Page 1

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318Cable/DSLFirewall and VPN Routers
NETGEAR,Inc.
4500 Great America Parkway
Santa Clara, CA 95054 USA
Phone 1-888-NETGEAR
SM-FR314NA-3
January 2002
Page 2

© 2001 by NETGEAR, Inc. Allrights reserved.
Trademarks
NETGEAR is a trademark of NETGEAR, Inc.
Microsoft, Windows, andWindowsNT are registered trademarksof M icrosoft Corporation.
Other brand and product names are registered trademarks or trademarks of their respective holders.
Statement of Conditions
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, NETGEAR reserves the right to
make changes to the products described in this document without notice.
NETGEAR does not assume any liability that may occur due to the use or applicationof the product(s) or circuit
layout(s) described herein.
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Com pliance Notice: Radio Frequency Notice
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Cl ass B digital device, pursuant to
part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protectionagainst harmful interferencein a
residential installation.This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions,may cause harmful interferenceto radio communications. However,there is no
guaranteethat interferencewill not occur in a particular installation. If this equipmentdoescauseharmfulinterference to
radioor televisionreception,whichcan be determined by turningthe equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try
to correct the interferenceby one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increasethe separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consultthe dealer or an experiencedradio/TV technician for help.
EN 55 022 Declaration of Conformance
This is to certify that the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewalland VPN Routers are shielded against
the generationof radio interference in accordance with the application of Council Directive 89/336/EEC, Article 4a.
Conformityis declared by t he application of EN 55 022 Class B (CISPR 22).
ii
Page 3

Bestätigung des Herstellers/Importeurs
Es wird hiermit bestätigt, daß das M odel FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers gemäß der
im BMPT-AmtsblVfg 243/1991 und Vfg 46/1992 aufgeführten Bestimmungenentstörtist. Das vorschriftsmäßige
Betreibeneiniger Geräte (z.B. Testsender) kann jedoch gewissen Beschränkungen unterliegen. Lesen Sie dazu bitte die
Anmerkungen in der Betriebsanleitung.
Das Bundesamt für Zulassungen in der Telekommunikation wurde davon unterrichtet, daß dieses Gerät auf den Markt
gebracht wurde und es ist berechtigt, die Serie auf die Erfüllungder Vorschriften hin zu überprüfen.
Certificate of the Manufacturer/Importer
It is hereby certifiedthat the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers have been
suppressed in accordancewith the conditions set out in the BMPT-AmtsblVfg243/1991and Vfg 46/1992. The operation
of some equipment (for example,test transmitters)i n accordance with the regulations may,however, be subject to
certain restrictions. Please refer to the notes in the operating instructions.
FederalOffice for Telecommunications Approvals has been notified of the placing of this equipmenton the market
and has been granted the right to test the series for compliance with the regulations.
Voluntary Contro l Council for Interference (VCCI) Statement
This equipment is in the second category (informationequipment to be used in a residential area or an adjacent area
thereto)and conforms to the standards set by the Voluntary Control Council for Interference by Data Processing
Equipmentand Electronic Office Machines aimed at preventingradio interference in such residential areas.
When used near a radio or TV receiver, it may become the cause of radio interference.
Read instructions for correct handling.
Customer Support
Referto the Support Information Card that shippedwith your Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and
VPN Ro uters.
World Wide Web
NETGEAR maintains a WorldWide Webhome page that you can access at the universal resource locator (URL)
http://www.netgear.com. A direct connectionto the Internet and a Web browsersuch as Internet Explorer
or Netscape are required.
iii
Page 4

iv
Page 5

Contents
About This Guide
Typographical Conventions .............................................................................................xv
Special Message Formats ...............................................................................................xvi
Technical Support . ...........................................................................................................xvi
Related Publications ........................................................................................................xvi
Chapter 1
Introduction
About t he Netgear Firewall/VPN Router .........................................................................1-1
Key Features ..................................................................................................................1-2
A Powerful, True Firewall .........................................................................................1-2
Virtual Private Networking (VPN) .............................................................................1-2
Content Filtering .......................................................................................................1-2
Configurable Ethernet Co nnec tion ...........................................................................1-3
Protocol S upport ......................................................................................................1-3
Easy Installation and Management .......................................................................... 1-4
Maintenance and S upport ........................................................................................1-4
Chapter 2
SettingUptheHardware
Package Contents ..........................................................................................................2-1
Local Network Hardware Requirements .........................................................................2-2
PC Requirements ..............................................................................................2-2
Access Device Requirement .............................................................................2-2
The Firewall Router’s Front Panel .................................................................................. 2-3
The Firewall Router’s Rear Panel ...................................................................................2-4
Connecting the Firewall Router ......................................................................................2-4
Connecting to Your Local Ethernet Network ............................................................2-5
Connecting to Your Internet Access Dev ice .............................................................2-6
Connecting the Power Adapter ................................................................................2-6
Verifying Connections .....................................................................................................2-6
Contents v
Page 6

Chapter 3
Preparing Your Network
Preparing Your Personal Computers for IP Networking .................................................3-1
Configuring Windows 95 or later for IP Networking ........................................................3-2
Configuring T CP /IP Properties .................................................................................3-4
Verifying TCP/IP Properties (Windows) ...................................................................3-4
Configuring the Macintosh for IP Networking .................................................................3-5
Verifying TCP/IP Properties (Macintosh) ..................................................................3-6
Your Internet Account .....................................................................................................3-7
Login Prot oc ols ........................................................................................................3-8
Account Information .................................................................................................3-8
Obtaining ISP Configuration Information (Windows) .........................................3-8
Obtaining ISP Configuration Information (Macintosh) .......................................3-9
Ready for Configuration ................................................................................................3-10
Chapter 4
Initial Configuration of the Firewall Router
Accessing the Web Management Interface ....................................................................4-1
Chapter 5
General Configuration
Status ..............................................................................................................................5-2
Network Settings ............................................................................................................5-3
Network Addressing Mode ......................................................................................5-4
LAN Settings ...........................................................................................................5-4
WAN Settings ...........................................................................................................5-5
DNS Settings ...........................................................................................................5-5
MAC Address Proxy .................................................................................................5-6
MTU Settings ...........................................................................................................5-6
Selecting and Configuring a Network Addressing Mode ................................................ 5-7
Configuring for a PPPoE Connection .......................................................................5-7
Configuring for Dynamic Addressing ........................................................................5-8
Configuring for Fixed Addressing with a Single Address ......................................... 5-8
Configuring for NAT Disabled ...................................................................................5-9
Additional Not es ...........................................................................................................5-10
Chapter 6
Content Filtering
Categories ......................................................................................................................6-1
vi Contents
Page 7

RestrictWeb Features .............................................................................................6-3
Use Filter List (Web/News/FTP/Gopher) .................................................................6-3
Timeof Day ..............................................................................................................6-4
Bypassing the Filter ........................................................................................................6-5
Updating t he C onte nt Filter List .....................................................................................6-5
Customizingthe Filter List .............................................................................................6-7
Content Filter List Category Descriptions .......................................................................6-8
Chapter 7
Network Access Ru les
Services ..........................................................................................................................7-2
Network Access Rules Options ................................................................................7-3
Creating a Public LAN Server (Port Forwarding) ............................................................7-4
Notes on DM Z or Bastion Host ..........................................................................7-4
Additional Notes ................................................................................................7-4
Adding a Service ...........................................................................................................7-5
Adding a Known Service ..........................................................................................7-6
Adding a Custom Service .........................................................................................7-6
Disabling Logging ....................................................................................................7-7
Deleting a Service ....................................................................................................7-7
Stealth Mode ...................................................................................................................7-7
Node Licens e Count .......................................................................................................7-8
Excluding Devices from Node License Count ..........................................................7-9
Chapter 8
Logging and Alerting
Viewingthe Log .............................................................................................................8-1
Log Messages .........................................................................................................8-2
Log Settings ...................................................................................................................8-4
Sending the Log .......................................................................................................8-5
Automated Sending ..................................................................................................8-5
Log and Alert Categories ........................................................................................8-6
Log Cat egories . .................................................................................................8-6
Alert Categories ................................................................................................8-7
Log Reports ...................................................................................................................8-7
Data Collection .........................................................................................................8-8
View Data .................................................................................................................8-9
Contents vii
Page 8

Chapter 9
DHCP Server Configuration
DHCP Server Overview ..................................................................................................9-1
Configuring the DHCP Server ........................................................................................9-2
General S etup ..........................................................................................................9-3
WINS ........................................................................................................................9-4
Dynamic Ranges ......................................................................................................9-4
Static Entries ............................................................................................................9-4
Current DHCP Leases . ............................................................................................9-5
Chapter 10
Virtual Pri vate Networking
What is a VPN ..............................................................................................................1 0-1
Accessing Network Resources from a VPN Client PC ....................................10-2
Linking Two Networks Together ....................................................................... 1 0-3
Initial Setup of the VPN ................................................................................................10-3
Configuring a Security Association ........................................................................10-5
Deleting a Security Association ..............................................................................10-7
Security Association Notes .................................................................................... 1 0-7
Installing and Configuring the SafeNet VPN Client ......................................................10-8
Install the VPN Client Software ........................................................................1 0-8
Open the Security Policy Editor .......................................................................1 0-9
Create a VPN Connection ...............................................................................1 0-9
Configure the Security Policy ........................................................................1 0-11
Configure the VPN Client Identity ..................................................................10-12
Configure VPN Client Authentication Proposal .............................................10-14
Configure VPN Client Key Exchange Proposal .............................................10-14
Save the VPN Client Settings ........................................................................10-15
Monitoring the VPN Connection ....................................................................10-15
Accessing Remote Resources across a VPN ............................................................10-17
Chapter 11
System M aintenance
Restart .........................................................................................................................11-1
Preferences ..................................................................................................................11-1
Overview of Settings Files ......................................................................................11-3
Exporting the Settings File ..............................................................................11-3
viii Contents
Page 9

Importing the SettingsF ile ..............................................................................11-3
Restoring Factory Default Settings .......................................................................11-3
Launch the Setup Wizard .......................................................................................11-4
Updating Fi rmware ......................................................................................................11-5
Uploading New Firmware .......................................................................................11-6
Upgrade Features ..................................................................................................11-7
Diagnostic Tools ..........................................................................................................11-7
DNS Name Lookup ...............................................................................................11-8
Find Network Path .................................................................................................. 11-8
Ping .......................................................................................................................11-9
Packet Trace .........................................................................................................11-9
Tech Support Report .. ..........................................................................................11-11
Administrator Settings .......................................................................................... 11-11
Chapter 12
Troubleshooting
Basic Functioning .........................................................................................................12-1
PWR LED Not On ..................................................................................................12-1
Test LED Stays On .................................................................................................1 2-2
LNK/ACT LEDs Not On ..........................................................................................1 2-2
Troubleshooting the Web Management Interface .........................................................12-3
Troubleshooting the ISP Connection ............................................................................12-3
Troubleshooting a TC P/ IP Network Using a Ping Utility ...............................................12-5
Testing the LAN Path to Your Router ..................................................................... 1 2-6
Testing the Path from Your PC to a Remote Device ..............................................12-6
Recovering From a Lost Password ..............................................................................12-7
Appendix A
Technical S pecifications
General S pecifications ................................................................................................... A-1
Appendix B
Networks, Routing, and Firewall Basics
Basic Router Concepts .................................................................................................. B-1
What is a Router? ...................................................................................................B-1
Routing Information Protocol ...................................................................................B-2
IP Addresses and the Internet ................................................................................. B-2
Netmask ..................................................................................................................B-4
Contents ix
Page 10

Subnet A ddressing ..................................................................................................B-5
Private IP Addresses ...............................................................................................B-7
Single IP Address Operation Using NAT .................................................................B-8
MAC Addresses and Address Resolution P rotocol .................................................B-9
Domain Name Server .............................................................................................. B-9
IP Configuration by DHCP .................................................................................... B-10
Ethernet Cabling ..........................................................................................................B-10
Uplink Switches and Crossover Cables .................................................................B-11
Cable Quality ..........................................................................................................B-11
Internet Security and Firewalls .....................................................................................B-11
What is a Firewall? ................................................................................................ B-12
Stateful Packet Inspection .....................................................................................B-12
Denial of Service Attack ........................................................................................ B-12
Glossary
Index
x Contents
Page 11

Figures
Figure 2-1. FR314 Front Panel ...................................................................................2-3
Figure 2-2. FR314 Rear Panel ...................................................................................2-4
Figure 4 -1. Web Manager Login Window ...................................................................4-2
Figure 4-2. Setup Wizard, Password Window ............................................................4-2
Figure 4 -3. Setup Wizard, Time Zone Window ..........................................................4-3
Figure 4 -4. Setup Wizard, Connecting to the Internet Wi ndow .................................. 4-4
Figure 4 -5. Setup Wizard, PPPoE W indow ................................................................4-5
Figure 4-6. Setup Wizard, Static Address Window .....................................................4-6
Figure 4 -7. Setup Wizard, ISP Set tings Window ........................................................4-7
Figure 4 -8. Setup Wizard, Final W indow ....................................................................4-8
Figure 5 -1. General Status Window ........................................................................... 5-2
Figure 5-2. Network Settings Window ........................................................................5-3
Figure 6-1. Filter Categories Window .........................................................................6-2
Figure 6-2. Filter Customize Window .........................................................................6-7
Figure 7-1. Network Access Rules W indow .. .............................................................7-2
Figure 7-2. Add Service Window ................................................................................7-5
Figure 8 -1. View Log Window .. ..................................................................................8-2
Figure 8 -2. Log Settings Window ...............................................................................8-4
Figure 8-3 . Log Reports Window ................................................................................8-8
Figure 9-1. DHCP Server Conf igu ration Window .......................................................9-2
Figure 10-1. VPN S ummary Window .........................................................................10-4
Figure 10-2. VPN Configure Window .........................................................................10-5
Figure 11-1 . Preferences Window ..............................................................................11-2
Figure 11-2. Firmware Update Window ......................................................................11-5
Figure 11-3. Diagnostics Window ...............................................................................11-7
Figure B-1. Three Main Address Classes .................................................................. B-3
Figure B-2. Example of Subnetting a Class B Address . ............................................B -5
Figure B-3. Single IP Address Operation Using NAT ................................................ B-8
Figures xi
Page 12

xii Figures
Page 13

Tables
Table 2-1. LED Descriptions .....................................................................................2-3
Table 6-1. Content Filter List Categories ..................................................................6-4
Table 8-1. Content Filter List Categories ..................................................................8-3
Table B-1. Netmask Notation Translation Table for One Octet ................................. B-6
Table B-2. Netmask Formats ....................................................................................B-6
Table B-3. UTP Ethernet cable wiring, straight-through .........................................B-10
Tables xiii
Page 14

xiv Tables
Page 15

About This Guide
Congratulations on your purchase of the NETGEAR™Model FR314, F R318 or FV318 Cable/DSL
Firewall Router. The firewall router is a complete security solution that protects your network
from attacks and intrusions, filters objectionable Web content, and logs security threats.
This guide describes the features of the firewall router and provides installation and configuration
instructions.
Typographic al Conventions
This guide uses the following typographical conventions:
italics Book titles and UNIX file, command, and directory names.
courier font Screen text, user-typed command-line entries.
Initial Caps Menu titles and window and button names.
[Enter] Named keys in text are shown enclosed in square brackets. The notation
[Enter] is used for the Enter key and the Return key.
[Ctrl]+C Two or more keys that must be pressed simultaneously are shown in text
linked with a plus (+) sign.
ALL CAPS DOS file and directory names.
About This G uide xv
Page 16
Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Special Message Formats
This guide uses the following formats to highlight special messages:
Note: This format is used to highlight information of importance or special interest.
Caution: This format is used to highlight information that will help you prevent
equipment failure or loss of data.
Warning: This format is used to highlight information about the possibility of injury or
equipment damage.
Danger: This format is used to alert you that there is the potential for incurring an
electrical shock if you mishandle the equipment.
Technical Support
For help with any technical issues, c ontact Customer Support at 1-888-NETGEAR, or visit us on
the Web a t www.NETGEAR.com. The NETGEAR Web site includes a n extensive knowledge
base, answers to frequently asked questions, and a means for submitting technical questions
online.
Related Publications
As you read this document, you may be directed to various RFC documents for further
information. An RFC is a Request For Comment (RFC) published by the I nternet Engineering
Task Force (IETF), an open organizationthat defines the architecture a nd operationof the Internet.
The RFC documents outline and define the standard protocols and procedures for the Internet. The
documents are listed on the World Wide Web at w ww.ietf.org and are mirrored and indexed at
many other sites worldwide.
xvi About This Guide
Page 17

