Page 1

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
User Manual
350 East Plumeria Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
USA
November 2011
202-10604-02
v1.0
Page 2

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
© 2011 NETGEAR, Inc. All rights reserved
No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated
into any language in any form or by any means without the written permission of NETGEAR, Inc.
Technical Support
Thank you for choosing NETGEAR. To register your product, get the latest product updates, get support online, or
for more information about the topics covered in this manual, visit the Support website at
http://support.netgear.com.
Phone (US & Canada only): 1-888-NETGEAR
Phone (Other Countries): Check the list of phone numbers at
http://support.netgear.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/984
Trademarks
NETGEAR, the NETGEAR logo, and Connect with Innovation are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of
NETGEAR, Inc. and/or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries. Information is subject to change
without notice. Other brand and product names are registered trademarks or trademarks of their respective
holders. © 2011 NETGEAR, Inc. All rights reserved.
Statement of Conditions
To improve internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, NETGEAR reserves the right to make changes
to the products described in this document without notice. NETGEAR does not assume any liability that may occur
due to the use, or application of, the product(s) or circuit layout(s) described herein.
2
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1 Internet Configuration
Hardware Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Router Stand . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Router Front Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Router Back Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Router Label. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
System Setup. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Position Your Wireless Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Typical Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Log In to Your Wireless-N Modem Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Use the Setup Wizard after Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Fixed IP (Static) Account Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Manually Configure Your Internet Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Broadband Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Basic ISP Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
ADSL Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Mobile Broadband Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Chapter 2 Wireless Settings
Wireless Adapter Compatibility. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Preset Security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Security Basics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Turn Off Wireless Connectivity. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Disable SSID Broadcast. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Restrict Access by MAC Address. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Wireless Security Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Add Clients (Computers or Devices) to Your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Manual Method. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Wireless Settings Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Consider Every Device on Your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
View or Change Wireless Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Wireless Settings Screen Fields. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Change WPA Security Option and Passphrase. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Set WEP Encryption and Passphrase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Wireless Guest Networks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Chapter 3 Protecting Your Network
Protect Access to Your Wireless-N Modem Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
3
Page 4

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Change the Built-In Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Change the Administrator Login Time-Out. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Block Keywords, Sites, and Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Block Sites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Block Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Set Times and Schedule Firewall Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Set Your Time Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Schedule Firewall Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
View, Select, and Save Logged Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Examples of Log Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Enable Security Event Email Notification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Live Parental Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Chapter 4 Managing Your Network
Upgrade the Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Manually Check for Firmware Upgrades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Back Up, Restore, and Erase Your Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
Back Up the Configuration to a File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Restore the Configuration from a File. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Erase the Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Router Status and Usage Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .56
View Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
View the Connection Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
View Attached Devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Run Diagnostics and Reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
Configure Remote Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Chapter 5 USB Storage
USB Drive Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
File-Sharing Scenarios. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Share Photos with Friends and Family. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Store Files in a Central Location for Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Share Large Files with Colleagues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
USB Storage Basic Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Edit a Network Folder. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
Configure USB Storage Advanced Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
Create a Network Folder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Unmount a USB Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Specify Approved USB Devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .72
Connect to the USB Drive from a Remote Computer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Locate the Internet Port IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Access the Router’s USB Drive Remotely Using FTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Connect to the USB Drive with Microsoft Network Settings. . . . . . . . . . . .74
Enable File and Printer Sharing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
Chapter 6 Advanced Configuration
4
Page 5

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Configure WAN Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76
Set Up a Default DMZ Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
Configure Dynamic DNS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78
Configure LAN Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Configure DHCP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
Configure Reserved IP Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .81
Set Up Quality of Service (QoS). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82
Configure QoS for Internet Access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82
Advanced Wireless Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Restrict Wireless Access to Your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Configure WPS Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Use Static Routes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87
Static Route Example. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87
Configure Static Routes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88
Configure Universal Plug and Play. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .89
Build Wireless Bridging and Repeating Networks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .90
Point-to-Point Bridge Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .92
Multi-Point Bridge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .93
Repeater with Wireless Client Association. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .94
Port Forwarding and Port Triggering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .95
Port Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .96
Port Triggering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .96
Advanced USB Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
Traffic Meter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .98
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
Basic Functioning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .101
Welcome Screen Displays instead of Router Main Menu. . . . . . . . . . .101
Troubleshoot with the LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .101
Cannot Log In to the Wireless-N Modem Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103
Troubleshoot the Internet Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .104
DSL Link. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .104
Internet Port LED Is Red. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .105
Connecting to Mobile Broadband . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .105
Obtain an Internet IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .105
Troubleshoot PPPoE or PPPoA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .106
Troubleshoot Internet Browsing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .106
Troubleshoot a TCP/IP Network Using the Ping Utility. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107
Test the LAN Path to Your Wireless-N Modem Router . . . . . . . . . . . .107
Test the Path from Your Computer to a Remote Device . . . . . . . . . . .107
Restore the Default Configuration and Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .108
Use the Restore Factory Settings Button to Reset the Router. . . . . . .108
Problems with Date and Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .108
Appendix A Technical Specifications and Factory Default Settings
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .110
Factory Default Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .112
5
Page 6

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Appendix B Wall-Mounting
Appendix C Notification of Compliance
Index
6
Page 7

1. Internet Configuration
This chapter describes how to configure your N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router
DGN2200M Mobile Edition Internet connection. For help with installation, see the N300 Wireless
ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition Installation Guide.
This chapter covers the following topics:
• Hardware Features
• System Setup
• Log In to Your Wireless-N Modem Router
• Use the Setup Wizard after Installation
• Manually Configure Your Internet Settings
For more information about the topics covered in this manual, visit the support website at
http://support.netgear.com.
1
7
Page 8

