Page 1

MCUez HC12 Assembler User's Manual
MCUEZASM12/D
Rev. 1
Easy development software
from the company that
knows MCU hardware best
Page 2

Page 3

MCUEZASM12/D
Rev. 1
MCUez
HC12 Assembler
User’s Manual
NON-DISCLOSURE AGREEMENT REQUIRED
Page 4

User’s Manual
Important Notice to Users
While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of all information
in this document, Motorola assumes no liability to any party for any loss or
damage caused by errors or omissions or by statements of any kind in this
document, its updates,supplements, or special editions, whether such errors
are omissions or statementsresulting from negligence,accident, or any other
cause. Motorola further assumes no liability arising out of the application or
use of any information, product, or system described herein; norany liability
for incidental or consequential damages arising from the use of this
document. Motorola disclaims all warranties regarding the information
containedherein, whether expressed, implied, or statutory, includingimplied
warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. Motorola
makes no representation that the interconnection of products in the manner
described herein will not infringe on existing or future patent rights, nor do
the descriptions contained herein imply the granting or license to make, use
or sell equipment constructed in accordance with this description.
The computer program contains materialcopyrighted by Motorola, Inc., first
published in 1997, and may be used only under a license such as the License
For Computer Programs (Article 14) contained in Motorola’s Terms and
Conditions of Sale, Rev. 1/79.
Trademarks
This document includes these trademarks:
MCUez and MCUasm are trademarks of Motorola, Inc.
Microsoft Windows and Microsoft Developer Studio are registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the U.S. and other countries.
WinEdit is a trademark of Wilson WindowWare.
© Motorola, Inc., and HIWARE AG., 1999; All Rights Reserved
NON-DISCLOSURE AGREEMENT REQUIRED
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
4 MOTOROLA
Page 5

User’s Manual — MCUez HC12 Assembler
Section 1. General Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Section 2. Graphical User Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Section 3. Environment Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Section 4. Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Section 5. Assembler Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
Section 6. Sections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107
List of Sections
Section 7. Assembler Syntax. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .117
Section 8. Assembler Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .159
Section 9. Macros . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .203
Section 10. Assembler Listing File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .209
Section 11. Operating Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .217
Section 12. Assembler Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .243
Appendix A. MASM Compatibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .311
Appendix B. MCUasm Compatibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .315
Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .317
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA List of Sections 5
Page 6

List of Sections
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
6 List of Sections MOTOROLA
Page 7

User’s Manual — MCUez HC12 Assembler
Section 1. General Information
1.1 Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1.3 Structure of This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1.4 Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1.4.1 Creating a New Project . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1.4.2 Creating an Assembly Source File. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
1.4.3 Assembling a Source File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
1.4.4 Linking an Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table of Contents
Section 2. Graphical User Interface
2.1 Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
2.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
2.3 Starting the Motorola Assembler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
2.4 Assembler Graphical Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
2.4.1 Window Title . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
2.4.2 Content Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
2.4.3 Assembler Toolbar. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
2.4.4 Status Bar. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
2.4.5 Assembler Menu Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
2.4.6 File Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
2.4.6.1 Editor Settings Dialog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
2.4.6.2 Save Configuration Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
2.4.6.3 Assembler Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
2.4.7 View Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
2.4.7.1 Option Settings Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Table of Contents 7
Page 8

Table of Contents
2.4.8 Specifying the Input File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
2.4.8.1 Using the Editable Combo Box in the Toolbar. . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
2.4.8.2 Using the Entry File | Assembly ... . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
2.4.8.3 Using Drag and Drop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
2.5 Error Feedback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Section 3. Environment Variables
3.1 Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
3.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
3.3 Paths . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
3.4 Line Continuation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
3.5 Environment Variables Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
3.5.1 ASMOPTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
3.5.2 GENPATH. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
3.5.3 ABSPATH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
3.5.4 OBJPATH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
3.5.5 TEXTPATH. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
3.5.6 SRECORD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
3.5.7 ERRORFILE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
3.5.8 COPYRIGHT: Copyright Entry in Object File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
3.5.9 INCLUDETIME: Create Time in Object File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
3.5.10 USERNAME: User Name in Object File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Section 4. Files
4.1 Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
4.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
4.3 Input Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
4.3.1 Source Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
4.3.2 Include Files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
4.4 Output Files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
4.4.1 Object Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
4.4.2 Absolute Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
4.4.3 Motorola S Files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
8 Table of Contents MOTOROLA
Page 9

Table of Contents
4.4.4 Listing Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
4.4.5 Debug Listing Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
4.4.6 Error Listing Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Section 5. Assembler Options
5.1 Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
5.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
5.3 ASMOPTIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
5.4 Assembler Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
5.4.1 -CI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
5.4.2 -Env . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
5.4.3 -F2 -FA2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
5.4.4 -H . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
5.4.5 -L . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
5.4.6 -Lc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
5.4.7 -Ld . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
5.4.8 -Le . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
5.4.9 -Li. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
5.4.10 -Ms -Mb. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
5.4.11 -MCUasm. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
5.4.12 -N . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
5.4.13 -V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
5.4.14 -W1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
5.4.15 -W2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
5.4.16 -WmsgNe. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
5.4.17 -WmsgNi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
5.4.18 -WmsgNw . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
5.4.19 -WmsgFbv -WmsgFbm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
5.4.20 -WmsgFiv -WmsgFim. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Section 6. Sections
6.1 Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
6.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
6.3 Section Attributes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Table of Contents 9
Page 10

Table of Contents
6.3.1 Code Sections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
6.3.2 Constant Data Sections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
6.3.3 Data Sections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
6.4 Section Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
6.4.1 Absolute Sections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
6.4.2 Relocatable Sections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
6.4.3 Relocatable versus Absolute Section. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
6.4.3.1 Modularity. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
6.4.3.2 Multiple Developers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
6.4.3.3 Early Development . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
6.4.3.4 Enhanced Portability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
6.4.3.5 Tracking Overlaps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
6.4.3.6 Reusability. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Section 7. Assembler Syntax
7.1 Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
7.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
7.3 Comment Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
7.4 Source Line. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
7.4.1 Label Field . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
7.4.2 Operation Field . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
7.4.2.1 Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
7.4.2.2 Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
7.4.2.3 Macro Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
7.4.3 Operand Fields. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
7.4.3.1 Inherent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
7.4.3.2 Immediate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
7.4.3.3 Direct. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
7.4.3.4 Extended . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
7.4.3.5 Relative . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
7.4.3.6 Indexed, 5-Bit Offset. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
7.4.3.7 Indexed, 9-Bit Offset. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
7.4.3.8 Indexed, 16-Bit Offset. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
7.4.3.9 Indexed, Indirect 16-Bit Offset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
7.4.3.10 Indexed, Pre-Decrement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
10 Table of Contents MOTOROLA
Page 11

Table of Contents
7.4.3.11 Indexed, Pre-Increment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
7.4.3.12 Indexed, Post-Decrement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
7.4.3.13 Indexed, Post-Increment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
7.4.3.14 Indexed, Accumulator Offset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
7.4.3.15 Indexed-Indirect, D Accumulator Offset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
7.4.3.16 Indexed PC versus Indexed PC Relative
Addressing Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
7.4.4 Comment Field. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
7.5 Symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
7.5.1 User-Defined Symbols. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
7.5.2 External Symbols. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
7.5.3 Undefined Symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
7.5.4 Reserved Symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
7.6 Constants. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
7.6.1 Integer Constants . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
7.6.2 String Constants. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
7.6.3 Floating-Point Constants . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
7.7 Operators. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
7.7.1 Addition and Subtraction Operators (Binary) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
7.7.2 Multiplication, Division, and Modulo Operators (Binary) . . . . . 149
7.7.3 Sign Operators (Unary) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
7.7.4 Shift Operators (Binary). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
7.7.5 Bitwise Operators (Binary) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
7.7.6 Bitwise Operators (Unary). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
7.7.7 Logical Operators (Unary). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
7.7.8 Relational Operators (Binary) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
7.7.9 Memory PAGE Operator (Unary) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
7.7.10 Force Operator (Unary) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
7.8 Expressions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
7.8.1 Absolute Expressions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
7.8.2 Simple Relocatable Expression . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
7.9 Translation Limits. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Table of Contents 11
Page 12

Table of Contents
Section 8. Assembler Directives
8.1 Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
8.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
8.2.1 Section Definition Directives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
8.2.2 Constant Definition Directives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
8.2.3 Data Allocation Directives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
8.2.4 Symbol Linkage Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
8.2.5 Assembly Control Directives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
8.2.6 Listing File Control Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
8.2.7 Macro Control Directives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
8.2.8 Conditional Assembly Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
8.3 ABSENTRY — Application Entry Point. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
8.4 ALIGN — Align Location Counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
8.5 BASE — Set Number Base . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
8.6 CLIST — List Conditional Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
8.7 DC — Define Constant. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
8.8 DCB — Define Constant Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
8.9 DS — Define Space . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
8.10 ELSE — Conditional Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
8.11 END — End Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
8.12 ENDIF — End Conditional Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
8.13 ENDM — End Macro Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
8.14 EQU — Equate Symbol Value. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
8.15 EVEN — Force Word Alignment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
8.16 FAIL — Generate Error Message. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
8.17 IF — Conditional Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
8.18 IFCC — Conditional Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
8.19 INCLUDE — Include Text from Another File. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
12 Table of Contents MOTOROLA
Page 13

Table of Contents
8.20 LIST — Enable Listing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
8.21 LLEN — Set Line Length. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
8.22 LONGEVEN — Forcing Longword Alignment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
8.23 MACRO — Begin Macro Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
8.24 MEXIT — Terminate Macro Expansion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
8.25 MLIST — List Macro Expansions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
8.26 NOLIST — Disable Listing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
8.27 NOPAGE — Disable Paging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
8.28 ORG — Set Location Counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
8.29 OFFSET — Create Absolute Symbols. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
8.30 PAGE — Insert Page Break . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
8.31 PLEN — Set Page Length . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
8.32 SECTION — Declare Relocatable Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
8.33 SET — Set Symbol Value . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
8.34 SPC — Insert Blank Lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
8.35 TABS — Set Tab Length . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
8.36 TITLE — Provide Listing Title . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
8.37 XDEF — External Symbol Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
8.38 XREF — External Symbol Reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Section 9. Macros
9.1 Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
9.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
9.3 Macro Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
9.4 Defining a Macro . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
9.5 Calling Macros . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Table of Contents 13
Page 14

