Page 1
Symbol LS3478
Product Reference Guide
Page 2

Page 3

Symbol LS3478
Product Reference Guide
72E-67139-03
Revision A
July 2007
Page 4

ii Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
© 2007 by Motorola, Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced or used in any form, or by any electrical or mechanical means,
without permission in writing from Motorola. This includes electronic or mechanical means, such as
photocopying, recording, or information storage and retrieval systems. The material in this manual is subject to
change without notice.
The software is provided strictly on an “as i s” basis. All sof twar e, including firmware, furnished to the user is on
a licensed basis. Motorola grants to the user a non-transferab le and non-exclusive license to use each
software or firmware program delivered hereunder (licensed program). Except as noted below, such license
may not be assigned, sublicensed, or otherwise transferred by the user without prior written consent of
Motorola. No right to copy a licensed program in whole or in part is granted, except as permitted unde r
copyright law. The user shall not modify, merge, or incorporate any form or portion of a licensed program with
other program material, create a derivative work from a licensed program, or use a licensed program in a
network without written permission from Motorola. The user agrees to maintain Motorola’s copyright notice on
the licensed programs delivered hereunder, and to include the same on any authorized copies it makes, in
whole or in part. The user agrees not to deco mpile, disassemble, decode, or reverse engineer any licensed
program delivered to the user or any portion thereof.
Motorola reserves the right to make changes to any software or product to improve reliability, function, or
design.
Motorola does not assume any product liability arising out of, or in connection with, the application or use of
any product, circuit, or application described herein.
No license is granted, either expressly or by implication, estoppel, or otherwise under any Motorola, Inc.,
intellectual property rights. An implied license only exists for equipment, circuits, and subsystems contained in
Motorola products.
MOTOROLA and the Stylized M Logo and Symbol and the Symbol logo are registered in the US Patent &
Trademark Office. Bluetooth is a registered trademark of Bluetooth SIG. Microsoft, Windows and ActiveSync
are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. All other product or service names
are the property of their respective owners.
Motorola, Inc.
One Motorola Plaza
Holtsville, New York 11742-1300
http://www.symbol.com
Patents
This product is covered by one or more of the patents listed on the website: www.symbol.com/patents.
Page 5
Revision History
Changes to the original manual are listed below:
Change Date Description
-01 Rev A 2/2005 Initial release.
-02 Rev A 2/2007 Update service information, correct Symbol PTC Terminal bar code, specify that
-03 Rev A 7/2007 Motorola rebranding; added Battery Maintenance information in Chapter 3.
iii
multipoint mode does not support Beep on BEL.
Page 6

iv Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Page 7

Table of Contents
About This Guide
Introduction.................................................................................................................... xiii
Chapter Descriptions..................................................................................................... xiii
Notational Conventions.................................................................................................. xiv
Related Publications...................................................................................................... xiv
Service Information........................................................................................................ xv
Chapter 1: Getting Started
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 1-1
Unpacking the Scanner ................................................................................................ 1-2
The Scanner Cradle ...................................................................................................... 1-2
Cradle Parts ............................................................................................................ 1-3
Connecting the Cradle ............................................................................................ 1-4
Supplying Power to the Cradle ............................................................................... 1-5
Connecting a Synapse Cable Interface .................................................................. 1-6
Lost Connection to Host .......................................................................................... 1-6
Mounting the Cradle ................................................................................................ 1-6
Inserting the Battery ...................................................................................................... 1-7
Removing the Battery ............................................................................................. 1-7
Charging the Battery ..................................................................................................... 1-8
Charging LED ......................................................................................................... 1-8
Charging Problem LED ........................................................................................... 1-8
Inserting the Scanner in the Cradle .............................................................................. 1-9
Pairing ........................................................................................................................... 1-9
Unpairing ................................................................................................................. 1-10
Configuring the Scanner ............................................................................................... 1-10
Page 8

vi Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Chapter 2: Scanning
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 2-1
Beeper Definitions ........................................................................................................ 2-2
LED Definitions ............................................................................................................. 2-3
Scanning ....................................................................................................................... 2-4
Aiming ..................................................................................................................... 2-5
Decode Zone ................................................................................................................ 2-6
Chapter 3: Maintenance and Technical Specifications
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 3-1
Maintenance ................................................................................................................. 3-1
Battery Maintenance ............................................................................................... 3-1
Troubleshooting ............................................................................................................ 3-2
Technical Specifications ............................................................................................... 3-5
Scanner Signal Descriptions ......................................................................................... 3-8
Chapter 4: User Preferences
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 4-1
Scanning Sequence Examples ..................................................................................... 4-2
Errors While Scanning .................................................................................................. 4-2
User Preferences Default Parameters .......................................................................... 4-2
User Preferences .......................................................................................................... 4-3
Set Default Parameter ............................................................................................ 4-3
Beeper Tone ........................................................................................................... 4-3
Beeper Volume ....................................................................................................... 4-4
Power Mode ............................................................................................................ 4-5
Laser On Time ........................................................................................................ 4-5
Beep After Good Decode ........................................................................................ 4-6
Trigger Mode ........................................................................................................... 4-7
Aim Duration ........................................................................................................... 4-8
Radio Communications ................................................................................................. 4-9
Connection Maintenance Interval ........................................................................... 4-9
Radio Output Power ................................................................................................ 4-11
Parameter Broadcast .............................................................................................. 4-11
Single Point/Multipoint Operation ............................................................................ 4-12
Chapter 5: Keyboard Wedge Interface
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 5-1
Connecting a Keyboard Wedge Interface ..................................................................... 5-2
Keyboard Wedge Default Parameters .......................................................................... 5-3
Keyboard Wedge Host Types ....................................................................................... 5-4
Keyboard Wedge Host Types ................................................................................. 5-4
Keyboard Wedge Country Types (Country Codes) ................................................ 5-5
Ignore Unknown Characters ................................................................................... 5-7
Keystroke Delay ...................................................................................................... 5-7
Intra-Keystroke Delay ............................................................................................. 5-8
Alternate Numeric Keypad Emulation ..................................................................... 5-8
Page 9

Caps Lock On ......................................................................................................... 5-8
Caps Lock Override ................................................................................................ 5-9
Convert Wedge Data .............................................................................................. 5-9
Function Key Mapping ............................................................................................ 5-10
FN1 Substitution ..................................................................................................... 5-10
Send Make and Break ............................................................................................ 5-10
Keyboard Maps ............................................................................................................. 5-11
ASCII Character Set ..................................................................................................... 5-13
Chapter 6: RS-232 Interface
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 6-1
Connecting an RS-232 Interface .................................................................................. 6-2
RS-232 Default Parameters .......................................................................................... 6-3
RS-232 Host Parameters .............................................................................................. 6-4
RS-232 Host Types ................................................................................................. 6-6
Baud Rate ............................................................................................................... 6-7
Parity ....................................................................................................................... 6-9
Check Receive Errors ............................................................................................. 6-10
Stop Bit Select ........................................................................................................ 6-11
Data Bits ..................................................................................................... .......... .. 6-11
Hardware Handshaking .......................................................................................... 6-12
Software Handshaking ............................................................................................ 6-14
Host Serial Response Time-out .............................................................................. 6-16
RTS Line State ........................................................................................................ 6-17
Beep on <BEL> ....................................................................................................... 6-17
Intercharacter Delay ................................................................................................ 6-18
Nixdorf Mode A/B and OPOS/JPOS Beep/LED Options ........................................ 6-19
Ignore Unknown Characters ................................................................................... 6-20
ASCII / Character Set ................................................................................................... 6-21
Table of Contents vii
Chapter 7: USB Interface
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 7-1
Connecting a USB Interface ......................................................................................... 7-1
USB Default Parameters .............................................................................................. 7-3
USB Host Parameters .................................................................................................. 7-4
USB Device Type .................................................................................................... 7-4
USB Country Keyboard Types (Country Codes) .................................................... 7-5
USB Keystroke Delay ............................................................................................. 7-7
USB Caps Lock Override ........................................................................................ 7-8
USB Ignore Unknown Characters ........................................................................... 7-8
Emulate Keypad ...................................................................................................... 7-9
USB Keyboard FN 1 Substitution ............................................................................ 7-9
Function Key Mapping ............................................................................................ 7-10
Simulated Caps Lock .............................................................................................. 7-10
Convert Case .......................................................................................................... 7-11
ASCII Character Set ..................................................................................................... 7-12
Page 10

viii Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Chapter 8: IBM 468X/469X Interface
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 8-1
Connecting to an IBM 468X/469X Host ........................................................................ 8-2
IBM Default Parameters ............................................................................................... 8-3
IBM 468X/469X Host Parameters ................................................................................. 8-4
Port Address ........................................................................................................... 8-4
Convert Unknown to Code 39 ................................................................................. 8-4
Chapter 9: Wand Emulation Interface
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 9-1
Connecting a Wand Emulation Interface ...................................................................... 9-2
Wand Emulation Default Parameters ........................................................................... 9-3
Wand Emulation Host Parameters ............................................................................... 9-4
Wand Emulation Host Types .................................................................................. 9-4
Leading Margin (Quiet Zone) .................................................................................. 9-5
Polarity .................................................................................................................... 9-5
Ignore Unknown Characters ................................................................................... 9-6
Convert All to Code 39 ............................................................................................ 9-6
Convert Code 39 to Full ASCII ............................................................................... 9-7
Chapter 10: Scanner Emulation Interface
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 10-1
Connecting Using Scanner Emulation .......................................................................... 10-2
Scanner Emulation Default Parameters ....................................................................... 10-3
Scanner Emulation Host ............................................................................................... 10-4
Scanner Emulation Host Parameters ........................................................................... 10-5
Beep Style ............................................................................................................... 10-5
Parameter Pass-Through ........................................................................................ 10-6
Convert Newer Code Types .................................................................................... 10-7
Module Width .......................................................................................................... 10-7
Convert All Bar Codes to Code 39 .......................................................................... 10-8
Code 39 Full ASCII Conversion .............................................................................. 10-8
Transmission Timeout ............................................................................................. 10-9
Ignore Unknown Characters ................................................................................... 10-10
Leading Margin ....................................................................................................... 10-11
Check for Decode LED ........................................................................................... 10-12
Chapter 11: 123Scan
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 11-1
Setting Up 123Scan ...................................................................................................... 11-1
Chapter 12:
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 12-1
Scanning Sequence Examples ..................................................................................... 12-1
Errors While Scanning .................................................................................................. 12-1
Symbology Default Parameters .................................................................................... 12-2
Symbologies
Page 11

Table of Contents ix
UPC/EAN ...................................................................................................................... 12-5
Enable/Disable UPC-A ............................................................................................ 12-5
Enable/Disable UPC-E ............................................................................................ 12-5
Enable/Disable UPC-E1 .......................................................................................... 12-6
Enable/Disable EAN-13 .......................................................................................... 12-6
Enable/Disable EAN-8 ............................................................................................ 12-7
Enable/Disable Bookland EAN ............................................................................... 12-7
Decode UPC/EAN/JAN Supplementals .................................................................. 12-8
UPC/EAN/JAN Supplemental Redundancy ............................................................ 12-10
Transmit UPC-A/UPC-E/UPC-E1 Check Digit ........................................................ 12-10
UPC-A Preamble .................................................................................................... 12-12
UPC-E Preamble .................................................................................................... 12-13
UPC-E1 Preamble .................................................................................................. 12-14
Convert UPC-E to UPC-A ....................................................................................... 12-15
Convert UPC-E1 to UPC-A ..................................................................................... 12-16
EAN-8/JAN-8 Extend .............................................................................................. 12-17
Code 128 ...................................................................................................................... 12-17
Enable/Disable Code 128 ....................................................................................... 12-17
Enable/Disable UCC/EAN-128 ............................................................................... 12-18
Enable/Disable ISBT 128 ........................................................................................ 12-18
Code 39 ........................................................................................................................ 12-19
Enable/Disable Code 39 ......................................................................................... 12-19
Enable/Disable Trioptic Code 39 ............................................................................ 12-19
Convert Code 39 to Code 32 .................................................................................. 12-20
Code 32 Prefix ........................................................................................................ 12-20
Set Lengths for Code 39 ......................................................................................... 12-21
Code 39 Check Digit Verification ............................................................................ 12-22
Transmit Code 39 Check Digit ................................................................................ 12-22
Code 39 Full ASCII Conversion .............................................................................. 12-23
Code 93 ........................................................................................................................ 12-24
Enable/Disable Code 93 ......................................................................................... 12-24
Set Lengths for Code 93 ......................................................................................... 12-24
Code 11 ........................................................................................................................ 12-26
Code 11 .................................................................................................................. 12-26
Set Lengths for Code 11 ......................................................................................... 12-27
Code 11 Check Digit Verification ............................................................................ 12-28
Transmit Code 11 Check Digits .............................................................................. 12-29
Interleaved 2 of 5 (I 2 of 5) ............................................................................................ 12-30
Enable/Disable Interleaved 2 of 5 ........................................................................... 12-30
Set Lengths for Interleaved 2 of 5 ........................................................................... 12-30
I 2 of 5 Check Digit Verification ............................................................................... 12-32
Transmit I 2 of 5 Check Digit ................................................................................... 12-32
Convert I 2 of 5 to EAN-13 ...................................................................................... 12-33
Discrete 2 of 5 (D 2 of 5) ............................................................................................... 12-34
Enable/Disable Discrete 2 of 5 ................................................................................ 12-34
Set Lengths for Discrete 2 of 5 ............................................................................... 12-35
Codabar (NW - 7) ......................................................................................................... 12-36
Enable/Disable Codabar ......................................................................................... 12-36
Set Lengths for Codabar ......................................................................................... 12-37
CLSI Editing ............................................................................................................ 12-38
Page 12

x Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
NOTIS Editing ......................................................................................................... 12-38
MSI ............................................................................................................................... 12-39
Enable/Disable MSI ................................................................................................ 12-39
Set Lengths for MSI ................................................................................................ 12-40
MSI Check Digits .................................................................................................... 12-41
Transmit MSI Check Digit(s) ................................................................................... 12-42
MSI Check Digit Algorithm ...................................................................................... 12-42
GS1 DataBar ................................................................................................................ 12-43
GS1 DataBar-14 ..................................................................................................... 12-43
GS1 DataBar Limited .............................................................................................. 12-43
GS1 DataBar Expanded ......................................................................................... 12-43
Convert GS1 DataBar to UPC/EAN ........................................................................ 12-44
Redundancy Level ........................................................................................................ 12-45
Redundancy Level 1 ............................................................................................... 12-45
Redundancy Level 2 ............................................................................................... 12-45
Redundancy Level 3 ............................................................................................... 12-46
Redundancy Level 4 ............................................................................................... 12-46
Security Level ............................................................................................................... 12-47
Security Level 0 ...................................................................................................... 12-47
Security Level 1 ...................................................................................................... 12-47
Security Level 2 ...................................................................................................... 12-47
Security Level 3 ...................................................................................................... 12-47
Bi-directional Redundancy ............................................................................................ 12-48
Chapter 13:
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 13-1
Scanning Sequence Examples ..................................................................................... 13-1
Errors While Scanning .................................................................................................. 13-1
Miscellaneous Default Parameters ............................................................................... 13-2
Miscellaneous Scanner Parameters ............................................................................. 13-3
Chapter 14:
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 14-1
Rules: Criteria Linked to Actions ................................................................................... 14-1
Using ADF Bar Codes .................................................................................................. 14-2
ADF Bar Code Menu Example ..................................................................................... 14-2
Miscellaneous Scanner Options
Transmit Code ID Character ................................................................................... 13-3
Scan Angle .............................................................................................................. 13-3
Prefix/Suffix Values ................................................................................................. 13-4
Scan Data Transmission Format ............................................................................ 13-5
FN1 Substitution Values ......................................................................................... 13-7
Transmit “No Read” Message ................................................................................. 13-7
Synapse Interface ................................................................................................... 13-8
Advanced Data Formatting
Rule 1: The Code 128 Scanning Rule .................................................................... 14-3
Rule 2: The UPC Scanning Rule ............................................................................ 14-3
Alternate Rule Sets ................................................................................................. 14-3
Rules Hierarchy (in Bar Codes) .............................................................................. 14-4
Default Rules .......................................................................................................... 14-5
Page 13

