Mitsubishi M306V5ME-XXXSP, M306V5EESS, M306V5EESP Datasheet

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
1. DESCRIPTION
The M306V5ME-XXXSP and M306V5EESP are single-chip microcomputers using the high-performance
silicon gate CMOS process using a M16C/60 Series CPU core and are packaged in a 64-pin plastic molded
SDIP. These single-chip microcomputers operate using sophisticated instructions featuring a high level of
instruction efficiency. With 1M bytes of address space, they are capable of executing instructions at high
speed. They also feature a built-in OSD display function and data slicer, making them ideal for controlling
TV with a closed caption decoder.
The features of the M306V5EESP are similar to those of the M306V5ME-XXXSP except that this chip has
a built-in PROM which can be written electrically.
1.1 Features
• Memory size ........................................<ROM>192K bytes
<RAM> 5K bytes
<OSD ROM> 61K bytes
<OSD RAM> 2.2K bytes
• Shortest instruction execution time......100 ns (f(XIN)=10 MHz)
• Power sourse voltage ..........................4.5 V to 5.5V
• Power consumption .............................250 mW
• Interrupts..............................................21 internal and 3 external interrupt sources, 4 software
interrupt sources; 7 levels
• Multifunction 16-bit timer......................2 output timers + 1 input timer + 5 timers
• Serial I/O..............................................4 units
UART/clock synchronous: 2
Multi-master I2C-BUS interface 0 (2 systems): 1
Multi-master I2C-BUS interface 1 (1 systems): 1
• DMAC ..................................................2 channels (trigger: 23 sources)
• A-D converter.......................................8 bits ✕ 6 channels
• D-A converter.......................................8 bits ✕ 2 channels
• Data slicer............................................1 circuit
• HSYNC counter .....................................1 circuit (2 systems)
• OSD function .......................................1 circuit
• Watchdog timer....................................1 circuit
• Programmable I/O ...............................46 lines
• Clock generating circuit .......................2 built-in clock generation circuits
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
M306V5EESP
1.2 Applications
TV with a closed caption decoder
Rev. 1.0

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
------Table of Contents------
1. DESCRIPTION ..............................................1
1.1 Features...................................................1
1.2 Applications .............................................1
1.3 Pin Configuration ..................................... 3
1.4 Block Diagram .........................................4
1.5 Performance Outline................................5
2. OPERATION OF FUNCTIONAL BLOCKS .. 10
2.1 Memory..................................................10
2.2 Central Processing Unit (CPU) .............. 16
2.3 Reset .....................................................19
2.4 Single-chip Mode ................................... 23
2.5 Clock Generating Circuit........................27
2.6 Protection............................................... 35
2.7 Overview of Interrupt .............................36
2.8 Watchdog Timer ....................................56
2.9 DMAC .................................................... 58
2.10 Timer.................................................... 68
2.11 Serial I/O..............................................88
2.12 A-D Converter....................................138
2.13 D-A Converter....................................153
2.14 Data Slicer ......................................... 155
2.15 HSYNC Counter ..................................165
2.16 OSD Function .................................... 166
2.16.1 Triple Layer OSD ........................ 172
2.16.2 Display Position .......................... 174
2.16.3 Dot Size ...................................... 178
2.16.4 Clock for OSD.............................179
2.16.5 Field Determination Display........180
2.16.6 Memory for OSD.........................182
2.16.7 Character Color ..........................195
2.16.8 Character Background Color ...... 195
2.16.9 OUT1, OUT2 Signals..................200
2.16.10 Attribute ....................................201
2.16.11
2.16.12 Particular OSD Mode Block ...... 207
2.16.13 Multiline Display........................209
2.16.14 SPRITE OSD Function ............. 210
2.16.15 Window Function ...................... 213
2.16.16 Blank Function .......................... 214
2.16.17 Raster Coloring Function .......... 217
Automatic Solid Space Function.....
206
2.16.18 Scan Mode................................219
2.16.19 R, G, B Signal Output Control...219
2.16.20 OSD Reserved Register ........... 220
2.17 Programmable I/O Ports .................... 221
3. USAGE PRECAUTION..............................239
3.1 Timer A (timer mode)........................... 239
3.2 Timer A (event counter mode) ............. 239
3.3 Timer A (one-shot timer mode)............239
3.4 Timer A
3.5 Timer B
3.6 Timer B (pulse period/pulse width
measurement mode) ...........................240
3.7 A-D Converter......................................240
3.8 Stop Mode and Wait Mode ..................240
3.9 Interrupts..............................................241
3.10 Built-in PROM version .......................242
4. ITEM TO BE SUBMITTED WHEN ORDERING
MASKED ROM VERSION ......................... 243
5. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS..........244
5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings ................. 244
5.2 Recommended Operating Conditions..245
5.3 Electrical Characteristics .....................246
5.4 A-D Conversion Characteristics...........247
5.5 D-A Conversion Characteristics...........247
5.6
Analog R, G, B Output Characteristics .......
5.7 Timing Requirements...........................248
5.8 Switching Characteristics.....................250
6. MASK ROM CONFIRMATION FORM ....... 251
7. MARK SPECIFICATION FORM ................255
8.ONE TIME PROM VERSION
M306V5EESP MARKING...........................256
9. PACKAGE OUTLINE ................................. 257
(pulse width modulation mode)....
(timer mode, event counter mode) .....
239
240
247
Rev. 1.0
2
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
T
S
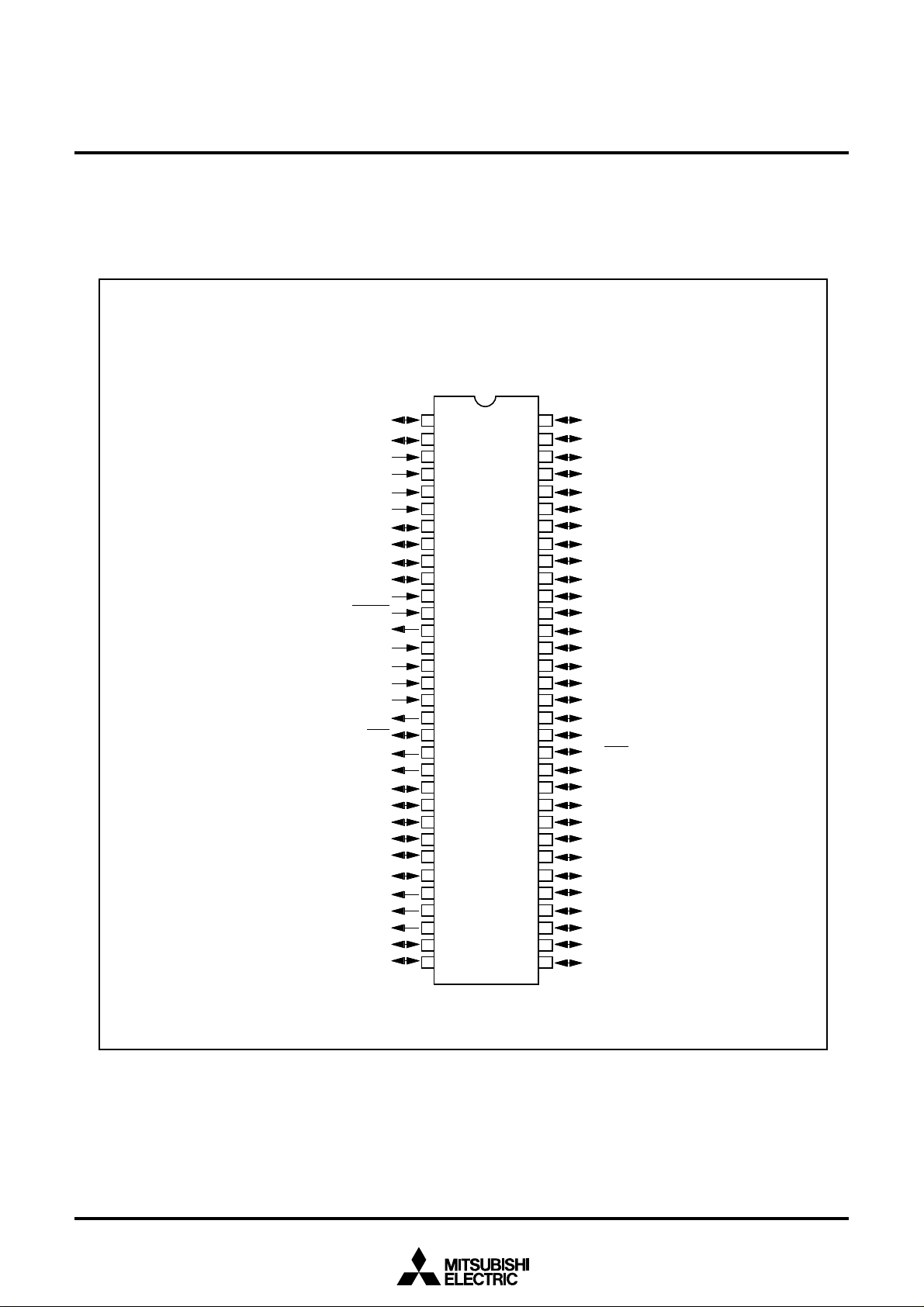
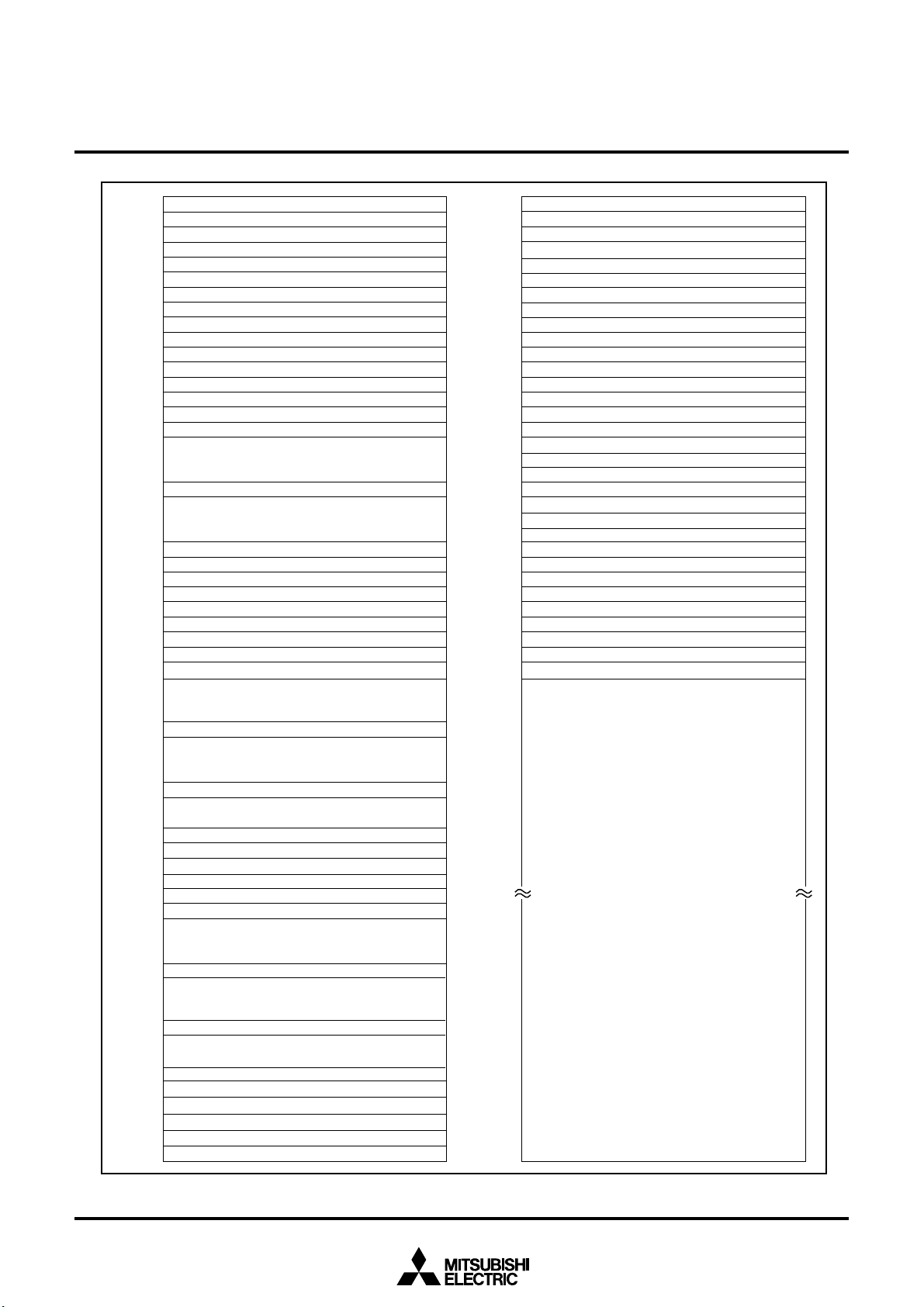
1.3 Pin Configuration
Figure 1.3.1 shows the pin configuration (top view).