Table of Contents
9.6 Macro Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
9.7 Labels Inside Macros . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
9.8 Macro Expansion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
9.9 Nested Macros . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 208
Section 10. Assembler Listing File
10.1 Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
10.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
10.3 Page Header . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
10.4 Source Listing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
10.4.1 Absolute (Abs.) Listing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
10.4.2 Relative (Rel.) Listing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
10.4.3 Location (Loc.) Listing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 213
10.4.4 Object (Obj.) Code Listing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
10.4.5 Source Line Listing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
Section 11. Operating Procedures
11.1 Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
11.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
11.2.1 Working with Absolute Sections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
11.2.2 Defining Absolute Sections in the Assembly Source File. . . . . . 218
11.2.3 Linking an Application Containing Absolute Sections . . . . . . . . 219
11.3 Working with Relocatable Sections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
11.3.1 Defining Relocatable Sections in the Assembly Source File. . . . 221
11.3.2 Linking an Application Containing Relocatable Sections. . . . . . 222
11.4 Initializing the Vector Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 224
11.4.1 Initializing the Vector Table in the Linker PRM File . . . . . . . . . 224
11.4.2 Initializing Vector Table in Assembly Source Files
Using a Relocatable Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
11.4.3 Initializing the Vector Table in the Assembly Source File
Using an Absolute Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 228
11.5 Splitting an Application into Different Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 231
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
14 Table of Contents MOTOROLA
Page 15

Table of Contents
11.6 Using Direct Addressing Mode to Access Symbols. . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
11.6.1 Using Direct Addressing Mode to Access
External Symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
11.6.2 Using Direct Addressing Mode to Access
Exported Symbols. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
11.6.3 Defining Symbols in the Direct Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
11.6.4 Using a Force Operator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
11.6.5 Using SHORT Sections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
11.7 Directly Generating an .abs File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
11.7.1 Assembler Source File. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236
11.7.2 Assembling and Generating the Application. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
Section 12. Assembler Messages
12.1 Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
12.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
12.2.1 Warning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
12.2.2 Error. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
12.2.3 Fatal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246
12.3 Message Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246
12.3.1 A1000: Conditional Directive not Closed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
12.3.2 A1001: Conditional Else not Allowed Here . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 248
12.3.3 A1051: Zero Division in Expression . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249
12.3.4 A1052: Right Parenthesis Expected. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249
12.3.5 A1053: Left Parenthesis Expected. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250
12.3.6 A1054: References on Non-Absolute Objects Are not Allowed
When Options -FA1 or -FA2 Are Enabled. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 251
12.3.7 A1101: Illegal Label: Label is Reserved . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 252
12.3.8 A1103: Illegal Redefinition of Label. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 253
12.3.9 A1104: Undeclared User-Defined Symbol <symbolName>. . . . 254
12.3.10 A1201:Label <labelName> Referenced in Directive
ABSENTRY is not Defined in Code Segment . . . . . . . . . . . . 255
12.3.11 A2301: Label is Missing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256
12.3.12 A2302: Macro Name is Missing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256
12.3.13 A2303: ENDM is Illegal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 257
12.3.14 A2304: Macro Definition Within Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 258
12.3.15 A2305: Illegal Redefinition of Instruction or Directive Name . . 259
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Table of Contents 15
Page 16

Table of Contents
12.3.16 A2306: Macro not Closed at End of Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260
12.3.17 A2307: Macro Redefinition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261
12.3.18 A2308: Filename Expected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 262
12.3.19 A2309: File not Found . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 262
12.3.20 A2310: Illegal Size Character . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 263
12.3.21 A2311: Symbol Name Expected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
12.3.22 A2312: String Expected. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
12.3.23 A2313: Nesting of Include Files Exceeds 50. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 265
12.3.24 A2314: Expression Must Be Absolute. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 265
12.3.25 A2316: Section Name Required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 266
12.3.26 A2317: Illegal Redefinition of Section Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 267
12.3.27 A2318: Section not Declared . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 268
12.3.28 A2320: Value too Small. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 269
12.3.29 A2321: Value too Big . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 270
12.3.30 A2323: Label is Ignored . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 271
12.3.31 A2324: Illegal Base (2, 8, 10, 16) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 272
12.3.32 A2325: Comma or Line End Expected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
12.3.33 A2326: Label is Redefined . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 274
12.3.34 A2327: ON or OFF Expected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 275
12.3.35 A2328: Value is Truncated . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 275
12.3.36 A2329: FAIL Found. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 276
12.3.37 A2330: String is not Allowed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 277
12.3.38 A2332: FAIL Found. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 278
12.3.39 A2333: Forward Reference not Allowed. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 279
12.3.40 A2334: Only Labels Defined in the Current Assembly Unit
Can Be Referenced in an EQU Expression. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 280
12.3.41 A2335: Exported Absolute SET Label is not Supported . . . . . . . 281
12.3.42 A2336: Value too Big . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
12.3.43 A2338: <Message String> . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 283
12.3.44 A2341: Relocatable Section not Allowed: Absolute File
is Currently Directly Generated . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 284
12.3.45 A12001: Illegal Addressing Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 285
12.3.46 A12002: Complex Relocatable Expression not Supported . . . . . 286
12.3.47 A12003: Value is Truncated to One Byte . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 287
12.3.48 A12005: Value Must Be Between 1 and 8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 288
12.3.49 A12007: Comma Expected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 288
12.3.50 A12008: Relative Branch with Illegal Target . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 289
12.3.51 A12009: Illegal Expression . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 290
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
16 Table of Contents MOTOROLA
Page 17

Table of Contents
12.3.52 A12010: Register Expected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
12.3.53 A12011: Size Specification Expected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 292
12.3.54 A12102: Page Value Expected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 293
12.3.55 A12103: Operand not Allowed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 294
12.3.56 A12104: Immediate Value Expected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 295
12.3.57 A12105: Immediate Address Mode not Allowed . . . . . . . . . . . . 296
12.3.58 A12107: Illegal Size Specification for HC12 Instruction . . . . . . 297
12.3.59 A12109: Illegal Character at the End of Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 298
12.3.60 A12110: No Operand Expected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 299
12.3.61 A12201: Lexical Error in First or Second Field . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300
12.3.62 A12202: Not an HC12 Instruction or Directive. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 301
12.3.63 A12203: Reserved Identifiers not Allowed
as Instruction or Directive. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 301
12.3.64 A12401: Value Out of Range –128...127. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 302
12.3.65 A12402: Value Out of Range –32,768...32,767. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304
12.3.66 A12403: Value Out of Range –256...255. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 305
12.3.67 A12405: PAGE with Initialized RAM not Supported . . . . . . . . . 307
12.3.68 A12408: Code Size Per Section Is Limited to 32 Kbytes . . . . . . 308
12.3.69 A12409: In PC Relative Addressing Mode,
References to Object Located in Another Section
or File Only Allowed for IDX2 Addressing Mode. . . . . . . . . 309
12.3.70 A12411: Restriction: Label Specified in a DBNE, DBEQ,
IBNE, IBEQ, TBNE, or TBEQ Instruction Should
Be Defined in the Same Section They Are Used . . . . . . . . . . 310
Appendix A. MASM Compatibility
A.1 Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 311
A.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 311
A.3 Comment Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 311
A.4 Constants. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 311
A.5 Operators. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 312
A.6 Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 313
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Table of Contents 17
Page 18

Table of Contents
Appendix B. MCUasm Compatibility
B.1 Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315
B.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315
B.3 Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315
B.4 Set Directive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 316
B.5 Obsolete Directives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 316
Index
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 317
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
18 Table of Contents MOTOROLA
Page 19

User’s Manual — MCUez HC12 Assembler
Figure Title Page
1-1 MCUez Shell. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1-2 Environment Configuration Dialog Box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1-3 Working Project Directory Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
1-4 New Configuration Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
1-5 Assembler Window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
1-6 Options Settings Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
1-7 Selecting an Object File Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
1-8 Assembling a File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
1-9 Linker Window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
1-10 Link Process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
List of Figures
2-1 Tip of the Day Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
2-2 Assembler Window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
2-3 Assembler Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
2-4 Assembler Status Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
2-5 Starting the Global Editor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
2-6 Starting the Local Editor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
2-7 Starting the Editor with the Command Line. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
2-8 Starting the Editor with DDE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
2-9 Save Configuration Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
4-1 Assembler Structural Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
6-1 Absolute Section Programming Example. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
6-2 PRM File Example Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
6-3 Relocatable Section Programming Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
6-4 Defining One RAM and One ROM Area. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
6-5 Defining Multiple RAM and ROM Areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA List of Figures 19
Page 20

List of Figures
Figure Title Page
7-1 Relocatable Symbols Program Example. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
7-2 Set or EQU Directive Program Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
7-3 External Symbol Program Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
7-4 Undefined Symbol Example. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
11-1 Starting the MCUez Assembler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
11-2 Options Setting Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
11-3 Selecting the Object File Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
11-4 Generating an .abs File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
20 List of Figures MOTOROLA
Page 21

User’s Manual — MCUez HC12 Assembler
Table Title Page
2-1 Menu Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
2-2 Assembler Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
2-3 Advanced Options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
3-1 Environment Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
5-1 Assembler Option Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
5-2 Scope of Each Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
5-3 Assembler Option Details. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
7-1 ExecuInstructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
7-2 Addressing Mode Notations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
7-3 Operator Precedence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
7-4 Expression — Operator Relationship (Unary) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
7-5 Expression — Operator Relationship (Binary). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
List of Tables
8-1 Section Directives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
8-2 Constant Directives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
8-3 Data Allocation Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
8-4 Symbol Linkage Directives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
8-5 Assembly Control Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
8-6 Assembler List File Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
8-7 Macro Directives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
8-8 Conditional Assembly Directives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
8-9 Conditional Types. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
A-1 Operators. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 312
A-2 Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 313
B-1 Obsolete Directives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 316
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA List of Tables 21
Page 22

