NSC LP3982ILD-3.0, LP3982ILD-2.82, LP3982ILD-2.77, LP3982ILD-1.8, LP3982IMMX-3.0 Datasheet
...
LP3982
Micropower, Ultra Low-Dropout, Low-Noise, 300mA
CMOS Regulator
General Description
The LP3982 low-dropout (LDO) CMOS linear regulator is
available in 1.8V, 2.5V, 2.77V, 2.82V, 3.0V, 3.3V, and adjustable versions. They deliver 300mA of output current. Packaged in an 8-Pin MSOP, the LP3982 is pin and package
compatible with Maxim’s MAX8860. The LM3982 is also
available in the small footprint LLP package.
The LP3982 suits battery powered applications because of
its shutdown mode (1nA typ), low quiescent current (90µA
typ), and LDO voltage (120mV typ). The low dropout voltage
allows for more utilization of a battery’s available energy by
operating closer to its end-of-life voltage. The LP3982’s
PMOS output transistor consumes relatively no drive current
compared to PNP LDO regulators.
This PMOS regulator is stable with small ceramic capacitive
loads (2.2µF typ).
These devices also include regulation fault detection, a
bandgap voltage reference, constant current limiting and
thermal overload protection.
Features
n MAX8860 pin, package and spec. compatible
n LLP space saving package
n 300mA guaranteed output current
n 120mV typical dropout
@
300mA
n 90µA typical quiescent current
n 1nA typical shutdown mode
n 60dB typical PSRR
n 2.5V to 6V input range
n 120µs typical turn-on time
n Stable with small ceramic output capacitors
n 37µV RMS output voltage noise (10Hz to 100kHz)
n Over temperature/over current protection
n
±
2% output voltage tolerance
Applications
n Wireless handsets
n DSP core power
n Battery powered electronics
n Portable information appliances
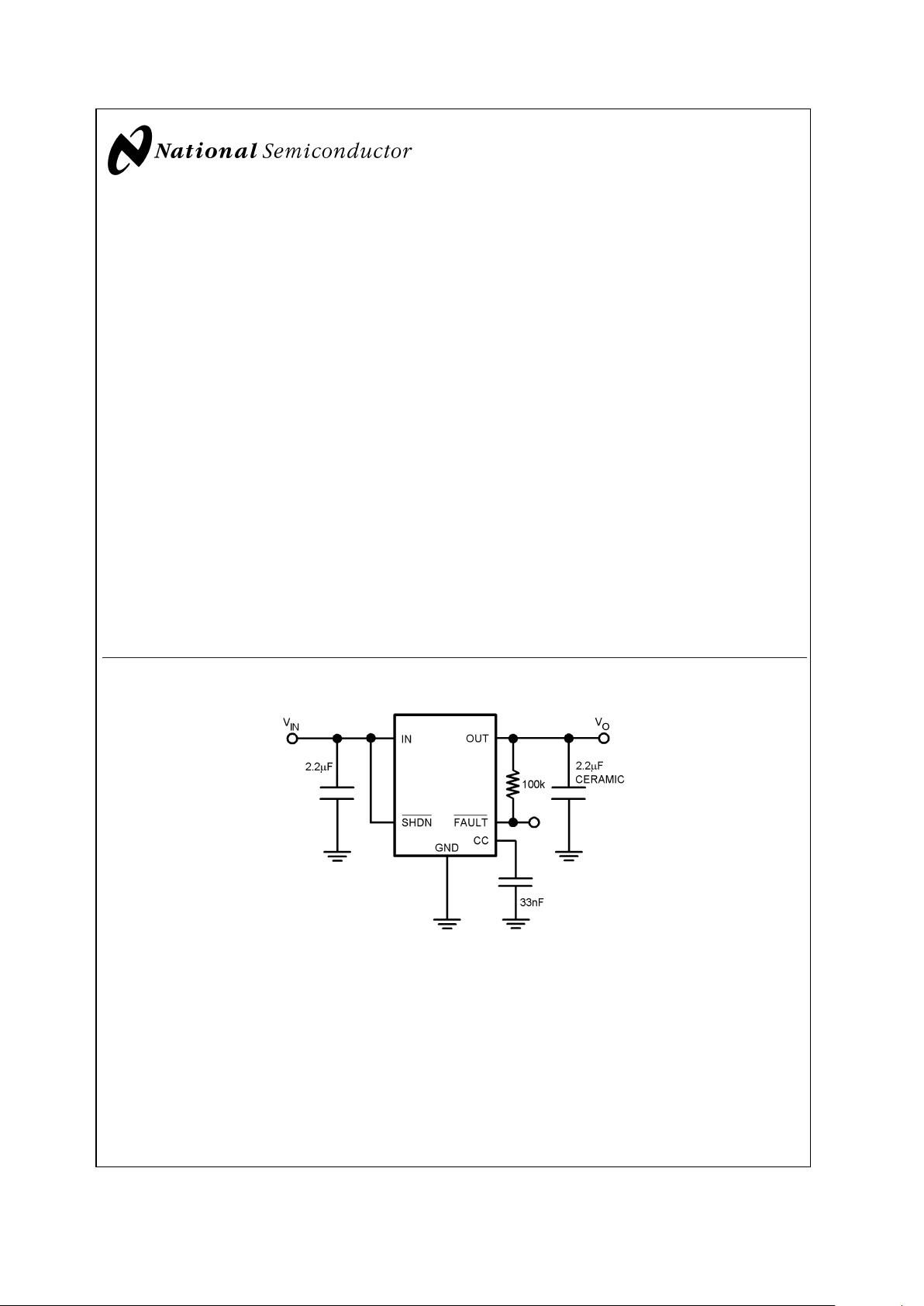
Application Circuit
20036931
July 2002
LP3982 Micropower, Ultra Low-Dropout, Low-Noise, 300mA CMOS Regulator
© 2002 National Semiconductor Corporation DS200369 www.national.com
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Notes 1,
2)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