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Hardware Features
This section acquaints you with the physical aspects of your N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem
Router.
Router Stand
Since the router is a vertical-only device, use the stand to position your wireless modem
router upright.
To assemble the router and its stand:
1. Insert the tabs of the stand into the slot on the bottom of your router.
2. Place your router near an AC power outlet in a location where you can connect cables as
needed for your home network.
If you are planning to connect to the Internet using mobile broadband, the router needs to
be located where you can receive a strong mobile broadband signal while indoors.
To mount the router to a wall, see Wall-Mounting on page 114.
For additional considerations on router placement, see Position Your Wireless Router on
page 13.
Internet Configuration
8
Page 9
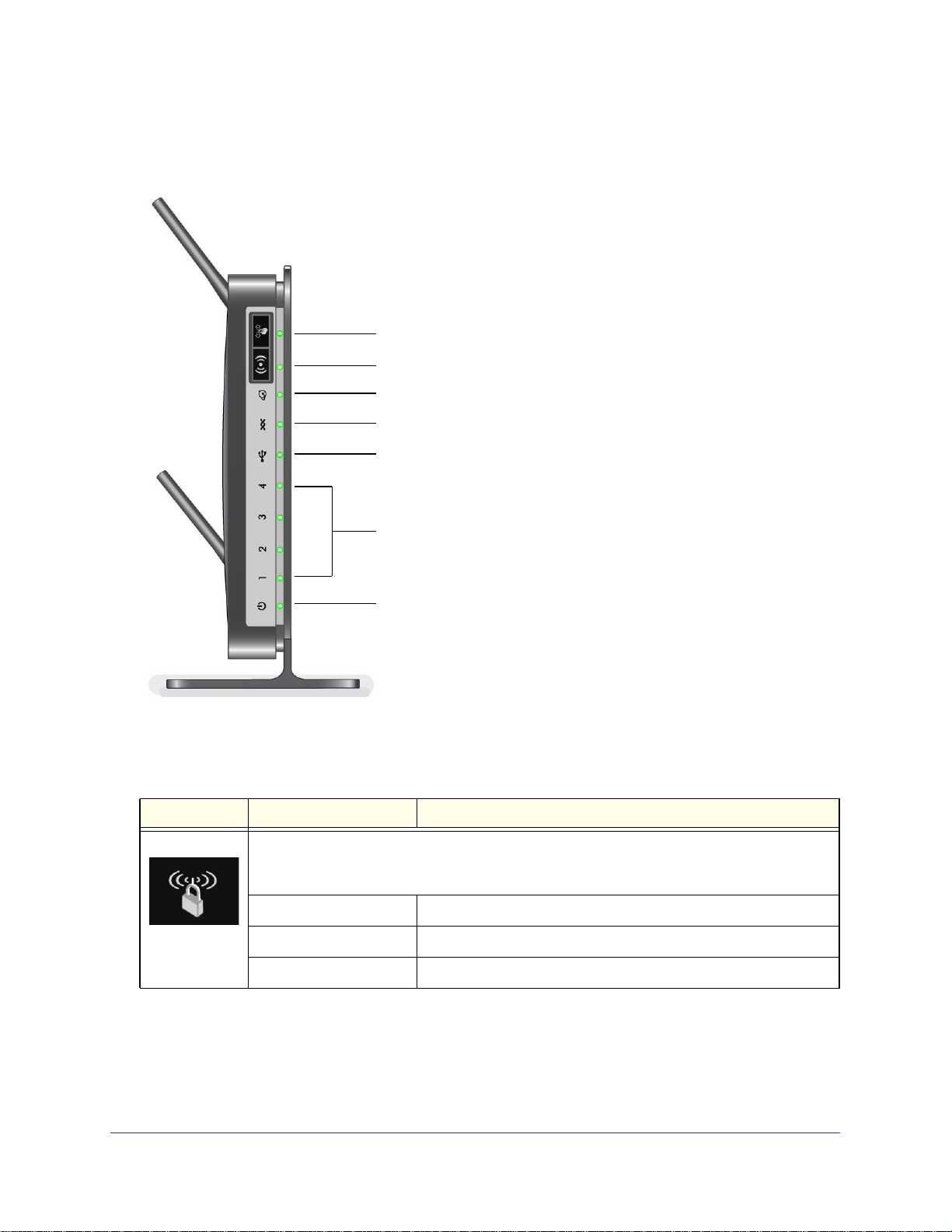
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Router Front Panel
The wireless modem router front panel contains control buttons and status LEDs.
WPS
WiFi On/Off
Internet
DSL
USB Mobile Broadband
Ethernet LAN Ports
Power
You can use the LEDs to verify status and connections. The following table lists and
describes each LED and button on the front panel of the wireless modem router.
Table 1. Front panel button and LED descriptions
Button/LED Activity Description
WPS
Press this button to open a 2-minute window for the wireless modem router to connect with
other WPS-enabled devices. For more information about using the WPS method to implement
security, see Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) Method on page 32.
Solid green WPS wireless security is being enabled.
Blinking green The device is in the 2-minute interval to synchronize security.
Off WPS is not being set or enabled.
Internet Configuration
9
Page 10
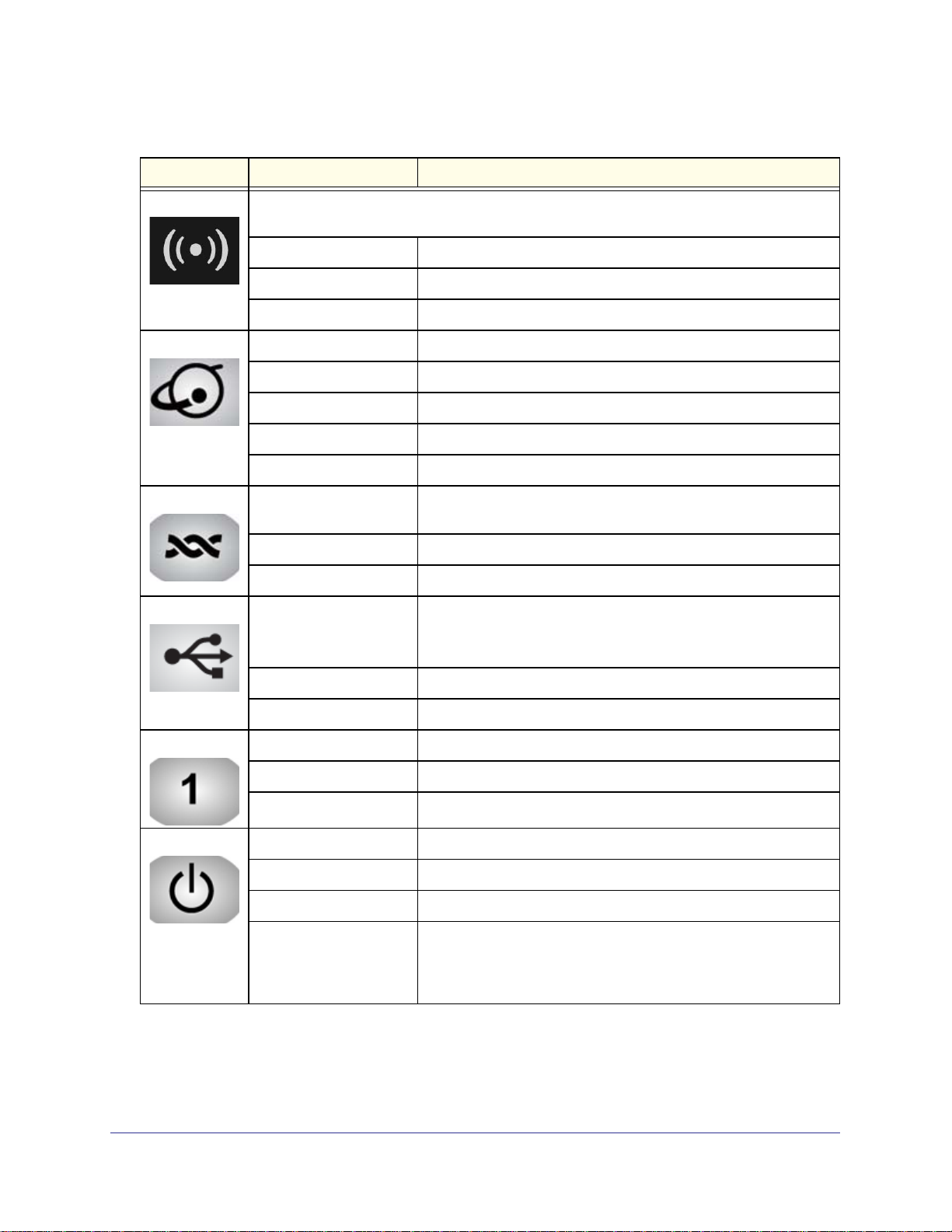
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Table 1. Front panel button and LED descriptions (continued)
Button/LED Activity Description
WiF Turn the wireless radio in the wireless modem router on and off. The wireless radio is on by
default. The LED located below this button indicates if the wireless radio is on or off.
Solid green Indicates that the wireless port is initialized.
Blinking green Data is being transmitted or received over the wireless link.
Off The wireless access point is turned off.
Internet Port
DSL
USB
LAN Ports
Solid green There is an Internet session.
Solid red There is no Internet connection.
Blinking green Data is being transmitted over the Internet connection.
Blinking green and red Traffic meter limit has been reached.
Off No Internet connection detected or device in bridge mode.
Solid green The ADSL port is synchronized with an ISP’s network access
device.
Blinking green Indicates ADSL training—ADSL is synchronizing with the DSLAM.
Off The unit is off, or there is no IP connection.
Off • No USB device connected.
• “Safely Remove Hardware” has been activated.
• An error has occurred with the device.
Solid blue USB device is ready to use.
Blinking blue USB device is in use.
Solid green The local Ethernet ports have detected wired links with computers.
Blinking Data is being transmitted or received.
Power
Off No link is detected on these ports.
Solid green The router is powered on and operating normally.
Solid amber POST (power-on self-test) in progress.
Off Power is not supplied to the router.
Restore Factory Settings
button
Press the Restore Factory Settings button for 6 seconds. The
Power LED lights briefly. When the button is released, the LED
blinks red three times and then turns green as the router resets to
the factory defaults.
Internet Configuration
10
Page 11
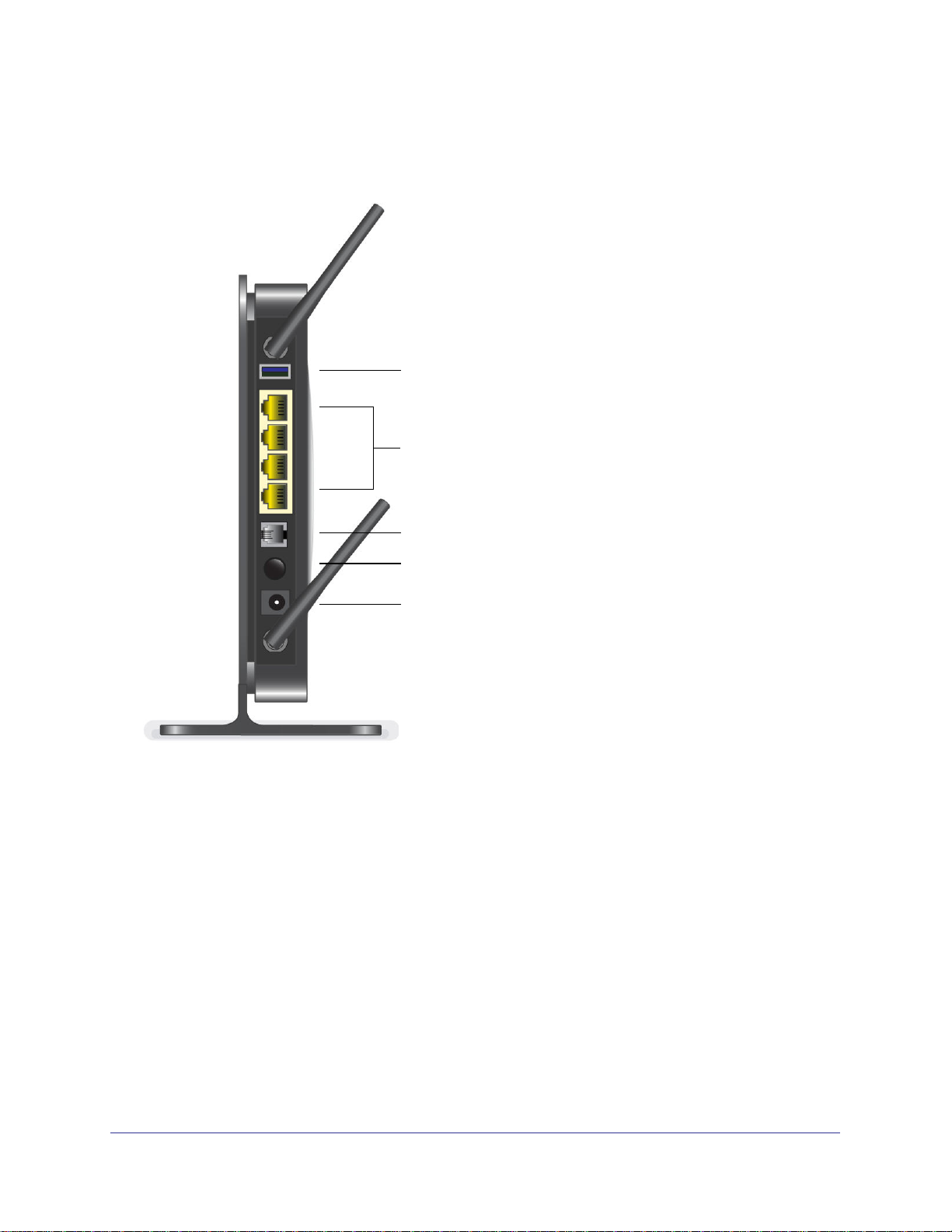
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Router Back Panel
The back panel of the wireless modem router contains port connections.
USB mobile broadband
Ethernet LAN ports
DSL
Power On/Off button
Power adapter input
Internet Configuration
11
Page 12
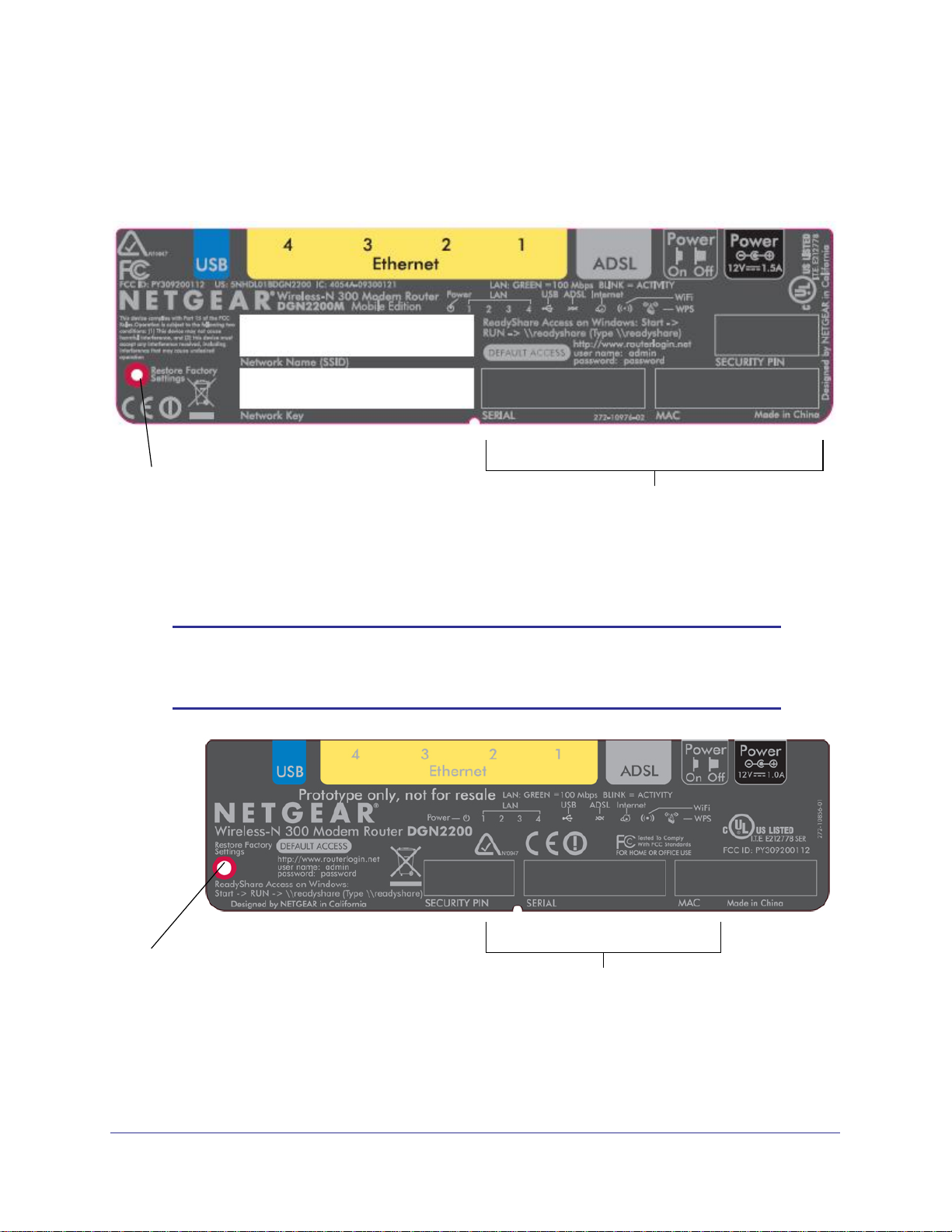
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
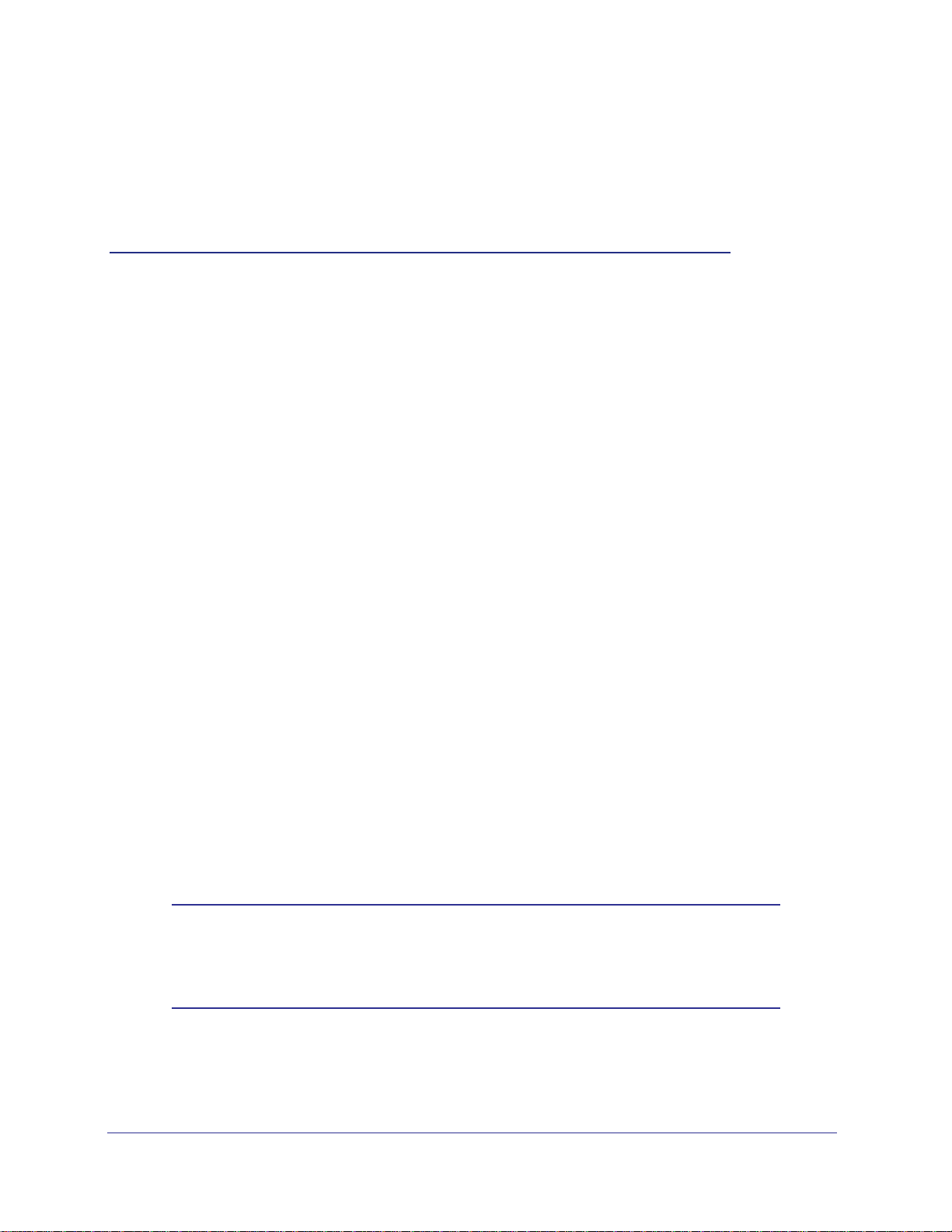
Router Label
The label on the left side of the wireless modem router shows the router’s MAC address,
serial number, security PIN, and factory default login information.
Restore Factory
Settings: Press for
6 seconds.
Router information
- Default access address
- Default user name and password
- Security PIN
- Serial number
- MAC address
Note: If the label on your router looks like the one in the following figure,
then your router has no preset wireless security. You need to set the
wireless security to protect your network.
Restore Factory
Settings: Press for
6 seconds.
Router information
- Default access address
- Default user name and password
- Security PIN
- Serial number
- MAC address
Internet Configuration
12
Page 13
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
System Setup
The N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition requires the
considerations described in the following sections for successful operation.
• Position Your Wireless Router
• Typical Systems on page 14
Position Your Wireless Router
The wireless modem router lets you access your network from virtually anywhere within the
operating range of your wireless network. However, the operating distance or range of your
wireless connection can vary significantly depending on the physical placement of your
router. For example, the thickness and number of walls the wireless signal needs to pass
through might limit the range. For best results, place your router:
• Near the center of the area where your computers and other devices will operate,
preferably within line of sight to your wireless devices.
• Accessible to an AC power outlet and near Ethernet cables for wired computers.
• In an elevated location such as a high shelf, keeping the number of walls and ceilings
between the wireless modem router and your other devices to a minimum.
• Away from electrical devices that are potential sources of interference, such as ceiling
fans, home security systems, microwaves, or the base for a cordless phone.
• Away from any large metal surfaces, such as a solid metal door or aluminum studs. Large
expanses of other materials such as glass, insulated walls, fish tanks, mirrors, brick, and
concrete can also affect your wireless signal.
Note: Failure to follow these guidelines can result in significant
performance degradation or an inability to wirelessly connect to the
Internet.
Internet Configuration
13
Page 14
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Typical Systems
The wireless modem router allows you to have the types of systems described in the
following sections. Your choice of system will determine how you configure the settings
described in Broadband Settings on page 21.
• ADSL Only
• Mobile Broadband Only on page 15
• ADSL with Failover to Mobile Broadband on page 16
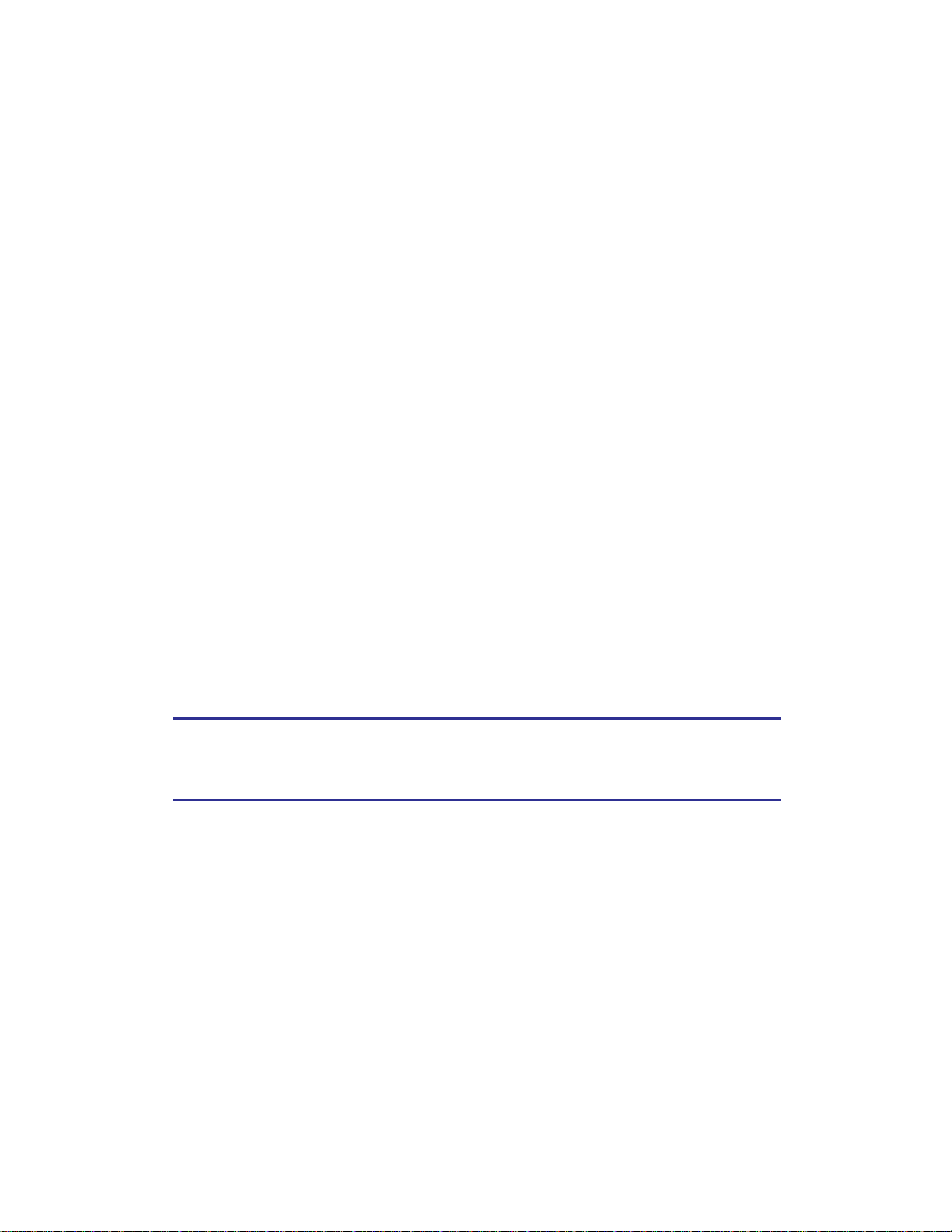
ADSL Only
Note: Incorrectly connecting a filter to your wireless modem router will
block your ADSL connection.
Internet Configuration
14
Page 15
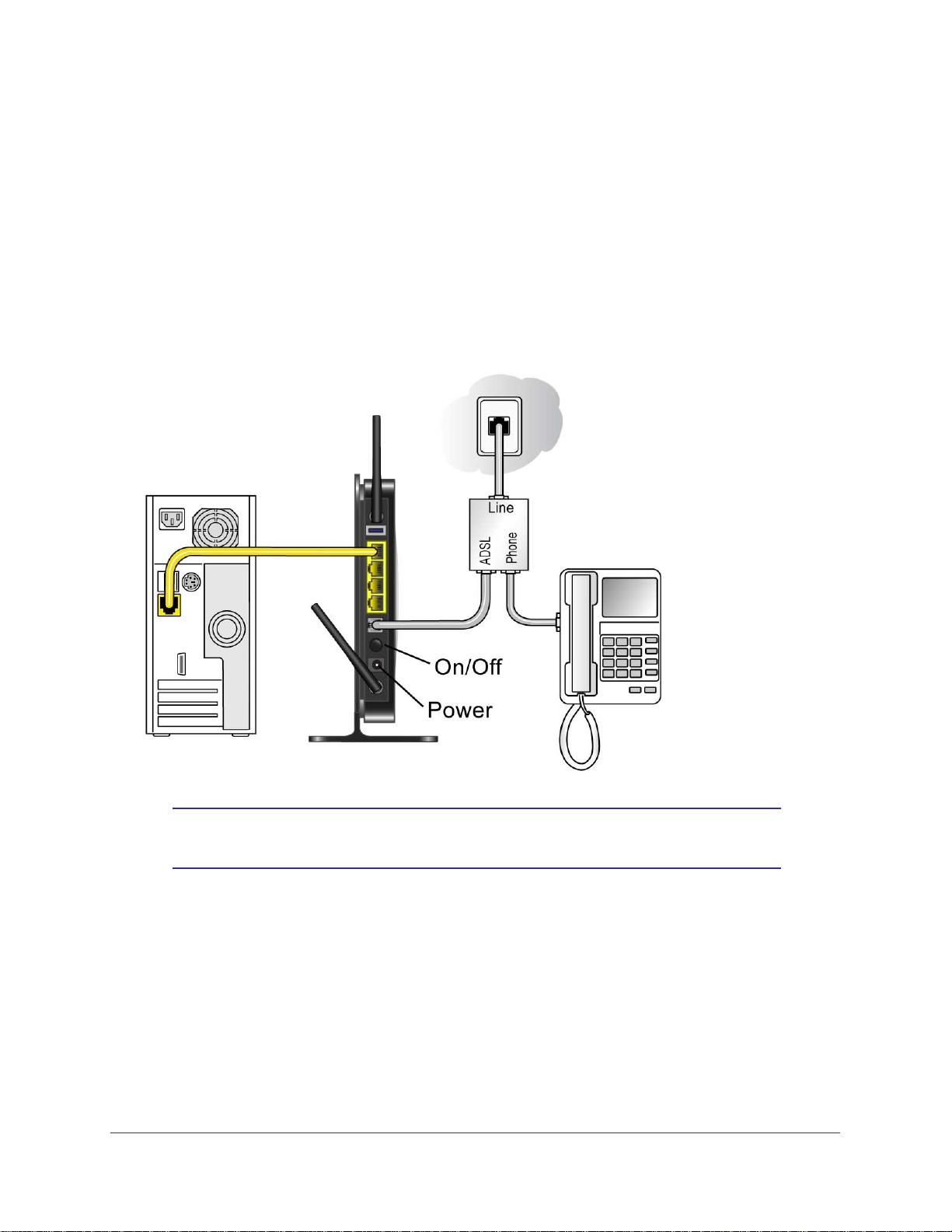
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Mobile Broadband Only
Note: Because the USB port on the wireless modem router is used for
connecting the broadband mobile modem cable, you are not able to
use the USB port for both a ReadyShare storage and a broadband
mobile Internet connection at the same time even when using a USB
hub to fan out the USB port.
Internet Configuration
15
Page 16
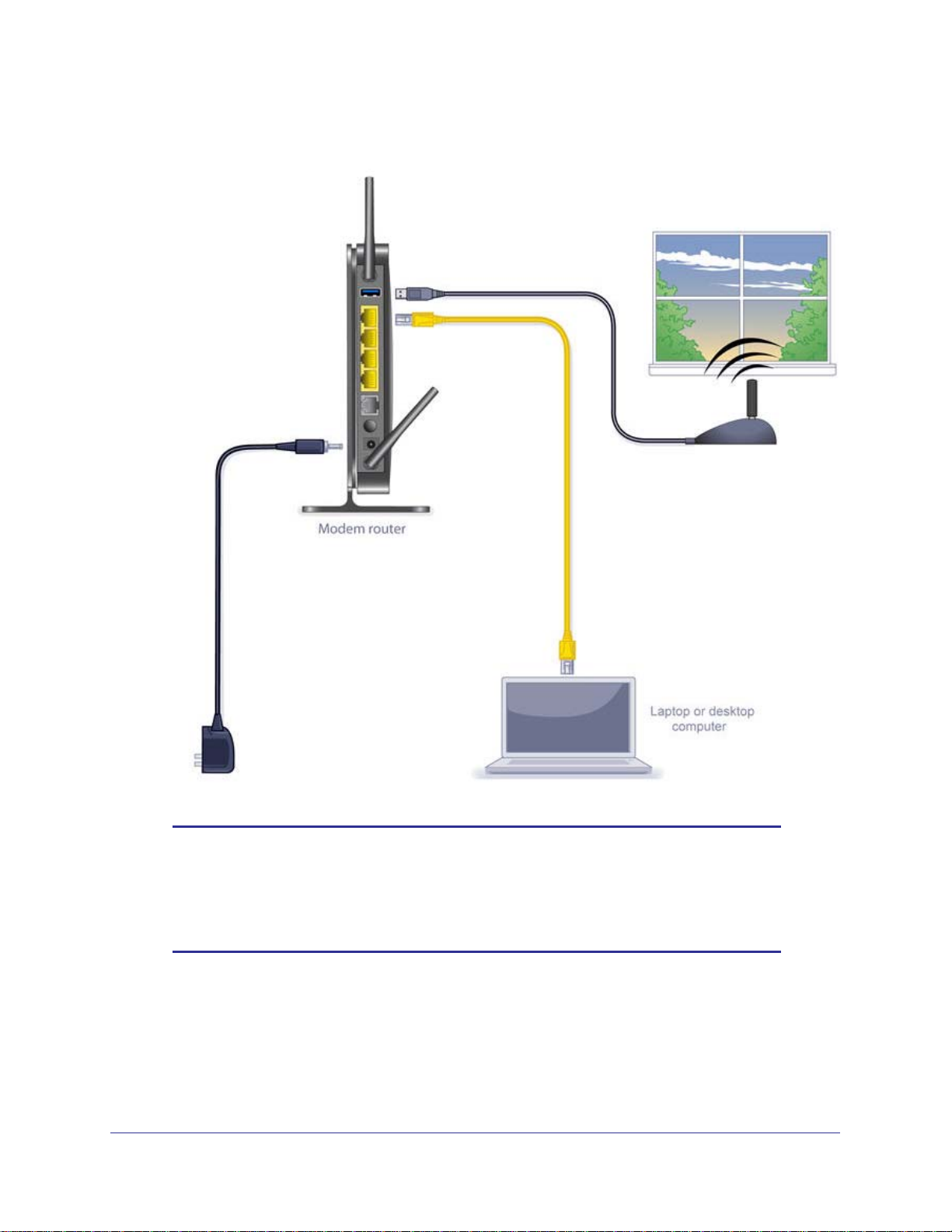
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
ADSL with Failover to Mobile Broadband
Note: Incorrectly connecting a filter to your wireless modem router will
block your ADSL connection.
Note: Because the USB port on the wireless modem router is used for
connecting the broadband mobile modem cable, you are not able to
use the USB port for both a ReadyShare storage and a broadband
mobile Internet connection at the same time even when using a USB
hub to fan out the USB port.
Internet Configuration
16
Page 17
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Log In to Your Wireless-N Modem Router
When you first connect to your wireless modem router during installation, a Setup Wizard
displays. For help using the Setup Wizard to configure your Internet and wireless network,
see the N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition Installation
Guide.
After the initial configuration, you can log in to the wireless modem router to view or change
its settings, and to access the Knowledge Base and documentation.
Note: Your computer needs to be configured for DHCP.
When you have logged in, if you do not click Logout, the wireless modem router waits for 5
minutes after no activity before it automatically logs you out.
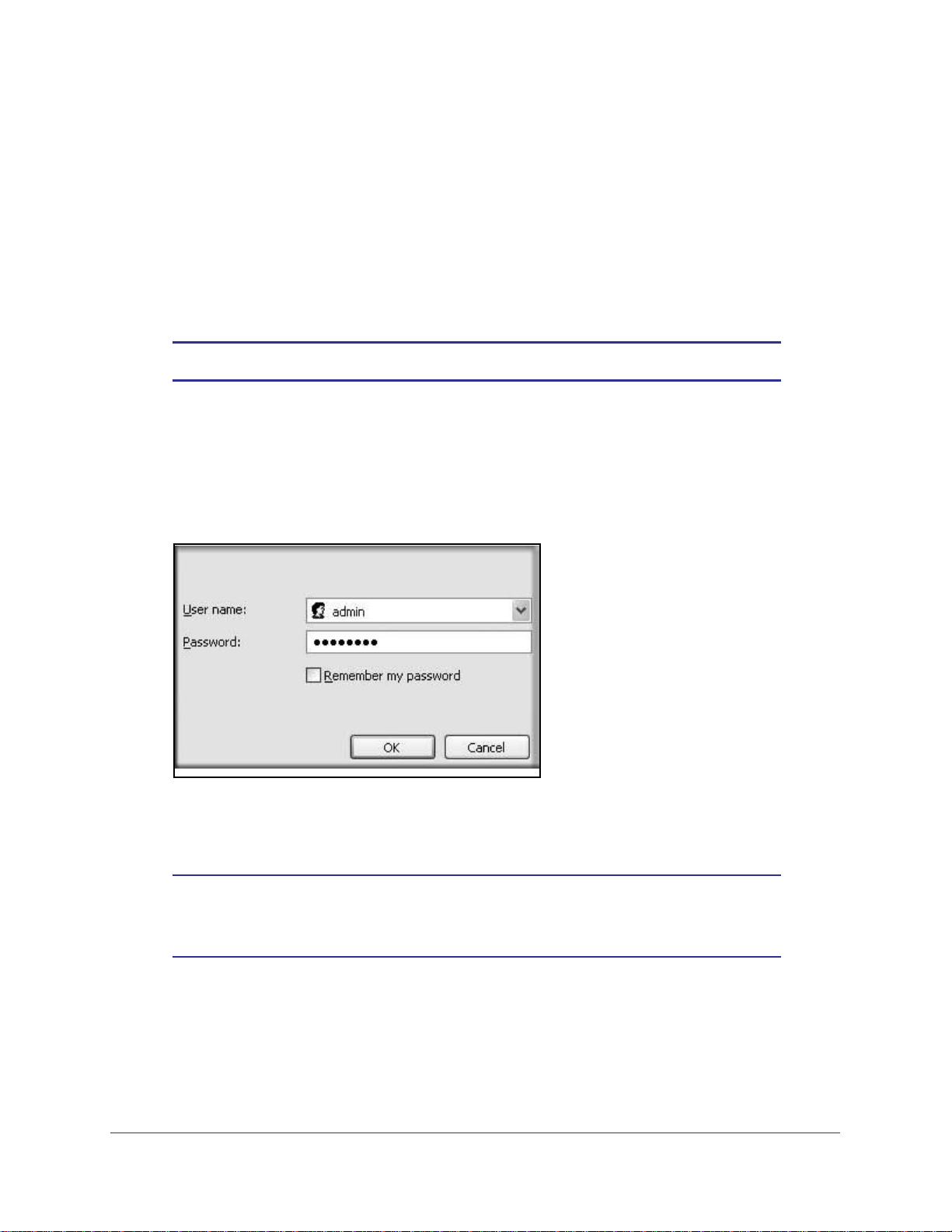
To log in to the wireless modem router:
1. Type http://www.routerlogin.net in the address field of your browser, and then press
Enter or Return. A login window displays:
2. Enter admin for the user name and your password (or the default, password). For
information about how to change the password, see Change the Built-In Password on
page 42.
Note: If you changed your password and do not remember what it is, you
can restore the wireless modem router to its factory settings. See
Factory Default Configuration on page 112.
3. If the router has not been configured, the Smart Wizard screen displays. After the router has
been configured, one of the following screens displays:
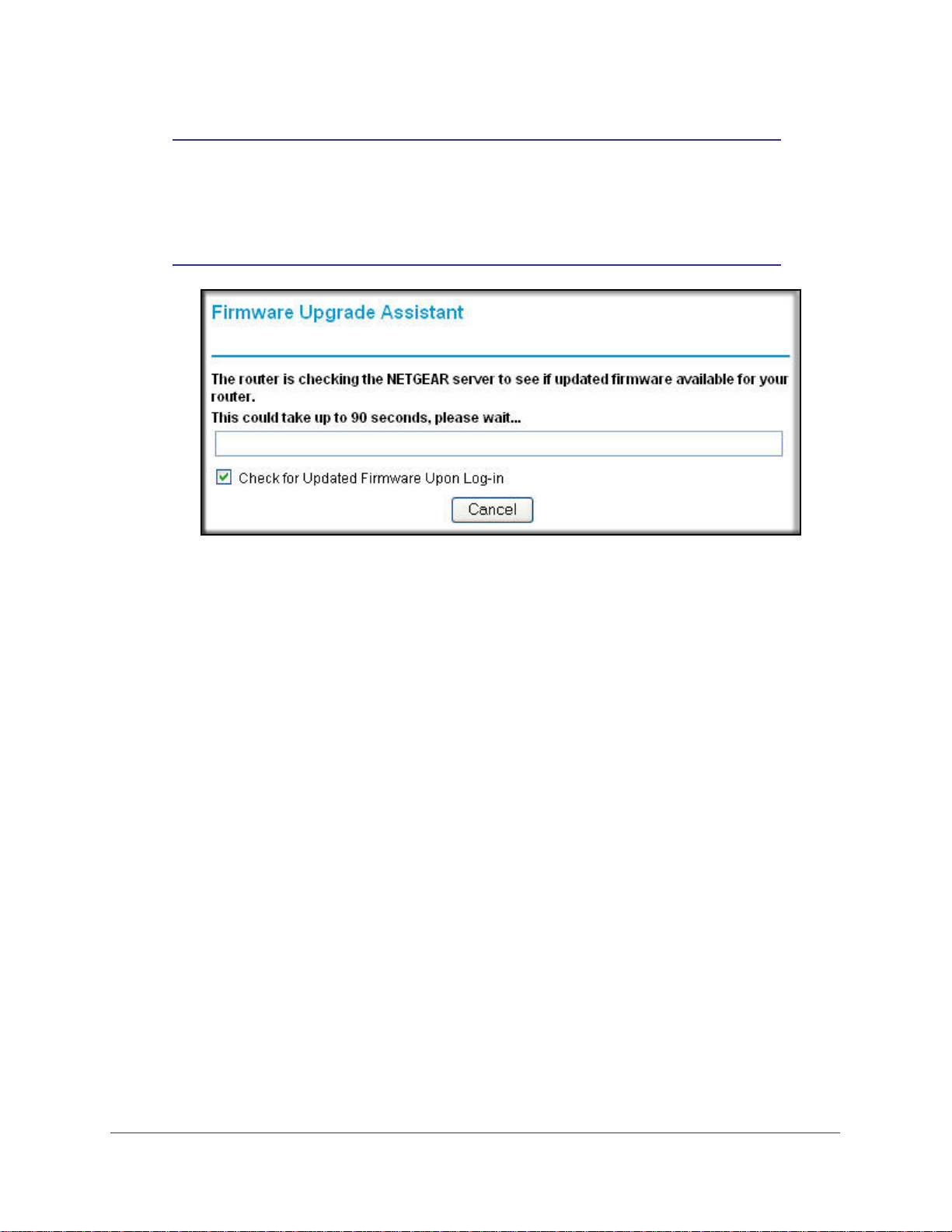
• Firmware Upgrade Assistant screen. After initial setup, the Firmware Upgrade
Assistant screen displays unless the Check for Updated Firmware Upon Log-in check
box is cleared.
Internet Configuration
17
Page 18
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Note: You can disable this automatic checking and updating feature during
future logins by clearing the Check for Updated Firmware Upon
Log-in check box, but NETGEAR recommends that you keep this
feature enabled to ensure that your router is using the latest updated
firmware.
• Router Status screen. The Router Status screen displays the current router
connection status. See Router Status and Usage Statistics on page 56.
4. You can use different methods to configure your router.
• Select Setup Wizard from the router menu to set up your Internet connection and
wireless network configuration. See Use the Setup Wizard after Installation on
page 19.
• You can manually configure the router settings. See Manually Configure Your Internet
Settings on page 21.
Internet Configuration
18
Page 19

