Page 1

W370/W375
Level 3
Circuit Description
10 August 2006
V1.0
Page 2

W370/W375 Level 3 C
Index
1 Receive.................................................................................................... 5
1.1 Band selection........................................................................................... 5
1.2 Frontend................................................................................................... 5
1.3 Demodulation............................................................................................ 7
1.4 Audio Codec.............................................................................................. 9
1.4.1 Voice Downlink Patch ...............................................................................9
1.5 Earpiece Receiver .................................................................................... 10
1.6 Headset.................................................................................................. 10
1.7 Speaker Phone ........................................................................................ 10
1.8 Data Download Receive Path.................................................................... 10
1.9 26MHz System Clock................................................................................ 11
2 Transmit ................................................................................................ 12
2.1 Audio (Voice uplink Patch)........................................................................ 12
2.2 Data Download Transmit Path .................................................................. 13
2.3 Stereo Audio Path.................................................................................... 13
2.4 Modulation.............................................................................................. 14
2.5 Transceiver IC......................................................................................... 16
2.5.1 Function Description .......................................................................... 16
2.5.2 Receiver Section................................................................................ 17
2.5.3 Transmit Section ............................................................................... 18
2.5.4 Digitally- Controlled Crystal Oscillator (DCXO)...................................... 19
2.6 RF TX PA ................................................................................................ 19
3 Syren Monitoring ADC ........................................................................... 20
4 Baseband Serial Port (BSP)................................................................... 21
5 Microcontroller Serial Port (USP).......................................................... 21
6 General purposes I/O (GPIO)................................................................ 22
7 TFT LCD Display..................................................................................... 22
7.1 Display Backlights.................................................................................... 23
7.2 Image Processor (For W375 only)............................................................. 24
7.3 Camera Module (For W375 only)............................................................... 24
8 32kHz RTC............................................................................................. 25
9 SIM Card Circuit .................................................................................... 25
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 2 -
Page 3

W370/W375 Level 3 C
9.1 SIM Card Supply Voltage Generation......................................................... 26
10 Keypad................................................................................................... 26
10.1 Keypad Matrix ......................................................................................... 27
11 Vibrator circuit ...................................................................................... 27
12 Memory ................................................................................................. 28
13 Power .................................................................................................... 28
13.1 Low-Dropout Voltage Regulators............................................................... 28
13.2 Power Down Methods .............................................................................. 29
14 Sleep Module......................................................................................... 30
14.1 Sleep Up Sequence.................................................................................. 30
14.2 Sleep off Sequence.................................................................................. 31
15 Power Tree ............................................................................................ 32
16 Charging Circuit and External Power .................................................... 32
16.1 Battery Support....................................................................................... 32
16.2 Charger Support...................................................................................... 32
16.3 USB Data Cable Support........................................................................... 33
17 FM Radio................................................................................................ 33
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 3 -
Page 4

