Page 1

Model RFT9739
Rack-Mount Transmitter
Instruction Manual
Version 3 Transmitters
February 2000
Page 2

Page 3

Model RFT9739
Copyright ©2000, Micro Motion, Inc. All rights res erved.
Micro Motion, ELITE, and ProLink are registered trademarks of Micro Motion, Inc.,
Boulder, Colorado. Rosemount and SMART FAMILY are registered tradema r k s of
Rosemount, Inc., Eden Prair i e, Minn eso ta . Fis her -Rosemount is a trademark o f
Fisher-Rosemount, C layton, Missouri. HART is a registered trademar k of the HART
Communication Foundation, Austin, Texas. Modbus is a registered tra dem ark of
Modicon, Inc., North Andover, Massachusetts. Tefzel is a registered trademark of E.I.
Du Pont de Nemours Co., Inc., Wilmington, Delaware.
Rack-Mount Transmitter
Instruction Manual
Version 3 Transmitters
For technical assistance, phone the Micro Motion Customer
Service Department:
• In the U.S.A., phone 1-800-522-6277, 24 hours
• Outside the U.S.A., phone 30 3-530-8400, 24 hours
• In Europe, phone +31 (0) 318 549 443
• In Asia, phone 65-770-8155
Page 4

Page 5

Contents
1 Before You Begin
1.1 About this manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.2 About the transmitter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
2 Getting Started
2.1 Hazardous area installations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Hazardous area installations in Europe. . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.2 Configuration, calibration, and characterization . . . . . 4
2.3 Switch settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Security modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Security mode 8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Communication settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Milliamp output scaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3 Transmitter Mounting
3.1 General guidelines. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.2 Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4 Power-Supply and Sensor Wiring
4.1 General guidelines. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4.2 Power supply and grounding. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Power-supply options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Power-supply wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Grounding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Fuses. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
4.3 Changing power-supply voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
4.4 Sensor wiring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Cable connections to sensor and transmitter . . . . . . . 22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
1
3
11
17
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
i
Page 6

Contents
continued
5 Output Wiring
5.1 General guidelines. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
5.2 Maximum wire length. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
5.3 Primary and secondary mA outputs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Connections for HART
5.4 Frequency outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Frequency/pulse output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Default configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Configuration for increased current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Configuration for constant current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Configuration for open collector mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Dual-channel frequency output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Setting voltage level for VDE output requirements . . . 37
Optocoupler output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
5.5 Control output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Control output in open collector mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
5.6 Peripheral device wiring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
5.7 Pressure transmitter wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
5.8 Remote-zero switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
5.9 RS-485 multidrop network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
5.10 Bell 202 multidrop network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
5.11 Security wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
®
communication devices. . . . . 29
25
6Startup
6.1 Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
6.2 Using the display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
6.3 Custody transfer event registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
6.4 Flowmeter zeroing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
6.5 Totalizer control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
6.6 Process measurement. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Process variables mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Communication configuration mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Zeroing procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Diagnosing zero failure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Additional information about flowmeter zeroing. . . . . . 66
59
ii
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 7

Contents
continued
7 Troubleshooting
7.1 General guidelines. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
7.2 Transmitter diagnostic tools. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Fault outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Diagnostic messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
7.3 Interrogation with a HART
7.4 Troubleshooting using the transmitter display. . . . . . . 73
Not configured. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Transmitter failure messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Overrange and sensor error messages. . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Slug flow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Output saturated messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Informational messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
7.5 Power supply. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
7.6 Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
7.7 Master reset. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
7.8 Additional information about troubleshooting . . . . . . . 81
7.9 Customer service. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
®
device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Appendixes
Appendix A RFT9739 Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Appendix B Ordering Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Appendix C Theory of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Appendix D HART
Appendix E Transmitter Version Identification . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Appendix F Replacing Older Transmitters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Appendix G Return Policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
®
Communicator Menu Trees. . . . . . . . . 97
69
Index
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
113
iii
Page 8