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Use the Setup Wizard after Installation
The Setup Wizard can check your Internet connection for servers and protocols to determine
your ISP configuration. You can also manually specify your Internet connection settings in the
Basic Settings screen.
Note: The Setup Wizard is also called the Configuration Assistant on
some systems.
To use the Setup Wizard:
1. From the top of the modem router main menu, select Setup Wizard.
2. Click Next.
The Setup Wizard prompts you to set up your Internet connection and wireless network
as described in the N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Installation Guide.
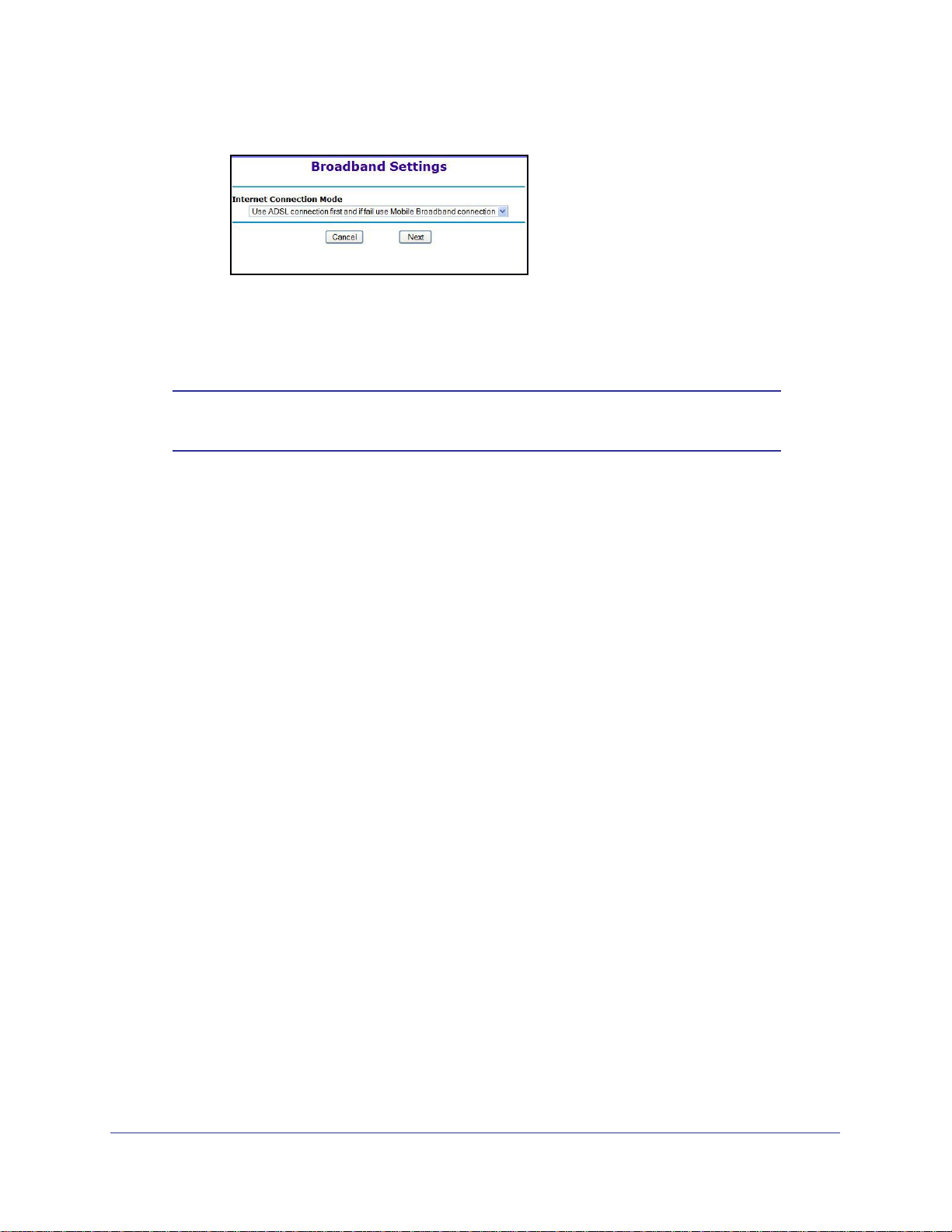
a. Select your Internet connection mode:
• Use ADSL first and if fail use Mobile Broadband connection
• Always use Mobile Broadband connection
Internet Configuration
19
Page 20
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
• Always use ADSL connection
b. Click Next.
c. Select your country and then your Internet service provider information.
d. Click Next.
Note: When failover mode is selected, ADSL is configured first, and then
mobile broadband is configured second.
3. Depending on the type of connection, you are prompted to enter your ISP settings.
• For PPPoE or PPPoA, enter the login user name and password. These fields are
case-sensitive.
• For a dynamic IP account setup, no entries are needed.
• For IP over ATM Classical IP assignment (RFC1577), enter the assigned IP address,
subnet mask, and the IP address of your ISP’s primary DNS server. If a secondary
DNS server address is available, enter it also. DNS servers translate an Internet
name such as www.netgear.com to a numeric IP address.
• For help with a static IP address, see Fixed IP (Static) Account Setup on page 20.
4. At the end of the Setup Wizard, click Test to check your Internet connection. If you have
trouble connecting to the Internet, see Troubleshooting on page 100.
Fixed IP (Static) Account Setup
To set up a fixed IP (static) account:
1. If required, enter the account name and domain name from your ISP.
2. Select Use Static IP Address or Use IP Over ATM (IPoA—RFC1483 Routed) according to
the information from your ISP. If you select IPoA, the router will detect the gateway IP
address, but you still need to provide the router IP address.
3. Enter your assigned IP address, subnet mask, and the IP address of your ISP’s gateway
wireless modem router. This information should have been provided to you by your ISP.
4. Enter the IP address of your ISP’s primary DNS server. If a secondary DNS server address
is available, enter it also. DNS servers translate an Internet name such as www.netgear.com
to a numeric IP address.
Internet Configuration
20
Page 21

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Manually Configure Your Internet Settings
For you to connect to the network, an active broadband service account is required. Contact
your ISP for your user name, password, and the network name. You also need to configure
some or all of the settings described in the following sections, depending on how you have
chosen to connect to the Internet:
• Broadband Settings
• Basic ISP Settings on page 22
• ADSL Settings on page 25 (not required if using mobile broadband connection only)
• Mobile Broadband Settings on page 26 (not required if using ADSL connection only)
Broadband Settings
To manually configure your broadband Internet settings:
1. Log in to the router as described in Log In to Your Wireless-N Modem Router on
page 17.
2. From the main menu, select Broadband Settings.
3. Adjust the settings as needed based on your Internet connection. The fields in this screen
are described in Table 2.
4. The following buttons are available:
• Apply. Apply the changes that you made.
• Cancel. Discard changes.
Internet Configuration
21
Page 22
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
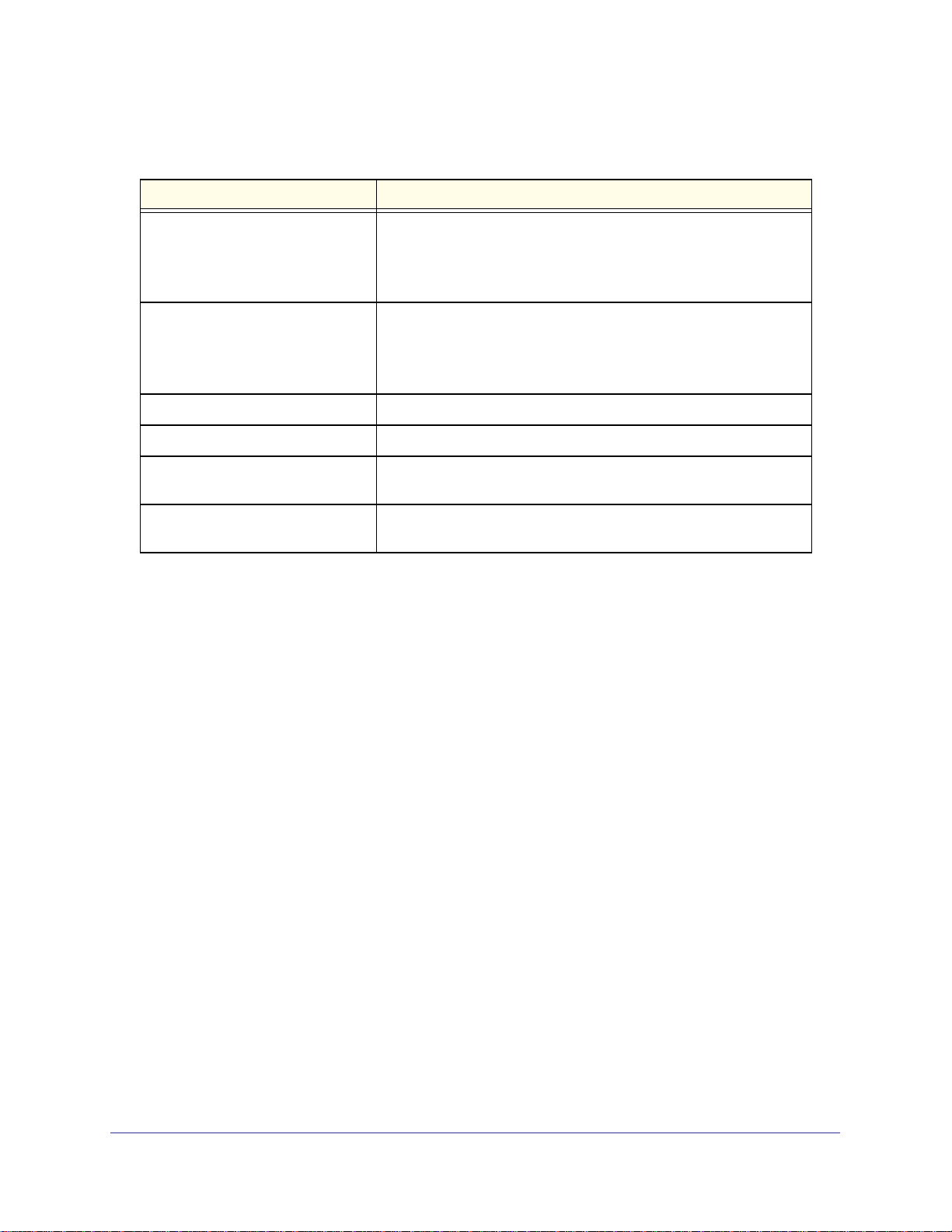
Table 2. Broadband Settings fields
Fields and check boxes Description
Internet Connection Mode The choices are:
• Use ADSL first and if fail use Mobile Broadband connection
• Always use Mobile Broadband connection
• Always use ADSL connection
Failover Detection Method
Retry Interval is
Failover after
Resume after
Enable Hardware link detection Enter when to fail over when the Ethernet link is dropped. This is
1. This field is available only when the internet connection Mode is Use ADSL first and if fail use Mobile
Broadband connection.
1
Enter the retry interval.
1
Enter how many retry attempts to make before failing over.
1
Enter how long to wait for the primary link to be stabilized before
1
Select the failover method, and enter the related information:
• DNS lookup using WAN DNS Server
• Perform a DNS lookup by a hostname
• Ping this IP address
resuming use of the primary link.
independent of the DNS or Ping detection method.
Basic ISP Settings
To view or configure the basic settings:
1. From the router menu, select Basic Settings.
Internet Configuration
22
Page 23

