
2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Description
32171 Group is a 32-bit, single-chip RISC microcomputer
with built-in flash memory, which was developed for use in
general industrial and household equipment.
To make full use of microcomputer built-in mass volume
flash memory, this microcomputer contains a variety of peripheral functions ranging from two independent blocks of
16-channel A-D converters to 37-channel multifunction timers, 10-channel DMAs, 3-channel serial I/Os, and 1-channel
real time debugger. Also included 1-channel Full-CAN modules and JTAG (boundary scan facility).
With lower power consumption and low noise characteristics
also considered, these microcomputers are ideal for embedded equipment applications.
Features
M32R RISC CPU core
• Uses the M32R family RISC CPU core (Instruction set
common to all microcomputers in the M32R family)
• Five-stage pipelined processing
• Sixteen 32-bit general-purpose registers
• 16-bit/32-bit instructions implemented
• DSP function instructions (sum-of-products calculation
using 56-bit accumulator)
• Built-in flash memory
• Built-in flash programming boot program
• Built-in RAM
• PLL clock generating circuit .............. Built-in × 4 PLL circuit
• Maximum operating frequency of the CPU clock
40MHz(when operating at -40 to +85
32MHz(when operating at -40 to +125oC)
o
C)
Real-time Debugger
• Includes dedicated clock-synchronized serial I/O that can
read and write the contents of the internalRAM independently of the CPU.
• Can look up and update the data table in real time while the
program is running.
• Can generate a dedicated interrupt based on RTD communication.
Abundant internal peripheral functions
In addition to the timers and real-time debugger, the
microcomputer contains the following peripheral functions.
• DMAC ............................................................ 10 channels
• A-D converter.................... 10-bit converter × 16 channels
• Serial I/O...........................................................3 channels
• Interrupt controller......... 22 interrupt sources, 8 priority levels
• Wait controller
• Full CAN ............................................................ 1 channel
• JTAG (Boundary scan function, Mitsubishi original)
Designed to operate at high temperatures
To meet the need for use at high temperatures, the microcomputer is designed to be able to operate in the temperature
range of -40 to +125oC when CPU clock operating
frequency = 32 MHz. When CPU clock operating frequency =
40 MHz, the microcomputer can be used in the temperature
o
range of -40 to +85
Note: This does not guarantee continuous operation at
o
125
puter at 125
C. If you are considering use of the microcom
C.
o
C, please consult Mitsubishi.
Table 1 Type Name List (32171 Group)
Type Name RAM Size ROM Size
M32171F4VFP 16K bytes 512K bytes
M32171F3VFP 16K bytes 384K bytes
M32171F2VFP 16K bytes 256K bytes
37-channel multijunction timers (MJT)
Multifunction timers are incorporated that support various
purposes of use.
16-bit output related timers ....................................... 35ch
16-bit input/output related timers .............................. 10ch
16-bit input related timers ........................................... 8ch
32-bit input related timers ........................................... 8ch
• Flexible configuration is possible through interconnection
of timers.
•
The internal DMAC and A-D converter can be started by a timer .
Applications
Automobile equipment control (e.g., Engine, ABS, AT), industrial equipment system control, and high-function OA equipment (e.g., PPC)
2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
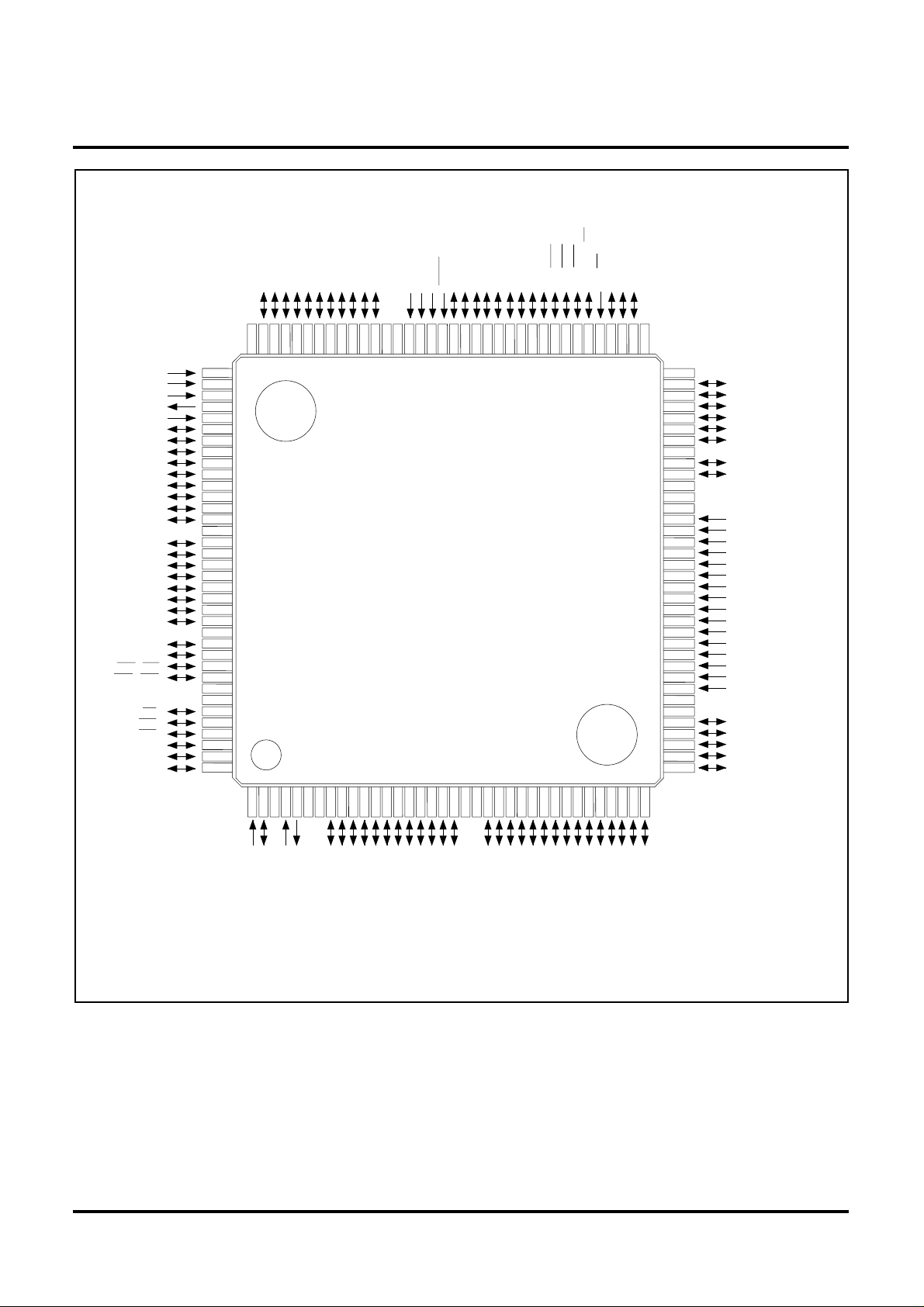
Pin Assignment(top view)
MS
JT
JTCK
JTRST
JTDO
JTDI
P103/TO11
P104/TO12
P105/TO
P106/TO14
P107/TO15
P124/TCLK
P125/TCLK1
P126/TCLK
P127/TCLK3
VCCI
P130/TIN16
P131/TIN1
P132/TIN1
P133/TIN19
P134/TIN2
P135/TIN2
P136/TIN2
P137/TIN23
VCCE
P150/TIN0
P153/TIN3
P41/ BLW / BLE
P42/ BHW / BHE
VCCI
VSS
P43/ RD
P44/ CS0
P45/ CS1
P46/A13
P47/A14
P220/CT
13
0
2
7
8
0
1
2
X
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
R
DTXD
4/RT
P7
82
W
/
Q
IT
K
L
C
WA
B
HACK
HRE
/
/
3
7
P71/
P70
P
P72/
0
8
81
8
79
7
4/ SBI
P6
77
CC
3
2
6
V
P
P6
P61
F
6
4
7
75
7
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
VSS
P87/SCLKI1/SCLKO1
D1
P86/RX
P85/TXD1
P84/SCLKI0/SCLKO0
P83/RXD0
P82/TXD0
VC
CE
P175/RXD2
P174/TXD2
VSS
VCCI
AVSS0
AD0IN15
AD0IN14
AD0IN13
AD0IN12
AD0IN11
AD0IN10
AD0IN9
AD0IN8
AD0IN7
AD0IN6
AD0IN5
AD0IN4
AD0IN3
AD0IN2
AD0IN1
AD0IN0
AVCC0
VREF0
P17/DB15
P16/DB14
P15/DB13
P14/DB12
P13/DB11
D
4/TO17
5/TO18
P9
P9
7
88
8
CK
A
6
1
D
DRX
O
T
/
3
6/RT
7
P9
P77/RTDCLK
P
P75/RT
83
86
85
84
1
102/TO10
P
107
P101/TO9
P100/TO8
05
106
1
116/TO6
P117/TO7
P
04
03
1
1
P115/TO5
02
1
DD
V
108
111/TO
114/TO4
112/TO2
P
P113/TO3
P
01
00
99
98
1
1
P
VSS
P
P110/TO0
VCCE
F
4
97
96
95
9
1
MOD
3
9
MOD0
2
1
9
9
19
TO20
RESET
P97/
P96/TO
9
90
8
M32171F4VFP
M32171F3VFP
M32171F2VFP
1
2
3
S
221/CRX
P225/A12
OSC-VS
P
8
5
XOUT
6
7
CNT
V
SC-VCC
O
9
P30/A15
P31/A16
4
IN
X
Figure 1 Pin Layout Diagram of the M32171
2
0
2
1
11
1
13
7
19
P32/A1
P33/A18
P34/A
P35/A20
8
9
17
14
15
16
1
1
20
21
22
7
6
CE
S
A2
/
3
VC
20/A23
P36/A21
P37/A22
P
VS
21/A24
22/A25
2
P
P24/A2
P
P
Package 144P6Q-A
6
24
6/A29
P2
8
25
2
27
2
29
30
0
3
A
DB3
DB0
/
7
1/DB1
2
P
4/DB4
P0
P02/DB2
P03/
P0
P00/
23
8
A2
/
5
2
P
31
5/DB5
P0
5
32
33
34
3
36
0
1
DB8
DB9
DB7
DB
/
6/DB6
2
0
1
P10/
P11/
P
P07/
P
2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
M32R CPU core
(max 40MHz)
Multiplieraccumulator
(32 × 16 + 56)
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
32171
Internal bus
interface
DMAC
(10 channels)
Multijunction timer
(MJT : 37 channels)
Internal flash memory
(M32171F4VFP : 512KB)
(M32171F3VFP : 384KB)
(M32171F2VFP : 256KB)
Internal RAM
(16KB )
Real-time debugger
(RTD)
PLL clock generation
circuit
Internal 32-bit bus
Internal 16-bit bus
External bus
Data
A-D converter
(10-bit, 16 channels)
Serial I/O
(3 channels)
Interrupt controller
(22 sources, 8 levels)
Wait controller
Full CAN
(1 channel)
interface
Address
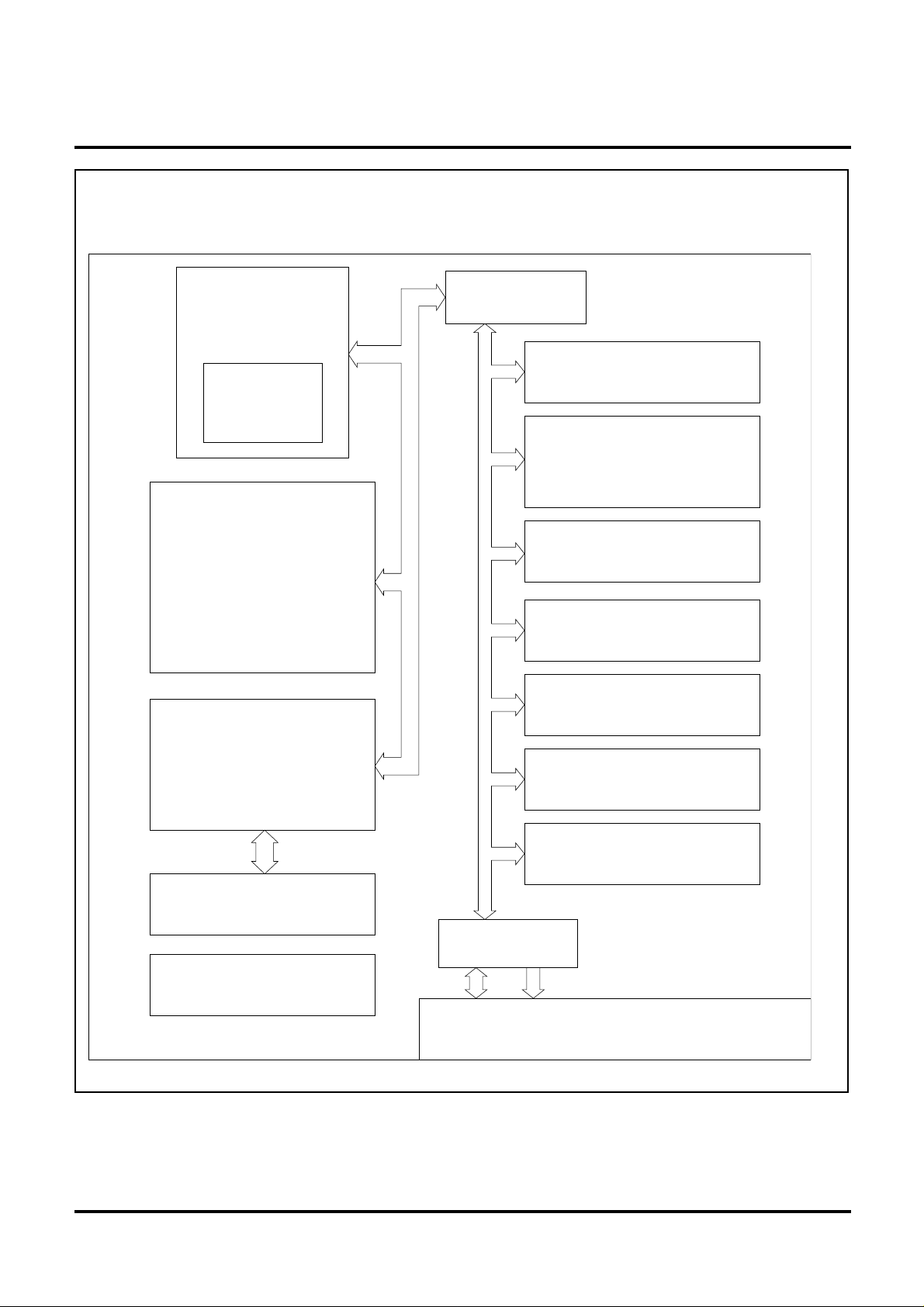
Figure 2 Block diagram
Input/output port(JTAG) 97 lines
3

