Page 1

PAMS Technical Documentation
NHN–5NT Transceiver
Chapter 3
System Module JF5
Originat 05/98
Copyright 1998 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved.
Page 2
NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
Amendment
Number
Technical Documentation
AMENDMENT RECORD SHEET
Date Inserted By Comments
Page 3 – 2
Originat 05/98
Page 3

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
CONTENTS
Transceiver NHN–5N – 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Introduction – 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Functional Description – 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Block Diagram – 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Baseband – 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Introduction – 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Baseband Technical Summary – 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Modes of Operation – 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Maximum Ratings – 7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DC Characteristics – 7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Signals – 7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
UIF Connector – 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Connector – 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connections – 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CTRLU Control Block – 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Block Description – 14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Main Components – 16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PWRU – 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Introduction – 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Technical Specifications – 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Block Description – 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Block Diagram of MUUMI ASIC – 22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Main components – 22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
AUDIO – 24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Introduction – 24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Main features – 24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Technical specifications – 25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Block description, Audio Processor – 28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Main components – 30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Module JF5
RF Section – 31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Technical Summary – 31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
List of Submodules – 31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Specification and Functional Description – 31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Characteristics of the Module – 32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DC Characteristics – 32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connections – 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Antenna – 37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Functional description , RF section – 38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Block Diagram – 38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RF Key components – 39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver – 39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RX Synthesizer – 39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 3
Page 4

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
RF Characteristics – 41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver – 41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RX Synthesizer – 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RX loop filter – 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TX Synthesizer – 43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TX Loop Filter – 43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmitter – 43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Regulators – 43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
AFC function – 44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parts List of JF5 system module – 45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Technical Documentation
Page 3 – 4
Originat 05/98
Page 5
PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
Transceiver NHN–5N
Introduction
Functional Description
The NHN–5N transceiver electronics consists of the UI module PCB and
the RF/system PCB. The UI module is connected to the system module
with a connector. The system and RF submodules are interconnected
with PCB wiring. The phone can be connected to accessories with a bot-
tom system connector, which includes charging and accessory control.
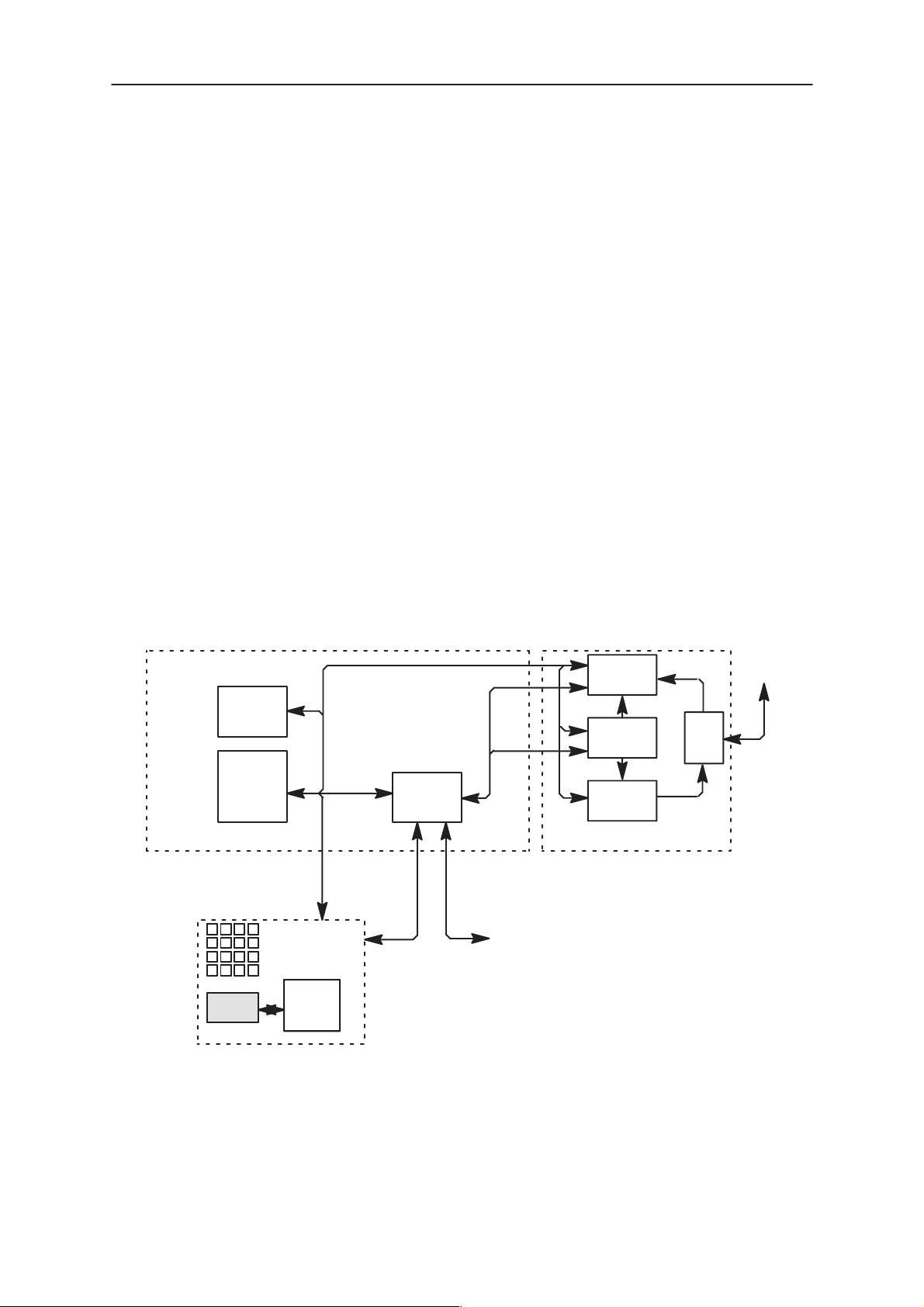
Block Diagram
The NHN–5N consist of 2 PCB’s: JF5 system module and GN4 user inter-
face module.
System Module JF5
The JF5 consists of 2 submodules, BASEBAND and RF. BASEBAND
consist of 3 functional blocks: PWRU, CTRLU and AUDIO; RF also con-
sists of 3 modules: RX, SYNT, TX; while the GN4 is the User Interface
module (UIF–module, kindly refer to section 4.).
RX
PWRU
CTRLU
BASEBAND–submodule
UIF–module
LCDLCD
LCD Driver
AUDIO
SYNT
TX
RF–submodule
BUZZER
MIC,EAR
DUP
ANT
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 5
Page 6