W370/W375 Level 3 C
Figures
Figure 1: Receiver Path ..............................................................................6
Figure 2: Syren and Calypso-Plus IC............................................................ 7
Figure 3: Baseband Downlink Block Diagram................................................8
Figure 4: Audio Codec Block Diagram ..........................................................9
Figure 5: Voice Codec Downlink Patch ....................................................... 11
Figure 6: Aero II 26MHz clock circuit ......................................................... 11
Figure 7: Voice Uplink Paths ..................................................................... 12
Figure 8: Stereo Audio Path ...................................................................... 14
Figure 9: Baseband Uplink Block Diagram .................................................. 16
Figure 10: Aero II IC................................................................................ 16
Figure 11: Aero II Transceiver Block Diagram............................................. 17
Figure 12: Aero II Receiver Block Diagram................................................. 18
Figure 13: Aero II Transmit Block Diagram.................................................19
Figure 14: Power Amplifier and Antenna Switch.......................................... 20
Figure 15: Baseband interface................................................................... 21
Figure 16: The pin connections of TFT LCD and U100 Calypso-Plus.............. 23
Figure 17: Function Block Diagram of PAP1312 ..........................................24
Figure 18: SIM interface ........................................................................... 25
Figure 19: Keyboard scanning sequence .................................................... 26
Figure 20: Keyboard connection................................................................ 27
Figure 21: Memory interface ..................................................................... 28
Figure 22: Power Distribution Tree ............................................................ 32
Figure 23: FM Radio Function....................................................................33
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 4 -
Page 5
W370/W375 Level 3 C
1 Receive
1.1 Band selection
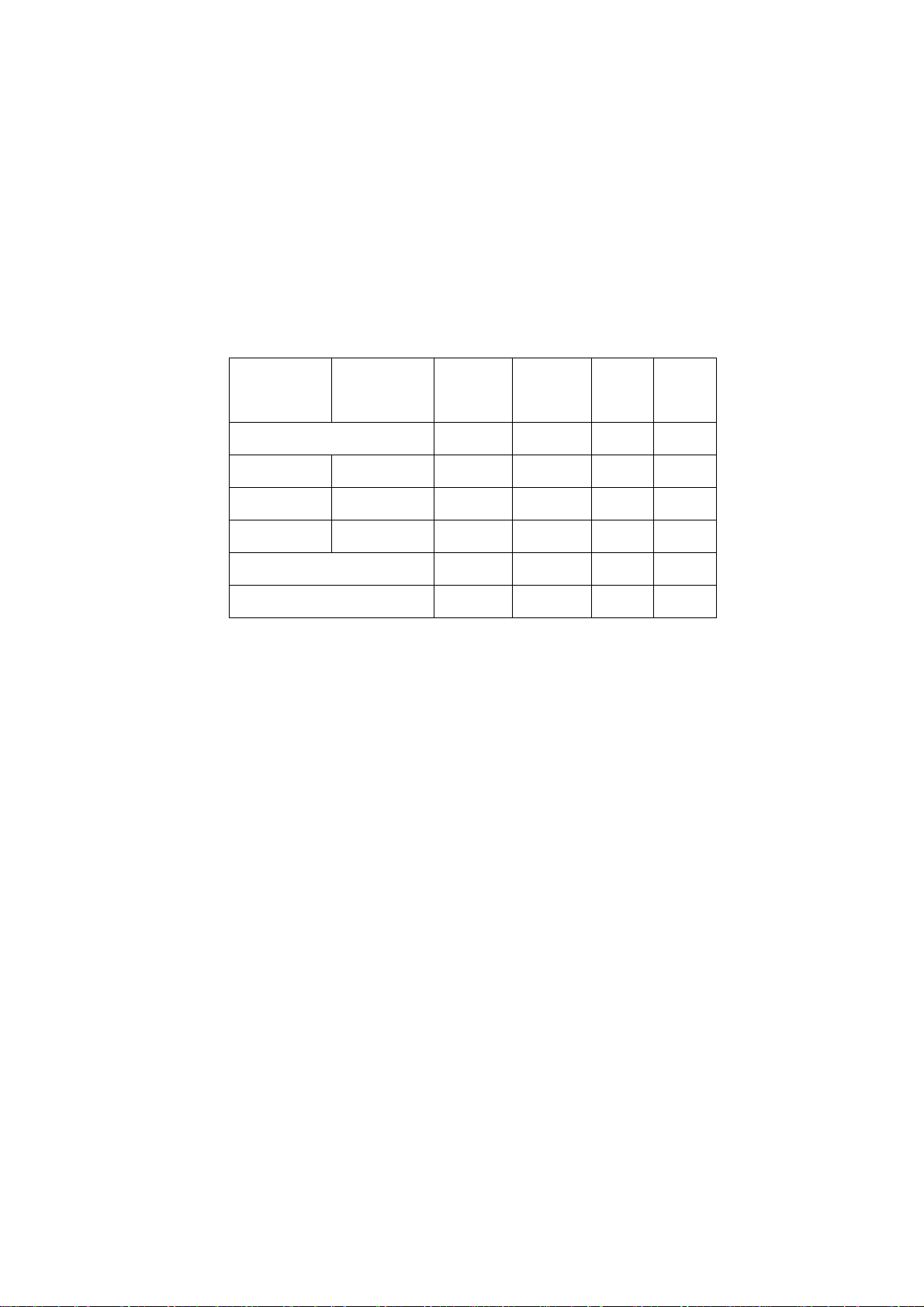
The radio frequency signal is received from the tri-band antenna. Received GSM RF signal
enters the unit at the antenna. L812, C825 and L811 components provide antenna
matching. The RF signal then enters mechanical 50-ohm RF connector J800. This RF
connector was used for conductive phasing testing. After J800 the RF signal enters
U803 (RF PA and front-end-module) on Pin 15 (ANT), where through control voltages
the RX path is isolated from the TX path. The following table describes how the voltages
control the switch of RF path:
W370/
W375 EU
W375 US
Standby Low x x x
EGSM900 GSM850 High Low Low Low
DCS1800 PCS1900 High Low High Low
PCS1900 DCS1800 High Low High High
TX GSM850/900 High High Low x
TX DCS1800/PCS1900 High High High x
The low band GSM850/900 RX signal from U803 (Pin 19) is connected to the SAW filter
BF800. The DCS1800 and PCS1900 band RX signals from U803 (Pin 22 and Pin 23) are
connected to the SAW filter BF801 and BR802 respectively. Those SAW filters also act as
Balun transformers. The balanced RF signal of the selected frequency band is then sent
to the front end IC U802 (Aero II).
1.2 Frontend
VLogic
PIN 27
TX_EN
PIN 28
BS1
PIN 2
BS2
PIN 1
The receiver block diagram in the Aero II IC U802 is shown in
U802 transceiver uses a digital low-IF receiver architecture that allows for the on-chip
integration of the channel selection filters, eliminating the external RF image reject filters,
and the IF SAW filter required in conventional superheterodyne architectures. Compared
with direct-conversion architectures, the digital low-IF architecture has a much greater
degree of immunity to dc offsets that can arise from RF local oscillator (RFLO) self-mixing,
second-order distortion of blockers (AM suppression), and device 1/f noise. The digital
low-IF receiver's immunity to dc offsets has the benefit of expanding part selection and
improving manufacturing.
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 5 -
Figure 1. The Aero II IC
Page 6
W370/W375 Level 3 C
Figure 1: Receiver Path
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 6 -
Page 7
W370/W375 Level 3 C
Figure 2: Syren and Calypso-Plus IC
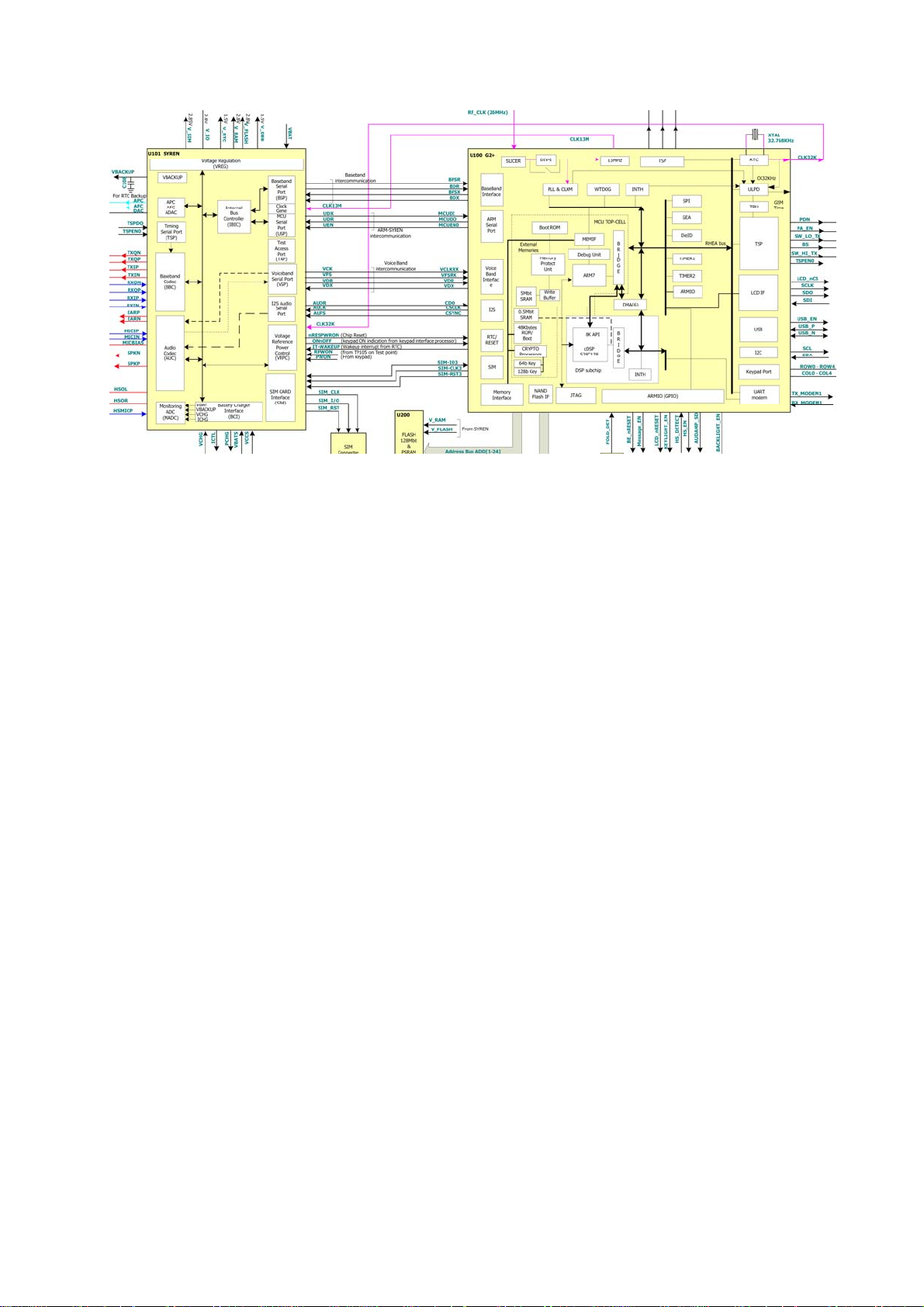
1.3 Demodulation The RXI and RXQ signals are feed in the - Dual ADC stage on Syren IC U101 (Pin
G11, G12, F11 and F12). The baseband codec (BBC) is composed of a baseband uplink
path (BUL) and a baseband downlink path (BDL).
The BDL path includes two identical circuits for processing the analog baseband I and Q
components generated by the RF circuits. The first stage of the BDL path is a continuous
second-order anti-aliasing filter that prevents aliasing of out-of-band frequency
components due to sampling in the ADC. This filter serves also as an adaptation stage
between external and on-chip circuitry.
The anti-aliasing filter is followed by a fourth-order - modulator that performs
analog-to-digital conversion at a sampling rate of 6.5 MHz. The ADC provides 2-bit words
to a digital filter that performs the decimation by a ratio of 24 to lower the sampling rate
to 270.833 kHz. The ADC also provides channel separation by providing enough rejection
of the adjacent channels to allow the demodulation performances required by the GSM
specification.
The BDL path includes an offset register, in which the value representing the channel dc
offset is stored. This value is subtracted from the output of the digital filter before
transmitting the digital samples to the Calypso-Plus IC U100 (DSP) via the BSP. Upon
reset, the offset register is loaded with 0s; its content is updated during the calibration
process.
The typical sequence of burst reception consists of:
1. Power up the BDL path
2. Perform an offset calibration
3. Convert and filter the I and Q components and transmit digital samples
Timing of this sequence is controlled via the TSP, which receives serial real-time control
signals from the TPU of the Calypso-Plus IC U100 (DSP) device. Three real-time signals
control the transmission of a burst: BDLON, BDLCAL, and BDLENA. Each signal
corresponds to a time window.
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 7 -
Page 8
W370/W375 Level 3 C
BDLON high sets the BDL path in power-on mode after a delay corresponding to the
power-on settling time of the analog block. BDLCAL enables the offset calibration
window. Two offset calibration modes are possible and are selected by the state of bit 9
(EXTCAL) of the baseband codec control register. When EXTCAL is 0, the analog inputs
are disconnected from the external world and internally shorted. The result of conversion
done in this state is stored in the offset register. When EXTCAL is 1, the analog input
remains connected to external circuitry, and the result of conversion, including in this
case internal offset plus external circuitry offset, is stored in the offset register. The
duration of the calibration window depends mainly on the settling time of the digital filter.
Data conversion starts with the rising edge of the BDLENA signal; however, the first
eight I and Q samples are not transmitted to the Calypso-Plus IC U100 (DSP), since they
are meaningless due to the group delay of the digital filter. The rising edge of BDLENA is
also used by the IBIC to affect the transmit path of the BSP to the BUL path during the
entire reception window. At the falling edge of BDLENA, the conversion in progress is
completed and samples are transmitted before stopping the conversion process. Finally,
BDLON low sets the BDL path in power-down mode.
Figure 3: Baseband Downlink Block Diagram
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 8 -
Page 9
W370/W375 Level 3 C
Figure 4: Audio Codec Block Diagram
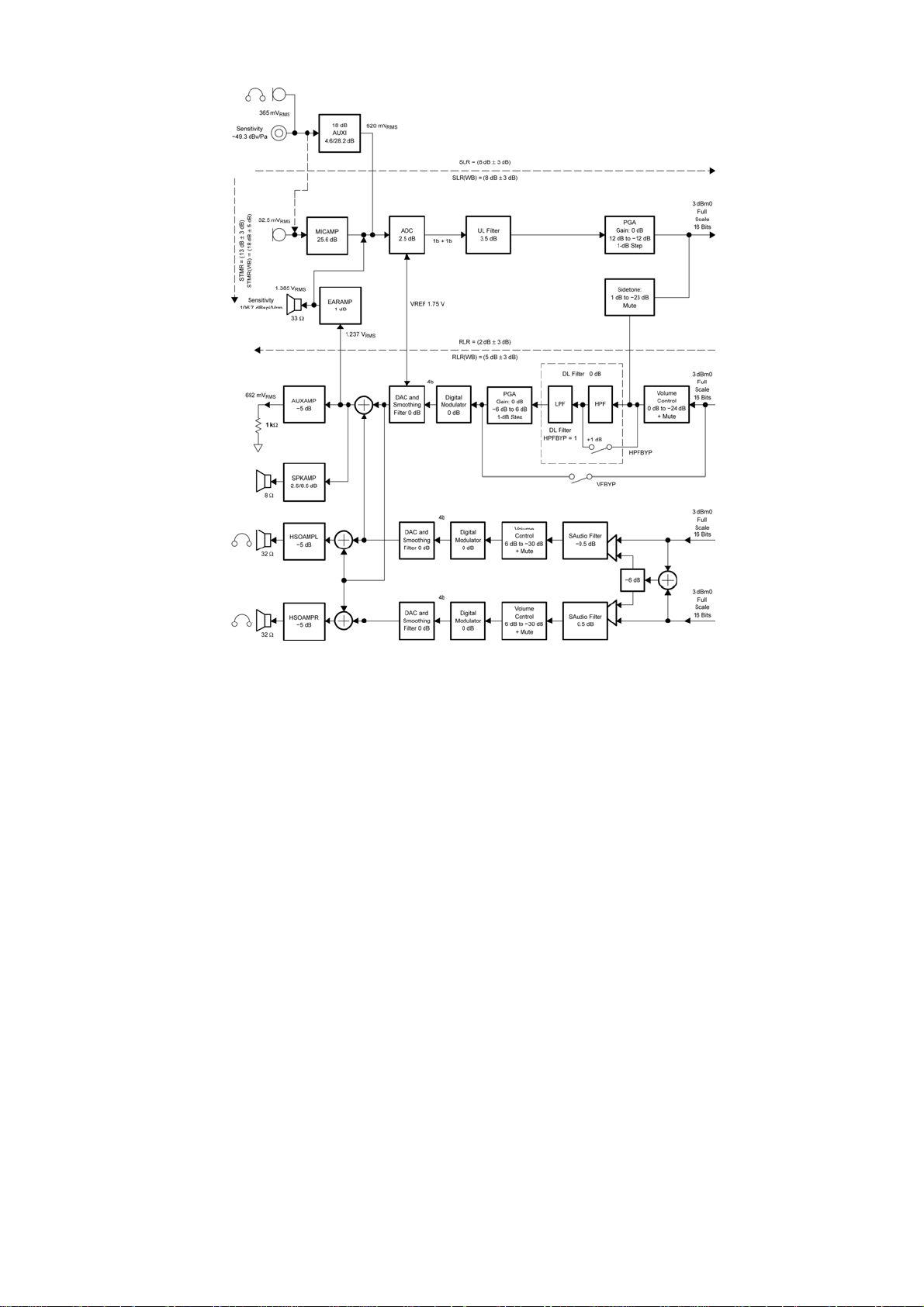
1.4 Audio Codec
The Audio codec consist of a voice codec dedicated to GSM application and an audio
stereo line. The voice codec circuitry processes analog audio components in the uplink
path and applies this signal to the voice signal interface for eventual baseband
modulation. In the downlink path, the codec circuitry changes voice component data
received from the voice serial interface into analog audio. The voice codec support an
8/16 kHz sampling frequency. The stereo audio path converts audio component data
received from the I2S serial interface into analog audio. The following paragraphs
describe these uplink/downlink and audio stereo functions in more details.
1.4.1 Voice Downlink Patch
The VDL path receives speech samples at the rate of 8 kHz from the Calypso-Plus IC U100
(DSP) via the VSP and converts them to analog signals to drive the external speech
transducer.
The digital speech coming from the Calypso-Plus IC U100 (DSP) is first fed to a speech
digital filter that has two functions. The first function is to interpolate the input signal and
to increase the sampling rate from 8 kHz up to 40 kHz to allow the digital-to-analog
conversion to be performed by an over-sampling digital modulator. The second function
is to band-limit the speech signal with both low-pass and high-pass transfer functions.
The filter, the PGA gain, and the volume gain can be bypassed by programming.
The interpolated and band-limited signal is fed to a second order - digital modulator
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 9 -
Page 10