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Table 2 Outline Performance (1/2)
Functional Block Features
M32R CPU core M32R family CPU core, internally configured in 32 bits
Built-in multiplier-accumulator (32 × 16 + 56)
Basic bus cycle : 25 ns (CPU clock frequency at 40 MHz, Internal peripheral clock frequency at 20 MHz)
Logical address space : 4G bytes, linear
General-purpose register : 32-bit register × 16, Control register: 32-bit register × 5
accumulator : 56 bits
External data bus 16 bits data bus
Instruction set 16-bit/32-bit instruction formats
83 instructions/ 9 addressing modes
Internal flash memory M32171F4VFP : 512K bytes
M32171F3VFP : 384K bytes
M32171F2VFP : 256K bytes
Rewrite durability : 100 times
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
Internal RAM 16K bytes
DMAC 10 channels (DMA transfers between internal peripheral I/Os, between internal
peripheral I/O and internal RAM, and between internal RAMs)
Channels can be cascaded and can operate in combination with internal peripheral I/O
Multijunction timer 37 channels of multijunction timers
• 16-bit output-related timers × 11 channels (single-shot, delayed single-shot)
• 16-bit input/output-related timers × 10 channels (event count mode, single-shot, PWM, measurement)
• 16-bit input-related timers × 8 channels (measurement, event count mode)
• 32-bit input-related timers × 8 channels (measurement)
Flexible timer configuration is possible through interconnection of channels using the event bus.
A-D converter 10-bit multifunction A-D converters
• Input 16 channels
• Scan-based conversion can be switched with 4, 8, and 16
• Capable of interrupt conversion during scan
• 8-bit/10-bit readout function available
Serial I/O 3 channels (The serial I/Os can be set for synchronous serial I/O or UART.
SIO2 is UART mode only)
Real-time debugger (RTD) 1-channels dedicated clock-synchronized serial
• The entire internal RAM can be read or rewritten from the outside without CPU intervention
Interrupt controller Controls interrupts from internal peripheral I/Os
(Priority can be set to one of 8 levels including interrupt disabled)
Wait controller Controls wait when accessing external extended area
(1 to 4 wait cycles inserted + prolonged by external WAIT signal input)
CAN 16-channels message slots
JTAG Boundary-Scan function
4

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Table 1 Outline Performance (2/2)
Function Block Features
Clock Maximum internal CPU memory clock : 40MHz (access to CPU, internal ROM, andinternal RAM)
Maximum internal peripheral clock : 20MHz (access to internal peripheral module)
Maximum external input clock : 10.0MHz, Built-in multiply-by-4 PLL circuit
Power Supply Voltage External I/O : 5V (±0.5V) or 3.3V (±0.3V)
Internal logic : 3.3V (±0.3V)
Operating temperature rang -40 to +125°C (CPU memory clock 32MHz , internal peripheral clock 16MHz)
-40 to +85°C (CPU memory clock 40MHz , internal peripheral clock 20MHz)
Package 0.5mm pitches / 144-pin plastic LQFP
5

