Datasheet SCANPSC110FE-QV, SCANPSC110FFMQB, SCANPSC110FJ-QV, SCANPSC110FLMQB, SCANPSC110FW-QV Datasheet (NSC)
...Page 1
SCANPSC110F
SCAN Bridge Hierarchical and Multidrop Addressable
JTAG Port (IEEE1149.1 System Test Support)
General Description
The SCANPSC110F Bridge extends the IEEE Std. 1149.1
test bus into a multidrop test bus environment. The advantage of a hierarchical approach over a single serial scan
chain is improved test throughput and the ability to remove a
board from the system and retain test access to the remaining modules. Each SCANPSC110F Bridge supports up to 3
local scan rings which can be accessed individually or combined serially.Addressingis accomplished by loading the instruction register with a value matching that of the Slot inputs. Backplane and inter-board testing can easily be
accomplished by parking the local TAP Controllers in one of
the stable TAP Controller states via a Park instruction. The
32-bit TCK counter enables built in self test operations to be
performed on one port while other scan chains are simultaneously tested.
Features
n True IEEE1149.1 hierarchical and multidrop addressable
capability
n The 6 slot inputs support up to 59 unique addresses, a
Broadcast Address, and 4 Multi-cast Group Addresses
n 3 IEEE 1149.1-compatible configurable local scan ports
n Mode Register allows local TAPs to be bypassed,
selected for insertion into the scan chain individually, or
serially in groups of two or three
n 32-bit TCK counter
n 16-bit LFSR Signature Compactor
n Local TAPs can be tri-stated via the OE input to allow
an alternate test master to take control of the local TAPs
n The IP version of this device supports features not
described in this datasheet such as 8 slot inputs for
enhanced address capability and additional instructions.
For a completed description of the additional instructions
supported, refer to the SCANPSC110 supplemental
datasheet.
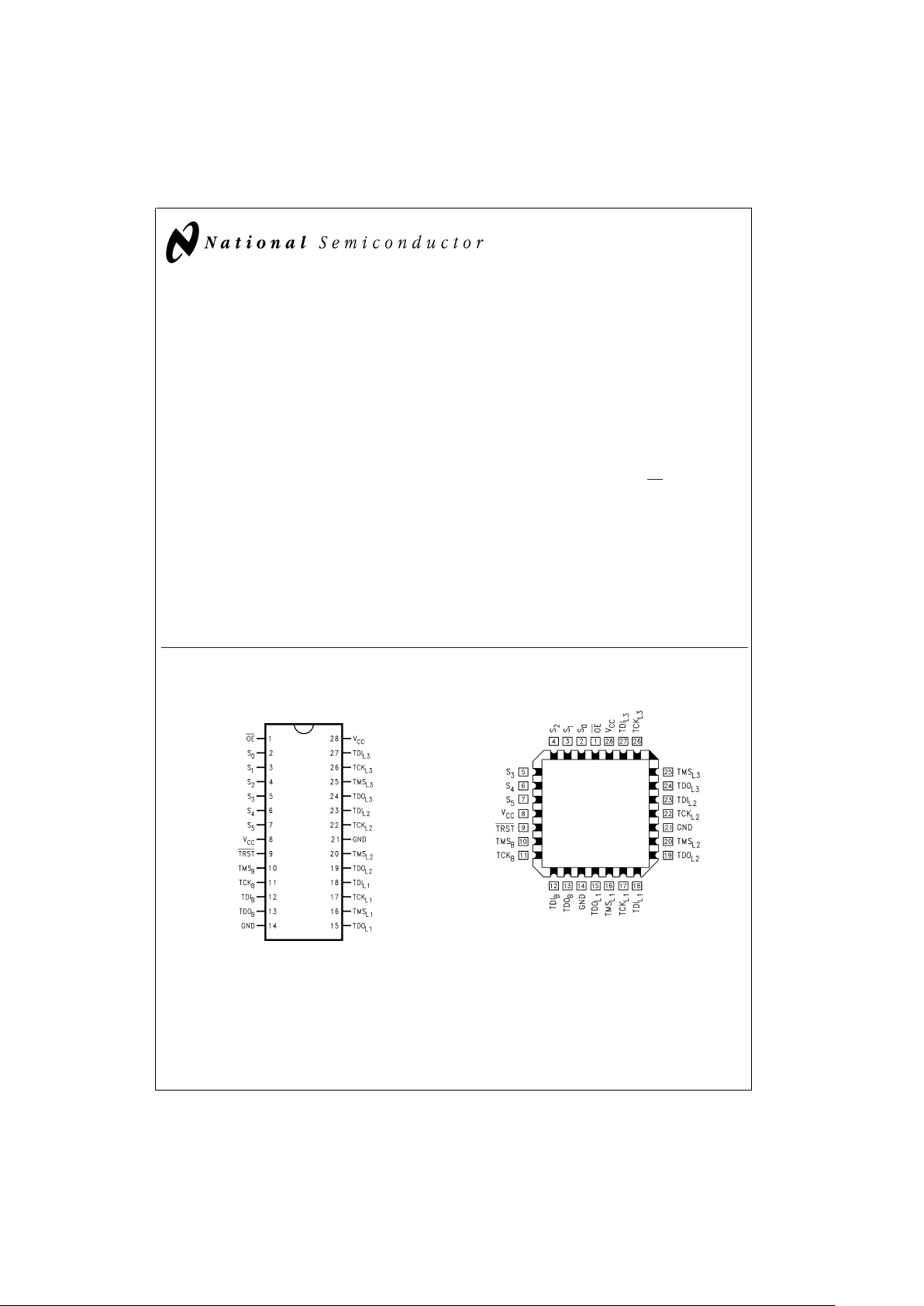
Connection Diagrams
TRI-STATE®is a registeredtrademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
28-Pin
CDIP and Flatpak
DS100327-1
Pin Assignment for LCC
DS100327-2
October 1999
SCANPSC110F SCAN Bridge
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS100327 www.national.com
Page 2
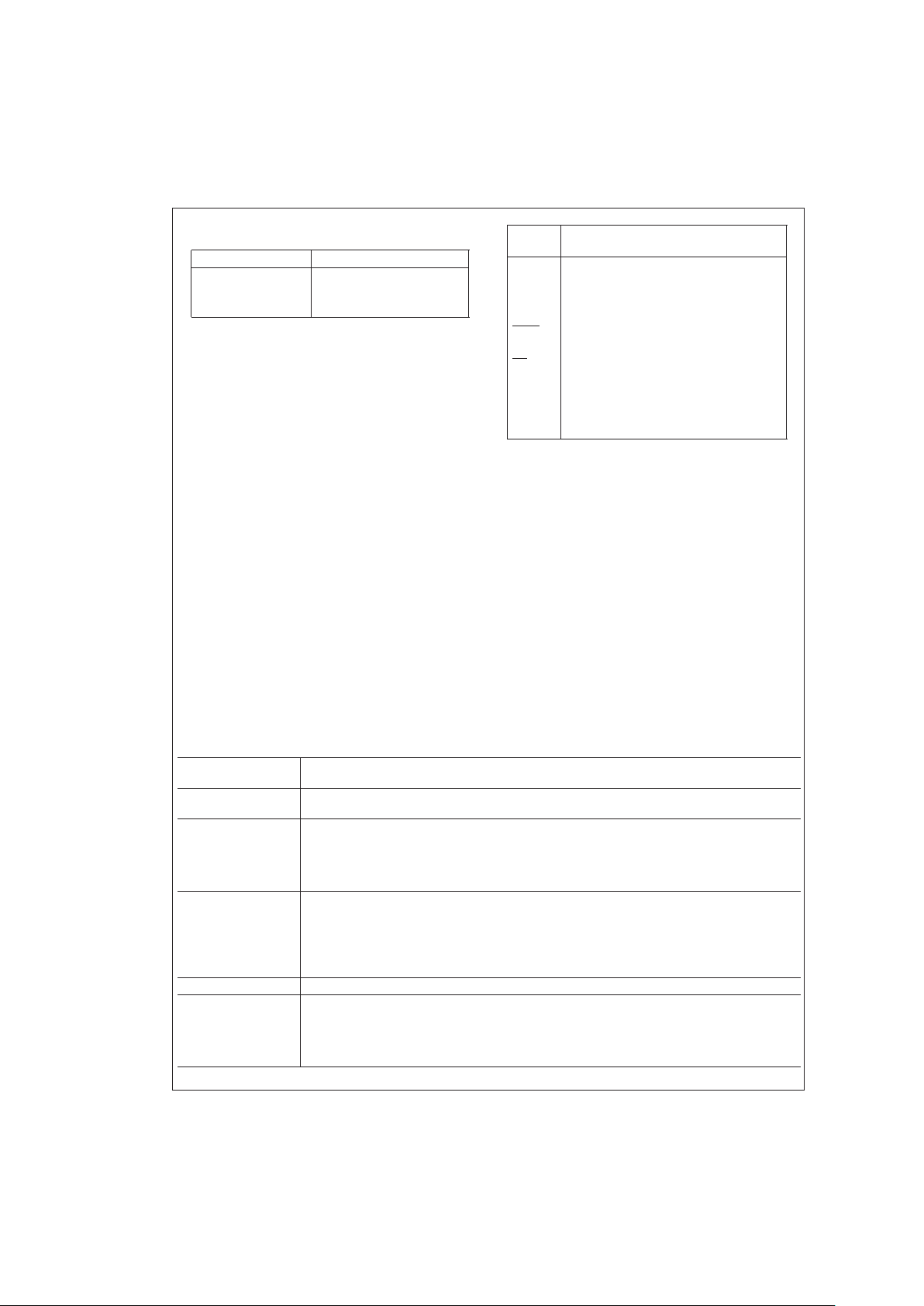
Connection Diagrams (Continued)
Order Number Description
SCANPSC110FFMQB Military Flatpak
SCANPSC110FDMQB Military DIP
SCANPSC110FLMQB Military Leadless Chip Carrier
Pin
Names
Description
TCK
B
Backplane Test Clock Input
TMS
B
Backplane Test Mode Select Input
TDI
B
Backplane Test Data Input
TDO
B
Backplane Test Data Output
TRST
Asynchronous Test Reset Input (Active low)
S
(0,5)
Address Select Port
OE
Local Scan Port Output Enable (Active low)
TCK
L(1–3)
Local Port Test Clock Output
TMS
L(1–3)
Local Port Test Mode Select Output
TDI
L(1–3)
Local Port Test Data Input
TDO
L(1–3)
Local Port Test Data Output
Table of Contents
1. GLOSSARY OF TERMS: 2
2. DETAILED PIN DESCRIPTION TABLE: 3
3. OVERVIEW OF SCAN BRIDGE FUNCTIONS: 4
A. SCANPSC110F Bridge Architecture: 4
B. SCANPSC110F Bridge State Machines: 4
4. TESTER/SCANPSC110F BRIDGE INTERFACE: 8
5. REGISTER SET: 8
6. ADDRESSING SCHEME: 8
7. HIERARCHICAL TEST SUPPORT: 9
8. LEVEL 1 PROTOCOL: 9
A. Addressing Modes: 9
B. Direct Addressing: 10
C. Broadcast Addressing: 10
D. Multi-Cast Addressing: 10
9. LEVEL 2 PROTOCOL: 11
A. Level 2 Instruction Types: 11
B. Level 2 Instruction Descriptions: 12
10. REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS: 14
11. SPECIAL FEATURES: 16
A. BIST Support: 16
B. RESET: 16
C. Port Synchronization: 16
12. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS: 18
13. RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS: 18
14. DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS: 18
15. AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS: 20
16. AC WAVEFORMS: 22
17. APPENDIX: 24
A. State Diagram for Boundary-Scan TAP Control-
ler: 24
18. APPLICATIONS EXAMPLE: 24
TABLE 1. Glossary of Terms
LFSR Linear Feedback Shift Register. When enabled, will generate a 16-bit signature of sampled serial
test data.
LSP Local Scan Port. A four signal port that drives a “local” (i.e. non-backplane) scan chain. (e.g.,
TCK
L1
, TMSL1, TDOL1, TDIL1)
Local Local is used to describe IEEE Std. 1149.1 compliant scan rings and the SCANPSC110F Bridge
Test Access Port that drives them. The term “local” was adopted from the system test architecture
that the ’PSC110F Bridge will most commonly be used in; namely, a system test backplane with a
’PSC110F Bridge on each card driving up to 3 “local” scan rings per card. (Each card can contain
multiple ’PSC110Fs, with 3 local scan ports per ’PSC110F.)
Park/Unpark Park, parked, unpark, and unparked, are used to describe the state of the LSP controller and the
state of the local TAP controllers (the “local TAP controllers” refers to the TAP controllers of the
scan components that make up a local scan ring). Park is also used to describe the action of
parking a LSP (transitioning into one of the Parked LSP controller states). It is important to
understand that when a LSP controller is in one of the parked states, TMS
L
is held constant,
thereby holding or “parking” the local TAP controllers in a given state.
TAP Test Access Port as defined by IEEE Std. 1149.1
Selected/Unselected Selected and Unselected refers to the state of the ’PSC110F Bridge Selection Controller. A
selected ’PSC110F has been properly addressed and is ready to receive Level 2 protocol.
Unselected ’PSC110Fs monitor the system test backplane, but do not accept Level 2 protocol
(except for the
GOTOWAIT
instruction). The data registers and LSPs of unselected ’PSC110Fs are
not accessible from the system test master.
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com 2
Page 3
Table of Contents (Continued)
TABLE 1. Glossary of Terms (Continued)
Active Scan Chain The Active Scan Chain refers to the scan chain configuration as seen by the test master at a given
moment. When a ’PSC110F is selected with all of its LSPs parked, the active scan chain is the
current scan bridge register only. When a LSP is unparked, the active scan chain becomes: TDI
B
→
the current ’PSC110F register→the local scan ring registers→a PAD bit→TDO
B
. Refer to
Table 4
for Unparked configurations of the LSP network.
Level 1 Protocol Level 1 is the protocol used to address a ’PSC110F.
Level 2 Protocol Level 2 is the protocol that is used once a ’PSC110F is selected. Level 2 protocol is IEEE Std.
1149.1 compliant when an individual ’PSC110F is selected.
PAD A one bit register that is placed at the end of each local scan port scan-chain. The PAD bit
eliminates the prop delay that would be added by the ’PSC110F LSPN logic between TDI
Ln
and
TDO
L(n+1)
or TDOBby buffering and synchronizing the TDILinputs to the falling edge of TCKB,
thus allowing data to be scanned at higher frequencies without violating set-up and hold times.
LSB Least Significant Bit, the right-most position in a register (bit 0)
MSB Most Significant Bit, the left-most position in a register
TABLE 2. Detailed Pin Description Table
Pin
#
Name I/O (Note 1) (SOIC Description
& LCC)
TMS
B
TTL Input w/Pull-Up
Resistor
10 BACKPLANE TEST MODE SELECT: Controls sequencing through the TAP
Controller of the SCANPSC110F Bridge. Also controls sequencing of the TAPs
which are on the three (3) local scan chains.
TDI
B
TTL Input w/Pull-Up
Resistor
12 BACKPLANE TEST DATA INPUT: All backplane scan data is supplied to the
’PSC110F through this input pin.
TDO
B
TRI-STATEable, 13 BACKPLANE TEST DATA OUTPUT: This output drives test data from the
’PSC110F and the local TAPs, back toward the scan master controller.
32 mA/64 mA Drive,
Reduced-Swing,
Output
TCK
B
TTL Schmitt Trigger
Input
11 TEST CLOCK INPUT FROM THE BACKPLANE: This is the master clock
signal that controls all scan operations of the ’PSC110F and of the three (3)
local scan ports.
TRST
TTL Input w/Pull-Up 9 TEST RESET: An asynchronous reset signal (active low) which initializes the
’PSC110F logic.
Resistor
S
(0–5)
TTL Inputs 2, 3, 4, SLOT IDENTIFICATION: The configuration of these six (6) pins is used to
identify (assign a unique address to) each ’PSC110F on the system backplane.
5, 6, 7
OE
TTL Input 1 OUTPUT ENABLE for the Local Scan Ports, active low. When high, this
active-low control signal TRI-STATEs all three local scan ports on the
’PSC110F, to enable an alternate resource to access one or more of the three
(3) local scan chains.
TDO
L(1–3)
TRI-STATEable, 15,19, TEST DATA OUTPUTS: Individual output for each of the three (3) local scan
ports.
24 mA/24 mA 24
Drive Outputs
TDI
L(1–3)
TTL Inputs w/Pull-Up 18, 23, TEST DATA INPUTS: Individual scan data input for each of the three (3) local
scan ports.
Resistors 27
TMS
L(1–3)
TRI-STATEable, 16, 20, TEST MODE SELECT OUTPUTS: Individual output for each of the three (3)
local scan ports. TMS
L
does not provide a pull-up resistor (which is assumed
to be present on a connected TMS input, per the IEEE 1149.1 requirement)
24 mA/24 mA 25
Drive Outputs
TCK
L(1–3)
TRI-STATEable, 17, 22, LOCAL TEST CLOCK OUTPUTS: Individual output for each of the three (3)
local scan ports. These are buffered versions of TCK
B
.
24 mA/24 mA 26
Drive Output
V
CC
Power Supply Voltage 8, 28 Power supply pins, 5.0V±10%.
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com3
Page 4
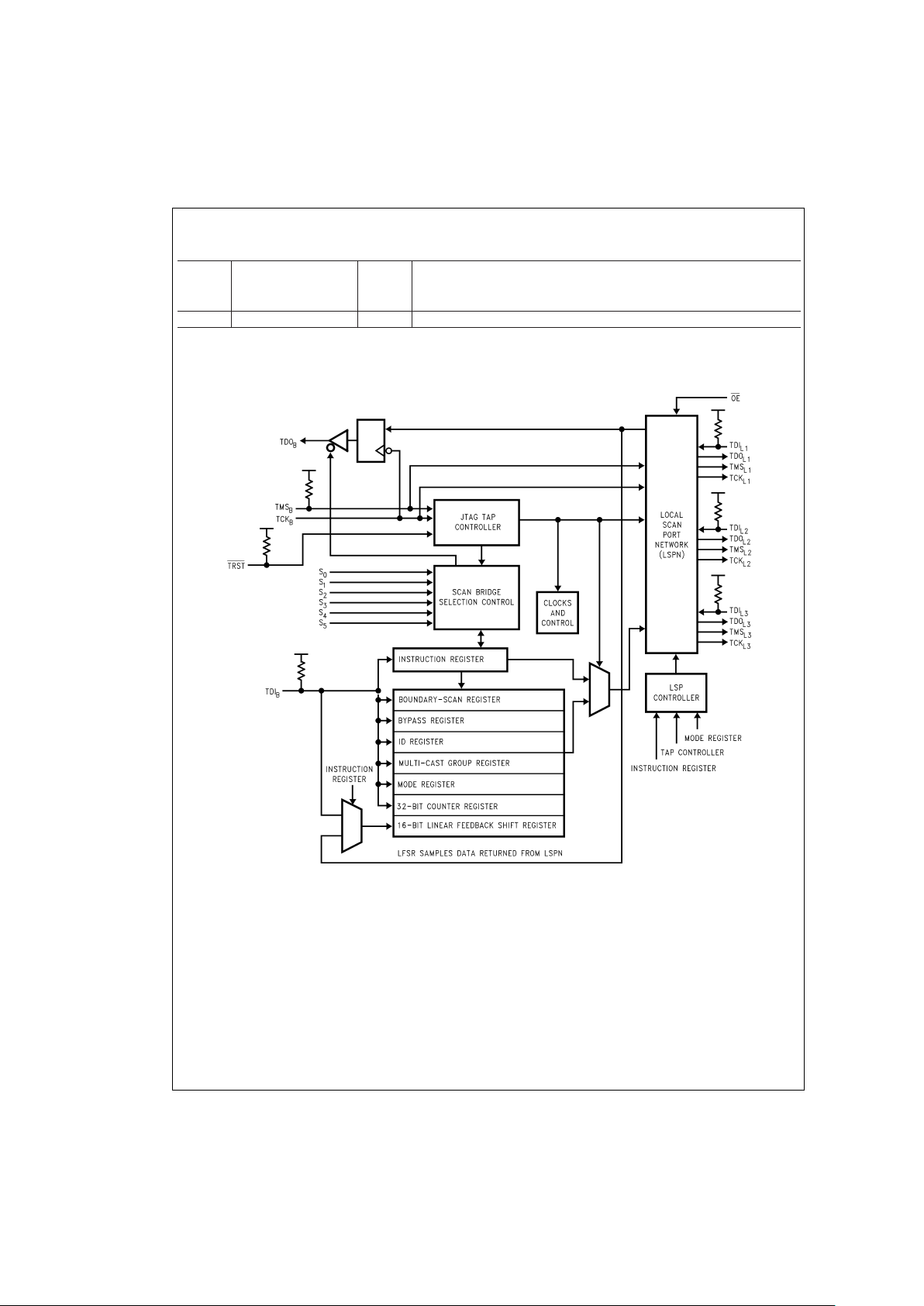
Table of Contents (Continued)
TABLE 2. Detailed Pin Description Table (Continued)
Pin
#
Name I/O (Note 1) (SOIC Description
& LCC)
GND Ground potential 14, 21 Power supply pins 0V.
Note 1: All pins are active HIGH unless otherwise noted.
Overview of SCANPSC110F Bridge Functions
SCANPSC110F BRIDGE ARCHITECTURE
Figure 1
shows the basic architecture of the ’PSC110F. The
device’s major functional blocks are illustrated here. The
TAPController, a 16-state state machine, is the central control for the device. The instruction register and various test
data registers can be scanned to exercise the various functions of the ’PSC110F (these registers behave as defined in
IEEE Std. 1149.1).
The ’PSC110F selection controller provides the functionality
that allows the 1149.1protocol to be used in a multi-drop environment. It primarily compares the address inputto the slot
identification and enables the ’PSC110F for subsequent
scan operations.
The Local Scan Port Network (LSPN) contains multiplexing
logic used to select different port configurations. The LSPN
control block contains the Local Scan Port Controllers
(LSPC) for each Local Scan Port (LSP
1
, LSP2, and LSP3).
This control block receives input from the ’PSC110F instruction register, mode register, and the TAP controller. Each local portcontains all four (4) boundary scan signals needed to
interface with the local TAPs.
SCANPSC110F BRIDGE STATE MACHINES
The ’PSC110Fis IEEE 1149.1-compatible,in that it supports
all required 1149.1 operations. In addition, it supports a
higher level of protocol, (Level 1), that extends the IEEE
1149.1 Std. to a multi-drop environment.
DS100327-3
FIGURE 1. SCANPSC110F Bridge Architecture
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com 4
Page 5
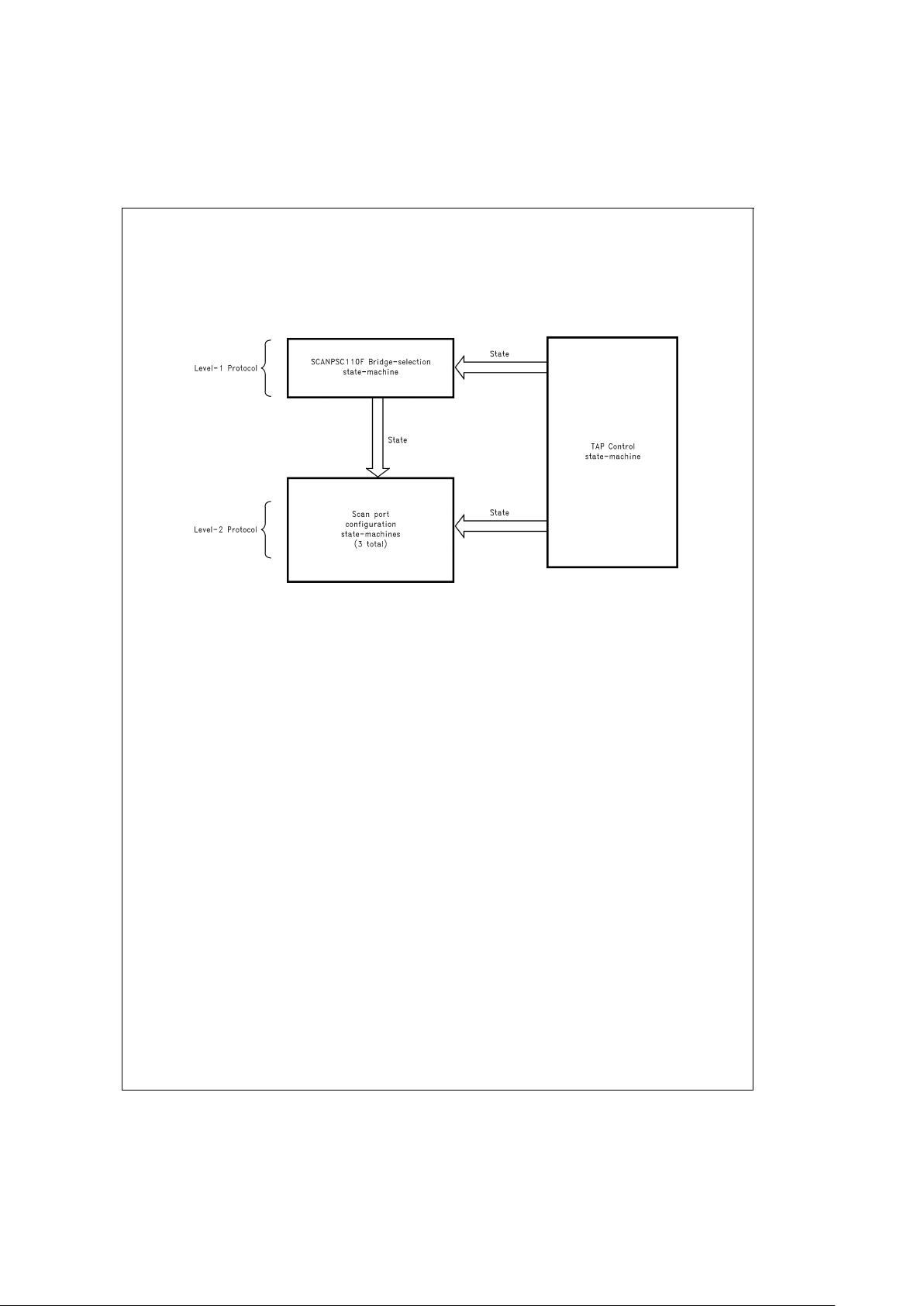
Overview of SCANPSC110F Bridge
Functions
(Continued)
In multi-drop scan systems, a scan tester can select individual ’PSC110Fs for participation in upcoming scan operations. ’PSC110F “selection” is accomplished by simultaneously scanning a device address out to multiple
’PSC110Fs. Through an on-chip address matching process,
only those ’PSC110Fs whose statically-assigned address
matches the scanned-out address become selected to receive further instructions from the scan tester. ’PSC110F selection is done using a “Level-1” protocol, while follow-on instructions are sent to selected ’PSC110Fs by using a
“Level-2” protocol.
The ’PSC110F contains three distinct but coupled
state-machines (see
Figure 2
). The first of these is the
TAP-control state-machine, which is used to drive the
’PSC110Fsscan ports in conformance with the 1149.1 Standard (see
Figure 17
of appendix). The second is the
’PSC110F-selection state-machine (
Figure 3
). The third
state-machine actually consists of three identical but independent state-machines (see
Figure 4
), one per ’PSC110F
local scan port. Each of these scan port-selection
state-machines allows individual local ports to be inserted
into and removed from the ’PSC110Fs overall scan chain.
The ’PSC110F selection state-machine performs the address matching which gives the ’PSC110F its multi-drop capability. That logic supports single-’PSC110F access,
multi-cast, and broadcast. The ’PSC110F-selection
state-machine implements the chip’s Level-1 protocol.
DS100327-4
FIGURE 2. SCANPSC110F Bridge State Machines
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com5
Page 6
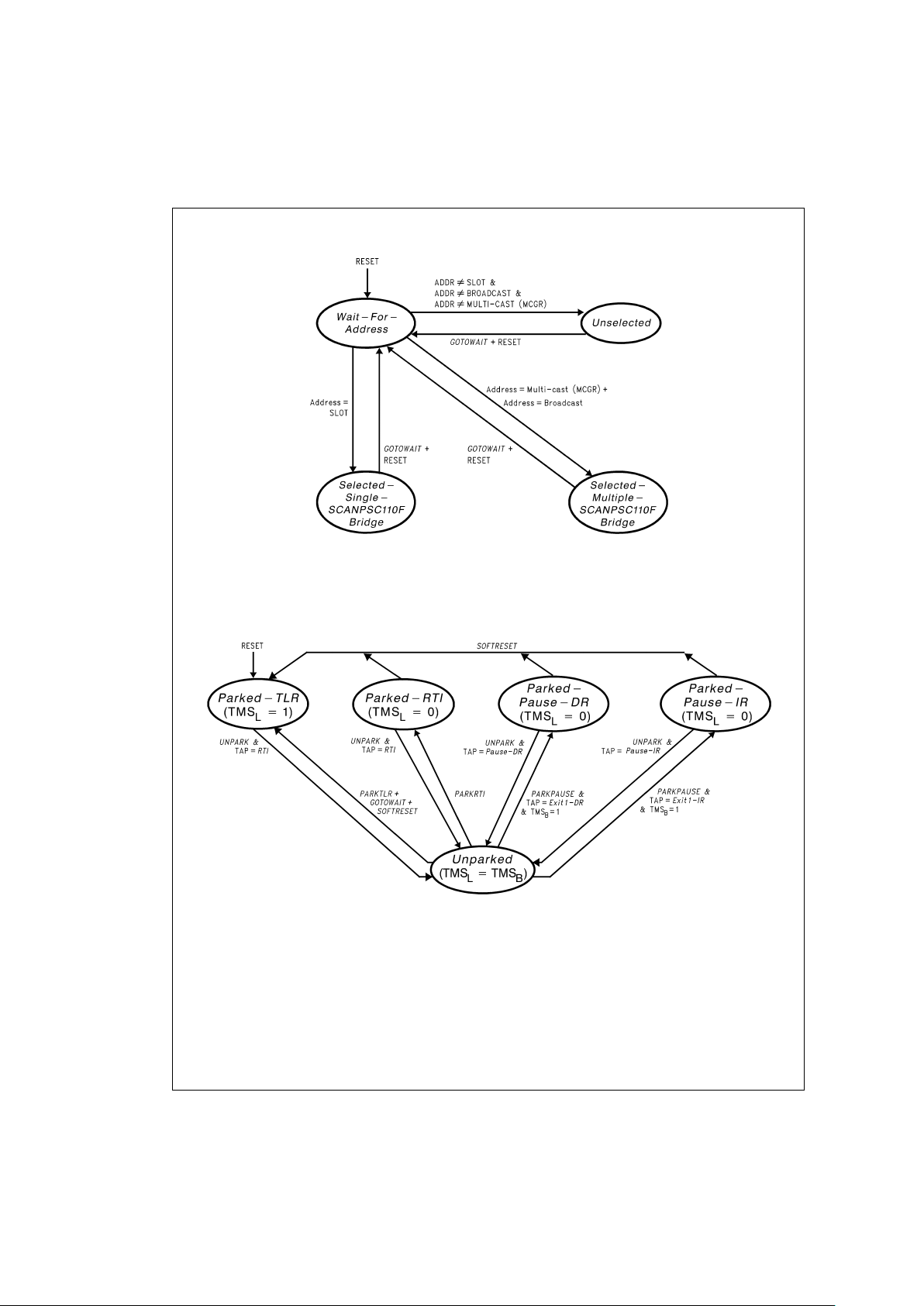
Overview of SCANPSC110F Bridge Functions (Continued)
The ’PSC110F’s scan port-configuration state-machine is
used to control the insertion of local scan ports into the overall scan chain, or the isolation of local ports from the chain.
From the perspective of a system’s (single) scan controller,
each ’PSC110F presents only one scan chain to the master.
The ’PSC110F architecture allows one or more of the
’PSC110F’s local ports to be included in the active scan
chain.
Each local port can be “parked” in one of four stable states
(Parked-TLR, Parked-RTI, Parked-Pause-DR or
Parked-Pause-IR)
, either individually or simultaneously with
other local ports. Parking a chain removes that local chain
from the active scan chain. Conversely, a parked chain can
be “unparked”, causing the corresponding local port to be inserted into the active scan chain.
As shown in
Figure 4
, the ’PSC110F’s three scan
port-configuration state-machines allow each of the part’s local ports tooccupy a different state atany given time. For example, some ports may be parked, perhaps in different
states, while other ports participate in scan operations. The
state-diagram shows that some state transitions depend on
the current state of the TAP-control state-machine.As an ex-
DS100327-5
KEY
+=OR
&=AND
ADDR=6-bit address in the Instruction Register
SLOT=Static address in the ’PSC110F Selection Controller
FIGURE 3. State Machine for SCANPSC110F Bridge Selection Controller
DS100327-12
FIGURE 4. Local SCANPSC110F Bridge Port Configuration State Machine
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com 6
Page 7
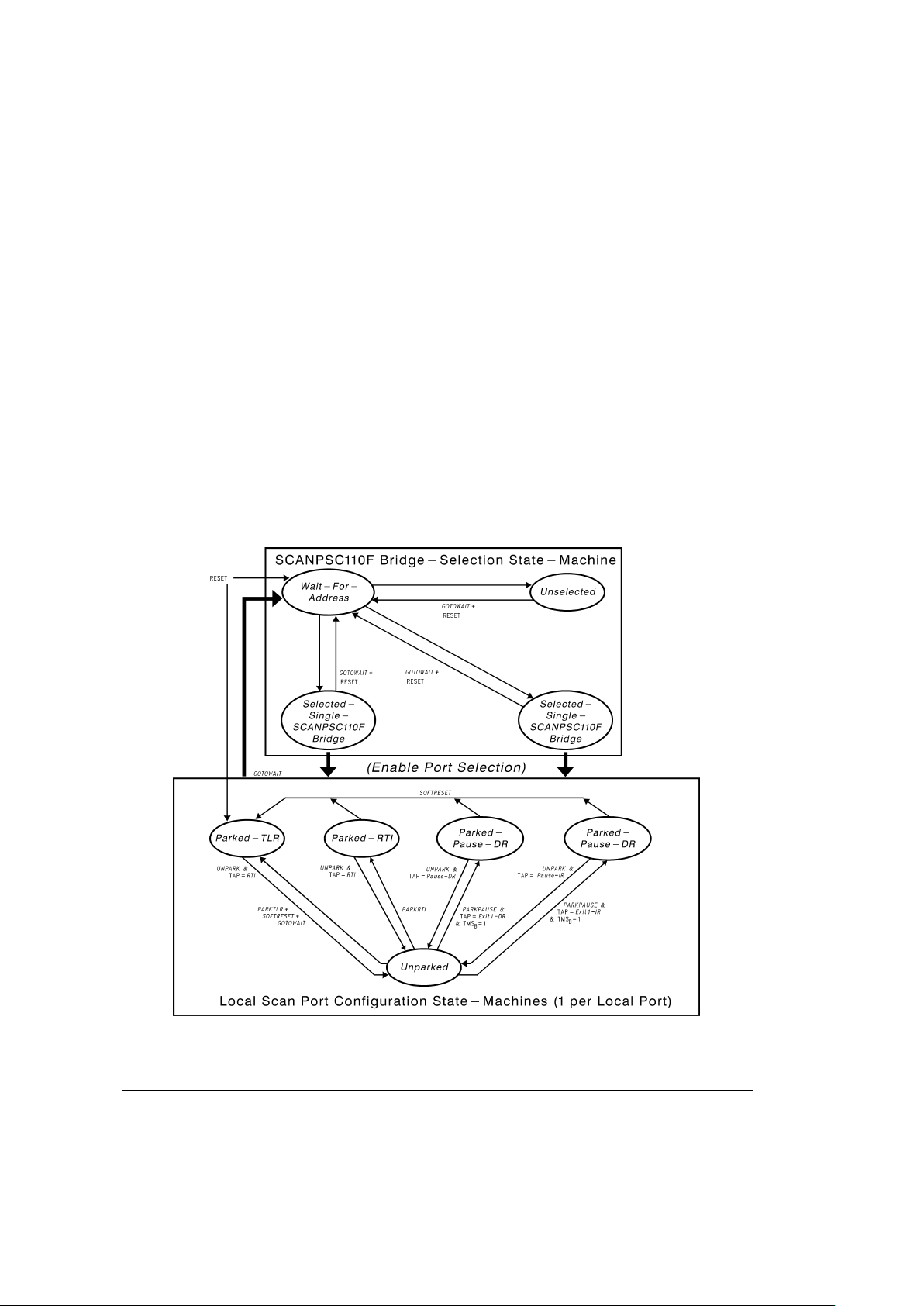
Overview of SCANPSC110F Bridge
Functions
(Continued)
ample, a local portwhich is presently in the
Parked-RTI
state
does not become unparked (i.e., enter the
Unparked
state)
until the ’PSC110F receives an
UNPARK
instruction and the
’PSC110F’s TAP state-machine enters the
Run-Test/Idle
state.
Similarly, certain transitions of the scan port-configuration
state-machine can force the ’PSC110F’s TAP-control
state-machine into specific states. For example, when a local port is in the
Unparked
state and the ’PSC110F receives
a PARKRTI instruction, the Local Port controller enters the
Parked-RTI
state in which TMSLnwill be held low until the
port is later unparked. While TMS
Ln
is held low, all devices
on that local scan chain remain in their current TAP State
(the
RTI
TAP controller state in this example).
The ’PSC110F’s scan port-configuration state-machine
implements part of the ’PSC110F’s Level-2 protocol. In addition, the ’PSC110F providesa number of Level-2 instructions
for functions other than local scan port confguration. These
instructions provide access to and control of various registers within the ’PSC110F. This set instructions includes:
BYPASS CNTRSEL
EXTEST LFSRON
SAMPLE/PRELOAD LFSROFF
IDCODE CNTRON
MODESEL CNTROFF
MCGRSEL GOTOWAIT
LFSRSEL
Figure 5
illustrates how the ’PSC110F’s state-machines interact. The ’PSC110F-selection state-machine enables or
disables operation of the chip’s three port-selection
state-machines. In ’PSC110Fs which are selected via
Level-1 protocol (either as individual ’PSC110Fs or as members of broadcast or multi-cast groups), Level-2 protocol
commands can be used to park or unpark local scan ports.
Note that most transitions of the port-configuration
state-machines are gated by particular states of the
’PSC110F’sTAP-control state-machine, as shown in
Figures
4, 5
.
DS100327-6
FIGURE 5. Relationship Between SCANPSC110F Bridge State Machines
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com7
Page 8
Overview of SCANPSC110F Bridge
Functions
(Continued)
Following a hardware reset, the TAP controller
state-machine is in the
Test-Logic-Reset (TLR)
state; the
’PSC110F-selection state-machine is in the
Wait-For-Address
state; and each of the three port-selection
state-machines is in the
Parked-TLR
state. The ’PSC110Fis
then ready to receive Level-1 protocol, followed by Level-2
protocol.
Tester/SCANPSC110F Bridge
Interface
An IEEE 1149.1 system tester sends instructions to a
’PSC110F via that ’PSC110F’s backplane scan-port. Following test logic reset, the ’PSC110F’s selection state-machine
is in the
Wait-For-Address
state. When the ’PSC110F’sTAP
controller is sequenced to the Shift-IR state, data shifted in
through the TDI
B
input is shifted into the ’PSC110F’sinstruction register. Note that prior to successful selection of a
’PSC110F, data is not shifted out of the instruction register
and out through the ’PSC110F’s TDO
B
output, as it is during
normal scan operations. Instead, as each new bit enters the
instruction register’s most-significant bit, data shifted out
from the least-significant bit is discarded.
When the instruction register is updated with the address
data, the ’PSC110F’s address-recognition logic compares
the six least-significant bitsof the instruction register with the
6-bit assigned address which is statically present on the
S
(0–5)
inputs. Simultaneously, the scanned-in address is
compared with the reserved Broadcast and Multi-cast addresses. If an address match is detected, the
’PSC110F-selectionstate-machine enters one of the two selected states. If the scanned address does not match a valid
single-slot address or one of the reserved broadcast/
multi-cast addresses, the ’PSC110F-selection state-machine
enters the
Unselected
state.
Note that the SLOT inputs
should not be set
to a value cor-
responding to
a multi-cast group
,ortothe
broadcast ad-
dress
. Also note that the single-’PSC110F selection process
must be performed for all ’PSC110Fs which are subsequently to be addressed in multi-cast mode. This is required
because each such device’s Multi-cast Group Register
(MCGR) must be programmed with a multi-cast group number,and the MCGR is notaccessible to the test controller until that ’PSC110F has first entered the
Selected-Single-’PSC110F
state.
Once a ’PSC110F has been selected, Level-2 protocol is
used to issue commands and to access the chip’s various
registers.
Register Set
The SCANPSC110F Bridge includes a number of registers
which are used for ’PSC110F selection and configuration,
scan datamanipulation, and scan-support operations. These
registers can be grouped as shown in
Table 3
.
The specific fields and functions of each of these registers
are detailed in the section of this document titled “Data Register Descriptions”.
Note that when any of these registers is selected for insertion into the ’PSC110F’s scan-chain, scan data enters
through that register’s most-significant bit. Similarly, data
that is shifted outof the register is fed to the scan inputof the
next-downstream device in the scan-chain.
TABLE 3. Registers
Register Name BSDL Name Description
Instruction Register INSTRUCTION ’PSC110F addressing and instruction-decode
IEEE Std. 1149.1 required register
Boundary-Scan Register BOUNDARY IEEE Std. 1149.1 required register
Bypass Register BYPASS IEEE Std. 1149.1 required register
Device Identification Register IDCODE IEEE Std. 1149.1 optional register
Multi-Cast Group Register MCGR ’PSC110F-group address assignment
Mode Register MODE ’PSC110F local-port configuration and control bits
Linear-Feedback Shift Register LFSR ’PSC110F scan-data compaction (signature generation)
TCK Counter Register CNTR Local-port TCK clock-gating (for BIST)
Addressing Scheme
The SCANPSC110F Bridge architecture extends the functionality of the IEEE 1149.1 Standard by supplementing that
protocol with an addressing scheme which allowsa test controller to communicate with specific ’PSC110Fs within a network of ’PSC110Fs. That network can include both
multi-drop and hierarchical connectivity. In effect, the
’PSC110Farchitecture allows a test controller to dynamically
select specific portions of such a network for participation in
scan operations. This allows a complex system to be partitioned into smaller blocks for testing purposes.
The ’PSC110F provides two levels of test-network partitioning capability. First, a test controller can select entire indi-
vidual ’PSC110Fs, specific sets of ’PSC110Fs (multi-cast
groups), or all ’PSC110Fs (broadcast). This
’PSC110F-selection process is supported by a “Level-1”
communication protocol. Second, within each selected
’PSC110F, a test controller can select one or more of the
chip’s three local scan-ports. That is, individual local ports
can be selected forinclusion in the (single) scan-chain which
a ’PSC110F presents to the test controller. This mechanism
allows a controller to select specific terminal scan-chains
within theoverall scan network. The port-selectionprocess is
supported by a “Level-2” protocol.
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com 8
Page 9
Hierarchical Test Support
Multiple SCANPSC110FBridges can be used to assemble a
hierarchical boundary-scan tree. In such a configuration, the
system tester can configure the local ports of a set of
’PSC110Fs so as to connect a specific set of local
scan-chains to the active scan chain. Using this capability,
the tester can selectively communicate with specific portions
of a target system.
The tester’s scan port is connected to the backplane scan
port of a “root” layer of ’PSC110Fs,each of which can be selected using multi-drop addressing. A second tier of
’PSC110Fs can be connected to this root layer, by connecting a local port (LSP) of a root-layer ’PSC110F to the backplane port of a second-tier ’PSC110F. This process can be
continued to construct a multi-level scan hierarchy.
’PSC110F local ports which are not cascaded into
higher-level ’PSC110Fs can be thought of as the terminal
“leaves” of a scan “tree”. The test master can select one or
more target leaves by selecting and configuring the local
ports of an appropriate set of ’PSC110Fs in the test tree.
Level 1 Protocol
ADDRESSING MODES
The SCANPSC110F Bridge supports “single” and “multiple”
modes of addressing a ’PSC110F.The “single” mode will select one ’PSC110F and is called Direct Addressing. More
than one ’PSC110F device can be selected via the Broadcast and Multi-Cast Addressing modes.
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com9
Page 10