V
IN,VOUT,VSHDN,VSET,VCC
,
V
FAULT
−0.3V to 6.5V
Fault Sink Current 20mA
Power Dissipation (Note 3)
Storage Temperature Range −65˚C to 160˚C
Junction Temperature (T
J
) 150˚C
Lead Temperature (10 sec.) 260˚C
ESD Rating
Human Body Model (Note 6) 2kV
Machine Model 200V
Thermal Resistance (θ
JA
)
8-Pin MSOP 223˚C/W
8-Pin LLP (Note 3)
Operating Ratings(Note 1), (Note 2)
Temperature Range −40˚C to 85˚C
Supply Voltage 2.5V to 6.0V
Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for VIN=VO+0.5V (Note 7), V
SHDN=VIN,CIN=COUT
= 2.2µF, CCC= 33nF,
TJ= 25˚C. Boldface limits apply for the operating temperature extremes: −40˚C and 85˚C.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min
(Note 5)
Typ
(Note 4)
Max
(Note 5)
Units
V
IN
Input Voltage 2.5 6.0 V
∆V
O
Output Voltage Tolerance 100µA ≤ I
OUT
≤ 300mA
V
IN=VO
+0.5V, (Note 7)
SET = OUT for the Adjust
Versions
−2 +2
%of
V
OUT (NOM)
−3 +3
V
O
Output Adjust Range Adjust Version Only 1.25 6 V
I
O
Maximum Output Current Average DC Current Rating 300 mA
I
LIMIT
Output Current Limit 330 770 mA
I
Q
Supply Current I
OUT
= 0mA 90 270
µA
I
OUT
= 300mA 225
Shutdown Supply Current V
O
= 0V, SHDN = GND 0.001 1 µA
V
DO
Dropout Voltage
(Note 7), (Note 8)
I
OUT
= 1mA 0.4
mVI
OUT
= 200mA 80 220
I
OUT
= 300mA 120
∆V
O
Line Regulation I
OUT
= 1mA, (VO+ 0.5V) ≤ VI≤ 6V
(Note 7)
−0.1 0.01 0.1 %/V
Load Regulation 100µA ≤ I
OUT
≤ 300mA 0.002 %/mA
e
n
Output Voltage Noise I
OUT
= 10mA, 10Hz ≤ f ≤ 100kHz 37 µV
RMS
Output Voltage Noise Density 10Hz ≤ f ≤ 100kHz, C
OUT
= 10µF 190 nV/
V
SHDN
SHDN Input Threshold VIH,(VO+ 0.5V) ≤ VI≤ 6V
(Note 7)
2
V
V
IL
,(VO+ 0.5V) ≤ VI≤ 6V
(Note 7)
0.4
I
SHDN
SHDN Input Bias Current SHDN = GND or IN 0.1 100 nA
I
SET
SET Input Leakage SET = 1.3V, Adjust Version Only
(Note 9)
0.1 2.5 nA
V
FAULT
FAULTDetection Voltage VO≥ 2.5V, I
OUT
= 200mA
(Note 10)
120 280 mV
FAULT Output Low Voltage I
SINK
= 2mA 0.115 0.25 V
I
FAULT
FAULT Off-Leakage Current FAULT = 3.6V, SHDN = 0V 0.1 100 nA
