Mitsubishi M5M4V64S30ATP-12 Datasheet
SDRAM (Rev.0.2)
Jan'97 Preliminary
PRELIMINARY
Some of contents are subject to change without notice.
MITSUBISHI LSIs
M5M4V64S30ATP-8, -10, -12
64M (4-BANK x 2097152-WORD x 8-BIT) Synchronous DRAM
DESCRIPTION
The M5M4V64S30ATP is a 4-bank x 2097152-word x 8-bit
Synchronous DRAM, with LVTTL interface. All inputs and
outputs are referenced to the rising edge of CLK. The
M5M4V64S30ATP achieves very high speed data rate up to
125MHz, and is suitable for main memory or graphic memory
in computer systems.
FEATURES
- Single 3.3v±0.3v power supply
- Clock frequency 125MHz / 100MHz / 83MHz
- Fully synchronous operation referenced to clock rising edge
- 4 bank operation controlled by BA0, BA1 (Bank Address)
- /CAS latency- 2/3 (programmable)
- Burst length- 1/2/4/8 (programmable)
- Burst type- sequential / interleave (programmable)
- Column access - random
- Auto precharge / All bank precharge controlled by A10
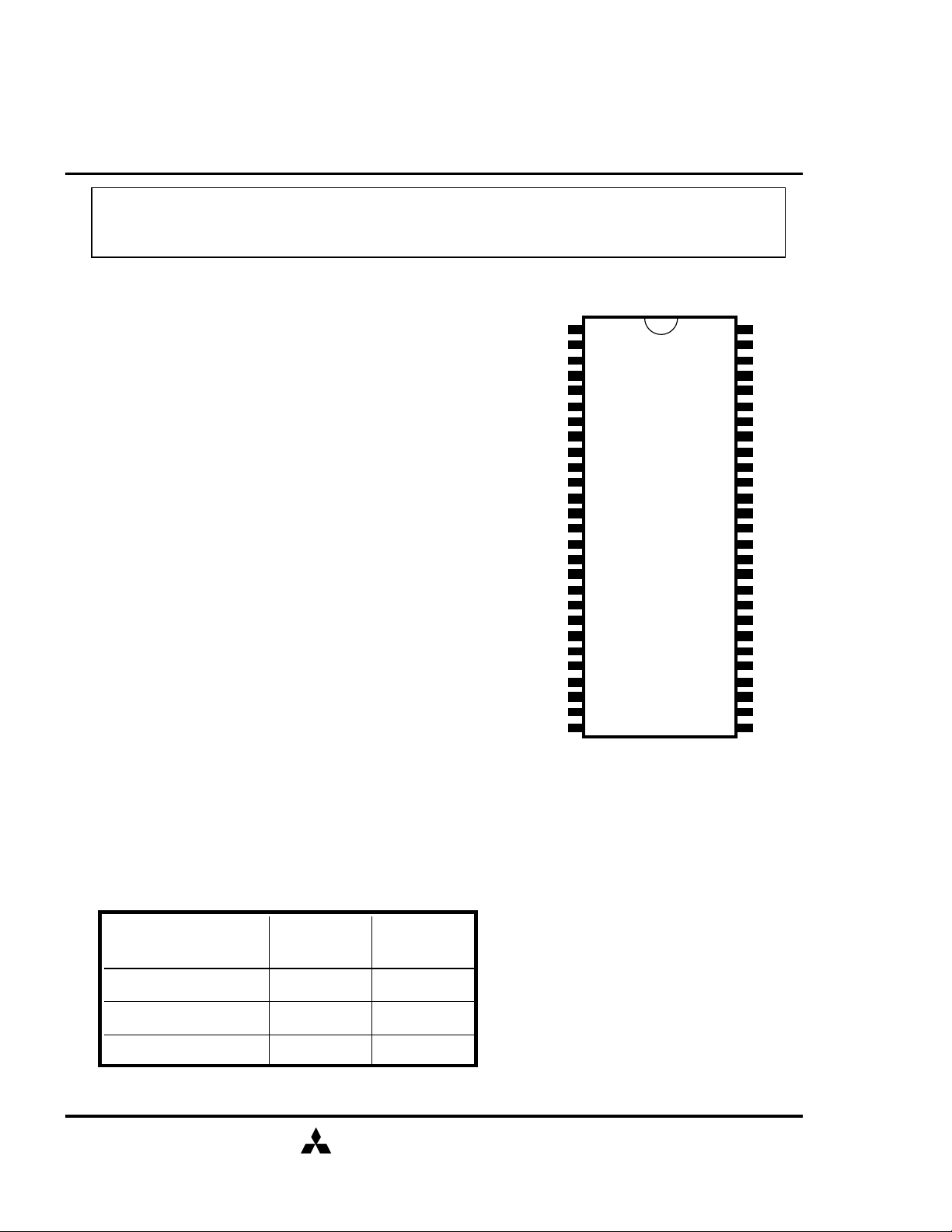
PIN CONFIGURATION
(TOP VIEW)
Vdd
DQ0
VddQ
DQ1
VssQ
DQ2
VddQ
DQ3
VssQ
Vdd
/WE
/CAS
/RAS
/CS
BA0(A13)
BA1(A12)
A10
Vdd
1
2
3
4
NC
5
6
7
NC
8
9
10
NC
11
12
13
NC
14
15
NC
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
A0
24 31
A1 A6
25 30
A2
26 29
A3
27 28
400mil 54pin TSOP(II)
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
Vss
DQ7
VssQ
NC
DQ6
VddQ
NC
DQ5
VssQ
NC
DQ4
VddQ
NC
Vss
NC (Vref)
DQM
CLK
CKE
NC
A11
A9
A8
A723 32
A5
A4
Vss
- Auto refresh and Self refresh
- 4096 refresh cycles /64ms
- Column address A0-A8
- LVTTL Interface
- 400-mil, 54-pin Thin Small Outline Package (TSOP II) with
0.8mm lead pitch
Max.
Frequency
M5M4V64S30ATP-8 125MHz 6ns
M5M4V64S30ATP-10 100MHz
M5M4V64S30ATP-12 83MHz 8ns
CLK Access
Time
8ns
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
CLK : Master Clock
CKE : Clock Enable
/CS : Chip Select
/RAS : Row Address Strobe
/CAS : Column Address Strobe
/WE : Write Enable
DQ0-7 : Data I/O
DQM : Output Disable/ Write Mask
A0-11 : Address Input
BA0,1 : Bank Address
Vdd : Power Supply
VddQ : Power Supply for Output
Vss : Ground
VssQ : Ground for Output
1
SDRAM (Rev.0.2)
Jan'97 Preliminary
MITSUBISHI LSIs
M5M4V64S30ATP-8, -10, -12
64M (4-BANK x 2097152-WORD x 8-BIT) Synchronous DRAM
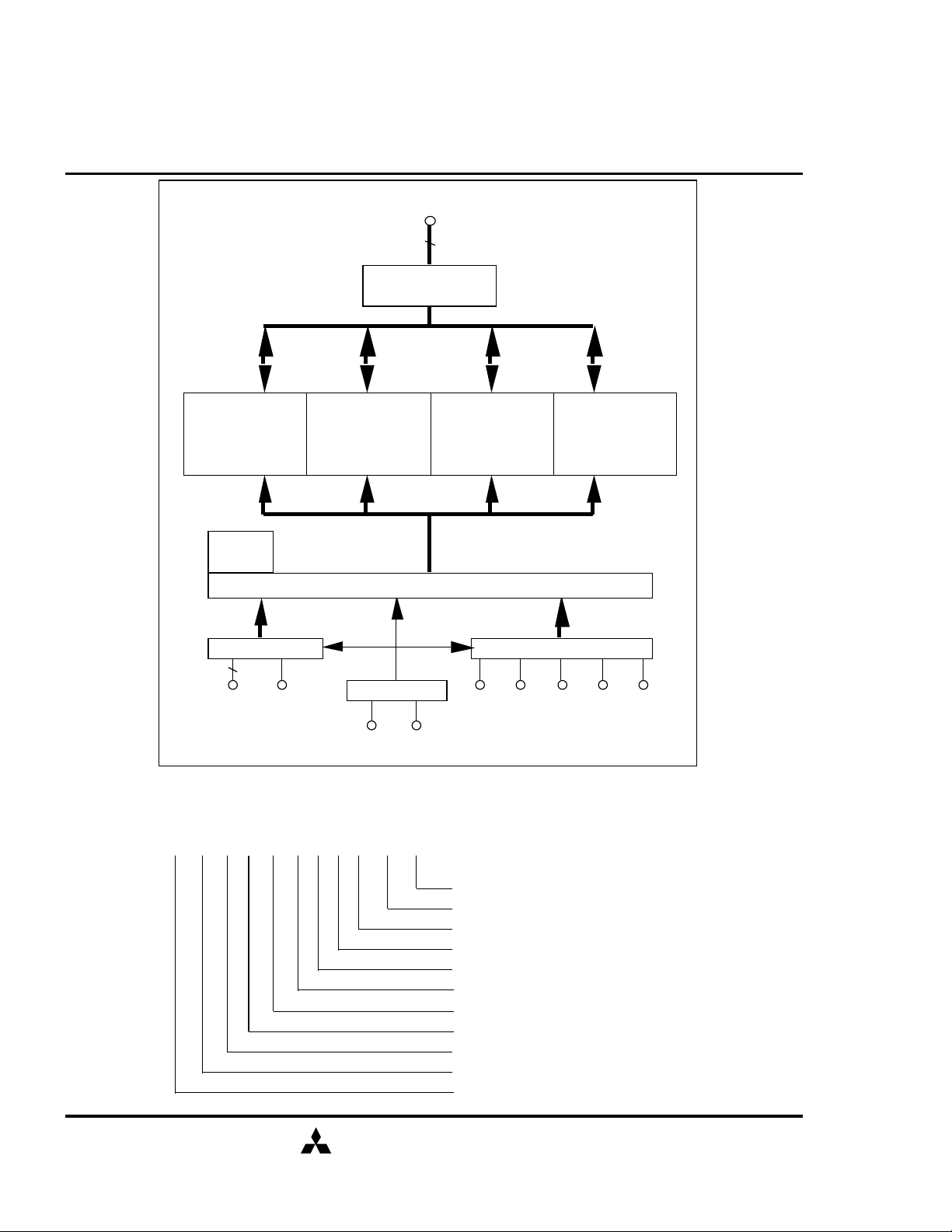
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Memory Array
Bank #0
Mode
Register
Address Buffer
Memory Array
I/O Buffer
Bank #1
Control Circuitry
DQ0-7(0-3)
Memory Array
Bank #2
Memory Array
Bank #3
Control Signal Buffer
A0-11 BA0,1
Type Designation Code
M 5M 4 V 64 S 3 0 A TP - 8
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
Clock Buffer
CLK CKE
This rule is applied to only Synchronous DRAM family.