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
2. Select Yes or No depending on whether your ISP requires a login. This selection changes
the fields available on the Basic Settings screen.
ISP does not require login ISP does require login
• Yes. If your ISP requires a login, select this radio button.
• No. If your ISP does not require a login, enter the account name, if required, and the
domain name, if required.
3. Enter the settings for the IP address and DNS server. If you enter or change a DNS
address, restart the computers on your network so that these settings take effect.
4. If no login is required, you can specify the MAC Address setting.
5. Click Apply to save your settings.
6. Click Test to test your Internet connection. If the NETGEAR website does not display within
1 minute, see Troubleshoot the Internet Connection on page 104.
Internet Configuration
23
Page 24
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
When your Internet connection is working, you do not need to launch the ISP’s login program
on your computer to access the Internet. When you start an Internet application, your
wireless modem router automatically logs you in.
Table 3. Basic Settings screen fields
Settings Description
Does Your ISP Require a Login? • Yes
• No
These fields
display only if no
login is required.
These fields
display only if
your ISP
requires a login.
Internet IP Address • Get Dynamically from ISP. Your ISP uses DHCP to assign your IP
Account Name
(If required)
Domain Name
(If required)
Login The login name provided by your ISP. This is often an e-mail address.
Password The password that you use to log in to your ISP.
Service Name If your ISP provided a service name, enter it here.
Connection
Mode
Idle Timeout (In
minutes)
Enter the account name provided by your ISP. This might also be called the
host name.
Enter the domain name provided by your ISP.
Select the connection mode: Always on, Dial on Demand, or Manually
Connect.
If you want to change the Internet login time-out, enter a new value in
minutes. This determines how long the wireless modem router keeps the
Internet connection active after there is no Internet activity from the LAN.
Entering an Idle Timeout value of 0 (zero) means never log out.
address. Your ISP automatically assigns these addresses.
• Use Static IP Address. Enter the IP address that your ISP assigned.
Also enter the IP subnet mask and the gateway IP address. The gateway
is the ISP’s wireless modem router to which your wireless modem router
will connect.
• Use IP Over ATM (PoA). This option is available only if your ISP does not
require a login.
Domain Name Server (DNS)
Address
The DNS server is used to look up site addresses based on their names.
• Get Automatically from ISP. Your ISP uses DHCP to assign your DNS
server address automatically.
• Use These DNS Servers. If you know your ISP does not automatically
transmit DNS addresses to the wireless modem router during login, select
this option, and enter the IP address of your ISP’s primary DNS server. If
a secondary DNS server address is available, enter it also.
Internet Configuration
24
Page 25
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Table 3. Basic Settings screen fields (continued)
Settings Description
NAT (Network Address
Translation)
This field
displays only if
your ISP does
not require a
login.
1. Disabling NAT reboots the wireless modem router and resets its configuration settings to the factory defaults.
Disable NAT only if you plan to install the wireless modem router in a setting where you will be manually
administering the IP address space on the LAN side of the router.
Router MAC
Address
NAT automatically assigns private IP addresses (10.1.1.x) to devices on
your LAN.
• Enable. Usually NAT is enabled.
• Disable. This disables NAT, but leaves the firewall active. Disable NAT
only if you are sure that you do not require it. When NAT is disabled, only
standard routing is performed by this router. Classical routing lets you
directly manage the IP addresses that the wireless modem router uses.
Classical routing should be selected only by experienced users.
Your computer’s local address is its unique address on your network. This is
also referred to as the computer’s MAC (Media Access Control) address.
• Use Default MAC Address. This is the usual setting.
• Use Computer MAC address. If your ISP requires MAC authentication,
you can use this setting to disguise the wireless modem router’s MAC
address with the computer’s own MAC address.
• Use This MAC Address. If your ISP requires MAC authentication, you
can manually type the MAC address for a different computer. The format
for the MAC address is XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX.
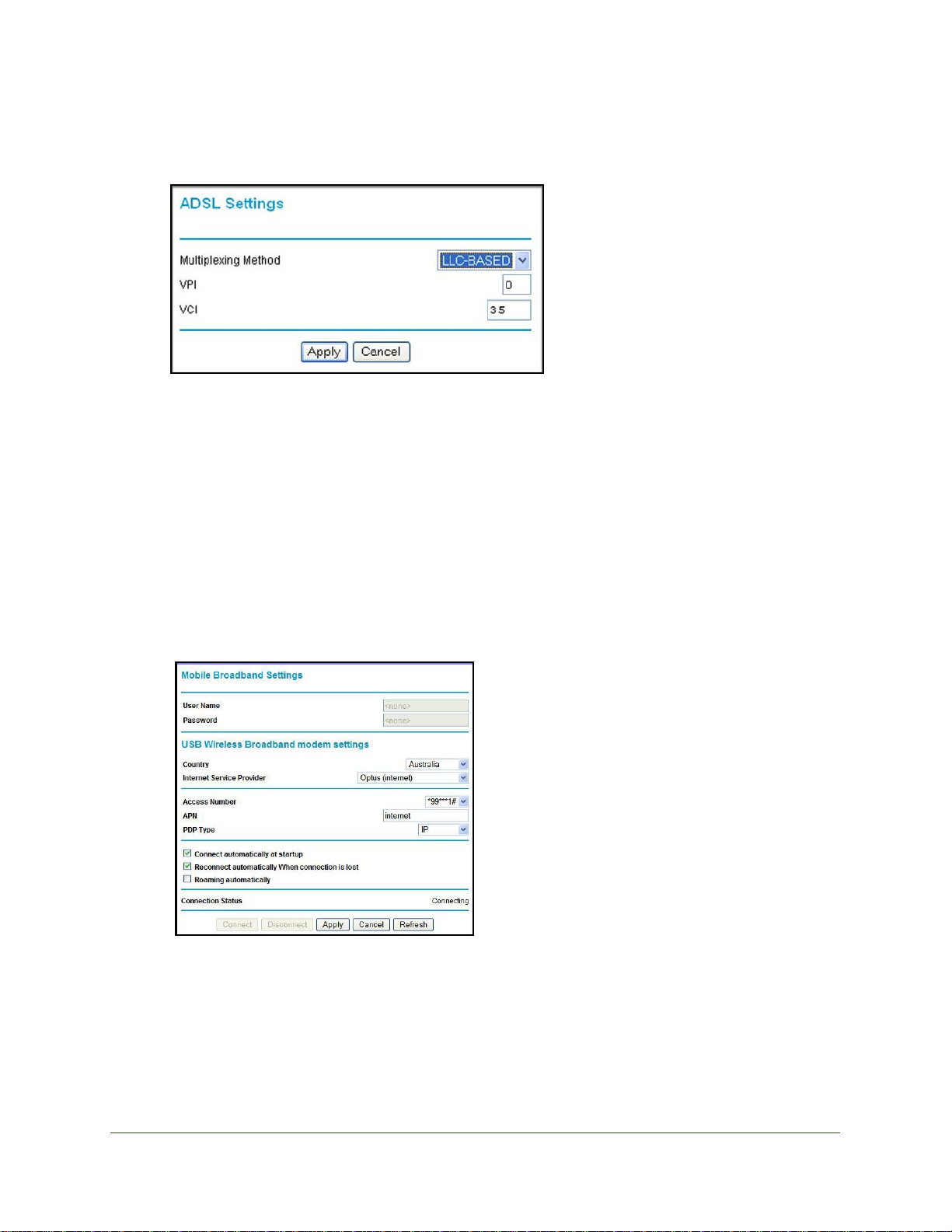
ADSL Settings
1
NETGEAR recommends that you use the Setup Wizard to automatically detect and configure
your ADSL settings. This usually works fine. However, if you have technical experience and
are sure of the multiplexing method and virtual circuit number for the virtual path identifier
(VPI) and virtual channel identifier (VCI), you can specify those settings here.
Note: Use the Setup Wizard to select the correct country to optimize
detection of the ADSL settings.
If your ISP provided you with a multiplexing method or VPI/VCI number, then enter the
setting.
Internet Configuration
25
Page 26
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
To manually specify ADSL settings:
1. From the main menu, select ADSL Settings, and the ADSL Settings screen displays.
2. In the Multiplexing Method drop-down list, select LLC-based or VC-based.
3. For the VPI, type a number between 0 and 255. The default is 8.
4. For the VCI, type a number between 32 and 65535. The default is 35.
5. Click Apply.
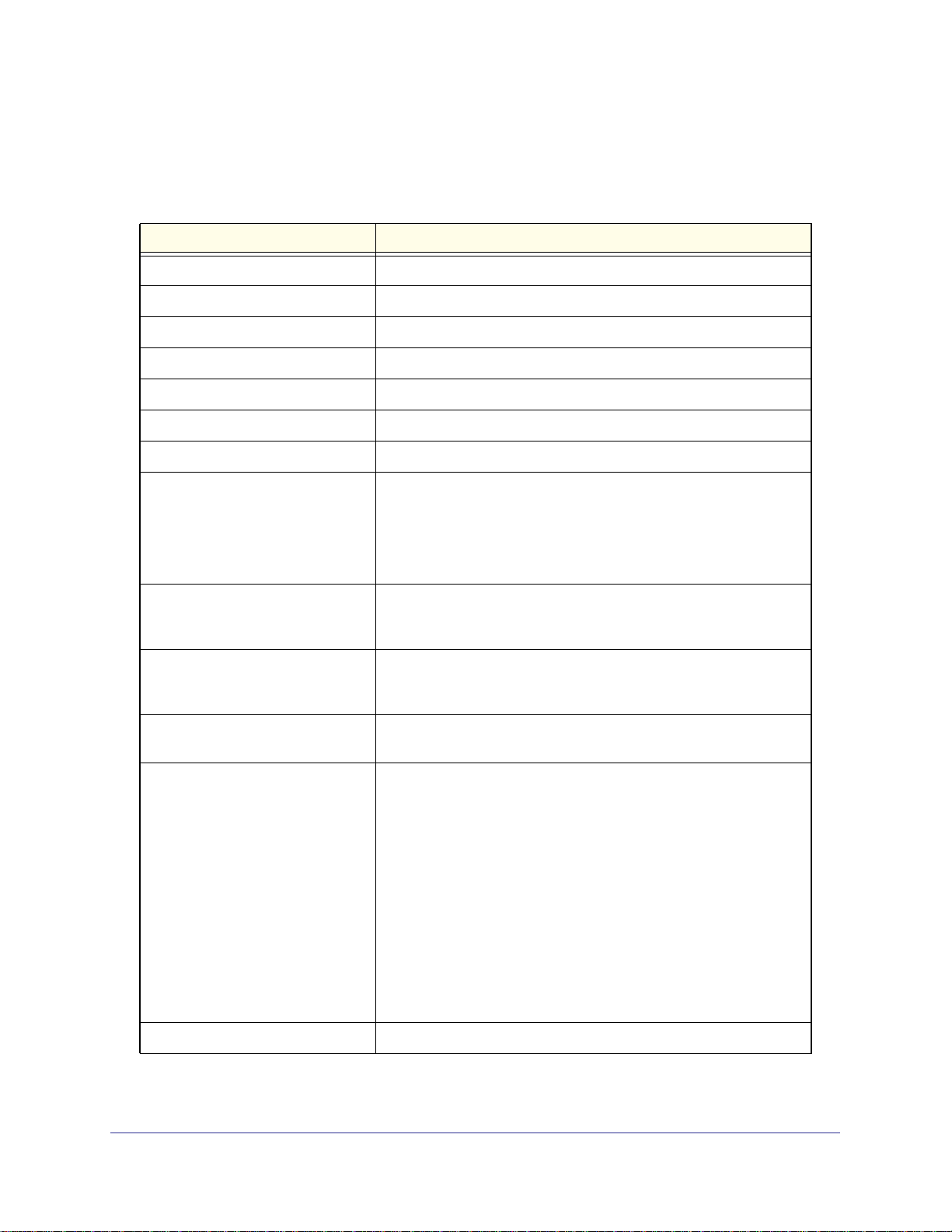
Mobile Broadband Settings
To manually configure your mobile broadband Internet settings:
1. Log in to the router as described in Log In to Your Wireless-N Modem Router on
page 17.
2. From the main menu, select Mobile Broadband Settings.
3. Adjust the settings as needed based on your Internet connection. The fields in this screen
depend on the network and are described in Table 4.
4. The following buttons are available:
• Connect. Manually connect to the network.
• Disconnect. Disconnect from the current network.
• Apply. Apply the changes that you made.
Internet Configuration
26
Page 27
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
• Cancel. Discard changes.
• Refresh. Update the connection status.
1
Table 4. Mobile Broadband Settings fields
Fields and check boxes Description
User Name Internet account login user name.
Password Internet account password for authentication.
Country Select your country from the drop-down list.
Internet Service Provider Select your Internet service provider from the drop-down list.
Access Number The remote site's phone number.
PIN code PIN code of the SIM card, where applicable.
APN Access point name.
PDP type Select the type of packet data protocol:
• IP
• PDP-IP
• PPP
• PPP-IP
Connect automatically at startup When this check box is selected, the modem automatically connects
to the network when powered up. This should be selected after login
information is provided.
Reconnect automatically when
connection is lost
Roaming automatically When this check box is selected, the unit might roam to any available
Wireless Button Configuration Select the option to determine the behavior of the WPS button on the
Connection status Current WAN port status.
When this check box is selected, the modem attempts to reconnect to
the network when the connection is lost. Under normal situations, this
setting check box should be selected.
operator in range and might incur roaming charges.
front panel when it is pressed.
• Control WiFi Only: Pressing the button toggles the WiFi function.
If WiFi is turned on, pressing the button turns off the WiFi. Pressing
it again turns on the WiFi. This function is available only if the WiFi
function is enabled. The wireless broadband function is unaffected.
• Control Both WiFi and Wireless Broadband: Pressing the button
toggles both the WiFi function and wireless broadband at the same
time. If WiFi is turned on, pressing the button turns off the WiFi. At
the same time, the wireless broadband connection is disconnected.
If you press the button again, WiFi is turned on, and the router
attempts to reestablish the wireless broadband connection.
Depending on the coverage, wireless broadband coverage might or
might not be connected successfully.
1. These fields and check boxes depend on the network.
Internet Configuration
27
Page 28
2. Wireless Settings
This chapter describes how to use the Wireless Settings screen to view and change (if needed)
your wireless network settings. Security features to prevent objectionable content from reaching
your computers are covered in Chapter 3, Protecting Your Network and Chapter 6, Advanced
Configuration.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Wireless Adapter Compatibility
• Preset Security
• Security Basics
• Add Clients (Computers or Devices) to Your Network
• Wireless Settings Screen
• Wireless Guest Networks
2
Wireless Adapter Compatibility
A wireless adapter is the wireless radio in your computer or laptop that lets the computer or
laptop connect to a wireless network. Most computers and laptops come with an adapter
already installed, but if it is outdated or slow, you can purchase a USB adapter to plug into a
USB port.
Make sure the wireless adapter in each computer in your wireless network supports the
same security settings as the wireless modem router. See Preset Security on page 29 for
information about the wireless modem router’s preconfigured security settings.
Note: If you connect devices to your wireless modem router using WPS
as described in Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) Method on page 32,
those devices assume the security settings of the wireless modem
router.
28
Page 29
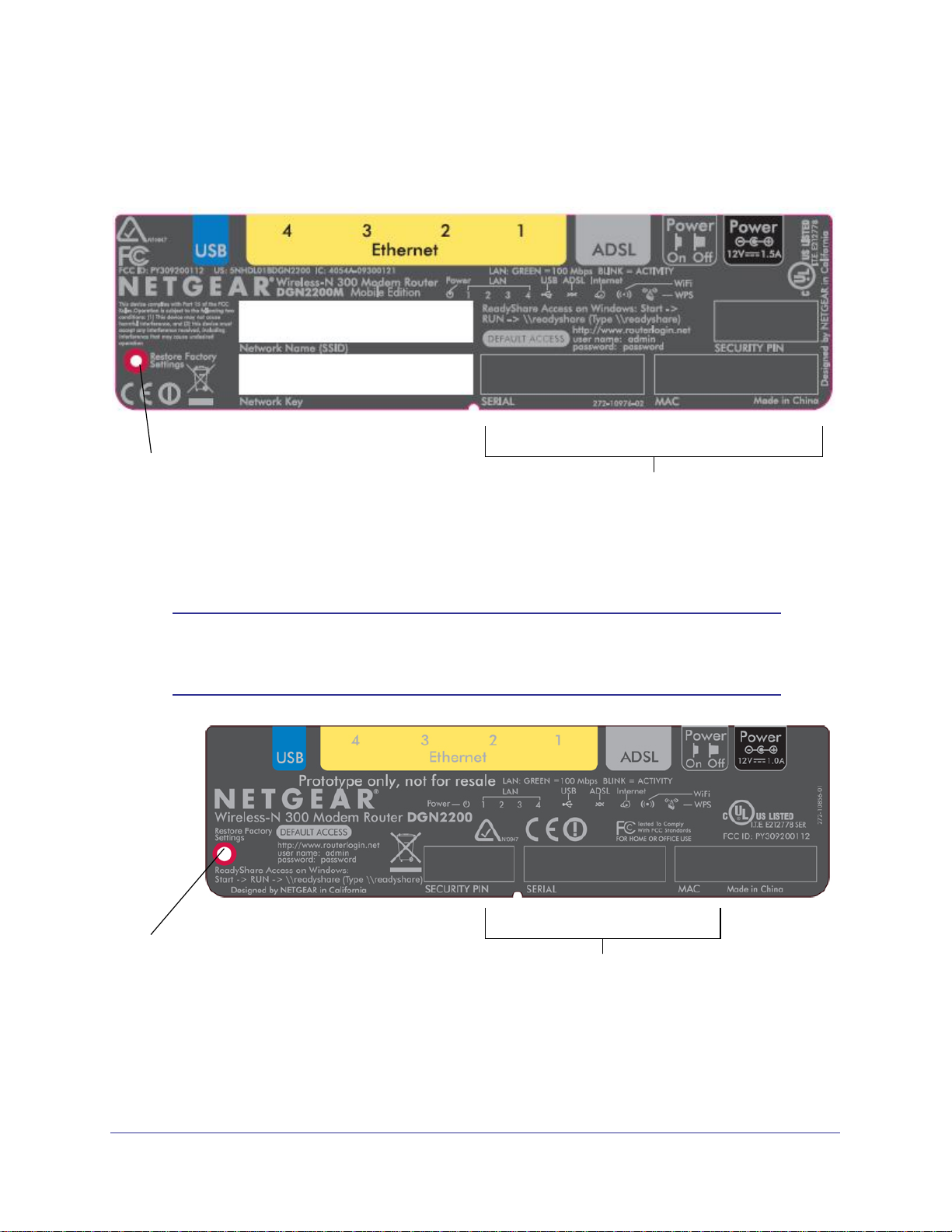
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Preset Security
If label on your router looks like this, then it has preset security.
Restore Factory
Settings: Press for
6 seconds.
Router information
- Default access address
- Default user name and password
- Security PIN
- Serial number
- MAC address
Note: If label on your router looks like the one in the following figure, then
your router has no preset wireless security. You need to set the
wireless security to protect your network.
Restore Factory
Settings: Press for
6 seconds.
Router information
- Default access address
- Default user name and password
- Security PIN
- Serial number
- MAC address
Wireless Settings
29
Page 30