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Outline of the CPU core
The M32171 Group uses the M32R RISC CPU core, and has
an instruction set which is common to all microcomputers in
the M32R family.
Instructions are processed in five pipelined stages consisting
of instruction fetch, decode, execution, memory access, and
write back. Thanks to its “out-of-order-completion” mechanism,
the M32R CPU allows for clock cycle efficient, instruction execution control.
The M32R CPU internally has sixteen 32-bit general-purpose
registers. The instruction set consists of 83 discrete instructions, which come in either a 16-bit instruction or a 32-bit instruction format. Use of the 16-bit instruction format helps to
reduce the code size of a program. Also, the availability of 32bit instructions facilitates programming and increases the performance at the same clock speed, as compared to
architectures with segmented address spaces.
Sum-of-products instructions comparable to DSP
The M32R CPU contains a multiplier/accumulator that can
execute 32 bits × 16 bits in one cycle. Therefore, it executes a
32 bit × 32 bit integer multiplication instruction in three cycles.
Also, the M32R CPU supports the following four sum-of-products instructions (or multiplication instructions) for DSP function use.
(1) 16 high-order register bits × 16 high-order register bits
(2) 16 low-order register bits × 16 low-order register bits
(3) All 32 register bits × 16 high-order register bits
(4) All 32 register bits × 16 low-order register bits
Furthermore, the M32R CPU has instructions for rounding the
value stored in the accumulator to 16 or 32 bits, and instructions for shifting the accumulator value to adjust digits before
storing in a register. Because these instructions also can be
executed in one cycle, DSP comparable data processing capability can be obtained by using them in combination with
high-speed data transfer instructions such as Load & Address
Update or Store & Address Update.
Address space
The M32171 Group’s logical addresses are always handled in
32 bits, providing 4 Gbytes of linear address space. The
M32171 Group’s address space consists of the following.
User space
A 2-Gbyte area from H’0000 0000 to H’7FFF FFFF is the user
space. Located in this space are the user ROM area, external
extended area, internal RAM area, and SFR (Special Function Register) area (internal peripheral I/O registers). Of
these, the user ROM area and external extended area are located differently depending on mode settings.
Boot program space
A 1-Gbyte area from H’8000 0000 to H’BFFF FFFF is the boot
program area. This space contains the on-board programming program (boot program) used in blank state by the internal flash memory.
System space
A 1-Gbyte area from H’C000 0000 to H’FFFF FFFF is the
system area. This space is reserved for use by development
tools such as an in-circuit emulator and debug monitor, and
cannot be used by the user.
Three operation modes
The M32170 and M32174 Group has three operation modes:
single-chip mode, external extended mode, and processor
mode. These operation modes are changed from one to another by setting the MOD0 and MOD1 pins.
6
2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Port 7
Port 22
Port 15
Port 13
Port 12
Port 11
Port 10
Port 9
Multijunction
converter
Clock
Reset
Mode
CAN
timer
A-D
XIN
XOUT
VC
NT
C
OSC-VC
S
OSC-VS
P70 / BCLK / W
RESET
D0
MO
D1
MO
FP
P220 / C
P221 / C
P150,P153 / TIN0,TIN3
P130-P137 / TIN16-TIN23
P124-P127 / TCLK0-TCLK3
P93-P97 / TO16-TO720
P100-P107 / TO8-TO15
P110-P117 / TO0-TO7
AD0IN0A-D0IN15
AVCC
AVSS
VREF
R
TX
RX
0
0
0
10
4
21
16
3.3V (Note)
2VFP
5V
M32171F4VFP, M32171F3VFP, M32171F
P45 / C
P44 / C
P43 / R
P42 / BHW / B
P41 / BLW / B
P71 / WAI
P72 / HREQ
P73 / HACK
19
P20-P27 / A23-A30
P30-P37 / A15-A22
P46, P47 / A13, A14
P225 / A12
16
P00-P07 / DB0-DB7
P10-P17 / DB8-DB15
P82 / TXD
P83 / RXD
5V
P84 / SCLKI 0 / SCLKO
P85 / TXD1
P86 / RXD
P87 / SCLKI 1 / SCLKO
P174 / TXD
P175 / RXD2
P74 / RTDTXD
P75 / RTDRXD
P76 / RTDACK
P77 / RTDCL
S1
S0
D
HE
LE
T
0
0
1
2
K
Bus
control
Address
bus
Data
bus
0
Serial
I/O
1
Real-time
debugger
Port 4
Port 7
Port 2
Port 3
Port 4
Port 22
Port 0
Port 1
Port 8
Port 17
Port 7
Port 6
Port 6
Interrupt
controller
Note:
P61-P63
P64 / S
VCCE
VCCI
3.3V
5V
BI
: Operates with a 3.3V power supply.
Operates with a 5V or 3.3V power supply.
:
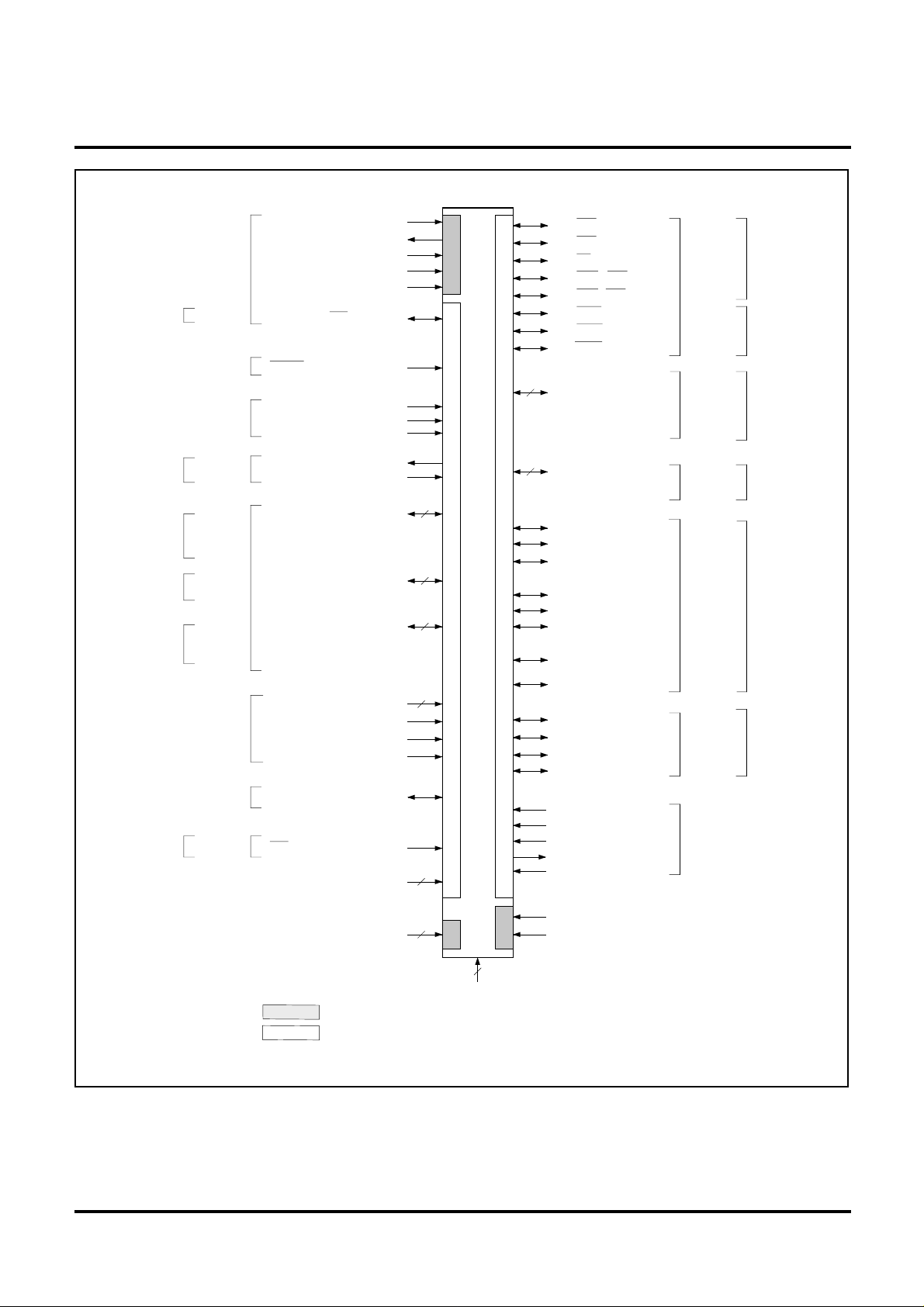
Figure 3 Pin Function Diagram of 240QFP
JTMS
JTCK
JTRST
DO
JT
DI
3V
3.
JT
VDD
FVCC
4
3
3.3V
5
S
VS
JT
AG
7
2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Table 4 Description of Pin Function (1/4 )
Type Pin Name Description Input/Output Function
Power VCCE Power supply — Supplies power (5 V or 3.3V) to external I/O ports.
supply VCCI Power supply — Supplies power (3.3 V) to the internal logic.
VDD RAM power supply — nternal RAM backup power supply (3.3 V).
FVCC Flash power supply — Internal flash memory backup power supply (3.3 V).
VSS Ground — Connect all VSS pins to ground (GND).
Clock XIN, Clock Input Clock input/output pins. These pins contain a PLL-based
XOUT Output frequency multiply-by-4, so input the clock whose frequency is quarter
the operating frequency. (XIN input = 10 MHz when CPU clock operates
at 40 MHz)
BCLK / System clock Output
______
WR external inpout clock. (BCLK output = 20 MHz when CPU clock operates at 40
When this signal is System Clock(BCLK), it outputs a clock whose is twice
MHz). Use this clock when circuits are synchronized externally.
When this signal is Write(WR), during external write access it indicates the
valid data on the data bus to transfer.
______
that of
OSC-VCC Power supply — Power supply to the PLL circuit. Connect OSC-VCC to the power supply(3.3V)
OSC-VSS Ground — Connect OSC-VSS to ground.
VCNT PLL control Input This pin controls the PLL circuit. Connect a resistor and capacitor to this pin.
Reset
Mode MOD0 Mode Input These pins set an operation mode.
Address A12-A30 Address Output 19 lines of address bus (A12-A30) are provided to accommodate two
bus bus
Data bus DB0-DB15 Data bus Input/output This 16-bit data bus connects to external device.
______
RESET Reset Input This pin resets the internal circuits.
MOD1 MOD0 MOD1 Mode
0 0 Single-chip mode
0 1 Expanded external mode
1 0 Processor mode
0 0 (Boot mode) (Note)
1 1 (Reserved)
channels of 1 MB memory space (max.) connected external to the chip.
A31 is not output.
In the write cycle, of the 16-bit data bus the valid byte positions to write are
output as BHW/ BHE and BLW/ BLE. In read cycle, data on the entire 16-bit
data bus is read. However, only the data at the valid byte positions are
transferred to the M32R’s internal circuit.
_________ ________ ________ _______
Note: FP pin should be “H” level in Boot Mode.
8

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Table 5 Description of Pin Function (2/4)
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Type Pin type Description Input/Output Function
Bus
___
CS0, Chip Output Chip select signals for external devices.
control CS1 select
__
RD Read Output This signal is output when reading external devices.
___
_______
BHW/ BHE Byte high Output Indicates the byte positions to which valid are transferred when writing to
___
write
_______
BLW/ BLE Byte low Output
external devices.BHW/ BHE and BLW/ BLE correspond to the upper address
side(D0-D7 effective) and the lower address side(D8-D15 effective),respectivel.
write
____
WAIT Wait Input
_________
If WAIT input is low when the M32R accesses external devices, the wait cycle
extended.
_____
HREQ Hold Input This pin is used by an external device to request control of the external bus.
____
request
HACK Hold Output This signal indicates to the external device that the M32R has entered a hold
The M32R goes to a hold state when HREQ input is pulled low.
acknowledge state and relinquished control of the external bus.
Multijunction
TIN0, TIN3 Timer input Input Input pins for multijunction timer.
timer TIN16-TIN23
TO0 Timer output Output Output pins for multijunction timer.
-TO20
TCLK0 Timer clock Input Clock input pins for multijunction timer.
-TCLK3
________ _______ ________ _______
__________
A-D AVCC0, Analog power – AVCC0 is the power supply for the A-D0 converters.Connect AVCC0
converter
upply
to the power supply (5V or 3.3V).
AVSS0 Analog ground – AVSS0 is the analog ground for the A-D0 converters. Connect AVCC0 to ground
AD0IN0 Analog input Input 16-channel analog input pin for A-D0 converter.
-AD0IN15
VREF0 Reference Input VREF0 is the reference voltage input pin (5V or 3.3V) for the A-D0 converters.
voltage input
___
Interrupt
SBI System Input System break interrupt(SBI) input pin of the interrupt controller.
controller break
interrupt
9