PIN CONFIGURATION (top view)
Y N
1/
VS
T V S E T B
A V
C VI
O L
VH
A1/ S C L 3
0/
P 9
C N VS
R E S E T
X
O S C 1
O S C 2
I N
P 8
2/
O U T 1
O U T 2
6/
3O
4/
2O
D2/ S C L 1
D2/ S D A 1
7/
P 6
T x
P 6
3/
R x
2/
P 6
H L F
0I
O U T
VS
XI
VC
C
C
C C
N
D
N
S
N
C
T0
T
2
R
G
B
D0
D0
P 1 0
Y N
P 1 00/ HS
D
P 9
4/
P 93/ D A0/ S D A 3
T B
U
T A
P 7
U
T A
P 7
P 72/ C L K2/ S C L 2
R x
P 7
1/
T x
P 7
0/
S D A
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
3 0 6 V 5 M E - X X X S
3 0 6 V 5 E E S
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1 0
1 1
1 2
1 3
1 4
1 5
1 6
1 7
1 8
1 9
2 0
2 1
2 2
2 3
2 4
2 5
2 6
2 7
2 8
2 9
3 0
3 1
3 2
M
M
P
P
6 4
6 3
6 2
6 1
6 0
5 9
5 8
5 7
5 6
5 5
5 4
5 3
5 2
5 1
5 0
4 9
4 8
4 7
4 6
4 5
4 4
4 3
4 2
4 1
4 0
3 9
3 8
3 7
3 6
3 5
3 4
3 3
0
P 0
P 01
P 02
P 03
P 04
P 05
P 06
P 07
P 20
P 21
P 22
P 23
P 24
P 25
P 26
P 27
P 30
P 31
P 32
P 33/ I N T1
P 34/ H C 0
H C
5/
P 3
A N
P 3
6/
P 37/ A N 1
A N
P 4
0/
A N
1/
P 4
P 42/ A N 4
A N
P 4
3/
P 5
0
P 52
P 53
P 55/ C L K0
1
0
2
3
5
Figure 1.3.1 Pin configuration (top view)
Rev. 1.0
Package: 64P4B
3
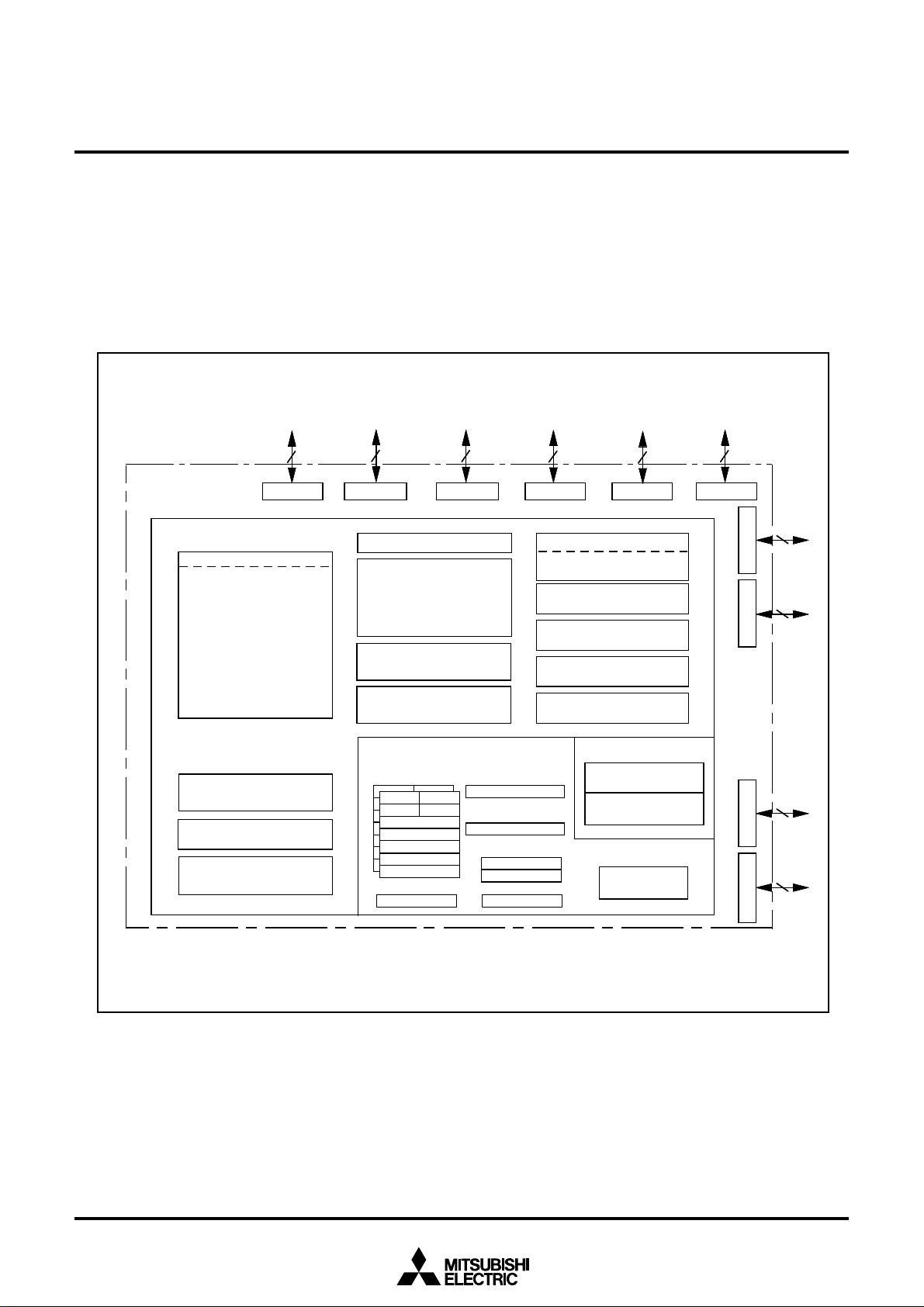
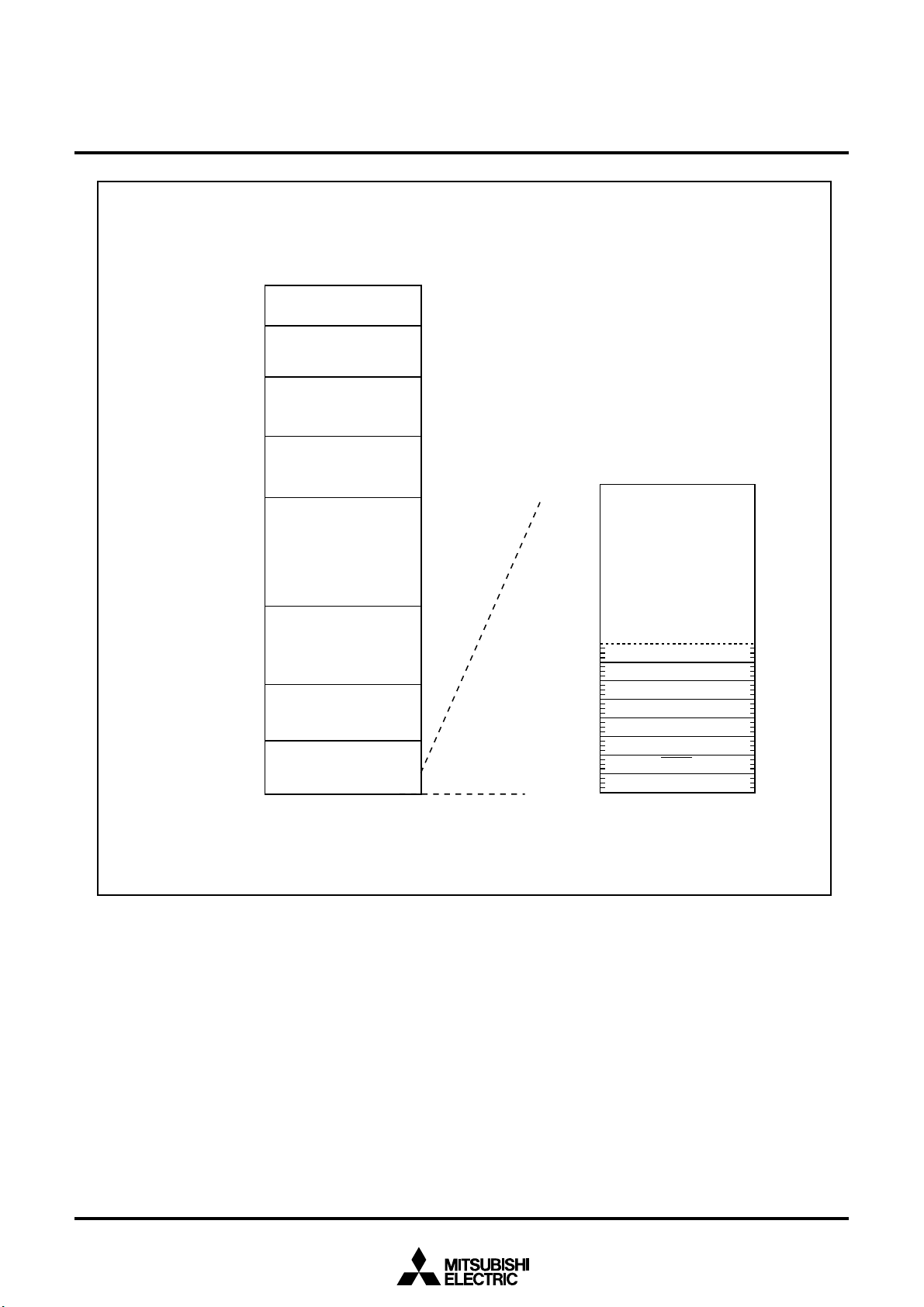
1.4 Block Diagram
0
Figure 1.4.1 is a block diagram.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
I / O p o r t s
I n t e r n a l p e r i p h e r a l f u n c t i o n s
T i m e r T A 0 ( 1 6 b i t s )
T i m e r T A 1 ( 1 6 b i t s )
T i m e r T A 2 ( 1 6 b i t s )
T i m e r T A 3 ( 1 6 b i t s )
T i m e r T A 4 ( 1 6 b i t s )
T i m e r T B 0 ( 1 6 b i t s )
T i m e r T B 1 ( 1 6 b i t s )
T i m e r T B 2 ( 1 6 b i t s )
W a t c h d o g t i m e r
( 2 c h a n n e l s )
D - A c o n v e r t e r
( 8 b i t s X 2 c h a n n e l s )
T i m e r
( 1 5 b i t s )
D M A C
8
P o r t P 0
8
P o r t P 2
A - D c o n v e r t e r
8
P o r t P 3
O S D
D a t a s l i c e r
H
S Y N C
c o u n t e r
M 1 6 C / 6 0 s e r i e s 1 6 - b i t C P U c o r e
R e g i s t e r s
R 0 LR 0 H
R 0 LR 0 H
R 1 HR 1 L
R 1 HR 1 L
R 2
R 2
R 3
R 3
A
A 0
A 1
A 1
F B
F B
S B F L G
P r o g r a m c o u n t e r
V e c t o r t a b l e
S t a c k p o i n t e r
4
P o r t P 4
S y s t e m c l o c k g e n e r a t o r
I N
– X
X
U A R T / c l o c k s y n c h r o n o u s S I / O
U A R T / c l o c k s y n c h r o n o u s S I / O
M u l t i - m a s t e r I2C - b u s
i n t e r f a c e 0
M u l t i - m a s t e r I2C - b u s
i n t e r f a c e 1
P C
I N T B
I S P
U S P
4
P o r t P 5
O U T
M e m o r y
R O M
1 9 2 K
R A M
5 K
M u l t i p l i e r
3
P o r t P 6
o r t P
P
7
o r t P
P
5 1
8
o r t P
P
9
3 2
o r t P 1
P
0
Figure 1.4.1 Block diagram
Rev. 1.0
4
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
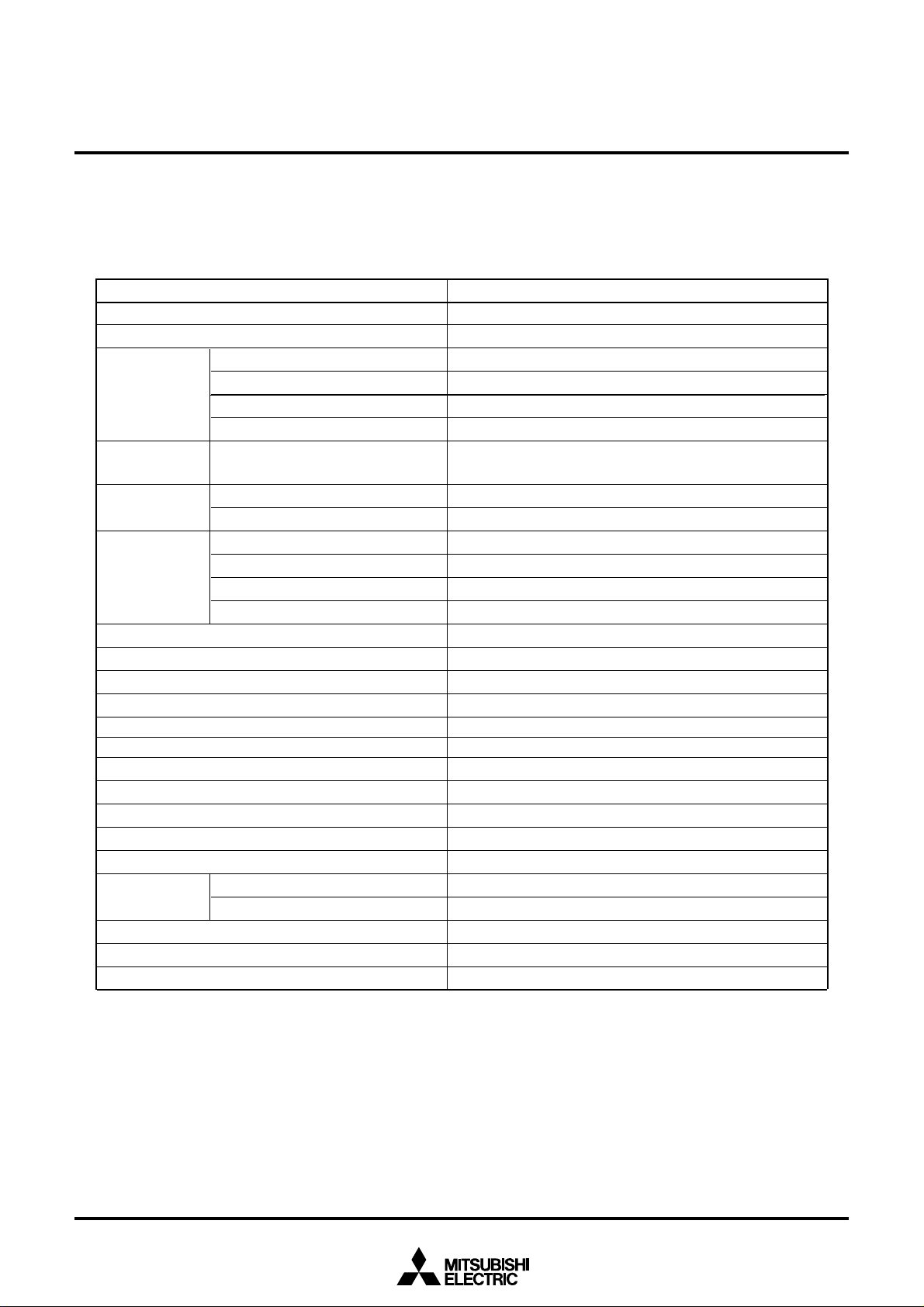
1.5 Performance Outline
Table 1.5.1 is a performance outline.
Table 1.5.1 Performance outline
Item Performance
Number of basic instructions 91 instructions
Shortest instruction execution time 100 ns(f(XIN)=10 MHz)
Memory ROM 192K bytes
size RAM 5K bytes
OSD ROM 61K bytes
OSD RAM 2.2K bytes
I/O port P0, P2 to P10 8 bits ✕ 3, 5 bits ✕ 1, 4 bits ✕ 2, 3 bits ✕ 2, 2 bits ✕ 1,
1 bit ✕ 1
Multifunction TA0, TA1, TA2, TA3, TA4 16 bits ✕ 5
timer TB0, TB1, TB2 16 bits ✕ 3
Serial I/O UART0 1 unit: UART or clock synchronous
UART2 1 unit: UART or clock synchronous
Multi-master I2C-BUS interface 0 1 unit (2 channels)
Multi-master I2C-BUS interface 1 1 unit (1 channels)
A-D converter 8 bits ✕ 6 channels
D-A converter 8 bits ✕ 2 channels
DMAC 2 channels (trigger: 23 sources)
OSD function
Data slicer 32-bit buffer
HSYNC counter 8 bits ✕ 2 channels
Watchdog timer 15 bits ✕ 1 (with prescaler)
Interrupt
Clock generating circuit 2 built-in clock generation circuits
Power source voltage 4.5 V to 5.5V (f(XIN ) = 10 MHz)
Power consumption
I/O I/O withstand voltage 5 V
characteristics Output current 5 mA
Operating ambient temperature –10 o C to 70 o C
Device configuration CMOS high performance silicon gate
Package 64-pin plastic molded SDIP
Triple layer, 890 kinds of fonts, 42 character ✕ 16 lines
21 internal and 3 external sources, 4 software sources, 7 levels
250 mW
Rev. 1.0
5
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
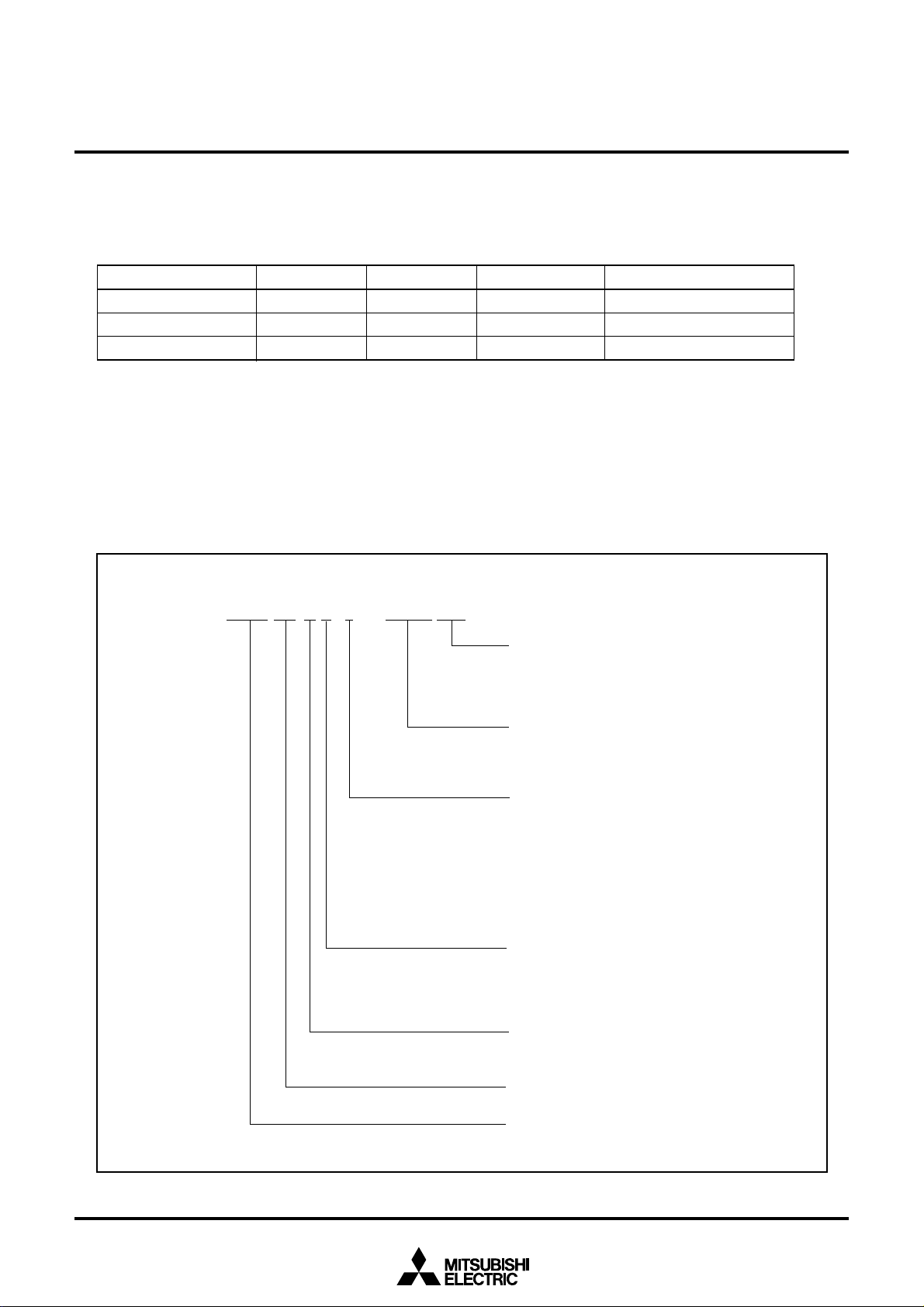
Currently supported products are listed below.
