NSC PC16550DN, PC16550DV, PC16550DVEF, PC16550DVX Datasheet
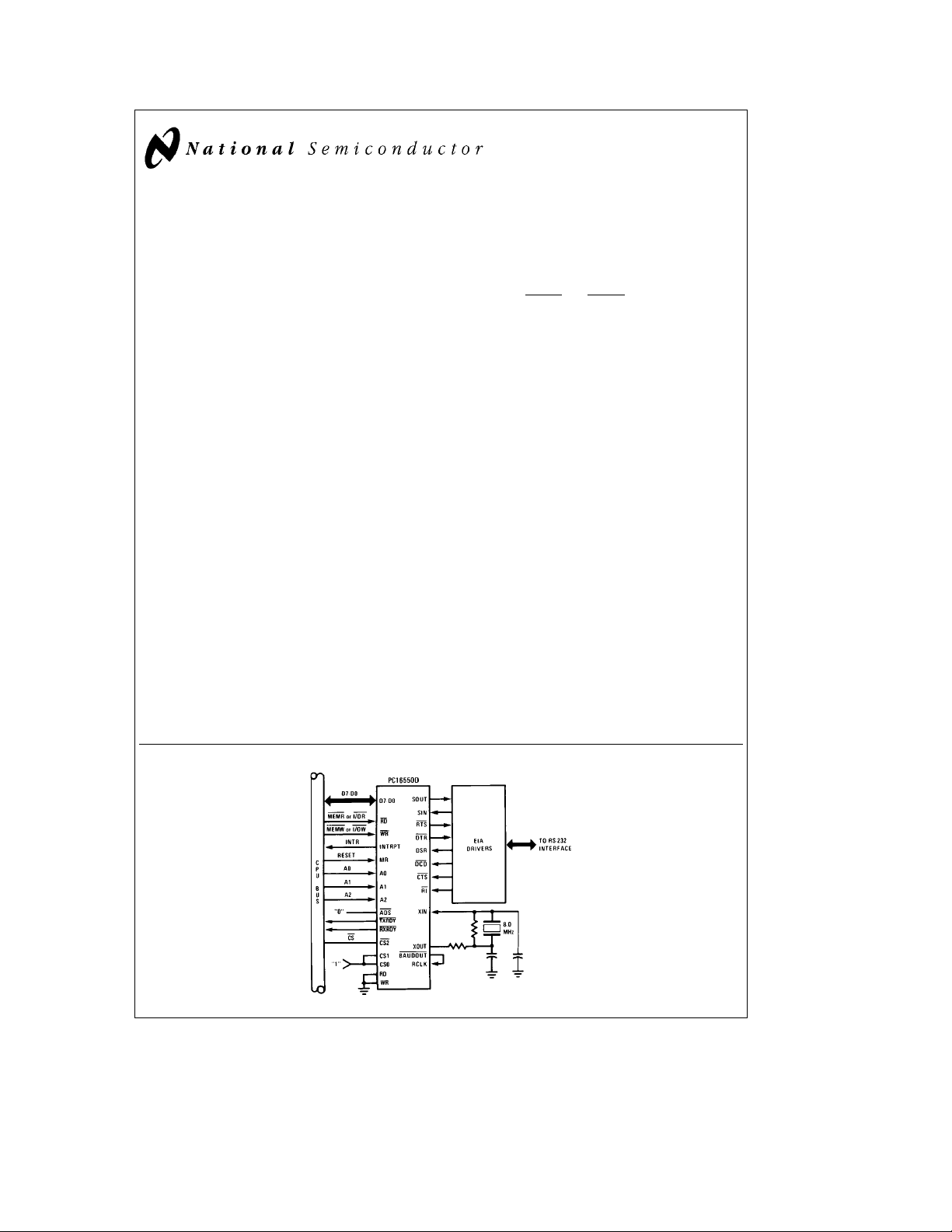
PC16550D Universal Asynchronous
Receiver/Transmitter with FIFOs
General Description
The PC16550D is an improved version of the original 16450
Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART).
Functionally identical to the 16450 on powerup (CHARACTER mode)* the PC16550D can be put into an alternate
mode (FIFO mode) to relieve the CPU of excessive software
overhead.
In this mode internal FIFOs are activated allowing 16 bytes
(plus 3 bits of error data per byte in the RCVR FIFO) to be
stored in both receive and transmit modes. All the logic is on
chip to minimize system overhead and maximize system efficiency. Two pin functions have been changed to allow signalling of DMA transfers.