Table of Contents xi
Special Considerations for Multipoint Networks ...................................................... 14-5
Special Commands ....................................................................................................... 14-6
Pause Duration ....................................................................................................... 14-6
Begin New Rule ...................................................................................................... 14-6
Save Rule ............................................................................................................... 14-6
Erase ....................................................................................................................... 14-7
Quit Entering Rules ................................................................................................. 14-7
Disable Rule Set ..................................................................................................... 14-8
Criteria .......................................................................................................................... 14-9
Code Types ............................................................................................................. 14-9
Code Lengths .......................................................................................................... 14-12
Message Containing A Specific Data String ........................................................... 14-16
Actions .......................................................................................................................... 14-20
Send Data ............................................................................................................... 14-20
Setup Field(s) .......................................................................................................... 14-23
Modify Data ............................................................................................................. 14-29
Pad Data with Spaces ............................................................................................. 14-30
Pad Data with Zeros ............................................................................................... 14-34
Beeps ...................................................................................................................... 14-38
Send Keystroke (Control Characters and Keyboard Characters) ........................... 14-39
Send Right Control Key .......................................................................................... 14-71
Send Graphic User Interface (GUI) Characters ...................................................... 14-71
Turn On/Off Rule Sets ............................................................................................ 14-77
Alphanumeric Keyboard ............................................................................................... 14-78
Appendix A: Standard Default Parameters
Appendix B: Programming Reference
Symbol Code Identifiers ................................................................................................ B-1
AIM Code Identifiers ..................................................................................................... B-2
Appendix C: Sample Bar Codes
UPC-A ........................................................................................................................... C-1
UPC-E ........................................................................................................................... C-1
UPC-E1 ......................................................................................................................... C-1
EAN-13 ......................................................................................................................... C-2
EAN-8 ........................................................................................................................... C-2
Code 39 ........................................................................................................................ C-2
Trioptic Code 39 ........................................................................................................... C-2
Code 93 ........................................................................................................................ C-3
Code 11 ........................................................................................................................ C-3
Codabar ........................................................................................................................ C-3
MSI ............................................................................................................................... C-3
Interleaved 2 of 5 .......................................................................................................... C-4
Page 14

xii Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Appendix D: Numeric Bar Codes
0, 1, 2, 3 ........................................................................................................................ D-1
4, 5, 6, 7 ........................................................................................................................ D-2
8, 9 ................................................................................................................................ D-3
Cancel ........................................................................................................................... D-3
Glossary
Index
Tell Us What You Think...
Page 15
About This Guide
Introduction
The Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide provides gene ral instructions for settin g up, ope rating, maint aining,
and troubleshooting the scanner. The Symbol LS3478 includes the following variations of the scanner:
•
LS3478-FZ: 1-D scanning
•
LS3478-ER: extended range 1-D scanning.
Chapter Descriptions
•
Chapter 1, Getting Started provides a product overview and unpacking instructions.
•
Chapter 2, Scanning describes parts of the scanner, beeper and LED definitions, and how to use the
scanner.
•
Chapter 3, Maintenance and Technical Specifications provides information on how to care for the scanner,
troubleshooting, and technical specifications.
•
Chapter 4, User Preferences provides the programming bar codes necessary for selecting user preference
features for the scanner.
•
Chapter 5, Keyboard Wedge Interface provides information for setting up the scan ne r fo r key bo a rd wedge
operation.
•
Chapter 6, RS-232 Interface provides information for setting up the scanner for RS-232 operation.
•
Chapter 7, USB Interface provides information for setting up the scanner for USB operation.
•
Chapter 8, IBM 468X/469X Interface provides information for setting up the scanner with IBM 468X/469X
POS systems.
•
Chapter 9, Wand Emulation Interface provides information for setting up the scanner for wand emulation
operation.
•
Chapter 10, Scanner Emulation Interface provides information for setting up the scanner for scanner
emulation operation.
•
Chapter 11, 123Scan provides information on the PC-based scanner configuration tool 123Scan.
Page 16

xiv Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
•
Chapter 12, Symbologies describes all symbology features and provides the programming bar codes for
selecting these features.
•
Chapter 13, Miscellaneous Scanner Option s includes commonly used bar codes to customize how data is
transmitted to the host device.
•
Chapter 14, Advanced Data Formatting (ADF) describes how to customize scanned data befo re transmitting
to the host.
•
Appendix A, Standard Defaul t Parameters provides a table of all host devices and miscellaneous scanne r
defaults.
•
Appendix B, Programming Reference provides a table of AIM code identifiers, ASCII character conversions,
and keyboard maps.
•
Appendix C, Sample Bar Codes includes sample bar codes.
•
Appendix D, Numeric Bar Codes includes the numeric bar codes to scan for parameters requiring specific
numeric values.
Notational Conventions
The following conventions are used in this document:
•
Bullets (•) indicate:
• action items
• lists of alternatives
• lists of required steps that are not necessarily sequential.
•
Sequential lists (e.g., those that describe step-by-s te p pr oc ed ur e s) ap pe a r as nu m be re d lists.
•
Throughout the programming bar code menus, asterisks (*) are used to denote default parameter settings.
Related Publications
The LS3478 Quick S tart Guid e (p/n 72-67137- xx) provide s general in formation to help the user get st arte d with the
scanner, including basic setup and operation instructions.
For the latest versions of the LS3478 Quick Start Guide and the Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide go to:
http://support.symbol.com.
* Indicates Default
*Baud Rate 9600
Feature/Option
Page 17

Service Information
If you have a problem with your equipment, contact Motorola Enterprise Mobility Support for your region. Go to
http://www.symbol.com/contactsupport
contact that Business Partner for service.
Before contacting, have the model number and serial number at hand. If your problem cannot be solved by the
Motorola Enterprise Mobility Support, you may need to return your equipment for servicing and you will be given
specific directions.
Motorola is not responsible for any damages incurred during shipment if the approved shipping container is not
used. Shipping the units improperly can possibly void the warranty.
About This Guide xv
. If you purchased your Motorola product from a Motorola Business Pa rtner,
Page 18

xvi Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Page 19
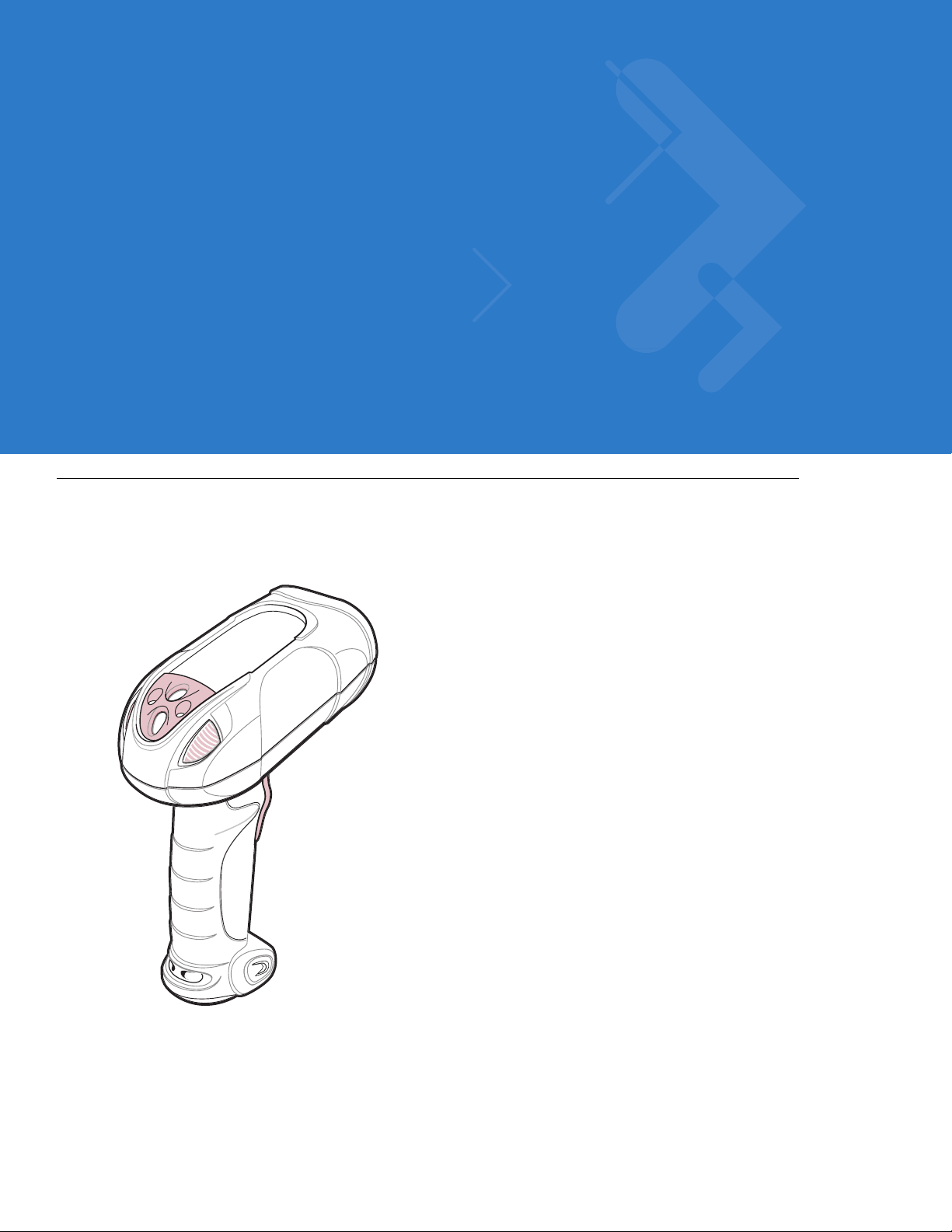
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Introduction
The Symbol LS3478 scanner combines excellent scanning performance and advanced ergonomics to provide the
best value in a lightweight laser scanner, ensuring comfort and ease of use for extended periods of time.
Figure 1-1
Symbol LS3478 Scanner
Page 20

