Page 1
S
UPERSCRIPT COLOR
LASER
NETWORK GUIDE
October, 1999
703-A0368-001
Page 2

Proprietary Notice and Liability Disclaimer
The information disclosed in this document, including all
designs and related materials, is the valuable property of
NEC Technologies and/or its licensors, as appropriate,
reserve all patent, copyright and other proprietary rights to
this document, including all design, manufacturing,
reproduction, use and sales rights thereto, except to the
extent said rights are expressly granted to others.
The NEC T echnologies product(s) discussed in this document
are warranted in accordance with the terms of the Limited
Warranty Statement accompanying each product. However,
actual performance of each such product is dependent upon
factors such as system configuration, customer data and
operator control. Since implementation by customers of each
product may vary, the suitability of specific product
configurations and applications must be determined by the
customer and is not warranted by NEC Technologies.
To allow for design and specification improvements, the
information in this document is subject to change at any time
without notice. Reproduction of this document or portions
thereof without prior approval of NEC Technologies is
prohibited.
© NEC Technologies, Inc., 1999
Microsoft, Windows, Windows 95, Windows 98,
Windows NT, Windows for Workgroups, and MS-DOS are
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Adobe PostScript® 3 is a trademark of Adobe Systems
Incorporated.
All other product, service, brand, or trade names used in this
publication are the trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective companies or organizations. NEC disclaims
any responsibility for specifying which marks are owned by
which companies or organizations.
Copyright 1999
NEC T echnologies, Inc.
1250 N. Arlington Heights Rd.
Itasca, IL 60143
All Rights Reserved.
Copyright 1999
NEC Corporation
7-1 Shiba 5-Chome, Minato-Ku
Tokyo 108-01, Japan
All Rights Reserved.
ii SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Chapter 1 Introduction 1
Overview 1
Network Setup Tasks 1
Typical Network Setups 2
Types of Network Topologies 2
Chapter 2 NIC Installation 5
Overview 5
Installing the Network Interface Card (NIC) 5
What You Will Need 5
Preparing the Printer 6
Installing the NIC 6
Testing the NIC 8
Network Settings Page 9
NIC Features 10
NIC Status Lights 10
Resetting the NIC 10
Restoring Factory Default Settings 10
Chapter 3 IP Address 11
Overview 11
Assigning the IP Address 11
Obtaining the Printer’s IP Address 11
Selecting an IP Address Assignment Method 11
Using the Operator Panel 12
Using MAP 13
Using BOOTPL32 14
Using ARP 15
Using DHCP 16
Chapter 4 Network Administration
Page 17
Using the Network Administration page 17
Accessing the Network Administration Page 17
Chapter 5 Windows Setup 21
Windows Peer-to-Peer 21
IP vs. IPX Peer-to-Peer Printing 21
Installing Peer-to-Peer Software 21
Adding the Peer-to-Peer Printer 22
Moving a Peer-to-Peer Printer 24
Removing Peer-to-Peer Software 24
Setting Up Windows NT 24
Setting LPR Printing on an NT Network 24
Shared Printing in Windows 95/98 25
Chapter 6 NetWare Setup 27
NetWare 5.x and 4.x 27
Attaching the Printer 27
Installing the Printer Driver 31
Configuring the Network Printer 31
NetWare 3.x 32
Starting PCONSOLE 32
Defining the Print Queue 32
Defining the Print Server 32
Defining the Printer 32
Assigning the Print Queue 32
Confirming Successful Configuration 32
Installing and Configuring Your Printer Driver 32
Chapter 8 Macintosh Setup 33
Overview 33
Macintosh Requirements 33
Software Requirements 33
Hardware Requirements 33
Setting Up the Printer 34
Installing the PPD 34
Configuring the Printer 34
Renaming Your Printer 35
Printing 35
Page Setup 36
Uninstalling the Driver 36
Mac Peer-to-Peer 36
iii
Page 4

Adding the Peer-to-Peer Printer 36
Chapter 8 UNIX Setup 37
Setting Up on a Unix System 37
Configuring the IP Address on the Printer 37
Setting Up Your Printing Mode 37
chapter 9 Web Printing Setup 39
Overview 39
PrintAgent Remote Printing 39
NEC PrintAgent Pull Printing 39
Remote Printing 40
System Requirements 40
Print Agent Remote Printing Setup 40
Remote Printing From Your Desktop 41
Getting Printer Status 42
PrintAgent Status Window Menu Bar 42
PrintAgent Buttons 43
PrintAgent Program Menus 44
PrintAgent Program Menu Commands 44
Pull Printing 46
Pull Printing from Your Desktop 46
Pull Printing User Settings 50
Setting Up a Pull Printing Server 51
Appendix A Troubleshooting 57
Network Printing Problems 57
Check the Printer Operation 57
Check the Network Settings Page 57
Check other Network Users 57
Review Recent System Changes 57
Check Hardware Connections 57
Check NIC Status Lights 57
Troubleshooting for NT Server 58
Troubleshooting for NetWare 58
Troubleshooting for MacOS 59
Copying the Files 61
Resetting Web JetAdmin Discovery 62
Appendix C Safety Information 65
Ozone Emission 65
Laser Safety 65
CDRH Regulations 65
FCC Statement 66
Appendix B Web JetAdmin 61
Using Web JetAdmin 61
Locating the Files 61
iv SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 5

