NSC PC97338VJG Datasheet
PC87338 /PC97338
ACPI 1.0 and PC98/9 9 Co mp l iant Sup erI/O
PC87338/PC97338 ACPI 1.0 and PC98/99 Compliant SuperI/O
November 1998
General D escription
The PC97338 is a fully ACPI 1.0 and PC98/99 c ompliant, ISA based Super I/O. It is functionally compatible with the PC87338. It includes a Floppy Disk
Controller (FDC), two Serial Communication Con trollers (SCC) for UART and Infrared support, one
IEEE1284 compatible Parallel Port, and two g eneral
purpose Chip Select signals for game port support.
The device supports powe r management as well as
3.3V and 5V mixed operation making it particularly
suitable for notebook and sub-notebook applications.
The PC87338 and PC97338 are fully compliant to the
Plug and Play specifications included in the "Hardware Design Guide for Microsoft Windows 95".
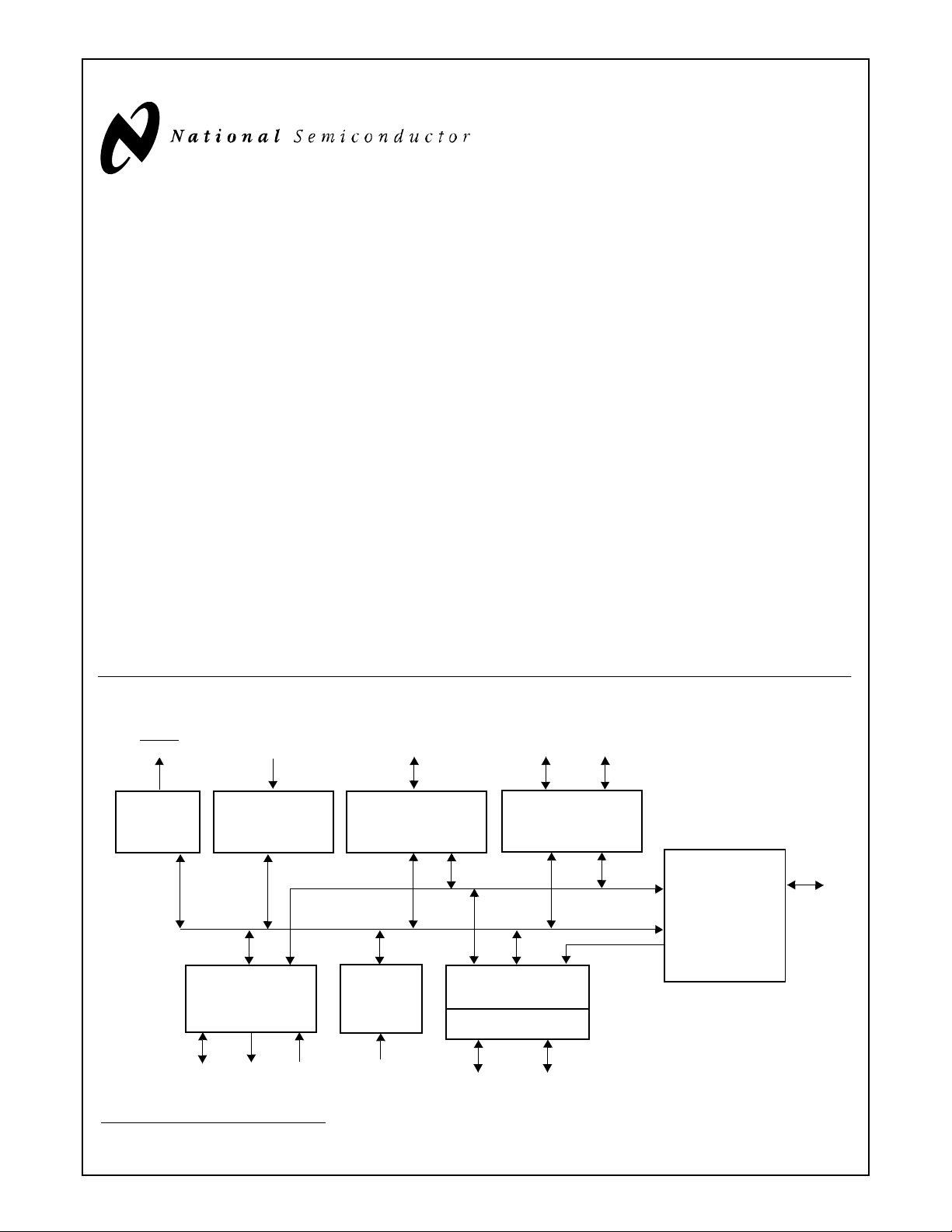
Block Diagram
Configuration Input
CS1,0
Signals
Serial Interfac e
Differences between the PC873 38 and PC97338 are
indicated in italics. These differences are summarized
in Appendix A.
Features
■ Meets ACPI 1.0 and PC98/99 requirements
■ Backward compatible with PC87338
■ 100% compatibility with Plug and Play require-
ments specified in the “
Microsoft Windows 95
Channel architectures
■ A special Plug and Play module includes:
Flexible IRQs, DMAs and base addresses
—
General Interrupt Requests (IRQs) that can be
—
multiplexed to the ten supported IRQs
Serial
Interface
Fast IR
Interface
Hardware Design Guide for
”, ISA, EISA, and Micro-
General
Chip Select
Microprocessor
Address
Data and
Control
©
1998 National Semiconductor Corporation
Channels
TRI-STATE® is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
®
IBM
, MicroChannel®, PC-AT® and PS/2® are registered trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation.
®
Microsoft
and Windows® are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Configuration
Plug and Play
Support
DMA
IRQ
Registers
IRQ Input
Signals
SCC1
(16550 UART)
Interrupt
and DMA
Power-
Down
Logic
Control
SCC2
(16550 UART +
INFRARED)
IEEE1284
Parallel Port
High Current Driver
Data Handshake
1
Floppy
Drive
Interface
Floppy Disk
Control ler (FDC)
with
Digital Data
Separator (DDS)
(Enhanced 8477)
www.national.com
Floppy
Drive
Interface
■ A new, high performance, on-chip Floppy Disk
Controller (FDC) provides:
— Software compatibility with the PC8477, which
contains a superset of the floppy disk controller
functions in the µDP8473, the NEC µP D 765A
and the N82077
— A modifiable 13-bit address
— Ten IRQ channel options
— Four 8-bit DMA channel options
— 16-byte FIFO
— Burst and non-burst modes
— Low-power CMOS with enhanced power-down
mode
— A new, high-performance, on-chip, digital data
separator without external filter components
— Support for 5.25"/3.5" floppy disk drives
— Automatic media sense support
— Perpendicular recording drive support
— Three mode Floppy Disk Drive (FDD) support
— Full support for IBM’s Tape Drive Register
(TDR) implementation
— Support for new fast tape drives (2 Mbps) and
standard tape drives (1 Mbps, 500 Kbps and
250 Kbps)
— Support for both
FM
and MFM modes
.
■ Two Serial Communication Controllers provide:
— Software compatibility with the 16550A and the
16450
— A modifiable 13-bit address
— Ten IRQ channel options
— MIDI baud rate support
— Four 8-bit DMA channel options on SCC2
— Shadow register support UART write-only bits
■ A fast universal Infrared interface on SCC2 supports the following:
— Data rates of up to 115.2 Kbps (SIR)
— A data rate of 1.152 Mbps (MIR)
— A data rate of 4.0 Mbps (FIR)
— Selectable internal or external modulation /de-
modulation (Shar p-IR)
— Consumer Electronic IR mode
■ A bidirectional parallel port that includes:
— A modifiable 13-bit address
— Ten IRQ channel options
— Four 8-bit DMA channel options
— An Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) compatible
with version EPP 1.9 (IEEE1284 compliant),
that also supports version EPP 1.7 of the Xircom specification.
— An Extended Capabilities Port (ECP) that is
IEEE1284 compliant, including level 2
— Bidirectional data transfer under either soft-
ware or hardware control
— Compatib ility with ISA, EISA , and M icroChan-
nel parallel ports
— Multiplexing of additional external FDC signals
on parallel port pins that enables use of an external Floppy Disk Drive (FDD)
— A protection circuit that prevents damage to the
parallel port when an external printer powers
up or operates at high voltages
— 14 mA output drivers
■ Two general purpose pins for two programm able
chip select signals can be program med for game
port control.
■ An address decoder that:
— Selects all primary and secondary ISA ad-
dresses, including COM1-4 and LPT1-3
— Decodes up to 16 address bits
■ Clock source:
— An internal clock multiplier generates all re-
quired internal frequencies.
— A clock input source 14.318 M Hz, 24 MHz, or
48 MHz may be selected
■ Enhanced power managem ent features:
— Special power-down configuration registers
— Enhanced programmable FDC command to
trigger power down
— Programmable power-down and wake-up
modes
— Two dedicated pins for FDC power manage-
ment
— Low power-down current consumption (typical-
ly for PC97338, 400 µA for 3.3V and 600 µA for
5V application)
— Reduced pin leakage current
— Low power CMOS technology
— The ability to shut off clocks to either the entire
chip or only to specific modules
■ Mixed voltage support provides:
— Standard 5 V operation
— Low voltage 3.3 V operation
— Simultaneous internal 3.3 V operation and re-
ception or transmission to devices that have either 3.3 V or 5 V power supply
■ 100-pin TQFP VJG package - PC87338/PC97338
■ 100-pin PQFP VLJ package - PC87338/PC 97338
2
www.national.com
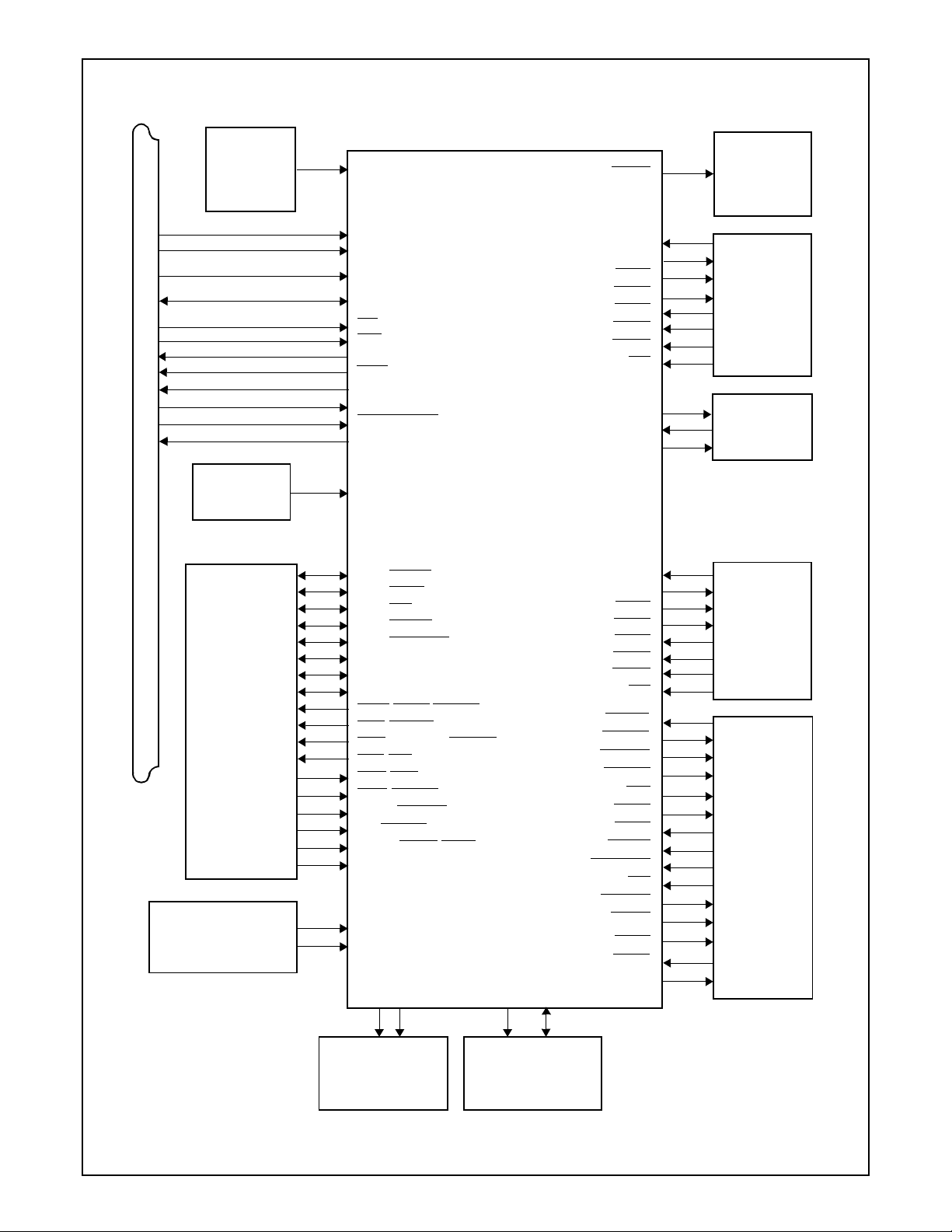
Basic Configuration
Clock
External
ISA Bus
Device
Parallel
Port
Connector
Configuration
Selectio n Logic
X1(CLKIN)
MR
AEN
A0-A15
D0-D7
RD
WR
IOCHRDY
ZWS
IRQ3-7, 9-12, 15
TC
DACK0,1,2,3
DRQ0,1,2,3
SIRQI1,2,3
PC87338VLJ
PC87338VJG
Super I/O
PD0/INDEX
PD1/TRK0
PD2/WP
PD3/RDATA
PD4/DSKCHG
PD5/MSEN0
PD6/DRATE0
PD7/MSEN1
SLIN
/STEP/ASTRB
STB/WRITE
AFD/DENSEL/DSTRB
INIT/DIR
ACK/DR1
ERR/HDSEL
SLCT/WGATE
PE/WDATA
BUSY/MTR1/WAIT
PNF
BADDR0,1
CFG0
IDLE
PD
BOUT1/SOUT1
BOUT2/SOUT2
DRATE0,1/MSEN0,1
ADRATE0,1
CS0,1
SIN1
RTS1
DTR1
CTS1
DSR1
DCD1
RI1
IRTX
IRRX1,2
IRSL0-2
SIN2
RTS2
DTR2
CTS2
DSR2
DCD2
RI2
RDATA
WDATA
WGATE
HDSEL
DIR
STEP
TRK0
INDEX
DSKCHG
WP
IDLE/MTR0,1
DR0,1
DR23
DRV2
DENSEL
Game
Port
EIA
Drivers
IR
Interface
EIA
Drivers
FDC
Connector
External
Power Dow n
Control
FDC
Configuration
Logic
3
www.national.com
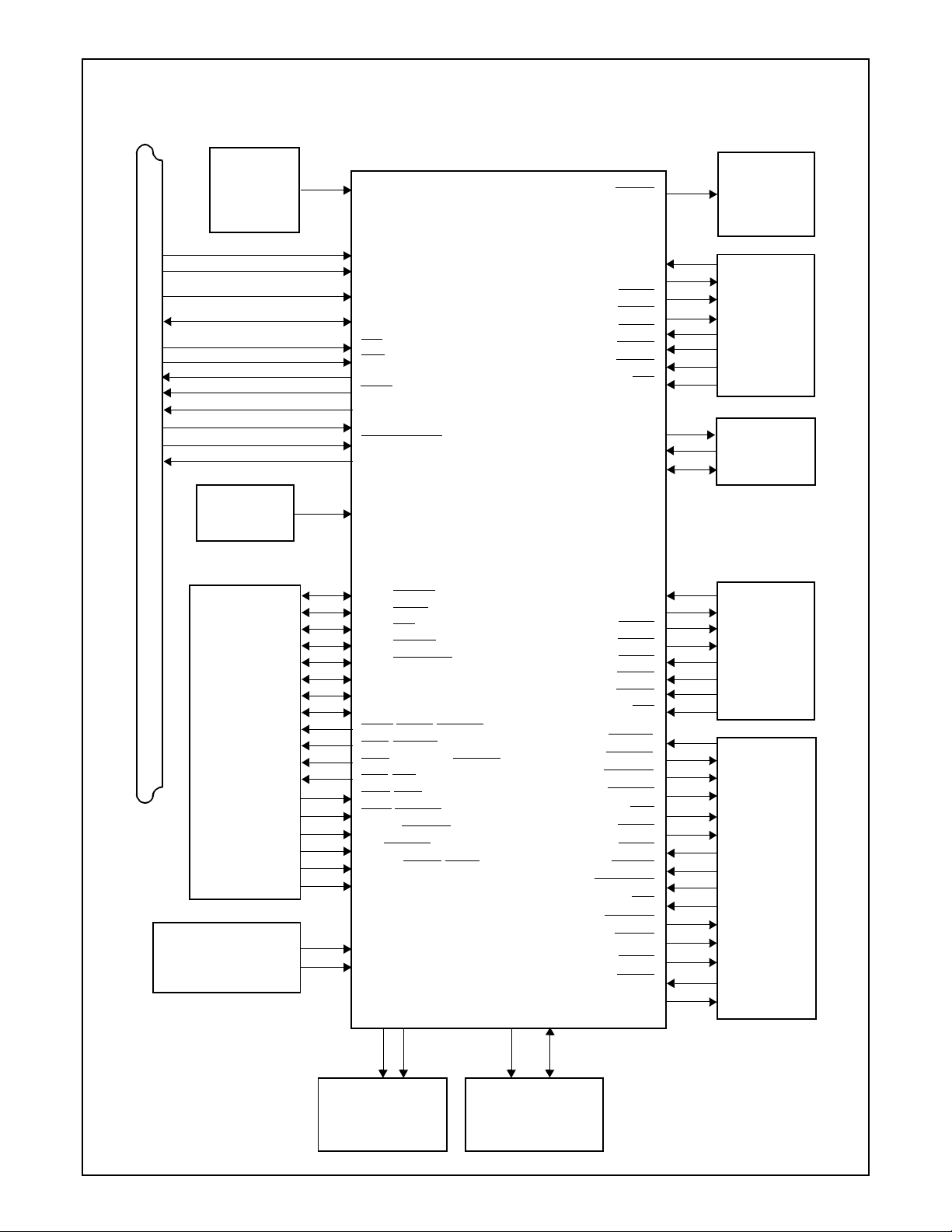
Basic Configuration
Clock
External
ISA Bus
Device
Parallel
Port
Connector
Configuration
Selectio n Logic
X1(CLKIN)
MR
AEN
A0-A15
D0-D7
RD
WR
IOCHRDY
ZWS
IRQ3-7, 9-12, 15
TC
DACK0,1,2,3
DRQ0,1,2,3
SIRQI1,2,3
PC97338VLJ
PC97338VJG
Super I/O
PD0/INDEX
PD1/TRK0
PD2/WP
PD3/RDATA
PD4/DSKCHG
PD5/MSEN0
PD6/DRATE0
PD7/MSEN1
SLIN
/STEP/ASTRB
STB/WRITE
AFD/DENSEL/DSTRB
INIT/DIR
ACK/DR1
ERR/HDSEL
SLCT/WGATE
PE/WDATA
BUSY/MTR1/WAIT
PNF
BADDR0,1
CFG0
IDLE
PD
CS0,1
SIN1
SOUT1
RTS1
BOUT1/DTR1
CTS1
DSR1
DCD1
RI1
IRTX
IRRX1,2
IRSL0-2/ID0-2
SIN2
SOUT2
RTS2
BOUT2/DTR2
CTS2
DSR2
DCD2
RI2
RDATA
WDATA
WGATE
HDSEL
DIR
STEP
TRK0
INDEX
DSKCHG
WP
IDLE/MTR0,1
DR0,1
DR23
DRV2
DENSEL
DRATE0,1/MSEN0,1
ADRATE0,1
Port
EIA
Drivers
IR
Interface
EIA
Drivers
FDC
Connec t or
Game
Exter n al
Power Down
Control
FDC
Configuration
Logic
4
www.national.com
Table of Contents
1.0 Pin Descriptions
1.1 CONNECTION DIAGRAMS .............................................................................................................18
1.2 SIGNAL/PIN DESCRIPTIONS ..........................................................................................................22
2.0 Configuration
2.1 OVERVIEW ......................................................................................................................................36
2.2 CONFIGURATION REGISTER SETUP ...........................................................................................36
2.2.1 Hardware Device Confi guration ..............................................................................................36
2.2.2 Software Device Configurat io n ............... ........................ ........................ ....................... ..........38
2.2.3 Updating Configuration Registers ........................................................................................... 38
2.2.4 Reserved Bits in Configurat ion Registers .... .......... ....................... ........................ ...................38
2.2.5 INDEX and DATA Register Locations .....................................................................................38
2.2.6 Plug and Play Protocol ............................................................................................................39
2.3 THE CONFIGURATION REGISTERS ..............................................................................................40
2.3.1 Configuration Register Bitmaps ...............................................................................................41
2.3.2 Function Enable Register (FER), Index 00h ............................................................................45
2.3.3 Function Address Register (FAR), Index01h .......................................................................... 47
2.3.4 Power and Test Register (PTR), Index 02h ........................................ ..... ....... ....... ....... ..... .....47
2.3.5 Function Control Register (FCR), Index03h ...........................................................................48
2.3.6 Printer Control Register (PCR), Index04h .............................................................................. 49
2.3.7 Power Management Control Register (PMC), Index 06h ........................................................50
2.3.8 Tape, SCCs and Parallel Port Configuration Register (TUP), Index 07h ................................51
2.3.9 SuperI/O Chip Identification Register (SID), Index 08h ...........................................................52
2.3.10 Advanced SuperI/O Chip Configuration Register (ASC), Index 09h .....................................52
2.3.11 Chip Select 0 Low Address Register (CS0LA), Index 0Ah ....................................................53
2.3.12 Chip Select 0 Configuration Register (CS0CF), Index 0B h ...................................................53
2.3.13 Chip Select 1 Low Address Register (CS1LA), Index 0Ch ....................................................54
2.3.14 Chip Select 1 Configuration Register (CS1CF), Index 0Dh ...................................................54
2.3.15 Chip Select 0 High Address Register (CS0HA), Index 10h ...................................................55
2.3.16 Chip Select 1 High Address Register (CS1HA), Index 11h ...................................................55
2.3.17 SuperI/O Chip Configuration Register 0 (SCF0), Index 1 2h .................................................55
2.3.18 SuperI/O Chip Configuration Register 1 (SCF1), Index 1 8h .................................................56
2.3.19 Plug and Play Configuration 0 Register (PNP0), Index 1Bh .................................................57
2.3.20 Plug and Play Configuration 1 Register (PNP1), Index 1Ch .................................................58
2.3.21 SuperI/O Chip Configuration Register 2 (SCF2), Index 4 0h .................................................58
2.3.22 Plug and Play Configuration 2 Register (PNP2), Index 41h ..................................................59
2.3.23 Parallel Port Base Address Low Byte Register (PBAL), Index42h .......................................60
2.3.24 Parallel Port Base Address High Byte Register (PBAH), Index 43h .....................................60
2.3.25 SCC1 Base Address Low Byte Register (S1BAL), Index 44h ...............................................61
2.3.26 SCC1 Base Address High Byte Register (S1BAH), Index 45h .............................................61
2.3.27 SCC2 Base Address Low Byte Register (S2BAL), Index 46h ...............................................61
2.3.28 SCC2 Base Address High Byte Register (S2BAH), Index 47h .............................................62
2.3.29 FDC Base Address Low Byte Register (FBAL), Index 48h ...................................................62
2.3.30 FDC Base Address High Byte Register (FBAH,) Index 49h . .................................................62
5
www.national.com
2.3.31 SIO Base Address Low Byte Register (SBAL), Index 4Ah ....................................................63
2.3.32 SIO Base Address High Byte Register (SBAH), Index4Bh .................................................. 63
2.3.33 System IRQ Input 1 Configuration Register (SIRQ1), Index 4Ch ..........................................63
2.3.34 System IRQ Input 2 Configuration Register (SIRQ2), Index 4Dh ..........................................64
2.3.35 System IRQ Input 3 Configuration Register (SIRQ3), Index 4Eh . .........................................65
2.3.36 Plug-and-Play Configuration 3 Register (PNP3), Index 4Fh .................................................66
2.3.37 SuperI/O Configuration 3 Register (SCF3), Index 50h ..........................................................67
2.3.38 Clock Co ntrol Register (CLK), Index 51h ..............................................................................68
2.3.39 Manufacturing Test Register (MTEST), Index 52h ................................................................68
3.0 The Digital Floppy Disk Controller (FDC)
3.1 FDC FUNCTIONS ............................................................................................................................69
3.1.1 Microprocessor Interface .........................................................................................................69
3.1.2 System Operation Modes ........................................................................................................ 70