List of Tables
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
22 List of Tables MOTOROLA
Page 23

User’s Manual — MCUez HC12 Assembler
Section 1. General Information
1.1 Contents
1.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1.3 Structure of This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1.4 Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1.4.1 Creating a New Project . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1.4.2 Creating an Assembly Source File. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
1.4.3 Assembling a Source File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
1.4.4 Linking an Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
1.2 Introduction
Features of the MCUez HC12 assembler include:
• Graphical user interface (GUI)
• Online help
• Support for absolute and relocatable assembler code
• 32-bit application
• Compatible with MCUasm Release 5.3
• Conforms to Motorola assembly language input standard and
ELF/DWARF 2.0 object code format
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA General Information 23
Page 24

General Information
1.3 Structure of This Manual
This list describes the topics contained in this manual.
• Graphical user interface — Description of the MCUez assembler GUI
• Environment — Description of the MCUez assembler environment
variables
• Assembler options — Detailed description of the full set of assembler
options
• Assembler syntax — Description of the assembler input file syntax
• Assembler directives — List of all directives supported by the
assembler
• Assembler messages — Description and examples produced by the
assembler
1.4 Getting Started
NOTE:
• Appendices
• Index
This section describes how to get started using MCUez. The locations of
specific working directories and the directories reflected in dialog window
reflect the directories that have been chosen.
This section provides instructions to:
• Create a new project
• Write the assembly source file
• Assemble the assembly source file
• Link the application to generate an executable file
All directory paths and listings are examples only. Paths and directory listings
may change depending upon the MCUez configuration.
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
24 General Information MOTOROLA
Page 25

1.4.1 Creating a New Project
The first step in creating an application is to define the new project. Do this by
using the MCUez Shell.
1. Start the MCUez Shell.
2. Click on the ezMCU button to open the Configuration dialog box.
General Information
Getting Started
Figure 1-1. MCUez Shell
Figure 1-2. Environment Configuration Dialog Box
3. Click on the New button to open the Project Directory dialog box.
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA General Information 25
Page 26

General Information
4. Enter the path for thenew project in the editbox. For example, substitute
C:\MCUEZ\MCuez12\DEMO\WMMDS12A with
C:\MCUEZ\MCUez12\DEMO\mydir as the example shows in
Figure 1-3.
Figure 1-3. Working Project Directory Dialog Box
NOTE:
The specified directory must be accessible from a PC.
5. Click on the OK button to close the Project Directory dialog box. The
New Configuration dialog box will then appear.
6. Define the editor to use with the project. Select the Editor tab. Select an
editor from the Editor drop down box. In the Executable command line,
enter the path and command used to start the editor.
For example:
C:\MCUEZ\MCUez12\Prog\Motpad.EXE
The command also can be selected by using the Browse... button.
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
26 General Information MOTOROLA
Page 27

General Information
Getting Started
Figure 1-4. New Configuration Dialog Box
7. Click on the OK button in the New Configuration dialog box to create
the MCUez configuration files in the specified project directory.
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA General Information 27
Page 28

General Information
1.4.2 Creating an Assembly Source File
Once the project has been configured, writing the application can begin. For
example, source code may be stored in a file named test.asm and may look as
like this:
initStk: EQU $AFE ; Initial value for SP
dataSec: SECTION ; Define a section
var1: DC.W 5 ; Assign 5 to the symbol var1
codeSec: SECTION ; Define a section for code
entry:
LDS #initStk ; Load stack pointer
LDD var1
BRA entry
When writing assembly source code, pay special attention to these points:
XDEF entry ; Make the symbol entry visible for
; external module.
; This is necessary to allow the
; linker to find the symbol and
; use it as the entry point for
; the application.
• All symbols referenced outside the current source file (in another source
file or in the linker configuration file) must be visible externally. Forthis
reason, the assembly directive XDEF entry has been inserted.
• To make debugging from the application easier, defining separate
sections for code, constant data (defined with DC (define constant)), and
variables (defined with DS (define space)) are strongly recommended.
This enables the symbols located in the variable or constant data sections
to be displayed in the data window component of the debugger.
• The stack pointer must be initialized when using BSR (branch to
subroutine) or JSR (jump to subroutine) instructions in an application.
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
28 General Information MOTOROLA
Page 29

1.4.3 Assembling a Source File
This procedure describes how to assemble a source file.
1. Start the assembler by clicking on the ezASM button in the MCUez
Shell. Enter the name of the file to be assembled in the editable combo
box, as shown in Figure 1-5.
General Information
Getting Started
Figure 1-5. Assembler Window
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA General Information 29
Page 30

General Information
2. Select the menu entry Assembler | Options to generate anELF/DWARF
2.0 object file. The Options Settings dialog is displayed as shown in
Figure 1-6.
Figure 1-6. Options Settings Dialog Box
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
30 General Information MOTOROLA
Page 31

General Information
Getting Started
3. In the Output folder, select the check box in front of the label Object
FileFormatshownin Figure1-7. Select the radio button ELF/DWARF
2.0 Object File Format and click OK.
Figure 1-7. Selecting an Object File Format
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA General Information 31
Page 32

General Information
4. The file is assembled, as shown in Figure 1-8, when the Assemble
button is clicked.
Figure 1-8. Assembling a File
The macro assembler indicates a successful assembler session by printing the
number of generated bytes of code. The message Code size: 10 indicates that
test.asm was assembled withouterrors. The macro assemblergenerates a binary
object file anda debug listing file for each source file.The binary object file has
the same name as the input module with an extension of .o. The debug listing
file has the same name as the input module, with an extension of .dbg.
When the assembly option -L is specified on the command line, the macro
assembler generates a list file containing the source instruction and
corresponding hexadecimal code.
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
32 General Information MOTOROLA
Page 33

General Information
Getting Started
The list file generated by the macro assembler looks like this:
Motorola HC12-Assembler
(c) COPYRIGHT MOTOROLA 1991-1997
Abs. Rel. Loc. Obj. code Source line
---- ---- ------ --------- ----------1 1 XDEF entry
...
4 4 0000 0AFE initStk: EQU $AFE ; SP Init
; value
5 5 dataSec: SECTION ;
6 6 000000 0005 var1: DC.W 5 ; Assign 5 to
; var1
77
8 codeSec: SECTION ;
9 9 entry:
10 10 000000 CF 0AFE LDS #initStk ; Load stack
11 11 000003 FC xxxx LDD var1
12 12 000006 20F8 BRA entry
1.4.4 Linking an Application
Once the object file is available, the application can be linked. The linker will
organize code and data sections according to the linker parameter file. Follow
this procedure to link an application:
1. Starttheeditor and create the linker parameter file. Copy thefilefibo.prm
to test.prm.
2. In the file test.prm, change the name of the executable and object files to
test.
3. Additionally, modify the start and end addresses for the ROM and RAM
memory areas.
The test.prm module appears like this:
LINK test.abs /* Name of the executable file generated.*/
NAMES test.o END /*Name of the object files in the application*/
SEGMENTS
MY_ROM = READ_ONLY 0x800 TO 0x8FF; /*READ_ONLY memory area */
MY_RAM = READ_WRITE 0xB00 TO 0xBFF; /*READ_WRITE memory area */
END
PLACEMENT
.data INTO MY_RAM; /* Variables should be allocated in MY_RAM */
.text INTO MY_ROM; /* Code should be allocated in MY_ROM */
END
INIT entry /* entry is the entry point to the application */
VECTOR ADDRESS 0xFFFE entry /* Initialization for Reset vector */
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA General Information 33
Page 34

General Information
NOTE:
The commands in thelinker parameter file aredescribed in detail inthe MCUez
Linker User’s Manual, Motorola document order number MCUEZLNK/D.
4. Click the eZLink button in the MCUez Shell. The linker is started as
shown in Figure 1-9.
5. Enter the nameof the file to be linked in the editable combo box. To start
linking, press the Enter key or click on the Link button.
Link
Button
Figure 1-9. Linker Window
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
34 General Information MOTOROLA
Page 35

General Information
Getting Started
Once the linker is started, the linker window displays the link process as shown
in Figure 1-10.
Figure 1-10. Link Process
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA General Information 35
Page 36

General Information
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
36 General Information MOTOROLA
Page 37

User’s Manual — MCUez HC12 Assembler
Section 2. Graphical User Interface
2.1 Contents
2.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
2.3 Starting the Assembler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
2.4 Assembler Graphical Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
2.4.1 Window Title . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
2.4.2 Content Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
2.4.3 Assembler Toolbar. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
2.4.4 Status Bar. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
2.4.5 Assembler Menu Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
2.4.6 File Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
2.4.6.1 Editor Settings Dialog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
2.4.6.2 Save Configuration Dialog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
2.4.6.3 Assembler Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
2.4.7 View Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
2.4.7.1 Option Settings Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
2.4.8 Specifying the Input File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
2.4.8.1 Using the Editable Combo Box in the Toolbar. . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
2.4.8.2 Using the Entry File | Assembly ... . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
2.4.8.3 Using Drag and Drop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
2.5 Error Feedback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
2.2 Introduction
The MCUez HC12 assembler uses a Microsoft Windowsapplication, which
is a graphical user interface (GUI).
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Graphical User Interface 37
Page 38

Graphical User Interface
2.3 Starting the Motorola Assembler
Start the assembler from the MCUez Shell by clicking on the ezASM icon in
the toolbar.
When the assembler is started, a standard Tip of the Day window, containing
tips about the assembler, is displayed.
Figure 2-1. Tip of the Day Window
Click Next Tip to see the next piece of information about the assembler. Click
Close to close the Tip of the Day dialog.
To bypass the standard Tip of the Day window when the assembler is started,
uncheck Show Tips on StartUp.
To re-enable the tips window, choose the Help|Tip of the Day ... menu option.
The Tip of the Day dialog will open. Then select Show Tips on StartUp.
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
38 Graphical User Interface MOTOROLA
Page 39

