NSC LM2435T Datasheet
LM2435
Monolithic Triple 5.5 ns CRT Driver
General Description
The LM2435 is an integrated high voltage CRT driver circuit
designed for use in color monitor applications. The IC contains three high input impedance, wide band amplifiers
which directly drivethe RGB cathodes of a CRT. Each channel has its gain internally set to −14 and can drive CRT capacitive loads as well as resistive loads present in other applications, limited only by the package’s power dissipation.
The IC is packaged in an industry standard 9-lead TO-220
molded plastic power package. See Thermal Considerations
section.
Features
n Dissipates approximately 45%less power than the
LM2405
Schematic and Connection Diagrams
n Well matched with LM1279 and LM1282/83 video
preamps
n 0V to 5V input range
n Stable with 0 pF–20 pF capacitive loads and inductive
peaking networks
n Convenient TO-220 staggered lead package style
n Standard LM243X Family Pinout which is designed for
easy PCB layout
Applications
n 1280 x 1024 Displays up to 75 Hz Refresh
n Pixel clock frequencies up to 135 MHz
n Monitors using video blanking
LM2435 Monolithic Triple 5.5 ns CRT Driver
August 1999
Note: TabisatGND
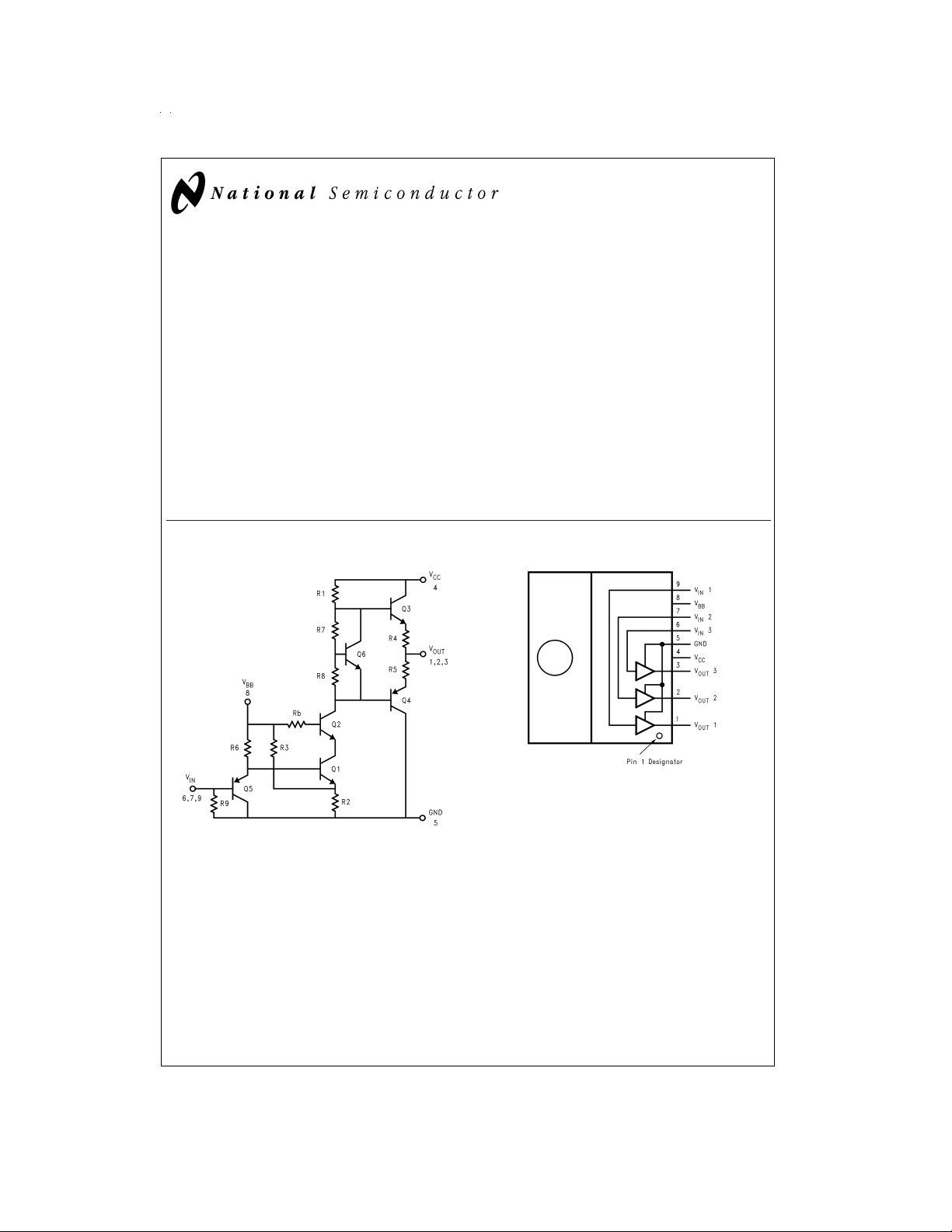
Top View
Order Number LM2435T
DS101044-1
FIGURE 1. Simplified Schematic Diagram
(One Channel)
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS101044 www.national.com
DS101044-2
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Notes 1, 3)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage, (V
Bias Voltage, (V
Input Voltage, (V
Storage Temperature Range, (T
) +90V
CC
) +16V
BB
) 0Vto6V
IN
) −65˚C to +150˚C
STG