W370/W375 Level 3 C
sampled at 1 MHz to generate a 4-bit (9 levels) over-sampled signal. This signal is then
passed through a dynamic element-matching block and then to a 4-bit digital-to-analog
converter (DAC).
Due to the over-sampling conversion, the analog signal obtained at the output of the
4–bit DAC is mixed with a high frequency noise. Because a 4–bit digital output is used, a
first–order RC filter (included in the output stage) is enough to filter this noise.
The volume control and the programmable gain are performed in the TX digital filter.
Volume control is performed in steps of 6 dB from 0 dB to -24 dB. In mute state,
attenuation is higher than 40 dB. A fine adjustment of gain is possible from -6 dB to +6
dB in 1–dB steps to calibrate the system depending on the earphone characteristics. The
earphone amplifier provides a full differential signal on the terminals EARP Syren Pin A8
and EARN Syren Pin B8. The 8Ohm speaker amplifier provides a differential signal on
the terminals SPKP Syren Pin A6, B6 and SPKN Syren Pin A7, B7.
1.5 Earpiece Receiver The Receiver J10 is connected to EARP Syren Pin A8 and EARN Syren Pin B8.
1.6 Headset
The headset uses a standard 2.5mm phone jack. The headset circuit contains analog
switches (U302 and U303), which are normally switched to receiver earpiece after power
on. When system turns on, the signal HS_EN1 and HS_EN2 (U100 Pin Y14, R13) are
applied. When earphone plug in, the phone will detect this action and make an
appropriate response to answer a call while incoming call occur. The interrupt for the
headphones is detected on the HS_DETECT (U100 Pin M4) line from Pin 6 of Headset
Jack J301. This signal will be pulled to high when the headset is connected.
1.7 Speaker Phone
When the handset set the hand-free mode, the Syren will switch from EARP/EARN to
SPKP/SPKN trace and receiver signal will be through Audio amplifier U301 to Speaker.
1.8 Data Download Receive Path
The External download cable is connected to the Earphone Jack J301, the headset
connector of the mobile phone. The download path is routed from J301 Pin 2 via U302
Pin 3 to RX_Modem. The RX_Modem signal connects to Calypso-Plus IC U100 Pin
C18 to provide this capability. When software is set to download mode, the signal
HS_EN1 (U100 Pin Y14) is applied low, the phone will entered to download state till
download cable pulls out.
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 10 -
Page 11

W370/W375 Level 3 C
Figure 5: Voice Codec Downlink Patch
1.9 26MHz System Clock
The Aero II U802 transceiver integrates the DCXO (Digitally-Controlled Crystal Oscillator)
circuitry required to generate a precise system reference clock using only an external
crystal resonator U800, without external varactors or trim capacitors.
A buffer is available to provide a reference clock output from the XOUT (U802 Pin 8) to
the Calypso-Plus U100 input (Pin J21). The XOUT buffer is enabled when the XEN (Pin
32) is set high, independent of the PDN (Pin 9). To achieve complete power down
during sleep, the XEN pin should be set low to disable the XOUT buffer. When XDIV
(Pin 26) is tied low, XOUT is 26 MHz, and when it is tied high, XOUT is 13 MHz. In the
case of this document, 26MHz is configured and used for synchronization between the
baseband and RF circuits.
Figure 6: Aero II 26MHz clock circuit
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 11 -
Page 12