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
For more information about address assignment, refer to the IETF documents RFC 1597, Address
Allocation for Private Internets, and RFC 1466, Guidelines for Management of IP Address Space.
For more information about IP address translation, refer to RFC 1631, The IP Network Address
Translator (NAT).
About This Guide xvii
Page 18

Page 19

Chapter 1
Introduction
This chapter describes the features of the NETGEAR Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/
DSL Firewall and VPN R outers.
About the Ne tg ear Firewall/VPN Router
The Model FR314, FR318 or FV318 C able/DSL Firewall Router is a complete security solution
that protects your network from attacks and intrusions. The firewall router prevents theft,
destruction, and malicious tampering, filters objectionable Web content, and logs security threats.
Unlike simple Internet sharing routers, the firewall router uses stateful packet inspection, widely
considered as the most effective method of filtering IP traffic, to ensure secure f irewall filtering.
The Netgear Firewall/VPN Router is a flexible, high-performance, easy-to-use firewall router that
provides a secure and cost-effective solution for connecting your network of PCs to a single-user
broadband line, such as a cable modem or DSL modem. When personal computers (PCs) on the
LAN need to communicate with locations on the Internet, the PCs send requests to the firewall
router. The firewall r outer translates those requests so that the requests appear to originate from a
single PC, rather than from a network of PCs. The firewall router delivers the requests to the
external access device for transmission to the Internet.
The FR314 and FR318 Firewall Routers allow Internet access for up to eight users. Optional
upgrades may be purchased for a total of 20 users or 45 users. The FV318 VPN Router allows
Internet access for up to 20 users, with an optional upgrade available for a total of 45 users.
A VPN upgrade may be purchased to give the FR318 Firewall Router VPN capability for
establishing a single VPN connection. The FV318 VPN Router is capable of five VPN
connections.
Introduction 1-1
Page 20

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Key Features
The Netgear Firewall/VPN Router offers the following features.
A Powerful, True Firewall
Unlike simple Internet sharing routers, the Netgear Firewall/VPN Router is a true firewall, using
stateful packet inspection to defend against hacker attacks, and lets you define rules for Internet
access and content viewing. Its firewall features include:
• Denial of Service (DoS) protection
Automatically detects and thwarts Denial of Service ( D oS) attacks such as Ping of Death,
SYN Flood, LAND Attack and IP Spoofing.
• Blocks unwanted traffic from the Internet to your LAN.
• Blocks access from your LAN to Internet locations that you specify as off-limits
• Logs and reports attempted breaches of security or access restrictions.
Virtual Private Networking (VPN)
The FR318 (with optional VPN upgrade) and the FV318 provide secure, encrypted
communication between your local network and a remote network or client. Once you have
created a VP N Security Association to a remote site, the firewall router can automatically encrypt
data and send it over the Internetto the remote site, where it will be decrypted and forwarded to the
intended destination.
The FR318 and FV318 support the IPSec standard for VPNs, using up to 168 bit encryption for
maximum security.
Content Filtering
With its content filtering features, the Netgear Firewall/VPN Router prevents objectionable
content from reaching your PCs. Its content filtering features include:
1-2 Introduction
Page 21

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
• Content filtering by subscription
The Netgear Firewall/VPN Router uses content filtering to enforce your network’s Internet
access policies. You can use the Content Filter List to block Web sites by category, such as
pornography or racial intolerance. Since content on the Internet is constantly changing, the
firewall router automatically updates the Content Filter List every week to ensure that access
restrictions to new and relocated sites are properly enforced.
• Content filtering by domain or keyword
In addition to filtering by the Content Filter List, the Netgear Firewall/VPN R outer allows you
to control access to Internet content by specifying Trusted or Forbidden domains, or by
screening for keywords within Web URLs.
• Protocol filtering
In addition to filtering access to Web sites, the Ne tgear Firewall/VPN Router can also block
ActiveX, Java, cookies, and Web proxies.
• Logging of security incidents and inappropriate use
You c an configure the Netgear Firewall/VPN Router to log and block access to objectional
Web sites, or to log inappropriate usage without blocking access. You can decide how often
you want to view the log, or direct the firewall router to send the log to you at a specified
e-mail address at specified intervals. You can configure the firewall router to send alert
messages to your e-mail address or e-mail pager whenever a high-priority event (including
attacks, system errors, and blocked Web sites) occurs.
Configurable Ethernet Connection
With its internal, 4-port (FR314) or 8-port (FR318 and FV318) 10/100 switch, the firewall router
can connect to either a 10 Mbps standard Ethernet network or a 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet network.
The local LAN interface is autosensing and is capable of full-duplex or half-duplex operation.
TM
The 8-port Netgear Firewall/VPN Routers incorporate Auto Uplink
Ethernet port will automatically sense whether the Ethernet c able plugged into the port should
have a 'normal' connection (e.g. connecting to a PC) or an 'uplink' connection (e.g. connecting to a
router, switch, or hub). That port will then configure itself to the correct configuration. This feature
also eliminates the need to wor ry about crossover cables, as Auto Uplink will accommodate either
type of cable to make the right connection.
technology. Each LOCAL
Protocol Support
The Netgear Firewall/VPN Router supports the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) and Routing Information Protocol (RIP). Relevant features include:
Introduction 1-3
Page 22

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
• IP address masquerading by dynamic NAT+
The firewall router allows several networked PCs to share an Internet account using only a
single IP address, which may be statically or dynamically assigned by your Internet service
provider (ISP). This technique, an extension of Network Address Translation (NAT), is also
known as IP address masquerading and allows the use of an inexpensive single-user ISP
account.
• Port forwarding (Public Servers)
The firewall router performs port-address translation. With this feature, you can direct
incoming traffic to be forwarded to specific local PCs, based on the service port of the
incoming request.
• Automatic configuration of attached P Cs by DHCP
The firewall router dynamically assigns network configuration information, including
IP, gateway, and domain name server (DNS) addresses, to attached PCs on the LAN using the
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). This feature greatly simplifies configuration
of LAN-attached PCs.
• PPP over Ethernet
PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) is a protocol for connecting remote hosts to the Internet over an
always-on connection by simulating a dial-up connection. The firewallrouter incorporates and
automatically launches a PPPoE client so that the user does not ne ed to manually log in for
Internet access.
Easy Installation and Management
You c an install, configure, and operate the Model FR314, FR318 or FV318 f irewall router within
minutes after connecting it to the network. The following fe atures sim plify installation and
management tasks:
• Browser-based management
Browser-based configuration allows you to easily configure your firewall router from almost
any type of personal computer, such as Windows, Macintosh, or Linux. A user-friendly Setup
Wizard is provided and online help documentation is built into the browser-based Web
Management Interface.
• Visua l monitoring
The firewall router’s front panel LEDs provide an easy way to monitor its status and activity.
Maintenance and Support
NETGEAR offers the following features to he lp you maximize your use of the firewall router:
1-4 Introduction
Page 23

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
• Flash EPROM for firmware upgrade
• Five-year warranty, two years on power adapter
• Free technical support seven days a week, twenty-four hours a day
Introduction 1-5
Page 24

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
1-6 Introduction
Page 25

Chapter 2
Setting Up the Hardware
This chapter describes the Netgear Firewall/VPN Router hardware and provides instructions for
installing it.
Package Contents
The product package should contain the following items:
• Model FR314, FR318 or FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall Router
• AC power adapter,12 V DC output
• Twisted-pair Category 5 (Cat 5) Ethernet cable, straight-through wiring
• Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Resource CD, including:
— This guide
— Application Notes
— Configuration and Troubleshooting Guides
• FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Router Installation Guide
• Registration and Warranty C ard
• Support Information Card
If any of the parts are incorrect, missing, or damaged, contact your NETGEAR dealer. Keep the
carton, including the original packing materials, in case you need to return the firewall router for
repair.
SettingUptheHardware 2-1
Page 26