The UART performs serial-to-parallel conversion on data
characters received from a peripheral device or a MODEM,
and parallel-to-serial conversion on data characters received from the CPU. The CPU can read the complete
status of the UART at any time during the functional operation. Status information reported includes the type and condition of the transfer operations being performed by the
UART, as well as any error conditions (parity, overrun, framing, or break interrupt).
The UART includes a programmable baud rate generator
that is capable of dividing the timing reference clock input
by divisors of 1 to (2
driving the internal transmitter logic. Provisions are also included to use this 16
UART has complete MODEM-control capability, and a processor-interrupt system. Interrupts can be programmed to
the user’s requirements, minimizing the computing required
to handle the communications link.
The UART is fabricated using National Semiconductor’s advanced M
*Can also be reset to 16450 Mode under software control.
²
2
Note: This part is patented.
16
b
c
clock to drive the receiver logic. The
CMOS process.
1), and producing a 16cclock for
²
Features
Y
Capable of running all existing 16450 software.
Y
Pin for pin compatible with the existing 16450 except
for CSOUT (24) and NC (29). The former CSOUT and
NC pins are TXRDY
Y
After reset, all registers are identical to the 16450 register set.
Y
In the FIFO mode transmitter and receiver are each
buffered with 16 byte FIFO’s to reduce the number of
interrrupts presented to the CPU.
Y
Adds or deletes standard asynchronous communication
bits (start, stop, and parity) to or from the serial data.
Y
Holding and shift registers in the 16450 Mode eliminate
the need for precise synchronization between the CPU
and serial data.
Y
Independently controlled transmit, receive, line status,
and data set interrupts.
Y
Programmable baud generator divides any input clock
by1to(2
Y
Independent receiver clock input.
Y
MODEM control functions (CTS, RTS, DSR, DTR, RI,
and DCD).
Y
Fully programmable serial-interface characteristics:
Ð 5-, 6-, 7-, or 8-bit characters
Ð Even, odd, or no-parity bit generation and detection
Ð 1-, 1(/2-, or 2-stop bit generation
Ð Baud generation (DC to 1.5M baud).
Y
False start bit detection.
Y