W370/W375 Level 3 C
2 Transmit
2.1 Audio (Voice uplink Patch)
The VUL path includes two input stages. The first stage is a microphone amplifier,
compatible with electric microphones containing a FET buffer with open drain output. The
microphone amplifier has a gain of typically 25.6 dB (±1 dB) and provides an external
voltage of 2.5V to bias the microphone (MICBIAS Syren Pin C9).
The auxiliary audio input can be used as an alternative source for higher-level speech
signals. This stage performs single-ended conversion and provides a programmable gain
of 4.6 dB or 28.2 dB. The third stage is a headset microphone amplifier, compatible with
electric microphones. The headset microphone amplifier has a gain of typically 18 dB and
provides an external voltage of 2.0V or 2.5V to bias the headset microphone
(HSMICBIAS Syren Pin B11). When one of the input stages (MICI, HSMICP) is in use,
the other input stages are disabled and powered down.
The resulting fully differential signal is fed to the analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The
ADC conversion slope depends on the value of the internal voltage reference.
Analog-to-digital conversion is performed by a third-order - modulator with a sampling
rate of 1 MHz. Output of the ADC is fed to a speech digital filter, which performs the
decimation down to 8 kHz and band-limits the signal with both low-pass and high-pass
transfer functions. Programmable gain can be set digitally from –12 dB to +12 dB in 1-dB
steps. The speech samples are then transmitted to the Calypso-Plus IC U100 via the VSP
at a rate of 8 kHz. There are 15 meaningful output bits.
Programmable functions of the VUL path, power-up, input selection, and gain are
controlled by the Baseband serial port (BSP) or the MCU serial port (USP) via the serial
interfaces. The VUL path can be powered down by Program.
Figure 7: Voice Uplink Paths
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 12 -
Page 13

W370/W375 Level 3 C
2.2 Data Download Transmit Path
The External download cable is connected to the Earphone Jack J301 Pin 3, the headset
connector of the mobile phone. The download path is routed from J301 Pin 3 via U303
Pin 3 to TX_Modem. The TX_Modem signal connects to Calypso-Plus IC U100 Pin
A20 to provide this capability. When software is set to download mode, the signal
HS_EN2 (U100 Pin R13) is applied low, the phone will entered to download state till
download cable pull out.
2.3 Stereo Audio Path
The stereo audio path receives Left and right signal samples at the rate of a
programmable frequency, from 8kHz to 48kHz, via the I2S serial interface and converts
them to analog signals to drive the external audio signal or speech transducers.
The digital audio signal is first fed to an audio digital filter that has two functions. The first
function is to interpolate the input signal and to increase the sampling rate to allow the
digital–to–analog conversion to be performed by an over-sampling digital modulator. The
second function is to band–limit the audio signal with a low–pass transfer functions. The
interpolated and band–limited signal is fed to a second order - digital modulator
sampled at fS1 frequency to generate a 4–bit (9 levels) over-sampled signal. This signal is
then passed through a dynamic element matching block and then to a 4–bit
digital–to–analog converter (DAC).
Due to the over-sampling conversion, the analog signal obtained at the output of the
4–bit DAC is mixed with a high frequency noise. Because a 4–bit digital output is used, a
first–order RC filter (included in the output stage) is enough to filter this noise.
The volume control is performed in the audio digital filter. Volume control is performed in
steps of 1 dB from 0 dB to -30 dB. In mute state, attenuation is higher than 40 dB. The
gain is independently programmable on the Left and Right channels, using the same
register VAUSCTRL. A common adjustment of gain is possible at 0dB or +6dB. A digital
Left/Right summer and 6dB attenuator allows output of a mono audio path. These
configurations are programmed with the register VAUDCTRL.
The Left and right head set amplifiers provide the stereo signal on terminals HSOL (U101
Pin A9) and HSOR (U101 Pin A10). The mono audio signal may be provided on the
Right or the Right and Left headset outputs. The mono audio signal may be sum to the
speech signal and provided on the Auxiliary, Earphone and/or 8Ohm Speaker outputs.
The Audio Stereo/Mono path can be powered down and configure with the PWDNG,
VAUDCTRL and VAUDPLL registers.
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 13 -
Page 14

W370/W375 Level 3 C
Figure 8: Stereo Audio Path
2.4 Modulation
The modulator circuit in the BUL path performs the Gaussian minimum shift keying
(GMSK) in accordance with the GSM specification 5.04. The data to be modulated flows
from the Calypso-Plus IC U100 radio interface (RIF) through the baseband serial port
(BSP).
The GMSK modulator is implemented digitally, the Gaussian filter computed on 3 bits of
the input data stream being encoded in the Sine/Cosine look-up tables in ROM, and it
generates the in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) digital samples with an interpolation ratio
of 16.
The raw burst data (as yet unmodulated) received via the BSP is loaded in a burst RAM
prior to performing the modulation. Burst RAM, and multi-slot operation will be described
in a paragraph below. The modulation procedure differs according to the modulated type
selected.
The GMSK modulator has a bit-rate of 270.833kHz, the same rate as its symbol rate. It
performs differential encoding on the 3 most recent input data stream bits. The resulting
bit stream is Gaussian filtered by means of a Sine/Cosine look–up table stored in a ROM,
from which the in–phase (I) and quadrature (Q) digital samples are generated with an
interpolation ratio of 16 from the symbol rate, i.e., at 4.33MHz
These digital I and Q words are sampled at 4.33 MHz and applied to the inputs of a pair of
10–bit DACs. The analog outputs are then passed through third–order Bessel filters to
reduce out–of–band noise and image frequency and to obtain a modulated output
spectrum consistent with 3GPP specification TS 05.05.
Fully differential signals are available at terminals BULIP, BULIM, BULQP, and
BULQM.
To minimize phase trajectory error, the dc offset of the I and Q channels can be
minimized using offset calibration capability. During offset calibration, input words of the
10–bit DACs are set to zero code and a 6–bit sub–DAC is used to minimize the dc offset at
analog outputs. The sub-DAC is capable of cancellation of internal offsets up to 6.25% of
the output dynamic range.
The entire content of a burst, including guard bits, tail bits, and data bits, is stored in one
of two 160–bit burst buffers before starting the transmission. The presence of two burst
buffers is dictated by the need to support multi-slot transmission: one buffer is loaded
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 14 -
Page 15

W370/W375 Level 3 C
with new data while the content of the second buffer is pushed into the GMSK modulator
for transmission.
Single–slot or multi-slot mode is selected by the MSLOT bit of the BBCTL register. When
single slot mode is selected, only the content of burst buffer 1 is used for modulation.
Output level can be selected with the OUTLEV[2:0] bits of the BBCTL register.
The typical sequence of burst transmission consists of:
1. Power up the BUL path
2. Perform an offset calibration (not mandatory)
3. Modulate the content of the burst buffer
Timing of this sequence is controlled via the timing serial port (TSP), which receives serial
real-time control signals from the time process unit (TPU) of Calypso-Plus IC U100 (DSP)
device. Three real-time signals control the transmission of a burst: BULON, BULCAL,
and BULENA. Each signal corresponds to a time window.
BULON high sets the BUL path in power-on mode after a delay corresponding to the
power-on settling time of the analog block. BULCAL enables the offset calibration
window. During BULCAL, inputs of 10-bit DACs are forced to code zero and a low-offset
comparator senses the dc level at the TXIP Syren Pin H12 (BULIP)/TXIN Syren Pin
H10 (BULIM) and TXQP Syren Pin F11 (BULQP)/ TXQN Syren Pin F12 (BULQM)
terminals. The result of the comparison modifies the content of the offset registers, which
drives the 6-bit sub-DACs to minimize the offset error. The duration of the calibration
phase depends on the time needed to sweep the sub-DAC dynamic range. Modulation
starts with the rising edge of BULENA and ends 32 one-quarter bits after the falling edge
of BULENA. At the end of modulation, the modulator is reinitialized by setting the
pointers of burst buffers and the filter ROM to the base address. The I vector is set to its
maximum value, while the Q vector is set to 0.
A capability exists to unbalance the gain between I and Q channels in order to allow
compensation of natural gain mismatch or imperfection of RF mixer via the IQSEL, G0,
and G1 bits of the BBCTL register.
The output common mode voltage of the TXIP Syren Pin H12 (BULIP)/TXIN Syren Pin
H10 (BULIM) and TXQP Syren Pin F11 (BULQP)/ TXQN Syren Pin F12 (BULQM)
terminals can be set to several values by bits 2–0 (SELVMID [2:0]) of the baseband codec
control register.
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 15 -
Page 16