Contents
continued
Tables
Table 2-1 Security modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Table 4-1 Selecting the proper grounding scheme . . . . . . 19
Table 4-2 Terminal designations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 5-1 Output wiring terminal designations . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 5-2 Peripheral wiring diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Table 5-3 Sensors affected by pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Table 6-1 Display screens. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Table 6-2 Parameters that affect event registers . . . . . . . 64
Table 6-1 Effect of security modes on flowmeter zeroing . 66
Table 6-2 Effect of security modes on totalizer control . . . 68
Table 7-1 Fault output levels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Table 7-2 Using transmitter failure messages. . . . . . . . . . 73
Table 7-3 Using overrange and sensor error messages. . 75
Table 7-4 Using slug flow and output saturated messages 75
Table 7-5 Using informational messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Table 7-6 Nominal resistance ranges for flowmeter
circuits. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Table 7-7 Default values after a master reset . . . . . . . . . . 80
Tables in appendixes
Table F-1 Resistance values for determining RTD type . . 104
Table F-2 RE-01 to RFT9739 terminal conversions . . . . . 106
Table F-3 RFT9712 to RFT9739 terminal conversions. . . 107
Table F-4 RFT9729 to RFT9739 terminal conversions. . . 108
iv
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 9

Contents
continued
Figures
Figure 1-1 RFT9739 exploded view. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Figure 2-1 Hazardous area approvals tag . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Figure 2-2 Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Figure 3-1 RFT9739 dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 3-2 Rack-mount connector locations . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 3-3 Space requirements for proper ventilation . . . . 14
Figure 3-4 Types of connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Figure 4-1 Power-supply wiring terminals . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 4-2a Grounding detail — typical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 4-2b Grounding detail — hazardous-area sensor
installations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 4-2c Grounding detail — high-integrity I.S.
installations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 4-3 Fuses and power-select switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 4-4 Wiring to ELITE sensors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 4- 5 Wiring to F-Series, Model D and DL sensors. . 23
Figure 4-6 Wiring to Model DT sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 5-1 Output terminals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 5-2 4-20 mA output performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Figure 5-3 Primary and secondary mA output wiring. . . . . 28
Figure 5-4 HART
Figure 5-5 Frequency/pulse output wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 5-6 Frequency/pulse output wiring for increased
Figure 5-7 Frequency/pulse output wiring for constan t
Figure 5-8 Frequency/pulse output wiring for open
Figure 5-9 RFT9739 back panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 5-10 Resistor R5 on inside of back panel . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 5-11 Dual-channel frequency output wiring . . . . . . . 36
Figure 5-12 RFT9739 back panel and power board . . . . . . 37
Figure 5-13 Jumper J10 on power board. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 5-14 Jumper JP1 on inside of back panel. . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 5-15 Optocoupler output wiring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 5-16 Control output wiring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Figure 5-17 Control output wiring for open collector mode . 42
Figure 5-18 RFT9739 back panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 5-19 Location of resistor R4 on inside of back panel 43
Figure 5-20 Wiring to DMS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 5-21a Wiring to DRT with LED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 5-21b Wiring to DRT with LCD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 5-22a Wiring to FMS-3 with LED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Figure 5-22b Wiring to FMS-3 with LCD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Figure 5-23 Wiring to NFC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Figure 5-24a Wiring to AC-powered NOC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Figure 5-24b Wiring to DC-powered NOC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Figure 5-25a Wiring to Model 3300 with screw-type or
Figure 5-25b Wiring to Model 3300 with I/O cable. . . . . . . . . 49
Figure 5-26 Wiring to Model 3350 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
®
Communicator, ProLink® PC-Interface,
and AMS modem connections . . . . . . . . . . 29
current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
collector mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
solder-tail terminals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
v
Page 10

Contents
continued
Figure 5-27a Wiring to pressure transmitter — analog output 52
Figure 5-27b Wiring to pressure transmitter — external power,
analog input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Figure 5-27c Wiring to pressure transmitter — digital
communications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Figure 5-28 Wiring to remote-zero switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Figure 5-29 RS-485 wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Figure 5-30 Typical HART
®
network wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Figure 5-31 Inhibit-switch wiring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Figure 7-1 HART
®
Communicator, ProLink® PC-Interface,
and AMS modem connections . . . . . . . . . . 71
Figures in appendixes
Figure C-1 Coriolis mass flow sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Figure D-1 On-line menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Figure E-1 RFT9739 back panels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Figure F-1 RFT9739 terminals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Figure F-2 RE-01 Remote Electronics Unit terminals. . . . . 106
Figure F-3 RFT9712 Remote Flow Transmitter terminals . 107
Figure F-4 RFT9729 Remote Flow Transmitter terminals . 108
vi
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 11

