NSC ADC0817CCN Datasheet
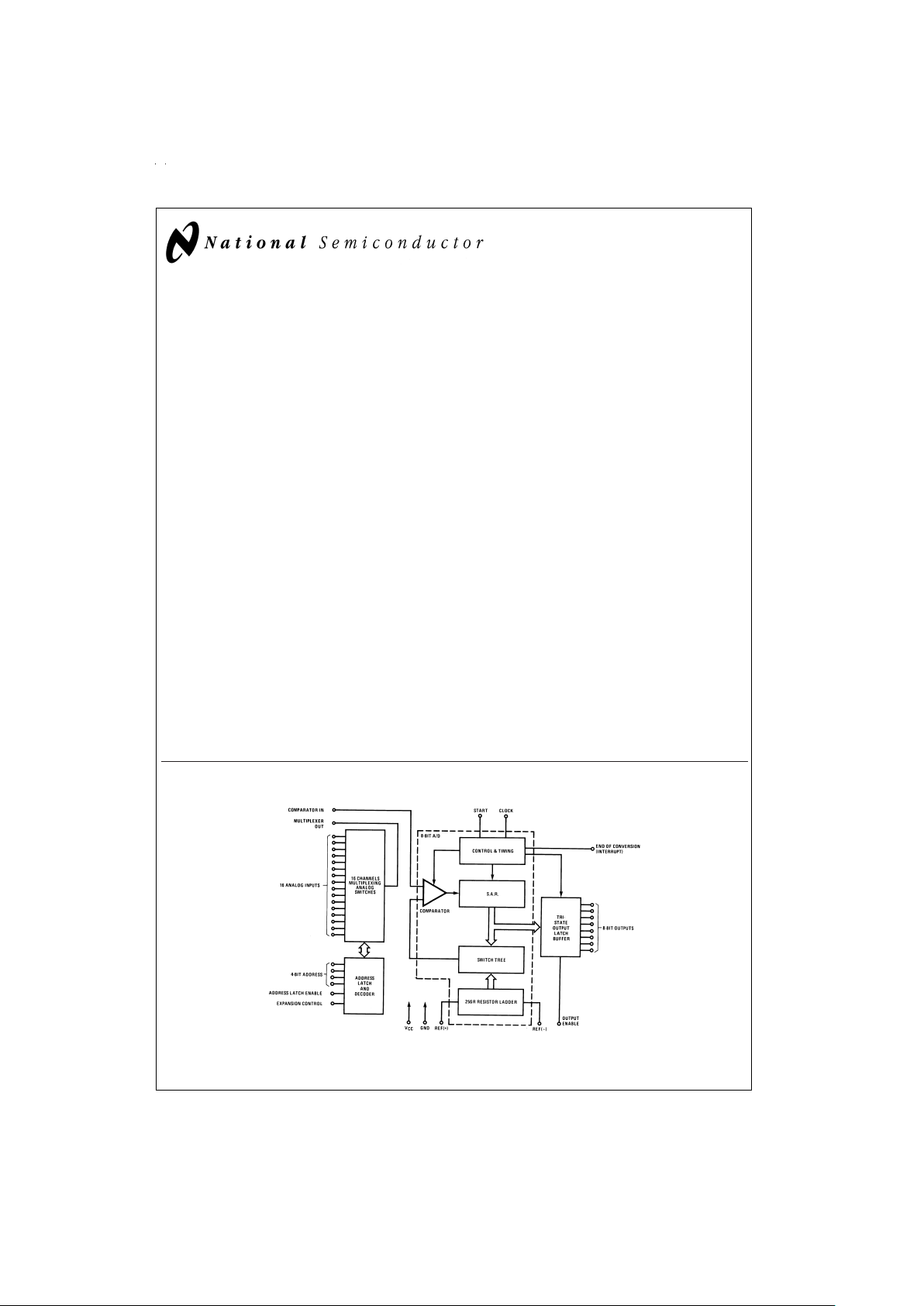
ADC0816/ADC0817
8-Bit µP Compatible A/D Converters
with 16-Channel Multiplexer
General Description
The ADC0816, ADC0817 data acquisition component is a
monolithic CMOS device with an 8-bit analog-to-digital converter, 16-channel multiplexer and microprocessor compatible control logic. The 8-bit A/D converter uses successive
approximation as the conversion technique. The converter
features a high impedance chopper stabilized comparator, a
256R voltage divider with analog switch tree and a successive approximation register. The 16-channel multiplexer can
directly access any one of 16-single-ended analog signals,
and provides the logic for additional channel expansion. Signal conditioning of any analog input signal is eased by direct
access to the multiplexer output, and to the input of the 8-bit
A/D converter.