/CS /RAS /CAS /WE DQM
Cycle Time (min.) 8: 8ns, 10: 10ns, 12: 12ns
Package Type TP: TSOP(II)
Process Generation
Function 0: Random Column, 1: 2N-rule
Organization 2n 2: x4, 3: x8, 4: x16
Synchronous DRAM
Density 64:64M bits
Interface S: SSTL, V:LVTTL
Memory Style (DRAM)
Use, Recommended Operating Conditions, etc
Mitsubishi Main Designation
2
SDRAM (Rev.0.2)
MITSUBISHI LSIs
Jan'97 Preliminary
M5M4V64S30ATP-8, -10, -12
64M (4-BANK x 2097152-WORD x 8-BIT) Synchronous DRAM
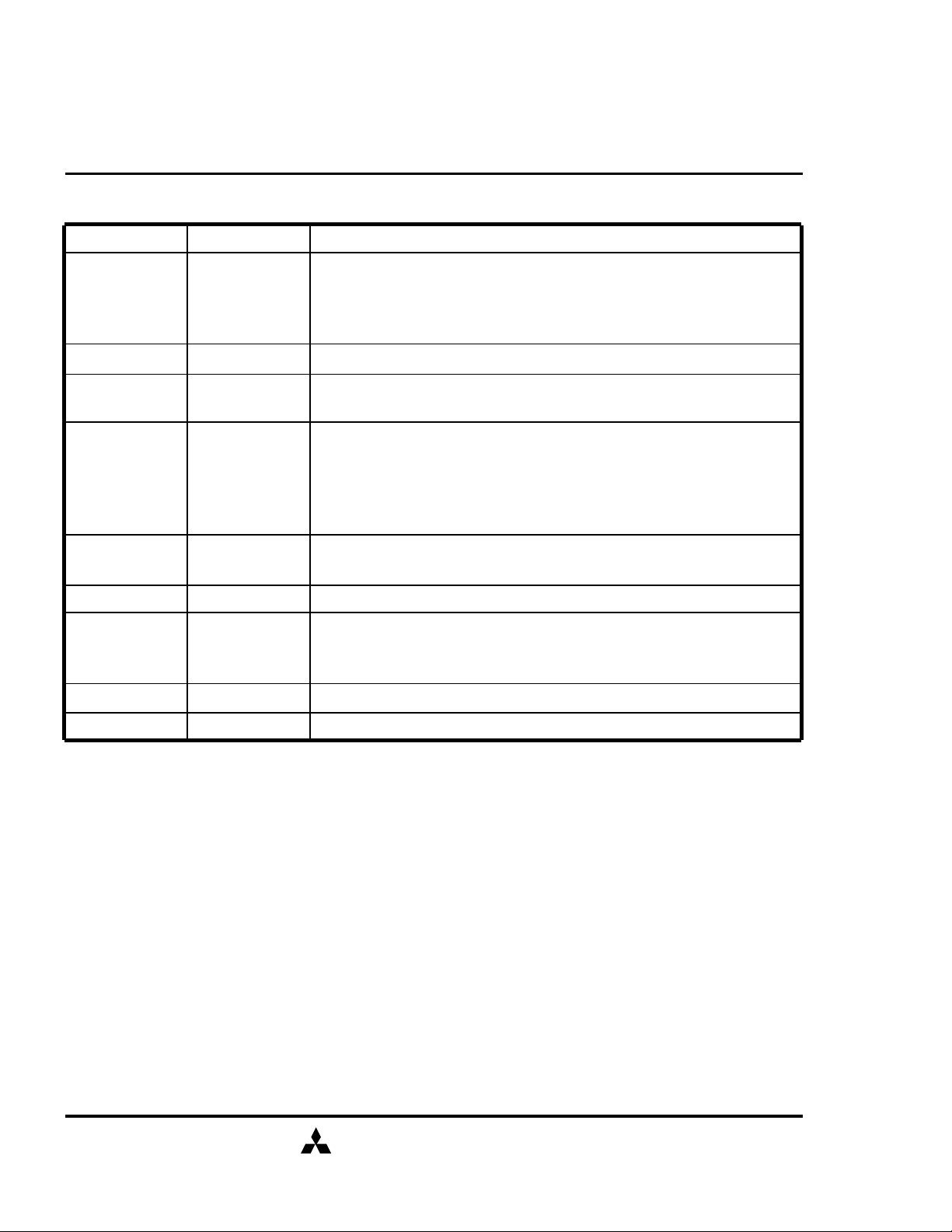
PIN FUNCTION
CLK Input Master Clock: All other inputs are referenced to the rising edge of CLK.
Clock Enable: CKE controls internal clock. When CKE is low, internal clock
CKE Input
/CS Input Chip Select: When /CS is high, any command means No Operation.
/RAS, /CAS, /WE Input Combination of /RAS, /CAS, /WE defines basic commands.
A0-11 Input
for the following cycle is ceased. CKE is also used to select auto / self
refresh. After self refresh mode is started, CKE becomes asynchronous
input. Self refresh is maintained as long as CKE is low.
A0-11 specify the Row / Column Address in conjunction with BA0,1. The
Row Address is specified by A0-11. The Column Address is specified by
A0-9 (x4), A0-8 (x8). A10 is also used to indicate precharge option. When
A10 is high at a read / write command, an auto precharge is performed.
When A10 is high at a precharge command, all banks are precharged.
BA0,1 Input
DQ0-7 (0-3) Input / Output Data In and Data out are referenced to the rising edge of CLK.
DQM Input
Vdd, Vss Power Supply Power Supply for the memory array and peripheral circuitry.
VddQ, VssQ Power Supply VddQ and VssQ are supplied to the Output Buffers only.
Bank Address: BA0,1 specifies one of four banks to which a command is
applied. BA0,1 must be set with ACT, PRE, READ, WRITE commands.
Din Mask / Output Disable: When DQM is high in burst write, Din for the
current cycle is masked. When DQM is high in burst read, Dout is disabled
at the next but one cycle.
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
3

SDRAM (Rev.0.2)
MITSUBISHI LSIs
Jan'97 Preliminary
M5M4V64S30ATP-8, -10, -12
64M (4-BANK x 2097152-WORD x 8-BIT) Synchronous DRAM
BASIC FUNCTIONS
The M5M4V64S30ATP provides basic functions, bank (row) activate, burst read / write, bank (row)
precharge, and auto / self refresh.
Each command is defined by control signals of /RAS, /CAS and /WE at CLK rising edge. In addition to 3
signals, /CS ,CKE and A10 are used as chip select, refresh option, and precharge option, respectively.
To know the detailed definition of commands, please see the command truth table.
CLK
/CS
/RAS
/CAS
/WE
CKE
A10
Chip Select : L=select, H=deselect
Command
Command
Command
Refresh Option @refresh command
Precharge Option @precharge or read/write command
define basic commands
Activate (ACT) [/RAS =L, /CAS =/WE =H]
ACT command activates a row in an idle bank indicated by BA.
Read (READ) [/RAS =H, /CAS =L, /WE =H]
READ command starts burst read from the active bank indicated by BA. First output data appears after
/CAS latency. When A10 =H at this command, the bank is deactivated after the burst read (auto-precharge,
READA).
Write (WRITE) [/RAS =H, /CAS =/WE =L]
WRITE command starts burst write to the active bank indicated by BA. Total data length to be written is
set by burst length. When A10 =H at this command, the bank is deactivated after the burst write (autoprecharge, WRITEA).
Precharge (PRE) [/RAS =L, /CAS =H, /WE =L]
PRE command deactivates the active bank indicated by BA. This command also terminates burst read /
write operation. When A10 =H at this command, both banks are deactivated (precharge all, PREA).