1 Before You Begin
1.1 About this manual
1.2 About the transmitter
This instruction manual explains how to:
• Install the Micro Motion
use with Micro Motion Coriolis flow sensors, including instructions for:
-
Power-supply and sensor wiring
-
Output wiring
• Initialize the transmitter
• Diagnose and troubleshoot problems with the transmitter
For more information about the Micro Motion sensors, see the
appropriate sensor instruction manual.
Instructions in this manual pertain to Version 3 transmitters. Do not use
this manual for transmitters shipped before January 1996. To identify the
transmitter version, see
Micro Motion rack-mount transmitters have enhanced EMI immunity that
complies with EMC directive 89/336/EEC and low-voltage directive
73/23/EEC, when properly installed in accordance with the guidelines
and instructions in this manual.
The Model RFT9739 transmitter is a microprocessor-based transmitter
for fluid process measurement. The transmitter works with Micro Motion
sensors to measure mass or volume flow, density, and temperature.
The rack-mount RFT9739 is for control-room mounting. The housing is a
1/3 rack cassette for 19-inch enclosure-dense packaging. Components
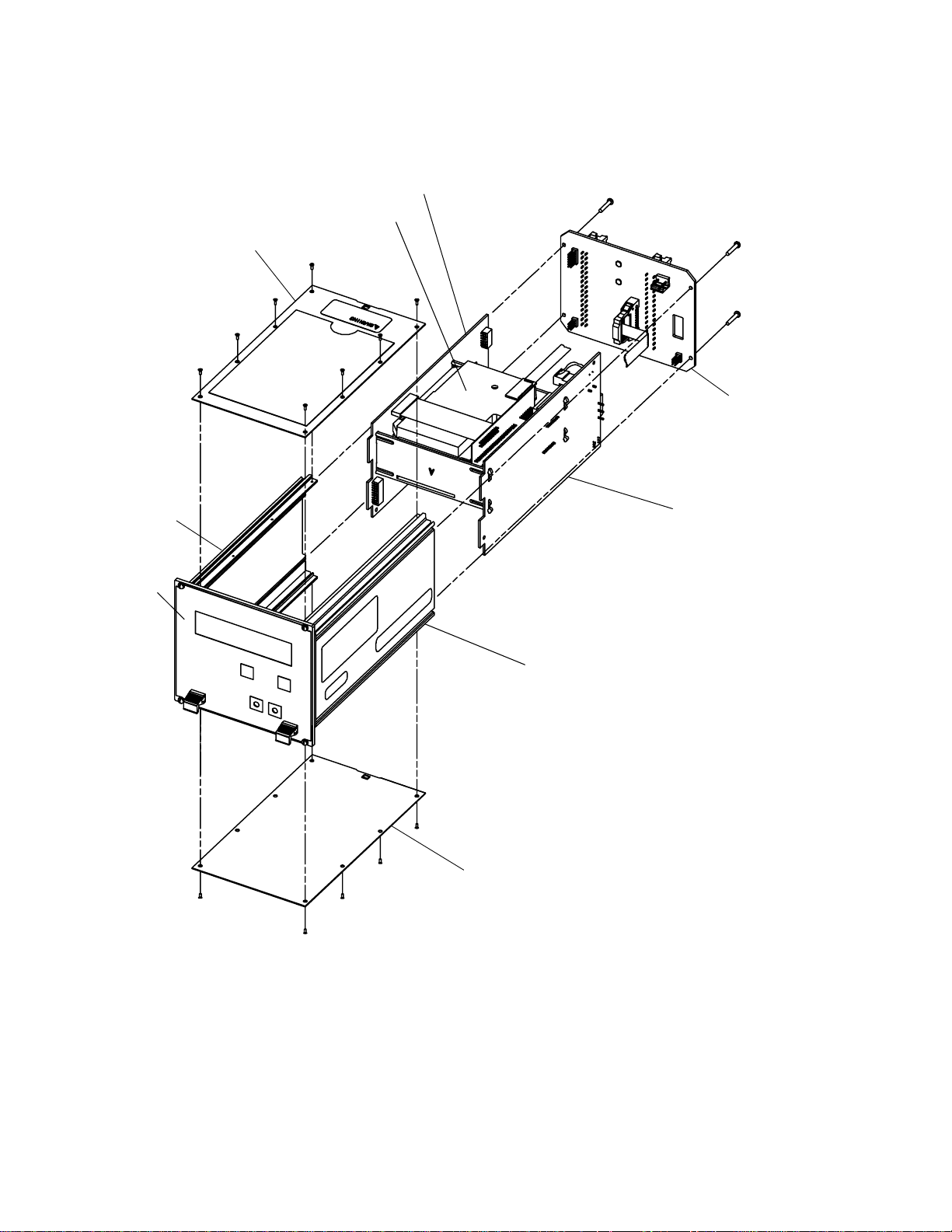
of the transmitter are shown in
®
Model RFT9739 rack-mount transmitter for
Appendix E
, page 101.
Figure 1-1
, page 2.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
The RFT9739 front panel has a two-line, 16-character, alphanumeric
liquid crystal display (LCD). Scroll and Reset buttons enable the user to
perform the following operations. Use of the display is described in
Section 6.2
• View the flow rate, density, temperature, mass and volume totals and
inventory levels, and status messages
• Set the transmitter's flow totalizers