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
The wireless modem router comes with preset security. This means that the WiFi network
name (SSID), passphrase, and security option (encryption protocol) are preset in the factory.
You can find the preset SSID and passphrase on the bottom of the unit.
• WiFi network name (SSID) identifies your network so devices can find it.
• Passphrase controls access to your network. Devices that know the SSID and the
passphrase can find your wireless network and connect.
Note: The preset SSID and passphrase are uniquely generated for every
device to protect and maximize your wireless security.
• Security option is the type of security protocol applied to your wireless network. The
security protocol in force encrypts data transmissions and ensures that only trusted
devices receive authorization to connect to your network. The preset security option is
WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK mixed mode, described in Wireless Security Options on page 31.
The Wireless Settings screen lets you view and change the preset security settings.
However, NETGEAR recommends that you not change your preset security settings. If
you do decide to change your preset security settings, make a note of the new settings and
store it in a safe place where you can easily find it.
Security Basics
Unlike wired network data, wireless data transmissions extend beyond your walls and can be
received by any device with a compatible wireless adapter (radio). For this reason, it is very
important to maintain the preset security and understand the other security features available
to you. Besides the preset security settings described in the previous section, your wireless
modem router has the security features described here and in Chapter 3, Protecting Your
Network.
• Turn off wireless connectivity
• Disable SSID broadcast
• Restrict access by MAC address
• Wireless security options
Turn Off Wireless Connectivity
You can turn off the wireless connectivity of the wireless modem router by pressing the WiFi
On/Off button on its front panel
to your wireless modem router and you take a business trip, you can turn off the wireless
portion of the wireless modem router while you are traveling. Other members of your
household who use computers connected to the wireless modem router through Ethernet
cables can still use the wireless modem router.
. For example, if you use your laptop to wirelessly connect
Wireless Settings
30
Page 31

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Disable SSID Broadcast
By default, the wireless modem router broadcasts its WiFi network name (SSID) so devices
can find it. If you change this setting to not allow the broadcast, wireless devices will not find
your wireless modem router unless they are configured with the same SSID. See Wireless
Access Point Settings on page 37 for the procedure.
Note: Turning off SSID broadcast nullifies the wireless network discovery
feature of some products such as Windows XP, but the data is still
fully exposed to a determined snoop using specialized test
equipment like wireless sniffers. If you allow the broadcast, be sure
to keep wireless security enabled.
Restrict Access by MAC Address
You can enhance your network security by allowing access to only specific computers based
on their Media Access Control (MAC) addresses. You can restrict access to only trusted
computers so that unknown computers cannot wirelessly connect to the wireless modem
router. The wireless station MAC address filtering adds additional security protection to the
wireless security option that you have in force. The access list determines which wireless
hardware devices are allowed to connect to the wireless modem router by MAC address.
See Advanced Wireless Settings on page 84 for the procedure.
Wireless Security Options
A security option is the type of security protocol applied to your wireless network. The
security protocol encrypts data transmissions and ensures that only trusted devices receive
authorization to connect to your network. There are several types of encryption: Wi-Fi
Protected Access II (WPA2), WPA, and Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP). WPA2 is the latest
and most secure, and is recommended if your equipment supports it. WPA has several
options including pre-shared key (PSK) encryption and 802.1x encryption for enterprises.
Note that it is also possible to disable wireless security. NETGEAR does not recommend this.
You can view or change the wireless security options in the Wireless Settings screen. See
Wireless Settings Screen on page 33.
Add Clients (Computers or Devices) to Your Network
Choose either the manual or the WPS method to add wireless computers or devices to your
wireless network.
Wireless Settings
31
Page 32

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Manual Method
To add clients manually:
1. Open the software that manages your wireless connections on the wireless device
(laptop computer, gaming device, iPhone) that you want to connect to your wireless
modem router. This software scans for all wireless networks in your area.
2. Look for your network and select it. If you did not change the name of your network during
the setup process, look for the default WiFi network name (SSID) and select it. The default
SSID is located on the product label on the bottom of the wireless modem router.
3. Enter the wireless modem router passphrase, and click Connect. The default wireless
modem router passphrase is located on the product label on the bottom of the wireless
modem router.
4. Repeat steps 1–3 to add other wireless devices.
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) Method
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) is a standard that lets you easily join a secure wireless network
with WPA or WPA2 wireless security. The wireless modem router automatically sets security
for each computer or device that uses WPS to join the wireless network. To use WPS, make
sure that your wireless devices are Wi-Fi certified and support WPS. NETGEAR products
that use WPS call it Push 'N' Connect.
1
Note: If the SSID changes each time you add a WPS client, the Keep
Existing Wireless Settings check box on the Advanced Wireless
Settings screen has been cleared. See Configure WPS Settings on
page 86 for more information about this setting.
You can use a WPS button or the wireless modem router interface method to add wireless
computers and devices to your wireless network.
WPS Button Method
To add clients using the WPS button:
1. Press the
2. Within 2 minutes, press the WPS button on your wireless computer or device, or follow the
WPS instructions that came with the computer. The device is now connected to your
wireless modem router.
3. Repeat steps 1–2 to add other WPS wireless computers or devices.
WPS button on the wireless modem router front panel.
1. For a list of other Wi-Fi-certified products available from NETGEAR, go to http://www.wi-fi.org.
Wireless Settings
32
Page 33

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Wireless Modem Router Interface Method
To add clients using the wireless modem router interface:
1. Select Add WPS Client at the top of the wireless modem router menus.
2. Click Next. The following screen lets you select the method for adding the WPS client.
WPS Push button method
3. Select either Push Button or PIN Number. With either method, the wireless modem
router tries to communicate with the computer or wireless device, set the wireless
security for wireless device, and allow it to join the wireless network.
The PIN method displays this screen so you can enter the client security PIN number:
WPS PIN method
While the wireless modem router attempts to connect, the WPS LED on the front of the
wireless modem router blinks green. When the wireless modem router establishes a
WPS connection, the LED is solid green, and the wireless modem router WPS screen
displays a confirmation message.
4. Repeat to add another WPS client to your network.
Wireless Settings Screen
The Wireless Settings screen lets you view or change the wireless network settings. Note
that your preset wireless modem router has a unique network name and password, located
on the product label. NETGEAR recommends that you use these settings. If you decide to
change them, note the new settings and save them in a secure location.
Wireless Settings
33
Page 34

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Note: If you use a wireless computer to change the wireless network name
(SSID) or security options, you are disconnected when you click
Apply. To avoid this problem, use a computer with a wired
connection to access the wireless modem router.
Consider Every Device on Your Network
Before you begin, check the following:
• Every wireless computer has to be able to obtain an IP address by DHCP from the
wireless modem router.
• Each computer or wireless adapter in your network needs to have the same SSID and
wireless mode (bandwidth and data rate) as the wireless modem router. Check that the
wireless adapter on each computer can support the mode and security option you want to
use.
• The security option on each wireless device in the network needs to match the wireless
modem router. For example, if you select a security option that requires a passphrase, be
sure to use same passphrase for each wireless computer in the network.
View or Change Wireless Settings
Your preset wireless modem router comes set up with a unique wireless network name
(SSID) and network password. This information is printed on the label for your wireless
modem router. You view or change these settings in the Wireless Settings screen. You can
also use this screen to set up guest wireless networks.
Wireless Settings
34
Page 35

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
To view or change wireless settings:
1. Select Setup > Wireless Settings to display the following screen.
Wireless Settings
35
Page 36

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Note: If your wireless security is not preset, the Wireless Settings screen
looks like this:
1. Change the name (SSID) to a
personalized setting.
2. Change the Security Options setting to
WPA-PSK (TKIP) + WPA2-PSK (AES).
3. Enter a passphrase that you can
remember but is hard for others to guess.
4. Click Apply to save your settings.
2. Select the wireless network that you want to configure.
3. Make any changes that are needed, and click Apply when done to save your settings.
Note: The screen sections, settings, and procedures are explained in the
following sections.
4. Set up and test your computers for wireless connectivity:
a. Use your wireless computer or device to join your network. When prompted, enter the
network password.
b. From the wirelessly connected computer, make sure that you can access the
Internet.
Wireless Settings
36
Page 37

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Wireless Settings Screen Fields
Wireless Network
The primary network is the one that you usually use. You can set up guest networks too. You
can customize access so that people who use their computers to access your guest network
can use the Internet, but they do not have access to the rest of your home network.
• Name (SSID). The SSID is also known as the wireless network name. Enter a
32-character (maximum) name in this field. This field is case-sensitive. The default SSID
for your primary network is randomly generated, and there is typically no need to change
it. If you want to set up guest networks, NETGEAR does recommend that you customize
the default guest network names (SSIDs).
• Region. The location where the wireless modem router is used. It might not be legal to
operate the wireless modem router in a region other than the regions listed.
• Channel. The wireless channel used by the gateway: 1 through 13. Do not change the
channel unless you experience interference (shown by lost connections or slow data
transfers). If this happens, experiment with different channels to see which is the best.
• Mode. Up to 150 Mbps is the default and allows 802.11n and 802.11g wireless devices to
join the network. g & b supports up to 54 Mbps. Up to 65 Mbps supports up to 65 Mbps.
Wireless Access Point Settings
• Enable this wireless network. When this check box is selected, the wireless modem
router accepts wireless clients for the network. By default, this check box is selected for
your primary network. If you clear this check box, the wireless modem router accepts
wired clients only.
• Allow Broadcast of Name (SSID). This setting allows the wireless modem router to
broadcast its SSID so that a wireless station can display this wireless name (SSID) in its
scanned network list. This check box is selected by default. To turn off the SSID
broadcast, clear the Allow Broadcast of Name (SSID) check box and click Apply.
• Wireless Isolation. When this check box is selected, wireless stations cannot
communicate with each other or with stations on the wired network. By default, this check
box is not selected.
Security Options Settings
The Security Options section of the Wireless Settings screen lets you change the security
option and passphrase. The primary network for your preset wireless modem router is
already set up with WPA2 and WPA security. NETGEAR recommends that you set up
wireless security for each guest network that you plan to use. For information about changing
these settings, see the following section, Change WPA Security Option and Passphrase, and
Set WEP Encryption and Passphrase on page 38.
Wireless Settings
37
Page 38

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Change WPA Security Option and Passphrase
To change the WPA security option and passphrase:
1. In the Security Options section, select the WPA option that you want.
2. Enter the passphrase that you want to use. It is a text string from 8 to 63 characters.
3. Click Apply.
Set WEP Encryption and Passphrase
To set WEP encryption and passphrase:
1. In the Security Options section of the Wireless Settings screen, select WEP:
2. Select the authentication type. The default is Automatic. Other choices are Open System
(any client can authenticate itself to the network) and Shared Key (a passphrase and a
four-way challenge are needed for authentication).
3. Select the encryption strength setting, either 64-bit or 128-bit.
Wireless Settings
38
Page 39

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
4. Enter the four data encryption keys either manually or automatically. These values need to
be identical on all computers and access points in your network.
• Automatic. Enter a word or group of printable characters in the Passphrase field and
click Generate. The four key fields are automatically populated with key values.
• Manual. The number of hexadecimal digits that you enter depends on the encryption
strength setting:
- For 64-bit WEP, enter 10 hexadecimal digits (any combination of 0–9, a–f, or
A–F).
- For 128-bit WEP, enter 26 hexadecimal digits (any combination of 0–9, a–f, or
A–F).
5. Select the radio button for the key you want to make active.
Make sure that you understand how the WEP key settings are configured in your wireless
adapter. Wireless adapter configuration utilities such as the one in Windows XP allow one
key entry, which has to match the default key you set in the wireless modem router.
6. Click Apply.
Wireless Guest Networks
A wireless guest network allows you to provide guests access to your wireless network
without prior authorization of each individual guest. You can configure wireless guest
networks and specify the security options for each wireless guest network.
To set up a wireless guest network:
1. Select Setup > Wireless Settings.
Wireless Settings
39
Page 40

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
2. Select the radio button for the network profile that you want to set up.
3. You can specify whether the SSID broadcast is enabled and whether you want to allow
guests to access your local network. You can also change the SSID.
• NETGEAR strongly recommends that you change the SSID to a different name. Note
that the SSID is case-sensitive. For example, GuestNetwork is not the same as
Guestnetwork.
• For guest networks, wireless security is disabled by default. NETGEAR strongly
recommends that you implement wireless security for the guest network.
4. Select a security option for the guest network, and specify the password.
5. When you have finished making changes, click Apply.
Wireless Settings
40
Page 41

3. Protecting Your Network
This chapter describes how to use the basic firewall features of the wireless modem router to
protect your network. The chapter includes:
• Protect Access to Your Wireless-N Modem Router
• Block Keywords, Sites, and Services
• Set Times and Schedule Firewall Services
• Enable Security Event Email Notification
• Live Parental Controls
Protect Access to Your Wireless-N Modem Router
For security reasons, the wireless modem router has its own user name and password. Also,
after a period of inactivity for a set length of time, the login automatically disconnects. You
can use the following procedures to change the wireless modem router’s password and the
period for the administrator’s login time-out.
3
Note: The user name and password are not the same as any other user
name or password your might use to log in to your Internet
connection.
NETGEAR recommends that you change this password to a more secure password. The
ideal password should contain no dictionary words from any language and should be a
mixture of both uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Your password can
be up to 30 characters.
41
Page 42

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Change the Built-In Password
To change the build-in password:
1. In the main menu, under Maintenance, select Set Password.
2. To change the password, first enter the old password, and then enter the new password
twice.
3. Click Apply to save your changes.
Note: After changing the password, you are required to log in again to
continue the configuration. If you have backed up the wireless
modem router settings previously, you should do a new backup so
that the saved settings file includes the new password.
Change the Administrator Login Time-Out
For security, the administrator’s login to the wireless modem router configuration times out
after a period of inactivity.
To change the login time-out period:
1. In the Set Password screen, type a number in the Administrator login times out field. The
suggested default value is 5 minutes.
2. Click Apply to save your changes, or click Cancel to keep the current period.
Block Keywords, Sites, and Services
The wireless modem router provides a variety of options for blocking Internet-based content
and communications services. With its content filtering feature, the wireless modem router
prevents objectionable content from reaching your computers. The wireless modem router
allows you to control access to Internet content by screening for keywords within web
addresses. Key content filtering options include:
• Keyword blocking of HTTP traffic.
Protecting Your Network
42
Page 43

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
• Outbound service blocking. Limits access from your LAN to Internet locations or services
that you specify as off-limits.
• Denial of service (DoS) protection. Automatically detects and thwarts denial of service
(DoS) attacks such as Ping of Death, SYN flood, LAND Attack, and IP spoofing.
• Blocking unwanted traffic from the Internet to your LAN.
Block Sites
To block keywords and sites:
1. In the main menu, under Content Filtering, select Block Sites:
2. To enable keyword blocking, select one of the following:
• Per Schedule. Turn on keyword blocking according to the settings in the Schedule
screen.
• Always. Turn on keyword blocking all the time, independent of the Schedule screen.
3. Enter a keyword or domain in the Keyword field, click Add Keyword, and then click Apply.
Some examples of keyword application follow:
• If the keyword XXX is specified, the URL http://www.badstuff.com/xxx.html is blocked.
• If the keyword .com is specified, only websites with other domain suffixes (such as
.edu or .gov) can be viewed.
• Enter a period (.) to block all Internet browsing access.
Up to 32 entries are supported in the Keyword list.
4. To delete a keyword or domain, select it from the list, click Delete Keyword, and then click
Apply.
5. To specify a trusted user, enter that computer’s IP address in the Trusted IP Address field,
and click Apply.
Protecting Your Network
43
Page 44

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
You can specify one trusted user, which is a computer that will be exempt from blocking
and logging. Since the trusted user will be identified by an IP address, you should
configure that computer with a fixed IP address.
6. Click Apply to save your settings.
Block Services
To block services:
1. In the main menu, under Content Filtering, select Block Services.
.
2. Select one of the following:
• Per Schedule. Turn on keyword blocking according to the settings in the Schedule
screen.
• Always. Turn on keyword blocking all the time, independent of the Schedule screen.
3. Click Add, and the following screen displays:
4. Either select a service from the Service Type drop-down list, or select User Defined to
create a custom service.
Protecting Your Network
44
Page 45

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
5. Click Add to create the service, and the service is listed in the Service Table:
6. Click Apply to save your settings.
Set Times and Schedule Firewall Services
The wireless modem router uses the Network Time Protocol (NTP) to obtain the current time
and date from one of several network time servers on the Internet. On the router menu,
select Schedule under Security to display the Security screen:
Protecting Your Network
45
Page 46

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Set Your Time Zone
To localize the time for your log entries:
1. In the Schedule screen, select your time zone.
This setting is used for the blocking schedule according to your local time zone and for
time-stamping log entries.
2. If your time zone is currently in daylight savings time, select the Adjust for Daylight
Savings Time check box.
Note: If your region uses daylight savings time, you need to manually
select Adjust for Daylight Savings Time on the first day of daylight
savings time, and clear it at the end. Enabling daylight savings time
causes 1 hour to be added to the standard time.
3. The wireless modem router has a list of NETGEAR NTP servers. If you would prefer to use
a particular NTP server as the primary server, select the Use this NTP Server check box,
and enter its IP address.
4. Click Apply to save your settings.
Schedule Firewall Services
If you enabled service blocking in the Block Services screen or port forwarding in the Port
Forwarding/Port Triggering screen, you can set up a schedule for when blocking occurs or
when access is not restricted.
To block Internet services based on a schedule:
1. From the Schedule screen, select Every Day, or select one or more days.
2. If you want to limit access completely for the selected days, select All Day. Otherwise, to
limit access during certain times for the selected days, or enter times in the Start Time and
End Time fields.
Note: Enter the values in 24-hour time format. For example, 10:30 a.m.
would be 10 hours and 30 minutes, and 10:30 p.m. would be 22
hours and 30 minutes. If you set the start time after the end time, the
schedule will be effective through midnight the next day.
3. Click Apply to save your changes.
Protecting Your Network
46
Page 47