1 - 2 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
This scanner supports the following host interfaces through communication with a cradle:
•
Standard RS-232 connection to a host.
•
Keyboard wedge connection to a host, where scanned data is interpreted as keystrokes. The following
international keyboards are supported (for Windows™ environment): North American, German, French,
French Canadian, Spanish, Italian, Swedish, UK English, Japanese, and Brazilian-Portuguese.
•
Wand emulation connection to a mobile computer, a controller, or host, which collects the data as wand data
and decodes it.
•
Scanner emulation connection to a mobile computer or a controller, which collects the data and interprets it
for the host.
•
IBM® 468X/469X hosts.
•
USB connection to a host. The scanner autodetects a USB host and defaults to the HID keyboard interface
type. Select other USB interface types by scanning programming bar codes. The following international
keyboards are supported (for Windows™ environment): North America, German, French, French Canadian,
Spanish, Italian, Swedish, UK English, Japanese, and Brazilian-Portuguese.
•
Synapse capability, which allows connection to a wide variety of host systems using a Synapse cable and
Synapse adapter cable. The scanner autodetects the Synapse interface.
•
Configuration via 123Scan.
Unpacking the Scanner
Remove the scanner from its packing and inspect it for damage. If the scanner was damaged in transit, call
Motorola Enterprise Mobility Support at one of the telephone numbers listed on page xv. KEEP THE PACKING. It
is the approved shipping container and should be used if the equipment ever needs to be returned for servicing.
The Scanner Cradle
The scanner cradle serves as a stand, charger, and host interface for the scanner. There are two versions of the
cradle:
•
Charging cradle with radio: All communication between the cordless scanner and the host computer is
accomplished through the cradle. Each bar code contains programming instructions or other da ta unique to
the bar code pattern. The scanner transmits b ar code data to the cradle via a wireless radio antenna. The
cradle then sends that information via an interface cable to the host computer for interpretation.
•
Charge-only cradle: This cradle serves as a sta nd and battery charger. Since one radio-enabled cradle can
receive information from up to four scanners, it is possible to have several charge-only cradles.
The charging cradle with radio supports two modes of operation:
•
Single point mode: the cradle communicates with one scanner.
•
Multipoint mode: the cradle communicates with more than one scanner.
The cradle sits on a desktop or mounts on a non-horizontal surface (such as a wall or forklift), depending on the
environment. For more information about mounting options and procedures, refer to the documentation included
with the cradle.
Page 21
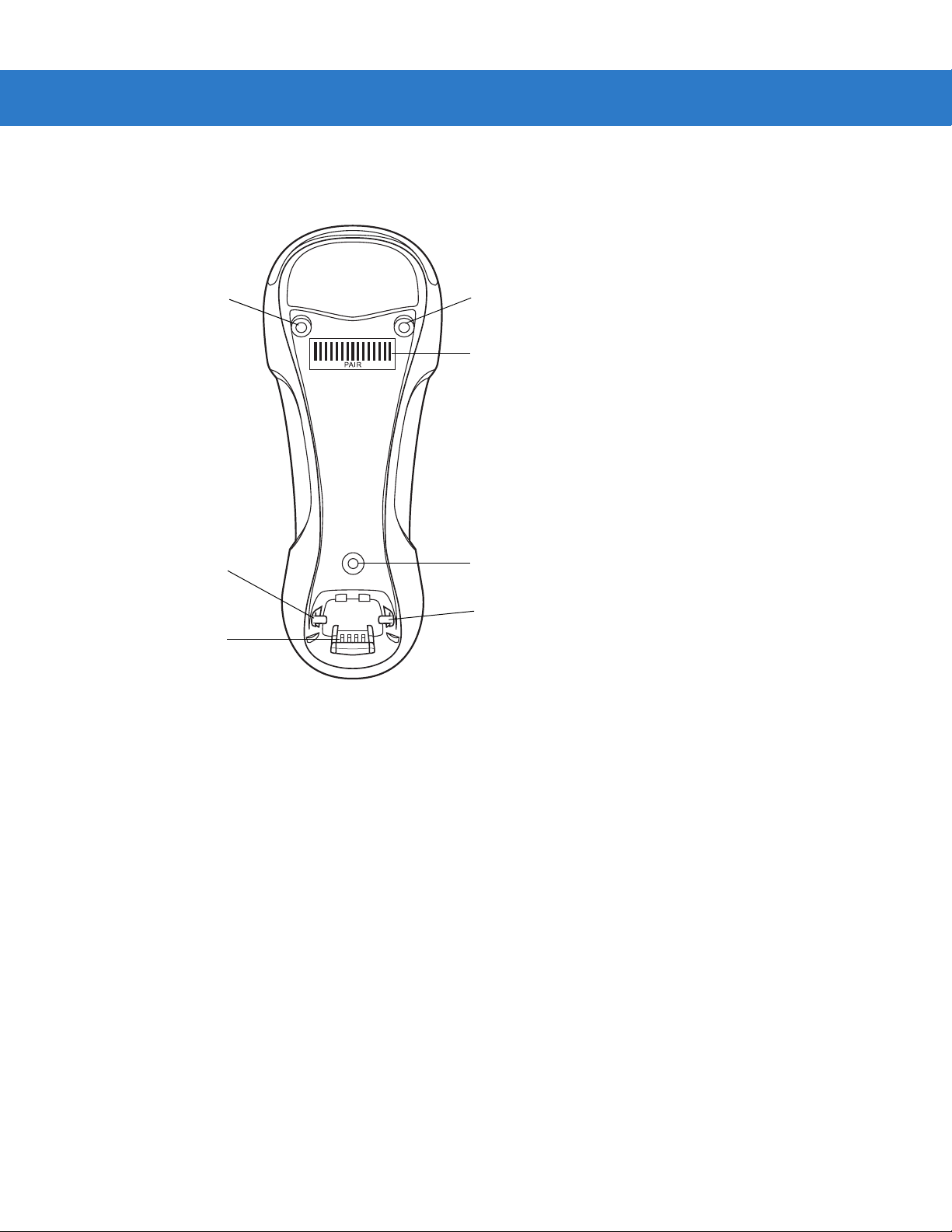
Cradle Parts
Getting Started 1 - 3
Mounting
Screw Hole
Latch
Charging/
Communications
Contacts
Figure 1-2
Cradle Front View
Mounting
Screw Hole
Pairing
Bar Code
Mounting
Screw Hole
Latch
Page 22
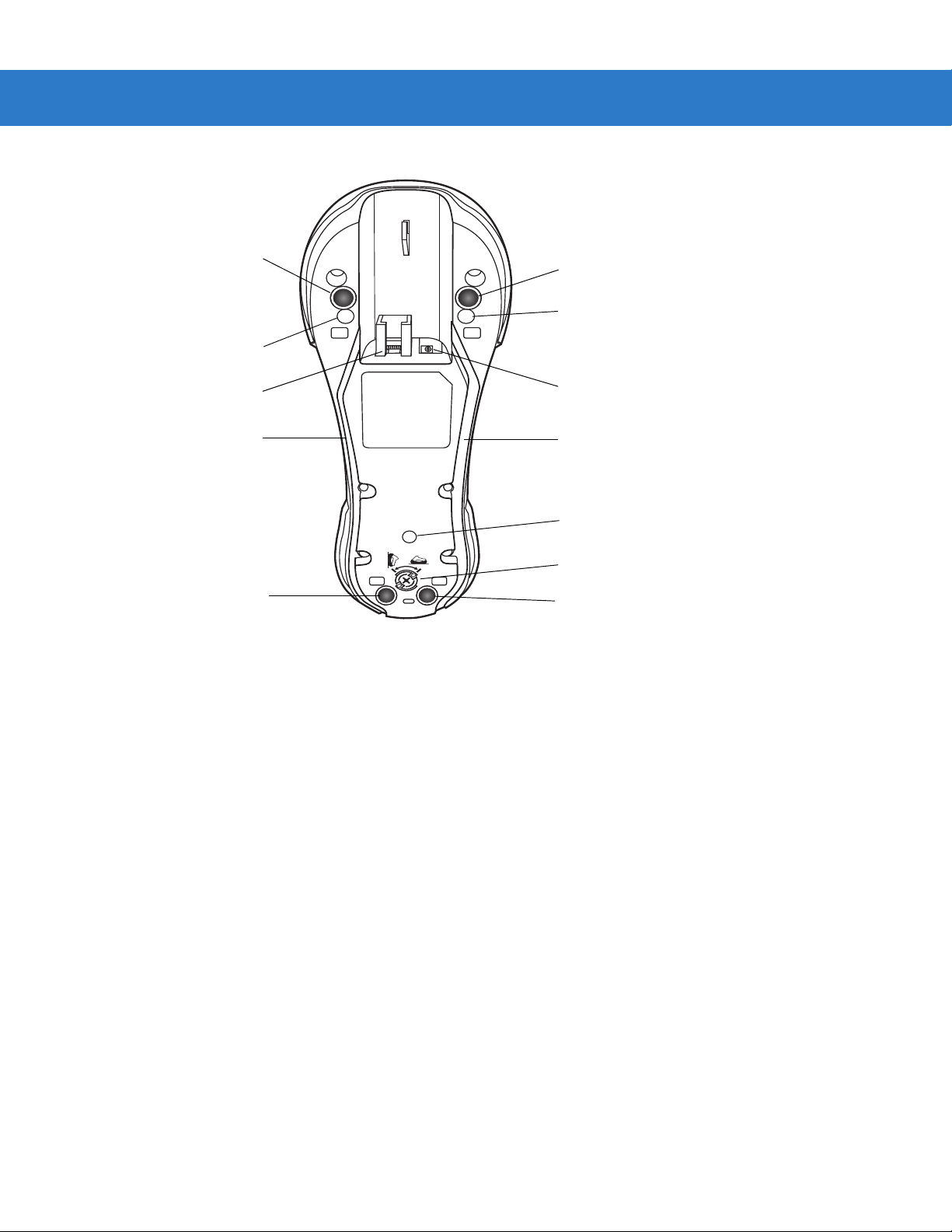
1 - 4 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Rubber Foot
Mounting Screw Hole
Host Port
Power Cable Groove
Rubber Foot
Figure 1-3
Cradle Back View
Connecting the Cradle
Rubber Foot
Mounting Screw Hole
Power Port
Host Cable Groove
Mounting Screw Hole
Converter Knob
Rubber Foot
Important: Connect the interface cable and power supply in the following order to ensure proper operation of the
scanner and cradle. Note that this procedure includes two different power supply options.
1. Disconnect the power supply from the scanner cradle. See Figure 1-4.
2. Insert the modular connector of the interface cable into the host interface port on the back of the scanner
cradle.
3. If using a power supply that connects to the interface cable, insert this power supply into the power connector
on the interface cable, and the other end to an AC supply (see the cradle’s Quick Reference Guide for more
information).
4. Insert the other end of the interface cable into the appropriate port on the host computer (see the specific host
chapter for information on host connections).
Page 23
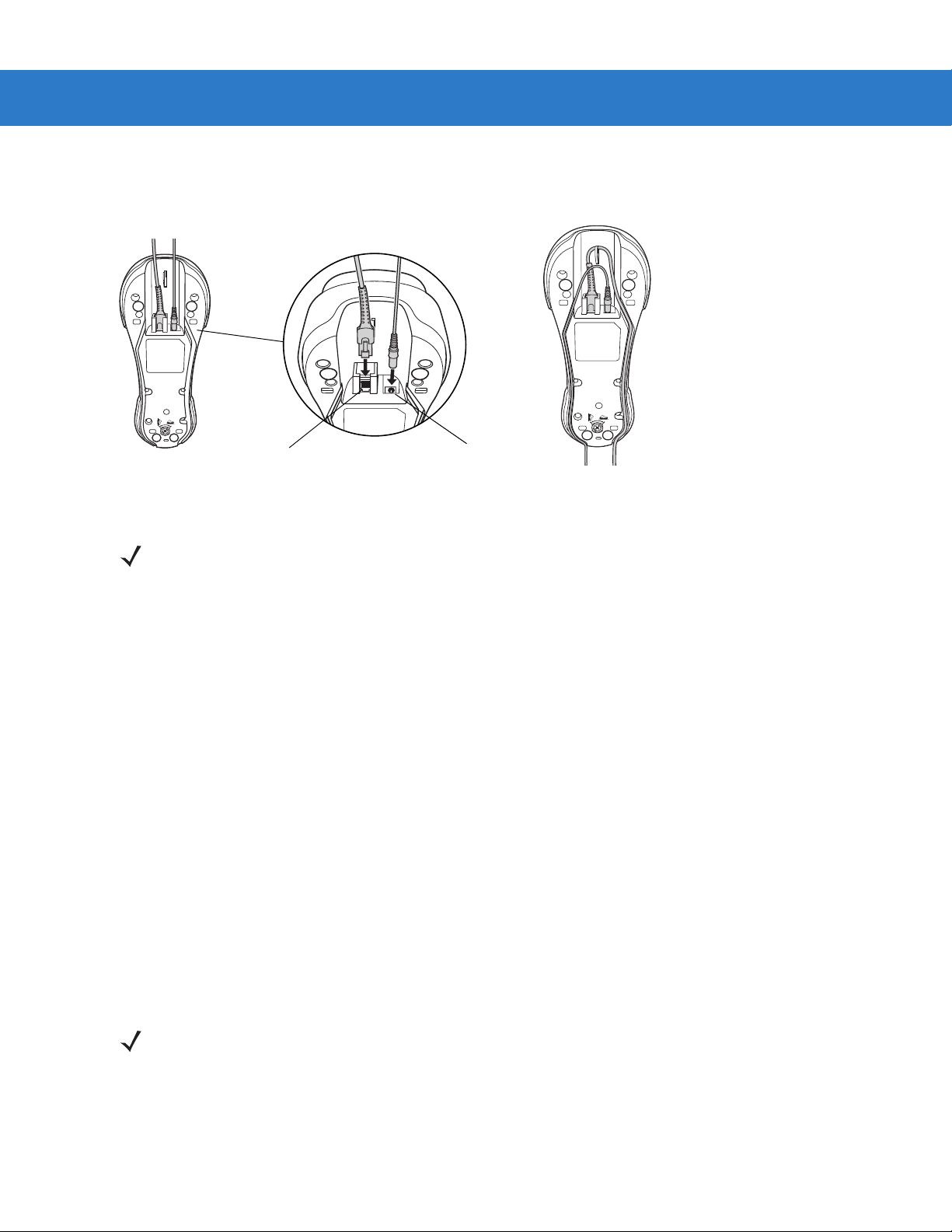
Getting Started 1 - 5
5. If using an external power supply, insert the power cable into the power port on the back of the scanner cradle,
and connect the power supply to an approved AC supply (see the cradle’s Quick Reference Guide for more
information).
Power Port
Figure 1-4
NOTE Disconnect the power supply before changing host cables, or the scanner may not recognize the new
Host Port
Connecting the Cables to the Cradle
host.
Different cables are required for different hosts. The connectors illustrated in each host chapter are
examples only. The connectors may be different from those illustrated, but the steps to connect the
scanner remain the same.
Supplying Power to the Cradle
The cradle receives power from one of two sources:
•
An external power supply.
•
When connected to the host through a host cable that supplies power.
The cradle detects whether the host or the external supply is supplying power. It always draws power from the
external supply when available, regardless of the presence of power from a host.
Using the USB Interface to Supply Power
When the cradle is connected to the host via the USB interface, it can be powered by the USB port instead of an
external power supply. Powering from a USB host limits charging as follows:
•
The scanner charges at a slower rate than when charging from an external power supply.
•
The cradle can charge a scanner only in single point mode. An external power supply is required to charge a
scanner in multipoint mode.
NOTE The radio link functions normally when the cradle draws power from a USB host.
For more information on single and multipoint operation, see Pairing on page 1-9.
Page 24
1 - 6 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
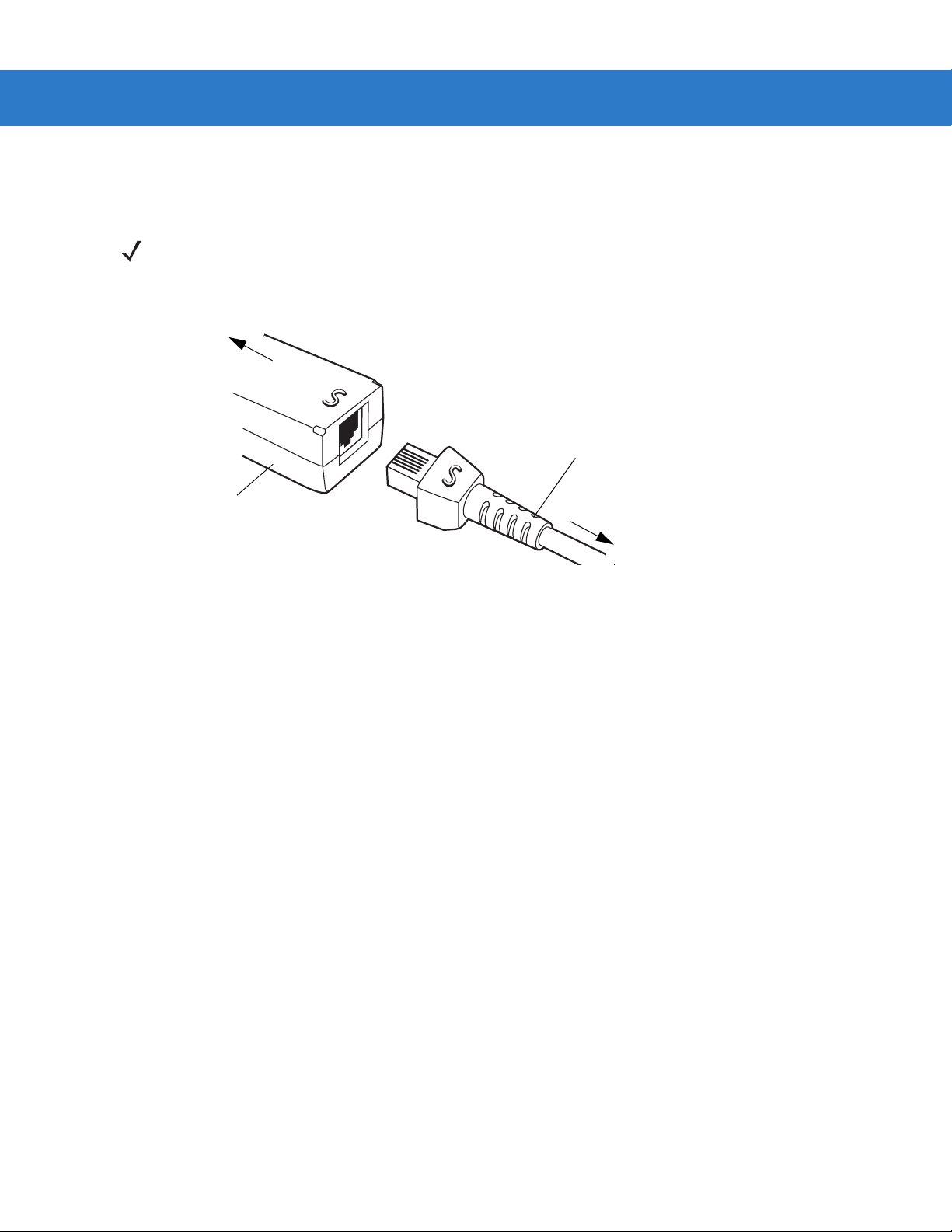
Connecting a Synapse Cable Interface
NOTE Refer to the Synapse Interface Guide provided with the Synapse cable for more information.
Symbol’s Synapse Smart Cables enable interfacin g to a variety of hosts. The appropriate Synapse cable detects
the host.
To host
Synapse Smart Cable
Synapse adapter cable
To scanner cradle
Figure 1-5
1. Plug the Synapse adapter cable into the bottom of the scanner cradle, as described in Connecting the Cables
Synapse Cable Connection
to the Cradle on page 1-5.
2. Align the ‘S’ on the Synapse adapter cable with the ‘S’ on the Synapse Smart Cable and plug the cable in.
3. Connect the other end of the Synapse Smart Cable to the host.
Lost Connection to Host
If scanned data does not transmit to the cradle’s host, ensure all cables are firmly inserted and the powe r su pply is
connected properly. If scanned data still does not transmit to the host, reestablish connection with the host:
1. Disconnect the power supply from the cradle.
2. Disconnect the host interface cable from the cradle.
3. Wait three seconds.
4. Reconnect the host interface cable to the cradle.
5. Reconnect the power supply to the cradle.
6. Re-establish pairing with the cradle.
Mounting the Cradle
For information on mounting the cradle, refer to the documentation included with the cradle.
Page 25
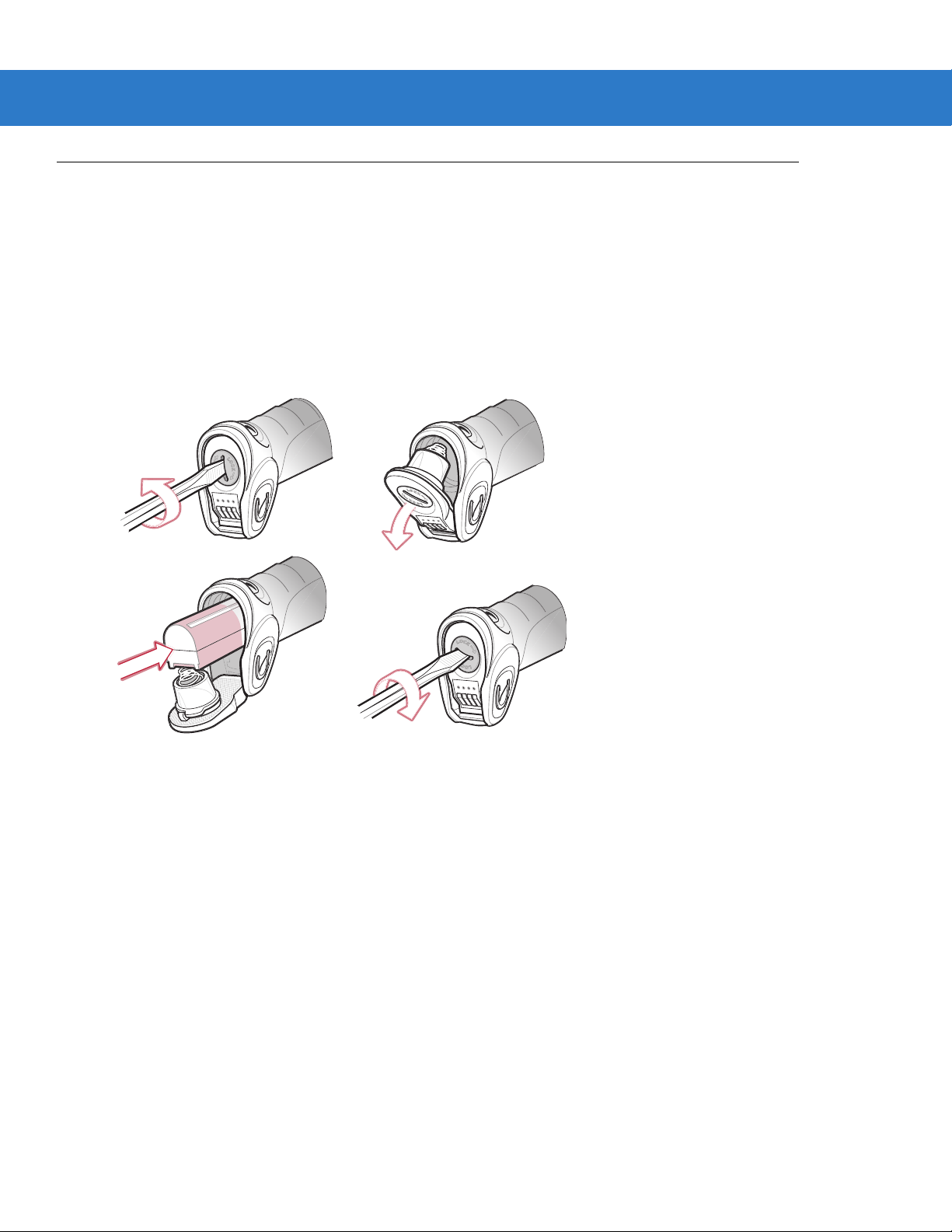
Inserting the Battery
The battery resides in a chamber in the scanner handle. To insert the battery:
1. Insert a coin or flathead screwdriver in the slot at the base of the scanner, then turn the slot counterclockwise
to release the latch.
2. Lift the latch.
3. If a battery is already installed, turn the scanner upright to slide the battery out.
4. Slide the new battery into the chamber, with the rounded side toward the back and the cont acts facing into the
chamber.
Getting Started 1 - 7
Figure 1-6
5. Close the latch.
6. Insert a coin or flathead screwdriver in the slot at the base of the scanner, press down gently, and turn the slot
clockwise to lock the latch in place.
Inserting the Battery
Removing the Battery
To remove the battery:
1. Insert a coin or flathead screwdriver in the slot at the base of the scanner, then turn the slot counterclockwise
to release the latch.
2. Lift the latch.
3. Turn the scanner upright to slide the battery out.
Page 26