• Reset communication paramete rs
• Zero the flowmeter
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
, page 60.
1
Page 12
continued
Before You Begin
Figure 1-1. RFT9739 exploded view
Module cassette
Top cover
Control board
Back pane l
Side panel
Front panel
Power board
Side panel
Bottom cover
2
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 13
2 Getting Started
Hazardous area
approvals tag
2.1 Hazardous area installations
WARNING
If the sensor is installed in a hazar do us area, fail ure to
comply with requirements for intrinsic safety could
result in an explosion.
• Install the transmitter in a non-hazardous area.
• For intrinsically safe sensor inst allations, use this
document with Micro Motion UL or CSA installation
instructions.
• For hazardous area installations in Europe, refer to
standard EN 60079-14 if nation al standards do not apply.
• Read the approvals tag before installing the RFT9739. The approvals
tag is attached to the side of the transmitter. See
• For a complete list of UL, CSA, and European approvals, see page 88.
• For an intrinsically safe installation of the sensor, use this manual with
the appropriate Micro Motion intrinsically safe installation instructions:
-
UL-D-IS Installation Instructions
-
CSA-D-IS Installation Instructions
• In Europe, refer to standard EN60079-14 if national standards do not
apply. To comply with CENELEC standards, see page 4.
The RFT9739 rack-mount transmitter is classified as a Class A product.
When used in a residential area or in an adjacent area thereto, radio
interference may be caused by radios, television receivers, and like
devices.
Figure 2-1
.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
Figure 2-1.
Hazardous area approvals
tag
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
3
Page 14

