Nikon Optiphot Quick Reference Manual

Digital Microscopy Center, University of Washington
July 29, 2016 1
Quick Reference Guide to Using the Nikon Optiphot
(Details begin on following page)
Start-up
1. Epi-fluorescence.
1.1. Turn on the xenon lamp before anything else
1.1.1. Power supply on shelf above microscope
1.1.2. Press black rocker switch
1.1.3. Press the orange button momentarily, and release
1.2. Turn on the microscope lamp
1.2.1. Green push button at left, front base of microscope
1.3. Select your objective lens;
1.4. Select desired epi-fluorescent filter with slider over objective turret
1.5. Open fluorescent shutter
1.6. Set the trinocular beamsplitter to direct the image to the eyepieces;
2. Brightfield.
2.1. Turn on the microscope lamp
2.1.1. black push button at left, front base of microscope
2.2. Select your objective lens;
2.3. Set the trinocular beamsplitter to direct the image to the eyepieces;
2.4. Select “DIA” on filter slider;
2.5. Adjust lamp intensity with slider across base of microscope
2.6. Focus on the specimen
2.7. Set Koehler illumination
2.8. See following pages for use of condenser for darkfield and phase contrast.
Shut down
3. Turn off the equipment.
3.1. Switch off the xenon lamp
3.1.1. Lamp must be on for at least 30 minutes
3.2. Turn off the transmitted lamp
3.3. Remove slide
3.4. Clean any immersion oil or mounting medium from lens and stage
Did you record your usage on the Nikon reservation calendar?
Digital Microsopy Center, University of Washington
July 29, 2016 2
Details on Getting Started With The Microscope
See the Nikon Optiphot manual for additional information about the microscope.
Start-up
1. Epi-fluorescence.
1.1. When using fluorescence, turn on the mercury lamp before anything else;
1.2. The xenon arc lamp power supply sits on the shelf over the microscope;
1.3. Press the rocker switch labeled “POWER” towards “I”, the green light will come on;
1.4. Press the button labeled “IGNITION” for about 3-4 seconds, never more than 10 seconds;
1.5. The amber “LAMP READY” flashes, then is steady in 1-2 minutes, after lamp stabilizes;
1.6. If the amber indicator doesn’t come on in 3 minutes, turn off the power, wait 5 minutes then
proceed from step 1.2;
1.7. If the bulb fails to ignite, it may be too hot from prior use, the bulb may be faulty or may
need to be reseated. Contact facility staff.
2. Transmitted Illumination with halogen lamp (Figure 1).
2.1. Power switch turned on by the black switch, left front corner of the microscope base;
2.1.1. This lamp is used for brightfield, phase contrast, and darkfield microscopy
2.2. Lamp intensity is controlled by 3 means:
2.2.1. Lamp voltage controlled by slider at front of the microscope base
2.2.2. Neutral density filters mounted below the condenser (Figure 1, Table 2)
2.2.2.1. Avoids need to change lamp voltage, which alters white balance
2.2.3. Photo Button – sets lamp to 9V, which is much too bright for the digital camera
3. Beam Splitter (Figure 3, Table 1)
3.1. 3 options for dividing the light between the eyepieces and camera port
Table 1. Beamsplitter positions.
Position
Image path
In#
100%#to#eyepieces#
Middle#
14%#to#eyepieces/86%#to#camera#
Fully#out#
100%#to#camera#
Digital Microscopy Center, University of Washington
July 29, 2016 3
Table 2. Neutral density filters and combinations for transmitted light.
