NSC LMV339MX, LMV339MTX, LMV339MT, LMV339M, LMV331M7X Datasheet
...
August 1999
LMV331 Single / LMV393 Dual / LMV339 Quad
General Purpose, Low Voltage, TinyPack Comparators
LMV331 Single / LMV393 Dual / LMV339 Quad General Purpose, Low Voltage, TinyPack
Comparators
General Description
The LMV393 and LMV339 are low voltage (2.7-5V) versions
of the dual and quad comparators, LM393/339, which are
specified at 5-30V. The LMV331 is the single version, which
is availableinspace saving SC70-5 and SOT23-5 packages.
SC70-5 is approximately half the size of SOT23-5.
The LMV393 is available in 8-pin SOICand 8-pin MSOP.The
LMV339 is available in 14-pin SOIC and 14-pin TSSOP.
The LMV331/393/339 is the most cost-effective solution
where space, low voltage, low power and price are the primary specification in circuit design for portable consumer
products. They offer specifications that meet or exceed the
familiar LM393/339 at a fraction of the supply current.
The chips are built with National’s advanced Submicron
Silicon-Gate BiCMOS process. The LMV331/393/339 have
bipolar input and output stages for improved noise performance.
Connection Diagrams
5-Pin SC70-5/SOT23-5
DS100080-1
Top View
Features
(For 5V Supply, Typical Unless Otherwise Noted)
n Space Saving SC70-5 Package (2.0 x 2.1 x 1.0
mm)
n Space Saving SOT23-5 Package (3.00 x 3.01 x
1.43 mm)
n Guaranteed 2.7V and 5V Performance
n Industrial Temperature Range −40˚C to +85˚C
n Low Supply Current 60µA/Channel
n Input Common Mode Voltage Range Includes Ground
n Low Output Saturation Voltage 200 mV
Applications
n Mobile Communications
n Notebooks and PDA’s
n Battery Powered Electronics
n General Purpose Portable Device
n General Purpose Low Voltage Applications
14-Pin SO/TSSOP
8-Pin SO/MSOP
Top View
DS100080-2
Top View
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS100080 www.national.com
DS100080-3
Ordering Information
Temperature Range Packaging
Package
5-pin SC70-5 LMV331M7 C13 1k Units Tape and Reel MAA05
5-pin SOT23-5 LMV331M5 C12 1k Units Tape and Reel MA05B
8-pin Small Outline LMV393M LMV393M Rails
8-pin MSOP LMV393MM LMV393 1k UnitsTape and Reel
14-pin Small Outline LMV339M LMV339M Rails
14-pin TSSOP LMV339MT LMV339MT Rails
Industrial
−40˚C to +85˚C
LMV331M7X C13 3k Units Tape and Reel
LMV331M5X C12 3k Units Tape and Reel
LMV393MX LMV393M 2.5k Units Tape and Reel
LMV393MMX LMV393 3.5k Units Tape and Reel
LMV339MX LMV339M 2.5k Units Tape and Reel
LMV339MTX LMV339MT 2.5k Units Tape and Reel
Marking
Transport
Media
NSC
Drawing
M08A
MUA08A
M14A
MTC14
www.national.com 2

Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
ESD Tolerance (Note 2)
Human Body Model
LMV331/ 393/ 339 800V
Machine Model LMV331/339/393 120V
Differential Input Voltage
Voltage on any pin
(referred to V
−
pin)
Soldering Information
Infrared or Convection (20 sec) 235˚C
Storage Temp. Range −65˚C to +150˚C
Junction Temperature (Note 3) 150˚C
±
Supply Voltage
5.5V
Operating Ratings(Note 1)
Supply Voltage 2.7V to 5.0V
Temperature Range
LMV393, LMV339,
LMV331
Thermal Resistance (θ
M Package, 8-pin Surface
Mount
M Package, 14-pin Surface
Mount
MTC Package, 14-pin
TSSOP
MAA05 Package, 5-pin
SC70-5
M05A Package 5 -pin
SOT23-5
MM Package, 8-pin Mini
)
JA
−40˚C ≤ T
≤ +85˚C
J
190˚C/W
145˚C/W
155˚C/W
478˚C/W
265˚C/W
235˚C/W
Surface Mount
2.7V DC Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for TJ= 25˚C, V+=2.7V, V−=0V. Boldface limits apply at the temperature
extremes.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typ
V
OS
TCV
I
B
I
OS
V
CM
Input Offset Voltage
Input Offset Voltage
OS
Average Drift
Input Bias Current
Input Offset Current
Input Voltage Range −0.1 V
(Note 4)
1.7 7
2.0 V
V
SAT
I
O
I
S
Saturation Voltage I
≤ 1mA 200 mV
sink
Output Sink Current VO≤ 1.5V 23 5 mA min
Supply Current LMV331 40 100 µA max
LMV393
Both Comparators
LMV339
140 200 µA max
All four Comparators
Output Leakage Current .003 1 µA max
LMV331/
393/339
Limit
(Note 5)
5 µV/˚C
10
5
250
400
50
150
70 140 µA max
Units
nA max
nA max
mV
max
2.7V AC Electrical Characteristics
TJ= 25˚C, V+=2.7V, R
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typ
t
PHL
t
PLH
Propagation Delay (High to Low) Input Overdrive=10 mV 1000 ns
Propagation Delay (Low to High) Input Overdrive=10 mV 500 ns
=
5.1 kΩ,V−=0V.