Level 1 Protocol (Continued)
TABLE 4. SCANPSC110F Bridge Address Modes
Address Types Hex Address
(Note 2)
Binary Address
(Note 3)
TDOBState
Direct Address 00 to 3A XX000000 to XX111010 Normal IEEE Std. 1149.1
Broadcast Address 3B XX111011 Always TRI-STATED
Multi-Cast Group 0 3C XX111100 Always TRI-STATED
Multi-Cast Group 1 3D XX111101 Always TRI-STATED
Multi-Cast Group 2 3E XX111110 Always TRI-STATED
Multi-Cast Group 3 3F XX111111 Always TRI-STATED
Note 2: Hex address ’7X’, ’BX’, or ’FX’ may be used instead of ’3X’.
Note 3: Only the six (6) LSB’s of the address is compared to the S
(0–5)
inputs. The two (2) MSB’s are “don’t cares”.
DIRECT ADDRESSING
The ’PSC110F enters the
Wait-For-Address
state when:
1. its TAP Controller enters the
Test-Logic-Reset
state, or
2. its instructionregister is updated with theGOTOWAIT instruction (while either selected or unselected).
Each ’PSC110F within a scan network must be statically
configured with a unique address via its S
(0–5)
inputs. While
the ’PSC110F controller is in the
Wait-For-Address
state,
data shifted into bits 5 through 0 of the instruction register is
compared with the address present on the S
(0–5)
inputs in
the
Update-IR
state. If the six (6) LSBs of the instruction reg-
ister match the address on the S
(0–5)
inputs, (see
Figure 6
)
the ’PSC110F becomes selected, and is ready to receive
Level 2 Protocol (i.e., further instructions). When the
’PSC110F is selected, its device identification register is inserted into the active scan chain.
All ’PSC110Fs whose S
(0–5)
address does not match the instruction register address become unselected. They will remain unselected until either their TAP Controller enters the
Test-Logic-Reset
state, or their instruction register is up-
dated with the
GOTOWAIT
instruction.
BROADCAST ADDRESSING
The BroadcastAddress allows a tester to simultaneously select all ’PSC110Fs in a test network. This mode is useful in
testing systems which contain multiple identical boards. To
avoid bus contention between scan-path output drivers on
different boards, each ’PSC110F’s TDO
B
buffer is always
tri-stated while in Broadcast mode. In this configuration, the
on-chip Linear Feedback Shift Register (LFSR) can be used
to accumulate a test result signature for each board that can
be read back later by direct-addressing each board’s
’PSC110F.
MULTI-CAST ADDRESSING
As a way to make the broadcast mechanism more selective,
the ’PSC110F provides a “Multi-cast” addressing mode. A
’PSC110F’s multi-cast group register (MCGR) can be programmed to assign that ’PSC110F to one of four (4)
Multi-Cast groups. When ’PSC110Fs in the
Wait-For-Address
state are updated with a Multi-Cast address, all ’PSC110Fs whose MCGR matches the Multi-Cast
group will become selected. As in Broadcast mode, TDO
B
is
always tri-stated while in Multi-cast mode.
DS100327-7
FIGURE 6. Direct Addressing: Device Address Loaded into Instruction Register
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com 10
Page 11