Complete status reporting capabilities.
Y
TRI-STATEÉTTL drive for the data and control buses.
Y
Line break generation and detection.
Y
Internal diagnostic capabilities:
Ð Loopback controls for communications link fault
isolation
Ð Break, parity, overrun, framing error simulation.
Y
Full prioritized interrupt system controls.
and RXRDY, respectively.
16
b
1) and generates the 16cclock.
PC16550D Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter with FIFOs
June 1995
Basic Configuration
TRI-STATEÉis a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corp.
C
1995 National Semiconductor Corporation RRD-B30M75/Printed in U. S. A.
TL/C/8652
TL/C/8652– 1
1.0 ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
2.0 DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
3.0 AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
4.0 TIMING WAVEFORMS
5.0 BLOCK DIAGRAM
6.0 PIN DESCRIPTIONS
7.0 CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
8.0 REGISTERS
8.1 Line Control Register
8.2 Typical Clock Circuits
Table of Contents
8.0 REGISTERS (Continued)
8.3 Programmable Baud Generator
8.4 Line Status Register
8.5 FIFO Control Register
8.6 Interrupt Identification Register
8.7 Interrupt Enable Register
8.8 Modem Control Register
8.9 Modem Status Register
8.10 Scratchpad Register
8.11 FIFO Interrupt Mode Operation
8.12 FIFO Polled Mode Operation
9.0 TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
2
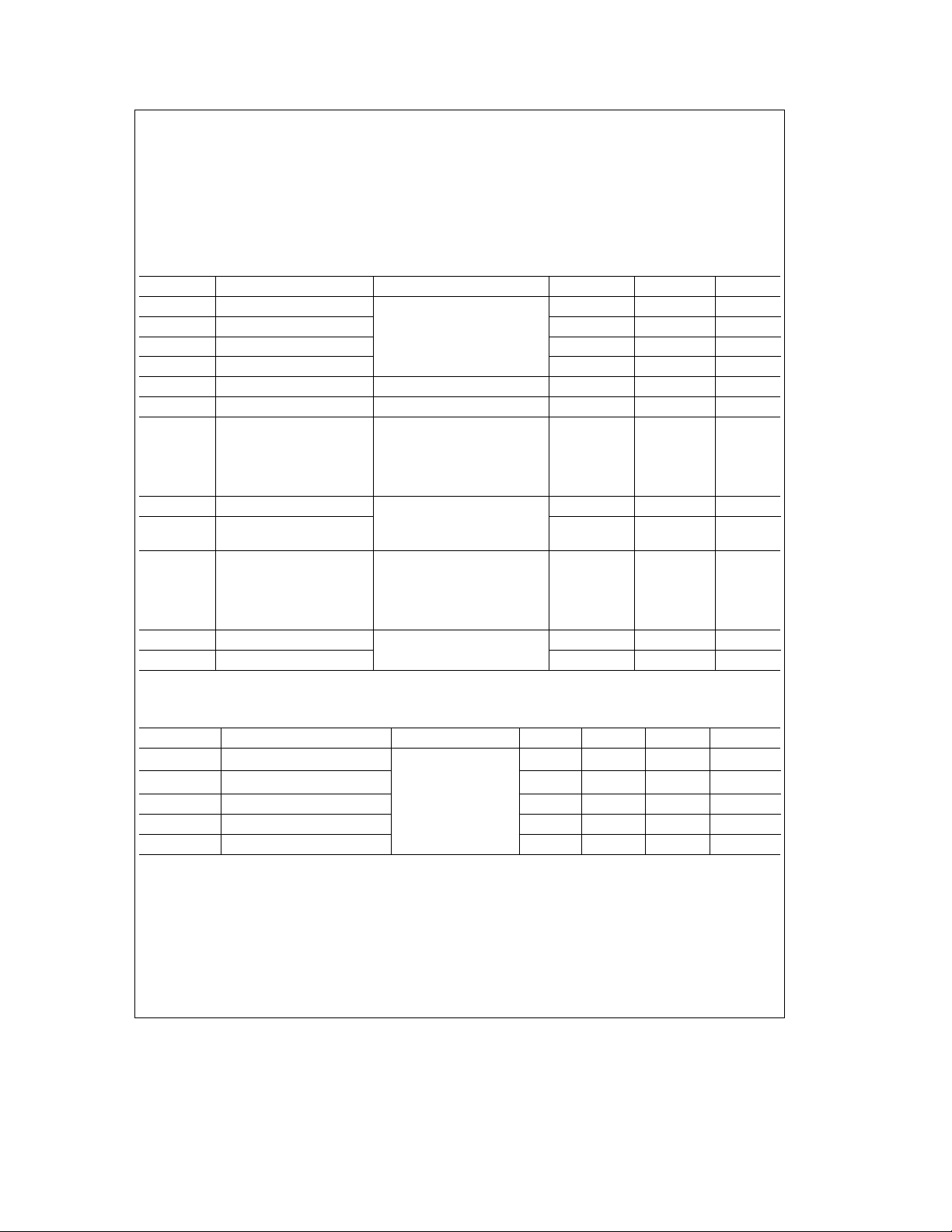
1.0 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Temperature Under Bias 0§Ctoa70§C
Storage Temperature
All Input or Output Voltages
with Respect to V
SS
b
65§Ctoa150§C
b
0.5V toa7.0V
Power Dissipation 1W
2.0 DC Electrical Characteristics
e
T
0§Ctoa70§C, V
A
DD
ea
5Vg10%, V
e
0V, unless otherwise specified.
SS
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Units
V
ILX
V
IHX
V
IL
V
IH
V
OL
V
OH
ICC(AV) Average Power Supply V
Clock Input Low Voltage
Clock Input High Voltage 2.0 V
Input Low Voltage
Input High Voltage 2.0 V
Output Low Voltage I
Output High Voltage I
Current No Loads on output
e
1.6 mA on all (Note 1) 0.4 V
OL
eb
1.0 mA (Note 1) 2.4 V
OH
e
5.5V, T
DD
SIN, DSR, DCD, 15 mA
e
CTS, RI
2.0V
All other inputs
I
IL
I
CL
I
OZ
Input Leakage V
Clock Leakage
TRI-STATE Leakage V
e
5.5V, V
DD
All other pins floating.