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Local Network Hardware Requirements
The Netgear Firewall/VPN Router is intended for use in a network of pe rsonal computers (PCs)
that are interconnected by twisted-pair Ethernet cables.
PC Requirements
To install and run the firewall router over your network of PCs, each P C must ha ve the following:
• An installed Ethernet Network Interface Card (NIC).
• A connection to the network via a hub or switch. If all PCs on the network will not run at the
same speed (10 Mbps or 100 Mbps), you need to use a dual-speed hub or switch. The firewall
router provides a 4-port (FR314) or 8-port (FR318 and FV318) switch capable of either 10
Mbps or 100 Mbps operation. Links operating at 100 Mbps must be connected with Category
5cable.
Access Device Requirement
The shared broadband access device (cable modem or DSL modem) must provide a standard
10BASE-T Ethernet interface.
2-2 Setting Up the Hardware
Page 27
Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
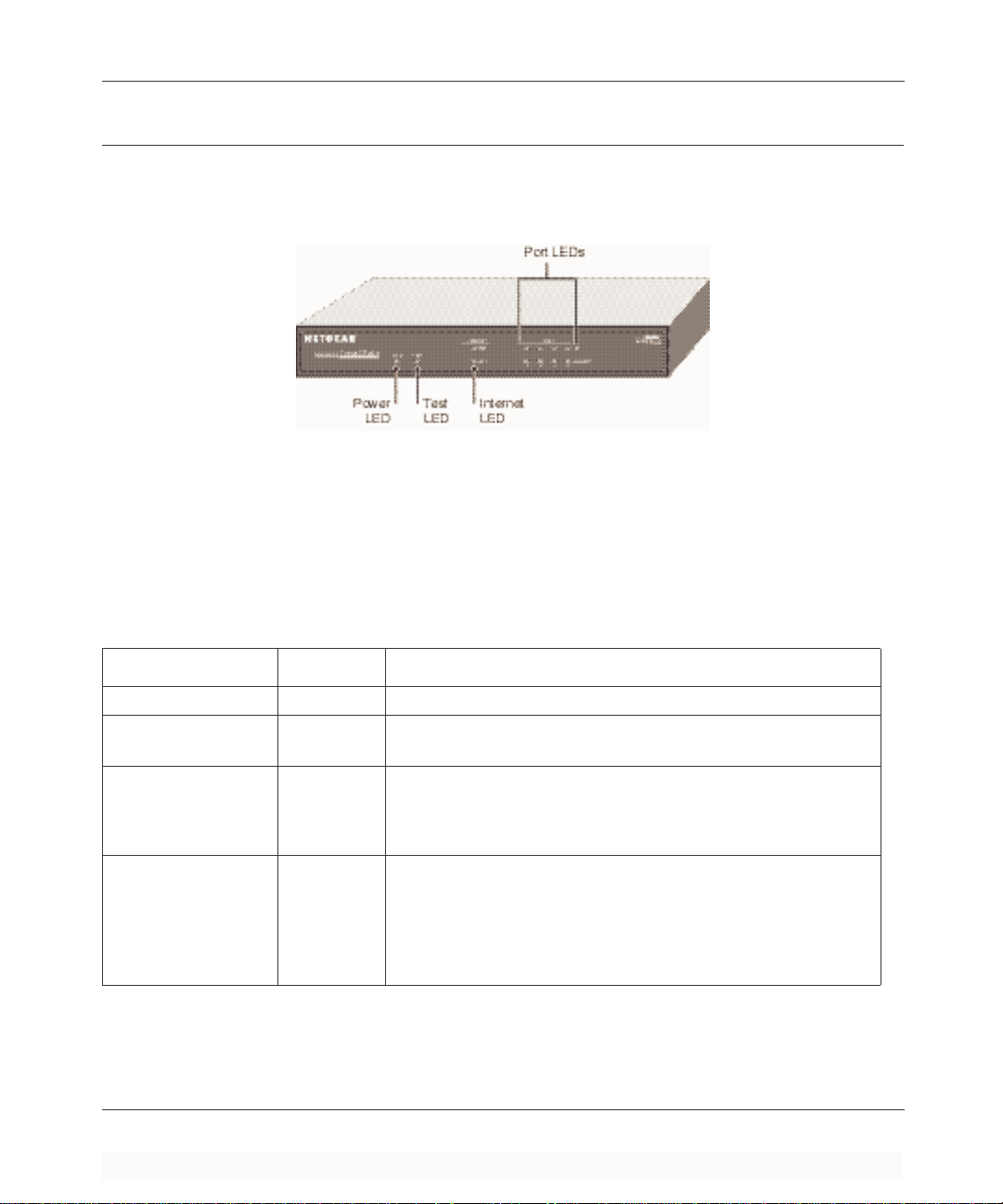
The Firewall Router ’s Front Panel
The front panel of the Model FR314, FR318 or FV318 firewall router (Figure 2-1) contains status
LEDs.
Figure 2-1. FR314 Front Panel
You c an use some of the LEDs to verify connections. Table 2-1 lists and describes each LED on
the front panel of the firewall router. These LEDs are green when lit, e xcept for the TES T LED,
which is amber.
Table 2-1. LED Descriptions
Label Activity Description
POWER On Power is supplied to the firewall router.
TEST On
Off
INTERNET
LINK On The Internet port has detected a link with an attached device.
ACT (Activity) Blinking Data is being transmitted or received by the Internet port.
LOCAL
LINK/ACT
(Link/Activity)
100 (100 Mbps) On
On
Blinking
Off
The system is initializing.
The system is ready and running.
The Local port has detected a link with an attached device.
Data is being transmitted or received by the Local port.
The Local port is operating at 100 Mbps.
The Local port is operating at 10 Mbps.
SettingUptheHardware 2-3
Page 28
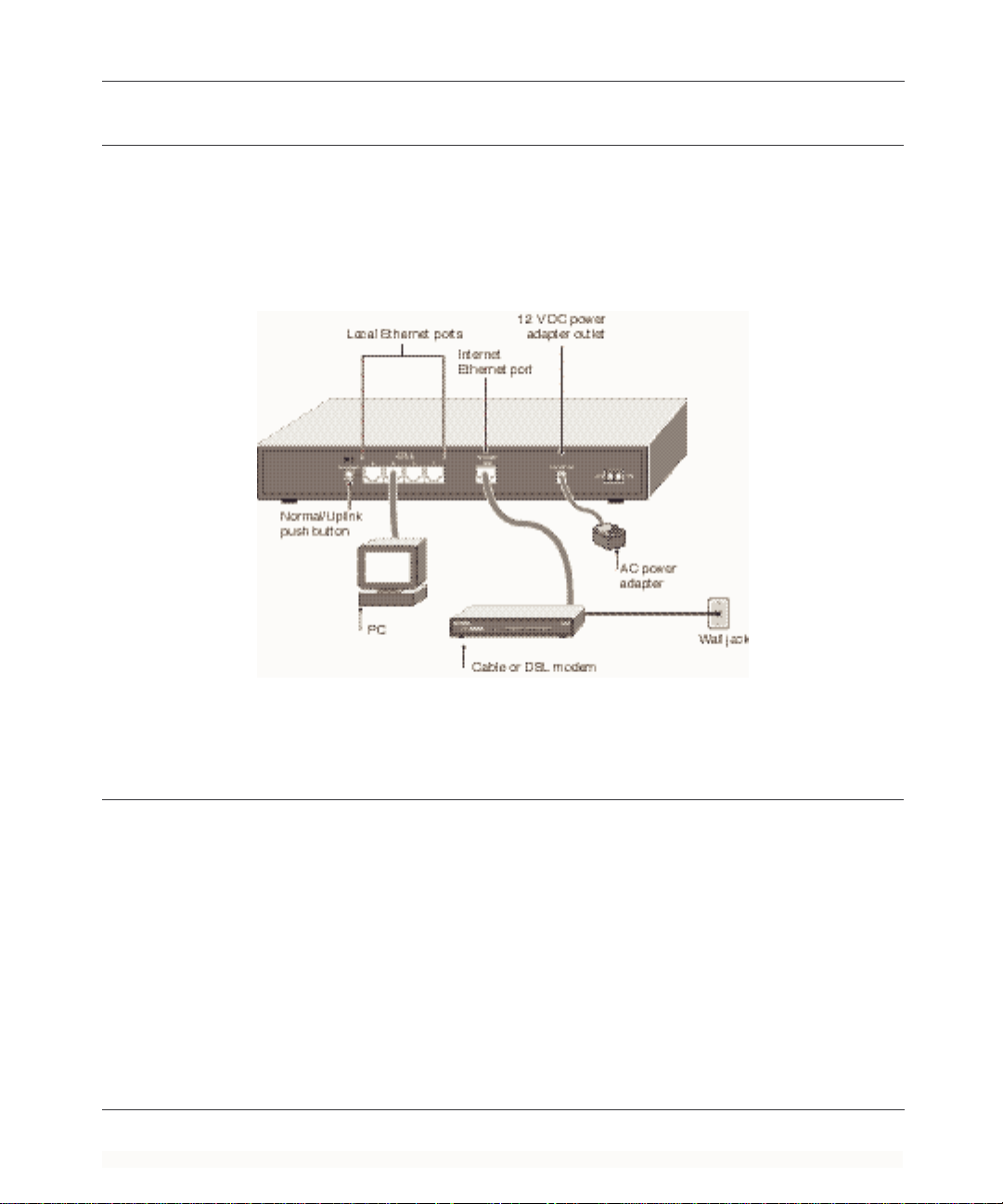
Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
The Firewall Router ’s Rear Panel
The rear panel of the FR314 is shown in Figure 2-2. The FR318 and FV318 differ only in the
number of ports and the absence of an Uplink switch. Refer to this diagram to identify the firewall
router ports before attempting to make any connections.
Figure 2-2. FR314 Rear Panel
Connecting the Firewall Router
Before using your firewall router, you need to do the f ollowing:
• Connect your local Ethernet network to the LOCAL port(s) of the firewall router (described
next).
• Connect your cable or DSL modem to the INTERNET port of the firewall router (see page
2-6).
• Connect the power adapter (see page 2-6).
2-4 Setting Up the Hardware
Page 29

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Connecting to Your Local Ethernet Network
Your local network attaches to the firewall router ports that are marked LOCAL. The LOCAL
ports of the firewall router are capable of ope ration at either 10 Mbps (10BASE-T) or 100 Mbps
(100BASE-TX), depending on the Ethernet interface of the attached PC, hub, or switch. If a ny
connection will operate at 100 Mbps, you must use a Category 5 (Cat 5) ra ted cable, such as the
Ethernet cable included with your firewall router.
The Netgear Firewall/VPN R outer incorporates a 4-port (FR314) or 8-port ( FR318 and FV318)
switch for connection to your local network.
To connect the firewall router to your LAN:
1. Connec t your PCs directly to any of the LOCAL ports of the firewall router using standard
Ethernet cables.
2. (FR314) Verify that the NORMAL/UPLINK switch of the last LOCAL port is set to
NORMAL.
If your local network consists of more hosts than LOCAL ports, you need to connect your firewall
router to another hub or switch. For the FR314, this can be done using either of the following
methods:
Connect the F R314’s last LOCAL port to any normal port of an Ethernet hub or switch using
standard Ethernet cable. Push in the NORMAL/UPLINK switch of the firewallrouter to select
UPLINK.
OR
Connect any LOC AL port of your FR314 to the UPLINK port of an Ethernet hub or switch.
For the FR318 and FV318, connect any LOCAL port of your f irewall router to any port of an
Ethernet hub or switch. The LOCAL port will automatically configure itself for the uplink
connection.
Note: The Netgear Firewall/VPN Router incorporates Auto Uplink
TM
technology. Each LOCAL
Ethernet port will automatically sense whether the Ethernet c able plugged into the port should
have a 'normal' connection (e.g. connecting to a PC) or an 'uplink' connection (e.g. connecting to a
router, switch, or hub). That port will then configure itself to the correct configuration. This feature
also eliminates the need to wor ry about crossover cables, as Auto Uplink will accommodate either
type of cable to make the right connection.
SettingUptheHardware 2-5
Page 30

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Connecting to Your Internet Access Device
To connect the firewall router to the Internet (or WAN):
1. Connec t the firewall router’s INTERNET port to the 10BASE-T Ethernet port on your existing
Internet access device (your cable modem or DSL modem).
Note: The a ttached modem device m ust provide a standard 10BASE-T Ethernet connection. The
firewall router does not include a cable for this connection. Instead, use the Ethernet cable
providedwith your access device or any other standard 10BASE-T Ethernet cable. If you are using
a DSL modem, the modem’s connection to the phone line remains unchanged.
Note: The Ethernet cable supplied by your ISP for connecting to your cable or DSL modem may
be an Ethernet crossover cable rather than a straight-through cable. I t is importantto use this cable
to connect the modem to your router, not to connect your PCs to your router.
Connecting the Power Adapter
To connect the firewall router to the power adapter:
1. Plug the connector of the power adapter into the 12 VDC adapter outlet on the rear panel of the
firewall router.
2. Plug the other end of the adapter into a standard wall outlet.
3. Turn the Power switch to the ON position.
4. Verify that the POWER LED on the firewall router is lit.
Ve rify ing Connections
After applying power to the f irewall router, complete the following steps to verify the connections
to it:
1. When power is first applied, verify that the POWER LED is on.
2. Verify that the TEST LED turns on within a few seconds.
3. After approximately 90 seconds, verify that:
a. The TEST LED has turned off.
b. TheLOCAL LINK/ACT LEDs are lit for any local ports that are connected.
c. The INTERNET LINK/ACT LED is lit.
2-6 Setting Up the Hardware
Page 31

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
If a LINK/ACT LED is lit, a link has been established to the connected device.
4. If any LOCAL port is connected to a 100 Mbps device, verify that the 100 LED for that port is
lit.
The firewall router is now properly attached to the network. Next, you need to prepare your
network to a ccess the Internet through the firewall router. See the following chapter.
SettingUptheHardware 2-7
Page 32

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
2-8 Setting Up the Hardware
Page 33

Chapter 3
Preparing Your Network
This chapter describes how to prepare your PC network to connect to the Internet through the
Model FR314, F R318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers a nd how to order
broadband Internet service from an Internet service provider (ISP).
Preparing Your Personal Computers for IP Networking
The Netgear Firewall/VPN Router uses the Transmission Control Protocol/InternetProtocol (TCP/
IP). In order to access the Internet through the f irewall router, each P C on your network must have
TCP/IP installed and selected as the networking protocol.
Note: In this chapter, we use the term “PC” to refer to personal computers in general, and not
necessarily Windows computers.
Most operating systems include the software components you need to install and use TCP/IP on
your PC:
®
• Windows
establishing a TCP/IP network.
• Windows 3.1 does not include a TCP/IP component. You need to purchase a third-party TCP/
IP application package such as Ne tManage Chameleon.
• Macintosh O perating System 7 or later includes the software components for establishing a
TCP/IP network.
• All versions of UNIX or Linux include TCP/IP components.
Preparing Y our Network 3-1
95 or later (including Windows NT®) includes the software components for
Page 34

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Follow the instructions provided with your operating system or networking software to install
TCP/IP on your computer. Although TCP/IP is built into the Windows operating system (starting
with Windows 95), you need to enable and configure it as described in “Configuring Windows 95
or later for IP Networking”onpage 3-2. To configure the M acintosh, see “Configuring the
Macintosh for IP Networking on page 3-5.
In your IP network, all PCs and the firewall router must be assigned IP addresses. Each PC must
also have certain other IP c onfiguration information such as a subnet mask (netmask), a domain
name server (DNS) address, and a default gateway address. In most cases, you should install TCP/
IP so that the PC obtains its specific network configuration information from a DHCP server
during bootup. For a detailed explanation of the meaning a nd purpose of these configuration items,
refer to “Appendix B, “Networks, Routing, and Firewall Basics.”
The firewall router is shipped preconfigured as a DHCP server. The firewall router assigns the
following TCP/IP configuration information automatically when the PCs are rebooted:
• PC or workstation IP addresses—192.168.0.2 through 192.168.0.9
• Subnet mask—255.255.255.0
• Gateway address (the firewall router)—192.168.0.1
These addresses are part of the IETF-designated private address range for use in private networks.
Configuring Windows 95 or later for IP Networking
As part of the PC preparation process, you need to manually install and configure TCP/IP on each
networked PC. Before starting, locate your Windows CD; you may need to insert it during the
TCP/IP installation process.
®
To configure Microsoft
1. On the Windows taskbar, click the Start button, point to Settings, a nd then click Control Panel.
2. Double -click the Network icon.
The Network window opens, which displays a list of installed components:
3-2 Preparing Yo ur Network
Windows 95 or later for IP networking:
Page 35

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
You m ust have an Ethernet adapter, the TCP/IP protocol, a nd Client for M icrosoft Networks.
Note: It is not necessary to remove any other network components shown in the
Network window in order to install the adapter, TCP/IP, or Client for Microsoft
Networks.
If you need the adapter:
a. Click the Add button.
b. Select Adapter, and then click Add.
c. Select the manufacturer and model of your Ethernet adapter, and then click OK.
If you need TCP/IP:
a. Click the Add button.
b. Se lect Protocol, and then click Add.
c. Select Microsoft.
Preparing Your Network 3-3
Page 36

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
d. Se lect TCP/IP, and then click OK.
If you need Client for Microsoft Networks:
a. Click the Add button.
b. Select Client, and then click Add.
c. Select Microsoft.
d. Select Client for Microsoft Networks, and then click OK .
3. Restart your PC for the changes to take effect.
Configuring TCP/IP Properties
After the TC P/IP protocol components are installed, each PC must be assigned specific
information about itself and resources that are available on its network. The simplest way to
configure this information is to allow the PC to obtain the information from the internal DHCP
server of the firewall router.
Note: If an ISP technician c onfigured your PC during the installation of a broadband
modem, or if you configuredit using instructions providedby your ISP,you may need to
copy the current configuration information for use in the configuration of your firewall
router. Refer to “O btaining ISP Configuration Information (Windows)”onpage 3-8 or
“Obtaining ISP Configuration Information (Macintosh)”onpage 3-9 for further
information.
If you are using DHCP with the recommended default addresses, you can configure your PCs by
following these steps:
1. Install TCP/IP on each PC, leaving the PC configured to obtain configuration settings
automatically (by DHCP).
2. Physically connect the PCs and the firewall router using a hub or a direct connection.
3. Restart the firewall router and allow it to boot.
4. Restart each PC.
Verifying TCP/IP Properties (Windows)
After your P C is configured a nd has r ebooted, you can c heck the TCP/IP configuration using the
Windows 95 and 98 utility winipcfg.exe (for Windows NT systems, use ipconfig.exe).
3-4 Preparing Yo ur Network
Page 37