Auto-Refresh (REFA) [/RAS =/CAS =L, /WE =CKE =H]
REFA command starts auto-refresh cycle. Refresh address including bank address are generated inter-
nally. After this command, the banks are precharged automatically.
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
4
SDRAM (Rev.0.2)
Jan'97 Preliminary
64M (4-BANK x 2097152-WORD x 8-BIT) Synchronous DRAM
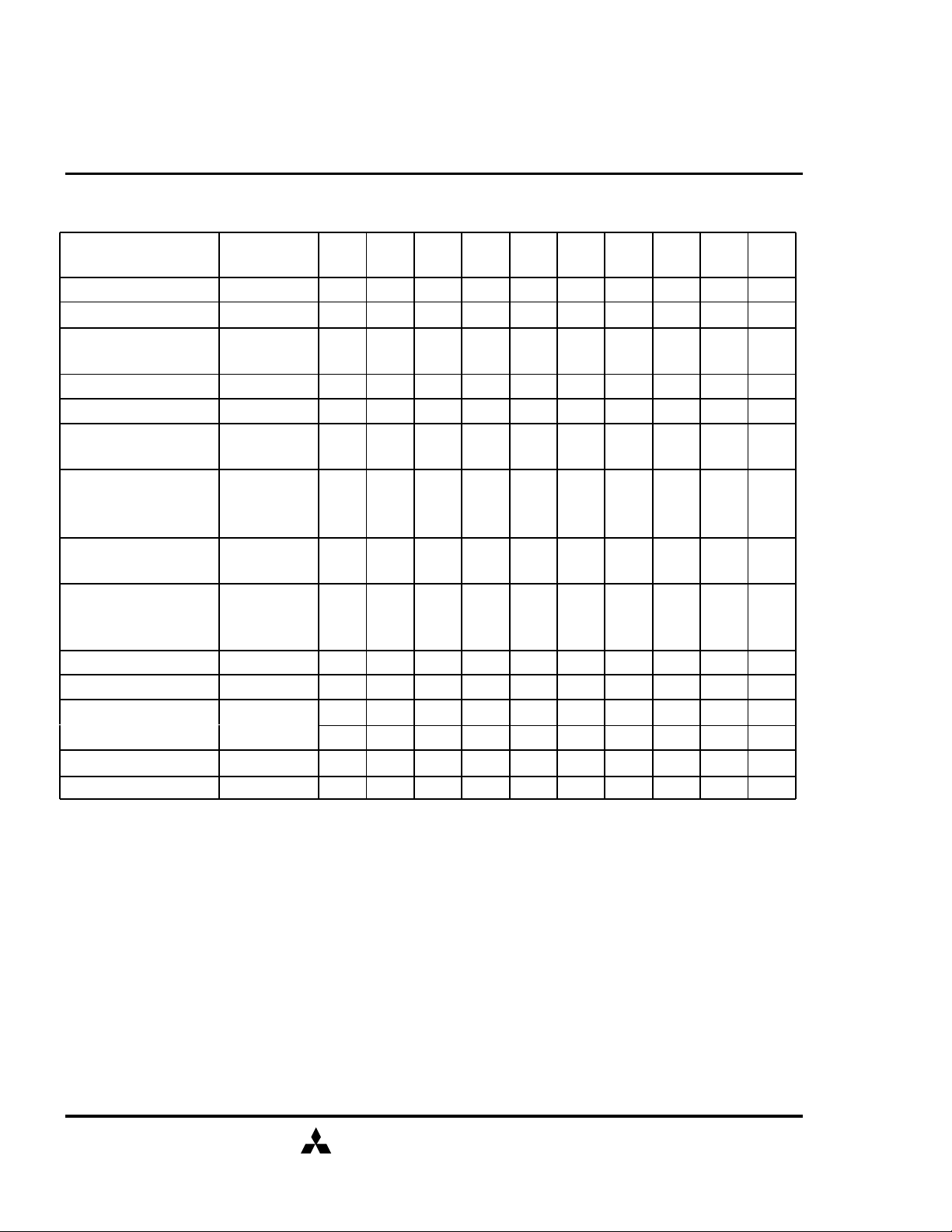
COMMAND TRUTH TABLE
MITSUBISHI LSIs
M5M4V64S30ATP-8, -10, -12
COMMAND MNEMONIC
Deselect DESEL H X H X X X X X X X
No Operation NOP H X L H H H X X X X
Row Address Entry &
Bank Activate
Single Bank Precharge PRE H X L L H L V X L X
Precharge All Banks PREA H X L L H L X H X
Column Address Entry
& Write
Column Address Entry
& Write with Auto-
Precharge
Column Address Entry
& Read
Column Address Entry
& Read with Auto-
Precharge
Auto-Refresh REFA H H L L L H X X X X
Self-Refresh Entry REFS H L L L L H X X X X
Self-Refresh Exit REFSX
Burst Terminate TERM H X L H H L X X X X
Mode Register Set MRS H X L L L L L L L V*1
ACT H X L L H H V V V V
WRITE H X L H L L V X L V
WRITEA H X L H L L V X H V
READ H X L H L H V X L V
READA H X L H L H V X H V
CKE
CKE
n-1
L H H X X X X X X X
L H L H H H X X X X
/CS /RAS /CAS /WE BA0,1 A11 A10 A0-9
n
X
H=High Level, L=Low Level, V=Valid, X=Don't Care, n=CLK cycle number
NOTE:
1. A7-A9 =0, A0-A6 =Mode Address
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
5
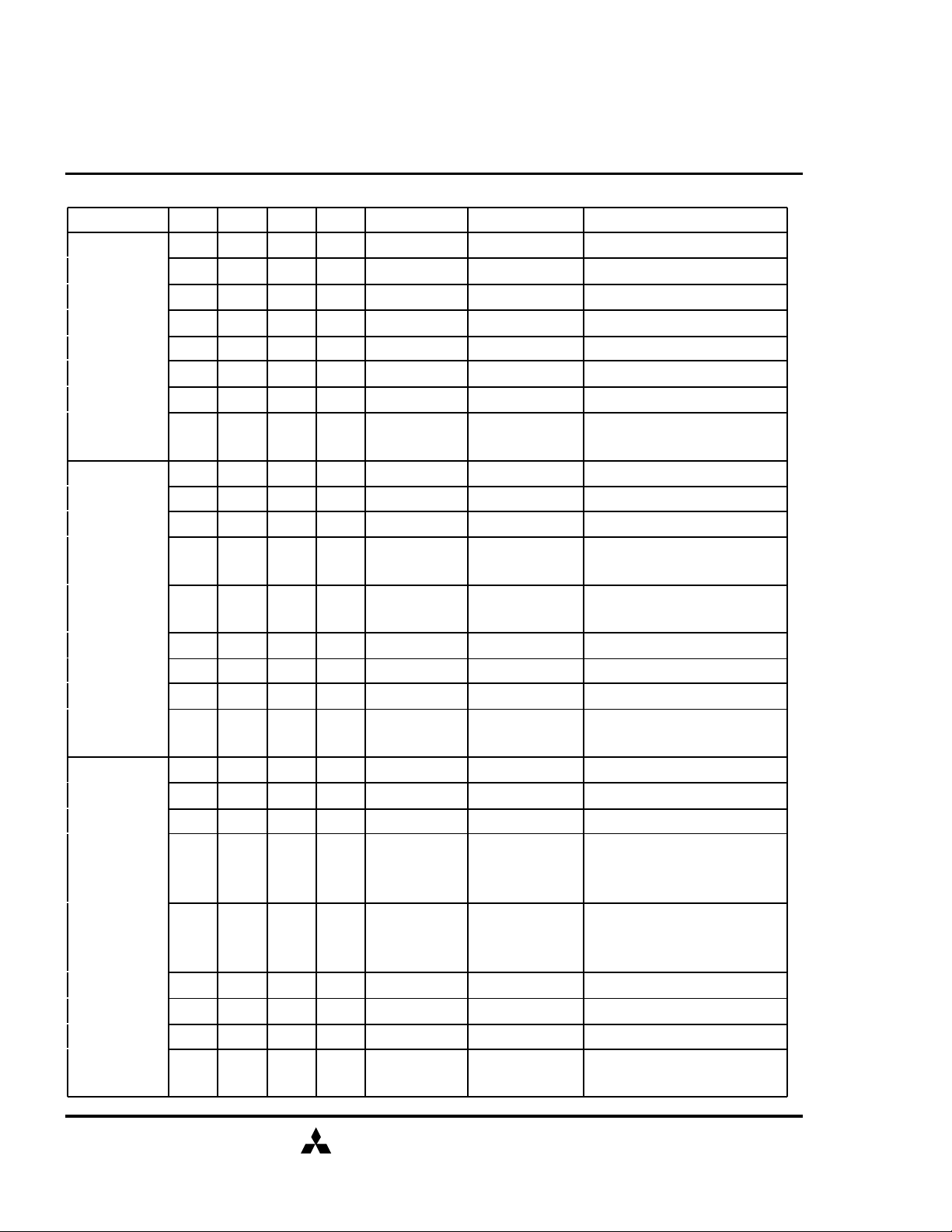
SDRAM (Rev.0.2)
MITSUBISHI LSIs
Jan'97 Preliminary
M5M4V64S30ATP-8, -10, -12
64M (4-BANK x 2097152-WORD x 8-BIT) Synchronous DRAM
FUNCTION TRUTH
TABLE
Current State /CS /RAS /CAS /WE Address Command Action
IDLE H X X X X DESEL NOP
L H H H X NOP NOP
L H H L BA TBST ILLEGAL*2
L H L X BA, CA, A10 READ / WRITE ILLEGAL*2
L L H H BA, RA ACT Bank Active, Latch RA
L L H L BA, A10 PRE / PREA NOP*4
L L L H X REFA Auto-Refresh*5
L L L L
ROW ACTIVE H X X X X DESEL NOP
L H H H X NOP NOP
L H H L BA TBST NOP
L H L H BA, CA, A10 READ / READA
L H L L BA, CA, A10
L L H H BA, RA ACT Bank Active / ILLEGAL*2
L L H L BA, A10 PRE / PREA Precharge / Precharge All
L L L H X REFA ILLEGAL
L L L L
READ H X X X X DESEL NOP (Continue Burst to END)
L H H H X NOP NOP (Continue Burst to END)
