Page 1

Nokia Customer Care
Service Manual
RM-659; RM-707 (Nokia X7-00.1; Nokia X7-00;
L3&4)
Mobile Terminal
Part No: (Issue 2)
COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 2
RM-659; RM-707
Amendment Record Sheet
Amendment Record Sheet
Amendment No Date Inserted By Comments
Issue 1 11/2010 MT
Issue 2 04/2011 MT Added RM-707 specific information
and updated sections
Information
and
Troubleshooting
specific tools: Camera assembly jig
and Camera insertion tool, and
added SS-252 Multi tool to section
General
Cellular RF
. Removed product
Service Tools and Service Concepts
.
Page ii COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 3

RM-659; RM-707
Copyright
Copyright
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Reproduction, transfer, distribution or storage of part or all of the contents in this document in any form
without the prior written permission of Nokia is prohibited.
Nokia, Nokia Connecting People, and Nokia X and Y are trademarks or registered trademarks of Nokia
Corporation. Other product and company names mentioned herein may be trademarks or tradenames of
their respective owners.
Nokia operates a policy of continuous development. Nokia reserves the right to make changes and
improvements to any of the products described in this document without prior notice.
Under no circumstances shall Nokia be responsible for any loss of data or income or any special, incidental,
consequential or indirect damages howsoever caused.
The contents of this document are provided "as is". Except as required by applicable law, no warranties of
any kind, either express or implied, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability
and fitness for a particular purpose, are made in relation to the accuracy, reliability or contents of this
document. Nokia reserves the right to revise this document or withdraw it at any time without prior notice.
The availability of particular products may vary by region.
IMPORTANT
This document is intended for use by qualified service personnel only.
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page iii
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 4

RM-659; RM-707
Warnings and cautions
Warnings and cautions
Warnings
•
IF THE DEVICE CAN BE INSTALLED IN A VEHICLE, CARE MUST BE TAKEN ON INSTALLATION IN VEHICLES FITTED
WITH ELECTRONIC ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS AND ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEMS. UNDER CERTAIN FAULT
CONDITIONS, EMITTED RF ENERGY CAN AFFECT THEIR OPERATION. IF NECESSARY, CONSULT THE VEHICLE DEALER/
MANUFACTURER TO DETERMINE THE IMMUNITY OF VEHICLE ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS TO RF ENERGY.
•
THE PRODUCT MUST NOT BE OPERATED IN AREAS LIKELY TO CONTAIN POTENTIALLY EXPLOSIVE ATMOSPHERES,
FOR EXAMPLE, PETROL STATIONS (SERVICE STATIONS), BLASTING AREAS ETC.
•
OPERATION OF ANY RADIO TRANSMITTING EQUIPMENT, INCLUDING CELLULAR TELEPHONES, MAY INTERFERE
WITH THE FUNCTIONALITY OF INADEQUATELY PROTECTED MEDICAL DEVICES. CONSULT A PHYSICIAN OR THE
MANUFACTURER OF THE MEDICAL DEVICE IF YOU HAVE ANY QUESTIONS. OTHER ELECTRONIC EQUIPMENT MAY
ALSO BE SUBJECT TO INTERFERENCE.
•
BEFORE MAKING ANY TEST CONNECTIONS, MAKE SURE YOU HAVE SWITCHED OFF ALL EQUIPMENT.
Cautions
•
Servicing and alignment must be undertaken by qualified personnel only.
•
Ensure all work is carried out at an anti-static workstation and that an anti-static wrist strap is worn.
•
Ensure solder, wire, or foreign matter does not enter the telephone as damage may result.
•
Use only approved components as specified in the parts list.
•
Ensure all components, modules, screws and insulators are correctly re-fitted after servicing and
alignment.
•
Ensure all cables and wires are repositioned correctly.
•
Never test a mobile phone WCDMA transmitter with full Tx power, if there is no possibility to perform the
measurements in a good performance RF-shielded room. Even low power WCDMA transmitters may disturb
nearby WCDMA networks and cause problems to 3G cellular phone communication in a wide area.
•
During testing never activate the GSM or WCDMA transmitter without a proper antenna load, otherwise
GSM or WCDMA PA may be damaged.
Page iv COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 5

RM-659; RM-707
For your safety
For your safety
QUALIFIED SERVICE
Only qualified personnel may install or repair phone equipment.
ACCESSORIES AND BATTERIES
Use only approved accessories and batteries. Do not connect incompatible products.
CONNECTING TO OTHER DEVICES
When connecting to any other device, read its user’s guide for detailed safety instructions. Do not connect
incompatible products.
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page v
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 6

RM-659; RM-707
ESD protection
ESD protection
Nokia requires that service points have sufficient ESD protection (against static electricity) when servicing
the phone.
Any product of which the covers are removed must be handled with ESD protection. The SIM card can be
replaced without ESD protection if the product is otherwise ready for use.
To replace the covers ESD protection must be applied.
All electronic parts of the product are susceptible to ESD. Resistors, too, can be damaged by static electricity
discharge.
All ESD sensitive parts must be packed in metallized protective bags during shipping and handling outside
any ESD Protected Area (EPA).
Every repair action involving opening the product or handling the product components must be done under
ESD protection.
ESD protected spare part packages MUST NOT be opened/closed out of an ESD Protected Area.
For more information and local requirements about ESD protection and ESD Protected Area, contact your local
Nokia After Market Services representative.
Page vi COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 7

RM-659; RM-707
Care and maintenance
Care and maintenance
This product is of superior design and craftsmanship and should be treated with care. The suggestions below
will help you to fulfil any warranty obligations and to enjoy this product for many years.
•
Keep the phone and all its parts and accessories out of the reach of small children.
•
Keep the phone dry. Precipitation, humidity and all types of liquids or moisture can contain minerals that
will corrode electronic circuits.
•
Do not use or store the phone in dusty, dirty areas. Its moving parts can be damaged.
•
Do not store the phone in hot areas. High temperatures can shorten the life of electronic devices, damage
batteries, and warp or melt certain plastics.
•
Do not store the phone in cold areas. When it warms up (to its normal temperature), moisture can form
inside, which may damage electronic circuit boards.
•
Do not drop, knock or shake the phone. Rough handling can break internal circuit boards.
•
Do not use harsh chemicals, cleaning solvents, or strong detergents to clean the phone.
•
Do not paint the phone. Paint can clog the moving parts and prevent proper operation.
•
Use only the supplied or an approved replacement antenna. Unauthorised antennas, modifications or
attachments could damage the phone and may violate regulations governing radio devices.
All of the above suggestions apply equally to the product, battery, charger or any accessory.
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page vii
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 8

RM-659; RM-707
Company policy
Company policy
Our policy is of continuous development; details of all technical modifications will be included with service
bulletins.
While every endeavour has been made to ensure the accuracy of this document, some errors may exist. If
any errors are found by the reader, NOKIA MOBILE PHONES Business Group should be notified in writing/email.
Please state:
•
Title of the Document + Issue Number/Date of publication
•
Latest Amendment Number (if applicable)
•
Page(s) and/or Figure(s) in error
Please send to:
NOKIA CORPORATION
Nokia Mobile Phones Business Group
Nokia Customer Care
PO Box 86
FIN-24101 SALO
Finland
E-mail: Service.Manuals@nokia.com
Page viii COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 9

RM-659; RM-707
Battery information
Battery information
Note: A new battery's full performance is achieved only after two or three complete charge and
discharge cycles!
The battery can be charged and discharged hundreds of times but it will eventually wear out. When the
operating time (talk-time and standby time) is noticeably shorter than normal, it is time to buy a new battery.
Use only batteries approved by the phone manufacturer and recharge the battery only with the chargers
approved by the manufacturer. Unplug the charger when not in use. Do not leave the battery connected to
a charger for longer than a week, since overcharging may shorten its lifetime. If left unused a fully charged
battery will discharge itself over time.
Temperature extremes can affect the ability of your battery to charge.
For good operation times with Li-Ion batteries, discharge the battery from time to time by leaving the product
switched on until it turns itself off (or by using the battery discharge facility of any approved accessory
available for the product). Do not attempt to discharge the battery by any other means.
Use the battery only for its intended purpose.
Never use any charger or battery which is damaged.
Do not short-circuit the battery. Accidental short-circuiting can occur when a metallic object (coin, clip or
pen) causes direct connection of the + and - terminals of the battery (metal strips on the battery) for example
when you carry a spare battery in your pocket or purse. Short-circuiting the terminals may damage the battery
or the connecting object.
Leaving the battery in hot or cold places, such as in a closed car in summer or winter conditions, will reduce
the capacity and lifetime of the battery. Always try to keep the battery between 15°C and 25°C (59°F and 77°
F). A phone with a hot or cold battery may temporarily not work, even when the battery is fully charged.
Batteries' performance is particularly limited in temperatures well below freezing.
Do not dispose of batteries in a fire!
Dispose of batteries according to local regulations (e.g. recycling). Do not dispose as household waste.
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page ix
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 10

RM-659; RM-707
Battery information
(This page left intentionally blank.)
Page x COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 11

RM-659; RM-707
Nokia X7-00.1; Nokia X7-00; L3&4 Service Manual
Structure
Nokia X7-00.1; Nokia X7-00; L3&4 Service Manual Structure
1 General Information
2 Service Tools and Service Concepts
3 BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
4 Cellular RF troubleshooting
5 Camera Module Troubleshooting
6 System Module
Glossary
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page xi
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 12

RM-659; RM-707
Nokia X7-00.1; Nokia X7-00; L3&4 Service Manual
Structure
(This page left intentionally blank.)
Page xii COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 13

Nokia Customer Care
1 — General Information
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 1 – 1
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 14

RM-659; RM-707
General Information
(This page left intentionally blank.)
Page 1 – 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 15

RM-659; RM-707
General Information
Table of Contents
Product selection................................................................................................................................................... 1–5
Product features and sales package.................................................................................................................... 1–6
Product and module list ....................................................................................................................................... 1–9
Mobile enhancements........................................................................................................................................... 1–9
Technical specifications..................................................................................................................................... 1–11
Transceiver general specifications .............................................................................................................. 1–11
Main RF characteristics for GSM850/900/1800/1900 and WCDMA V/II/I phones .................................... 1–12
Main RF characteristics for GSM850/900/1800/1900 and WCDMA VIII/V/IV/II/I phones........................ 1–13
Battery endurance......................................................................................................................................... 1–15
Environmental conditions ............................................................................................................................ 1–15
List of Tables
Table 1 Audio......................................................................................................................................................... 1–9
Table 2 Car........................................................................................................................................................... 1–10
Table 3 Data ........................................................................................................................................................ 1–11
Table 4 Power..................................................................................................................................................... 1–11
List of Figures
Figure 1 View of RM-707....................................................................................................................................... 1–6
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 1 – 3
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 16

RM-659; RM-707
General Information
(This page left intentionally blank.)
Page 1 – 4 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 17