e
V
0V, 5.5V
IN
e
5.5V, V
DD
e
V
0V, 5.25V
OUT
1) Chip deselected
2) WRITE mode,
chip selected
V
ILMR
V
IHMR
Note 1: Does not apply to XOUT
MR Schmitt V
MR Schmitt V
IL
IH
Maximum ratings indicate limits beyond which perma-
Note:
nent damage may occur. Continuous operation at these limits is not intended and should be limited to those conditions
specified under DC electrical characteristics.
b
0.5 0.8 V
DD
b
0.5 0.8 V
DD
e
25§C
A
e
0.8V
e
0V
SS
e
0V
SS
g
10 mA
g
10 mA
g
20 mA
0.8 V
2.0 V
V
V
Capacitance T
A
e
25§C, V
DD
e
e
V
0V
SS
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
C
C
C
C
C
XIN
XOUT
IN
OUT
I/O
Clock Input Capacitance 7 9 pF
e
f
1 MHz
Clock Output Capacitance 7 9 pF
Input Capacitance 5 7 pF
c
Unmeasured pins
returned to V
SS
Output Capacitance 6 8 pF
Input/Output Capacitance 10 12 pF
3
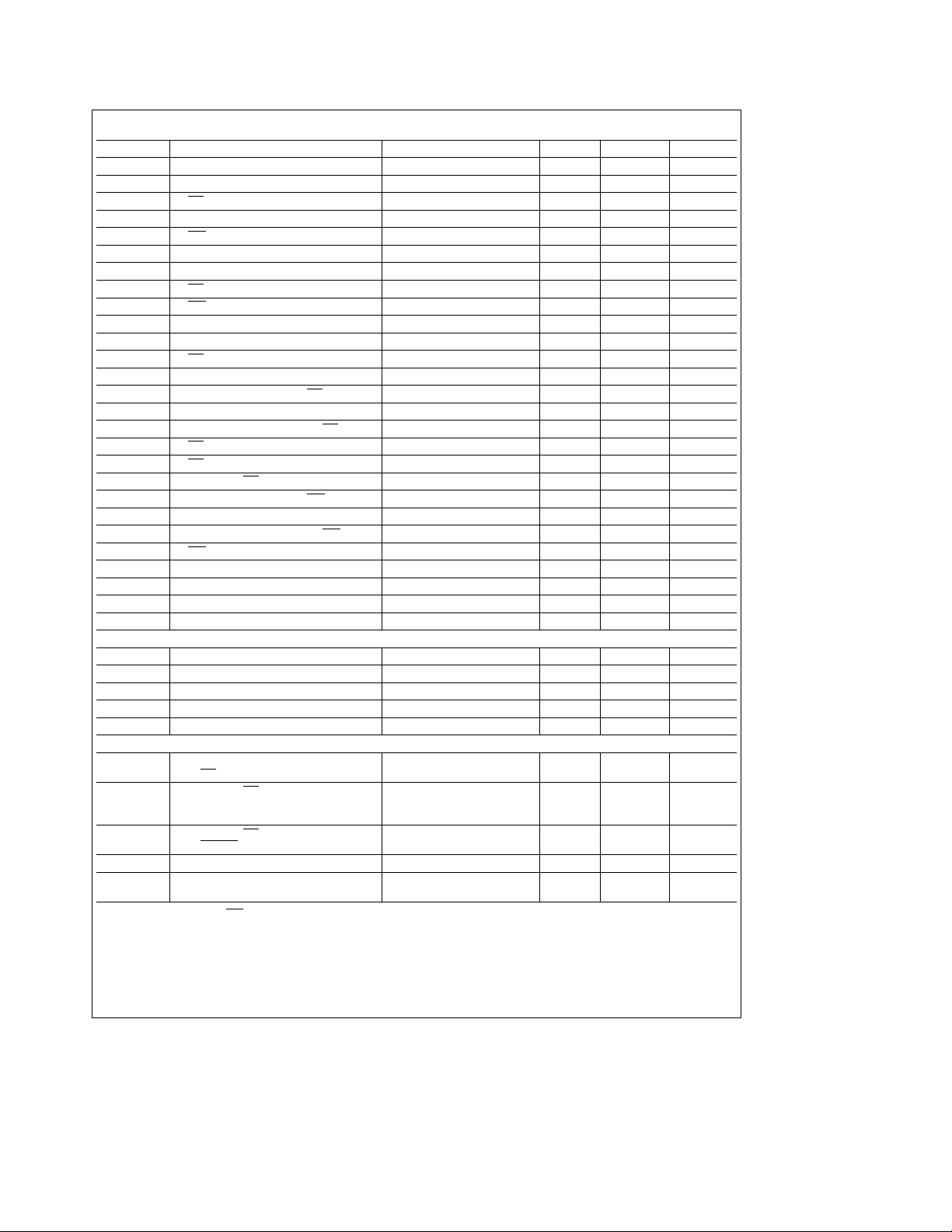
3.0 AC Electrical Characteristics T
e
0§Ctoa70§C, V
A
DD
ea
5Vg10%
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Units
t
ADS
t
AH
t
AR
t
AS
t
AW
t
CH
t
CS
t
CSR
t
CSW
t
DH
t
DS
t
HZ
t
MR
t
RA
t
RC
t
RCS
t
RD
t
RDD
t
RVD
t
WA
t
WC
t
WCS
t
WR
t
XH
t
XL
RC Read Cycleet
WC Write Cycleet
Address Strobe Width 60 ns
Address Hold Time 0 ns
RD, RD Delay from Address (Note 1) 30 ns
Address Setup Time 60 ns
WR, WR Delay from Address (Note 1) 30 ns
Chip Select Hold Time 0 ns
Chip Select Setup Time 60 ns
RD, RD Delay from Chip Select (Note 1) 30 ns
WR, WR Delay from Select (Note 1) 30 ns
Data Hold Time 30 ns
Data Setup Time 30 ns
RD, RD to Floating Data Delay
@
100 pF loading (Note 3) 0 100 ns
Master Reset Pulse Width 5000 ns
Address Hold Time from RD, RD (Note 1) 20 ns
Read Cycle Delay 125 ns