L H H L BA TBST Terminate Burst
L H L H BA, CA, A10 READ / READA
L H L L BA, CA, A10
L L H H BA, RA ACT Bank Active / ILLEGAL*2
L L H L BA, A10 PRE / PREA Terminate Burst, Precharge
L L L H X REFA ILLEGAL
L L L L
Op-Code,
Mode-Add
Op-Code,
Mode-Add
Op-Code,
Mode-Add
MRS Mode Register Set*5
Begin Read, Latch CA,
Determine Auto-Precharge
WRITE /
WRITEA
MRS ILLEGAL
WRITE /
WRITEA
MRS ILLEGAL
Begin Write, Latch CA,
Determine Auto-Precharge
Terminate Burst, Latch CA,
Begin New Read, Determine
Auto-Precharge*3
Terminate Burst, Latch CA,
Begin Write, Determine AutoPrecharge*3
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
6
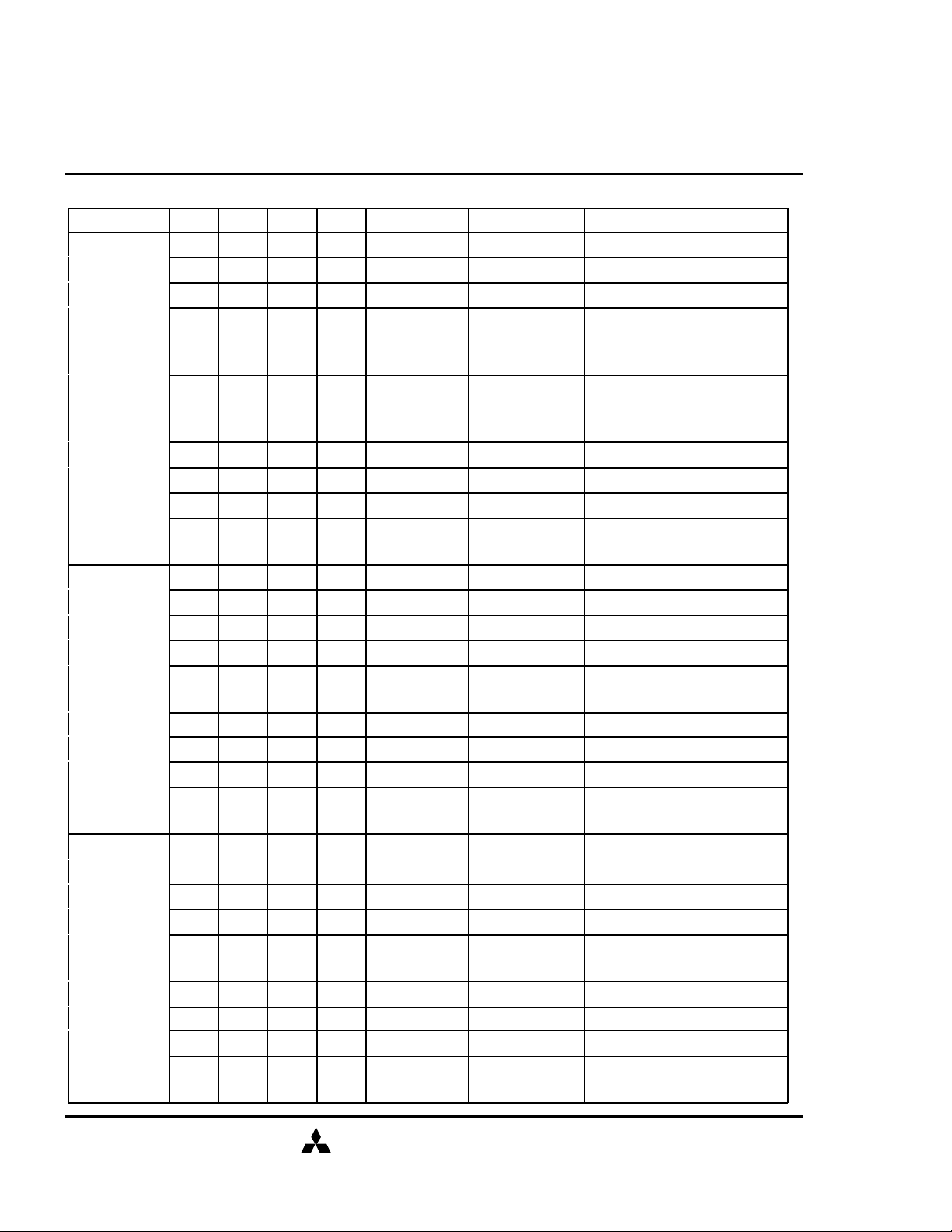
SDRAM (Rev.0.2)
MITSUBISHI LSIs
Jan'97 Preliminary
M5M4V64S30ATP-8, -10, -12
64M (4-BANK x 2097152-WORD x 8-BIT) Synchronous DRAM
FUNCTION TRUTH TABLE(continued)
Current State /CS /RAS /CAS /WE Address Command Action
WRITE H X X X X DESEL NOP (Continue Burst to END)
L H H H X NOP NOP (Continue Burst to END)
L H H L BA TBST Terminate Burst
Terminate Burst, Latch CA,
READ with
AUTO
PRECHARGE
WRITE with
AUTO
PRECHARGE
L H L H BA, CA, A10 READ / READA
L H L L BA, CA, A10
L L H H BA, RA ACT Bank Active / ILLEGAL*2
L L H L BA, A10 PRE / PREA Terminate Burst, Precharge
L L L H X REFA ILLEGAL
L L L L
H X X X X DESEL NOP (Continue Burst to END)
L H H H X NOP NOP (Continue Burst to END)
L H H L BA TBST ILLEGAL
L H L H BA, CA, A10 READ / READA ILLEGAL
L H L L BA, CA, A10
L L H H BA, RA ACT Bank Active / ILLEGAL*2
L L H L BA, A10 PRE / PREA ILLEGAL*2
L L L H X REFA ILLEGAL
L L L L
H X X X X DESEL NOP (Continue Burst to END)
L H H H X NOP NOP (Continue Burst to END)
L H H L BA TBST ILLEGAL
L H L H BA, CA, A10 READ / READA ILLEGAL
L H L L BA, CA, A10
L L H H BA, RA ACT Bank Active / ILLEGAL*2
L L H L BA, A10 PRE / PREA ILLEGAL*2
L L L H X REFA ILLEGAL
L L L L
Op-Code,
Mode-Add
Op-Code,
Mode-Add
Op-Code,
Mode-Add
WRITE /
WRITEA
MRS ILLEGAL
WRITE /
WRITEA
MRS ILLEGAL
WRITE /
WRITEA
MRS ILLEGAL
Begin Read, Determine AutoPrecharge*3
Terminate Burst, Latch CA,
Begin Write, Determine AutoPrecharge*3
ILLEGAL
ILLEGAL
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
7
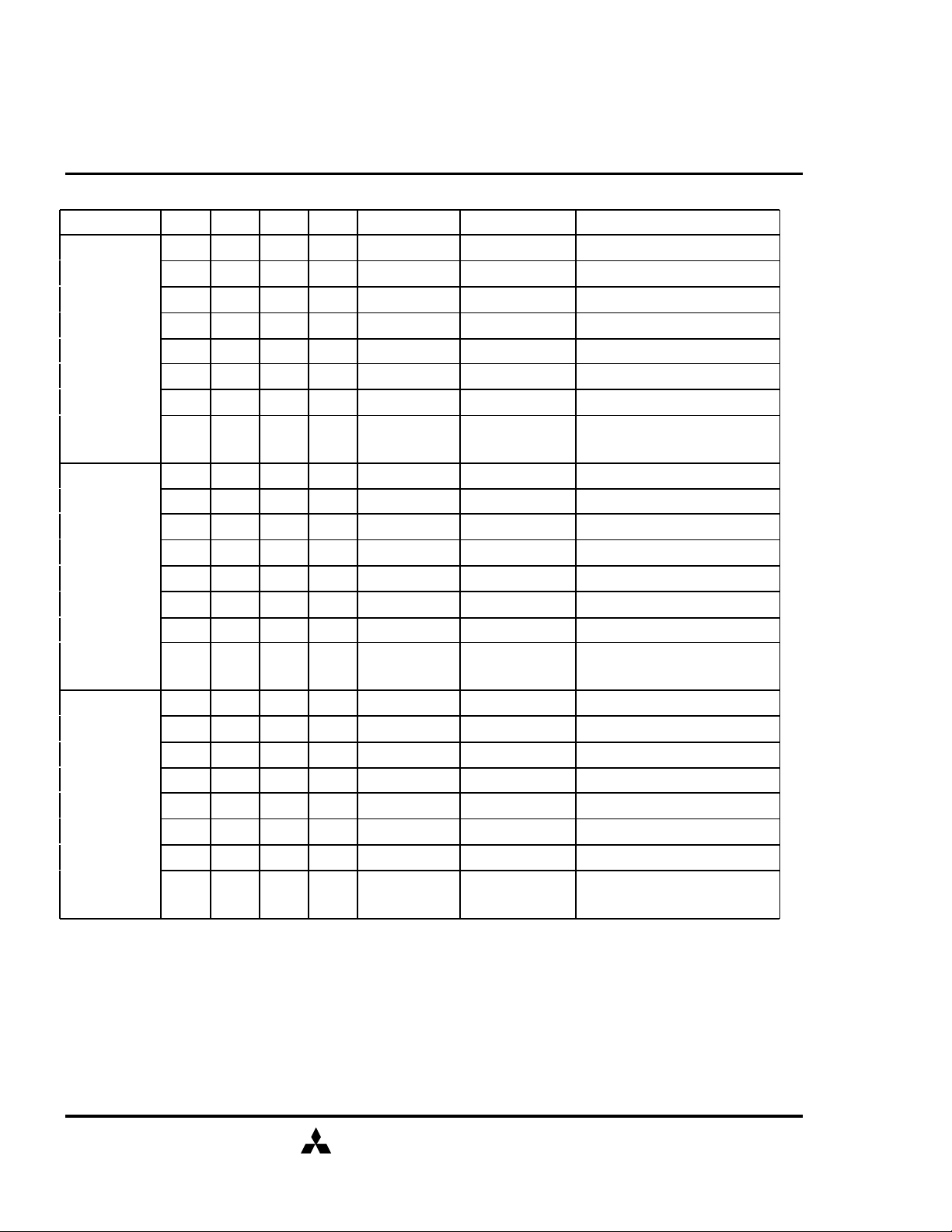
SDRAM (Rev.0.2)
Jan'97 Preliminary
M5M4V64S30ATP-8, -10, -12