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
Baseband
Introduction
The baseband submodule controls the internal operation of the phone. It
controls the user interface, i.e. LCD driver, keyboard and audio interface
functions. The module performs all signalling towards the system and car-
ries out audio–frequency signal processing. In addition, it controls the op-
eration of the transceiver and stores tuning data for the phone.
Baseband Technical Summary
All functional blocks of the baseband are mounted on a single multi layer
printed circuit board. This PCB contains also the RF–parts. The chassis
of the radio unit contains separating walls for baseband and RF. All com-
ponents of the baseband are surface mounted and soldered by reflow.
The connections to accessories are fed through the CAP (Common Ac-
cessory Platform) bottom connector of the radio unit. The connections to
User Interface –module (UIF) are fed through a board to board connector.
There is no physical connector between RF and baseband.
Technical Documentation
Modes of Operation
The module has three operating modes: stand–by, listening and con-
versation mode.
Standby mode:
MCU clock is switched off, only NIPA timer is running to enable battery
save timings.
If a charger is connected, the MCU doesn‘t go to standby mode.
Listening mode:
In the listening mode some blocks of the audio IC (NIPA) are in standby
state.
Conversation mode:
In the conversation mode all ICs are active.
Page 3 – 6
Originat 05/98
Page 7
PAMS
bits/s
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
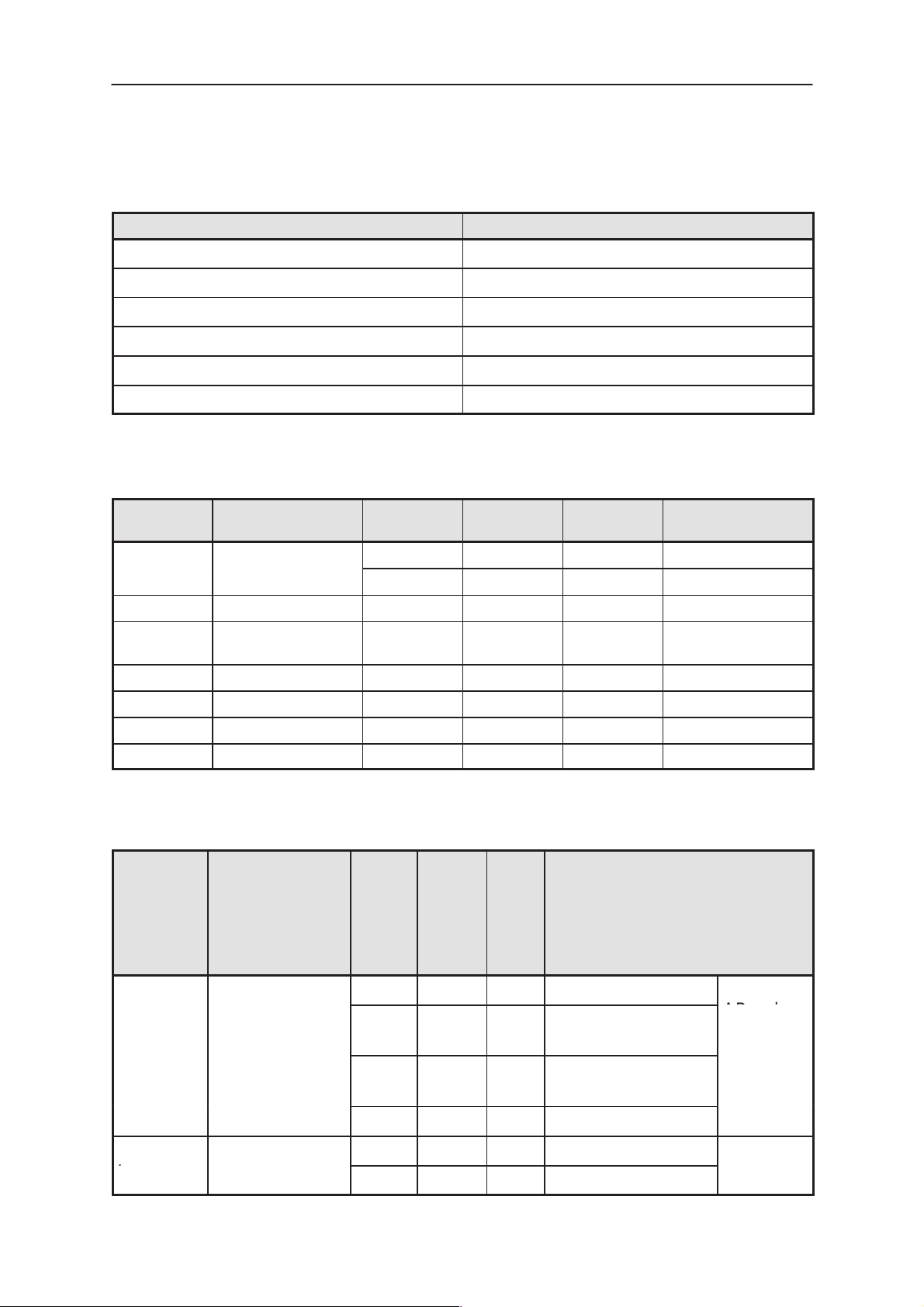
Maximum Ratings
Parameter Value
Operating temperature range –25 ... +55 deg. C
Storage temperature range –40 ... +85 °C
VBAT max. 8.8 V (TX off)
VBAT max. 7.5 V (TX on)
VC max. 16 V.
Battery charging is enabled +5 ... +45 °C
DC Characteristics
Pin / Conn. Line Symbol Minimum Typical /
Nominal
VCS
11.0V 12.0V 16.0V Slow charger
Maximum Unit / Notes
System Module JF5
VBA T 5.3V 6.0V 8.8V
VRF 5.3V 6.0V 8.8V VBAT for RF mod-
VA 3.2V 3.3V 3.42V Imax = 40mA
VL 3.2V 3.3V 3.42V Imax = 40mA
VL3 4.5V 4.75V 5.0V Imax = 180mA
VREF 3.2V 3.3V 3.42V Imax = 5mA
Signals
Pin /
Line Symbol Mini-
Conn.
6/system M2BUS
9.8V 10.3V 10.8V Fast charger
ule
mum
Typi-
cal /
Nomi-
Max-
i-
mum
Notes
nal
0V 0.7V Input low level
2.3V 5.25VInput high level
Isink<5m
ABaud
rate 9600
0V 0.2V 0.35VOutput low level
.
10/sys-
HOOK
tem
Originat 05/98
4.1V 4.5V 5.0V Output high level
0V 0.5V Input low level
2.4V 3.2V Input high level
Hook
Page 3 – 7
Page 8
NHN–5NT
detection
detection
resistor in
g
F
key ad
PAMS
System Module JF5
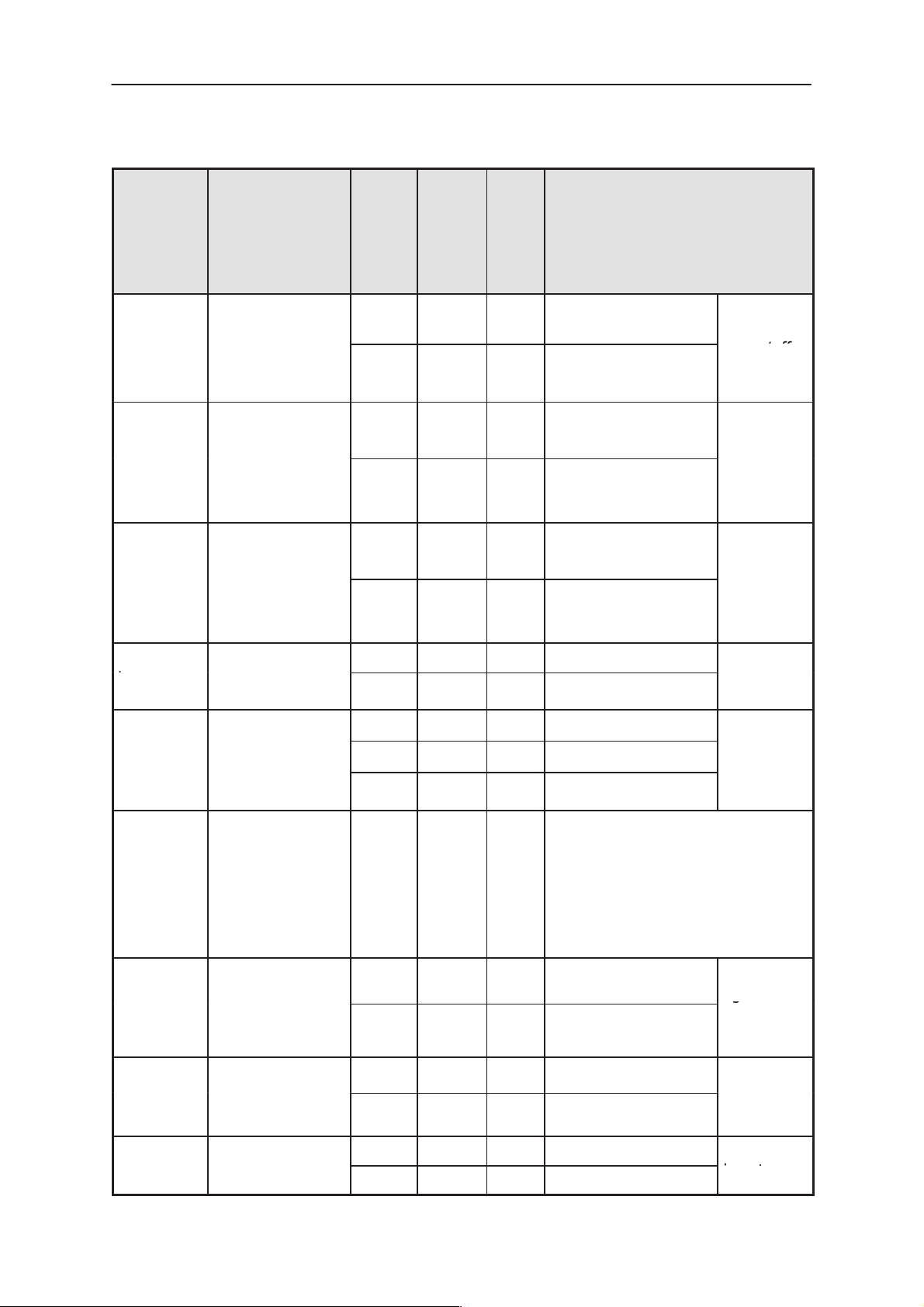
Line SymbolPin /
Conn.
2/system VOUT
5/system BOOST0
11/system
BOOST1
Technical Documentation
Minimum
0V 0.2V 0.4V Output low, power
4.1V 4.5V 5.0V Output high, power
Typi-
cal /
Nomi-
nal
0V booster detect /
3.3V booster detect /
0V booster detect /
i-
mum
off
on
power control ”0”
power control ”1”
power control ”0”
NotesMax-
HDA device power on/off
RF
booster
/ power
select
RF
booster
3.3V booster detect /
power control ”1”
12/system
2/battery BSI
3/battery BTEMP 1.0V 47k, B=4050 NTC between
3,4/UIF BACKLIGHT
VCS
9.8V 16V Isink < 730mA
1.95V 400mAh Li–ION
0.45V 550mAh NiMH
1.95V 1500mAh Li–ION
BTEMP and ground in battery
pack.
A 47k pull–up resistor in HP.
Vibrator control output (AC–
controlled)
0mA backlights off
40mA backlights on
/ power
select
A 47k
pull–up
HP.
Backlight–
ing for
keymat
17–24/UI
7–9/UIF ROW(0:2)
Page 3 – 8
LD(0:7)
0V 0.7V Output/Input low
2.3V 3.3V Output/Input high
0V 0.7V Input low
2.8V 3.3V Input high
LCD I/O,
p
output
Keypad
input
Originat 05/98
Page 9
PAMS
data/con
ON but
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
Line SymbolPin /
Conn.
25/UIF LCDREG
26/UIF LCDCS
27/UIF LCDRESET
11/UIF XNWR
Minimum
0V 0.7V Output low
2.8V 3.3V Output high
0V 0.7V Output low
2.8V 3.3V Output high
0V 0.7V Output low
2.8V 3.3V Output high
0V 0.7V Output low
2.8V 3.3V Output high
Typi-
cal /
Nomi-
nal
i-
mum
System Module JF5
NotesMax-
LCD
-
trol
LCD chip
select
LCD re-
set
LCD write
28/UIF XNRD
10/UIF LCDCLK
12/UIF XPWRON
0V 0.7V Output low
2.8V 3.3V Output high
0V 0.7V Output low
2.8V 3.3V Output high
0V 0.7V Input low
2.8V 3.3V Input high
LCD read
LCD
clock
Power
ton
UIF Connector
Signal Name Pin Notes
VL 1 Logic supply voltage 3.3V
CALLLED 2 Call LED
BACKLIGHT 3,4 Backlights on/off
VNEG 6 Negative voltage for LCD module
ROW0,1,2 7–9 Lines for keyboard read
-
LCDCLK 10 LCD Driver clock
XNWR 11 LCD Driver write selection input
XPWRON 12 Power on control from keyboard
GND 13,14,15,16 Ground
LD(0:7) 17–24 Parallel data for LCD driver
LCDREG 25 LCD Driver control/data select
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 9
Page 10
NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
LCDCS 26 LCD Driver chip select
LCDRESET 27 LCD Driver reset
XNRD 28 LCD Driver read selection input
Technical Documentation
NotesPinSignal Name
System Connector
Signal Name Pin Notes
GND 1, 8 Power supply ground.
XMIC 3 External audio input from accessories
or handsfree microphone. There is a
pull–down resistor in accessory for
identification
M2BUS 6 Serial bidirectional data and control be-
tween the handphone and accessories.
A 10k pull–up resistor in HP.
BOOST0,1 5,11 RF booster detection lines / RF power-
level control.
HOOK 10 HOOK–indication. The phone has a
47k pull–up resistor.
VOUT 2 Hand–free device power on/off.
XEAR 9 External audio output to accessories or
handsfree speaker. There is a DC volt-
age control for HF unit mute control.
BGND BGND Battery connector
BTEMP BTEMP Battery connector, Battery temperature
BSI BSI Battery connector
VBAT B+ Battery connector
VCS 12,CH+,
DC+
Battery charging voltage
Page 3 – 10
Originat 05/98
Page 11
PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
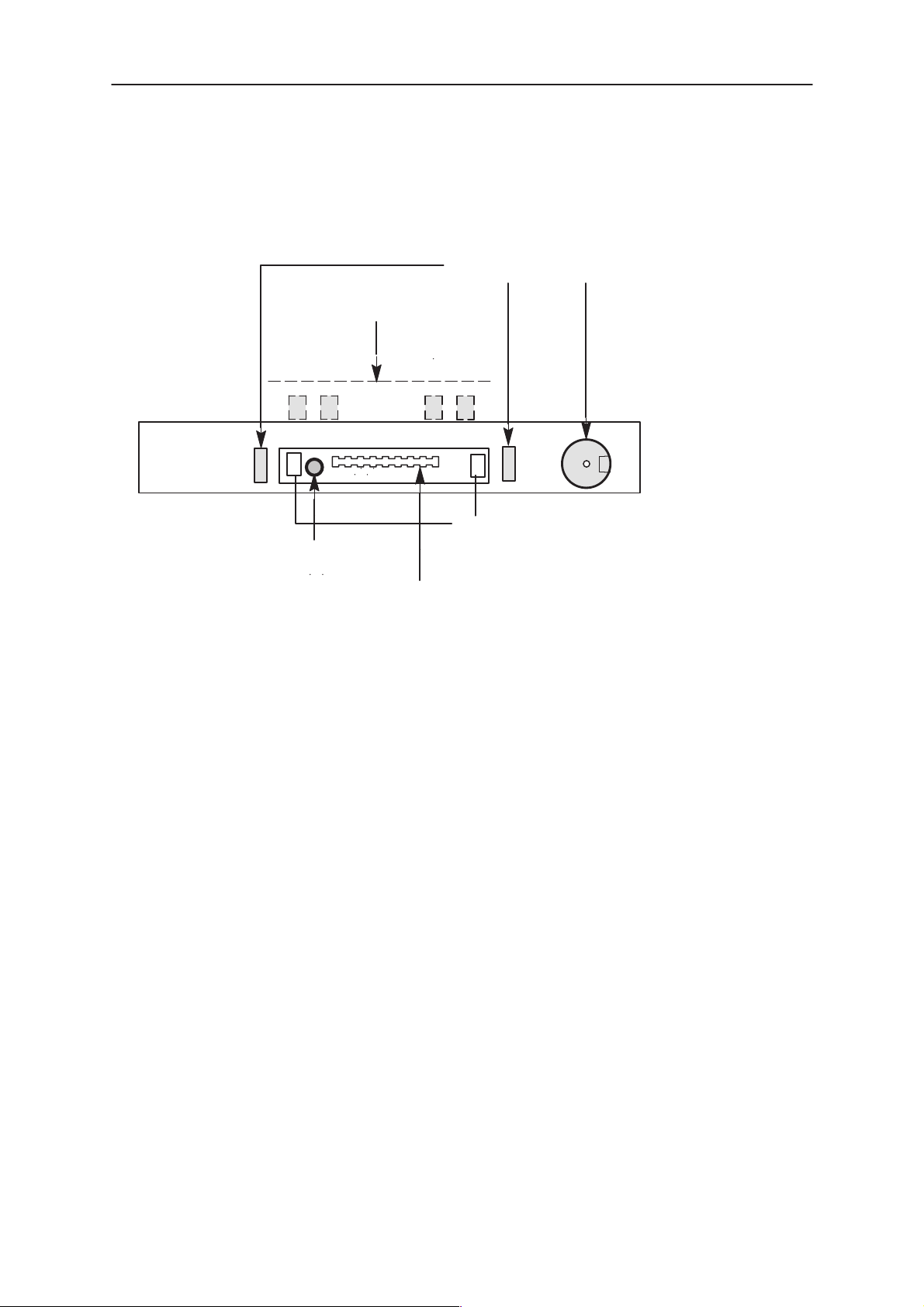
Connections
Battery Connector
4
+
34
Charging Connectors
3
12 7
1 6
12
Locking
System Module JF5
1
–
2
RF–connector
(not used)
System Connector
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 11
Page 12
NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
Technical Documentation
CTRLU Control Block
The Control block controls all phones functions and it includes modem
and SIS–processor too.
CTRLU internal signals, input
Signal Name Notes From
VL Logic supply voltage, 3.3V. PWRU
VL3 Logic supply voltage, 4.75V. PWRU
VREF Reference voltage 3.3V 3%. Max. PWRU
XRES Reset line from MUUMI PWRU
PWRON Power on signal from MUUMI PWRU
VCHARG Charger voltage to A/D converter PWRU
VBATSW Battery voltage to A/D converter. VCHARG
CLKMCU Clock signal from NIP A. AUDIO
NMI No maskable Interrupt reques from NIPA AUDIO
XINT Interrupt reques from NIPA. AUDIO
HOOK HOOK–indication SYSTEM
BTEMP Battery temperature SYSTEM
BSI Battery size indication SYSTEM
M2BUS Serial interface SYSTEM
RFTEMP RF temperature SYNT
RSSI Received signal strenght indication RX
TXI Transmitter output power level indication TX
XPWRON Power buttom from UIF. UIF
ROW0 Line for keyboard read. UIF
ROW1 Line for keyboard read. UIF
ROW2 Line for keyboard read. UIF
ACCDET Accessory detection line SYSTEM
Page 3 – 12
Originat 05/98
Page 13
PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
System Module JF5
CTRLU internal signals, output
Signal Name Notes To
CSW Charger control PWRU
VOUT Headset–adapter powersupply SYSTEM
M2BUS Common serial clock (NIPA,sis) SYSTEM
AGC Gain control RX
RXE RX Circuit power on/off RX
SCLK Synchronous data clock for synthesizers SYNT
SDAT Synchronous data for synthesizers /
TX duplex filter current control 2 (option)
SLE Synthesizer data latch enable SYNT
TXE Transmitter control (on/off) TX
TXC Transmitter Power Control TX
XNCS NIPA chip select signal AUDIO
XNWR NIPA/LCD write control signal AUDIO.UIF
SYNT, TX
XNRD NIPA/LCD read control signal AUDIO,UIF
NA0–3 NIPA/LCD address bus AUDIO,UIF
ND0–7 NIPA/LCD data bus AUDIO,UIF
EARENA Ear amplifier enable AUDIO
KBINT Keyboard interrupt AUDIO
MBUSINT MBUS interrupt AUDIO
MBUSOUT MBUS out PWRU
LIGHTS Backlights on/off UIF
LCDCS LCD Driver chip select UIF
LCDRESET LCD Driver reset UIF
XEARON External ear amplifier enable SYSTEM
XEARDC PHF5 DC mute control SYSTEM
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 13
Page 14