Filter
Light Reduction
% Transmission
ND2#
1/2#
50%#
ND4#
1/4#
25%#
ND16#
1/16#
6.25%#
ND2+ND4#
1/8#
12.5%#
ND2+ND16#
1/32#
3.125%#
ND4+ND16#
1/64#
1.562%#
ND2+ND4+ND16#
1/128#
0.781%#
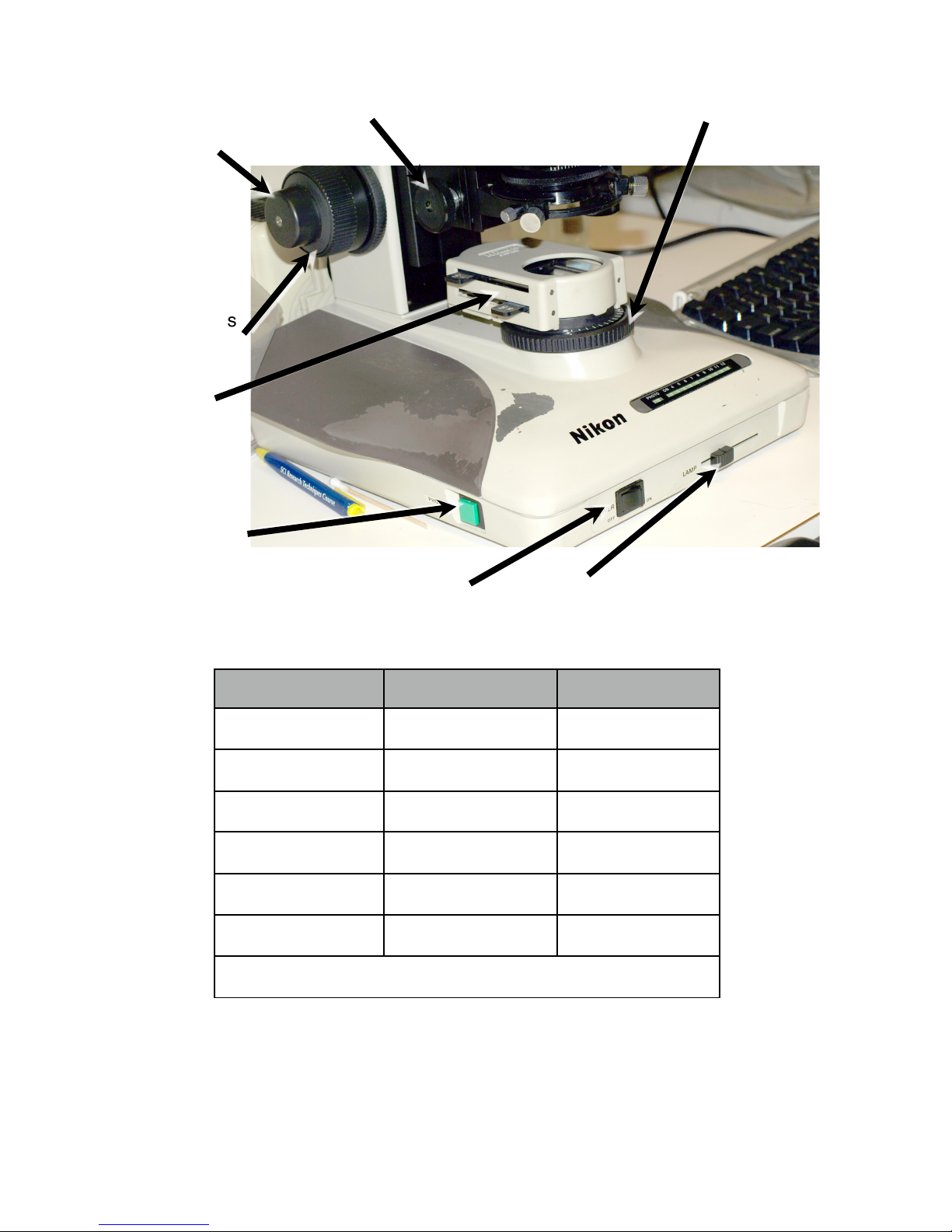
Condenser focus Substage field diaphragm
Brightfield lamp power Brightfield lamp voltage
Figure 1. Sub-stage Controls
Fine Focus
Coarse Focus
Transmitted
Light
ND Filters
“Photo” switch
 Loading...
Loading...