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Table 6 Description of Pin Functions (3/4)
Type Pin name Description Input/output Function
Serial SCLKI0/ UART transmit/ Input/output When channel 0 is in UART mode:
I/O
SCLKO0 receive clock Clock output derived from BRG output by dividing it by 2
output or CSIO
transmit/receive When channel 0 is in CSIO mode:
clock Transmit/receive clock input when external clock is selected
input/output Transmit/receive clock output when internal clock is selected
SCLKI1/ UART transmit/ Input/output When channel 1 is in UART mode:
SCLKO1 receive clock Clock output derived from BRG output by dividing it by 2
output or CSIO
transmit/receive When channel 1 is in CSIO mode:
clock Transmit/receive clock input when external clock is selected
input/output Transmit/receive clock output when internal clock is selected
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
TXD0 Transmit data Output Transmit data output pin for serial I/O channel 0
RXD0 Receive data Input Receive data input pin for serial I/O channel 0
TXD1 Transmit data Output Transmit data output pin for serial I/O channel 1
RXD1 Receive data Input Receive data input pin for serial I/O channel 1
TXD2 Transmit data Output Transmit data output pin for serial I/O channel 2
RXD2 Receive data Input Receive data input pin for serial I/O channel 2
Real-Time
Debugger
Flash- FP Flash protect Input This pin protects the flash memory against E/W in hardware.
only
CAN CTX Transmit data Output Data output pin from CAN module.
RTDTXD Transmit data Output Serial data output pin of the real-time debugger
RTDRXD Receive data Input Serial data input pin of the real-time debugger
RTDCLK Clock input Input Serial data transmit/receive clock input pin of the real-time debugger
RTDACK Acknowledge Output This pin outputs a low pulse synchronously with the real-time debugger’s
first clock of serial data output word. The low pulse width indicates the
type of the command/data the realtime debugger has received.
CRX Receive data Input Data input pin to CAN module.
JTAG JTMS Test mode Input Test select input for controlling the test circuit’s state transition
JTCK Clock Input Clock input to the debugger module and test circuit.
JTRST Test reset Input Test reset input for initializing the test circuit asynchronously.
JTDO Serial output Output Serial output of test instruction code or test data.
JTDI Serial input Input Serial input of test instruction code or test data.
10

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Table 7 Description of Pin Functions (4/4)
Type Pin name Description Input/output Function
Input/
output
port
(Note)
P00-P07 Input/output port 0 Input/output Programmable input/output port.
P10-P17 Input/output port 1 Input/output Programmable input/output port.
P20-P27 Input/output port 2 Input/output Programmable input/output port.
P30-P37 Input/output port 3 Input/output Programmable input/output port.
P41-P47 Input/output port 4 Input/output Programmable input/output port.
P61-P64 Input/output port 6 Input/output Programmable input/output port.
(However, P64 is an input-only port)
P70-P77 Input/output port 7 Input/output Programmable input/output port.
P82-P87 Input/output port 8 Input/output Programmable input/output port.
P93-P97 Input/output port 9 Input/output Programmable input/output port.
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
P100 Input/output port 10 Input/output Programmable input/output port.
-P107
P110 Input/output port 11 Input/output Programmable input/output port.
-P117
P124 Input/output port1 2 Input/output Programmable input/output port.
-P127
P130 Input/output port 13 Input/output Programmable input/output port.
-P137
P150, P153 Input/output port 15 Input/output Programmable input/output port.
P174, P175 Input/output port 17 Input/output Programmable input/output port.
P220, Input/output port 22 Input/output Programmable input/output port.
P221, P225 (However, P221 is an input-only port)
Note: Input/output port 5 is reserved for future use.
Input/output ports 14, 16, 18, 19, 20, and 21 do not exist.
11
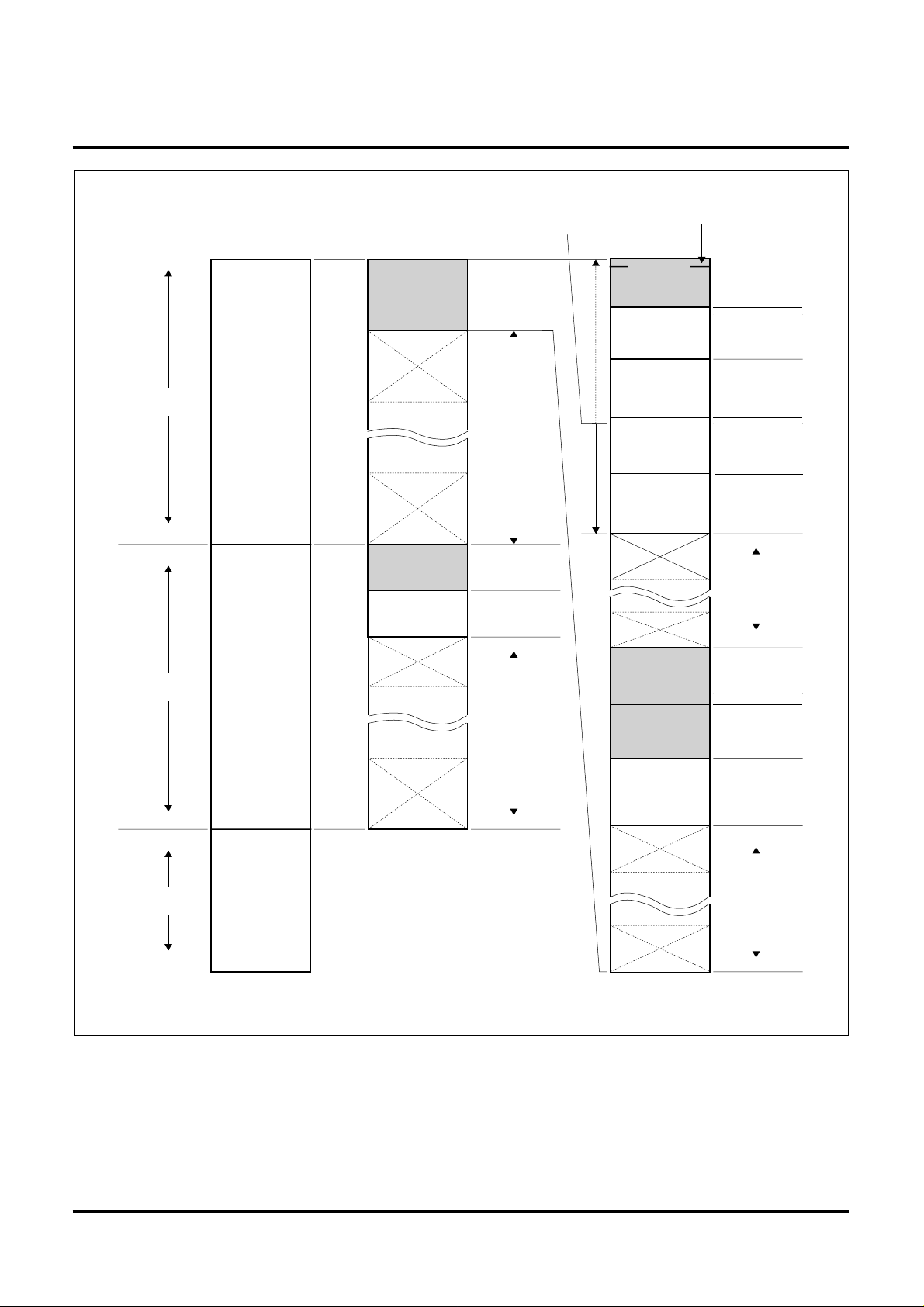
2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
< Logical space of the M32171F4VFP >
Logical address
H'0000 0000
(16M bytes)
2G bytes
H'7FFF FFFF
H'8000 0000
1G bytes
H'BFFF FFFF
H'C000 0000
User space
Boot
program
space
BOOT ROM
area
(8K bytes)
Reserved area
(8K bytes)
Expanded external area
(4M bytes)
Ghost area
in units of
16M bytes
H'8000 0000
H'8000 1FFF
H'8000 2000
H'8000 3FFF
H'8000 4000
Ghost area
in units of
16K bytes
H'BFFF FFFF
EIT vector entry
User ROM
area
Reserved area
(512K bytes)
CS0 area
CS1 area
Ghost area in
CS1
(1M byte)
SFR area
(16K bytes)
Internal RAM
(16K bytes)
Reserved area
(96K bytes)
H'0000 0000
H'0007 FFFF
H'000F FFFF
H'0010 0000
H'001F FFFF
H'0020 0000
H'002F FFFF
H'0030 0000
H'003F FFFF
H'0040 0000
Ghost area in
units of 4M bytes
H'007F FFFF
H'0080 0000
H'0080 3FFF
H'0080 4000
H'0080 7FFF
H'0080 8000
H'0081 FFFF
H'0082 0000
1G bytes
System
space
H'FFFF FFFF
Figure 4 Address Space of the M32171F4VFP
12
Ghost area in
units of 128K bytes
H'00FF FFFF

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
< Logical space of the M32171F3VFP >
Logical address
H'0000 0000
(16M bytes)
2G bytes
H'7FFF FFFF
H'8000 0000
1G bytes
H'BFFF FFFF
H'C000 0000
User space
Boot
program
space
BOOT ROM
area
(8K bytes)
Reserved area
(8K bytes)
Expanded external area
(4M bytes)
Ghost area
in units of
16M bytes
H'8000 0000
H'8000 1FFF
H'8000 2000
H'8000 3FFF
H'8000 4000
Ghost area
in units of
16K bytes
H'BFFF FFFF
EIT vector entry
User ROM
area
Reserved area
(640K bytes)
CS0 area
CS1 area
Ghost area in
CS1
(1M byte)
SFR area
(16K bytes)
Internal RAM
(16K bytes)
Reserved area
(96K bytes)
H'0000 0000
H'0005 FFFF
H'000F FFFF
H'0010 0000
H'001F FFFF
H'0020 0000
H'002F FFFF
H'0030 0000
H'003F FFFF
H'0040 0000
Ghost area in
units of 4M bytes
H'007F FFFF
H'0080 0000
H'0080 3FFF
H'0080 4000
H'0080 7FFF
H'0080 8000
H'0081 FFFF
H'0082 0000
1G bytes
System
space
H'FFFF FFFF
Figure 5 Address Space of the M32171F3VFP
Ghost area in
units of 128K bytes
H'00FF FFFF
13