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
Block Description
– CTRLU – PWRU
MCU controls the watchdog timer in the MUUMI ASIC. It sends a positive
pulse approximately once every 1 s to the XPWROFF pin of the MUUMI
to keep the power on. If the CTRLU fails to deliver this pulse, the MUUMI
will remove power from the system. The CTRLU controls also the charger on/off switching in the PWRU block. When power off is requested,
the CTRLU leaves the MUUMI watchdog without reset. After the watchdog has elapsed the MUUMI cuts off the supply voltages from the phone.
Battery charging is controlled by CSW line.
VBATSW , Battery voltage measurement
Battery voltage can be measured from 5.4 V to 10.3 V nominal with 3.3 V
reference voltage. The absolute accuracy is low because of the reference 3 % accuracy and A/D–converter +/– 8 LSB accuracy . This battery
voltage measurement offset error must be calibrated with input voltage
6.0 V and 8.2 V. The A/D conversion result can be calculated from the
following equation:
Technical Documentation
A/D readout = 1024 * (VBATSW* ( 47/147)) / VREF
VREF=3.3 V
For example:
8.2 V results 814 = 32EH
6.0 V results 595 = 253H
VCHARG , Charger voltage measurement
Charger voltage can be measured up to 18.3 V nominal. The A/D–conversion result can be calculated from equation :
A/D readout = 1024 * (VCSW*(22/122)) / VREF VREF=3.3 V
For example:
12.0 V gives 671 = 29FH
6.0 V gives 336 = 150H
BSI , Battery size indication
Battery type can be defined with the BSI resistor value. A NiMH battery
has a different BSI resistor compared with a Li–ION battery. Different
sizes of the Li–ION batteries cannot be identified.
BTEMP , Battery temperature measurement
Battery temperature measurement is implemented with a 47 kohm NTC
with N value of 4050 and 47 kohm pullup resistor. The A/D conversion
readout can be calculated from equation:
Page 3 – 14
A/D readout= 1024* ( R
For example:
45 C gives ?
25 C gives ?
5 C gives ?
0 C gives ?
NTC
/( R
NTC
+47k))
Originat 05/98
Page 15

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
Battery voltage is measured over the VBATSW and charging voltage over
the VCHARG. Battery temperature is measured over the BTEMP line.
Battery size is determined by reading the BSI line. This is pulled to +3,3V
by a 47kohm resistor. In the battery pack a ”size” resistor is connected
between BSI and GND. Battery charging is controlled by the CSW line.
Muumi watchdog is refreshed by controlling XPWROFF line.
– CTRLU – AUDIO
Interface between the MCU and the NIPA circuit is a bidirectional 8–bit
data bus with 4 address lines. Address, data and control lines are used in
the MCU as I/O–port pins. The data lines direction is controlled with the
MCU data direction register. The interface includes address outputs
NA0–3, data inputs (read) / outputs (write) ND0–7, chip select control output XCS , read control output XRD, write control output XWR and interrupt input XINT. When the MCU is in sleep state, the control signals XRD
and XCS must be in ’0’ state and the address output NA0–3 and NWR in
’1’ state and data lines ND0–7 must be in ‘0‘ state.
– CTRLU – UIF
System Module JF5
The keyboard is connected directly to the controller. ND0–6 are the output lines and ROW0–2 are the input lines. Keyboard scanning is done by
driving one ND line to 0 V at the time. If any key is pressed, then the corresponding ROW line goes to 0V and the phone knows which key is
pressed.
Data to the LCD Driver is written and read by ND(0:7) lines. XNRD/
XNWT are the read / write selection lines and NA0 is the instruction / data
register selection line. LCDCS line enables the LCD driver.
ND(0:7) lines are in 0 V state when phone is in sleep mode so that any
key pressing can be indicated.
Keyboard and LCD lights are controlled by LIGHTS signal.
– CTRLU – RX
RX circuit power is switched on/off by RXE signal.
The received signal strength is measured over the RSSI and the inter-
mediate frequency is measured over the IF.
– CTRLU – SYNT
RF temperature is measured over the RFTEMP. Frequency is controlled
by the AFC signal. The synthesizer is controlled via the synchronous serial bus SDAT/SCLK. The data is latched to the synthesizer by the positive edge of SLE line. The TX synthesizer power on/off (TXS/port P3) line
is controlled via PLL circuit.
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 15
Page 16
NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
– CTRLU – TX
The transmitter output power level is measured over the TXI. TXE line
activates the power module. The power is controlled via TXC line which
is a PWM–controlled output port.
Technical Documentation
Main Components
– MCU
The phone MCU H8/3092 is a CMOS MCU. All the memory needed (128
kB ROM, 4 kB RAM) except the EEPROM, is located in the controller.
MCU operating clock (7.3728 MHz) is generated on the NIPA.
MCU Pins are listed in the table:
Pin No Port Signal Description
1 PB0 SISCLK Clock for SIS prosessor
2 PB1 SISDATA Serialdata to SIS prosessor
3 PB2 EDATA Serial data to EEPROM
4 PB3 RXD Serial interface (M2BUS)
5 PB4 SCLK Serial clock for synthesiz
6 PB5 HOOK Handset hook signal
7 PB6 PWRON Power button
8 PB7 SLE RX/TX synthesizer latch
9 P90 TXD Serial interface (M2BUS)
10 P92 RXD M2BUS net free timer input
11 P94 ECLK Clock to EEPROM
12 Vss GND MCU Ground
13–20 P30–P37 ND0–7 Paraller data bus for NIPA,LCD & keys
21 Vcc VL Power supply for processor
22 P10 NA0 Address line for NIPA and LCD regis-
ter
23 P11 NA1 Address line for NIPA
24 P12 NA2 Address line for NIPA
25 P13 NA3 Address line for NIPA
26 P14 XNCS NIPA chip select
27 P15 XNWR Read/write control to NIPA
28 P16 XNRD Read/write control to NIPA
29 P17 LCDCD LCD chip select
30 GND MCU Ground
Page 3 – 16
Originat 05/98
Page 17
PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
31
32–35 P21–P24 ROW0–3 Keypad inputs
36 P25 protoseries indicator, pull–down if pro-
37 P26
38 P27 CALLCNT Call continue during battery change
39 P50 XPWROFF Muumi watchdog refresh
40 P51 EARENA EAR amplifier enable
41 P52
42 P53 LCDRESET Reset to LCD
43 P60
44 MD0
45 MD1
46
P20 LIGHTS Backlight control
to
System Module JF5
47 STBY
48 RES XRES Reset from MUUMI
49 NMI NMI Interrupt request from NIPA
50 Vss GND Ground
51 EXTAL EXTAL External system clock from NIPA
52 XTAL
53 Vcc VL
54 P63 TXE Transmitter on/off
55 P64 AGC Gain control
56 P65 RXE RX circuit power on/off
57 RESO
58 AVcc
59 P70 VBATSW Battery voltage
60 P71 VCHARG Charger voltage
61 P72 RSSI Received signal strength
62 P73 TXI Transmitter power monitor
63 P74 BTEMP Battery temperature
64 P75 BSI Battery size indication
65 P76 RFTEMP RF temperature
66 P77 ACCDET Accessory detection
67 Vref Vref Reference voltage for processor
68 AVcc Vref Reference voltage for processor
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 17
Page 18