L
(Note 4)
Input Overdrive=100 mV 350 ns
Input Overdrive=100 mV 400 ns
Units
www.national.com3

5V DC Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for TJ= 25˚C, V+=5V, V−=0V. Boldface limits apply at the temperature
extremes.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typ
V
OS
TCV
I
B
I
OS
V
CM
Input Offset Voltage 1.7 7
Input Offset Voltage
OS
Average Drift
Input Bias Current
Input Offset Current
Input Voltage Range −0.1 V
(Note 4)
4.2 V
A
V
V
sat
I
O
I
S
Voltage Gain 50 20 V/mV min
Saturation Voltage I
≤ 4 mA 200 400
sink
Output Sink Current VO≤ 1.5V 84 10 mA
Supply Current LMV331 60 120
LMV393
100 200
Both Comparators
LMV339
170 300
All four Comparators
Output Leakage Current .003 1 µA max
5 µV/˚C
25
2
LMV331/
393/339
Limit
(Note 5)
9
250
400
50
150
700
150
250
350
Units
mV
max
nA max
nA max
mV
max
µA max
µA max
µA max
5V AC Electrical Characteristics
TJ= 25˚C, V+=5V, R
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typ
t
PHL
t
PLH
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is intended to be functional, but specific performance is not guaranteed. For guaranteed specifications and the test conditions, see the Electrical characteristics.
Note 2: : Human body model, 1.5kΩ in series with 100 pF. Machine model, 200Ω in series with 100 pF.