Chip Select Hold Time from RD, RD (Note 1) 20 ns
RD, RD Strobe Width 125 ns
RD, RD to Driver Enable/Disable
Delay from RD, RD to Data
@
100 pF loading (Note 3) 60 ns
@
100 pF loading 60 ns
Address Hold Time from WR, WR (Note 1) 20 ns
Write Cycle Delay 150 ns
Chip Select Hold Time from WR, WR (Note 1) 20 ns
WR, WR Strobe Width 100 ns
Duration of Clock High Pulse External Clock (8, Max.) 55 ns
Duration of Clock Low Pulse External Clock (8, Max.) 55 ns
a
a
t
AR
AW
t
RD
a
RC
a
t
t
WR
WC
280 ns
280 ns
Baud Generator
16
N Baud Divisor 1 2
t
BHD
t
BLD
t
HW
t
LW
Baud Output Positive Edge Delay 100 pF Load 175 ns
Baud Output Negative Edge Delay 100 pF Load 175 ns
Baud Output Up Time f
Baud Output Down Time f
e8,d
2, 100 pF Load 75 ns
X
e8,d
2, 100 pF Load 100 ns
X
b
1
Receiver
t
RAI
t
RINT
t
RXI
t
SCD
t
SINT
Note 1: Applicable only when ADS is tied low.
Note 2: In the FIFO mode (FCR0
will be delayed 3 RCLKs. Status indicators (PE, FE, BI) will be delayed 3 RCLKs after the first byte has been received. For subsequently received bytes these
indicators will be updated immediately after RDRBR goes inactive. Timeout interrupt is delayed 8 RCLKs.
Note 3: Charge and discharge time is determined by V
Note 4: These specifications are preliminary.
Delay from Active Edge
of RD
to Reset Interrupt
Delay from RD, RD 100 pF Load
(RD RBR/or RD LSR) 1000 ns
to Reset Interrupt
Delay from RD RBR
to RXRDY
Inactive
Ðns
290 ns
Delay from RCLK to Sample Time 2000 ns
Delay from Stop to Set Interrupt (Note 2)
e
1) the trigger level interrupts, the receiver data available indication, the active RXRDY indication and the overrun error indication
and the external loading.