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
< Logical space of the M32171F2VFP >
Logical address
H'0000 0000
(16M bytes)
2G bytes
H'7FFF FFFF
H'8000 0000
1G bytes
H'BFFF FFFF
H'C000 0000
User space
Boot
program
space
BOOT ROM
area
(8K bytes)
Reserved area
(8K bytes)
Expanded external area
(4M bytes)
Ghost area
in units of
16M bytes
H'8000 0000
H'8000 1FFF
H'8000 2000
H'8000 3FFF
H'8000 4000
Ghost area
in units of
16K bytes
H'BFFF FFFF
EIT vector entry
User ROM
area
Reserved area
(768K bytes)
CS0 area
CS1 area
Ghost area in
CS1
(1M byte)
SFR area
(16K bytes)
Internal RAM
(16K bytes)
Reserved area
(96K bytes)
H'0000 0000
H'0003 FFFF
H'000F FFFF
H'0010 0000
H'001F FFFF
H'0020 0000
H'002F FFFF
H'0030 0000
H'003F FFFF
H'0040 0000
Ghost area in
units of 4M bytes
H'007F FFFF
H'0080 0000
H'0080 3FFF
H'0080 4000
H'0080 7FFF
H'0080 8000
H'0081 FFFF
H'0082 0000
1G bytes
System
space
H'FFFF FFFF
Figure 6 Address Space of the M32171F2VFP
14
Ghost area in
units of 128K bytes
H'00FF FFFF

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
H'0080 0000
to
H'0080 007E
H'0080 0080
to
H'0080 00EE
H'0080 0100
to
H'0080 0146
H'0080
0180
H'0080 0200
to
H'0080 023E
H'0080 0240
to
H'0080 02FE
H'0080 0300
to
H'0080 03BE
H'0080 03C0
to
H'0080 03D8
0 7 8 15
+0
address+1address
Interrupt
controller
(ICU)
A-D converter
Serial I/O
Wait controller
MJT (common part)
MJT (TOP)
MJT (TIO)
MJT (TMS)
Multijunction
timer
(MJT)
H'0080 07E0
to
H'0080 07F2
H'0080 0FE0
to
H'0080 0FFE
H'0080 1000
to
H'0080 11FE
H'0080 3FFE
0 7 8 15
+0
address+1address
Flash control
MJT (TML1)
CAN
Figure 7 SFR Area
H'0080 03E0
to
H'0080 03F
H'0080 0400
H'0080 047E
H'0080 0700
H'0080 0756
Note: The Real-time debugger (RTD) is an independent module operated from external circuits,
and is transparent to the CPU.
E
to
to
MJT (TML0)
DMAC
Input/output ports
15

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Built-in Flash Memory and RAM
The M32171F4VFP contains 512-Kbyte flash memory and
16-Kbyte RAM. The M32171F3VFP contains 384-Kbyte
flash memory and 16-Kbyte RAM. The M32171F2VFP contains 256-Kbyte flash memory and 16-Kbyte RAM.
The internal flash memory can be programmed on-board
(i.e., while being mounted on the printed circuit board). This
means that the same chip as will be used in mass-production can be used directly from the development stage on,
allowing for system development without having to change
the printed circuit board when proceeding from trial production to mass-production.
< Internal flash >
H'0000 0000
H'0000 1FFF
H'0000 2000
H'0000 3FFF
H'0000 4000
H'0000 5FF
H'0007 C000
H'0007 DFF
H'0007 E000
H'0007 FFFF
F
F
L bank 0
(8K bytes)
L bank 1
(8K bytes)
L bank 2
(8K bytes)
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
L bank 62
(8K bytes)
L bank 63
(8K bytes)
Built-in Virtual-Flash Emulation Function
Internal flash memory, which is divided from the first address
in units of 8 Kbyte (L banks), can be replaced in 8 -Kbyte
blocks (H70080 4000-H’0080 5FFF) from the beginning of
the internal RAM. And also the internal flash memory, which
is divided from the first address in units of 4-Kbyte area (All S
banks), can be replaced within two 4 Kbytes areas (H’0080
6000-H’0080 7FFF).
This function allows parts of the program which are frequently changed during development to be altered or evaluated without having to reset the microcomputer each time.
What’s more, when combined with the realtime debugger,
this function helps to reduce the program evaluation period,
because data in the RAM can be rewritten without requiring
any CPU load.
< Internal RAM >
8K bytes
4K bytes
4K bytes
H'0080 4000
H'0080 5FF
H'0080 6000
H'0080 7FFF
F
Note 1: If the same bank area is set in multiple virtual-flash bank registers and the virtual-flash emulation enable bit is enabled,
the corresponding internal RAM area is assigned to either bank register according to the priority FELBANK0 > FESBANK0
> FESBANK1.
Note 2: When access is made to the 8-Kbyte area (L bank) specified with pseudo-flash bank register 0, the internal RAM
area is accessed. During pseudo-flash emulation mode, RAM data can read and written to and from both the internal RAM
area and the virtual-flash setup area.
Figure 8 Virtual-Flash Emulation Areas of the M32171F4VFP (Replaced in Units of 8 Kbytes)
16

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
H'0000 0000
H'0000 0FFF
H'0000 1000
H'0000 1FFF
H'0000 2
000
H'0000 2FF
H'0007 E000
H'0007 EFFF
H'0007 F000
H'0007 FFFF
F
S bank 0
(4K bytes)
S bank 1
(4K bytes)
S bank 2
(4K bytes)
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
S bank 126
(4K bytes)
S bank 127
(4K bytes)
< Internal RAM>
8K bytes
4K bytes
4K bytes
H'0080 4000
H'0080 5FF
H'0080 6000
H'0080 7000
F
Note 1: If the same bank area is set in multiple virtual-flash bank registers and the virtual-flash emulation enable bit is enabled,
the corresponding internal RAM area is assigned to either bank register according to the priority FELBANK0 > FESBANK0
> FESBANK1.
Note 2: When access is made to the 4-Kbyte area (S bank) specified with virtual-flash bank registers 0 and 1, the internal RAM
area is accessed. During virtual-flash emulation mode, RAM data can read and written to and from both the internal RAM
area and the virtual-flash setup area.
< Internal flash >
Figure 9 Virtual-Flash Emulation Areas of the M32171F4VFP (Replaced in Units of 4 Kbytes)
Virtual-Flash Emulation Areas of M32171F4VFP, M32171F3VFP,
and M32171F2VFP are shown as follows.
Table 8 Virtual-Flash Emulation Areas
Type Name Virtual-Flash Emulation Areas
M32171F4VFP H’ 0000 0000 - H’ 0007 FFFF
M32171F3VFP H’ 0000 0000 - H’ 0005 FFFF
M32171F2VFP H’ 0000 0000 - H’ 0003 FFFF
17

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Input/output Ports
The microcomputer has a total of 97 input/output ports
P0-P22. (However, P5 is reserved for future use, P14, P16,
and P18-P21 do not exist.) The input/output ports can be
used as input ports or output ports by setting uptheir direction
registers.
Table 9 Outline of Input/output Ports
Item Specification
Number of Port Total 97 ports
P0 : P00 - P07 (8 lines)
P1 : P10 - P17 (8 lines)
P2 : P20 - P27 (8 lines)
P3 : P30 - P37 (8 lines)
P4 : P41 - P47 (7 lines)
P6 : P61 - P64 (4 lines)
P7 : P70 - P77 (8 lines)
P8 : P82 - P87 (6 lines)
P9 : P93 - P97 (5 lines)
P10 : P100 - P107 (8 lines)
P11 : P110 - P117 (8 lines)
P12 : P124 - P127 (4 lines)
P13 : P130 - P137 (8 lines)
P15 : P150, P153 (2 lines)
P17 : P174, P175 (2 lines)
P22 : P220, P221, P225 (3 lines)
Each input/output port is a dual-function pin shared with
otherinternal peripheral I/O or external extended bus signal
lines. These pin functions are selected by using the chip operation mode select or the input/output port operation mode
registers. These input/output ports are interfaced using a
dedicated power supply to allow for connections to the peripheral circuits operating with 5V or 3.3V.
Port function The input/output ports can be set for input or output mode bitwise by using the input/output port
direction control register. (However, P64 is an SBI input-only port, and P221 is CAN input-only port.)
Pin function Dual-functions shared with peripheral I/O or external extended signals (or multi-functions shared with
peripheral I/Os which have multiple functions.)
Pin function P0 - P4: Changed by setting CPU operation mode (MOD0 and MOD1 pins)
changeover P6 - 22 : Changed by setting the input/output port operation mode register.
(However, peripheral I/O pin functions are selected using the peripheral I/O register.)
Note: Input/output ports P14, P16, and P18-P21 do not exist.
___
Table 10 CPU Operation Modes and P0-P4 Pin Functions
MOD0 MOD1 Operation mode Pin functions of P0-P4
VSS VSS Single-chip mode Input/output port pin
VSS VCCE External extended mode
VCCE VSS Processor mode (FP pin = VSS)
VCCE VCCE Reserved (use inhibited) –
Note: VCCE connects to +5V or +3.3V, and VSS connects to GND.
External extended signal pin
18

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
CPU
operation mode
settings (Note1)
(Reserved)
P0
P1
P2
P3
P4
P5
P6
P7
P8
P9
P10
02 57
DB0
DB8 DB9 DB10 DB11 DB12 DB13 DB14 DB15
A23 A24 A25 A26 A27 A28 A29 A30
A15 A16 A17 A18 A19 A20 A21 A22
BCLK/
WR
13
DB1 DB2 DB3 DB4 DB5 DB6 DB7
BLW/BLE
(P61)
WAIT HREQ HACK RTDTXD RTDRXD RTDACK RTDC
BHW/BHE
(P62)
TXD0 RXD0
RD CS0 CS1 A13 A14
(P63)
TO 16 TO 1 7 TO 18 T O 19 TO 20
TO 11 TO 1 2 TO 13 T O 14 TO 15TO 10TO 9TO 8
4
SBI
SCLKI 0/
SCLKO 0
TXD1 RXD1
6
LK
SCLKI 1/
SCLKO 1
Input/output
port operation
mode register
settings
P11
P12
TI N 16 TIN 17 TIN 18 TIN 19 TIN 20 TIN 21 TIN 22 TIN 23
P13
P14
TIN 0 TIN
P15
P16
P17
P18
P19
P20
P21
P22
CTX CRX A12
TO 3 TO 4 TO 5 TO 6 TO 7TO 2TO 1TO 0
TCLK 0 TCLK 1 TCLK 2 TCLK 3
3
TXD 2 RXD 2
Note 1: The pin function are selected by setting the MOD0 and MOD1 pins.
Note 2: P14, P16, P18, P19, P20, and P21 do not exist.
Figure 10 Input/output Ports and Pin Function Assignments
19