Note 3: The maximum power dissipation is a functionof T
-TA)/θJA. All numbers apply for packages soldered directly into a PC board.
Note 4: Typical Values represent the most likely parametric norm.
Note 5: All limits are guaranteed by testing or statistical analysis.
www.national.com 4
Propagation Delay (High to Low) Input Overdrive=10 mV 600 ns
Propagation Delay (Low to High) Input Overdrive=10 mV 450 ns
=
5.1 kΩ,V−=0V.
L
(Note 4)
Input Overdrive=100 mV 200 ns
Input Overdrive=100 mV 300 ns
, θJA, and TA. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is P
J(max)
D
Units
=
(T
J(max)
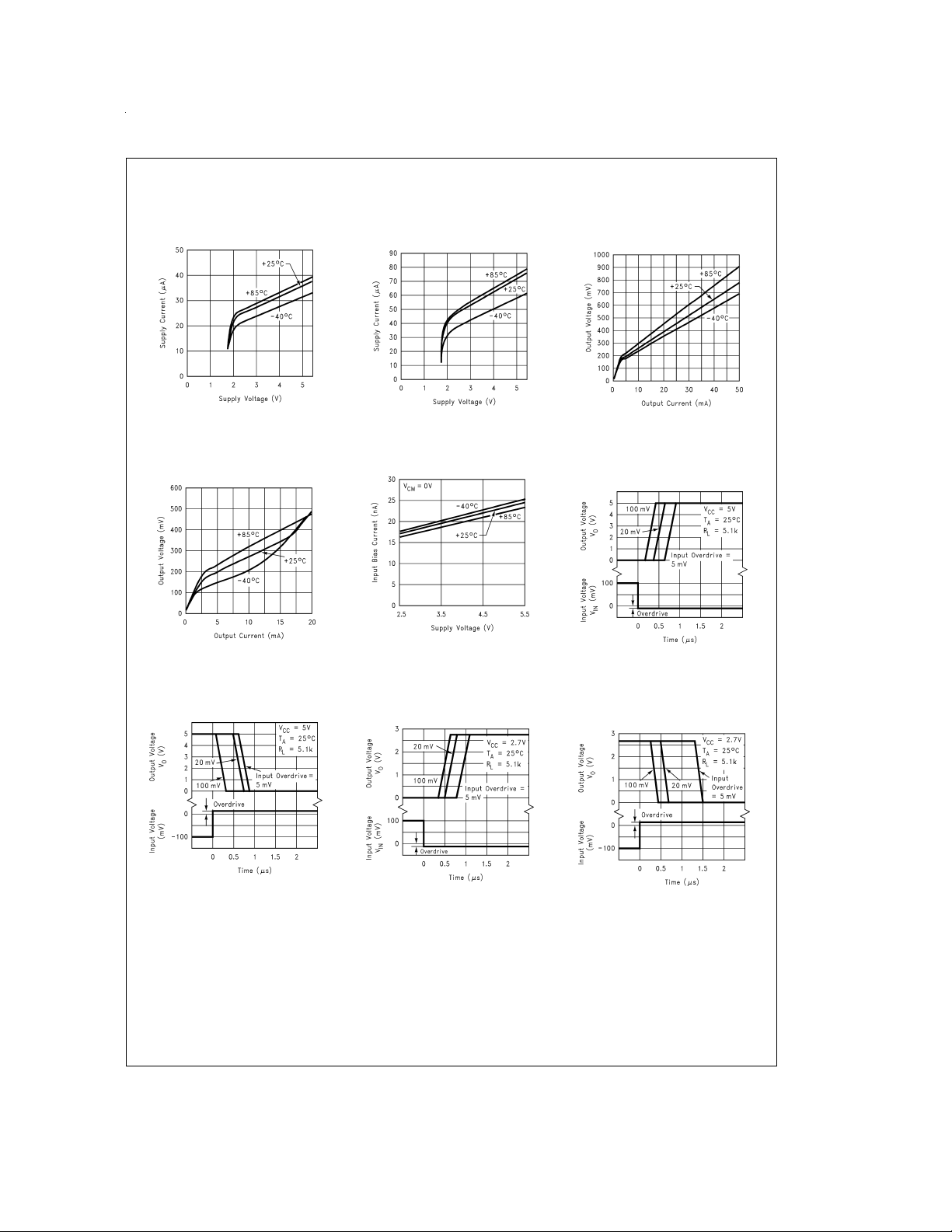
Typical Performance Characteristics Unless otherwise specified, V
Supply Current vs
Supply Voltage Output High
(LMV331)
Supply Current vs
Supply Voltage Output Low
(LMV331)
Output Voltage vs
Output Current at 5V Supply
=
+5V, single supply, T
S
=
25˚C
A
Output Voltage vs
Output Current
at 2.7 Supply
Response Time for
Input Overdrive
Positive Transition
DS100080-34
DS100080-38
Input Bias Current vs
Supply Voltage
Response Time vs
Input Overdrives
Negative Transition
DS100080-33
DS100080-36
DS100080-37
Response Time vs
Input Overdrives
Negative Transition
DS100080-42
Response Time for
Input Overdrive
Positive Transition
DS100080-43
DS100080-41
DS100080-40