2.4 Assembler Graphical Interface
If the assembler was started without specifying a filename, the window in
Figure 2-2 is displayed. The assembler window provides a window title, menu
bar, toolbar, content area, and status bar.
Graphical User Interface
Assembler Graphical Interface
Menu Bar
Toolbar
Content
Area
2.4.1 Window Title
Status Bar
Figure 2-2. Assembler Window
The window title displays the assembler name and project name. If no project
is currently loaded, Default Configuration is displayed. An * (asterisk) after
the project name indicates that some values have been changed. The * indicates
changes in options, editor configuration, or appearance (window position, size,
font, etc.).
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Graphical User Interface 39
Page 40

Graphical User Interface
2.4.2 Content Area
The content area displays logging information about the assembly session and
consists of:
• Name of file being assembled
• Complete path and name of files processed (main assembly file and all
• List of error, warning, and information messages
• Size of code generated during the assembly session
If a filename is dragged and dropped into the content area, the file is either
loaded as a configuration file or is assembled. It is loaded as a configuration file
if the file hasa .ini extension. Ifnot, the file is assembled with thecurrent option
settings. (See 2.4.8 Specifying the Input File.)
included files)
Assembly information in the content area includes:
• Files created or modified
• Location within file where errors occurred
• A message number
Some files listedin the content area can be opened inthe editor specified during
project configuration. Double click on a filename to open an editable file or
select a line that contains a filename and click the right mouse button to display
a menu that contains an Open ... entry (if file is editable).
A message number is displayed with message output. From this output, there
are three ways to open the corresponding help information.
1. Select one line of the message and press F1. Help for the associated
message number is displayed. If the selected line does not have a
message number, the main help is displayed.
2. PressShift-F1and then click on the message text.Ifthereisno associated
message number, the main help is displayed.
3. Click the right mouse button on the message text and select Help on ....
This menu entry is available only if a message number is available.
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
40 Graphical User Interface MOTOROLA
Page 41

After an assembly session has completed, error feedback can be performed
automatically by double clickingon the messagein the content area. The source
file containing the error or warning message will open to the line containing the
problem.
2.4.3 Assembler Toolbar
Figure 2-3 illustrates the assembler toolbar.
Graphical User Interface
Assembler Graphical Interface
Displays Program Help Information
Saves the Current Configuration
Loads a Configuration
New Configuration
Command Line (Editable Combo Box)
Context Help
Assemble
Option Settings
Stop Current Assembly
Figure 2-3. Assembler Toolbar
The three buttons on the left correspond with entries in the File menu. The New
Configuration, Load Configuration, and SaveConfiguration buttons enable
the user to reset, load, and save configuration files for the assembler.
The Help and Context Help buttons open the help file or use the
context-sensitive help feature.
Press the Context Help button to change the mouse cursor to a question mark
and arrow. Then click on an item within the application to display help
information. Help is available for menus, toolbar buttons, and window areas.
The command line box contains a drop down list of the last commands
executed. Once a command line has been selected or entered in the combo box,
click the Assemble button to execute the command.
The Options Setting button opens the Options Setting dialog box.
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Graphical User Interface 41
Page 42

Graphical User Interface
2.4.4 Status Bar
Figure 2-4 shows the assembler status bar.
Message Area
Point to a menu entry or button in the toolbar to display a brief explanation in
the message area.
2.4.5 Assembler Menu Bar
The entries in Table 2-1 are available in the Menu Bar.
Menu entry Description
File Assembler configuration file management
Assembler Assembler option settings
View Assembler window settings
Help Standard windows help menu
Current Time
Figure 2-4. Assembler Status Bar
Table 2-1. Menu Bar
2.4.6 File Menu
An assembler configuration file typically contains the following information:
• Assembler option settings specified in the assembler dialog boxes
• Last command line executed and current command line
• Window position, size, and font
• Editor associated with the assembler
• Tip of the Day settings
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
42 Graphical User Interface MOTOROLA
Page 43

Graphical User Interface
Assembler Graphical Interface
Assembler configuration information is stored in the specified configuration
file. As many configuration filesas required for a projectcan be defined. Switch
to different configuration files by selecting File|Load Configuration and
File|Save Configuration, or by clicking the corresponding toolbar buttons.
For instance:
• Choose File|Assemble to open a standard Open File dialog box
. A list
of all .asm files in the project directory is displayed. Select an input file.
Click OK to close the dialog box and assemble the selected file.
• Choose File|New/Default Configuration to reset assembler options to
the default values. Default values are specified in the section titled
Command Line Options.
• Choose File|Load Configuration to open a standard Open File dialog
box. A list of all .ini files in the project directory is displayed. Select a
configuration file to be used by subsequent assembly sessions.
• Choose File|Save Configuration to store the current settings in the
configuration file specified in the title bar.
• ChooseFile|SaveConfigurationas ... to open a standardSaveAsdialog
box and display the list of all .ini files in the project directory. Specify
the name and location of the configuration file. Click OK to save the
current settings in the specified configuration file.
• Choose File|Configuration ... to open the Configuration dialog box.
Specify an editor and related information to be used for error feedback,
then save the configuration.
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Graphical User Interface 43
Page 44

Graphical User Interface
2.4.6.1 Editor Settings Dialog
This dialog box has several radio buttons for selecting a type of editor.
Depending on the type selected, the content below it changes.
These are the main entries:
• Global Editor (Configured by the Shell)
Figure 2-5. Starting the Global Editor
This entry is enabled only when an editor is defined in the [Editor] section of
the global initialization file mcutools.ini.
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
44 Graphical User Interface MOTOROLA
Page 45
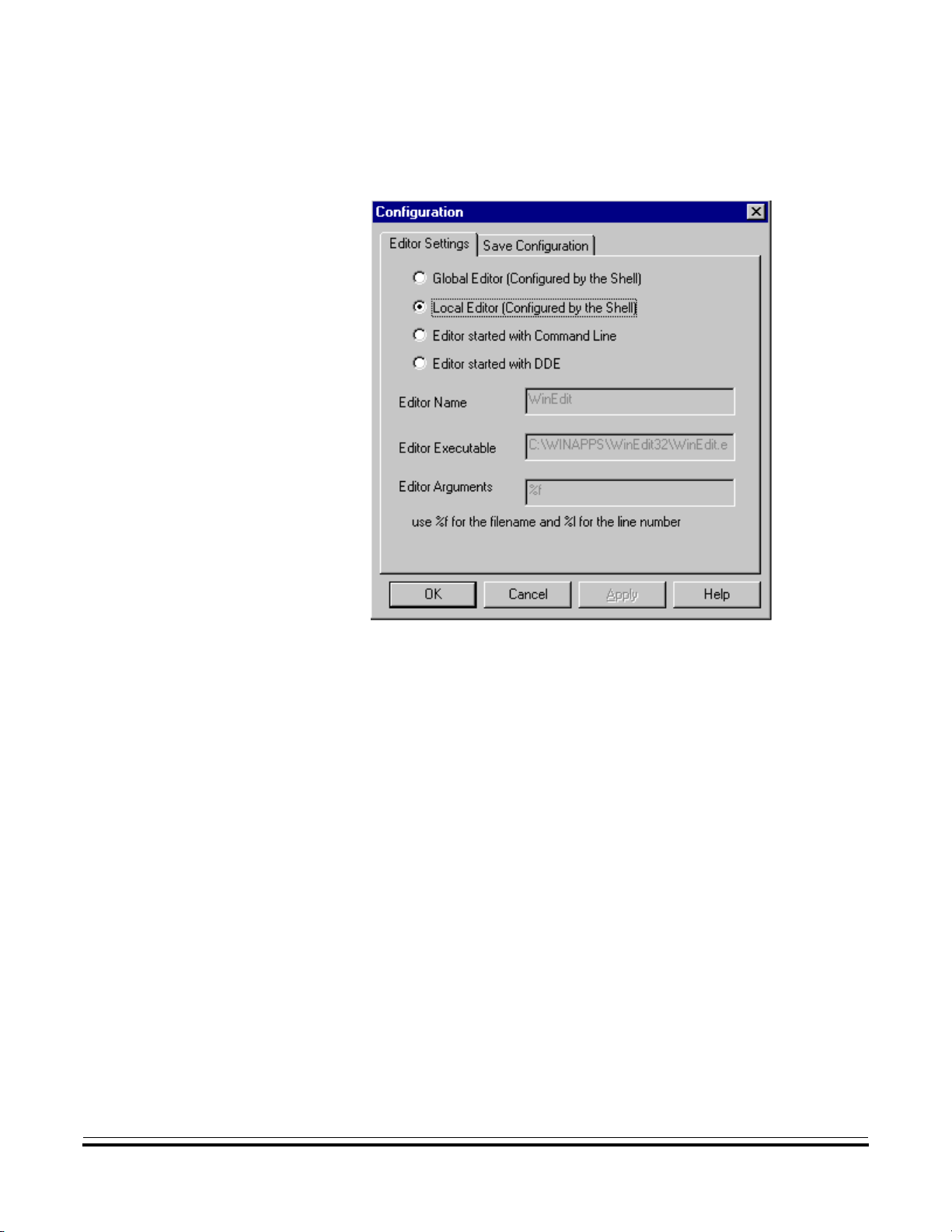
• Local Editor (Configured by the Shell)
Graphical User Interface
Assembler Graphical Interface
Figure 2-6. Starting the Local Editor
This entry is only enabled if an editor is defined in the local configuration file,
usually project.ini in the project directory.
The Global Editor and Local Editor settings cannot be edited within this
dialog box, since they are read only. These entries can be configured with the
MCUez Shell application.
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Graphical User Interface 45
Page 46

Graphical User Interface
• Editor started with Command Line
Figure 2-7. Starting the Editor with the Command Line
When this editor type is selected, a separate editor is associated with the
assembler for error feedback. Theeditor configured in the shell will notbe used
for error feedback. Enter the appropriate path and command name to start the
editor. Command modifiers are specified on the command line.
Example:
For WinEdit 32-bit version
C:\WinEdit32\WinEdit.exe %f /#:%l
For Write
C:\Winnt\System32\Write.exe %f
Write does not support line number modifier.
For Motpad
C:\TOOLS\MOTPAD\MOTPAD.exe %f::%l
Motpad supports line numbers.
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
46 Graphical User Interface MOTOROLA
Page 47