Table 1.5.2 List of supported products
R A M c a p a c i t yR O M c a p a c i t y
M 3 0 6 V 5 M E - X X X S P5
1 9 2 K b y t e s
9 2 K b y t e
9 2 K b y t e
s6
s6
K b y t e
5 K b y t e s
s M a s k R O M v e r s i o n
Note: Since EPROM version is for development support tool (for evaluation), do not use for mass produc-
tion.
P a c k a g e t y p e
6 4 P 4 B
4 P 4
B
4 S 1
B5 K b y t e s
R e m a r k sT y p e N o
O n e T i m e P R O M v e r s i o nM 3 0 6 V 5 E E S P1
E P R O M v e r s i o nM 3 0 6 V 5 E E S S1
T y p e N o . M 3 0 6 V 5 M E – X X X S P
P a c k a g e t y p e :
S P : P a c k a g e6 4 P 4 B
S S : P a c k a g e6 4 S 1 B
R O M N o .
O m i t t e d f o r O n e T i m e P R O M v e r s i o n
a n d E P R O M v e r s i o n
R O M c a p a c i t y :
E : 1 9 2 K b y t e s
M e m o r y t y p e :
M : M a s k R O M v e r s i o n
E : O n e T i m e P R O M v e r s i o n o r E P R O M
v e r s i o n
S h o w s R A M c a p a c i t y , p i n c o u n t , e t c
( T h e v a l u e i t s e l f h a s n o s p e c i f i c m e a n i n g )
Figure 1.5.1 Type No., memory size, and package
6
M 1 6 C / 6 V G r o u p
M 1 6 C F a m i l y
Rev. 1.0

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
1.5.1 As For M16C/6V (64-Pin Version) Group
M16C/6V (64-pin version) group is packaged in a 64-pin plastic molded SDIP. Note that the number of
pins is reduced when it is compared with a 100-pin package product.
(1) M16C/6V (64-pin version) group supports only the shingle-chip mode. It does not support the memory
expansion and the microprocessor modes.
(2) Be sure to initialize in the sequence below immediately after reset release.
➀ Set OSD reserved register i (i = 1 to 4) to the specified values.
➁
Set each reserved bit of the port Pi direction register, the port Pi register, and pull-up control register
to the specified values.
➂ Set port reserved register i (i = 1 to 3) to the specified values.
➃ Set other reserved registers and each reserved bit of other registers to the specified values.
i
Rev. 1.0
7
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
Table 1.5.3 Pin description (1)
P i n n a m e
VC
C,
VS
C N VS
S
S
S i g n a l n a m e
P o w e r s u p p l y
i n p u t
C N V
S S
I n p u t
I / O t y p e
p i n . S u p p l y 0 V t o t h e
p i n
S u p p l y 4 . 5 V t o 5 . 5 V t o t h e V
p i n
C o n n e c t t h i s p i n t o t h e V
S S
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
F u n c t i o n
C C
.
VS
S
.
R E S E T
XI
N
U
XO
T
A VC
C
P 00 t o P 07
P 20 t o P 27
P 30 t o P 37
P 40 t o P 43
P
P 50, P 52,
P 5
3,
55
P 62, P 63,
P 6
7
R e s e t i n p u t
C l o c k i n p u t
C l o c k o u t p u t
I n p u t
I n p u t
O u t p u t
A n a l o g p o w e r
s u p p l y i n p u t
I / O p o r t P 0
I / O p o r t P 2
I / O p o r t P 3
I / O p o r t P 4
I / O p o r t P 5I
I n p u t / o u t p u t
I n p u t / o u t p u t
I n p u t / o u t p u t
I n p u t / o u t p u t
n p u t / o u t p u
I n p u t / o u t p u tI / O p o r t P 6
A “ L ” o n t h i s i n p u t r e s e t s t h e m i c r o c o m p u t e r .
a n d t h e
p i n s .
p i n a n d l e a v e t h e
U
p i n o p e n
T h e s e p i n s a r e p r o v i d e d f o r t h e m a i n c l o c k g e n e r a t i n g c i r c u i t . C o n n e c t
a c e r a m i c r e s o n a t o r o r c r y s t a l b e t w e e n t h e X
u s e a n e x t e r n a l l y d e r i v e d c l o c k , i n p u t i t t o t h e X
X
O U T
.
I N
I N
XO
T
T h i s p i n i s a p o w e r s u p p l y i n p u t f o r t h e A - D c o n v e r t e r . C o n n e c t t h i s
p i n t o V
C C.
T h i s i s a n 8 - b i t C M O S I / O p o r t . I t h a s a n i n p u t / o u t p u t p o r t d i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r t h a t a l l o w s t h e u s e r t o s e t e a c h p i n f o r i n p u t o r o u t p u t
i n d i v i d u a l l y . W h e n s e t f o r i n p u t , t h e u s e r c a n s p e c i f y i n u n i t s o f f o u r b i t s
v i a s o f t w a r e w h e t h e r o r n o t t h e y a r e t i e d t o a p u l l - u p r e s i s t o r .
T h i s i s a n 8 - b i t I / O p o r t e q u i v a l e n t t o P 0 .
c o u n t e r I / O p i n s , a n d A - D c o n v e r t e r i n p u t
T h i s i s a n 8 - b i t I / O p o r t e q u i v a l e n t t o P 0 . P i n s i n t h i s p o r t f u n c t i o n a s
e x t e r n a l i n t e r r u p t p i n , H
S Y N C
p i n s a s s e l e c t e d b y s o f t w a r e .
T h i s i s a n 8 - b i t I / O p o r t e q u i v a l e n t t o P 0 . P i n s i n t h i s p o r t f u n c t i o n a s A - D
c o n v e r t e r i n p u t p i n s a s s e l e c t e d b y s o f t w a r e .
T h i s i s a 4 - b i t I / O p o r t e q u i v a l e n t t o P 0 . P 57 i n t h i s p o r t f u n c t i o n s a s
t
U A R T 0 I / O p i n a s s e l e c t e d b y s o f t w a r e .
T h i s i s a 3 - b i t I / O p o r t e q u i v a l e n t t o P 0 . P i n s i n t h i s p o r t a l s o f u n c t i o n a s
U A R T 0 a n d m u l t i - m a s t e r I
2
C - B U S i n t e r f a c e 0 I / O p i n s a s s e l e c t e d b y
s o f t w a r e .
To
P 70 t o P 72
,
P 74, P 76
P 82
P 90, P 93, P 94
I / O p o r t P 7
I / O p o r t P 8
I / O p o r t P 9
I n p u t / o u t p u t
I n p u t / o u t p u t
I n p u t / o u t p u t
T h i s i s a 5 - b i t I / O p o r t e q u i v a l e n t t o P 0 ( P 70 a n d P 71 a r e N - c h a n n e l
o p e n - d r a i n o u t p u t ) . P i n s i n t h i s p o r t a l s o f u n c t i o n a s t i m e r s A 2 a n d A 3 ,
U A R T 2 , m u l t i - m a s t e r I
s o f t w a r e .
c a n b e m a d e t o f u n c t i o n a s t h e I / O p i n f o r t h e i n p u t p i n s f o r e x t e r n a l
P 82 i s I / O p o r t w i t h t h e s a m e f u n c t i o n s a s P 0 .
P 8
2
2
C - B U S i n t e r f a c e 0 I / O p i n s a s s e l e c t e d b y
i n t e r r u p t s a s s e l e c t e d b y s o f t w a r e .
T h i s i s a n 3 - b i t I / O p o r t e q u i v a l e n t t o P 0 . P i n s i n t h i s p o r t a l s o f u n c t i o n
a s T i m e r B 0 i n p u t p i n , D - A c o n v e r t e r o u t p u t p i n s , a n d m u l t i - m a s t e r I
2
C -
B U S i n t e r f a c e 1 I / O p i n s a s s e l e c t e d b y s o f t w a r e .
Rev. 1.0
8
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
Table 1.5.4 Pin description (continued) (2)
S i g n a l n a m eF
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
u n c t i o
nP i n n a m e I / O t y p e
1
R , G , B
O U T 1 , O U T 2
O S C 1
O S C 2
I N
C V
V
H O L D
H L F
T V S E T B
I n p u t / o u t p u tI / O p o r t P 1 0P 1 00, P 1 0
O S D o u t p u t
O S D o u t p u tO u t p u t
C l o c k i n p u t
f o r O S D
C l o c k o u t p u t
f o r O S D
I / O f o r d a t a
s l i c e r
T e s t i n p u t
O u t p u t
I n p u t
O u t p u t
I n p u t
I n p u t
I n p u t / o u t p u t
I n p u t
T h i s i s a 2 - b i t I / O p o r t e q u i v a l e n t t o P 0 . P i n s i n t h i s p o r t a l s o f u n c t i o n
a s a i n p u t p i n s f o r O S D f u n c t i o n a s s e l e c t e d b y s o f t w a r e .
T h e s e a r e O S D o u t p u t p i n s ( a n a l o g o u t p u t ) .
T h e s e a r e O S D o u t p u t p i n s ( d i g i t a l o u t p u t ) .
T h i s i s a n O S D c l o c k i n p u t p i n .
T h i s i s a n O S D c l o c k o u t p u t p i n .
I n p u t c o m p o s i t e v i d e o s i g n a l t h r o u g h a c a p a c i t o r .
C o n n e c t a c a p a c i t o r b e t w e e n V
C o n n e c t a f i l t e r u s i n g o f a c a p a c i t o r a n d a r e s i s t o r
b e t w e e n H L F a n d V s s .
T h i s i s a t e s t i n p u t p i n . F i x i t t o “ L . ”
H O L D
a n d V s s .
Rev. 1.0
9

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
2. OPERATION OF FUNCTIONAL BLOKS
This microcomputer accommodates certain units in a single chip. These units include ROM and RAM to
store instructions and data and the central processing unit (CPU) to execute arithmetic/logic operations.
Also included are peripheral units such as timers, serial I/O, D-A converter, DMAC, OSD circuit, data slicer,
A-D converter, and I/O ports.
The following explains each unit.
2.1 Memory
Figure 2.1.1 is a memory map. The address space extends the 1M bytes from address 0000016 to
FFFFF16. From FFFFF16 down is ROM. There is 192K bytes of internal ROM from D000016 to FFFFF16.
The vector table for fixed interrupts such as the reset mapped to FFFDC16 to FFFFF16. The starting address of the interrupt routine is stored here. The address of the vector table for timer interrupts, etc., can be
set as desired using the internal register (INTB). See the section on interrupts for details.
5K bytes of internal RAM is mapped to the space from 02C0016 to 03FFF16. In addition to storing data, the
RAM also stores the stack used when calling subroutines and when interrupts are generated.
The SFR area is mapped to 0000016 to 003FF16. This area accommodates the control registers for peripheral devices such as I/O ports, A-D converter, serial I/O, and timers, etc. Figures 2.1.2 to 2.1.5 are location
of peripheral unit control registers. Any part of the SFR area that is not occupied is reserved and cannot be
used for other purposes.
The special page vector table is mapped to FFE0016 to FFFDB16. If the starting addresses of subroutines
or the destination addresses of jumps are stored here, subroutine call instructions and jump instructions
can be used as 2-byte instructions, reducing the number of program steps.