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
View, Select, and Save Logged Information
The wireless modem router logs security-related events such as denied incoming service
requests, hacker probes, and administrator logins. If you enable content filtering in the Block
Sites screen, the Logs screen show you when someone on your network tries to access a
blocked site. If you enable email notification, you will receive these logs in an email message.
To view the log, under Content Filtering, select Logs. A screen similar to the following
displays:
You can write the logs to a computer running a syslog program. To activate this feature,
select Broadcast on LAN, or enter the IP address of the server where the syslog file will be
written.
Table 5. Security log entry descriptions
Field Description
Date and time The date and time the log entry was recorded.
Description or action The type of event and what action was taken, if any.
Source IP The IP address of the initiating device for this log entry.
Source port and interface The service port number of the initiating device, and whether it
originated from the LAN or WAN.
Destination The name or IP address of the destination device or website.
Destination port and interface The service port number of the destination device, and whether it is
on the LAN or WAN.
Protecting Your Network
47
Page 48

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Examples of Log Messages
Following are examples of log messages. In all cases, the log entry shows the time stamp as
day, year-month-date hour:minute:second.
Activation and Administration
Tue, 2011-05-21 18:48:39 - NETGEAR activated
This entry indicates a power-up or reboot with initial time entry.
Tue, 2011-05-21 18:55:00 - Administrator login successful-IP:192.168.0.2
Thu, 2011-05-21 18:56:58 - Administrator logout - IP:192.168.0.2
This entry shows an administrator logging in to and out from IP address 192.168.0.2.
Tue, 2011-05-21 19:00:06 - Login screen timed out - IP:192.168.0.2
This entry shows a time-out of the administrator login.
Wed, 2011-05-22 22:00:19 - Log emailed
This entry shows when the log was emailed.
Dropped Packets
Wed, 2011-05-22 07:15:15 - TCP packet dropped - Source:64.12.47.28,4787,WAN Destination:134.177.0.11,21,LAN - [Inbound Default rule match]
Sun, 2011-05-22 12:50:33 - UDP packet dropped - Source:64.12.47.28,10714,WAN Destination:134.177.0.11,6970,LAN - [Inbound Default rule match]
Sun, 2011-05-22 21:02:53 - ICMP packet dropped Source:64.12.47.28,0,WAN - Destin
rule match]
These entries show an inbound FTP (port 21) packet, a User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
packet (port 6970), and an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packet (port 0) being
dropped as a result of the default inbound rule, which states that all inbound packets are
denied.
ation:134.177.0.11,0,LAN - [Inbound Default
Protecting Your Network
48
Page 49

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Enable Security Event Email Notification
To receive logs and alerts by email, you need to provide your email information in the E-mail
screen and specify which alerts you would like to receive and how often.
In the main menu, under Security, select E-mail. The E-mail screen displays.
You can make the following selections:
• Turn E-mail Notification On. Select this check box if you want to receive email logs and
alerts from the wireless modem router.
• Your Outgoing Mail Server. Enter the name or IP address of your ISP’s outgoing
(SMTP) mail server (such as mail.myISP.com). You might be able to find this information
in the configuration settings of your email program.
• Send to This E-mail Address. Enter the email address to which logs and alerts are sent.
This email address is also used as the From address. If you leave this field blank, log and
alert messages are not sent through email.
• My mail server requires authentication. If you use an outgoing mail server provided by
your current ISP, you do not need to select this check box. If you use an email account
that is not provided by your ISP, select this check box, and enter the required user name
and password information.
• Send Alert immediately. Select this check box if you would like immediate notification of
a significant security event, such as a known attack, port scan, or attempted access to a
blocked site.
• Send logs according to this schedule. Specifies how often to send the logs: Hourly,
Daily, Weekly, or When Full.
Protecting Your Network
49
Page 50

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
- Day for sending log
Specifies which day of the week to send the log. Relevant when the log is sent weekly.
- Time for sending log
Specifies the time of day to send the log. Relevant when the log is sent daily or
weekly.
If the Weekly, Daily, or Hourly option is selected and the log fills up before the specified
period, the log is automatically emailed to the specified email address. After the log is
sent, it is cleared from the wireless modem router’s memory. If the wireless modem router
cannot email the log file, the log buffer might fill up. In this case, the wireless modem
router overwrites the log and discards its contents.
Live Parental Controls
NETGEAR Live Parental Controls, powered by OpenDNS, is a router-based web filtering
solution available on NETGEAR Wireless-N router and gateway products. Designed to
protect you from identity theft and scams, Live Parental Control blocks up to 50 categories of
Internet content.
Live Parental Controls helps keep your family safe online, but like all web filtering tools, it is
not perfect. NETGEAR reminds you there is no substitute for keeping the family computer in
a common area and in plain sight where you can monitor the websites your kids are visiting,
and taking caution when visiting websites requesting personal or financial information.
Download Live Parental Controls from this website: http://www.netgear.com/lpc
Web-Based Access
Live Parental Controls is the first to allow parents or network administrators to manage
settings while away from home or office. This is particularly convenient when access
exceptions need to be made. And since settings are stored on the web, using a browser
interface to manage them is not difficult at all.
Total Home Protection
Live Parental Controls protects all Internet-connected devices through the router. It protects
not only computers, but also set-top boxes, iPhones, iPods, and gaming consoles that are
attached to your network. You no longer need to worry about phones and gaming consoles
not being protected when kids use them in their own rooms. Even guest computers
accessing the Internet through your network are protected.
Flexible Settings
You might have your own computer, or you might be sharing a computer with other members
in the family. Default and settings for individual users allow you to customize configuration for
different computing arrangements and personalize the settings for each person. Setting
according to time allow Internet access during scheduled time slots to help manage the
balance between work and play.
Protecting Your Network
50
Page 51

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Minimal Software Installation
Installation requires a one-time installation of a management utility program. Once Live
Parental Controls is set up, the software runs in the background and does not interfere with
normal Internet usage.
Protecting Your Network
51
Page 52

4. Managing Your Network
This chapter describes how to perform network management tasks with your wireless modem
router. This chapter includes these sections:
• Upgrade the Firmware
• Back Up, Restore, and Erase Your Settings
• Router Status and Usage Statistics
• View Attached Devices
• Run Diagnostics and Reboot
• Configure Remote Management on page 62
Upgrade the Firmware
The wireless modem router’s firmware (routing software) is stored in flash memory. By
default, when you log in to your wireless modem router, it automatically checks the
NETGEAR website for new firmware and alerts you if there is a newer version.
4
Note: To turn off the automatic firmware check at login, clear the Check
for Updated Firmware Upon Log-in check box on the Router
Upgrade screen.
52
Page 53

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
If the wireless modem router discovers a newer version of firmware, the message on the left
displays. If no new firmware is available, the message on the right displays.
To upgrade, click Yes to allow the wireless modem router to download and install the new
firmware.
WARNING:
When uploading firmware to the wireless modem router, do not
interrupt the web browser by closing the window, clicking a link,
or loading a new page. If the browser is interrupted, it could
corrupt the firmware.
When the upload is complete, your wireless modem router automatically restarts. The
upgrade process could take a few minutes. Read the new firmware release notes to
determine whether you need to reconfigure the wireless modem router after upgrading.
Manually Check for Firmware Upgrades
You can use the Router Upgrade screen to manually check the NETGEAR website for newer
versions of firmware for your product.
To manually check for new firmware and install it on your wireless modem router:
1. On the main menu, under Maintenance, select Router Status. Note the version number
of your wireless modem router firmware.
2. Go to the DGN2200M Mobile Edition support page on the NETGEAR website at
http://www.netgear.com/support.
3. If the firmware version on the NETGEAR website is newer than the firmware on your
wireless modem router, download the file to your computer.
Managing Your Network
53
Page 54

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
4. On the main menu, under Maintenance, select Router Upgrade.
5. Click Browse, and locate the firmware you downloaded (the file ends in .img or .chk).
6. Click Upload to send the firmware to the wireless modem router.
WARNING:
When uploading firmware to the wireless modem router, do not
interrupt the web browser by closing the window, clicking a link,
or loading a new page. If the browser is interrupted, it could
corrupt the firmware.
When the upload is complete, your wireless modem router automatically restarts. The
upgrade process typically takes about 1 minute. Read the new firmware release notes to
determine whether you need to reconfigure the wireless modem router after upgrading.
Back Up, Restore, and Erase Your Settings
The configuration settings of the wireless modem router are stored in a configuration file. This
file can be backed up to your computer, restored, or reverted to factory default settings.
Managing Your Network
54
Page 55

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Back Up the Configuration to a File
To back up the configuration to a file:
1. From the main menu, under Maintenance, select Backup Settings to display this
screen:
2. Click Save to save a copy of the current settings.
3. Store the .cfg file on a computer on your network.
Restore the Configuration from a File
To restore the configuration from a file:
1. In the main menu, under Maintenance, select Backup Settings.
2. Enter the full path to the file on your network, or click the Browse button to locate the file.
3. When you have located the .cfg file, click the Restore button to upload the file to the
wireless modem router.
4. The wireless modem router then reboots automatically.
Erase the Configuration
Sometimes you might want to restore the wireless modem router to the factory default
settings. You can do this by using the erase function.
To erase the configuration:
1. In the main menu, under Maintenance, select Backup Settings, and click the Erase
button.
2. The wireless modem router then reboots automatically.
After an erase, the wireless modem router’s password is password, the LAN IP address
is 192.168.0.1, and the wireless modem router’s DHCP client is enabled.
Managing Your Network
55
Page 56

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Note: To restore the factory default configuration settings when you do not
know the login password or IP address, press the Restore Factory
Settings button on the bottom of the wireless modem router for 6
seconds.
Router Status and Usage Statistics
In the main menu, under Maintenance, select Router Status.
Table 6. Router Status fields
Field Description
Account Name The host name assigned to the router in the Basic Settings screen.
Firmware Version The wireless modem router firmware version.
Managing Your Network
56
Page 57

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Table 6. Router Status fields (continued)
Field Description
ADSL Port MAC Address The Ethernet MAC address being used by the Internet (ADSL) port.
IP Address The IP address used by the Internet (ADSL) port. If no address is shown,
the wireless modem router cannot connect to the Internet.
Network Type The network type depends upon your ISP.
IP Subnet Mask The IP subnet mask used by the Internet (ADSL) port.
Gateway IP
Address
Domain Name
Server
LAN Port MAC Address This field displays the Ethernet MAC address being used by the local (LAN)
IP Address This field displays the IP address being used by the local (LAN) port of the
DHCP If Off, the wireless modem router does not assign IP addresses to
IP Subnet Mask This field displays the IP subnet mask being used by the local (LAN) port of
Modem ADSL Firmware
Version
Modem Status The connection status of the modem.
DownStream
Connection
Speed
IP address used as a gateway to the Internet for computers configured to
use DHCP.
The DNS server IP addresses used by the wireless modem router. These
addresses are usually obtained dynamically from the ISP.
port of the wireless modem router.
wireless modem router. The default is 192.168.0.1.
computers on the LAN.
If On, the wireless modem router does assign IP addresses to computers on
the LAN.
the wireless modem router. The default is 255.255.255.0.
The version of the firmware.
The speed at which the modem is receiving data from the ADSL line.
UpStream
Connection
Speed
VPI The Virtual Path Identifier setting.
VCI The Virtual Channel Identifier setting.
The speed at which the modem is transmitting data to the ADSL line.
Managing Your Network
57
Page 58

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Table 6. Router Status fields (continued)
Field Description
Wireless Port Name (SSID) The service set ID, also known as the wireless network name for WLAN.
Region The country where the unit is set up for use.
Channel The current channel, which determines the operating frequency.
Wireless AP Indicates if the access point feature is enabled for WLAN. If disabled, the
WiFi LED on the front panel is off.
Broadcast
Name
Indicates if the wireless modem router is configured to broadcast its SSID
for WLAN.
View Statistics
On the Router Status screen, click the Show Statistics button to display wireless modem
router usage statistics.
The Show Statistics screen displays the following statistics:
Table 7. Router Statistics fields
Field Description
WAN, LAN, or WLAN The statistics for the WAN (Internet), LAN (local), and wireless LAN (WLAN)
ports. For each port, the screen displays the following:
Status The link status of the port.
TxPkts The number of packets transmitted on this port since reset or manual clear.
RxPkts The number of packets received on this port since reset or manual clear.
Collisions The number of collisions on this port since reset or manual clear.
Tx B/s The current line utilization—percentage of current bandwidth used on this
port.
Managing Your Network
58
Page 59

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Table 7. Router Statistics fields (continued)
Field Description
Rx B/s The average line utilization for this port.
Up Time The time elapsed since the last power cycle or reset.
ADSL Link Downstream
or Upstream
Connection Speed Typically, the downstream speed is faster than the upstream speed.
Line Attenuation The line attenuation increases the farther you are physically from your ISP’s
WAN, LAN, or WLAN The statistics for the WAN (Internet), LAN (local), and wireless LAN (WLAN)
Status The link status of the port.
The statistics for the upstream and downstream ADSL link. These statistics
will be of interest to your technical support representative if you are having
problems obtaining or maintaining a connection.
facilities.
ports. For each port, the screen displays the following:
View the Connection Status
On the Router Status screen, click the Connection Status button to display wireless modem
router connection status.
This screen shows the following statistics:
Table 8. Connection Status fields (PPPoE network type example)
Field Description
Connection Time The time elapsed since the last connection to the Internet through the ADSL
port.
Connecting to sender The connection status.
Negotiation Success or Failed.
Managing Your Network
59
Page 60

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Table 8. Connection Status fields (PPPoE network type example) (continued)
Field Description
Authentication Success or Failed.
Obtaining IP Address The IP address assigned to the WAN port by the ADSL Internet service provider.
Obtaining Network Mask The network mask assigned to the WAN port by the ADSL Internet service
provider.
View Attached Devices
The Attached Devices screen contains a table of all IP devices that the wireless modem
router has discovered on the local network. In the main menu, under Maintenance, select
Attached Devices to view the table.
For each device, the table shows the IP address, device name if available, and the Ethernet
MAC address. Note that if the wireless modem router is rebooted, the table data is lost until
the wireless modem router rediscovers the devices. To force the wireless modem router to
look for attached devices, click the Refresh button.
Managing Your Network
60
Page 61

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Run Diagnostics and Reboot
In the main menu, under Maintenance, select Diagnostics.
The wireless modem router has a diagnostics feature. You can use the Diagnostics screen to
perform the following functions from the wireless modem router:
• Ping an IP address to test connectivity to see if you can reach a remote host.
• Perform a DNS lookup to test if an Internet name resolves to an IP address to verify that
the DNS server configuration is working.
• Display the Routing table to identify what other wireless modem routers the wireless
modem router is communicating with.
• Reboot the wireless modem router to enable new network configurations to take effect or
to clear problems with the wireless modem router’s network connection.
Managing Your Network
61
Page 62

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Configure Remote Management
Using the Remote Management screen, you can allow a user or users on the Internet to
configure, upgrade, and check the status of your wireless modem router.
Note: Be sure to change the wireless modem router’s default password to
a very secure password. The ideal password should contain no
dictionary words from any language and should be a mixture of
letters (both uppercase and lowercase), numbers, and symbols.
Your password can be up to 30 characters.
To configure remote management:
1. Under Advanced in the main menu, select Remote Management.
2. Select the Turn Remote Management On check box.
3. Specify the external addresses allowed to access the router remotely. For security, restrict
access to as few as practical:
• To allow access from any IP address on the Internet, select Everyone.
• To allow access from a range of IP addresses, select IP address Range. Then enter
a beginning and ending IP address to define the allowed range.
• To allow access from a single IP address on the Internet, select Only This Computer.
Enter the IP address that will be allowed access.
4. Specify the port number that will be used for accessing the router menu.
Web browser access usually uses the standard HTTP service port 80. For greater
security, you can specify a custom port by entering that number in the field provided.
Managing Your Network
62
Page 63

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Choose a number between 1024 and 65535, but do not use the number of any common
service port. The default is 8080, which is a common alternate for HTTP.
5. Click Apply to have your changes take effect.
To access the router from the Internet, type the router’s WAN IP address in the browser’s
Address field, followed by a colon (:) and the port number. For example, if your external
address is 134.177.0.123 and you use port 8080, enter the following in your browser:
http://134.177.0.123:8080
In this case, the http:// needs to be included in the address.
Managing Your Network
63
Page 64

5. USB Storage
This chapter describes how to access and configure a USB storage drive attached to your
wireless modem router.
5
64
Page 65

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Note: The USB port on the wireless modem router can be used only to
connect USB storage devices like flash drives or hard drives. Do not
connect computers, USB modems, printers, CD drives, or DVD
drives to the USB port.
Note: Because the USB port on the wireless modem router is used for
connecting the broadband mobile modem cable, you are not able to
use the USB port for both a ReadyShare storage and a broadband
mobile Internet connection at the same time even when using a USB
hub to fan out the USB port.
This chapter includes the following sections:
• USB Drive Requirements
• File-Sharing Scenarios
• USB Storage Basic Settings
• Configure USB Storage Advanced Settings
• Unmount a USB Drive
• Specify Approved USB Devices
• Connect to the USB Drive from a Remote Computer
• Connect to the USB Drive with Microsoft Network Settings
USB Drive Requirements
The wireless modem router works with 1.0 and 1.1 (USB full speed) and 2.0 (USB high
speed) standards. The approximate USB bus speeds are shown in the following table.
Bus Speed/Second
USB 1.1 12 Mbits
USB 2.0 480 Mbits
Actual bus speeds can vary, depending on the CPU speed, memory, speed of the network,
and other variables. The wireless modem router should work with USB 2.0-compliant or
1.1-compliant external flash and hard drives. For the most up-to-date list of USB drives
supported by the wireless modem router, go to
http://kb.netgear.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/12345.
When selecting a USB device, bear in mind the following:
USB Storage
65
Page 66

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
• The USB port on the wireless modem router can be used with one USB hard drive at a
time. Do not attempt to use a USB hub attached to the USB port.
• According to the USB 2.0 specification, the maximum available power is 5V at 0.5A.
Some USB devices might exceed this requirement, in which case the device might not
function or might function erratically. Check the documentation for your USB device to be
sure.
• The wireless modem router supports FAT, FAT32, NTFS (read-only), and Linux file
systems.
File-Sharing Scenarios
You can share files on the USB drive for a wide variety of business and recreational
purposes. The files can be any Windows, Mac, or Linux file type including text files, Word,
PowerPoint, Excel, MP3, pictures, and multimedia. USB drive applications include:
• Sharing multimedia with friends and family. You can share MP3 files, pictures, and other
multimedia with local and remote users.
• Sharing resources on your network. Store files in a central location so that you do not
have to power up a computer to perform local sharing. In addition, you can share files
between Macintosh, Linux, and Windows computers by using the USB drive as a
go-between.
• Sharing files with offsite coworkers. Share files such as Word documents, PowerPoint
presentations, and text files with remote users.
A few common uses are described in the following sections.
Share Photos with Friends and Family
You can create your own central storage location for photos and multimedia. This eliminates
the need to log in to (and pay for) an external photo-sharing site.
To share files with your friends and family:
1. Insert your USB drive into the USB port on the wireless modem router either directly or
with a USB cable.
Computers on your local area network (LAN) can access this USB drive using a web
browser or Microsoft Networking.
2. If you want to specify read-only access, or to allow access from the Internet, see Configure
USB Storage Advanced Settings on page 70.
Store Files in a Central Location for Printing
This scenario is for a family that has one high-quality color printer directly attached to a
computer, but not shared on the local area network (LAN). This family does not have a print
server:
USB Storage
66
Page 67