Level 1 Protocol (Continued)
Level 2 Protocol
Once the SCANPSC110F Bridge has been successfully addressed and selected, its internalregisters may be accessed
via Level-2 Protocol. Level-2 Protocol is compliant to IEEE
Std. 1149.1 TAP protocol with one exception: if the
’PSC110F is selected via the Broadcast or Multi-Cast address, TDO
B
will always be TRI-STATED. (The TDOBbuffer
must be implemented this way to prevent bus contention.)
Upon being selected,(i.e., the ’PSC110F Selectioncontroller
transitions from the
Wait-For-Address
state to one of the
Se-
lected
states), each of the local scan ports (LSP1, LSP2,
LSP
3
) remains parked in one of the following four TAP Con-
troller states:
Test-Logic-Reset,Run-Test/Idle, Pause-DR
,or
Pause-IR
and the active scan chain will consist of: TDI
B
through the instruction register (or the IDCODE register) and
out through TDO
B
.
TDI
B
→
Instruction Register→TDO
B
The
UNPARK
instruction (described later) is used to insert
one or more local scan ports into the active scan chain.
Table 4
describes which local ports are inserted into the
chain, and in what order.
LEVEL 2 INSTRUCTION TYPES
There are two types of instructions (reference
Table 5
):
DS100327-8
FIGURE 7. Broadcast Addressing: Address Loaded into Instruction Register
DS100327-9
FIGURE 8. Multi-Cast Addressing: Address Loaded into Instruction Register
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com11
Page 12