CHAPTER 1
I
NTRODUCTION
O
VERVIEW
The main purpose of this book is to help the network
administrator integrate SuperScript Color Laser printers into
an Ethernet network. The first eight chapters describe setting
up the printer on traditional networks using such systems as
NetWare or Windows NT. Chapter 9 describes Web or
Internet printing using NEC’s unique PrintAgent software.
As described in the user’s guide that came with your
particular SuperScript color laser printer, each printer comes
with its own built-in web server and home page. You can set
up driverless printing and perform network administration
tasks directly from the printer’s home page. See Chapter 9 for
more information on this topic.
Some simplified instructions are included in this guide, but
ideally we assume that you have the following:
• A working knowledge of your network utilities and
system.
• The correct network software.
• A completely operational system.
• Access to the supervisor account as a network
administrator , or access to an account that has supervisor
privileges.
ETWORK SETUP TASKS
N
To begin using the SuperScript Color Laser Printer as a
network printer follow these tasks:
1.
Connect the printer to your network
note:
SuperScript printer, such as 4600N, it already has a
network interface card (NIC) installed. If it is a printer like
the 4400, you can purchase a Network Interface Upgrade
Kit and install a NIC yourself. See Chapter 2 of this user’s
guide for instructions.
2.
Obtain the printer’s IP address
3.
Assign the IP address to the printer
necessary if a DHCP server is present.) See chapter 3 for
details.
4.
Access the Network Administration page to configure
the NIC.
Reconfiguring or modifying the NIC parameters can be
done using the Network Configuration page or MAP.
Chapter 4 explains more about this.
5.
Configure the network and workstations to use the
SuperScript Color Laser network printer.
After configuring the NIC, you are now ready to setup
the computer to print. Select your operating system and
continue configuring your system. The SuperScript CD
that came with the printer contains network printing
tools to support the following operating systems and
network protocols.
From Windows 95/98
• If you have a NetWare network, see Chapter 6 for
NetWare 5.x, 4.x, and 3.x configuration information.
• If you do not have a designated server, you can print
directly to the network printer using the peer-to-peer
software provided on the SuperScript CD that came with
the printer.
• Without a designated network server, you can also set up
shared printing, see page 25.
If there is an N in the model number on the
.
.
. (This step is not
1
Page 6
From Windows NT 4.0
A
f
• If you have a NetWare network, see Chapter 6 for
Netware 5.x, 4.x, and 3.x configuration information.
• In a Windows NT network you can use LPR printing. See
Chapter 5.
From Windows for Workgroups
• If you have a NetWare network, see Chapter 6 for
Netware 5.x, 4.x, and 3.x configuration information.
• You can also use shared printing, see Chapter 5.
From Mac OS
See Chapter 7 of this user’s guide to set up and print from
Macintosh computers over EtherTalk.
10 or fewer computers because peer-to-peer networking
software limits the number of users attached to any one
shared resource.
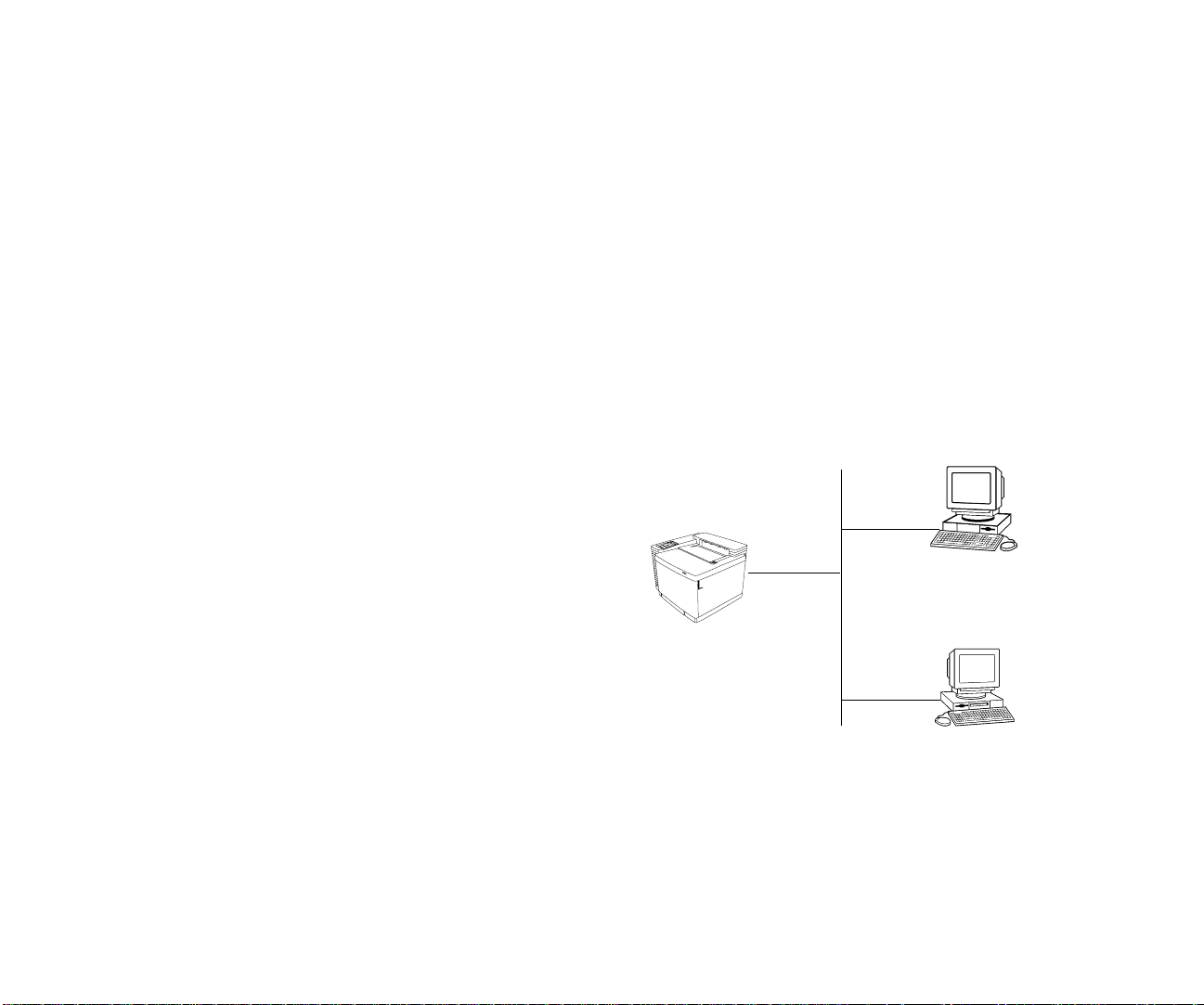
In this scenario,
print clients
use the network to send print
jobs directly to the printer. There is no intermediary
computer (server) that gets involved between the printer and
print clients.
Each client must compete with other clients for printer
availability. If the printer is busy processing a print job, each
client must store their jobs until the printer is ready to accept
them. However, the printer can be upgraded with more
memory to temporarily store multiple jobs until they are
printed. Shown below is an illustration of the peer-to-peer
topology.
From Unix
See Chapter 8 for installing the printer on a UNIX system in
Solaris 2.x and SCO.
T
YPICAL NETWORK SETUPS
Peer -to-Peer T opology
n Ethernet LAN is used to interconnect the printer and print clients.
Print clients send print jobs directly to the printer, but each must wait
or printer availability.
Typical Ethernet networks fall into basically three different
categories or topologies. Network topologies describe how a
network interconnects computers with other equipment such
as a printer . The following describes three topologies that can
be used as solutions for networking your printer. For web
printing options see Chapter 9.
Note:
a computer that can send a print job to the printer.
In this user’s guide, the term “print client” means
Printer
Print Client
Types of Network Topologies
Three networking topologies can be used for networking
your SuperScript color laser printer.
• Peer-to-Peer Topology
• Printer Server Topology
• Printer Sharing Topology
Ethernet
Network
Print Client
Peer -to-Peer T opology
Peer-to-peer topology is the simplest way to network your
printer. It involves print clients, a printer, and a network to
interconnect everything. The network operating system
(NOS) can be Microsoft NT Server, Novell NetWare, or
UNIX. Peer-to-peer is used primarily in smaller networks of
2 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
A local area network (LAN) interconnects the printer and all
the print clients. The network can be a 10MB or 100MB
Ethernet LAN that transports TCP/IP or IPX protocols.
Page 7
The printer and each print client use their own network cable
to connect to the network.
Print jobs sent by clients must not pass through a router to
get to the printer.
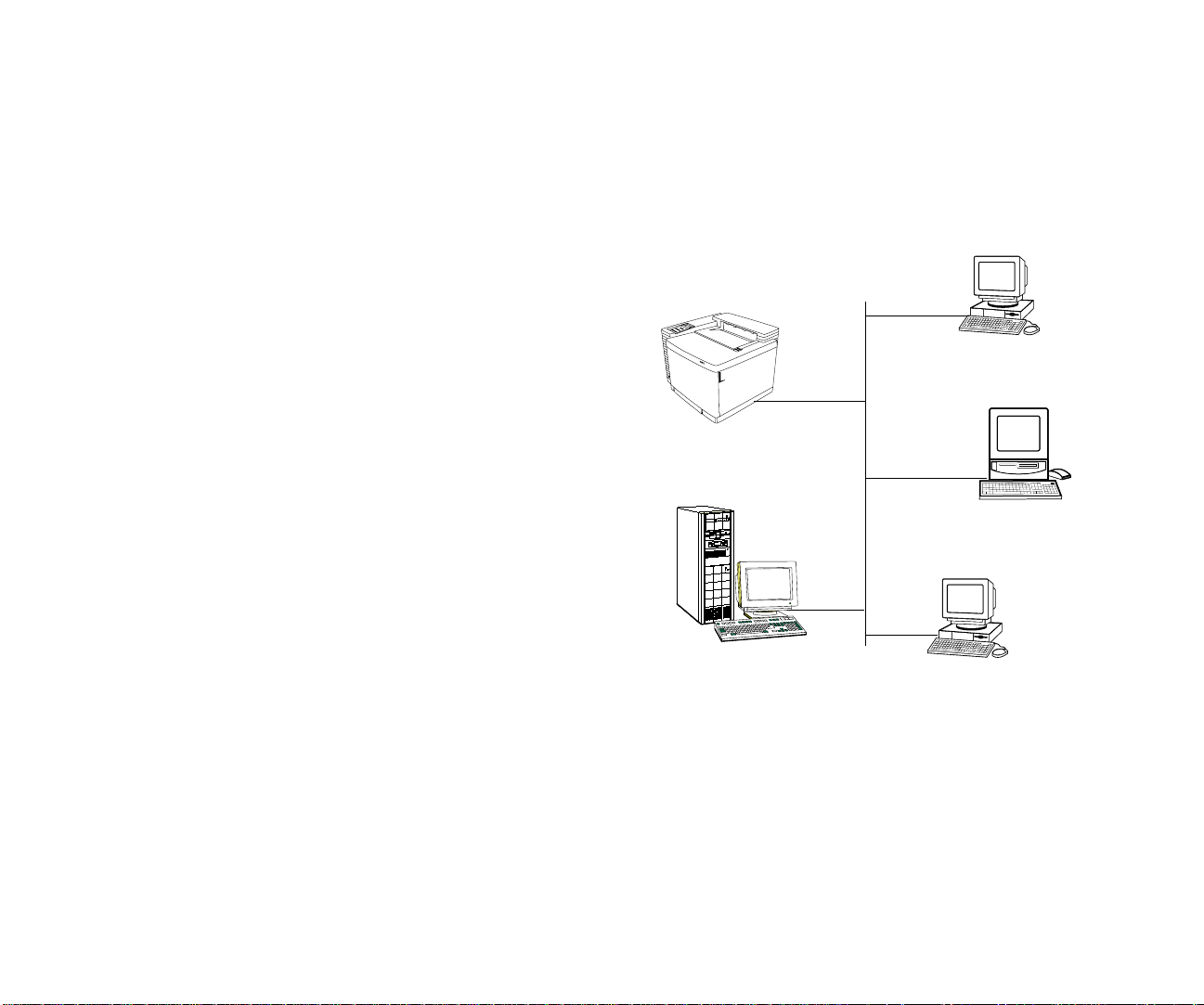
Printer Server Topology
The printer server topology involves a computer, called a
printer server
. All print clients send their print jobs to the
printer server. The printer server then sends the jobs to the
printer. The network operating system (NOS) can be
Microsoft NT Server, Novell NetWare, or UNIX.
In this scenario,
jobs directly to a computer that is configured as a
server
. The server then sends the jobs to the printer.
print clients
use the network to send print
printer
The server can receive and store multiple print jobs; this is
called queuing. Jobs are sent to the printer in the sequence
that they are received. This process relieves a client from
having to process the print job and allows them to focus on
other computing tasks. The server can also be configured for
controlling access to the printer and recording all printing
activity.
Shown below is a diagram of the printer server topology. A
LAN that interconnects the printer, the print clients, and the
printer server . The network can be a 10MB or 100MB Ethernet
LAN that transports TCP/IP or IPX protocols.
Print jobs sent by clients must not pass through a router to
get to the printer.
Printer Server Topology
An Ethernet LAN is used to interconnect the printer, printer
server, and print clients. Print clients send their print jobs to
the printer server where they are queued. The server then
sends the jobs to the printer. The server also controls access to
the printer.
Ethernet
Network
Print Client
Printer
Print Client
Printer Server
Print Client
I
NTRODUCTION
Typical Network Setups 3
Page 8
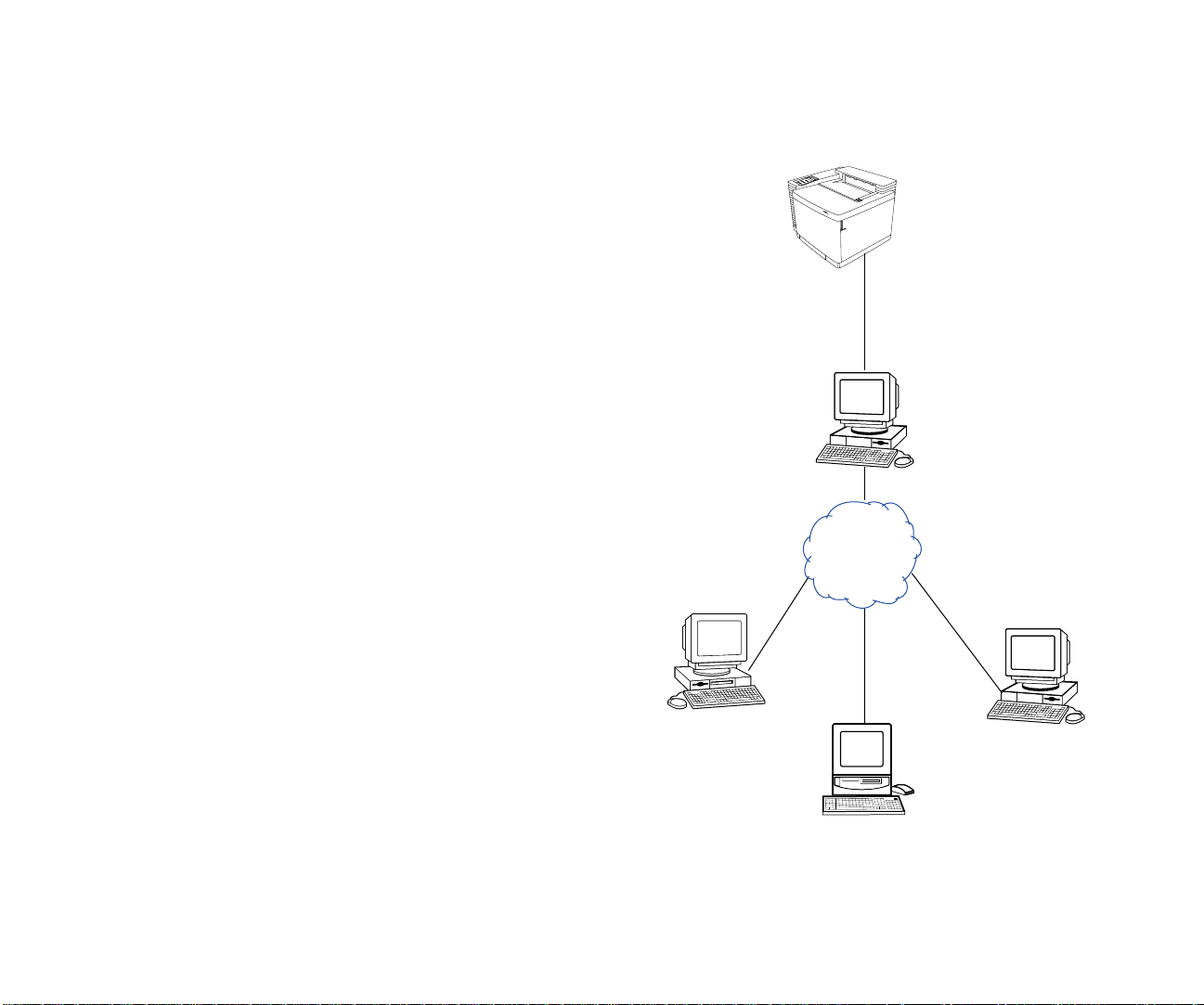
Microsoft Printer Sharing Topology
A
Microsoft Printer Sharing topology involves a LAN that
interconnects the print clients. The printer is directly
connected to one print client using a parallel cable. The client
then is configured to share its printer. Clients that want to use
Printer Sharing Topology
LAN is used to interconnect the print clients. One print client
is connected to the printer using a parallel cable, and is also
configured to share it with other print clients. The sharing client
can control access to the printer.
the printer must be configured so they can connect to the
printer.
If the sharing client receives a print job while its performing
other computing tasks, it may slow down. The network
operating system (NOS) can be Microsoft NT Server, Novell
NetWare, or UNIX.
The LAN can be any type of network that can interconnect
Printer
Parallel Cable
the print clients.
Print client sharing
its printer with other
print clients.
Ethernet
Corporate
Intranet
4 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Print Client
Print Client
Print Client
Page 9
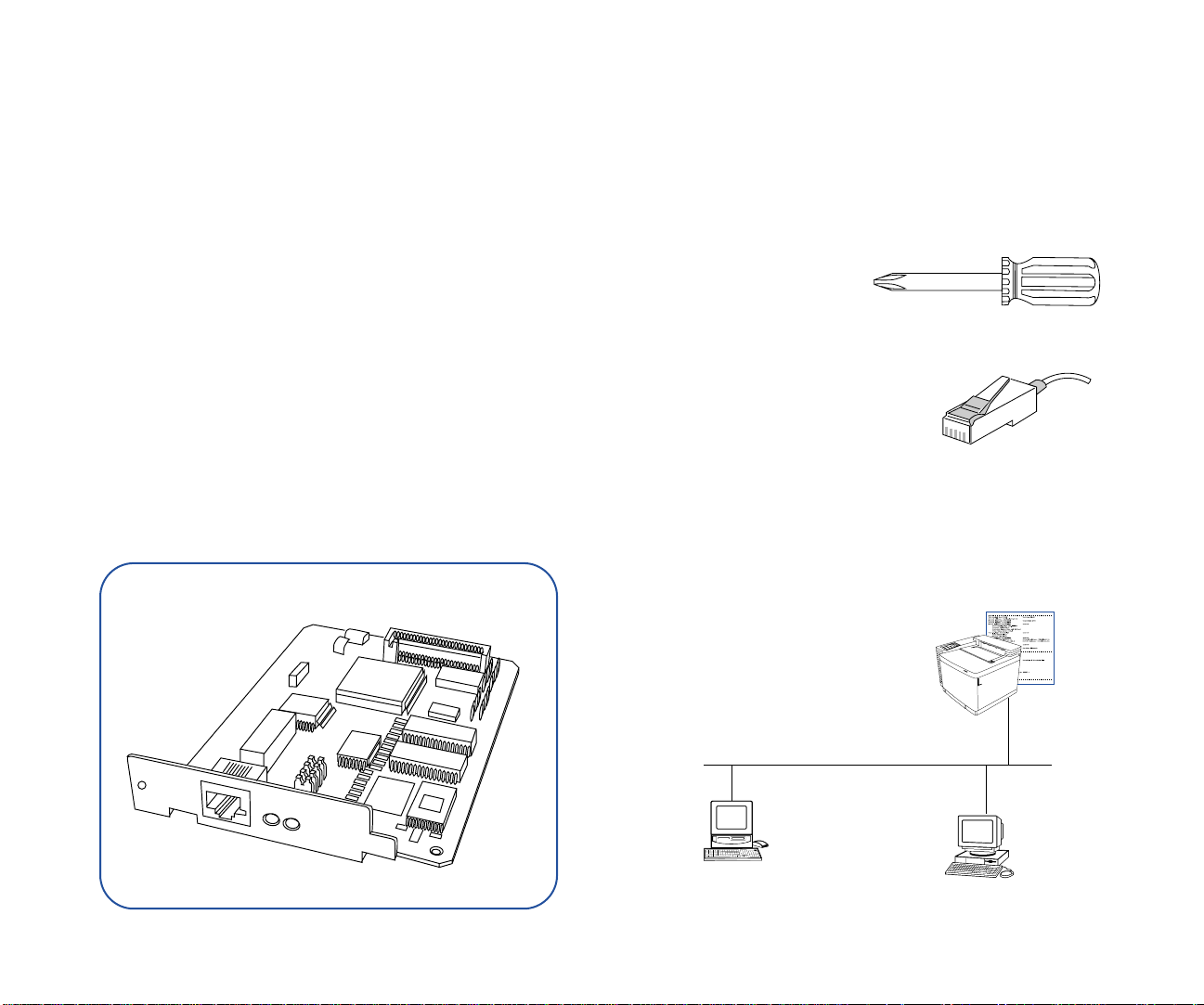
CHAPTER 2
NIC I
O
VERVIEW
If you have an NEC SuperScript™ printer already equipped
with a Network Interface Card (NIC) there is an N in the
model number. For example, the SuperScript 4600N. If you
have a printer without a NIC, such as the SuperScript 4400,
you can upgrade it by installing a NIC. A NIC is a printed
circuit board containing hardwar e for connecting a printer or
computer to a network.
The SuperScript Network Interface Upgrade Kit contains a
NIC that allows you to connect your SuperScript color laser
printer to a network. This makes it the ideal printer for
workgroups and small offices.
NSTALLATION
NSTALLING THE NETWORK
I
NTERFACE CARD
I
Order # 4010
(NIC)
What Y ou Will Need
You will need to provide the following hardware to install
the NIC in your printer and connect it to your network:
• A phillips-head screwdriver
• a Category 5 twisted pair cable with RJ-45 connectors for
10/100Base-T Ethernet®
SuperScript Network Interface Card
note:
10 Mbps or 100 Mbps Ethernet connection. For better
performance, NEC recommends you use shielded cable
and connectors when connecting to 100 Mbps Ethernet.
Installation Steps
1. Assemble what you need
2. Prepare the printer
3. Attach the NIC
4. Test the NIC
5. Print a Network Settings page
6. Get to know the NIC’s features
The NIC automatically detects whether you have a
5
Page 10
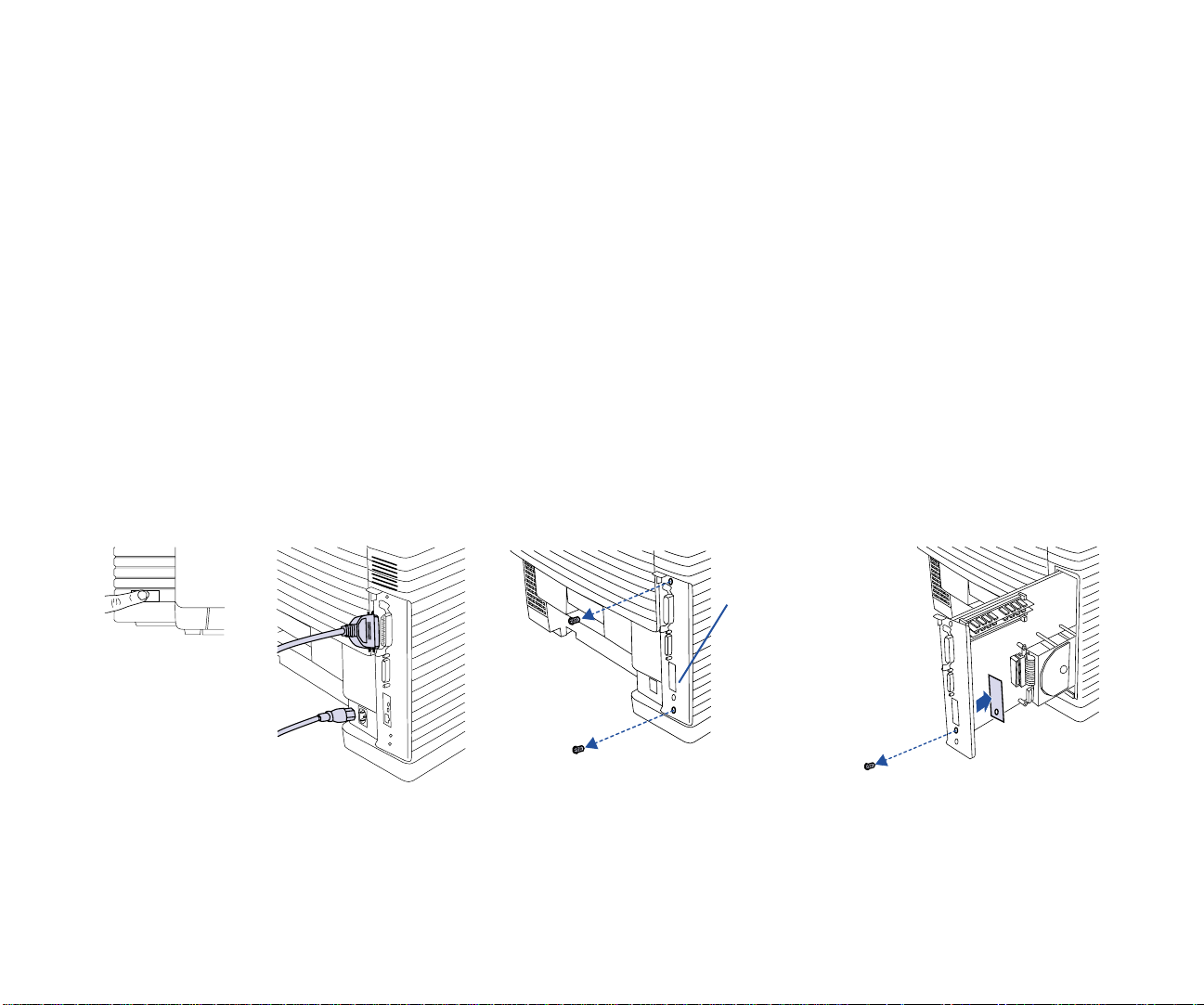
Preparing the Printer
1. T urn of f the printer, remove the power cord from the rear
of the printer, and disconnect the printer cable from the
port
(A)
. Position the printer so you are facing the side
and back corner where the cable port is located. Make
sure that you have enough room to work.
2. Using a small phillips-head screw driver remove the two
screws from the Interface Panel (expansion slot) on the
rear of the printer
3. Remove the screw that holds the small 1.5” x 3.75” plate
over the Network Slot. Remove the plate. Keep the screw
(C)
.
Preparing the Printer
(B)
, and pull out the Controller Board.
Installing the NIC
These steps are illustrated on the opposite page.
4. Two posts are used for fastening the NIC to the
Controller Board. Remove the screw from the lower one,
loosen the screw of the upper one and rotate the small
bracket
circuitry and components!
5. Remove the NIC from its protective bag
NIC only by its edges.
6. Hold the NIC so that its circuitry faces inside the printer
and its LED’s face the back of the printer. Carefully align
the standoff pin with the lower right corner of the NIC.
7. Plug the NIC’s connector to the Controller Board as
shown
8. Use the mounting screws and bracket to fasten the NIC
to the standoff pins as shown. Attach the screw removed
from the front in step 3
9. Slide the Controller Board back in the expansion slot.
Reinstall and tighten the screws
(D)
. Avoid touching the Controller Board
(F)
.
(G)
.
(H)
.
(E)
. Handle the
A
6 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
B
Network Slot
C
Page 11
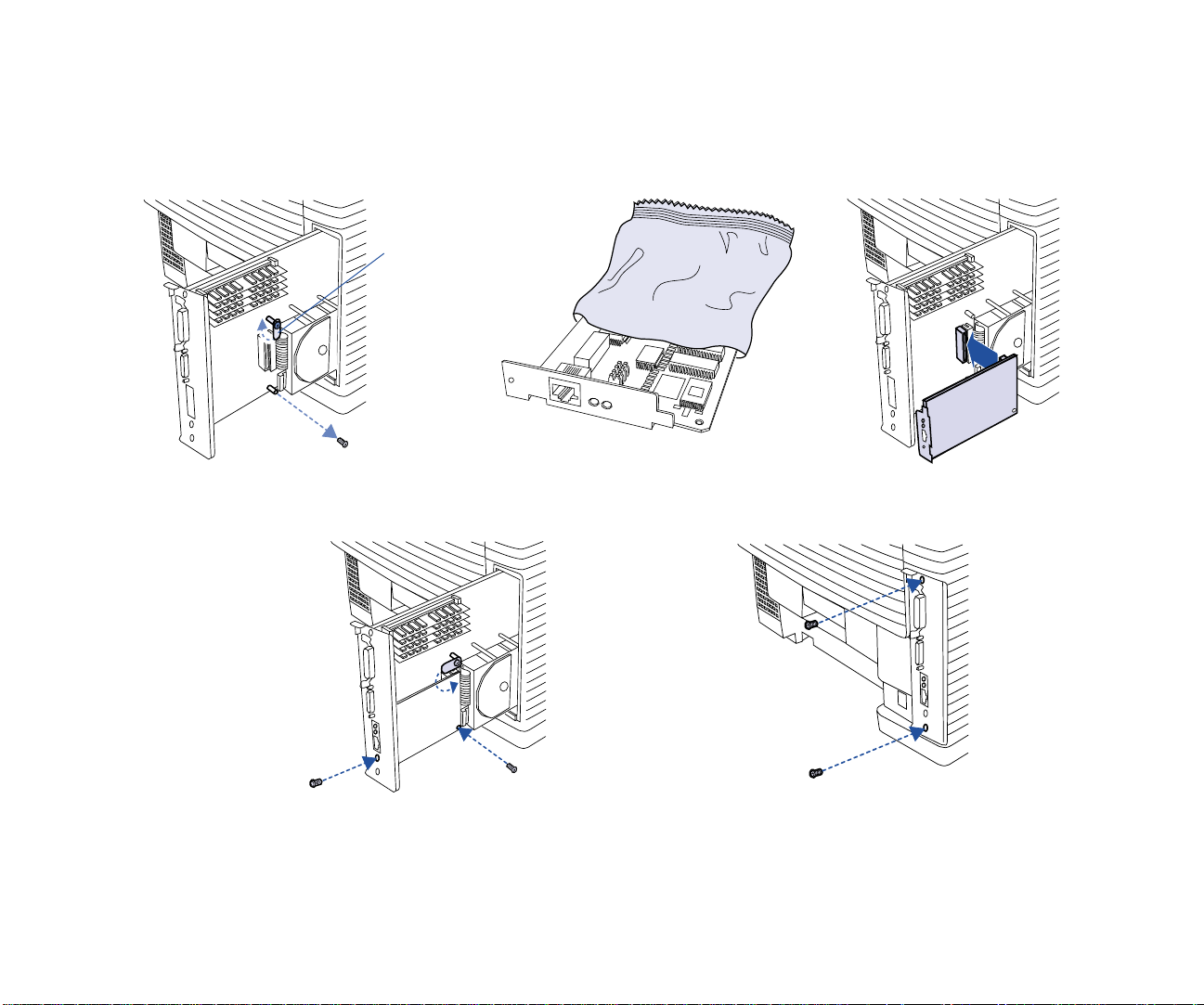
NIC I
Installing the NIC
D
NSTALLATION
E
Bracket
G
H
F
Installing the Network Interface Card (NIC) 7
Page 12
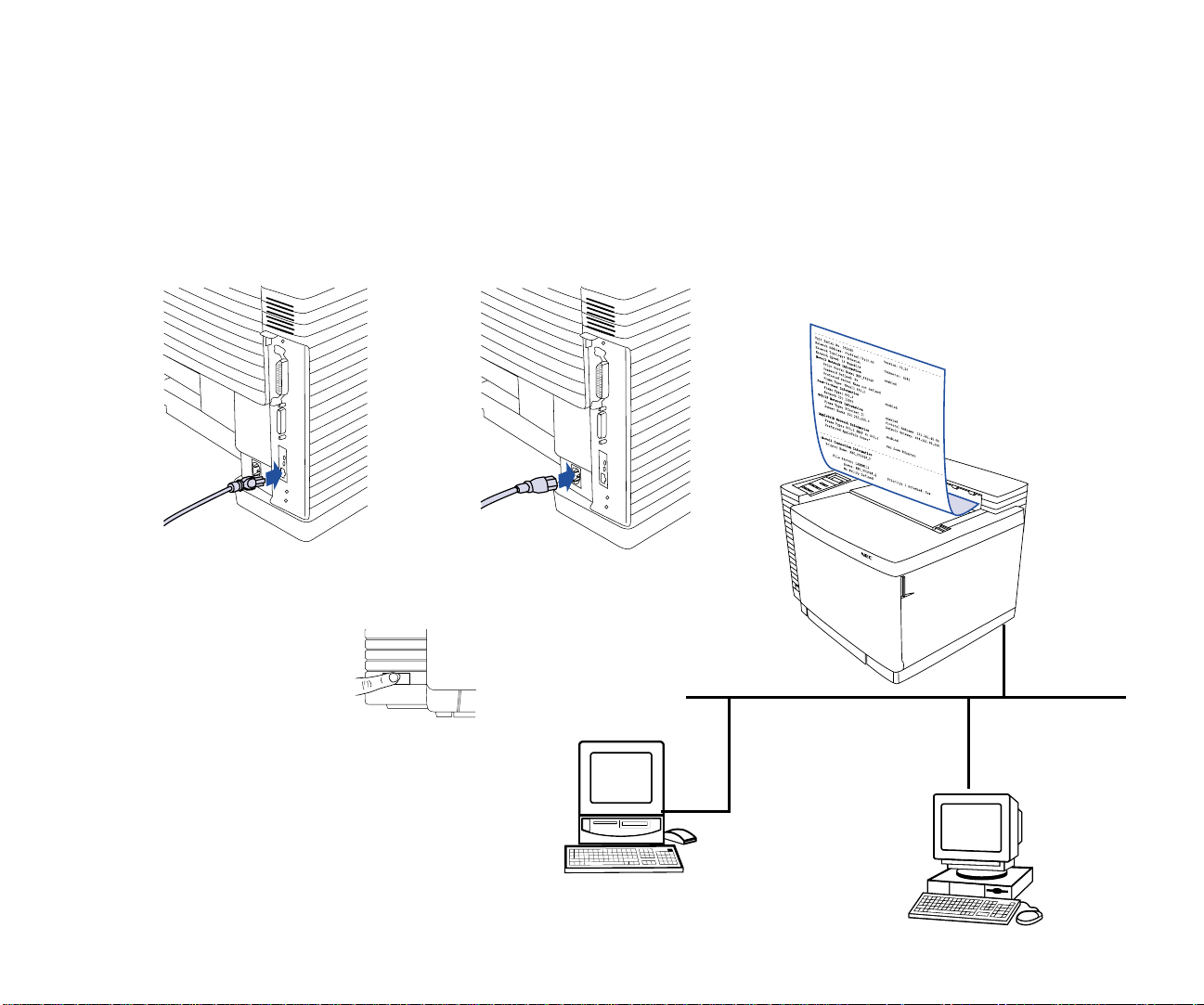
ESTING THE
T
Follow these steps to verify that the NIC is installed and
operating properly.
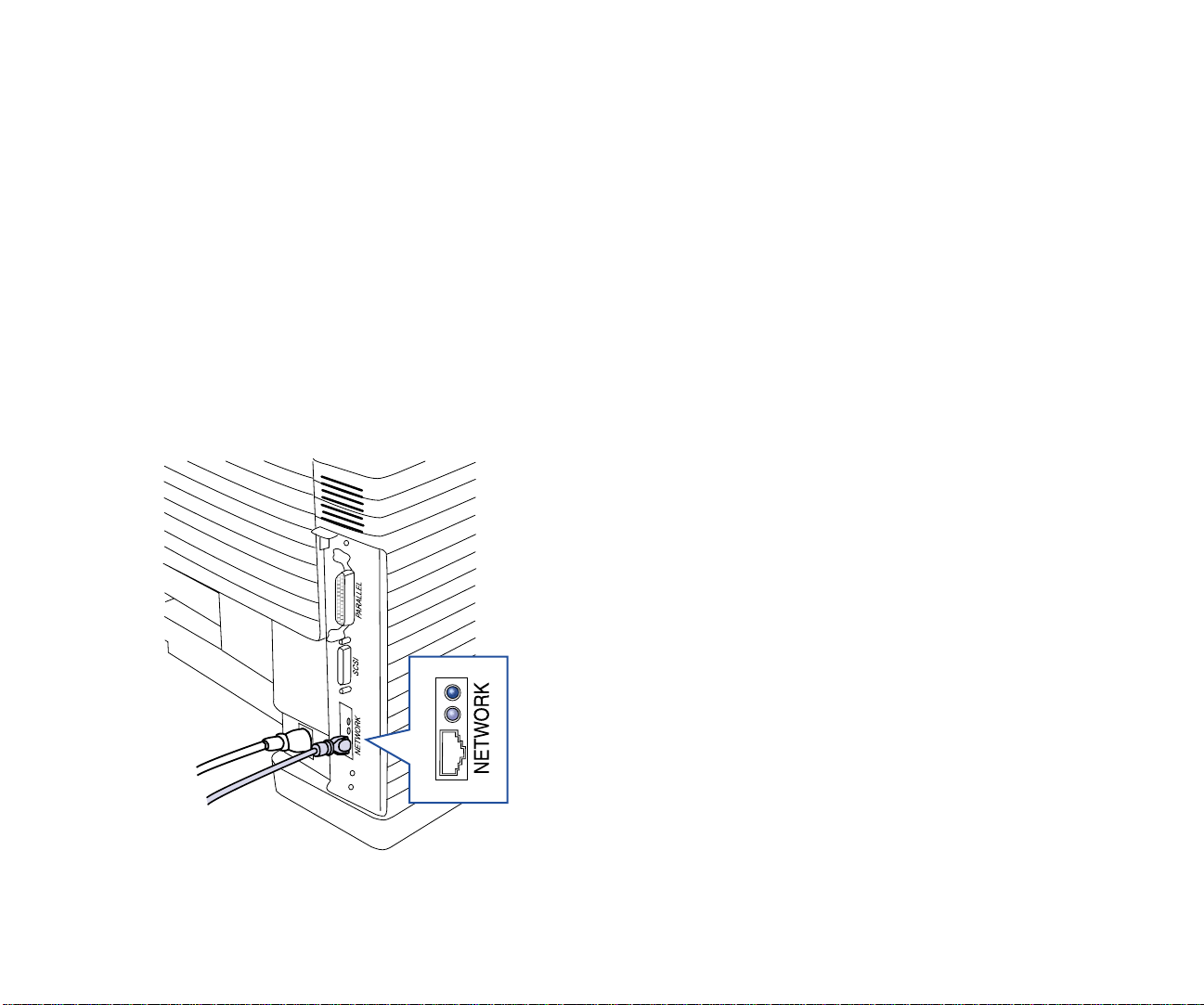
1. Connect the network’s twisted pair cable with RJ-45
connectors to the new network port on your printer
Reattach the power cord to the printer
printer.
Connecting the NIC
NIC
(B)
, plug in the
(A)
2. Turn on the printer
warm up, and then it prints a Network Settings page
with NIC status information.
note:
.
this information when configuring the NIC for your
network.
Keep the Network Settings page. You will need
(C)
. It may take up to 90 seconds to
A
C
B
The SuperScript Color Laser is now a network
printer. The rest of this guide gives information for
configuring your system to use the network printer.
8 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 13
ETWORK SETTINGS PAGE
N
Each time you turn on the networked printer, it prints a
Network Settings page. The Network Settings page provides
information about the network printer settings and network
connections. You should review this page immediately after
NIC installation and any time you change the configuration
to verify that the procedure was done properly.
In the illustration at the right, important features are circled.
The
Print Server Name.
(which is also on the back of the
NIC), is used for printer identification in peer-to-peer and
NetWare protocols. The
address or MAC address. The
address you assign the printer. You can set a new
Printer Name
using the Apple Printer Utility.
Network Address
Protocol Address
is the hardware
is the IP
AppleTalk
Another way to print the Network Settings page is:
1. Go to the URL Configuration Page, the URL is
http://<IP address>/configure.html
2. Click on the
Network Administration
.
link. This displays
the Network Administration Page.
3. Click
Configure Status Page
, then click
Generate Now
.
(The Network Administration Page is described in
Chapter 4.)
The Network Settings Page
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Unit Serial No: 992048 Version: 05.20
Network Address: 00:40:af:79:19:80
Network Topology: Ethernet Connector:RJ45
Network Speed: 10 Megabits
Novell Network Information enabled
Print Server Name: NEC_992048
Password Defined: No
Preferred Server Name not defined
Directory Services Context not defined
Frame Type: Novell 802.3
Peer-to-Peer Information enabled
Frame Type: 802.3
Network ID: 32803
TCP/IP Network Information enabled
Frame Type: Ethernet II Protocol Address: 131.241.45.84
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway: 131.241.45.254
DNS Address: 0.0.0.0
AppleTalk Network Information enabled
Frame Type: 802.2 SNAP On 802.3
Preferred Appletalk Zone:* San Jose EtherNet
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Novell Connection Information
Printer Name: NEC_992048_P
File Server: LABNW312
Queue: NEC_992048_Q Priority: 1 Attached: Yes
No Notify Defined
Peer-to-Peer Connection Information
Printer Name: NEC_992048
AppleTalk Connection Information
AppleTalk Printer Name: Peggy’s SS4600 4
TCP/IP Connection Information
Port Number: 10001
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
NIC I
NSTALLATION
Network Settings Page 9
Page 14
NIC FEATURES
NIC Status Lights
When the NIC is installed, its two status lights, amber and
green, are located on the Interface Panel on the back of the
printer. Light patterns for normal operation are:
Green light is on solid: This shows normal operation
while the printer is awaiting print jobs.
Amber light blinks continuously: This shows that the
NIC is receiving a print job.
Green light blinks 3 times and stays on: This occurs
when the printer has performed a successful self-test. It
then prints a Network Settings page.
Light patterns that identify error conditions are
described in Appendix A, “Troubleshooting” see page 57.
Resetting the NIC
If you change network settings, you may need to reset the
NIC for the new settings to take effect.Turn the printer off
and then on again, or:
1. Go to the URL Configuration Page, the URL is
http://<IP address>/configure.html.
2. Click on the Network Administration link. This displays
the Network Administration Page.
3. Click Reset in the System column,
Restoring Factory Default Settings
You can reset the NIC to its factory default settings. This
means that the NIC clears data such as names and IP
addresses. It does not lose its serial number or Network
Address. If you have changed the printer’s name, it will
revert to its default name.
note: You should restore factory defaults when the
printer is moved to a different network.
To reset the NIC to factory default settings
Go to the Network Administration Page and click Factory
Defaults in the System column. You will need to enter a
password (the default is sysadm). Then turn the printer off
and on again. The Network Administration Page is described
in Chapter 4.
10 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 15
CHAPTER 3
IP ADDRESS
OVERVIEW
T o take advantage of the many SuperScript network featur es,
you must assign an IP address to the printer network
interface card or NIC. This chapter explains several ways of
assigning an IP address.
ASSIGNING THE IP ADDRESS
Obtaining the Printer’s IP Address
Obtain the printer’s IP Address from your network
administrator . (This step is not necessary for Macintosh users
or if you have a DHCP server.)
note: If a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
server is present, an IP address will automatically be
processed and returned to the NIC. A Network Settings
page will print showing the printer IP address. See page
16 for more information about DHCP.
Selecting an IP Address Assignment Method
If a DHCP server is not present, there are several ways to
assign a TCP/IP address to your printer.
Operator Panel
Use the printer’s Operator Panel to assign the IP address to
the printer.
SuperScript MAP Utility
Use the printer’s Management Access Program (MAP) to
assign the IP address from the following operating systems
Windows 95/98
Windows NT 4.0
BOOTPL32
Use BOOTPL32 to assign the IP address from the following
operating systems
Windows 95/98
Windows NT 4.0
ARP
Use ARP to assign the IP address from the following
operating system
Windows 95/98
11
Page 16
Using the Operator Panel
You can use the Operator Panel to enable and set up the
TCP/IP networking parameters for the printer. This is
particularly useful for setting the network IP address so you
can use it as the printer’s URL in Web-based printing (see
Chapter 9). Also, use the Operator Panel to set the IP addr ess
on a UNIX system. Follow these steps:
1. Press the Online button of the Operator Panel. OFFLINE
appears on the display.
2. Press the Menu button to enter menu mode. CONTROL
appears on the display.
3. Press the Next button until COMMUNICATIONS appears
on the display, and press the Select button.
4. Press the Next button until NETWORK appears on the
display, and press the Select button.
5. Press the Next button until TCP/IP appears on the display,
and press the Select button.
6. Press the Next button until NET ADDRESS appears on the
display, and press the Select button.
7. Use the Operator Panel buttons to set values for each of
the 12 digits in this manner.
First press Next to set the cursor to the first digit.
For the first digit, press Select to increment to the correct
value. Then press Next to move to the next digit and
press Select to increment to its correct value. Continue
until all twelve digits are set. When the final digit is set,
press Next to confirm the Net Address you set and then
press Select.
8. Press Menu to exit menu mode and press Online to
bring the printer online.
To validate any changes to network settings, you must turn
the printer off, and then on again.
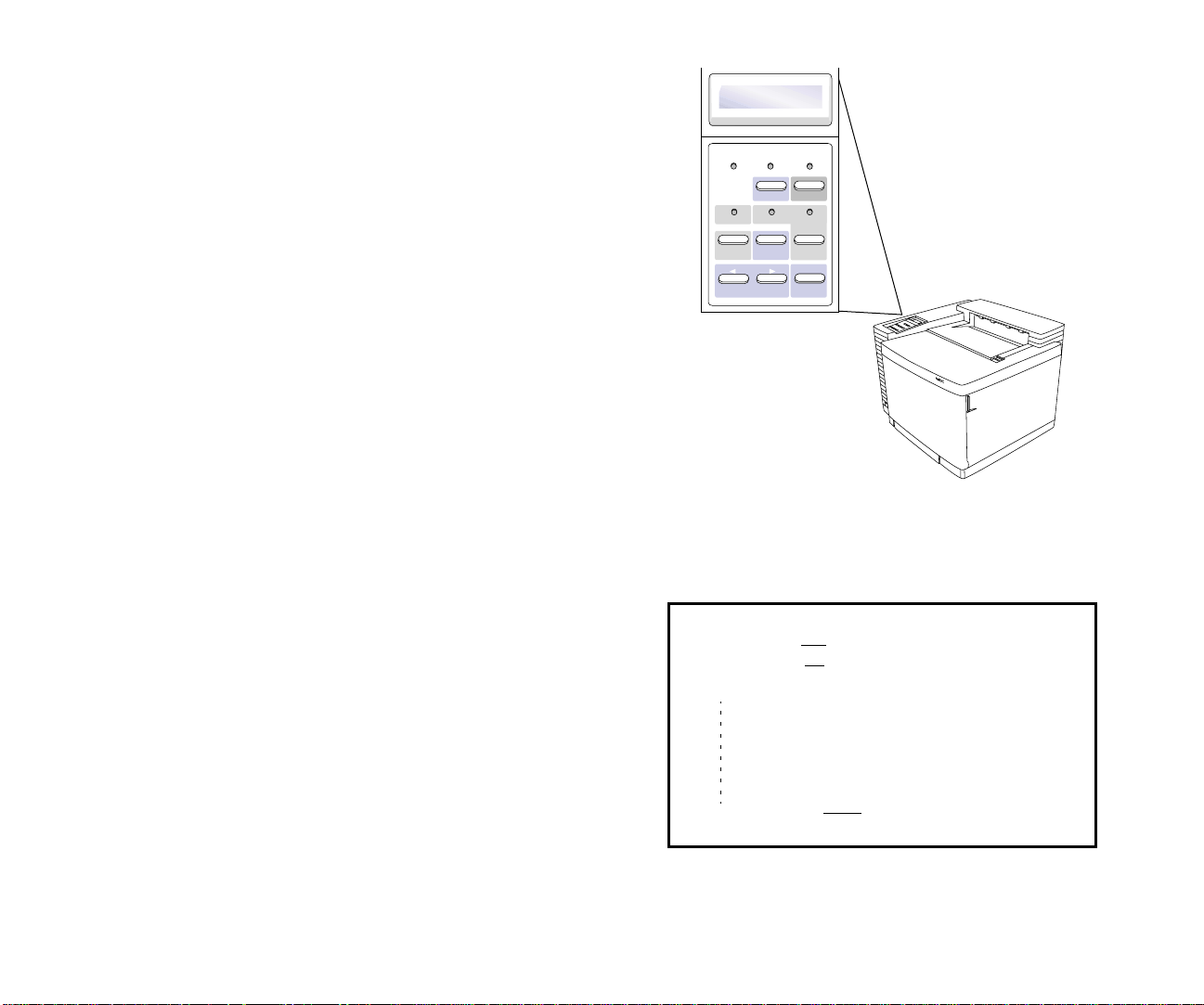
Communications Menu
This menu contains settings that enable the printer to receive
print jobs from the NIC. It can be used to configure
emulations and networking protocols. A diagram of the
Network choices are shown in the box at left. For more
information on the Operator Panel see your SuperScript
printer user’s guide.
Power Warning Online
Menu OnLine
Data OHT Label
Feed Item Media
Previous Next
NETWORK
ETHERTALK
NOVELL IPX
TCP/IP
PERSONALITY
Select
ENABLE* / DISABLE
ENABLE* / DISABLE
ENABLE* /DISABLE
NET ADDRESS
SUBNET MASK
GATEWAY
AIS* / POSTSCRIPT / PCL
*Default selection for the setting.
12 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 17