W370/W375 Level 3 C
Figure 9: Baseband Uplink Block Diagram
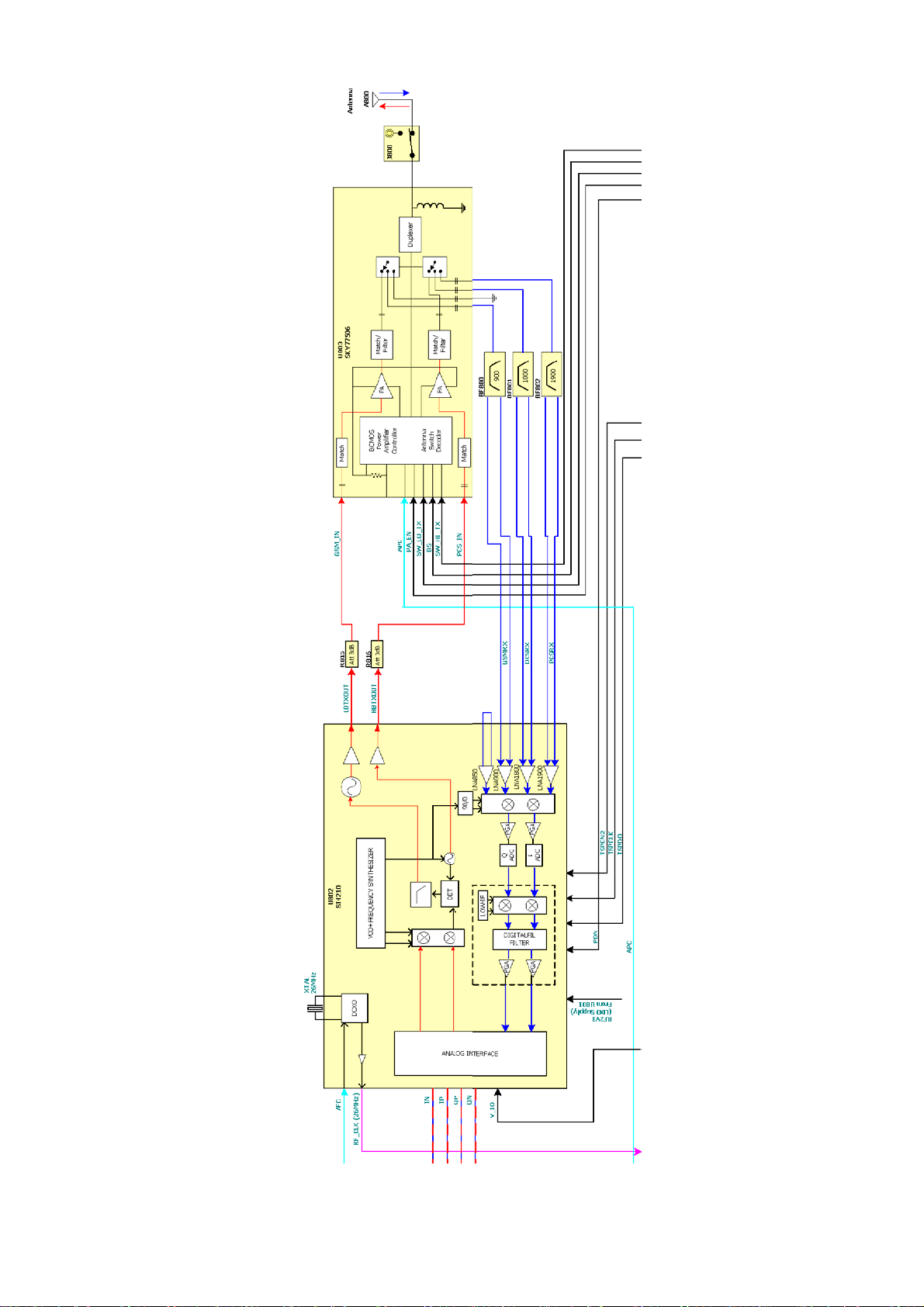
2.5 Transceiver IC
The Aero II IC U802 transceiver is a complete RF front end for multi-band GSM and GPRS
wireless communications. The receive section interfaces between the RF band-select
SAW filters and the baseband subsystem. The Aero II receiver leverages a proven digital
low-IF architecture and enables a universal baseband interface without the need for
complex dc offset compensation. The transmit section of Aero II provides a complete up
conversion path from the baseband subsystem to the power amplifier (PA U803) using an
offset phase-locked loop (OPLL) integrated with Silicon Laboratories’ patented
synthesizer technology. All sensitive components, such as TX/RF VCOs, loop filters,
tuning inductors, and varactors are completely integrated into a single integrated circuit.
The Aero II transceiver includes a digitally-controlled crystal oscillator (DCXO) and
completely integrates
Figure 10: Aero II IC
2.5.1 Function Description
The Aero II transceiver is the industry's most integrated RF front end for multi-band
GSM/GPRS digital cellular handsets and wireless data modems.
The receive section uses a digital low-IF architecture that avoids the difficulties
associated with direct conversion. The baseband interface is compatible with any
supplier's baseband subsystem.
The transmit section is a complete up-conversion path from the baseband subsystem to
the power amplifier, and uses an offset phase-locked loop (OPLL) with a fully integrated
transmit VCO.
The frequency synthesizer uses Silicon Laboratories' proven technology that includes an
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 16 -
Page 17

W370/W375 Level 3 C
integrated RF VCO, loop filter, and varactor. The unique integer-N PLL architecture
produces a transient response superior in speed to fractional-N architectures without
suffering the high phase noise or spurious modulation effects often associated with those
designs. This fast transient response makes the Aero II transceiver well suited to GPRS
multi-slot applications where channel switching and settling times are critical.
The analog baseband interface is used with conventional GSM baseband ICs (BBIC). The
receive and transmit baseband I/Q pins are multiplexed together in a 4-wire IN, IP, QN
and QP interface. A standard three-wire TSPCLK, TSPEN2 and TSPDO serial interface
is used to control the transceiver. The Aero II transceiver is Silicon Laboratories'
third-generation transceiver to be implemented in a 100% CMOS process.
Figure 11: Aero II Transceiver Block Diagram
2.5.2 Receiver Section
The receive (RX) section integrates four differential input low noise amplifiers (LNAs)
supporting the GSM 850 (869–894 MHz), E-GSM 900 (925–960 MHz), DCS 1800
(1805–1880 MHz), and PCS 1900 (1930– 1990 MHz) bands. The LNA inputs are matched
to 150 or 200 balanced-output SAW filters through external matching networks
A quadrature image-reject mixer downconverts the RF signal to a low intermediate
frequency (IF). The mixer output is amplified with an analog programmable gain amplifier
(PGA). The quadrature IF signal is digitized with high resolution analog-to-digital
converters (ADCs).
The ADC output is downconverted to baseband with a digital quadrature local oscillator
signal. Digital decimation and FIR filters perform digital filtering, and remove ADC
quantization noise, blockers, and reference interferers. The response of the FIR filter is
programmable to a flat passband setting and a linear phase setting. After filtering, the
digital output is scaled with a PGA
Digital-to-analog converters (DACs) drive differential I and Q analog signals onto the BIP,
BIN, BQP, and BQN pins to interface to Syren IC U101.
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 17 -
Page 18

W370/W375 Level 3 C
Figure 12: Aero II Receiver Block Diagram
2.5.3 Transmit Section
The transmit section consists of an I/Q baseband upconverter, an offset phase-locked
loop (OPLL), and two 50 output buffers that can drive an external power amplifier (PA
U803). One output is for the GSM 850 (824– 849 MHz) and E-GSM 900 (880–915 MHz)
bands and one output is for the DCS 1800 (1710–1785 MHz) and PCS 1900 (1850–1910
MHz) bands.
The OPLL requires no external filtering to attenuate transmitter noise and spurious
signals in the receive band, saving both cost and power. The output of the transmit VCO
(TXVCO) is a constant-envelope signal that reduces the problem of spectral spreading
caused by non-linearity in the PA U803. Additionally, the TXVCO benefits from isolation
provided by the transmit output buffers. This significantly minimizes any load pull effects
and eliminates the need for off-chip isolation networks.
A quadrature mixer upconverts the differential in-phase (BIP, BIN) and quadrature
(BQP, BQN) baseband signals to an intermediate frequency (IF) that is filtered and
which is used as the reference input to the OPLL. The OPLL consists of a feedback mixer,
a phase detector, a loop filter, and a fully integrated TXVCO.
Low-pass filters before the OPLL phase detector reduce the harmonic content of the
quadrature modulator and feedback mixer outputs.
The receive and transmit baseband I/Q pins are multiplexed together in a 4-wire interface
(TXQN, TXQP, TXIN, and TXIP). In transmit mode, the BIP, BIN, BQP, and BQN pins
provide the analog I/Q input from the baseband subsystem. The I and Q signals are
automatically swapped within the Aero II transceiver when switching bands. The transmit
output path is automatically selected by program.
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 18 -
Page 19