Level 2 Protocol (Continued)
1. Instructions that insert a ’PSC110F register into the active scan chain so that the register can be captured or
updated
(BYPASS, SAMPLE/PRELOAD, EXTEST, ID-
CODE, MODESEL, MCGRSEL, LFSRSEL, CNTRSEL).
2. Instructions that configure local ports or control the operation of the linear feedback shift register and counter
registers
(UNPARK, PARKTRL, PARKRTI, PARKPAUSE, GOTOWAIT, SOFTRESET, LFSRON, LFSROFF, CNTRON, CNTROFF).
These instructions, along
with any other yet undefined Op-Codes, will cause the
device identification register to be inserted into the active scan chain.
LEVEL 2 INSTRUCTION DESCRIPTIONS
BYPASS:
The
BYPASS
instruction selects the bypass register for insertion into the active scan chain when the
’PSC110F is selected.
EXTEST:
The
EXTEST
instruction selects the
boundary-scan register for insertion into the active scan
chain. The boundary-scan register consists of seven
“sample only” shift cells connected to the S
(0–5)
and OE in-
puts. Onthe ’PSC110F, the
EXTEST
instruction performsthe
same function as the
SAMPLE/PRELOAD
instruction, since
there aren’t any scannable outputs on the device.
SAMPLE/PRELOAD:
The
SAMPLE/PRELOAD
instruction
selects the boundary-scan register for insertion into the active scan chain. The boundary-scan register consists of
seven “sample only” shift cells connected to the S
(0–5)
and
OE inputs.
IDCODE:
The
IDCODE
instruction selects the device identi-
fication registerfor insertion into the active scanchain. When
IDCODE
is the current active instruction the device identifi-
cation “0FC0E01F” Hex is captured upon exiting the
Capture-DR
state.
TABLE 5. Level 2 Protocol and Op-Codes
Instructions Hex Op-Code Binary Op-Code Data Register
BYPASS
FF 11111111 Bypass Register
EXTEST
00 00000000 Boundary-Scan Register
SAMPLE/PRELOAD
81 10000001 Boundary-Scan Register
IDCODE
AA 10101010 Device Identification Register
UNPARK
E7 11100111 Device Identification Register
PARKTLR
C5 11000101 Device Identification Register
PARKRTI
84 10000100 Device Identification Register
PARKPAUSE
C6 11000110 Device Identification Register
GOTOWAIT
*
C3 11000011 Device Identification Register
MODESEL
8E 10001110 Mode Register
MCGRSEL
03 00000011 Multi-Cast Group Register
SOFTRESET
88 10001000 Device Identification Register
LFSRSEL
C9 11001001 Linear Feedback Shift Register
LFSRON
0C 00001100 Device Identification Register
LFSROFF
8D 10001101 Device Identification Register
CNTRSEL
CE 11001110 32-Bit TCK Counter Register
CNTRON
0F 00001111 Device Identification Register
CNTROFF
90 10010000 Device Identification Register
Other Undefined TBD TBD Device Identification Register
Note 4: All other instructions act on selected ’PSC110Fs only.
UNPARK:
This instruction unparks the Local Scan Port Network and inserts it into the active scan chain as configured
by the Mode register (see
Table 4
). Unparked LSPs are se-
quenced synchronously with the ’PSC110F’s TAPcontroller.
When a LSP has been parked in the
Test-Logic-Reset
or
Run-Test/Idle
state, it will not become unparked until the
’PSC110F’s TAP Controller enters the
Run-Test/Idle
state
following the
UNPARK
instruction. If an LSP has been
parked in one of the stable pause states (
Pause-DR
or
Pause-IR
), it will not become unparked until the ’PSC110F’s
TAP Controller enters the respective pause state. (See
Fig-
ures 9, 10, 11, 12
).
PARKTLR:
This instruction causes all unparked LSPs to be
parked in the
Test-Logic-Reset
TAP controller state and removes the LSPnetwork from the active scan chain. The LSP
controllers keep the LSPs parked in the
Test-Logic-Reset
state by forcing their respective TMSLoutput with a constant
logic “1” while the LSP controller is in the
Parked-TLR
state
(see
Figure 4
).
PARKRTI:
This instruction causes all unparked LSPs to be
parked in the
Run-Test/Idle
state. When aLSPnis active (un-
parked), its TMS
L
signals follow TMSBand the LSPncontroller state transitions are synchronized with the TAP Controller
state transitions of the ’PSC110F. When the instruction register is updated with the
PARKRTI
instruction, TMSLwill be
forced to a constant logic “0”, causing the unparked local
TAP Controllers to be parked in the
Run-Test/Idle
state.
When an LSP
n
is parked, it is removed from the active scan
chain.
PARKPAUSE:
The
PARKPAUSE
instruction has dual functionality. It can be used to park unparked LSPs or to unpark
parked LSPs. The instruction places all unparked LSPs in
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com 12
Page 13