3.2 DATA TRANSFER ............................................................................................................................70
3.2.1 Data Rates ..............................................................................................................................70
3.2.2 The Data Separator .................................................................................................................70
3.2.3 Perpendicular Recording Mode Support ........................................................... .......... ....... .....71
3.2.4 Data Rate Selection ................................................................................................................72
3.2.5 Write Precompensation ...........................................................................................................72
3.2.6 FDC Low-Power Mode Logic ..................................................................................................73
3.2.7 Reset .................. ....................... ........................ ........................ ....................... ............... .......73
3.3 THE REGISTERS OF THE FDC ......................................................................................................74
3.3.1 FDC Register Bitmaps .............................................................................................................74
3.3.2 Status Register A (SRA), Offset 000 .......................................................................................75
3.3.3 Status Register B (SRB), Offset 001 .......................................................................................76
3.3.4 Digital Output Re gister (DOR), Offset 010 ..............................................................................77
3.3.5 Tape Drive Register (TDR), Offset 011 ...................................................................................79
3.3.6 Main Status Register (MSR), Offset 100 .. ...............................................................................80
3.3.7 Data Rate Select Register (DSR), Offset 100 .........................................................................82
3.3.8 Data Register (FIFO), Offset 101 ............................................................................................83
3.3.9 Digital Input Register (DIR), Offset 111 ...................................................................................83
3.3.10 Configuration Control Register (CCR), Offset 111 ................................................................84
3.4 THE PHASES OF FDC COMMANDS ..............................................................................................85
3.4.1 Command Phase .............. ......... ........................ ........................ ....................... ......................85
3.4.2 Execution Phase .....................................................................................................................85
3.4.3 Result Phase ........................................................................................................................... 87
3.4.4 Idle Phase ........ ........................ ........................ ....................... ........................ ........................88
3.4.5 Drive Polling Phase .................................................................................................................88
3.5 THE RESULT PHASE STATUS REGIST ER S ....... .......... ........................ ....................... .................88
3.5.1 Result Phase Status Register 0 (ST0) ....................................................................................88
3.5.2 Result Phase Status Register 1 (ST1) ....................................................................................89
3.5.3 Result Phase Status Register 2 (ST2) ....................................................................................90
3.5.4 Result Phase Status Register 3 (ST3) ....................................................................................91
3.6 THE FDC COMMAND SET ..............................................................................................................91
3.6.1 Abbreviations Used in FDC Commands ................................................... .. ....... .......... .. ....... ...92
6
www.national.com
3.6.2 The CONFIGURE Command ....................................................... ....... ....... ..... ....... ....... ..... .....94
3.6.3 The DUMPREG Command ............................................ .. ....... .......... ....... .. ....... .......... .. ....... ...95
3.6.4 The FORMAT TRACK Command ................................................................... .. .......... ....... .....96
3.6.5 The INVALID Command .................................................. ..... ....... ....... ....... ..... ....... ....... ..... .....99
3.6.6 The LOCK Command ............................................................................................................100
3.6.7 The MODE Command ........................................................... ....... ....... ..... ....... ....... ....... ..... .. .100
3.6.8 The NSC Command ................... ..... ..... ..... .... ..... ..... .. ..... .. ..... .. ..... ..... .. ..... .. ..... .. ..... ..... .. ... .....103
3.6.9 The PERPENDICULAR MODE Command .......................................................................... .103
3.6.10 The READ DATA Command ...............................................................................................105
3.6.11 The READ DELETED DATA Command .............................................................................108
3.6.12 The READ ID Command .....................................................................................................109
3.6.13 The READ A TRACK Command .........................................................................................110
3.6.14 The RECALIBRATE Command ...........................................................................................110
3.6.15 The RELATIVE SEEK Command ........................................................................................111
3.6.16 The SCAN EQUAL, the SCAN LO W OR EQUAL and the SCAN HI GH
OR EQUAL Commands ......................................................................................................112
3.6.17 The SEEK Command ..........................................................................................................113
3.6.18 The SENSE DRIVE STATUS Command ............................................................................114
3.6.19 The SENSE INTERRUPT Command ..................................................................................114
3.6.20 The SET TRACK Command ...............................................................................................115
3.6.21 The SPECIFY Command ....................................................................................................116
3.6.22 The VERIFY Command ......................................................................................................118
3.6.23 The VERSION Comm and ...................................................................................................119
3.6.24 The WRITE DATA Command .............................................................................................120
3.6.25 The WRITE DELETED DATA Command ............................................................................121
3.7 EXAMPLE OF A FOUR-DRIVE CIRCUIT USING THE PC87338/PC97338 ..................................121
4.0 Parallel Port
4.1 INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................................123
4.1.1 The Chip Parallel Port Modes ...............................................................................................123
4.1.2 Device Conf igu r a tion ......... ......... ........................ ........................ ....................... ............... .....123
4.2 STANDARD PARALLEL PORT MODES ........................................................................................123
4.2.1 Standard Parallel Port (SPP) Modes Register Set . ...............................................................124
4.2.2 SPP Mode Parallel Port Register Bitmaps ....... ......... ........................ ........................ ............124
4.2.3 Data Register (DTR), Offset 0 ...............................................................................................124
4.2.4 Status Register (STR), Offset 1 .............................................................................................125
4.2.5 Control Register (CTR), Offset 2 ...........................................................................................126
4.3 ENHANCED PARALLEL POR T (EPP) MO D ES ........................... ....................... ........................ ... 127
4.3.1 Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) Modes Register Set ..............................................................128
4.3.2 EPP Modes Parallel Port Regist e r Bitm a ps ................... ........................ ....................... ........128
4.3.3 SPP or EPP Data Register (DTR), Offset 0 ..........................................................................129
4.3.4 SPP or EPP Status Regi ste r ( ST R ), Offset 1 ............................... ........................ .................129
4.3.5 SPP or EPP Control Register (CTR), Offset 2 ......................................................................129
4.3.6 EPP Address Register, Offset 3 ............................................................................................130
4.3.7 EPP Data Port 0, Offse t 4 ........ ........................ ....................... ........................ ......................130
4.3.8 EPP Data Port 1, Offse t 5 ........ ........................ ....................... ........................ ......................130
4.3.9 EPP Data Port 2, Offse t 6 ........ ........................ ....................... ........................ ......................130
7
www.national.com
4.3.10 EPP Data Port 3, Offset 7 ...................................................................................................131
4.3.11 EPP Mode Transfer Operations ..........................................................................................131
4.4 EXTENDED CAPABILITIES PARALLEL PORT (ECP) MODES ....................................................133
4.4.1 Accessing the ECP Registers ...............................................................................................134
4.4.2 Software Operation in ECP Modes .......................................................................................134
4.4.3 Hardware Operation in ECP Modes ......................................................................................134
4.4.4 ECP Modes Parallel Port Register Bitmaps ..........................................................................135
4.4.5 ECP Data Register (DATAR), Bits 7-5 of ECR = 000 or 001, Offset 000h ............................136
4.4.6 ECP Address FIFO (AFIFO) Register, Bits 7-5 of ECR = 011, Offset 000h ..........................137
4.4.7 ECP Status Register (DSR), Offset 001h ..............................................................................137
4.4.8 ECP Control Register (DCR), Offset 002h ........................................................................... .137
4.4.9 Parallel Port Data FIFO (CFIFO) Register, Bits 7-5 of ECR = 010, Offset 400h ...................138
4.4.10 ECP Data FIFO (DFIFO) Register, Bits 7-5 of ECR = 011, Offset 400h .............................138
4.4.11 Test FIFO (TFIFO) Register, Bits 7-5 of ECR = 110, Offset 400h ......................................139
4.4.12 Configuration Register A (CNFGA), Bits 7-5 of ECR = 111, Offset 400h ............................139
4.4.13 Configuration Register B (CNFGB), Bits 7-5 of ECR = 111, Offset 401h ............................139
4.4.14 Extended Control Register (ECR), Offset 402h ...................................................................140
4.5 ECP MODE DESCRIPTIONS .........................................................................................................142
4.5.1 Software Controlled Data Transfer (Modes 000 and 001) .....................................................142
4.5.2 Automatic Data Transfer (Modes 010 and 011) ................................................ .......... ....... .. .142
4.5.3 FIFO Test Access (Mode 110) ................................................ ..... ....... ....... ..... ....... ....... ........143
4.5.4 Configuration Registers Access (Mode 111) ... ......................................................................143
4.5.5 Interrupt Generation ..............................................................................................................143
4.6 THE PARALLEL PORT MULTIPLEXER (PPM) ............................................................................. 144
4.7 PARALLEL PORT PIN/SIGNAL LIST .............................................................................................144
5.0 Serial Communications Controllers (SCC1 and SCC2)
5.1 FEATURES .....................................................................................................................................146
5.2 FUNCTIONAL MODES OVERVIEW .............................................................................................. 146
5.3 UART MODE ..................................................................................................................................146
5.4 SHARP-IR MODE ...........................................................................................................................147
5.5 IRDA 1.0 SIR MODE ...................................................................................................................... 147