1 - 8 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Charging the Battery
For best performance, fully charge the scanner battery before using the scanner for the first time. To charge the
battery, place the scanner in the cradle, ensuring that the metal contacts on the bottom of the scanner touch the
contacts on the cradle. The battery begins charging. A complete charge can take up to four hours, depending on
the remaining charge in the battery.
Charge within the recommended temperature of 32° to 104° F (0° to 40° C) nominal, 41° to 95° F (5° to 35° C)
ideal.
For information on maximizing battery life, see Battery Maintenance on page 3-1.
Charging LED
The flashing green LED indicates charging activity. See Table 2-2 on page 2-3. If the scanner is charging in fast
mode (external power supply is present), the green LED blinks quickly (on for 0.25 seconds, off for 0.75 seconds).
If the scanner is charging in slow mode (host-powere d mode), the LED blinks slowly (o n for 0.5 seconds, of f for 1.5
seconds).
Charging Problem LED
A solid or flashing red LED during charging indicates a charging problem. See Table 2-2 on page 2-3 for definitions
of error conditions and the appropriate action to take.
Page 27
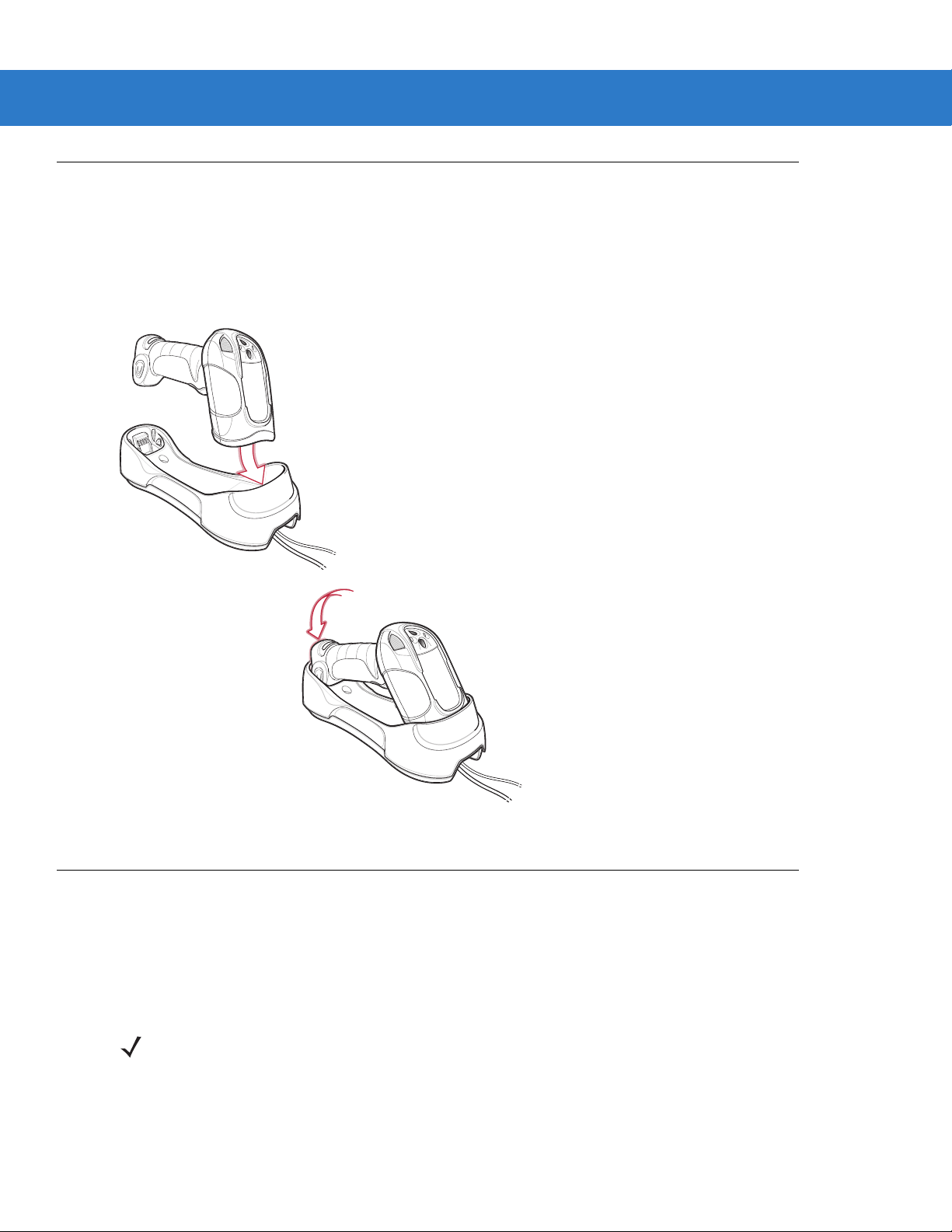
Inserting the Scanner in the Cradle
Insert the scanner in the cradle so that the metal contacts on the bottom of the scanner handle touch th e con tacts
on the cradle:
1. With a slightly rotated motion, insert the scanner into the cradle top first.
2. Push the handle until it clicks into place, engaging the contacts in the cradle and scanner.
Getting Started 1 - 9
Figure 1-7
Pairing
Pairing is the process by which a scanner initiates communication with a cradle. The cradle has multipoint
capability, and can pair with up to four scanners at a time. The cradle includes a pairing bar code.
To pair the scanner with the cradle, scan the pairing bar code on the cradle. A short low-high beep indicates
successful pairing.
Inserting the Scanner in the Cradle
NOTE The pairing bar code that connects the scanner to a cradle is unique to each cradle.
Do not scan data or parameters until pairing completes.
Page 28

1 - 10 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Unpairing
Unpair the scanner from the cradle to make the cradle available for pairing with another scanner. Scan the bar
code on page 4-12 to unpair the scanner from its cradle.
NOTE An unpairing bar code is also included in the LS3478 Quick Start Guide.
Configuring the Scanner
Use the bar codes in this manual or the 123Scan configuration program to configure the scanner. See Chap te r 4,
User Preferences and each host chapter for information about programming the scanner using bar code menus.
See Chapter 11, 123Scan to configure the scanner using this configuration program. 123Scan includes a help file.
Page 29
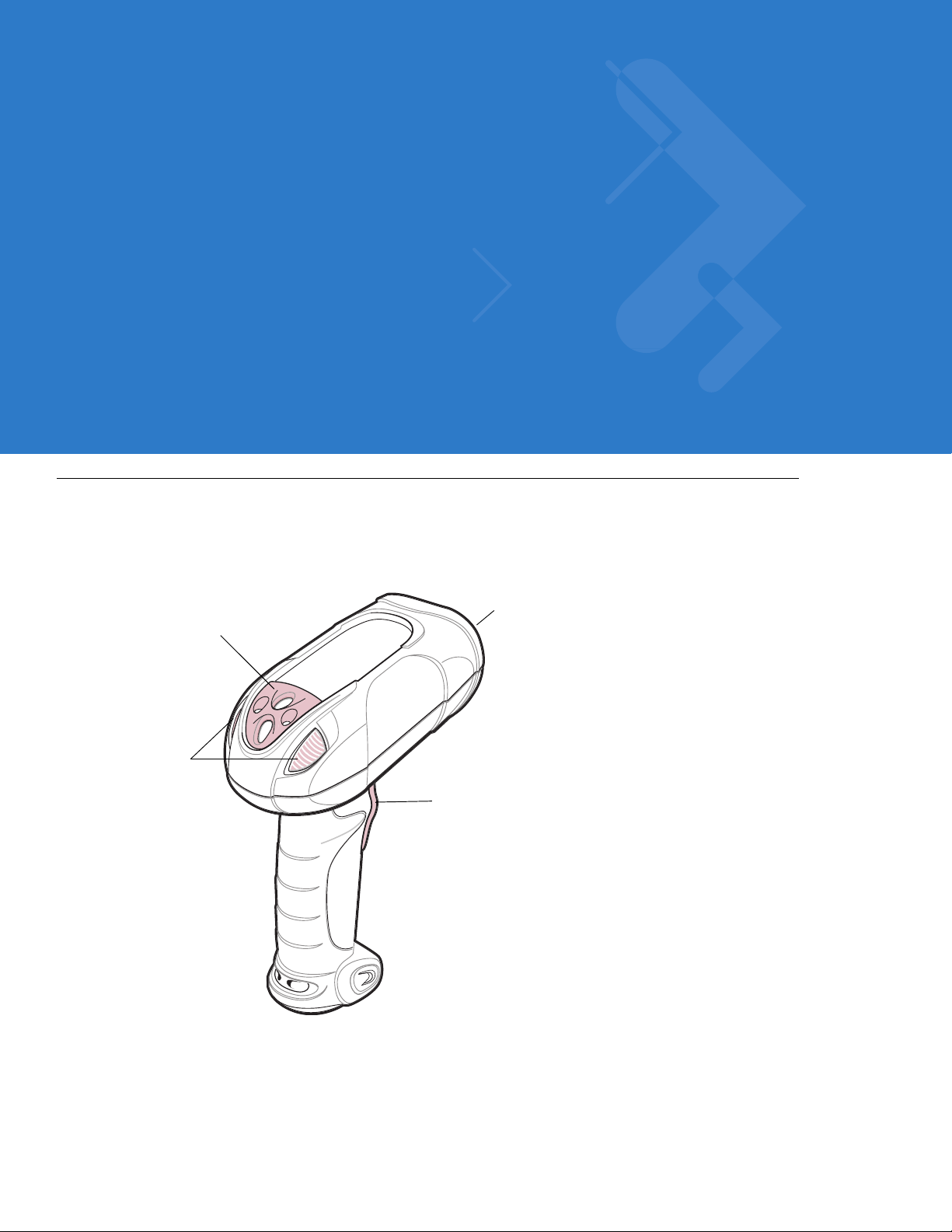
Chapter 2 Scanning
Introduction
This chapter provides beeper and LED definitions, scanning techniques, general scanning instructions and tips,
and decode zone diagrams.
Tether Plate
LED
Indicators
Scan Window
Scan Trigger
Figure 2-1
Parts of the Scanner
Page 30
2 - 2 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Beeper Definitions
The scanner emits different beeper sequences and patterns to indicate its status. Table 2-1 defines beep
sequences that occur during both normal scanning and while programming the scanner.
Table 2-1
Standard Use
Short low-short medium-short high beeps Power up.
One short high beep A bar code symbol was decoded (if decode beeper is enabled).
Four long low beeps A communication error occurred while transmitting a scanned symbol
Long low-high beeps Attempt to pair with the cradle was unsuccessful. Ensure that the
Four short high beeps Low battery indication.
Long low-high-low-high beeps Attempt to pair with a cradle that is already paired with the maximum
Five long low beeps Conversion or format error.
Low-high-low beeps ADF transmit error.
Short high-short high-short low-short low
beeps
Standard Beeper Definitions
Beeper Sequence Indication
to a host. The data is ignored. This occurs if the scanner i s not properly
configured or if the scanner has disconnected from the cradle.
cradle has power; if not, cycle power to the cradle and re-attempt the
pairing.
number of scanners.
Radio failure.
Cordless Scanner Connection
Short low-short high beeps The scanner has connected to the cradle after scanning a pairing bar
code or automatically after a disconnect.
Short high-short low beeps The scanner disconnected from the cradle either because the scanner
moved out of range of the cradle, the USB host suspended the cradle,
or cradle power was interrupted.
Parameter Menu Scanning
Short high beep Correct entry scanned or correct menu sequence performed.
Long low-long high beeps Input error; incorrect bar code, programming sequence or ‘
scanned. Scanner remains in ADF program mode.
Short high-short low beeps Keyboard parameter selected. Enter value using numeric bar codes.
Short high-short low-short high-short low
beeps
Successful program exit with change in the parameter setting.
Cancel
’
Page 31

