NSC LF444MWC, LF444MD-883, LF444CN, LF444CMX, LF444CM Datasheet
LF444
Quad Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier
General Description
The LF444 quad low power operational amplifier provides
many of the same AC characteristics as the industry standard LM148 while greatly improving the DC characteristics
of the LM148. The amplifier has the same bandwidth, slew
rate, and gain (10 kΩ load) as the LM148 and only draws
one fourth the supply current of the LM148. In addition the
well matched high voltage JFET input devices of the LF444
reduce the input bias and offset currents by a factor of
10,000 over the LM148. The LF444 also has a very low
equivalent input noise voltage for a low power amplifier.
The LF444 is pin compatible with the LM148 allowing an immediate 4 times reduction in power drain in many applications. The LF444 should be used wherever low power dissipation and good electrical characteristics are the major
considerations.
Features
n
1
⁄4supply current of a LM148: 200 µA/Amplifier (max)
n Low input bias current: 50 pA (max)
n High gain bandwidth: 1 MHz
n High slew rate: 1 V/µs
n Low noise voltage for low power
n Low input noise current
n High input impedance: 1012Ω
n High gain V
O
=
±
10V, R
L
=
10k: 50k (min)
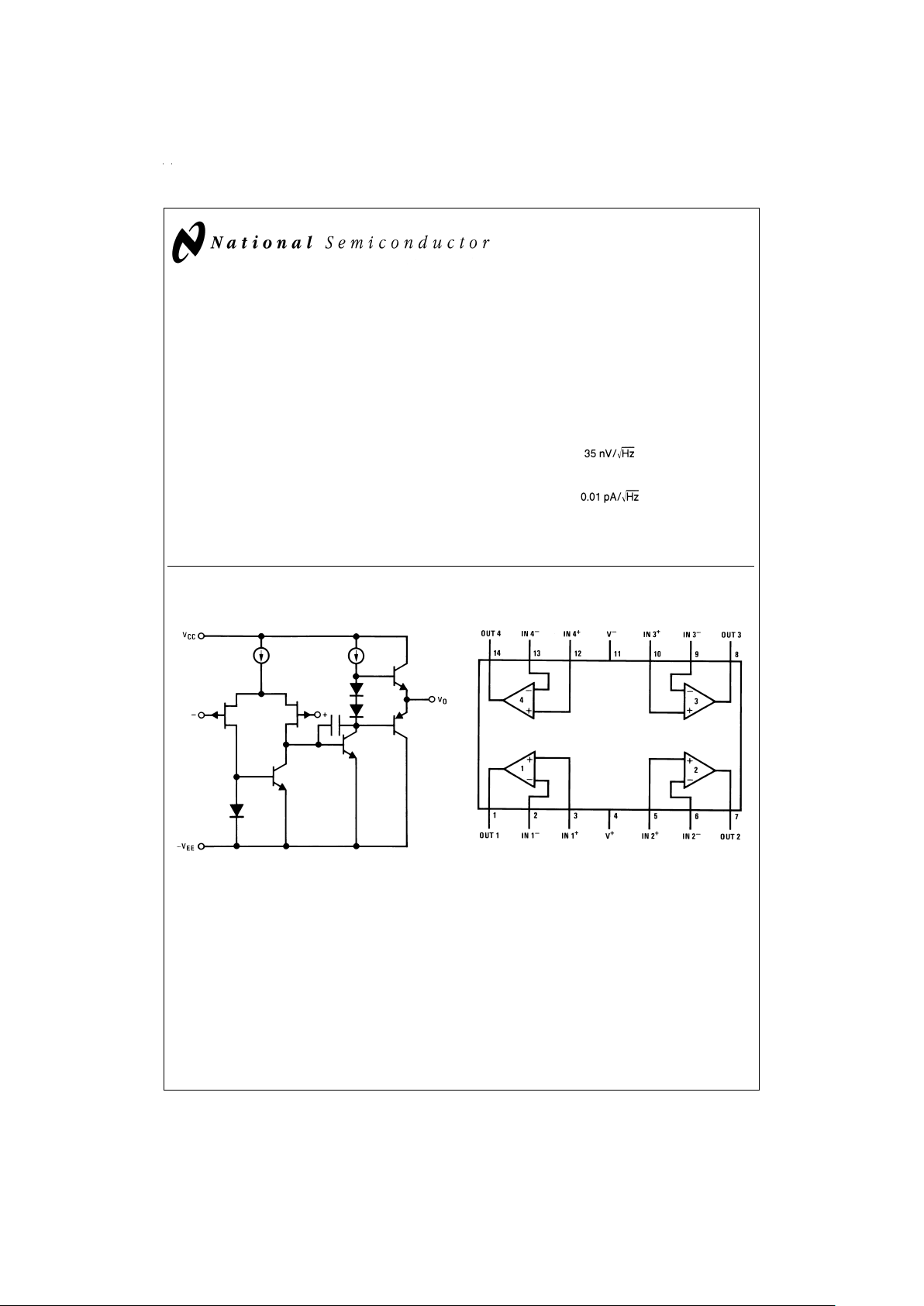
Simplified Schematic
Ordering Information
LF444XYZ
X indicates electrical grade
Y indicates temperature range
“M” for military, “C” for commercial
Z indicates package type “D”, “M” or “N”
Connection Diagram
BI-FET™and BI-FET II™are trademarks of National Semiconductor Corporation.
1/4 Quad
DS009156-1
Dual-In-Line Package
DS009156-2
Top View
Order Number LF444AMD, LF444CM,
LF444ACN, LF444CN or LF444MD/883
See NS Package Number D14E, M14A or N14A
May 1998
LF444 Quad Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS009156 www.national.com