Getting Started
continued
Hazardous area installations in Europe
2.2 Configuration, calibration, and characterization
To comply with CENELEC standards for hazardous area installations in
Europe, adhere to the following CENELEC conditions for safe use.
Location
The RFT9739 must be installed outside the hazardous area. The
transmitter installation must meet (at least) IP20 safety requirements,
per IEC 529.
Potential equalization
To achiev e potential equalization, the RFT9739 ground conductor should
be connected to the appropriate ground terminals within the hazardous
area, using a potential equalizing line.
Output wiring
Nonintrinsically-safe connections between the RFT9739 and other
devices may be made
or equal to 250 V.
The following information explains the differences among configuration,
calibration, and characterization. Certain parameters might require
configuration
even when
Configuration parameters
measurement units, flow direction, damping values, slug flow
parameters, and span values for the milliamp and frequency outputs. If
requested at time of order, the transmitter is configured at the factory
according to customer specifications.
only
to devices that maintain a voltage less than
calibration
include items such as transmitter tag,
is not necessary.
Calibration
density, and temperature. Field calibration is optional.
Characterization
density, and temperature directly into transmitter memory. Calibration
factors can be found on the sensor serial number tag and on the
certificate that is shipped with the sensor.
For configuration, calibration, or characterization procedures, see one of
the following communications manuals:
Using the HART Communicator with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using ProLink Software with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using Modbus Protocol with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
You can also use Fisher-Rosemount™ Asset Management Solutions
(AMS) software for configuration, calibration, and characterization. For
more information, see the AMS on-line help.
A basic software tree for the HART Communicator is shown in
Appendix D
accounts for an individual sensor’s sensitivity to flow,
is the process of entering calibration factors for flow,
, page 97.
4
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 15
Getting Started
Switches 1 through 10 at left
are shown in the OFF position.
continued
2.3 Switch settings
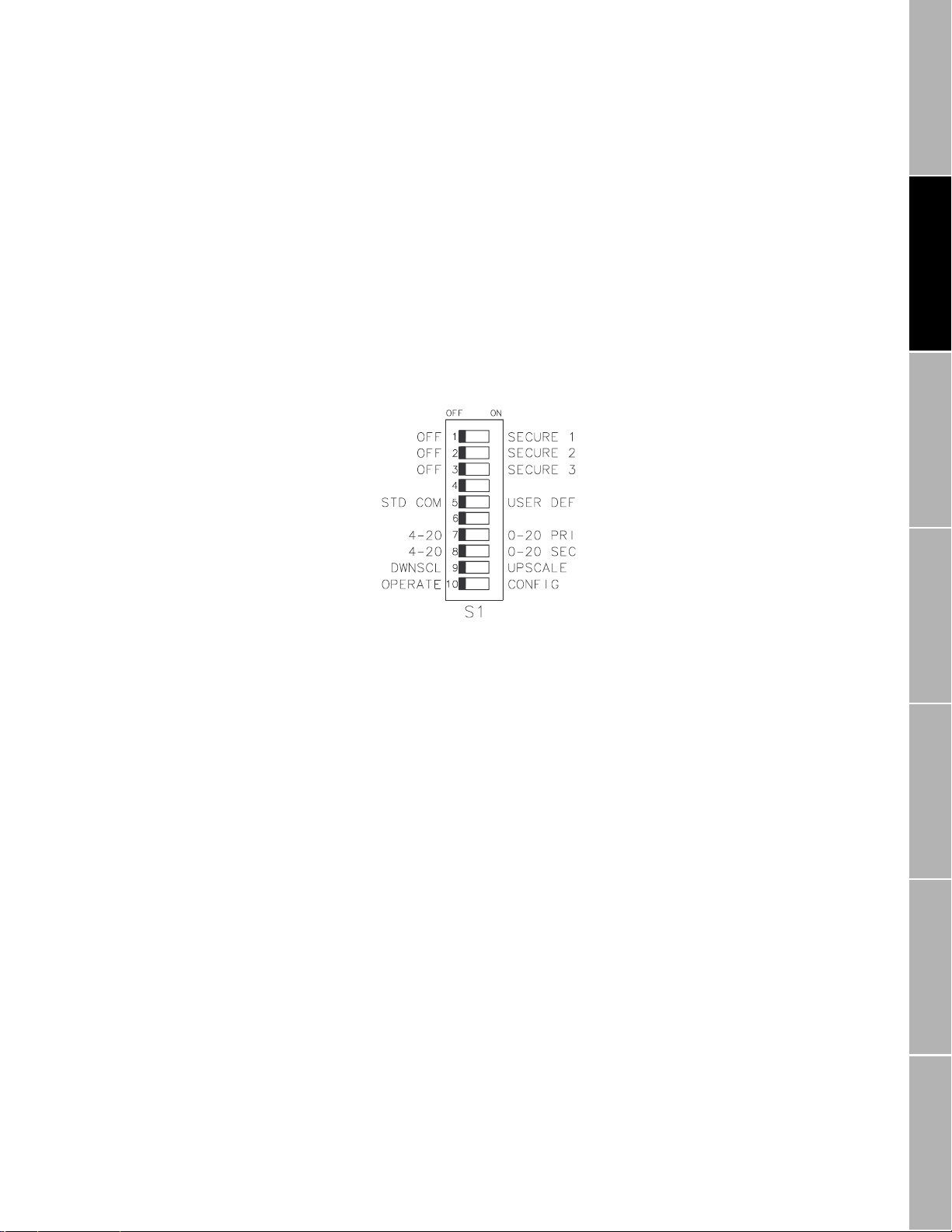
Figure 2-2.
Switches
Switches 1 through 10, located inside the transmitter on the control
board, control the following transmitter functions (see
Figure 1-1
,
page 2, for the location of the control board):
• Communications settings, including baud rate, stop bits and parity,
data bits, communication protocol, and physical layer
• mA outputs
• Zeroing method
• Write-protection of transmitter configuration
Switches are shown in
Figure 2-2
, and described in the following
sections. To access switches, remove the bottom cover of the transmitter
housing. Normally, switch settings do not require adjustment.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
5
Page 16