Scanning 2 - 3
Table 2-1
ADF Programming Normal Data Entry
High-low beeps Enter another digit. Add leading zeros to the front if necessary.
Low-low beeps Enter another alphabetic character or scan the End of Message bar
High-high beeps Enter another criterion or action, or scan the Save Rule bar code.
High-low-high-low beeps Rule saved. Rule entry mode exited.
High-low-low beeps All criteria or actions cleared for current rule, continue entering rule.
Low beep Delete last saved rule. The current rule is left intact.
Low-high-high beeps All rules have been deleted.
Short low-short high-short low-short high
beeps
ADF Programming Error Indications
Low-high-low-high beeps Out of rule memory. Erase some existing rules, then try to save rule
Standard Beepe r Definitions (Continued)
Beeper Sequence Indication
code.
Out of host ADF parameter storage space. Scan
Parameter on page 4-3
again. (It is not necessary to re-enter the current rule.)
.
Set Default
Low-high-low beeps Cancel rule entry. Rule entry mode exited because of an error or the
Low-high beeps Entry error, wrong bar code scanned. Re-enter criterion or action. All
LED Definitions
In addition to beeper sequences, the scanner uses a two-color LED to indicate its status. Ta b l e 2- 2 explains LED
sequences.
Table 2-2
Standard Use
Off No power is applied to the scanner, or the scanner is on and ready to scan.
Green A bar code was successfully decoded.
Red A data transmission error or scanner malfunction occurred.
Charging Use
LED Status Indications
LED Indication
user asked to exit rule entry.
previously entered criteria and actions are retained. Criteria or action
list is too long for a rule.
Green Slow Flash The scanner is in the cradle and is charging in slow mode (used when the cradle is
powered from the host cable).
Green Fast Flash The scanner is in the cradle and is charging in rapid mode (used when the cradle is
powered from an external power supply).
Page 32

2 - 4 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Table 2-2
Red fast flash
(two flashes per second)
Red slow flash
(one flash per second)
Red and green flash
Scanning
See Chapter 1, Getting Started to install and program the scanner. To scan.
1. Aim the scanner at the bar code.
2. Press the scan trigger.
LED Status Indications (Continued)
LED Indication
Overcharge condition. Contact Motorola Enterprise Mobility Support.
Battery voltage not increasing with charge. Replace the battery.
Temperature fault. Move the cradle to a location where the temperature is 0
optimal charging temperature is 5
o
- 35o C.
o
- 40o C;
Figure 2-2
3. Ensure the scan line crosses every bar and space of the symbol.
4. The scanner beeps and the LED turns green to indicate a successful decode. See Table 2-1 and Table 2-2 for
Aiming the Scanner
RIGHT
012345
WRONG
012345
beeper and LED definitions.
Page 33

Scanning 2 - 5
Aiming
Do not hold the scanner directly over the bar code. Laser light reflecting directly back into the scanner from the bar
code is known as specular reflection which can make de cod in g difficult.
Tilt the scanner up to 65° forward or back to achieve a successful decode. Simple practice shows what tolerances
to work within.
65°
Figure 2-3
65°
Optimum Scan Angles
Page 34

2 - 6 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Decode Zone
in. cm
30
20
76.2
50.8
Note: Typical performance at 68˚F (20˚C)
on high quality Code 39 and UPC symbols.
LS 3408
FZ
5 mil
7.25"
2.5"
7.5 mil
2.0" 15.75"
13 mil
1.0" 24"
100% UPC
20 mil (80%MRD)
0"*
20 mil (31%MRD)
40 mil
2.0"*
55 mil
4.0"*
in.
0 1020304050607080
0 25.4 50.8 76.2 101.6 127.0 152.4 177.8 203.2
cm
*Minimum distance determined by symbol length and scan angle
Figure 2-4
Symbol LS3478-FZ Decode Zone
26.5"
39.5"
67.0"
Depth of Field
84.0"
90
228.6
10
25.4
00
10
25.4
20
50.8
30
76.2
W
i
d
t
h
o
f
F
i
e
l
d
Page 35

W
Note: Typical performance at 73.4˚F (23˚C)
W
on high quality Code 39 symbols.
LS 3478
ER
0.25" 20"
in.
cm
LS 3478
ER
7.5 mil
10 mil
2" 32"
15 mil
3" 69"
20 mil
3" 94"
0 102030405060708090 100
0 25.4 50.8 76.2 101.6 127.0 152.4 177.8 203.2 228.6 254.0
Depth of Field
Note: Typical performance at 73.4˚F (23˚C)
on high quality Code 39 symbols.
15" 180"
*
55 mil
70 mil reflective
100 mil reflective
365"
540"
in. cm
12
8
4
0
4
8
12
in. cm
72
48
24
0
24
48
72
182.9
121.9
61.0
0
61.0
121.9
182.9
30.5
20.3
10.2
0
10.2
20.3
30.5
Scanning 2 - 7
i
d
t
h
o
f
F
i
e
l
d
i
d
t
h
o
f
F
i
e
l
d
in.
0 60 120 180 240 300 360 420 480 540 600
0 152.4 304.8 457.2 609.6 762.0 914.4 1066.8 1219.2 1371.6 1524.0
cm
Depth of Field
*Near range determined by degree of reflectivity and width of bar code.
Figure 2-5
Symbol LS3478-ER Decode Zone
Page 36

2 - 8 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Page 37

Chapter 3 Maintenance and Technical
Specifications
Introduction
This chapter provides suggested scanner maintenance, troubleshooting, technical specifications, and signal
descriptions (pinouts).
Maintenance
Cleaning the scan window is the only maintenance required. A dirty window can affect scanning accuracy.
•
Do not allow any abrasive material to touch the window.
•
Remove any dirt particles with a damp cloth.
•
Wipe the window using a tissue moistened with ammonia/water.
•
Do not spray water or other cleaning liquids directly onto the window.
Battery Maintenance
When batteries are stored over a year, battery cell manufacturers advise that some irreversible deterioration in
overall battery quality may occur. To minimize this los s, the y re co mm e nd sto ring ba tte r i es ha lf ch arge d in a dr y,
cool place between 41° and 77°F (5° and 25°C), the coo ler the better, and removed from the equipment to prevent
the loss of capacity . Batteries should be charged to half capacity at least once a year. In order to charge a battery
to half capacity , t ake a fully discharged battery and cha rge it for 2 hours. If an electrolyte leakage is observed, avoid
any contact with the affected area and properly dispose of the battery.
Page 38

3 - 2 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Troubleshooting
Table 3-1
Scanner emits short low-short
medium-short high beep
sequence.
Scanner emits short high-short
high-short low-short-low beep
sequence.
Nothing happens when scan
trigger is pressed.
Laser comes on, but scanner
does not decode the bar code.
Troubleshooting
Problem Possible Causes Possible Solutions
Scanner is powering up. Normal when scanner battery is inserted.
Radio failure. Cycle power to the cradle and re-attempt pairing.
No power to the scanner. Check battery.
Ensure that end cap to battery chamber is
secured.
Scanner is disabled. For Simple Serial Interface (SSI), Synapse, or
IBM-468x mode, enable the scanner via the host
interface. Otherwise, call Motorola Enterprise
If using RS-232 Nixdorf B
mode, CTS is not asserted.
Scanner is not programmed
for the correct bar code
type.
Mobility Support (see
information).
Assert CTS line.
Ensure the scanner is programmed to read the
type of bar code being scanned.
page xv
) for contact
Scanner emits four short high
beeps.
Scanner emits a disconnect
(short high-short low) beep
sequence.
Bar code symbol is
unreadable.
Bar code is out of range
from the scanner.
Battery is low. Charge the battery. See
Scanner has disconnected
from cradle because it is too
far from the cradle.
Scanner has disconnected
from the cradle because the
cradle has lost power or
been placed in USB
suspend mode.
Check the symbol to ensure it is not defaced. Try
scanning test bar codes of the same bar code
type. See
bar codes.
Move scanner closer to or further from bar code.
page 1-8
Move closer to the cradle and listen for a
reconnection beep (short low-short high).
Check power connections to cradle, and if using a
USB cable, check to make sure PC has not
entered a power save mode.
Appendix C, Sample Bar Codes
.
for test
Charging the Battery on
Page 39

Maintenance and Technical Specifications 3 - 3
Table 3-1
Scanner emits four long low
beeps after scanning a bar
code.
Bar code is decoded, but data
is not transmitted to the host.
Troubleshooting (Continued)
Problem Possible Causes Possible Solutions
Cradle has not completed
USB initialization.
Incorrect host interface
cable is used.
Interface/power cables to
cradle are loose.
Scanner is not paired to a
cradle.
Scanner has disconnected. See disconnect beep sequence above.
A transmission error was
detected.
Scanner not paired to
host-connected interface.
Cradle not programmed for
correct host interface
Interface cable is loose. Ensure all cable connections are secure.
Wait several seconds and scan again.
Ensure that correct host interface cable is used.
Ensure all cable connections are secure.
Scan the PAIR bar code on the cradle that is
connected to the host that is to receive data.
Ensure the cradle’s communication parameters
match the host's setting.
Pair the scanner to the cradle (using PAIR bar
code on the cradle)
Check scanner host parameters or edit options.
Five long low beeps are heard
after a bar code is decoded
Scanned data is incorrectly
displayed on the host.
Scanner emits short high-short
high- short high-long low beep
sequence when it is not in use.
Scanner emits long low-long
high beep sequence during
programming.
Cradle has lost connection
to host.
A conversion error or format
error has been detected.
Cradle host communication
parameters do not match
host’s parameters.
RS-232 receive error. Normal during host reset. Otherwise, ensure the
Input error or ’Cancel’ bar
code was scanned.
In this exact order: disconnect power supply;
disconnect host cable; wait three seconds;
reconnect host cable; reconnect power supply;
reestablish pairing.
Ensure the scanner’s conversion parameters are
properly configured.
Ensure proper host is selected.
For RS-232, ensure the cradle’s communication
parameters match the host’s settings.
For a Keyboard Wedge configuration, ensure the
system is programmed for the correct keyboard
type, and the CAPS LOCK key is off.
Ensure editing options (e.g., UPC-E to UPC-A
conversion) are properly programmed.
scanner’s RS-232 parity setting matches the host
setting.
Ensure the correct numeric bar codes, that are
within range for the parameter being pr ogrammed,
are being scanned.
Page 40

3 - 4 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Table 3-1
Troubleshooting (Continued)
Problem Possible Causes Possible Solutions
Scanner emits short low-short
high- short low-short high beep
sequence while it is being
programmed.
Scanner emits one short high
beep when it is not in use.
Out of ADF parameter
storage space.
Out of Synapse parameter
storage space.
In RS-232 mode, a <BEL>
character is received and
Beep on <BEL> option is
enabled.
Scanner emits short low-short
Scanner is powering up. Normal when scanner battery is inserted.
medium-short high beep
sequence.
Battery does not charge. Cradle is outside the
charging temperature range.
Erase all rules and re-program with shorter rules.
Scan ’Set Synapse Defaults’ bar code, from the
appropriate Synapse Interface Guide, for cables
no longer in use and re-program the scanner for
the current host interface.
Normal when Beep on <BEL> is enabled and the
scanner is in RS-232 mode.
Charge within the recommended temperature of
32° to 104° F
(0° to 40° C) nominal, 41° to 95° F (5° to 35° C)
ideal.
NOTE If problems still occur, contact the distributor or contact Motorola Enterprise Mobility Support. See page xv
for the telephone numbers.
Page 41

Technical Specifications
Maintenance and Technical Specifications 3 - 5
Table 3-2
Battery Rechargeable Lithium-Ion 2200 mAh (3.7V)
Decode Capability UPC/EAN, Bookland EAN, UPC/EAN with supplementals, Code 128, UCC/EAN 128,
Beeper Operation User-selectable: Enable, Disable
Beeper Volume User-selectable: Three levels
Beeper Tone User-selectable: Three tones
Scan Repetition Rate 36 scans/second
Yaw Tolerance ± 50° from nominal ± 60° from nominal
Pitch Tolerance ± 65° from nominal ± 65° from nominal
Roll Tolerance ± 20° from nominal ± 10° from nominal
Print Contrast Minimum 25% minimum reflectance differential, measured at 650 nm.
Ambient Light Immunity
Indoor:
Outdoor:
Technical Specifications - Scanner
Item
Symbol LS3478-FZ Symbol LS3478-ER
ISBT 128, Code 39, Trioptic Cod e 39, Cod e 93, Cod e 11, Interleaved 2 of 5, Discrete 2
of 5, Codabar (NW-7), MSI, GS1 DataBar.
450 Ft Candles (4,842 Lux)
8,000 Ft Candles (86,080 Lux)
Description
450 Ft Candles (4,842 Lux)
4,000 Ft Candles (43,040 Lux)
Durability 6.5 ft (2.0 m) drops to concrete;
5 ft (1.5 m) at -4° F (-20° C)
Operating Temperature -4° to 122° F (-20° to 50° C)
Storage Temperature -40° to 140° F (-40° to 60° C)
Charging Temperature 32° to 104° F (0° to 40° C) nominal, 41° to 95° F (5° to 35° C) ideal
Humidity 5% to 95% (non-condensing)
ESD 15 kV air discharge
8 kV contact discharge
Weight 14.6 oz (414 grams) 14.8 oz (420 grams)
Dimensions:
Height
Width
Depth
Laser 650nm laser diode
Laser Classifications IEC 825-1 Class 2
7.34 in. (18.65 cm)
4.82 in. (12.25 cm)
2.93 in. (7.43 cm)
Page 42

3 - 6 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Table 3-2
Minimum Element Width 5 mil (0.127 mm)
Interfaces Supported Keyboard Wedge, RS-232, USB, IBM 468X/469X, Wand Emulation, Scanner
Radio Link Bluetooth Class 1 (2.4 GHz), Class 2
Electrical Safety Certified Pending to UL1950, CSA C22.2 No.950. EN60950/IC950
Input Transient
Protection
EMI FCC Part 15 Class B, ICES-003 Class B European Union EMC Directive,
Technical Specifications - Scanner (Continued)
Description
Item
Symbol LS3478-FZ Symbol LS3478-ER
7.5 mil (0.191 mm)
Emulation, Synapse, 123Scan
IEC 1000-4-(2,3,4,5,6,11)
Australian SMA, Taiwan EMC, Japan VCCI/MITI/Dentori
Page 43