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
69
P80 XINT Interrupt request from NIPA
Technical Documentation
70 P81
71 P82
72 P83
73 PA0 BOOST1 RF booster control
74 PA1 BOOST0 RF booster control
75 PA2 XEARDC DC to XEAR line control
76 PA3 XEARON XEAR amplifier ON
77 PA4 CSW Charging control
78 PA5 SDAT Serial data for synthesiz
79 PA6 TXC TX syntetisizer enable. Active high.
80 PA7 VOUT Power supply to HDA
– SIS
Motorola SIS 68HC11A8 (subscriber identification) circuit connected to
the controller over serial bus IIC.
SIS processor signals:
Pin Description
EXTAL Clock input from NIPA
RESET Reset input
PD0 IIC bus data
PD1 IIC bus clock
– EEPROM
There is two 8k EEPROM in phone. EEPROM is a nonvolatile memory
into which is stored the tuning data for the phone. In addition, it contains
the short code memory locations to retain user selectable phone numbers.
EEPROM signals:
Pin Description
SDA IIC bus data
SCL IIC bus clock
Page 3 – 18
Originat 05/98
Page 19

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
System Module JF5
PWRU
Introduction
The power block generates the supply voltages for the baseband and includes also the charging electronics.
Technical Specifications
TPWRU internal signals, inputs
Signal Name Notes From
CSW Charger control CTRLU
MBUSOUT Serial interface CTRLU
XPWRON Power on control from keyboard UIF
XPWROFF Power off control from controller (watch dog) CTRLU
VBAT Battery voltage input SYSTEM
VCS Charging supply voltage from charger SYSTEM
TPWRU internal signals, outputs
Signal Name Signal description To
XRES Master reset CTRLU
PWRON Power on signal for microprosessor. CTRLU
VL Logic supply voltage, 3.3V CTRLU,AU-
DIO,UIF
VL3 Logic supply voltage, 4.75V CTRLU,
AUDIO
VA Analog supply voltage. Max 40 mA. SYNT,
AUDIO
VREF Reference voltage 3.3V 3%. Max. 5mA. CTRLU, RF,
TX
VBATSW Battery voltage to A/D converter. CTRLU
VCHARG Charger voltage to A/D converter. CTRLU
VRF Battery voltage to RX–unit RX
VBAT Battery voltage to TX–unit TX
M2BUS Serial interface SYSTEM
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 19
Page 20

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
Block Description
The baseband power supplying circuit includes:
– the supply voltages:
– Regulator has been used before MUUMI – switched output of battery
(VBATSW) and charger voltage (VCHARG) measurements to the MCU
A/D–converter
– battery voltage detection and reset logic
– charger switch control output used to limit battery voltage VBAT < 8.8V
– power on/off switch input (XPWRON), buffered output to MCU
(PWRON)
– watchdog timer using oscillator in COFF pin , cleared by falling edge
input in PWROFFX, elapsing time for watchdog timer is 3 ... 4 seconds
– M2BUS open drain output driver is not used.
Technical Documentation
VL 40mA for digital circuits
VL3 20mA for RF
VA 20mA for analog circuits
VREF 5mA reference voltage for A/D–converters and
regulators
The charge switch driving circuit is implemented with discrete components. This circuit includes transient voltage protection, soft charge
switching, low voltage battery charging and battery disconnecting with
charger connected protection. This circuit also limits battery voltage when
charger is connected to protect MUUMI and TX transistors.
Power circuitry have three different operating modes: POWER OFF , RESET and POWER ON. In POWER OFF state MUUMI regulator outputs
are disabled and reset control output signal (PURX) is active low.
MUUMI internal oscillator at pin COFF is working in all operating modes.
MUUMI goes through short RESET state (100ms ) to POWER ON–state
, if PWR–button is pressed or charger voltage input is connected to
charging input VCS (charging voltage detection in MUUMI input VCHAR
is level active). In RESET–state regulator outputs VL,VA and VREF are
active and PURX–signal is active low. If battery voltage on MUMMIs pin
is lower than 4.1 V (3.9V...4.3V) the circuit cannot go to POWER ON
state. MUUMI goes also to RESET state, when battery voltage on MUUMIs pin is falling below 3.9 V (3.7V...4.1V). This situation is possible, when
battery is fully discharged or battery is disconnected.
In POWER ON mode all regulator outputs are active and MUUMI reset
signal output PURX is inactive high. MCU XPWROFF–output signal
clears at falling edge the watchdog inside MUUMI. If the watchdog is not
cleared , MUUMI goes to POWER OFF state. When the charger is connected and battery voltage on MUUMIs pin is higher than 4.1V , module
stays in POWER ON mode.
The MCU controls battery charging with CSW output (which is PWM–controlled output port) and MUUMI limits the maximum battery voltage to 8.8
V with CHRGSW–output.
Page 3 – 20
Originat 05/98
Page 21

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
No current flows from charger (VCHARG) to battery , if MCU output CSW
is active low and XRES signal is inactive high. The battery is charged
also, when charger is connected and XRES signal is active low. The
charging circuit charges the battery during RESET to higher than 5.3 V.
The charging electronics is controlled by the CTRLU. When the charging
voltage is applied to the phone while the phone is powered up, the
CTRLU detects it and starts controlling the charging.
If the phone is in power–off, the MUUMI will detect the charging voltage .
If the battery voltage is high enough the reset will be released and the
CTRLU will start controlling the charging. If the battery voltage is too low
the phone is in reset and charging control circuitry will pass the charging
current to the battery. When the battery voltage on MUUMIs pin has
reached 4.1V (3.9...4.3V) the reset will be removed and the CTRLU
starts controlling the charging. This all is invisible to the user.
V116 is the charging switch; it is governed by the controller (CSW line) via
voltage regulator V114 and V115. In fast charge mode CSW is ”1” and in
maintain charge mode there is controller controlled pulses. In charge off
state CSW is ”0”. In maintain charge mode pulse ratio depends of charger
and temperature.
System Module JF5
There are three different ways to switch the power on:
– Power key pressing grounds the XPWRON line. The MUUMI defects
that and switches the power on.
– Charger detection on MUUMI detects that charger is connected and
switches power on.
– MUUMI will switch power on when the battery is connected. If the bat-
tery is changed during the call, the power is kept on. If not the power
is switched off.
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 21
Page 22

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
Block Diagram of MUUMI ASIC
VBAT1
1
VBAT2
22
VBAT3
5
M2BUSIN
11
760k
PWM
15
760k
CHARGER
CTRL
LOGIC
BANDGAP
REF
Technical Documentation
70k
40k
VBATSW
M2BUSOUT
VREF
17
12
VL
23
VA
2
4
VCHAR
21
PWRONX
13
PWROFFX
14
TEST
3
Main components
– MUUMI asic
VBAT
32k
760k
760k
LOW VBAT
& CHARGER
DETECT
PWR ON/OFF
&
RESET LOGIC
Creset
20
16
Coff
VL_ENA
VA_ENA
VREF_ENA
VSW_ENA
VCHAR
GND1
24
GND2
19
GND3
7
CHRGSW
PWRONXBUFF
VCHARSW
Cref
6
PURX
8
10
9
18
– Transistor V116 and diode V118
– Regulators N130 and N140
Page 3 – 22
Creates the voltages, comprises power switch, charger, battery
detection and watchdog.
The charging current is passed through these components.
Originat 05/98
Page 23

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
N130 decreases battery voltage to 4.75 volts which is suitable
for MUUMI asic.
N140 creates the supply voltage VL3 (4.75 volts) to display
and logic circuits.
System Module JF5
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 23
Page 24

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
AUDIO
Introduction
The block includes a NIPA audio/signalling prosessor in a 64 TQFP package.
Main features
– Single chip FFSK modem and audio circuit
– Full duplex 1200 baud signalling
– DMS facility
– Low power consumption modes
– Programmable output clocks with clock stop for MCU and LCD
– 8 bit parallel interface with pull ups
– FSK indicator and level detector
– Speech volume indicator
– Programmable timer
– IF counter
– 8 bit DAC
– FII filter and gain control
– Low noise microphone amplifier
– Input for a handset microphone or an accessory
– Microphone sensitivity compensation +4.8/–4.2 dB range (4 bits)
– Compandor
– RX and TX filters
– Tx hard limiter
– Tx AGC
– Internal reference compensation +1.00/–0.75 dB range(3 bits)
– Summing stage for voice/data, signalling and fii
– Transmitter compensation amplifier with +3.75/–3.75 dB range (4 bits)
– Receiver compensation amplifier with +3.75/–3.75 dB range (4 bits)
– Volume control amplifier with –20/+17.5 range (4 bits)
– Earphone amplifier with drive capability for ceramic earpiece
– Buffered output for a handset or an accessory
– Mute switches
– Dual and single tone multifrequency generator
– Driver for buzzer amplifier
– Hands free functions
Technical Documentation
Page 3 – 24
Originat 05/98
Page 25

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
System Module JF5
Technical specifications
AUDIO internal signals, inputs
Signal Name Notes From
VL Logic supply voltage, 3.3V PWRU
VA Analog supply voltage, 3.3V PWRU
VL3 Logic supply voltage, 4.75V PWRU
XRES Reset line from MUUMI PWRU
XNRD Read control signal CTRLU
XNCS Chip select signal CTRLU
XNWR Write control signal CTRLU
NA0...A3 4–bit address bus CTRLU
ND0...D7 8–bit bidirectional data bus CTRLU
EARENA Earphone amplifier enable CTRLU
XEARON external earphone amplifier enable CTRLU
XEARDC External earphone DC enable CTRLU
KBINT Keyboard interrupt CTRLU
MBUSINT MBUS interrupt CTRLU
DAF Detected audio signal from receiver RX
IF (2nd) Intermediate frequency for AFC function RX
XMIC External audio input from accessories SYSTEM
MICP Microphone (positive node) SYSTEM
MICN Microphone (negative node) SYSTEM
AUDIO internal signals, outputs
Signal Name Notes To
XEAR External audio output to accessories SYSTEM
ACCDET Accessory detection signal SYSTEM
MOD Audio output to synthesizer SYNT
AFC VCTCXO control SYNT
BUZZER Buzzer signal SYSTEM
EARP Earpiece (positive node) UIF
EARN Earpiece (negative node) UIF
CLKMCU Clock signal for MCU CTRLU
XINT Interrupt reques to MCU CTRLU
NMI No maskable Interrupt reques to MCU CTRLU
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 25
Page 26

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
Technical Documentation
Pin list of NIPA audio/signalling processor
Pin no Symbol Pin type Notes
1 VDD1 + 3.3 V Supply voltage, digital
2 XRD DIN/pd Read control signal, active state LOW, pull–down > 50
k
3 XCS DIN/pd Chip select signal, active state LOW, pull–down > 50
k
4 A3 DIN/pu 4–bit address bus, MSB, pull–up > 50 k
5 A2 DIN/pu 4–bit address bus, pull–up > 50 k
6 A1 DIN/pu 4–bit address bus, pull–up > 50 k
7 A0 DIN/pu 4–bit address bus, LSB, pull–up > 50 k
8 D7 DIO 8–bit bidirectional data bus MSB
9 D6 DIO 8–bit bidirectional data bus
10 D5 DIO 8–bit bidirectional data bus
11 D4 DIO 8–bit bidirectional data bus
12 D3 DIO 8–bit bidirectional data bus
13 D2 DIO 8–bit bidirectional data bus
14 D1 DIO 8–bit bidirectional data bus
15 D0 DIO 8–bit bidirectional data bus LSB
16 VDD2 + 3.3 V Supply voltage, digital
17 NMI DOUT Non maskable Interrupt request
18 XCLR DIN HW reset input, active state LOW
19 TMODE DIN/pd Test mode selection, pull–down > 50 k
20 TSEL DIN/pd Test select, pull–down > 50 k
21 XINT DOUT Interrupt request to MCU, active state LOW
22 MBUSINT DIN MBUS interrupt request, falling edge active
23 KBINT DIN Keyboard interrupt request, falling edge active
24 IF AIN IF input
25 VSS2 0 V Supply voltage, digital ground
26 VSA2 0 V Supply voltage, analog ground
27 DAF AIN Signal input
28 FILO AOUT Rxfilter output
29 EXPI AIN Expander input
30 EAMPBO AOUT Expander Amplifier B output
31 EWCI AIN Expander Window Comparator input
32 EXPO AOUT Expander output
33 VDA2 + 3.3 V Supply voltage, analog
34 VOLI AIN Volume control ampl. input (Volume)
Page 3 – 26
Originat 05/98
Page 27