• Editor started with DDE
Graphical User Interface
Assembler Graphical Interface
Figure 2-8. Starting the Editor with DDE
Enter the service, topic, and client name to be used for a DDE connection to the
editor. All entries can have modifiers forfilename and linenumber as explained
in the next example.
Example: For Microsoft Developer Studio
Service Name : "msdev"
Topic Name : "system"
ClientCommand : "[open(%f)]"
, use this setting:
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Graphical User Interface 47
Page 48

Graphical User Interface
• Modifiers
The editor format depends on the command syntax used to start the editor.
Check the editor manual for modifiers that can be used to define the editor
command line.
When either entry Editor Started with the Command line or Editor
started with DDE is selected, the configuration may contain modifiers
to identify which file to open and which line to select.
– The %f modifier refers to the name of the file (including path) where
the error has been detected.
– The %l modifier refers to the line number where the message has
been detected.
NOTE:
NOTE:
Be cautious whenusing the%lmodifier. This modifiercan be used only with an
editor that can be started with a line number as a parameter. Editors such as
WinEdit version 3.1 or lower and Notepad do not allow this kind of parameter.
When using a word processing editor, such as Microsoft Word or Wordpad,
make sure to save the input file as an ASCII text file; otherwise, the assembler
will have trouble processing the file.
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
48 Graphical User Interface MOTOROLA
Page 49

2.4.6.2 Save Configuration Dialog
Figure 2-9 shows the Save Configuration dialog box.
Graphical User Interface
Assembler Graphical Interface
Figure 2-9. Save Configuration Dialog Box
The second page of the configuration dialog consists of save operations. In the
SaveConfiguration dialog, select attributesto be stored intheproject file. This
dialog box provides the following configurations:
• Options — When set, the current option settings are stored in the
configuration file. Disable this option to retain the last saved options.
• Editor configuration — When set, the current editor settings are stored
in the configuration file. Disable this option to retain the last saved
options.
• Appearance—Whenset, the current application appearance, such asthe
window position (only loaded at startup time) and the command line
content and history, is saved. Disable to keep previous settings.
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Graphical User Interface 49
Page 50

Graphical User Interface
• Save on exit — If this option is set, the assembler will save the
configuration on exit. No prompt will appear to confirm this operation.
If this option is not set, the assembler will ignore any changes.
NOTE:
Almost all settings are stored in the configuration file. Exceptions are the
recently used configuration listandall settings in thisdialog. These settings are
stored in the assembler section of the mcutools.ini file.
Assembler configurations can coexist in the same file used for the project
configuration (defined by the shell application) along with other MCUez tool
specifications. When an editor is configured by the shell, the assembler can
read this information from the project file, if present. The project configuration
file created by the shell is named project.ini. Therefore, this filename is also
suggested (but not mandatory) to the assembler.
2.4.6.3 Assembler Menu
Table 2-2 depicts the Assembler menu that allows customization of the
assembler and setting or resetting of assembler options.
Table 2-2. Assembler Menu
Item Description
Options
Allows defining of the options to be activated when assembling
an input file
2.4.7 View Menu
This menu enables customization of the assembler window. For instance,
whether the status baror toolbar will bedisplayed or hidden canbe defined. The
user also can define the font used in the window or clear the window.
• Choose View|Tool Bar to switch on/off the assembler window toolbar.
• Choose View|Status Bar to switch on/off the assembler window status
bar.
• Choose View|Log ... to customize the output in the assembler window
content area.
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
50 Graphical User Interface MOTOROLA
Page 51

• Choose View|Log ...|Change Font to open a standard Font Selection
dialog box. Options selected in this dialog are applied to the assembler
window content area.
• Choose View|Log ...|Clear Log to clear the assembler window content
area.
2.4.7.1 Option Settings Dialog Box
This dialog box enables the user to set/reset assembler options, as shown in
Figure 2-10.
Graphical User Interface
Assembler Graphical Interface
Figure 2-10. Option Settings Dialog Box
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Graphical User Interface 51
Page 52

Graphical User Interface
Available options are arranged in different groups as shown in Table 2-3.
Option Group Description
Table 2-3. Advanced Options
NOTE:
Output
Input Lists options related to the input file
Host Lists options related to the host
Code
Generation
Messages Lists options controlling the generation of error messages
Lists options related to the output files generated
(type of files to be generated)
Lists options related to code generation
(memory models, ...)
An assembly option is set when the corresponding check box is checked. To
obtain more information about a specific option, select the option and press the
F1 key or the Help button. To select an option, click once on the option text.
Options that require additional parameters will display an edit box or an
additional subwindow where additional parameters can be set.
Assembler options specified in the project file (using the MCUez Shell) are
automatically displayed in the Option Settings dialog box.
2.4.8 Specifying the Input File
The input file to be assembled can be specified in several ways. During the
assembly session, options will beset according to the configurationprovided by
the user in the Option Settings dialog box. Before assembling a file, make sure
a project directory is associated with the assembler.
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
52 Graphical User Interface MOTOROLA
Page 53

2.4.8.1 Using the Editable Combo Box in the Toolbar
The following describes how to use the Editable Combo box.
• Assembling a new file — A new filename and additional assembler
options can be entered on the command line. Click on the Assemble
button or press the Enter key to assemble the specified file.
• Reassembling a file — The previously executed command can be
displayed by clicking on the arrowon the rightside of the command line.
From the drop down list, select a command. Click on the Assemble
button or press the Enter key to assemble the specified file.
2.4.8.2 Using the Entry File | Assembly ...
Select the menu entry File | Assemble to display the File to Assemble dialog
box. Browse to and select the desired file. Click Open to assemble the selected
file.
Graphical User Interface
Error Feedback
2.4.8.3 Using Drag and Drop
A filename can be dragged from an external program (for example, the File
Manager) and dropped into the assembler window. The dropped file is
assembled as soon as the mouse button is released in the assembler window. If
the dragged file has the extension .ini, it is a configuration file and will be
loaded and not assembled.
2.5 Error Feedback
Aftera source file has been assembled, thecontentareadisplays a list of all error
or warning messages detected. The message format is:
>> <FileName>, line <line number>, col <column number>
pos <absolute position in file>
<Portion of code generating the problem>
<message class> <message number>: <Message string>
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Graphical User Interface 53
Page 54

Graphical User Interface
Example:
>> in “C:\DEMO\fiboerr.asm”, line 76, col 20, pos 1932
BRA label
^
ERROR A1104: Undeclared user defined symbol: label
Errorscanbe corrected by using the editor definedduringconfiguration.Editors
such as WinEdit Version 95 (or higher) or Codewright from Premia
Corporation can be started with a line number in the command line. If
configured correctly, these editors are activated automatically by double
clicking on an error message. The editor will open the file containing the error
and position the cursor on the line with the error.
Editors like WinEdit Version 31 or lower, Notepad, or Wordpad cannot be
started with a line number. These editors can be activated automatically by
double clicking on a message. The editor will open the file containing the error.
To locate the error, use the find or search feature of the editor. In the assembler
content area, select the line containing the message class, number, and string
and press CTRL+C to copy the message. Paste the message in the Find dialog
box of the editor to search for the error.
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
54 Graphical User Interface MOTOROLA
Page 55

User’s Manual — MCUez HC12 Assembler
Section 3. Environment Variables
3.1 Contents
3.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
3.3 Paths . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
3.4 Line Continuation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
3.5 Environment Variables Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
3.5.1 ASMOPTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
3.5.2 GENPATH. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
3.5.3 ABSPATH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
3.5.4 OBJPATH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
3.5.5 TEXTPATH. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
3.5.6 SRECORD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
3.5.7 ERRORFILE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
3.5.8 COPYRIGHT: Copyright Entry in Object File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
3.5.9 INCLUDETIME: Create Time in Object File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
3.5.10 USERNAME: User Name in Object File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Environment Variables 55
Page 56

Environment Variables
3.2 Introduction
This section describes environment variables used by the MCUez assembler.
Environment variables are set in thePaths or Additionaltab of the MCUez shell
New Configuration or Current Configuration dialog box. Refer to the MCUez
Installation and Configuration User’s Manual, Motorola document order
number MCUEZINS/D. Environment variables that define paths (such as
GENPATH, OBJPATH, ABSPATH, etc.) are used by the assembler and other
MCUez applications.
3.3 Paths
Environmentvariables that contain pathsindicatewhere to look for files.A path
list is a list of directory names separated by semicolons or a directory name
preceded by an asterisk. If a directory name is preceded by an asterisk (*), the
programs recursively search the wholedirectory tree for afile, not just thegiven
directory. Directories are searched in the order they appear in the path list.
Syntax:
DirSpec;DirSpec;DirSpec
*DirectoryName
Examples: GENPATH=C:\INSTALL\LIB;D:\PROJECTS\TESTS;
LIBPATH=*C:\INSTALL\LIB
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
56 Environment Variables MOTOROLA
Page 57

3.4 Line Continuation
It is possible to specify an environment variable over more than one line by
using the line continuation character \ (back slash).
Example:
This is the same as
Observe the following when using the continuation character in path
definitions:
Environment Variables
Line Continuation
ASMOPTIONS=\
-W2 \
-WmsgNe=10
ASMOPTIONS=-W2 -WmsgNe=10
GENPATH=.\
TEXTFILE=.\txt
Will result in
GENPATH=.TEXTFILE=.\txt
To avoid syntax errors, use a semicolon (;) at the end of a path if there is a \ at
the end of the code line, such as:
GENPATH=.\;
TEXTFILE=.\txt
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Environment Variables 57
Page 58

Environment Variables
3.5 Environment Variables Description
The remainder of this section describes each of the environment variables
available for the assembler. The information in Table 3-1 describes the
structure for explaining each environment variable.
Table 3-1. Environment Variables
Topic Description
Syntax
Arguments Describes and lists optional and required arguments for the variable
Default Shows the default setting for the variable, if applicable
Description
Example
Tools Lists tools that use this variable, if applicable
MCUez
Shell
See also Lists related sections, if applicable
Specifies the syntax of the option in EBNF (Extended Backus-Naur
Form) format
Provides a detailed description of the environment variable and how
to use it
Gives an example of usage and effects of the variable where
possible
Explains how the environment variable can be initialized
in the MCUez Shell
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
58 Environment Variables MOTOROLA
Page 59