OL,VOH
1
RCLK
Cycles
4
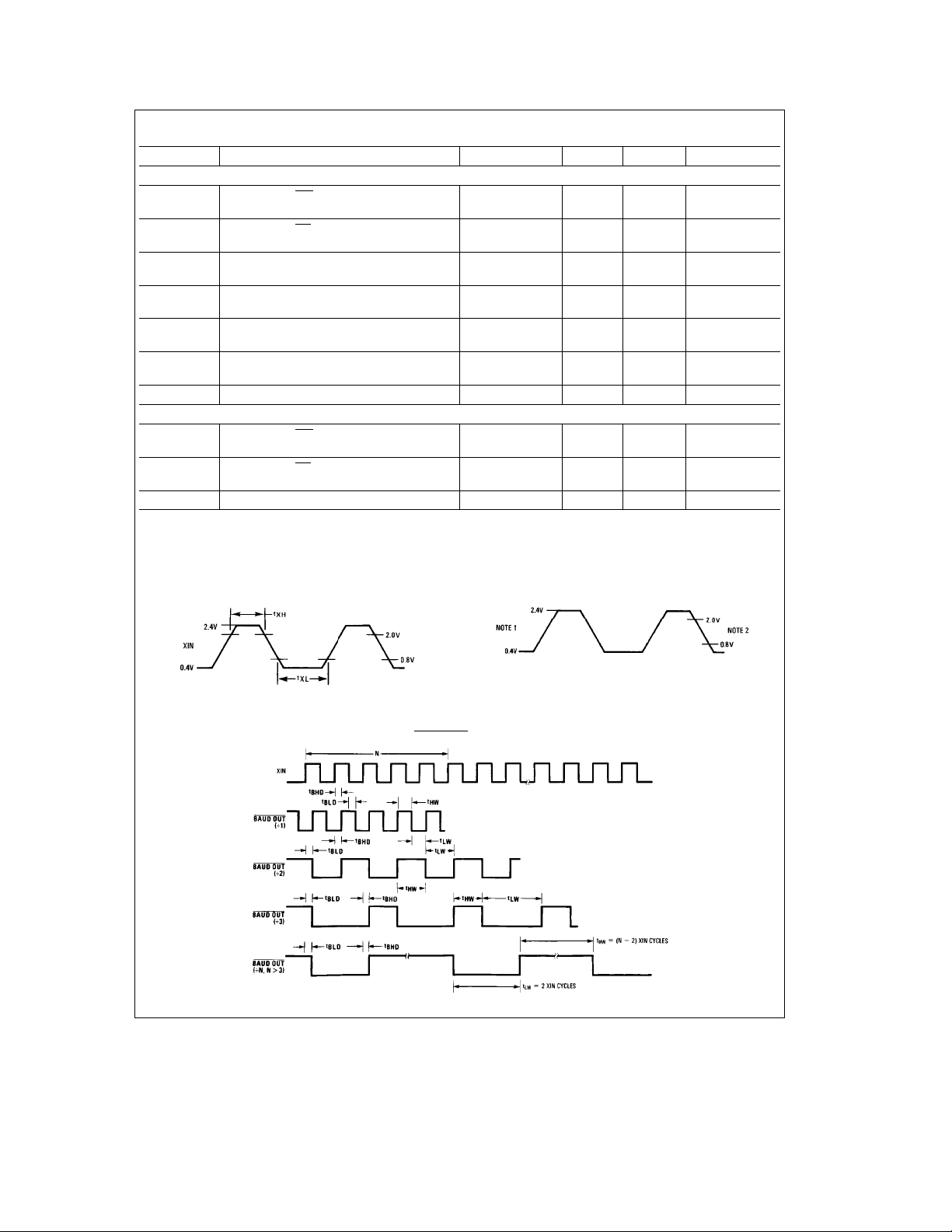
3.0 AC Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Units
Transmitter
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
HR
IR
IRS
SI
STI
SXA
WXI
Delay from WR, WR (WR THR) 100 pF Load
to Reset Interrupt
Delay from RD, RD (RD IIR) to Reset 100 pF Load
Interrupt (THRE)
Delay from Initial INTR Reset to Transmit
Start Cycles
Delay from Initial Write to Interrupt (Note 1)
Delay from Stop to Interrupt (THRE) (Note 1)
824
16 24
88
Delay from Start to TXRDY active 100 pF Load
175 ns
250 ns
BAUDOUT
BAUDOUT
Cycles
BAUDOUT
Cycles
8
BAUDOUT
Cycles
Delay from Write to TXRDY inactive 100 pF Load 195 ns
Modem Control
t
MDO
t
RIM
t
SIM
Note 1: This delay will be lengthened by 1 character time, minus the last stop bit time if the transmitter interrupt delay circuit is active. (See FIFO Interrupt Mode
Operation).
Note 2: These specifications are preliminary.