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
To check your PC’s TC P/IP configuration:
1. On the Windows taskbar, click the Start button, and then click Run.
The Run window opens.
2. Type winipcfg, and then click OK.
The IP Configurationwindow opens, which lists (among other things), your IP address, subnet
mask, and default gateway.
3. Se lect your Ethernet adapter.
The window is updated to show your settings, which should match the va lues below if you are
using the default TC P/IP settings that NETGEAR recommends:
• The IP address is between 192.168.0.2 and 192.168.0.9
• The subnet mask is 255. 255.255.0
• The default gateway is 192.168.0.1
At this point, your PCs can communicate with each other and with the firewall router, but they still
require DNS Server addresses in order to browse the Internet. The DNS Server addresses are not
assigned until after the firewall router is configured and the PCs are rebooted.
Note: Reboot all attached PCs again after your firewall router is configured, or the PCs
will not be able to browse the Internet. The firewall router cannot assign DNS addresses
to your PCs until after it is configured.
Configuring the Macintosh for IP Networking
Beginning with Macintosh Operating System 7, TCP/IP is already installed on the Macintosh. On
each networked Macintosh, you will need to configure TCP/IP to use DHCP by following these
steps:
1. From the Apple menu, select C ontrol Panels, then TCP/IP.
Preparing Your Network 3-5
Page 38

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
The TCP/IP Control Panel opens:
2. From the “Connect via” box, se lect your Macintosh’s Ethernet interface.
3. From the “Configure” box, select Using DHCP Server.
You c an leave the DHCP Client ID box empty.
4. Close the TCP/IP Control Panel.
5. Repeat this for each Macintosh on your ne twork.
Verifying TCP/IP Properties (Macintosh)
After your M acintosh is configured and has rebooted, you can check the TCP/IP configuration by
returning to the TCP/IP Control Panel. From the Apple menu, select Control Panels, then TCP/IP.
3-6 Preparing Yo ur Network
Page 39

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
The panel is updated to show your settings, which should match the values below if you are using
the default TCP/IP settings that NETGEAR recommends:
• The IP Address is between 192.168.0.2 and 192.168.0.9
• The Subnet mask is 255.255.255.0
• The Router address is 192.168.0.1
If you do not see these values, you may need to restart your Macintosh or you may need to switch
the “Configure” setting to a different option, then back again to “Using DHCP Server”.
At this point, your Macintosh computers can communicate with each other and with the firewall
router, but they still require Name Server (DNS) addresses in order to browse the Internet. The
Name Server a ddresses are not assigned until after the firewall router is configured and the
Macintosh computers are rebooted.
Your Internet Account
For access to the Internet, you need to contract with an Internet service provider (ISP) for a
single-user Internet access account using an external broadband access device such as a cable
modem or DSL modem. This modem must be a separate physical box (not a card) and must
provide an Ethernet port intended for c onnection to a Network Interface Card (NIC) in a PC.
For a single-user Internet account, your I SP supplies TCP/IP c onfiguration information for one
PC. With a typical account, much of the configuration information is dynamically assigned when
your PC is first booted up while connected to the ISP,and you will not need to know that dynamic
information.
In order to share the Internet connection among several computers, your firewall router takes the
place of the single PC, and you need to configure it with the TC P/IP information that the single PC
would normally use. When the firewall router’s INTERNET port is connected to the broadband
modem, the firewall router appears to be a single PC to the ISP. The firewall router then allowsthe
PCs on the local network to masquerade as the single PC to access the Internet through the
broadband modem. The method used by the firewall router to accomplish this is c alled Network
Address Translation (NAT) or IP masquerading.
Preparing Your Network 3-7
Page 40

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Login Protocols
Some ISPs require a special login protocol, such as PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE). If your ISP
requires one, you need a login name and password, and you also need to select P PPoE when you
configure the firewall router. After your network and firewall router are configured, the firewall
router performs the login task when needed, and you will no longer need to log in from your PC.
Account Information
Unless these items are dynamically assigned by the ISP, your ISP should give you the following
basic information for your account:
• An IP address and subnet mask
• A gateway IP address, which is the address of the ISP’s router
• One or more dom ain name server (DNS) IP addresses
• Host name and domain suffix
For example, your account’s full server names may look like this:
mail.xxx.yyy.com
In this example, the domain suffix is xxx.yyy.com.
If any of these items are dynamically supplied by the I SP, your firewall router automatically
acquires them. If an ISP technician configured your PC during the installation of the broadband
modem, or if you configured it using instructions provided by your ISP, you need to copy
configuration information from your PC’s Ne twork TCP/IP Properties window (or Macintosh
TCP/IP Control Panel) before reconfiguring your PC for use with the firewall router. These
procedures are described next.
Obtaining ISP Configuration Information (Windows)
As mentioned above, you may need to collect configuration information from your PC so that you
can use this information when you configure the firewall router. Following this procedure is only
necessary when your ISP does not dynamically supply the account information.
To get the information you need to c onfigure the firewall router for Internet access:
1. On the Windows taskbar, click the Start button, point to Settings, a nd then click Control Panel.
2. Double -click the Network icon.
3-8 Preparing Yo ur Network
Page 41

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
The Network window opens, which displays a list of installed components.
3. Select TCP/IP, and then click Properties.
The TCP/IP Properties dialog box opens.
4. Select the IP Address tab.
If an IP address and subnet mask are shown, write down the information. If an address is
present, your account uses a fixed (static) IP address. I f no address is present, your account
uses a dynamically-assigned IP address. Click “Obtain an IP address automatically”.
5. Select the Gateway tab.
If an IP address appears under Installed Gateways, write down the address. This is the ISP’s
gateway address. Select the address and then click Remove to remove the gateway address.
6. Se lect the DNS Configuration tab.
If any DNS server addresses a re shown, write down the addresses. If any information appears
in the Host or Domain information box, write it down. Click Disable DNS.
7. Click OK to save your changes and close the TCP/IP Properties dialog box.
You are returned to the Network window.
8. Click OK.
9. Reboot your PC at the prompt. You m ay also be prompted to insert your Windows CD.
Obtaining ISP Configuration Information (Macintosh)
As mentioned above, you may need to collect configuration information from your Macintosh so
that you can use this information when you configure the firewall router. Following this procedure
is only necessary when your ISP does not dynamically supply the account information.
To get the information you need to c onfigure the firewall router for Internet access:
1. From the Apple menu, select C ontrol Panels, then TCP/IP.
The TCP/IP Control Panel opens, which displays a list of configuration settings. If the
“Configure” setting is “Using DHCP Server”, your account uses a dynamically-assigned IP
address. In this case, close the Control Panel a nd skip the rest of this section.
2. If an IP address a nd subnet mask are shown, write down the information.
3. If an IP address a ppears under Router address, wr ite down the address. This is the ISP’s
gateway address.
Preparing Your Network 3-9
Page 42

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
4. If any Name Server addresses are shown, write down the addresses. These are your ISP’sDNS
addresses.
5. If any information appears in the Search domains information box, write it down.
6. Change the “ Configure” setting to “Using DHCP Server”.
7. Close the TCP/IP Control Panel.
Ready for Configuration
After configuring all of your PCs for TCP/IP networking and connecting them to the LOCAL
network of your firewall router, you are r eady to access and configure the firewall router. Proceed
to the next chapter.
3-10 Preparing Your Network
Page 43

Chapter 4
Initial Configuration of the Firewall Router
This chapter describes how to perform the initial configuration of your Model FR314, FR318 and
FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers using the Setup Wizard, which wa lks you through
the configuration process. The Setup Wizard should result in a working and secure configuration,
but you will need to use the main menus to download the Content Filter List and set any other
desired firewall rules. These procedures are de scribed in subsequent chapters.
Accessing the Web Management Interface
You c an manage the Netgear Firewall/VPN Router f rom any computer connected to the local
network of the firewall router. The computer you use to manage the firewall router is called the
Management Station.
Your Management Station must have a Web browser (for example, Microsoft Internet Explorer or
Netscape Navigator) installed on it. The Netgear Firewall/VPN Router uses Java for security and
other functions, so your Web browser must be Java-enabled and support HTTP uploads.
NETGEAR recommends using Netscape Navigator 3.0 or above. Free browser programs are
readily available for Windows, Macintosh, or UNIX/Linux.
To perform the initial configuration:
1. Turn on the firewall router and wait for initialization to complete.
Allow at least one minute and verify that the TEST LED is off.
2. Reboot your PC to obtain DHCP configuration from the firewall router.
3. Launch your Web browser.
4. Type http://192.168.0.1 in the browser’s Address box and press Enter.
A login window opens as shown in Figure 4-1 below:
Initial Configurat ion of the Firewall Router 4-1
Page 44
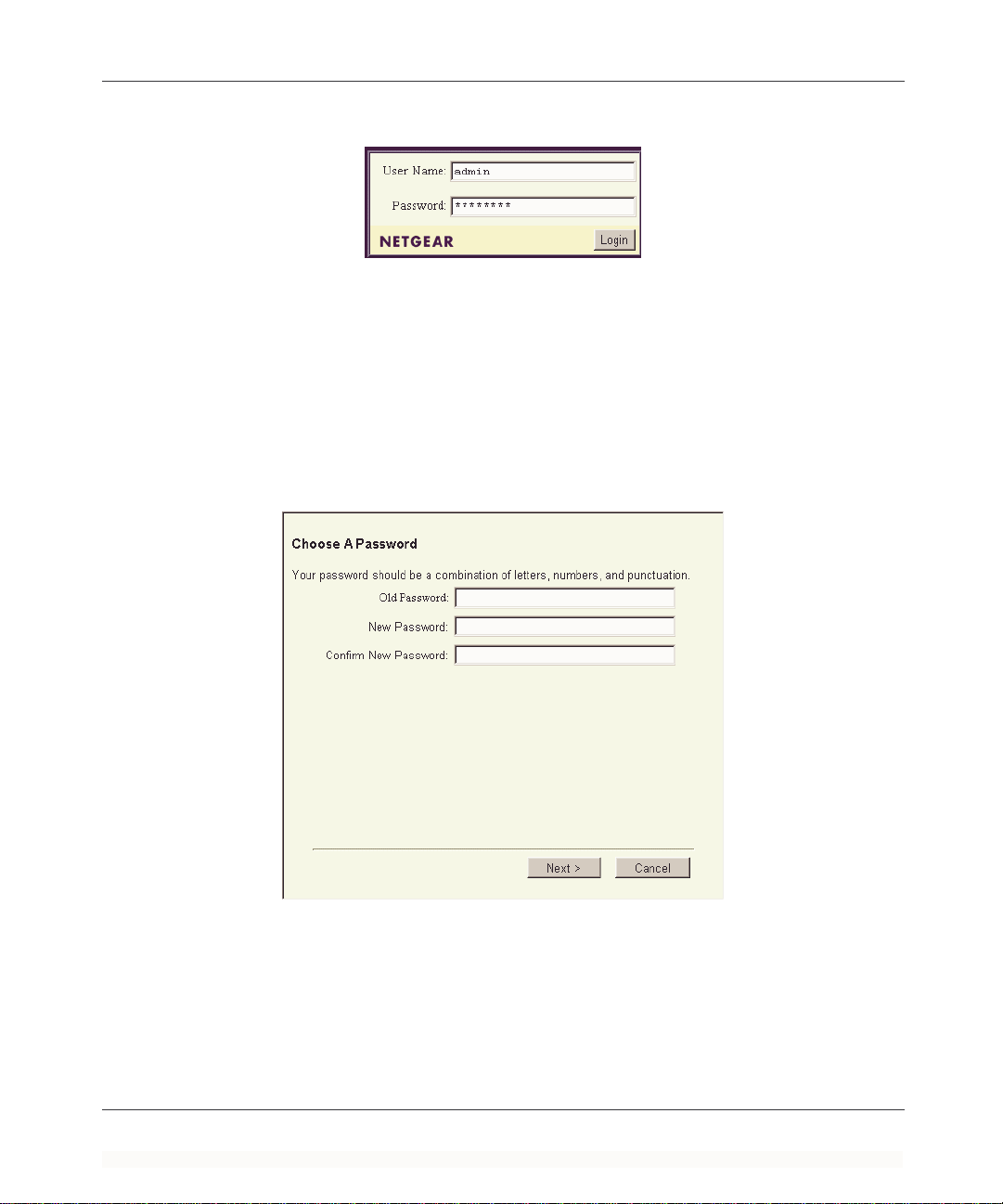
Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Figure 4-1. Web Manager Login Window
Type admin in the User Name box, password in the Password box, and then click OK.
5.
If your firewall router password was previously changed, enter the current password.
6. If the Setup Wizard does not automatically launch when the Web Management Interface
appears, select Setup Wizard from the navigation bar on the left.
7. In the first Wizard window, as shown in Figure 4-2 below, choose a new Password:
Figure 4-2. Setup Wizard, Password Window
As you complete this step, keep the following in mind:
• This password is only for access to the Web Management Interface, not to your Internet
account.
4-2 Initial Configuration of the Firewall Router
Page 45

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
• Choose a password that cannot be easily guessed. First enter the old password, and then
enter the new password twice. If you do not enter the new password exactly the same in
both New Password boxes, the operation fails. The reason that you must type the new
password exactly the same in both boxes is to protect you against accidentally mistyping
your password in the future, which would result in your being locked out of the f irewall
router.
• The first time you set your password, remember that the firewall router's default password
is "password".
• The password cannot be recovered if it is lost or forgotten. If you lose the password, you
will need to clear the firewall router’s software and reload it. See Chapter 11, “System
Maintenance” for instructions.
8. Click Next.
The Time Zone window opens:
Figure 4-3. Setup Wizard, Time Zone Window
Select your time zone from the pull-down menu.
9.
The firewall router's internal clock is automatically set by a Network Time Server on the
Internet using the Network Time Protocol (NTP). The firewall router uses the time and date
settings to time stamp log events, to automatically update the C ontent Filter List, and f or other
internal purposes.
Initial Conf iguration of the Firewall Router 4-3
Page 46

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
10. Click Next.
The firewall router attempts to automatically determine your network addressing mode. If it
cannot automatically determine the mode, the Connecting to the Internet window opens.
Figure 4-4. Setup Wizard, Connecting to the Internet Window
If this window appears, you must manually select your addressing mode. Unless your ISP
account uses a PPPoE login procedure or does not dynamically assign network address
information, you can skip the next two steps.
4-4 Initial Configuration of the Firewall Router
Page 47

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
11. If your ISP account uses a PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) login procedure, you a re prompted to
enter your account’s Login Name and Password in the PPPoE window:
Figure 4-5. Setup Wizard, PPPoE Window
Enter the user name and password provided by your ISP for your I nternet account. These
entries are case sensitive. This password is for logging into your ISP account. It is not the same
as the password you use to access your Netgear Firewall/VPN R outer’s Web Management
Interface.
Initial Conf iguration of the Firewall Router 4-5
Page 48