The device eliminates the need for external zero and
full-scale adjustments. Easy interfacing to microprocessors
is provided by the latched and decoded multiplexer address
inputs and latched TTL TRI-STATE
®
outputs.
The design of the ADC0816, ADC0817 has been optimized
by incorporating the most desirable aspects of several A/D
conversion techniques. The ADC0816, ADC0817 offers high
speed, high accuracy, minimal temperaturedependence,excellent long-term accuracy and repeatability, and consumes
minimal power. These features make this device ideally
suited to applications from process and machine control to
consumer and automotive applications. For similar performance in an 8-channel, 28-pin, 8-bit A/D converter, see the
ADC0808, ADC0809 data sheet. (See AN-258 for more information.)
Features
n Easy interface to all microprocessors
n Operates ratiometrically or with 5 V
DC
or analog span
adjusted voltage reference
n 16-channel multiplexer with latched control logic
n Outputs meet TTL voltage level specifications
n 0V to 5V analog input voltage range with single 5V
supply
n No zero or full-scale adjust required
n Standard hermetic or molded 40-pin DIP package
n Temperature range −40˚C to +85˚C or −55˚C to +125˚C
n Latched TRI-STATE output
n Direct access to “comparator in” and “multiplexer out” for
signal conditioning
n ADC0816 equivalent to MM74C948
n ADC0817 equivalent to MM74C948-1
Key Specifications
n Resolution 8 Bits
n Total Unadjusted Error
±
1
⁄2LSB and±1 LSB
n Single Supply 5 V
DC
n Low Power 15 mW
n Conversion Time 100 µs
Block Diagram
TRI-STATE®is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
DS005277-1
June 1999