Level 2 Protocol (Continued)
one of the TAPController pause states. A local port does not
become parked until the ’PSC110F’s TAP Controller is sequenced through
Exit1-DR/IR
into the
Update-DR/IR
state.
When the ’PSC110F TAP Controller is in the
Exit1-DR
or
Exit1-IR
state and TMSBis high, the LSP controller forces a
constant logic “0” onto TMS
L
thereby parking the port in the
Pause-DRorPause-IR
state respectively (see
Figure 4
).
Another instruction can then be loaded to reconfigure the local ports or to deselect the ’PSC110F (i.e.,
MODESEL, GO-
TOWAIT,
etc.).
If the
PARKPAUSE
instruction is given to a bridge whose
LSPs areparked in
Pause-IRorPause-DR
, theparked LSPs
will become unparked when the ’PSC110F’s TAP controller
is sequenced into the respective Pause state.
The
PARKPAUSE
instruction was implemented with this
dual functionality to enable backplane testing (interconnect
testing between boards) with simultaneous Updates and
Captures.
Simultaneous Update and Capture of several boards can be
performed by parking LSPs of the different boards in the
Pause-DR
TAP controller state, after shifting the data to be
updated into the boundary registers of the components on
each board. The broadcast address is used to select all
’PSC110Fs connected to the backplane. The
PARKPAUSE
instruction is scanned into the selected ’PSC110Fs and the
’PSC110F TAP controllers are sequenced to the
Pause-DR
state where the LSPs of all ’PSC110Fs become unparked.
The local TAP controllers are then sequenced through the
Update-DR, Select-DR, Capture-DR, Exit1-DR, and parked
in thePause-DR state, as the ’PSC110FTAPcontroller is sequenced into the Update-DR state. When a LSP is parked, it
is removed from the active scan chain.
GOTOWAIT:
This instruction is used to return all ’PSC110Fs
to the
Wait-For-Address
state. All unparked LSPs will be
parked in the
Test-Logic-Reset
TAPcontroller state (see
Fig-
ure 5
).
MODESEL:
The
MODESEL
instruction inserts the mode
register into the active scan chain. The mode register determines the LSPN configuration. Bit 7 of the mode register is a
read-only counter status flag.
MCGRSEL:
This instruction inserts the multi-cast group register (MCGR) into the active scan chain. The MCGR is used
to group ’PSC110Fs into multi-cast groups for parallel TAP
sequencing (i.e., to simultaneously perform identical scan
operations).
SOFTRESET:
This instruction causes all 3 Port configura-
tion controllers (
Figure 4
) to enter the
Parked-TLR
state,
which forces TMS
Ln
high; this parks each local port in the
Test-Logic-Reset
state within 5 TCKBcycles.
LFSRSEL:
This instruction inserts the linear feedback shift
register (LFSR) into the active scan chain, allowing a compacted signature to be shifted out of the LFSR during the
Shift-DR
state. (The signature is assumed to have been
computed during earlier
LFSRON
shift operations.) This instruction disables the LFSR register’s feedback circuitry,
turning the LFSR into a standard 16-bit shift register.This allows a signature to be shifted out of the register, or a seed
value to be shifted into it.
LFSRON:
Once this instruction is executed, the linear feedback shift register samples data from the active scan path
(including all unparked TDI
Ln
) during the
Shift-DR
state.
Data from the scan path is shifted into the linear feedback
shift register and compacted. This allows a serial stream of
data to be compressed into a 16-bit signature that can subsequently be shifted out using the
LFSRSEL
instruction. The
linear feedback shift register is not placed in the scan chain
during this mode. Instead, the register samples the active
scan-chain data as it flows from the LSPN to TDO
B
.
LFSROFF:
This instruction terminates linear feedback shift
register sampling.The LFSR retains its current state after receiving this instruction.
CNTRSEL:
This instruction inserts the 32-bit TCK counter
shift register into the active scan chain. This allows the user
to program the number of “n” TCK cycles to send to the
parked local ports once the
CNTRON
instruction is issued
(e.g., for BIST operations). Note thatto ensure completion of
count-down, the ’PSC110F should receive at least “n” TCK
B
pulses.
CNTRON:
This instruction enables the TCK counter. The
counter begins counting down on the first rising edge of
TCK
B
following the
Update-IR
TAP controller state and is
decremented on each rising edge of TCK
B
thereafter. When
the TCK counter reaches terminal count, “00000000” Hex,
TCK
L
of all parked LSP’s is held low.
The CNTROFF instruction must be issued before unparking the LSPs of a
’PSC110F whose counter has reached terminal count.
This function over-rides the mode register TCK control bit
(bit-3).
CNTROFF:
This instruction disables the TCK counter, and
TCK
L
control is returned to the mode register (bit-3).
DS100327-10
FIGURE 9. Local Scan Port Synchronization from
Parked-TLR
Instruction
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com13
Page 14