Lead Temperature
<
(Soldering,
10 sec.) 300˚C
ESD Tolerance, Human Body Model 2 kV
Machine Model 250V
Operating Ranges (Note 2)
V
CC
V
BB
V
IN
V
OUT
+60V to +85V
+8V to +15V
+0V to +5V
+15V to +75V
Case Temperature −20˚C to +100˚C
Do not operate the part without a heat sink.
Electrical Characteristics
(See
Figure 2
Unless otherwise noted: V
DC Tests: VIN= +2.8 V
AC Tests: Output = 40 VPP(25V to 65V) at 1 MHz.
for Test Circuit)
Symbol Parameter Condition
I
I
V
A
∆A
CC
BB
OUT
V
Supply Current Per Channel, No Input Signal, No
Bias Current All Three Channels 14 mA
DC Output Voltage No AC Input Signal, VIN= 1.35V 62 65 68 V
DC Voltage Gain No AC Input Signal −12 −14 −16
Gain Matching (Note 4), No AC Input Signal 1.0 dB
V
LE Linearity Error (Notes 4, 5), No AC Input Signal 8
t
R
t
F
Rise Time (Note 6), 10%to 90
Fall Time (Note 6), 90%to 10
OS Overshoot (Note 6) 5
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur.
Note 2: Operating ratings indicate conditions for which the device is functional, but do not guarantee specific performance limits. For guaranteed specifications and
test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics. The guaranteed specifications apply only for the test conditions listed. Some performance characteristics may
change when the device is not operated under the listed test conditions.
Note 3: All voltages are measured with respect to GND, unless otherwise specified.
Note 4: Calculated value from Voltage Gain test on each channel.
Note 5: Linearity Error is the variation in dc gain from V
Note 6: Input from signal generator: t
= +80V, VBB= +12V, CL= 8 pF, TC= 50˚C
CC
DC
Output Load
= 1.0V to VIN= 4.5V.
1 ns.