Using MAP
The Management Access Program (MAP), runs only under
Windows 95/98 and Windows NT 4.0. You use MAP to list
SuperScript network printers connected to your network.
Then you select one to go to its Network Administration
page for network administration options.
MAP Operating Requirements
To use MAP, you must have installed on your PC
• Netscape Navigator or Internet Explorer
• The Microsoft TCP/IP protocol stack, if printer is going
to support TCP/IP.
For IPX Search Functions: The IPX protocol must be
installed and enabled on your PC. Both Microsoft and the
NetWare 32-bit stacks are supported.
Installing MAP
MAP is available on the SuperScript printer driver that came
with your printer. MAP must be installed from Windows 95/
98 or Windows NT 4.0. It cannot be installed from Windows
3.1x or the MS-DOS® command prompt.
1. Insert the your SuperScript CD.
2. Press the Windows Start button and select Run.
At Run, type <drive>:\map\Setup.exe
Then click OK. Follow the Install wizard prompts.
3. Choose the Destination Directory to install the MAP and
click Next.
4. When the Select Program Folder is displayed, type a new
folder name, or select one from the existing Folder list
and click Next.
5. When the “Setup is Complete” Information dialog box is
displayed, click OK, then complete the installation.
Running MAP and Selecting a Printer
In Windows 95/98 or Windows NT 4.0:
1. Press the Start button.
2. Select MAP from the program group you specified
during installation.
3. When MAP starts, a list of all available units on the
network is displayed by unit IP address or serial number.
The unit listing will be divided by TCP/IP units and
IPX/SPX units. See the illustration below.
note: If a unit is enabled for both IP and IPX, it will
appear in both lists.
4. Click on a unit under IPX/SPX in the list to display its
Network Administration Page.
5. Click on a unit under TCP/IP to display the printer’s
Home page.
The Network Administration page options are explained in
Chapter 4. An example using MAP and the Network
Administration page to configure the printer for NetWare 4.x
is shown in Chapter 6.
Management Access Program 3.30
[Refresh] [Help]
Units supporting TCP/IP
http://131.241.45.61/NEC_991142 NEC SuperScript 4600 Ethernet Card
http://131.241.45.203/NEC_991149 NEC SuperScript 4600 Ethernet Card
http://131.241.45.64/NEC_991151 NEC SuperScript 4400 Ethernet Card
http://131.241.45.83/NEC_991650 Print Server Card
http://131.241.45.191/NEC_991653 Print Server Card
http://131.241.45.189/NEC_991655 NEC SuperScript 4400 Ethernet Card
http://131.241.45.127/NEC_999999 Print Server Card
Units supporting IPX/SPX
NEC 991142 NEC SS 4600
NEC 991149
NEC 991151
NEC 991650
NEC 991653
MAP lists the SuperScript printers on your network.
Select one to display its Network Administration page.
NEC SS 4400
NEC SS 4400
NEC SS 4200
NEC SS 4200
IP ADDRESS
Assigning the IP Address 13
Page 18
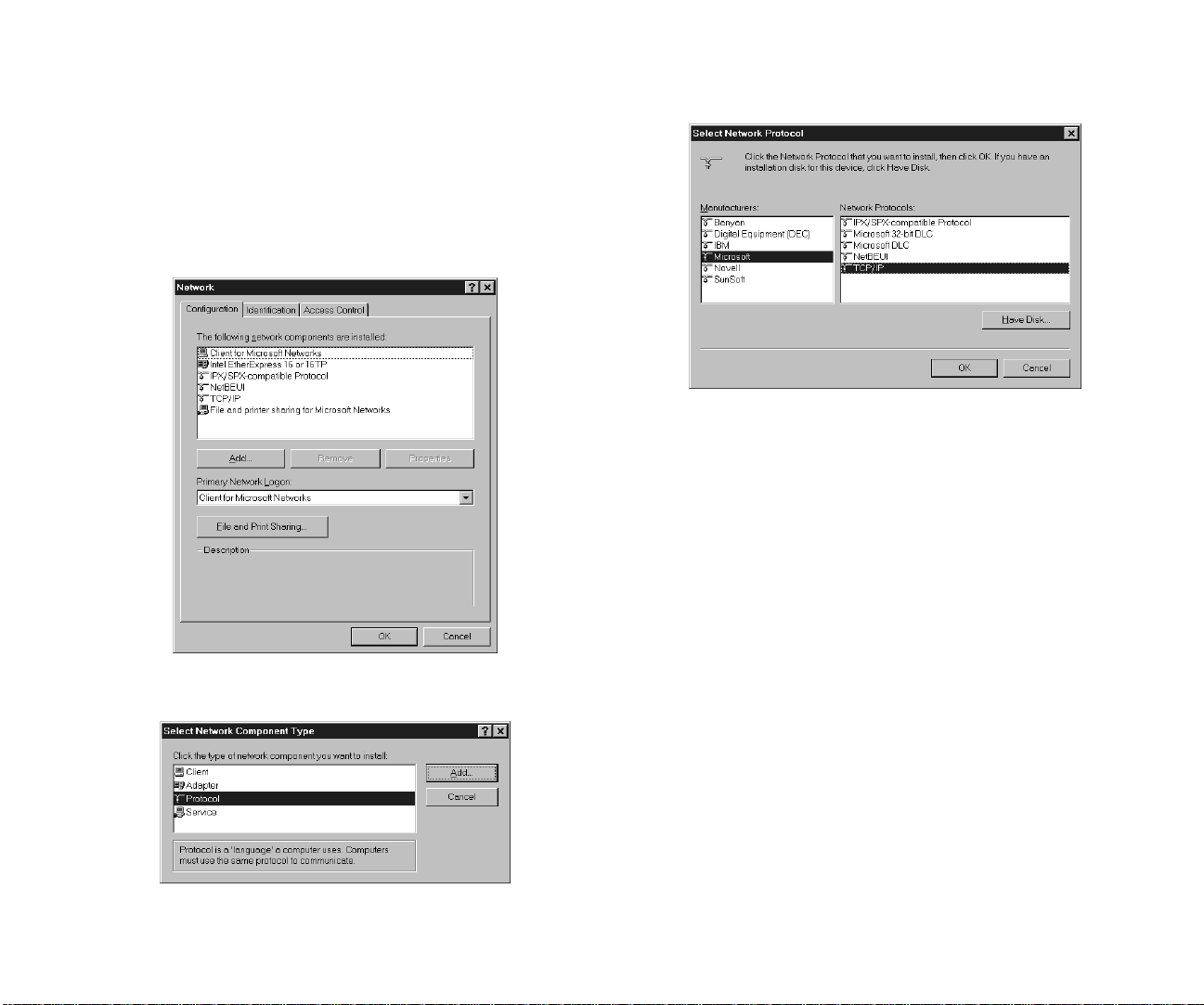
Using BOOTPL32
First follow these directions to set up TCP/IP in Windows
95/98 and Windows NT 4.0:
Installing the TCP/IP Protocol
1. In Windows, open the Network control panel.
2. If TCP/IP Protocol is not installed, install it in the
following step (in Windows 95).
a. Select Configuration Tab in the Network control
panel and click Add button.
b. When Select Network Component Type dialog box is
displayed, select Protocol and click Add button.
c. When Select Network Protocol dialog box is
displayed, select Microsoft and TCP/IP and click OK
button.
d. Then, TCP/IP Protocol is installed.
e. Restart. The new protocol and service will not be
available until system is restarted.
Assigning the IP Address
Use BOOTPL32 to set the IP address and other TCP/IP
parameters manually. You can also use ARP/ping commands
if you prefer.
1. Insert the SuperScript Color Laser CD.
2. Launch BOOTPL32
In Windows access the CD ROM drive and launch
BOOTPL32 from the bootp directory
or T ype E:\BOOTP\BOOTPL32.EXE from the Start>Run
dialog box.
14 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 19