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
12. If your ISP account does not dynamically assign a network address, you are prompted to enter
your static (fixed) address information in the next window.
Figure 4-6. Setup Wizard, Static Address Window
Enter the following information for each option:
• WAN IP Address and Subnet Mask
Enter the IP Address and Subnet Mask assigned to your account by your ISP.
• Gateway
Enter the IP Address of your ISP’s gateway router.
• Primary DNS Server and Optional Second DNS Server
A DNS server is a host on the Internet that translates Internet names (such as www
addresses) to numeric I P addresses. If you enter DNS addresses here, you should reboot
your PCs after configuring the firewall router.
4-6 Initial Configuration of the Firewall Router
Page 49

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
13. Click Next. The ISP Settings window opens:
Figure 4-7. Setup Wizard, ISP Settings Window
Enter your account’s Host Name and Domain Na me. These parameters may be necessary to
access your ISP’s services such as mail or news se rvers. If you leave the Domain Name field
blank, the router will attempt to automatically obtain the domain name from the ISP. If the
attempt fails, you will need to manually enter this information.
Initial Conf iguration of the Firewall Router 4-7
Page 50

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
14. Click Next.The final Setup Wizard window opens:
Figure 4-8. Setup Wizard, Final Window
Reboot your firewall router in order for the configuration to take effect, and then reboot any
15.
attached PCs.
Your PCs should now have secure Internet access. You can test this by browsing to any Internet
location, such as NETGEAR’s Web site at www.NETGEAR .com.
If your PCs are unable to browse the Internet after initial firewall router configuration, refer to
Chapter 12, “Troubleshooting.”
If you wish to perform further configuration of your firewall router’s features, refer to the next
three chapters.
4-8 Initial Configuration of the Firewall Router
Page 51

Chapter 5
General Configuration
This chapter describes how to interpret current status informationand how to configure the Model
FR314, FR318 and FV318 firewall routers' network settings, which include the firewall router's IP
addressing method and settings.
If you need to configure the firewall’s more advanced features, see Chapter 6, “Content Filtering,”
and Chapter 7, “Network Access Rules.”
General Configuration 5-1
Page 52

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Status
To view the firewall router's status information, click General from the navigation bar on the left,
and then click the Status subtopic. The Status window opens as shown in Figure 5-1 below:
Figure 5-1. General Status Window
The Status window provides information on the current operating conditions of the router. Please
view this window periodically for helpful status information."
5-2 General Configuration
Page 53

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Network Settings
This section describes how to configure the firewall router's IP address information.
To configure the firewall router's network settings, click General from the navigation bar on the
left, and then click the Network subtopic. The Network Settings window opens as shown as shown
in Figure 5-2 below:
Figure 5-2. Network Settings Window
From here, you can configure network addressing mode options,LAN settings, WAN settings, and
DNS settings.
General Configuration 5-3
Page 54

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Network Addressing Mode
You c an use the Network Addressing Mode menu to configure how the firewall router determines
its network address and accesses the network. This section describes each option; for configuration
procedures for each option, see “Selecting and Configuring a Network Addressing Mode,” starting
on page 5-7.
The Network Addressing Mode options a re:
• NAT w ith Dynamic Addressing(Default)
The firewall router will request TCP/IP settings f rom a DHCP server on the Internet. This is
the most common application in cable and DSL environments where the IP a ddress is
dynamically assigned by the ISP's DHCP server. See page 5-8 for instructions on configuring
for dynamic addressing.
• NAT w ith PPPoE
Your ISP requires the installation of desktop login software and a user name a nd password
authentication to connect to the Internet. PPPoE is common in DSL environments. See page
5-7 for instructions on configuring for a PPPoE connection.
• NAT with Static Addressing
Your ISP assigns a single, valid IP address for your account. See page 5-8 for instructions on
configuring for static addressing.
• NAT D isabled
Your ISP assigns valid IP addresses for all computers on your network. See page 5-9 for
instructions on configuring for NAT disabled mode.
LAN Settings
The LAN Settings options are:
• NETGEAR Firewall LAN IP Address
This is the IP address assigned to the firewall router's LAN port for accessing and managing
the firewall router from your local PCs. This IP address should be a unique address within the
LAN address range. Unless you have a need to c hange it, NETGEAR recommends that you
use the default address of
• LAN Subnet Mask
5-4 General Configuration
192.168.0.1.
Page 55

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
The LAN Subnet Mask defines the range of IP addresses that are on the LAN. The default
Class C subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 supports up to 254 IP addresses on the LAN. If the
Class C subnet mask is used, all local area network addresses should contain the same first
three numbers as the firewall router’s LAN IP Address (for example,
have a need to c hange it, NETGEAR recommends that you use the default subnet mask of
255.255.255.0.
192.168.0). Unless you
WAN Settings
The WAN Settings options are:
• WAN Gateway (Router) Address
The WAN Gateway (Router) Address is the IP address of the next router or gateway to which
your firewall router connects to access the Internet. In c able a nd DSL environments, the WAN
router is located at the ISP. The Gateway (Router) Address is automatically assigned when
Dynamic Addressing or PPPoE is selected as your addressing mode.
• NETGEAR Firewall WAN IP Address
This is the IP Address assigned to the WAN port of the firewall router. When NAT is enabled,
this will be the only address seen by Internet users, and all activity on the Internet will appear
to originate from this address. The WAN IP address is assigned automatically when Dynamic
Addressing or PPPoE is selected as your addressing m ode. The WAN IP Address is the same
as the LAN IP Address when NAT Disabled mode is selected.
• WAN Subnet Mask
The WAN Subnet Mask determines which IP addresses are located on the WAN. This subnet
mask should be assigned by your ISP.
The WAN Subnet Mask is assigned automatically when Dynamic Addressing or PPPoE is
selected as your addressing mode. The WAN Subnet Mask is the same as the LAN Subnet
Mask when NAT Disabled mode is selected.
DNS Settings
There is one DNS S ettings option: DNS Servers.
General Configuration 5-5
Page 56

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
DNS Servers, or Domain Name Servers, resolve descriptive names of network resources (such as
www.NETGEAR.com) to numeric IP addresses. One or m ore DNS Server addresses should be
assigned by your ISP for your use. DNS Server addresses are assigned automatically when
Dynamic Addressing or PPPoE is selected as your addressing mode. These DNS addresses are
used by the firewall router to locate and access the Content Filter List server and for the built-in
DNS lookup tool.
Note: The f irewall router will not automatically relay these DNS settings to the LAN. You must
enable and c onfigure the firewall router's DHCP server or manually configure your computers'
DNS settings to obtain DNS name resolution.
MAC Address Proxy
Some ISPs, pa rticularly cable providers, allow a customer to ac cess the Internet from only one
specific PC, which is identified by that PC’s unique Ethernet MAC (Media Access Control)
address. In this case, you can have your firewall router obtain and use (“proxy” or “spoof”) that
MAC address from your PC.
To have the firewall router proxy your PC’sMAC address, first you must use that PC to access the
Network Settingsmenu. If you arecurrently configuring the routerfrom a different P C, logoff and
loginfromthedesiredPC.
In the MAC Address Proxy menu section, check the box titled “Use this PC’s MAC Address on
the WAN Port.” Then click Update.
MTU Settings
The MTU (Maximum Transmit Unit) is the largest size packet, including all headers and data, that
can be transmitted over a given network. You can set the MTU size in the MTU Settings menu
section of the Network Settings menu. To set the MTU size, check the box titled “Fragment
outbound packets larger than WAN MTU”, enter a new MTU value in the WAN M TU box, then
click Update.
Ethernet networks typically use an MTU of 1500 bytes, but some ISPs, particularly DSL
providers, add additional bytes to each packet resulting in a packet size of greater than 1500.
(These extra bytes typically result from the use of a name-and-password login client such as
EnterNet or WinPOET). A downstream router receiving these larger packets may send back an
ICMP message asking your router to use a smaller packet size. Since this type of request can be
used as a type of DoS attack, your router will discard the request, possibly resulting in a slower or
lostconnection.
5-6 General Configuration
Page 57

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
If your ISP requires a user name and password to connect (using a PPPoE client like EnterNet or
WinPOET, for example) then you may find it necessary or beneficial to set your MTU to a lower
value than the standard 1500. You should try 1492, 1452, or 1404 (subtracting 8, 48, or 96),
working from higher to lower to see which results in a higher speed connection.
Selecting and Configuring a Network A ddressing Mode
Use the following information to determine which network addressing mode to use:
• If your ISP requires the installation of desktop login software (for example, EnterNet or
WinPOET)and provides a login user name and password authenticationto access the Internet,
select NAT with PPPoE. PPPoE is commonly used in DSL connections.
• If your ISP did not provide you with any valid IP a ddress, but instructed you to obtain an IP
address automatically, select NAT with Dynamic Addressing. This is the most common
configuration used with home or small office cable and DSL connections.
• If your ISP provided you with one single valid IP address, select NAT with Static Addressing.
• If your ISP provided you with multiple valid IP addresses (one for each PC), select NAT
Disabled.
The following sections provide configuration procedures for each mode.
Configuring for a PPPoE Connection
To configure for a PPPoE connection:
1. From the Network Addressing Mode window, select NAT with PPPoE.
2. NETGEAR recommends that you leave the LAN IP A ddress field and the LAN Subnet Mask
field at their default values of
3. Under ISP Settings, in the User Name box, type the login user name provided by your ISP.
The user name identifies the PPPoE client.
4. Under ISP Settings, in the Password box, type the login password provided by your ISP.
The password authenticates the PPPoE session. This field is case sensitive.
5. Check the Disconnect after __ Minutes of Inactivity checkbox to automaticallydisconnect the
PPPoE connection after a specified period of inactivity.
6. In the Minutes box, define a maximum number of minutes of inactivity.
General Configuration 5-7
192.168.0.1 and 255.255.255.0,respectively.
Page 58

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
You c an enter a number from 1 to 99 minutes.
7. Click Update.
Once the firewall router has been updated, a message confirming the update is shown at the
bottom of the browser window.
8. Click Restart for these changes to take effect.
The restart may take up to 90 seconds, during which time the firewall router is inaccessible and all
network traffic through the firewall router is ha lted.
When your firewall router has successfully established a PPPoE connection, the Network page
displays the firewall router's WAN IP settings. The WAN Ga teway (Router) Address, WAN IP
(NAT Public) Address, and DNS Servers are shown.
Configuring for Dynamic Addressing
To obtain IP settings dynamically:
1. From the Network Addressing Mode window, select NAT with Dynamic Addressing.
2. NETGEAR recommends that you leave the LAN IP A ddress field and the LAN Subnet Mask
field at their default values of
192.168.0.1 and 255.255.255.0,respectively.
3. Under DNS Settings, enter the Host Name assigned to your PC by your ISP.
4. Click Update.
Once the firewall router has been updated, a message confirming the update is shown at the
bottom of the browser window.
5. Click Restart for these changes to take effect.
The restart may take up to 90 seconds, during which time the firewall router is inaccessible and all
network traffic through the firewall router is ha lted.
When your firewall router has suc cessfully received a DHCP lease, the Network page displays the
firewall router's WAN IP settings. The WAN Gateway (Router) Address, WAN IP (NAT Public)
Address, and DNS Servers are shown.
Configuring for Fixed Addressing with a Single Address
To use NAT with a single valid IP a ddress:
5-8 General Configuration
Page 59

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
1. From the Network Addressing Mode window, select NAT with Fixed Addressing.
2. NETGEAR recommends that you leave the NETGEAR Firewall LAN IP Address field and
the LAN Subnet Mask f ield at their default values of
192.168.0.1 and 255.255.255.0,
respectively.
3. In the NETGEAR Firewall WAN IP (NAT Public) Address box, type the single va lid IP
address assigned by your ISP.
All network activity will appear to originate from this address.
4. In the WAN S ubnet Mask box, type your WAN subnet mask.
This subnet mask should be assigned by your ISP with your single valid IP address.
5. In the WAN Ga teway (Router) Address box, type the IP address of the next router or gateway
to which your firewall router connects to access the Internet.
In cable a nd DSL environments, the WAN Gateway is located at the ISP.
6. In the DNS Servers box, type the IP address or IP a ddresses of your DNS servers.
The firewall router will use these DNS servers for diagnostic tests and for upgrade a nd
registration functionality.
7. Click Update.
Once the firewall router has been updated, a message confirming the update is shown at the
bottom of the browser window.
8. Click Restart for these changes to take effect.
The restart may take up to 90 seconds, during which time the firewall router is inaccessible and all
network traffic through the firewall router is ha lted.
Configuring for NAT Disabled
If you plan to disable NAT, you need to assign valid IP addresses to all computers and network
devices on your LAN. However, you must begin the firewall router configuration by assigning
your Management Station to an address within the factory de fault address range of the firewall
router. After changing the firewall router’s LAN IP Addr ess and LAN Subnet Mask, you must
reconfigure your Management Station to use the fixed addressing scheme in order to reconnect to
the firewall router for further configuration.
To use valid IP addresses throughout your local ne twork:
1. From the Network Addressing Mode window, select NAT Disabled.
General Configuration 5-9
Page 60

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
2. In the NETGEAR Firewall LAN IP Address box, type a unique, valid IP address from your
LAN address range.
The firewall router LAN IP Address is the address assigned to the firewall router's LAN port
and is used for management of the firewall router.
3. In the LAN Subnet Mask box, type your network's subnet mask. The LAN Subnet Mask
notifies your firewall router which IP addresses are on your LAN. The default value,
255.255.255.0, supports up to 254 IP addresses.
4. In the WAN Ga teway (Router) Address box, type the IP address of the next router or gateway
to which your firewall router connects to access the Internet.
In cable a nd DSL environments, the WAN Gateway is located at the ISP.
5. In the DNS Servers box, type the IP address or IP a ddresses of your DNS servers.
The firewall router uses these DNS servers for diagnostic tests and for upgrade and
registration functionality.
6. Click Update.
Once the firewall router has been updated, a message confirming the update is displayed at the
bottom of the browser window.
7. Click Restart for these changes to take effect.
The restart may take up to 90 seconds, during which time the firewall router is inaccessible
and all network traffic through the firewall router is halted. After the reboot, your firewall
router’s IP address will be changed to the IP address you entered in Step 2.
8. Reconfigure your Management Station’s IP address to an address on the same subnet as the
firewall router’s new LAN IP Address.
You will need to reconfigureall PCs on your LAN to use addresses on the new subnet. In addition,
you need to configure all connected PCs to use the firewall router’s IP address as their gateway.
Additional Notes
Unless you have selected the NAT Disabled addressing m ode, your firewall router use s Network
Address Translation (NAT) to share a single-user Internet account among all of your attached PCs.
In addition to the network settings described in this chapter,you must enable and configure the
firewall router's DHCP server or manually configure your computers' DNS settings in order to
obtain DNS name resolution.
5-10 General Configuration
Page 61