5.6 IRDA 1.1 M IR AND FIR MODES ....................................................................................................147
5.6.1 High Speed Infrared Transmit Operation ..............................................................................148
5.6.2 High Speed Infrared Receive Operation ...............................................................................149
5.7 CONSUMER ELECTRONIC IR (CEIR) MODE ..............................................................................149
5.7.1 CEIR Transmit Operation ......................................................................................................149
5.7.2 CEIR Receive Operation .......................................................................................................150
5.8 FIFO TIME-OUTS ...........................................................................................................................150
5.9 TRANSMIT DEFERRAL .................................................................................................................151
5.10 AUTOMATIC FALLBACK TO 16550 COMP A TIBILITY MO DE ....................................................151
5.11 PIPELINING ..................................................................................................................................152
5.12 OPTICAL TRANSCEIVER INTERFACE ......................................................................................152
8
www.national.com
5.13 ARCHITECTURAL DESCRIPTION ..............................................................................................153
5.14 BANK 0 ......................................................................................................................................... 153
5.14.1 TXD/RXD – Transmit/Receive Data Ports ...........................................................................153
5.14.2 IER – Interrupt Enable Register ..........................................................................................154
5.14.3 EIR/FCR – Event Identification/FIFO Control Registers ......................................................154
5.14.4 LCR/BSR – Link Control/Bank Select Register ...................................................................157
5.14.5 MCR – Modem/Mode Control Register .. .............................................................................159
5.14.6 LSR – Link Status Register .................................................................................................160
5.14.7 MSR – Modem Status Register ...........................................................................................162
5.14.8 SPR/ASCR – Scratchpad/Auxiliary Status and Control Register ........................................162
5.15 BANK 1 ......................................................................................................................................... 163
5.15.1 LBGD – Legacy Baud Generator Divisor Port . ....................................................................164
5.15.2 LCR/BSR – Link Control/Bank Select Registers .................................................................164
5.16 BANK 2 ......................................................................................................................................... 164
5.16.1 BGD – Baud Generator Divisor Port ...................................................................................164
5.16.2 EXCR1 – Extended Control Register 1 ...............................................................................166
5.16.3 LCR/BSR – Link Control/Bank Select Registers .................................................................167
5.16.4 EXCR2 – Extended Control Register 2 ...............................................................................167
5.16.5 TXFLV – TX_FIFO Level, Read-Only ..................................................................................168
5.16.6 RXFLV – RX_FIFO Level, Read-Only .................................................................................168
5.17 BANK 3 ......................................................................................................................................... 168
5.17.1 MID – Module Identification Register, Read Only ...............................................................168
5.17.2 SH_LCR – Link Control Register Shadow, Read Only .................................... .......... .. ....... .168
5.17.3 SH_FCR – FIFO Control Register Shadow, Read-Only ......................................................168
5.17.4 LCR/BSR – Link Control/Bank Select Registers .................................................................168
5.18 BANK 4 ......................................................................................................................................... 169
5.18.1 TMR – Timer Register .........................................................................................................169
5.18.2 IRCR1 – Infrared Control Register 1 ...................................................................................169
5.18.3 LCR/BSR – Link Control/Bank Select Registers .................................................................169
5.18.4 TFRL/TFRCC – Transmitter Frame-Length/Current-Count .................................................170
5.18.5 RFRML/RFRCC – Receiver Frame Maximum-Length/Current-Count ................................170
5.19 BANK 5 ......................................................................................................................................... 170
5.19.1 P_BGD – Pipelined Baud Generator Divisor Register ........................................................170
5.19.2 P_MDR – Pipelined Mode Register .....................................................................................170
5.19.3 LCR/BSR – Link Control/Bank Select Registers .................................................................171
5.19.4 IRCR2 – Infrared Control Register 2 ...................................................................................171
5.19.5 ST_FIFO – Status FIFO ......................................................................................................172
5.20 BANK 6 ......................................................................................................................................... 173
5.20.1 IRCR3 – Infrared Control Register 3 ...................................................................................173
5.20.2 MIRPW – MIR Pulse Width Register ...................................................................................173
5.20.3 SIR_PW – SIR Pulse Width Registe r ..................................................................................174
5.20.4 LCR/BSR – Link Control/Bank Select Registers .................................................................174
5.20.5 BFPL – Beginning Flags/P reamble Length Register ...........................................................174
5.21 BANK 7 ......................................................................................................................................... 175
5.21.1 IRRXDC – Infrared Receiver Demodulator Control Register ..............................................175
9
www.national.com
5.21.2 IRTXMC – Infrared Transmitter Modulator Control Register ...............................................178
5.21.3 RCCFG – CEIR Configuration Register ..............................................................................179
5.21.4 LCR/BSR – Link Control/Bank Select Registers .................................................................179
5.21.5 IRCFG [1–4] – Infrared Interface Configuration Registers ..................................................179
5.22 SERIAL COMMUNICATION CONTROLLER2 REGISTER BITMAPS .........................................182
6.0 DMA and Interrupt Mapping
6.1 DMA SUPPORT .............................................................................................................................190
6.1.1 Legacy Mode .............................................................................................. ...........................190
6.1.2 Plug and Play Mode .......................................................................................... ............ ........190
6.2 INTERRUPT SUPPORT .................................................................................................................191
6.2.1 Legacy Mode .............................................................................................. ...........................191
6.2.2 Plug and Play Mode .......................................................................................... ............ ........192
7.0 Power Management
7.1 POWER-DOWN STATE .................................................................................................................194
7.1.1 Recommended Power-Down Methods - Group 1 ................... .......... .. ....... ....... .......... .. ....... .194
7.1.2 Recommended Power-Down Methods - Group 2 ................... .......... .. ....... ....... .......... .. ....... .195
7.1.3 Special Power-Down Cases ..................................................................................................195
7.2 POWER-UP ....................................................................................................................................195
7.2.1 The Clock Multiplier ...............................................................................................................195
7.2.2 Chip Power-Up Procedure ...................................................... .......... ....... .. ....... .......... .. ....... .195
7.2.3 SCC1 and SCC2 Power-Up ..................................................................................................196
7.2.4 FDC Power-Up ......................................................................................................................196
8.0 Device Description
8.1 GENERAL ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS ............................................................................197
8.1.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings ................................................................................................... 197
8.1.2 Capacitance ..................................................................... ................... .............. ....................197
8.1.3 Electrical Characteristics .......................................................................................................197
8.2 DC CHARACTERISTICS OF PINS, BY GROUP ...........................................................................198
8.2.1 Group 1 ................................................................................... ................... ...........................198
8.2.2 Group 2 ................................................................................... ................... ...........................198
8.2.3 Group 3 ................................................................................... ................... ...........................198
8.2.4 Group 4 ................................................................................... ................... ...........................199
8.2.5 Group 5 ................................................................................... ................... ...........................199
8.2.6 Group 6 ................................................................................... ................... ...........................199
8.2.7 Group 7 ................................................................................... ................... ...........................200
8.2.8 Group 8 ................................................................................... ................... ...........................200
8.2.9 Group 9 ................................................................................... ................... ...........................201
8.2.10 Group 10 .............................................................................................................................201
8.2.11 Group 11 .............................................................................................................................201
8.2.12 Group 12 .............................................................................................................................202
8.2.13 Group 13 .............................................................................................................................202
10
www.national.com
8.3 AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS .........................................................................................202
8.3.1 AC Test Conditions T
= 0° C to 70° C, VDD = 5.0 V ± 10%, 3.3 V ± 10% ...........................202
A
8.4 SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS ................................................................................................203
8.4.1 Timing Table .........................................................................................................................203
8.4.2 Timing Diagrams ..................................................................................................................207
9.0 Appendix A
COMPARISON OF PC87338 A ND PC97338 .......................................................................................216
11
www.national.com
List of Figures
FIGURE 1 Plug and Play Protocol Flowchart ..................................................................................................39
FIGURE 2 LFSR Circuit ...................................................................................................................................40
FIGURE 3 FER Register Bitmap .....................................................................................................................45