3. Select Configure from the Admin menu.
a. Enter the IP address to assign to the printer.
b. Enter the subnet mask.
c. Enter the default gateway address (if applicable) or
leave blank.
d. Enter the hardware address of your printer. This
address is listed on the Network Settings page under
Network Address, for example,
00:40:af:c9:f0:d8. Enter it exactly as it appears
on the Network Settings page.
4. Click on Go to send the new settings to the printer.
After a few minutes (usually between 1 and 2 minutes, but
possibly up to 5 minutes on very large or busy networks), the
printer will reset and print a Network Settings page. The new
IP settings will be listed in the TCP/IP Network Information
section of the Network Settings page.
If the new IP address does not appear on the Network
Settings page under “Protocol Address,” you may have
entered the hardware address incorrectly in BOOTPL32.
Repeat Steps 2 and 3, and check the IP address on the new
Network Settings page.
The new IP address can also be verified in BOOTPL32 by
turning the printer off and on, and selecting Verify from the
Admin menu. It should report that the Unit is Active.
Using ARP
You can use the following procedure to set the IP address on
the printer. Then, you can set the other IP parameters from
the Network Administration page. The network printer must
be on the same network segment as the workstation that you
are using to configure it. The TCP/IP stack must be installed
and operating.
1. From Windows, start an MS DOS session.
2. At the command prompt enter: arp -s
[IP address] [Hardware Address]
(for the hardware address, use hyphens as separators,
instead of colons.)
(e.g. >C:arp -s 123.123.123.1 00-40-0f-12-
34-56)
Then enter ping [IP address]
(request should time out)
(e.g. >C:ping 123.123.123.1)
3. Turn the printer off and on, and use the ping command
again to verify that the printer has its IP address. If it has
the address, the result is a confirmation message: [IP
address] is alive
4. Remove the entry from the ARP cache using this
command: arp -d [IP address]
(e.g. >C:arp -d 123.123.123.1)
IP ADDRESS
Assigning the IP Address 15
Page 20
Using DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) allows
automatic assignment of IP address and other IP parameters
for attached devices. The SuperScript color laser printer
works with DHCP in the following way.
At power-up, the printer’s NIC broadcasts a DHCP request
for an IP address. If a DHCP server is present, the request
will be processed, and an IP address will be returned to the
NIC. Upon receipt of the IP address, the NIC resets, and
prints a Network Settings page. This shows the new IP
address (and subnet mask, and default gateway, if any).
Under factory default settings, once an IP address has been
assigned to it, the NIC will no longer broadcast DHCP requests. If
you uncheck IP Address in NVRAM, in the Network
Administration Page, the printer will broadcast a DHCP request
each time you turn on the printer.
The DHCP server may grant a temporary IP address, called a
temporary lease or temporary reservation, which expires
later, or may grant a permanent or unlimited lease or
reservation which does not expire.
Devices that are granted a temporary lease will be notified
before the lease expires and asked if they would like to
extend the lease. The NIC will continue extending its lease
indefinitely (unless prohibited by your DHCP server
configuration), and thus maintain a consistent IP address.
Important: If the NIC is not turned on or is not connected to
the network when the DHCP server is sending requests to extend
the lease, the lease will not be extended. The DHCP server will
cancel the lease and may assign the IP address to another device.
Therefore, it is highly recommended to explicitly specify the NIC
lease as permanent or unlimited in your DHCP server
configuration.
Verify that your printer was assigned an IP address through
the Network Settings page, then proceed to setting up your
workstation to use the printer.
he Network Settings Page
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Unit Serial No: 992048 Version: 05.20
Network Address: 00:40:af:79:19:80
Network Topology: Ethernet Connector:RJ45
Network Speed: 10 Megabits
Novell Network Information enabled
Print Server Name: NEC_992048
Password Defined: No
Preferred Server Name not defined
Directory Services Context not defined
Frame Type: Novell 802.3
Peer-to-Peer Information enabled
Frame Type: 802.3
Network ID: 32803
TCP/IP Network Information enabled
Frame Type: Ethernet II Protocol Address: 131.241.45.84
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway: 131.241.45.254
DNS Address: 0.0.0.0
AppleTalk Network Information enabled
Frame Type: 802.2 SNAP On 802.3
Preferred Appletalk Zone:* San Jose EtherNet
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Novell Connection Information
Printer Name: NEC_992048_P
File Server: LABNW312
Queue: NEC_992048_Q Priority: 1 Attached: Yes
No Notify Defined
Peer-to-Peer Connection Information
Printer Name: NEC_992048
AppleTalk Connection Information
AppleTalk Printer Name: Peggy’s SS4600 4
TCP/IP Connection Information
Port Number: 10001
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
16 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 21
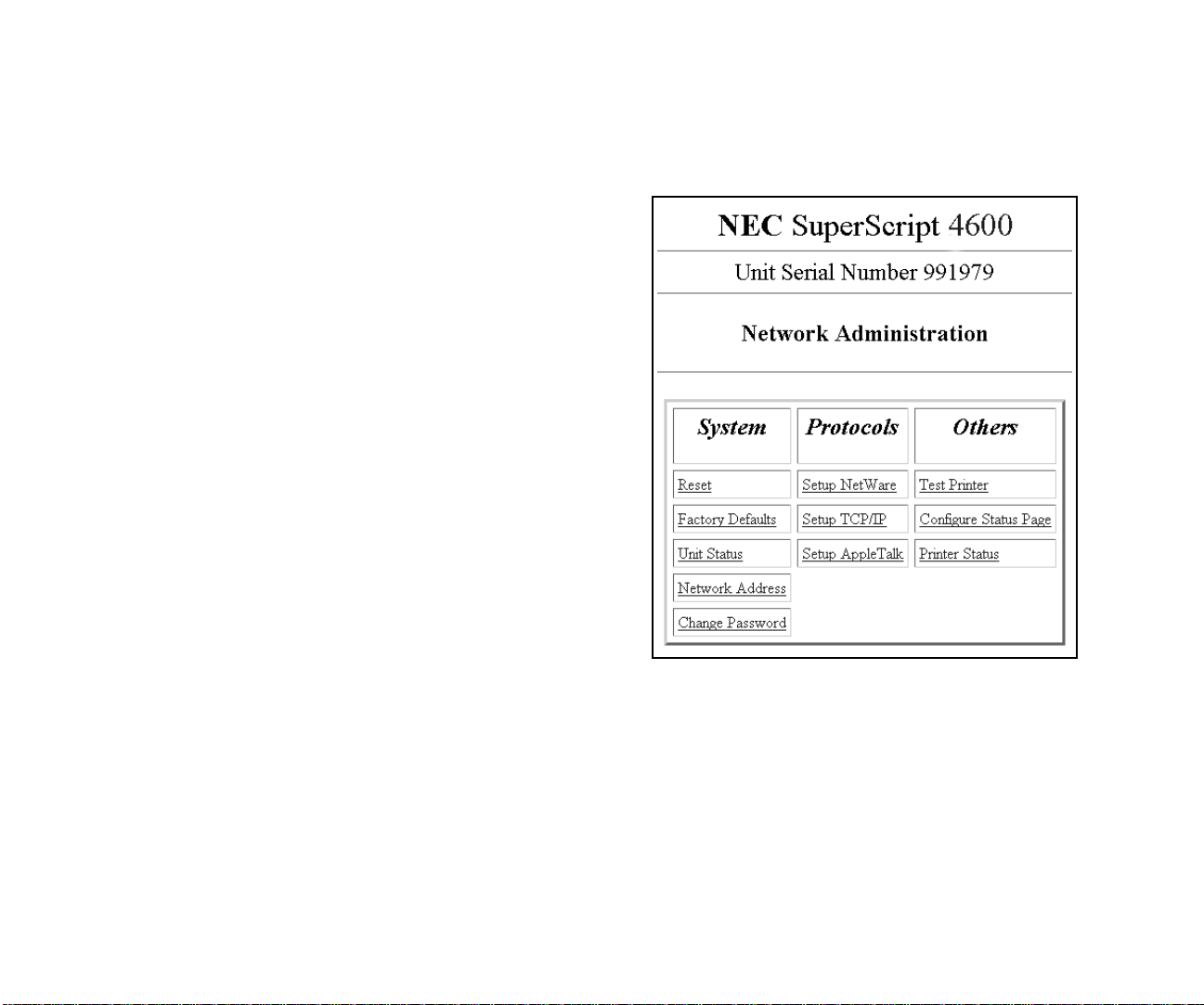
CHAPTER 4
NETWORK ADMINISTRATION
PAGE
USING THE NETWORK
DMINISTRATION PAGE
A
Each SuperScript laser printer has a built-in web page that
allows you to perform network administration tasks.
Accessing the Network Administration Page
You must assign an IP address to your printer’s NIC. Then
you can use a web browser, such as Navigator or Internet
Explorer, to access the Network Administration page.
note: See Chapter 3 for instructions on assigning the
printer’s IP address. The printer’s IP address then appears
on the Network Settings page under the TCP/IP Network
Information section, protocol address entry.
To access the Network Administration page, open your
browser by double-clicking on its icon.
1. Go to the URL Configuration Page, the URL is
http://<IP address>/configure.html.
2. Click on the Network Administration link. This displays
the Network Administration page.
You can access the following functions through the Network
Administration page:
that this option clears all settings you have defined for
the NIC. You must turn the printer off and on again for
the factory default settings to take effect.
The Network Administration Page
System Functions
Reset: Click here to reset the NIC and allow new
settings to take effect. The NIC’s connection with the
network is fully reinitialized, but its connection with the
printer controller is not. To reset the connection with the
printer controller, turn the printer off and on.
Factory Defaults: Click here to restore factory default
values on all NIC parameters. You should restore factory
defaults if you move the printer to a new network or if
the NIC was set up improperly the first time. Remember
17
Page 22
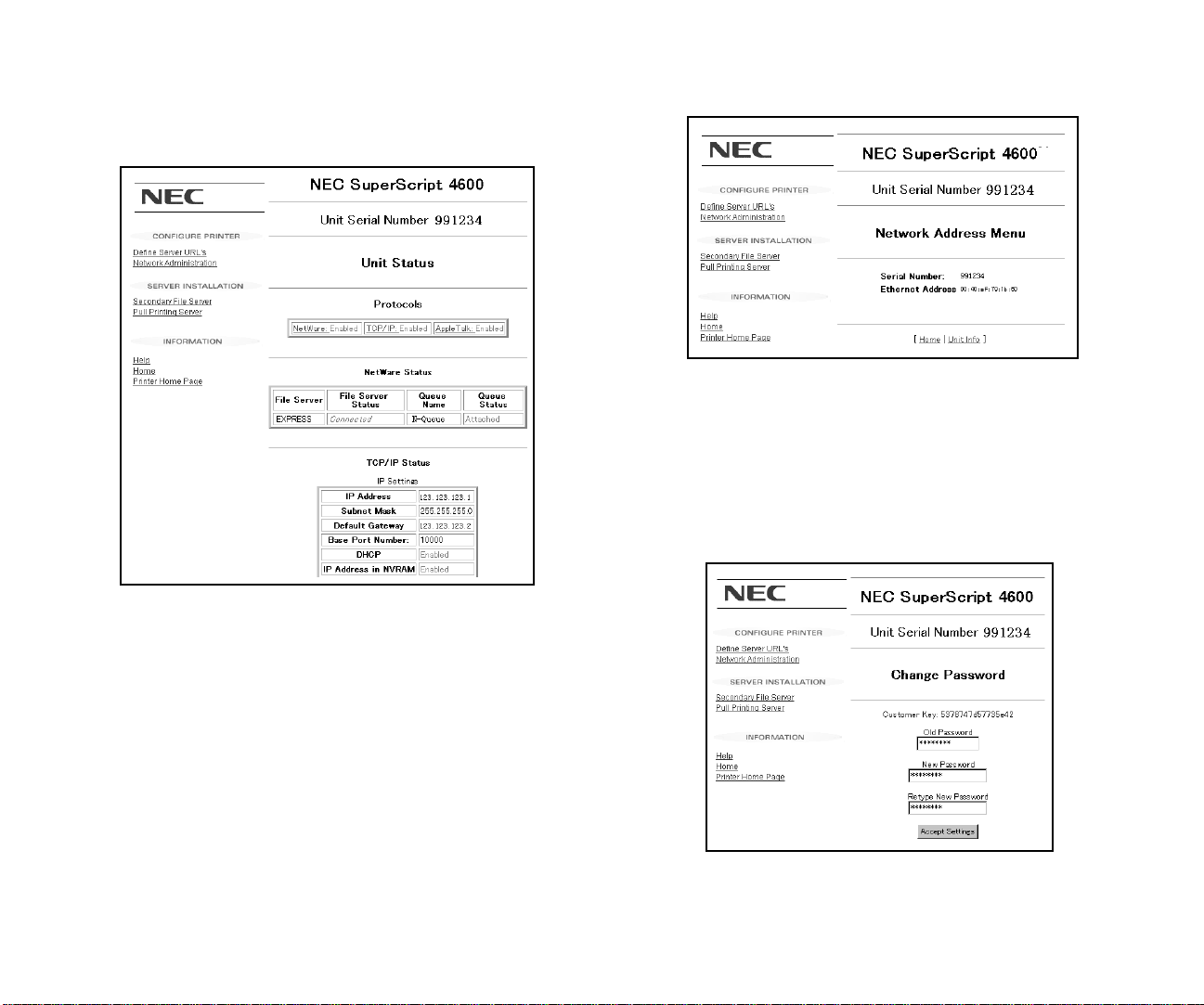
Unit Status: Click here to view the current state for each
protocol and NIC port available on your NIC. For each
supported protocol (Novell NetWare, TCP/IP, or
AppleT alk), the top line displays the pr otocols supported
and if the protocol is enabled or disabled.
Network A ddress: Click here to view the serial number
and the Ethernet MAC (Media Access Control) address
for the NIC.
Change Password: Changing any parameters using the
Network Administration Page requir es a password. Click
here to change your password. The default password is
sysadm. Your password can contain letters, numbers, and
punctuation, and is case sensitive.
note: If you forget your password, you can restore the
NIC to its factory defaults manually. See page 10.
18 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 23

Protocol Functions
The Protocols area is used for setting up network options and
parameters. It provides extensive access to NIC parameters,
and allows you to setup IP parameters (IP address, subnet
mask, and default gateway). You can enable/disable
AppleTalk and NetWare, but not TCP/IP. (We recommend
that you disable any protocol that you are not using.)
note: The entries in these pages
should reflect your network setup.
Contact your system administrator
for the correct configuration.
DHCP Settings in the Network Administration Page
You can control the way the NIC handles DHCP from the
Network Administration Page. To go there,
1. Go to the URL Configuration Page, the URL is
http://<IP address>/configure.html.
2. Click on the Network Administration link. This displays
the Network Administration Page.
3. Under Protocols, click Setup TCP/IP. The two DHCP
Settings are shown here.
The factory default is that both settings are checked.
When Enable DHCP is not checked, the NIC will not
make DHCP requests.
When IP Address in NVRAM is not checked, the NIC
will always make a new DHCP address request at printer
power on.
NETWORK ADMINISTRATION PAGE
Using the Network Administration page 19
Page 24

Other Functions
Test Printer: Click here, and then click on the Start Test
button in the dialog box that appears, to send a test
document to the printer.
Configure Status Page: Click here to configure
Network Settings page options. In the dialog box that
appears, select the checkbox by Print Status Page on
Startup to generate a status page (the Network Settings
page) each time you turn on the printer or reset the NIC.
note: We recommend that you leave this setting
checked to print at power-on.
To print out a Network Settings page immediately, click
Generate Now.
Printer Status: Click here to display status information
for the printer and NIC, as well as errors and messages.
20 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 25