Maintenance and Technical Specifications 3 - 7
Table 3-3
Power Requirements 4.75 - 14.0 VDC
Typical Current Draw
Not Charging: 10 mA 105 mA @ 5V
Fast Rate Charge: 915 mA @ 5V
Slow Rate Charge: 480 mA @ 5V
Interfaces Supported None Keyboard Wedge, RS-232, USB,
Operating Temperature -4° to 122° F (-20° to 50° C)
Storage Temperature -40° to 140° F (-40° to 60° C)
Charging Temperature 32° to 104° F (0° to 40° C) nominal, 41° to 95° F (5° to 35° C) ideal
Technical Specifications - Cradles
Item
STB 3408 and FLB 3408 STB 3478 and FLB 3478
660 mA @ 9V
345 mA @ 9V
Description
45 mA @ 9V
955 mA @ 5V
660 mA @ 9V
480 mA @ 5V
345 mA @ 9V
IBM 468X/469X, Wand Emulation,
Scanner Emulation, Synapse
Humidity 5% to 95% (non-condensing)
ESD 15 kV air discharge
8 kV contact discharge
Weight 10.5 oz (298 grams)
Dimensions:
Height
Width
Depth
Radio Link N/A Bluetooth Class 1 (2.4 GHz)
Electrical Safety Certified Pending to UL1950, CSA C22.2 No.950. EN60950/IC950
Input Transient Protection IEC 1000-4-(2,3,4,5,6,11)
EMI FCC Part 15 Class B, ICES-003 Class B European Union EMC Directive,
9.5 in. (24.1 cm)
4.0 in (10.2 cm)
2.9 in (7.4 cm)
Australian SMA, Taiwan EMC, Japan VCCI/MITI/Dentori
Page 44

3 - 8 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Scanner Signal Descriptions
The signal descriptions in Table 3-4 apply to the 10-pin RJ connector on the scanner cradle and are for referenc e
only .
Table 3-4
Pin IBM Synapse RS-232
1 Reserved SynClock Reserved Reserved Reserved Jump to Pin 6 DBP
2 Power Power Power Power Power Power Power
3 Ground Ground Ground Ground Ground Ground Ground
4 IBM_A(+) Reserved TxD KeyClock DBP Reserved SOS
5 Reserved Reserved RxD TermData CTS D + Decode
6 IBM_B(-) SynData RTS KeyData RTS Jump to Pin 1 Trigger
7 Reserved Reserved CTS TermClock Reserved D - Enable
8 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
9 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
10 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
Figure 3-1 illustrates the positions of the cradle pins.
Scanner Cradle to Host Pin-outs
Keyboard
Wedge
Wand USB
Scanner
Emulation
Pin 4 Pin 3 Pin 2
Figure 3-1
The signal descriptions in Table 3-5 apply to the connector from the scanner to the scanner cradle and are for
reference only.
Table 3-5
Pin Description
1VCC
2CRADLE_TXD
3 CRADLE_RXD
4GND
Cradle Pin Assignments
Scanner to Scanner Cradle Pin-outs
Pin 1
Page 45

Chapter 4 User Preferences
Introduction
This chapter describes each user preferen ce fea tu re an d provides the programming bar codes for selecting these
features for the scanner.
The scanner ships with the settings shown in the User Preferences Default Table on page 4-2 (also see Appendix
A, Standard Default Parameters for all host device and miscellaneous scanner defaults). If the default values suit
the requirements, programming is not necessary.
Set feature values by scanning single bar codes or short bar code sequences. The settings are stored in
non-volatile memory and are preserved when the scanner powers down.
The scanner communicates with the host through the scanner cradle. During scanner setup, the scanner is paired
with a cradle, which is connected to the host through one of several interfaces (see Pairing on page 1-9 and the
applicable host interface chapter). Each cradle can pair with up to four scanners.
If not using a Synapse or USB cable, select the host type (see the specific host chapter) after the scanner emits
power-up beeps. This is only done upon the first power-up when connecting to a new host.
NOTE Disconnect the power supply before changing host cables or the scanner may not recognize the new host.
To return all features to their default values, scan Set All Defaults on page 4-3. Throughout the programming bar
code menus, default values are indicated with asterisks (
* Indicates Default
*High Frequency
*).
Feature/Option
Page 46

4 - 2 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Scanning Sequence Examples
In most cases, scan only one bar code to set a parameter value. For example, to set the beeper tone to high, scan
the High Frequency (beeper tone) bar code under Beeper Tone on page 4-3. The scanner issues a fast warble
beep and the LED turns green, indicating a successful parameter entry.
Other parameters, such as Laser On Time or Data Transmission Formats, require scanning several bar codes.
See the parameter description for this procedure.
Errors While Scanning
Unless otherwise specified, if an error is made during a scanning sequence, re-scan the correct parameter.
User Preferences Default Parameters
T able 4-1 lists the default s for user preference p arameters. To change any option, scan the appropriate bar code (s)
provided in User Preferences on page 4-3.
NOTE See Appendix A, Standard Default Parameters for all user preference, host, symbology, and
miscellaneous default parameters.
Table 4-1
User Preferences
Set Default Parameter All Defaults
Beeper Tone Medium
Beeper Volume High
Power Mode Reduced
Laser On Time 3.0 sec
Beep After Good Decode Enable
Trigger Mode Level
Aim Duration 0.0 sec
Connection Maintenance Interval 15 minutes
User Preferences Default Table
Parameter Default
Page
Number
4-3
4-3
4-4
4-5
4-5
4-6
4-7
4-8
4-9
Radio Output Power Bluetooth Class 1
Parameter Broadcast Enable
Single Point/Multipoint Operation Single Point
4-11
4-11
4-12
Page 47

User Preferences
Set Default Parameter
Scan this bar code to return all parameters to the default values listed in Table A-1 on page A-1.
Beeper Tone
To select a decode beep frequency (tone), scan the Low Frequency, Medium Frequency, or High Frequency bar
code.
User Preferences 4 - 3
Set All Defaults
Low Frequency
*Medium Frequency
High Frequency
Page 48

4 - 4 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Beeper Volume
To select a beeper volume, scan the Low Volume, Medium Volume, or High Volume bar code.
Low Volume
Medium Volume
*High Volume
Page 49

User Preferences 4 - 5
Power Mode
This parameter determines whether or not the scanner ente rs re duced po wer mo de a fter a decode attempt. When
in reduced power mode, the scanner draws less current from its battery.
Continuous On
*Reduced Power Mode
Laser On Time
This parameter sets the maximum time that decode processing continues during a scan attempt. It is
programmable in 0.1 second increments from 0.5 to 9.9 seconds. The default Laser On Time is 3.0 seconds.
To set a Laser On Time, scan the bar code below. Next, scan two numeric bar codes from Appendix D, Numeric
Bar Codes that correspond to the desired on time. Include a leading zero for single digit numbe rs. For examp le, to
set a Laser On Time of 0.5 seconds, scan the bar code below, then scan the 0 and 5 bar codes. T o co rrect an error
or change the selection, scan Cancel on page D-3.
Laser On Time
Page 50

4 - 6 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Beep After Good Decode
Scan one of the following bar codes to select whether the scanner beep s after a good decode. If Do Not Beep
After Good Decode is selected, the beeper still operates during parameter menu scanning and indicates error
conditions.
Do Not Beep After Good Decode
*Beep After Good Decode
(Enable)
(Disable)
Page 51

User Preferences 4 - 7
Trigger Mode
Scan one of the following bar codes to set the scanner’s trigger mode.
Level Trigger
Upon trigger pull, an aiming dot appears for a programmable duration of time. After this time, the aiming dot turns
into a standard laser scanning beam for a full decode sessio n. The laser scanning beam st ays on until the laser-on
timeout occurs, a decode occurs, or the trigger is released. If the trigger is released before the aiming duration
expires, the laser shuts off an d no decode occurs.
*Level
Two Stage - Option 1
Upon trigger pull, an aiming dot appears. This aiming dot remains while the trigger is pulled. When the trigger is
released, the aiming dot turns into a standard laser scanning beam for a fu ll decode session. The laser scanning
beam stays on until the laser-on timeout occurs or a decode occurs. If the trigger is pulled again while in a decode
session, the scanner beam returns to an aiming dot.
Two Stage - Option 1
Two Stage - Option 2
Upon trigger pull, an aiming dot appears. When the trigger is released, the aiming dot turns off. Pulling the trigger
twice quickly turns on the standard laser scanning beam for a full decode session. The laser scanning beam stays
on until the laser-on timeout occurs, a decode occurs, or the trigger is released.
Two Stage - Option 2
Page 52

4 - 8 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Aim Duration
When the scanner is in Level trigger mode (default mode), Aim Duration sets the amount of time the aiming dot
appears before turning into a scanning beam. This parameter has no affect when the scanner is in either of the
Two Stage trigger modes. See Trigger Mode on page 4-7 for a description of each of the trigger modes.
The aim duration is programmable in 0.1 second increments, from 0.0 to 9.9 seconds. The defa ult Aim Duration is
0.0 seconds. When set to 0.0 seconds, no aiming pattern ap pe a rs be fo re a decod e sessio n .
To set an aim duration, scan the bar code below. Then scan two numeric bar codes from Appendix D, Numeric Bar
Codes that correspond to the desired aim duration. In clude a leading zero for dur ations less tha n 1.0 seconds. For
example, to set an aim duration of 0.5 seconds, scan the bar code below followed by the 0 and the 5 bar codes. T o
correct an error or change the selection, scan Cancel on page D-3.
Aim Duration
Page 53

Radio Communications
Connection Maintenance Interval
When a scanner disconnects from a cradle due to a Link Supervision Timeout, the scanner immediately attempts
to reconnect to the cradle for 30 seconds. If the scanner does not reconnected within 30 seconds, it enters low
power mode. Thereafter, when a bar code is scanned, the scanner attempts to reconnect before transmitting the
data.
To guarantee that a disconnected scanner can reconnect when it comes back in range, the cradle reserves the
connection for that scanner for a period of time defined by the Connection Main tenance Interval. If the cradle is
already supporting the maximum four scanners, and one sc anner disconnects, a fifth scanner cannot pair to the
cradle during this interval. Connection Maintenance Interval options are:
•
15 minutes
•
30 minutes
•
One hour
•
Two hours
User Preferences 4 - 9
•
Four hours
•
Eight hours
•
24 hours
•
Indefinitely.
Considerations
The system administrator determines the Connection Maintenance Interval. A shor ter interval allows new users to
gain access to abandoned connections more quickly, but causes problems if users leave the work area for
extended periods. A longer interval allows existing users to leave the work area for longer periods of time, but ties
up the system for new users.
To avoid this conflict, users who are going off-shift can scan the unpair bar code on page 4-12 to ignore the
Connection Maintenance Interval and make the connection immediately available.
Page 54

4 - 10 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
To set the Connection Maintenance Interval, select one of the following bar codes.
*Set Interval to 15 Minutes
Set Interval to 30 Minutes
Set Interval to 60 Minutes
Set Interval to 2 Hours
Set Interval to 4 Hours
Set Interval to 8 Hours
Set Interval to 24 Hours
Set Interval to Forever
Page 55

User Preferences 4 - 11
Radio Output Power
The Symbol LS3478 uses a Class 1 Bluetooth radio with a transmission range of up to 100m. Optionally place the
radio in a Class 2 operating mode to restrict the transmission range to 10m and reduce the effect of the radio on
neighboring wireless systems.
Scan a bar code to select Class 1 or Class 2 operation.
*Bluetooth Class 1
Bluetooth Class 2
Parameter Broadcast
Enable Parameter Broadcast to broadcast all parameter bar codes scanned to all other scanners in the piconet. If
disabled, parameter bar codes are processed by the individual scanner only, and the scanner ignores parameters
broadcast from other scanners or from the cradle (e.g., parameters sent via 123Scan).
*Enable Parameter Broadcast
Disable Parameter Broadcast
Page 56

4 - 12 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Single Point/Multipoint Operation
The cradle supports communication from up to four scanners simultaneously. This multipoint mode requires an
external power supply to charge the scanners in the cradle. To power the cradle from the interface cable (either
from the USB hub or from a power supply attached to the interface cable), place the cradle in single point mode. In
single point mode, only one scanner can connect to the cradle at a time.
NOTE When operating in bus-powered mode, the cradle must turn off the Bluetooth radio to charge the scanner.
For this reason, only charge the scanner paired with the cradle in the cradle. Placing another scanner in
the cradle for charging disrupts communication with the paired scanner.
When setting options while in multipoint mode, allow time for the setting changes to apply to all scanners
To select single point or multipoint mode, scan the appropriate bar code.
Multipoint Mode
*Single Point Mode
Unpair
Scan the following bar code to disconnect the scanner from its cradle.
Unpairing
NOTE The LS3478 Quick Start Guide also includes the unpairing bar code.
Page 57

Chapter 5 Keyboard Wedge Interface
Introduction
This chapter provides instructions for programming the scanner for keyboard wedge host interface, used to
connect the scanner between the keyboard and host computer. The scanner translates the bar code data into
keystrokes, and transmits the information to the host computer via the cradle interface. The host computer accept s
the keystrokes as if they originated from the keyboard.
This interface adds bar code reading functionality to a system designed for manual keyboard input. In this mode
the keyboard keystrokes are simply passed through.
Throughout the programming bar code menus, default values are indicated with asterisks (
* Indicates Default
*North American
Feature/Option
*).
Page 58

5 - 2 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Connecting a Keyboard Wedge Interface
Male DIN Host Connector
Keyboard
Connector
Female DIN Keyboard
Connector
Y-cable
Figure 5-1
Keyboard Wedge Interface Connection with Y-cable
To connect the keyboard wedge interface Y-cable:
1. Turn off the host and unplug the keyboard connector.
2. Attach the modular connector of the Y-cable to the cable interface port on the scanner cradle. See Connecting
the Cradle on page 1-4.
3. Connect the round male DIN host connector of the Y-cable to the keyboard port on the host.
4. Connect the round female DIN keyboard connector of the Y-cable to the keyboard connector.
5. If required, attach the optional power supply to the connector in the middle of the Y-cable.
6. Ensure that all connections are secure.
7. Turn on the host system.
8. Pair the scanner to the cradle by scanning the bar code on the cradle.
9. Select the keyboard wedge host type by scanning the appropriate bar code from the Keyboard Wedge Host
Types section on page 5-4.
10. To modify any other parameter options, scan the appropriate bar codes in this chapter.
11. Connect an external power supply if desired.
NOTE Interface cables vary depending on configuration. The connectors illustrated in Figure 5-1 are examples
only. The connectors may be different from those illustrated, but the steps to connect the scanner cradle
remain the same.
Disconnect the power supply before changing host cables or the scanner may not recognize the new host.
Page 59

Keyboard Wedge Default Parameters
Table 5-1 lists the defaults for keyboard wedge host parameters. To change any option, scan the appropriate bar
code(s) provided in this chapter.
NOTE See Appendix A, Standard Default Parameters for all user preference, host, symbology, and
miscellaneous default parameters.
Keyboard Wedge Interface 5 - 3
Table 5-1
Keyboard Wedge Host Parameters
Keyboard Wedge Host Type IBM PC/AT& IBM PC Compatibles
Keyboard Wedge Country Types (Country Codes) North American
Ignore Unknown Characters Enable
Keystroke Delay 0 msec (No Delay)
Intra-Keystroke Delay Disable
Alternate Numeric Keypad Emulation Disable
Caps Lock On Disable
Caps Lock Override Disable
Convert Wedge Data Do Not Convert Wedge Data
Function Key Mapping Disable
FN1 Substitution Disable
Send Make and Break Send Make and Break Scan Codes
Keyboard Wedge Host Default Table
Parameter Default
Page
Number
5-4
5-5
5-7
5-7
5-8
5-8
5-8
5-9
5-9
5-10
5-10
5-10
Page 60