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
NotesPin typeSymbolPin no
35 EXTEAR AOUT Buffered output for handset or an accessory
36 EVGND AIN Earphone driver virtual ground
37 EARM AOUT Earphone driver output
38 EARP AOUT Earphone driver output
39 CWCI AIN Compressor window comparator input
40 DACO AOUT DA converter output
41 SIDEAR AOUT Sidetone output
42 REF AIN Internal analog signal ground 1.65 V
43 MIC AIN Microphone amplifier input
44 BIMIC AOUT Microphone bias current output
45 CMIC AIN Microphone current stabilization capacitor
46 EXTMIC AIN Audio input for a handset or an accessory
47 TXBPO AOUT Transmit bandpass filter output
System Module JF5
48 VDA1 + 3.3 V Supply voltage, analog
49 COMI AIN Compressor input
50 COMO AOUT Compressor output
51 EMPI AIN Pre emphasis input
52 FIIOUT AOUT Received FII signal
53 TOUT DOUT Test output, digital
54 ATST AOUT Audio Filter Test output
55 MOD AOUT Transmit path output
56 VSA1 0 V Supply voltage, analog ground
57 VSS1 0 V Supply voltage, digital ground
58 BUZZ DOUT Buzzer output
59 ATOUT AOUT Test pin
60 CLKOUT COUT (7.3728 MHz) 3.6864 MHz crystal oscillator output
61 CLKIN CIN (7.3728 MHz) 3.6864 MHz crystal oscillator input or
input for the external clock
62 CLKLCD DOUT Clock signal for LCD, 230.4 kHz or 57.6 kHz
63 CLKMCU DOUT Clock signal for MCU, 3.6864 MHz or 7.3728 MHz
64 XWR DIN/pu Write control signal, active state LOW, pull–up > 50
k
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 27
Page 28

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
Block description, Audio Processor
WPOSFIL
WTRFIL
SUM
TRREG
STATUS
BITS
RECREG
DPLL
MOD
BUZZ
BUZZ
ddtmf
SMUX
DFLAG
loop (to MODRXFIL)
MODTRPOST
DRIV
CONTROL BITS
DETED
TXAAF
PREEMP
EMPI
CWCI
COMI COMO
TXBPO
ATST
LIM
AGC
SUM
TXTRI
SINGEN
MODTRFIL
TXLP TXTRI+TXPOSTFIL
AGC
PREEM LIM
COMPR
ATOUT
VOL
RXAAF
MODRXFIL
DATACOMP
aloop (to RXMUX)
SINGEN MODTRFIL
TRSTBY
TFLAG
txbpo
(to SIDEAR)
FSKMOD
TR
RFLAG
RECCTRL
INTERNAL
CLOCKS
CTRL
AFC
XBSSBY
XTALKSBY
XBUZZSBY
XIFSBY
CREG
TIMER
DETFIL
DACO
D/A
8 bit
XDACSBY
XDTMFSBY
INTERFACE
Technical Documentation
FIIOUT
FIIBUF
A0 A1 A2 A3 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7
NMI
XINT
XWR
XRD
XCS
EARP
EAR
HF
FIIPOST
EARM
CONTR
EVGND
DEEMP+RXFIL
SIDEAR
EXTEAR
RXATT ACC
EXP VOL
SIDEAR
txbpo
(from TXBP)
64 pins
VOLI
EXPO
EWCI
EAMPBO
EXPI
FILO
Page 3 – 28
TXMUX+TXAAF TXATT MICTRI TXBP
MICAM
MIC
CMIC
BIMIC
ddtmf (to BUZZDRIV)
DTMFCOMP
dtmf
DTMF GEN
EXTMIC
CLKLCD CLKMCU
XCLR
TMODE
(to RXMUX)
REF GEN
CLKIN
CLOCKDIV
TSEL
OSC
IFAMP
CLKOUT
IFCNTR
FSKDIS
IF
FSKIND
MBUSINT
DATACOMP
MODRXFIL
GND GEN
REF
KBINT
LEVEL
FSKLEV
VDD2
VDD1
Figure 1. NIPA block diagram
FIIFIL(4kHz)+FIITRI
dtmf
loop (from WPOSFIL)
VSS2
VSA1
VDA1
VDA2
RXMUX+AAFIL
VSA2
VSS1
aloop (from TXPOSTFIL)
RXTRI RXAAF
DAF
Originat 05/98
Page 29

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
Transmitting data path
The data to be transmitted will be loaded into the transmitting register
TRREG. From the TRREG register the 8 bit data is transformed to serial
data which is sent to the FSK modulator (FSKMOD) and sine wave generator (SINGEN) and then to the summing block (SUM).
Receiving data path
The data from anti alias filter is connected through the modems RX filter
(MODRXFIL) to the data comparator (DA TACOMP) and then to FSK discriminator. Further from FSK discriminator data is connected to detecting filter
(DETFIL) and from there to digital phase locked loop (DPLL).
IF
Intermediate frequency counter (IFCTR) is on the modem to measure
the frequency of IF signal.
AFC
AFC makes the synthesizer fine tuning. It can be used for channel sidestep also.
AFC DA–converter output DC level tunes RF oscillator (VCXO). See section 2.4.2.
System Module JF5
FII path
The FII signal is filtered and amplified with a 4 kHz bandpass filter (FIIFIL). FIITRI is for FII sensitivity compensation. The filtered FII is then fed to
summing block (SUM).
Buzzer driver
Buzzer driver is a ’semi PWM’ signal generator. It detects rising edges of
DTMF signal and generates a pulse on every rising edge. The length of the
pulse can be set by writing length control word to the register BUZZVOL. The
length is N * 2.17 us, where N is a value in BUZZVOL register.
Value 0x0H in the BUZZVOL register disables the buzzer driver, i.e. BUZZ
output is always low.
Clock divider
Clock divider generates the internal clock frequencies by dividing the
master clock frequency which is created by an internal crystal oscillator
and an external 7.3728 MHz or 3.6864 MHz crystal. An external clock
signal can also be used. If the crystal is used, the oscillator output
CLKOUT must not be loaded. The buffered crystal frequency can be obtained at pin CLKMCU directly or divided by two. The 230.4kHz / 57.6kHz
clock can be obtained at pin CLKLCD. Frequency is selected with control
bit SELLCDC.
Earphone amplifier
NIPA can drive ceramic earphone only. Because of the dynamic earphone, it need power amplifier for earphone, for that purpose is used
N761 and N762 IC’s.
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 29
Page 30

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
Main components
– NIPA (asic).
– IC’s N761 and N762
Technical Documentation
NIPA is a single chip audio/signalling processor.
Power amplifier for earphone/external earphone.
Page 3 – 30
Originat 05/98
Page 31

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
RF Section
Technical Summary
The RF module is designed for handportable cellular phone which operates in the NMT900 system (specification NMT DOC.900–3). The purpose of the module is to receive and demodulate the radio frequency signal from base station and transmit modulated RF signal to base station.
EMC leakage is prevented with magnesium shield on component side
and metallic inner surface of B–cover.
List of Submodules
Name of submodule
Rx module
Tx module
Synthesizer module
System Module JF5
All submodules are only functional blocks, They are constructed on same
PCB and have no material codes by themselves.
Specification and Functional Description
Parameter Value
RX frequency band 935.0125 – 959.9875 MHz
TX frequency band 890.0125 – 914.9875 MHz
RX LO frequency band 980.0125 – 1004.9875 MHz
Duplex spacing 45 MHz
Channel numbers 1 – 1000, 1025 – 2023
Number of channels 1999
Channel spacing 12.5/25 kHz
TX output power 0.1 W low power, 0.55 W high power
Method of frequency synthesis Dual PLL with two UHF signals for RX LO and
TX
Frequency control AFC with +/– 2.5 kHz limits
Receiver type Superheterodyne with double IF
Modulator type FM–modulator
Current consumption, reception 60 mA
Current consumption, extended standby 5 mA
Current consumption, transmission 500 mA max. 400 mA typ.
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 31
Page 32

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
Characteristics of the Module
The maximum battery voltage during transmission should not exceed 8.5
V. Higher battery voltages may destroy the power amplifier module.
Parameter Value
Battery voltage 8.5 V,
Regulated supply voltage 3.6 V +/– 5 %
Operating temperature range –25 ... +55 deg. C
DC Characteristics
Maximum ratings
There are two regulators in the RF unit. Regulators get their reference
voltages 3.3 V (Vref) from BB unit. Regulators regulate the battery voltage
to the fixed 3.6 V level.
Technical Documentation
Control Signals
In the following table the RF current consumption can be seen with different status of the control signals. RX and TX synthesizer phase locked
loops are switched on/off by a control byte that is loaded to the PLL circuit.
Table 1. Control Signals and Current Consumtion
RXE + SW powerup for RX synthe-
sizer
H H H 400 mA Power Level 2
H H L 60 mA Stanby mode
L L L 1 mA All RF parts has
TXS + SW powerup for TX synthe-
sizer
TXE Typical Current
Consumption /mA
been powered off
Power distribution diagram is shown in the figure next page.
Note
Page 3 – 32
Originat 05/98
Page 33

Originat 05/98
PAMS
Technical Documentation
Figure: Power distribution diagran
740 mA (high)
320 mA (low)
30 mA
switch
synthesizer
IC
battery
6.0 V
regulator
VCCR 3.6 V
6 mA (TX off)10 mA
9 mA (TX on)
LNA
10 mA (AGC off)
1 mA (AGC on)
IF amp
regulator
VRXVCO 3.6 V
4 mA2 mA
FM DETTX buffer TX VCOPA
9 mA
RX buffer
RX VCO
2 mA10 mA
VCTCXO
TXE
System Module JF5
Page 3 – 33
NHN–5NT
Page 34

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
Technical Documentation
Connections
Connections to the Baseband Module
Signal Name Type Function
AFC Analog out The reference oscillator frequency adjust.
AGC Digital out Automatic gain Control for LNA. Active state: High
DAF Analog in Demodulated received signal (audio + fii+ data)
GND Power Common ground
IF Analog out 2nd IF signal (450 kHz)
MOD Analog out Modulation signal for transmitter (audio + fii + data)
RFTEMP Analog in RF temperature which is determined by NTC resistor.
RSSI Analog in Received signal strength indicator. Voltage measurement.
RXE Digital out Receiver on/off control. Active state: High
SCLK Digital out Serial clock for synthesizer. Active state: Rising edge
SDAT Digital out Serial data for synthesizer. Active state: High
SLE Digital out Synthesizer latch enable
TXC PWM out Transmitter power control
TXE Digital out Transmitter enable. Active state: High
TXI Analog in ”TX power on” –indicator
TXS Digital out TX synthesizer enable. Active state: High
VBAT Power Battery voltage
VRF Power Unregulated voltage from battery
VREF Power Reference voltage
Values of digital control signal
Supply voltage VDD 3.3 V
Logical 1 VOH >VDD*0,7
Logical 0 VOL <VDD*0,3
Logical 1 IOH <1mA , 1mA (typical)
Logical 0 IOL <1mA , 1mA (typical)
AFC VCTCXO control voltage
Type analog signal (DC–level)
Level 0.3...3,0 V DC
Source impedance Zs < 1.5 kohm
Load impedance 10 kohm // 10 pF ± 10 %
Control step size for TX freq. 100 Hz (typical)
Page 3 – 34
Originat 05/98
Page 35