64M (4-BANK x 2097152-WORD x 8-BIT) Synchronous DRAM
FUNCTION TRUTH TABLE(continued)
Current State /CS /RAS /CAS /WE Address Command Action
PRE -
CHARGING
ROW
ACTIVATING
WRITE RECOVERING
H X X X X DESEL NOP (Idle after tRP)
L H H H X NOP NOP (Idle after tRP)
L H H L BA TBST ILLEGAL*2
L H L X BA, CA, A10 READ / WRITE ILLEGAL*2
L L H H BA, RA ACT ILLEGAL*2
L L H L BA, A10 PRE / PREA NOP*4 (Idle after tRP)
L L L H X REFA ILLEGAL
L L L L
H X X X X DESEL NOP (Row Active after tRCD)
L H H H X NOP NOP (Row Active after tRCD)
L H H L BA TBST ILLEGAL*2
L H L X BA, CA, A10 READ / WRITE ILLEGAL*2
L L H H BA, RA ACT ILLEGAL*2
L L H L BA, A10 PRE / PREA ILLEGAL*2
L L L H X REFA ILLEGAL
L L L L
H X X X X DESEL NOP
L H H H X NOP NOP
L H H L BA TBST ILLEGAL*2
L H L X BA, CA, A10 READ / WRITE ILLEGAL*2
L L H H BA, RA ACT ILLEGAL*2
L L H L BA, A10 PRE / PREA ILLEGAL*2
L L L H X REFA ILLEGAL
L L L L
Op-Code,
Mode-Add
Op-Code,
Mode-Add
Op-Code,
Mode-Add
MRS ILLEGAL
MRS ILLEGAL
MRS ILLEGAL
MITSUBISHI LSIs
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
8
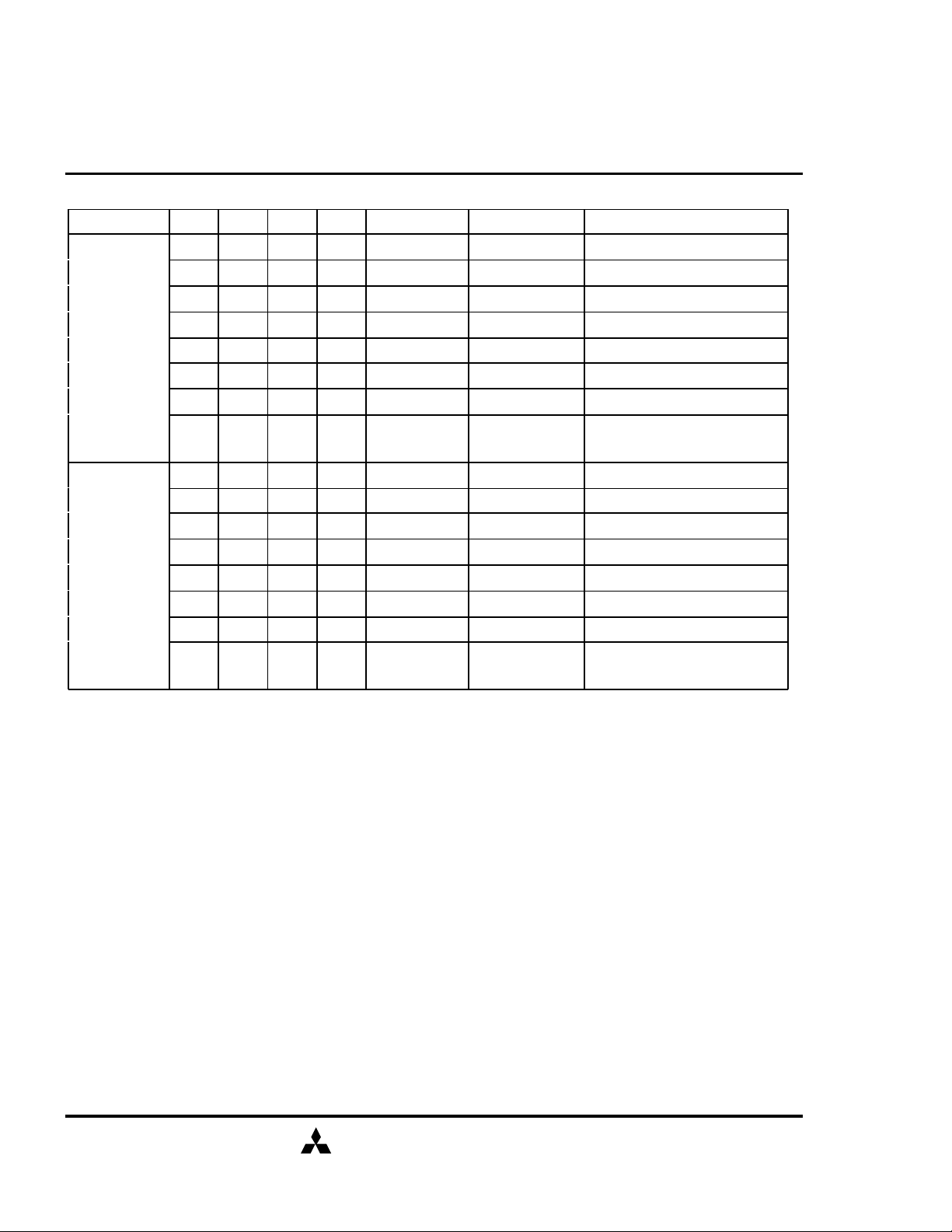
SDRAM (Rev.0.2)
MITSUBISHI LSIs
Jan'97 Preliminary
M5M4V64S30ATP-8, -10, -12
64M (4-BANK x 2097152-WORD x 8-BIT) Synchronous DRAM
FUNCTION TRUTH TABLE(continued)
Current State /CS /RAS /CAS /WE Address Command Action
RE-
FRESHING
MODE
REGISTER
SETTING
H X X X X DESEL NOP (Idle after tRC)
L H H H X NOP NOP (Idle after tRC)
L H H L BA TBST ILLEGAL
L H L X BA, CA, A10 READ / WRITE ILLEGAL
L L H H BA, RA ACT ILLEGAL
L L H L BA, A10 PRE / PREA ILLEGAL
L L L H X REFA ILLEGAL
L L L L
H X X X X DESEL NOP (Idle after tRSC)
L H H H X NOP NOP (Idle after tRSC)
L H H L BA TBST ILLEGAL
L H L X BA, CA, A10 READ / WRITE ILLEGAL
L L H H BA, RA ACT ILLEGAL
L L H L BA, A10 PRE / PREA ILLEGAL
L L L H X REFA ILLEGAL
L L L L
Op-Code,
Mode-Add
Op-Code,
Mode-Add
MRS ILLEGAL
MRS ILLEGAL
ABBREVIATIONS:
H=High Level, L=Low Level, X=Don't Care
BA=Bank Address, RA=Row Address, CA=Column Address, NOP=No OPeration
NOTES:
1. All entries assume that CKE was High during the preceding clock cycle and the current clock cycle.
2. ILLEGAL to bank in specified state; function may be legal in the bank indicated by BA, depending on the state of
that bank.