RM-659; RM-707
General Information
Product selection
RM-659 and RM-707 are GSM/WCDMA dual-mode handportable monoblock multimedia computers with a
capacitive touch UI, integrated GPS (A-GPS OMA SUPL) and WLAN. RM-659 supports GSM 850/900/1800/1900
and WCDMA I/II/V bands, GPRS/EGPRS and WCDMA/HSDPA data bearers. RM-707 supports GSM
850/900/1800/1900 and WCDMA I/II/IV/V/VIII bands, GPRS/EGPRS and WCDMA/HSDPA/HSUPA data bearers.
For WCDMA the maximum bit rate is up to 384 kbit/s for downlink and 384 kbit/s for uplink with simultaneous
CS speech or CS video (max. 64 kbit/s). RM-659 supports HSDPA category 8 with downlink peak data rate up
to 7.2 Mbit/s (in limited use cases). RM-707 supports HSDPA category 9 with downlink peak data rate up to
10.2 Mbit/s (in limited use cases), HSUPA belongs to category 5 with uplink peak data rate up to 2.0 Mbit/s
(in limited use cases).
In PS/CS mode, the device supports DTM with multi slot class 32 (max. 5 RX + 3 TX, sum 6). With EGPRS this
means maximum download speed of up to 236.8 kbit/s simultaneously with speech. With GPRS this means
maximum download speed of up to 85.6 kbit/s simultaneously with speech.
In PS only mode, RM-659 supports MSC 10 (max. 4 Rx + 2 TX, sum 5) timeslots resulting in maximum download
speed of up to 236 kbit/s with EGPRS, and up to 177 kbit/s with GPRS. In PS only mode, RM-707 supports MSC
33, a maximum of 5 Rx + 4 Tx timeslots (maximum Rx and Tx timeslot sum 6) resulting in maximum download/
upload speed of up to 296/177.6 kbit/s with EGPRS, and up to 107/64.2 kbit/s with GPRS.
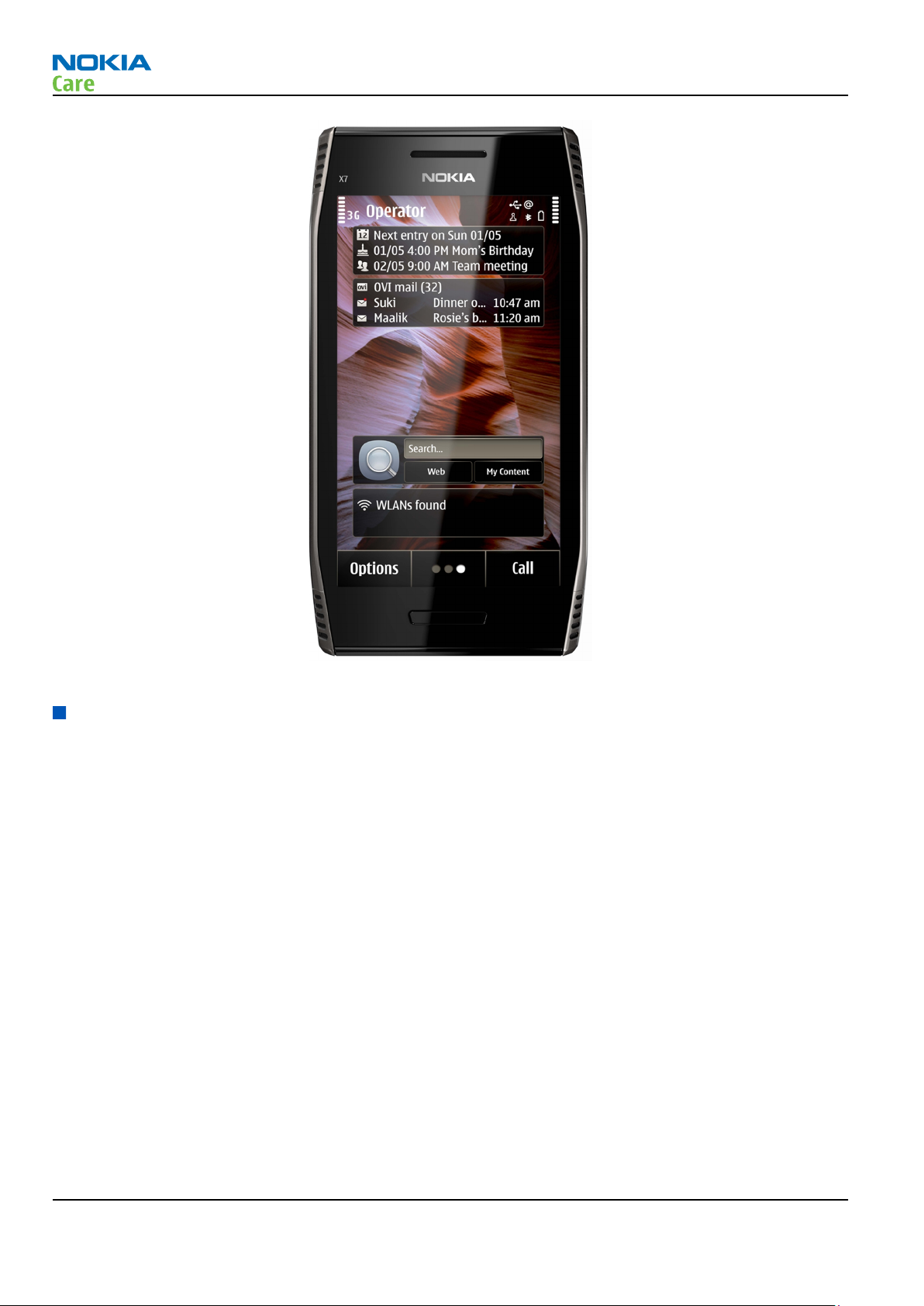
The device has a large AMOLED nHD 4.0” (640 x 360 pixels) colour display (active area 43.2 mm x 76.8 mm)
with 16 million colors. It also has an 8 megapixel EDOF camera, 4 x (RM-659) or 2 x (RM-707) digital zoom
and an integrated dual LED flash.
The MMS implementation follows the OMA MMS standard release 1.3. The browser is a highly advanced
Internet browser also capable of viewing operator domain XHTML Mobile Profile (MP) content. The device
also supports Bluetooth 3.0 standard.
RM-659 uses Symbian 9.2 operating system, S60 (release 3.2) UI, and RM-707 uses Symbian ^3 for Nokia
devices operating system. The device supports the full Web Browser for S60, which brings desktop-like Web
browsing experience to mobile devices. It also supports MIDP Java 2.1 , providing a good platform for
compelling 3rd party applications.
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 1 – 5
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 18
RM-659; RM-707
General Information
Figure 1 View of RM-707
Product features and sales package
Imaging
Main camera:
•
Sensor: 8 megapixel EDOF (Extended Depth of Field)
•
F number/Aperture: F2.8
•
Digital zoom: 4x (RM-659), 2x (RM-707)
•
Fixed focus
•
Focus range: 60 cm ~ infinity
•
Flash: Integrated dual LED flash
Video:
•
Video resolution: nHD 25 fps (720p)
•
Audio recording: AAC (AMR for MMS)
•
Video stabilization
•
Video clip length: Max. 90 min
•
Video file format: .mp4 (default), .3gp (for MMS)
•
White balance: automatic, sunny, cloudy, incandescent, fluorescent
•
Scene: Auto, Night
•
Colour tone: normal, sepia, B&W, vivid, negative
Page 1 – 6 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 19

RM-659; RM-707
General Information
•
Zoom (digital): 3x
•
Video recording indicator
Photo:
•
Aspect ratio: 16:9
•
View finder: Full screen view finder
•
Still image resolutions: up to 8 megapixel: 3280 x 2464
•
Still image file format: JPEG/EXIF
•
Auto exposure: center weighted AE
•
Image orientation: automatic
•
Automatic red eye removal
•
Automatic motion blur reduction
•
Face tracking
•
Exposure compensation: +2 ~ -2EV at 0.5 step
•
White balance: automatic, sunny, cloudy, incandescent, fluorescent
•
Scene: auto, portrait, landscape, night, user defined
•
Colour tone: normal, sepia, B&W, vivid, negative
•
Zoom (digital): 4x (RM-659), 2x (RM-707)
Edit
•
On device Photo editor and Video editor (manual & automatic)
View
•
4.0” nHD (640 x 360 pixels) colour display (active area 43.2 mm x 76.8 mm), up to 16M colors, 16:9 aspect
ratio
•
Dipro Sensor - a combination of ALS and proximity. ALS to optimize display brightness and power
consumption. Proximity for turning off the display when in a call for power consumption.
•
Slideshow from Gallery
Share
•
Share effortlessly from Gallery or after capture
•
Video sharing support (WCDMA services)
•
Online Album: Image/Video uploading from Gallery
Store
•
350 MB internal user memory
•
Hot swappable microSD up to 32 GB
•
Easy to transfer and organize photos and video between your device and a compatible PC
Music
•
Digital music player: supports MP3/ AAC/ eAAC/ eAAC+/ WMA/ AMR-NB/ WB-AMR (RM-707) with playlists,
equalizer and album art
•
Synchronise music with Microsoft Windows Media Player 10 & 11
•
Stereo FM radio (87.5-108 MHz /76-90 MHz) with Visual Radio™ support
•
Bluetooth speakers
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 1 – 7
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 20

RM-659; RM-707
General Information
•
Integrated handsfree speaker
•
Nokia Music Headset (WH-702 for RM-659, WH-701 for RM-707)), inbox
Media
•
Full-screen video playback to view downloaded, streamed or recorded video clips
•
Supported video formats: MPEG-4 , H.264/AVC, H.263/3GPP, VC-1, Real Video 10, ON2 VP6, Flash video
Productivity
Context management:
•
OMA DRM version 2.0
•
OTA provisioning & over the air SW update (FOTA)
•
Ovi Suite
•
Web Browser (OSS), Java ™ MIDP 2.1, XHTML browsing over TCP/IP
Messaging:
•
E-mail (SMTP, IMAP4, POP3), MMS, SMS, unified editor
•
IM client
Office applications:
•
Viewing of email attachments – .doc, .xls, .ppt, .pdf, .zip
•
Mail for Exchange
PIM:
•
Contacts, calendar, to-do, notes, recorder, calculator, clock
Synchronization:
•
Local/Remote (using SyncML)
•
Data: Calendar, Contacts, To-do, Notes, E-mail
•
PC Applications: Microsoft Outlook (98, 2000, 2002, 2003), Outlook Express, Lotus Organizer (5.0, 6.0),
Lotus Notes (5.0, 6.0)
Call management:
•
Call logs, speed dial, voice dialling (with SIND) and voice commands
Connectivity
•
Integrated GPS (A-GPS OMA SUPL)
•
Nokia Maps 3.0
•
WLAN - IEEE802.11 g/b/n with UPnP support
•
Micro USB interface with USB 2.0 high speed
•
Bluetooth wireless technology 3.0
•
MicroSD memory card - support up to 32 GB
•
Nokia 3.5 mm AHJ connector (RM-659)
•
Nokia 3.5 mm A/V connector (RM-707)
Add-on software framework
•
Symbian ^3 for Nokia devices OS (RM-707)
•
Symbian 9.2 OS (RM-659)
•
Nokia Series 60, 5th edition, feature pack 2
Page 1 – 8 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 21
RM-659; RM-707
General Information
•
Java: MIDP2.1
•
C++ and Java SDKs
•
Flash Lite 4.0
Additional technical specifications
•
Vibrating alert
•
3GPP Rel 5/6 WCDMA , Rel 4 EGSM compliant
•
Speech codecs supported: AMR, NB AMR, FR, EFR, WB-AMR (RM-707)
•
GPRS/EGPRS Class B, Multi slot class 10 (RM-659)
•
GPRS/EGPRS Rel 6, Multi slot class 33 (RM-707)
•
Dual Transfer Mode (DTM) class A, multi slot class 32
•
WCDMA DL 384 kbit/s, UL 384 kbit/s
•
HSDPA up to 7.2 Mbps (RM-659)
•
HSDPA up to 10.2 Mbps, HSUPA 2 Mbps (RM-707)
Sales package
•
Transceiver RM-659 or RM-707
•
Charger AC-10UC (RM-659) or AC-10 (RM-707)
•
Music headset WH-702 (RM-659) or WH-701 (RM-707)
•
Connectivity cable (CA-101)
•
MicroSD card 8GB (MU-43)
•
Quick Start Guide
Product and module list
Module name Type code Notes
System/RF module PWB 3HF
HSJ flex module 3HT
UI flexi module 3HR
Volume keys flex module 3HS
Mobile enhancements
Table 1 Audio
Enhancement Type
Music headsets WH-701 (for RM-707, inbox)
WH-702 (for RM-659, inbox)
Mini speakers MD-6
MD-8
MD-9
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 1 – 9
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 22