Level 2 Protocol (Continued)
Register Descriptions
Instruction Register
The instruction shift register is an 8-bit register that is in series with the scan chain whenever the TAP Controller of the
SCANPSC110F Bridge is in the
Shift-IR
state. Upon exiting
the
Capture-IR
state, the value “XXXXXX01” is captured into
the instruction register, where “XXXXXX” represents the
value on the S
(0–5)
inputs.
When the ’PSC110F controller is in the
Wait-For-Address
state, the instruction register is used for ’PSC110F selection
via address matching. In addressing individual ’PSC110Fs,
the chip’s addressing logic performs a comparison between
a statically-configured (hard-wired) value on that ’PSC110F’s
slot inputs, and an address which is scanned into the chip”s
instruction register. Binary address codes “000000” through
“111010” (“00” through “3A” Hex) are reserved for addressing individual ’PSC110Fs.Address “3B” Hex is for Broadcast
mode.
In doingmulti-cast (group) addressing, a scanned-inaddress
is compared against the (previously scanned-in) contents of
a ’PSC110F’s Multi-Cast Group register. Binary address
codes “111110” through “111111” (“3A” through “3F” Hex) are
reserved for multi-cast addressing, and should not be assigned as ’PSC110F slot-input values.
Boundary-Scan Register
The boundary-scan register is a “sample only” shift register
containing cells from the S
(0–5)
and OE inputs. The register
allows testing of circuitry external to the ’PSC110F. It permits
the signals flowing between the system pins to be sampled
and examined without interfering with the operation of the
on-chip system logic.
The scan chain is arranged as follows:
TDI
B
→OE→
S
5
→
S
4
→
S
3
→
S
2
→
S
1
→
S
0
→
LSPN→TDO
B
Bypass Register
The bypass register is a1-bit register that operates as specified in IEEE Std. 1149.1 once the ’PSC110F has been selected. The register provides a minimum length serial path
for the movement of test data between TDI
B
and the LSPN.
This path can be selected when no other test data register
needs to be accessed during a board-level test operation.
Use of the bypassregister shortens the serial access-path to
test data registers located in other components on a
board-level test data path.
Multi-Cast Group Register
“Multi-cast” is a method of simultaneously communicating
with more than one selected ’PSC110F.
The multi-cast group register(MCGR) is a 2-bit register used
to determine which multi-cast group a particular’PSC110F is
assigned to. Four addresses are reserved for multi-cast addressing. When a ’PSC110F is in the
Wait-For-Address
state
and receives a multi-cast address, and if that ’PSC110F’s
MCGR contains a matching value for that multi-cast address, the ’PSC110F becomes selected and is ready to receive Level 2 Protocol (i.e., further instructions).
The MCGR is initialized to “00” upon entering the
Test-Logic-Reset
state.
The following actions are used to perform multi-cast addressing:
1. Assign all target ’PSC110Fs to a multi-cast group by
writing each individual target ’PSC110F’s MCGR with
the same multi-cast group code (see
Table6
). This configuration step must be done by individually addressing
each target ’PSC110F, using that chip’s assigned slot
value.
2. Scan out the multi-cast group address through the TDI
B
input of
all
’PSC110Fs. Note that this occurs in parallel,
resulting inthe selection of only those’PSC110Fs whose
MCGR was previously programmed with the matching
multi-cast group code.
TABLE 6. Multi-Cast Group Register Addressing
MCGR Hex Address Binary Address
Bits 1, 0
00 3C XX111100
01 3D XX111101
10 3E XX111110
11 3F XX111111
DS100327-11
FIGURE 10. Local Scan Port Synchronization from
Parked-RTI
State
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com 14
Page 15
Register Descriptions (Continued)
TABLE 7. Mode Register Control of LSPN
Mode Register Scan Chain Configuration (If unparked)
XXX0X000 TDI
B
→
Register→TDO
B
XXX0X001 TDI
B
→
Register→LSP
1
→
PAD→TDO
B
XXX0X010 TDI
B
→
Register→LSP
2
→
PAD→TDO
B
XXX0X011 TDI
B
→
Register→LSP
1
→
PAD→LSP
2
→
PAD→TDO
B
XXX0X100 TDI
B
→
Register→LSP
3
→
PAD→TDO
B
XXX0X101 TDI
B
→
Register→LSP
1
→
PAD→LSP
3
→
PAD→TDO
B
XXX0X110 TDI
B
→
Register→LSP
2
→
PAD→LSP
3
→
PAD→TDO
B
XXX0X111 TDI
B
→
Register→LSP
1
→
PAD→LSP
2
→
PAD→LSP
3
→
PAD→TDO
B
XXX1XXXX TDI
B
→
Register→TDO
B
(Loopback)
X=don’t care
Register=’PSC110F instruction register or any of the ’PSC110F test data registers
PAD=insertion of a 1-bit register for synchronization
Mode Register
The mode register is an 8-bit data register used primarily to
configure the Local Scan Port Network. The mode register is
initialized to “00000001” binary upon entering the
Test-Logic-Reset
state.
Bits 0, 1, 2, and 4 are used for scan chain configuration as
described in
Table 7
. When the
UNPARK
instruction is ex-
ecuted, the scan chain configuration will be as shown in
Table 7
above. When all LSPs are parked, the scan chain
configuration will be TDI
B
→
’PSC110F-register→TDO
B
. Bit 3
is used for TCK
Ln
configuration, see
Table 8
.
TABLE 8. Test Clock Configuration
Bit 3 LSP
n
TCK
Ln
1 Parked Stop
0 Parked Run
1 Unparked Run
0 Unparked Run
Bit 3 is normally set to logic “0” so that TCK
L
is free-running
when the local scan ports are parked. When the local ports
are parked, bit 3 can be programmed with logic “1”, forcing
all of the LSP TCK
L
’s to stop. This feature can be used in
power sensitive applications to reduce the power consumed
by the test circuitry in parts of the system that are not under
test.
Bit 3 of the mode register must be reset to logic “0”
before the UNPARK instruction is executed.
Bit 7 is a status bit for the TCK counter. When the counter is
on and has reached terminal count (Zero) Bit 7 of the mode
register will be high (logic “1”). Bit 7 is read-only and will be
low in all other conditions.
Bits 5 and 6 are reserved for future use.
Device Identification Register
The device identification register (IDREG) is a 32-bit register
compliant with IEEE Std. 1149.1. When the
IDCODE
instruction is active, the identification register is loaded with the
value “0FC0E01F” Hex upon leaving the
Capture-DR
state
(on the rising edge of the TCK
B
).
TABLE 9. Detailed Device Identification (Binary)
Bits
31–28
Bits 27–12 Bits 11–1 Bit
0
Version Part Number Manufacturer 1
Identity
0000 1111 1100 0000
1110
0000 0001 111 1
Linear Feedback Shift Register
The ’PSC110F contains a “signature compactor” which supports test result evaluation in a multi-chain environment. The
signature compactorconsists of a 16-bit linear-feedbackshift
register (LFSR) which can monitor local-port scan data as it
is shifted “upstream” from the ’PSC110F’s local-port network. Once the LFSR is enabled, the LFSR’s state changes
in a reproducible way as each local-port data bit is shifted in
from the local-port network. When all local-port data has
been scanned in, the LFSR contains a16-bit signature value
which can be compared against a signature computed for
the expected results vector.
The LFSR uses the following feedback polynomial:
F(x)=X
16+X12+X3
+X+1
This signature compactor is used to compress serial data
shifted in from the local scan chain, into a 16-bit signature.
This signaturecan then be shifted out for comparison with an
expected value. This allows users to test long scan chains in
parallel, via Broadcast or Multi-Cast addressing modes, and
check only the 16-bit signatures from each module.
The LFSR is initialized with a value of “0000” Hex upon reset.
32-Bit TCK Counter Register:
The 32-bitTCK counter register enables BIST testingthat requires “n” TCK cycles, to be run on a parked LSP while another ’PSC110F port is being tested. The
CNTRSEL
instruction can be used to load a count-down value into the counter
register via the active scan chain. When the counter is enabled (via the
CNTRON
instruction), and the LSP is parked,
the local TCKs will stopand be held low when terminal count
is reached.
The TCK counter is initialized with a value of “00000000”
Hex upon reset.
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com15
Page 16

Special Features
BIST SUPPORT
The sequence of instructionsto run BIST testing on a parked
SCANPSC110F Bridge port is as follows:
1. Pre-load the Boundaryregister of the device under test if
needed.
2. Initialize the TCK counter to 00000000 Hex. Note that
the TCK counter is initialized to 00000000 Hex upon
Test-Logic-Reset
, so this step may not be necessary.
3. Issue the
CNTRON
instruction to the ’PSC110F, to en-
able the TCK counter.
4. Shift the
PARKRTI
instruction into the ’PSC110Finstruc-
tion register and
BIST
instruction into the instruction reg-
ister of the device under test.
5. Issue the
CNTRSEL
instruction to the ’PSC110F.
6. Load the TCK counter (Shift the 32-bit value representing the number of TCK
L
cycles needed to execute the
BIST operation into the TCK counter register).
7. Bit 7 of the Mode register can be scanned to check the
status of the TCK counter, (
MODESEL
instruction fol-
lowed by a
Shift-DR
). Bit 7 logic “0” means the counter
has not reached terminal count, logic “1” means that the
counter has reached terminal count and the BIST operation has completed.
8. Execute the
CNTROFF
instruction.
9. Unpark the LSP and scan out the result of the BIST operation (the
CNTROFF
instruction must be executed be-
fore unparking the LSP).
The Self test will begin on the rising edge of TCK
B
following
the
Update-DR
TAP controller state.
RESET
Reset operations canbe performed at three levels.The highest level resets all ’PSC110F registers and all of the local
scan chains of selected and unselected ’PSC110Fs. This
“Level 1” reset is performed whenever the ’PSC110F TAP
Controller enters the
Test-Logic-Reset
state.
Test-Logic-Reset
can be entered synchronously by forcing
TMS
B
high for at least five (5) TCKBpulses, or asynchronously by asserting the TRST pin.A “Level 1” reset forces all
’PSC110Fs into the
Wait-For-Address
state, parks all local
scan chains in the
Test-Logic-Reset
state, and initializes all
’PSC110F registers.
TABLE 10. Reset Configurations for Registers
Register Bit Width Initial Hex Value
MCGR 2 0
Instruction 8 AA (
IDCODE
Instruction)
Mode 8 01
LFSR 16 0000
32-Bit Counter 32 00000000
The
SOFTRESET
instruction is provided to perform a “Level
2” reset of all LSP’s of selected ’PSC110Fs.
SOFTRESET
forces all TMSLsignals high, placing the corresponding local
TAP Controllers in the
Test-Logic-Reset
state within five (5)
TCK
B
cycles.
The third level of reset is the resetting of individual local
ports. An individual LSP can be reset by parking the port in
the
Test-Logic-Reset
state via the
PARKTLR
instruction. To
reset an individual LSP that is parked in one of the other
parked states, the LSP must first be unparked via the
UN-
PARK
instruction.
PORT SYNCHRONIZATION
When a LSP is not being accessed, it is placed in one of the
four TAP Controller states:
Test-Logic-Reset, Run-Test/Idle,
Pause-DR,
or
Pause-IR.
The ’PSC110F is able to park a local chain by controlling the local Test Mode Select outputs
(TMS
L(1–3)
) (see
Figure 4
). TMSLnis forced high for parking
in the
Test-Logic-Reset
state, and forced low for parking in
Run-Test/Idle, Pause-IR,orPause-DR
states. Local chain
access is achieved by issuing the
UNPARK
instruction. The
LSPs do not become unparkeduntil the ’PSC110F TAP Controller is sequenced through a specified synchronization
state. Synchronization occurs in the
Run-Test/Idle
state for
LSPs parked in
Test-Logic-ResetorRun-Test/Idle;
and in the
Pause-DRorPause-IR
state for ports parked in
Pause-DR
or
Pause-IR,
respectively.
Figures 11, 12
show the waveforms for synchronization of a
local chain that was parked in the
Test-Logic-Reset
state.
Once the
UNPARK
instruction is received in the instruction
register, the LSPC forces TMS
L
low on the falling edge of
TCK
B
.
This moves the local chain TAPControllers to the synchronization state
(Run-Test/Idle)
, where they stay until synchroni-
zation occurs. If the next state of the ’PSC110F TAPControl-
ler is
Run-Test/Idle
, TMSLis connected to TMSBand the
local TAP Controllers aresynchronized to the ’PSC110FTAP
Controller as shown in
Figure 12
. If the next state after
DS100327-15
FIGURE 11. Local Scan Port Synchronization on Second Pass
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com 16
Page 17