3. Must satisfy bus contention, bus turn around, write recovery requirements.
4. NOP to bank precharging or in idle state. May precharge bank indicated by BA.
5. ILLEGAL if any bank is not idle.
ILLEGAL = Device operation and/or data-integrity are not guaranteed.
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
9
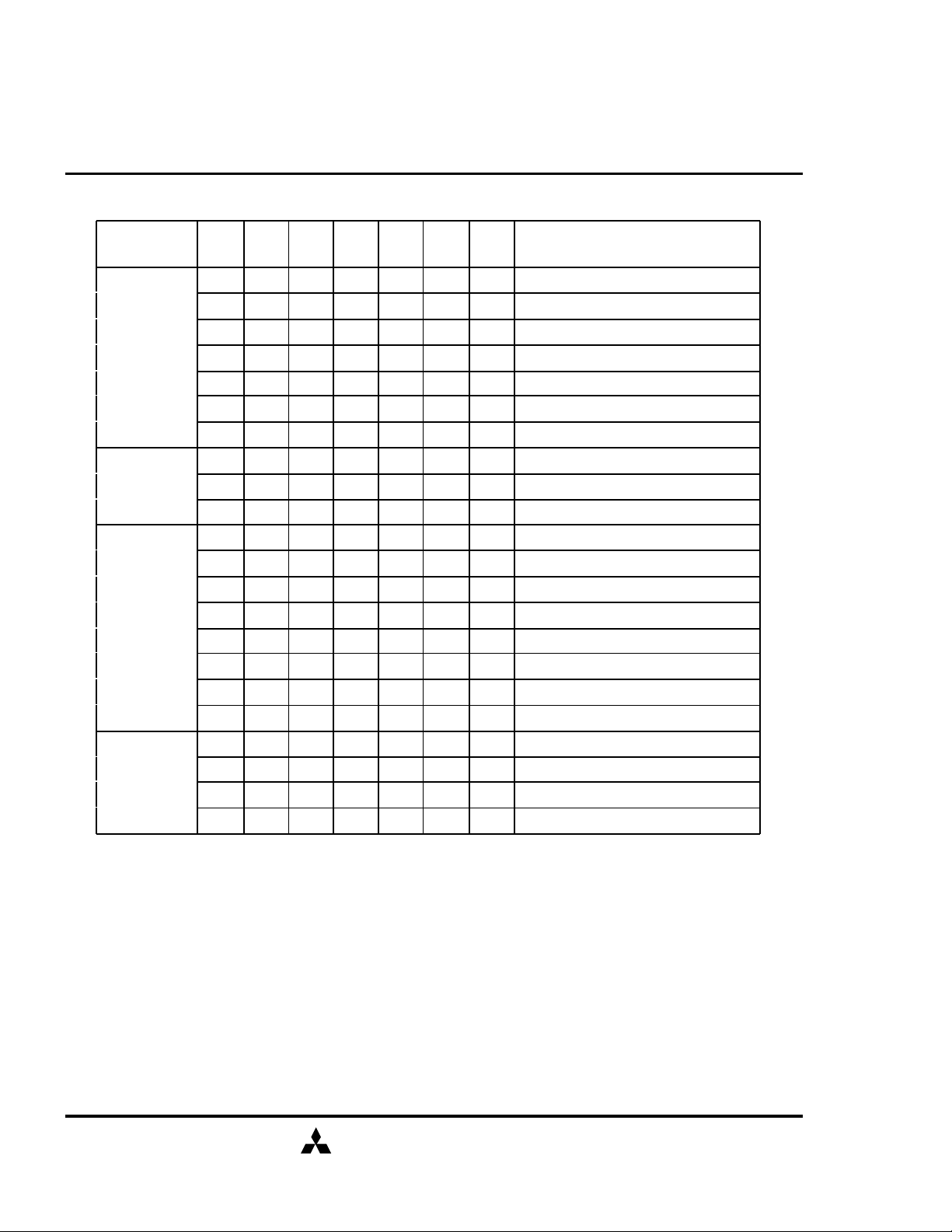
SDRAM (Rev.0.2)
Jan'97 Preliminary
64M (4-BANK x 2097152-WORD x 8-BIT) Synchronous DRAM
FUNCTION TRUTH TABLE for CKE
CKE
Current State
SELF-
REFRESH*1
POWER
DOWN
ALL BANKS
IDLE*2
ANY STATE
other than
listed above
CKE
n-1
H X X X X X X INVALID
L H H X X X X Exit Self-Refresh (Idle after tRC)
L H L H H H X Exit Self-Refresh (Idle after tRC)
L H L H H L X ILLEGAL
L H L H L X X ILLEGAL
L H L L X X X ILLEGAL
L L X X X X X NOP (Maintain Self-Refresh)
H X X X X X X INVALID
L H X X X X X Exit Power Down to Idle
L L X X X X X NOP (Maintain Self-Refresh)
H H X X X X X Refer to Function Truth Table
H L L L L H X Enter Self-Refresh
H L H X X X X Enter Power Down
H L L H H H X Enter Power Down
H L L H H L X ILLEGAL
H L L H L X X ILLEGAL
H L L L X X X ILLEGAL
L X X X X X X Refer to Current State =Power Down
H H X X X X X Refer to Function Truth Table
H L X X X X X Begin CLK Suspend at Next Cycle*3
L H X X X X X Exit CLK Suspend at Next Cycle*3
L L X X X X X Maintain CLK Suspend
/CS /RAS /CAS /WE Add Action
n
MITSUBISHI LSIs
M5M4V64S30ATP-8, -10, -12
ABBREVIATIONS:
H=High Level, L=Low Level, X=Don't Care
NOTES:
1. CKE Low to High transition will re-enable CLK and other inputsasynchronously. A minimum setup time must be
satisfied before any command other than EXIT.
2. Power-Down and Self-Refresh can be entered only from the All Banks Idle State.
3. Must be legal command.
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
10
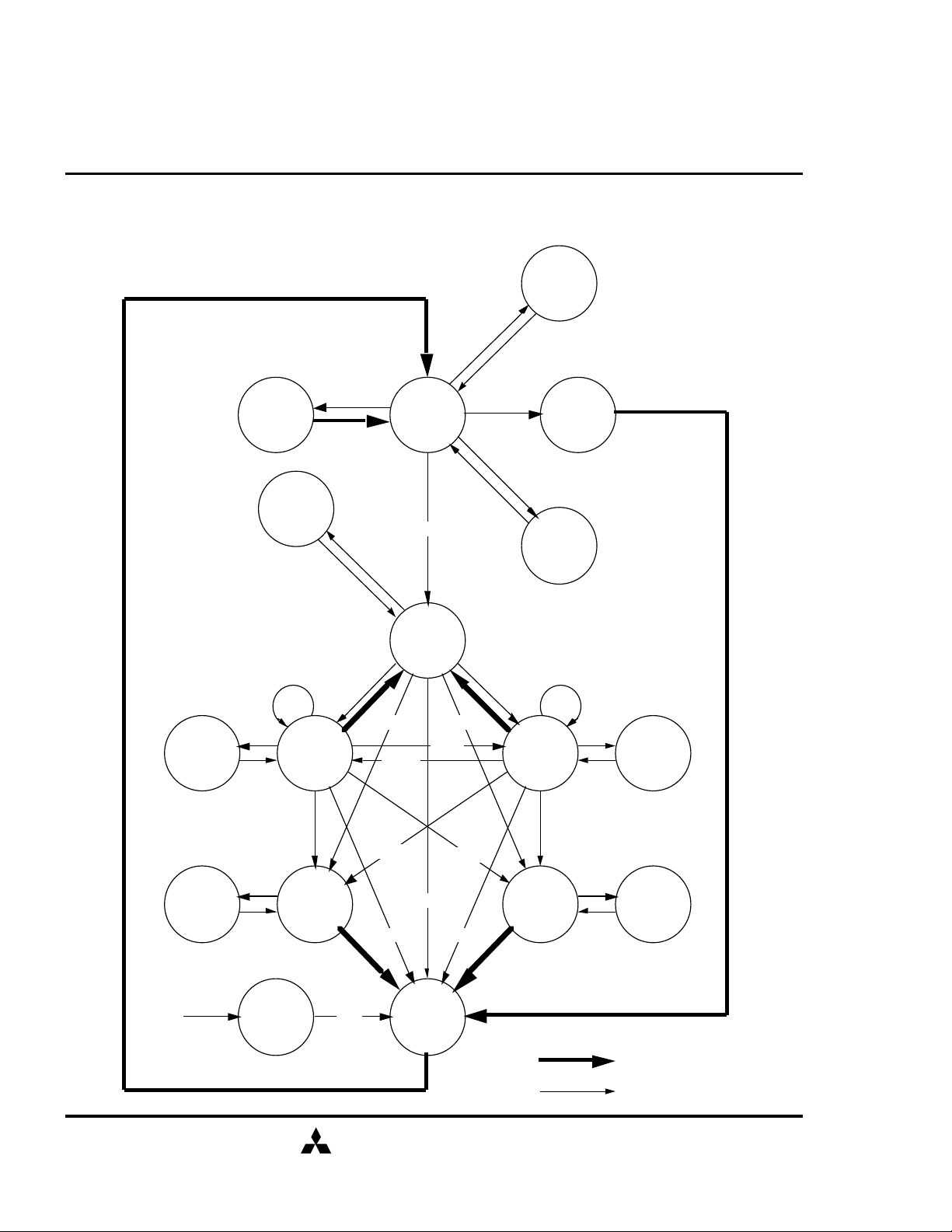
SDRAM (Rev.0.2)
Jan'97 Preliminary
64M (4-BANK x 2097152-WORD x 8-BIT) Synchronous DRAM
SIMPLIFIED STATE DIAGRAM
MITSUBISHI LSIs
M5M4V64S30ATP-8, -10, -12
SELF
REFRESH
REFS
REFSX
WRITE
SUSPEND
MODE
REGISTER
MRS
IDLE
REFA
SET
CKEL
CLK
SUSPEND
CKEH
ACT
POWER
CKEL
CKEH
ROW
ACTIVE
WRITE READ
CKEL
WRITE
CKEH
WRITEA READA
WRITEA
WRITE
WRITEA
READA
READ
READA
READ
AUTO
REFRESH
DOWN
CKEL
CKEH
READ
SUSPEND
WRITEA
SUSPEND
POWER
APPLIED
CKEL
CKEH
POWER
ON
WRITEA
PRE
PRE PRE
PRE
PRE
CHARGE
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
READA
CKEL
READA
SUSPEND
CKEH
Automatic Sequence
Command Sequence
11
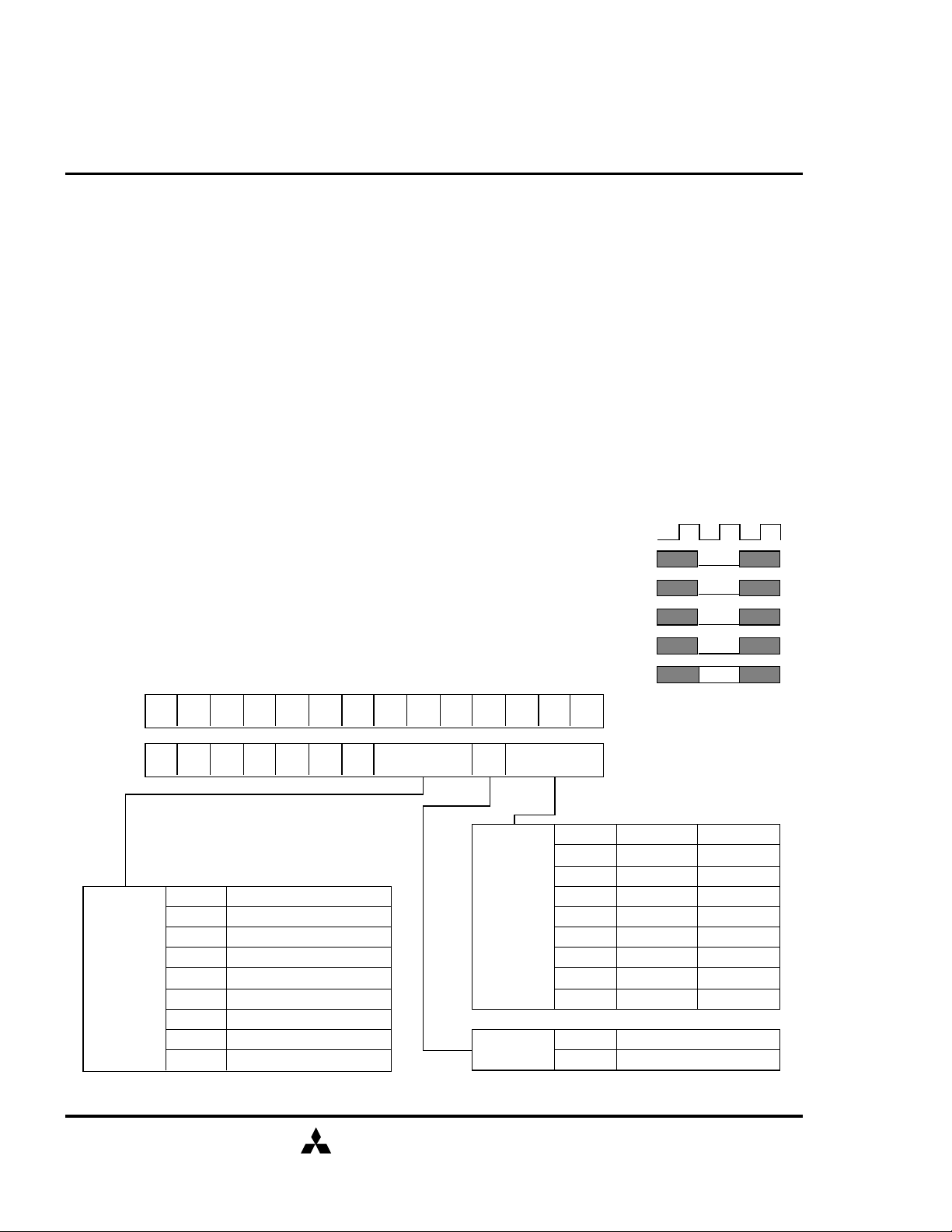
SDRAM (Rev.0.2)
MITSUBISHI LSIs
Jan'97 Preliminary
M5M4V64S30ATP-8, -10, -12