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
• The family’s color printer is directly attached to the mother’s computer.
• The daughter has some photos on her Macintosh computer that she wants to print.
• Their computers are not visible to each other on the network.
To print her photos on the color printer:
1. The daughter types \\readyshare in the address field of her web browser.
This gives her access to the USB drive in the router.
2. She copies the photos from the Mac to the router USB drive.
3. The mother uses a her web browser or Microsoft Networking to transfer the files from the
USB drive to her computer. Then she prints the files.
Share Large Files with Colleagues
Sending files larger than 5 MB can pose a problem for many email systems. The router
allows you to share very large files such as PowerPoint presentations or .zip files with
colleagues at another site. Rather than tying up their mail systems will large files, your
colleagues can use FTP to easily download shared files from the wireless modem router.
To share files with a remote colleague:
1. To protect your network, set up security. Create a user name and password for the
colleague with appropriate access.
2. If you want to limit USB drive access to read-only access, from the wireless modem router
USB Storage (Basic Settings) screen, click Edit a Network folder. In the Write Access field,
select admin, and then click Apply.
Note: The password for admin is the same one that you use to access the
wireless modem router. By default it is password.
3. Enable FTP via Internet in the USB Storage (Advanced Settings) screen. See Configure
USB Storage Advanced Settings on page 70.
USB Storage
67
Page 68

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
USB Storage Basic Settings
You can view or edit basic settings for the USB storage device attached to your wireless
modem router. On the wireless modem router main menu under USB, select Basic Settings.
The following screen displays:
By default, the USB storage device is available to all computers on your local area network
(LAN). To access your USB device from this screen, you can click the network or device
name or the share name.
Network or device name:
\\readyshare
Share name:
\\readyshare\USB_Storage
You can also type \\readyshare in the address field of your web browser. If you logged in to
the wireless modem router before you connected your USB device, you might not see your
USB device in the wireless modem router screens until you log out and then log in again.
Table 9. USB Storage (Basic Settings)
Fields and buttons Description
Network Device Name The default is \\readyshare. This is the name used to access the
USB device connected to the wireless modem router.
USB Storage
68
Page 69

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Table 9. USB Storage (Basic Settings) (continued)
Fields and buttons Description
Available
Network Folders
Edit button You can click the Edit button to edit the Available Network Folders
Safely Remove USB Device
button
Folder Name Full path of the used by the network folder.
Volume name Volume name from the storage device (either USB drive or HDD).
Total/Free
Space
Share Name • You can click the name shown, or you can type it in the address
Read and Write
Access
Shows the current utilization of the storage device.
field of your web browser.
• If Not Shared is shown, then the default share has been deleted,
and no other share for the root folder exists. Click the link to
change this setting.
Shows the network folder permissions and access controls.
• All-no password allows all users to access the network folder.
• admin uses the same password that you use to log in to the
wireless modem router main menu.
settings. See Edit a Network Folder on page 69.
Click to safely remove the USB device attached to your wireless
modem router. See Unmount a USB Drive on page 72.
Edit a Network Folder
This process is the same from either the USB Storage (Basic Settings) screen or the USB
Storage (Advanced Settings) screen. Click the Edit button to open the Edit Network Folder
screen:
You can use this screen to select a folder, to change the share name, or to change read
access or write access from All-no password to admin. The password for admin is the same
one that is used to log in to the router main menu. By default it is password.
USB Storage
69
Page 70

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Note: You need to click Apply for your changes to take effect.
Configure USB Storage Advanced Settings
To configure advanced USB settings, from the router menu, under USB, select Advanced
Settings. The USB Storage (Advanced Settings) screen displays:
You can use this screen to specify access to the USB storage device. The following table
explains the fields and buttons in the USB Storage (Advanced Settings) screen.
Table 10. USB Storage (Advanced Settings)
Fields Description
Network Device Name The default is readyshare. This is the name used to access the USB
device connected to the wireless modem router from your computer.
Workgroup If you are using a Windows workgroup rather than a domain, the
workgroup name is displayed here.
USB Storage
70
Page 71

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Table 10. USB Storage (Advanced Settings) (continued)
Fields Description
Access Method Network
Connection
HTTP Disabled by default. If you enable this setting, you can type
HTTP (via
Internet)
FTP Disabled by default.
FTP (via
Internet)
Available
Network Folders
Folder Name Full path of the used by the network folder.
Volume name Volume name from the storage device (either USB drive or HDD).
Total/Free
Space
Share Name • You can click the name shown, or you can type it into the address
Read and Write
Access
Enabled by default, this allows all users on the LAN to have access
to the USB drive.
http://readyshare to access the USB drive.
Disabled by default. If you enable this setting, remote users can type
http://readyshare to access the USB drive over the Internet.
Disabled by default. If you enable this setting, remote users can
access the USB drive through FTP over the Internet.
The current utilization of the storage device.
field of your web browser.
• If Not Shared is shown, then the default share has been deleted,
and no other share for the root folder exists. Click the link to
change this setting.
Shows the permissions and access controls on the network folder.
• All-no password allows all users to access the network folder.
• admin prompts you to enter the same password that you use to
log in to the wireless modem router main menu.
Create a Network Folder
To create a network folder:
1. From the USB Storage (Advanced Settings) screen, click the Create a Network Folder
button to open the Create a Network Folder screen:
USB Storage
71
Page 72

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
2. Create a folder.
• You can specify the folder’s share name read access and write access from All-no
password to
• The password for admin is the same one that is used to log in to the wireless modem
router main menu. By default it is password.
3. Click Apply so that your changes take effect.
admin.
Unmount a USB Drive
WARNING:
Unmount the USB drive first before physically unplugging it from
the wireless modem router. If the USB disk is removed or a cable
is pulled while data is being written to the disk, it could result in
file or disk corruption.
To unmount a USB disk drive so that no users can access it, from the USB Settings screen,
click the Safely Remove USB button. This takes the drive offline.
Specify Approved USB Devices
You can specify which USB devices are approved for use when connected to the router.
To specify approved USB devices:
1. On the router main menu, under Advanced, select USB Settings.
USB Storage
72
Page 73

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
2. Click Approved Devices.
3. On the USB Drive Approved Devices screen, select the USB device from the Available USB
Devices list.
4. Click Add.
5. Select the Allow only approved devices check box.
6. Click Apply so that your change takes effect.
If you want to approve another USB device, you need to first click the Safely Remove USB
Device button to unmount the currently connected USB device. Connect the other USB
device, and then repeat this process.
Connect to the USB Drive from a Remote Computer
To connect to the USB drive from remote computers using a web browser, you need to use
the router’s Internet port IP address.
Locate the Internet Port IP Address
To view the Internet port IP address:
1. Log in to the wireless modem router.
2. In the main menu, under Maintenance, select Router Status.
3. Record the IP address that is listed for the Internet port. This is the IP address you can use
to connect to the router remotely.
Access the Router’s USB Drive Remotely Using FTP
To connect to the router’s USB drive using a web browser:
1. Connect to the router by typing ftp:// and the Internet port IP address in the address field
of Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator, for example, ftp://10.1.65.4. If you are using
Dynamic DNS, you can type the DNS name rather than the IP address.
2. Type the account name and password that provide access rights to the USB drive.
USB Storage
73
Page 74

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
3. The directories of the USB drive that your account has access to display, for example,
share/partition1/directory1. You can now read and copy files from the USB directory.
Connect to the USB Drive with Microsoft Network Settings
You can access the USB drive from local computers on your home or office network using
Microsoft network settings. You need to be running Microsoft Windows 2000, XP, or older
versions of Windows with Microsoft Networking enabled. You can use normal Explorer
operations such as dragging and dropping, opening files, or cutting and pasting files from:
• Microsoft Windows Start menu, Run option
• Windows Explorer
• Network Neighborhood or My Network Place
Enable File and Printer Sharing
Each computer’s network properties need to be set to enable network communication with
the USB drive. File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networking needs to be enabled, as
described in the following sections.
Note: In Windows 2000 and Windows XP, File and Printer Sharing is
enabled by default.
Configure Windows 98SE and Windows ME
The easiest way to get to your network properties is to go to your desktop, right-click
Network Neighborhood, and then select Properties. File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft
Windows should be listed. If it is not, click Add, and follow the installation prompts.
Note: If you have any questions about File and Printer Sharing, contact
Microsoft for assistance.
Configure Windows 2000 and Windows XP
Right-click the network connection for your local area network. File and Printer Sharing for
Microsoft Windows should be listed. If it is not, click Install, and follow the installation
prompts.
USB Storage
74
Page 75

6. Advanced Configuration
This chapter describes how to configure the advanced features of your wireless modem router.
For information about remote management, see Configure Remote Management on page 62.
The following features are discussed in this chapter:
• Configure WAN Settings
• Configure Dynamic DNS
• Configure LAN Settings
• Set Up Quality of Service (QoS)
• Advanced Wireless Settings
• Use Static Routes
• Configure Universal Plug and Play
• Build Wireless Bridging and Repeating Networks
• Port Forwarding and Port Triggering
• Advanced USB Settings
• Traffic Meter
6
75
Page 76

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Configure WAN Settings
In the main menu, under Advanced, select WAN Setup to display the following screen.
Table 11. WAN settings
Setting Description
Disable SPI Firewall The SPI (stateful packet inspection) firewall protects your LAN against
denial of service attacks. This should be disabled only in special
circumstances.
Default DMZ Server See Set Up a Default DMZ Server on page 77.
Respond to a Ping on an Internet
WAN Port
MTU Size The normal MTU (maximum transmit unit) value for most Ethernet
NAT Filtering This option determines how the router deals with inbound traffic. The
If you want the wireless modem router to respond to a ping from the
Internet, select the Respond to Ping on Internet Port check box. This
should be used only as a diagnostic tool, since it allows your wireless
modem router to be discovered. Do not select this check box unless you
have a specific reason to do so.
networks is 1500 bytes, or 1492 bytes for PPPoE connections. For some
ISPs you might need to reduce the MTU. But this is rarely required and
should not be done unless you are sure it is necessary for your ISP
connection.
Secured option provides a secured firewall to protect the computers on
LAN from attacks from the Internet, but it might cause some Internet
games, point-to-point applications, or multimedia applications not to work.
The Open option, on the other hand, provides a much less secured
firewall, while it allows almost all Internet applications to work.
Disabling the SIP ALG The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Application Level Gateway (ALG) is
enabled by default to optimize VoIP phone calls that use the SIP. The
Disable SIP ALG check box allows you to disable the SIP ALG. Disabling
the SIP ALG might be useful when running certain applications.
Advanced Configuration
76
Page 77

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Set Up a Default DMZ Server
The default demilitarized zone (DMZ) server feature is helpful when you use some online
games and videoconferencing applications that are incompatible with NAT. The wireless
modem router is programmed to recognize some of these applications and to work correctly
with them, but there are other applications that might not function well. In some cases, one
local computer can run the application correctly if that computer’s IP address is entered as
the default DMZ server.
Note: For security reasons, you should avoid using the default DMZ server
feature. When a computer is designated as the default DMZ server,
it loses much of the protection of the firewall, and is exposed to
many exploits from the Internet. If compromised, the computer can
be used to attack your network.
Incoming traffic from the Internet is usually discarded by the wireless modem router unless
the traffic is a response to one of your local computers or a service that you have configured
in the Port Forwarding/Port Triggering screen. Instead of discarding this traffic, you can have
it forwarded to one computer on your network. This computer is called the default DMZ
server.
To assign a computer or server to be a default DMZ server:
1. In the main menu, under Advanced, select WAN Setup.
2. Select the Default DMZ Server check box.
3. Type the IP address for that server.
4. Click Apply to save your changes.
Advanced Configuration
77
Page 78

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Configure Dynamic DNS
If your network has a permanently assigned IP address, you can register a domain name and
have that name linked with your IP address by public Domain Name Servers (DNS).
However, if your Internet account uses a dynamically assigned IP address, you will not know
in advance what your IP address will be, and the address can change frequently. In this case,
you can use a commercial Dynamic DNS service that will allow you to register your domain to
their IP address and will forward traffic directed at your domain to your frequently changing IP
address.
The router contains a client that can connect to a Dynamic DNS service provider. To use this
feature, you need to select a service provider and obtain an account with them. After you
have configured your account information in the router, whenever your ISP-assigned IP
address changes, your router automatically contacts your Dynamic DNS service provider,
logs in to your account, and registers your new IP address.
To configure Dynamic DNS:
1. In the main menu, under Advanced, select Dynamic DNS.
2. Access the website of one of the Dynamic DNS service providers whose names appear in
the Service Provider drop-down list, and register for an account. For example, for
dyndns.org, go to www.dyndns.org.
3. Select the Use a Dynamic DNS Service check box.
4. Select the name of your Dynamic DNS service provider.
5. Type the host name that your Dynamic DNS service provider gave you. The Dynamic DNS
service provider might call this the domain name. If your URL is myName.dyndns.org, then
your host name is myName.
6. Type the user name for your Dynamic DNS account.
7. Type the password (or key) for your Dynamic DNS account.
8. If your Dynamic DNS provider allows the use of wildcards in resolving your URL, you can
select the Use Wildcards check box to activate this feature. For example, the wildcard
feature causes *.yourhost.dyndns.org to be aliased to the same IP address as
yourhost.dyndns.org.
Advanced Configuration
78
Page 79

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
9. Click Apply to save your configuration.
Note: If your ISP assigns a private WAN IP address such as 192.168.x.x
or 10.x.x.x, the Dynamic DNS service will not work because private
addresses are not routed on the Internet.
Configure LAN Settings
The LAN Setup screen allows configuration of LAN IP services such as DHCP.
Note: If you change the LAN IP address of the wireless modem router
while connected through the browser, you will be disconnected. You
need to then open a new connection to the new IP address and log
in again.
The wireless modem router is shipped preconfigured to use private IP addresses on the LAN
side and to act as a DHCP server. The wireless modem router’s default LAN IP configuration
is as follows:
• LAN IP address. 192.168.0.1
• Subnet mask. 255.255.255.0
These addresses are part of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)–designated private
address range for use in private networks and should be suitable in most applications. If your
network has a requirement to use a different IP addressing scheme, you can make those
changes by opening the LAN Setup screen.
Advanced Configuration
79
Page 80

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Under Advanced in the main menu, select LAN Setup.
Table 12. LAN Setup
Setting Description
Device Name This is a user-friendly name of the router. You can see this name for
the router in Network Explorer on Windows systems.
IP Address This is the LAN IP address of the wireless modem router.
IP Subnet Mask This is the LAN subnet mask of the wireless modem router.
Combined with the IP address, the IP subnet mask allows a device to
know which other addresses are local to it, and which need to be
reached through a gateway or wireless modem router.
Use Router as DHCP Server See the following section, Configure DHCP.
Address Reservation See Configure Reserved IP Addresses on page 81.
Configure DHCP
By default, the wireless modem router functions as a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP) server, allowing it to assign IP, DNS server, and default gateway addresses to all
computers connected to the wireless modem router’s LAN. The assigned default gateway
address is the LAN address of the router. IP addresses are assigned to the attached
computers from a pool of addresses specified in this screen. Each pool address is tested
before it is assigned to avoid duplicate addresses on the LAN.
For most applications, the default DHCP and TCP/IP settings of the router are satisfactory.
Advanced Configuration
80
Page 81

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Use Router as DHCP Server
If another device on your network will be the DHCP server, or if you will manually configure
the network settings of all of your computers, clear the Use Router as DHCP Server check
box. Otherwise, leave it selected.
Specify the pool of IP addresses to be assigned by setting the starting IP address and ending
IP address. These addresses should be part of the same IP address subnet as the router’s
LAN IP address. Using the default addressing scheme, you should define a range between
192.168.0.2 and 192.168.0.254, although you might want to save part of the range for
devices with fixed addresses.
The router delivers the following settings to any LAN device that requests DHCP:
• An IP address from the range you have defined
• Subnet mask
• Gateway IP address, which is the router’s LAN IP address
• Primary DNS server, if you entered a primary DNS address in the Basic Settings screen;
otherwise, the router’s LAN IP address
• Secondary DNS server, if you entered a secondary DNS address in the Basic Settings
screen
• WINS server, short for Windows Internet Naming Service Server, determines the IP
address associated with a particular Windows computer. A WINS server records and
reports a list of names and IP addresses of Windows computers on its local network. If
you connect to a remote network that contains a WINS server, enter the server’s IP
address here. This allows your computers to browse the network using the Network
Neighborhood feature of Windows.
Configure Reserved IP Addresses
When you specify a reserved IP address for a computer on the LAN, that computer will
always receives the same IP address each time it accesses the router’s DHCP server.
Reserved IP addresses should be assigned to servers that require permanent IP settings.
To reserve an IP address:
1. In the LAN Setup screen, click the Add button.
2. In the IP Address field, type the IP address to assign to the computer or server. Choose an
IP address from the router’s LAN subnet, such as 192.168.0.x.
3. Type the MAC address of the computer or server.
Tip: If the computer is already present on your network, you can copy its
MAC address from the Attached Devices screen and paste it here.
4. Click Apply to enter the reserved address into the table.
Advanced Configuration
81
Page 82

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Note: The reserved address will not be assigned until the next time the
computer contacts the router’s DHCP server. Reboot the computer
or access its IP configuration and force a DHCP release and renew.
To edit or delete a reserved address entry:
1. Select the radio button next to the reserved address that you want to edit or delete.
2. Click Edit or Delete.
Set Up Quality of Service (QoS)
Quality of Service (QoS) is an advanced feature that can be used to prioritize some types of
traffic ahead of others. The modem router can provide QoS prioritization over the wireless
link and on the Internet connection.
The modem router supports WiFi Multimedia Quality of Service (WMM QoS) to prioritize
wireless voice and video traffic over the wireless link. WMM QoS provides prioritization of
wireless data packets from different applications based on four access categories: voice,
video, best effort, and background. For an application to receive the benefits of WMM QoS,
both it and the client running that application need to be WMM enabled. Legacy applications
that do not support WMM, and applications that do not require QoS, are assigned to the best
effort category, which receives a lower priority than voice and video.
Configure QoS for Internet Access
To add or create a policy to prioritize traffic:
1. From the main menu, under Advanced, select QoS Setup.
Advanced Configuration
82
Page 83

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
2. Click Setup QoS rule. The QoS Priority Rule list displays:
3. To change a rule, select its radio button, and scroll down to the bottom of the screen:
4. To edit a rule, click Edit. To add a custom rule, click Add Priority Rule, and enter the
requested information on the screen that displays.
5. Click Apply to save this rule to the QoS Policy list and return to the QoS Setup screen.
6. In the QoS Setup screen, click Apply.
Advanced Configuration
83
Page 84

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Advanced Wireless Settings
From the main menu, under the Advanced heading, select Wireless Settings:
Restrict Wireless Access to Your Network
By default, any wireless computer that is configured with the correct SSID can access your
wireless network. For increased security, the wireless modem router provides several ways to
restrict wireless access to your network.
You can do the following:
• Turn off wireless connectivity completely.
• Restrict access based on the wireless network name (SSID).
• Restrict access based on the Wireless Card Access List.
These options are discussed in the following sections.
Turn Off Wireless Connectivity Completely
You can completely turn off the wireless connectivity of the wireless modem router by
pressing the WiFi On/Off button on the front panel of the wireless modem router. For
example, if you use your notebook computer to wirelessly connect to your wireless modem
router and you take a business trip, you can turn off the wireless portion of the wireless
modem router while you are traveling. Other members of your household who use computers
connected to the wireless modem router through Ethernet cables can still use the wireless
modem router. To do this, clear the Enable Wireless Access Point check box on the Wireless
Settings screen, and then click Apply.
Advanced Configuration
84
Page 85