www.national.com5
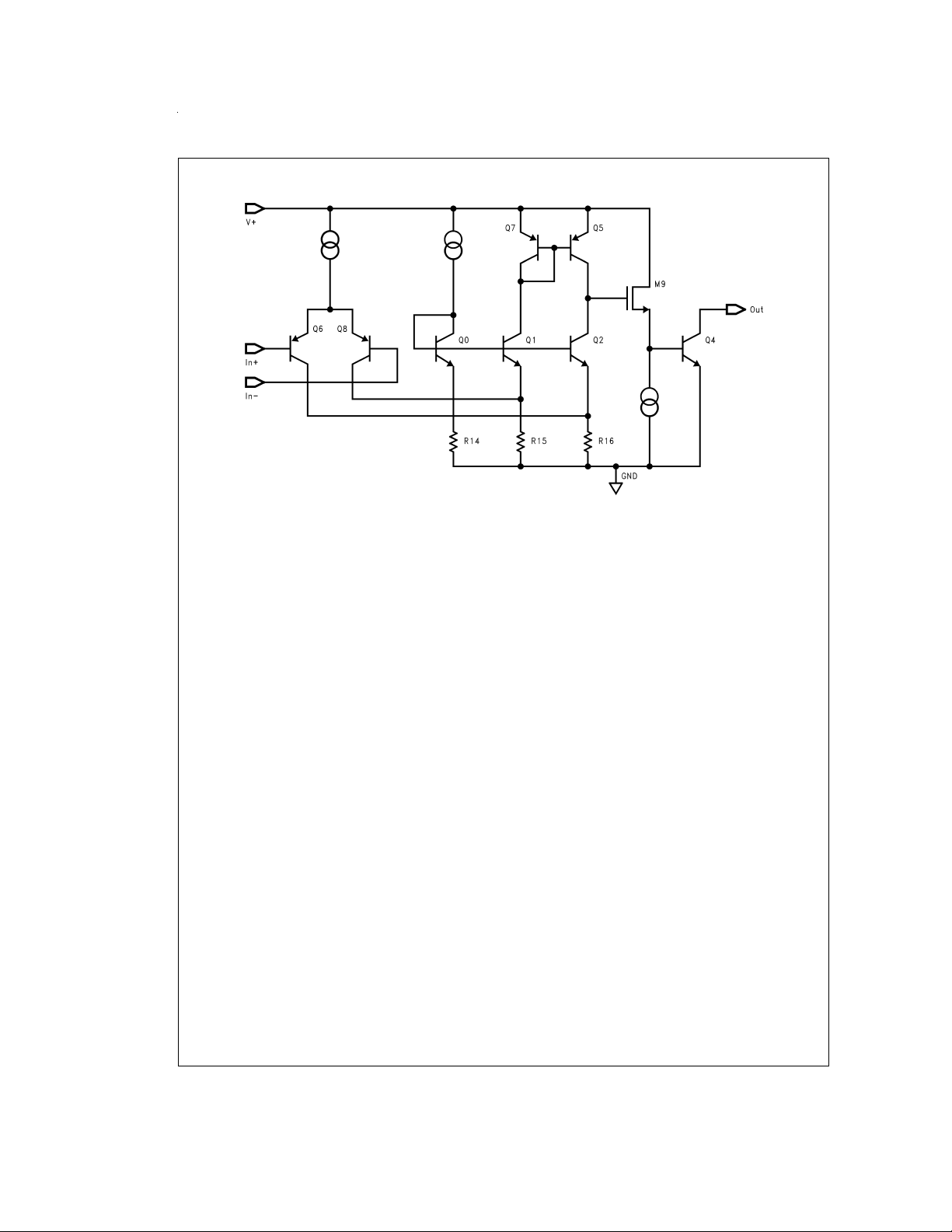
Simplified Schematic
DS100080-47
www.national.com 6
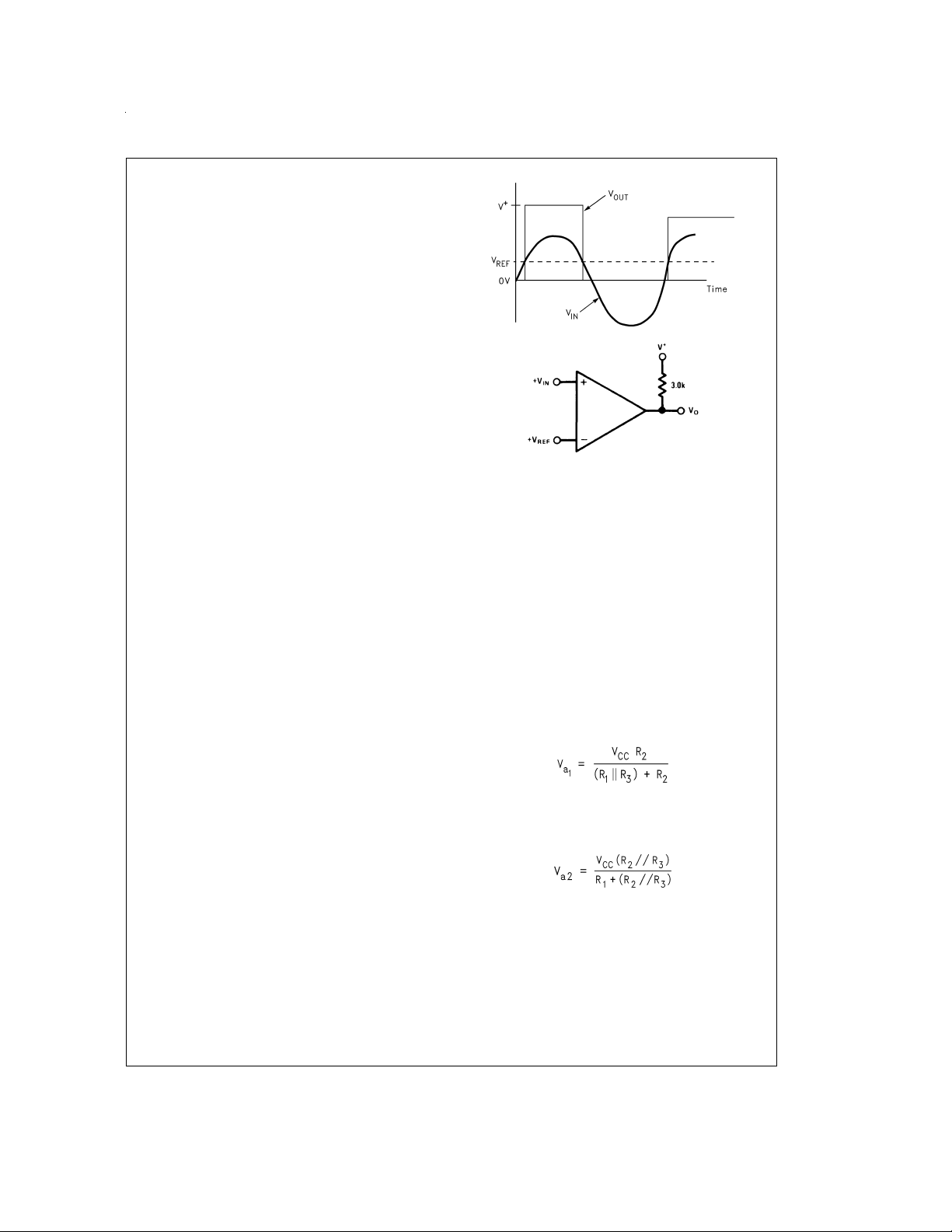
Application Circuits
Basic Comparator
A basic comparator circuit is used for converting analog signals to a digital output. The LMV331/393/339 have an
open-collector output stage, which requires a pull-up resistor
to a positive supply voltage for the output to switch properly.
When the internal output transistor is off, the output voltage
will be pulled up to the external positive voltage.
The output pull-up resistor should be chosen high enough so
as to avoid excessive power dissipation yet low enough to
supply enough drive to switch whatever load circuitry is used
on the comparator output. On the LMV331/393/339 the
pull-up resistor should range between 1k to 10kΩ.
The comparator compares the input voltage (V
non-inverting pin to the reference voltage (V
ing pin. If V
saturation voltage. On the other hand, if V
V
ref
is less than V
in
, the output voltage (Vo)isatthe
ref
, the output voltage (Vo)isatV
.
cc.
)atthe
in
) at the invert-
ref
is greater than
in
DS100080-26
DS100080-4
FIGURE 1. Basic Comparator
Comparator with Hysteresis
The basic comparator configuration may oscillate or produce
a noisy output if the applied differential input voltage is near
the comparator’s offset voltage. This usually happens when
the input signal is moving very slowly across the comparator’s switching threshold. This problem can be prevented by
the addition of hysteresis or positive feedback.
Inverting Comparator with Hysteresis
The inverting comparator with hysteresis requires a three resistor network that are referenced to the supply voltage V
of the comparator. When Vin at the inverting input is less
than V
, the voltage at the non-inverting node of the com-
a
parator (V
assume V
sistors can be represented as R
lower input trip voltage V
<
Va), the output voltage is high (for simplicity
in
switches as high as Vcc). The three network re-
o
//R3in series with R2. The
1
is defined as
a1
cc
When Vinis greater than Va (VinVa), the output voltage is
low very close to ground. In this case the three network resistors can be presented as R
per trip voltage V
is defined as
a2
//R3in series with R1. The up-
2
The total hysteresis provided by the network is defined as
=
∆V
V
a
a1-Va2
To assure that the comparator will always switch fully to V
and not be pulled down by the load the resistors values
should be chosen as follow:
<<
R
pull-up
and R
R
load
>
R
pull-up
.
www.national.com7
1
cc
 Loading...
Loading...