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Built-in 10-Channel DMAC
The microcomputer contains 10 channels of DMAC, allowing
for data transfer between internal peripheral I/Os, between
internal RAM and internal peripheral I/O, and between internal RAMs.
The microcomputer also supports cascaded connection between DMA channels (starting DMA transfer on a channel at
end of transfer on another channel). This makes advanced
transfer processing possible without causing any additional
CPU load.
DMA transfer requests can be issued from the user-cre
ated software, as well as can be triggered by a signal generated by the internal peripheral I/O (A-D converter, MJT, or
serial I/O).
Table 11 Outline of the DMAC
Item Content
Number of channels 10 channels
Transfer request • Software trigger
• Request from internal peripheral I/O: A-D converter, multijunction timer, or serial I/O
(reception completed, transmit buffer empty)
• Cascaded connection between DMA channels possible (Note)
Maximum number of times transferred 256 times
Transferable address space • 64 Kbytes (address space from H’0080 0000 to H’0080 FFFF)
• Transfers between internal peripheral I/Os, between internal RAM and internal peripheral IO,
and between internal RAMs are supported
Transfer data size 16 bits or 8 bits
Transfer method Single transfer DMA (control of the internal bus is relinquished for each transfer performed),
dual-address transfer
Transfer mode Single transfer mode
Direction of transfer One of three modes can be selected for the source and destination of transfer:
• Address fixed
• Address increment
• 32-channel ring buffer
Channel priority Channel 0 > channel 1 > channel 2 > channel 3 > channel 4 >
channel 5 > channel 6 > channel 7 > channel 8 > channel 9
(Fixed priority)
Maximum transfer rate 13.3 Mbytes per second (when internal peripheral clock = 20 MHz)
Interrupt request Group interrupt request can be generated when each transfer count register underflows
Transfer area 64 Kbytes from H’0080 0000 to H’0080 FFFF (Transfer is possible in the entire internal
RAM/SFR area)
Note: The following DMA channels can be cascaded.
DMA transfer on channel 1 started at end of one DMA transfer on channel 0
DMA transfer on channel 2 started at end of one DMA transfer on channel 1
DMA transfer on channel 0 started at end of one DMA transfer on channel 2
DMA transfer on channel 4 started at end of one DMA transfer on channel 3
DMA transfer on channel 6 started at end of one DMA transfer on channel 5
DMA transfer on channel 7 started at end of one DMA transfer on channel 6
DMA transfer on channel 5 started at end of one DMA transfer on channel 7
DMA transfer on channel 9 started at end of one DMA transfer on channel 8
DMA transfer on channel 5 started at end of all DMA transfers on channel 0 (underflow of transfer count register)
20

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
One DMA2 transfer completed
Software start
A-D conversion completed
MJT (TIO8_udf)
MJT (input event bus 2)
Software
MJT (output event bus 0)
One DMA0 transfer completed
Software
MJT (output event bus 1)
MJT (TIN18 input signal)
One DMA1 transfer completed
Serial I/O0 (transmit buffer empty)
Serial I/O1 (reception completed)
One DMA3 transfer completed
Serial I/O0 (reception completed)
One DMA7 transfer completed
All DMA0 transfers completed (udf)
Serial I/O2 (reception completed)
Software start
MJT (TIN0 input signal)
Software
MJT (TIN19 input signal)
Software start
MJT (TIN20 input signal)
start
start
start
DMA channel 0
DMA
request
selector
DMA channel
DMA
request
selector
DMA channel
DMA
request
selector
DMA channel
DMA
request
selector
DMA channel
DMA
request
selector
DMA channel
DMA
request
selector
Source
Destination
Transfer count
1
Source
Destination
Transfer count
2
Source
Destination
Transfer count
3
Source
Destination
Transfer count
4
Source
Destination
Transfer count
5
Determination block
Source
Destination
Transfer count
udf
udf
udf
udf
udf
DMA start
udf
Internal bus
Internal bus arbitration
Interrupt
request
Software start
Serial I/O1 (transmit buffer empty)
One DMA5 transfer completed
Software start
Serial I/O2 (transmit buffer empty)
One DMA6 transfer completed
Software start
MJT (input event bus 0)
Software start
One DMA8 transfer
completed
Figure 11 Block Diagram of the DMAC
DMA channel
DMA
request
selector
DMA channel
DMA
request
selector
DMA channel
DMA
request
selector
DMA channel
DMA
request
selector
6
Source
Destination
DMA start
udf
udf
udf
udf
Internal bus arbitration
Interrupt
request
Transfer count
7
Source
Destination
Transfer count
8
Source
Destination
Transfer count
9
Source
Destination
Transfer count
Determination block
21

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Built-in 37-Channel Multijunction Timers (MJT)
The microcomputer contains a total of 37 channels of
multijunction timers consisting of 11 channels of 16-bit output related timers, 10 channels of 16-bit input/output related
timers, eight channels of 16-bit input related timers, eight
channels of 32-bit input related timers, Each timer has multiple operation modes to choose from, depending on the pur-
poses of use.
Also, the maltijunction timers internally have a clock bus, input event bus, and an output event bus, so that multiple timers can be used in combination allowing for a flexible timer
configuration.
The output related timers have a correcting function that
allows the timer’s count value to be incremented or
decremented as necessary while count is in progress, mak-
ing real time output control possible.
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Output related timer : 11ch
Input/output related timer : 10ch
16-bit input related timer : 8ch
TCLK pin
1/2 internal
peripheral clock
TIN pin
Note: This is a conceptual diagram and does not show the actual timer configuration.
PRS
Clock bus
E/L
E/L
32-bit input related timer : 8ch
Input event bus
CLK
EN
CLK
EN
·
·
·
Timer
Timer
·
·
·
·
Figure 12 Conceptual Diagram of the Multijunction Timer (MJT)
To DMAC,
A-D converter
Output event bus
Interrupt output
F/F
Interrupt output
F/F
E/L
PRS
: Junction box (Selector)
F/F
TO pin
TO pin
: Edge/Level selector
: Prescaler
: Output flip-flop
22

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Table 12 Outline of Multijunction Timers
Name Type Number of channels Content
TOP Output-related 11 One of three input modes can be selected in software.
(Timer Output) 16-bit timer < With correction function >
(down-counter) • Single-shot output mode
• Delayed single-shot output mode
< Without correction function >
• Continuous output mode
TIO Input/output-related 10 One of three input modes or four output modes can be
(Timer 16-bit timer selected by software.
Input Output)
(down-counter) < Input modes >
• Measure clear input mode
• Measure free-run input mode
• Noise processing input mode
< Output mode without correction function
• PWM output mode
• Single-shot output mod
• Delayed single-shot output mode
• Continuous output mode
TMS Input-related 8 16-bit input measure timer.
(Timer 16-bit timer
Measure Small)
TML Input-related 8 32-bit input measure timer.
(Timer 32-bit timer
Measure Large)
(up counter)
(up counter)
23

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
0
TCLK
TIN
TIN3
/2 internal
peripheral
clock
TCLK1
TCLK2
TCLK0S
0
TCLK1
TCLK2
TIN0
TIN3
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Clock bus Input event bus Output event bus
3 2 1 0
PRS
PRS
PRS
3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3
S
9
IRQ
S
7
DRQ
S
S
S
clk
clk
clk
clk
clk
clk
clk
clk
en
en
en
en
en
en
en
en
S
S
S
2
IRQ1
S
S
clk
en
clk
en
clk
en
clk
en/
cap
S
clk
en/
cap
S
clk
en/
cap
S
clk
en/
cap
S
0
1
2
S
S
clk
en/
cap
S
clk
en/
cap
S
S
S
clk
en/cap
S
S
clk
en/
cap
S
S
clk
en/
cap
S
S
clk
en/
cap
S
IRQ2
udfTOP 0
IRQ2
udfTOP 1
IRQ2
udfTOP 2
IRQ2
udfTOP 3
IRQ2
udfTOP 4
IRQ2
udfTOP 5
IRQ1
udfTOP 6
IRQ1
udfTOP 7
IRQ6
udfTOP 8
IRQ6
udfTOP 9
IRQ5
udfTOP 10
IRQ0
udfTIO 0
IRQ0
udfTIO 1
IRQ0
udfTIO 2
IRQ0
udfTIO 3
IRQ4
udfTIO 4
S
IRQ4
udfTIO 5
IRQ4
udfTIO 6
IRQ4
udfTIO 7
DRQ0
IRQ3
udfTIO 8
IRQ3
udfTIO 9
32171 Group
F3
F8
F1
F2
F4
F6
F7
F9
F0
F5
TO 0
TO 1
TO 2
TO 3
TO 4
TO 5
TO 6
TO 7
TO 8
TO 9
TO 10
0
TO 11
1
TO 12
2
TO 13
3
TO 14
4
TO 15
5
6
TO 16
TO 17
7
TO 18
8
TO 19
9
TO 20
0
F/
F/
F/
F/
F/
F/
S
F/
S
F/
S
F/
F/
S
F/F1
S
S
F/F1
F/F1
S
S
F/F1
S
F/F1
S
F/F1
S
F/F1
F/F1
S
F/F1
S
F/F1
S
F/F2
3 2 1 0 3 2 1 0
PSC0-2
: Prescaler
F/F
Figure 13 Block Diagram of Multijunction Timers (MJT) (1/3)
24
: Output flip-flop
S
0 1 2 3
: Selector