Special Features (Continued)
Update-IR
were
Select-DR
, TMSLwould remain low and
synchronization would not occur until the ’PSC110F TAP
Controller entered the
Run-Test/Idle
state, as shown in
Fig-
ure 11
.
Each local port has its own Local Scan Port Controller. This
is necessary because the LSPN can be configured in any
one of eight (8) possible combinations. Either one, some, or
all of the local ports can be accessed simultaneously. Configuring the LSPN is accomplished with the mode register, in
conjunction with the
UNPARK
instruction.
The LSPN can be unparked in one of seven different configurations, as specified by bits 0-2 of the mode register. Using multiple ports presents not only the task of synchronizing
the ’PSC110F TAPController with the TAPControllers of an
individual local port, but also of synchronizing the individual
local ports to one another.
When multiple local ports are selected for access, it is possible that two ports are parked in different states. This could
occur when previous operations accessed the two ports
separately and parked them in the two different states. The
LSP Controllers handle this situation gracefully.
Figure 12
shows the
UNPARK
instruction being used to access LSP1,
LSP
2
, and LSP3in series (mode register=“XXX0X111” bi-
nary). LSP
1
and LSP2become active as the ’PSC110F con-
troller is sequenced through the
Run-Test/Idle
state. LSP
3
remains parked in the
Pause-DR
state until the ’PSC110F
TAPController is sequenced through the
Pause-DR
state.At
that point, all three local ports are synchronized for access
via the active scan chain.
DS100327-14
FIGURE 12. Synchronization of the Three Local Scan Ports (LSP1, LSP2, and LSP3)
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com17
Page 18
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 5)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage (V
CC
) −0.5V to +7.0V
DC Input Diode Current (I
IL
)
V
I
=
−0.5V −20 mA
V
I
=
V
CC
+0.5V +20 mA
DC Input Voltage (V
I
) −0.5V to VCC+0.5V
DC Output Diode Current (I
OK
)
V
O
=
−0.5V −20 mA
V
O
=
V
CC
+0.5V +20 mA
DC Output Voltage (V
O
) −0.5V to VCC+0.5V
DC Output Source/Sink Current (I
O
)
±
50 mA
DC V
CC
or Ground Current
±
50 mA
per Output Pin
DC Latchup Source or Sink Current
±
300 mA
Junction Temperature
Ceramic +175˚C
Storage Temperature −65˚C to +150˚C
ESD Last Passing Voltage (Min) 4000V
Recommended Operating
Conditions
Supply Voltage (VCC)
SCANPSC110F 4.5V to 5.5V
Input Voltage (V
I
) 0VtoV
CC
Output Voltage (VO) 0VtoV
CC
Operating Temperature (TA)
Military −55˚C to +125˚C
Minimum Input Edge Rate dV/dt
SCAN “F” Series Devices 125 mV/ns
V
IN
from 0.8V to 2.0V
V
CC
@
4.5V, 5.5V
Note 5: Absolute maximum ratings are those values beyond which damage
to the device may occur. The databook specifications should be met, without
exception, to ensure that the system design is reliable over its power supply
temperature, and output/input loading variables. National does not recommended operation of SCAN outside of recommended operation conditions.
DC Electrical Characteristics
Symbol Parameter V
CC
(V)
Military Units Conditions
T
A
=
−55˚C to +125˚C
Guaranteed
Limits
V
IH
Minimum High 4.5 2.0 V V
OUT
=
0.1V or
Input Voltage 5.5 2.0 V
CC
−0.1V
V
IL
Maximum Low 4.5 0.8 V V
OUT
=
0.1V or
Input Voltage 5.5 0.8 V
CC
−0.1V
V
OH
Minimum High 4.5 4.4 I
OUT
=
−50 µA
(TCK
Ln
, TMSLn, Output Voltage 5.5 5.4 V VIN(TDIB, TMSB,
TDO
Ln
) TCKB)=V
IH
V
OH
Minimum High 4.5 3.7 I
OUT
=
−24 mA
(TCK
Ln
, TMSLn, Output Voltage 5.5 4.7 V VINon S
(0-5)
and
TDO
Ln
) TDl
(1–3)
=
V
IH,VIL
All Outputs Loaded
V
OH
Minimum High 4.5 3.15 V I
OUT
=
−50 µA
(TDO
B
) Output Voltage 5.5 4.15
V
OH
Minimum High 4.5 2.4 V I
OUT
=
−24 mA
(TDO
B
) Output Voltage 5.5 2.4 All Outputs Loaded
V
OL
Maximum Low 4.5 0.1 I
OUT
=
+50 µA
(TCK
Ln
,TMSLn, Output Voltage 5.5 0.1 V VIN(TDIB, TMSB,
TDO
Ln
) TCKB)=V
IL
V
OL
Maximum Low 4.5 0.50 I
OUT
=
+24 mA
(TCK
Ln
,TMSLn, Output Voltage 5.5 0.50 V VINon S
(0–5)
and
TDO
Ln
) TDI
(1–3)
=
V
IH,VIL
All Outputs Loaded
V
OL
Maximum Low 4.5 0.1
V
I
OUT
=
+50 µA
(TDO
B
) Output Voltage 5.5 0.1
V
OL
Maximum Low 4.5 0.55 V I
OUT
=
+48 mA
(TDO
B
) Output Voltage 5.5 0.55 All Outputs Loaded
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com 18
Page 19

DC Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Symbol Parameter V
CC
(V)
Military Units Conditions
T
A
=
−55˚C to +125˚C
Guaranteed
Limits
I
IN
(OE, Maximum Input 5.5
±
1.0 µA V
IN
=
V
CC
or
TCK
B,S(0–5)
) Leakage Current V
IN
=
GND
I
IN, MAX
Maximum Input V
IN
=
V
CC
(TRST, TDILn, Leakage Current 5.5 3.7 µA
TDI
B
, TMSB)
I
IN, MAX
Maximum Input V
IN
=
GND
(TRST, TDI
Ln
, Leakage Current 5.5 −385 µA
TDI
B
, TMSB)
I
IN, MIN
Minimum Input V
IN
=
GND
(TDI
B
, TMSB, Leakage Current 5.5 −160 µA
TRST, TDI
Ln
)
I
CCT
Maximum
I
CC
/Input
5.5 1.6 mA V
IN
=
V
CC
−2.1V
I
CCT
Maximum V
IN
=
V
CC
−2.1V
(TDI
B
, TMSB,I
CC
/Input 5.5 1.75 mA Test one at a time
TRST, TDI
L
) with others floating
I
CC
Maximum
Quiescent
5.5 168 µA
TDIB, TMSB, TRST,
Supply Current TDI
L
=
V
CC
I
CC, MAX
Maximum
Quiescent
5.5 2.5 mA
TDIB, TMSB, TRST,
Supply Current TDI
L
=
GND
I
OLD
Minimum V
OLD
=
1.65V max
(TCK
Ln
, TMSLn, Dynamic 5.5 50 mA VIN(OE)=V
IL
TDOLn) Output Current (Note 6)
I
OLD
Minimum V
OLD
=
0.8V
(TDO
B
) Dynamic 5.5 63 mA VIN(TRST)=V
IH
Output Current (Note 6)
I
OHD
Minimum V
OHD
=
3.85V max
(TCK
Ln
, TMSLn, Dynamic 5.5 −50 mA (Note 6)
TDO
Ln
) Output Current
I
OHD
Minimum Dynamic V
OHD
=
2.0V max
(TDO
B
) Output Current 5.5 −27 mA (Note 6)
I
OZ
Maximum VIN(OE)=V
IH
TRI-STATE
®
5.5
±
10.0 µA VIN(TRST)=V
IL
Leakage Current V
O
=
V
CC
, GND
I
OS
Output Short 5.5 −100 mA V
O
=
0.0V
(TDO
B
) Circuit Current min (Note 7)
Note 6: Maximum test duration of 2 ms. One output loaded at a time.
Note 7: Maximum test duration not to exceed 1 second.
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com19
Page 20

AC Electrical Characteristics
Symbol Parameter V
CC
(V)
Military Units Fig.
No.
T
A
=
−55˚C
to +125˚C
C
L
=
50 pF
Min Max
t
PHL
, Propagation Delay
t
PLH
TCK
B
↓
to TCK
Ln
5.0 3.0 15.0 ns
Figure 13
TCK
B
↑
to TCK
Ln
2.5 15.0
t
PHL
, Propagation Delay
t
PLH
TCK
B
↓
to TDO
Ln
5.0 3.0 16.5 ns
Figure 13
TCK
B
↓
to TDO
Ln
3.0 17.0
t
PHL
, Propagation Delay
t
PLH
TCK
B
↓
to TMS
Ln
5.0 3.5 26.5 ns
Figure 13
TCK
B
↓
to TMS
Ln
4.5 24.5
t
PHL
, Propagation Delay
t
PLH
TCK
B
↓
to TDO
B
5.0 3.0 17.0 ns
Figure 13
TCK
B
↓
to TDO
B
2.5 16.5
t
PHL
, Propagation Delay 5.0 2.5 14.5 ns
Figure 13
t
PLH
TMSBto TMS
Ln
1.5 14.5
t
PLH
Propagation Delay 5.0 4.5 30.0 ns
Figure 15
TRST to TMS
Ln
t
PZL
, Enable Time 5.0
t
PZH
TCK
B
↓
to TDO
Ln
4.0 22.5 ns
TCK
B
↓
to TDO
Ln
3.0 19.0
t
PLZ
, Disable Time
t
PHZ
TCK
B
↓
to TDO
Ln
5.0 1.5 15.5 ns
TCK
B
↓
to TDO
Ln
2.0 17.0
t
PZL
, Enable Time
t
PZH
TCK
B
↓
to TDO
B
5.0 4.0 20.5 ns
TCK
B
↓
to TDO
B
2.5 16.5
t
PLZ
, Disable Time
t
PHZ
TCK
B
↓
to TDO
B
5.0 2.0 16.5 ns
TCK
B
↓
to TDO
B
2.0 17.5
t
PZL
, Enable Time 5.0 3.0 19.5 ns
Figure 16
t
PZH
OE to TDO
Ln
3.0 17.5
t
PLZ
, Disable Time 5.0 1.0 14.0 ns
Figure 16
t
PHZ
OE to TDO
Ln
1.0 15.5
t
PZL
, Enable Time 5.0 2.0 14.5 ns
Figure 16
t
PZH
OE to TMS
Ln
1.5 13.0
t
PLZ
, Disable Time 5.0 1.0 12.0 ns
Figure 16
t
PHZ
OE to TMS
Ln
1.0 12.5
t
PZL
, Enable Time 5.0 2.0 14.5 ns
Figure 16
t
PZH
OE to TCK
Ln
1.5 13.0
t
PLZ
, Disable Time 5.0 1.0 12.0 ns
Figure 16
t
PHZ
OE to TCK
Ln
1.0 12.5
t
PLZ
, Disable Time 5.0 2.5 20.0 ns
Figure 15
t
PHZ
TRST to TDO
B
3.0 20.0
t
PLZ
, Disable Time 5.0 2.5 21.0 ns
Figure 15
t
PHZ
TRST to TDO
Ln
1.5 21.0
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com 20
Page 21

AC Electrical Characteristics
Symbol Parameter
V
CC
(V)
Military
Units
Fig.
No.
T
A
=
−55˚C
to +125˚C
C
L
=
50 pF
Guaranteed
Minimum
t
S
Setup Time 5.0 8.0
TMS
B
to TCK
B
↑
t
H
Hold Time 5.0 4.0 ns
Figure 13
TMSBto TCK
B
↑
t
S
Setup Time 5.0 6.0 ns
Figure 13
TDIBto TCK
B
↑
t
H
Hold Time 5.0 4.0 ns
Figure 13
TdIBto TCK
B
↑
t
S
Setup Time
S
n
to TCK
B
↓
5.0 12.5 ns
(in
Update-DR
state)
t
H
Hold Time
S
n
to TCK
B
↓
5.0 0.0 ns
(in
Update-DR
state)
t
S
Setup Time
S
n
to TCK
B
↑
5.0 4.0 ns
(in
Capture-DR
or
Capture-IR
state)
t
H
Hold Time
S
n
to TCK
B
↑
5.0 6.0 ns
(in
Capture-DR
or
Capture-IR
state)
t
S
Setup Time 5.0 2.0 ns
Figure 13
TDILnto TCK
B
↑
t
H
Hold Time 5.0 6.0 ns
Figure 13
TDILnto TCK
B
↑
t
S
Setup Time
OE to TCK
B
↑
5.0 4.0 ns
(in
Capture-DR
state)
t
H
Hold Time
OE to TCK
B
↑
5.0 4.0 ns
(in
Capture-DR
State)
t
W
Clock Pulse Width 5.0 24.0 ns
Figure 13
TCKB(H or L)
t
WL
Clock Pulse Width 5.0 10.0 ns
Figure 15
TRST (L)
t
REC
Recover Time 5.0 2.0 ns
Figure 15
TCK
B
↑
from TRST
t
OSHL
, Output-to-Output Skew 5.0 1.0 ns (Note 8)
t
OSLH
TCK
Ln
t
OSHL
, Output-to-Output Skew 5.0 2.0 ns (Note 8)
t
OSLH
TMSLn(unparked)
F
MAX
Maximum Clock Frequency 5.0 MHz
Note 8: Skew is defined as the absolute value of the difference between the actual propagation delays for any two separate outputs of the same device. The specification applies to any outputs switching HIGH to LOW (t
OSHL
), or LOW to HIGH (t
OSLH
). The specification is guaranteed but not tested.
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com21
Page 22