CHAPTER 5
WINDOWS SETUP
WINDOWS PEER-TO-PEER
Peer-to-peer printing allows Windows 95/98 computers to
print directly to a networked printer without an intervening
file server. Below are the main features of peer-to-peer
printing.
• Runs on Windows 95/98 and workstations or servers
“out of the box.”
• Runs on networks with or without a NetWare file server.
• Implements peer-to-peer direct printing between
Windows computers and networked printers.
• You can configure network printers the same way you
configure printers directly attached to a computer.
note: In isolated, serverless networks, the NIC should
be used with its factory default settings.
IP vs. IPX Peer-to-Peer Printing
Your network configuration will dictate whether IP or IPX is
more appropriate. However, we recommend you use IP peerto-peer printing if possible.
For IP Peer-to-Peer Printing: You must install
PeerToPeer-IP. This protocol allows you to access the
network printer over an IP network. The Microsoft TCP/
IP protocol stack must also be installed and properly
configured on your workstation. The network and the
network print servers must support IP.
For IPX peer-to-peer Printing: You must install
PeerToPeer-IPX. It is not necessary to have a NetWare file
server on the network to use this protocol.
Installing Peer-to-Peer Software
Follow these steps to install the correct software.
IP Peer-to-Peer
1. Insert the printer driver CD that came with your printer,
for example, SuperScript 4400 Series CD.
2. Press the Windows Start button and select Run.
At Run, type: <drive>:\p2pip\Setup.exe
Then click OK. Follow the Install wizard prompts.
3. Choose the Destination Directory to install the P2P-IP
and click Next.
4. When the Select Program Folder is displayed, type a
new folder name, or select one from the existing Folder
list and click Next.
5. When the Setup is Complete information dialog box is
displayed, click OK button, then complete the
installation.
IPX Peer-to-Peer
1. Insert the printer driver CD that came with your printer,
for example, SuperScript 4400 Series CD.
2. Press the Windows Start button and select Run.
At Run, type: <drive>:\p2pipx\Setup.exe
Then click OK. Follow the Install wizard prompts.
3. When the Installation Complete dialog box is displayed,
click Finish button, then complete the installation.
note: If you use IPX peer-to-peer and there is no
NetWare server in the network, make sure that the
Ethernet frame types for both printer and PC match. Do
not use “Auto.” The printer’s Ethernet frame type can be
changed in the NetWare Configuration menu. See page
19.
21
Page 26
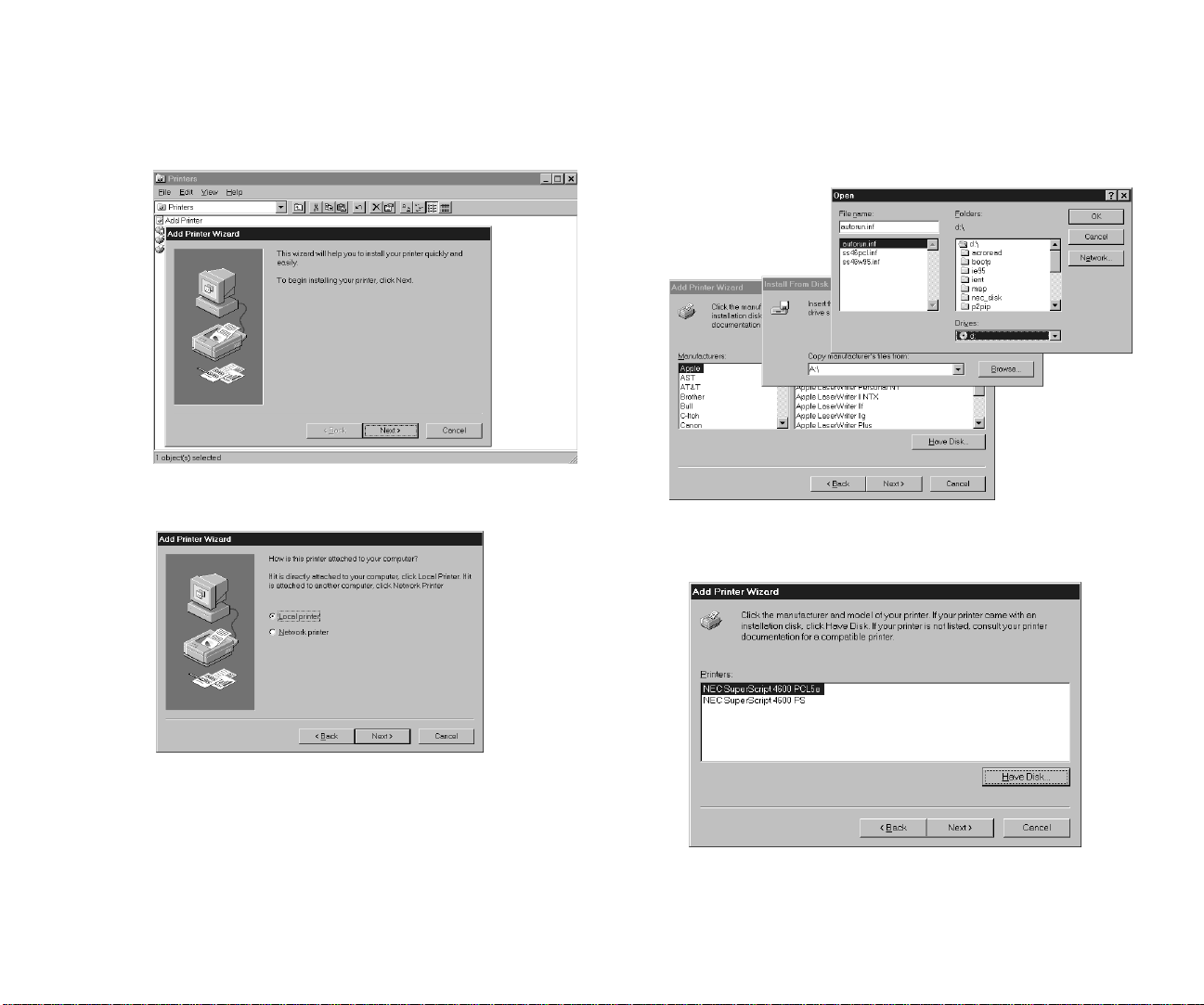
Adding the Peer-to-Peer Printer
1. In Window 95/98, pr ess the Start button, select Settings,
then select Printers.
2. In the Printers window, double-click Add Printer. Then
Add Printer wizard will launch and click Next.
3. When the Add Printer wizard asks how the printer is
attached, select Local printer and click Next.
4. When the Add Printer Wizard dialog box is displayed,
click Have Disk and click Browse in the Install From
Disk dialog box.
5. When the Open dialog box is displayed, select your
printer’s CD icon in the Drives field. Then select
autorun.inf.
6. Exit both the Open dialog box and the Install From Disk
dialog box by clicking OK.
22 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
7. Click Next in the Add Printer Wizard dialog box.
8. Your peer-to-peer network printer will be listed under
local printer ports and identified using the printer’s
Page 27

serial number. For example, NEC_991234.
Select your new peer-to-peer printer, and click Next.
9. Continue responding to the Add Printer Wizard until the
process is complete.
10. From the Windows Start button, select Settings then
Printers.
11. Click on the printer icon and select Properties.
12. Click on the Details tab.
13. Click on the Spool Settings button to open the following
dialog box:
14. Select the Disable bi-directional support for this printer
radio button.
15. Click OK.
16. Under the General tab, click on the Print Test Page
button to make sure that the driver is installed correctly.
WINDOWS SETUP
Windows Peer-to-Peer 23
Page 28

Moving a Peer-to-Peer Printer
If you move your printer to a new network, you must restore
the NIC to its factory defaults (see page 10). If you have
changed your printer’s name, it will revert to its original
factory name.
Removing Peer-to-Peer Software
You should delete all printers which have been installed to
use peer-to-peer printing before you delete the peer-to-peer
software. Follow these steps.
1. Press the Windows Start button, select Settings, then
select Printers.
2. In the Printers window, select the peer-to-peer printer
that you want to remove.
3. Select Delete from the File menu.
Removing P2P-IP
To remove the IP peer-to-peer software from your computer,
use the Add/Remove Programs control panel.
1. Press the Windows Start button, select Settings, then
select Control Panel.
2. Open Add/Remove Programs. Select P2P-IP in the list
and click Remove.
Removing Peer-to-Peer-IPX
To remove the IPX peer-to-peer software from your
computer, use the PeerToPeer-IPX Uninstall program. Follow
these steps.
1. Insert the SuperScript CD into the drive.
2. Press the Windows Start button and select Run.
3. At Run, type:
<drive>:\P2PIPX\UNINSTAL.EXE
Then click OK.
Follow the Uninstall wizard prompts. When removal is
complete, click OK.
SETTING UP WINDOWS NT
Setting LPR Printing on an NT Network
The following procedure can be used to set up the LPR
spooler for a Windows NT 4.0 workstation/server.
1. In the Windows Network control panel, install the
Microsoft TCP/IP Printing service.
2. Use the Windows Add Printer wizard to install the
SuperScript printer driver for Windows NT 4.0.
note: SuperScript printer drivers are provided on the
SuperScript CD that came with the printer.
3. In Windows NT 4.0, click the Start button, select
Settings, then select Printers.
4. Select the NEC SuperScript 4600 printer icon, and then
select Properties from the File menu.
5. Click on the Ports tab (the SuperScript printer driver
installs to LPT1 by default).
6. Then select Add Port.
7. Under Available Printer Port select LPR Port and click
the New Port button.
8. In the Name or address of server providing lpd field,
enter the IP (Protocol) address of the printer, for example,
128.191.184.50.
9. In the Name of printer or print queue on that server
field, enter PORT1 (the word “PORT” must be in
uppercase). Click OK, then click Close to assign that
newly created port to the SuperScript printer.
10. Click on the Sharing tab in the NEC SuperScript
Properties window.
11. Click on the radio button Shared and enter a name for
your SuperScript printer.
12. Click OK to apply these settings to your printer.
24 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 29
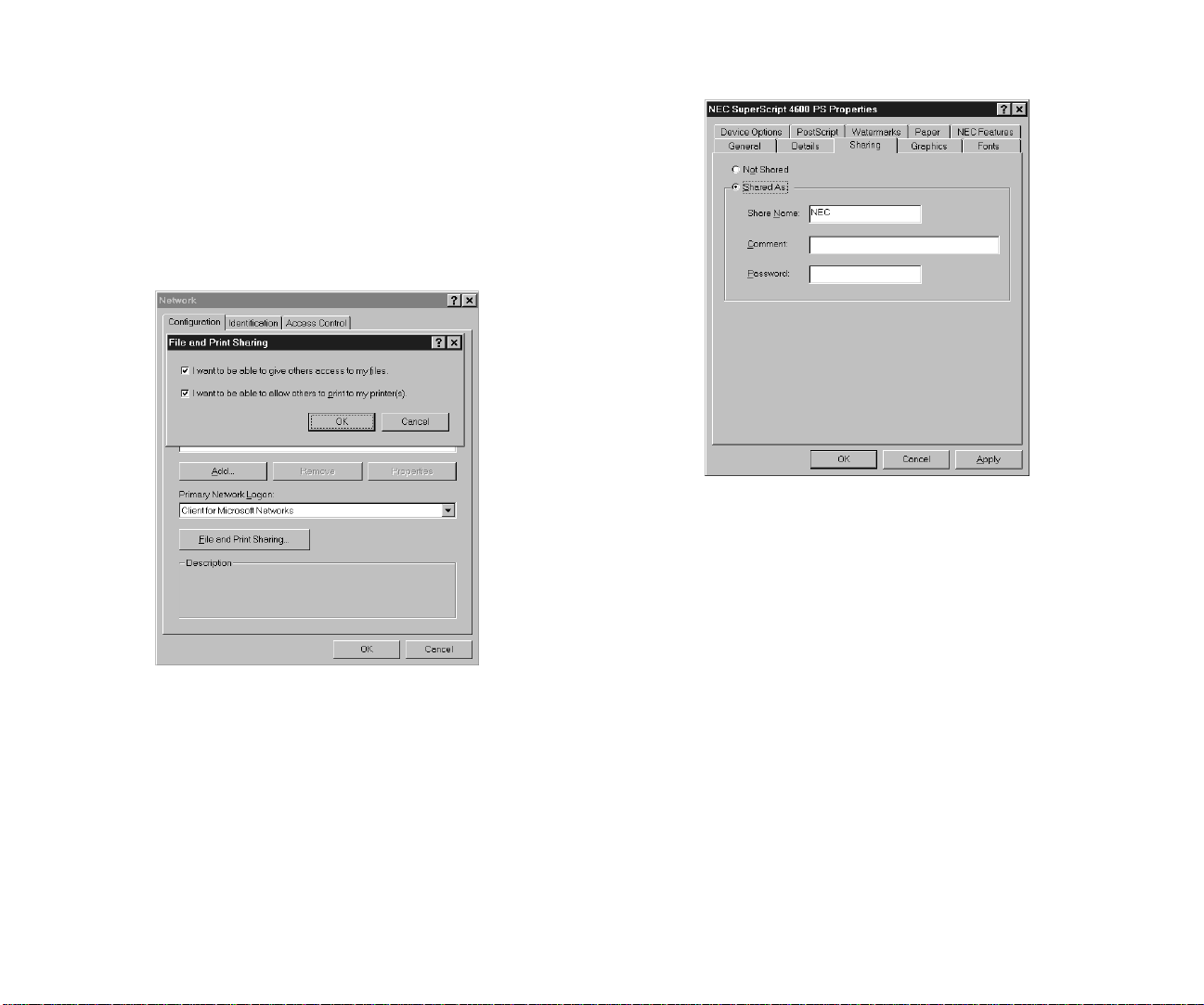
Shared Printing in Windows 95/98
Use these steps to set up shared printing in Windows 95/98.
1. Install the printer as a “local” printer using LPT1 port.
2. Press the Windows Start button, select Settings, then
select Control Panel.
3. In the Control Panel window, double-click the Network
icon.
4. Click on the File and Print Sharing button and in the
dialog box that appears, make sure that I want to be able
to allow others to print to my printer(s) is checked.
5. Click OK and Click OK in the Network window.
6. Next, press the Windows Start button, select Settings,
then select Printers.
7. In the Printers window, select the printer installed on
LPT1. Click on it with the right mouse button and select
Sharing from the pop-up menu.
8. Select Shared as and enter a name to identify the printer
on the network. Then click OK.
9. On another PC, press the Windows Start button, select
Settings, then select Printers.
10. In the Printers window, double-click the Add Printer
icon.
11. Click Next to begin installation and specify Network
when prompted.
12. When prompted for Network Path or Queue Name, click
on Browse, and browse to the name of the computer
where the printer was installed locally.
WINDOWS SETUP
Setting Up Windows NT 25
Page 30

13. Select the name of the shared printer and click OK.
14. Proceed with normal installation as directed.
26 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 31

CHAPTER 6
NETWARE SETUP
NETWARE 5.X AND 4.X
Follow these instructions if your network operating system is
NetWare 5.x or 4.x. Begin by:
Attaching the Printer
1. Log in to NetWare 5.x or 4.x with administrator rights
and open the NetWare Administrator window.
2. Create Printer Object.
a. Highlight the Organizational Unit or Organization where
you want to create the print service in the Directory Tree.
From the Object menu, select Create.
b. In the New Object window that appears, scroll down the
Class of New Object list, select the Printer icon and click
the OK button.
c. When the Create Printer window appears, type a name
in the Printer Name field and click on the Create button.
3. Create Print Server Object.
a. Highlight the Organizational Unit. From the Object
menu, select Create.
b. In the New Object window appears, scroll down the
Class of New Object list, select the Print Server icon,
and click the OK button.
c. At the Create Print Server window, type a name in the
27
Page 32

Print Server Name field and click the Create button.
note: The Print Server name you enter should match
the name shown on the Network Settings page under
Novell Network Information.
4. Create Print Queue Object.
a. Highlight the Organizational Unit. From the Object
menu, select Create.
b. In the New Object window that appears, scroll down the
Class of New Object list, select the Print Queue icon,
and click the OK button.
c. At the Create Print Queue window, click the Directory
Service Queue button, then type in a name for Print
Queue Name.
d. Click the icon to the right of Print Queue Volume field to
display the browser, and select a specific Print Queue
Volume (or type the name in the field).
28 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
e. Click the Create button.
Page 33

5. Assign Printer Object
a. In the Directory Tree, double click on the printer object
just created to open its Printer window. Click on the
Assignments button on the right-side of the window and
click on the Add button.
b. In the Select Object window that appears, find the print
queue object just created among the choices listed in the
Objects box and select it by clicking on it.
the OK button again.
6. Assign Print Server Object
a. In the Directory Tree, double-click on the print server
object you just created to open its Print Server window.
NETWARE SETUP
c. Click on the OK button and the print queue is added to
the Print Queues: box in the Printer: window. Click on
NetWare 5.x and 4.x 29
Page 34

b. In the Print Server window that appears, click on the
Assignments button and Add button to bring up the
Select Object window. Select the printer object just
created from the Objects box and click on the OK button.
Now the printer (with its context) appears in the
Printers: box of the Print Server window. Click on
the OK button.
a. At the Directory Tree, double click on the Print Queue
object you just created. At the Print Queue window, click
on the Assignments button.
b. If you configured the print queue and printer correctly
they will appear in the proper boxes on the Print Queue
window. Press the Cancel button.
7. Check Assignments
30 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 35

Installing the Printer Driver
In Windows, use the Add Printer feature to install and
configure a SuperScript printer driver in each workstation
that will access the network printer.
note: SuperScript printer drivers are on the SuperScript
CD that came with the printer.
Specify that the printer will be attached as a Network Printer ,
and set the Port to the printer queue you just created. (The
Windows NT 4.0 driver installs automatically to LPT1:. After
installation, you can manually reset the port to your NetWare
queue.)
Configuring the Network Printer
Now you must specify the Print Server Name, Preferred
NDS Context, and Preferred NDS Tree using the Network
Administration Page options. Continue with the instructions
below, to do this.
1. Click on the SuperScript printer you want to configure to
display its Network Administration page.
2. NetWare 4.x/5.x (NDS) Configuration
a. On the Network Administration Page, click on Setup
NetWare in the Protocols column.
b. In the NetWare Configuration menu that appears, enter a
name in the Print Server Name and Preferred File Server
fields, enter a name in the Preferred NDS Context field,
and enter a name in the Preferred NDS Tree field. (Leave
the Preferred File Server field blank.)
c. Enter the password and click on the Accept Settings
button. (The default password is sysadm.)
NETWARE SETUP
3. Turn the printer off and then on again to validate
network settings changes.
4. Confirm Successful Configuration.
a. In the Systems column, click on Reset. After the Reset,
turn the printer off and then on again.
b. Go back to the Network Administration Page, click the
Network Administration button. Then, in the System
column, click on Unit Status.
c. In the dialog box that appears, scr oll down to display the
NetWare Status. The Queue Status should be Attached.
d. If the Queue Status is not shown as Attached, please
verify that the entries for Print Server Name, Preferred
NDS Context, and Print Server Password match those
defined in NWADMIN.
NetWare 5.x and 4.x 31
Page 36