5 - 4 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Keyboard Wedge Host Types
Keyboard Wedge Host Types
Select the keyboard wedge host by scanning one of the following bar codes.
*IBM PC/AT & IBM PC Compatibles
IBM AT NOTEBOOK
NCR 7052
Page 61

Keyboard Wedge Interface 5 - 5
Keyboard Wedge Country Types (Country Codes)
Scan the bar code corresponding to the keyboard type. If the particular keyboard type is not listed, see Alternate
Numeric Keypad Emulation on page 5-8.
*North American
German Windows
French Windows
French Canadian Windows 95/98
French Canadian Windows XP/2000
Page 62

5 - 6 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Keyboard Wedge Country Types (Country Codes) (continued)
Spanish Windows
Italian Windows
Swedish Windows
UK English Windows
Japanese Windows
Brazilian-Portuguese Windows
Page 63

Keyboard Wedge Interface 5 - 7
Ignore Unknown Characters
Unknown characters are characters the host does not recognize. When Send Bar Codes With Unknown
Characters is selected, all bar code data is sent except for unknown characters, an d the scanner emits no error
beeps. When Do Not Send Bar Codes W ith Unknown Charact ers is selected, bar code d ata is sent until the first
unknown character is encountered, and the scanner emits an error beep.
*Send Bar Codes with Unknown Characters
(Enable)
Do Not Send Bar Codes with Unknown Characters
(Disable)
Keystroke Delay
This is the delay in milliseconds between emulated keystrokes. Scan a bar code below to increase the delay when
hosts require a slower data transmission.
*0 msec (No Delay)
20 msec (Medium Delay)
40 msec (Long Delay)
Page 64

5 - 8 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Intra-Keystroke Delay
Enable Intra-Keystroke Delay to insert an additional delay between each emulated key press and release. This
also sets the Keystroke Delay parameter to a minimum of 5 msec.
Enable Intra-Keystroke Delay
*Disable Intra-Keystroke Delay
Alternate Numeric Keypad Emulation
This allows emulation of most other country keyboard types not listed in Keyboard W ed ge Co untry Types (Country
Codes) on page 5-5 in a Microsoft
®
operating system environment.
Enable Alternate Numeric Keypad
*Disable Alternate Numeric Keypad
Caps Lock On
When enabled, the scanner emulates keystrokes as if the Caps Lock key is always pressed.
Enable Caps Lock On
*Disable Caps Lock On
Page 65

Keyboard Wedge Interface 5 - 9
Caps Lock Override
When enabled, on AT or AT Notebook hosts, the keyboard igno res the st ate of the Ca ps Lock key an d matches the
case (upper or lower) of the sent character. Therefore, an upper case ‘A’ in the bar code is sent as an upper case
‘A,’ and a lower case ‘a’ in the bar code is sent as a lower case ‘a,’ no matter what the st ate of the keyboard’ s Cap s
Lock key.
Enable Caps Lock Override
*Disable Caps Lock Override
NOTE If both Caps Lock On and Caps Lock Override are enabled, Caps Lock Override takes precedence.
Convert Wedge Data
When enabled, the scanner converts all bar code dat a to the selected case.
Convert Wedge Data to Upper Case
Convert Wedge Data to Lower Case
*Do Not Convert Wedge Data
Page 66

5 - 10 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Function Key Mapping
ASCII values under 32 are normally sent as control key sequences (see Table 5-2 on page 5-13). Enable this
parameter to send the keys in bold in place of the standard key mapping. Table entries that do not have a bold
entry remain the same regardless of this parameter.
Enable Function Key Mapping
*Disable Function Key Mapping
FN1 Substitution
When enabled, this parameter replaces any FN1 character in an EAN128 b ar code with a keystroke chosen by the
user. See FN1 Substitution Values on page 13-7.
Enable FN1 Substitution
*Disable FN1 Substitution
Send Make and Break
When enabled, the scan codes for releasing a key are not sent.
*Send Make and Break Scan Codes
Send Make Scan Code Only
Page 67

Keyboard Maps
The following keyboard maps are provided for pr efix/suffix keystroke parameters. To program the prefix/suffix
values, see the bar codes on page 13-4.
Keyboard Wedge Interface 5 - 11
7014 5001 5002 5003 5004 5005 5006 5007 5008 5009 5010
7009
Figure 5-2
Figure 5-3
IBM PS2 Type Keyboard
5001
5003
5005
5007
5009
5002
5004
5006
5008
5010
7014
7009
IBM PC/XT
5011
7008
7013
7013
5012
7010 7007
7012
7011
7002 7004 7005
7015
7017 7016
7006
7001
7003
7018
7008
7012
7013
7004
7011 7002
7003
7006
5001
5002
5003
5004
5005
5006
5007
5008
5009
5010
Figure 5-4
7009
IBM PC/AT
7008
7013
7014
7012
7004
7011
7003
7002
Page 68

5 - 12 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
5001
5003
5005 5006
5007
5009
Figure 5-5
1065
1072
1079 1080
5001
5003
5002
5011
5004
5008
5010
1048
(1048 if double key)
NCR 7052 32-KEY
1066
1073
5002
5004
1067
1074
1081
5011
5012
1068
1075
1082
1046
1045
5014
1043
5017
7013
(7013 if double key)
1070
1069
1076
1077
1083 1084
1045
5013
5014
5015
5013
5015
5016
5018
5019
1071
1078
1085
1086
1087
5005 5006
5007
5009
Figure 5-6
5008
5010
(1048 if double key)
1048
5012
NCR 7052 58-KEY
1046
1043
5016
5018
5017
7013
5019
(1043 if double key)
1088
1089
1090
Page 69

ASCII Character Set
NOTE Code 39 Full ASCII interprets the bar code special character ($ + % /) preceding a Code 39 character and
assigns an ASCII character value to the pair. For example, when Code 39 Full ASCII is enabled and a +B
is scanned, it is interpreted as b, %J as ?, and %V as @. Scanning ABC%I outputs the keystroke
equivalent of ABC >.
Keyboard Wedge Interface 5 - 13
Table 5-2
Keyboard Wedge ASCII Character Set
ASCII Value
Full ASCII Code 39
Encode Character
1001 $A CTRL A
1002 $B CTRL B
1003 $C CTRL C
1004 $D CTRL D
1005 $E CTRL E
1006 $F CTRL F
1007 $G CTRL G
1008 $H
1009 $I
CTRL H/
CTRL I/
1010 $J CTRL J
1011 $K CTRL K
1012 $L CTRL L
Keystroke
BACKSPACE
1
HORIZONTAL TAB
1
1013 $M
CTRL M/
ENTER
1
1014 $N CTRL N
1015 $O CTRL O
1016 $P CTRL P
1017 $Q CTRL Q
1018 $R CTRL R
1019 $S CTRL S
1020 $T CTRL T
1021 $U CTRL U
1
The keystroke in bold is sent only if the “Function Key Mapping” is
enabled. Otherwise, the unbolded keystroke is sent.
Page 70

5 - 14 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Table 5-2
Keyboard Wedge ASCII Character Set (Continued)
ASCII Value
Full ASCII Code 39
Encode Character
1022 $V CTRL V
1023 $W CTRL W
1024 $X CTRL X
1025 $Y CTRL Y
1026 $Z CTRL Z
1027 %A
CTRL [/
1028 %B CTRL \
1029 %C CTRL ]
1030 %D CTRL 6
1031 %E CTRL 1032 Space Space
1033 /A !
Keystroke
1
ESC
1034 /B “
1035 /C #
1036 /D $
1037 /E %
1038 /F &
1039 /G ‘
1040 /H (
1041 /I )
1042 /J *
1043 /K +
1044 /L ,
1045 - 1046 . .
1047 /O /
1048 0 0
1049 1 1
1
The keystroke in bold is sent only if the “Function Key Mapping” is
enabled. Otherwise, the unbolded keystroke is sent.
Page 71

Keyboard Wedge Interface 5 - 15
Table 5-2
Keyboard Wedge ASCII Character Set (Continued)
ASCII Value
Full ASCII Code 39
Encode Character
1050 2 2
1051 3 3
1052 4 4
1053 5 5
1054 6 6
1055 7 7
1056 8 8
1057 9 9
1058 /Z :
1059 %F ;
1060 %G <
1061 %H =
1062 %I >
Keystroke
1063 %J ?
1064 %V @
1065 A A
1066 B B
1067 C C
1068 D D
1069 E E
1070 F F
1071 G G
1072 H H
1073 I I
1074 J J
1075 K K
1076 L L
1077 M M
1
The keystroke in bold is sent only if the “Function Key Mapping” is
enabled. Otherwise, the unbolded keystroke is sent.
Page 72

5 - 16 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Table 5-2
Keyboard Wedge ASCII Character Set (Continued)
ASCII Value
Full ASCII Code 39
Encode Character
1078 N N
1079 O O
1080 P P
1081 Q Q
1082 R R
1083 S S
1084 T T
1085 U U
1086 V V
1087 W W
1088 X X
1089 Y Y
1090 Z Z
Keystroke
1091 %K [
1092 %L \
1093 %M ]
1094 %N ^
1095 %O _
1096 %W ‘
1097 +A a
1098 +B b
1099 +C c
1100 +D d
1101 +E e
1102 +F f
1103 +G g
1104 +H h
1105 +I i
1
The keystroke in bold is sent only if the “Function Key Mapping” is
enabled. Otherwise, the unbolded keystroke is sent.
Page 73

Keyboard Wedge Interface 5 - 17
Table 5-2
Keyboard Wedge ASCII Character Set (Continued)
ASCII Value
Full ASCII Code 39
Encode Character
1106 +J j
1107 +K k
1108 +L l
1109 +M m
1110 +N n
1111 +O o
1112 +P p
1113 +Q q
1114 +R r
1115 +S s
1116 +T t
1117 +U u
1118 +V v
Keystroke
1119 +W w
1120 +X x
1121 +Y y
1122 +Z z
1123 %P {
1124 %Q |
1125 %R }
1126 %S ~
1
The keystroke in bold is sent only if the “Function Key Mapping” is
enabled. Otherwise, the unbolded keystroke is sent.
Table 5-3
Keyboard Wedge ALT Key Character Set
ALT Keys Keystroke
2065 ALT A
2066 ALT B
2067 ALT C
2068 ALT D
2069 ALT E
Page 74

5 - 18 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Table 5-3
2070 ALT F
2071 ALT G
2072 ALT H
2073 ALT I
2074 ALT J
2075 ALT K
2076 ALT L
2077 ALT M
2078 ALT N
2079 ALT O
2080 ALT P
2081 ALT Q
2082 ALT R
Keyboard Wedge ALT Key Character Set (Continued)
ALT Keys Keystroke
2083 ALT S
2084 ALT T
2085 ALT U
2086 ALT V
2087 ALT W
2088 ALT X
2089 ALT Y
2090 ALT Z
Table 5-4
3000 Right Control Key
3048 GUI 0
3049 GUI 1
3050 GUI 2
3051 GUI 3
Keyboard Wedge GUI Key Character Set
GUI Keys Keystrokes
3052 GUI 4
3053 GUI 5
Page 75

Keyboard Wedge Interface 5 - 19
Table 5-4
3054 GUI 6
3055 GUI 7
3056 GUI 8
3057 GUI 9
3065 GUI A
3066 GUI B
3067 GUI C
3068 GUI D
3069 GUI E
3070 GUI F
3071 GUI G
3072 GUI H
3073 GUI I
Keyboard Wedge GUI Key Character Set (Continued)
GUI Keys Keystrokes
3074 GUI J
3075 GUI K
3076 GUI L
3077 GUI M
3078 GUI N
3079 GUI O
3080 GUI P
3081 GUI Q
3082 GUI R
3083 GUI S
3084 GUI T
3085 GUI U
3086 GUI V
3087 GUI W
3088 GUI X
3089 GUI Y
3090 GUI Z
Page 76

5 - 20 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Table 5-5
5001 F1
5002 F2
5003 F3
5004 F4
5005 F5
5006 F6
5007 F7
5008 F8
5009 F9
5010 F10
5011 F11
5012 F12
5013 F13
Keyboard Wedge F Key Character Set
F Keys Keystroke
5014 F14
5015 F15
5016 F16
5017 F17
5018 F18
5019 F19
5020 F20
5021 F21
5022 F22
5023 F23
5024 F24
Page 77

Keyboard Wedge Interface 5 - 21
Table 5-6
6042 *
6043 +
6044 undefined
6045 6046 .
6047 /
6048 0
6049 1
6050 2
6051 3
6052 4
6053 5
6054 6
Keyboard Wedge Numeric Keypad Character Set
Numeric Keypad Keystroke
6055 7
6056 8
6057 9
6058 Enter
6059 Num Lock
Page 78

5 - 22 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Table 5-7
7001 Break
7002 Delete
7003 Pg Up
7004 End
7005 Pg Dn
7006 Pause
7007 Scroll Lock
7008 Backspace
7009 Tab
7010 Print Screen
7011 Insert
7012 Home
7013 Enter
Keyboard Wedge Extended Keypad Character Set
Extended Keypad Keystroke
7014 Escape
7015 Up Arrow
7016 Dn Arrow
7017 Left Arrow
7018 Right Arrow
Page 79

Chapter 6 RS-232 Interface
Introduction
This chapter provides instructions for programming the scanner to interface with an RS-232 host interface. The
RS-232 interface is used to attach the scanner cradle to point-of-sale devices, host computers, or other devices
with an available RS-232 port (i.e., COM port).
If the particular host is not listed in Table 6-2, set the communication parameters to match the host device. Refer to
the documentation for the host device.
NOTE This scanner uses TTL RS-232 signal levels, which interface with most system architectures. For system
architectures requiring RS-232C signal levels, Motorola offers different cables providing the TTL to
RS-232C conversion. Contact Motorola Enterprise Mobility Support for more information.
Throughout the bar code menus, default values are indicated with asterisks (
* Indicates Default
*Baud Rate 9600
Feature/Option
*).
Page 80

6 - 2 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Connecting an RS-232 Interface
This connection is made directly from the scanner cradle to the host computer.
Serial Port Connector to Host
Interface Cable
Figure 6-1
1. Attach the modular connector of the RS-232 interface cable to the cable interface port on the scanner
RS-232 Direct Connection
NOTE Interface cables vary depending on configuration. The connectors illustrated in Figure 6-1 are examples
only. The connectors may be different from those illustrated, but the steps to connect the scanner cradle
remain the same.
Disconnect the power supply before changing host cables or the scanner may not recognize the new host.
cradle.(See Connecting the Cradle on page 1-4.
2. Connect the other end of the RS-232 interface cable to the serial port on the host.
3. Connect the power supply to the serial connector end of the RS-232 interface cable, then plug the power
supply to an appropriate outlet, or connect an external power supply to the cradle.
4. Ensure that all connections are secure.
5. Pair the scanner to the cradle by scanning the bar code on the cradle.
6. Select the RS-232 host type by scanning the appropriate bar code from the RS-232 Host Types section on
page 6-6.
7. To modify any other parameter options, scan the appropriate bar codes in this chapter.
Page 81