ADC0816/ADC0817 8-Bit µP Compatible A/D Converters with 16-Channel Multiplexer
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS005277 www.national.com
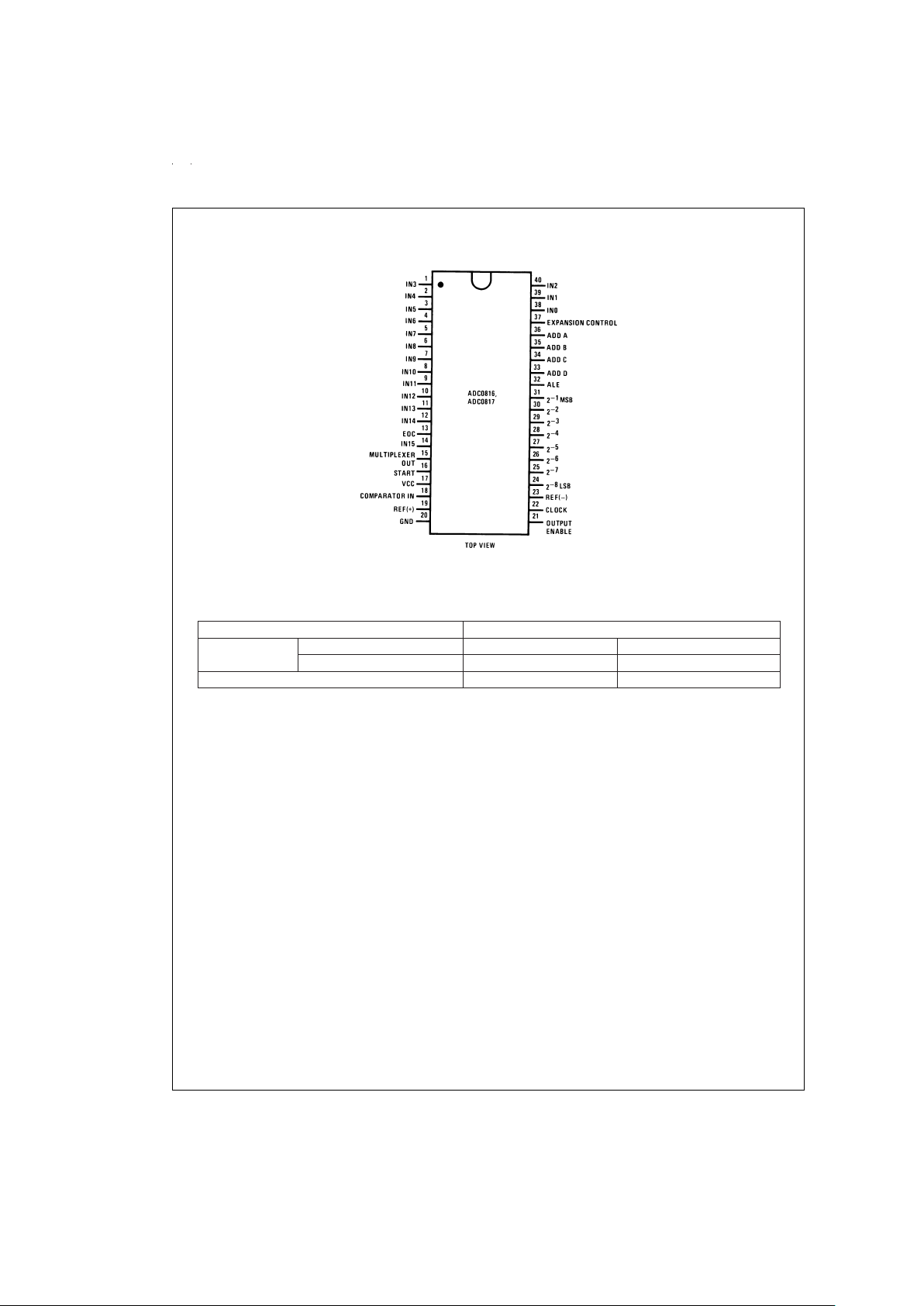
Connection Diagram
Ordering Information
TEMPERATURE RANGE −40˚C to +85˚C
Error
±
1
⁄2Bit Unadjusted ADC0816CCN ADC0816CCJ
±
1 Bit Unadjusted ADC0817CCN
Package Outline N40A Molded DIP J40A Hermetic DIP
Dual-In-Line Package
DS005277-6
Order Number ADC0816CCN or ADC0817CCN
See NS Package Number N40A
www.national.com 2
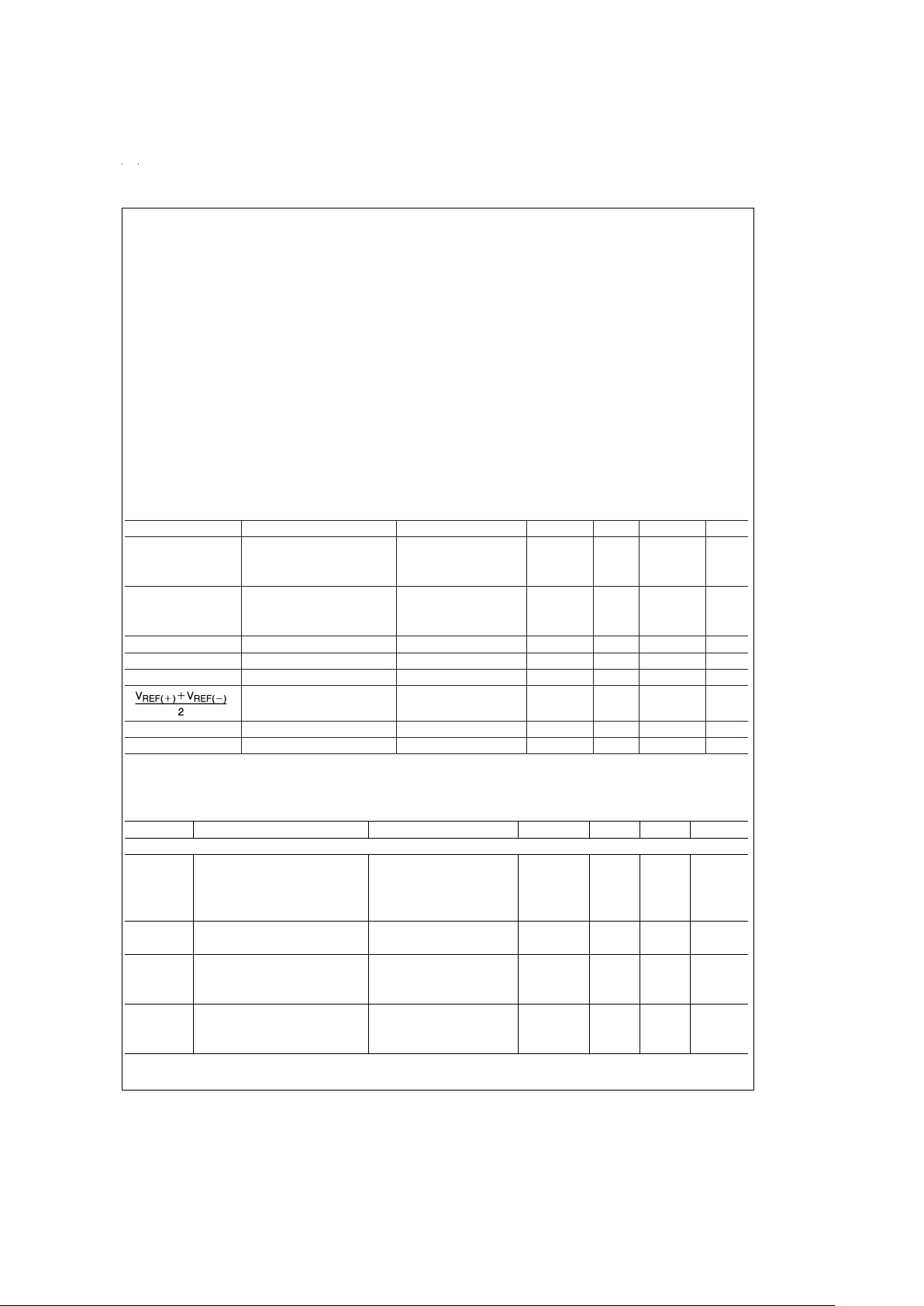
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Notes 1, 2)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage (V
CC
) (Note 3) 6.5V
Voltage at Any Pin −0.3V to (V
CC
+0.3V)
Except Control Inputs
Voltage at Control Inputs −0.3V to 15V
(START, OE, CLOCK, ALE, EXPANSION CONTROL,
ADD A, ADD B, ADD C, ADD D)
Storage Temperature Range −65˚C to + 150˚C
Package Dissipation at T
A
=
25˚C 875 mW
Lead Temp. (Soldering, 10 seconds)
Dual-In-Line Package (Plastic) 260˚C
Molded Chip Carrier Package
Vapor Phase (60 seconds) 215˚C
Infrared (15 seconds) 220˚C
ESD Susceptibility (Note 9) 400V
Operating Conditions (Notes 1, 2)
Temperature Range (Note 1) T
MIN≤TA≤TMAX
ADC0816CCN, ADC0817CCN −40˚C≤TA≤+85˚C
Range of V
CC
(Note 1) 4.5 VDCto 6.0 V
DC
Voltage at Any Pin 0V to V
CC
Except Control Inputs
Voltage at Control Inputs 0V to 15V
(START, OE, CLOCK, ALE, EXPANSION CONTROL,
ADD A, ADD B, ADD C, ADD D)
Electrical Characteristics
Converter Specifications: V
CC
=
5V
DC
=
V
REF(+),VREF(−)
=
GND, V
IN
=
V
COMPARATOR IN,TMIN≤TMAX
and f
CLK
=
640 kHz unless
otherwise stated.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