FIGURE 4 FAR Register Bitmap .....................................................................................................................47
FIGURE 5 PTR Register Bitmap .....................................................................................................................48
FIGURE 6 FCR Register Bitmap .....................................................................................................................48
FIGURE 7 PCR Register Bitmap .....................................................................................................................49
FIGURE 8 PMC Register Bitmap .....................................................................................................................50
FIGURE 9 TUP Register Bitmap .....................................................................................................................51
FIGURE 10 SID Register Bitmap .....................................................................................................................52
FIGURE 11 ASC Register Bitmap ...................................................................................................................52
FIGURE 12 CS0LA Register Bitmap ............................................................................................................... 53
FIGURE 13 CS0CF Register Bitmap ...............................................................................................................53
FIGURE 14 CS1LA Register Bitmap ............................................................................................................... 54
FIGURE 15 CS1CF Register Bitmap ...............................................................................................................54
FIGURE 16 CS0HA Register Bitmap ...............................................................................................................55
FIGURE 17 CS1HA Register Bitmap ...............................................................................................................55
FIGURE 18 SCF0 Register Bitmap .................................................................................................................55
FIGURE 19 SCF1 Register Bitmap .................................................................................................................56
FIGURE 20 PNP0 Register Bitmap .................................................................................................................57
FIGURE 21 PNP1 Register Bitmap .................................................................................................................58
FIGURE 22 SCF2 Register Bitmap .................................................................................................................58
FIGURE 23 Busy Flag Timing .........................................................................................................................59
FIGURE 24 PNP2 Register Bitmap .................................................................................................................59
FIGURE 25 PBAL Register Bitmap .................................................................................................................60
FIGURE 26 PBAH Register Bitmap .................................................................................................................61
FIGURE 27 S1BAL Register Bitmap ...............................................................................................................61
FIGURE 28 S1BAH Register Bitmap ...............................................................................................................61
FIGURE 29 S2BAL Register Bitmap ...............................................................................................................61
FIGURE 30 S2BAH Register Bitmap ...............................................................................................................62
FIGURE 31 FBAL Register Bitmap ..................................................................................................................62
FIGURE 32 FBAH Register Bitmap .................................................................................................................62
FIGURE 33 SBAL Register Bitmap .................................................................................................................63
FIGURE 34 SBAH Register Bitmap .................................................................................................................63
FIGURE 35 SIRQ1 Register Bitmap ................................................................................................................63
FIGURE 36 SIRQ2 Register Bitmap ................................................................................................................64
FIGURE 37 SIRQ3 Register Bitmap ................................................................................................................65
FIGURE 38 PNP3 Register Bitmap .................................................................................................................66
FIGURE 39 SCF3 Register Bitmap .................................................................................................................67
FIGURE 40 CLK Register Bitmap ....................................................................................................................68
FIGURE 41 FDC Functional Block Diagram ........................................... .. ..... .. ..... ..... .. ..... .. ..... .. ..... .................69
FIGURE 42 PC87338/PC97338 D ynamic Window Ma rgin Performance ........................................................70
FIGURE 43 Read Algorithm State Diagram ....................................................................................................71
FIGURE 44 Perpendicular Recording Drive Read/Write Head and Pre-Erase Head . .....................................72
FIGURE 45 SRA Register Bitmap ...................................................................................................................75
FIGURE 46 SRB Register Bitmap ...................................................................................................................76
FIGURE 47 DOR Register Bitmap ...................................................................................................................78
FIGURE 48 TDR Register Bitmap ...................................................................................................................79
FIGURE 49 MSR Register Bitmap ...................................................................................................................81
12
www.national.com
FIGURE 50 DSR Register Bitmap ................................................................................................................... 82
FIGURE 51 FDC Data Register Bitmap ...........................................................................................................83
FIGURE 52 DIR Register Bitmap ....................................................................................................................84
FIGURE 53 CCR Register Bitmap ...................................................................................................................84
FIGURE 54 ST0 Result Phase Register Bitmap ..............................................................................................88
FIGURE 55 ST1 Result Phase Register Bitmap ..............................................................................................89
FIGURE 56 ST2 Result Phase Register Bitmap ..............................................................................................90
FIGURE 57 ST3 Result Phase Register ..........................................................................................................91
FIGURE 58 IBM, Perpendicular, and ISO Formats Supported by FORMAT TRACK Command ....................99
FIGURE 59 PC87338/PC97338 Four Floppy Disk Drive Circuit ...................................................................122
FIGURE 60 DTR Register Bitmap (SPP Mode) .............................................................................................125
FIGURE 61 STR Register Bitmap (SPP Mode) .............................................................................................125
FIGURE 62 CTR Register Bitmap (SPP Mode) in PC87338 .........................................................................126
FIGURE 63 CTR Register Bitmap (SPP Mode) in PC97338 .........................................................................126
FIGURE 64 DTR Register Bitmap (EPP Mode) .............................................................................................129
FIGURE 65 STR Register Bitmap (EPP Mode) .............................................................................................129
FIGURE 66 CTR Register Bitmap (EPP Mode) .............................................................................................130
FIGURE 67 DTR Register Bitmap (EPP Mode) .............................................................................................130
FIGURE 68 DTR Register Bitmap (EPP Mode) .............................................................................................130
FIGURE 69 DTR Register Bitmap (EPP Mode) .............................................................................................130
FIGURE 70 EPP Data Port 2 Bitmap .............................................................................................................130
FIGURE 71 EPP Data Port 3 Bitmap .............................................................................................................131
FIGURE 72 EPP 1.7 Address Write ..............................................................................................................131
FIGURE 73 EPP 1.7 Address Read ..............................................................................................................132
FIGURE 74 EPP Write with Zero Wait States ...............................................................................................132
FIGURE 75 EPP 1.9 Address Write ..............................................................................................................133
FIGURE 76 EPP 1.9 Address Read ..............................................................................................................133
FIGURE 77 DATAR Register Bitmap ............................................................................................................136
FIGURE 78 AFIFO Register Bitmap ..............................................................................................................137
FIGURE 79 ECP DSR Register Bitmap .........................................................................................................137
FIGURE 80 DCR Register Bitmap .................................................................................................................137
FIGURE 81 CFIFO Register Bitmap ..............................................................................................................138
FIGURE 82 DFIFO Register Bitmap ..............................................................................................................139
FIGURE 83 TFIFO Register Bitmap ..............................................................................................................139
FIGURE 84 CNFGA Register Bitmap ............................................................................................................ 139
FIGURE 85 CNFGB Register Bitmap ............................................................................................................ 140
FIGURE 86 ECR Register Bitmap ................................................................................................................. 140
FIGURE 87 ECP Forward Write Cycle ..........................................................................................................142
FIGURE 88 ECP (Reverse) Read Cycle .......................................................................................................143
FIGURE 88 Composite Serial Data ...............................................................................................................146
FIGURE 88 Register Bank Architecture ........................................................................................................153
FIGURE 88 Interrupt Enable Register .... .......................................................................................................154
FIGURE 88 Event Identification Register, Non-Extended Mode ...................................................................155
FIGURE 88 Event Identification Register, Extended Mode ...........................................................................156
FIGURE 88 FIFO Control Register ................................................................................................................157
FIGURE 88 Link Control Register ..................................................................................................................158
FIGURE 88 Modem Control Register, Non-Extended Mode ...................................................................... .. .159
FIGURE 88 Modem Control Register, Extended Modes .................................................. ....... .. .......... ....... ...159
FIGURE 88 Link Status Register ...................................................................................................................160
FIGURE 88 Modem Status Register ......................................................... ....... .......... .. ....... ....... ..... ...............162
FIGURE 88 Auxillary Status and Control Register .......................................................................................162
13
www.national.com
FIGURE 88 Extended Control Register 1 . .....................................................................................................166