Delay from WR, WR (WR MCR) to 100 pF Load
Output
Delay from RD, RD to Reset Interrupt 100 pF Load
(RD MSR)
200 ns
250 ns
Delay from MODEM Input to Set Interrupt 100 pF Load 250 ns
4.0 Timing Waveforms (All timings are referenced to valid 0 and valid 1)
External Clock Input (24.0 MHz Max.)
AC Test Points
Note 1: The 2.4V and 0.4V levels are the voltages that the inputs are driven to during AC testing.
Note 2: The 2.0V and 0.8V levels are the voltages at which the timing tests are made.
TL/C/8652– 2
BAUDOUT Timing
5
TL/C/8652– 3
TL/C/8652– 4
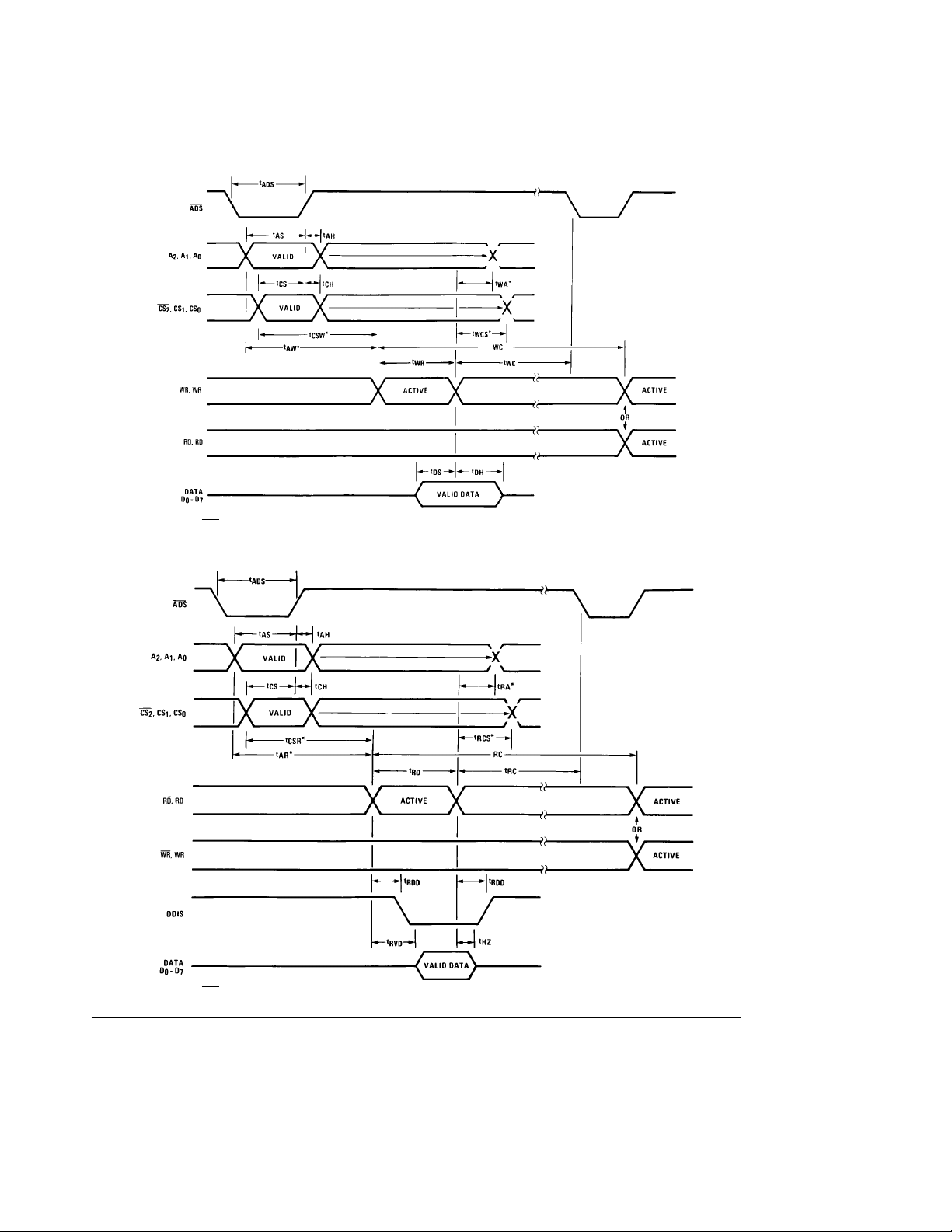
4.0 Timing Waveforms (Continued)
Write Cycle
*Applicable Only When ADS is Tied Low.