W370/W375 Level 3 C
Figure 13: Aero II Transmit Block Diagram
2.5.4 Digitally- Controlled Crystal Oscillator (DCXO)
As shown in Figure 6, the Aero II transceiver integrates the DCXO circuitry required to
generate a precise system reference clock using only an external crystal resonator. The
DCXO replaces a discrete VC-TCXO module. The DCXO allows for the use of a standard 26
MHz crystal. There are no external varactors or trim capacitors required.
The DCXO uses the CDAC and CAFC arrays to correct for both static and dynamic
frequency errors, respectively. An internally digitally programmable capacitor array
(CDAC) provides a coarse method of adjusting the reference frequency in discrete steps.
The CDAC[6:0] bits in Register 03h are programmed to compensate for static variations
in PCB design, manufacturing, and crystal tolerance, and are typically set to center the
oscillator frequency during production.
A second capacitor array (CAFC) allows for fine and continuous dynamic adjustment of
the reference frequency by an external control voltage (AFC). This control voltage is
supplied by the AFC DAC of the baseband and should be connected to the transceiver
AFC Aero II Pin 27. The baseband determines the appropriate frequency adjustment
based on the receipt of the FCCH burst. The baseband then adjusts the AFC voltage to
correct for frequency variations caused by temperature drift.
The transceiver can be adjusted for the corresponding baseband AFC input full-scale
voltage by program.
The Aero II transceiver can be configured in DCXO mode or VC-TCXO mode by the
XMODE Aero II Pin 25. To use the transceiver in DCXO mode, the XMODE pin is tied
high. The XTAL1 Aero II Pin 31 and XTAL2 Aero II Pin 30 are then connected directly
to the 26 MHz crystal U800. No additional components are required.
A buffer is available to provide a reference clock output from the XOUT Aero II Pin 8 to
the baseband input. The XOUT buffer is enabled when the XEN Aero II Pin 32 is set
high, independent of the PDN Aero II Pin 9. To achieve complete power-down during
sleep, the XEN pin should be set low to disable the XOUT buffer. The XOUT buffer is
specified to drive a 26 MHz when XDIV is tied low.
2.6 RF TX PA The TX signal outputs at LBTXOUT Aero II Pin 15 (low-band) and HBTXOUT Aero II
Pin 16 (high-band). The high-band signal passes through R815, and the low-band signal
passes through R816. The SKY77506 PA IC U803 has two independent RF paths (one for
the high-band signal and one for the low-band signal). A linear power amplifier in each
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 19 -
Page 20

W370/W375 Level 3 C
path. The SKY77506 U803 also contains band-select switch circuitry to select GSM (logic0)
or DCS/PCS (logic1) as determined from the Band Select (BS1) Pin 2 signal. The
module consists of separate GSM850/900 PA and DCS1800/PCS1900 PA blocks,
impedance-matching circuitry for 50 input and output impedances, and a Power
Amplifier Control (APC SKY77506 Pin 26) block with an internal current-sense resistor.
The SKY77506 U803 also integrates TX harmonics filtering, high linearity and low
insertion loss RF switches and diplexer. The output of each PA block and the outputs to
the four receive pads are connected to the antenna pad U803 Pin 15 through RF
switches and a diplexer.
Band selection and control of transmit and receive modes are performed using three
external control (BS1 Pin 2, BS2 Pin 1 and TX_EN Pin 28). Refer to the table in
section 1.1 Band Selection. The two band-select (BS1, BS2) select between
GSM850/900 and DCS/PCS modes of operation. The transmit enable (TX_EN) controls
receive or transmit mode of the respective RF switch. Proper timing between transmit
enable (TX_EN) and Analog Power Control (APC SKY77506 Pin 26) allows for high
isolation between the antenna and TX-VCO while the VCO is being tuned prior to the
transmit burst. The TX_EN input allows initial turn-on of the PAC circuitry to minimize
battery drain.
The amplified RF signal then outputs from SKY77506 Pin 15 to the antenna A800.
Figure 14: Power Amplifier and Antenna Switch
3 Syren Monitoring ADC
The monitoring section includes a 10-bit ADC and 10-bit/9-word RAM. The ADC monitors:
z Four internal analog values:
– Battery voltage (VBAT)
– Battery charger voltage (VCHG)
– Current charger (current-to-voltage (I-to-V) converter) (ICHG)
– Backup battery voltage (VBACKUP)
z Five external analog values:
– ADIN1: Reserve for model detect
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 20 -
Page 21

W370/W375 Level 3 C
– BATTEMP Syren Pin J12 for monitor the battery temperature
– HS_MODE Syren Pin J10 for detect download cable or headset
– ADIN4: not used
– ADIN5: not used
Figure 15: Baseband interface
4 Baseband Serial Port (BSP)
The baseband serial port (BSP) is a bidirectional (transmit/receive) serial port. Both
receive and transmit operations are double-buffered and permit a continuous
communication stream. Format is a 16-bit data packet with frame synchronization.
The CK13M master clock is used as a clock for both transmit and receive. The BSP allows
read and write access of all internal registers under the arbitration of the internal bus
controller. But its transmit path is allocated to the BDL path during burst reception for I
and Q data transmissions.
5 Microcontroller Serial Port (USP)
The microcontroller serial port (USP) is a synchronous serial port. It consists of three
terminals: data transmit (MCUDI Syren Pin K3), data receive (MCUDO Syren Pin L3),
and port enable (MCUEN0 Syren Pin M2). The clock signal is the CK13M master clock.
Transfers are initiated by the external microcontroller, which pushes data into the USP via
the MCUDO, while synchronous data contained in the transmit buffer of the USP is
pushed out via the MCUDI. The USP allows read and write access of all internal registers
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 21 -
Page 22

W370/W375 Level 3 C
T
T
T
T
T
under the arbitration of the internal bus controller.
6 General purposes I/O (GPIO)
Calypso-Plus provides 16 GPIOs in read or write mode by internal registers.
GPIO Pin Used As. Description
GPIO0
GPIO1
GPIO2
GPIO3
GPIO4
GPIO5
GPIO6
GPIO7
GPIO8
GPIO9
GPIO10
GPIO11
GPIO12
GPIO13
GPIO14
GPI015
KEYLIGHT_EN Pin W5
BACKLIGHT_EN Pin Y4
AUDAMP_SD Pin AA4
CHG_DET Pin V7
LCD_nRESET Pin M3
SEND_END Pin R19
FM_nRESET Pin D18
BATTERY_EN Pin C19
HS_DETECT Pin M4
BE_nReset Pin P18
INCOM_EN1 Pin E18
INCOM_EN2Pin C21
MESSAGE_EN Pin D19
Band select Pin G11
BYPASS Pin B7
FOLD_DET Pin C7
7 TFT LCD Display
Keypad light controller
LCD backlight controller
Audio amplifier controller
he interrupt for the detection of USB
charger or USB data cable
LCD reset
he interrupt from the headset when the
end call button is pressed
FM radio reset
The LED indication of low battery
The interrupt for the headset or data cable
detection
Reset Backend IC (W375: PixArt PAP1312
Image Processor)
he LED indication of incoming call while the
caller is unknown
he LED indication of incoming call while the
caller is known
The LED indication of new message
Low: EGSM/DCS, High: GSM850/PCS
For the bypass function of Backend IC
(W375: PixArt PAP1312 Image Processor)
he interrupt for the detection of the
clamshell flip open or close.
The 1.8” (4.487cm) LCD module is an active matrix color TFT LCD module. LTPS (Low
Temperature Poly Silicon) TFT technology is used. Vertical drivers are built on the panel.
The following is general specifications of Toppoly TFT LCD. (Model name is TD018THEE3)
1. Display Size (Diagonal) : 1.8 (4.487) Inch (cm)
2. Display Type : Transmissive
3. Active Area (HxV) : 28.032 x 35.04 mm
4. Number of Dots (HxV) : 128 x RGB x 160 dot
5. Dot Pitch (HxV) : 0.073 x 0.219 mm
6. Color Arrangement : RGB Stripe
7. Color Numbers : 65 K
8. Outline Dimension (HxVxT) : 35.6 x 47.6 x 3.15 mm
9. Weight : 6.6 +/- 0.5 g
For W370, the 65K TFT LCD display is controlled by the micro wire (uWire) and GPIO
interface of Calypso-Plus. Figure 16 shows the pin connections between TFT LCD and
Calypso-Plus. And the functions of those pins are described as the following:
SDO – LCD serial data bus from Calypso-Plus
SCLK – LCD serial clock derived from reference 13MHz clock
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 22 -
Page 23