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
AGC Receiver gain control
Type Digital signal
Function 0 = AGC off
1 = AGC on
DAF Demodulated audio and data
signal
Type analog signal
Nominal level 50 mVrms @3,0 kHz deviation
Unit to unit variation 35 mV ...65 mV
Source impedance ZS < 5 kohm
Load impedance ZL > 50 kohm
IF 450 kHz 2nd IF signal
Level 250 mVpp (typical) not speci-
fied by manufacturer
Source impedance < 10 k W
System Module JF5
Load impedance > 50 k W
MOD Modulation signal for trans-
mitter (Audio + data)
Type Analog signal
Nominal level 300 mVpp @3,0 kHz deviation
Load impedance ZL > 10 kW
Source impedance Zs < 5 kW
RFTEMP VCTCXO temperature
Type analog signal
Level 0...3,3 V DC
Temp. range –25...+55 degrees centigrade
RSSI Received signal strength in-
dicator
DC–level 0.2...3.0 V
Source impedance 56 kW (typical)
RXE Receiver enable
Type Digital signal
Function 0 = RX off
1 = RX on
On–state current 150 mA (typical) (300 mA max.)
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 35
Page 36

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
SCLK Serial clock for synthesizer
Type digital signal
Pulse width > 1 us
SDAT Serial data for synthesizer
Type digital signal
Pulse width > 1 us
VALUES:
Control byte x110 011x x001 11xx
Reference divider 1188
Divider formulas for RX oscilla-
tor (ch 1...1000)
Divider formulas for RX oscilla-
tor (ch 1025...2023)
Divider formulas for TX oscilla-
tor (ch 1...1000)
Divider formulas for TX oscilla-
tor (ch 1025...2023)
Technical Documentation
(x = don‘t care bit)
N = 2*ch +78400
N = 2*(ch–1024) +78401
N = 2*ch +71200
N = 2*(ch–1024) +71201
SLE Synthesizer enable
Type Digital signal
Function 0 = synthesizer enabled
1 = syntheziser disabled
TXC Transmitter power control
Type PWM signal
Function Duty cycle of the TXC signal
defines the TX power level
PWM frequency 5 kHz
Level 0...3.3 V DC
Number of duty cycle steps 256
Load impedance > 100 kohm
TXE Transmitter on/off control
Type Digital signal
Function 0 = TX off
1 = TX on
TXI ”TX power on” –indicator
Type Analog signal
Source impedance > 47 k
Level < 1 V = TX off
> 1 V = TX on
Page 3 – 36
Originat 05/98
Page 37

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
TXS TX synthesizer on/off
Type Digital signal
Function 0 = Supply off
1 = Supply on
VBAT Battery voltage
Nominal value 6.5 V
Minimum value 5.3 V (NiMh)
Absolute maximum 8.8 V (Li–ion)
Max. current 700 mA
VRF Battery voltage for RX regula-
tor
Nominal value 6.5 V
Minimum value 5.8 V
System Module JF5
Absolute maximum 8.5 V
Max. current 600 mA
VREF Reference voltage
Level 3.3 V 4%
Antenna
The phone is fitted with a retractable antenna. Electrical lenght of the antenna is 1/4 wave lenght.
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 37
Page 38

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
Functional description , RF section
Block Diagram
Block diagram of the RF module is below.
RSSI
DAF
IF
PHASE SHIFTER
TX VCO
TX BUFFER
MOD
SLE
SCLK
AGC
SDATA
TXC
TXE
AFC
VCTCXO 14.85 MHz
Technical Documentation
TXI
VBAT
RXE
REGULATOR
4.75 V
VCCR
TSYN SWITCH
REGULATOR
4.75 V
450 kHz FILTER
IF AMPLIFIER
45 MHz
CRYSTAL FILTER
DIODE MIXER
IF CIRCUIT
TANK CIRCUIT FOR 2.ND LO
UMA 1015
SYNTHESIZER IC
LOOP FILTER
RX LO BUFFER
PLL
PLL
LOOP FILTER
VRXVCO
RX VCO
AMPLIFIER MODULE
TX POWER CONTROL
Page 3 – 38
RX–FILTER
LNA
ANTENNA
DUPLEX–FILTER
POWER DETECTOR
DIR_COUPLER
Originat 05/98
Page 39

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
System Module JF5
RF Key components
Name Manufacturer Type NMP Code
Antenna LK–Products RS1–GS7HH1.0 0660168
Duplexer LK–Products HY–4F/NN1 4512059
Saw Filter Toshiba SRF947–VDC–TB12R 4511016
45 MHz IF filter KDS DSF753SB 4510085
450 kHz IF filter NTK MLF–HSR12N–450 4510061
IF circuit Toshiba TA31136 4349694
VCTCXO KSS VC–TCXO–112CB 4510043
PLL IC Philips UMA1015M / C2 4349616
RX VCO Kyocera EK–301R0993A1 4350015
TX VCO Kyocera EK–301T0903A1 435001 1
Power Amplifier RF Micro Devices RF2131 4340163
Receiver
The receiver is a dual–conversion superheterodyne using two intermediate
frequencies, 45 MHz and 450 kHz.
The RF signal from the duplexer RX port is applied to the low noise RF
amplifier. The amplifier has 17 dB gain and 1,5 dB noise figure.
Next the signal is filtered with Z321. The filter is followed by a single balanced
diode mixer, which has 6 dB conversion loss.
After the mixer signal is filtered with the crystal filter Z350, which has 7,5 kHz
bandwidth. Next the IF signal is amplified by V380. From the amplifier the
IF–signal is applied to the second mixer.
The second mixer, the LO buffer transistor, IF amplifier and quadrature
detector are all integrated in the circuit N370. The second LO frequency,
44.55 MHz, is third harmonic of the VCTCXO frequency . LO signal is realized
with tank circuit C372 and L371. After the mixer the 450kHz IF signal is
filtered with ceramic filter Z370. The IF amplifier output signal is phase
shifted by resonance circuit. After this the signal is fed to a quadrature
detector.
Signal DAF is low pass filtered by R372 and C379. The DAF, RSSI and 2nd
IF signal (450 kHz) are fed to the audio/logic unit.
RX Synthesizer
The first injection frequency for receiver is generated by a digital phase
locked loop (PLL). The output frequency of the loop (LO) is obtained from
a voltage–controlled oscillator (VCO) G530. The VCO output signal is
amplified by RX–LO–buffer and fed to the receiver mixer . The injection level
required by the receiver mixer is about +3 dBm. In addition, the signal is
feeded back to the dualsynthesizer circuit N820.
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 39
Page 40

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
The overall divisor of the chain is selected according to the desired channel.
The internal dividers of N820 are programmed with 17 bits, which are
transferred serially on the SDAT (synthesizer data) line from the processor
into an internal shift register also located in N820. Data transfer is timed with
SCLK clock pulses.
The divided frequency is compared with a highly stable reference frequency
by a phase comparator in the PLL circuit. The phase comparator controls the
VCO frequency by means of a DC voltage through the loop filter so as to keep
the divided frequency applied to the phase comparator equal to the fixed
reference frequency.
The reference frequency is 12,5 kHz. This reference frequency is obtained
from voltage and temperature controlled crystal oscillator (VCTCXO).
Oscillator frequency is 14.85 MHz. The VCTCXO frequency is divided by
1188.
RX loop filter
Phase comparator output is pin 3. If the VCO frequency is too high, the
output goes low and discharge integrator capacitor C521. After this, the DC
control voltage and the VCO frequency will decrease.
Technical Documentation
If the VCO frequency is too low, the output goes high and charge the
integrator capacitor C521. Thereafter the DC control voltage and the VCO
frequency will go up.
Output pulses from the phase detector have to be supplied to the loop filter.
The function of the integrator is to convert positive and negative pulses to DC
voltage. The remaining ripple and AC components are filtered in the lowpass
filter.
TX synthesizer and TX loop filter
The transmitter synthesizer generates a frequency modulated transmitter
signal for the transmitter section. The modulated TX injection frequency is
generated in TX–VCO (G430). The TX modulated TX signal is amplified in
TX–buffer before the transmitter.
Output pulses from the phase detector N820 pin 17 have to be supplied to
the loop filter. The integrator, which consists of R420 and C421, converts
positive and negative pulses to DC voltage. The remaining ripple is filtered
in the low–pass filter.
Transmitter
The transmitter is realized with a power amplifier module N601. The
modulated RF signal from the TX synthesizer is applied to the 50 ohm input
of the module. The power level is controlled by the voltage supplied to the
pin 1. Zener diode V642 protects the module against too high control
voltages (>4.5 V). Amplifier module has two pairs of output pins ( pins 10, 1 1
and 14, 15 ). The real part of the output impedance is 10 ohms. Amplified RF
Page 3 – 40
Originat 05/98
Page 41

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
signals are compined symmetrically and impedance is matched to 50 ohms.
After that signal is fed to the duplex filter. The harmonics of the transmitter
are attenuated in the matching circuit and in the duplex filter. A voltage
proportional to the output power is rectified from a directional coupler by
DC–biased Schottky diode V640. This rectified voltage is fed to a differential
amplifier which consists of transistor V650. The reference voltage is filtered
from the PWM signal provided by the TXC line. The differential amplifier
adjusts the control voltage so that the reference voltage and the voltage
proportional to the output power are equal. The transmitter is switched on
when TXE goes high (logic 1). TXE enables the transmitter power control
circuit by transistor V653. When the transmitter is inactive (TXE low) the RF
level from the transmitter is reduced below –57 dBm.
Regulators
Voltages (3.6 V) for RF parts are realized by two regulator–components
(N310, N311). Voltage from N311 is used for receiver VCO and VCTCXO.
V oltage from N310 is used for other RF–parts excluding P A module. TX synthesizer and transmitter VCO get supply voltage via switch (V41 1). It is controlled by PLL circuit. Regulators are controlled by RXE–line.
System Module JF5
AFC Function
The transceiver unit is equipped with AFC function, i.e. it uses the incoming
receive signal from base station as a frequency reference. The control loop
consists of the receiver, the IF counter in the NIPA, MCU, an 8–bit D/A
converter in the NIPA and the VCTCXO, which is used as a reference
oscillator for the synthesizer.
The 2nd IF signal (450 kHz) from receiver is fed to the NIP A. The IF counter
counts the received frequency. If the frequency differs from programmed
value, MCU adjusts the frequency of the VCTCXO by changing output
voltage of the D/A converter. This adjustment continues until the desired
receive frequency is achieved. AFC is not active during a channel scan and
below –90 dBm RX signal level.
RF Characteristics
Temperature range
Line Symbol Minimum Typical /
Nominal
Operating temperature –25 +55 °C
Maximum Unit / Notes
Receiver
The receiver is a dual–conversion superheterodyne using two intermediate
frequencies, 45 MHz and 450 kHz.
The RF signal from the duplexer RX port is applied to the RF amplifier. The
amplifier has 18 dB gain and 1,5 dB noise figure.
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 41
Page 42