3.5.1 ASMOPTIONS
Environment Variables
Environment Variables Description
Syntax: ASMOPTIONS=<option>
Arguments: <option>: Assembler command line option
Description: If this environment variable is set, the assembler appends its
contents to its command line each time a file is assembled. It
can be used to globally specify certain options that should
alwaysbe set, so theydon’t haveto be specifiedeach time afile
is assembled.
Options listed here must be valid assembler options and are
separated by space characters.
Example: ASMOPTIONS=-W2 -L
MCUez Shell: Open the Current Configuration dialog box.
Select the Additional tab.
Enter the environment variable definition in the edit box.
See also: Section 5. Assembler Options
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Environment Variables 59
Page 60

Environment Variables
3.5.2 GENPATH
Syntax: GENPATH=<path>
Arguments: <path>: Paths separated by semicolons, without spaces.
Description: The macro assembler will look for the source or included files
first in the project directory, then in the directories listed in the
environment variable GENPATH.
NOTE:
If a directory specification in this environment variable starts with an asterisk
(
*
), the entire directory tree is searched recursively, for instance, all
subdirectories are searched.
Example: GENPATH=\sources\include;..\..\headers;*\user
MCUez Shell: Open the Current Configuration dialog.
Select the Paths tab.
In the Configure combo box, select General Path.
Enter the directories in the list box (one directory on each line).
See also: None
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
60 Environment Variables MOTOROLA
Page 61

3.5.3 ABSPATH
Environment Variables
Environment Variables Description
Syntax: ABSPATH=<path>
Arguments: <path>: Paths separated by semicolons, without spaces
Description: This environment variable is only relevant when absolute files
are directly generated by the macro assemblerinstead of object
files. When this environment variable is defined, the assembler
will store the absolute files it produces in the first directory
specified. If ABSPATH is not set, the generated absolute files
will be stored in the directory where the source file was found.
Example:
ABSPATH=\sources\bin;..\..\headers;\usr\local\bin
MCUez Shell: Open the Current Configuration dialog.
Select the Paths tab.
In the Configure combo box, select Absolute.
Enter the directories in the list box (one directory on each line).
See also: None
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Environment Variables 61
Page 62

Environment Variables
3.5.4 OBJPATH
Syntax: OBJPATH=<path>
Arguments: <path>: Paths separated by semicolons, without spaces
Description: When this environment variable is defined, the assembler will
store the object files it produces in the first directory specified.
If OBJPATH is not set, the generated object files will be stored
in the directory where the source file was found.
Example:
OBJPATH=\sources\bin;..\..\headers;\usr\local\bin
MCUez Shell: Open the Current Configuration dialog.
Select the Paths tab.
In the Configure combo box, select Object.
Enter the directories in the list box (one directory on each line).
See also: None
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
62 Environment Variables MOTOROLA
Page 63

3.5.5 TEXTPATH
Environment Variables
Environment Variables Description
Syntax: TEXTPATH=<path>
Arguments: <path>: Paths separated by semicolons, without spaces
Description: When this environment variable is defined, the assembler will
store the listing files it produces in the first directory specified.
If TEXTPATH is not set, the generated listing files will be
stored in the directory where the source file was found.
Example:
TEXTPATH=\sources\txt;..\..\headers;\usr\local\txt
MCUez Shell: Open the Current Configuration dialog.
Select the Paths tab.
In the Configure combo box, select Text.
Enter the directories in the list box (one directory on each line).
See also: None
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Environment Variables 63
Page 64

Environment Variables
3.5.6 SRECORD
Syntax: SRECORD=<RecordType>
Arguments: <Record Type>: Force the type for the Motorola S record that
Description: This environment variable is only relevant when absolute files
must be generated. This parameter may take the value S1, S2,
or S3.
are generated directly by the macro assemblerinstead of object
files. When this environment variable is defined, the assembler
will generate a Motorola S file containing records from the
specified type (S1 records when S1 is specified, S2 records
when S2 is specified, and S3 records when S3 is specified).
When this variable is not set, the type of S record generated
will depend on the size of the address loaded there. If the
address can be coded on two bytes, an S1 record is generated.
If the address is coded on three bytes, an S2 record is
generated. Otherwise, an S3 record is generated.
NOTE:
If the environment variable SRECORD is set, it is the user’s responsibility to
specify the appropriate S record type. If S1 is specified while the code is loaded
above 0xFFFF, the Motorola S file generated will not be correct because the
addresses will all be truncated to 2-byte values.
Example: SRECORD=S2
MCUez Shell: Open the Current Configuration dialog.
Select the Additional tab.
Enter the environment variable in the list box.
See also: None
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
64 Environment Variables MOTOROLA
Page 65

3.5.7 ERRORFILE
Environment Variables
Environment Variables Description
Syntax: ERRORFILE=<
filename>
Arguments: <filename>: Filename with possible format specifiers
Description: The environment variable ERRORFILE specifies the name of
the error file used by the assembler.
Possible format specifiers are:
%n: Substitute with the filename, without the path
%p: Substitute with the path of the source file
%f: Substitute with the full filename (path included; same as
%p%n)
Examples: ERRORFILE=MyErrors.err
Logs all errors in the file MyErrors.err in the current
directory
ERRORFILE=\tmp\errors
Logs all errors in the filenamed errors in the directory \tmp
ERRORFILE=%f.err
Logs all errors in a file with the same name as the source file
(with extension .err) into the same directory as the source
file.Forexample,ifthefile\sources\test.asmisassembled,an
error file \sources\test.err will be generated.
ERRORFILE=\dir1\%n.err
An error file \dir1\test.err will be generated for a source file
named test.asm.
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Environment Variables 65
Page 66

Environment Variables
MCUez Shell: Open the Current Configuration dialog.
See also: None
ERRORFILE=%p\errors.txt
An error file \dir1\dir2\errors.txt will be generated for a
source file \dir1\dir2\test.asm.
If the environment variable ERRORFILE is not set, errors
arewritten to the defaulterrorfile.The default error filename
is dependent upon how the assembler is configured and
started. If no filename is provided, errors are written to the
err.txt file in the project directory.
Select the Additional tab.
Enter the environment variable definition in the list box.
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
66 Environment Variables MOTOROLA
Page 67

3.5.8 COPYRIGHT: Copyright Entry in Object File
Tools: Assembler and linker
Syntax: COPYRIGHT=<copyright string>
Arguments: <copyright string>: String for the copyright entry in the object
file
Default: None
Description: Each object file contains an entry for a copyright string. This
information may be retrieved from the object files.
Example: COPYRIGHT=Copyright by Motorola
MCUez Shell: Open the Current Configuration dialog.
Select the Additional tab.
Enter the environment variable definition in the list box.
Environment Variables
Environment Variables Description
See also: Environment variable 3.5.9 INCLUDETIME: Create Time
in Object File
Environment variable 3.5.10 USERNAME: User Name in
Object File
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Environment Variables 67
Page 68

Environment Variables
3.5.9 INCLUDETIME: Create Time in Object File
Tools: Assembler and linker
Syntax: INCLUDETIME=(ON | OFF)
Arguments: ON: Include time information in object file
OFF: Do not include time information in object file.
Default: ON
Description: Normally, each object file created contains a time stamp
indicating the creation time and data as strings. So whenever a
new file is created by one of the tools, the new file gets a new
time stamp entry.
This behavior may be undesirable if a binary file compare has
to be performed. Even if the information in two object files is
the same, the files do not match exactly because the time
stamps are not the same. Toavoid such problems, this variable
may be set to OFF. In this case, the time stamp strings for date
and time are “none” in the object file.
The time stamp may be retrieved from the object files using a
decoder.
Example: INCLUDETIME=OFF
MCUez Shell: Open the Current Configuration dialog.
Select the Additional tab.
Enter the environment variable definition in the list box.
See also: Environment variable3.5.8 COPYRIGHT: CopyrightEntry
in Object File
Environment variable 3.5.10 USERNAME: User Name in
Object File
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
68 Environment Variables MOTOROLA
Page 69

3.5.10 USERNAME: User Name in Object File
Tools: Assembler and linker
Syntax: USERNAME=<user>
Arguments: <user>: Name of user
Default: None
Description: Each object file contains an entry identifying the user who
created the object file. This information may be retrieved from
the object files using a decoder.
Example: USERNAME=MOTOROLA
MCUez Shell: Open the Current Configuration dialog.
Select the Additional tab.
Enter the environment variable definition in the list box.
Environment Variables
Environment Variables Description
See also: Environment variable3.5.8 COPYRIGHT: CopyrightEntry
in Object File
Environment variable 3.5.9 INCLUDETIME: Create Time
in Object File
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Environment Variables 69
Page 70

Environment Variables
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
70 Environment Variables MOTOROLA
Page 71

User’s Manual — MCUez HC12 Assembler
4.1 Contents
4.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
4.3 Input Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
4.3.1 Source Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
4.3.2 Include Files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
4.4 Output Files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
4.4.1 Object Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
4.4.2 Absolute Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
4.4.3 Motorola S Files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
4.4.4 Listing Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
4.4.5 Debug Listing Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
4.4.6 Error Listing Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Section 4. Files
4.2 Introduction
This chapter describes all file types associated with the MCUez application.
4.3 Input Files
The following sections describe input files:
• Source files
• Include files
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Files 71
Page 72

Files
4.3.1 Source Files
4.3.2 Include Files
The macro assembler takes any file as input and does not require the filename
to have a special extension. However, it is suggested that all source filenames
have the extension .asm and all included files have the extension .inc. Source
files will be searched first in the project directory and then in the GENPATH
directory.
Thesearch for include files is governed bytheenvironmentvariable GENPATH.
Include files are searched first in the project directory, then in the directories
specified in the environment variable GENPATH. The project directory is set
from the MCUez Shell or the environment variable DEFAULTDIR.
4.4 Output Files
4.4.1 Object Files
The following sections describe six types of output files:
1. Object files
2. Absolute files
3. Motorola S files
4. Listing files
5. Debug listing files
6. Error listing files
After a successful assembly session, the macro assembler generates an object
file containing the target code as well as some debugging information. This file
is written to the directory given in the environment variable OBJPATH. If that
variable contains more than one path, the object file is written to the first
directory given. If this variable is not set, the object file is written to the
directory where the source file was found. Object files always get the
extension .o.
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
72 Files MOTOROLA
Page 73