FIGURE 88 DMA Control Signals Routing ............................ ..... ..... .. ..... .. ..... ..... ..... .... ..... .. ..... .. ..... ...............167
FIGURE 88 Extended Control Register 2 . .....................................................................................................167
FIGURE 88 Transmit FIFO Level .................................................................................................................168
FIGURE 88 Receive FIFO Level ..................................................................................................................168
FIGURE 88 Infrared Control Register 1 .........................................................................................................169
FIGURE 88 Pipelined Mode Register ...........................................................................................................171
FIGURE 88 IInfrared Control Register 2 ........................................................................................................171
FIGURE 88 Frame Status Byte Register .......................................................................................................172
FIGURE 88 Infrared Control Register 3 .........................................................................................................173
FIGURE 88 MIR Pulse Width Register ..........................................................................................................173
FIGURE 88 SIR Pulse Width Register ..........................................................................................................174
FIGURE 88 Beginning Flags/Preamble Length Register . .............................................................................174
FIGURE 88 Intrared Receiver Demodulator Control Register ......................................................................175
FIGURE 88 Intrared Transmitter Modulator Control Register .................................................. ....... ....... ........178
FIGURE 88 CEIR Configuration Register .....................................................................................................179
FIGURE 88 Infrared Configuration Register 1 ...............................................................................................180
FIGURE 88 Infrared Configuration Register 2 ...............................................................................................180
FIGURE 88 Infrared Configuration Register 3 ...............................................................................................181
FIGURE 88 Infrared Configuration Register 4 ...............................................................................................181
FIGURE 89 Load Circuit ................................................................................................................................202
FIGURE 90 Testing Specification Standard ..................................................................................................203
FIGURE 91 Clock Timing ..............................................................................................................................207
FIGURE 92 CPU Read Timing ......................................................................................................................208
FIGURE 93 CPU Write Timing ......................................................................................................................208
FIGURE 94 DMA Access Timing ...................................................................................................................209
FIGURE 95 UART, Sharp-IR and CEIR Timing ............................................................................................209
FIGURE 96 SIR, MIR and FIR Timing ...........................................................................................................210
FIGURE 97 IRSLn Write Timing ....................................................................................................................210
FIGURE 98 Modem Control Timing ................................................... ....... ..... ....... ....... ....... ..... ....... ...............211
FIGURE 99 FDC Write Data Timing ..............................................................................................................211
FIGURE 100 FDC Read Data Timing ............................................................................................................211
FIGURE 101 FDC Control Signal s Ti mi n g ............................. ........................ ........................ ........................212
FIGURE 102 Parallel Port Interrupt Timing (Compatible Mode) ....................................................................212
FIGURE 103 Parallel Port Interrupt Timing (Extended Mode) .......................................... .. ....... .......... ....... .. .212
FIGURE 104 Parallel Port Data Transfer Timing (Compatible Mode) ......................... ....... ....... .......... .. ....... .213
FIGURE 105 Parallel Port Data Transfer Timing (EPP 1.7 Mode) ...............................................................213
FIGURE 106 Parallel Port Data Transfer Timing (EPP 1.9 Mode) ...............................................................214
FIGURE 107 Parallel Port Forward Transfer Timing (ECP Mode) ...............................................................214
FIGURE 108 Parallel Port Reverse Transfer Timing (ECP Mode) ......................................... .. ..... ..... .. ..... .. .215
FIGURE 109 System Interrupts Timing .........................................................................................................215
FIGURE 110 CS1-0 Signals Timing ................................................ ....... ....... .. .......... ....... .. ....... ....................215
FIGURE 111 Reset Timing ............................................................................................................................ 215
14
www.national.com
List of Tables
TABLE 1 Signal/Pin Description Table ............................................................................................................22
TABLE 2 Multi-Function Pins (Excluding Strap Pins) ...................................................................................... 34
TABLE 3 IRQ12, A15-11 / SCC2 / Infrared Pin Allocation ...............................................................................35
TABLE 4 SCC2 Mode Configurations 1 . ..........................................................................................................35
TABLE 5 SCC2 Mode Configurations 2 .......................................................................................................... 35
TABLE 6 Default Configurations Controlled by Hardware .............................................................................. 36
TABLE 7 Configuration Registers ...................................................................................................................36
TABLE 8 IND E X a nd DA T A R egister Addre s s Op tio n s and Con figuration Re gis te r Ac cessibility .......... .... ... . 38
TABLE 9 Primary and Secondary Drive Address Selection ............................................................................ 46
TABLE 10 Encoded Drive and Motor Pin Information (Bit 4 of FER = 1) .........................................................46
TABLE 11 Parallel Port Addresses ..................................................................................................................47
TABLE 12 COM Port Selection for SCC1 ........................................................................................................47
TABLE 13 COM Port Selection for SCC2 ........................................................................................................47
TABLE 14 Address Selection for COM3 and COM4 ......................................................................................47
TABLE 15 Parallel Port Mode ..........................................................................................................................49
TABLE 16 Bit Settings to Enable MRT 1
TABLE 17 Bit Settings to Enable DR1
TABLE 18 ECP DMA Option Selection ...........................................................................................................56
TABLE 19 Parallel Port Plug and Play DMA Settings .....................................................................................56
TABLE 20 Parallel Port Plug and Play Interrupt Assignment ..........................................................................57
TABLE 21 Parallel Port Plug and Play Interrupt Mapping .............................................................................57
TABLE 22 TDR Bit 5 Values ............................................................................................................................58
TABLE 23 FDC Plug and Play Interrupt Mapping ...........................................................................................59
TABLE 24 FDC Plug and Play DMA Settings ..................................................................................................60
TABLE 25 SBAL Reset Values .......................................................................................................................63
TABLE 26 SBAH Reset Values ......................................................................................................................63
TABLE 27 SIRQI1 Plug and Play Interrupt Mapping .......................................................................................64
TABLE 28 SIRQ1 Interrupt Settings 64
TABLE 29 SIRQI2 Plug and Play Interrupt Mapping .................................................................................... 65
TABLE 30 Selecting MSEN1, DRATE1, CS0
TABLE 31 SIRQI3 Plug and Play Interrupt Mapping ......................................................................................66
TABLE 32 Selecting DRV2
TABLE 33 SCC2 Receiver Channel Selection ...............................................................................................67
TABLE 34 SCC2 Transmission Channel Selection .........................................................................................67
TABLE 35 The FDC Registers and Their Addresses ......................................................................................74
TABLE 36 Drive and Motor Pin Encoding When FER 4 = 1 ...................................................................... .....77
TABLE 37 Drive Enable Hexadecimal Values .................................................................................................77
TABLE 38 TDR Bit Utiliz at ion and Reset Val ues in Different Drive M odes .......................... ....... ............ ........ 79
TABLE 39 Media Type Bit Settings ................................................................................................................80
TABLE 40 Data Transfer Rate Encoding .........................................................................................................82
TABLE 41 Write Precompensation Dela ys ......................................................................................................82
TABLE 42 Default Precompensat ion Delays ...................................................................................................82
TABLE 43 FDC Command Set Summary ........................................................................................................92
TABLE 44 Bytes per Sector Codes ................................................................................................................. 97
TABLE 45 Typical Values for PC Compati ble Diskette Media .........................................................................97
TABLE 46 Typical Gap Values ........................................................................................................................98
TABLE 47 Multipliers and Head Settle Time Ranges for Different Data Transfer Rates ..............................102
TABLE 48 DENSEL Encoding ......................................................................................................................102
TABLE 49 Effect of Drive Mode and Data Rate on FORMAT TRACK and WRITE DATA Commands .........104
, DR23, PNF or SIRQI3 ..................................................................................66
, IDLE or IRSL2 ................................................................................51
or PD ..................................................................................................51
or SIRQI2 .................................................................................65
15
www.national.com
TABLE 50 Effect of GDC Bits on FORMAT TRACK and WRITE DATA Commands ....................................104
TABLE 51 Skip Control Effect on READ DATA Command ...........................................................................107
TABLE 52 Result Phase Termination Values with No Error ..........................................................................108
TABLE 53 SK Effect on READ DELETED DATA Command .. ......................................................................108
TABLE 54 Maximum RECALIBRATE Step P ulses for Values of R255 and ETR ..........................................111
TABLE 55 The Effect of Scan Commands on the ST2 Register ...................................................................113
TABLE 56 Interrupt Causes Reported by SENSE INTERRUPT .......... ......... .......................... .......... ............ 114
TABLE 57 Defining Bytes to Read or Write Using SET TRACK ....................................................................116
TABLE 58 Constant Multipliers for Delay After Processing Factor and Delay Ranges ................................117
TABLE 59 Constant Multipliers for Delay Before Processing Factor and Delay Ranges . ............................117
TABLE 60 STEP