64M (4-BANK x 2097152-WORD x 8-BIT) Synchronous DRAM
POWER ON SEQUENCE
Before starting normal operation, the following power on sequence is necessary to prevent a SDRAM
from damaged or malfunctioning.
1. Apply power and start clock. Attempt to maintain CKE high, DQM high and NOP condition at the inputs.
2. Maintain stable power, stable clock, and NOP input conditions for a minimum of 500µs.
3. Issue precharge commands for all banks. (PRE or PREA)
4. After all banks become idle state (after tRP), issue 8 or more auto-refresh commands.
5. Issue a mode register set command to initialize the mode register.
After these sequence, the SDRAM is idle state and ready for normal operation.
MODE REGISTER
Burst Length, Burst Type and /CAS Latency can be programmed by
setting the mode register (MRS). The mode register stores these data
until the next MRS command, which may be issued when both banks
are inÅ@idle state. After tRSC from a MRS command, the SDRAM is
ready for new command.
A11 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0BA1BA0
0 0 0 0 0
LATENCY
MODE
00
CL
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 0 1
1 1 0
1 1 1
/CAS LATENCY
R
R
2
3
R
R
R
R
R: Reserved for Future Use
LTMODE BT BL
BURST
LENGTH
BURST
TYPE
CLK
/CS
/RAS
/CAS
/WE
BA0,1 A11-A0
BL
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 0 1
1 1 0
1 1 1
0
SEQUENTIAL
INTERLEAVED
1
V
BT= 0 BT= 1
1
2
4
8
R
R
R
R
1
2
4
8
R
R
R
R
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
12
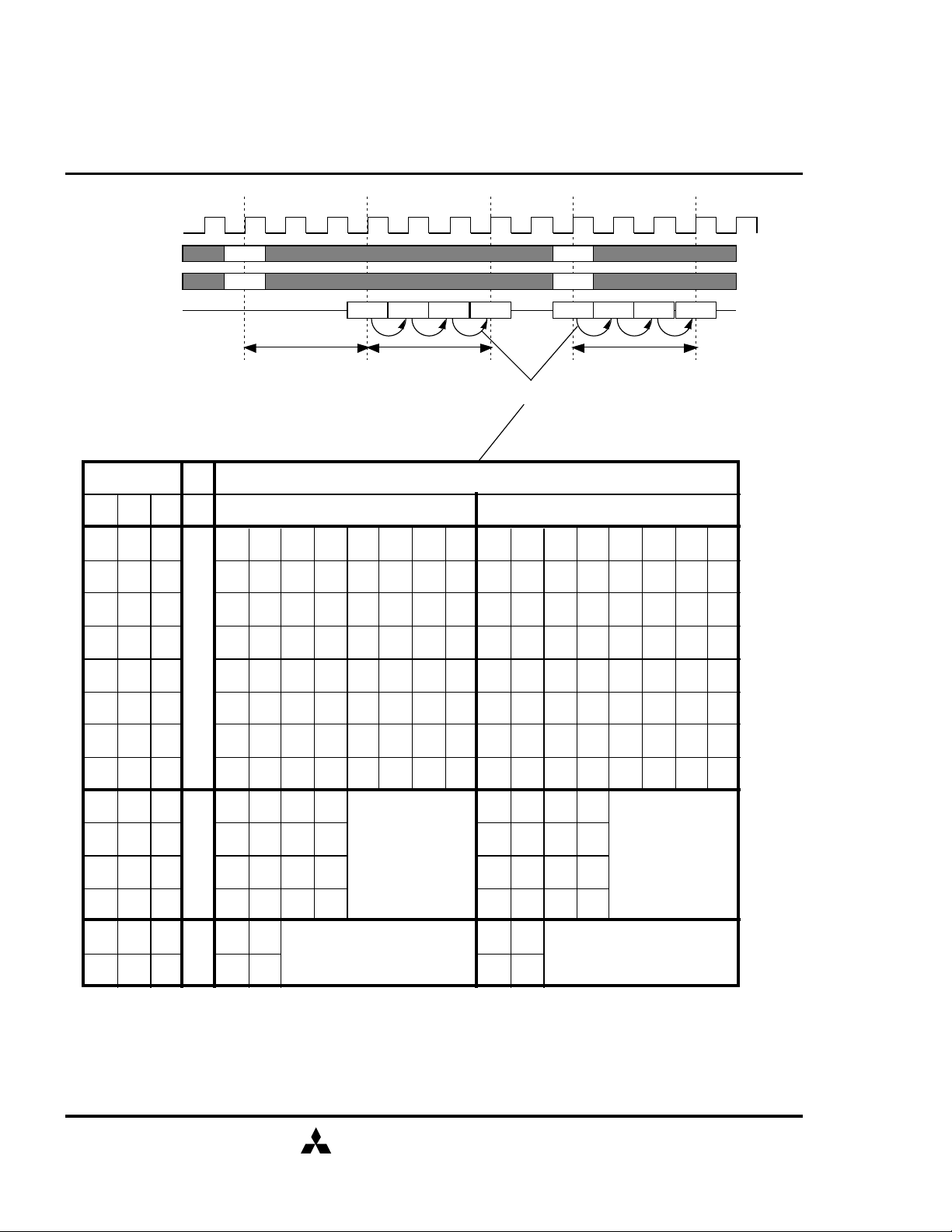
SDRAM (Rev.0.2)
Jan'97 Preliminary
CLK
Command
Address
DQ
MITSUBISHI LSIs
M5M4V64S30ATP-8, -10, -12
64M (4-BANK x 2097152-WORD x 8-BIT) Synchronous DRAM
Read
Y
Q0 Q1 Q2 Q3
Write
Y
D0 D1 D2 D3
CL= 3
BL= 4
Initial Address BL
A2 A1 A0
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 1
8
1 0 0
1 0 1
1 1 0
1 1 1
/CAS Latency Burst Length Burst Length
Burst Type
Column Addressing
Sequential Interleaved
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 0 3 2 5 4 7 6
2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 0 1 6 7 4 5
3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 2 1 0 7 6 5 4
4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3
5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 4 7 6 1 0 3 2
6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 4 5 2 3 0 1
7 0 1 2
3 4 5 6 3 2 1 0
7 6 5 4
- 0 0
- 0 1
- 1 0
- 1 1
- - 0
- - 1
0 1 2 3
1 2 3 0
4
2 3 0 1
3 0
0 1
2
1 0
1 2
0 1 2 3
1 0 3 2
2 3 0 1
3 2
0 1
1 0
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
1 0
13
SDRAM (Rev.0.2)
MITSUBISHI LSIs
Jan'97 Preliminary
M5M4V64S30ATP-8, -10, -12