NETWARE 3.X
Complete these basic tasks to configure NetWare 3.x binderybased services for your printer. Begin by:
Starting PCONSOLE
Log in to NetWare 3.x with Administrator rights and start
PCONSOLE.
Defining the Print Queue
1. Select Print Queue Information from the Available
Options menu and press ENTER.
2. Press INSERT, type a name for the new queue to be
serviced by the NIC and press ENTER. Press ESCAPE to
return to the Available Options Menu.
Defining the Print Server
1. Select Print Server Information from the Available
Options menu and press ENTER.
2. Press INSERT, type the NIC Print Server Name and press
ENTER.
note: The Print Server Name you enter should match
the name shown on the Network Settings page under
Novell Network Information.
Defining the Printer
1. Press ENTER with the new Print Server Highlighted,
select Print Server Configuration and press ENTER, then
select Printer Configuration and press ENTER.
2. In the Configured Printers list, select an unused printer
number and press ENTER. In the Printer <#>
Configuration screen, define a new name for the printer
if desired. (The printer name is displayed in various
NetWare printing messages.)
3. Press ESCAPE to exit and select Yes to save the changes.
Press ESCAPE again to return to the Printer Server
Configuration menu.
Assigning the Print Queue
1. Select Queues Serviced By Printer and press ENTER.
Highlight the desired printer on the Defined Printers list
and press ENTER.
2. Press INSERT to display the Available Queues list. Select
the desired queue and press ENTER. Assign a Priority
level (recommended choice is 1) and press ENTER.
3. Press Alt-F10 to exit PCONSOLE.
Confirming Successful Configuration
1. Turn the printer off and on and wait for a Network
Settings page to print. If the network is large, this may
take several minutes.
2. The Novell Connection Information area on the Network
Settings page displays the printer name, file server,
queue, etc. If it displays Attached: Y es , this confirms that
the NIC Print Server is ready to accept print jobs. If not,
verify that the Print Server name matches exactly the
Print Server name that was entered in PCONSOLE.
Check the Novell Connection
Information area on the
Network Settings page. If you
experience difficulty call NEC
printer tech support at 1-800632-4650.
Installing and Configuring Your Printer Driver
In Windows, use the Add Printer feature to install and
configure a SuperScript printer driver in each workstation
that will access the network printer.
note: SuperScript printer drivers are on the SuperScript
CD that came with the printer.
Specify that the printer will be attached as a Network Printer ,
and set the Port to the printer queue you just created. (The
Windows NT 4.0 driver installs automatically to LPT1:. After
installation, you can manually reset the port to your NetWare
queue.)
32 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 37

CHAPTER 7
MACINTOSH SETUP
OVERVIEW
The following chapter contains information on how to
configure your PowerMac to work with a SuperScript color
laser printer. It also explains how to install the printer
software
M
ACINTOSH REQUIREMENTS
This section describes the hardware and software
requirements for Macintosh computers to connect with
SuperScript color laser printers.
Software Requirements
For Macintosh computers to connect to the printer , they must
meet the following requirements.
• EtherTalk software must be installed in your computer
and active.
• The operating system must be Mac OS 7.1 or higher.
• The standard LaserWriter 8 printer driver must be
installed. Check the Chooser in the Apple menu to assure
that it is installed. If it isn’t, use the Mac OS help system
for information about installing it.
• The standard Apple Script program must be installed
and active before configuring your network
configuration.
• The NEC SuperScript PPD must be installed.
Hardware Requirements
Hardware requirements are categorized into requirements
for the Macintosh and requirements for the printer.
Macintosh Hardware Requirements
• The computer must already be connected to the network
and able to communicate with the network via Ethernet.
note: PowerMacs have built-in Ethernet capabilities.
Older Macs need to have an Ethernet expansion card
installed.
• An appropriate 10/100Base-T cable must be connected to
the Ethernet port.
Printer Hardware Requirements
• To receive print jobs from a Macintosh computer, the
printer must be an “N” model or have a SuperScript NIC
installed.
• The printer must already be connected to an Ethernet
network.
33
Page 38

SETTING UP THE PRINTER
Installing the PPD
Follow these steps for installing the SuperScript Color Laser
PPD:
1. Insert the SuperScript Color Laser CD that came with the
printer into your Macintosh.
2. Double-click on the SuperScript Color Laser Mac CD
icon.
3. In the SuperScript Color Laser Mac window, doubleclick on the AdobePS Installer icon.
4. Double-click the SuperScript Color Laser Installer icon
to begin installing the PPD. If there is an installer 2, as
above, it will automatically launch with the first installer .
no difference if you choose Custom Install or Easy Install.
6. Click the Install button.
7. The SuperScript printer driver will load.
8. The installer will let you know when installation is
complete. To install other programs, such as Adobe
Acrobat 4.0, you must go back to the first window.
Configuring the Printer
1. Select Chooser from the Apple menu and make sure the
AppleTalk Active button is selected.
2. In the Chooser, select the AdobePS printer icon.
3. Select the AppleTalk zone your printer is on.
4. Select the printer’s name, for example SuperScript 4600
2, in the printer list.
5. Make sure to select Install NEC SuperScript...It makes
34 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 39

5. Click the Setup button in the Chooser.
6. In the Setup dialog box, click Auto Setup. The driver will
attempt to determine the correct PPD (PostScript Printer
Description) file to associate with the printer.
7. In the Printer Descriptions dialog box, select
SuperScript 4600 2 (or what ever printer you are
configuring) and click Select. The following status box
appears:
Renaming Y our Printer
Rename your printer if you have more than one SuperScript
color laser printer on your network. To do this you need a
copy of Apple Printer Utility. Obtain this online from Apple
Computer at this URL:
http://asu.info.apple.com
Search for “Apple Printer Utility,” or you can request the
Apple LaserWriter 8.5.1 driver installer disk set from Apple
by calling 800-SOS-APPL.
Then perform a custom install of the Apple Printer Utility:
1. Launch the Apple Printer Utility.
2. Select the zone in which your SuperScript printer resides.
3. Select the printer you wish to rename and click Open
Printer.
4. Select the Name section of the window by clicking the
arrow.
5. Type your desired name into the field labeled AppleTalk
Name.
6. Click the Send button.
MACINTOSH SETUP
8. When the Setup dialog box reappears, click the
Configure button.
9. In the Configure dialog box, use the pull-down menus to
specify options currently installed in your printer.
Printing
To print a document from your Macintosh computer:
1. Select Print from the File menu.
2. A Print dialog box appears that allows you to select the
settings you want. Change the center “Panel” of settings
by selecting categories from the Settings pull-down
menu.
3. Select one of the following options from the Destination
pull-down menu.
Printer: Your document is printed out on your printer
(the default).
File: The document can be saved as either a PostScript
Job or an Encapsulated PostScript file.
4. When all settings are specified, click the Print button to
print the document.
Setting Up the Printer 35
Page 40

Page Setup
To view and change Page Setup settings
1. Select Page Setup from the File menu.
2. A dialog box appears that allows you to select the
settings you want. Change the center “Panel” of settings
by selecting Page Attributes or PostScript Options from
the drop-down menu.
3. Select options and click OK to return to the document.
UNINSTALLING THE DRIVER
T o uninstall the SuperScript Color Laser printer driver follow
these steps:
1. Insert the CD that came with your printer and doubleclick on its icon.
2. In the SuperScript Color Laser Mac window, doubleclick on the AdobePS Installer icon.
3. Double-click on the Uninstall icon.
4. Choose Uninstall from the drop-down menu.
5. Select the Remove NEC SuperScript...box.
6. Click on the Uninstall button.
MAC PEER-TO-PEER
Peer-to-peer printing allows PowerMac computers to print
directly to a networked printer without an intervening file
server. Below are the main features of peer-to-peer printing.
• Runs on PowerMacs or servers “out of the box.”
• Runs on networks with or without a NetWare file server.
• Implements peer-to-peer direct printing between mixed
platform computers and networked printers.
• You can configure network printers the same way you
configure printers directly attached to a computer.
Adding the Peer-to-Peer Printer
note: Before accessing the SuperScript Color Laser
network printer, you need the following information from
your system administrator. The AppleTalk Zone where the
printer is located and the printer’s name.
1. Select the Chooser from the Apple menu.
7. Removal progress will be shown on your screen and a
dialog box will appear letting you know that the printer
driver has been removed from your system.
36 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
2. Check to make sure that AppleTalk is Active.
3. From the upper left-hand list box, select LaserWriter8.
4. From the AppleTalk Zone list box, select the proper
zone, as designated by your system administrator.
5. Select the name of the printer (as designated by your
system administrator) in the Select a PostScript Printer:
list box. Click on the name even if it is the only one
shown.
6. Close the Chooser.
Page 41

CHAPTER 8
UNIX SETUP
SETTING UP ON A UNIX SYSTEM
Here we provide basic instructions for installing the printer
on your UNIX system in Solaris 2.x and SCO. For additional
information, refer to your operating system administration
manuals.
Configuring the IP Address on the Printer
First the SuperScript color laser printer must be assigned an
IP address and routing parameters. We suggest you use the
instructions in Chapter 3 for using the printer Operator Panel
to set the Net (IP) Address.
Setting Up Your Printing Mode
Use these instructions to set up the printer for SCO Open
Server Enterprise 5.0 and Solaris 2.x.
Installing the Printer in Your System
lpd is an implementation of the standard UNIX line printer
daemon which lets you print across a TCP/IP network,
without the need to install software on your workstation, and
with all filtering and banners done by the printer. Remote
printing uses the same commands (lpr, lpq, lpc) as local
printing.
The process begins when the LPR call finds a printer on a
remote system by looking at the remote (rm) entry in the
/etc/printcap file for that printer. LPR handles a print
job for a remote printer by opening a connection with the lpd
process on the remote system and sending the data file
(followed by the control file containing control information
for this job) to the remote system. The printer-based lpd then
filters the data and prints the job according to information
contained in the control file and its own printcap file.
Adding a SuperScript Color Laser Printer to Solaris 2.x
Log into your system as root. Add the printer’s IP address
you already assigned into the /etc/hosts file. Using
lpsystem follow these steps to open a terminal and enter
the printer’s IP address from the command line.
1. lpsystem -t bsd <IP address of printer>
[ENTER]
Enter the 4400N print server host name from the
/etc/hosts file. Your system may want its IP address
instead of the remote host name.
2. lpadmin -p <printername> -s <remote host
name or IP address>!PORT1 [ENTER]
note: There is no space after the remote host name.
3. Enable<printername> [ENTER]
4. Accept<printername> [ENTER]
Then, make sure that the printer content type is set to PS” by
typing lpstat -p -l to display the current printer settings. If it
is not set to PS, type the following on the command line to
change the printer settings.
5. lpadmin -p <printername> -I ps [ENTER]
6. lpadmin -p <printername> -T PS [ENTER]
To test that the printer was installed into the system, send a
print job using any application in your operating system.
Make sure that the printer you choose is the SuperScript
printer that you installed earlier.
The following sections give specific lpd setup instructions for
various systems. The SuperScript 4400N printer will be used
as an example. You must log in as root in order to execute the
commands.
37
Page 42

Adding a SuperScript Color Laser Printer to SCO
OpenServer 5.x
Log into your system as root. Add the printer’s IP address
you already assigned into the /etc/hosts file. Using
lpsystem follow these steps to open a terminal and enter
the printer’s IP address from the command line. A
SuperScript 4400N printer will be used for this example.
1. Set up the SuperScript 4400N printer as a remote printer
on a host that sends jobs to a Print Server using lpd. Use
the following procedures to do this:
At the prompt, type: mkdev rlp
note: You cannot run mkdev rlp twice. If you have
additional printers to be configured, use the rlpconf
command.
2. You will now be asked a series of questions. Respond as
follows. Do you want to install or remove a remote
printer? Type: I
3. Do you want to change printer description file
/etc/printcap? Type: Y
4. Write a printer name. For example,
type: lprprinter1
5. Is lprprinter1 a remote printer or a local printer? Type: R
6. Enter remote host name: type host name entered in
printcap for the 4400N. For example, type: lprprinter
7. Confirm the information you have entered. Type: Y
8. Confirm the preceding connection as your system
default. Type: Y
9. Enter another printer name or quit setup. Type: Q
10. Do you want to start the remote daemon now? Type: Y
11. Using a line editor of your choice, verify the following on
your /etc/printcap file. If necessary, use the
following steps to change the “rp” entry.
lprprinter1:\
:lp=:\
:rm=lprprinter:\
:rp=PORT1:\
:sd=/usr/spool/lpd/lprprinter1:
example, from a browser, to verify that the installation
was successful.
note: This information was based on the sample input
in the earlier steps. Actual parameters may vary
depending on prior setup.
12. Change the :rp=lprprinter: entry to :rp=PORT1.
13. Set this printer as the default printer and print a page, for
38 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 43

CHAPTER 9
WEB PRINTING SETUP
OVERVIEW
NEC PrintAgent is innovative software that allows you to
print over the Internet in two ways, Remote Printing and Pull
Printing. PrintAgent is powered by redipS® Core software,
and available just by browsing to your printer’s home page.
Printer Home Page Features
The URL is the IP address or host name
you assign to the Printer,
for example, http://131.241.45.65
PrintAgent Remote Printing
If you are a Windows 95/98 or Windows NT user, Remote
Printing is the easiest way to print over the web and get
instant printer status. You can print to any SuperScript color
laser printer anywhere, as long as you have its URL.
All you do is browse to the printer’s home page and
download/install the PrintAgent driver to your system or
install directly from the CD that came with your SuperScript
color laser printer. When you print with the PrintAgent
driver, the job goes over the web to the printer, and printer
status comes back to your desktop on the PrintAgent Status
window. The first part of this chapter covers the following
topics about Remote Printing:
• System requirements
• Remote Printing setup
• Remote Printing from your desktop
• Getting printer status
• PrintAgent features
• PrintAgent menus and commands
NEC PrintAgent Pull Printing
Pull Printing is an ideal solution for busy offices that print
long, complex, or color rich documents. With Pull Printing,
your job is sent to a Pull Printing server to be processed. Then
the Pull Printing server delivers the job to the printer. This
frees your computer, and reduces network traffic. You can
also set up a secondary server to deliver printer Help files
and drivers to users, making the printer more efficient.
Pull Printing is also called “driverless” printing because you
don’t need a SuperScript Color Laser printer driver on your
system. You can pull print any Microsoft Word, Excel,
PowerPoint, .PDF file, or web page without opening it— just
by sending its location to the Pull Printing server. The server
does all the work and leaves your computer free for other
tasks. The second part of this chapter covers the following
topics about Pull Printing:
• Pull Printing from your desktop
• Server system requirements
• Server software installation
• Secondary server
• Configuring URLs
• Starting the Pull Printing server
39
Page 44
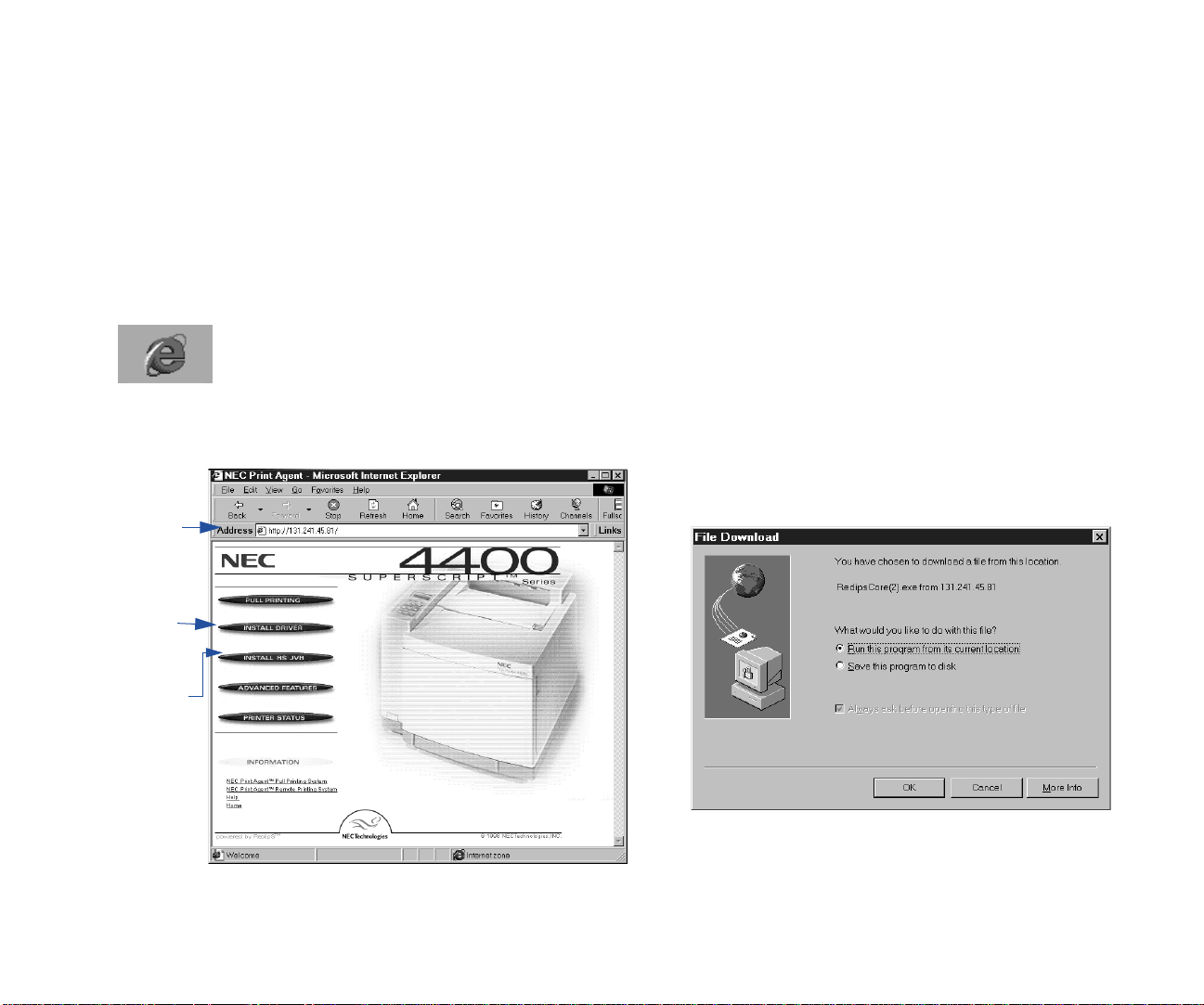
REMOTE PRINTING
NEC PrintAgent’s Remote Printing lets you deliver today’s
complex, graphic-rich documents in vivid color around the
world using the Internet.
System Requirements
You must have the following on your computer:
• A Windows 95/98 or Windows NT operating system.
• Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.01 SP1 or higher or
Microsoft Java V irtual Machine. You can download either
program from the SuperScript color laser home page or
from Microsoft’s website.
A
The SuperScript Color Laser Home Page
B
Enter Printer’s
IP address here
Install
PrintAgent
software here
Print Agent Remote Printing Setup
First, you or your system administrator must set the IP
Address on the printer. For instructions, see Chapter 3 of this
user’s guide.
Second, you must install the PrintAgent (redipS) software.
Go to the Printer Home page to download and install the
NEC PrintAgent software and driver.
1. Launch your web browser (A).
2. Enter the printer’s IP Address as the URL to reach the
printer’s Home page.
3. Click on the Install Driver button to download
PrintAgent software (B).
4. In the File Download dialog box that appears, choose
Run this program from its current location and then
click OK to begin installation (C).
File Download Dialog Box
C
Install Microsoft
Java Virtual
Machine here
40 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 45

5. During installation, you will be prompted with the Add
RedipS Enabled Printer... dialog box to enter the URL (IP
Address or fully qualified DNS name) of your printer.
Click Install so it can be added to your system as the
default printer (D).
6. When installation is finished, you can see the special
NEC PrintAgent driver icon in the printer’s window by
selecting Settings and then Printers from the Windows
Start menu (E).
7. Restart your computer for the new driver to take effect.
note: You can also install Remote Printing software
from the SuperScript CD that came with your printer.
Simply choose NEC PrintAgent from the Select
Components dialog box during Custom/Network Client
installation (F).
The Add RedipS Enabled Printer Dialog Box
D
Remote Printing From Your Desktop
Now you can print as usual from your applications—just
select Print from the File menu and choose PrintAgent
printer. The jobs will be sent to the printer using browser
technology, and you will receive instant printer status reports
from the PrintAgent Status window.
The Printer’s Window
E
WEB PRINTING SETUP REMOTE PRINTING
Select Components Dialog Box
F
Remote Printing 41
Page 46