Getting Started
continued
Security modes
Table 2-1. Security modes
Switch settings
Switch 1
Switch 2
Switch 3
Mode
1
OFF
OFF
OFF
Switches 1, 2, and 3 are security switches, which enable the user to
disable flowmeter zeroing, disable resetting of totalizers, and writeprotect all configuration and calibration parameters.
Switch settings enable any of eight possible security modes. Different
modes determine which functions are disabled and whether
configuration and calibration parameters are write-protected. The
following functions can be disabled:
• Flowmeter zeroing using digital communications
• Flowmeter zeroing using the Scroll and Reset buttons
• Totalizer control, with flow, using digital communications
• Totalizer control, with flow, using the Scroll and Reset buttons
• Totalizer control, with zero flow, using digital communications
• Totalizer control, with zero flow, using the Scroll and Reset buttons
Table 2-1
lists the parameters that are write-protected and functions that
are disabled for each security mode. Security modes 1 through 7 are
entered immediately when switches are set.
For information about security mode 8, see pages 7 through 8.
Mode
2
OFF
OFF
ON
Mode
3
OFF
ON
OFF
Mode
4
OFF
ON
ON
Mode
5
ON
OFF
OFF
Mode
6
ON
OFF
ON
Mode
7
ON
ON
OFF
Mode
8*
ON
ON
ON
Function/
parameter
Flowmeter
zeroing
Totalize r
control,
no flow
Totalize r
control,
with flow
Configuration and
calibration parameters
* C hanging the settings of switches 1, 2, and 3 does not immediately impl em ent security mode 8. For more information about
security mode 8, see pages 7 through 8.
Performed
with
Zero but t on or
Reset button
HART or
Modbus
Scroll and
Reset buttons
HART or
Modbus
Scroll and
Reset buttons
HART or
Modbus
Mode
1
Mode
2
Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled
Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled
Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled
Mode
3
Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled
Disabled Disabled Disabled
Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled
Write-
protected
Mode
4
Write-
protected
Mode
5
Write-
protected
Mode
6
Write-
protected
Mode
7
Write-
protected
Mode
8
Write-
protected
6
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 17
Getting Started
continued
Security mode 8
When transmitter security is set for mode 8, the transmitter meets
security requirements for custody transfer described in National Institute
of Standards and Technology (NIST) Handbook 44.
Once the transmitter is configured for security mode 8, the security
mode cannot be changed unless a master reset is performed. A master
reset causes all configuration parameters to return to their default
values, and
requires complete characterization and reconfiguration
of the trans m i tt e r.
If the user attempts to enter a new security mode or change the
transmitter configuration after entering security mode 8:
• Internal totalizers stop counting
• The frequency/pulse output goes to 0 Hz
• mA outputs go to 4 mA
• The display reads "SECURITY BREACH; SENSOR OK"
• Custody transfer event registers record each change made to defined
configuration and calibration parameters. (For a list of these
parameters, see
Table 6-2
, page 64.)
The security breach continues, and totalizers and outputs remain
inactive, until the transmitter is reconfigured for security mode 8, or until
a master reset has been performed. Custody transfer ev ent registers are
not affected by a master reset.
• For information about event registers, see
• To perform a master reset, see
Section 7.7
Section 6.3
, page 79.
, page 64.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Milliamp output trim, milliamp output test, and frequency/pulse output
test procedures cannot be performed after security mode 8 is entered.
Before entering security mode 8,
perform milliamp trim and/or test
procedures, if necessary , as described in any of the following manuals or
in AMS on-line help:
Using the HART Communicator with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using ProLink Software with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using Modbus Protocol with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
To enter security mode 8:
1. Note the position of switch 5.
2. Set switches 1, 2, 3, and 10 to the ON position.
3. Set switches 4, 5, and 6 to the OFF position.
4. Locate the Reset button on the transmitter front panel.
5. Press and hold the Reset button for ten seconds.
6. Reset switch 5 to the desired position (as noted in Step 1).
7. Reset switch 10 to the OFF (OPERATE) position.
8. To verify the transmitter is in security mode 8, use the Scroll button to
scroll through the display screens. The transmitter is in security
mode 8 if the CONFIG REG and CALIBRATE REG screens appear.
9. Leave switches 1, 2 and 3 in the ON position to maintain security
mode 8.
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
7
Page 18