ADC0816
Total Unadjusted Error 25˚C
±
1
⁄
2
LSB
(Note 5) T
MIN
to T
MAX
±
3
⁄
4
LSB
ADC0817
Total Unadjusted Error 0˚C to 70˚C
±
1 LSB
(Note 5) T
MIN
to T
MAX
±
11⁄
4
LSB
Input Resistance From Ref(+) to Ref(−) 1.0 4.5 kΩ
Analog Input Voltage Range (Note 4) V(+) or V(−) GND−0.10 V
CC
+0.10 V
DC
V
REF(+)
Voltage, Top of Ladder Measured at Ref(+) V
CC
VCC+0.1 V
Voltage, Center of Ladder VCC/2−0.1 VCC/2 VCC/2+0.1 V
V
REF(−)
Voltage, Bottom of Ladder Measured at Ref(−) −0.1 0 V
Comparator Input Current f
c
=
640 kHz, (Note 6) −2
±
0.5 2 µA
Electrical Characteristics
Digital Levels and DC Specifications: ADC0816CCN, ADC0817CCN— 4.75V≤VCC≤5.25V, −40˚C≤TA≤+85˚C unless other-
wise noted.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
ANALOG MULTIPLEXER
R
ON
Analog Multiplexer ON (Any Selected Channel)
Resistance T
A
=
25˚C, R
L
=
10k 1.5 3 kΩ
T
A
=
85˚C 6 kΩ
T
A
=
125˚C 9 kΩ
∆R
ON
∆ON Resistance Between Any (Any Selected Channel) 75 Ω
2 Channels R
L
=
10k
I
OFF+
OFF Channel Leakage Current V
CC
=
5V, V
IN
=
5V,
T
A
=
25˚C 10 200 nA
T
MIN
to T
MAX
1.0 µA
I
OFF(−)
OFF Channel Leakage Current V
CC
=
5V, V
IN
=
0,
T
A
=
25˚C −200 nA
T
MIN
to T
Max
−1.0 µA
www.national.com3
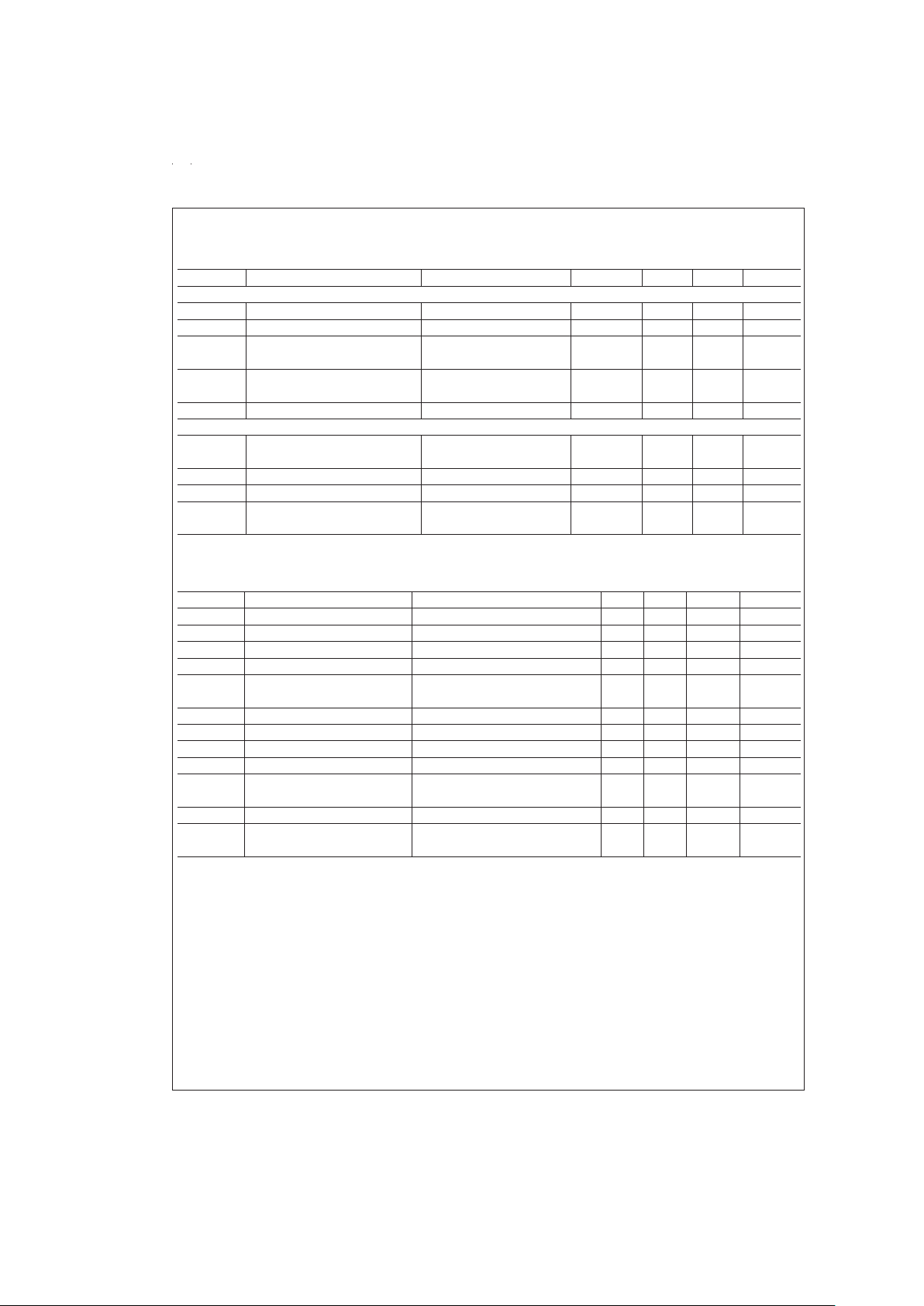
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Digital Levels and DC Specifications: ADC0816CCN, ADC0817CCN— 4.75V≤VCC≤5.25V, −40˚C≤TA≤+85˚C unless other-
wise noted.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
CONTROL INPUTS
V
IN(1)
Logical “1” Input Voltage VCC−1.5 V
V
IN(0)
Logical “0” Input Voltage 1.5 V
I
IN(1)
Logical “1” Input Current V
IN
=
15V 1.0 µA
(The Control Inputs)
I
IN(0)