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
Next the signal is filtered with Z321. The filter is followed by a single balanced
diode mixer, which has 6 dB conversion loss.
After the mixer signal is filtered with the crystal filter Z350, which has 7,5 kHz
bandwidth. Next the IF signal is amplified by V380. From the amplifier the
IF–signal is applied to the second mixer.
The second mixer, the LO buffer transistor, IF amplifier and quadrature
detector are all integrated in the circuit N370. The second LO frequency,
44.55 MHz, is third harmonic of the VCTCXO frequency . LO signal is realized
with tank circuit C372 and L371. After the mixer the 450kHz IF signal is
filtered with ceramic filter Z370. The IF amplifier output signal is phase
shifted by resonance circuit. After this the signal is fed to a quadrature
detector.
Signal DAF is low pass filtered by R372 and C379. The DAF, RSSI and 2nd
IF signal (450 kHz) are fed to the audio/logic unit.
RX Synthesizer
Technical Documentation
The first injection frequency for receiver is generated by a digital phase
locked loop (PLL). The output frequency of the loop (LO) is obtained from
a voltage–controlled oscillator (VCO) G530. The VCO output signal is
amplified by RX–LO–buffer and fed to the receiver mixer . The injection level
required by the receiver mixer is about +3 dBm. In addition, the signal is
feeded back to the dualsynthesizer circuit N820.
The overall divisor of the chain is selected according to the desired channel.
The internal dividers of N820 are programmed with 17 bits, which are
transferred serially on the SDAT (synthesizer data) line from the processor
into an internal shift register also located in N820. Data transfer is timed with
SCLK clock pulses.
The divided frequency is compared with a highly stable reference frequency
by a phase comparator in the PLL circuit. The phase comparator controls the
VCO frequency by means of a DC voltage through the loop filter so as to keep
the divided frequency applied to the phase comparator equal to the fixed
reference frequency.
The reference frequency is 12,5 kHz. This reference frequency is obtained
from voltage controlled crystal oscillator (VCXO or VCTCXO). Oscillator
frequency is 14.85 MHz. The VCXO frequency is divided by 1188.
RX loop filter
Phase comparator output is pin 3. If the VCO frequency is too high, the
output goes low and discharge integrator capacitor C521. After this, the DC
control voltage and the VCO frequency will decrease.
If the VCO frequency is too low, the output goes high and charge the
integrator capacitor C521. Thereafter the DC control voltage and the VCO
frequency will go up.
Page 3 – 42
Originat 05/98
Page 43

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
Output pulses from the phase detector have to be supplied to the loop filter.
The function of the integrator is to convert positive and negative pulses to DC
voltage. The remaining ripple and AC components are filtered in the lowpass
filter.
TX Synthesizer
The transmitter synthesizer generates a frequency modulated transmitter
signal for the transmitter section. The modulated TX injection frequency is
generated in TX–VCO (G430). The TX modulated TX signal is amplified in
TX–buffer before the transmitter.
TX Loop Filter
Output pulses from the phase detector N820 pin 17 have to be supplied to
the loop filter. The integrator, which is constituted of R420 and C421,
converts positive and negative pulses to DC voltage. The remaining ripple
is filtered in the low–pass filter.
System Module JF5
Transmitter
The transmitter is realized with a power amplifier module. The modulated RF
signal from the TX synthesizer is applied to the 50 ohm input of the module.
The power level is controlled by the voltage supplied to the pin 1. Zener diode
V642 protects the module against too high control voltages (>4.5 V).
Amplifier module has two pairs of output pins ( pins 10, 11 and 14,15 ).
Amplified RF signals are compined symmetrically and fed through a
low–pass filter to the duplex filter. The harmonics of the transmitter are
reduced by the duplex filter. A voltage proportional to the output power is
rectified from a directional coupler by DC–biased Schottky diode V640. This
rectified voltage is fed to a differential amplifier which consists of transistor
V650. The reference voltage is filtered from the PWM signal by TXC line. The
differential amplifier adjusts the control voltage so that the reference voltage
and the voltage proportional to the output power are equal. The transmitter
is switched on when TXE goes high (logic 1), which enables the transmitter
power control circuit by transistor V653. When the transmitter is inactive
(TXE low) the RF level from the transmitter is reduced below –57 dBm.
Regulators
The voltage regulators for RF parts consist of the transistors V310, 31 1, 313
and 314. The first regulator (V310, 311) provides the operating voltage for
the receiver, PLL circuit and RX–VCO buffer. The other one is used to
regulate the operating voltage of the RX–VCO. These regulators are
realized using discrete transistors because the output noise has to be very
low. The 3.3 V reference voltage (VREF) is fed from the logic module. TX
synthesizer gets the supply voltage via a switch which is realized using
transistors V411 and V410. The switch is controlled by the digital TXS–line
from the logic module.
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 43
Page 44

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
AFC function
The transceiver unit is equipped with AFC function, i.e. it uses the incoming
receive signal from base station as a frequency reference. The control loop
consists of the receiver, the IF counter in the NIPA, MCU, an 8–bit D/A
converter in the NIPA and the VCTCXO, which is used as a reference
oscillator for the synthesizer.
The 2nd IF signal (450 kHz) from receiver is fed to the NIP A. The IF counter
counts the received frequency. If the frequency differs from programmed
value, MCU adjusts the frequency of the VCXO by changing output voltage
of the D/A converter. This adjustment continues until the desired receive
frequency is achieved. AFC is not active during a channel scan and below
–90 dBm RX signal level.
Technical Documentation
Page 3 – 44
Originat 05/98
Page 45

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
System Module JF5
Parts List of JF5 system module
Issue 5.0 Code: 0201130
ITEM CODE DESCRIPTION VALUE TYPE
R44 1430690 Chip jumper 0402
R101 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R102 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R111 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R112 1430788 Chip resistor 22 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R113 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R114 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R115 1430738 Chip resistor 270 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R116 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R117 1430788 Chip resistor 22 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R118 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R119 1430730 Chip resistor 150 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R120 1430764 Chip resistor 3.3 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R121 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R122 1430780 Chip resistor 12 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R123 1430780 Chip resistor 12 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R124 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R130 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R140 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R152 1430740 Chip resistor 330 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R153 1430726 Chip resistor 100 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R157 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R158 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R170 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R171 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R172 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R173 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R202 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R203 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R204 1430792 Chip resistor 33 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R205 1430792 Chip resistor 33 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R206 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R208 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R210 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R214 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R215 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R217 1430788 Chip resistor 22 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R221 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R222 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R223 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R224 1430792 Chip resistor 33 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R225 1430792 Chip resistor 33 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 45
Page 46

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
R226 1430792 Chip resistor 33 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R230 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R231 1430830 Chip resistor 1.0 M 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R232 1430814 Chip resistor 270 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R233 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R234 1430792 Chip resistor 33 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R235 1430802 Chip resistor 82 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R241 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R243 1430792 Chip resistor 33 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R244 1430792 Chip resistor 33 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R245 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R246 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R251 1430792 Chip resistor 33 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R252 1430792 Chip resistor 33 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R270 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R271 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R272 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R310 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R311 1430710 Chip resistor 22 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R319 1430690 Chip jumper 0402
R320 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R321 1430786 Chip resistor 18 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R322 1430726 Chip resistor 100 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R330 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R331 1430808 Chip resistor 150 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R332 1430734 Chip resistor 220 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R333 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R334 1430710 Chip resistor 22 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R335 1430764 Chip resistor 3.3 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R340 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R341 1430764 Chip resistor 3.3 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R342 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R343 1430734 Chip resistor 220 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R350 1430726 Chip resistor 100 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R360 1430744 Chip resistor 470 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R361 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R362 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R363 1430756 Chip resistor 1.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R365 1430690 Chip jumper 0402
R366 1430714 Chip resistor 33 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R370 1430758 Chip resistor 1.5 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R371 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R372 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R373 1430714 Chip resistor 33 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R374 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R381 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R411 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
Technical Documentation
Page 3 – 46
Originat 05/98
Page 47

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
R414 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R420 1430766 Chip resistor 3.9 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R421 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R422 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R423 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R430 1430718 Chip resistor 47 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R431 1430734 Chip resistor 220 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R432 1430788 Chip resistor 22 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R433 1430786 Chip resistor 18 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R434 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R440 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R441 1430772 Chip resistor 5.6 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R442 1430734 Chip resistor 220 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R443 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R444 1430690 Chip jumper 0402
R520 1430764 Chip resistor 3.3 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R521 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R522 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R523 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R530 1430724 Chip resistor 82 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R531 1430734 Chip resistor 220 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R532 1430690 Chip jumper 0402
R601 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R632 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R641 1430726 Chip resistor 100 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R642 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R643 1430786 Chip resistor 18 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R644 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R646 1430776 Chip resistor 8.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R647 1430744 Chip resistor 470 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R649 1430806 Chip resistor 120 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R651 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R652 1430786 Chip resistor 18 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R653 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R654 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R656 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R659 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R660 1430690 Chip jumper 0402
R711 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R712 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R721 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R722 1430788 Chip resistor 22 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R723 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R724 1430812 Chip resistor 220 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R725 1430812 Chip resistor 220 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R731 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R732 1430792 Chip resistor 33 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
System Module JF5
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 47
Page 48

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
R733 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R734 1430816 Chip resistor 330 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R740 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R741 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R742 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R743 1430718 Chip resistor 47 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R744 1430718 Chip resistor 47 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R751 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R752 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R753 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R766 1430820 Chip resistor 470 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R767 1430788 Chip resistor 22 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R768 1430788 Chip resistor 22 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R769 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R770 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R771 1430792 Chip resistor 33 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R772 1430798 Chip resistor 56 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R773 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R774 1430788 Chip resistor 22 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R775 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R776 1430830 Chip resistor 1.0 M 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R777 1430788 Chip resistor 22 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R778 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R779 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R780 1430788 Chip resistor 22 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R781 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R782 1430784 Chip resistor 15 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R783 1430772 Chip resistor 5.6 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R785 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R786 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R789 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R790 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R791 1430764 Chip resistor 3.3 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R793 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R800 1800673 NTC resistor 15 k 10 % 0.12 W 0805
R811 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R812 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R816 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R820 1430786 Chip resistor 18 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R821 1430714 Chip resistor 33 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R822 1430714 Chip resistor 33 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R826 1430786 Chip resistor 18 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R840 1430714 Chip resistor 33 5 % 0.063 W 0402
C101 2611668 Tantalum cap. 4.7 u 20 % 10 V
C102 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C103 2310791 Ceramic cap. 33 n 20 % 50 V 0805
C104 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
Technical Documentation
Page 3 – 48
Originat 05/98
Page 49

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
C105 2604199 Tantalum cap. 2.2 u 20 % 3.2x1.6x1.6
C106 2604199 Tantalum cap. 2.2 u 20 % 3.2x1.6x1.6
C107 2604199 Tantalum cap. 2.2 u 20 % 3.2x1.6x1.6
C108 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C109 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C111 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C112 2604209 Tantalum cap. 1.0 u 20 % 16 V
C113 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C114 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C120 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C121 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C122 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C123 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C130 2604209 Tantalum cap. 1.0 u 20 % 16 V
C131 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C132 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C142 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C143 2611668 Tantalum cap. 4.7 u 20 % 10 V
C144 2604209 Tantalum cap. 1.0 u 20 % 16 V
C145 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C151 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C152 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C153 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C156 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C157 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C158 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C160 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C162 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C163 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C164 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C167 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C168 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C169 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C170 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C171 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C172 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C173 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C174 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C175 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C176 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C177 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C178 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C189 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C190 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C191 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C192 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C193 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
System Module JF5
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 49
Page 50

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
C194 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C195 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C196 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C197 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C198 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C199 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C201 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C202 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C203 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C205 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C206 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C207 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C228 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C229 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C230 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C231 2312296 Ceramic cap. Y5 V 1210
C241 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C242 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C243 2320781 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 16 V 0603
C251 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C252 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C301 2604209 Tantalum cap. 1.0 u 20 % 16 V
C302 2312296 Ceramic cap. Y5 V 1210
C310 2320778 Ceramic cap. 10 n 10 % 16 V 0402
C311 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C312 2312296 Ceramic cap. Y5 V 1210
C313 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C314 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C315 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C316 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C317 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C319 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C320 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C322 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C323 2320518 Ceramic cap. 1.8 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C324 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C325 2320534 Ceramic cap. 8.2 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C326 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C327 2320526 Ceramic cap. 3.9 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C328 2611668 Tantalum cap. 4.7 u 20 % 10 V
C331 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C332 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C333 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C340 2320520 Ceramic cap. 2.2 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C341 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C342 2320518 Ceramic cap. 1.8 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C343 2320526 Ceramic cap. 3.9 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
Technical Documentation
Page 3 – 50
Originat 05/98
Page 51