4.4.2 Absolute Files
4.4.3 Motorola S Files
Files
Output Files
When an application is encoded in a single module and all the sections are
absolute sections, the user can decide to generate an absolute file instead of an
object file. Thisfile is written to the directory given inthe environment variable
ABSPATH. If that variable contains more than one path, the absolute file is
written in the first directory given. If this variable is not set, the absolute file is
written in the directory where the source file was found. Absolute files always
get the extension .abs.
When an application is encoded in a single module and all the sections are
absolute sections, the user can decide to generate an absolute file instead of an
object file. In that case, a Motorola S record file is generated at the same time.
This file can be burnt into an EPROM. It contains information stored in all
READ_ONLY sections in the application. The extension for the generated
Motorola S record file depends on the SRECORD variable setting.
For instance:
• If SRECORD = S1, the Motorola S record file gets the extension
.s1.
• If SRECORD = S2, the Motorola S record file gets the extension
.s2.
• If SRECORD = S3, the Motorola S record file gets the extension
.s3.
• If SRECORD is not set, the Motorola S record file gets the
extension .sx.
Thisfile is written to thedirectorygiven in the environment variable ABSPATH.
If that variable contains more than one path, the motorola S file is written in the
first directory given. If this variable is not set, the file is written in the directory
the source file was found.
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Files 73
Page 74

Files
4.4.4 Listing Files
4.4.5 Debug Listing Files
After a successful assembly session,the macro assembler generates alisting file
containing each assembly instruction with its associated hexadecimal code.
This file is generated when the option -L is activated, even if the macro
assembler generates an absolute file. This file is written to the directory given
in the environment variableTEXTPATH. If that variablecontains more thanone
path, the listing file is written in the first directory specified. If this variable is
not set, the listing fileis written in thedirectory where the source filewas found.
Listing files always get the extension .lst. Section 10. Assembler Listing File
describes the format of this file.
After a successful assembling session, the macro assembler generates a debug
listing file, which will be used to debug the application. This file is always
generated, even when the macro assembler generates an absolute file. The
debug listing file is a duplicateof the source, where all the macros are expanded
and the include files merged. This file (with the extension .dbg) is written to the
directory listed in the environment variable OBJPATH. If that variable contains
more than one path, the debug listing file is written to the first directory given.
If this variable is not set, the file is written in the directory where the source file
was found. Debug listing files always get the extension .dbg.
4.4.6 Error Listing Files
If the macro assembler detects any errors, it creates an error file. The name and
location of this file depend on the settings from the environment variable
ERRORFILE.
If the macro assembler’s window is open, it displays the full path of all include
files read. After successful assembly, the number of code bytes generated and
the number of global objects written to the object file are displayed. Figure 4-1
shows the different structures associated with the assembler.
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
74 Files MOTOROLA
Page 75

Files
Output Files
.asm
.o
or
.abs
.dbg
1. Current Directory
2. GENPATH
1. OBJPATH
2. Source File Path
ASSEMBLER
.lst
1. Current Dir
.inc
1. TEXTPATH
2. Source File Path
2. GENPATH
ERRORFILE
err.txt
or
EDOUT
Figure 4-1. Assembler Structural Diagram
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Files 75
Page 76

Files
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
76 Files MOTOROLA
Page 77

User’s Manual — MCUez HC12 Assembler
Section 5. Assembler Options
5.1 Contents
5.2 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
5.3 ASMOPTIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
5.4 Assembler Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
5.4.1 -CI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
5.4.2 -Env . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
5.4.3 -F2 -FA2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
5.4.4 -H . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
5.4.5 -L . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
5.4.6 -Lc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
5.4.7 -Ld . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
5.4.8 -Le . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
5.4.9 -Li. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
5.4.10 -Ms -Mb . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
5.4.11 -MCUasm. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
5.4.12 -N . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
5.4.13 -V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
5.4.14 -W1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
5.4.15 -W2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
5.4.16 -WmsgNe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
5.4.17 -WmsgNi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
5.4.18 -WmsgNw . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
5.4.19 -WmsgFbv -WmsgFbm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
5.4.20 -WmsgFiv -WmsgFim . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Assembler Options 77
Page 78

Assembler Options
5.2 Introduction
The assembler offers a number of options that control how the assembler
operates. Options consist of a dash (-) followed by one or more letters or digits.
Anything not starting with a dash is assumed to be the name of a source file to
be assembled. Assembler options may be specified on the command line or in
the ASMOPTIONS environment variable. Typically, each assembler option is
specified only once per assembly session.
NOTE:
NOTE:
5.3 ASMOPTIONS
Arguments for an option must not exceed 128 characters.
Command line options are not case sensitive. –Li is the same as –li. For
options that belong tothe same group, forexample –Lc and –Li,the assembler
allows options to be combined, for example, –Lci or –Lic instead of –Lc
–Li.
Itis not possible to combineoptionsin different groups, for instance,
cannot be abbreviated by the terms
If this environment variable is set, the assembler appends the values (options)
defined for this variableto its commandline each time afile is assembled.It can
be used to globally specify certain options that should always be set, so the user
doesn’t have to specify them each time a file is assembled.
–LC1
or
–LCW1
.
–Lc –W1
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
78 Assembler Options MOTOROLA
Page 79

5.4 Assembler Options
Table 5-1 describes how assembler options are grouped and Table 5-2
describes the scope of each option.
Group Description
HOST Lists options related to the host
Assembler Options
Assembler Options
Table 5-1. Assembler Option Group
OUTPUT
INPUT Lists options related to input file
CODE
MESSAGE Lists options controlling generation of error messages
VARIOUS Lists various options
Lists options related to output file generation (type of file
to be generated)
Lists options related to code generation (memory models,
float format, etc.)
Table 5-2. Scope of Each Option
Scope Description
The option has to be set for all files (assembly units) of an
Application
Assembly
unit
None
application. A typical example is an option to set the memory
model. Mixing object files will have unpredictable results.
The option can be set differently for each assembly unit of an
application. Mixing objects in an application is possible.
The option is not related to a specific code part. A typical example is
options for message management.
Available options are arranged in separate groups, and a dialog box tab is
available for each group. The content of the list box depends on the tab selected
in the dialog box.
The remainder of this section describes each of the options available for the
assembler. The options are listed in alphabetical order and described by the
categories shown in Table 5-3.
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Assembler Options 79
Page 80

Assembler Options
Group HOST, OUTPUT, INPUT, CODE, MESSAGE, VARIOUS
Scope Application, assembly unit, or none
Syntax Specifies the syntax of the option in EBNF format
Arguments Describes and lists optional and required arguments for the option
Default Shows the default setting for the option
Description Provides a detailed description of the option and how to use it
Example
See also Related options
Table 5-3. Assembler Option Details
Topic Description
Gives an example of usage and effectsof the option where possible.
Assembler settings, source code and/or linker PRM files are
displayed where applicable.
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
80 Assembler Options MOTOROLA
Page 81

5.4.1 -CI
Assembler Options
Assembler Options
-CI: Set case sensitivity for label names OFF
Group: INPUT
Scope: Assembly unit
Syntax: -CI
Arguments: None
Default: ON
Description: Switches case sensitivity OFF for label names. When this
option is activated, the assembler ignores case sensitivity for
label names.
Thisoptioncan be only specified when the assembler generates
an absolute file. (Option -FA2 must be activated.)
Example: When case sensitivity for label names is switched off, the
assembler will not generate error messages for this code:
ORG $200
entry: NOP
BRA Entry
The instruction BRA Entry will branch on the label entry.
By default, the assembler is case sensitivefor label names. The
labels Entry and entry are two distinct labels.
See also: None
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Assembler Options 81
Page 82

Assembler Options
5.4.2 -Env
-Env: Set environmental variable
Group: HOST
Scope: Assembly unit
Syntax: -Env <EnvironmentVariable>=<VariableSetting>
Arguments: <EnvironmentVariable>: Environment variable to be set
<VariableSetting>: Assigned value
Default: None
Description: This option sets an environment variable.
Example: ASMOPTIONS=-EnvOBJPATH=\sources\obj
This is the same as OBJPATH=\sources\obj in the
default.env file.
See also: Section 3. Environment Variables
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
82 Assembler Options MOTOROLA
Page 83

5.4.3 -F2 -FA2
Assembler Options
Assembler Options
-F: Object file format
Group: OUTPUT
Scope: Application
Syntax: -F (2 | A2)
Arguments: 2: ELF/DWARF 2.0 object file format
A2: ELF/DWARF 2.0 absolute file format (default)
Default: -FA2
Description: Defines format for the output file generated by the assembler
With the option -F2 set, the assembler produces an
ELF/DWARF 2.0 object file.
With the option -FA2 set, the assembler produces an
ELF/DWARF 2.0 absolute file.
Example: ASMOPTIONS=-F2
See also: None
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Assembler Options 83
Page 84

Assembler Options
5.4.4 -H
-H: Short help
Scope: None
Syntax: -H
Arguments: None
Default: None
Description: The -H option will display a short list of available options.
No other option or source file should be specified when the -H
option is invoked.
Example: The following is a portion of the list produced by the option
-H:
MESSAGE:
-N Show Notification box in case of
errors
-W1 Don’t print INFORMATION messages
-W2 Don’t print INFORMATION or WARNING
messages
VARIOUS:
-H Prints this list of options
-V Prints the Assembler version
See also: None
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
84 Assembler Options MOTOROLA
Page 85