Enhancement Type
Wired headsets HS-82 (for RM-707)
WH-203 (for RM-707)
WH-501 (for RM-707)
Bluetooth headsets BH-102
BH-103
BH-104
BH-105
BH-106
BH-108
BH-212
BH-214
BH-216
RM-659; RM-707
General Information
BH-501
BH-504
BH-505
BH-604
BH-606
BH-607
BH-703
BH-804
BH-903
BH-905
Bluetooth speakers MD-7W
Table 2 Car
Enhancement Type
Nokia Universal Mobile Holder CR-114 (for RM-707)
CR-122
HH-20 (for RM-707)
Wireless plug-in car handsfree HF-200
HF-310
HF-510
Car kit CK-100
Multimedia car kit CK-300
Display car kit CK-600
Page 1 – 10 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 23
RM-659; RM-707
General Information
Enhancement Type
Mobile charger DC-6 (for RM-659)
DC-10 (for RM-659)
DC-11 (for RM-659)
Table 3 Data
Enhancement Type
Connectivity cable CA-101 (inbox)
CA-101D
CA-126
CA-179 (for RM-707)
Micro USB OTG to USB adapter cable CA-157
MicroSD card MU-22, 1GB
MU-37, 2GB
MU-41, 4GB
MU-43, 8GB (inbox)
MU-44, 16GB
Table 4 Power
Enhancement Type
Battery 1200 mAh Li-ion BL-5K
Travel charger AC-6 (for RM-659)
AC-10 (for RM-707, inbox)
AC-10UC (for RM-659, inbox)
Multiple charger DT-600 (for RM-659)
Technical specifications
Transceiver general specifications
Unit Dimensions (L x W x T)
Weight (g)
Volume (cm3)
(mm)
Transceiver with BL-5K
119.7 x 62.8 x 11.9 150 73
1200 mAh Li-ion battery
pack
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 1 – 11
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 24
RM-659; RM-707
General Information
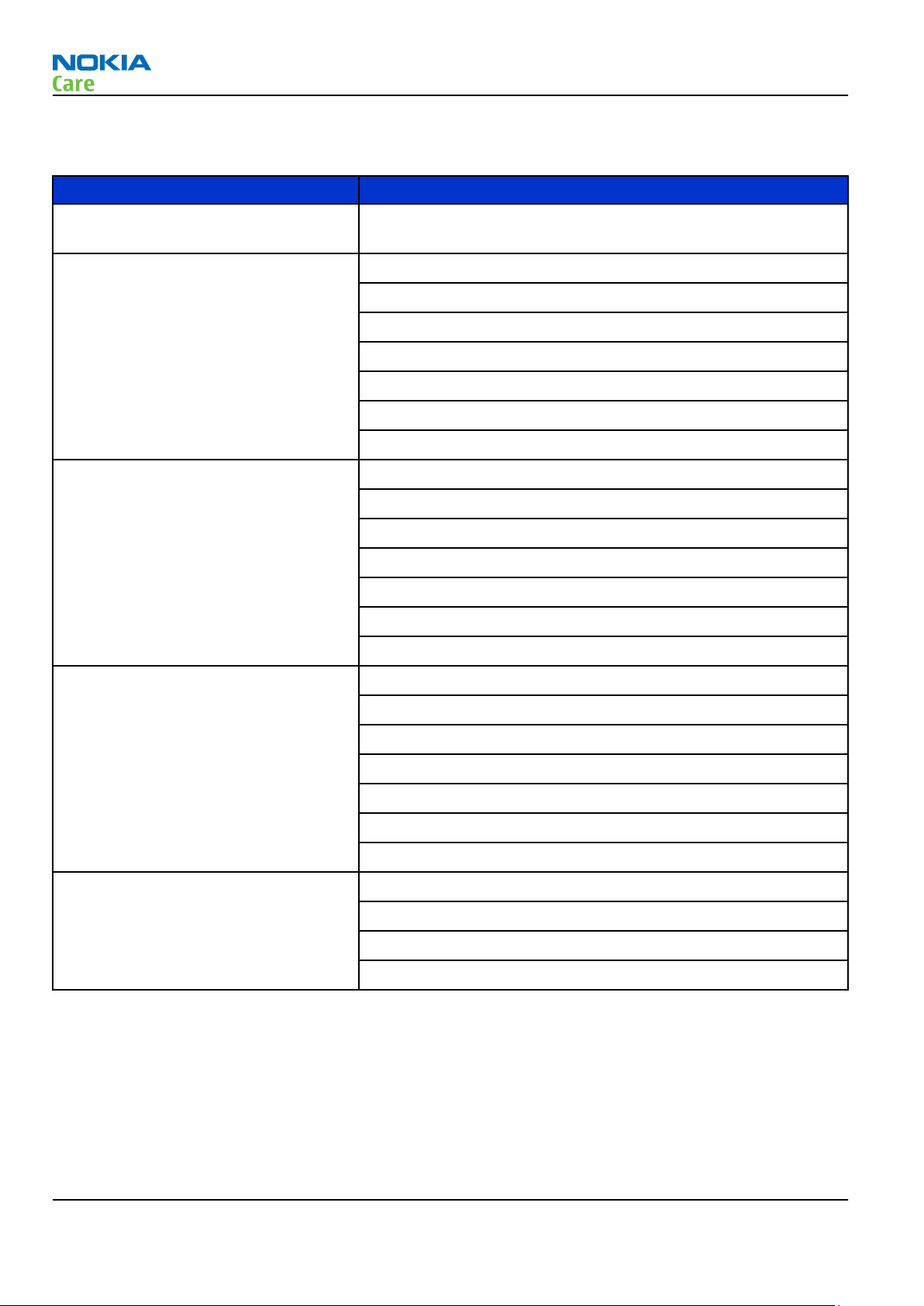
Main RF characteristics for GSM850/900/1800/1900 and WCDMA V/II/I phones
Parameter Unit
Cellular system GSM850, EGSM900, GSM1800/1900, WCDMA V (850), WCDMA II
(1900) and WCDMA I (2100)
Rx frequency band GSM850: 869 - 894MHz
EGSM900: 925 - 960 MHz
GSM1800: 1805 - 1880 MHz
GSM1900: 1930 - 1990 MHz
WCDMA V (850): 869 - 894 MHz
WCDMA II (1900): 1930 - 1990 MHz
WCDMA I (2100): 2110 - 2170 MHz
Tx frequency band GSM850: 824 - 849 MHz
EGSM900: 880 - 915 MHz
GSM1800: 1710 - 1785 MHz
GSM1900: 1850 - 1910 MHz
WCDMA V (850): 824 - 849 MHz
WCDMA II (1900): 1850 - 1910 MHz
WCDMA I (2100): 1920 - 1980 MHz
Output power GSM850: +5 ...+33 dBm/3.2 mW ... 2 W
GSM900: +5 … +33 dBm/3.2 mW … 2 W
GSM1800: +0 … +30 dBm/1.0 mW … 1 W
GSM1900: +0 … +30 dBm/1.0 mW … 1 W
WCDMA V (850): -50 ... +23.5 dBm/0.01 μW ... 251 mW
WCDMA II (1900): -50 ... +23.5 dBm/0.01 μW ... 251 mW
WCDMA I (2100): -50 ... +22.5 dBm/0.01 μW ... 251 mW
EDGE output power EDGE850: +5 … +27 dBm/3.2 mW … 501 mW
EDGE900: +5 … +27 dBm/3.2 mW … 501 mW
EDGE1800: +0 … +26 dBm/1.0 mW … 398 mW
EDGE1900:+0 … +26 dBm/1.0 mW … 398 mW
Page 1 – 12 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 25
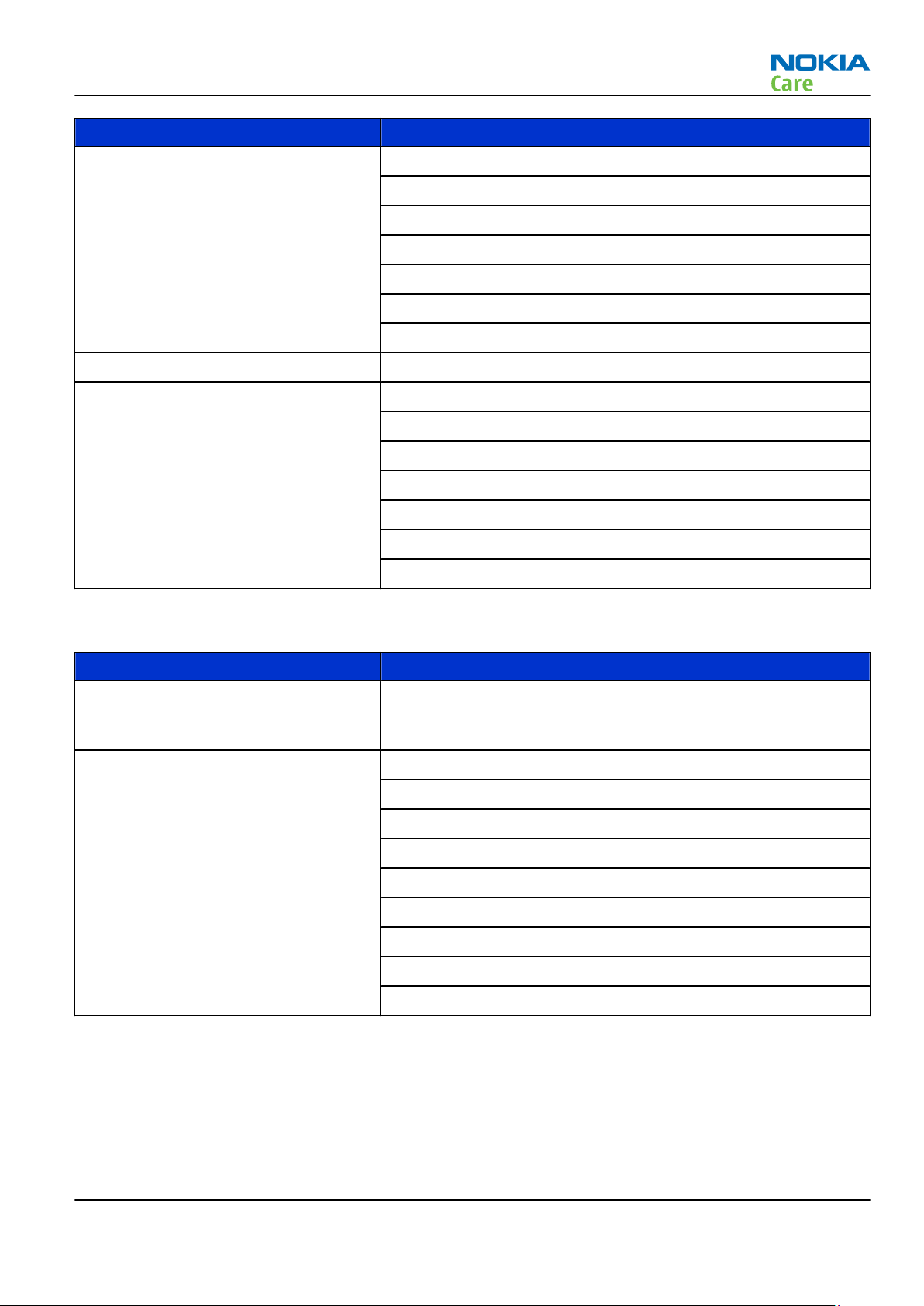
RM-659; RM-707
General Information
Parameter Unit
Number of RF channels GSM850: 124
GSM900: 174
GSM1800: 374
GSM1900: 299
WCDMA V (850): 108
WCDMA II (1900): 289
WCDMA I (2100): 277
Channel spacing 200 kHz (WCDMA II and V 100/200 kHz)
Number of Tx power levels GSM850: 15
GSM900: 15
GSM1800: 16
GSM1900: 16
WCDMA V (850): 75
WCDMA II (1900): 75
WCDMA I (2100): 75
Main RF characteristics for GSM850/900/1800/1900 and WCDMA VIII/V/IV/II/I phones
Parameter Unit
Cellular system GSM850, EGSM900, GSM1800/1900, WCDMA VIII (900), WCDMA V