Logical “0” Input Current V
IN
=
0 −1.0 µA
(The Control Inputs)
I
CC
Supply Current f
CLK
=
640 kHz 0.3 3.0 mA
DATA OUTPUTS AND EOC (INTERRUPT)
V
OUT(1)
Logical “1” Output Voltage I
O
=
−360 µA, T
A
=
85˚C V
CC
−0.4 V
I
O
=
−300 µA, T
A
=
125˚C
V
OUT(0)
Logical “0” Output Voltage I
O
=
1.6 mA 0.45 V
V
OUT(0)
Logical “0” Output Voltage EOC I
O
=
1.2 mA 0.45 V
I
OUT
TRI-STATE Output Current V
O
=
V
CC
3.0 µA
V
O
=
0 −3.0 µA
Electrical Characteristics
Timing Specifications: V
CC
=
V
REF(+)
=
5V, V
REF(−)
=
GND, t
r
=
t
f
=
20 ns and T
A
=
25˚C unless otherwise noted.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
t
WS
Minimum Start Pulse Width (
Figure 5
) (Note 7) 100 200 ns
t
WALE
Minimum ALE Pulse Width (
Figure 5
) 100 200 ns
t
s
Minimum Address Set-Up Time (
Figure 5
)2550ns
T
H
Minimum Address Hold Time (
Figure 5
)2550ns
t
D
Analog MUX Delay Time R
S
=
OΩ (
Figure 5
) 1 2.5 µs
from ALE
t
H1,tH0
OE Control to Q Logic State C
L
=
50 pF, R
L
=
10k (
Figure 8
) 125 250 ns
t
1H,t0H
OE Control to Hi-Z C
L
=
10 pF, R
L
=
10k (
Figure 8
) 125 250 ns
t
C
Conversion Time f
c
=
640 kHz, (
Figure 5
) (Note 8) 90 100 116 µs
f
c
Clock Frequency 10 640 1280 kHz
t
EOC
EOC Delay Time (
Figure 5
) 0 8+2µs Clock
Periods
C
IN
Input Capacitance At Control Inputs 10 15 pF
C
OUT
TRI-STATE Output At TRI-STATE Outputs (Note 8) 10 15 pF
Capacitance
Note 1: AbsoluteMaximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. DC and AC electrical specifications do not apply when operating
the device beyond its specified operating conditions.
Note 2: All voltages are measured with respect to GND, unless otherwise specified.
Note 3: Azener diode exists, internally, from V