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
3 2 1 0 3 2 1 0
clk
TMS 0
ovf
cap3 cap2 cap1 cap0
S
clk TML 0
cap3 cap2 cap1 cap0
S
S
S
S
TIN20
TIN2
1
TIN2
2
TIN2
3
IRQ11
IRQ11
IRQ11
IRQ11
0 1 2 3
IRQ
7
3 2 1 0 3 2 1 0
0 1 2 3
TIN20
S
TIN21
S
TIN22
S
TIN23
S
S
DRQ12
clk TMS 1
ovf
cap3 cap2 cap1 cap0
S
S
S
S
S
DRQ5
TIN16
TIN1
7
TIN1
8
TIN19
DRQ6
IRQ10
IRQ10
IRQ10
IRQ10
IRQ
7
TIN16
S
TIN17
S
TIN18
S
TIN19
S
(Note1)
clk TML 1
cap3 cap2 cap1 cap0
S
TCLK3
TCLK3
S
S
S
S
S
S
S
S
S
AD0TRG
(To A-D0 converter)
Clock bus
Input event bus
Output event bus
1/2 internal
peripheral
clock
1/2 internal
peripheral
clock
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Figure 14 Block Diagram of Multijunction Timers (MJT) (2/3)
25

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
s
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Clock bus Input event bus Output event bu
3 2 1 0 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3
TIN18
TIN0
TIN19
TIN20
AD0 completed
TIO8-udf
SIO0-TXD
SIO1-RXD
SIO0-RXD
RXD
SIO2-
SIO1-
TXD
TXD
SIO2-
S
S
S
S
S
S
S
S
S
DMA
DMA
DMA
DMA
DMA
DMA
DMA
DMA
DMA
udf
0
end
udf
1
end
udf
2
end
udf
3
end
udf
4
udf
5
end
udf
6
end
udf
7
end
udf
8
end
DMAIRQ
DMAIRQ
DMAIRQ
DMAIRQ
DMAIRQ
DMAIRQ
DMAIRQ
DMAIRQ
DMAIRQ
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
S
3 2 1 0 3 2 1 0
Figure 15 Block Diagram of Multijunction Timers (MJT) (3/3)
DMA
udf
9
DMAIRQ
1
0 1 2 3
26

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Built-in Two Independent A-D Converters
The microcomputer contains two 16-channel converters with
10-bit resolution (A-D0 converter and A-D1 converter). In
addition to single conversion on each channel, continuous
A-D conversion on a combined group of 4, 8, and 16 channels is possible. The A-D converted value can be read out in
either 10 bits or 8 bits.
In addition to ordinary A-D conversion, the converters support comparator mode in which the set value and A-D converted value are compared to determine which is larger or
smaller than the other.
When A-D conversion is finished, the converters can generated
a DMA transfer request, as well as an interrupt.
The A-D converters are interfaced using a dedicated power
supply to allow for connections to the peripheral circuits op-
erating with 5V or 3.3V.
Table 13 Outline of the A-D Converters
Item Content
Analog input 16 channels
A-D conversion method Successive approximation method.
Resolution 10 bits (Conversion results can be read out in either 10 or 8 bits.)
Absolute accuracy Normal rate mode
(Conditions: Ta = -40 ~ +125°C,
AVCC0 = VREF0 = 5.12V)
Conversion mode A-D conversion mode,comparator mode
Operation mode Single mode, scan mode
(Note 1)
Double rate mode
+
2 LSB
+
2 LSB
Scan mode Single -shot scan mode, continuous scan mode.
Conversion start trigger Software start Started by setting A-D conversion start bit to 1.
Hardware start A-D0 converter started by MJT output event bus 3.
Conversion rate During single mode Normal 299 × 1/ f (BCLK)
f(BCLK) : Internal peripheral clock
(Note 2)
Interrupt request generation When A-D conversion is finished, when comparate operation is finished, when single-shot
DMA transfer request generation When A-D conversion is finished, when comparate operation is finished, when single-shot
Note 1: The rated value of conversion accuracy here is that of the microcomputer's own as a single unit which can be exhibited when the
microcomputer is used in an environment where it may not be affected by the power supply wiring or noise on the board.
Note 2: When input clock (XIN) = 10 MHz, f(BCLK) = 20 MHz.
operating frequency
(Shortest time ) Double speed 173 × 1/ f (BCLK)
During comparator mode Normal 47 × 1/ f (BCLK)
(Shortest time ) Double speed 29 × 1/ f (BCLK)
scan is finished, or when one cycle of continuous scan is finished.
scan is finished, or when one cycle of continuous scan is finished.
27

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
10-bit readout
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Internal data bus
8-bit readout
Shifter
AD0DT0
AD0DT1
AD0DT2
AD0DT3
AD0DT4
AD0DT5
AD0DT6
AD0DT7
AD0DT8
AD0DT9
AD0DT10
AD0DT11
AD0DT12
AD0DT13
AD0DT14
AD0DT15
AD0CMP
AVCC0
AVSS0
VREF0
AD0IN0
AD0IN1
AD0IN2
AD0IN3
AD0IN4
AD0IN5
AD0IN6
AD0IN7
AD0IN8
AD0IN9
AD0N10
AD0IN11
AD0IN12
AD0IN13
AD0IN14
AD0IN15
10-bit A-D0 Data Register 0
10-bit A-D0 Data Register 1
10-bit A-D0 Data Register 2
10-bit A-D0 Data Register 3
10-bit A-D0 Data Register 4
10-bit A-D0 Data Register 5
10-bit A-D0 Data Register 6
10-bit A-D0 Data Register 7
10-bit A-D0 Data Register 8
10-bit A-D0 Data Register 9
10-bit A-D0 Data Register 10
10-bit A-D0 Data Register 11
10-bit A-D0 Data Register 12
10-bit A-D0 Data Register 13
10-bit A-D0 Data Register 14
10-bit A-D0 Data Register 15
A-D comparate
Data Register
10-bit A-D Successive
Approximation Register
(AD0SAR)
10-bit D-A Converter
Selector
Successive Approximation
-type A-D Converter Unit
AD0SIM0,1
Output event bus 3
(multijunction timer)
Comparator
Single Mode Register
Scan Mode RegisterAD0SCM0,1
A-D Control Circuit
• Mode selection
• Channel selection
• Conversion time
selection
• Flag control
• Interrupt control
Interrupt request
DMA transfer request
Figure 16 Block Diagram of the A-D0 Converter
28

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
3-channel High-speed Serial I/Os
The microcomputer contains three channels of serial I/Os
consisting of two channels that can be set for CSIO mode
(clock-synchronized serial I/O) or UART mode (asynchronous serial I/O) and one other channel that can only be set
for UART mode.
The SIO has the function to generate a DMA transfer request when data reception is completed or the transmit register becomes empty, and is capable of high-speed serial
communication without causing any additional CPU load.
Table 14 Outline of Serial I/O
Item Content
Number of channels CSIO/UART: 2 channels (SIO0,SIO1)
UART only : 1 channels (SIO2)
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Clock During CSIO mode : Internal clock / external clock, selectable (Note1)
During UART mode : Internal clock only
Transfer mode Transmit half-duplex, receive half-duplex, transmit/receive full-duplex
BRG count sourcef (BCLK), f(BCLK)/8, f(BCLK)/32, f(BCLK)/256 (When internal clock is selected) (Note2)
Data format CSIO mode : Data length = Fixed to 8 bits
Order of transfer = Fixed to LSB first
UARTmode : Start bit = 1 bit
Character length = 7, 8, or 9 bits
Parity bit = Added or not added (When added, selectable between odd and even parity)
Stop bit = 1 or 2 bits
Order of transfer = Fixed to LSB first
Baud rate CSIO mode : 152 bits per second to 2 Mbits per second (when operating with f(BCLK) = 20 MHz)
UARTmode : 19 bits per second to 156 Kbits per second (when operating with f(BCLK) = 20 MHz)
Error detection CSIO mode : Overrun error only
UARTmode : Overrun, parity, and framing errors
(The error-sum bit indicates which error has occurred)
Fixed cycle clock When using SIO0 and SIO1 as UART, this function outputs a divided-by-2 BRG clock from the SCLK pin.
output function
Note 1: During CSIO mode, the maximum input frequency of an external clock is f(BCLK) divided by 16.
Note 2: When f(BCLK) is selected for the BRG count source, the BRG set value is subject to limitations.
29

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
SIO0
TXD0
RXD0
SIO1
SIO0 Transmit Buffer Register
SIO0 Transmit Shift Register
SIO0 Receive Shift Register
SIO0 Receive Buffer Register
BCLK,
BCLK/8,
BCLK/32,
BCLK/256
BCLK
Clock divider
Transmit/receive
UART
mode
1
(Set value + 1)
generator (BRG)
control circuit
1/16
Baud rate
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Transmit interrupt
Receive interrupt
Transmit DMA transfer request
Receive DMA transfer request
CSIO
mode
When external clock selected
When internal clock selected
1/2
CSIO mode
When internal clock selected
When UART mode selected
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
To interrupt
controller
To DMA3
To DMA4
SCLKI0/ SCLKO0
Internal data bus
TXD1
RXD1
SIO1 Transmit Shift Register
SIO1 Receive Shift Register
SIO2
TXD2
RXD2
SIO2 Transmit Shift Register
SIO2 Receive Shift Register
Note 1 : When BCLK is selected, the BRG set value is subject to limitations.
Note 2 : SIO2 does not have the SCLKI/SCLKO function.
Figure 17 Block Diagram of Serial I/O
Transmit/receive
control circuit
Transmit/receive
control circuit
Transmit interrupt
Receive interrupt
Transmit DMA transfer request
Receive DMA transfer request
Transmit interrupt
Receive interrupt
Transmit DMA transfer request
Receive DMA transfer request
To interrupt
controller
To DMA6
To DMA3
SCLKI1/ SCLKO1
To interrupt
controller
To DMA7
To DMA5
30

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
CAN Module
The M32171 Group contains two Full CAN modules compliant with CAN Specification V2.0B (CAN0 and CAN1), each
of which has 16-channel message slots and three mask reg-
isters.
Data bus
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
CAN0 Message
Control Register
CAN0 Extended
CAN0 Configuration
CAN0 Time Stamp
CTX
CRX
CAN0 Status
Register
CAN0 REC
Register
CAN0 TEC
Register
CAN0 Protocol
Controller
2.0B active
Figure 18 Block Diagram of the CAN Module
Slot 0-15
Register
Register
CAN0 Control
Register
Acceptance
Filtering
16-bit Timer
Register
CAN0 Global
Mask Register
CAN0 Local
Mask Register A
CAN0 Local
Mask Register B
Message Memory
(1) Message ID
(2) Data length code
(3) Message data
(4) Time stamp
CAN0 Slot
Status Register
CAN0 Slot
Interrupt Control
Register
CAN0 Error
Interrupt Control
Register
Interrupt Control
Circuit
CAN0 Transmit/Receive
& Error Interrupt
31