Getting Printer Status
When you send a print job, the PrintAgent Status window
opens automatically with status information. The animated
printer image reflects printer status.
Eyebrows Moving: The Status Monitor and the printer
are successfully communicating.
Eyebrows Stop, Printer Looks Sad: Check the power
to the printer.
Pages Printing Out: The printer is printing.
Printer Sleeping: The printer is warming up.
Critical messages, such as NO PAPER IN TRAY 1, OUT OF
TONER
, or TOP COVER OPEN, will interrupt a print job. These
are shown with a descriptive image and message. Noncritical messages, such as LOW TONER and some service
errors, will appear only in the text field.
PrintAgent Status Window Menu Bar
The menu bar at the top of the PrintAgent window provides
several options for configuring PrintAgent and managing
print jobs.
Under File Menu
Select Cancel Print Job to cancel the job currently being
processed.
Select Print PostScript File to display a browser for selecting
a PostScript file to transfer to the printer.
Select V iew Print Queue to display the Print Queue window
to view and delete jobs.
Select Exit to quit the PrintAgent program.
Under View Menu
Select options from this menu to view Text Only, Text and
Animation, or Full View of the PrintAgent window.
Under Options Menu
Select General to display a dialog box for setting preferences
about version updates, Status Monitor frequency and
display, and the web browser path.
Select Network to display a dialog box for setting prefer ences
about proxy host, port, domain, and host name.
Under Help Menu
Select Index to display a list of online Help topics.
Select About to view information about copyright,
manufacturer model number, and software version.
Window Menu Bar
Printer Status
Reports Here
42 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
PrintAgent Status Window
Page 47
PrintAgent Buttons
In addition to providing printer status and Help, PrintAgent
buttons provide access to the features described below.
Details Button
Click this to view more information about the printer. Tray
information, emulations, pages per minute, installed
memory, and printer IP address are available. Service
messages are described in more detail.
Admin Button
Click this to perform administrative functions, including,
changing the printer name, password, changing the reference
URLs, cancelling a print job, or sending files to the printer . To
make changes in Printer Administration, you must enter the
Administration Password. The default password is Seattle.
Help Button
When a message is present in the PrintAgent window, press
the Help button for more details or instructions. When no
messages are present, clicking on the Help button displays
the Help Index.
Home Button
Click this to display a web page specified by your
administrator—possibly the manufacturer’s home page or
the printer’s home page.
WEB PRINTING SETUP REMOTE PRINTING
Window Menus
Printer Status
Reports Here
PrintAgent Status Window
Admin Button
Remote Printing 43
Page 48

PrintAgent Program Menus
PrintAgent program menus are available two ways.
• In Windows 95/98 or Windows NT, press the Start
button, select Programs, and NEC PrintAgent System to
display PrintAgent commands.
• Once you have started PrintAgent, you can click on the
PrintAgent icon (the green planet) in the taskbar at the
bottom right corner of your Windows desktop.
First access the PrintAgent program from here...
PrintAgent Program Menu Commands
Start
PrintAgent will also start automatically when you decide to
print or use the Property pages. Keeping it running speeds
print time because you won’t have to wait for PrintAgent to
start up every time you print. In order to monitor printer
status, PrintAgent must be running. When PrintAgent first
starts, a red planet icon appears in the Windows taskbar in
the lower right-hand corner of the screen. If the planet
doesn’t turn green after five seconds, PrintAgent did not
launch properly. Restart your computer and try again.
Stop
To stop PrintAgent, select Stop from the taskbar or Program
menu.
Monitor a Printer
Select this from the taskbar to monitor any PrintAgent
printer on your network.
...then you can access PrintAgent
from the icon on the taskbar
44 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
PrintAgent
taskbar Icon
Page 49

Add Printer
Once the PrintAgent software is installed, you can add any
SuperScript color laser printer to your system as long as has
an accessible IP address. Select Add Printer, enter the URL of
the printer and click Install (A).
If you get a message box indicating that the PrintAgent could
not access the printer, first verify that the URL you typed is
correct by retyping it.
If the URL was correct and PrintAgent still cannot establish
communication, select Network Properties from the
PrintAgent menu on the taskbar and check your proxy
settings (B). If you are trying to reach a printer using a proxy
server, you must check the Default Proxy host and port box,
then enter your proxy host and port. To reach a printer
without using a proxy, you must either de-select the Default
Proxy host and port checkbox, or enter the URL or domain
name in the No Proxy For text area.
If PrintAgent is still unable to establish communication with
the printer, go to the printer’s home page using your Web
browser. If the proxy settings are correct in the browser and
the Web page is not found, the problem is with the printer,
and you should contact the network administrator.
Add printers here...
A
Remove Printers
To remove a PrintAgent printer, select Remove Printer from
the PrintAgent menu. In the Printer Selection dialog box that
appears, select the printer you wish to remove and press OK.
Select Reset from the PrintAgent for the removal to take
effect.
Reset
If there are any communication or animation problems with
the Status window and the printer has power , selecting Reset
often resolves the problem.
About
Select this to view copyright and version information.
Uninstall
To uninstall the PrintAgent System, including all PrintAgent
printers and the NEC PrintAgent System, press the W indows
Start button, select Programs, and select NEC PrintAgent
System to display PrintAgent commands. Choose Uninstall
(C). Respond Yes to the confirmation dialog boxes, and
PrintAgent will be removed from your computer.
Check proxy settings here...
B
WEB PRINTING SETUP REMOTE PRINTING
Uninstall PrintAgent here...
C
Remote Printing 45
Page 50

PULL PRINTING
NEC PrintAgent’s Pull Printing capability allows you to pull
documents from internet sites or servers. You can also print
without running your applications or using a printer driver,
thus reducing the CPU cycles required for printing. To do this
a Pull Printing server must be set up. If you are a system
administrator, go to page 51 for instructions on how to
configure a Pull Printing server.
Pull Printing from Your Desktop
Once the Pull Printing Server is running, any local user can
Pull Print just by browsing to the Pull Printing page. To pull
print from your desktop, you must have
• Microsoft’s Internet Explorer 5.0 or Netscape
Communicator 4.6 and above with Java 1.1 support.
Sending a Pull Print Job
1. Launch the Web browser.
2. Enter the printer’s URL to reach the printer’s
home page.
3. Click on Pull Printing.
You can print the following types of documents using the
Pull Printing page.
• Word (.doc), Excel (.xls), and PowerPoint (.ppt) files*
• Adobe Acrobat .pdf files*
• Any Web page on the Internet.
• .gif, .jpg, .jpeg, .txt, .c, h, .java, .bak, .rtf, .ps, .html, and
.htm files can also be printed.
*Supported Microsoft applications and PDF file types can be
printed if your system administrator installed the
corresponding applications or plug-ins on the Pull Printing
server. Otherwise, a message will appear, notifying you that
you cannot print that file type.
46 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 51

4. The Pull Printing page appears as shown below.
5. Enter a file location in the Browser text field.
To print a local file, type the drive, path and name of the
file in the text entry field, or use the Browse button to
select a file. The drive and full path must be specified. If
the plug-in for that particular type of file has been
Pull Printing Page
To get this page, go to your printer’s home page and select Pull Printing.
installed on the secondary server , the file is r ender ed and
sent to the printer. If the plug-in is not installed, you will
be notified.
To print a web page, press the Print a URL button.
“http://” appears in the text field. Type in the desired
URL.
WEB PRINTING SETUP PULL PRINTING
Send document to
printer.
Send a web page to a
designated printer.
Shows job status in
print queue.
Shows print history for
up to 30 days.
Logon as a different
user.
redipS icon changes
colors if there is a
problem.
Monitor the printer’s
status to show if your
job has printed.
Use the Browser text
field to enter a file
location or the URL of
a web page.
Use this button to print
a file or Web page.
Change printer
settings on the driver
property pages.
Pull Printing 47
Page 52

6. Click the Set Printer Properties button.
7. The printer driver properties tabs appear. Make any
changes in settings here.
8. Click the Print Local File or Print a URL button. The job
will be rendered by the Pull Printing server and sent to
the printer.
Changing Properties and Saving Settings
The Set Printer Properties button functions in the same way
as the local printer drivers. You simply point and click to
change settings for your print job. Click on any tab to view
more settings.
With Pull Printing, you can save different preferences for
each printer you use. If you are accepting cookies, the
property settings, along with any watermarks you may have
created, will be saved upon sending the print job. The next
time you pull print to that particular printer, the property
pages will preset to match your previous preferences.
View Status Monitor
When you click the View Status Monitor button, the
PrintAgent Status Monitor appears. The animated printer
image shows the printer status.
Eyebrows Moving: The Status Monitor and the printer
are successfully communicating.
Eyebrows Stop, Printer Looks Sad: Check the power
to the printer.
Pages Printing Out: The printer is printing.
Printer Sleeping: The printer is warming up.
Printer Properties
48 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
PrintAgent Status Monitor
note: The “Warning: Applet Window”
message at the bottom of the status
monitor is a Java security feature and
does not indicate a problem.
Page 53

Server Status
The Server Status button on the Server Status page allows
you to see the server status queue: print jobs waiting to be
processed by the printer. As the mouse pointer passes over
the icon of a particular job an information window pops up.
If you want to cancel a job, select the job and press the cancel
button. Only the person who sent the job can cancel it. Print
jobs from other users can only be canceled by a network
administrator.
Server Status Page
Print Job History
Clicking the Print Job Status button brings up the Print Job
Status page. The following information about your print jobs
can be found here:
• Job name
• Print status
• Printer name
• Job history
Although you can track your job history for a maximum of 30
days, you can also indicate a shorter period of time.
Print Job History
WEB PRINTING SETUP PULL PRINTING
Pull Printing 49
Page 54

Logon as...
The Logon as... button allows another user to log in and print
with their user ID so their print jobs can be tracked.
redipS Icon
The small redipS icon located on the Pull Printing web page
(below the Print Local File button) can change colors.
Normally the icon color is green, indicating no errors or
warnings. A yellow icon indicates a warning, such as “low
toner.” Under these conditions you can still print. A red icon
indicates a more serious error, such as “out of paper.” You
can still send a print job but the driverless server cannot send
the job until the error is cleared. Until then the job waits in
the queue.
Canceling a Job
You can cancel a print job before it is rendered as long as you
are accepting cookies. To cancel, click on the print job in the
Print Queue frame. You will see a yellow highlight around
the text. Click the Cancel button. After it is sent to the
secondary server, the job can only be canceled using the
Admin dialog box from the PrintAgent window.
Getting Help
When a message is present in the PrintAgent window, press
the Help button for more details or instructions. When no
messages are present, clicking on the Help button displays
the Help Index.
Pull Printing User Settings
You can customize your web browser settings to enhance
your Pull Printing capabilities.
Cookies
If you would like the ability to save your printer settings and
any watermarks you make, you must accept any cookies we
set. This also gives you the ability to cancel any print jobs you
send that are still in the print queue. A cookie is a small piece
of data that the browser stores on your hard drive. Each
cookie has a maximum limit of 4 kilobytes. Although
driverless printing will work if cookies are not accepted, it
will not be customized for your needs. You can choose to
always accept a cookie, which will allow all web pages to set
cookies. You can choose to have a message box appear each
time a cookie is set and you will then have the option of
accepting or rejecting the cookie.
Accepting Cookies in Internet Explorer 5.0: Click on
the Tool menu item and select Internet Options. Click on
the Security tab. Click on Custom Level button. In the
Security section, there are three cookie options. Select the
Enable Option radio button.
You can distinguish your print job from others if you accept
the PrintAgent cookies. Your print job will display the name
of the file or URL you sent, while other print jobs will show
only the URL of the printer to which the job will be sent. To
see which printer your jobs will be sent to, place the mouse
over the icon next to your print job. The name of the printer
will be displayed, along with the name of the file or URL of
the web page. It will also signify whether your job is waiting
to be rasterized or has already been sent to the status
monitor.
The section below shows system administrators how to
configure a Pull Printing server to support clients.
50 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 55

Setting Up a Pull Printing Server
Server System Requirements
The Pull Printing server must be installed prior to server
installation.
• A Windows 95/98 or Windows NT operating system.
• Microsoft Word, Excel, and PowerPoint.
• The web server included on the SuperScript CD that
came with your printer that is automatically installed
when pull printing server is selected under the
Administrator installation.
• Internet Explorer 5.0 (this is available on the SuperScript
CD that came with your printer).
Folder list and Click Next.
WEB PRINTING SETUP PULL PRINTING
Server System Recommendation
For best performance it is recommended that your server
have a minimum of 64MB RAM.
Then, to use Pull Printing, you must
1. Set the IP Address on the printer. For instructions, see
Chapter 3.
2. Install the PrintAgent core software, Pull Printing Server
and/or Secondary File Server software.
3. Configure URLs.
This section also provides instructions for
• Setting Local User’s Web Browser Preferences (optional).
• Pull Printing from Your Desktop
PrintAgent Core and Server Installation
You must install the NEC PrintAgent Core software, and the
Pull Printing server software. You can also install the
Secondary File server software. All three can be installed at
once using the Administrator Setup option. The SuperScript
4400 color laser printer is used for an example. Follow these
steps.
1. Insert the SuperScript CD that came with your printer
into the CD-ROM drive. The Installer will launch
automatically.
2. Select Program Folder
When the Select Program Folder dialog box is displayed,
type a new folder name, or select one from the Existing
3. After you choose a location, the Setup Type dialog box is
displayed, select the Network Server/Administrator
setup option and click Next.
4. Select components w hen the Components list is
displayed, select PrintAgent and click the Change
button.
Pull Printing 51
Page 56

5. Select Sub-components In the Sub-components list, make
sure that PrintAgent, Pull Printing Server, and
optionally, Secondary File Server are selected and click
Continue. Then click Next in the Select Components
dialog box.
6. When the P2P-IP Setup dialog box is displayed, click
Next.
7. When the SuperScript Color Laser Setup Information
dialog box is displayed, click Continue to proceed to
NEC PrintAgent or click Exit to exit the SuperScript
setup.
8. When the Adobe PS 4.2 PostScript Printer Driver Setup
dialog box is displayed, click Next.
a. When the Printer T ype dialog box is displayed, select
Local Printer and click Next.
52 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 57

b. When the Install PostScript Printer from PPD dialog
box is displayed, choose for example NEC
SuperScript 4400 PS and click Next.
d. When the Add Printer dialog box is displayed,
choose a Printer Name and click Next.
WEB PRINTING SETUP PULL PRINTING
c. When the Local Port Selection list is displayed,
choose Available port and click Next.
e. When the NEC SuperScript property box is
displayed, check it and click OK.
f. If there are no more printers to be installed, click
Exit.
9. PrintAgent System Setup
When the Welcome to NEC PrintAgent dialog box is
displayed, click Next. Then, the PrintAgent Setup starts.
When the Add RedipS Enable Printer dialog box is
displayed, enter the URL (IP Address of the printer) and
click Install.
10. When the SuperScript Setup Information dialog box is
displayed, click Continue to proceed to Pull Printing
server or click Exit to exit SuperScript Color Laser Setup.
11. Pull Printing Server Setup
When the Choose Destination Location dialog box is
displayed, check the Destination Folder and click Next.
Then, the Pull Printing server setup starts. When the
Pull Printing 53
Page 58
Admin Setup dialog box is displayed, enter the admin
login name and password for the web server and click
Next.
12. Secondary Server Setup
The Secondary Server Setup program starts after the Pull
Printing Setup program is finished.
13. When installation is complete, restart Windows.
About the Secondary File Server
The PrintAgent Driver, Help files, and the PrintAgent Core
software reside on the printer. However, you have the option
of putting these files on a secondary server and then
changing the URLs to point to that server. This frees the
printer to process print jobs.
When Secondary File Server installation is complete, the
PrintAgent core files have been copied into the htdocs
directory, so the Secondary File server is ready to respond to
file transfer requests. However, if you want the Secondary
File server to deliver the two server .exe files, you must
manually copy the files DriverlessServer.exe and
SecondaryFileServer.exe from
<CD-ROM Drive>:\NEC_disk\redips_downloads
to
c:\program files\xitami\htdocs\
redips_downloads
You can manually copy the Help and Images Folders from
<CD-ROM drive>:\NEC_disk\ncss44rn
to
c:\program files\xitami\htdocs\ncss44rn
(keeping the directory structures intact.)
note: You can also install the Secondary Server
Software from a link on the URL Configuration Page.
note: You can also install the PrintAgent Pull Printing
server, and Secondary File server software from links on
the URL Configuration page.
54 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 59

Configuring Server URLs
Once the IP address is assigned to the printer, you can go to
the printer URL Configuration Page to set URLs for the
server(s).
1. Launch your web browser and enter this URL
http://<Printer IP Address>/configure.html
This displays the printer’s URL Configuration Page.
2. In the Pull Print server text field, enter the IP Address of
the Pull Printing server as its URL.
Pull Printing will NOT work unless the Pull Print server
URL has been entered. The Driver, Help files, and the
PrintAgent core software reside on the printer, which is
identified as localhost. However, you have the option
of putting these files on a Secondary File server and then
changing the URLs to point to that server.
note: To specify the printer as the file source, you must
enter
localhost in the text field, (not the printer’s IP
address).
URL Configuration Page
3. If you have a Secondary File server, enter its IP Address
as URL for the Driver, Help files, and PrintAgent
software.
4. You can also specify any URL as the Home Page for
clients.
5. Click on the Submit Values to Printer button.
note: Printer URLs can use either the printer’s IP
Address, or the printer’s Domain Name, if one has been
assigned. For example:
http://4400NSecondFloor/configure.html
Plug Ins
If you have Microsoft Word, Excel, and PowerPoint installed
on the Pull Printing Server , clients can print Word, Excel, and
PowerPoint documents from the Pull Printing Page. For
clients to print .PDF files, Adobe Acrobat Reader must be
installed on the Pull Printing Server. Acrobat Reader is
provided on the CD that came with your SuperScript printer.
WEB PRINTING SETUP PULL PRINTING
Install Pull Printing Server and
Secondary File Server software
from the SuperScript CD
that came with the printer.
You can also download them by
clicking these links.
You must enter a URL
for the Pull Printing Server.
Pull Printing 55
Page 60

You can find out what file types are currently supported by
the Pull Printing server by reviewing the kickIE.ini file
located in the cgi-bin directory on the Pull Printing Server.
If you find other plug-ins for Internet Explore 4.01, you can
add the file types supported by the plug-ins to the
inetpub\cgi-bin\kickIE.ini file, under the Support
Type tag. Please remember to increase the value of the
NumberOfTypes variable.
Starting the Pull Printing Server
You can launch the Pull Printing server by pressing the
Windows Start button, selecting Programs, selecting NEC
PrintAgent Pull Service, and then selecting Start all.
56 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 61