(850), WCDMA IV (1700/2100), WCDMA II (1900) and WCDMA I
(2100)
Rx frequency band GSM850: 869 - 894MHz
EGSM900: 925 - 960 MHz
GSM1800: 1805 - 1880 MHz
GSM1900: 1930 - 1990 MHz
WCDMA VIII (900): 925 - 960 MHz
WCDMA V (850): 869 - 894 MHz
WCDMA IV (1700/2100): 2110 - 2155 MHz
WCDMA II (1900): 1930 - 1990 MHz
WCDMA I (2100): 2110 - 2170 MHz
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 1 – 13
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 26
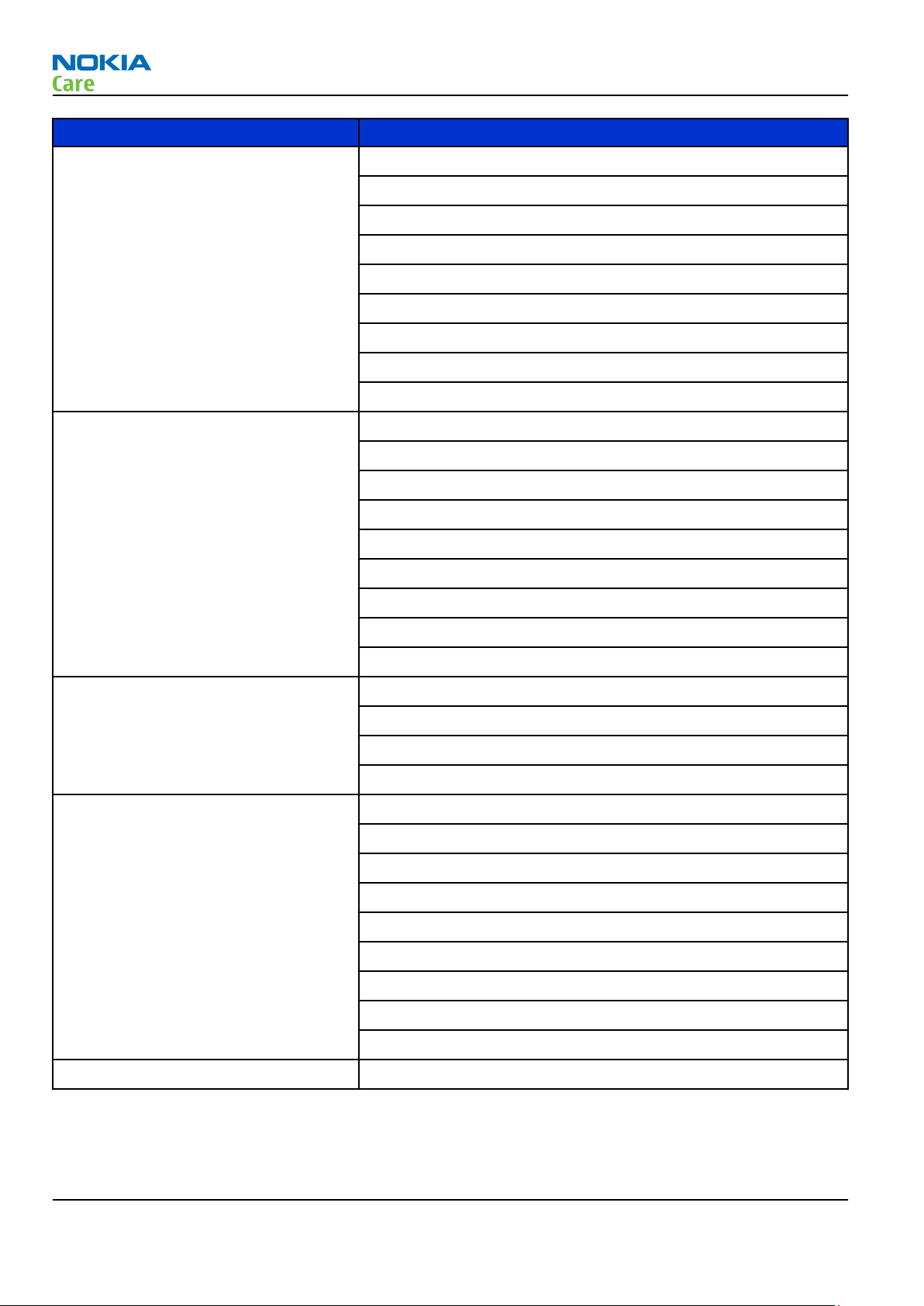
Parameter Unit
Tx frequency band GSM850: 824 - 849 MHz
EGSM900: 880 - 915 MHz
GSM1800: 1710 - 1785 MHz
GSM1900: 1850 - 1910 MHz
WCDMA VIII (900): 880 - 915 MHz
WCDMA V (850): 824 - 849 MHz
WCDMA IV (1700/2100): 1710 - 1755 MHz
WCDMA II (1900): 1850 - 1910 MHz
WCDMA I (2100): 1920 - 1980 MHz
Output power GSM850: +5 ...+33 dBm/3.2 mW ... 2 W
GSM900: +5 … +33 dBm/3.2 mW … 2 W
GSM1800: +0 … +30 dBm/1.0 mW … 1 W
RM-659; RM-707
General Information
GSM1900: +0 … +30 dBm/1.0 mW … 1 W
WCDMA VIII (900): -50 ... +23.5 dBm/0.01 μW ... 251 mW
WCDMA V (850): -50 ... +23.5 dBm/0.01 μW ... 251 mW
WCDMA IV (1700/2100): -50 ... +23.5 dBm/0.01 μW ... 251 mW
WCDMA II (1900): -50 ... +23.5 dBm/0.01 μW ... 251 mW
WCDMA I (2100): -50 ... +22.5 dBm/0.01 μW ... 251 mW
EDGE output power EDGE850: +5 … +27 dBm/3.2 mW … 501 mW
EDGE900: +5 … +27 dBm/3.2 mW … 501 mW
EDGE1800: +0 … +26 dBm/1.0 mW … 398 mW
EDGE1900:+0 … +26 dBm/1.0 mW … 398 mW
Number of RF channels GSM850: 124
GSM900: 174
GSM1800: 374
GSM1900: 299
WCDMA VIII (900): 152
WCDMA V (850): 108
WCDMA IV (1700/2100): 211
WCDMA II (1900): 289
WCDMA I (2100): 277
Channel spacing 200 kHz (WCDMA II, IV and V 100/200 kHz)
Page 1 – 14 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 27
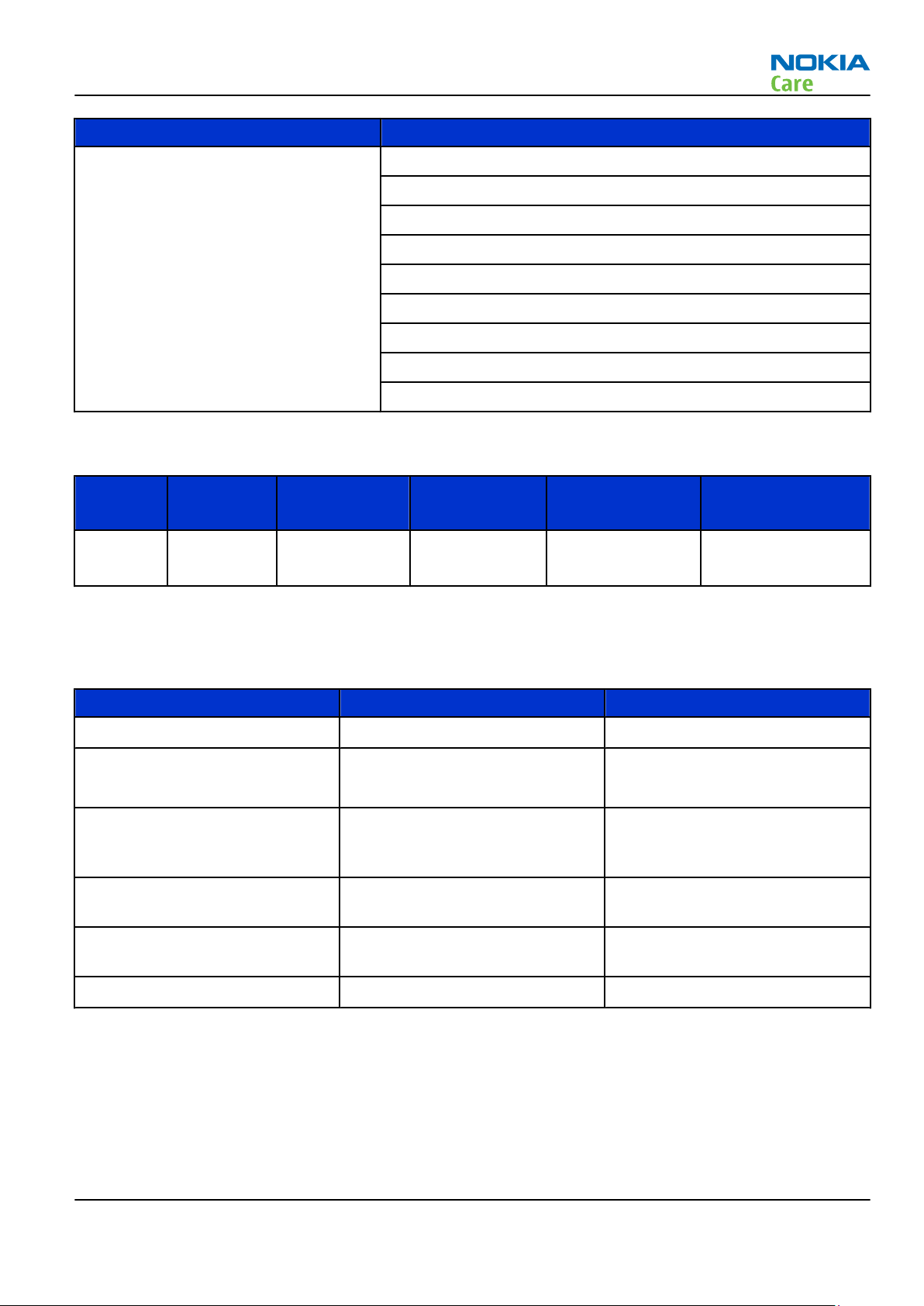
RM-659; RM-707
General Information
Parameter Unit
Number of Tx power levels GSM850: 15
GSM900: 15
GSM1800: 16
GSM1900: 16
WCDMA VIII (900): 75
WCDMA V (850): 75
WCDMA IV (1700/2100): 75
WCDMA II (1900): 75
WCDMA I (2100): 75
Battery endurance
Battery Capacity
(mAh)
BL-5K 1200 6.5 h (GSM)
Talk time Stand-by Music playback Video playback
4.5 h (WCDMA)
450 h (GSM)
450 h (WCDMA)
50 h 6 h
Environmental conditions
Temperature conditions
Environmental condition Ambient temperature Notes
Normal operation
Reduced performance
Intermittent operation
No operation or storage
-15oC...+55oC
-25oC...-15oC
+55oC...+70oC
-40oC...-15oC
+70oC...+85 oC
<-40oC...>+85oC
Specifications fulfilled
Operational for shorts periods
only
Operation not guaranteed but an
attempt to operate does not
damage the phone.
No storage or operation: an
attempt may damage the phone.
H.264 720p 30fps
Charging allowed
Long term storage conditions
-10oC...+60oC
0oC...+85oC
BTemp measurement range for
charging.
Humidity
Relative humidity range is 5...95%.
The HW module is not protected against water. Condensed or splashed water might cause malfunction. Any
submersion of the phone will cause permanent damage. Long-term high humidity, with condensation, will
cause permanent damage because of corrosion.
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 1 – 15
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 28