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
For more information about NAT, DNS, DHC P, and other networking concepts, refer to
Appendix B, “ Networks, R outing, and Firewall Basics.”
General Configuration 5-11
Page 62

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
5-12 General Configuration
Page 63

Chapter 6
Content Filtering
This chapter describes how to use the the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall
and VPN Routers’ content filtering features. With these features, you can prevent objectional
content from reaching the PCs on your LAN. You can block access to Web sites by c ategory,
domain name, or keyword.
Categories
To configure content filtering and blocking options by category, click Filter from the navigation
bar on the left, and then click on the Categories subtopic. The Filter Categories window opens as
shown in Figure 6-1 below:
Content Filtering 6-1
Page 64

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Figure 6-1. Filter Categories Windo w
Using the options in the Filter Categories window, you can configure content filtering and
blocking in three different ways:
• Restrict Web Features
• Use Filter List (Web/News/FTP/Gopher)
•TimeofDay
6-2 Content Filtering
Page 65

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Each category and its options are described in the sections that follow.
Restrict Web Features
You can restrict access to the following Web features:
• ActiveX
ActiveX is a programming language that embeds scripts in Web pages. Malicious
programmers use ActiveX to delete files or compromise security. Select the ActiveX check
box to block ActiveX controls.
•Java
Java is used to embed small programs, called applets, in Web pages. It is safer than ActiveX
since it has built-in security mechanisms. Select the Java check box to prevent attacks and
other threats created by Java applets.
• Cookies
Cookies are used by Web servers to track Web usage and remember user identity. Cookies can
also invade users' privacy by tracking Web activities. Select the Cookies check box to disable
cookies.
• Disable Web P roxy
When a proxy server is located on the WAN, LAN users can circumvent content filtering by
pointing to this proxy server. The Disable Web Proxy check box disables access to proxy
servers located on the WAN. It does not block Web proxies located on the LAN.
Use Filter List (Web/News/FTP/Gopher)
You use the options in this category in conjunction with the filter list. You can use these options to
block access to certain types of content, log all access attempts, or both:
• Log and Block Access
The firewall router logs access attempts and blocks access to all sites on the Content Filter,
custom, and keyword lists.
•LogOnly
This option lets you monitor inappropriateusage without restrictingaccess. The firewall router
logs and allows access to all sites on the Content Filter, custom, and keyword lists.
• Block all categories
The firewall router uses a Content Filter List to block access to objectional Web sites. The
Content Filter List classifies objectional Web sites based upon input from a wide range of
social, political, and civic organizations.
Content Filtering 6-3
Page 66

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
When you register the firewall router at <http://fr3.netgear.com>, you may download a
one-month subscription to Content Filter List updates.
The following is a list of the Content Filter List categories:
Table 6-1. Content Filter List Categories
Violence/Profanity Partial Nudity
Full Nudity Sexual Acts
Gross Depictions Intolerance
Satanic/Cult Drugs/Drug Culture
Militant/Extremist Sex Education
Gambling/Questionable/
Alcohol/Tobacco
Illegal
See “Content Filter List Category Descriptions”onpage 6-8 for a detailed description of
the criteria used to define Content Filter List categories.
Time of Day
The Timeof Day feature allows you to define specifictimes when content filtering is e nforced. For
example, you may want to filter your e mployees’ Internet access during normal business hours,
but allow unrestricted access at night and on weekends.
Note: Time of Day restrictions only a pply to the Content Filter,Customized blocking and
Keyword blocking. Restrict Web Features are not affected.
The Time of Day options a re:
•AlwaysBlock
Content filtering is enforced at all times.
• Block Between
Content filtering is enforced during the specified time and days. Enter the time period, in
24-hour format, and select the starting and ending day of the week to enforce content f iltering.
6-4 Content Filtering
Page 67

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Bypassing the Filter
You m ay allow a trusted user to bypass the content filtering and have access to sites that would
otherwise be blocked by the router. This can be done by defining a user name and password in the
Filter Bypass section of the F ilter Categories m enu.
To set up filter bypassing:
1. Go to the Filter C ategories m enu.
2. In the Filter Bypass section, enter an arbitrary name and password to be used by the trusted
user.
3. Click on the Update button.
When the trusted user wishes to access the Internet without being subject to blocking, he should
follow these steps:
1. Open your browser.
2. Ente r the router’s LAN IP address (usually 192.168.0.1) in the browser’s Address (or
Location) box. The router’s login screen will appear.
3. Ente r the name and password that you previously defined in the F ilter Bypass menu.
4. A message box will appear saying “<username>, you now have access to privileged services.”
Tip: Set the router’s LAN IP address as your browser’s default page.
Updating the Content Filter List
Since content on the Internet is constantly changing, the Content Filter List needs to be updated
regularly. When you register the Netgear Firewall/VPN Router with NETGEAR, you can activate
the Content Filter List and sign up to receive a one-month trial of the Content Filter List
subscription at no charge. For information about purchasing a Content Filter List subscription,
please contact NETGEAR at <http://www.buyne tgear.com>.
With a Content F ilter List subscription, you can download an updated Content Filter List at any
time, or configure the firewall router to automatically download a new list e ve ry week.
To update the Content Filter List, click Filter from the navigation bar on the left, and then click the
Categories subtopic. The Filter C ategories window opens as shown in Figure 6-1 above. Scroll to
the Filter Updates section at the bottom of the menu.
Content Filtering 6-5
Page 68

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
To configure Content Filter List updates, click one of the following options:
• Download Now
Immediately downloads and installs a new Content Filter List. This process m ay take several
minutes and requires a current subscription to Content Filter List updates. Downloading the
Content Filter List interrupts Internet access, so NETGEAR recommends that you download
new lists when Internet access is at a minimum.
• Automatic Download
Enables automatic, weekly downloads of the Content Filter List. The default download time
and day are determined using a simple algorithm that results in a default time between 10 p.m.
to 6 a.m. and can be any day of the week. Once loaded, the creation date of the current active
list is displayed at the top of the window. A current subscription to the Content Filter List
updates is required.
After configuring these options, click the Update button. Once the firewall router is updated, a
message confirming the update is displayed at the bottom of the window.
The Content Filter List expires 30 days after it is downloaded unless you purchase a subscription.
The filter list may also be erased if there is a failure downloading a new list. If the filter list has
expired or is not loaded, access to your manually-defined forbidden domains and ke ywords is still
blocked. See “Customizing the Filter List” for information on blocking access to specific domains
or to Web sites that contain specific keywords.
6-6 Content Filtering
Page 69

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Customizing the Filter List
To customize the Content Filter List, click F ilter from the navigation bar on the left, and then c lick
the Customize subtopic.The Filter Customize window opens as shown in Figure 6-2 below:
Figure 6-2. Filter Customize W i ndow
You c an customize the Content Filter List by specifying trusted domains, forbidden domains, and
blocking access to Web sites whose addresses contain specified keywords:
Content Filtering 6-7
Page 70

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
•TrustedDomains
To allow access to a Web site that is blocked by the Content Filter List, enter the host name,
such as "www.ok-site.com", into the Trusted Domains boxes. Do not include the prefix "http:/
/". All subdomains are allowed. For example, entering "yahoo.com" will allow
"mail.yahoo.com" and "my.yahoo.com". Up to 256 entries are supported in the Trusted
Domains list.
• Forbidden Domains
To block a We b site that is not blocked by the Content Filter List, enter the host name, such as
"www.bad-site.com" into the Forbidden Dom ains box. Do not include prefix "http://". All
subdomains are blocked. For example, entering "yahoo.com" will also block
"mail.yahoo.com" and "my.yahoo.com". Up to 256 entries are supported in the Forbidden
Domains list.
• Blocking by Keyword
The Netgear Firewall/VPN R outer allows you to block Web URLs containing keywords
specified by you. For example, if the keyword "XXX" is specified, the URL <http://
www.new-site.com/xxx.html> is blocked, even if it is not included in the Content Filter List.
Up to 100 entries are supported in the Keyword list.
After customizing your Content Filter List, click the Update button. Once the firewall router has
been updated, a message confirming the update is displayed a t the bottom of the window.
Note: Customized domains do not need to be reentered when the Content Filter List is updated
each week and do not require a filter list subscription.
To remove a trusted domain, forbidden domain, or keyword, select it from the appropriate list, and
click Delete Domain or Delete Keyword. After you delete an item from one of these lists, a
message confirming the change is displayed at the bottom of the window.
Content Filter List Category Descriptions
Violence/Profanity (graphics or text)
Pictures or text exposing extreme cruelty, or physical or emotional acts against any animal or
person which are primarily intended to hurt or inflict pa in. Obscene words, phrases, and profanity
is defined as text that uses, but is not limited to, George Carlin's seven c ensored wor ds more often
than once every 50 messages (Newsgroups) or once a page (Web sites).
6-8 Content Filtering
Page 71

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Partial Nudity
Picturesexposing the female breast or fullexposure of either male or female buttocks except when
exposing genitalia. (Excludes all swimsuits, including thongs.)
Full Nudity
Pictures exposing any or all portions of the human genitalia. Excluded from the Partial Nudity and
Full Nudity categories are sites containing nudity or partial nudity of a wholesome nature. For
example: Web sites containing publications such as National Geographic or Smithsonian
Magazine. Or sites hosted by museums such as the Guggenheim, the Louvre, or the Museum of
Modern Art.
Sexual Acts
Pictures or text exposing anyone or anything involved in explicit sexual acts and or lewd and
lascivious behavior, including m asturbation, copulation, pedophilia, and intimacy involving nude
or partially nude people in he terosexual, bisexual, lesbian or homosexual encounters. Also
includes phone sex ads, dating services, and adult personals, C D-ROM's, and videos.
Gross Depictions
Pictures or descriptive text of anyone or anything which are crudely vulgar or grossly deficient in
civility or behavior, or which show scatological impropriety. Includes such depictions as maiming,
bloody figures, or indecent depiction of bodily functions.
Intolerance
Pictures or text advocating prejudice or discrimination against any race, color, national origin,
religion, disability or handicap, gender, or sexual orientation. Any picture or text that elevates one
group over another. Also includes intolerant jokes or slurs.
Satanic/Cult
Pictures or text advocating devil worship, an affinity for evil or wickedness, or the advocacy to
join a cult. A cult is de fined as: A closedsociety that is headed by a single individual where loyalty
isdemanded and leaving is punishable.
Content Filtering 6-9
Page 72

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Drugs/Drug Culture
Pictures or text advocating the illegal use of drugs for entertainment. Includes substances used for
other than their primary purpose to alter the individual's state of mind, such as glue sniffing. This
excludes currently illegal drugs legally prescribed for medicinalpurposes (for example, drugs used
to treat glaucoma or cancer).
Militant/Extremist
Pictures or text advocating extremely aggressive and combative behaviors, or advocacy of
unlawful political measures. Topics include groups that advocate violence as a means to achieve
their goals. Includes "how to" information on weapons making, ammunition making, or the
making or use of pyrotechnics materials. Also includes the use of weapons for unlawful reasons.
Sex Education
Picturesor text advocating the proper use of contraceptives. This topic would include condom use,
the correct way to wear a condom and how to put a condom in place. Also included are sites
relating to discussionabout the use of the Pill, IUDs, and other types of contraceptives. In addition
to the above, this category includes discussion sites on discussing diseases with a partner,
pregnancy, and respecting boundaries. Excluded from this category are commercial sites wishing
to sell sexual paraphernalia.
Questionable/Illegal Gambling
Pictures or text advocating materials or activities of a dubious nature which may be illegal in any
or all jurisdictions, such as illegal business schemes, c hain letters, copyright infringement,
computer hacking, phreaking (using someone's phone lines without permission), and software
piracy. Also includes text advocating gambling relating to lotteries, casinos, betting, numbers
games, on-line sports, or financial betting, including non-monetary dares.
Alcohol & Tobacco
Pictures or text advocating the sale, consumption, or production of alcoholic beverages and
tobacco products.
6-10 Content Filtering
Page 73

Chapter 7
Network Access Rules
This chapter describes the Model FR314, FR318 or FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall Router’s Network
Access Rules. Network Access Rules include inbound and outbound access policy, user
authentication and remote management.
Network A c ce ss Rules 7-1
Page 74

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Services
To configure inbound and outbound access policies by service, click Firewall from the navigation
bar on the left, then Access, and then Services. The Network Access R ules window opens as
shown in Figure 7-1 below:
Figure 7-1. Network Access Rules Window
Note: The LAN In column is not displayed if NAT is enabled.
7-2 Network Access Rules
Page 75

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
The Serviceswindow allows you to customize Network Ac cess Rules by service. The Default rule,
at the bottom of the table, encompasses all Services.
Network Access Rules Options
This section describes the options you can configure in the Network Access Rules window. For
procedural information, also see “Creating a Public LAN S erver (Port Forwarding)”onpage 7-4
and “Adding a Service”onpage 7-5.
• LAN Out
If a LAN Out check box is checked (the default), users on your LAN are able to access that
service on the Internet. Otherwise, they are blocked from accessing that service.
•LANIn
The LAN In column is not visible when NAT is enabled (the default). If a LAN In check box
is checked, users on the Internet may access all computers on your LAN for that service. By
default, LAN In check boxes are not checked; use caution whe n enabling this option.
• Public LAN Server
A Public LAN Server is a server on your network that is designated to receive inbound traffic
for a specific service, such as Web access or e-mail. You may define a Public LAN Server by
entering the server's IP address in the Public LAN Server box for the appropriate se rvice. If
you do not have a Public LAN Server for a service, enter "0.0.0.0" in the box. See “Creating a
Public LAN Server (Port Forwarding),” next for more information.
• Network Connection Inactivity Timeout
If a connection to a remote server r emains idle for more than five minutes, the firewall r outer
closes the connection. Without this timeout, Internet connections could stay open indefinitely
and create potential security holes. You may increase the Inactivity Timeout if applications,
such as Telnet and FTP, are frequently disconnected.
• Detection Prevention
To prevent all unforwarded ports from responding to outside requests, check the box titled
“Enable Stealth Mode.” Please refer to “Stealth Mode“ on page 7-7 for details and
considerations on the use of this mode.
• Exclude IP Address from Node License count
If your local network contains active IP devices that do not require Internet access, such as
print servers, enter those IP addresses here to prevent these devices from being counted toward
your maximum node count. Please refer to “Node License Count“ on page 7-8 for details and
on the use of this feature.
Network Access Rul es 7-3
Page 76