RS-232 Default Parameters
Table 6-1 lists the defaults for RS-232 host parameters. To change any option, scan the appropriate bar code(s)
provided in the parameter descriptions section beginning on page 6-4.
NOTE See Appendix A, Standard Default Parameters for all user preference, host, symbology, and
miscellaneous default parameters.
RS-232 Interface 6 - 3
Table 6-1
RS-232 Host Parameters
RS-232 Host Types Standard RS-232
Baud Rate 9600
Parity None
Check Receive Errors Enable
Stop Bit Select 1 Stop Bit
Data Bits 8-Bit
Hardware Handshaking None
Software Handshaking None
Host Serial Response Time-out Minimum: 2 sec
RTS Line State Host: Low RTS
Beep on <BEL> Disable
Intercharacter Delay Minimum: 0 msec
RS-232 Host Default Table
Parameter Default
Page
Number
6-6
6-7
6-9
6-10
6-11
6-11
6-12
6-14
6-16
6-17
6-17
6-18
Nixdorf Beep/LED Options Normal Operation
Ignore Unknown Characters Send Bar Code
6-19
6-20
Page 82

6 - 4 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
RS-232 Host Parameters
Various RS-232 host types are set up with their own parameter default settings. Selecting the host type sets the
parameter defaults as listed in Table 6-2.
Table 6-2
Parameter
Transmit Code IDNo Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Data
Transmission
Format
Suffix CR/LF
Baud Rate 9600 9600 9600 9600 9600 9600 9600 9600
Parity None Even Odd Odd Even None Odd None
Hardware
Handshaking
Software
Handshaking
Serial
Response
Time-out
Terminal Specific RS-232
Standard
RS-232
(Default)
Data as is Data/
Suffix
CR
(7013)
None RTS/CTS
None None None None Ack/NakNone None None
2 Sec. 9.9 Sec. 9.9 Sec. 9.9 Sec. 9.9 Sec. 9.9 Sec. 9.9 Sec. 2 Sec.
(1013)
Option 3
ICL
Wincor-
Nixdorf
Mode A
Data/Suffix Data/
CR (1013) CR
RTS/CTS
Option 3
Wincor-
Nixdorf
Mode B
Suffix
(1013)
RTS/CTS
Option 3
Olivetti Omron
Prefix/
Data/
Suffix
ETX
(1002)
None None RTS/CTS
Data/
Suffix
CR
(1013)
OPOS/
JPOS
Data/
Suffix
CR
(1013)
Option 3
Fujitsu
Data/
Suffix
CR
(1013)
None
Stop Bit Select One One One One One One One One
ASCII Format 8-Bit 8-Bit 8-Bit 8-Bit 7-Bit 8-Bit 8-Bit 8-Bit
Beep On
<BEL>
RTS Line State Low High Low Low = No
Prefix None None None None STX
*In the Nixdorf Mode B or OPOS/JPOS, if CTS is Low, scanning is disabled. When CTS is High, the
user can scan bar codes.
**If Nixdorf Mode B or OPOS/JPOS is scanned without the scanner connected to the proper host, it
may appear unable to scan. If this happens, scan a different RS-232 host type within 5 seconds of
cycling power to the scanner.
Disable Disable Disable Disable Disable Disable Disable Disable
data to
send
Low High Low = No
data to
send
None None None
(1003)
Low
Page 83

RS-232 Host Parameters (continued)
Selecting the ICL, Wincor-Nixdorf Mode A, Wincor-Nixdorf Mode B, Olivetti, Omron, OPOS/JPOS or Fujitsu host
type enables the transmission of code ID characters listed in Table 6-3. These code ID characters are not
programmable and are separate from the Transmit Code ID feature. Do not enable the Transmit Code ID feature
for these terminals.
RS-232 Interface 6 - 5
Table 6-3
UPC-A A A A A A A A
UPC-E E C C C E C E
EAN-8/JAN-8 FF B B B FF B FF
EAN-13/JAN-13 F A A A F A F
Code 39 C <len> M M M <len> C <len> M None
Codabar N <len> N N N <len> N <len> N None
Code 128 L <len> K K K <len> L <len> K No ne
I 2 of 5 I <len> I I I <len> I <len> I None
Code 93 None L L L <len> None L None
D 2 of 5 H <len> H H H <len> H <len> H None
UCC/EAN 128 L <len> P P P <len> L <len> P None
MSI None O O O <len> None O None
Terminal Specific Code ID Characters
Wincor-
Code Type ICL
Nixdorf
Mode A
Wincor-
Nixdorf
Mode B
Olivetti Omron
OPOS/
JPOS
Fujitsu
Bookland EAN F A A A F A F
Trioptic None None None None None None None
Code 11 None None None None None None None
IATA H<len> H H None None H None
Code 32 None None None None None None None
Page 84

6 - 6 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
RS-232 Host Types
To select an RS-232 host type, scan one of the following bar codes.
*Standard RS-23 2
ICL RS-232
Wincor-Nixdorf RS-232 Mode A
Wincor-Nixdorf RS-232 Mode B
Olivetti ORS4500
Omron
Page 85

RS-232 Interface 6 - 7
RS-232 Host Types (continued)
OPOS/JPOS
Fujitsu RS-232
Baud Rate
Baud rate is the number of bits of data tran smitted pe r second. Set the scanner’s baud r ate to match th e baud ra te
setting of the host device. Otherwise, data may not reach the host device or may reach it in distorted form.
Baud Rate 600
Baud Rate 1200
Baud Rate 2400
Page 86

6 - 8 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Baud Rate (continued)
Baud Rate 4800
*Baud Rate 9600
Baud Rate 19,200
Baud Rate 38,400
Page 87

RS-232 Interface 6 - 9
Parity
A parity check bit is the most significant bit of each ASCII coded character. Select the parity type according to host
device requirements.
Select Odd parity to set the parity bit value to 0 or 1, based on data, to ensure that an odd number of 1 bits are
contained in the coded character.
Odd
Select Even parity to set the parity bit value to 0 or 1, based on data, to ensure that an even number of 1 bits are
contained in the coded character.
Select Mark parity and the parity bit is always 1.
Even
Mark
Page 88

6 - 10 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Parity (continued)
Select Space pari ty and the parity bit is always 0.
Select None when no parity bit is required.
Space
*None
Check Receive Errors
Select whether or not to check the parity, framing, and overrun of received characters. The pari ty value of received
characters is verified against the parity parameter selected above.
*Check For Received Errors (Enable)
Do Not Check For Received Errors (Disable)
Page 89

RS-232 Interface 6 - 11
Stop Bit Select
The stop bit(s) at the end of each transmitted character marks the end of transmission of one character and
prepares the receiving device for the next character in the serial data stream. The number of stop bits selected
(one or two) depends on the number the receiving terminal is programmed to accommodate. Set the number of
stop bits to match host device requirements.
*1 Stop Bit
2 Stop Bits
Data Bits
This parameter allows the scanner to interface with devices requiring a 7-bit or 8-bit ASCII protocol.
7-Bit
*8-Bit
Page 90

6 - 12 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Hardware Handshaking
The data interface consists of an RS-232 port designed to operate either with or without the ha rdware handshaking
lines, Request to Send (RTS), and Clear to Send (CTS).
If Standard RTS/CTS handshaking is not selected, scan data is transmitted as it becomes available. If Standard
RTS/CTS handshaking is selected, scan data is transmitted according to the following sequence:
•
The scanner reads the CTS line for activity. If CTS is asserted, the scanner waits up to the Host Serial
Response Time-out for the host to de-assert the CTS line. If, after Host Serial Response Time-out (default),
the CTS line is still asserted, the scanner sounds a transmit error, and any scanned data is lost.
•
When the CTS line is de-asserted, the scanner asserts the RTS line and waits up to the Host Serial
Response Time-out for the host to assert CTS. When the host asserts CTS, data is transmitted. If, after Host
Serial Response Time-out (default), the CTS line is still de-asserted, the scanner sounds a transmit error,
and discards the data.
•
When data transmission is complete, the scanner de-asserts RTS 10 msec after sending the last character.
•
The host should respond by de-asserting CTS. The scanner checks for a de-asserted CTS upon the next
transmission of data.
During the transmission of data, the CTS line should be asserted. If CTS is de-asserted for mo re than 50 ms
between characters, the transmission is aborted, the scanner sounds a transmission error, and the data is
discarded.
If this communications sequence fails, the scanner issues an error indication. In th is case, the dat a is lost and m ust
be rescanned.
If Hardware Handshaking and Software Handshaking are both enabled, Hardware Handshaking takes
precedence.
NOTE The DTR signal is jumpered (set) to the active state.
None
Scan the bar code below if no Hardware Handshaking is desired.
*None
Standard RTS/CTS
Scan the bar code below to select Standard RTS/CTS Hardware Handshaking.
Standard RTS/CTS
Page 91

RS-232 Interface 6 - 13
Hardware Handshaking (continued)
RTS/CTS Option 1
When RTS/CTS Option 1 is selected, the scanner asserts RTS before transmitting and ignores the state of CTS.
The scanner de-asserts RTS when the transmission is complete.
RTS/CTS Option 1
RTS/CTS Option 2
When Option 2 is selected, RTS is always high or low (user-programmed logic level). However, the scanner waits
for CTS to be asserted before transmitting data. If CTS is not asserted within Host Serial Response Time-out
(default), the scanner issues an error indication and discards the data.
RTS/CTS Option 2
RTS/CTS Option 3
When Option 3 is selected, the scanner asserts RTS p rior to any dat a transmission, regardless of the st ate of CTS.
The scanner waits up to Host Serial Response Time-out (default) for CTS to be asserted. If CTS is not asserted
during this time, the scanner issues an error indication and discards the data. The scanner de-asserts RTS when
transmission is complete.
RTS/CTS Option 3
Page 92

6 - 14 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Software Handshaking
This parameter offers control of the data transmission process in addition to, or instead of, that offered by hardwa re
handshaking. There are five options.
If Software Handshaking and Hardware Handshaking are both enabled, Hardware Handshaking takes
precedence.
None
When this option is selected, data is transmitted immediately. No response is expected from the host.
ACK/NAK
When this option is selected, after transmitting dat a, the scanner expect s eithe r an ACK or NAK response from the
host. When a NAK is received, the scanner transmits the same data again and waits for either an ACK or NAK.
After three unsuccessful attempts to send data when NAKs are received, the scanner issues an error indication
and discards the data.
*None
The scanner waits up to the programmable Host Serial Response Time-out to receive an ACK or NAK. If the
scanner does not get a response in this time, it issues an error indication and discards the data. There are no
retries when a time-out occurs.
ACK/NAK
Page 93

RS-232 Interface 6 - 15
Software Handshaking (continued)
ENQ
When this option is selected, the scanner waits for an ENQ character from the host before transmitting data. If an
ENQ is not received within the Host Serial Response Time-out, the scanner issues an error indication and discards
the data. The host must transmit an ENQ character at least every Host Serial Response Time-out to prevent
transmission errors.
ENQ
ACK/NAK with ENQ
This combines the two previous options. For re-transmissions of data, due to a NAK from the host, an additional
ENQ is not required.
ACK/NAK with ENQ
XON/XOFF
An XOFF character turns the scanner transmission off unt il the scanne r receives an XON character. There are two
situations for XON/XOFF:
•
XOFF is received before the scanner has data to send. When the scanner has data to send, it waits up to
Host Serial Response Time-out for an XON character before transmission. If the XON is not received within
this time, the scanner issues an error indication and discards the data.
•
XOFF is received during a transmission. Data transmission then stops after sending the current byte. When
the scanner receives an XON character, it sends the rest of the data message. The scanner waits up to 30
seconds for the XON.
XON/XOFF
Page 94

6 - 16 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Host Serial Response Time-out
This parameter specifies how long the scanner waits for an ACK, NAK, or CTS before determining that a
transmission error has occurred. This only applies when in one of the ACK/NAK Software Handshaking modes, or
RTS/CTS Hardware Handshaking option.
NOTE This parameter does not apply to the Wincor-Nixdorf RS-232 Mode A/B and the OPOS/JPOS host types.
*Minimum: 2 sec
Low: 2.5 Sec
Medium: 5 Sec
High: 7.5 Sec
Maximum: 9.9 Sec
Page 95

RS-232 Interface 6 - 17
RTS Line State
This parameter sets the idle state of the Serial Host RTS line. Scan a bar code below to select Low RTS or High
RTS line state.
*Host: Low RTS
Host: High RTS
Beep on <BEL>
Single Point Mode Only
When this parameter is enabled, the scanner issues a beep when a <BEL> character is detected on the RS-232
serial line. <BEL> is issued to indicate an illegal entry or other important event.
NOTE This parameter is not supported in Multipoint mode.
Beep On <BEL> Character
(Enable)
*Do Not Beep On <BEL> Character
(Disable)
Page 96

6 - 18 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Intercharacter Delay
This parameter specifies the intercharacter delay inserted between character transmissions.
*Minimum: 0 msec
Low: 25 msec
Medium: 50 msec
High: 75 msec
Maximum: 99 msec
Page 97

RS-232 Interface 6 - 19
Nixdorf Mode A/B and OPOS/JPOS Beep/LED Options
When Nixdorf Mode A, Nixdorf Mode B, or OPOS/JPOS is selected, this parameter indicates when the scanner
should beep and turn on its LED after a decode.
NOTE The Beep/LED After CTS Pulse option is not valid when Nixdorf Mode A is selected.
*Normal Operation
(Beep/LED Immediately After Decode)
Beep/LED After Transmission
Beep/LED After CTS Pulse
Page 98

6 - 20 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Ignore Unknown Characters
Unknown characters are characters the host does not recognize. When Send Bar Codes with Unknown
Characters is selected, all bar code data is sent except for unknown characte rs, and no erro r be eps sound on the
scanner. When Do Not Send Bar Codes With Unknown Characters is selected, bar code data is sent up to the
first unknown character and then an error beep sounds on the scanner.
*Send Bar Code with Unknown Characters
(Enable)
Do Not Send Bar Codes with Unknown Characters
(Disable)
Page 99

ASCII / Character Set
The values in Table 6-4 can be assigned as prefixes or suffixes for ASCII character data transmission.
RS-232 Interface 6 - 21
Table 6-4
1000 %U NUL
1001 $A SOH
1002 $B STX
1003 $C ETX
1004 $D EOT
1005 $E ENQ
1006 $F ACK
1007 $G BELL
1008 $H BCKSPC
1009 $I HORIZ TAB
1010 $J LF/NW LN
1011 $K VT
1012 $L FF
RS-232 Prefix/Suffix Values
Prefix/Suffix
Value
Full ASCII Code 39
Encode Character
ASCII Character
1013 $M CR/ENTER
1014 $N SO
1015 $O SI
1016 $P DLE
1017 $Q DC1/XON
1018 $R DC2
1019 $S DC3/XOFF
1020 $T DC4
1021 $U NAK
1022 $V SYN
1023 $W ETB
1024 $X CAN
1025 $Y EM
1026 $Z SUB
Page 100

6 - 22 Symbol LS3478 Product Reference Guide
Table 6-4
1027 %A ESC
1028 %B FS
1029 %C GS
1030 %D RS
1031 %E US
1032 Space Space
1033 /A !
1034 /B "
1035 /C #
1036 /D $
1037 /E %
1038 /F &
1039 /G ‘
RS-232 Prefix/Suffix Values (Continued)
Prefix/Suffix
Value
Full ASCII Code 39
Encode Character
ASCII Character
1040 /H (
1041 /I )
1042 /J *
1043 /K +
1044 /L ,
1045 - 1046 . .
1047 /O /
1048 0 0
1049 1 1
1050 2 2
1051 3 3
1052 4 4
1053 5 5
1054 6 6
1057 7 7
1056 8 8
 Loading...
Loading...