T
SD
Thermal Shutdown
Temperature
160
˚C
Thermal Shutdown Hysteresis 10
T
ON
Start-Up Time C
OUT
= 10µF, VOat 90% of Final
Value
120 µs
LP3982
www.national.com 2
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Note 1: Absolute Maximum ratings indicate limits beyond which damage may occur. Electrical specifications do not apply when operating the device outside of its
rated operating conditions.
Note 2: All voltages are with respect to the potential at the ground pin.
Note 3: Maximum Power dissipation for the device is calculated using the following equations:
where T
J(MAX)
is the maximum junction temperature, TAis the ambient temperature, and θJAis the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance. E.g. for the MSOP-8
package θ
JA
= 223˚C/W, T
J(MAX)
= 150˚C and using TA= 25˚C, the maximum power dissipation is found to be 561mW. The derating factor (−1/θJA) = −4.5mW/˚C,
thus below 25˚C the power dissipation figure can be increased by 4.5mW per degree, and similarity decreased by this factor for temperatures above 25˚C. The value
of the θ
JA
for the LLP package is specifically dependent on the PCB trace area, trace material, and the number of layers and thermal vias. For improved thermal
resistance and power dissipation for the LLP package, refer to Application Note AN-1187.
Note 4: Typical Values represent the most likely parametric norm.
Note 5: All limits are guaranteed by testing or statistical analysis.
Note 6: Human body model: 1.5kΩ in series with 100pF.
Note 7: Condition does not apply to input voltages below 2.5V since this is the minimum input operating voltage.
Note 8: Dropout voltage is measured by reducing V
IN
until VOdrops 100mV from its nominal value at VIN-VO= 0.5V. Dropout Voltage does not apply to the 1.8
version.
Note 9: The SET pin is not externally connected for the fixed versions.
Note 10: The FAULT detection voltage is specified for the input to output voltage differential at which the FAULT pin goes active low.