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Creating a Public LAN Server (Port Forwarding)
A Public LAN Server is a server on your LAN that is a ccessible to users on the Internet. Creating a
Public LAN Server in the Services window is the easiest wa y to set up a mail server, Web server,
or other public server, on your LAN.
To create a Public LAN Server:
1. Determine what type of service your server uses, such as FTP, Web, or Mail. Locate this
service in the Services window. If the service does not appear in the Services window, you
need to define it in the Add Service window (see “Adding a Service,” next).
2. Ente r the server's IP address in the Public LAN Server box for the appropriate service.
Note: If NAT is enabled, this IP address should be a private LAN address. Users on the
Internet will access the Public LAN Server at the WAN IP (NAT Public) Address.
You do not need to select the LAN In checkbox (for NAT Disabled Addressing Mode) to
allow inbound access to a Public LAN Server.
3. Click Update.
After the firewall router is updated, a message confirming the update is displayed at the
bottom of the window.
To configure additional Public LAN Servers, r epeat these steps.
Notes on DMZ or Bastion Host
Some routers allow the user to specify one server on the local network to receive all inbound
traffic that is not otherwise forwarded. This feature is referred to a s Default Server, DMZ ( a
misnomer in this application), or Bastion Host. By indiscriminately exposing a ll ports of the
designated PC, the user defeats the purpose of a hardware firewall and createsa large security risk.
Therefore this feature is not supported in this product. We recommend that the user determine
which ports are used by network applications, and only forward those ports that are necessary.
Additional Notes
• In NAT Disabled Network Addressing Mode, users on the Internet will a ccess Public LAN
Servers at their valid, LAN I P addresses.
• If NAT is enabled, users on the Internet will access Public LAN Servers at the WAN IP (NAT
Public) Address.
7-4 Network Access Rules
Page 77
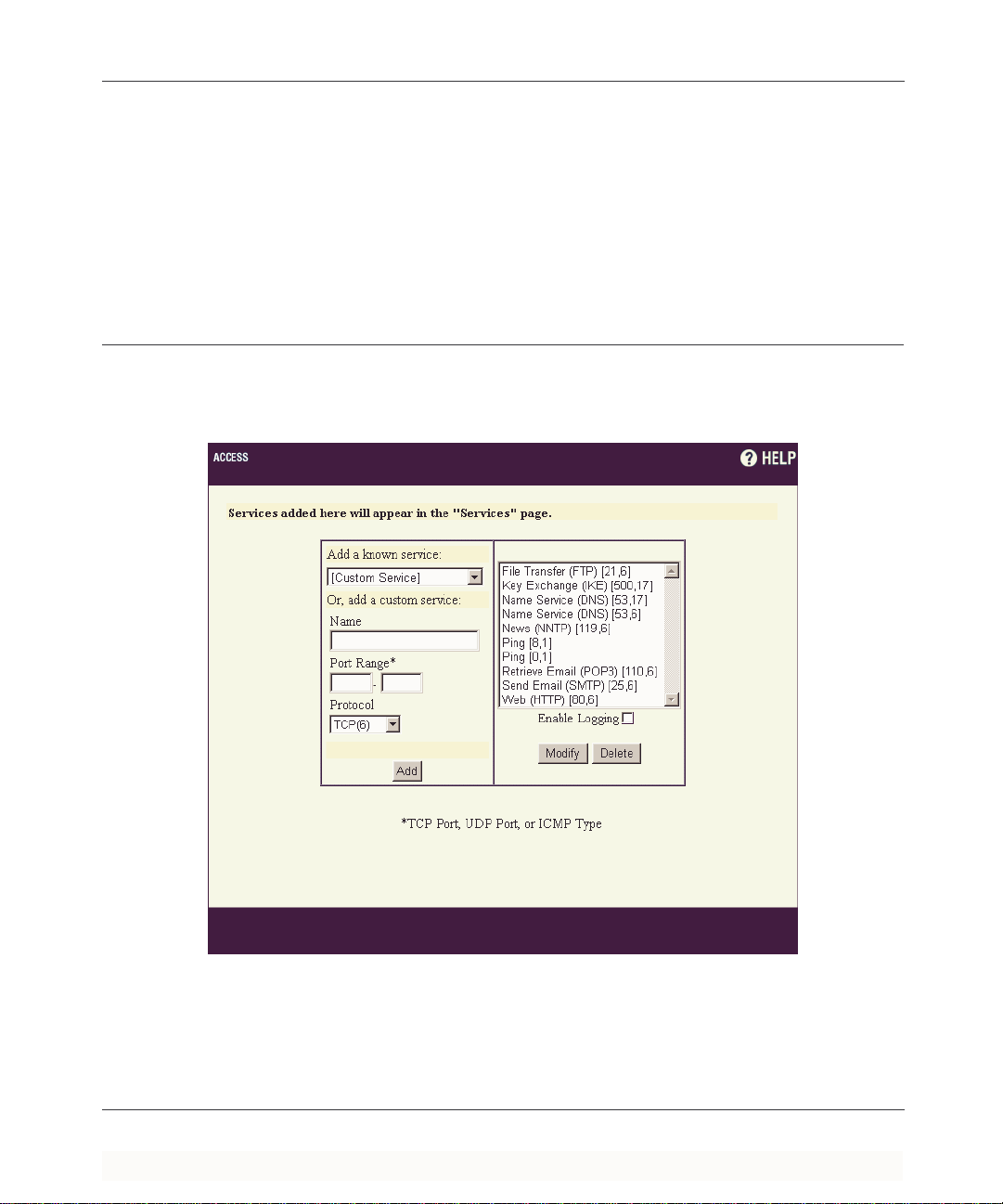
Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
• If users on the Internet cannot access Public LAN Servers, make sure that the Public LAN
Servers are properly c onfigured and have Internet c onnectivity. If you are trying to access the
serversby na me ratherthan by I P address, confirm that the DNS m x-record points to the correct IP
address: the WAN I P (NAT Public) Address, if NAT is enabled.
• If NAT is enabled, you cannot have multiple LAN servers of the same service, such as multiple
Web servers.
Adding a Service
To add a service that is not listed in the Services window, click Access from the navigation bar on
the left, and then click the Add Service subtopic. The Add Service window opens:
Figure 7-2. Add Service Window
Currently defined services are listed on the right side. These services also appear in the Services
window.
Network Access Rul es 7-5
Page 78

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Two numbers appear in brackets ne xt to each service. The first num ber indicates the service's IP
port number. The second number indicates the IP protocol type (6 for TCP, 17 for UDP, or 1 for
ICMP).
Note: You may notice multiple entries with the same name. For example, the default
configuration has two e ntries labeled "Name Service (DNS)"--for UDP port 53 and TCP port 53.
Multipleentries with the same name are grouped together,and are treated as a single service. Up to
128 entries are supported.
From the Add Service window,you can add a known service or a custom service.You can also use
this window to disable logging and to r emove services. The following sections provide procedures
for each task.
Adding a Known Service
To add a known service:
1. From the “Add a known service” list box, select the name of the service you want.
2. Click Add.
The new service will appear in the listbox on the right side of the window. Note that some services
add more than one entry to the list box.
Adding a Custom Service
To add a custom service:
1. From the “Add a known service” list box, select [Custom Service].
2. In the Name box, type a unique name, such as "CC:mail" or "Quake".
3. In the Port Range boxes, type the beginning number of the IP port range and ending number of
the IP port range. If the service only requires one IP port, enter the single port number in both
Port Range boxes.
Note: Visit <http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1700.txt> for a list of IP port numbers.
4. In the Protocol box, select the IP protocol type: TCP, UDP, or ICMP.
5. Click Add.
The new service will appear in the listbox on the right side of the window.
7-6 Network Access Rules
Page 79

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Note: If multiple entries with the same name are created, they are grouped together as a single
service and may not function as expected.
Disabling Logging
You c an disable logging of events in the Event Log. For example, if LINUX's authentication
messages are filling up your log, you m ay disable logging of LINUX authentication.
To disable logging:
1. From the list of currently defined services, select the name of the relevant service.
2. Clea r the Enable Logging check box.
3. Click Modify to apply the change.
Deleting a Service
To delete a service:
1. In the Network Access Rules window, make sure the LAN In a nd LAN Out boxes for this
service are not checked.
2. From the list of currently defined services in the Add Service window, select the name of the
relevant service.
3. Click Delete Service.
4. If multiple entries with the same name exist, delete all entries to remove the service.
Stealth Mode
When a remote computer attempts a connection to your router, the router first checks to see if the
requested port is configured for forwarding to a host on the LAN. If not, the router sends a reset
packet back to the remote client indicating that the connection is refused. This is the correct
behavior based on the IP protocol specifications. However, you may prefer that the router not
respond at all, as any response confirms that a device exists at the IP address the client tried to
connect to. If no response is made, the router’s IP address appears to be unused. This is known as
stealth mode.
Network Access Rul es 7-7
Page 80

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Stealth mode may cause problems with some applications, such as sending email. If your ISP's
mail server runs on UNIX or Linux (common for large ISPs), that mail server will attempt to send
you traffic whenever you try to se nd mail to it. That traffic is called authentication (or Identd) and
it uses TCP port 113. If your router is in Stealth mode, it will ignore the incoming authentication
packet, and the mail server may not forward your mail. If your routeris not in Stealth-mode,it will
send a NACK-RST packet, which may allow the ISP's m ail server to continue anyway.
If you have enabled stealth m ode and you are having difficulties sending regular email or
NETGEAR logs or alerts out through a mail server run by your ISP, you may want to enable
forwarding of authentication (Identd) traffic in the Add Services menu. Follow these steps:
1. Go to the Add Service menu.
2. Find Authentication in the “Add a known service” dropdown menu.
3. Click the Add button.
4. Go to the Services m enu.
5. Find the Public LAN Server box for Authentication near the bottom.
6. Type in the router’s LAN IP address.
7. Click Update.
This change will allow the router to respond to the ISP mail server’s authentication request.
Node License Count
The Netgear Firewall/VPN Routers provide Internet access sharing capability for multiple users. A
“User” or “Node” is a networked device w ith an IP address, most commonly a computer. The
FR314 and FR318 firewall routers allow a maximum of 8, 20 or 45 users/nodes, while the FV318
allows 20 or 45 users/nodes. The router’s 'node license' is initially the smallest of these numbers,
but can be increased in the amounts shown by purchasing node license upgrades from Netgear.
These node licenses a re counted cumulatively, not simultaneously. When the firewall router is
powered on or rebooted, it starts counting LAN IP addresses against the license. When a computer
or other device connects to the LAN port of the firewall, the router detects it via broadcast, and
stores the computer ’s IP address in m emory. Restarting the router will erase the stored IP
addresses and start the process all over again. When 8, 20, or 45 IP addresses have been stored in
the router’s memory, the router will not permit a ny additional addresses to a ccess the Internet.
Therefore, the router restricts the number of IP addresses on the LAN, not the number of
simultaneous connections to the Internet.
7-8 Network Access Rules
Page 81

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
When the number of IP addresses allowed by your node license is exceeded, the General Status
menu will display the message: “License exceeded: too many IP addresses are in use on your
LAN.”
Excluding Devices from Node License Count
If you have devices on your network that do not need Internet access, such as print servers or file
servers, you should exclude them from counting toward your node license. F or example, the
FR314 allows Internet access for up to 8 users. If your local network contains 8 PCs and a print
server, it is possible that your router will detect the print server and count it toward your node
license. Then only 7 of your users will have Internet a ccess. To avoid this situation, use the
“Exclude IP Address from Node License count” feature in the Firewall Access Services menu to
enter IP addresses to be excluded.
You m ay also discover that a c omputer with two NIC cards can take up two IP licenses. You will
need to reconfigure your network to avoid these problems. Turn off IP forwarding on Windows
NT or 2000 Servers that use two NICs.
Network Access Rul es 7-9
Page 82

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
7-10 Network Access Rules
Page 83

Chapter 8
Logging and Alerting
This chapter describes the Model FR314, FR318 or FV318 firewall router’s logging, alerting and
reporting features.
Viewing the Log
The firewall router maintains an event log that lists potential security threats. You can view this log
from the Web Management Interface or you can specify that the log is automatically sent to an
e-mail address for convenience and archiving.
You can also configure the firewall router to alert you of important events, such as an attack to the
router. The firewall router immediately sends alerts to the specified e-mail address or e-mail pag er.
Logging and Alerting 8-1
Page 84

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
To view the log, click Firewall from the navigation bar at the left and then click the Log subtopic
and then the View Log subtopic. The View Log window opens.
Figure 8-1. View Log Window
The log is displayed in a table. Each log entry contains the date and time of the event and a brief
message describing the event. Some log entries contain additional information such as IP
addresses, port numbers, or notes. You can sort the messages by Time, Message, Source address,
Destinationaddress, or Notes by clicking on the desired column heading. Youcan also specify that
the sorted messages are displayed in either ascending or descending order by clicking the small
arrow to the right of the column heading.
Depending on your Web browser, you should be able to copy entries from the log and paste them
into documents. You can also configure the Log Settings (described on page 8-4) to specify that
the event log is sent to you via e-mail.
Log Messages
The most common messages are:
8-2 Logging and Alerting
Page 85

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
• TCP, UDP, or ICMP packets dropped
When IP packets are blocked by the firewall router, dropped TCP, UDP and ICMP messages
are displayed.The messages include the source and destination IP addressesof the packet. The
TCP or UDP port number or the ICMP code follows the IP address. Log messages usually
include the name of the service in quotation marks.
• Web, FTP, Gopher,or Newsgroup blocked
When a PC on your network attempts to connect to a blocked site or newsgroup, a log is
displayed. The PC’s IP address, Ethernet address, the name of the blocked Web site, and the
Content Filter List Code are displayed. Code definitions for the 12 Content Filter List
categories are shown below.
Table 8-1. Content Filter List Categories
Code Category
a
b Partial nudity
c Full nudity
d Sexual acts
e Gross depictions
f Intolerance
g Satanic/cult
h Drug culture
i Militant/extremist
j Sex education
k Gambling/illegal
l Alcohol/tobacco
Violence/profani ty
For descriptions of these categories, see “C ontent Filter List Category Descriptions”onpage
6-8.
• ActiveX, Java, Cookie or Cod e Archive blocked
When ActiveX, Java or Web cookies are blocked, messages with the source and destination IP
addresses of the connection attempt are displayed.
Logging and Alerting 8-3
Page 86