Getting Started
continued
To verify the transmitter is in security mode 8:
Use the Scroll button to scroll through process variable screens to event
register screens. If event register screens appear, the transmitter is in
security mode8. For more information about us ing the Scr oll b u tt on an d
transmitter display, see
Section 6.2
, page 60.
To make changes to configuration or calibration parameters once
security mode 8 is entered:
1. Set switches 1, 2, and 3 to the OFF position.
2. Make changes through digital communication or with the Scroll and
Reset buttons (see "Communication configuration mode", page 61).
Custody transfer event registers record changes made to defined
configuration and calibration parameters. For more information about
digital communications, see the following instruction manuals or use
AMS on-line help:
Using the HART Communicator with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using ProLink Software with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using Modbus Protocol with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
3. Set switches 1, 2, and 3 to the ON position.
To reenter security mode 8:
If security mode 8 has been established previously, and the security
mode has been temporarily changed, it is not necessary to use the
Reset button to reenter security mode 8. In such a case, resetting
switches 1, 2, and 3 to the ON position will reenter security mode 8
immediately.
If a master reset has been performed, it is necessary to use the Reset
button method to reenter security mode 8. See the procedure, above.
To change to a security mode other than mode 8:
1. Perform a master reset (see
Section 7.7
, page 79, for master reset
procedure).
2. Perform characterization and re-configuration procedures as
described in any of the following instruction manuals or AMS on-line
help:
Using the HART Communicator with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using ProLink Software with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using Modbus Protocol with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
3. Set switches 1, 2, and 3 to the desired positions. See
Table 2-1
,
page 6.
8
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 19
Getting Started
continued
Communication settings
Switch 5 enables the user to choose the standard communication
configuration or user-defined parameters. With switch 10 in the ON
(CONFIG) position, switches 1 through 6 can be used for setting userdefined communication parameters.
Standard communication setting
To use the standard communication configuration, set switch 5 to the
STD COMM position. Setting the switch in this position establishes the
following parameters:
• HART protocol on the Bell 202 standard, at 1200 baud, on the primary
mA output
• Modbus protocol in RTU mode, at 9600 baud, on the RS-485 output
• 1 stop bit, odd parity
For RFT9739 software versions 3.6 and later, if switch 5 is in the STD
COMM position, an error message will appear on the RFT9739 display
when an attempt is made to change the communication configuration
using the RFT9739 display controls.
User-defined communication settings
To establish user-defined settings, set switch 5 to the USER-DEFINED
position, then use the buttons on the front panel to set baud rate; stop
bits and parity; data bits, protocol, and physical layer.
• When the transmitter is shipped from the factory, the default settings
are HART protocol, over RS-485, at 1200 baud, with 1 stop bit and odd
parity .
• For more information on using the display, see
Section 6.2
, page 60.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Milliamp output scaling
Switches 7, 8, and 9 allow the user to choose 0-20 mA or 4-20 mA
scaling for mA outputs, and upscale or downscale fault outputs.
Switch 7 defines the primary mA output scaling. Switch 8 defines the
secondary mA output scaling. Either switch may be set in the 0-20
position or the 4-20 position.
• The mA outputs are NAMUR compliant when switches 7 and 8 are in
the 4-20 position. See
Section 5.3
, page 27.
• Communication using the HART protocol over the primary mA output
requires switch 7 to be set in the 4-20 position.
• If switch 7 is in the 0-20 mA position, communication may be lost if
output is less than 2 mA. T o re-establish communication, move s witch 7
to the 4-20mA position.
Switch 9 defines the RFT9739 fault outputs. Fault outputs can be set for
downscale or upscale levels.
• If switch 9 is set to the DWNSCALE position, mA outputs go to 0 mA if
they produce a 0-20 mA current, or to 0-2 mA if they produce a
4-20 mA current; the frequency/pulse output goes to 0 Hz.
• If switch 9 is set to the UPSCALE position, mA outputs go to 22-24 mA;
the frequency/pulse output goes to 15-19 kHz.
• For more information, see "Fault outputs", page 69.
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
9
Page 20