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Hide Your Wireless Network Name (SSID)
By default, the wireless modem router is set to broadcast its wireless network name (SSID).
You can restrict wireless access to your network by not broadcasting the wireless network
name (SSID). To do this, clear the Allow Broadcast of Name (SSID) check box on the
Wireless Settings screen, and then click Apply. Wireless devices will not “see” your wireless
modem router. You need to configure your wireless devices to match the SSID of the wireless
modem router.
Note: The SSID of any wireless access adapters need to match the SSID
you specify in the wireless modem router. If the SSIDs do not match,
you will not get a wireless connection to the wireless modem router.
Restrict Access by MAC Address
For increased security, you can restrict access to the wireless network to allow only specific
computers based on their MAC addresses. You can restrict access to only trusted computers
so that unknown computers cannot wirelessly connect to the wireless modem router. MAC
address filtering adds an obstacle against unwanted access to your network, but the data
broadcast over the wireless link is fully exposed.The Wireless Card Access List determines
which wireless hardware devices will be allowed to connect to the wireless modem router.
To restrict access based on MAC addresses:
1. In the Wireless Settings screen, click the Set Up Access List button to display the list.
2. Select the Turn Access Control On check box to enable the restricting of wireless
computers by their MAC addresses.
Note: If you are using a wireless connection, do not click Apply until you
have added your computer’s MAC address in this screen.
3. Click the Add button to add wireless stations so that they will have access.
• You can select currently connected wireless computers from the Available Wireless
Cards List.
Advanced Configuration
85
Page 86

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
• You can type in the MAC address for the wireless computer or device. The MAC
address is usually printed on the wireless card, or on the label of a wireless device. It
might appear in the wireless modem router’s DHCP table. The MAC address is
12 hexadecimal digits.
• You can copy and paste the MAC addresses from the wireless modem router’s
Attached Devices screen into the MAC Address field of this screen. To do this,
configure each wireless computer to obtain a wireless link to the wireless modem
router. The computer should then appear in the Attached Devices screen.
4. Click Add to add each entry. You can add several stations to the list.
5. When you are finished adding stations, click Apply.
Now, only computers and devices on this list can wirelessly connect to the wireless modem
router. This prevents unauthorized access to your network.
Configure WPS Settings
The advanced WPS settings cannot be displayed if you have selected WEP as the security
option.
To display and specify advanced WPS settings:
1. Log in to the wireless modem router as described in Log In to Your Wireless-N Modem
Router on page 17.
2. In the main menu, under Advanced, select Wireless Settings to display the Advanced
Wireless Settings screen:
By default the Enable WPS check box is selected. If you clear this check box and click
Apply, you will not be able to use WPS.
3. Under WPS Settings, you can configure the following settings:
Advanced Configuration
86
Page 87

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
• Disable Router’s PIN. Only when the wireless modem router’s PIN is enabled can
you configure the wireless modem router’s wireless settings or add a wireless client
through WPS with the wireless modem router’s PIN number. If the wireless modem
router detects suspicious attempts to access the network with a PIN, the PIN function
might be disabled temporarily. You can manually enable the PIN function by clearing
the Disable Router’s PIN check box.
• Keep Existing Wireless Settings. By default, the Keep Existing Wireless Settings
check box is cleared. This allows the modem router to automatically generate the
SSID and WPA/WPA2 security settings when it implements WPS. After WPS is
implemented, the modem router automatically selects this check box so that your
SSID and wireless security settings remain the same if other WPS-enabled devices
are added later.
If you configure your wireless router settings and security manually, the Keep Existing
Wireless Settings check box will also be selected. This allows you to use WPS (Push 'N'
Connect) to connect additional WPS-capable devices to your wireless network using the
existing settings.
4. Click Apply to save your settings.
Use Static Routes
Static routes provide additional routing information to your router. Under normal
circumstances, the router has adequate routing information after it has been configured for
Internet access, and you do not need to configure additional static routes. You need to
configure static routes only for unusual cases such as multiple routers or multiple IP subnets
located on your network.
Static Route Example
As an example of when a static route is needed, consider the following case:
• Your primary Internet access is through a cable modem to an ISP.
• You have an ISDN router on your home network for connecting to the company where
you are employed. This router’s address on your LAN is 192.168.0.100.
• Your company’s network address is 134.177.0.0.
When you first configured your router, two implicit static routes were created. A default route
was created with your ISP to the wireless modem router, and a second static route was
created to your local network for all 192.168.0.x addresses. With this configuration, if you
attempt to access a device on the 134.177.0.0 network, your router forwards your request to
the ISP. The ISP forwards your request to the company where you are employed, and the
request is likely to be denied by the company’s firewall.
In this case you need to define a static route, telling your router that 134.177.0.0 should be
accessed through the ISDN router at 192.168.0.100.
In this example:
Advanced Configuration
87
Page 88

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
• The Destination IP Address and IP Subnet Mask fields specify that this static route applies
to all 134.177.x.x addresses.
• The Gateway IP Address field specifies that all traffic for these addresses should be
forwarded to the ISDN router at 192.168.0.100.
• The value in the Metric field represents the number of routers between your network and
the destination. This is a direct connection, so it can be set to the minimum value of 2.
• The Private check box is selected only as a precautionary security measure in case RIP is
activated.
Configure Static Routes
To add a static route:
1. In the main menu, under Advanced, select Static Routes.
2. Click Add to open the Static Routes screen.
3. Enter a route name for this static route in the Route Name field. This name is for
identification purpose only.
4. Select Private if you want to limit access to the LAN only. The static route will not be
reported in RIP.
5. Select Active to make this route effective.
6. Enter the IP address of the final destination.
Advanced Configuration
88
Page 89

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
7. Enter the IP subnet mask for this destination. If the destination is a single host, type
255.255.255.255.
8. Enter the gateway IP address, which needs to be a router on the same LAN segment as the
router.
9. Enter a number between 2 and 15 in the Metric field. This represents the number of routers
between your network and the destination. Usually, a setting of 2 or 3 works.
10. Click Apply. The Static Routes table is updated to show the new entry.
Configure Universal Plug and Play
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) helps devices such as Internet appliances and computers
access the network and connect to other devices as needed. UPnP devices can
automatically discover the services from other registered UPnP devices on the network.
To configure Universal Plug and Play:
1. On the main menu, select UPnP:
2. Fill in the settings on the UPnP screen:
• Turn UPnP On. UPnP can be enabled or disabled for automatic device configuration.
The default setting for UPnP is enabled. If UPnP is disabled, the wireless modem
router does not allow any device to automatically control the resources, such as port
forwarding (mapping), of the wireless modem router.
• Advertisement Period. The advertisement period is how often the wireless modem
router advertises (broadcasts) its UPnP information. This value can range from 1 to
Advanced Configuration
89
Page 90

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
1440 minutes. The default period is 30 minutes. Shorter durations ensure that control
points have current device status at the expense of additional network traffic. Longer
durations might compromise the freshness of the device status but can significantly
reduce network traffic.
• Advertisement Time to Live. The time to live for the advertisement is measured in
hops (steps) for each UPnP packet sent. Hops are the steps allowed to propagate for
each UPnP advertisement before it disappears. The number of hops can range from 1
to 255. The default value for the advertisement time to live is 4 hops, which should be
fine for most home networks. If you notice that some devices are not being updated or
reached correctly, then it might be necessary to increase this value a little.
• UPnP Portmap Table. The UPnP Portmap Table displays the IP address of each
UPnP device that is currently accessing the wireless modem router and which ports
(internal and external) that device has opened. The UPnP Portmap Table also
displays what type of port is opened and if that port is still active for each IP address.
3. Save, cancel your changes, or refresh the table:
• Click Apply to save the new settings to the wireless modem router.
• Click Cancel to disregard any unsaved changes.
• Click Refresh to update the portmap table and to show the active ports that are
currently opened by UPnP devices.
Build Wireless Bridging and Repeating Networks
With the DGN2200M Mobile Edition wireless modem router, you can build large bridged
wireless networks that form an IEEE 802.11n Wireless Distribution System (WDS). Using the
modem router with other access points (APs) and wireless devices, you can connect clients
by using their MAC addresses rather than by specifying IP addresses.
Here are some examples of wireless bridged configurations:
• Point-to-point bridge. The wireless modem router communicates with another
bridge-mode wireless station. See Point-to-Point Bridge Configuration on page 92.
• Multi-point bridge. The wireless modem router is the “master” for a group of bridge-mode
wireless stations. Then all traffic is sent to this master, rather than to other access points.
See Multi-Point Bridge on page 93.
• Repeater with wireless client association. Sends all traffic to the remote access point.
See Repeater with Wireless Client Association on page 94.
Note: The wireless bridging and repeating feature uses the default
security profile to send and receive traffic.
Advanced Configuration
90
Page 91

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
To view or change these configurations, from the main menu, select Wireless Repeating
Function:
Advanced Configuration
91
Page 92

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Point-to-Point Bridge Configuration
In point-to-point bridge mode, the wireless modem router communicates as an access point
with another bridge-mode wireless station. When used as a bridge, wireless client
associations are disabled—only wired clients can be connected. You need to enter the MAC
address of the other bridge-mode wireless station in the field provided. Use wireless security
to protect this communication. The following figure shows an example of point-to-point bridge
mode.
Both access points (APs) are in
point-to-point bridge mode.
AP 1 (DGN2200M modem router)
Internet
192.168.0.1
AP 2
Switch or hub
Computers
LAN Segment 1
Figure 1. Point-to-point bridge mode
To set up a point-to-point bridge configuration:
LAN Segment 2
Computers
1. Configure the DGN2200M Mobile Edition wireless modem router (AP 1) on LAN
Segment 1 in point-to-point bridge mode.
2. Configure the other access point (AP 2) on LAN Segment 2 in point-to-point bridge mode.
The DGN2200M Mobile Edition wireless modem router needs to have AP 2’s MAC
address in its Remote MAC Address field, and AP 2 needs to have the DGN2200M Mobile
Edition’s MAC address in its Remote MAC Address field.
3. Configure both APs, and verify that both APs are using the same SSID, channel,
authentication mode, if any, and security settings if security is in use.
4. Disable the DHCP server on AP 2. AP 1 will then be the DHCP server.
5. Verify connectivity across LAN Segment 1 and LAN Segment 2. A computer on either LAN
segment should be able to connect to the Internet or share files and printers of any other
computers or servers connected to LAN Segment 1 or LAN Segment 2.
Advanced Configuration
92
Page 93

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Multi-Point Bridge
Multi-point bridge mode allows a router to bridge to multiple peer access points
simultaneously. Wireless client associations are disabled. Only wired clients can be
connected. Multi-point bridge mode configuration includes the following steps:
1. Enter the MAC addresses of the other access points in the fields provided.
2. Set the other bridge-mode access points to point-to-point bridge mode, using the MAC
address of this DGN2200M Mobile Edition as the remote MAC address.
3. Use wireless security to protect this traffic.
Point-to-point
bridge mode
DGN2200M
AP 1
Point-to-point
Internet
192.168.0.1
Computers
LAN Segment 1
LAN Segment 2
Figure 2. Multi-point bridge mode
To set up the multi-point bridge configuration:
bridge mode
AP 2
Hub or switch
1. Configure the operating mode of the wireless modem routers.
• Because it is in a central location, configure the DGN2200M Mobile Edition wireless
modem router (AP 1) on LAN segment 1 in point-to-multi-point bridge mode, and
enter the MAC addresses of AP 2 and AP 3 in the Remote MAC Address 1 and
Remote MAC Address 2 fields.
AP 3
Hub or switch
Computers
LAN Segment 3
Computers
• Configure the access point (AP 2) on LAN segment 2 in point-to-point bridge mode
with the remote MAC address of the DGN2200M Mobile Edition wireless modem
router.
• Configure the access point (AP 3) on LAN segment 3 in point-to-point bridge mode
with the remote MAC address of the DGN2200M Mobile Edition wireless modem
router.
2. Disable the DHCP server on AP 2 and AP 3. AP 1 will then be the DHCP server.
3. Verify the following for all access points:
Advanced Configuration
93
Page 94

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
• The LAN networks of the wireless modem router and other access points are
configured to operate in the same LAN network address range as the LAN devices.
• Only one access point, the DGN2200M Mobile Edition wireless modem router in
Figure 2, Multi-point bridge mode, is configured in point-to-multi-point bridge mode; all
the others are in point-to-point bridge mode.
• All APs, including the DGN2200M Mobile Edition wireless modem router, need to be
on the same LAN. That is, all the access point LAN IP addresses need to be in the
same network.
• If you are using DHCP, for all access points, in the Internet IP Address section of the
Basic Settings screen, the Get Dynamically from ISP check box should be selected.
• All APs, including the DGN2200M Mobile Edition wireless modem router, need to use
the same SSID, channel, authentication mode, if any, and WEP security settings if
security is in use.
• All point-to-point APs need to have the MAC address of AP 1 (the DGN2200M Mobile
Edition wireless modem router in the previous figure) in the Remote AP MAC address
field.
4. Verify connectivity across the LANs. A computer on any LAN segment should be able to
connect to the Internet or share files and printers with any other computers or servers
connected to any of the three LAN segments.
Note: Wireless stations configured as they are in Figure 1 on page 92 will
not be able to connect to the wireless modem router or access
points. If you require wireless stations to access any LAN segment,
you can use additional access points configured in wireless access
point mode in any LAN segment.
Repeater with Wireless Client Association
In the repeater mode with wireless client association, the DGN2200M Mobile Edition wireless
modem router sends all traffic to a remote access point. For the repeater mode, you need to
enter the MAC address of the remote “parent” access point. Alternatively, you can configure
the DGN2200M Mobile Edition wireless modem router as the parent by entering the address
of a “child” access point. Note that the following restrictions apply:
• You do not have the option of disabling client associations with this DGN2200M Mobile
Edition wireless modem router.
• You cannot configure a sequence of parent-child APs. You are limited to only one parent
access point, although if the DGN2200M Mobile Edition wireless modem router is the
parent access point, it can connect with up to four child APs.
Advanced Configuration
94
Page 95

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
The following figure shows an example of a repeater mode configuration.
Wireless computer
associated with AP 1
DGN2200M
AP 2 in repeater mode
Internet
192.168.0.1
Computers
AP 1 (parent AP in repeater mode)
AP 3 in repeater mode
Figure 3. Repeater mode
To set up a repeater with wireless client association:
1. Configure the operating mode of the devices.
• Configure AP 1 (the DGN2200M Mobile Edition wireless modem router in Figure 3,
Repeater mode) with the MAC address of AP 2 and AP 3 in the first two Remote MAC
Address fields.
• Configure AP 2 with the MAC address of AP 1 in the Remote MAC Address field.
• Configure AP 3 with the MAC address of AP 1 in the Remote MAC Address field.
Wireless computer
associated with AP 2
Wireless computer
associated with AP 3
2. Verify the following for both access points:
• The LAN network configuration of each access point is configured to operate in the
same LAN network address range as the LAN devices.
• The access points need to be on the same LAN. That is, the LAN IP addresses for the
access points need to be in the same network.
• If you are using DHCP, for all access points, in the Internet IP Address section of the
Basic Settings screen, the Get Dynamically from ISP check box should be selected.
• Access point devices need to use the same SSID, channel, authentication mode, and
encryption.
3. Verify connectivity across the LANs. A computer on any LAN segment should be able to
connect to the Internet or share files and printers with any other computers or servers
connected to any of the three WLAN segments.
Port Forwarding and Port Triggering
Port forwarding and port triggering are advanced features that affect the behavior of the
firewall in your wireless modem router. Using the Port Forwarding / Port Triggering screen,
you can make local computers or servers available to the Internet for different services (for
Advanced Configuration
95
Page 96

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
example, FTP or HTTP), to play Internet games (like Quake III), or to use Internet
applications (like CU-SeeMe).
• Port triggering monitors outbound traffic. When the router detects traffic on the specified
outbound port, it remembers the IP address of the computer that sent the data and
triggers the incoming port. Incoming traffic on the triggered port is then forwarded to the
triggering computer. Port triggering allows requests from the Internet only after a
designated port is triggered. Port triggering applies to chat and Internet games.
• Port forwarding is designed for FTP, web server, or other server-based services. Once
port forwarding is set up, requests from the Internet are forwarded to the correct server.
Port Forwarding
To set up port forwarding:
1. From the main menu, under the Advanced Heading, select Port Forwarding/Port
Triggering.
2. You can select a service or create a custom service.
• Select a service from the Service Name drop-down list, and specify the computer’s IP
address.
• If you want to add a service that is not in the list, click the Add Custom Service button.
Fill in the fields in the Add Custom Service screen.
The service displays in the list.
Port Triggering
To set up port triggering:
1. From the main menu, under the Advanced Heading, select Port Forwarding/Port
Triggering.
Advanced Configuration
96
Page 97

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
2. Select the Port Triggering radio button to display the following screen:
3. Click Add Service, and fill in the fields in the Add Service screen.
The service displays in the list. For more detailed information, see the Port
Forwarding/Port Triggering help.
Advanced USB Settings
For added security the router can be set up to share only approved USB devices. To enable
this feature, select No, and click Apply.
To define the approved devices, click USB Drive Approved Devices.
Advanced Configuration
97
Page 98

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
Traffic Meter
Traffic metering allows you to monitor the volume of Internet traffic passing through your
wireless modem router’s Internet port. With the traffic meter utility, you can set limits for traffic
volume, set a monthly limit, and get a live update of traffic usage.
To monitor traffic on your router:
1. Under Advanced on the main menu, select Traffic Meter.
2. To enable the traffic meter, select the Enable Traffic Meter check box.
3. If you would like to record and restrict the volume of Internet traffic, select the Traffic
volume control by radio button. You can select one of the following options for controlling
the traffic volume:
• No Limit. No restriction is applied when the traffic limit is reached.
• Download only. The restriction is applied to incoming traffic only.
• Both Directions. The restriction is applied to both incoming and outgoing traffic.
4. You can limit the amount of data traffic allowed per month:
• By specifying how many Mbytes per month are allowed.
• By specifying how many hours of traffic are allowed.
Advanced Configuration
98
Page 99

N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition
5. Set the traffic counter to begin at a specific time and date.
6. Set up traffic control to issue a warning message before the monthly limit of Mbytes or hours
is reached. You can select one of the following to occur when the limit is attained:
• The Internet LED flashes green or amber.
• The Internet connection is disconnected and disabled.
7. Set up Internet traffic statistics to monitor the data traffic.
8. Click the Traffic Status button if you want a live update on Internet traffic status on your
router.
9. Click Apply to save your settings.
Advanced Configuration
99
Page 100

7. Troubleshooting
This chapter provides information about troubleshooting your N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem
Router DGN2200M Mobile Edition. After each problem description, instructions are provided to
help you diagnose and solve the problem. For the common problems listed, go to the section
indicated.
• Is the router on?
Go to Basic Functioning on page 101.
• Have I connected the router correctly?
Go to Basic Functioning on page 101.
• What are the LEDs on the front panel telling me?
Go to Troubleshoot with the LEDs on page 101.
• I cannot access the router’s configuration with my browser.
Go to Cannot Log In to the Wireless-N Modem Router on page 103.
7
• I have configured the router, but I cannot access the Internet.
Go to Troubleshoot the Internet Connection on page 104.
• Can my computer communicate with my router or with a remote device on the Internet?
Go to Troubleshoot a TCP/IP Network Using the Ping Utility on page 107.
• I cannot remember the router’s configuration password.
Go to Restore the Default Configuration and Password on page 108.
• I want to clear the configuration and start over again.
Go to Restore the Default Configuration and Password on page 108.
• The date or time is wrong.
Go to Problems with Date and Time on page 108.
100
 Loading...
Loading...