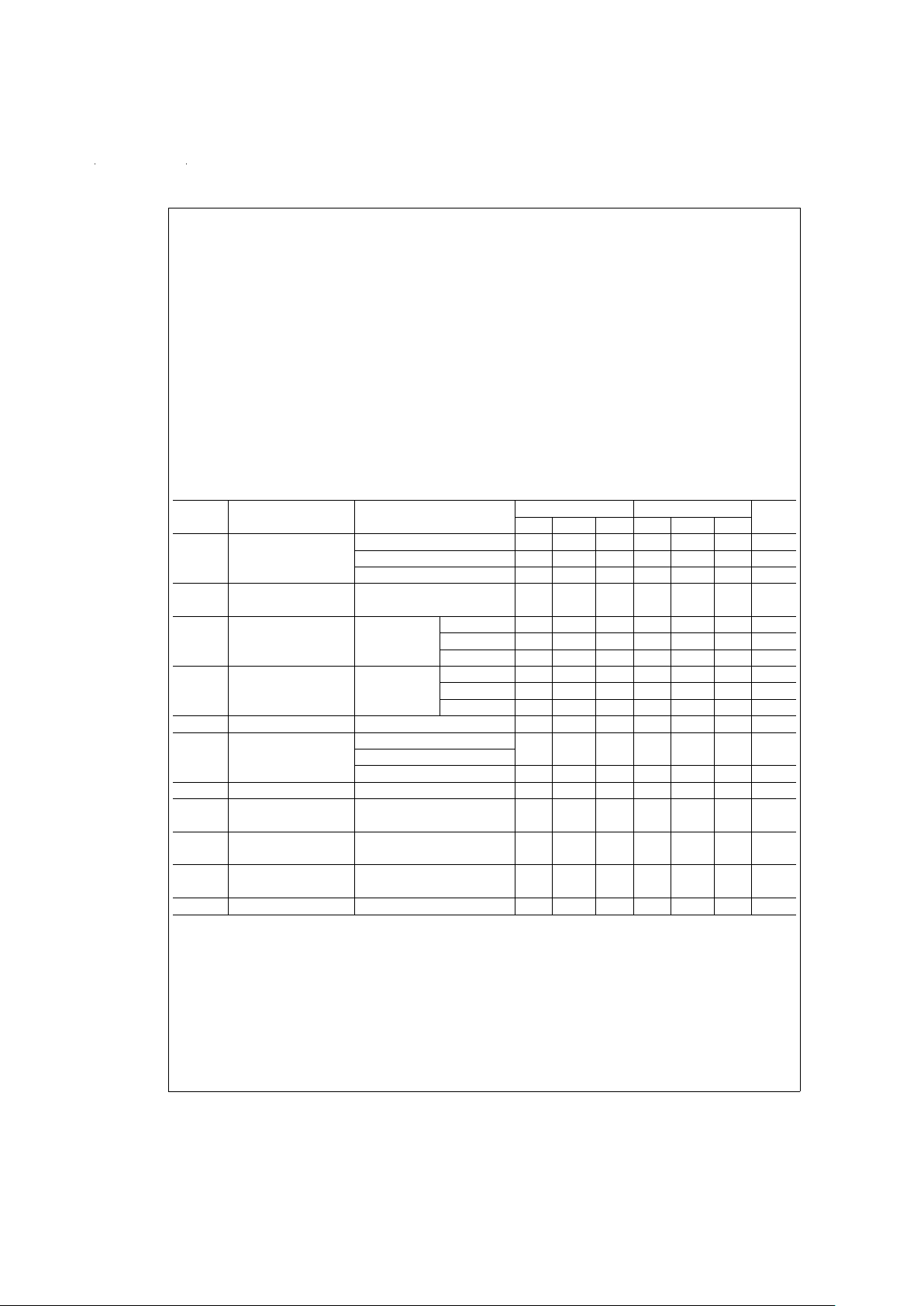
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 11)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
LF444A LF444
Supply Voltage
±
22V
±
18V
Differential Input Voltage
±
38V
±
30V
Input Voltage Range
±
19V
±
15V
(Note 1)
Output Short Circuit Continuous Continuous
Duration (Note 2)
D Package N, M Packages
Power Dissipation 900 mW 670 mW
(Notes 3, 9)
T
j
max 150˚C 115˚C
θ
jA
(Typical) 100˚C/W 85˚C/W
LF444A/LF444
Operating Temperature Range (Note 4)
Storage Temperature Range −65˚C ≤ T
A
≤ 150˚C
ESD Tolerance (Note 10) Rating to
be determined
Soldering Information
Dual-In-Line Packages
(Soldering, 10 sec.) 260˚C
Small Outline Package
Vapor Phase (60 sec.) 215˚C
Infrared (15 sec.) 220˚C
See AN-450 “Surface Mounting Methods and Their Effect on
Product Reliability” for other methods of soldering surface
mount devices.