W370/W375 Level 3 C
LCD_nCS – This is used as Chip Enable for the LCD.
LCD_nRESET – LCD reset
V_IO – LCD driver IC power supply
LED – LCD backlight LED power supply
Figure 16: The pin connections of TFT LCD and U100 Calypso-Plus
For W375, the 65K TFT LCD display is controlled by the back-end IC U20 (PixArt Image
Processor, PAP1312). Figure 16 shows the pin connections among PAP1312, Camera
module and TFT LCD.
The functions of those pins between LCD and U20 PAP1312 are described as the
following:
LCD_SDATA – LCD serial data bus from the back-end IC
LCD_SCLK – LCD serial clock derived from reference 13MHz clock
LCD_CS – This is used as Chip Enable for the LCD.
LCD_nRESET – LCD reset
V_IO – LCD driver IC power supply
LED – LCD backlight LED power supply
7.1 Display Backlights
The Display backlights are provided by the control signal BACKLIGHT_EN Calypso-Plus
Pin Y4. After BACKLIGHT_EN Calypso-Plus Pin Y4 control signal turned on, Charge
Pump U700 will charge the flying capacitor (C705) to supply 5V for two shunt LEDs in
LCM. On another side, when KEYLIGHT_EN Calypso-Plus Pin W5 control signal is high,
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 23 -
Page 24

W370/W375 Level 3 C
the keypad light will be turned on.
7.2 Image Processor (For W375 only)
U20 PAP1312 is a multimedia imaging processor targeted to the cellular phone
application. It integrates host interface, CMOS sensor interface, LCM interface, LCM
resizing engine, JPEG CODEC engine and ISP (Image Signal Process) engine. Besides, it
also integrates the 64kB SRAM to make the PAP1312 working without any external
memory.
Figure 16 has shown the pin connections between U20 PAP1312 and Calypso-Plus. Figure
17 shows the Function Block Diagram of PAP1312. It supports bypass mode by setting
BYPASS pin as high. Under bypass mode, Calypso-Plus can directly control LCM. For
W375, the parallel sensor interface (CAM_DATA[0:7]) is connected to camera module,
the serial LCM interface (LCD_CS Pin 14, LCD_SCLK Pin 11, LCD_SDATA Pin 15) is
connected to LCD and SPI host interface (BYPASS Pin 2, LCD_nCS Pin 47, SCLK Pin
3, SDI Pin 48, SDO Pin 48) is connected to Calypso-Plus U100.
The rest of the pins between camera module and U20 PAP1312 are described as the
following:
Figure 17: Function Block Diagram of PAP1312
7.3 Camera Module (For W375 only)
The camera module (CM-5628) is a sensor on-board camera and lens module designed
for mobile application.
CM-5628 can be programmed to provide image output in various fully processed and
Automatic image function include AEC, AGC, AWB... and image quality control such as
color saturation, hue, gamma, edge enhancement functions
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 24 -
Page 25

W370/W375 Level 3 C
Also the Figure 16 has shown the pin connections of camera module. The functions of
those pins between the camera module and U20 PAP1312 are described as the following:
CAM_DATA[0:7] – YUV/RGB Video Output, total are 8 bits.
SIO_C – SCCB serial interface clock input
SIO_D – SCCB serial interface data input and output
OV_RESET – Chip reset, with active high
XCLK – System clock input
PCLK – Pixel clock output
HREF – Horizontal synchronization output
VSYNC – Vertical synchronization output
PWDN – Power Down Mode Selection, 0: Normal mode, 1: power down mode
8 32kHz RTC
The Real-time Clock Interface is part of the Calypso-Plus U100 in use with the crystal
X100. The clock signal is running on 32kHz as reference for the clock module and as deep
sleep clock.
9 SIM Card Circuit
To allow the use of both 1.8V and 3V SIM card types, there is a SIM level-shifter module
in the Syren U101. The SIM card digital interface ensures the translation of logic levels
between the Syren U101 device and the SIM card J701 for the transmission of three
different signals:
SIM-SIO – Data Communications path between SIM connector J701 Pin 2 and Syren
Pin K4
SIM-CLK – SIM data Clock from Syren Pin M4
SIM-RST – SIM Reset from Syren Pin L4
V_SIM is an LDO voltage regulator providing the power supply to the SIM card driver of
the Syren device.
SIM_IO
SIM_CLK
SIM_RST
SIM-IO3
SIM-CLK3
SIM-RST3
DBBSI
O
DBBSCK
DBBSRS
T
SIMIO
SIMCK
SIMRST
V_SIM
SIM-IO
SIM-CLK
SIM-RST
VCCVRSIM
I/O
CLK
RST
GND
Calypso-Plus
Syren
SIM Connecter
Figure 18: SIM interface
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 25 -
Page 26

W370/W375 Level 3 C
9.1 SIM Card Supply Voltage Generation
To accommodate the 1.8V or 3V SIM cards, the Syren includes an LDO voltage regulator
that delivers supply voltage V_SIM Pin M3 to the SIM module.
The LDO voltage regulator is configured to generate the 1.8V or 2.9V (V_SIM U101 Pin
M3) supply. The V_SIM J701 Pin 4 and 5 terminals are decoupled by a capacitor
(C706).
The SIM Card Supply Voltage Generation is controlled by the following setoff control bits:
z Bit 0 (SIMSEL) of the SIM Card control register selects the V_SIM output voltage
(1.8V or 2.9V).
z Bit 1 (RSIMEN) of the SIM Card control register enables the 1.8V/2.9V series
regulator.
z Bit 2 (SIMRSU) of the SIM Card control register is the V_SIM regulator status.
z Bit 3 (SIMLEN) of the SIM Card control register enables the SIM interface level
shifter (on the SIMCK, SIMRST, and SIMIO terminals).
10 Keypad
The keyboard is connected to the chip using:
ROW0-ROW4 (KBR[0:5]) input pins for row lines
COL0-COL4 (KBC[0:5]) output pins for column lines
If a key button of the keyboard matrix is pressed, the corresponding row and column
lines are shorted.
To allow key press detection, all input pins (KBR[0:5]) are pulled up to VCC and all
output pins (KBC[0:5]) are driving a low level. Any action on a button will generate an
interrupt to the microcontroller which will, as answer, scan the column lines with the
sequence describe below.
This sequence is written to allow detection of simultaneous press actions on several key
buttons.
Figure 19: Keyboard scanning sequence
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 26 -
Page 27

W370/W375 Level 3 C
10.1 Keypad Matrix
Figure 20: Keyboard connection
The keypad matrix is as follow:
Function Key Col 0 Col 1 Col 2 Col 3 Col 4 Row 0 Row1 Row 2 Row 3 Row 4
1 S10 V V
2 S11 V V
3 S12 V V
SEND S13 V V
4 S14 V V
5 S15 V V
6 S16 V V
UP S17 V V
7 S18 V V
8 S19 V V
9 S20 V V
DOWN S21 V V
* S22 V V
0 S23 V V
# S24 V V
LEFT S25 V V
SOFT-L S26 V V
MENU S27 V V
SOFT-R S28 V V
RIGHT S29 V V
POWER/ENDS30 V
11 Vibrator circuit
DAC Syren U101 Pin D9 is used to control the vibrational level. D700 is used to
protection the vibrator. The DAC output voltage is 2V and drain current is around 80mA.
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 27 -
Page 28

W370/W375 Level 3 C
12 Memory
The W370/W375 portable will be using the stacked combination memory parts that
include flash die and PSRAM die. The Flash memory is 128Mbit size and the PSRAM
memory is 32Mbit size.
ADD [1:23] – Address Bus for Flash memory/PSRAM.
DATA [0:15] – Data Bus for Flash memory/PSRAM
V_FLASH – This is provided Flash memory I/O voltage.
V_MEM_18 – This is provided Flash memory supply voltage.
RnW – Read and Write allows information to be written or read from the memory
devices.
nFOE – Flash and PSRAM output enable (Active Low).
FDP – The Flash reset/deep power-down mode control.
nCS5 – This is used as Chip Enable for the Flash Memory.
nCS4 – This is used as Chip Enable for the PSRAM Memory.
nBHE – Enable to address High Byte Information.
nBLE – Enable to address Low Byte Information.
V_RAM – This provides PSRAM memory power supply
WPZ – Flash write protection
Figure 21: Memory interface
13 Power
13.1 Low-Dropout Voltage Regulators
The voltage regulation block consists of seven subblocks.
Several low-dropout (LDO) regulators perform linear voltage regulation. These regulators
supply power to internal analog and digital circuits, to the Calypso-Plus IC U100 (DSP)
processor, and to external memory.
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 28 -
Page 29