5.4.5 -L
Assembler Options
Assembler Options
-L: Generates a listing file
Group: OUTPUT
Scope: Assembly unit
Syntax: -L
Arguments: None
Default: None
Description: Switches on generation of the listing file. This listing file will
have the same name as the source file, but with the extension
.lst. The listing file contains macro definitions, invocation, and
expansion lines as well as expanded include files.
Example: ASMOPTIONS=-L
In the following assembly code example, the macro cpChar
accepts two parameters. The macro copies the value of the first
parameter to the second one.
When option -L is specified, the following portion of code:
INCLUDE "macro.inc"
CodeSec: SECTION
Start:
cpChar char1, char2
NOP
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Assembler Options 85
Page 86

Assembler Options
Generates the following output in the assembly listing file:
5 5 INCLUDE
"macro.inc"
6 1i cpChar: MACRO
7 2i LDD \1
8 3i STD \2
9 4i ENDM
10 5i
11 6 codeSec:
SECTION
12 7 Start:
13 8 cpChar
ch1, ch2
14 2m 000000 FC xxxx + LDD
ch1
15 3m 000003 7C xxxx + STD
ch2
16 9 000006 A7 NOP
17 10 000007 A7 NOP
Contents of included files, as well as macro definition,
invocation and expansion are stored in the listing file. Refer to
Section 10. Assembler Listing File for detailed information.
See also: 5.4.6 -Lc, 5.4.7 -Ld, 5.4.8 -Le, and 5.4.9 -Li
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
86 Assembler Options MOTOROLA
Page 87

5.4.6 -Lc
Assembler Options
Assembler Options
-Lc: No macro call in listing file
Group: OUTPUT
Scope: Assembly unit
Syntax: -Lc
Arguments: None
Default: None
Description: Switches on generation of the listing file, but macro
invocations are not present in the listing file. The listing file
contains macro definitions and expansion lines as well as
expanded include files.
Example: ASMOPTIONS=-Lc
In the following assembly code example, the macro cpChar
accepts two parameters. The macro copies the value of the first
parameter to the second one.
When option -Lc is specified, the following portion of code:
cpChar: MACRO
LDD \1
STD \2
ENDM
codeSec: SECTION
Start:
cpChar char1, char2
NOP
NOP
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Assembler Options 87
Page 88

Assembler Options
Generates the following output in the assembly listing file:
5 5 cpChar:
MACRO
66
LDD \1
77
STD \2
8 8
ENDM
9 9 codeSec:
SECTION
10 10 Start:
12 6m 000000 FC xxxx +
LDD char1
13 7m 000003 7C xxxx +
STD char2
14 12 000006 A7
NOP
15 13 000007 A7
NOP
Contents of included files, macro definitions, and expansion
are stored in the list file. The source line containing the macro
call is not present in the listing file. Refer to Section 10.
Assembler Listing File for detailed information.
See also: 5.4.5 -L
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
88 Assembler Options MOTOROLA
Page 89

5.4.7 -Ld
Assembler Options
Assembler Options
-Ld: No macro definition in listing file
Group: OUTPUT
Scope: Assembly unit
Syntax: -Ld
Arguments: None
Default: None
Description: Switches on generation of the listing file, butmacro definitions
are not present in the listing file. The listing file contains macro
invocation and expansion lines as well as expanded include
files.
Example: ASMOPTIONS=-Ld
In the following example, the macro cpChar accepts two
parameters. The macro copies the value of the first parameter
to the second one. When option -Ld is specified, the
following portion of code:
cpChar: MACRO
LDD \1
STD \2
ENDM
codeSec: SECTION
Start:
cpChar char1, char2
NOP
NOP
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Assembler Options 89
Page 90

Assembler Options
Generates this output in the assembly listing file:
5 5 cpChar:
MACRO
9 9 codeSec:
SECTION
10 10 Start:
11 11
cpChar char1, char2
12 6m 000000 FC xxxx +
LDD char1
13 7m 000003 7C xxxx +
STD char2
14 12 000006 A7
NOP
15 13 000007 A7
NOP
Contents of included files, as well as macro invocation and
expansion are stored in the listing file. Source code from the
macro definition is not present in the listing file. Refer to
Section 10. Assembler Listing File for detailed information.
See also: 5.4.5 -L
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
90 Assembler Options MOTOROLA
Page 91

5.4.8 -Le
Assembler Options
Assembler Options
-Le: No macro expansion in listing file
Group: OUTPUT
Scope: Assembly unit
Syntax: -Le
Arguments: None
Default: None
Description: Switchesongeneration of the listing file,butmacroexpansions
are not present in the listing file. The listing file contains macro
definitions and invocation lines as well as expanded include
files.
Example: ASMOPTIONS=-Le
In the following example, the macro cpChar accepts two
parameters. The macro copies the value of the first parameter
to the second one. When option -Le is specified, the following
portion of code:
cpChar: MACRO
LDD \1
STD \2
ENDM
codeSec: SECTION
Start:
cpChar char1, char2
NOP
NOP
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Assembler Options 91
Page 92

Assembler Options
Generates this output in the assembly listing file:
5 5 cpChar:
MACRO
66
LDD \1
77
STD \2
8 8
ENDM
9 9 codeSec:
SECTION
10 10 Start:
11 11
cpChar char1, char2
14 12 000006 A7
NOP
15 13 000007 A7
NOP
Contents of included files, as well as macro definitions and
invocation are stored in the listing file. Macro expansion lines
are not present in the listing file. Refer to Section 10.
Assembler Listing File for detailed information.
See also: 5.4.5 -L
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
92 Assembler Options MOTOROLA
Page 93

5.4.9 -Li
Assembler Options
Assembler Options
-Li: No included file in listing file
Group: OUTPUT
Scope: Assembly unit
Syntax: -Li
Arguments: None
Default: None
Description: Switches on generation of the listing file, but include files are
not expanded in the listing file. The listing file contains macro
definitions, invocation, and expansion lines.
Example: ASMOPTIONS=-Li
When option -Li is specified, this portion of code:
INCLUDE "macro.inc"
codeSec: SECTION
Start:
cpChar char1, char2
NOP
Generates the following output in the assembly listing file:
55
INCLUDE "macro.inc"
12 6 codeSec:
SECTION
13 7 Start:
15 3m 000000 FC xxxx +
LDD char1
16 4m 000003 7C xxxx +
STD char2
17 9 000006 A7
NOP
18 10 000007 A7
NOP
Macro definition, invocation, and expansion are stored in the
listing file.
See also: 5.4.5 -L
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Assembler Options 93
Page 94

Assembler Options
5.4.10 -Ms -Mb
-M: Memory model
Group: CODE
Scope: Application
Syntax: -M (s | b)
Arguments: s: Small memory model
b: Banked memory model
Default: -Ms
Description: The assembler for the MC68HC12 supports two different
memory models. Default is the small memory model, which
corresponds to the normal setup, for example, a 64-Kbyte
code-address space. If a code memory expansion scheme is
used, the banked memory model may be changed.
Memory models should be observed when mixing ANSI C and
assembler files. For compatibility reasons, the memory model
usedby the differentfiles must be the same. Additionally, when
assembling in the small memory model, thelinker will check if
all variables or code sections are located on the first page
between 0 and FFFF.
Example: ASMOPTIONS=-Ms
See also: None
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
94 Assembler Options MOTOROLA
Page 95

5.4.11 -MCUasm
Assembler Options
Assembler Options
-MCUasm: Switch ON MCUasm compatibility
Group: VARIOUS
Scope: Assembly unit
Syntax: -MCUasm
Arguments: None
Default: None
Description: Switches ON MCUasm assembler compatibility mode.
Additional features supported are listed in Appendix B.
MCUasm Compatibility.
Example: ASMOPTIONS=-MCUasm
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Assembler Options 95
Page 96

Assembler Options
5.4.12 -N
-N: Display error notification box
Group: MESSAGES
Scope: Assembly unit
Syntax: -N
Arguments: None
Default: None
Description: Causes the assembler to display an alert box if an error occurs
during assembly.This is useful when running a makefile, since
the assembler waits for the user to acknowledge the message,
thus suspending makefile processing.
Example: ASMOPTIONS=-N
If an error occurs during assembly, a dialog box is displayed
indicating the file where the error occurred.
See also: None
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
96 Assembler Options MOTOROLA
Page 97

5.4.13 -V
Assembler Options
Assembler Options
-V: Displays the assembler version
Group: VARIOUS
Scope: None
Syntax: -V
Arguments: None
Default: None
Description: Prints the assembler version and the current directory
NOTE:
This option is useful to determine the current directory.
Example: -V produces this list:
Directory: C:\MCUEZ\demo\WMMDS12A
Limitation Status: none
Common Module V-5.0.4, Date Mar 18 1998
Assembler Kernel, V-5.0.9, Date Mar 20 1998
User Interface Module, V-5.0.14, Date Mar 18 1998
Assembler Target, V-5.0.13, Date Mar 20 1998
See also: None
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Assembler Options 97
Page 98

Assembler Options
5.4.14 -W1
-W1: No information messages
Group: MESSAGES
Scope: Assembly unit
Syntax: -W1
Arguments: None
Default: None
Description: INFORMATION messages are not displayed. Only
WARNING and ERROR messages are listed.
Example: ASMOPTIONS=-W1
See also: None
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
98 Assembler Options MOTOROLA
Page 99

5.4.15 -W2
Assembler Options
Assembler Options
-W2: No information and warning messages
Group: MESSAGES
Scope: Assembly unit
Syntax: -W2
Arguments: None
Default: None
Description: INFORMATION and WARNING messages are not displayed.
Only ERROR messages are listed.
Example: ASMOPTIONS=-W2
See also: None
MCUez HC12 Assembler User’s Manual
MOTOROLA Assembler Options 99
Page 100

Assembler Options
5.4.16 -WmsgNe
-WmsgNe: Number of error messages
Group: MESSAGES
Scope: Assembly unit
Syntax: -WmsgNe <number>
Arguments: <number>: Maximum number of error messages
Default: 50
Description: Sets the number of errors detected before the assembler stops
processing
Example: ASMOPTIONS=-WmsgNe2
The assembler stops assembling after two error messages.
See also: 5.4.17 -WmsgNi and 5.4.18 -WmsgNw
User’s Manual MCUez HC12 Assembler
100 Assembler Options MOTOROLA
 Loading...
Loading...