64M (4-BANK x 2097152-WORD x 8-BIT) Synchronous DRAM
OPERATIONAL DESCRIPTION
BANK ACTIVATE
The SDRAM has four independent banks. Each bank is activated by the ACT command with the bank
addresses (BA0,1). A row is indicated by the row addresses A11-0. The minimum activation interval between one bank and the other bank is tRRD.Maximum 2 ACT commands are allowed within tRC, although
the number of banks which are active concurrently is not limited.
PRECHARGE
The PRE command deactivates the bank indicated by BA0,1. When multiple banks are active, the precharge
all command (PREA, PRE + A10=H) is available to deactivate them at the same time. After tRP from the
precharge, an ACT command to the same bank can be issued.
Bank Activation and Precharge All (BL=4, CL=3)
CLK
2 ACT command / tRCmin
tRCmin
Command
A0-9
A10
A11 Xa Xb Xb
BA0,1
DQ
READ
ACT
Xa
Xa
00
tRRD
tRCD
ACT
Xb
Xb
01
READ
Y
0
00
PRE
tRAS tRP
1
Qa0 Qa1 Qa2 Qa3
Precharge all
ACT
Xb
Xb
01
After tRCD from the bank activation, a READ command can be issued. 1st output data is available after
the /CAS Latency from the READ, followed by (BL -1) consecutive data when the Burst Length is BL. The
start address is specified by A8-0 (x 8) / A9-0 (x 4), and the address sequence of burst data is defined by the
Burst Type. A READ command may be applied to any active bank, so the row precharge time (tRP) can be
hidden behind continuous output data by interleaving the multiple banks. When A10 is high at a READ
command, the auto-precharge (READA) is performed. Any command (READ, WRITE, PRE, ACT) to the
same bank is inhibited till the internal precharge is complete. The internal precharge starts at BL after
READA. The next ACT command can be issued after (BL + tRP) from the previous READA.
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
14

SDRAM (Rev.0.2)
Jan'97 Preliminary
CLK
MITSUBISHI LSIs
M5M4V64S30ATP-8, -10, -12
64M (4-BANK x 2097152-WORD x 8-BIT) Synchronous DRAM
Multi Bank Interleaving READ (BL=4, CL=3)
Command
A0-9
A10
ACT
tRCD
Xa
Xa
A11 Xa Xb
BA0,1
00
DQ
READ with Auto-Precharge (BL=4, CL=3)
CLK
Command
A0-9
A10
ACT
tRCD tRP
Xa
Xa
READ
Y
0
00
READ
Y
1
ACT
Xb
Xb
10
/CAS latency
BL
READ
PRE
Y
0
0
10
00
Qa0 Qa1 Qa2 Qa3 Qb0 Qb1 Qb2
Burst Length
BL + tRP
ACT
Xa
Xa
A11
BA0,1
DQ
CLK
Command
CL=3
CL=2
DQ
DQ
Xa Xa
00
00
Qa0 Qa1 Qa2 Qa3
Internal precharge start
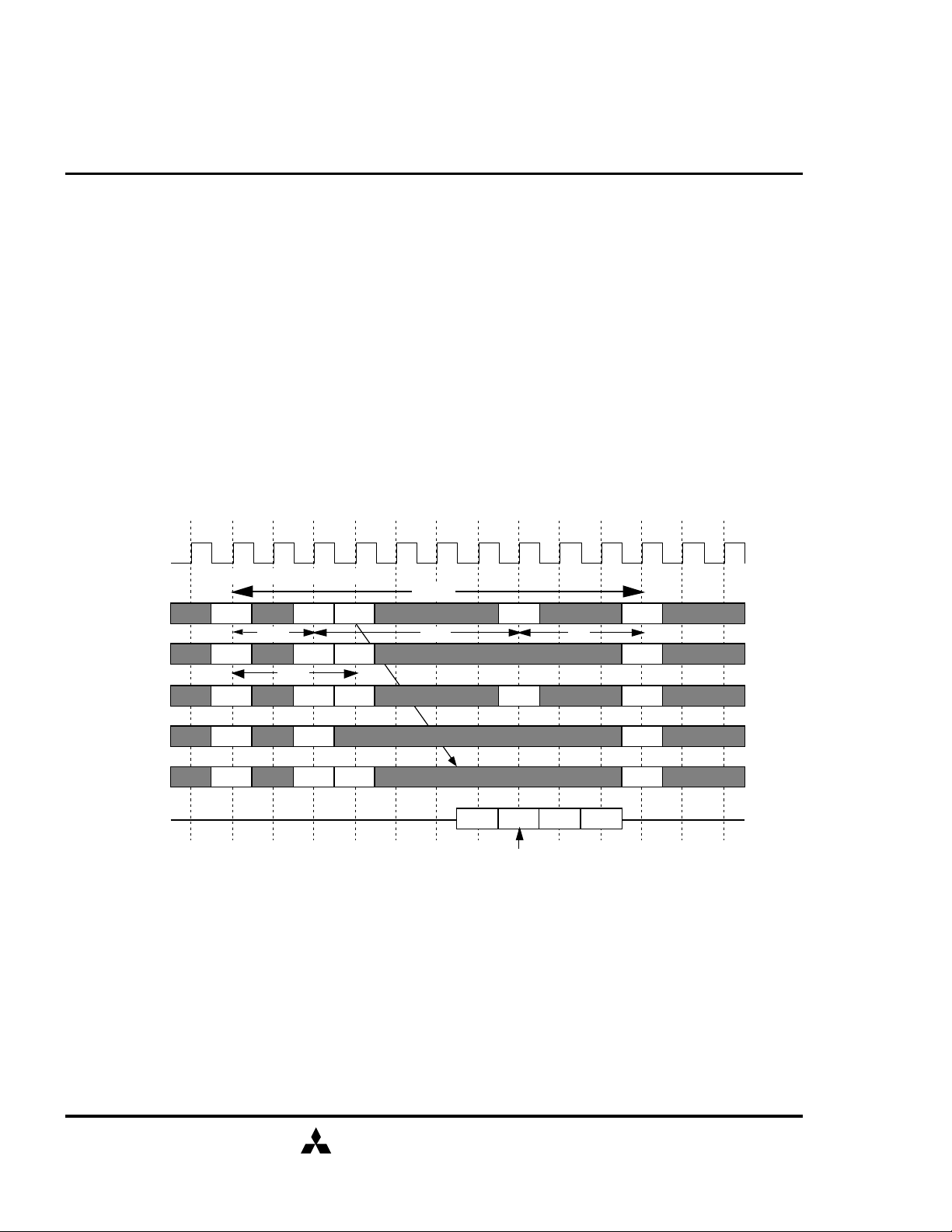
READ Auto-Precharge Timing (BL=4)
ACT READ
BL
Qa1 Qa2 Qa3Qa0
Qa1 Qa2 Qa3Qa0
Internal Precharge Start Timing
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
00
15
 Loading...
Loading...