W370/W375 Level 3 C
The first LDO (V_DBB Syren Pin A3) is a programmable regulator that generates the
supply voltages 1.5 V for Calypso-Plus IC U100 (DSP). During all modes, the main battery
directly supplies V_DBB.
The second LDO (V_IO Syren Pin L2 and M1) generates the supply voltage (2.8 V) for
the Calypso-Plus IC U100 (DSP), Analog Switch U301/U302 and Aero II U802 Interface
supply voltage. During all modes, the main battery directly supplies V_IO.
The third LDO (V_FLASH Syren Pin D1) is a programmable regulator that generates the
supply voltages 2.8 V for flash memory U200 and Calypso-Plus IC U100 (DSP) memory
interface I/Os. During all modes, the main battery directly supplies V_FLASH.
The fourth LDO (V_RAM Syren Pin F1) is a programmable regulator that generates the
supply voltages 2.8 V for external memories (PSRAM memory). The main battery directly
supplies V_RAM.
The fifth LDO (V_ABB) generates the supply voltage (2.8 V) for the analog functions of
the Syren U101 device. During all modes, the main battery directly supplies V_ABB.
The sixth LDO (V_SIM Syren Pin M3) is a programmable regulator that generates the
supply voltages (2.9 V and 1.8 V) for SIM card and SIM card drivers. During all modes,
the main battery directly supplies V_SIM.
The Syren U101 allows three operating modes for each of these voltage regulators:
1. ACTIVE mode during which the regulator is able to deliver its full power.
2. SLEEP mode during which the output voltage is maintained with very low power
consumption but with a low current capability (1mA).
3. OFF mode during which the output voltage is not maintained and the power
consumption is null.
The regulators rise up in ACTIVE mode only and each of them has a regulation ready
signal RSU. In switched-off and backup states of the mobile phone, the voltage regulators
will be set to a SLEEP or OFF mode depending on the system requirements. The regulator
voltages are decoupled by a low ESR capacitor connected across the corresponding VCC
and ground terminals. Besides its voltage filtering function, this capacitor also has a
voltage storage function that could give a delay for data protection purposes when the
main battery is unplugged.
The seventh LDO (V_RTC Syren Pin H1) is a programmable regulator that generates the
supply voltages 1.5 V for the real-time clock and the 32kHz oscillator located in the
Calypso-Plus IC U100 (DSP) device during all modes. The main or backup battery supplies
V_RTC.
13.2 Power Down Methods
The phone is disabled by one of the following conditions:
1. Software-initiated power down.
When the user requests to turn the phone off by pressing the POWER/END key, or
put RPWON TP11 to GND, or when a low battery voltage is detected by software
through VBATS Syren Pin K8 (typical value is 3.53V) measurement and therefore
the phone turns off.
2. Hardware-initiated power down.
On main battery remove or deep discharge, when the main battery voltage is
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 29 -
Page 30

W370/W375 Level 3 C
lower than 2.8V.
14 Sleep Module
The Sleep Module allowed for optimal power savings in idle modes. Syren U101 internal
LDOs (VRDBB, VRIO, VRRAM, VRMEM, VRSIM, and VRABB) have very low current
consumption and can provide 1mA current.
14.1 Sleep Up Sequence
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 30 -
Page 31

W370/W375 Level 3 C
14.2 Sleep off Sequence
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 31 -
Page 32

W370/W375 Level 3 C
e
15 Power Tree
W370/W375 Power Distribution Tre
VBAT
RF PA
FEM
Vibrator
Keypad
Light
FM Radio
V_SIM
1.8/2.9V
20mA
SIM
Card
V_FLASH
2.8V
60mA
Flash
128Mbit
Syren
V_RAM
2.8V
50mA
PSRAM
32Mbit
V_DBB
1.5V
170mA
Calypso-
Plus
V_IO
2.8V
100mA
Calypso-
Plus
LDO
2.5V
150mA
Camera
Supply
Voltage
FM Radio
Audio
Ampifier
Camera
Digital
Core
Foler
Sensor
LDO
1.8V
150mA
Back-end
IC Core
Aero II
I/O
Interface
Supply
Voltage
Charge
Pump
5V
60mA
LCD
Backlight
Back-end
IC I/O
Interface
Supply
Voltage
LDO
2.8V
150mA
Aero II
Supply
Voltage
Camera
I/O
Interface
Supply
Voltage
Speaker
Audio
Amplifier
Speaker
Figure 22: Power Distribution Tree
16 Charging Circuit and External Power
We can obtain power from battery, external charger and USB data cable. Power source
via the accessory connector are not supported.
16.1 Battery Support
The Battery connecter J700 is made up of 4 contacts, these are
♦ Pin 1 – VBAT- (BATTGND)
♦ Pin 2 – BATTEMP is used to measure the Battery temperature during charging, fed
from the battery connector to Syren U101 Pin J12
♦ Pin 3 – DATA-EPROM for charge/discharge control (No Used for W370/
W375)
♦ Pin 4 – VBAT+
16.2 Charger Support
When the battery voltage is less than 3.2V, and adapter is inserted, the charging system
will enter the ‘Pre-CHARGE’ mode. The pre-charging current will pass through Syren
pre-charge path and charger IC U504 (ISL6292C). The current limit resisters, (R513 and
R514), are set the safe magnitude of pre-charging current.
When a charger is plugged in and VBUS is less than 6.85V, the overvoltage protection IC
U502 (NCP345) will enable U503 (P-MOSFET) to start charging process. The process
starts charge state until VBAT is full.
When the battery voltage is less than 3.2V (deeply discharged), the Battery Charge
Interface (BCI) of Syren will enter the pre-charge mode (charging current is under 100mA)
as soon as the charger is plugged-in. At this moment, software cannot control the
charging process. Until battery voltage VBAT is larger than 3.2V, Syren will wake up and
then enter to normal charging status. The normal charge will start as constant current
mode (MAX current is 440mA). When the battery voltage is reach 4.15V, charging system
will enter the constant voltage mode till minimum current is less than 50mA, then the
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 32 -
Page 33

W370/W375 Level 3 C
charge process finishes. If charge current is larger than 0.5A then U504 will limit the
charge current to less than 0.5A. When the battery voltage VBAT is higher than 4.28V,
U503 (P-MOSFET) will be turned off and stop charging.
16.3 USB Data Cable Support
The charge process via a USB data cable is the same as an external charger in previous
section 16.2. Once the USB data cable is plugged-in, the 5V power source is supplied
from USB connector J500 Pin 1 along the VBUS trace to U502 and U503. If VBUS is
lower than 6.85V, the overvoltage protection IC U502 (NCP345) will enable U503
(P-MOSFET) to start charging process. The process starts charge state until VBAT is full.
17 FM Radio
The Si4700 U400 integrates the complete tuner function from antenna input to stereo
audio output for FM broadcast radio reception. The string of headset plays the role of FM
antenna and the broadcast radio signal is received through Pin 5 of headset jack J301
and goes into Si4700 U400 Pin 2.
An image-reject mixer downconverts the RF signal to low-IF. The quadrature mixer
output is amplified, filtered, and digitized with high resolution analog-to-digital converters
(ADCs). This advanced architecture achieves superior performance by using digital signal
processing (DSP) to perform channel selection, FM demodulation, and stereo audio
processing compared to traditional analog architectures. High-fidelity stereo
digital-to-analog converters (DACs) drive analog audio signals onto the LOUT Pin 16 and
ROUT Pin 15 of U400.
Shown as Figure 23, the FM radio sound connects to an audio amplifier LM4901 U401.
Afterwards the radio sound reaches to headset jack Pin 3 and Pin 6.
There is also an alternative way to let users hear FM radio through the loud speaker J302.
Under this situation, the audio signal from U400 ROUT Pin 15 goes through Syren Pin
B11 and outputs at trace SPKP and SPKN. Audio amplifier TPA6204 U301 magnifies the
radio sound and feeds the signal to speaker J302.
Figure 23: FM Radio Function
Motorola Proprietary Information
- 33 -
 Loading...
Loading...