10
Rev. 1.0
00000
003FF
00400
013FF
01400
02BFF
02C00
03FFF
04000
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
16
(Refer to Figures 2.1.2 to 2.1.5)
16
16
SFR area
OSD RAM area
16
16
Internal reserved
16
16
area
Internal RAM area
16
16
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
FFE00
16
8FFFF
16
90000
16
AFFFF
16
B0000
16
CFFFF
16
D0000
16
FFFFF
16
Figure 2.1.1 Memory map
Internal reserved
area
OSD ROM area
Internal reserved
area
Internal ROM area
FFFDC
FFFFF
Special page
vector table
16
Undefined instruction
Overflow
BRK instruction
Address match
Single step
Watchdog timer
16
DBC
Reset
Rev. 1.0
11
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
0 0 0 0
1 6
0 0 0 1
1 6
0 0 0 2
1 6
0 0 0 3
1 6
0 0 0 4
1 6
P r o c e s s o r m o d e r e g i s t e r 0 ( P M 0 )
0 0 0 5
1 6
P r o c e s s o r m o d e r e g i s t e r 1 ( P M 1 )
0 0 0 6
1 6
S y s t e m c l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 0 ( C M 0 )
0 0 0 7
1 6
S y s t e m c l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 ( C M 1 )
0 0 0 8
1 6
0 0 0 9
1 6
A d d r e s s m a t c h i n t e r r u p t e n a b l e r e g i s t e r ( A I E R )
0 0 0 A
1 6
P r o t e c t r e g i s t e r ( P R C R )
0 0 0 B
1 6
0 0 0 C
1 6
0 0 0 D
1 6
0 0 0 E
1 6
W a t c h d o g t i m e r s t a r t r e g i s t e r ( W D T S )
0 0 0 F
1 6
W a t c h d o g t i m e r c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( W D C )
0 0 1 0
1 6
0 0 1 1
1 6
A d d r e s s m a t c h i n t e r r u p t r e g i s t e r 0 ( R M A D 0 )
0 0 1 2
1 6
0 0 1 3
1 6
0 0 1 4
1 6
A d d r e s s m a t c h i n t e r r u p t r e g i s t e r 1 ( R M A D 1 )
0 0 1 5
1 6
0 0 1 6
1 6
0 0 1 7
1 6
0 0 1 8
1 6
0 0 1 9
1 6
0 0 1 A
1 6
0 0 1 B
1 6
0 0 1 C
1 6
0 0 1 D
1 6
0 0 1 E
1 6
0 0 1 F
1 6
0 0 2 0
1 6
0 0 2 1
1 6
D M A 0 s o u r c e p o i n t e r ( S A R 0 )
0 0 2 2
1 6
0 0 2 3
1 6
0 0 2 4
1 6
0 0 2 5
1 6
D M A 0 d e s t i n a t i o n p o i n t e r ( D A R 0 )
0 0 2 6
1 6
0 0 2 7
1 6
0 0 2 8
1 6
D M A 0 t r a n s f e r c o u n t e r ( T C R 0 )
0 0 2 9
1 6
0 0 2 A
1 6
0 0 2 B
1 6
0 0 2 C
1 6
D M A 0 c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( D M 0 C O N )
0 0 2 D
1 6
0 0 2 E
1 6
0 0 2 F
1 6
0 0 3 0
1 6
0 0 3 1
1 6
D M A 1 s o u r c e p o i n t e r ( S A R 1 )
0 0 3 2
1 6
0 0 3 3
1 6
0 0 3 4
1 6
D M A 1 d e s t i n a t i o n p o i n t e r ( D A R 1 )
0 0 3 5
1 6
0 0 3 6
1 6
0 0 3 7
1 6
0 0 3 8
1 6
D M A 1 t r a n s f e r c o u n t e r ( T C R 1 )
0 0 3 9
1 6
0 0 3 A
1 6
0 0 3 B
1 6
0 0 3 C
1 6
D M A 1 c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( D M 1 C O N )
0 0 3 D
1 6
0 0 3 E
1 6
0 0 3 F
1 6
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
0 0 4 0
1 6
0 0 4 1
1 6
0 0 4 2
1 6
0 0 4 3
1 6
0 0 4 4
1 6
O S D 1 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( O S D 1 I C )
0 0 4 5
1 6
I n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e s e r v e d r e g i s t e r 0 ( R E 0 I C )
0 0 4 6
1 6
I n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e s e r v e d r e g i s t e r 1 ( R E 1 I C )
0 0 4 7
1 6
I n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e s e r v e d r e g i s t e r 2 ( R E 2 I C )
0 0 4 8
1 6
O S D 2 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( O S D 2 I C )
0 0 4 9
1 6
M u l t i - m a s t e r I2C - B U S i n t e r f a c e 1 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( I I C 1 I C )
0 0 4 A
1 6
B u s c o l l i s i o n d e t e c t i o n i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( B C N I C )
0 0 4 B
1 6
D M A 0 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( D M 0 I C )
0 0 4 C
1 6
D M A 1 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( D M 1 I C )
0 0 4 D
1 6
M u l t i - m a s t e r I2C - B U S i n t e r f a c e 0 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( I I C 0 I C )
0 0 4 E
1 6
A - D c o n v e r s i o n i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( A D I C )
0 0 4 F
1 6
U A R T 2 t r a n s m i t i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( S 2 T I C )
0 0 5 0
1 6
U A R T 2 r e c e i v e i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( S 2 R I C )
0 0 5 1
1 6
U A R T 0 t r a n s m i t i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( S 0 T I C )
0 0 5 2
1 6
U A R T 0 r e c e i v e i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( S 0 R I C )
0 0 5 3
1 6
D a t a s l i c e r i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( D S I C )
0 0 5 4
1 6
V
S Y N C
0 0 5 5
0 0 5 6
0 0 5 7
0 0 5 8
0 0 5 9
0 0 5 A
0 0 5 B
0 0 5 C
0 0 5 D
0 0 5 E
0 0 5 F
0 0 6 0
0 1 F F
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( V S Y N C I C )
T i m e r A 0 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( T A 0 I C )
T i m e r A 1 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( T A 1 I C )
T i m e r A 2 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( T A 2 I C )
T i m e r A 3 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( T A 3 I C )
T i m e r A 4 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( T A 4 I C )
T i m e r B 0 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( T B 0 I C )
T i m e r B 1 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( T B 1 I C )
T i m e r B 2 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( T B 2 I C )
I N T 0 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( I N T 0 I C )
I N T 1 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( I N T 1 I C )
I n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e s e r v e d r e g i s t e r 3 ( R E 3 I C )
Figure 2.1.2 Location of peripheral unit control registers (1)
12
Rev. 1.0

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
0 2 0 01
6
0 2 0 11
6
S P R I T E O S D c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( S C )
0 2 0 21
6
O S D c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 ( O C 1 )
0 2 0 31
6
O S D c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2 ( O C 2 )
0 2 0 41
6
H o r i z o n t a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r ( H P )
0 2 0 51
6
C l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( C S )
0 2 0 61
6
I / O p o l a r i t y c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( P C )
0 2 0 71
6
O S D c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 3 ( O C 3 )
0 2 0 81
6
R a s t e r c o l o r r e g i s t e r ( R S C )
0 2 0 91
6
0 2 0 A1
6
0 2 0 B1
6
0 2 0 C1
6
T o p b o r d e r c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( T B R )
0 2 0 D1
6
0 2 0 E1
6
B o t t o m b o r d e r c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( B B R )
0 2 0 F1
6
0 2 1 01
6
B l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 ( B C 1)
0 2 1 11
6
B l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2 ( B C 2)
0 2 1 21
6
B l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 3 ( B C 3)
0 2 1 31
6
B l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 4 ( B C 4)
0 2 1 41
6
B l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 5 ( B C 5)
0 2 1 51
6
B l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 6 ( B C 6)
0 2 1 61
6
B l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 7 ( B C 7)
0 2 1 71
6
B l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 8 ( B C 8)
0 2 1 81
6
B l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 9 ( B C 9)
0 2 1 91
6
B l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 0 ( B C 1 0)
0 2 1 A1
6
B l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 1 ( B C 1 1)
0 2 1 B1
6
B l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 2 ( B C 1 2)
0 2 1 C1
6
B l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 3 ( B C 1 3)
0 2 1 D1
6
B l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 4 ( B C 1 4)
0 2 1 E1
6
B l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 5 ( B C 1 5)
0 2 1 F1
6
B l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 6 ( B C 1 6)
0 2 2 01
6
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 1 ( V P 1 )
0 2 2 11
6
0 2 2 21
6
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 2 ( V P 2 )
0 2 2 31
6
0 2 2 41
6
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 3 ( V P 3 )
0 2 2 51
6
0 2 2 61
6
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 4 ( V P 4 )
0 2 2 71
6
0 2 2 81
6
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 5 ( V P 5 )
0 2 2 91
6
0 2 2 A1
6
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 6 ( V P 6 )
0 2 2 B1
6
0 2 2 C1
6
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 7 ( V P 7 )
0 2 2 D1
6
0 2 2 E1
6
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 8 ( V P 8 )
0 2 2 F1
6
0 2 3 01
6
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 9 ( V P 9 )
0 2 3 11
6
0 2 3 21
6
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 1 0 ( V P 1 0 )
0 2 3 31
6
0 2 3 41
6
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 1 1 ( V P 1 1 )
0 2 3 51
6
0 2 3 61
6
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 1 2 ( V P 1 2 )
0 2 3 71
6
0 2 3 81
6
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 1 3 ( V P 1 3 )
0 2 3 91
6
0 2 3 A1
6
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 1 4 ( V P 1 4 )
0 2 3 B1
6
0 2 3 C1
6
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 1 5 ( V P 1 5 )
0 2 3 D1
6
0 2 3 E1
6
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 1 6 ( V P 1 6 )
0 2 3 F1
6
0 2 4 01
6
C o l o r p a l e t t e r e g i s t e r 1 ( C R 1 )
0 2 4 11
6
0 2 4 21
6
C o l o r p a l e t t e r e g i s t e r 2 ( C R 2 )
0 2 4 31
6
0 2 4 41
6
C o l o r p a l e t t e r e g i s t e r 3 ( C R 3 )
0 2 4 51
6
0 2 4 61
6
C o l o r p a l e t t e r e g i s t e r 4 ( C R 4 )
0 2 4 71
6
0 2 4 81
6
C o l o r p a l e t t e r e g i s t e r 5 ( C R 5 )
0 2 4 91
6
0 2 4 A1
6
C o l o r p a l e t t e r e g i s t e r 6 ( C R 6 )
0 2 4 B1
6
0 2 4 C1
6
C o l o r p a l e t t e r e g i s t e r 7 ( C R 7 )
0 2 4 D1
6
0 2 4 E1
6
C o l o r p a l e t t e r e g i s t e r 9 ( C R 9 )
0 2 4 F1
6
0 2 5 01
6
C o l o r p a l e t t e r e g i s t e r 1 0 ( C R 1 0 )
0 2 5 11
6
0 2 5 21
6
C o l o r p a l e t t e r e g i s t e r 1 1 ( C R 1 1 )
0 2 5 31
6
0 2 5 41
6
C o l o r p a l e t t e r e g i s t e r 1 2 ( C R 1 2 )
0 2 5 51
6
0 2 5 61
6
C o l o r p a l e t t e r e g i s t e r 1 3 ( C R 1 3 )
0 2 5 71
6
0 2 5 81
6
C o l o r p a l e t t e r e g i s t e r 1 4 ( C R 1 4 )
0 2 5 91
6
0 2 5 A1
6
C o l o r p a l e t t e r e g i s t e r 1 5 ( C R 1 5 )
0 2 5 B1
6
0 2 5 C1
6
0 2 5 D1
6
O S D r e s e r v e d r e g i s t e r 1 ( O R 1 )
0 2 5 E1
6
0 2 5 F1
6
O S D c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 4 ( O C 4 )
0 2 6 01
6
D a t a s l i c e r c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 ( D S C 1 )
0 2 6 11
6
D a t a s l i c e r c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2 ( D S C 2 )
0 2 6 21
6
C a p t i o n d a t a r e g i s t e r 1 ( C D 1 )
0 2 6 31
6
0 2 6 41
6
C a p t i o n d a t a r e g i s t e r 2 ( C D 2 )
0 2 6 51
6
0 2 6 61
6
C a p t i o n p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r ( C P S )
0 2 6 71
6
D a t a s l i c e r r e s e r v e d r e g i s t e r 2 ( D R 2 )
0 2 6 81
6
D a t a s l i c e r r e s e r v e d r e g i s t e r 1 ( D R 1 )
0 2 6 91
6
C l o c k r u n - i n d e t e c t r e g i s t e r ( C R D )
0 2 6 A1
6
D a t a c l o c k p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r ( D P S )
0 2 6 B1
6
0 2 6 F1
6
0 2 7 01
6
L e f t b o r d e r c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( L B R )
0 2 7 11
6
0 2 7 21
6
R i g h t b o r d e r c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( R B R )
0 2 7 31
6
0 2 7 41
6
S P R I T E v e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 1 ( V S 1 )
0 2 7 51
6
0 2 7 61
6
S P R I T E v e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 2 ( V S 2 )
0 2 7 71
6
0 2 7 81
6
S P R I T E h o r i z o n t a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r ( H S )
0 2 7 91
6
0 2 7 A1
6
O S D r e s e r v e d r e g i s t e r 4 ( O R 4 )
0 2 7 B1
6
O S D r e s e r v e d r e g i s t e r 3 ( O R 3 )
0 2 7 C1
6
O S D r e s e r v e d r e g i s t e r 2 ( O R 2 )
0 2 7 D1
6
P e r i p h e r a l m o d e r e g i s t e r ( P M )
0 2 7 E1
6
H
S Y N C
0 2 7 F1
0 2 8 01
0 2 D F1
6
6
6
c o u n t e r r e g i s t e r ( H C )
S Y N C
c o u n t e r l a t c h
H
Figure 2.1.3 Location of peripheral unit control registers (2)
Rev. 1.0
13
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
02E0
02E1
02E2
02E3
02E4
02E5
02E6
02E7
02E8
02E9
02EA
02EB
02EC
02ED
02EE
02EF
0339
0340
0341
0342
0343
0344
0345
0346
0347
0348
0349
035E
035F
0360
0361
0362
0363
0364
0365
0366
0367
0368
0369
036A
036B
036C
036D
036E
036F
0370
0371
0372
0373
0374
0375
0376
0377
0378
0379
037A
037B
037C
037D
037E
037F
2
I
C0 data shift register (IIC0S0)
16
2
I
C0 address register (IIC0S0D)
16
2
16
I
C0 status register (IIC0S1)
2
16
C0 control register (IIC0S1D)
I
2
16
C0 clock control register (IIC0S2)
I
2
16
C0 port selection register (IIC0S2D)
I
2
16
C0 transmit buffer register (IIC0S0S)
I
16
2
16
I
C1 data shift register (IIC1S0)
2
16
C1 address register (IIC1S0D)
I
16
I2C1 status register (IIC1S1)
2
16
C1 control register (IIC1S1D)
I
2
I
C1 clock control register (IIC1S2)
16
2
16
I
C1 port selection register (IIC1S2D)
2
16
I
C1 transmit buffer register (IIC1S0S)
16
16
16
Reserved register 1 (INVC1)
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
Reserved register 0 (INVC0)
16
16
16
Interrupt request cause select register (IFSR)
16
16
16
Reserved register 3 (INVC3)
16
16
16
16
Reserved register 4 (INVC4)
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
Reserved register 5 (INVC5)
16
UART2 special mode register (U2SMR)
16
UART2 transmit/receive mode register (U2MR)
16
16
UART2 bit rate generator (U2BRG)
16
UART2 transmit buffer register (U2TB)
16
16
UART2 transmit/receive control register 0 (U2C0)
16
UART2 transmit/receive control register 1 (U2C1)
16
UART2 receive buffer register (U2RB)
16
0380
0381
0382
0383
0384
0385
0386
0387
0388
0389
038A
038B
038C
038D
038E
038F
0390
0391
0392
0393
0394
0395
0396
0397
0398
0399
039A
039B
039C
039D
039E
039F
03A0
03A1
03A2
03A3
03A4
03A5
03A6
03A7
03A8
03A9
03AA
03AB
03AC
03AD
03AE
03AF
03B0
03B1
03B2
03B3
03B4
03B5
03B6
03B7
03B8
03B9
03BA
03BB
03BC
03BD
03BE
03BF
16
Count start flag (TABSR)
16
Reserved register 6 (INVC6)
16
One-shot start flag (ONSF)
16
Trigger select register (TRGSR)
16
Up-down flag (UDF)
16
16
Timer A0 register (TA0)
16
16
Timer A1 register (TA1)
16
16
Timer A2 register (TA2)
16
16
Timer A3 register (TA3)
16
16
Timer A4 register (TA4)
16
16
Timer B0 register (TB0)
16
16
Timer B1 register (TB1)
16
16
Timer B2 register (TB2)
16
16
Timer A0 mode register (TA0MR)
16
Timer A1 mode register (TA1MR)
16
Timer A2 mode register (TA2MR)
16
Timer A3 mode register (TA3MR)
16
Timer A4 mode register (TA4MR)
16
Timer B0 mode register (TB0MR)
16
Timer B1 mode register (TB1MR)
Timer B2 mode register (TB2MR)
16
16
16
16
UART0 transmit/receive mode register (U0MR)
16
UART0 bit rate generator (U0BRG)
16
UART0 transmit buffer register (U0TB)
16
16
UART0 transmit/receive control register 0 (U0C0)
16
UART0 transmit/receive control register 1 (U0C1)
16
UART0 receive buffer register (U0RB)
16
16
Reserved register 2 (INVC2)
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
UART transmit/receive control register 2 (UCON)
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
DMA0 request cause select register (DM0SL)
16
DMA1 request cause select register (DM1SL)
16
16
16
16
16
16
Figure 2.1.4 Location of peripheral unit control registers (3)
14
Rev. 1.0

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
03C016
03C116
03C216
03C316
03C416
A-D register 0 (AD0)
03C516
03C616
A-D register 1 (AD1)
03C716
03C816
A-D register 2 (AD2)
03C916
03CA16
A-D register 3 (AD3)
03CB16
03CC16
A-D register 4 (AD4)
03CD16
03CE16
A-D register 5 (AD5)
03CF16
03D016
03D116
03D216
03D316
03D416
A-D control register 2 (ADCON2)
03D516
03D616
A-D control register 0 (ADCON0)
03D716
A-D control register 1 (ADCON1)
03D816
D-A register 0 (DA0)
03D916
03DA16
D-A register 1 (DA1)
03DB16
03DC16
D-A control register (DACON)
03DD16
03DE16
03DF16
03E016
Port P0 register (P0)
03E116
Port reserved register 1 (PR1)
03E216
Port P0 direction register (PD0)
03E316
Port reserved register 2 (PR2)
03E416
Port P2 register (P2)
03E516
Port P3 register (P3)
03E616
Port P2 direction register (PD2)
03E716
Port P3 direction register (PD3)
03E816
Port P4 register (P4)
03E916
Port P5 register (P5)
03EA16
Port P4 direction register (PD4)
03EB16
Port P5 direction register (PD5)
03EC16
Port P6 register (P6)
03ED16
Port P7 register (P7)
03EE16
Port P6 direction register (PD6)
03EF16
Port P7 direction register (PD7)
03F016
Port P8 register (P8)
Port P9 register (P9)
03F116
Port P8 direction register (PD8)
03F216
Port P9 direction register (PD9)
03F316
03F416
Port P10 register (P10)
03F516
Port P10 direction register (PD10)
03F616
03F716
03F816
03F916
03FA16
03FB16
Pull-up control register 0 (PUR0)
03FC16
Pull-up control register 1 (PUR1)
03FD16
Pull-up control register 2 (PUR2)
03FE16
Port reserved register 3 (PR3)
03FF16
Figure 2.1.5 Location of peripheral unit control registers (4)
Rev. 1.0
15
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
2.2 Central Processing Unit (CPU)
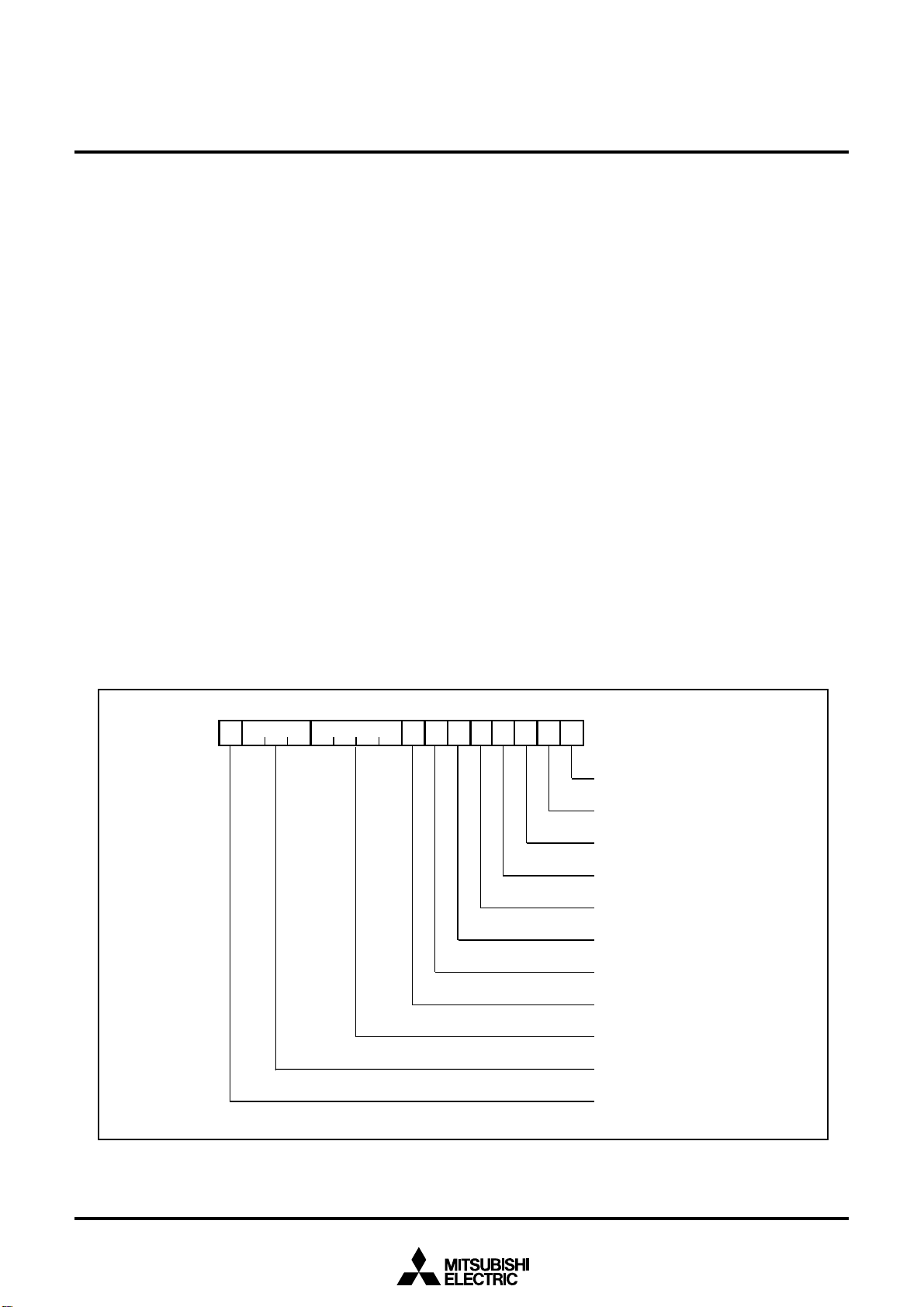
The CPU has a total of 13 registers shown in Figure 2.2.1. Seven of these registers (R0, R1, R2, R3, A0,
A1, and FB) come in two sets; therefore, these have two register banks.