APPENDIX A
TROUBLESHOOTING
Network Printing Problems
Use the checklists in this section to identify the cause of
network printing problems. If a problem persists, contact
NEC Printer Technical Support at NecTech’s web site
(www.nectech.com) or phone 1-800-632-4650.
Check the Printer Operation
Verify that the printer is plugged in, turned on, and online—
the green Online light on the Operator Panel should be lit, or
nothing will print.
Check the Network Settings Page
On power-up, the network printer produces a Network
Settings page which has useful information for
troubleshooting. Check the Network Settings page to see
which protocols are enabled and active. Confirm that the
network protocol you configured appears on the page. If not,
it should be reconfigured correctly for the network printer.
Check other Network Users
Determine if other network users can print. If they cannot
and they are all on the same network operating system, the
problem is most likely in the network configuration.
Review Recent System Changes
Verify that any hardware changes (installations,
modifications, removals), to the printer or network, were
done correctly. If you added a new software application,
make sure the program is compatible and installed correctly
on the network.
Check Hardware Connections
• Be sure that your cable is a Category 5 twisted pair cable
with RJ-45 connectors for 10/100Base-T ethernet.
• Check that the network connector is plugged into the RJ45 connector on the NIC.
• Try another cable to make sure you do not have a bad
cable.
• If you are using a 10/100Base-T concentrator hub that
does not support the link signal, use Manual Ethernet
Port selection instead of the factory default, Automatic
Ethernet Port selection.
Check NIC Status Lights
Check the NIC’s status lights to ensure that there is no error
condition. The two status lights, amber and green, are located
on the interface panel on the back of the printer. The green
light should be lit and steady. Light patterns that indicate
serious hardware problems or software errors are shown
below. If you see one of these patterns, you should contact
NEC Printer Technical Support.
Green light blinks rapidly: This occurs when the
printer performs a self-test and detects bad SIMM.
Green light blinks rapidly 4 times, pauses: This
occurs when the printer performs a self-test and detects a
problem in the Ethernet hardware.
Amber light blinks short for 10 seconds, then goes
out, and the green light blinks continuously: This
occurs when the printer performs a flash memory selftest and the checksum fails.
Green light blinks slowly: When this happens after
power-on completes, it indicates an interface error.
Green light blinks rapidly: When this happens while
the printer awaits print jobs, it indicates that the NetW ar e
connection has been lost.
Green and amber lights blink alternately: This would
occur when you turn on the printer after restoring
factory defaults, and indicates an error.
57
Page 62

Troubleshooting for NT Server
If you have a problem printing large files from the Pull
Printing server the problem may be that the server “timed
out.” If this is the case help can be found by accessing the
following URL:
http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/
articles/Q209/3/91.asp
Troubleshooting for NetWare
Use the Network Administration page options to
troubleshoot in an IPX environment. The checklists in this
section show what to look for. If you are still having
problems phone NecTech support at 1-800-632-4650.
NetWare Checklist
• Is the NIC name entered correctly? The factory-default
name is NEC_<serial number>
The serial number is on the back of the NIC and also
shown at the top of the Network Settings page.
• Did you assign print queues to the printer? It is
recommended you assign each print queue to a specific
printer NIC. If print queues are assigned to other
network printers, the print jobs may be going to another
network printer.
• Did you assign the printer to the type Remote Other /
Unknown?
If the PCONSOLE NWAdmin settings are correct, the
connection between the printer and network may have been
broken. Turn the printer off and, using PCONSOLE, wait for
the status message Not Connected. Turn the printer on and
the status should change to Waiting for Job.
File Server Checklist
• Is there enough disk space on the file server and is it
running?
• Is the correct file server associated with the printer? Use
PCONSOLE to check.
• Did you have the proper rights to configure the printer?
NetWare documentation.
• Is the application set up to print to the printer? Are you
using the correct driver?
• Is the workstation connected to the correct print queue?
Print a file and verify that the file goes to the queue.
• Are the print queues assigned to the NIC-connected
printer also assigned to another network printer? If they
are, the print jobs may be going to that printer.
• Is AUTO ENDCAP enabled? AUTO ENDCAP lets you
send data to a network printer . If it is not enabled, enable
it.
• Are text files printing but graphic files not? The printing
may be timing out. Use NetWare's PRINTCON or
CAPTURE to set a longer timeout period. Set the time to
at least two minutes for graphics applications.
NIC Configuration Checklist
If all your hardware connections are correct, check the
following
• The Network Settings page shows the status for the
selected network interface card. This report includes the
status of file servers and queues assigned to a printer
along with a description of any problems.
• The printer may not be assigned to the correct print
queues. Use PCONSOLE to direct print jobs to the correct
queues, then check to see if the print job is in the queue.
• If devices were added or changed, use PCONSOLE to
make sure you configured the new devices correctly.
• Make sure the printer name has been entered correctly. If
you changed the name using the NIC Home Page, you
must also change the name in PCONSOLE.
• You cannot use PCONSOLE Version 1.0 to configure the
NIC. Contact Novell for an upgrade.
Computer Checklist
• Is the network loaded onto the computer? See your
58 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 63

NIC/File Server/Printer Checklist
Check the following to see if the NIC and file server are
sending data to the printer . If the NIC cannot log onto the file
server, or cannot service jobs from a file server
• The network printer is not created on that file server. Use
PCONSOLE to create the print server on the correct file
server.
• Use PCONSOLE to check if the print jobs are being sent
to the printer. Be sure the print job is in the print queue
and waiting to be printed.
Computer to NIC Connection Checklist
To make sure the computer is communicating with the NIC,
perform these tests.
• Print a file from the workstation and make sure the print
job gets to the print queue using PCONSOLE. If the print
job does get to the queue, the problem is not with the
workstation/NIC connection.
• Use CAPTURE to send data to the printer from a
workstation software application. See your NetWare
print server manual for information.
• Make sure another printer is not taking the print jobs
from the queues before the NIC can service the job. To do
this, disable the other printer and send another
print job.
NIC Loses Its File Server Connection: If the network
printer loses its connection to the file server, it will take
approximately five to 10 minutes to reconnect. If the
connection is not made after a reasonable amount of
time, check the error conditions to troubleshoot the
problem.
Unable to Print from a Different Context: The NIC
does not support printing from a context other than the
one you specified using the MAP utility on your Web
browser. To do this, you must create an alias queue. See
your NetWare Manual for more info.
Troubleshooting for MacOS
• Is the Macintosh computer connected to the network
through Ethernet, and has the correct network port been
selected?
• Did you select the correct printer driver, zone, and
printer name in the Chooser?
• If you renamed the printer in the Apple Utility, you must
turn the printer off then on, and then reselect the printer
under its new name in the Chooser.
• If you placed the printer in a new zone, be sure you
reselected the zone and the printer name in the Chooser.
• In the following example the printer’s name changed.
The default name for the printer is SuperScript 4600N #,
where # is the sequential number of 4600N printers
installed. If a user changes the name of SuperScript 4600
2 to Mary’s Printer, the last printer in line will be
reassigned the name Superscript 4600 2, and the print
path must be changed using the Chooser for the system
to work again.
TROUBLESHOOTING
Network Printing Problems 59
Page 64

60 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 65

APPENDIX B
WEB JETADMIN
USING WEB JETADMIN
If you are using Web JetAdmin, you must copy certain
NEC SuperScript files from the CD that came with your
printer to Web JetAdmin folders so that the
NEC SuperScript 4600 (or 4200/4400) will appear properly.
Locating the Files
(This assumes your CDROM is drive E and your printer is
4600:)
E:\WebJetAD\nec_super_script_4600.glf
E:\WebJetAD\Icons\Nss4600i.gif
E:\WebJetAD\Images\Nss4600.gif
Copying the Files
Copy Files to corresponding Web JetAdmin Folders (Path
may vary depending on your Web JetAdmin version)
C:\Program Files\HP Web JetAdmin4.0\doc\
devices\nec_super_script_4600.glf
C:\Program Files\HP Web JetAdmin4.0\doc\
devices\Icons\Nss4600i.gif
C:\Program Files\HP Web JetAdmin4.0\doc\
devices\Images\Nss4600.gif
C:\Program Files\HP Web JetAdmin4.0\doc\
devices\nec_super_script_4600\CoverOpen.gif
C:\Program Files\HP Web JetAdmin4.0\doc\
devices\nec_super_script_4600\NoPaper.gif
E:\WebJetAD\
nec_super_script_4600\CoverOpen.gif
E:\WebJetAD\
nec_super_script_4600\NoPaper.gif
E:\WebJetAD\
nec_super_script_4600\NoToner.gif
E:\WebJetAD\
nec_super_script_4600\Offline.gif
E:\WebJetAD\
nec_super_script_4600\PaperJam.gif
C:\Program Files\HP Web JetAdmin4.0\doc\
devices\nec_super_script_4600\NoToner.gif
C:\Program Files\HP Web JetAdmin4.0\doc\
devices\nec_super_script_4600\Offline.gif
C:\Program Files\HP Web JetAdmin4.0\doc\
devices\nec_super_script_4600\PaperJam.gif
61
Page 66

Resetting Web JetAdmin Discovery
1. Launch Web JetAdmin 4.0.
4. This displays the Discovery Mechanisms page. Scroll
down to the Clear Database section and click on the
Clear! button.
2. In the W eb JetAdmin main page, click on Web JetAdmin
Settings.
3. Click on Modify Discovery Settings on the right side
under HP Web JetAdmin Global Settings.
5. The Success page appears. At the top of the frame, click
the Discovery Settings button to re-enter the Discovery
Mechanisms page.
62 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 67
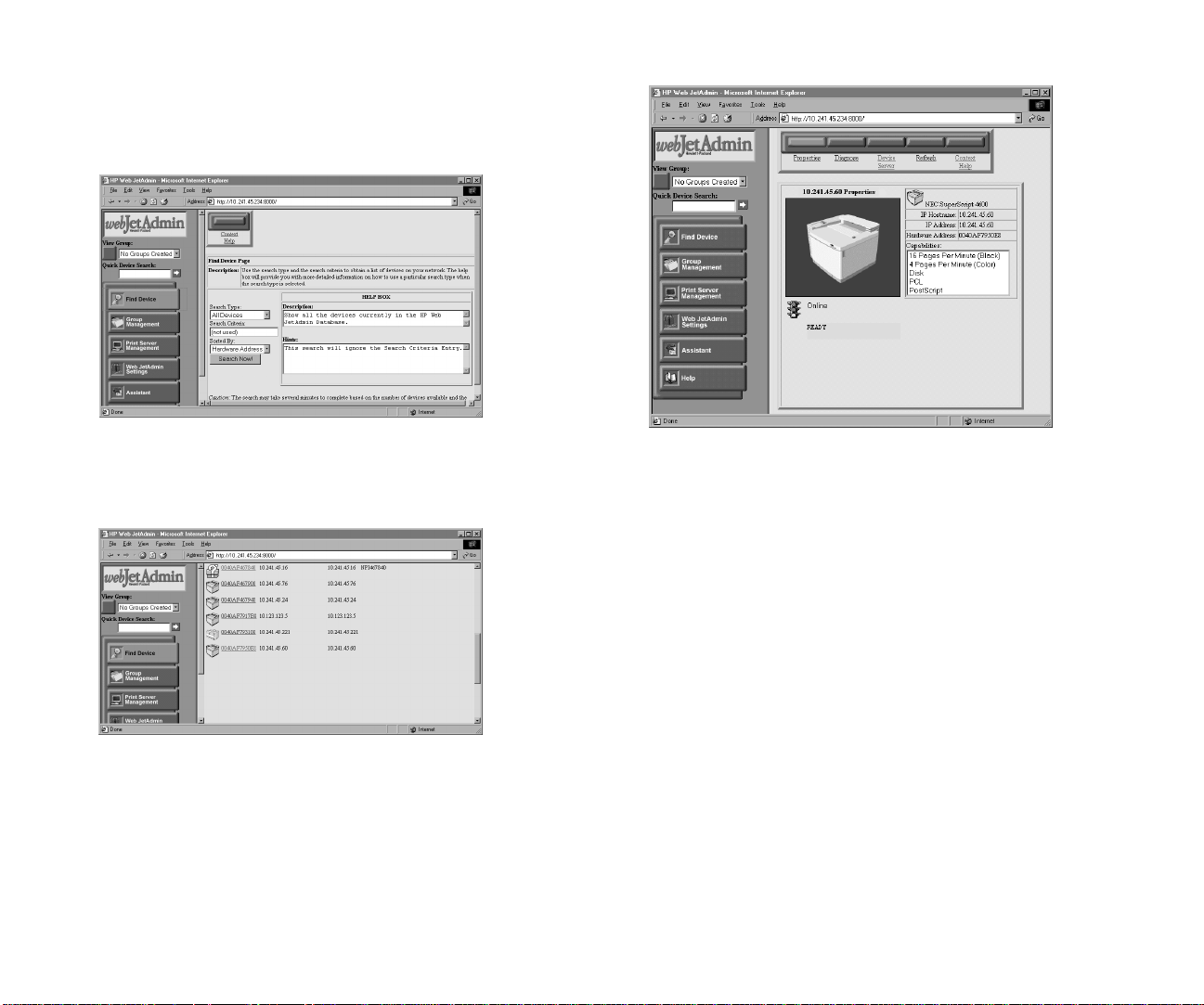
6. Scroll down to the Start New Discovery section and click
on the Start! button.Check to see if the Discovery is still
in progress by clicking on the Discovery Settings button.
7. If it is done, click on the Find Device button, then click
on Search Now.
8. When the list of discovered printers is displayed, select
your printer based on its Network/MAC Address from
the Network Settings page.
9. You will then see the printer’s properties and status.
WEB JETADMIN
Using Web JetAdmin 63
Page 68

64 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 69

APPENDIX C
SAFETY INFORMATION
This chapter provides safety information and product
specifications for SuperScript color laser printers. As you
operate your printer, please be aware of the following safety
considerations.
It takes two people to lift this printer and keep it level!
Ozone Emission
The corona assemblies found in laser printers and
photocopiers generate ozone gas (O3) as a by-product of the
electrophotographic process. Ozone is only generated while
the printer is printing (while the coronas are energized).
UL Standards for Ozone
The only existing standard for ozone emissions has been
established by Underwriters Laboratory (UL). All
SuperScript family printers meet this standard when shipped
from the factory to our customers.
Employer Responsibilities
Because ozone can be an irritant, various regulatory agencies
have established limits to the amount of ozone to which
employees may be exposed. The employer is responsible for
providing a safe work environment that meets the agencies’
standards.
Recommendations for Minimizing Ozone Exposure
Almost all ozone concerns arise from abnormal site or
operating conditions. The following conditions may generate
an ozone complaint:
• Installation of multiple laser printers in a confined area
• Extremely low relative humidity
• Poor room ventilation
• The exhaust port of the printer is directed towards the
face of personnel
• The existing ozone filter is in poor condition
• Long, continuous printing combined with any of the
above
Inspect your work environment for the operating conditions
listed above if you believe ozone emissions are a problem in
your area. Some people may be ultra-sensitive to ozone odor.
If these situations are encountered, it is advisable to position
the printer away from the sensitive user.
Laser Safety
This printer is certified as a Class 1 laser product under the
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS)
Radiation Performance Standard according to the Radiation
Control for Health and Safety Act of 1968. This means that
the printer does not produce hazardous laser radiation.
Since radiation emitted inside the printer is completely
confined within protective housings and external covers, the
laser beam cannot escape from the machine during any phase
of user operation.
CDRH Regulations
The Center of Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) of
the U.S. Food and Drug Administration implemented
regulations for laser products on August 2, 1976. These
regulations apply to laser products manufactured after
August 1, 1976. Compliance is mandatory for products
marketed in the United States. The printer’s rear panel
indicates compliance with the CDRH regulations and must
be attached to laser products marketed in the United States.
Caution! Use of controls, adjustments, or
performance of procedures other than those
specified in this user’s guide may result in
hazardous radiation exposure.
65
Page 70

FCC Statement
(For United States Use Only)
Federal Communications Commission Radio Frequency
Interference Statement.
WARNING! Changes or modifications to this unit not
expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the
equipment.
note: This equipment has been tested and found to
comply with the limits for a Class B
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are
designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not
occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which
can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the
user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or
more of the following measures.
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and
receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different
from the one to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio or TV
technician for help.
Use a shielded and properly grounded I/O cable to ensure
compliance of this unit to the specified limits of the rules.
If your printer is a model already equiped with a network
card, such as the NEC SuperScript 4600N or if you have
installed the optional Network Interface Card (NIC), the
printer meets the requirements of FCC Class A when
connected to an Ethernet cable.
digital device,
(For Canadian Use Only)
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits for
radio noise emissions from digital apparatus as set out in the
radio interference regulations of the Canadian Department of
Communications.
Le présent appareil numerique n’émet pas de bruits
radioélectriques dépassant les limites applicables aux
appareils numériques de Classe B présentes dans le
règlement sur le brouillage radioélectrique édicaté par le
Ministère des Communications du Canada.
Declaration of Conformity
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
U.S. Responsible Party: NEC Technologies, Inc.
Address:
Telephone Number: 630-467-5000
Type of product: Laser Printer
Equipment Classification: Class A Peripheral
Model: SuperScript 4200N, 4400N, 4600N
We hereby declare that the equipment specified
above conforms to the technical standards as
specified in the FCC rules.
1250 N. Arlington Heights Road,
Itasca, Illinois 60143
66 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
Page 71

INDEX
A
Acrobat Reader
Apple Printer Utility 9, 35
AppleTalk 19, 36
AppleTalk printer name 9
ARP 15
B
BOOTPL32
C
CDRH regulations
controller board 6
cookies 50
D
defaults
restoring
DHCP 16, 19
driverless printing 39
E
emulations
configuring
Ethernet 1
Excel 46
expansion slot 6
F
factory defaults
restoring
FCC 66
H
hardware connections
help button 50
home page 39
55
14
65
10, 17
12
10
57
I
Internet
Internet Explorer 46, 50
IP address 16, 17, 40
obtaining 11
IPX protocol 3
L
LAN
laser safety 65
lifting the printer 65
M
Macintosh driver
installing
uninstalling 36
MacOS 33, 59
hardware
LaserWriter 8 33
peer-to-peer 36
software requirements 33
MAP
installing
Microsoft Internet
Explorer
Microsoft Office 97 46
Microsoft printer sharing 4
N
NEC PrintAgent
NetWare 19, 58
attaching printer 27
NetWare 3.x 32
assign print queue 32
configure printer
46
2–4
34
requirements
13
46
driver
32
33
39, 51
define print queue 32
define print server 32
define printer 32
print queue
information
print server
configuration
print server
information
printer configuration 32
queues serviced by
printer
NetWare 4.x
attaching printer
configure printer 31
printer driver 31
NetWare 5.x
attaching printer
configure printer 31
printer driver 31
NetWare Administrator
Select Object
NetWare administrator 27
create printer 27
new object 27
print queue 28
print server 27
network address 9
network administration
resetting the NIC
network administration
page
Network Interface Upgrade
17, 58
setup NetWare 31
32
32
32
32
27
27
29
17
67
Page 72

Kit 5
network printing
problems
network settings page 8, 9, 20,
57–59
57, 58
network setup 1
network topologies 2
networking protocols 12
NIC
connection
installing 5–8
resetting 10
status lights 10
NIC status lights
normal operations
O
operator panel
IP address
ozone safety 65
P
password
PCONSOLE 32
PDF 46, 55
peer-to-peer 21, 24
IPX 21
Macintosh 36
removing software 24
peer-to-peer topology 2
plug ins 55
PowerPoint 46
PPD 53
configuring for Mac 34
print job history 49
PrintAgent 43
59
10
12
18
cookies 50
installing 40
uninstalling 45
PrintAgent core software 51
printer server topology 3
printer sharing 4
printer status 20
printer’s home page 39
printing
driverless
peer-to-peer 21
shared 25
protocol address 9
protocol functions 19
Pull Printing 39, 46
canceling a job 50
secondary file server 54
sending a job 47
Server installation 51
server system
recommendation
server system
requirements
Pull Printing page 46
Pull Printing server 46, 51, 56
R
redipS
redipS icon 50
Remote Printing 39, 40
S
safety
secondary file server 54
server status 49
39
printer status 42
65
39
51
51
server URLs 55
shared printing 25
status monitor 48
status page 9
status window
PrintAgent
SuperScript PPD 33
T
TCP/IP protocol
technical support 57
U
UL
65
unit status 18
UNIX 2, 37
URL 17, 39
W
Web browser
Web JetAdmin 61
copy files 61
locate files 61
settings 62
Web page 46
Windows 95/98 1
Windows for Workgroups 2
Windows NT 4.0 2
42
3, 14
46
68 SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
 Loading...
Loading...