Time Interval Calculation .................................................................................................. 117
TABLE 61 VERIFY Command Termination Condi tions .... ............................................................................. 119
TABLE 62 Parallel Port Reset States ...........................................................................................................124
TABLE 63 Standard Parallel Port Registers ................................................................................................124
TABLE 64 SPP Data Register Read and Write Modes .................................................................................125
TABLE 65 EPP Revision Selection ................................................................................................................127
TABLE 66 Parallel Po rt Registers in EPP Mod es ........... .......... ....................... ........................ ......................128
TABLE 67 ECP Modes Encoding ..................................................................................................................133
TABLE 68 Parallel Port Registers in ECP Modes ..........................................................................................134
TABLE 69 ECP Mode DMA Selection ..........................................................................................................140
TABLE 70 ECP Mode Interrupt Selection ......................................................................................................140
TABLE 71 ECP Modes .................................................................................................................................141
TABLE 72 Parallel Port Pin Out .....................................................................................................................144
TABLE 73 Register Bank Summary ............................................................................................................. 153
TABLE 74 Bank 0 Serial Controller Base Registers þ ...................................................................................153
TABLE 75 Non-Extended Mode Interrupt Priorities .......................................................................................155
TABLE 76 TX_FIFO Level Selection ............................................................................................................157
TABLE 77 RX_FIFO Level Selection .............................................................................................................157
TABLE 78 Word Length Select Encoding ......................................................................................................158
TABLE 79 Bit Settings for Parity Control .......................................................................................................158
TABLE 80 Bank Selection Encoding .............................................................................................................159
TABLE 81 The Module Operation Mod es ......................................................................................................160
TABLE 82 Bank 1 Register Set .....................................................................................................................163
TABLE 83 Bank 2 Register Set .....................................................................................................................164
TABLE 84 Baud Generator Divisor Settings ..................................................................................................165
TABLE 85 Bank 3 Register Set .....................................................................................................................168
TABLE 86 Bank 4 Register Set .....................................................................................................................169
TABLE 87 Bank 5 Register ............................................................................................................................170
TABLE 88 Bank 6 Register Set .....................................................................................................................173
TABLE 89 MIR Pulse Width Settings .............................................................................................................174
TABLE 90 FIR Preamble Length ...................................................................................................................174
TABLE 91 MIR Beginning Flags ....................................................................................................................175
TABLE 92 Bank 7 Register Set .....................................................................................................................175
TABLE 93 CEIR, Low Speed Demodulator (RXHSC = 0) (Frequency Ranges in kHz)þ ..............................176
TABLE 94 Consumer IR High Speed Demodulator Frequency Ranges in kHz (RXHSC = 1) .....................177
TABLE 95 Sharp-IR Demodulator Frequency Ranges in kHz .......................................................................177
TABLE 96 CEIR Carrier Frequency Encoding ...............................................................................................178
TABLE 97 Infrared Receiver Input Selection .................................................................................................182
TABLE 98 DMA Support in Legacy Mode ....................................................................................................190
TABLE 99 DMA Support in Plug and Play Mode ..................................................................... .. .......... ..........190
TABLE 100 Interrupt Support in Legacy Mode for IRQ3, 4, 6, 7, 9 10 and 11 .............................................191
16
www.national.com
TABLE 101 Interrupt Support in Legacy Mode for IRQ 5, 12 and 15 ...........................................................191
TABLE 102 TRI-STATE Condition for Interrupts in Legacy Mode .................................................................192
TABLE 103 Interrupt Support in Plug and Play Mode for IRQ3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10 or 11 ......................................193
TABLE 104 Interrupt Support in Plug and Play Mode for IRQ 5, 12 or 15 .. ...................................................193
TABLE 105 TRI-STATE Conditions fo r Interrupts in Plug and Play Mode ....................................................193
TABLE 106 Group 1 Power-Down ................................................................................................................194
TABLE 107 Clock Multiplier Encoding Options .... .........................................................................................196
TABLE 108 Capacitance: T
0°C to 70°C, VDD = 5V +/- 10% or 3.3V +/- 10%, VSS = 0V ...........................197
A
TABLE 109 Power Consumption ...................................................................................................................197
TABLE 110 DC Characteristics of Group 1 Pins ..........................................................................................198
TABLE 111 DC Characteristics of Group 2 Pins ...........................................................................................198
TABLE 112 DC Characteristics of Group 3 Pins ...........................................................................................199
TABLE 113 DC Characteristics of Group 4 Pins ..........................................................................................199
TABLE 114 DC Characteristics of Group 5 Pins ..........................................................................................199
TABLE 115 DC Characteristics of Group 6 Input Pins .................................................................................. 200
TABLE 116 DC Characteristics of Group 6 Output Pins .. .............................................................................200
TABLE 117 DC Characteristics of Group 7 Pins ...........................................................................................200
TABLE 118 DC Characteristics of Group 8 Pins ..........................................................................................200
TABLE 119 DC Characteristics of Group 9 Pins ..........................................................................................201
TABLE 120 DC Characteristics of Group 10 Pins ........................................................................................201
TABLE 121 DC Characteristics of Group 11 Pins ........................................................................................201
TABLE 122 DC Characteristics of Group 12 Pins ........................................................................................202
TABLE 123 DC Characteristics of Group 13 Pins ........................................................................................202
17
www.national.com
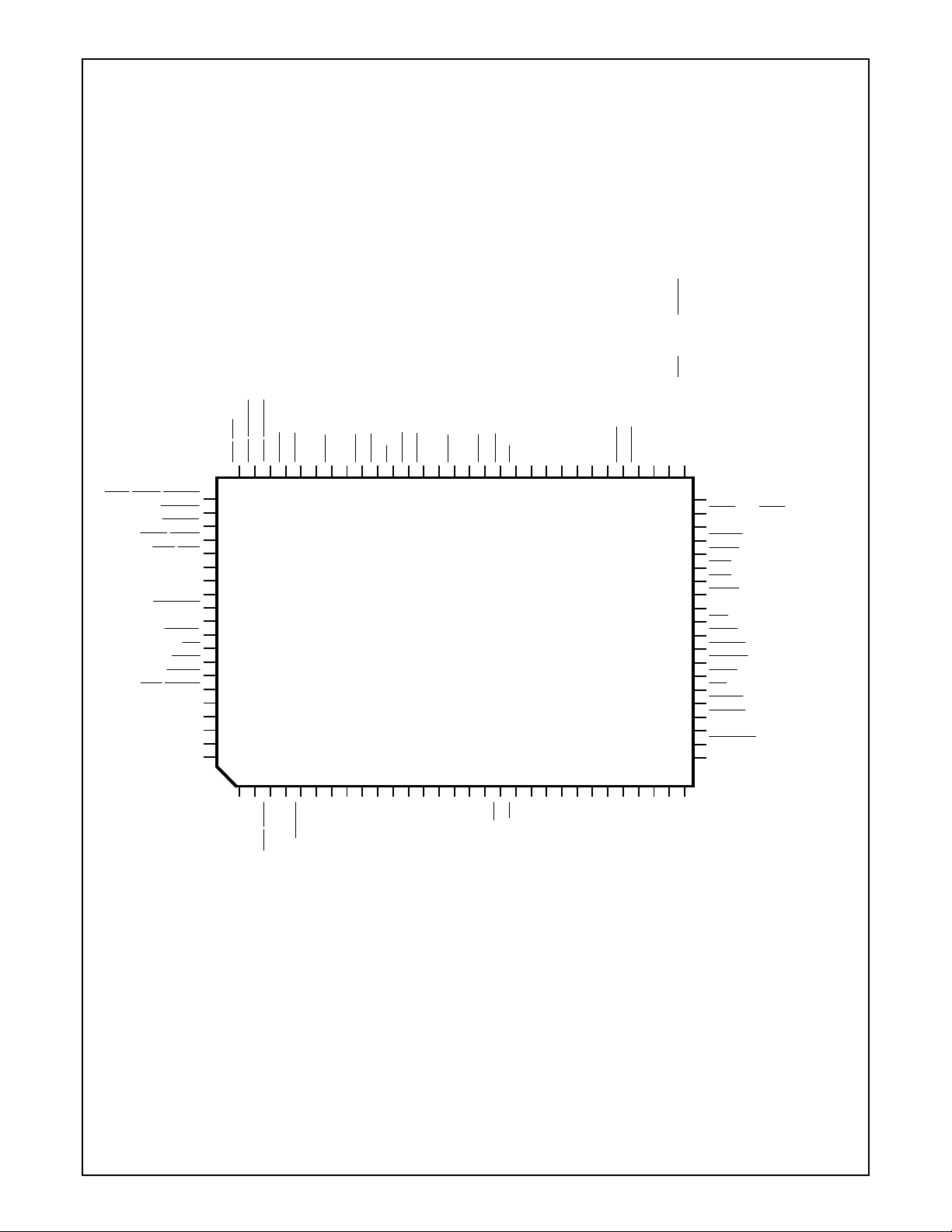
1.0 Pin Descriptions
1.1 CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
Plastic Quad Flatpack (PQFP), EIAJ
/SIRQI2/DACK3
/STEP/ASTRB
SLIN
SLCT/WGATE
PE/WDATA
BUSY/WAIT/MTR1
ACK/DR1
PD7/MSEN1
PD6/DRATE0
PD5/MSEN0
PD4/DSKCHG
IRQ5/ADRATE0
VSS
PD3/RDATA
PD2/WP
PD1/TRK0
PD0/INDEX
STB/WRITE
IRQ7
IRQ6
VDD
IRQ4
/BADDR0
AFD/DSTRB/DENSEL
DSR1
SOUT1/BOUT1/BADDR1
SIN1
TC
RTS1
X1
CTS1
VSS
IRSL1
DCD1
INIT/DIR
ERR/HDSEL
80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 63 62 6 1 60 59 58 57 5 6 55 54 53 52 51
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930
MR
IRQ3
/ZWS
DRQ2
DACK2
CS1
/IRQ12/IRRX2/IRSL0
/A14
DSR2
DTR1
RI1
DCD2/A15
SIN2/IRRX1
RTS2
PC87338VLJ
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
/A12
/A13
/A11
SOUT2/BOUT2/CFG0/IRTX
CTS2
DTR2
VSS
D0
IRQ11
IRQ15/SIRQI1/DRQ3
RI2
A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2A1
RD
WR
AEN
DRQ0
DACK0
IRQ10
DACK1
IRQ9
IOCHRDY
DRATE0/MSEN0
DRATE1/MSEN1/CS0
VDD
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
A0
/PNF/DR23/SIRQI3/IRSL2
DR V2
DENSEL/ADRATE1
INDEX
MTR0
DR1/PD
DR0
MTR1/IDLE/IRSL2
VSS
DIR
STEP
WDATA
WGATE
TRK0
WP
RDATA
HDSEL
DRQ1
DSKCHG
A10
Order Number PC87338VLJ
See NS Package Number VLJ100A
18
www.national.com
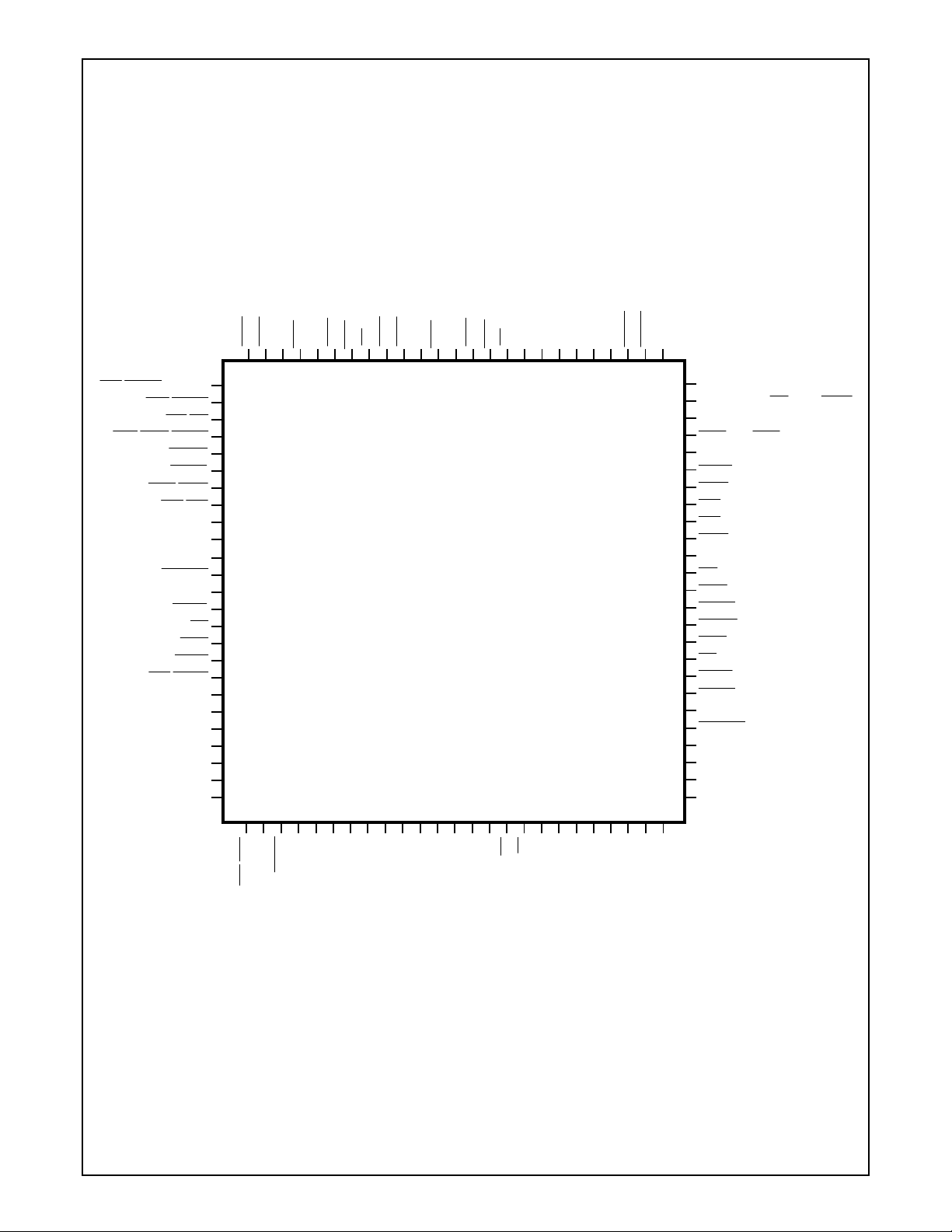
Thin Quad Flatpack (TQFP), JEDEC
AFD
/DSTRB/DENSEL
ERR
INIT/DIR
SLIN/STEP/ASTRB
SLCT/WGATE
PE/WDATA
BUSY/WAIT/MTR1
ACK/DR1
PD7/MSEN1
PD6/DRATE0
PD5/MSEN0
PD4/DSKCHG
PD3/RDATA
PD2/WP
PD1/TRK0
PD0/INDEX
STB/WRITE
IRQ5/ADRATE0
/HDSEL
VSS
IRQ7
IRQ6
VDD
IRQ4
IRQ3
MR
/BADDR0
DCD1
DSR1
SIN1
75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10111213141516171819202122232425
CTS1
RTS1
SOUT1/BOUT1/BADDR1
DTR1
/IRQ12/IRRX2/IRSL0
RI1
SIN2/IRRX1
DSR2
DCD2/A15
PC87338VJG
/A13
/A14
RTS2
/A12
/A11
RI2
CTS2
DTR2
SOUT2/BOUT2/CFG0/IRTX
IRQ11
IRQ10
IRQ15/SIRQI1/DRQ3
VSS
IRQ9
DACK0
DRQ0
DACK1
IOCHRDY
50
DRATE0/MSEN0
49
DRA TE1 /MSEN1/ CS0
48
VDD
47
DRV2
46
DENSEL/ADRATE1
45
INDEX
44
MTR0
43
DR1/PD
42
DR0
41
MTR1/IDLE/IRSL2
40
VSS
39
DIR
38
STEP
37
WDATA
36
WGATE
35
TRK0
34
WP
33
RDATA
HDSEL
32
DRQ1
31
DSKCHG
30
A10
29
28
A0
27
A1
26
A2
/PNF/DR23/SIRQI3/IRSL2
/SIRQI 2/ D AC K3
X1
TC
DRQ2
DACK2
CS1/ZWS
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
VSS
IRSL1
D0
WR
A9A8A7A6A5
RD
AEN
A4
A3
Order Number PC87338VJG
See NS Package Number VJG100A
19
www.national.com
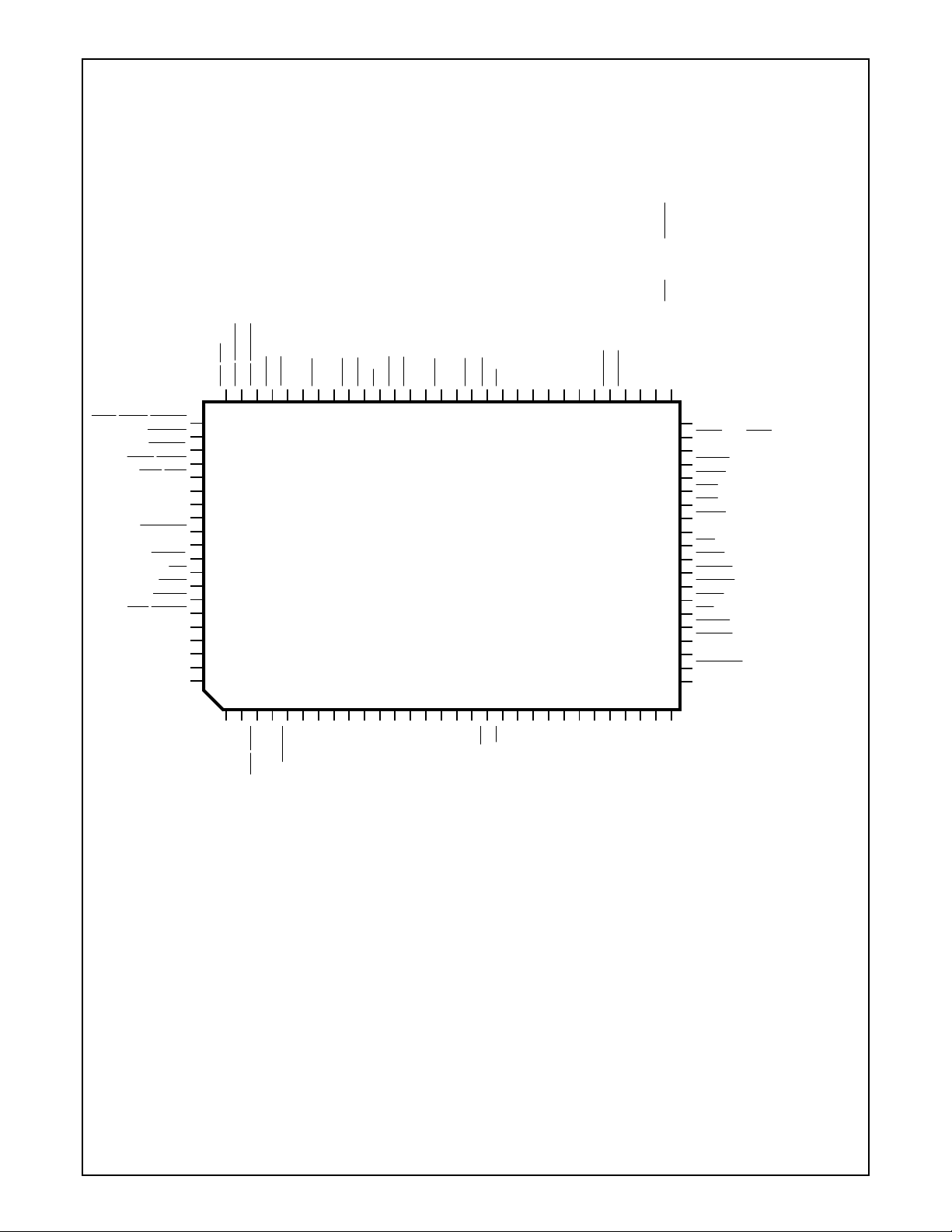
Plastic Quad Flatpack (PQFP), EIAJ
/SIRQI2/DACK3
/STEP/ASTRB
SLIN
SLCT/WGATE
PE/WDATA
BUSY/WAIT/MTR 1
ACK/DR1
PD7/MSEN1
PD6/DRATE0
PD5/MSEN0
PD4/DSKCHG
IRQ5/ADRATE0
VSS
PD3/RDATA
PD2/WP
PD1/TRK0
PD0/INDEX
STB/WRITE
IRQ7
IRQ6
VDD
IRQ4
/BADDR0
AFD/DSTRB/DENSEL
DSR1
DCD1
INIT/DIR
ERR/HDSEL
80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930
MR
IRQ3
SIN1
RTS1
SOUT1/BADDR1
CTS1
X1
TC
/ZWS
DRQ2
DACK2
CS1
VSS
IRSL1/ID1
/IRQ12/IRRX2/IRSL0ID0
/A14
DSR2
DTR1/BOUT1
DCD2/A15
RI1
SIN2/IRRX1
RTS2
PC97338VLJ
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
/A12/BOUT2
/A13
/A11
DTR2
VSS
IRQ11
IRQ15/SIRQI1/DRQ3
RI2
SOUT2/CFG0/IRTX
CTS2
D0
A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2A1
RD
WR
AEN
DRQ0
DACK0
IOCHRDY
IRQ10
DACK1
IRQ9
DRATE0/MSEN0
DRATE1/MSEN1/CS0
VDD
50
DRV2
49
DENSEL/ADRATE1
48
INDEX
47
MTR0
46
DR1/PD
45
DR0
44
MTR1/IDLE/IRSL2/ID2
43
VSS
42
DIR
41
STEP
40
WDATA
39
WGATE
38
TRK0
37
WP
36
RDATA
35
HDSEL
34
DRQ1
33
DSKCHG
32
A10
31
A0
/PNF/DR23/SIRQI3/IRSL2/ID2
Order Number PC97 338VLJ
See NS Package Number VLJ100A
20
www.national.com
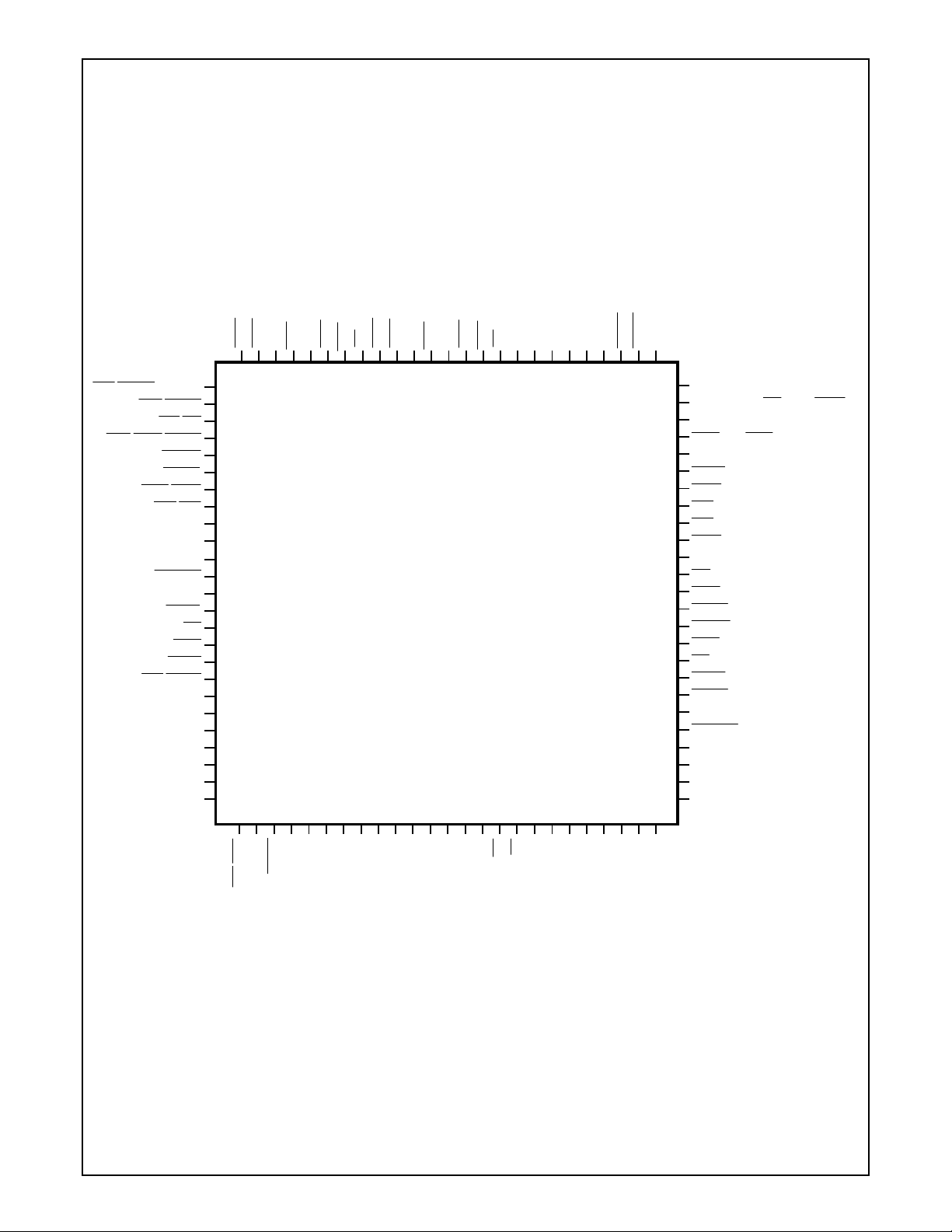
Thin Quad Flatpack (TQFP), JEDEC
AFD
/DSTRB/DENSEL
ERR
/HDSEL
INIT/DIR
SLIN/STEP/ASTRB
SLCT/WGATE
PE/WDATA
BUSY/WAIT/MTR1
ACK/DR1
PD7/MSEN1
PD6/DRATE0
PD5/MSEN0
PD4/DSKCHG
PD3/RDATA
PD2/WP
PD1/TRK0
PD0/INDEX
STB/WRITE
IRQ5/ADRATE0
VSS
IRQ7
IRQ6
VDD
IRQ4
IRQ3
MR
/BADDR0
DCD1
DSR1
SIN1
75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
CTS1
RTS1
SOUT1/BADDR1
DTR1/BOUT1
/IRQ12/IRRX2/IRSL0/ID0
RI1
SIN2/IRRX1
DSR2
DCD2/A15
PC97338VJG
/A13
/A14
RTS2
/A12/BOUT2
/A11
RI2
CTS2
SOUT2/CFG0/IRTX
DTR2
VSS
IRQ10
IRQ11
IRQ15/SIRQI1/DRQ3
IRQ9
DRQ0
DACK1
DACK0
IOCHRDY
50
DRATE0/MSEN0
49
DRATE1/MSEN1/CS0
48
VDD
47
DRV2
/PNF/DR23/SIRQI3/IRSL2/ID2
46
DENSEL/ADRATE1
45
INDEX
44
MTR0
43
DR1/PD
42
DR0
41
MTR1/IDLE/IRSL2/ID2
40
VSS
39
DIR
38
STEP
37
WDATA
36
WGATE
35
TRK0
34
WP
RDATA
33
HDSEL
32
DRQ1
31
DSKCHG
30
A10
29
28
A0
27
A1
26
A2
/SIRQI 2/D A CK3
X1
TC
DRQ2
DACK2
CS1/ZWS
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
VSS
IRSL1/ID1
D0
WR
A9A8A7A6A5
RD
AEN
A4
A3
Order Number PC97338VJG
See NS Package Number VJG100A
21
www.national.com
1.2 SIGNAL/PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Table 1 lists the signals of the Chip in alphabetical order. It also shows the pin associated with each signal for
the Plastic Quad Flatpack, (PQFP) and Thin Quad Flatpack (TQFP) options. The I/O column describes whether
the pin is an input, output, or bidirectional pin (marked as I, O or I/O, respectively). This column also specifies
which group in Section 8.2 describes the pin’s DC characteristics.