RM-659; RM-707
General Information
Vibration
The module should withstand the following vibrations:
•
5 - 10 Hz; +10dB / octave
•
10 - 50 Hz; 5.58 m2 / s3 (0.0558 g2/ Hz)
•
50 - 300 Hz; - 10 dB / octave
ESD strength
Conducted discharge is 8 kV (>10 discharges) and air contact 15 kV ( >10 discharges ).
The standard for electrostatic discharge is IEC 61000-4-2, and this device fulfils level 4 requirements.
RoHS
This device uses RoHS compliant components and lead-free soldering process.
Page 1 – 16 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 29

Nokia Customer Care
2 — Service Tools and Service
Concepts
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 2 – 1
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 30

RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
(This page left intentionally blank.)
Page 2 – 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 31

RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
Table of Contents
Service tools........................................................................................................................................................... 2–5
Product specific tools....................................................................................................................................... 2–5
SS-252........................................................................................................................................................... 2–5
General tools..................................................................................................................................................... 2–5
CU-4............................................................................................................................................................... 2–6
FPS-21........................................................................................................................................................... 2–7
MJ-300 .......................................................................................................................................................... 2–8
PK-1............................................................................................................................................................... 2–8
RJ-230 ........................................................................................................................................................... 2–9
SRT-6............................................................................................................................................................. 2–9
SS-112........................................................................................................................................................... 2–9
SS-210........................................................................................................................................................... 2–9
SS-227........................................................................................................................................................ 2–10
SS-93.......................................................................................................................................................... 2–10
SX-4............................................................................................................................................................ 2–10
Removing a camera with the removal tool SS-210 .............................................................................. 2–10
Cables.............................................................................................................................................................. 2–12
CA-101 ....................................................................................................................................................... 2–12
CA-158RS ................................................................................................................................................... 2–12
CA-31D ....................................................................................................................................................... 2–13
CA-89DS ..................................................................................................................................................... 2–13
CA-99PS...................................................................................................................................................... 2–13
PCS-1.......................................................................................................................................................... 2–14
XRS-6.......................................................................................................................................................... 2–14
Service concepts ................................................................................................................................................. 2–15
POS (Point of Sale) flash concept ................................................................................................................. 2–15
Flashing, certificate restore and product code change option 1 ............................................................. 2–16
Flashing, certificate restore and product code change option 2 ............................................................. 2–17
Flashing, certificate restore, product code change and EM calibration option 2 ................................... 2–18
BB and RF tuning option 2............................................................................................................................ 2–19
List of Figures
Figure 2 POS flash concept ................................................................................................................................ 2–15
Figure 3 Flashing, certificate restore and product code change................................................................... 2–16
Figure 4 Flashing, certificate restore and product code change................................................................... 2–17
Figure 5 Flashing, certificate restore, product code change and EM calibration......................................... 2–18
Figure 6 BB and RF tuning option 2.................................................................................................................. 2–19
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 2 – 3
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 32

RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
(This page left intentionally blank.)
Page 2 – 4 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 33

RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
Service tools
Product specific tools
The table below gives a short overview of service devices that can be used for testing, error analysis, and
repair of product RM-659; RM-707. For the correct use of the service devices, and the best effort of workbench
setup, please refer to various concepts.
SS-252 Multi tool SS-252 multi tool is an optional assembly jig.
General tools
The table below gives a short overview of service devices that can be used for testing, error analysis, and
repair of product RM-659; RM-707. For the correct use of the service devices, and the best effort of workbench
setup, please refer to various concepts.
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 2 – 5
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 34

RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
CU-4 Control unit CU-4 is a general service tool used with a module jig and/or a flash
adapter. It requires an external 12 V power supply.
The unit has the following features:
•
Software controlled via USB
•
EM calibration function
•
Forwards FBUS/Flashbus traffic to/from terminal
•
Forwards USB traffic to/from terminal
•
Software controlled BSI values
•
Regulated VBATT voltage
•
2 x USB2.0 connector (Hub)
•
FBUS and USB connections supported
When using CU-4, note the special order of connecting cables and
other service equipment:
Instructions
1 Connect a service tool (jig, flash adapter) to CU-4.
2 Connect CU-4 to your PC with a USB cable.
3 Connect supply voltage (12 V)
4 Connect an FBUS cable (if necessary).
5 Start service software.
Note: Service software enables CU-4 regulators via USB when
it is started.
Reconnecting the power supply requires a service software
restart.
Page 2 – 6 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 35

RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
FPS-21 Flash prommer
FPS-21 sales package:
•
FPS-21 prommer
•
AC-35 power supply
•
CA-31D USB cable
FPS-21 interfaces:
Front
•
Service cable connector
Provides Flashbus, USB and VBAT connections to a mobile device.
•
SmartCard socket
A SmartCard is needed to allow DCT-4 generation mobile device
programming.
Rear
•
DC power input
For connecting the external power supply (AC-35).
•
Two USB A type ports (USB1/USB3)
Can be used, for example, for connecting external storage memory
devices or mobile devices
•
One USB B type device connector (USB2)
For connecting a PC.
•
Phone connector
Service cable connection for connecting Flashbus/FLA.
•
Ethernet RJ45 type socket (LAN)
For connecting the FPS-21 to LAN.
Inside
•
Four SD card memory slots
For internal storage memory.
Note: In order to access the SD memory card slots inside
FPS-21, the prommer needs to be opened by removing the
front panel, rear panel and heatsink from the prommer body.
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 2 – 7
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 36

RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
MJ-300 Module jig Module jig MJ-300 can be used for flashing via USB and RF, battery and
system testing.
The main functions are:
•
Powering with external power
•
CU-4 interface adapter to phone (requires SS-227)
•
WLAN/BT/GPS RF-interfaces with probes
•
GSM/WCDMA RF-interfaces with probes
•
BSI mode selector (Tabby and Lynx interface, selected with battery
cable)
•
VBATT interface (Tabby and Lynx interface, selected with battery
cable)
•
CA-158RS cable is used together with this jig for RF testing
•
Attenuation values for CA-158RS cable
Band Default f/
MHz RX
GSM 850 881.6 -0.2 836.6 -0.2
GSM 900 942.4 -0.2 897.4 -0.2
GSM 1800 1842.8 -0.3 1747.8 -0.3
GSM 1900 1960.0 -0.3 1880.0 -0.3
WCDMA I 2140.0 -0.4 1950.0 -0.3
WCDMA II 1960.0 -0.3 1880.0 -0.3
WCDMA IV 2140.0 -0.4 1740.0 -0.3
WCDMA V 880.0 -0.2 835.0 -0.2
WCDMA VIII 942.6 -0.2 897.6 -0.2
WLAN n/a n/a 2442.0 -0.4
FM / Tx n/a n/a
PK-1 Software protection
key
PK-1 is a hardware protection key with a USB interface. It has the same
functionality as the PKD-1 series dongle.
PK-1 is meant for use with a PC that does not have a series interface.
To use this USB dongle for security service functions please register
the dongle in the same way as the PKD-1 series dongle.
Att. RX Default f/
MHz TX
Att. TX
Page 2 – 8 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 37

RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
RJ-230 Soldering jig RJ-230 is a soldering jig used for soldering and as a rework jig for the
engine module.
SRT-6 Opening tool SRT-6 is used to open phone covers.
Note: The SRT-6 is included in the Nokia Standard Toolkit.
SS-112 Camera recess 00 bit ¼” bit for the Torque screwdriver to be added as part of the service
box.
SS-210 Camera removal tool The camera removal tool SS-210 is used to remove/attach the camera
module from/to the socket.
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 2 – 9
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 38

RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
SS-227 Interface for CU-4
control unit
SS-227 is designed for regional Central Services to be able to use CU-4
with MJ-300 module jig. With SS-227, CU-4 can be used for battery
testing.
The main functions of SS-227 are:
•
CU-4 interface adapter to MJ-300
•
BSI mode selector (Lynx and Tabby mode selection)
•
VBATT interface
All functions are performed in the CU-4. Calibration voltages and
currents e.g. are protected and monitored by the CU-4 interface
software (protection for over-current, overvoltage and reverse
voltage).
SS-93 Opening tool SS-93 is used for opening JAE connectors.
Note: The SS-93 is included in Nokia Standard Toolkit.
SX-4 Smart card SX-4 is a BB5 security device used to protect critical features in tuning
and testing.
SX-4 is also needed together with FPS-21 when DCT-4 phones are
flashed.
Removing a camera with the removal tool SS-210
Steps
1. Insert the camera tool on top of the camera, do not press the metal sheets down.
Page 2 – 10 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 39

RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
2. Press the camera down a little bit with the camera tool black plastic part.
3. Press the metal sheets down.
4. Press the metal plates from the sides to tighten them to the camera.
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 2 – 11
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 40

5. Pull out the camera.
RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
Cables
The table below gives a short overview of service devices that can be used for testing, error analysis, and
repair of product RM-659; RM-707. For the correct use of the service devices, and the best effort of workbench
setup, please refer to various concepts.
CA-101 Micro USB cable The CA-101 is a USB-to-microUSB data cable that allows connections
between the PC and the phone.
CA-158RS RF tuning cable Product-specific adapter cable for RF tuning.
Page 2 – 12 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 41

RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
CA-31D USB cable The CA-31D USB cable is used to connect FPS-21 to a PC. It is included
in the FPS-21 sales package.
CA-89DS Cable Provides VBAT and Flashbus connections to mobile device
programming adapters.
CA-99PS Adapter CA-99PS adapter, 3.5 jack to 5.5 plug.
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 2 – 13
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 42

RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
PCS-1 Power cable The PCS-1 power cable (DC) is used with a docking station, a module
jig or a control unit to supply a controlled voltage.
XRS-6 RF cable The RF cable is used to connect, for example, a module repair jig to
the RF measurement equipment.
SMA to N-Connector approximately 610 mm.
Attenuation for:
•
GSM850/900: 0.3+-0.1 dB
•
GSM1800/1900: 0.5+-0.1 dB
•
WCDMA/WLAN: 0.6+-0.1dB
Page 2 – 14 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 43

RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
Service concepts
POS (Point of Sale) flash concept
Figure 2 POS flash concept
Type Description
Product specific tools
BL-5K Battery
Other tools
PC with Care Suite
Cables
CA-101 Micro USB cable
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 2 – 15
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 44

Flashing, certificate restore and product code change option 1
RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
Figure 3 Flashing, certificate restore and product code change
Type Description
Product specific devices
BL-5K Battery
Other devices
PK-1 SW security device
SX-4 Smart card
PC with service software
Smart card reader
Cables
CA-101 Micro USB cable
USB cable
Page 2 – 16 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 45

RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
Flashing, certificate restore and product code change option 2
Figure 4 Flashing, certificate restore and product code change
Type Description
Product specific devices
BL-5K Battery
Other devices
FPS-21 Flash prommer box
AC-35 Power supply
PK-1 SW security device
SX-4 Smart card
PC with service software
Cables
CA-101 Micro USB cable
USB cable
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 2 – 17
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 46

Service Tools and Service Concepts
Flashing, certificate restore, product code change and EM calibration option 2
RM-659; RM-707
Figure 5 Flashing, certificate restore, product code change and EM calibration
Type Description
Product specific tools
MJ-300 Module jig
Other tools
CU-4 Control unit
FPS-21 Flash prommer box
PK-1 SW security device
SX-4 Smart card
PC with service software
Cables
Page 2 – 18 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 47

RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
Type Description
CA-101 Micro USB cable
CA-89DS Service cable
CA-99PS Adapter
PCS-1 Power cable
USB cable
BB and RF tuning option 2
Figure 6 BB and RF tuning option 2
Type Description
Phone specific devices
MJ-300 Module jig
Other devices
CU-4 Control unit
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 2 – 19
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 48

Type Description
SS-227 CU-4 interface part
FPS-21 Flash prommer box
PK-1 SW security device
SX-4 Smart card
PC with service software
Measurement equipment
Cables
CA-101 Micro USB cable
PCS-1 DC power cable
XRS-6 RF cable
USB cable
GPIB control cable
RM-659; RM-707
Service Tools and Service Concepts
CA-158RS Product specific RF adapter cable
Page 2 – 20 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 49

Nokia Customer Care
3 — BB Troubleshooting and
Manual Tuning Guide
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 1
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 50

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
(This page left intentionally blank.)
Page 3 – 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 51

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Table of Contents
Baseband main troubleshooting......................................................................................................................... 3–5
Power and charging troubleshooting................................................................................................................. 3–9
Battery current measuring fault troubleshooting ........................................................................................ 3–9
General power checking troubleshooting ..................................................................................................... 3–9
Dead or jammed device troubleshooting................................................................................................... 3–12
Clocking troubleshooting ............................................................................................................................. 3–13
USB charging troubleshooting..................................................................................................................... 3–14
Interface troubleshooting ................................................................................................................................. 3–15
USB flashing fault troubleshooting ............................................................................................................. 3–15
USB data interface troubleshooting............................................................................................................ 3–16
SIM card troubleshooting ............................................................................................................................. 3–16
Memory troubleshooting.............................................................................................................................. 3–19
MicroSD card troubleshooting ................................................................................................................ 3–19
NOR troubleshooting ............................................................................................................................... 3–19
SDRAM troubleshooting........................................................................................................................... 3–21
IVE troubleshooting ........................................................................................................................................... 3–22
Introduction to IVE troubleshooting........................................................................................................... 3–22
IVE troubleshooting ...................................................................................................................................... 3–23
TV out troubleshooting...................................................................................................................................... 3–24
Introduction to SDTV troubleshooting........................................................................................................ 3–24
SDTV out troubleshooting ............................................................................................................................ 3–25
Display module troubleshooting ...................................................................................................................... 3–27
General instructions for display troubleshooting...................................................................................... 3–27
Introduction to display troubleshooting.................................................................................................... 3–28
Display fault troubleshooting ...................................................................................................................... 3–30
Touch panel troubleshooting....................................................................................................................... 3–30
Keyboard troubleshooting ................................................................................................................................ 3–32
Keys troubleshooting.................................................................................................................................... 3–32
Power key troubleshooting.......................................................................................................................... 3–33
Sensors troubleshooting ................................................................................................................................... 3–34
Accelerometer troubleshooting................................................................................................................... 3–34
Proximity sensor troubleshooting............................................................................................................... 3–35
ALS technical description and troubleshooting ......................................................................................... 3–35
Proximity sensor and ambient light sensor (ALS)................................................................................. 3–35
ALS troubleshooting ................................................................................................................................ 3–37
Audio troubleshooting....................................................................................................................................... 3–38
Audio troubleshooting test instructions..................................................................................................... 3–38
External earpiece troubleshooting.............................................................................................................. 3–40
External microphone troubleshooting........................................................................................................ 3–40
Internal earpiece troubleshooting .............................................................................................................. 3–42
Internal handsfree (IHF) troubleshooting................................................................................................... 3–43
Internal microphone troubleshooting........................................................................................................ 3–44
Vibra troubleshooting................................................................................................................................... 3–45
Connectivity module troubleshooting ............................................................................................................. 3–45
Introduction to connectivity module troubleshooting ............................................................................. 3–45
Bluetooth/FM radio and WLAN troubleshooting........................................................................................ 3–47
Introduction to Bluetooth/FM radio troubleshooting.......................................................................... 3–47
Introduction to WLAN troubleshooting ................................................................................................. 3–48
Bluetooth and FM radio self tests in Phoenix............................................................................................. 3–49
WLAN self test in Phoenix............................................................................................................................. 3–50
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 3
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 52

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Bluetooth functionality test......................................................................................................................... 3–50
FMRX radio receiver testing.......................................................................................................................... 3–51
WLAN TX and RX testing in Phoenix ............................................................................................................ 3–51
WLAN TX BiP testing procedure in Phoenix................................................................................................ 3–51
WLAN TX BiP testing procedure in Testing and Tuning Tool .................................................................... 3–52
Bluetooth troubleshooting .......................................................................................................................... 3–55
FMRX receiver troubleshooting.................................................................................................................... 3–56
WLAN troubleshooting ................................................................................................................................. 3–57
GPS troubleshooting .......................................................................................................................................... 3–57
Introduction to GPS troubleshooting.......................................................................................................... 3–57
GPS settings for Phoenix............................................................................................................................... 3–59
Quick Test window................................................................................................................................... 3–59
GPS control................................................................................................................................................ 3–60
GPS failure troubleshooting......................................................................................................................... 3–61
GPS basic checks troubleshooting ............................................................................................................... 3–62
Baseband manual tuning guide........................................................................................................................ 3–64
Certificate restoring ...................................................................................................................................... 3–64
Product code change .................................................................................................................................... 3–67
Energy management calibration................................................................................................................. 3–71
List of Tables
Table 5 Display module troubleshooting cases............................................................................................... 3–27
Table 6 Pixel defects .......................................................................................................................................... 3–28
Table 7 Defects table.......................................................................................................................................... 3–28
Table 8 Calibration value limits ........................................................................................................................ 3–72
List of Figures
Figure 7 Top cap removed to access VBAT test pad........................................................................................ 3–11
Figure 8 Power supply probes connected to VBAT test pad and micro USB casing..................................... 3–11
Figure 9 Expected Crystal clock input to BCM2727B on Oscilloscope ............................................................ 3–23
Figure 10 Expected SDTV CVBS PAL signal on Oscilloscope............................................................................. 3–26
Figure 11 Expected SDTV CVBS NTSC signal on Oscilloscope........................................................................... 3–27
Figure 12 DiPro proximity sensor and ambient light sensor......................................................................... 3–36
Figure 13 Hardware connections between BB and BOB1.0M-b..................................................................... 3–46
Figure 14 Bluetooth/WLAN/GPS antenna......................................................................................................... 3–46
Figure 15 Bluetooth and FM radio self tests in Phoenix................................................................................. 3–50
Figure 16 Component layout, bottom side...................................................................................................... 3–58
Figure 17 GPS layout and basic test points...................................................................................................... 3–59
Figure 18 GPS Quick Test window .................................................................................................................... 3–60
Figure 19 GPS Control dialogue box ................................................................................................................. 3–61
Page 3 – 4 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 53

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Baseband main troubleshooting
Context
Always start the troubleshooting procedure by running the Phoenix self tests. If a test fails, please follow the
diagrams below. If the phone is dead and you cannot perform the self tests, go to
troubleshooting
.
Dead or jammed device
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 5
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 54

Troubleshooting flow - Page 1 of 3
RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Page 3 – 6 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 55

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Troubleshooting flow - Page 2 of 3
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 7
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 56

Troubleshooting flow - Page 3 of 3
RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Page 3 – 8 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 57

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Power and charging troubleshooting
Battery current measuring fault troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 9
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 58

General power checking troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Page 3 – 10 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 59