CC
to GND and has a typical breakdown voltage of 7 VDC.
Note 4: Two on-chip diodes are tied to each analog input which will forward conduct for analog input voltages one diode drop below ground or one diode drop greater
than the V
CC
supply.The spec allows 100 mV forward bias of either diode. This means that as long as the analog VINdoes not exceed the supply voltage by more
than 100 mV, the output code will be correct. To achieve an absolute 0 V
DC
to5VDCinput voltage range will therefore require a minimum supply voltage of 4.900
V
DC
over temperature variations, initial tolerance and loading.
Note 5: Total unadjusted error includes offset, full-scale, and linearity errors. See
Figure 3
. None of these A/Ds requires a zero or full-scale adjust. However, if an
all zero code is desired for an analog input other than 0.0V, or if a narrow full-scale span exists (for example: 0.5V to 4.5V full-scale) the reference voltages can be
adjusted to achieve this. See
Figure 13
.
Note 6: Comparatorinput current is a bias current into or out of the chopper stabilized comparator.The bias current varies directly with clock frequency and has little
temperature dependence (
Figure 6
). See paragraph 4.0.
Note 7: Ifstart pulse is asynchronous with converter clock or if f
c
>
640 kHz, the minimum start pulse width is 8 clock periods plus 2 µs. For synchronous operation
at f
c
≤ 640 kHz take start high within 100 ns of clock going low.
Note 8: The outputs of the data register are updated one clock cycle before the rising edge of EOC.
Note 9: Human body model, 100 pF discharged through a 1.5 kΩ resistor.
www.national.com 4
 Loading...
Loading...