DC Electrical Characteristics (Note 5)
Symbol Parameter Conditions LF444A LF444 Units
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
V
OS
Input Offset Voltage R
S
=
10k, T
A
=
25˚C 2 5 3 10 mV
0˚C ≤ T
A
≤ +70˚C 6.5 12 mV
−55˚C ≤ T
A
≤ +125˚C 8 mV
∆V
OS
/∆T Average TC of Input R
S
=
10 kΩ 10 10 µV/˚C
Offset Voltage
I
OS
Input Offset Current V
S
=
±
15V T
j
=
25˚C 5 25 5 50 pA
(Notes 5, 6) T
j
=
70˚C 1.5 1.5 nA
T
j
=
125˚C 10 nA
I
B
Input Bias Current V
S
=
±
15V T
j
=
25˚C 10 50 10 100 pA
(Notes 5, 6) T
j
=
70˚C 3 3 nA
T
j
=
125˚C 20 nA
R
IN
Input Resistance T
j
=
25˚C 10
12
10
12
Ω
A
VOL
Large Signal Voltage V
S
=
±
15V, V
O
=
±
10V 50 100 25 100 V/mV
Gain R
L
=
10 kΩ,T
A
=
25˚C
Over Temperature 25 15 V/mV
V
O
Output Voltage Swing V
S
=
±
15V, R
L
=
10 kΩ
±
12±13
±
12±13 V
V
CM
Input Common-Mode
±
16 +18
±
11 +14 V
Voltage Range −17 −12 V
CMRR Common-Mode R
S
≤ 10 kΩ 80 100 70 95 dB
Rejection Ratio
PSRR Supply Voltage (Note 7) 80 100 70 90 dB
Rejection Ratio
I
S
Supply Current 0.6 0.8 0.6 1.0 mA
www.national.com 2
AC Electrical Characteristics (Note 5)
Symbol Parameter Conditions LF444A LF444 Units
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
Amplifier-to-Amplifier −120 −120 dB
Coupling
SR Slew Rate V
S
=
±
15V, T
A
=
25˚C 1 1 V/µs
GBW Gain-Bandwidth Product V
S
=
±
15V, T
A
=
25˚C 1 1 MHz
e
n
Equivalent Input Noise Voltage T
A
=
25˚C, R
S
=
100Ω,
35 35
f=1 kHz
i
n
Equivalent Input Noise Current T
A
=
25˚C, f=1 kHz 0.01 0.01
Note 1: Unless otherwise specified the absolute maximum negative input voltage is equal to the negative power supply voltage.
Note 2: Any of the amplifier outputs can be shorted to ground indefinitely, however, more than one should not be simultaneously shorted as the maximum junction
temperature will be exceeded.
Note 3: For operating at elevated temperature, these devices must be derated based on a thermal resistance of θ
jA
.
Note 4: The LF444A is available in both the commercial temperature range 0˚C ≤ T
A
≤ 70˚C and the military temperature range −55˚C ≤ TA≤ 125˚C. The LF444 is
available in the commercial temperature range only. The temperature range is designated by the position just before the package type in the device number. A“C”
indicates the commercial temperature range and an “M” indicates the military temperature range. The military temperature range is available in “D” package only.
Note 5: Unless otherwise specified thespecificationsapply over the full temperature range and for V
S
=
±
20V for the LF444Aand for V
S
=
±
15V for the LF444. VOS,
I
B
, and IOSare measured at V
CM
=
0.
Note 6: The input bias currents are junction leakage currents which approximately double for every 10˚C increase in the junction temperature, T
j
. Due to limited production test time, the input bias currents measured are correlated to junction temperature. In normal operation the junction temperature rises above the ambient temperature as a result of internal power dissipation, P
D.Tj
=
T
A+θjAPD
where θjAis the thermal resistance from junction to ambient. Use of a heat sink is recommended
if input bias current is to be kept to a minimum.
Note 7: Supply voltage rejection ratio is measured for both supply magnitudes increasing or decreasing simultaneously in accordance with common practice from
±
15V to±5V for the LF444 and from±20V to±5V for the LF444A.
Note 8: Refer to RETS444X for LF444MD military specifications.
Note 9: Max. Power Dissipation is defined by the package characteristics. Operating the part near the Max. Power Dissipation may cause the part to operate outside
guaranteed limits.
Note 10: Human body model, 1.5 kΩ in series with 100 pF.
Note 11: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limitsbeyond which damage to the device may occur.Operating ratings indicate conditions for which the deviceis func-
tional, but do not guarantee specific performancelimits. Electrical Characteristics state DC and AC electrical specifications underparticular test conditions which guarantee specific performance limits. This assumes that the device is within the Operating Ratings. Specifications are not guaranteed for parameters where no limit is
given, however, the typical value is a good indication of device performance.