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
C344 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C345 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C350 2320544 Ceramic cap. 22 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C351 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C354 2320532 Ceramic cap. 6.8 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C360 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C361 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C362 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C370 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C371 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C372 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C373 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C374 2320598 Ceramic cap. 3.9 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C375 2604329 Tantalum cap. 4.7 u 20 % 10 V
C376 2320598 Ceramic cap. 3.9 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C377 2310490 Ceramic cap. 360 p 2 % 50 V 0805
C378 2320556 Ceramic cap. 68 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C379 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C380 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C381 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C382 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C410 2611668 Tantalum cap. 4.7 u 20 % 10 V
C411 2320778 Ceramic cap. 10 n 10 % 16 V 0402
C420 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C421 2604209 Tantalum cap. 1.0 u 20 % 16 V
C422 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C423 2320120 Ceramic cap. 22 n 10 % 25 V 0603
C424 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C430 2611668 Tantalum cap. 4.7 u 20 % 10 V
C431 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C432 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C433 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C434 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C440 2320778 Ceramic cap. 10 n 10 % 16 V 0402
C441 2320530 Ceramic cap. 5.6 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C442 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C443 2320778 Ceramic cap. 10 n 10 % 16 V 0402
C520 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C521 2604209 Tantalum cap. 1.0 u 20 % 16 V
C522 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C523 2320120 Ceramic cap. 22 n 10 % 25 V 0603
C524 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C530 2604209 Tantalum cap. 1.0 u 20 % 16 V
C531 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C532 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C601 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C602 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
System Module JF5
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 51
Page 52

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
C603 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C604 2320520 Ceramic cap. 2.2 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C605 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C625 2611668 Tantalum cap. 4.7 u 20 % 10 V
C631 2320524 Ceramic cap. 3.3 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C633 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C634 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C635 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C641 2320524 Ceramic cap. 3.3 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C642 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C643 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C644 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C645 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C646 2320598 Ceramic cap. 3.9 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C648 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C650 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C663 2320530 Ceramic cap. 5.6 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C700 2320530 Ceramic cap. 5.6 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C701 2320552 Ceramic cap. 47 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C702 2320556 Ceramic cap. 68 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C703 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C704 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C711 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C712 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C713 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C714 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C715 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C716 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C717 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C721 2310777 Ceramic cap. 22 n 20 % 50 V 0805
C723 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C724 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C731 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C732 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C733 2604209 Tantalum cap. 1.0 u 20 % 16 V
C734 2320778 Ceramic cap. 10 n 10 % 16 V 0402
C735 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C740 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C741 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C742 2312296 Ceramic cap. Y5 V 1210
C750 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C762 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C763 2604209 Tantalum cap. 1.0 u 20 % 16 V
C766 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C767 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C768 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C777 2604209 Tantalum cap. 1.0 u 20 % 16 V
Technical Documentation
Page 3 – 52
Originat 05/98
Page 53

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
C778 2312296 Ceramic cap. Y5 V 1210
C779 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C780 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C782 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C783 2604209 Tantalum cap. 1.0 u 20 % 16 V
C785 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C790 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C791 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C792 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C793 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C794 2307816 Ceramic cap. 47 n 20 % 25 V 0805
C795 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C812 2604209 Tantalum cap. 1.0 u 20 % 16 V
C813 2320534 Ceramic cap. 8.2 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C814 2320598 Ceramic cap. 3.9 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C815 2320598 Ceramic cap. 3.9 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C820 2611668 Tantalum cap. 4.7 u 20 % 10 V
3.2x1.6x1.6
C821 2320778 Ceramic cap. 10 n 10 % 16 V 0402
C823 2611668 Tantalum cap. 4.7 u 20 % 10 V
3.2x1.6x1.6
C824 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C825 2611668 Tantalum cap. 4.7 u 20 % 10 V
3.2x1.6x1.6
C826 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
L101 3641262 Ferrite bead 30r/100mhz 2a 1206 1206
L102 3641262 Ferrite bead 30r/100mhz 2a 1206 1206
L103 3641262 Ferrite bead 30r/100mhz 2a 1206 1206
L151 3640035 Filt z>450r/100m 0r7max 0.2a 0603 0603
L154 3640035 Filt z>450r/100m 0r7max 0.2a 0603 0603
L155 3640035 Filt z>450r/100m 0r7max 0.2a 0603 0603
L156 3640035 Filt z>450r/100m 0r7max 0.2a 0603 0603
L157 3640035 Filt z>450r/100m 0r7max 0.2a 0603 0603
L321 3645191 Chip coil 8n2 5 % Q=10/100 MHz 0603
L350 3645015 Chip coil 560 n 10 % Q=15/25 MHz 0603
L370 3640103 Chip coil 320 u2 % Q=40/796 kHz 1812
L371 3641302 Chip coil 470 n5 % Q=30/25 MHz 1008
L631 3641262 Ferrite bead 30r/100mhz 2a 1206 1206
B701 4510012 Crystal 7.3728 M +–50PPM 11x4x2mm
G430 4350011 SM, vco 890–915mhz4.3v/10ma tx NMT9
G530 4350015 SM, vco980–1005mhz3.4v/10ma rx NMT
G810 4510043 SM, VCTCXO112cb 14.85mhz+–2ppm3.3v
F101 5119011 SM, fuse f2a 63v 1206
F102 5119011 SM, fuse f2a 63v 1206
Z321 4510065 Saw filter 947.5+–12.5 M 4X4
Z350 4510085 XTAL filter 45 M +–7.5KHZ 4POLE
Z370 4510061 Cer.filt 450+–6khz 11.8x7.5 11.8x7.5
System Module JF5
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 53
Page 54

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
Z660 4512059 Dupl 890–915/935–960mhz 45x15.9
V110 4113828 Trans. supr. SMB J28A DO214AA
V111 4219904 Transistor x 2 UMX1 npn 40 V SOT363
V113 4210102 Transistor BC858Wpnp 30 V 100 mA 200MW SOT323
V114 4200226 Darl. transistor BCV27 npn 30 V 300 mA SOT23
V115 4200226 Darl. transistor BCV27 npn 30 V 300 mA SOT23
V116 4210020 Transistor BCP69–25 pnp 20 V 1 A SOT223
V117 4210100 Transistor BC848W npn 30 V SOT323
V118 4110034 Schottky diode MBRS140 40 V 1 A DO214AA
V140 4100285 Diode x 2 BAV99 70 V 200 mA SER. SOT23
V151 4200811 Transistor BC849C npn 30 V 0.1 A SOT23
V170 4210102 Transistor BC858Wpnp 30 V 100 mA 200MW SOT323
V171 4210102 Transistor BC858Wpnp 30 V 100 mA 200MW SOT323
V172 4210100 Transistor BC848W npn 30 V SOT323
V210 4210102 Transistor BC858Wpnp 30 V 100 mA 200MW SOT323
V231 4210102 Transistor BC858Wpnp 30 V 100 mA 200MW SOT323
V263 4119902 Diode x 4 IMP11 80 V 0.3 A IMD
V271 4210102 Transistor BC858Wpnp 30 V 100 mA 200MW SOT323
V320 4210074 Transistor BFP420 npn 4. V SOT343
V330 4210102 Transistor BC858Wpnp 30 V 100 mA 200MW SOT323
V331 4219922 Transistor x 2 UM6
V340 4115802 Sch. diode x 2 4V 30 mA SOT23
V341 4210090 Transistor BFG540/X npn 15 V 129 mA SOT143
V380 4210066 Transistor BFR93AW npn 12 V 35 mA SOT323
V411 4210102 Transistor BC858Wpnp 30 V 100 mA 200MW SOT323
V440 4210090 Transistor BFG540/X npn 15 V 129 mA SOT143
V640 4100567 Sch. diode x 2 BAS70–04 70V15 mA SER SOT23
V641 4116536 Zener diode BZX84 5 % 2.4 V 0.3 W SOT23
V650 4219904 Transistor x 2 UMX1 npn 40 V SOT363
V651 4210054 Transistor ***
V653 4210100 Transistor BC848W npn 30 V SOT323
V723 4100285 Diode x 2 BAV99 70 V 200 mA SER. SOT23
V741 4200226 Darl. transistor BCV27 npn 30 V 300 mA SOT23
V742 4111824 Diode BAS16 75 V 250 mA 6 ns SOT23
V772 4100285 Diode x 2 BAV99 70 V 200 mA SER .SOT23
V775 4100285 Diode x 2 BAV99 70 V 200 mA SER. SOT23
V777 4210102 Transistor BC858Wpnp 30 V 100 mA 200MW SOT323
V778 4210100 Transistor BC848W npn 30 V SOT323
V790 4100567 Sch. diode x 2 BAS70–04 70V15 mA SER SOT23
V791 4100567 Sch. diode x 2 BAS70–0470V15 mA SER SOT23
V792 4100285 Diode x 2 BAV99 70 V 200 mA SER. SOT23
D241 4370029 IC, ASIC PQFP64
D251 4342264 IC, EEPROM SO8S
D252 4342264 IC, EEPROM SO8S
D790 4341611 IC, 2xbin.counter 4bit so14 74HC393 SO14S
N101 4370084 IC, mas1013s–t muumi ssop2NMP70084 SSOP24
N140 4340164 IC, regulator TK11247 4.75 V 180 mA SSO6
Technical Documentation
Page 3 – 54
Originat 05/98
Page 55

PAMS
NHN–5NT
Technical Documentation
N141 4340164 IC, regulator TK11247 4.75 V 180 mA SSO6
N310 4340415 IC, regulator TK11236BMC 3.6 V SOT23L
N311 4340415 IC, regulator TK11236BMC 3.6 V SOT23L
N370 4349694 IC, if amp+fm detector TA31136 SSO16
N601 4340163 IC, pow.amp. SO16SB
N701 4370137 IC Nipa3 nmt audio/signalling TQFP64
N761 4340331 IC, Power amp. LM4862 P W SO8S
N762 4340331 IC, Power amp. LM4862 P W SO8S
N763 4340059 IC, lp opamp+3/15v r&r LMC7101 SSOP5
N820 4349616 IC, 2xsynth 1.1ghz 3v UMA1015M SSO20
S100 5219005 IC, SWsp–no 30vdc 50ma smSW TACT SMD
S101 5219005 IC, SWsp–no 30vdc 50ma smSW TACT SMD
X001 5469031 SM, conn chp2502–0101 1x2 m P1.25
X002 5469031 SM, conn chp2502–0101 1x2 m P1.25
X003 5469031 SM, conn chp2502–0101 1x2 m P1.25
X120 5469007 Syst.conn 12af+jack+dc dct2 SMD
X130 5460021 SM, conn 2x14m spring p1.0 pcb/p PCB/PCB
X600 5429007 SM, coax conn m sw 50r 0.4–2ghz
9854261 PCB JF5 131.0X43.95X1.0 M4 4/PA
0240522 IC, SWMCU SW PROGR.
System Module JF5
Originat 05/98
Page 3 – 55
Page 56

NHN–5NT
PAMS
System Module JF5
Technical Documentation
This page intentionally left blank.
Page 3 – 56
Originat 05/98
 Loading...
Loading...