b15 b8 b7 b0
(Note)
R0
H
L
R1
R2
R3
A0
A1
FB
b15
(Note)
b15
(Note)
b15 b0
(Note)
b15 b0
(Note)
b15
(Note)
b15 b0
(Note)
b8 b7 b0
H
b19
L
PC
b0
Program counter
Data
b0
registers
INTB
b0 b19
HL
Interrupt table
register
b15 b0
USP
b15 b0
ISP
User stack pointer
Interrupt stack
pointer
Address
b0
registers
Frame base
registers
b15
SB
b15 b0
FLG
b0
Static base
register
Flag register
IPL
Note: These registers consist of two register banks.
Figure 2.2.1 Central processing unit register
CDZSBOIU
Rev. 1.0
16

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
2.2.1 Data Registers (R0, R0H, R0L, R1, R1H, R1L, R2, and R3)
Data registers (R0, R1, R2, and R3) are configured with 16 bits, and are used primarily for transfer and
arithmetic/logic operations.
Registers R0 and R1 each can be used as separate 8-bit data registers, high-order bits as (R0H/R1H),
and low-order bits as (R0L/R1L). In some instructions, registers R2 and R0, as well as R3 and R1 can
use as 32-bit data registers (R2R0/R3R1).
2.2.2 Address Registers (A0 and A1)
Address registers (A0 and A1) are configured with 16 bits, and have functions equivalent to those of data
registers. These registers can also be used for address register indirect addressing and address register
relative addressing.
In some instructions, registers A1 and A0 can be combined for use as a 32-bit address register (A1A0).
2.2.3 Frame Base Register (FB)
Frame base register (FB) is configured with 16 bits, and is used for FB relative addressing.
2.2.4 Program Counter (PC)
Program counter (PC) is configured with 20 bits, indicating the address of an instruction to be executed.
2.2.5 Interrupt Table Register (INTB)
Interrupt table register (INTB) is configured with 20 bits, indicating the start address of an interrupt vector
table.
2.2.6 Stack Pointer (USP/ISP)
Stack pointer comes in two types: user stack pointer (USP) and interrupt stack pointer (ISP), each configured with 16 bits.
Your desired type of stack pointer (USP or ISP) can be selected by a stack pointer select flag (U flag).
This flag is located at the position of bit 7 in the flag register (FLG).
2.2.7 Static Base Register (SB)
Static base register (SB) is configured with 16 bits, and is used for SB relative addressing.
2.2.8 Flag Register (FLG)
Flag register (FLG) is configured with 11 bits, each bit is used as a flag. Figure 2.2.2 shows the flag
register (FLG). The following explains the function of each flag:
• Bit 0: Carry flag (C flag)
This flag retains a carry, borrow, or shift-out bit that has occurred in the arithmetic/logic unit.
• Bit 1: Debug flag (D flag)
This flag enables a single-step interrupt.
When this flag is “1”, a single-step interrupt is generated after instruction execution. This flag is
cleared to “0” when the interrupt is acknowledged.
• Bit 2: Zero flag (Z flag)
This flag is set to “1” when an arithmetic operation resulted in 0; otherwise, cleared to “0”.
• Bit 3: Sign flag (S flag)
This flag is set to
• Bit 4: Register bank select flag (B flag)
This flag chooses a register bank. Register bank 0 is selected when this flag is “0” ; register bank 1 is
selected when this flag is “1”.
“1”
when an arithmetic operation resulted in a negative value; otherwise, cleared to
“0”
.
Rev. 1.0
17
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
g
r
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
• Bit 5: Overflow flag (O flag)
This flag is set to “1” when an arithmetic operation resulted in overflow; otherwise, cleared to “0”.
• Bit 6: Interrupt enable flag (I flag)
This flag enables a maskable interrupt.
An interrupt is disabled when this flag is “0”, and is enabled when this flag is “1”. This flag is cleared to
“0” when the interrupt is acknowledged.
• Bit 7: Stack pointer select flag (U flag)
Interrupt stack pointer (ISP) is selected when this flag is “0” ; user stack pointer (USP) is selected
when this flag is “1”.
This flag is cleared to “0” when a hardware interrupt is acknowledged or an INT instruction of software
interrupt Nos. 0 to 31 is executed.
• Bits 8 to 11: Reserved area
• Bits 12 to 14: Processor interrupt priority level (IPL)
Processor interrupt priority level (IPL) is configured with three bits, for specification of up to eight
processor interrupt priority levels from level 0 to level 7.
If a requested interrupt has priority greater than the processor interrupt priority level (IPL), the interrupt
is enabled.
• Bit 15: Reserved area
The C, Z, S, and O flags are changed when instructions are executed. See the software manual for
details.
b0b15
IPL
Flag register (FLG)
CDZSBOIU
Carry flag
Debug flag
Zero flag
Sign flag
Register bank select fla
Overflow flag
Interrupt enable flag
Stack pointer select flag
Reserved area
Processor interrupt prio
Reserved area
Figure 2.2.2 Flag register (FLG)
18
Rev. 1.0
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
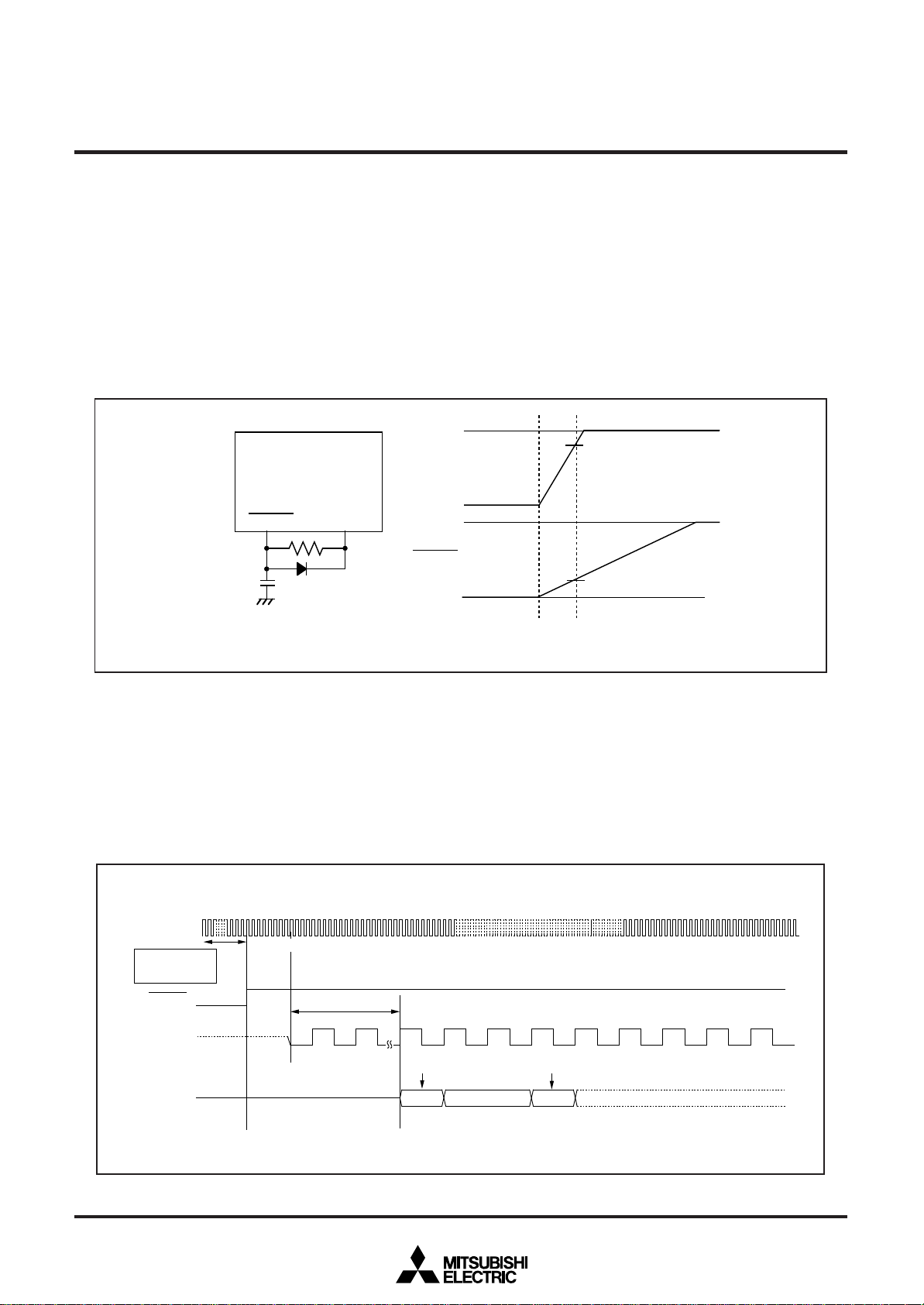
2.3 Reset
There are two kinds of resets; hardware and software. In both cases, operation is the same after the reset.
(See “Software Reset” for details of software resets.) This section explains on hardware resets.
When the supply voltage is in the range where operation is guaranteed, a reset is effected by holding the
reset pin level “L” (0.2VCC max.) for at least 20 cycles. When the reset pin level is then returned to the “H”
level while main clock is stable, the reset status is cancelled and program execution resumes from the
address in the reset vector table.
Figure 2.3.1 shows the example reset circuit. Figure 2.3.2 shows the reset sequence.
RESET
5V
V
CC
0V
V
CC
5V
RESET
0V
4.5V
0.9V
Example when f(XIN) = 10 MHz and VCC = 5V.
Figure 2.3.1 Example reset circuit
2.3.1 Software Reset
Writing “1” to bit 3 of the processor mode register 0 (address 000416) applies a (software) reset to the
microcomputer. A software reset has almost the same effect as a hardware reset. The contents of internal
RAM are preserved.
XIN
More than 20 cycles are needed
Single-chip
mode
RESET
BCLK
Address
Figure 2.3.2 Reset sequence
Rev. 1.0
BCLK 24cycles
FFFFC16
Content of reset vector
Content of reset vector
FFFFE16
19
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
____________
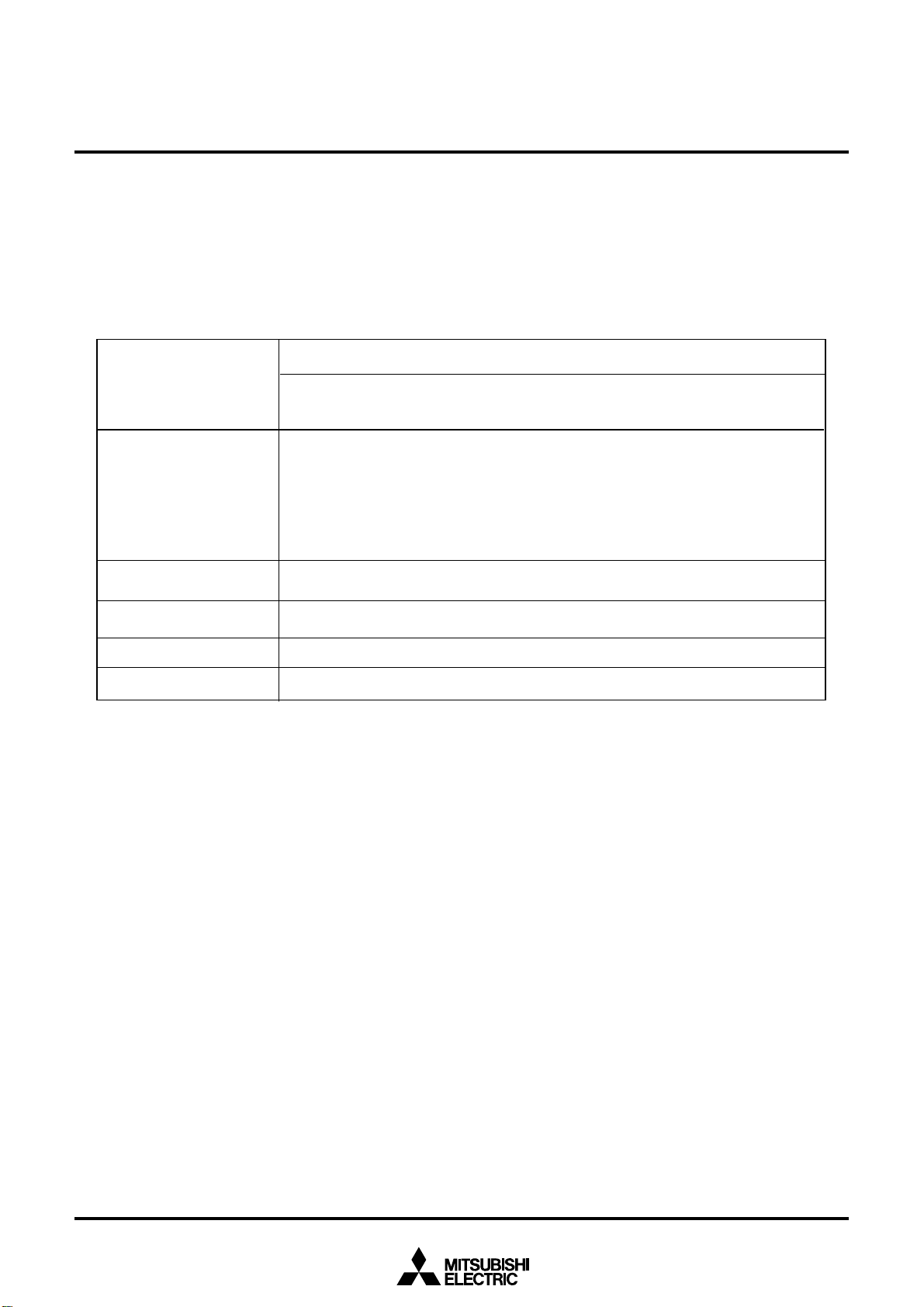
2.3.2 Pin Status When RESET Pin Level is “L”
Table 2.3.1 shows the statuses of the other pins while the RESET pin level is “L”. Figures 2.3.3 and 2.3.4
show the internal status of the microcomputer immediately after the reset is cancelled.