IN
r,tf
<
LM2435
Min Typ Max
Units
13 mA
%
%
5.5 ns
6.0 ns
DC
%
%
AC Test Circuit
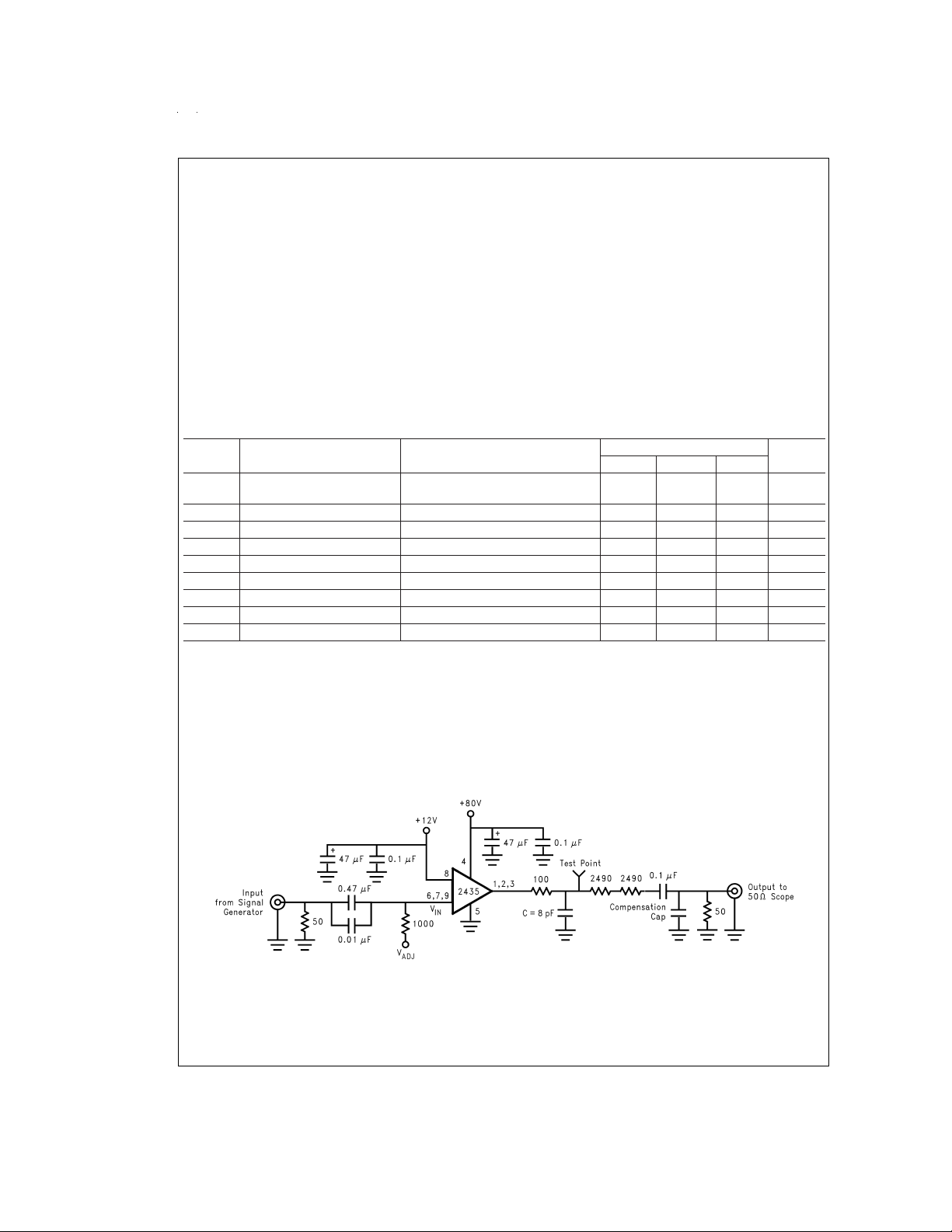
Note: 8 pF load includes parasitic capacitance.
FIGURE 2. Test Circuit (One Channel)
Figure 2
shows a typical test circuit for evaluation of the LM2435. This circuit is designed to allow testing of the LM2435 in a 50Ω
environment without the use of an expensive FET probe. The two 2490Ω resistors at the output form a 200:1 voltage divider when
connected to a 50Ω load. The compensation cap is used to flatten the frequency response of the 200:1 divider.