Capacitance
Symbol Parameter Typ Units Conditions
C
IN
Input Pin Capacitance 5.0 pF VCCis Open
C
OUT
Output Pin Capacitance 6.5 pF VCCis Open
C
PD
Power Dissipation Capacitance 50 pF V
CC
=
5.0V
AC Waveforms
DS100327-16
FIGURE 13. Waveforms for an Unparked SCANPSC110F Bridge in the SHIFT-DR (IR) TAP Controller State
DS100327-13
Note A: V
OHV
and V
OLP
are measured with respect to ground reference.
Note B: Input pulses have the following characteristics: f=1 MHz, t
r
=
3 ns, t
f
=
3 ns, skew ≤ 150 ps.
FIGURE 14. Quiet Output Noise Voltage Waveform
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com 22
Page 23

AC Waveforms (Continued)
DS100327-18
FIGURE 15. Reset Waveforms
DS100327-19
FIGURE 16. Output Enable Waveforms
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com23
Page 24

Appendix
Applications Example
The following sequence gives an example of how one might
use the SCANPSC110F Bridge to perform 1149.1 operations
via a multi-drop scan backplane. The system involved has
10 card slots, 8 of which are filled with modules, and 2 slots
are empty. (See
Figure 18
).
DS100327-17
Note: The value of the TMS during the rising edge of TCK is located next to each transition.
FIGURE 17. IEEE 1149.1 TAP Controller State Diagram
DS100327-20
FIGURE 18. Boundary Scan Backplane with 10 Card Slots, 8 Slots Are Filled with Boards
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com 24
Page 25

Applications Example (Continued)
More Information can be found in Application Notes:
AN-1023 Structural System Test via IEEE Std. 1149.1 with
SCANPSC110F Hierarchical and Multidrop Addressable JTAG Port
AN-1022 Boundary Scan, An Enabling Technology for
System Level Embedded Test
1. After the system is powered up a level-1 reset is performed via the TRST input. All TAP Controllers (both
’PSC110F and local) are asynchronously forced into the
Test-Logic-Reset
state. All LSP Controllers are in the
parked
Test-Logic-Reset
state; this forces the TMSLoutputs of each portto a logic “1”, keeping all board TAPsin
the
Test-Logic-Reset
state.
2. The first task of the tester is to find out which slots are
occupied onthe backplane. This is accomplishedby performing a serial poll of each slot address in the system,
as assigned by the S
0–5
value of each ’PSC110F in the
system.
Each target slot address is addressed by first sequenc-
ing all ’PSC110Fson the backplane to the
Shift-IR
state,
and then by shifting in the address of the target slot.The
’PSC110FTAP controller is then sequenced through the
Update-IR state. If a ’PSC110F with the matching slot
identification is present, it is selected. All other
’PSC110Fs are unselected. To determine whether that
slot contains a selected ’PSC110F, the tester must read
back the ’PSC110Fs S
0–5
value (if present).
The tester moves the selected ’PSC110F from the
Update-IR
state back to the
Shift-IR
state, and the instruction register is then scanned while loading the next
instruction
(GOTOWAIT)
. During the
Capture-IR
state of
the TAP Controller, a “01” pattern is loaded into the two
least significant bits of the ’PSC110F’s instruction register,and the most significant six bits capture the value on
the S
0–5
pins. The captured data is shifted out while the
GOTOWAIT command is shifted in. If an “all ones” pattern is returned, a board does not exist at that location.
(The “all ones” pattern is caused by the pull-up resistor
on the TDI input of the controller, as required for 1149.1
compliance.)
At the end of instruction register scan, the
GOTOWAIT
command is issued and all ’PSC110F selection controllers enter the
Wait-For-Address
state. This allows the
next ’PSC110Fin the polling sequence to be addressed.
The polling process is repeated for every possible board
address in the system. In this example, the tester finds
that boards
#
1 through#8 are present, and boards#9
and
#
10 are missing. Therefore, it will report back its
findings and will not attempt to test the missing boards.
3. Infrastructure testing of the populated boards may now
proceed. The tester addresses the ’PSC110F on Board
#
1 for test operations. ’PSC110F#1 is now selected,
while all others are unselected.
Board
#
1 is wired such that all LSPn’s are connected to
individual scan chains. The first objective is to test the
scan chain integrity of the board. For this task, it is more
efficient to configure the LSPN such that all three chains
are placed in series. To accomplish this, the
MODESEL
instruction is issued to place the mode register into the
active scan chain, and the binary value “00000111” is
shifted into the mode register. The
UNPARK
instruction
is then issued to access all three local chains.
Once the
UNPARK
instruction has been updated and
the ’PSC110FTAPcontroller is synchronized with the local TAP’s,the scan chain integrity test can be performed
on the local scan chains. This test is done by performing
a
Capture-IR
and then shifting the scan chain checking
the 2 least significant bits of each components instruction register for “01”. If the LSB’s of any component in
the scan chain are not “01”, the test fails. Diagnostic
software can be used to narrow down the cause of the
failure. Next the device identification of each component
in the scan chain is checked. This is done by issuing the
IDCODE
instruction to each component in the scan
chain. Components that do not support
IDCODE
will in-
sert their bypass register into the active scan chain.
After the IDCODE register scan, the
GOTOWAIT
instruction is issued to reset the local scan ports and return the ’PSC110F Selection controller to the
Wait-For-Address state. A sequence similar to step 3 is
repeated for each board in the system.
4. Next, the testeraddresses Board
#
1 to performinterconnect testing. For this task, it is efficient to configure the
LSPN such that all three chains are placed in series.
Therefore, the Mode register should be programmed
with the binary value “00000111” (this was done in step
3 above and need not be repeated unless a
Test-Logic-Reset
was performed since then). The
UN-
PARK
instruction is issued to access all three local
chains.
Once the
UNPARK
instruction has been loaded and the
’PSC110F is synchronized with the local TAPs, normal
1149.1 scan operations may commence. To test the interconnect on Board
#
1, an instruction register scan se-
quence is performed and the
SAMPLE/PRELOAD
instruction is loaded into the instruction register of all
target devices. The
BYPASS
instruction is loaded into
the instruction register of ’PSC110F
#
1. A data register
scan is now performed to preload the first test vector to
be applied to the interconnect.
5. After the preload operation is performed, an instruction
register scan is usedto load the
EXTEST
instruction into
all TAPs (
BYPASS
loaded into ’PSC110F#1). The appropriate sequencing is nowperformed to apply patterns
in order to test the interconnect on Board
#
1.
6. Upon completion of the interconnect test on Board
#
1,
the local chains must be parked. The
PARKTLR
command is loaded into the instruction register, and the
TMS
Ln
outputs of the three local chains are forced high,
sending the three local TAPs into the
Test-Logic-Reset
state.
7. Now that the Board
#
1 interconnect has been tested, the
interconnect on the other boards in the system must be
checked. All ’PSC110F are returned to the
Wait-For-Address
state by issuing the
GOTOWAlT
in-
struction. Board
#
2 is addressed next, followed by the
rest of the boards in the system. A sequence similar to
steps 4 through 6 is used for each board.
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com25
Page 26

Applications Example (Continued)
8. Assume that boards
#6,#
7 and#8 are identical, so that
it is possible to test them simultaneously. The tester first
addresses Board
#
6. Next the
MCGRSEL
instruction is
issued to place theMulti-Cast Group register into the active scan chain, and the binary value “01” is shifted into
the MCGR. The
GOTOWAIT
instruction is then issued
returning all ’PSC110F’s to the
Wait-For-Address
state.
The MCGR for ’PSC110F
#
7 and ’PSC110F#8 are pro-
grammed the sameas Board
#
6. Next theMulti-Cast address “00111101” is issued by the tester, which causes
the ’PSC110F Selection controller of ’PSC110F
#6–#
8
to enter the
Selected-Multi-Cast
state. The
LFSRON
instruction is then issued to enable the signature compaction circuitry on the selected ’PSC110Fs. The
SAMPLE/
PRELOAD
and
EXTEST
instructions are then used to
test the interconnects, similar to steps 4 and 5 above.
When the test sequence is complete, the
GOTOWAIT
instruction is issued returning all ’PSC110Fs to the
Wait-For-Address state
. ’PSC110Fs#6,#7, and#8 are
then addressed one at a time to read back the test signature from the LFSR (the LFSR is read by selecting it
with the
LFSRSEL
instruction, then scanning out itscon-
tents.
9. After testing the interconnect on the individual boards,
the next step is to test the backplane interconnect. This
is a pair-wise test between Board
#
1 and each of the
other boards. Board
#
1 drives test patterns onto th backplane wiring, and the currently addressed slave board
senses the written data via its backplane scan interface.
In this example, the interconnect between Board
#
1 and
Board
#
2 is tested first. To test this interconnect, the
1149.1-compliant backplane transceivers,
SCAN182245A, SCAN ABT TestAccess Logic, on each
board must beaccessed for scan operations (see
Figure
19
). For more information on SCAN ABT live insertion
capabilities, refer to the SCAN182245A datasheet.
First, the system master (Board
#
1) is addressed and
selected. The 1149.1-compliantSCAN ABT transceivers
reside on thechain connected to LSP
2
on Board#1. The
mode register is re-configured so that only port LSP
2
is
in the chain, and the
UNPARK
instruction is then used to
access this chain. The appropriate instruction register
and data register scan sequencing is then performed to
apply a pattern to the backplane using the SCAN ABT
bus transceiver.
10. To test the backplane interconnect, LSP
2
of Board#1
must be parked in the
Run-Test/Idle
TAP controller
state, so that the EXTEST command will stay active
when Board
#
1 is de-selected (the
PARKRTI
instruction
is issued). The
GOTOWAIT
instruction is then issued to
return all boards to the
Wait-For-Address
state. Each
one of the slave boards is then addressed, one at a
time, to sample the backplane signals being driven by
Board
#
1. For example, Board#2 is addressed. The
mode register is reconfigured, (if needed), to select the
scan chain (LSP
2
) that includes the SCAN ABT back-
plane transceivers for Board
#
2. The
UNPARK
instruc-
tion is issued to unpark LSP
n
and insert it into the active
scan chain. The
SAMPLE/PRELOAD
instruction is is-
sued to the SCAN ABT backplane transceivers, (
BY-
PASS
to other components in the scan chain). The
backplane is sampled by sequencing the TAP controller
through the
Capture-DR
state and the data is shifted out
and checked by the tester. The
PARKRTI
instruction is
then given to parkLSP
n
of Board#2inthe
Run-Test/Idle
state, and the
GOTOWAIT
instruction is issued to return
all ’PSC110Fs to the
Wait-For-Address
state so that the
next board, (Board
#
3), can be sampled.This procedure
is repeated for boards
#3–#
8, then Board#1 is selected
again, a new pattern is shifted out and driven by the
EX-
TEST
command, and the slave boards are again
sampled.
11. Step 10 is repeated until the backplane interconnect has
been sufficiently tested.
12. When testing is complete, the controller sends out the
SOFTRESET
instruction to all ’PSC110Fs. This is accomplished by first using the broadcast address, “3B”
Hex, to select all ’PSC110Fs. The
SOFTRESET
com-
mand is then loaded, causing TMS
L(1–3)
signals to go
high; this drives all local TAPs into the
Test-Logic-Reset
state within five TCK cycles.
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com 26
Page 27

Applications Example (Continued)
DS100327-21
FIGURE 19. Testing the Backplane Interconnections
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com27
Page 28

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
28-Pin Leadless Chip Carrier (LCC)
NS Package Number E28A
28-Pin Ceramic DIP
NS Package Number J28A
SCANPSC110F
www.national.com 28
Page 29

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted (Continued)
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL
COUNSEL OF NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or
systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and
whose failure to perform when properly used in
accordance with instructions for use provided in the
labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a
significant injury to the user.
2. A critical component is any component of a life
support device or system whose failure to perform
can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of
the life support device or system, or to affect its
safety or effectiveness.
National Semiconductor
Corporation
Americas
Tel: 1-800-272-9959
Fax: 1-800-737-7018
Email: support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Europe
Fax: +49 (0) 1 80-530 85 86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-530 85 85
English Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-532 78 32
Français Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-532 93 58
Italiano Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-534 16 80
National Semiconductor
Asia Pacific Customer
Response Group
Tel: 65-2544466
Fax: 65-2504466
Email: sea.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Japan Ltd.
Tel: 81-3-5639-7560
Fax: 81-3-5639-7507
www.national.com
28-Pin Flatpak
NS Package Number WA28D
SCANPSC110F SCAN Bridge
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
 Loading...
Loading...