____________
Table 2.3.1 Pin status when RESET pin level is “L”
____________
Pin name
P0, P2 , P3,
0
to P43,
P4
0
, P52, P53, P55,
P5
2
, P63, P67,
P6
0
to P72, P74, P76,
P7
2
,
P8
0
, P93, P94,
P9
0
, P10
P10
1
R, G, B, OUT1,OUT2
IN
, V
HOLD
CV
,
HLF
OSC1
OSC2
Input port (floating)
Output port
Input/output port
Input port
Output port
Status
CNVSS = V
SS
20
Rev. 1.0
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
·
·
·
6
6
·
r
6
6
6
6
6
6
·
r
r
·
r
r
·
·
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
1 6
) · · ·P r o c e s s o r m o d e r e g i s t e r 0 ( N o t e ) 0 0
( 0 0 0 4
( 0 0 0 5
1 6
) · · ·P r o c e s s o r m o d e r e g i s t e r 1
( 0 0 0 6
1 6
) · · ·S y s t e m c l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 0
( 0 0 0 7
1 6
) · · ·S y s t e m c l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1
A d d r e s s m a t c h i n t e r r u p t
e n a b l e r e g i s t e r
P r o t e c t r e g i s t e r(
M u l t i - m a s t e r I2C - B U S i n t e r f a c e 1
i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
B u s c o l l i s i o n d e t e c t i o n i n t e r r u p t
c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
D M A 0 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e
2
M u l t i - m a s t e r I
i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
A - D c o n v e r s i o n i n t e r r u p t
c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
U A R T 2 t r a n s m i t i n t e r r u p t
c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
U A R T 2 r e c e i v e i n t e r r u p t
c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
U A R T 0 t r a n s m i t i n t e r r u p t
c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
U A R T 0 r e c e i v e i n t e r r u p t
c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
C - B U S i n t e r f a c e 0
D a t a s l i c e r i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
V
S Y N C
i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
T i m e r A 0 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
T i m e r A 1 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
T i m e r A 2 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
T i m e r A 3 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
T i m e r A 4 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
( 0 0 0 9
1 6
) · · ·
0 0 0
A
1 6
) · ·
( 0 0 0 F
1 6
) · · ·W a t c h d o g t i m e r c o n t r o l r e g i s t e
1 6
) · · ·A d d r e s s m a t c h i n t e r r u p t r e g i s t e r 0
( 0 0 1 0
( 0 0 1 1
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 0 1 2
1 6
) · · · 0
( 0 0 1 4
1 6
) · · ·A d d r e s s m a t c h i n t e r r u p t r e g i s t e r 1
( 0 0 1 5
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 0 1 6
1 6
) · · · 0
( 0 0 2 C
1 6
) · · ·D M A 0 c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 00000?00
( 0 0 3 C
1 6
) · · ·D M A 1 c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 00000?00
( 0 0 4 4
1 6
) · · ·O S D 1 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ?000
( 0 0 4 8
1 6
) · · ·O S D 2 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
( 0 0 4 9
1 6
) · · ·
1 6
) · ·
( 0 0 4 A
( 0 0 4 B
1 6
) · ·
( 0 0 4 C
1 6
) · · ·D M A 1 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e
( 0 0 4 D
1 6
) · · · ? 0 0 0
1 6
) · · · ? 0 0 0
( 0 0 4 E
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 0 4 F
( 0 0 5 0
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 0 5 1
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 0 5 2
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 0 5 3
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 0 5 4
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 0 5 5
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 0 5 6
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 0 5 7
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 0 5 8
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 0 5 9
1 6
) · · ·
00 0
4 8
2 0
00?0????
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
1
0
1
1
000
1
1
0 0 0
1
1
0 0 0
?000
?00000
0 0 0?
? 0 0 0
? 0 0 0
? 0 0 0
? 0 0 0
? 0 0 0
? 0 0 0
? 0 0 0
? 0 0 0
? 0 0 0
? 0 0 0
? 0 0 0
? 0 0 0
? 0 0 0
1 6
T i m e r B 0 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
000
T i m e r B 1 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
T i m e r B 2 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
I N T 0 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
00
I N T 1 i n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
S P R I T E O S D c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
O S D c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1
O S D c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2
H o r i z o n t a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r
C l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
I / O p o l a r i t y c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
O S D c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 3
R a s t e r c o l o r r e g i s t e r
O S D r e s e r v e d r e g i s t e r 1(
O S D c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 4
D a t a s l i c e r c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1
D a t a s l i c e r c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2
C a p t i o n p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r
D a t a s l i c e r r e s e r v e d r e g i s t e r 2(
D a t a s l i c e r r e s e r v e d r e g i s t e r 1(
C l o c k r u n - i n d e t e c t r e g i s t e r
D a t a c l o c k p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r
L e f t b o r d e r c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
R i g h t b o r d e r c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r
S P R I T E h o r i z o n t a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r
( h i g h - o r d e r )
O S D r e s e r v e d r e g i s t e r 4
O S D r e s e r v e d r e g i s t e r 3
O S D r e s e r v e d r e g i s t e r 2
P e r i p h e r a l m o d e r e g i s t e
H
S Y N C
c o u n t e r r e g i s t e
) · ·
( 0 0 5 A
( 0 0 5 B
1 6
) · ·
( 0 0 5 C
1 6
) · · · ? 0 0 0
( 0 0 5 D
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 0 5 E
1 6
) · ·
1 6
) · · · 00000
( 0 2 0 1
( 0 2 0 2
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 2 0 3
1 6
) · · · 0 0
( 0 2 0 4
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 2 0 5
1 6
) · · · 0 0
( 0 2 0 6
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 2 0 7
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 2 0 8
1 6
) · · ·
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 2 0 9
0 2 5
D
1 6
) · · · 0 0
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 2 5 F
( 0 2 6 0
1 6
) · · · 0 0
( 0 2 6 1
1 6
) · · · 000
( 0 2 6 6
1 6
) · · ·
0 2 6
1 6
) · · · 0 0
7
0 2 6
8
1 6
) · · · 0 0
( 0 2 6 9
1 6
) · · · 0 0
( 0 2 6 A
1 6
) · ·
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 2 7 0
( 0 2 7 1
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 2 7 2
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 2 7 3
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 2 7 9
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 2 7 A
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 2 7 B
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 2 7 C
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 2 7 D
1 6
) · · ·
( 0 2 7 E
1 6
) · ·
? 0 0 0
? 0 0 0
? 00000
? 00000
0 0
1 6
1 6
0 0
1 6
1 6
00000010
0 0
1 6
0 0
1 6
0 0
1 6
1 6
00
1 6
????
?
0000
000
?
1 6
1 6
1 6
00 010
0 1
1 6
000
0 0
1
000
000
00 00000
0 0
1 6
0 0
1 6
0
00000
00 00
X : N o t h i n g i s m a p p e d t o t h i s b i t
? : U n d e f i n e d
T h e c o n t e n t o f o t h e r r e g i s t e r s a n d R A M i s u n d e f i n e d w h e n t h e m i c r o c o m p u t e r i s r e s e t . T h e i n i t i a l v a l u e s
m u s t t h e r e f o r e b e s e t .
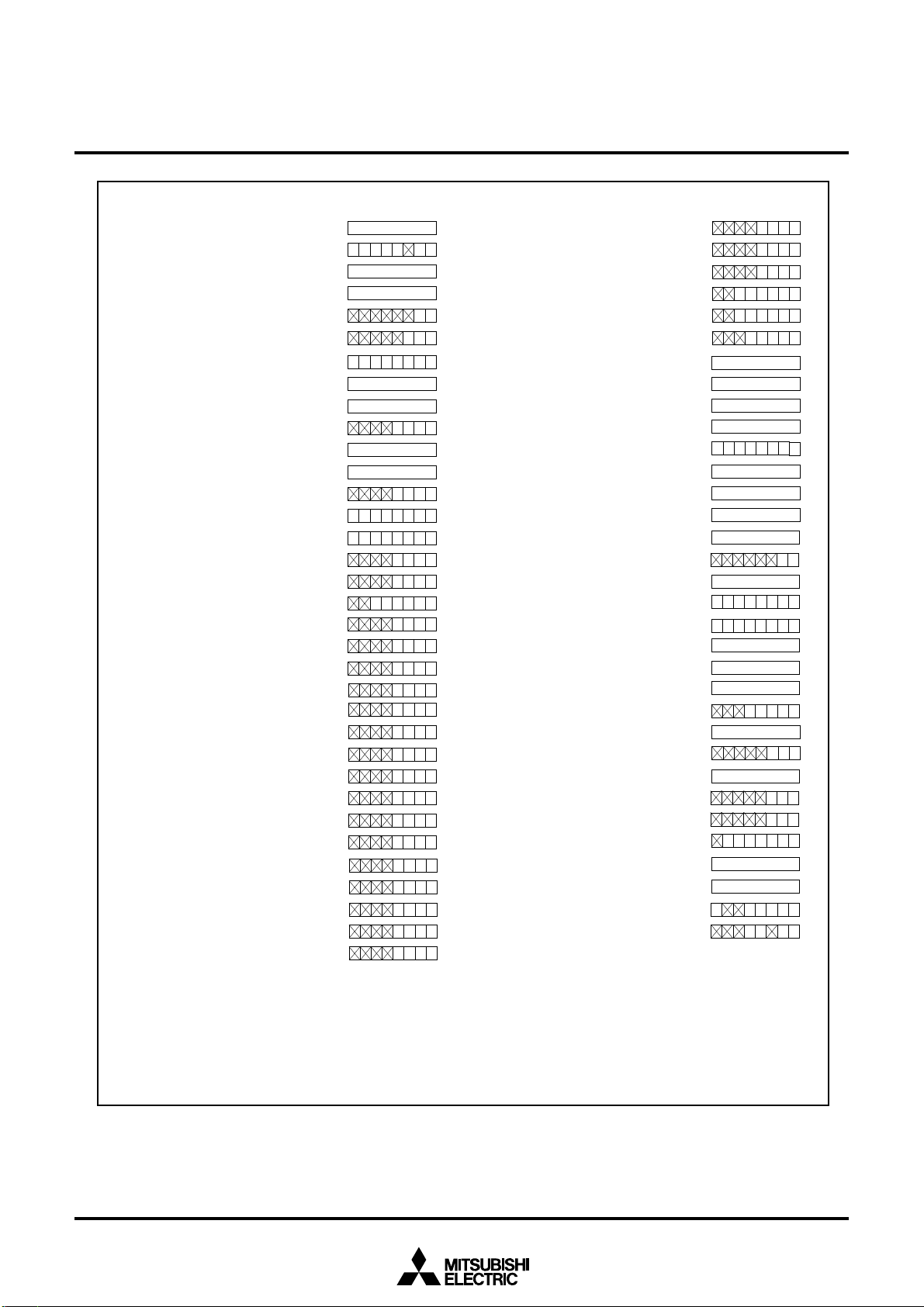
Figure 2.3.3 Device’s internal status after a reset is cleared (1)
Rev. 1.0
21
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
2
C0 address register
I
2
C0 status register
I
I2C0 control register
I2C0 clock control register
2
I
C0 port selection register
2
I
C1 address register
2
I
C1 status register
I2C1 control register
I2C1 clock control register
2
I
C1 port selection register
Reserved register 1
Reserved register 0
Interrupt request cause select register
Reserved register 3
Reserved register 4
Reserved register 5
UART2 special mode register
UART2 transmit/receive mode register
UART2 transmit/receive control register 0
UART2 transmit/receive control register 1
Count start flag
Reserved register 2
16
)···
(02E1
(02E216)···
(02E3
(02E4
(02E5
(02E9
(02EA
(02EB
(02EC
(02ED
(0340
(0348
(035F
(0362
(0366
(0376
16
)··· 00
16
)··· 00
16
)···
16
)···
16
)···
16
)··· 00
16
)··· 00
16
)···
16
)···
16
)··· 00
16
)··· 00
16
)··· 40
16
)··· 40
16
)··· 00
000
?00
000
?00
000
(037716)··· 00
(037816)··· 00
16
)···
(037C
16
)···
(037D
(0380
16
)··· 00
(0381
(0382
(0383
(0384
(0396
(0397
(0398
(0399
(039A
(039B
(039C
(039D
(03A0
(03A4
(03A5
(03A8
0
16
)···Reserved register 6
16
)···One-shot start flag
0000 000
16
)···Trigger select register
16
)···Up-down flag
16
)···Timer A0 mode register
16
)···Timer A1 mode register
16
)···Timer A2 mode register
16
)···Timer A3 mode register
16
)···Timer A4 mode register
16
)···Timer B0 mode register
0
0? 0000
16
)···Timer B1 mode register
00? 0000
16
)···Timer B2 mode register
00? 0000
16
)···UART0 transmit/receive mode register
16
)···UART0 transmit/receive control register 0
16
)···UART0 transmit/receive control register 1
16
)··· 00
00
16
000
1?
16
16
000
?0
00
16
000
1?
16
16
000
?0
???
??
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
08
16
02
16
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
08
16
02
16
16
A-D control register 0
A-D control register 1
D-A control register
Port P0 direction register
Port reserved register 2
Port P2 direction register
Port P3 direction register
Port P4 direction register
Port P5 direction register
Port P6 direction register
Port P7 direction register
Port P8 direction register
Port P9 direction register
Port P10 direction register
Pull-up control register 0
Pull-up control register 1(Note)
Pull-up control register 2
Port reserved register 3
Data registers (R0/R1/R2/R3)
Address registers (A0/A1)
Frame base register (FB)
Interrupt table register (INTB)
User stack pointer (USP)
Interrupt stack pointer (ISP)
Static base register (SB)
Flag register (FLG)
16
)···UART transmit/receive control register 2
(03B0
(03B816)···DMA0 request cause select register
(03BA
16
)···DMA1 request cause select register
(03D416)···A-D control register 2 0???
(03D616)···
(03D7
16
000 0???0
)···
(03DC16)··· 00
16
)··· 00
(03E2
16
)···
(03E3
(03E6
16
)···
(03E7
16
)···
(03EA
16
)···
(03EB
16
)···
(03EE
16
)···
(03EF
16
)···
(03F2
(03F3
(03F6
(03FC
(03FD
(03FE
(03FF
00 00000
16
)···
16
)···
16
)···
16
)···
16
)···
16
)···
16
)··· 00
0000
0000
0000
00000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000000
00
16
00
16
0000
00
16
16
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
00
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
x : Nothing is mapped to this bit
? : Undefined
The content of other registers and RAM is undefined when the microcomputer is reset. The initial values
must therefore be set.