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
• Ping of Death, IP Spoof, and SYN Flood At tacks
The IP address of the PC under attack and the source of the attack are displayed. In m any
attacks, the source address shown is forged and does not reflect the real source of the attack.
Note: Varying conditions c an produce symptoms that appear as an attack, even when no one is
deliberately a ttacking the LAN. To follow up on a possible attack, contact your ISP to determine
the source of the attack. R egardless of the nature of the a ttack, the LAN is protected; you do not
need to take further steps.
Log Settings
To configure log settings, click Firewall from the navigation bar on the left. Click Log, and the
click Log S ettings. The Log Settings window opens.
Figure 8-2. Log Settings Window
8-4 Logging and Alerting
Page 87

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
The Log Settings options are grouped as follows:
• Sending the Log
These options specify where logs a nd alerts are sent, and are described on page 8-5.
• Automation
These options specify how often logs are sent to the specified e-mail address, and are
described on page 8-5.
• Categories
These options specify what types of messages appear in the log, and are described on page 8-6.
After making any changes to the Log S ettings, click Update. Once the firewall router is updated, a
message confirming the update is displayed at the bottom of the window.
Sending the Log
You c an configure where to send logs and alerts:
•MailServer
Specifies the name or IP address of your outgoing (SMTP) mail server. If you leave this box
blank, log and alert messages are not sent via e-mail to any address.
•SendLogTo
Specifies the e-mail address to which event logs a re sent. After the log is sent, the log is
cleared from the firewall router’s memory. If you leave this box blank, the log is not sent via
e-mail to a ny address.
•SendAlertsTo
Specifies the e-mail address to which alerts are sent when attacks or system events occur. You
can enter a standard e-mail a ddress or the address of an e-mail pager. If you leave this box
blank, alerts are not sent via e-mail to any address.
•E-mailLogNow
Specifies that the log is im mediately sent to the address in the Send Log box. After the log is
sent, the log is cleared f rom the firewall router’s memory.
•ClearLogNow
Deletes the contents of the log.
Automated Sending
You c an specify that logs are automatically sent to the specified e-mail address with these options:
Logging and Alerting 8-5
Page 88

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
•SendLog
Specifies how often to send the logs: Daily, We ekly, or When Full.
•Every
Specifies which day of the week to send the log. R elevant when the log is sent weekly or daily.
•At
Specifies the time of day to send the log. Relevant when the log is sent daily.
If the Weekly or Daily option is selected and the log fills up, the log is automatically e-mailed to
the specified e-mail address.
Note: If the firewall router cannot e-mail the log file, the log buffer may fill up. In this case, the
router overwrites the log and discards its contents.
Log and Alert Categories
You c an define which log messages appear in the firewall router’s Event Log, and which events
trigger an alertmessage.
Log Ca tegories
Use these check boxes to specify which messages appear in the Event Log.
• System Maintenance
When enabled, log messages showing general system activity, such as administrator logins,
automatic downloads of the Content Filter Lists, and system activations, are displayed.
• System Errors
When enabled, log messages showing problems with DNS, E-mail, and automatic downloads
of the Content Filter List a re displayed.
• Blocked Web Sites
When enabled, log messages showing Web sites or ne wsgroups blocked by the Content Filter
List or by customized filtering are displayed.
• Blocked Java, A ctiveX, and Cookies
When enabled, log messages showing blocking of Java, ActiveX, and Cookies a re displayed.
•Attacks
When enabled, log messages showing Denial of Service a ttacks, suc h as SYN Flood, Ping of
Death, and IP spoofing, are generated.
• Dropped TCP
When enabled, log messages showing blocked incoming TCP connections are displayed.
8-6 Logging and Alerting
Page 89

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
• Dropped UDP
When enabled, log messages showing blocked incoming UDP packets are displayed.
• Dropped ICMP
When enabled, log messages showing blocked incoming ICMP packets are displayed.
•DeniedLANIP
When enabled, log messages showing denied LAN IP addresses are displayed.
By default, all messages are shown except Denied LAN IP messages.
Alert Categories
Alerts are events, such as attacks, that warrant immediate attention. When events generate alerts,
messages are immediately sent to the e- mail address specified in the Send Alerts to Box (see page
8-5). You can specify which types of events generate alert messages.
•Attacks
When enabled, log entries categorized as Attacks generate an alert message.
• System Errors
When enabled, log entries categorized as System Errors generate an alert message.
• Blocked Web Sites
When enabled, log entries categorized as Blocked Web Sites generate an alert message.
By default, the Attacks and System Errors check boxes are selected, and the Blocked Web Sites
check box is cleared.
Log Reports
The firewall router is able to perform a rolling analysis of the event log to show the top 25 most
frequentlyaccessed Websites, the top 25 users of bandwidth by IP address, and the top 25 services
consuming the most bandwidth.
To configure log reporting options, click F irewall fr om the navigation bar on the left. Click Log,
and then click Log Reports. The Log Reports window opens.
Logging and Alerting 8-7
Page 90

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Figure 8-3. Log Reports Window
In this window, you can configure how data is collected and view available reports. The Log
Report options are grouped as f ollows:
• Data Collection
•ViewData
These options are described in the following sections.
Data Collection
The Data Collection options are:
• Start Data Collection
Click the Start Data Collection button to begin log analysis. When log analysis is enabled, the
button reads Stop Data Collection.
• ResetData
Click the Reset button to c lear the r eport statistics and begin a new sample period. The sample
period is also reset when data collection is stopped or started, and when the firewall router is
restarted.
8-8 Logging and Alerting
Page 91

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
View Data
You c an select which r eport to view in the “Report to view” list box. The available reports are:
• We b Site Hits
Lists the URLs for the 25 most frequently accessed Web sites and the number of hits to that
site during the current sample period. You can use this report to help ensure that, for the most
part, users are accessing appropriate Web sites. If leisure, sports, or other inappropriate sites
top this list, you may want to consider changing or m ore strictly enforcing your Acceptable
Use Policy.
• Bandwidth Usage by IP Address
Lists IP a ddresses of the 25 top users of Internet bandwidth on your network and the number
of megabytes transmitted during the current sample period.
• Bandwidth Usage by Service
Lists the names of the 25 top Internet services (for example, HTTP, FTP, or RealAudio) and
the number of megabytes r eceived f rom the service during the current sample period. You can
use this report to determine whether services being used are appropriate for your situation. If
services such as video or push broadcasts are consuming a large portion of your available
bandwidth, you may choose to block these services.
To update the selected report, click Refresh Data.
Logging and Alerting 8-9
Page 92

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
8-10 Logging and Alerting
Page 93

Chapter 9
DHCP Server Configuration
This chapter describes how to configure the Model FR314, FR318 or FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall
Router’s DHCP server.
DHCP Server Overview
DHCP, or Dynamic Host ConfigurationProtocol, is a method for distributingTCP/IP settings from
a centralized server to the computers on a network. The firewall router’s DHCP server distributes
IP addresses, gateway addresses, DNS server addresses, and other IP configuration information to
the computers on your LAN.
The firewall router is shipped with its DHCP server enabled and preconfigured to automatically
assign the following TCP/IP configuration information to attached PCs on its local network:
• PC or workstation IP addresses—192.168.0.2 through 192.168.0.9
• Subnet mask—255.255.255.0
• Gateway address (the router)—192.168.0.1
These addresses are part of the IETF-designated private address range for use in private networks.
Note: Make sure there are no other active DHCP servers on the LAN before you connect the
firewall router.
DHCP Server Configuration 9-1
Page 94

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
Configuring the DHCP Server
To modify the configuration of the DHCP server, click General from the navigation bar on the left,
and then click the DHCP subtopic. The DHCP Server C onfiguration window opens.
Figure 9-1. DHCP Server Configuration Window
The DHCP Server configuration options are grouped into these categories:
• General Setup
• DNS Setup
9-2 DHCP Server Con figuration
Page 95

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
•WINSSetup
• Dynamic Ranges
• Static Entries
• Current DHCP Leases
All options are described in the sections that follow.
General Setup
The General Setup options are:
• Enable DHCP Server
By default, the firewall router’s DHCP server is enabled. To disable the DHCP server, clear
this check box.
• Client Default Gateway
In most cases, the firewall router is the only or primary router on a local network. Therefore,
the firewall router assigns its own LAN I P Address as Gatewayto the attached PCs on its local
network by de fault. To specify a nother address, type it in the Client Default Gateway box.
DNS Setup
The DNS Setup options are:
•DomainName
Specifies the registered domain name for your network or Internet service provider. An
example of a domain name is "your-domain.com". If you do not have a domain name, leave
this box blank.
• Set DNS Servers using NETGEAR Firewall’s Network settings
Specifies that the DNS servers that you specified in the Network Settings window are used.
• Specify manually
Specifies that different DNS servers than the ones specified in the Network S ettings window
are used. If you select this check box, enter the ne w DNS Server addresses in the DNS
Server 1, D NS Server 2, and DNS Server 3 boxes.
DNS servers are used by computers on your LAN to resolve domain names to IP addresses.
You only need to enter one DNS Server address, but multiple DNS entries will improve
performance and reliability.
DHCP Server Configuration 9-3
Page 96

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
WINS
WINS, or Windows Internet Naming Service, is a server process for resolving Windows-based
computer names to I P addresses. If a remote network contains a WINS server,your Windows PCs
can gather information from that WINS server about its local hosts. This allows your PCs to
browse that remote network using Ne twork Neighborhood.
If you will be c onnecting to a remote network that operates a WINS server, enter the WINS Server
address(es) in the WINS Server 1 and WINS Server 2 boxes. Otherwise, leave these boxes blank.
Dynamic Ranges
The Dynamic Range is the range of IP addresses dynamically assigned by the DHCP server. The
Dynamic range should be in the same subnet as the firewall router’s LAN IP address.
By default, the firewall router assigns addresses from 192.168.0.2 through 192.168.0.9.Tospecify
another range for assigning addresses, type the beginning IP a ddress in the Range Start box, type
the ending IP address in the Range End box, and then click Update. When the firewall router is
updated, a message confirming the update is displayed at the bottom of the window.
Note: The DHCP server may a ssign a total of 254 dynamic a nd static IP addresses. However, only
eight addresses are allowed to access the I nternet through the firewall router unless you purchase a
user-limit upgrade.
Note: The DHC P Server will not assign an IP address from the dynamic range if the address is
already being used by a computer on your LAN.
Static Entries
The DHCP Server can also assign Static Entries, or static IP addresses, to computers on the LAN.
With a Static Entry, the PC will always receive the same IP address each time it access the DHCP
server. Static IP addresses should be assigned to servers that require permanent IP settings.
Note: When a ssigning a Static Entry, choose an IP address from the firewall router’s LAN subnet
(such as 192.168.0.n), but do not choose an address within the Dyna mic Range defined in the
previous section.
To assign static IP addresses:
1. In the Static IP Address box, type the IP address to assign to your computer or server.
2. In the Ethernet Address box, type the Ethernet (MAC) address of your computer or server.
9-4 DHCP Server Con figuration
Page 97

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV 318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
3. Click Update.
When the firewall router is updated, a message confirming the update is displayed at the
bottom of the window.
4. Continue this process until you have added all the necessary static entries.
To remove a static address:
1. Select the address from the list of static entries.
2. Click Delete Static.
When the static entry is deleted, a message confirming the update is displayed at the bottom of the
window.
Current DHCP Leases
IP addresses a ssigned (“leased”) by the DHCP Server a re shown in the Current DHC P Leases box.
Each entry lists the IP address, the Ethernet M AC address, and whether the entry is Dynamic or
Static. To cancel a current lease, select the entry a nd click the Delete button.
If the firewall router is rebooted a fter assigning an IP address, the a ddress will not appear in the
Current DHCP Leases box until the lease is renewed. Addresses assigned by the firewall r outer
have a lease period of one week.
DHCP Server Configuration 9-5
Page 98

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
9-6 DHCP Server Con figuration
Page 99

Chapter 10
Virtual Private Networking
This chapter describes how to use the the virtual private networking (VPN) features of the FR318
and FV318. A VPN provides secure, encrypted communication between your local network and a
remote network.
Note: In order to perform the VPN function, the FR318 must be upgraded by purchasingthe VPN
Upgrade Option. The FV318 does not require an upgrade. The FR314 does not support VPN.
What is a VPN
A VPN can be thought of as a secure tunnel passing through the Internet, connecting two devices
such as a PC or router,which form the two tunnel e ndpoints. At one endpoint, data is encapsulated
and encrypted, then transmitted through the Internet. At the far endpoint, the data is received,
unencapsulated a nd decrypted. Although the data may pass through several I nternet routers
between the endpoints, the encapsulation and encryption forms a virtual “tunnel” for the data.
DATA PACKET
ENCRYPTION AND ENCAPSULATION
INTERNET
TRANSMISSION
VIA INTERNET
UNENCAPSULATION AND DECRYPTION
DATA PACKET
Virtual Private Networking 10-1
Page 100

Reference Guide for the Model FR314, FR318 and FV318 Cable/DSL Firewall and VPN Routers
The tunnel e ndpoint device, which encodes or decodes the data, can either be a PC running VPN
client software or a VPN-enabled router or server. S everal software standards exist for VPN data
encapsulation and encryption, such as PPTP and IPSec. Your Netgear Firewall/VPN Router uses
IPSec.
To set up a VPN connection, you must configure each endpoint with specific identification and
connection information describing the other endpoint. This set of configuration information
defines a security association ( SA) between the two points. The FR318 with the VPN option
installed is capable of creating one security association. The FV318 is capable of five Security
Associations.
Two common applications of VPN are
• secure access from a remote PC, such as a telecommuter connecting to a n office network
• secure access between two networks, such as a branch office and a main office
These applications are described be low.
Accessing Network Resources from a VPN Client PC
VPN client remote access allows a remotePC to connect to your network from any location on the
Internet. In this case, the remote PC is one tunnel endpoint, running VPN client software. The
Netgear VPN-enabled router on your network is the other tunnel endpoint, as shown below.
VPN
CLIENT
ATLANTA BA Y
SANTACL ARA
INTERNET
ROUTER
LAN
In some cases, the client P C may connect to the Internet through a local non-VPN-enabled router,
as shown below:
CLIENT
ATLANTA BA Y
SANTACL ARA
SIMPLE
ROUTER
INTERNET
VPN
ROUTER
LAN
If the non-VPN router is performing NAT, it must support “VPN-passthrough” of IPSec-encoded
data.
10-2 Virtual Private Networking
 Loading...
Loading...