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Open battery protection circuit due to short circuit during assembly
This phone is susceptible to short-circuiting of the VBAT line during display assembly due to the exposed
VBAT at the Dipro IR LED. This results in the battery protection circuit opening. The following steps will close
the battery protection circuit:
1 Remove the top end cap of the phone by removing the plastic covers and then remove the two screws.
Figure 7 Top cap removed to access VBAT test pad
2 Set power supply to 3.8 VDC with current limited to 500 mA. Put the negative side of the power supply to
the micro USB connector casing (see the black probe in the following figure) and the positive side to the
VBAT test pad (J2070) (see the red probe in the following figure). The power supply should show current
draw when the battery protection circuit closes. The phone should then power up provided the VBAT level
is high enough for SW to start up. If the phone does not power on, at this point you can plug a charger
into the phone and it should charge, and when VBAT reaches the proper level it should power on.
Figure 8 Power supply probes connected to VBAT test pad and micro USB casing
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 11
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 60

Dead or jammed device troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Page 3 – 12 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 61

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Clocking troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 13
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 62

USB charging troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Page 3 – 14 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 63

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Interface troubleshooting
USB flashing fault troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 15
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 64

USB data interface troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Page 3 – 16 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 65

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
SIM card troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 17
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 66

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Page 3 – 18 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 67

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Memory troubleshooting
MicroSD card troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 19
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 68

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
NOR troubleshooting
Context
NOR flash interface is an electrical interface between the memory and the digital ASIC. It is used for accessing
the memory IC for SW instructions and data.
Troubleshooting flow
Page 3 – 20 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 69

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
SDRAM troubleshooting
Context
SDRAM interface is an electrical interface between the memory and the digital Asic. It is used for accessing
the memory IC for SW instructions and data.
Troubleshooting flow
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 21
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 70

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
IVE troubleshooting
Introduction to IVE troubleshooting
The IVE engine is a next generation imaging and video engine based on BCM2727B. The BCM2727B acts as
imaging, video, display, and HDTV and SDTV hardware accelerator.
The following references on the PWB help in the effective debugging and troubleshooting of IVE.
Sr. No Reference Description
1 B1400 19.2MHz Crystal
2 D1400 IVE/BCM2727B IC
The following test points on the PWB help in the effective debugging and troubleshooting.
Sr. No Signal name Measuring point Description
1 VIVE_2V5_FILT C1419/C1417 2.5V supply to BCM2727B
2 VIVE_2V8_FILT C1414 2.8V supply to BCM2727B
3 VIVE_1V8_FILT L1402/C1450 1.8V supply to BCM2727B
4 VBAT L1403/C1466 VBAT supply to BCM2727B
5 RUN J1425 Enable signal to IVE. This needs to be
High for IVE to be Up.
6 XIN C1448 19.2MHz clock to IVE
Page 3 – 22 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 71

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
IVE troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 23
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 72

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Figure 9 Expected Crystal clock input to BCM2727B on Oscilloscope
TV out troubleshooting
Introduction to SDTV troubleshooting
SDTV
The phone has SDTV capability. The phone can be connected to an analog TV through a TV Out cable.
The following references on the PWB help in the effective debugging and troubleshooting of SDTV Out.
Sr. No Reference Description
1 R1419 DAC termination resistor. Resistor value 15 OHMS.
2 D1400 BCM2727B IC
3 N2001 Analog switch
4 L2001 Ferrite bead on the CVBS signal
5 X1201 AV/AHJ connector
The following test points on the PWB help in the effective debugging and troubleshooting.
Sr No Signal name Measuring point Description
1 CVBS J2006 SDTV signal
Page 3 – 24 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 73

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
SDTV out troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 25
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 74

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Figure 10 Expected SDTV CVBS PAL signal on Oscilloscope
Page 3 – 26 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 75

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Figure 11 Expected SDTV CVBS NTSC signal on Oscilloscope
Display module troubleshooting
General instructions for display troubleshooting
The first step is to verify with a working display that the fault is not on the display module itself. The display
module cannot be repaired.
The second step is to check that the engine is working normally. This can be done by connecting the phone
to a docking station and starting Phoenix service software. With the help of Phoenix read the phone
information to check that also the application engine is functioning normally (you should be able to read the
APE ID).
After these checks proceed to the display troubleshooting flowcharts. Use the Display Test tool in Phoenix to
find the detailed fault mode.
Pixel defects
Table 5 Display module troubleshooting cases
Display blank There is no image on the display. The display looks
the same when the phone is on as it does when the
phone is off.
Image on the display not correct Image on the display can be corrupted or a part of
the image can be missing. If a part of the image is
missing, change the display module. If the image is
otherwise corrupted, follow the appropriate
troubleshooting diagram.
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 27
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 76

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Visual defects (pixel) Pixel defects can be checked by controlling the
display with Phoenix. Use both colors, black and
white, on a full screen. R, G, B are also helpful.
The display may have some random pixel defects
that are acceptable for this type of display. The
criteria when pixel defects are regarded as a display
failure, resulting in a replacement of the display, are
presented in the following table.
Table 6 Pixel defects
Bright sub-pixels (sometimes called on-pixels or stuck-on) are
characterized by the appearance of bright/colored
pixels in, for example, black full screen picture.
Dark sub-pixels (sometimes called off-pixels, stuck-off, or black
pixels) are characterized by the appearance of dark
pixels in white, red, green, or blue full-screen
picture.
Combined sub-pixel defects are characterized by at least two sub-pixels
defects (bright or dim) being closer than 5 mm to
each other.
Temporal sub-pixels (sometimes called blinking defects) exhibit
temporal variations not related to any steady-state
video input. Temporal sub-pixel defects may be
intermittent, exhibit a sudden change of state, or
be flickering.
Table 7 Defects table
Item Bright dot (sub-
pixel) defect
Dark dot (sub-
pixel) defect
Total
1 Defect counts Not allowed
2 Combined sub-
Not allowed
pixel defect
3 Temporal sub-
Not allowed
pixel defect
Note: Blinking pixels are not allowed in normal operating temperatures and light conditions.
Introduction to display troubleshooting
The display module used is based on AM OLED technology and supports display format of 360 columns x 640
rows. The dimension of the display module is 52.7 mm x 97.16 mm x 2.21 mm. The module will interface to
the phone via FPC with a 20 pins board to board connector.
The following references on the PWB help in the effective debugging and troubleshooting of the display.
Page 3 – 28 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 77

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Sr No Reference Description
1 X1650 Display connector
2 Z1620, Z1621 Common Mode Choke on DSI bus
3 J1610/C1624
4 D1400 BCM2727B IC
The following test points on the PWB help in the effective debugging and troubleshooting.
Sr. No Signal name Measuring point Description
1 VIO L1620/C1621 1.8V supply to display
2 VBAT L1621/C1623 VBAT supply to display
3 TE0 C1625 Tearing effect signal from display module.
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 29
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 78

Display fault troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Page 3 – 30 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 79

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Touch panel troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 31
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 80

Keyboard troubleshooting
Keys troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Page 3 – 32 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 81

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Power key troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 33
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 82

Sensors troubleshooting
Accelerometer troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Page 3 – 34 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 83

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Proximity sensor troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
ALS technical description and troubleshooting
Proximity sensor and ambient light sensor (ALS)
This phone uses a combined proximity and ambient light sensor called DiPro. The proximity part of the device
uses an external IR LED supplied by VBAT. The current this LED consumes is controlled by DiPro and set using
software. The interrupt output of DiPro changes state when the infra red light from the LED is reflected back
by a suitable reflective surface. The ambient light sensor detects the level of ambient light and adjusts the
display brightness accordingly whenever the display is active. Covering this sensor results in dimmed display
lights.
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 35
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 84

BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Figure 12 DiPro proximity sensor and ambient light sensor
RM-659; RM-707
Page 3 – 36 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 85

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
ALS troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 37
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 86

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Audio troubleshooting
Audio troubleshooting test instructions
Single-ended external earpiece and differential internal earpiece outputs can be measured either with a
single-ended or a differential probe.
When measuring with a single-ended probe each output is measured against the ground.
Internal handsfree output is measured using a current probe, if a special low-pass filter designed for
measuring a digital amplifier is not available. Note also that when using a current probe, the input signal
frequency must be set to 2 kHz.
The input signal for each loop test can be either single-ended or differential. Exception to this is a digital
microphone which needs input signal from an external sound source (laptop speaker) to playback, eg. 1 kHz
sine wave from 5 cm distance.
Required equipment
The following equipment is needed for the tests:
•
Oscilloscope
•
Function generator (sine waveform)
•
Current probe (Internal handsfree DPMA output measurement)
•
Phoenix service software
•
Battery voltage 3.7V
•
Sound source (laptop speaker or B&K type 4231 calibrator)
Test procedure
Audio can be tested using the Phoenix audio routings option. Three different audio loop paths can be
activated:
•
External headset mic to earpiece
•
External headset mic to IHF mono
•
Internal digital microphone to headset
Each audio loop sets routing from the specified input to the specified output enabling a quick in-out test.
Loop path gains are fixed and they cannot be changed using Phoenix. Correct pins and signals for each test
are presented in the following table.
Phoenix audio loop tests and test results
The results presented in the table apply when no accessory is connected and battery voltage is set to 3.7V.
Earpiece, internal microphone and speaker are in place during measurement. Applying a headset accessory
during measurement causes a significant drop in measured quantities.
The gain values presented in the table apply for a differential output vs. single-ended/differential input.
Loop test Input
terminal
External
headset
mic to
earpiece
HS_MIC & GND EAR 1 & GND 0 300 1.35 300
Output
terminal
EAR 0 & GND
Path gain
[dB]
(fixed)
Input
voltage
[mVp-p]
Output DC
level [V]
Output
voltage
[mVp-p]
Page 3 – 38 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 87

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Loop test Input
terminal
External
headset
mic to IHF
mono
Internal
digital
microphon
e to
headset
HS_MIC & GND L4855 &
Acoustical
Input, 1kHz
sine wave
Output
terminal
L4856
L4857 &
L4858
HS_L & GND NA 94 dBSPL 70
HS_R & GND
Path gain
[dB]
(fixed)
10 200 630
Input
voltage
[mVp-p]
Output DC
level [V]
[mVp-p]
Output
voltage
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 39
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 88

External earpiece troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Page 3 – 40 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 89

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
External microphone troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 41
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 90

Internal earpiece troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Page 3 – 42 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 91

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Internal handsfree (IHF) troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 43
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 92

Internal microphone troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Page 3 – 44 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 93

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Vibra troubleshooting
Troubleshooting flow
Connectivity module troubleshooting
Introduction to connectivity module troubleshooting
The BOB1.0M-b module supports WLAN, BT, FMRX and FMTX. From a troubleshooting point of view, WLAN is
tested separately, but BT, FMRX and FMTX are checked in parallel.
REFOUT_EXT1 single ended 38.4 MHz analog clock from Linko RF is provided to BOB1.0M-b. The clock request
for the reference clock in the BOB1.0M-b module is shared between WLAN and BT blocks. When either system
requires a clock, this signal will be active. The CLK_REQ is connected to ExtSysClkReq pin of RAPU. The SLEEPCLK
input of 32.768 KHz clock from EM ASIC is used for power management and for FM in low power mode. The
internal SMPS supplies the whole BOB1.0M-b solution from the phone battery supply, VBAT, apart from VIO
which is needed for interface signal reference levels.
The following figure shows a top level block diagram of the BOB1.0M-b module.
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 45
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 94