Refer to the glossary for an explanation of abbreviations and terms used in this table and throughout this document. Use the Table of Contents to find more information about each register.
Symbol
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
ACK
PQFP
Pin
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
31
62
63
64
66
69
85 83 I
TQFP
Pin
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
29
60
61
62
64
67
TABLE 1.
I/O an d
Group #
I
Group 1
Group 3
Signal/Pin Description Table
Function
Address.
which internal register is accessed. T he values of A15-0 have no
effect during DMA transfers.
If CFG0 = 0 during reset, A15-0 are u sed for address decoding.
If CFG0 = 1 during reset, only A10 -0 are used for address
decoding, and A15-11 are ignored (mas ked to 0).
In Legacy mode, A10 is used only for ECP decodi ng.
A15-11 are multiplexed with SCC2’s signals.
Acknow ledg e.
external printer to indicate it received data from the pa rallel port.
This pin is internally connec ted to a n ominal 25 KΩ pull-up resistor.
ACK
These address lines from the m icroprocessor determine
This parallel port input sig nal is pulsed low by an
is multip lexed wit h DR1. (See Table 72 for more information).
ADRATE0
ADRATE1
AEN 20 18 I
AFD
98
48
78 76 O
96
46
Group 10
Group 1
Group 11
O
Additional Data Rate signals 0 and 1.
are provided in addition to DRATE1,0 and ha ve a similar function.
They reflect the currently selected FDC data rate, (bits 0 a nd 1 in
the Configuration Control Register (CCR) or the Data Rate Select
Register (DSR), whichever was written to last).
ADRATE0 is configured whe n bit 0 of ASC is 1. ADRATE1 is
configured when bit 4 of ASC is 1.
ADRATE0 is multiplexed with IRQ5 and A DRATE1 is multiplexed
with DENSEL.
Address Enable.
and disables the microprocesso r Address. The address lines
disabled will be A15-0 o r A10-0, depending on whether CFG0 wa s
set to 0 or 1 during reset (respectively).
Access during DMA transfer is NOT affected by this pin.
Automatic Feed XT.
the external printer that it should automatically line feed after each
Carriage Return byte. This signal enters a TRI-STATE
within 10 nsec after a 0 is loaded into the Control Register bit.
An external 4.7 KΩ pull-up resistor should be attached to this pin.
AFD
is multip lexed wit h DSTRB and DENSEL. See Table 72 for
more information.
When set to 1, this pin enables DMA addressing
When low this parallel port signal indicates to
These FDC output signals
®
condition
22
www.national.com
Symbol
PQFP
Pin
TQFP
Pin
I/O an d
Group #
Function
ASTRB 81 79 O
Group 11
BADDR0
BADDR1
BOUT1
BOUT2
73
65
74
73
(71)
(63)
71
63
72
71
(69)
(61)
Group 1
Group 7
Address Strobe. This active-low signal is used in EPP mode as an
address strobe.
ASTR B
is multip lexed with SLIN and STEP. See Table 72 for more
information.
SIO Base Address Straps 0 and 1. These bits must be externally
I
strapped to determine whi ch one of four base address options for
the INDEX and DATA regist ers will be used by the system after
reset. See Table 8.
If BADDR1 = 0 and BADDR0 = 1 during reset, the chip “wakes up”
without a base address and th e Plug and Play protocol should be
applied. For more details see Section 2.
These pins are internal ly grounded by a 30 KΩ pull-down resistor.
To strap these pins high, pull them up to V
BADDR0 is multiplexed with RTS1
, and BADDR1 is multiplexed with
with a 10 KΩ resistor.
cc
SOUT1 (and BOUT1 in PC87338 only).
SCC Baud Output signals 1 and 2. These multi-function pins
O
provide the associated serial channel Baud Rat e generator output
signal for SCC1 or SCC2, if test mode is selected in the Power and
Test Configuration Register (PTR) and the DLAB bit (LCR7) is set.
BOUT1 is multiplexed with SOUT1 and BADDR1. BOUT2 is
multiplexed with SOUT2, IRTX and CFG0 (in PC87 338 only).
BOUT1 is multiplexed wit h D TR1. BO UT2 is multiplexed with DTR2
and A12 (in PC97338 only ).
BUSY 84 82 I
Group 2
CFG0 65 63 I
Group 9
CS0
CS1
51
3
49
1
Group 8
Busy. This parallel port signal is set high by the external printer
when it cannot accept another charac ter.
This pin is internally grounded by a nominal 25 KΩ pull-down
resi stor.
BUSY is multiplexed w ith MT R1
and WAIT. (See Table 72 for more
information).
Configuration. This CMOS i nput signal is externally strapped to
select one of two default configurations in which the Chip p owers
up (see Table 6).
This pin is internally grounded by a 30 KΩ pull-down resistor. To
strap this pin high, pull it up to V
with a 10 KΩ resistor.
CC
CFG0 is mult iplexed with SO UT2 and IRTX .
Programmable Chip Select signals 0 and 1. CS
O
1,0 are
programmable chip select and/or latch e nable and/or out put ena ble
signals that can be used as gam e port, I/O expander, etc.
The decoded address and th e assertion conditions are c onfigured
via the Chip co nfiguration registers, indexed by 0Ah-0Dh, 10h-11h,
03h and 4Dh.
CS
1,0 are push-pull output signals.
CS0
is multiplexed with DRATE1, MS EN1, SIRQI2 and DACK3.
CS1
is multipl exed with ZWS.
23
www.national.com
Symbol
PQFP
Pin
TQFP
Pin
I/O an d
Group #
Function
CTS1
CTS2
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
DACK0
72
64
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
70
62
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
Group 1
I/O
Group 6
55 53 I
Group 1
UART Clear to Send signals 1 and 2. When low, this signal
I
indicates that the modem or d ata transfer device is ready to
exchange data.
The CTS
signal is a modem status input signal who se condition can
be tested by reading bit 4 (CTS) of the Modem Stat us Register
(MSR) for the appropriate ser ial channel. B it 4 i s the c om plem ent of
the CTS
CTS
MSR. CTS
signal. Bit 0 (DCTS) of the MSR indic ates whether the
input has changed state sinc e the previous reading of the
has no effect on the transmitte r.
If modem status interrupts are en abled, an interrupt is generated
whenever the DCTS bit of the MSR is set.
CTS2
is multiplexed with A13. When CTS2 is not selected, it is
masked to 0.
Data. Th ese signals are bi-directional data lines to the
microprocessor. D0 is the LSB and D7 is th e MSB.
DMA Acknowledge 0. An active low input signal used to
acknowledge DMA request 0 (DRQ0), and to enable the R D
WR
input signals during a DMA transfer. It can be used by either
the FDC, or the SCC2 or the parallel port. If none of them uses this
input signal, it is ignored. If the device which uses this si gnal is
disabled or configured with no DMA, the signal is also ignored.
Upon reset, it is ignored.
and
DACK1
DACK2
DACK3
54 52 I
Group 1
53 I
Group 1
51 49 I
Group 1
DMA Acknowledge 1. An active low input signal used to
acknowledge DMA request 1 (DRQ1), and enable the RD
and WR
input signals during a DMA transfer. It can be used by one of the
following: FDC, SCC2 or parallel port. If none of them us es this
input signal, it is ignored. If the device which uses this si gnal is
disabled or configured with no DMA, the signal is also ignored.
Upon reset, it is ignored.
DMA Acknowledge 2. An active low input signal used to
acknowledge DMA request 2 (DRQ2), and enable the RD
and WR
input signals during a DMA transfer. It can be used by one of the
following: FDC, SCC2 or parallel port. If none of them us es this
input signal, it is ignored. If the device which uses this si gnal is
disabled or configured with no DMA, the signal is also ignored.
Upon reset, it is used by the FDC.
DMA Acknowledge 3. An active low input signal used to
acknowledge DMA request 3 (DRQ3), and enable the RD
and WR
inputs during a DMA transfer. It can be used by one of the following:
FDC, SCC2 or parallel port. If none of them uses this input signal,
it is ignored. If the device which uses this signal is disabled or
configured with no D MA, the signal is also ig nored. Upon reset, it is
used by the FDC. DACK3
CS0
and SIRQI2.
is multip lexed wit h DRATE1, MSE N1,
24
www.national.com
Symbol
PQFP
Pin
TQFP
Pin
I/O an d
Group #
Function
DCD1
DCD2
DENSEL
(Normal
Mode)
(PPM
Mode)
77
69
75
67
Group 1
48 46 O
Group 10
78 76 O
Group 10
UART Data Carrier Detect signals 1 and 2. When low, this signal
I
indicates that the mode m or data transfer device has de tected the
data carrier.
The DCD
2,1 signals are mode m status input signals whose
condition can be tested by reading bit 7 (DCD) of the Modem
Status Register (MSR) for the appropriate serial channel . Bit 7 is
the complement of the DCD
indicates whether the DCD
signal. Bit 3 (DDCD) of the MSR
input signal has changed state since the
previous reading of the MSR.
If modem status interrupts are enabled, an interrupt is generated
whenever the DDCD bit of the MSR is set to 1.
DCD2
is multiplexed with A15. When DCD2 is not selected, it is
masked to 1.
Density Select. Indicates that a high density FDC data rate (500
Kbps, 1 Mbps or 2 Mbps) or a l ow density data rate (250 Kbps or
300 Kbps) is selected. The polarity of DENS EL is controlled via bit
6 of the ASC register. The default is active high for high density.
DENSEL is also programmable via the MODE command .
DENSEL is multiplexed with A DRATE1.
Density Select. This pin provides an additional Density Select
signal in PPM mode when PNF = 0.
DENSEL is multiplexed with A FD
, DSTR B. See Table 72 for more
information.
DIR
(Normal
41 39 O
Group 10
Mode)
(PPM
Mode)
DR0
DR1
80 78 O
Group 10
44
45
42
43
Group 10
(Normal
Mode)
DR1
(PPM
85 83 O
Group 10
Mode)
DR23 49 47 O
Group 10
Direction. This FDC output signal determines the direction of the
Floppy Disk Drive (FDD) head movement (active = step in, inactive
= step out) during a seek ope ration. During read or write
operations, DIR
is inactive.
Direction. This FDC pin provides an additional direction signal in
PPM Mode when PNF = 0. DIR
is multiplexed with INIT. See Table
72 for more information.
FDC Drive Select signals 0 and 1. These FDC s ignals are
O
decoded drive select output sig nals controlled by Digital Output
Register bits D0 and D1.
These signals are gated with DOR bi ts 7 through 4. These are
active low output signals. They are encoded with information to
control four FDDs when bit 4 of the Function Enable Re giste r (FER)
is set. DR0,1
are exchanged only via the TDR register. (Bit 4 of the
FCR register is reserved.)
DR1
is multip lexed with PD.
FDC Drive Select 1. This signal provides an additional drive select
signal in PPM mode when PNF = 0. It is drive select 1 when bit 4
of FCR is 0. It is drive select 0 when bit 4 of FCR is 1. This signal
is active low. DR1
is multip lexed with ACK. See Table 72 for more
information.
Drive 2 or 3. This FDC signal is assert ed when either drive 2 or
drive 3 is accessed (except during logical dr ive exchange, see bit 3
of TDR). This pin is configured when bits 7, 6 of SIRQ3 are 01.
DR23
is multip lexed with IRSL 0, DRV2, SIRQI3 and PNF.
25
www.national.com

Symbol
PQFP
Pin
TQFP
Pin
I/O an d
Group #
Function
DRATE0
DRATE1
(Normal
Mode)
DRATE0
(PPM
Mode)
DRQ0
DRQ1
DRQ2
DRQ3
DRV2
52
51
50
49
O
Group 8
87 85 O
Group 8
56
33
4
60
54
31
2
58
O
Group 6
49 47 I
Group 4
Data Rates 0 and 1. These FDC outpu t signals reflect the currently
selected FDC data rate, (bits 1 and 0 in the Configuration Control
Register (CCR) or the Data Rate Select Register (DSR), whi chever
was written to last). The pins are totem-pole buffered output signals
(6 mA sink, 6 mA source).
DRATE0 is multiplexed with MSEN0. DRATE1 is multiplexed with
MSEN1, SIRQI2, CS0
and DACK3.
Data Rate 0. This pin prov ides an additional FDC data rate signal,
in PPM mode, when PN F = 0.
DRATE0 is multiplexed with PD6. See Table 72 for m ore
information.
DMA Requests 0, 1, 2 and 3. These active high outputs signal the
DMA controller that a data transfer is required.
This DMA request can be sourced by one of the following: FDC,
SCC2 or parallel port. When n ot sourced by any of them, it is in
TRI-STATE. In Plug and Play mode, when the sourced device is
disabled or when the s ourced device is configured with no D MA, it
is also in TRI-STATE. Upon reset, DRQ2 is used by the FDC; and
DRQ0,1 and 3 are in TRI-STATE.
DRQ3 is multiplexed with IRQ15, and SIRQI1.
Drive2. This FDC input s ignal indicates (low) when a second disk
drive has been installed. The state of t his signal is available from
Status Register A in P S/2 m ode. This p in is conf igured when bits 7
and 6 of SIRQ3 are 00.
DRV2
is multip lexed with DR23, PNF, SIRQI3 and IRSL2.
DSKCHG
(Normal
Mode)
(PPM
Mode)
DSR1
DSR2
DSTRB
32 30 I
Group 4
89 87 I
Group 4
76
68
74
66
Group 1
78 76 O
Group 11
Disk Change. This FDC input signal indicates if t he drive door is
open. The state of this signal is ava ilable from the Digital Input
Register (DIR). This signal can also be configured as the RGATE
data separator diagnostic input signal via the MODE comm and (see
“The MODE Comm and” on page -101)
Disk Change. This signal provides an additional FDC Disk Change
signal in PPM Mode when PNF = 0. DSKCHG
is multip lexed with
PD4. See Table 36 for more information.