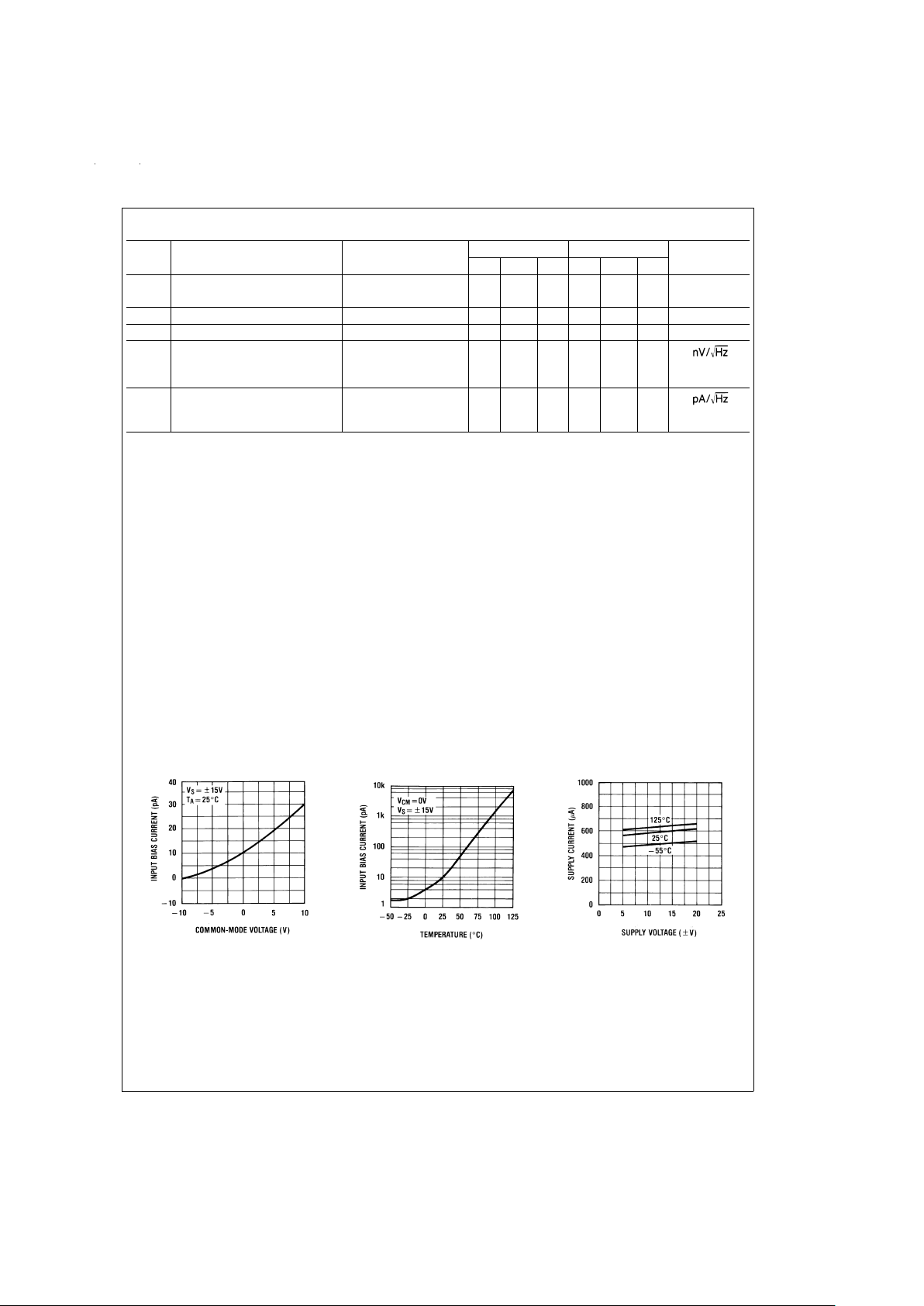
Typical Performance Characteristics
Input Bias Current
DS009156-12
Input Bias Current
DS009156-13
Supply Current
DS009156-14
www.national.com3
 Loading...
Loading...