www.national.com 2
DS101044-3
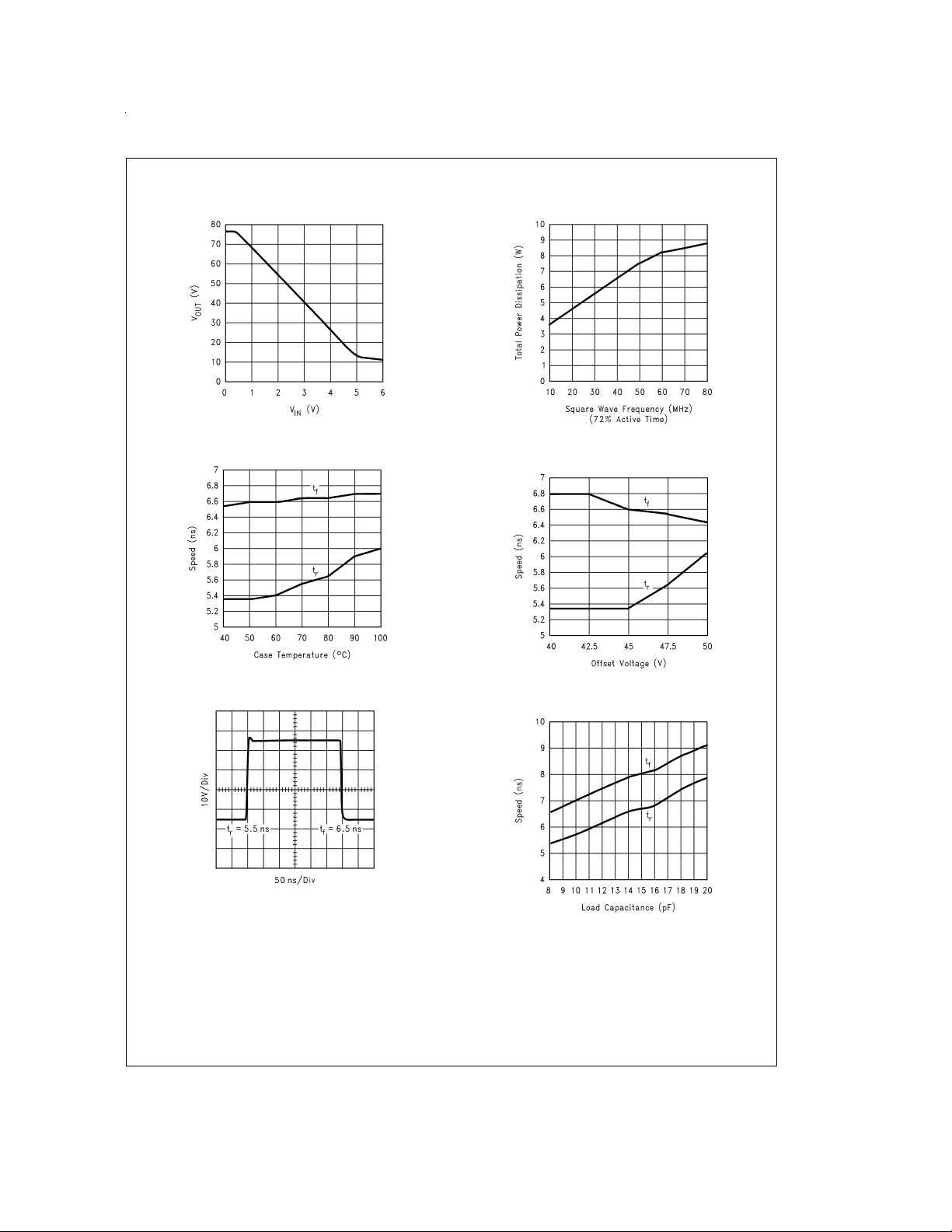
Typical Performance Characteristics (V
(25V-65V), Test Circuit -
Figure 2
unless otherwise specified)
=
+80 V
CC
DC,VBB
=
+12 V
DC,CL
=
8pF,V
OUT
=
40V
PP
DS101044-4
FIGURE 3. V
OUT
vs V
IN
DS101044-5
FIGURE 4. Speed vs Temperature
DS101044-7
FIGURE 6. Power Dissipation vs Frequency
DS101044-8
FIGURE 7. Speed vs Offset
DS101044-6
FIGURE 5. LM2435 Pulse Response
DS101044-9
FIGURE 8. Speed vs Load Capacitance
www.national.com3
 Loading...
Loading...