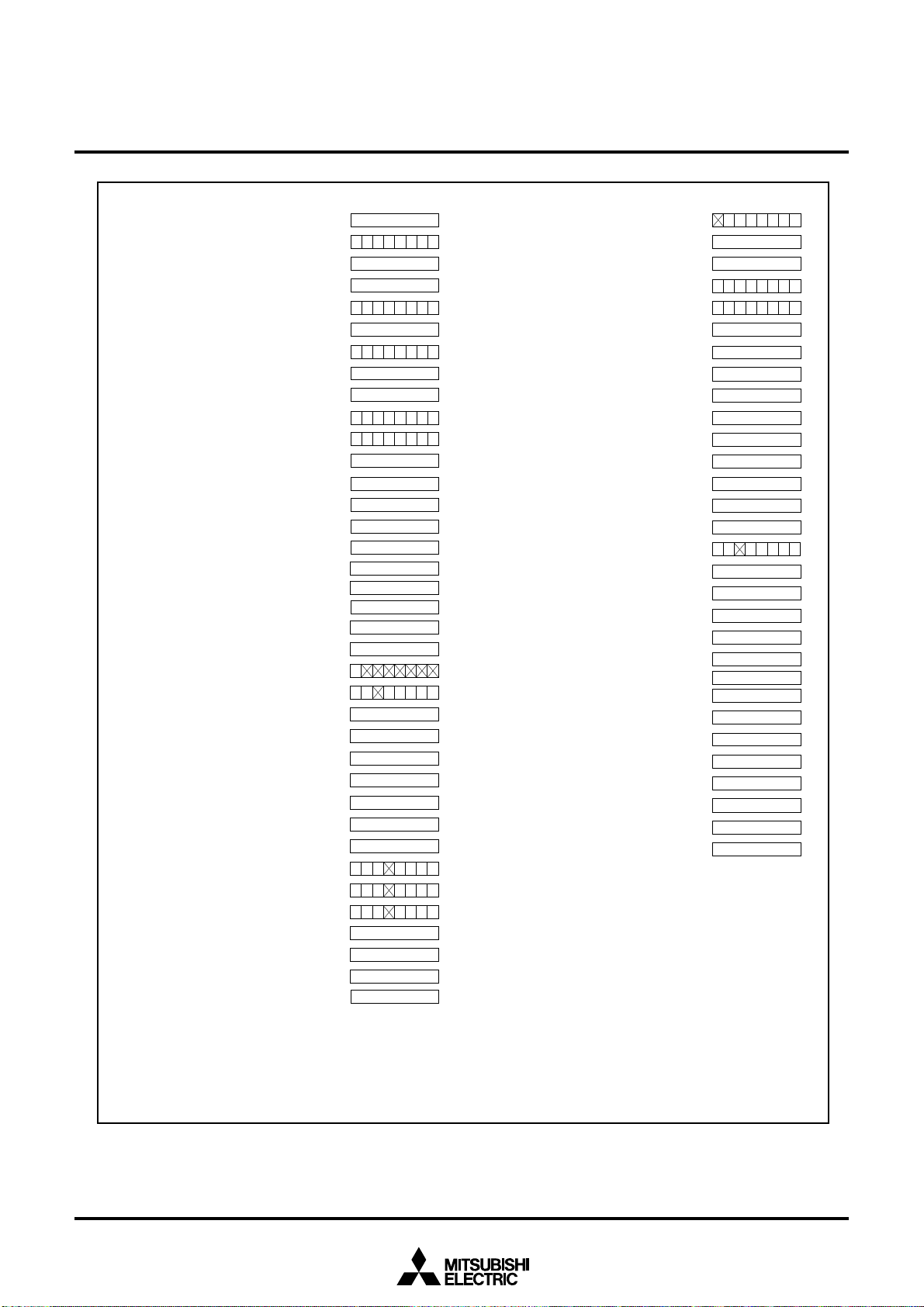
Figure 2.3.4 Device’s internal status after a reset is cleared (2)
22
Rev. 1.0
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
2.4 Single-chip Mode
This microcomputer supports single-chip mode only.
In single-chip mode, only internal memory space (SFR, OSD RAM, internal RAM, and internal ROM) can
be accessed. Ports P0, P2 to P10 can be used as programmable I/O ports or as I/O ports for the internal
peripheral functions.
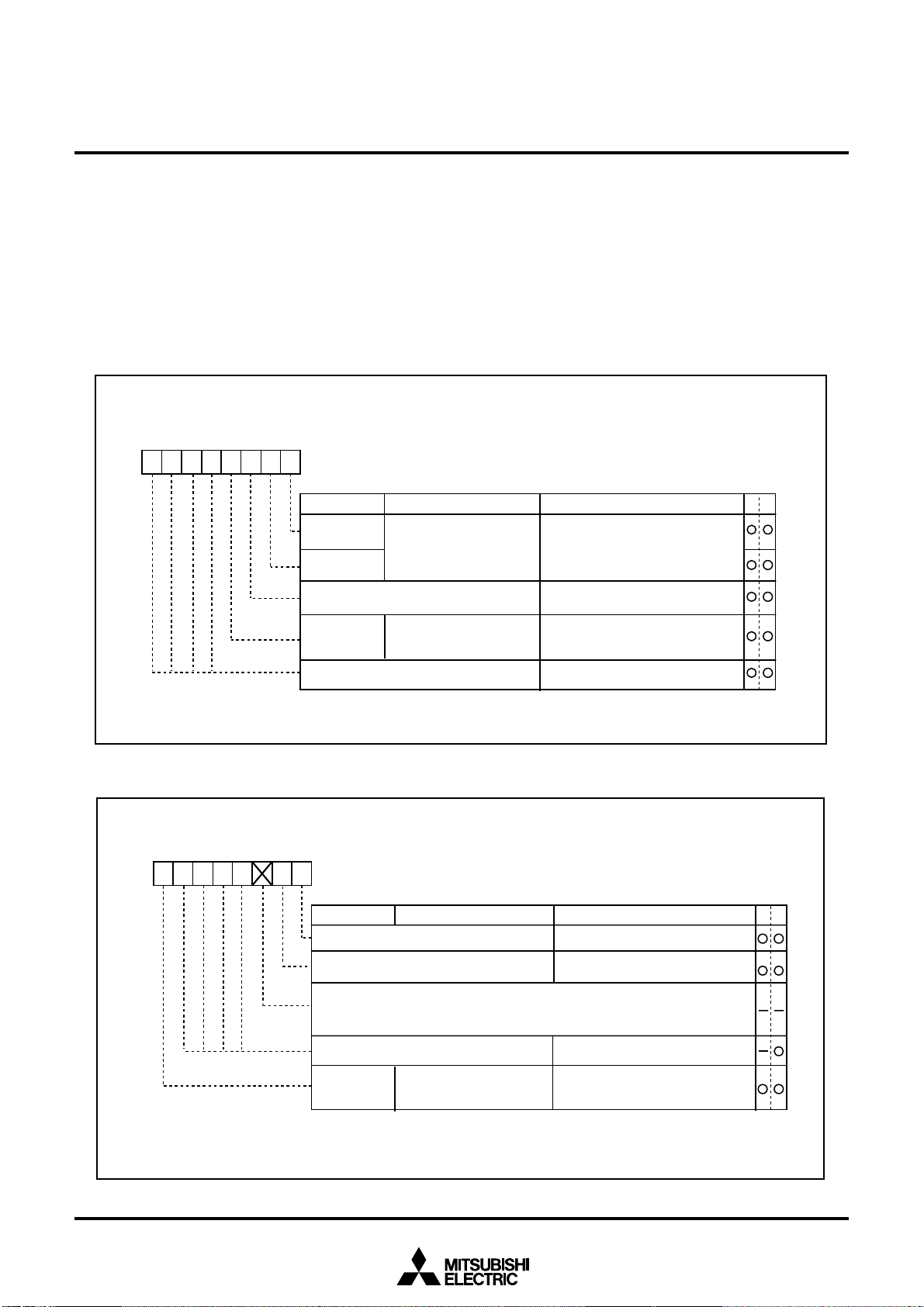
Figure 2.4.1 shows the processor mode register 0 and Figure 2.4.2 shows the processor mode register 1.
Figure 2.4.3 shows the memory map.
P r o c e s s o r m o d e r e g i s t e r 0 ( N o t e )
d d r e s
h e n r e s e
0 0
b 7b 6b 5b 4b 3b 2b 1b 0
S y m b o lA
P M 00
0000 000
P M 0 0
P M 0 1
R e s e r v e d b i t
P M 0 3
R e s e r v e d b i t s
N o t e : S e t b i t 1 o f t h e p r o t e c t r e g i s t e r ( a d d r e s s 0 0 0 A
v a l u e s t o t h i s r e g i s t e r .
Figure 2.4.1 Processor mode register 0
P r o c e s s o r m o d e r e g i s t e r 1 ( N o t e 1 )
d d r e s
h e n r e s e
0 0
b 7b 6b 5b 4b 3b 2b 1b 0
0
000
1
0 0 0 0 X 0
S y m b o lA
P M 10
0
sW
1 6
4
B i t n a m eF
P r o c e s s o r m o d e b i t
S o f t w a r e r e s e t b i t
sW
5
1 6 0
t
0 0
1 6
u n c t i o
b 1 b 0
0 0 : S i n g l e - c h i p m o d e
0 1 : I n h i b i t e d
1 0 : I n h i b i t e d
1 1 : I n h i b i t e d
M u s t a l w a y s b e s e t t o “ 0 ”
T h e d e v i c e i s r e s e t w h e n t h i s b i t i s s e t
t o “ 1 ” . T h e v a l u e o f t h i s b i t i s “ 0 ” w h e n
r e a d .
M u s t a l w a y s b e s e t t o “ 0 ”
1 6
) t o “ 1 ” w h e n w r i t i n g n e w
t
02
nB i t s y m b o l
WR
R e s e r v e d b i t
R e s e r v e d b i t ( N o t e 2 )
N o t h i n g i s a s s i g n e d .
I n a n a t t e m p t t o w r i t e t o t h i s b i t , w r i t e “ 0 . ” T h e v a l u e , i f r e a d , t u r n s o u t t o b e
i n d e t e r m i n a t e .
R e s e r v e d b i t s
P M 1 7
t o “ 1 ” w h e n w r i t i n g n e w
N o t e s 1 : S e t b i t 1 o f t h e p r o t e c t r e g i s t e r ( a d d r e s s 0 0 0 A
Figure 2.4.2 Processor mode register 1
Rev. 1.0
1 6)
u n c t i o
nB i t s y m b o l
B i t n a m eF
M u s t a l w a y s b e s e t t o “ 0 ”
M u s t a l w a y s b e s e t t o “ 1 ”
M u s t a l w a y s b e s e t t o “ 0 ”
W a i t b i t
v a l u e s t o t h i s r e g i s t e r .
2: A s t h i s b i t b e c o m e s “ 0 ” a t r e s e t , m u s t a l w a y s b e s e t t o “ 1 ” a f t e r r e s e t
r e l e a s e .
0 : N o w a i t s t a t e
1 : W a i t s t a t e i n s e r t e d
WR
23
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
00000
16
003FF
00400
013FF
01400
02BFF
02C00
03FFF
04000
SFR area
16
16
OSD RAM
16
16
Internal
reserved area
16
16
Internal
RAM area
16
16
Internal
reserved area
8FFFF
16
90000
16
AFFFF
16
B0000
16
CFFFF
16
D0000
16
FFFFF
16
Figure 2.4.3 Memory map in single-chip mode
OSD ROM
Internal
reserved area
Internal
ROM area
24
Rev. 1.0

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
2.4.1 Software Wait
A software wait can be inserted by setting the wait bit (bit 7) of processor mode register 1 (address
000516).
A software wait is inserted in the internal ROM/RAM area by setting the wait bit of the processor mode
register 1. When set to “0”, each bus cycle is executed in one BCLK cycle. When set to “1”, each bus cycle
is executed in two BCLK cycles. After the microcomputer has been reset, this bit defaults to “0”.
The SFR area and the OSD RAM area is always accessed in two BCLK cycles regardless of the setting
of these control bits.
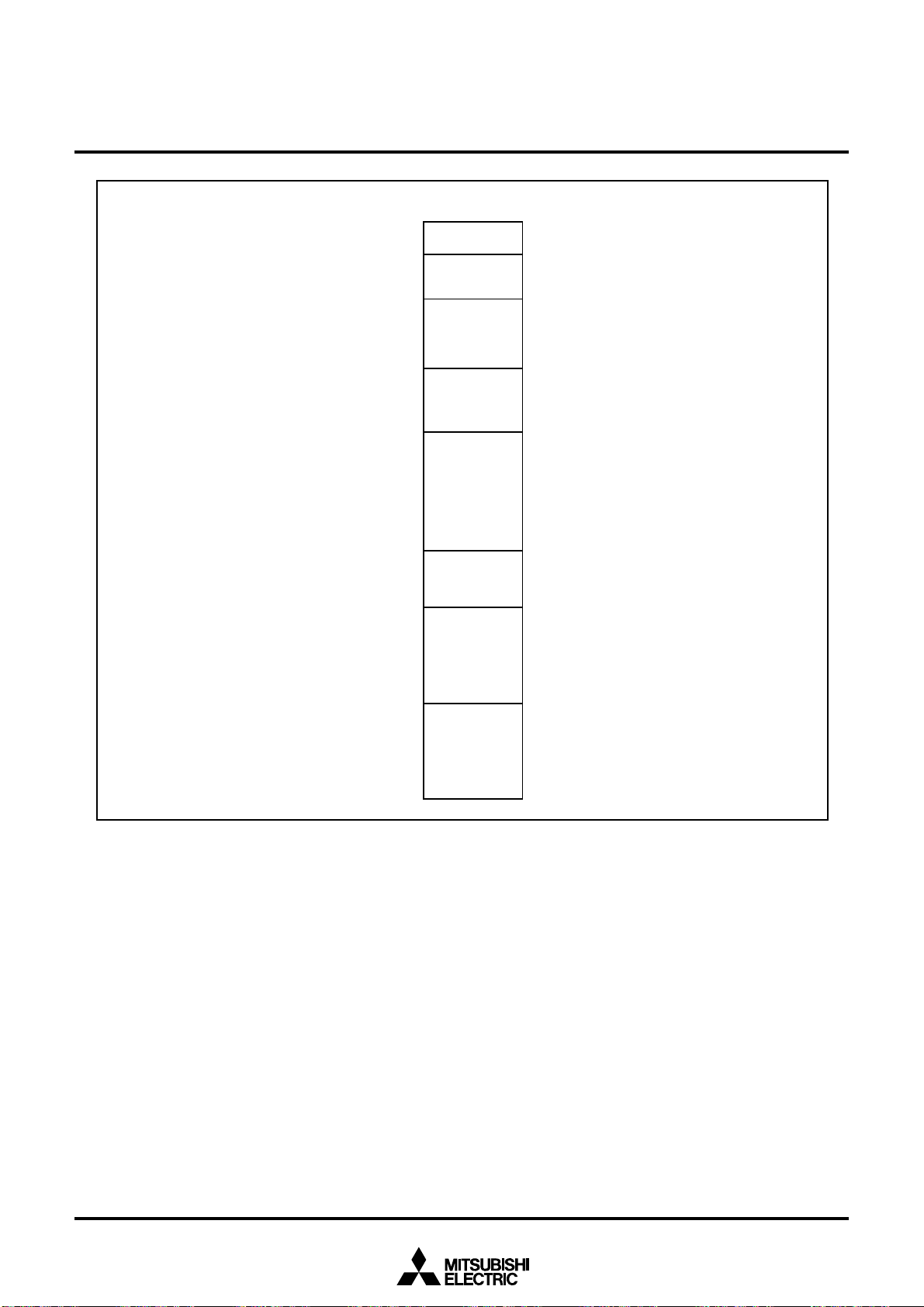
Table 2.4.1 shows the software wait and bus cycles. Figure 2.4.4 shows example bus timing when using
software waits.