TL/C/8652– 5
Read Cycle
*Applicable Only When ADS is Tied Low.
TL/C/8652– 6
6
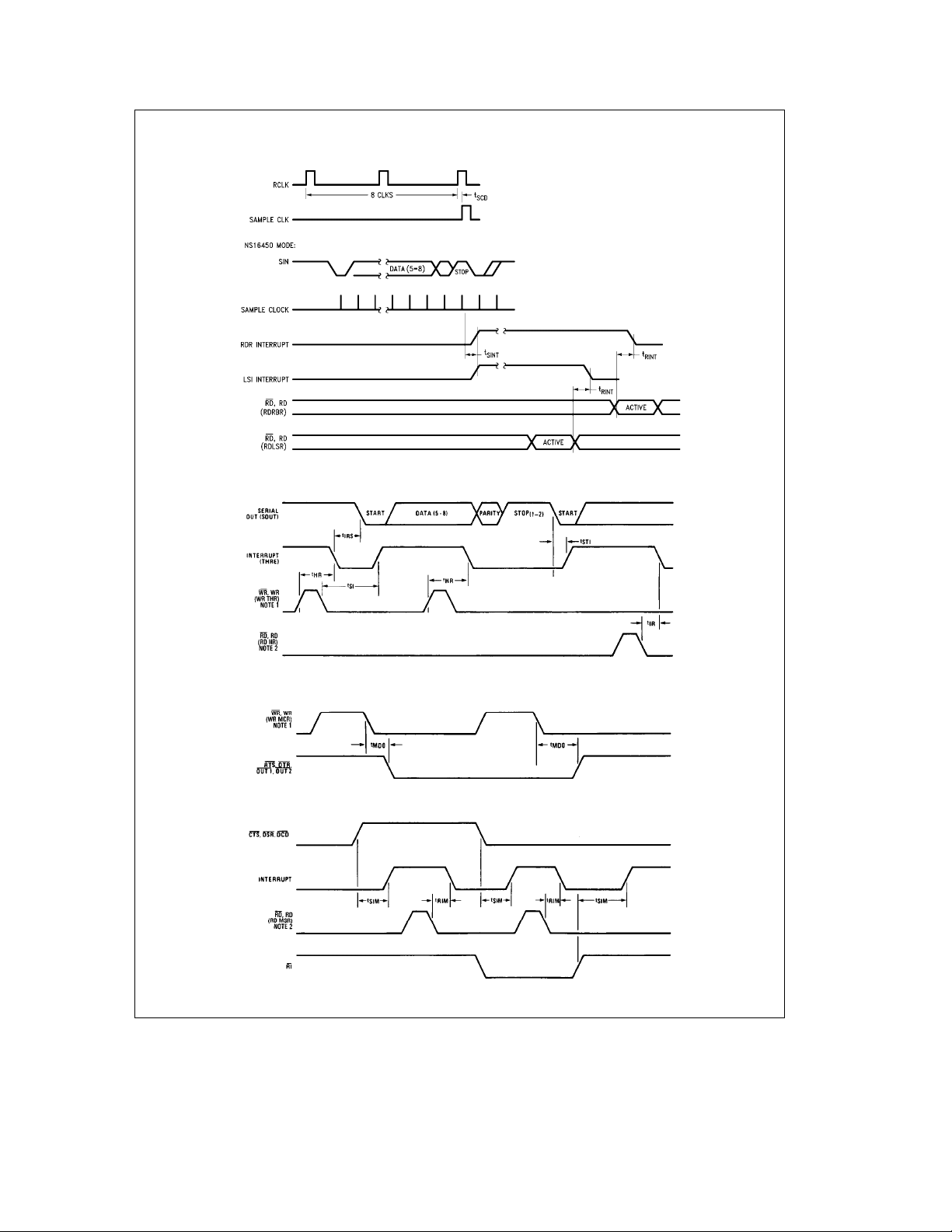
4.0 Timing Waveforms (Continued)
Receiver Timing
TL/C/8652– 7
Transmitter Timing
Note 1: See Write Cycle Timing
Note 2: See Read Cycle Timing
TL/C/8652– 8
MODEM Control Timing
TL/C/8652– 9
7
 Loading...
Loading...