Data Set Ready signals 1 and 2. When low, these UART signals
I
indicates that the appropriate data transfer device or m odem is
ready to establish a communications link. The DSR
signal is a
modem status input whos e condition can b e tested by reading bi t 5
(DSR) of the Modem Status Regi ster (MSR) for the appropriate
channel. Bit 5 is the complement of the DSR
of the MSR indicates whether the DS R
signal. Bit 1 (DDSR)
input signal has changed
state since the previous reading of the MS R.
If modem status interrupts are enabled an interrupt is generated
whenever the DDSR bit of the MSR is set.
When DSR2
DSR2
is not selected, it is masked to 0.
is multiplexed with IRRX2, IRQ12 an d IRSL0.
Data Strobe. This signal is used in EPP mode as a data strobe. It
is active low.
DSTRB
is multip lexed with AFD, DENSEL. See Table 72 for more
information.
26
www.national.com
Symbol
PQFP
Pin
TQFP
Pin
I/O an d
Group #
Function
DTR1
DTR2
ERR
HDSEL
(Normal
Mode)
(PPM
Mode)
ID2
ID1
ID0
71
63
69
61
Group 7
79 77 I
Group 3
34 32 O
Group 10
79 77 O
Group 10
43 or
49
8
68
41 or
47
6
66
Group 1
Data Terminal Ready signals 1 and 2. When low, these UART
O
output signals indicate to the appropriate m odem or data transfer
device that the UART is ready to establish a communications li nk.
The DTR
signal can be set to active low by programming bit 0
(DTR) of the Modem Control Register (MCR ) to a high level. A
Master Reset (MR) operation sets this signal to its inactive (high)
state. Loop mode operation holds this signal to it s inactive state.
DTR2
is multip lexed with A12
(and BOUT2 in PC9733 8 only)
Error. This parallel port input signal is set low by the external printer
when it has detected an error.
This pin is internally connec ted to a nomina l 25 KΩ pull-up resistor.
ERR
is multiplexed with HDSEL. See Table 72 for more information.
Head Select. This FDC output signal determines which side of the
FDD is accessed. Active (low) selects side 1, inactive (high) selects
side 0.
Head Select. This signal provides an additional head select signal in
PPM mode when PNF = 0. HDSEL
is multiplexed with ERR. See
Table 72 for more inform ation.
Identification –
I
and Play support. These pins are read after reset. These pins are available
only in PC97338.
ID2 is multiplexed with
DR23
, SIRQI3 and IRSL2.
ID1 is multiplexed with IRSL1.
ID0 is multiplexed with
These ID signals identify the infrared transceiver for Plug
MTR1
, IDLE and I RSL2 or with
DSR2
, IRQ12, IRRX2 and IRSL0.
DRV2
.
, PNF,
IDLE 43 41 O
Group 10
INDEX
(Normal
47 45 I
Group 4
Mode)
(PPM
Mode)
94 92 I
Group 4
INIT 80 78 O
Group 11
IOCHRDY 53 51 O
Group 13
Idle . This FDC output pin is used for an IDLE output signal when bit
4 of PMC is 1. It is used for MTR1
when bit 4 of PMC is 0. IDLE
indicates that the FDC is in the Idle state and ca n be powered
down. Whenever the FDC is in the Idle state, or whenever the FDC
is in a power-down state, the pin is active high.
IDLE is mu ltiplexed with MTR 1
and IRSL2.
Index. Thi s input signal indicates the beginning of an FDD track.
FDC Index. This signal provides an additional index signal in PPM
mode when PNF = 0.INDE X
is multiplexed with PD0. See Table 72
for more information.
Parallel Port Initialize. When this signal is low, it causes the printer
to be initialized. This signal is in a TRI-S TATE c ondition 10 nsec
after a 1 is loaded into the corresponding Control R egister bit. The
system should pull this pin high usi ng a 4.7 KΩ resistor.
INIT
is multip lexed with DIR.
I/O Channel Ready. This is the I/O Channel Ready open-drain
output signal. When IOCHRDY is driven low, the EPP extends the
host cycle.
27
www.national.com
Symbol
PQFP
Pin
TQFP
Pin
I/O an d
Group #
Function
IRQ3
IRQ4
IRQ5
IRQ6
IRQ7
IRQ9
IRQ10
IRQ11
IRQ12
IRQ15
(Plug and
Play mode)
IRQ3
IRQ4
(Legacy
mode)
1
100
98
97
96
57
58
59
68
60
1
100
99
98
96
95
94
55
56
57
66
58
99
98
I/O
Group 6
O
Group 6
Interrupts Requests 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12 and 15. These
signals are used to request an interrup t from the host processor,
when appropriate. These output pin s can be configured as totempole or open-drain outputs (see below).
Any of these interrupt request lines may be assigned to any one of
the following: SCC1, SCC2, parallel port, FDC, SIRQI1 signal,
SIRQI2 signal, or SIRQI3 signal. For more details, refer to Sections
2 and 6.
When the parallel port’s interrupt is routed to one of these pins, bit
6 of the PCR determ ines whether the o utput signal is totem pole or
open drain. Otherwise, they are totem-pole outputs.
This pin is I/O only wh en t he p arallel port’s interrupt is routed to this
pin, ECP is enabled and bit 6 of PCR is 1.The Plug and P lay mode
is determined by bit 3 of PNP0.
IRQ5 is mul tiplexed with A DRAT E0.
IRQ12 is multiplexe d with DSR2
, IRRX2 and IRSL0.
IRQ15 is multiplexed with SIRQI1 and DRQ3.
Interrupts 3 and 4. These are active high interrupts associated with
the serial ports. IRQ3 presents the device interr upt request if the
serial channel has been des ignated as COM2 or COM4. IRQ4
presents the device interrupt requ est if the serial p ort is designa ted
as COM1 or COM3.
The appropriate interrupt is enabled via IER, the as sociated
Interrupt Enable bit (Modem Control Register (MCR) bit 3), and the
interrupt request is actually triggered whe n one of the following
events occur : Receiver Error, Receive Data available, Transmitter
Holding Register Empty, or a Modem Status Flag is s et.
The interrupt request signal becom es inactive (low) after the
appropriate interrupt serv ice routine is executed, after being
disabled via the IER, or after a Master Reset. Either interrupt can
be disabled and put in TRI-STATE by setting bit 3 of the MCR low.
IRQ5
(Legacy
mode)
IRQ6
(Legacy
mode)
IRQ7
(Legacy
mode)
98 96 I/O
Group 6
97 95 O
Group 6
96 94 I/O
Group 6
Interrupt 5. This active high output signal indicates a parallel port
interrupt request. When enabled, this signal follows the ACK
signal
input. When bit 4 in the pa rallel port Control Re gister is set and the
parallel port address is desi gnated as shown in Table 11, this
interrupt is enabled. When no t enabled this signal is TRI-STATE.
This pin is I/O only when ECP i s enabled, and IRQ5 is configured.
Interrupt 6. This active high output signal indicates an interrupt
request upon completion of the exec ution phase for cert ain FDC
commands. It also signals when a da ta transfer is ready during a
non-DMA operation. In PC-AT or Model 30 mode, this signal is
enabled by bit D3 of the DOR. In PS/2 mode, IRQ6 is always
enabled, and bit D3 of the DOR is reser ved.
Interrupt 7. This active high output signal indicates a parallel port
interrupt request. When enabled, this signal follows the ACK
signal
input. When bit 4 in the pa rallel port Control Re gister is set and the
parallel port address is desi gnated as shown in Table 11, this
interrupt is enabled. When not enabled, this signal is in TRI-STATE.
This pin is I/O only when ECP is enabled, and IRQ7 is configured.
For ECP operation, refer to the interrupt ECP in Sect ion 4.5.5.
28
www.national.com
Symbol
PQFP
Pin
TQFP
Pin
I/O an d
Group #
Function
IRRX1
IRRX2
IRSL0
IRSL1
IRSL2
IRTX 65 63 O
MR 2 100 I
MSEN0
MSEN1
(Normal
Mode)
67
68
68
8
43 or 49
52
51
65
66
66
6
41 or 47
50
49
Group 1
Group 12
Group 12
Group 1
Group 4
Infrared Received data signals 1 and 2. Infrared serial data inp ut
I
signals. The infrared Analog Front End (AFE) is expected to send 1
to IRRX if there is no transmission. If it sends 0, the input signal
should be inverted by RXINV (bit 4 of register 7, in bank 7 of SCC2
- See Figure 88).
IRRX1 is m ultiplexed with SI N2.
IRRX2 is multiplexed with DSR2
Infrared Control signals 0, 1 and 2. These signals control the
O
infrared Analog Front End (AFE).
IRSL0 is m ultiplexed with DS R2
PC97338)
.
, IRQ12 and IRSL0 .
, IRQ12, IRRX2
(and ID0 in
IRSL1 is multiplexed with ID1 in PC97338.
IRSL2 is multiplexed with either DRV2, PNF, DR23, SIRQI3
ID2 in PC97338)
Infrared Transmitted data. Infrared serial data output.
IRTX is multiplexed with SOUT2, CFG0 (and BOUT2 in PC87338).
Master Reset. Active high input signa l that re s ets the controller to t he
idle state. The c onfiguration registers are s et to their se lected default
values. See the reset stat us for each functi onal unit.
Media Sense signals 0 and 1. MSEN0 is selected as a m edia
I
sense input signal when bit 1 of the FCR register is 0. MSEN1 is
selected as a media sense input signal when bits 7 and 6 of the
SIRQ2 register are 00.
Each pin is internally connected t o a 10 KΩ pull-up resistor. When
bit 1 of FCR is 1, pin 52 is used as a Data Rate 0 output pin, and
the pull-up resistor is disabled.
When DACK3
MSEN1 is masked to 1.
MSEN0 is multiplexed with DRATE0.
MSEN1 is multiplexed with DACK3
, or with MTR1, IDLE
, DRATE1, CS0 or SIRQI2 is selected on the pin ,
(and ID2 in PC97338)
, CS0, SIRQI2 and DRATE1.
(and
.
MSEN0
MSEN1
(PPM
Mode)
MTR0
MTR1
(Normal
Mode)
MTR1
(PPM
Mode)
88
86
46
43
84 82 O
86
84
44
41
Group 4
O
Group 10
Group 10
Media Sense signals 0 and 1. These signals provide additional
I
media sense signals in PPM mode when PNF = 0.
MSEN0 and MSEN1 are multiplexed with PD5 and PD7,
respectively. See Table 72 for more information.
FDC Motor Select signals 0 and 1. These motor en able lines for
drives 0 and 1 are controlled by bits 7 through 4 of the Digital
Output register. They are active low output signals. They are
encoded with information to control four FDDs (MTR0
logical mo tor values w ith MTR1
settings.
Bit 4 of the FCR register is reserved.
MTR1
is multiplexed with IDLE and IR SL2.
FDC Motor Select 1. This signal provides an additional motor select
1 signal in PPM mode when PNF = 0. It i s ac tive low. This pin is t he
motor enable line for drive 1 or drive 0, according to the TDR
register. Bit 4 of the FCR register is reserved.
MTR1
is multiplexed with BUSY and W AIT. See Table 72 for more
information.
29
) according to the TDR register
exchanges
www.national.com
Symbol
PQFP
Pin
TQFP
Pin
I/O an d
Group #
Function
PD 45 43 O
Group 10
PD0
PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
PD5
PD6
PD7
94
93
92
91
89
88
87
86
92
91
90
89
87
86
85
84
I/O
Group 1
and
Group 11
PE 8 3 81 I
Group 2
PNF 4 9 47 I
Group 1
Power Down . Thi s pin is used for the FDC Power-Down (PD)
output signal when bit 4 of PMC is 1. It is used for DR1
when bit 4
of PMC is 0. PD is active high whenever the FDC is put into a
power-down state by bit 6 of DSR (or bit 3 of FER, or bit 0 of PTR),
or by the MODE command.
PD is mult iplexed with DR 1
.
Parallel- Port Data signals 0 through 7. These bidirection al pins
transfer data to and from the peripheral data bus and the parallel
port Data Register. These pins have high current drive capability.
See “Device Description” on page -197.
PD7-0 are multiplexed with INDEX
, TRK0, WP, RDATA, DSKCHG,
MSEN0, DRAT E0 and MSEN1, respecti vely. See Table 72 for m ore
information.
Paper End. This parallel port input signal is set high by the ext ernal
printer when it is out of paper.
This pin is internally grounded by a nominal 25 KΩ pull-down
resi stor.
PE is mult iplexed with WDAT A
. See Table 72 for more information.
Printer Not Floppy. PNF is the Printer Not Floppy signal. It selects
the device which is connected to the PPM p ins.
When a parallel printer is connec ted, PNF must be set to 1, and
when a floppy disk drive is connected, PNF must be set to 0. This
pin is configured as PNF whe n bits 7 and 6 of SIRQ3 are 10.
PNF is multip lexed with DRV2
, DR23, SIRQI3 and IRSL2.
RD
RDATA
(Normal
Mode)
(PPM
Mode)
RI1
RI2
19 17 I
Group 1
35 33 I
Group 4
91 89 I
Group 4
70
62
68
60
Group 1
Read. Active low input signal to indicate a data read by the
microprocessor.
Read Data. This input signal is the raw serial data read from the
floppy disk drive.
Read Data. This pin provides an additional read data signal in PPM
mode when PNF = 0.
R
DATA is multiplexed with PD3. See Table 72 for more information.
Ring Indicators 1 and 2. When low, these UART signals indicates
I
that a telephone ring signal has be en received by the appropriate
modem.
The RI
signal is a modem status in put signal whose condition ca n
be tested by reading bit 6 (RI) of the Modem S tatus Regi ster (M SR )
for the appropriate serial channel. Bit 6 is the complement of the RI
signal. Bit 2 (TERI) of the MSR indicates whe ther the RI
signal has changed from low to high since t he previous reading of
the MSR.
When the TERI bit of MSR is set to 1, an i nterrupt is generated if
modem status interrupts are ena bled.
RI2
is multiplexed with A11. When RI2 is not sele cted, it is m asked
to 1.
input
30
www.national.com
 Loading...
Loading...