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
8-level Interrupt Controller
The Interrupt Controller controls interrupt requests from
each internal peripheral I/O (31 sources) by using eight priority levels assigned to each interrupt source, including interrupts disabled. In addition to these interrupts, it handles
System Break Interrupt (SBI), Reserved Instruction Exception (RIE), and Address Exception (AE) as nonmaskable in-
terrupts.
Wait Controller
The Wait Controller supports access to external devices.
For access to an external extended area of up to 1 Mbytes
(during external extended or processor mode), the Wait
Controller controls bus cycle extension by inserting one to
four wait cycles or using external WAIT signal input.
M32171F4VFP, M32171F3VFP, M32171F2VFP
____
Realtime Debugger (RTD)
The Realtime Debugger (RTD) provides a function for accessing directly from the outside to the internal RAM. It uses
a dedicated clock-synchronized serial I/O to communicate
with the outside.
Use of the RTD communicating via dedicated serial lines allows the internal RAM to be read out and rewritten without
having to halt the CPU.
M32R
CPU
Data Bus(CPU
Internal RAM
(16KB)
Virtual-DPRAM
structure
) Data Bus(RTD)
R/W without CPU intervention
Real-Time Debugger
(RTD)
Figure 19 Conceptual Diagram of the Realtime Debugger (RTD)
RTDCLK
RTDRXD
RTDTXD
RTDAC
Command
K
address Data
DataData
32

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
CPU Instruction Set
The M32R employs a RISC architecture, supporting a total
of 83 discrete instructions.
(1) Load/store instructions
Perform data transfer between memory and registers.
LD Load
LDB Load byte
LDUB Load unsigned byte
LDH Load halfword
LDUH Load unsigned halfword
LOCK Load locked
ST Store
STB Store byte
STH Store halfword
UNLOCK Store unlocked
(2) Transfer instructions
Perform register to register transfer or register to immediate
transfer
LD24 Load 24-bit immediate
LDI Load immediate
MV Move register
MVFC Move from control register
MVTC Move to control register
SETH Set high-order 16-bit
.
(3) Branch instructions
Used to change the program flow.
BC Branch on C-bit
BEQ Branch on equal
BEQZ Branch on equal zero
BGEZ Branch on greater than or equal zero
BGTZ Branch on greater than zero
BL Branch and link
BLEZ Branch on less than or equal zero
BLTZ Branch on less than zero
BNC Branch on not C-bit
BNE Branch on not equal
BNEZ Branch on not equal zero
BRA Branch
JL Jump and link
JMP Jump
NOP No operation
(4) Arithmetic/logic instructions
Perform comparison, arithmetic/logic operation, multiplication/division, or shift between registers.
• Comparison
CMP Compare
CMPI Compare immediate
CMPU Compare unsigned
CMPUI Compare unsigned immediate
• Logical operation
AND AND
AND3 AND 3-operand
NOT Logical NOT
OR OR
OR3 OR 3-operand
XOR Exclusive OR
XOR3 Exclusive OR 3-operand
• Arithmetic operation
ADD Add
ADD3 Add 3-operand
ADDI Add immediate
ADDV Add (with overflow checking)
ADDV3 Add 3-operand
ADDX Add with carry
NEG Negate
SUB Subtract
SUBV Subtract (with overflow checking)
SUBX Subtract with borrow
• Multiplication/division
DIV Divide
DIVU Divide unsigned
MUL Multiply
REM Remainder
REMU Remainder unsigned
• Shift
SLL Shift left logical
SLL3 Shift left logical 3-operand
SLLI Shift left logical immediate
SRA Shift right arithmetic
SRA3 Shift right arithmetic 3-operand
SRAI Shift right arithmetic immediate
SRL Shift right logical
SRL3 Shift right logical 3-operand
SRLI Shift right logical immediate
(5) Instructions for the DSP function
Perform 32 bit × 16 bit or 16 bit × 16 bit multiplication or sumof-products calculation. These instructions also perform
rounding of the accumulator data or transfer between accumulator and general-purpose register.
MACHI Multiply-accumulate high-order
halfwords
MACLO Multiply-accumulate low-order
halfwords
MACWHI Multiply-accumulate word and
high-order halfword
MACWLO Multiply-accumulate word and
low-order halfword
MULHI Multiply high-order halfwords
MULLO Multiply low-order halfwords
MULWHI Multiply word and high-order
halfword
MULWLO Multiply word and low-order
halfword
MVFACHI Move from accumulator high-order word
MVFACLO Move from accumulator low-order word
MVFACMI Move from accumulator middle-order
word
MVTACHI Move to accumulator high-order word
MVTACLO Move to accumulator low-order word
RAC Round accumulator
RACH Round accumulator halfword
(6) EIT related instructions
Start trap or return from EIT processing.
RTE Return from EIT
TRAP Trap
33

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
< Multiply instruction > < Multiply-accumulate instruction >
Rsrc
Rsrc1
0151631
H
L
0151631
×
×
0
ACC
Rsrc1
031
32 bit
0151631
2
H L
MULLO instructionMULHI instruction
63
Rsrc2
HL
Rsrc1
0151631
HL
×
0
×
×
0
MULWLO instructionMULWHI instruction
ACC
63
Rsrc1
031
32 bit
×
< Ropund off instruction >
0
ACC
63
0
0
Rsrc2
0151631
H L
×
+
+
MACLO instructionMACHI instruction
ACC
0
Rsrc2
0151631
H L
×
+
+
MACWLO instructionMACWHI instruction
ACC
63
ACC
63
63
ACC
63
RAC
0
sign 0data
0
0
sign 0data
instruction
RACH
instruction
63
63
ACC
63
Figure 20 Instructions for the DSP Function
< Accumulator - register transfer instruction >
MVFACMI
0
instruction
ACC
Rdest
48
MVFACLO
instruction
1
0
MVFACHI
instruction
6315 16 31 32 47
0
031
Rsrc
ACC
MVTACLO
instruction
MVTACHI
instruction
6331 32
34

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
LQFP144-P-2020-0.50
Weight(g)
–
JEDEC Code
EIAJ Package Code
Lead Material
Cu Alloy
144P6Q-A
Plastic 144pin 20✕20mm body LQFP
–
0.125
–
––
0.2
–
–
––
–
–
––
–
Symbol
Min Nom Max
A
A
2
b
c
D
E
H
E
L
L
1
y
b
2
Dimension in Millimeters
H
D
A
1
0.225
––
I
2
1.0
––
M
D
20.4
––
M
E
20.4
8°0°
0.1
1.0
0.650.50.35
22.222.021.8
22.222.021.8
0.5
20.120.019.9
20.120.019.9
0.1750.1250.105
0.270.220.17
1.4
0.05
1.7
e
Recommended Mount Pad
M
D
l
2
b
2
M
E
e
A
H
D
D
H
E
E
1
36
37
72
73
108
109
144
F
b
e
L
A
2
A
1
L
1
c
Detail F
y
Package Dimensions Diagram
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
35

2001-5-14 Rev.1.0
Mitsubishi Microcomputers
32171 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
HEAD OFFICE: 2-2-3, MARUNOUCHI, CHIYODA-KU, TOKYO 100-8310, JAPAN
Keep safety first in your circuit designs!
• Mitsubishi Electric Corporation puts the maximum effort into making semiconductor products better and more reliable, but there is always the possibility that trouble may occur with them. Trouble with semiconductors may lead to
personal injury, fire or property damage. Remember to give due consideration to safety when making your circuit designs, with appropriate measures such as (i) placement of substitutive, auxiliary circuits, (ii) use of non-flammable
material or (iii) prevention against any malfunction or mishap.
Notes regarding these materials
• These materials are intended as a reference to assist our customers in the selection of the Mitsubishi semiconductor product best suited to the customer’s application; they do not convey any license under any intellectual property
rights, or any other rights, belonging to Mitsubishi Electric Corporation or a third party.
• Mitsubishi Electric Corporation assumes no responsibility for any damage, or infringement of any third-party’s rights, originating in the use of any product data, diagrams, charts, programs, algorithms, or circuit application examples
contained in these materials.
• All information contained in these materials, including product data, diagrams, charts, programs and algorithms represents information on products at the time of publication of these materials, and are subject to change by
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation without notice due to product improvements or other reasons. It is therefore recommended that customers contact Mitsubishi Electric Corporation or an authorized Mitsubishi Semiconductor product
distributor for the latest product information before purchasing a product listed herein.
The information described here may contain technical inaccuracies or typographical errors. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation assumes no responsibility for any damage, liability, or other loss rising from these inaccuracies or errors.
Please also pay attention to information published by Mitsubishi Electric Corporation by various means, including the Mitsubishi Semiconductor home page (http://www.mitsubishichips.com).
• When using any or all of the information contained in these materials, including product data, diagrams, charts, programs, and algorithms, please be sure to evaluate all information as a total system before making a final decision
on the applicability of the information and products. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation assumes no responsibility for any damage, liability or other loss resulting from the information contained herein.
• Mitsubishi Electric Corporation semiconductors are not designed or manufactured for use in a device or system that is used under circumstances in which human life is potentially at stake. Please contact Mitsubishi Electric
Corporation or an authorized Mitsubishi Semiconductor product distributor when considering the use of a product contained herein for any specific purposes, such as apparatus or systems for transportation, vehicular, medical,
aerospace, nuclear, or undersea repeater use.
• The prior written approval of Mitsubishi Electric Corporation is necessary to reprint or reproduce in whole or in part these materials.
• If these products or technologies are subject to the Japanese export control restrictions, they must be exported under a license from the Japanese government and cannot be imported into a country other than the approved
destination.
Any diversion or reexport contrary to the export control laws and regulations of Japan and/or the country of destination is prohibited.
• Please contact Mitsubishi Electric Corporation or an authorized Mitsubishi Semiconductor product distributor for further details on these materials or the products contained therein.
© 2001 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP.
New publication, effective May 2001.
Specifications subject to change without notice.

Revision Description List 32171Group Data Sheet
Rev. Revision Description Rev.
No.
Page Point
1.0 First Edition 010514
date
(1/1)
 Loading...
Loading...