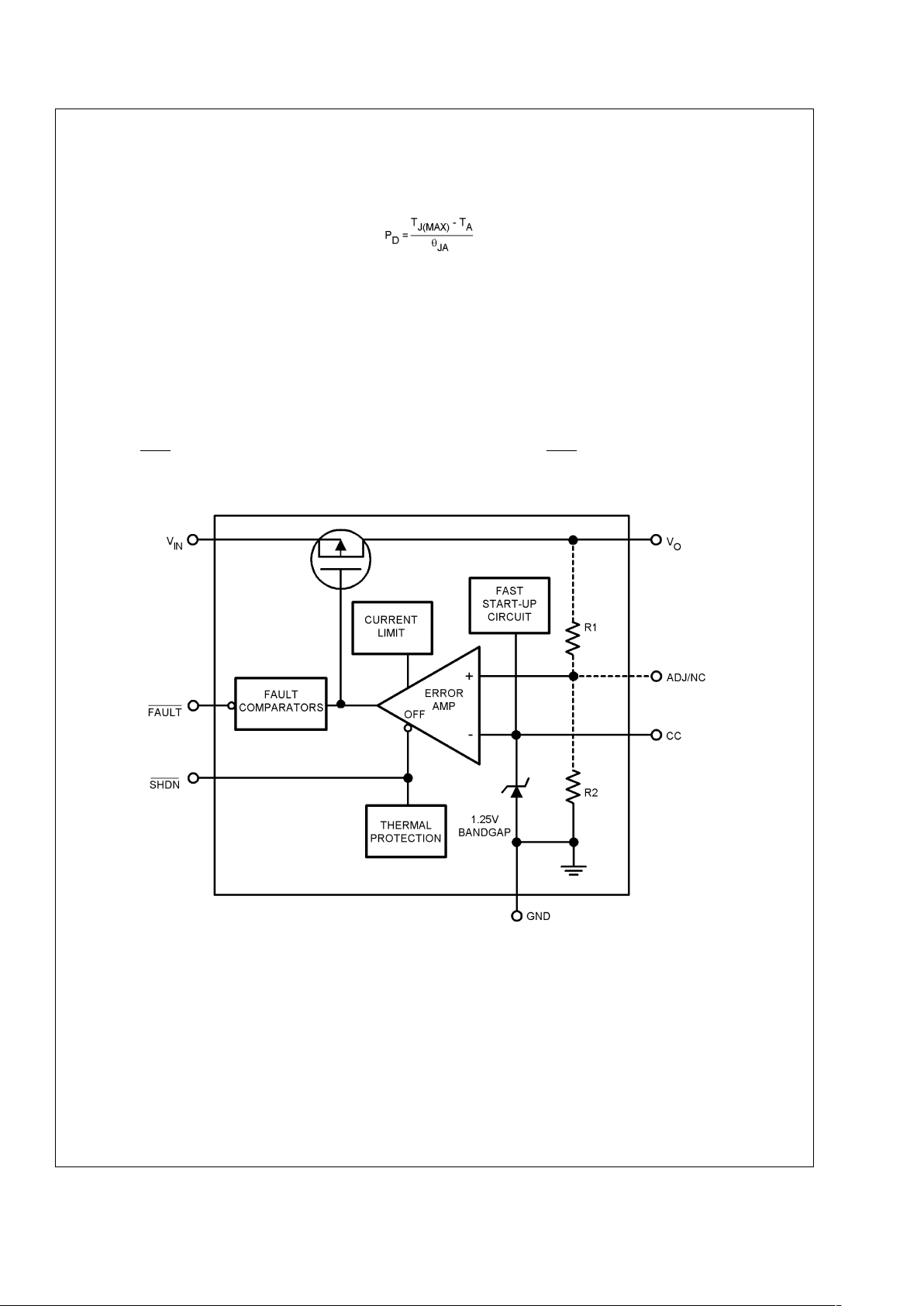
Functional Block Diagram
20036913
LP3982
www.national.com3
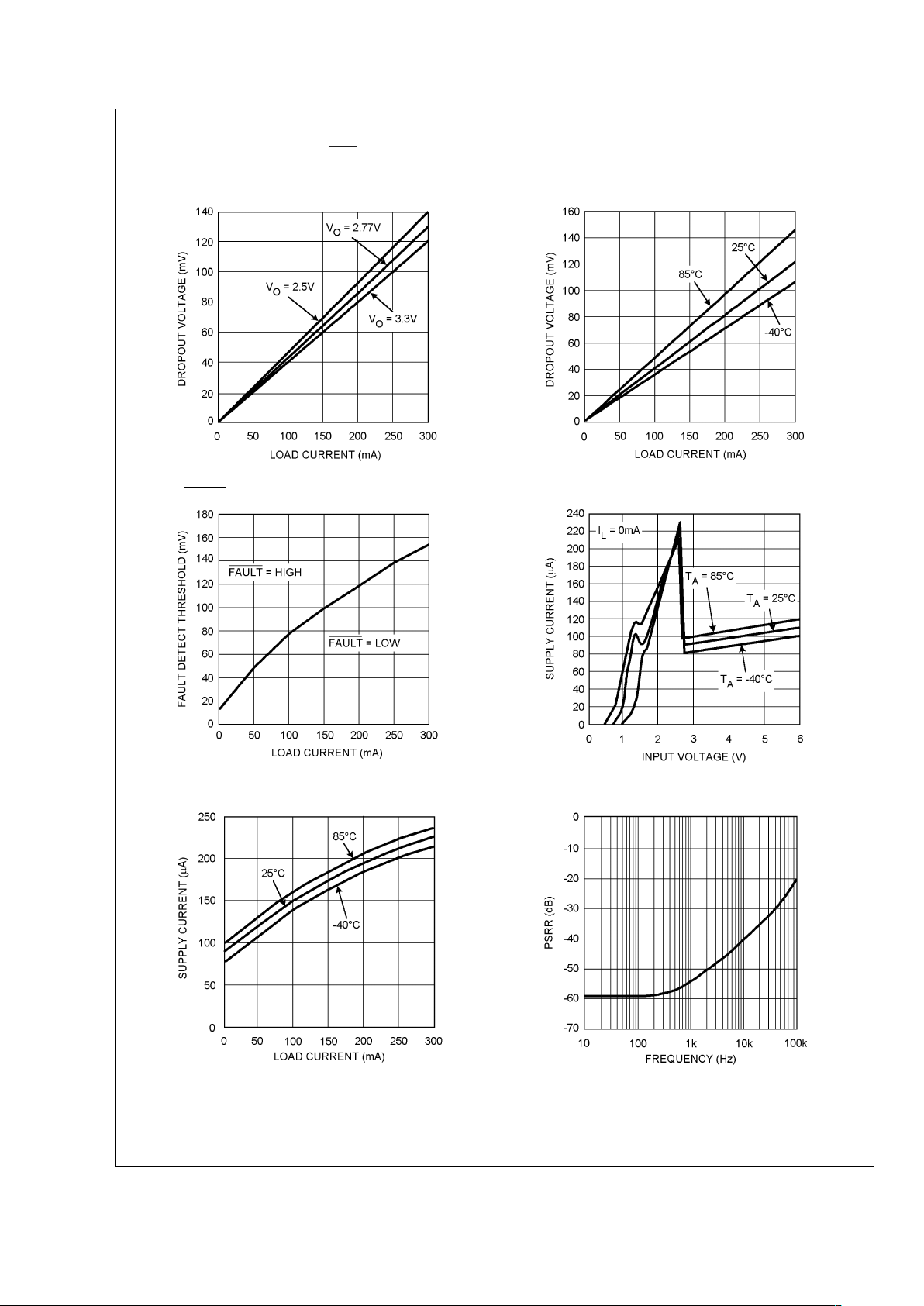
Typical Performance Characteristics Unless otherwise specified, V
IN=VO
+ 0.5V, CIN=C
OUT
=
2.2µF, C
CC
= 33nF, TJ= 25˚C, V
SHDN=VIN
.
Dropout Voltage vs. Load Current
(For Different Output Voltages)
Dropout Voltage vs. Load Current
(For Different Output Temperatures)
20036903 20036927
FAULT Detect Threshold vs. Load Current Supply Current vs. Input Voltage
20036928
20036929
Supply Current vs. Load Current Power Supply Rejection Ratio vs. Frequency
20036930
20036904
LP3982
www.national.com 4
 Loading...
Loading...