Table 2.4.1 Software waits and bus cycles
Area Wait bit
SFR/
OSD RAM
Internal
ROM/RAM
Invalid 2 BCLK cycles
0 1 BCLK cycle
1 2 BCLK cycles
Bus cycle
Rev. 1.0
25
BCLK
Write signal
Read signal
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
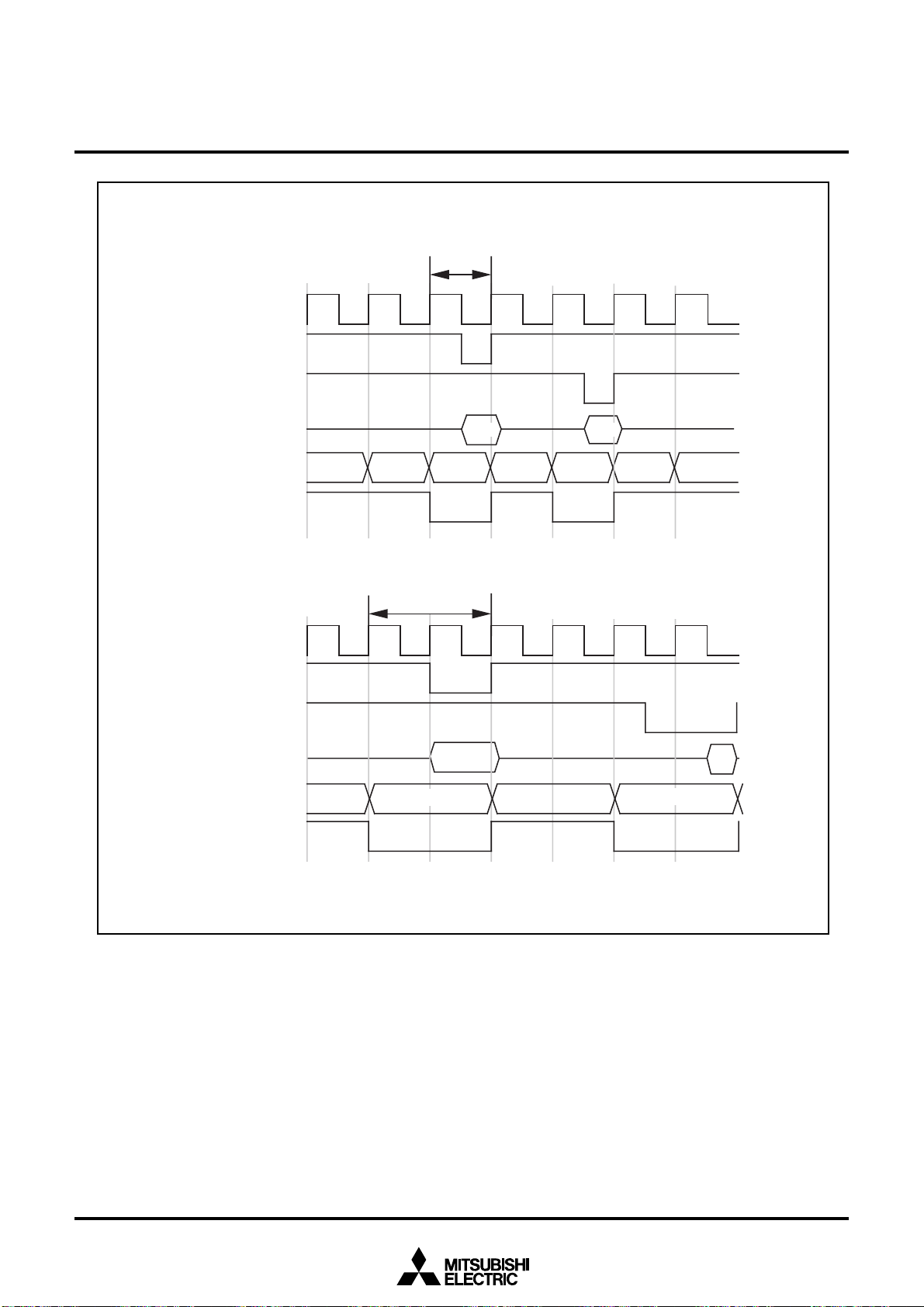
Bus cycle< No wait >
Address bus
Chip select
< With wait >
Write signal
Read signal
Address bus
Chip select
Data bus
BCLK
Data bus
Address
Bus cycle
Output
Address
Output
Input
Address
Input
Address
Figure 2.4.4 Typical bus timings using software wait
26
Rev. 1.0
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
O
C
C
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
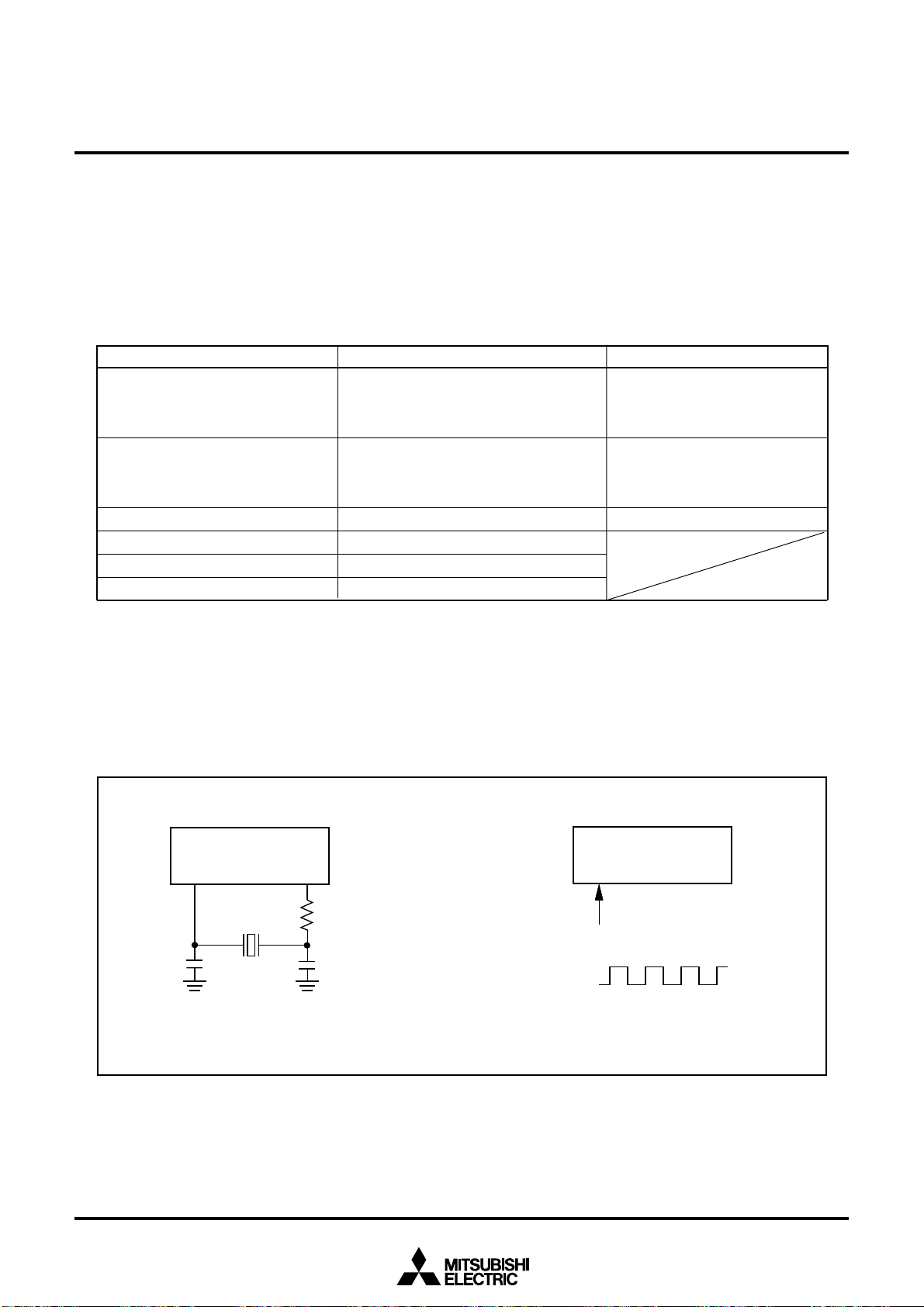
2.5 Clock Generating Circuit
The clock generating circuit contains each oscillator circuit that supplies the operating clock sources to the
CPU and internal peripheral units and that supplies the operating clock source to OSD.
Table 2.5.1. Clock oscillation circuits
Main clock oscillation circuit OSD oscillation circuit
Use of clock • CPU’s operating clock source
• Internal peripheral units’
operating clock source
Usable oscillator • Ceramic resonator • Ceramic resonator
(or quartz-crystal oscillator) (or quartz-crystal oscillator)
Pins to connect oscillator XIN, XOUT OSC1, OSC2
Oscillation stop/restart function Available
Oscillator status immediately after reset
Oscillating
Other Externally derived clock can be input
• OSD’s operating clock source
• LC oscillator
2.5.1 Example of Oscillator Circuit
Figure 2.5.1 shows some examples of the main clock circuit, one using an oscillator connected to the
circuit, and the other one using an externally derived clock for input. Circuit constants in Figure 2.5.1 vary
with each oscillator used. Use the values recommended by the manufacturer of your oscillator.
M i c r o c o m p u t e r
( B u i l t - i n f e e d b a c k r e s i s t o r )
X
I N
I N
N o t e : I n s e r t a d a m p i n g r e s i s t o r i f r e q u i r e d . T h e r e s i s t a n c e w i l l v a r y d e p e n d i n g o n t h e o s c i l l a t o r a n d t h e o s c i l l a t i o n d r i v e
c a p a c i t y s e t t i n g . U s e t h e v a l u e r e c o m m e n d e d b y t h e m a k e r o f t h e o s c i l l a t o r .
W h e n t h e o s c i l l a t i o n d r i v e c a p a c i t y i s s e t t o l o w , c h e c k t h a t o s c i l l a t i o n i s s t a b l e . W h e n b e i n g s p e c i f i e d t o c o n n e c t a
f e e d b a c k r e s i s t o r e x t e r n a l l y b y t h e m a n u f a c t u r e , c o n n e c t a f e e d b a c k r e s i s t o r b e t w e e n p i n s X
X
O U T
( N o t e )
R
d
O U T
Figure 2.5.1 Examples of main clock
M i c r o c o m p u t e r
( B u i l t - i n f e e d b a c k r e s i s t o r )
X
I N
E x t e r n a l l y d e r i v e d c l o c k
V c c
V s s
I N
a n d X
X
O U T
p e
n
O U T
.
Rev. 1.0
27
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
2.5.2 OSD Oscillation Circuit
The OSD clock oscillation circuit can obtain simply a clock for OSD by connecting an LC oscillator or a
ceramic resonator (or a quartz-crystal oscillator) across the pins OSC1 and OSC2. Which of LC oscillator
or a ceramic resonator (or a quartz-crystal oscillator) is selected by setting bits 1 and 2 of the clock control
register (address 020516).
Microcomputer
OSC2OSC1
L
C1 C2
Figure 2.5.2 OSD clock connection example
2.5.3 Clock Control
Figure 2.5.3 shows the block diagram of the main clock generating circuit.
Sub clock
RESET
Software reset
Interrupt request
level judgment
output
CM10 “1”
Write signal
WAIT instruction
CM0i : Bit i at address 0006
CM1i : Bit i at address 0007
WDCi : Bit i at address 000F
QS
R
QS
R
X
IN
X
OUT
Main clock
CM02
a
16
16
16
1/2 1/2 1/2 1/2
CM06=0
CM17,CM16=10
CM06=0
CM17,CM16=01
CM06=0
CM17,CM16=00
f
1
f
AD
f
8
f
32
c
b
a
Divider
d
b
CM06=1
f1SIO2
f8SIO2
f32SIO2
BCLK
c
1/2
CM06=0
CM17,CM16=11
d
Details of divider
Figure 2.5.3 Clock generating circuit
28
Rev. 1.0

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
The following paragraphs describes the clocks generated by the clock generating circuit.
(1) Main clock
The main clock is generated by the main clock oscillation circuit. After a reset, the clock is divided by
8 to the BCLK. The clock can be stopped using the main clock stop bit (bit 5 at address 000616).
After the oscillation of the main clock oscillation circuit has stabilized, the drive capacity of the main
clock oscillation circuit can be reduced using the XIN-XOUT drive capacity select bit (bit 5 at address
000716). Reducing the drive capacity of the main clock oscillation circuit reduces the power dissipation. This bit changes to “1” when shifting from high-speed/medium-speed mode to stop mode and at
a reset.
(2) BCLK
The internal clock φ is the clock that drives the CPU, and is the clock derived by dividing the main
clock by 1, 2, 4, 8, or 16. The BCLK is derived by dividing the main clock by 8 after a reset.
The main clock division select bit 0 (bit 6 at address 000616) changes to “1” when shifting from highspeed/medium-speed to stop mode and at reset.
(3) Peripheral function clock (f1, f8, f32, f1SIO2, f8SIO2, f32SIO2, fAD)
The clock for the peripheral devices is derived by dividing the main clock by 1, 8 or 32. The peripheral
function clock is stopped by stopping the main clock or by setting the WAIT peripheral function clock
stop bit (bit 2 at 000616) to “1” and then executing a WAIT instruction.
Rev. 1.0
29
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
)
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER with CLOSED CAPTION DECODER
and ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Figures 2.5.4 and 2.5.5 shows the system clock control registers 0 and 1.
S y s t e m c l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 0 ( N o t e 1 )
d d r e s
b 7b 6b 5b 4b 3b 2b 1b 0
00100
0
0 0
S y m b o lA
C M 00
B i t n a m eF
R e s e r v e d b i t s
sW h e n r e s e t
1 6
6
M u s t a l w a y s b e s e t t o “ 0 ”
4 8
1 6
u n c t i o
nB i t s y m b o l
M306V5ME-XXXSP
M306V5EESP
WR
C M 0 2
R e s e r v e d b i t
R e s e r v e d b i t s
C M 0 6
R e s e r v e d b i t
N o t e s 1 : S e t b i t 0 o f t h e p r o t e c t r e g i s t e r ( a d d r e s s 0 0 0 A
2 : T h i s b i t c h a n g e s t o “ 1 ” w h e n s h i f t i n g f r o m h i g h - s p e e d / m e d i u m - s p e e d m o d e t o s t o p m o d e a n d a t a r e s e t .
W A I T p e r i p h e r a l f u n c t i o n
c l o c k s t o p b i t
M a i n c l o c k d i v i s i o n s e l e c t
b i t 0 ( N o t e 2 )
Figures 2.5.4 System clock control register 0
S y s t e m c l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 ( N o t e 1 )
b 7b 6b 5b 4b 3b 2b 1b 0
00
00
d d r e s
0 0
S y m b o lA
C M 10
C M 1 0
A l l c l o c k s t o p c o n t r o l b i t
0 : D o n o t s t o p p e r i p h e r a l f u n c t i o n c l o c k i n w a i t m o d e
1 : S t o p p e r i p h e r a l f u n c t i o n c l o c k i n w a i t m o d e
M u s t a l w a y s b e s e t t o “ 1 ”
M u s t a l w a y s b e s e t t o “ 0 ”
0 : C M 1 6 a n d C M 1 7 v a l i d
1 : D i v i s i o n b y 8 m o d e
M u s t a l w a y s b e s e t t o “ 0 ”
1 6
) t o “ 1 ” b e f o r e w r i t i n g t o t h i s r e g i s t e r .
sW h e n r e s e t
7
1 6
B i t n a m eF
( N o t e 4
2 0
1 6
u n c t i o
nB i t s y m b o l
0 : C l o c k o n
1 : A l l c l o c k s o f f ( s t o p m o d e )
WR
R e s e r v e d b i t s
C M 1 5
C M 1 6
C M 1 7
N o t e s 1 : S e t b i t 0 o f t h e p r o t e c t r e g i s t e r ( a d d r e s s 0 0 0 A
2 : T h i s b i t c h a n g e s t o “ 1 ” w h e n s h i f t i n g f r o m h i g h - s p e e d / m e d i u m - s p e e d m o d e t o s t o p m o d e a n d a t a
r e s e t .
3 : C a n b e s e l e c t e d w h e n b i t 6 o f t h e s y s t e m c l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 0 ( a d d r e s s 0 0 0 6
“ 1 ” , d i v i s i o n m o d e i s f i x e d a t 8 .
I f
4 : I f t h i s b i t i s s e t t o “ 1 , ” X
O U T
Figure 2.5.5 System clock control register 1
30
“ 0 ”
X
I N
- X
O U T
s e l e c t b i t ( N o t e 2 )
M a i n c l o c k d i v i s i o n
s e l e c t b i t 1 ( N o t e 3 )
d r i v e c a p a c i t y
1 6
M u s t a l w a y s b e s e t t o
0 : L O W
1 : H I G H
b 7 b 6
0 0 : N o d i v i s i o n m o d e
0 1 : D i v i s i o n b y 2 m o d e
1 0 : D i v i s i o n b y 4 m o d e
1 1 : D i v i s i o n b y 1 6 m o d e
) t o “ 1 ” b e f o r e w r i t i n g t o t h i s r e g i s t e r .
t u r n s “ H , ” a n d t h e b u i l t - i n f e e d b a c k r e s i s t o r i s c u t o f f .
1 6
) i s “ 0 . ”
Rev. 1.0
 Loading...
Loading...