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Figure 13 Hardware connections between BB and BOB1.0M-b
Bluetooth/WLAN/GPS antenna
The Bluetooth/WLAN/GPS antenna is product specific (antenna integrated into phone's top cap). On phones
with WLAN, the Bluetooth RF signal is routed from the connectivity module through the RF diplexer and a
shared Bluetooth/WLAN/GPS antenna is used. The FM receiver RF signal is routed through a product specific
FM antenna matching circuit to the phone headset connector. The FM radio audio signal is routed to the
headset connector through the BB ASIC shared by the phone audio functions.
The antenna positions are presented in the following figure.
Figure 14 Bluetooth/WLAN/GPS antenna
Page 3 – 46 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 95

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Bluetooth/FM radio and WLAN troubleshooting
Introduction to Bluetooth/FM radio troubleshooting
The Bluetooth and FM radio receiver functions are combined so these features are checked when
troubleshooting.
The following problems can occur with the Bluetooth and FM radio hardware:
Symptom Problem Repair solution
Unable to switch on Bluetooth on
phone user interface
Able to send data file to another
Bluetooth device, but unable to
hear audio through functional
Bluetooth headset
Able to switch on Bluetooth on
phone user interface, but unable
to detect other Bluetooth devices
Problems connecting to specific
manufacturer/model Bluetooth
accessory (specific Bluetooth
profile supported by phone and
accessory in product
specification)
Able to turn on FM radio and
Bluetooth on phone user
interface, but unable to detect
local FM radio stations with FM
headset inserted
Open circuit solder joints or
component failure of BOB
module or SMD components
Open circuit solder joints or
component failure of BOB
module (PCM interface)
Open circuit solder joints or
detached component in
Bluetooth antenna circuit
Possible interoperability issue
with accessory fixed in recent
Nokia phone software release
(check Nokia Service Bulletin for
the latest information)
Open circuit solder joints or
detached component in FM
antenna circuit
Replacement of BOB module
Replacement of BOB module
Repair of Bluetooth antenna
circuit
Update phone software to
the latest version if advised
in Nokia Service Bulletin
Note: The phone
Bluetooth Address and
software version are
displayed by pressing
*#2820# when Bluetooth
is on.
Repair of FM receiver antenna
circuit
Able to perform scans to detect
local FM radio stations with
functional FM headset inserted,
but unable to hear FM audio
through headset
Users may experience the following problems resulting in functional phones being returned to the repair
centre:
Symptom Problem Repair solution
Bluetooth feature does not
operate as desired with another
Bluetooth device
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 47
Open circuit solder joints or
detached component in FM
receiver audio path between
Bluetooth/FM ASIC and headset
Bluetooth Profile implemented
in Bluetooth accessory not
supported in Nokia phone
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Repair of FM audio circuit
Use Bluetooth accessory with
Bluetooth profiles supported
by phone
Page 96

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Symptom Problem Repair solution
Poor FM radio reception (unable
to detect many radio stations)
Nokia headset not being used Use Nokia headset
BT and FM radio test coverage
The tests listed in the table below should be performed to verify whether the Bluetooth and FM receiver are
functional. The use of self tests is described in section
Test Test Coverage Repair solution
Blueooth Self Test: ST_LPRF_IF_TEST Bluetooth-FM ASIC UART interface
(controls Bluetooth and FM
receiver and transmitter)
Bluetooth Self Test:
ST_BT_WAKEUP_TEST
Bluetooth Self Test:
ST_LPRF_AUDIO_LINES_TEST
Bluetooth Functional Test: BER test
with BT-Box or functional test with
other Bluetooth device
FM Radio Functional Test: Perform
scan for local radio stations and
check station list displayed on
phone
Bluetooth ASIC interrupt control
interface
Bluetooth ASIC PCM interface Replacement of BOB module
Bluetooth antenna circuit Repair of Bluetooth antenna
FM receiver antenna circuit Repair of FM antenna circuit
Bluetooth and FM radio self tests in Phoenix
Replacement of BOB module
(or repair of phone BB)
Replacement of BOB module
(or repair of phone BB)
(or repair of phone BB)
circuit (including RF filter or
WLAN switch if fitted)
(between BTHFMWLAN ASIC
and headset connector)
.
FM Radio Functional Test: Listen to
local radio station
The self tests run from Phoenix software are used for fault diagnosis.
If Phoenix software is not available, the functional tests with phone accessories are sufficient to verify the
functionality of Bluetooth and FM radio receiver.
If Bob1.0M-b module has been replaced, the WLAN tuning must be performed to ensure that the
output complies with ETSI/ FCC legal limits.
FM receiver audio circuit Repair of FM receiver audio
circuit (between BTHFMWLAN
ASIC and headset connector)
Introduction to WLAN troubleshooting
The following problems can occur with the WLAN hardware:
Symptom Problem Repair solution
Unable to switch on WLAN on
phone user interface
Able to turn on WLAN via phone
user interface, but unable to
detect any WLAN APs or other
WLAN devices
Open circuit solder joints or
component failure of BOB
module
Open circuit solder joints or
component failure of BOB
module or filter
Replacement of BOB module
or Host
Replacement of BOB module
or filter
Page 3 – 48 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 97

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Symptom Problem Repair solution
Able to turn on WLAN via phone
user interface and find APs and
other WLAN devices, but not able
to connect
Slow download speed when
using WLAN as connection
method
Users may experience the following problems resulting in functional phones being returned to the repair
centre:
Symptom Problem Repair solution
WLAN does not operate as desired
with another WLAN device
Problem with TX part of WLAN
circuit
System clock possibly degraded Change system clock source
Other WLAN device is not
conforming to ETSI/FCC
specifications
Replacement of BOB module
Use only certified WLAN
products
WLAN test coverage
The tests listed in the table below should be performed to verify whether WLAN is functional. WLAN should
be re-tested after repair.
Test Test Coverage Repair solution
WLAN Self Test: ST_WLAN_TEST WLAN SPI and control interface
(data interface and control of
WLAN)
Bluetooth Functional Test: BER test
with BT-Box or functional test with
another Bluetooth device
WLAN TX Tuning Checks WLAN TX path up to
The self tests run from Phoenix software are used for fault diagnosis.
If Phoenix software is not available, the functional tests with phone accessories are sufficient to verify the
functionality of WLAN.
Antenna connection from module,
including filter
module output and calibrates the
new module if fitted
Replacement of BOB module
Replacement of BOB module or
antenna components
Replacement of BOB module or
antenna components
Bluetooth and FM radio self tests in Phoenix
Prerequisites
A flash adapter (or phone data cable) connected to a PC with Phoenix service software is required.
Steps
1. Place the phone in the flash adapter or connect data cable to phone.
2. Start
3. Choose File → Scan Product.
Phoenix
service software.
4. From the Mode drop-down menu, set mode to Local.
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 49
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 98

5. Choose Testing → Self Tests.
RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
6. In the
•
•
•
7. To run the tests, click Start.
Self Tests
ST_LPRF_IF_TEST
ST_LPRF_AUDIO_LINES_TEST
ST_BT_WAKEUP_TEST
window check the following Bluetooth and FM radio related tests:
Figure 15 Bluetooth and FM radio self tests in
Phoenix
WLAN self test in Phoenix
Prerequisites
A flash adapter (or phone data cable) connected to a PC with Phoenix service software is required.
Steps
1. Place the phone in the flash adapter or connect data cable to phone.
2. Start
3. Choose File → Scan Product.
4. From the Mode drop-down menu, set mode to Local.
5. Choose Testing → Self Tests.
6. In the
7. To run the test, click Start.
Bluetooth functionality test
Bluetooth functionality can be checked by transferring a file to another Bluetooth phone.
Phoenix
Self Tests
•
ST_WLAN_TEST
service software.
window check the following WLAN test:
Page 3 – 50 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 99

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
FMRX radio receiver testing
Steps
1. Set signal generator parameters:
•
FM modulation on
•
Frequency 100MHz
•
FM deviation 22kHz
•
Modulation frequency 1kHz
•
RF level should be varied during the test to obtain good audio signal quality
•
Connect suitable antenna to signal generator
Note: You may alternately use a known good FM radio broadcast as a test signal.
2. Attach the Nokia headset to the phone’s AV connector.
3. Use Scroll button to autotune to the radio frequency.
4. Set volume to suitable level.
5. Check audio quality with a headset.
WLAN TX and RX testing in Phoenix
Context
The basic WLAN RX and TX functionality can be checked with Phoenix.
Steps
1. Place the phone in the flash adapter or connect data cable to phone.
2. Start
3. Choose File → Scan Product.
4. Choose Testing → WLAN RX Tests or WLAN TX Tests. See the following figures.
Phoenix
service software.
WLAN TX BiP testing procedure in Phoenix
Context
Note: This is an alternative procedure to tune the WLAN TX. The other, recommended procedure is
described in chapter WLAN TX BiP testing procedure in Testing and Tuning Tool (page 3–52 ) .
Issue 2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Page 3 – 51
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Page 100

RM-659; RM-707
BB Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Note: No external measurement equipment is required as the calibration is completely handled
internally. RF cable and adapter losses do not need to be taken into account while WLAN TX tuning
is proceeded.
WLAN TX has been BiP (Build in Prduction line testing) tuned correctly in production. There is no reason to
do re-calibration unless the Bob1.0M-b (N6300) is changed or memory (D3000) is corrupted.
WLAN TX can be tuned automatically with Testing and Tuning Tool. It performs calibrations and tunings of
WLAN TX. The results are displayed and logged in a result file, if initiated.
Steps
1. Place the phone in the flash adapter or connect data cable to phone.
2. Start
3. Choose File → Scan Product.
4. Choose Tuning → WLAN_TX_TUNING. See the following figure.
Phoenix
service software.
5. Select “Sub-Band 0” as indicated in the figure.
6. Click Start Power Calibration and read the result from the Result box.
7. If TXPowerCal response returns ‘Passed’ results, the WLAN TX BiP test is successful.
WLAN TX BiP testing procedure in Testing and Tuning Tool
Context
Note: No external measurement equipment is required as the calibration is completely handled
internally. RF cable and adapter losses do not need to be taken into account while WLAN TX tuning
is proceeded.
WLAN TX has been BiP (Build in Prduction line testing) tuned correctly in production. There is no reason to
do re-calibration unless the Bob1.0M-b (N6300) is changed or memory (D3000) is corrupted.
WLAN TX can be tuned automatically with Testing and Tuning Tool. It performs calibrations, tunings and
measurements of WLAN TX. The results are displayed and logged in a result file, if initiated.
Steps
1. Make sure the phone is connected to the PC.
Page 3 – 52 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 2
Copyright © 2011 Nokia. All rights reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...