10
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 21
3 Transmitter Mounting
3.1 General guidelines
Follow these guidelines when installing the rack-mount RFT9739
transmitter:
•Locate the transmitter where it is accessible for service and calibration.
•Install the transmitter in a location that is compliant with the area
specified on the RFT9739 approvals tag (see
•To comply with CENELEC standards for hazardous area installations in
Europe, the RFT9739 must be installed outside the hazardous area.
The transmitter installation must meet (at least) IP20 safety
requirements, per IEC 529.
•Total length of cable from the sensor to the transmitter must not exceed
1000 feet (300 meters).
•Locate the transmitter where the ambient temperature remains
between 32 and 122°F (0 and 50°C).
The rack-mount RFT9739 meets DIN standard 41494, 19-inch
configuration for control-room equipment.
•Transmitter dimensions are shown in
•Three transmitters fit into one 19-inch enclosure with a Eurocard
220mm depth, as indicated in
•When installing multiple transmitters in a single rack, 15 watts of
forced-air cooling, per transmitter, is required. Minimum spacing is
shown in
Figure3-3
, page14.
Figure3-1
Figure3-2
Figure2-1
, page12.
, page13.
, page3).
CAUTION
Failure to maintain an ambient temperature below
maximum temperature rating could result in
operational failure and product damage.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
Install transmitter in an area with sufficient air flow to keep
the ambient temperature below 122°F (50°C).
The back panel of the transmitter housing has two 32-pin connectors for
sensor wiring and output wiring. These connectors meet DIN standard
41612, Model F (male). For more information, see
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
Section3.2
, page15.
11
Page 22
continued
Transmitter Mounting
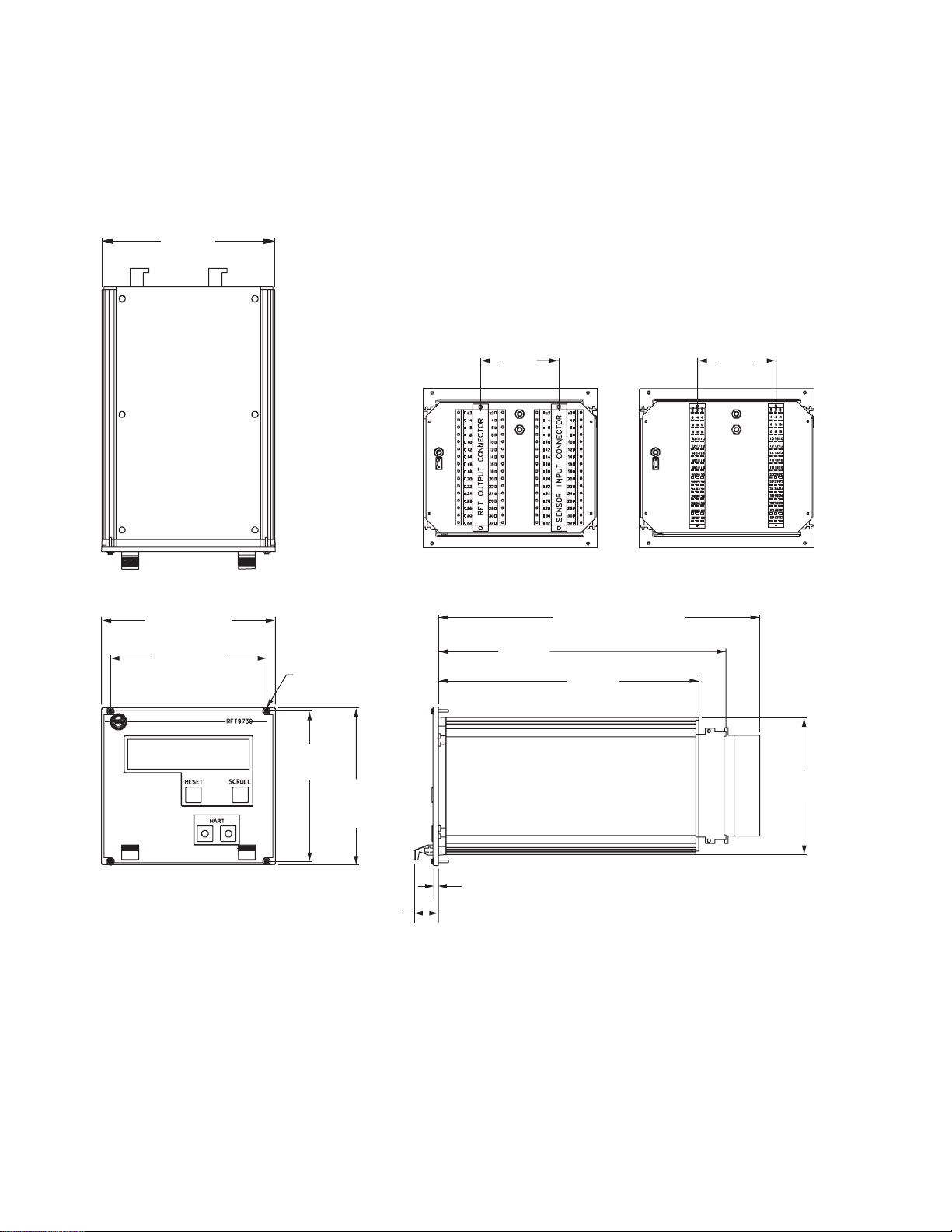
Figure 3-1. RFT9739 dimensions
Dimensions in
5 37/64
(141.7)
(127)
inches
(mm)
5 17/32
(140.4)
5
28TE
25TE
4X M2.5 x 11
Back panel with
DIN 41612 male
Y-shaped screw terminals
2 19/32
(66)
13TE
With Y-shaped
screw terminals
10 5/16
(281.9)
9 15/64
(234.6)
8 23/64
(212.3)
Back panel with
DIN 41612 male
fast-on/solder terminals
2 19/32
(66)
13TE
With fast-on/solder
terminals
10 1/16
(255.6)
12
4 13/16
(122.4)
5 3/64
(128.4)
3HE
4 3/8
(111.1)
3/16
(4.7)
47/64
(18.7)
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 23
continued
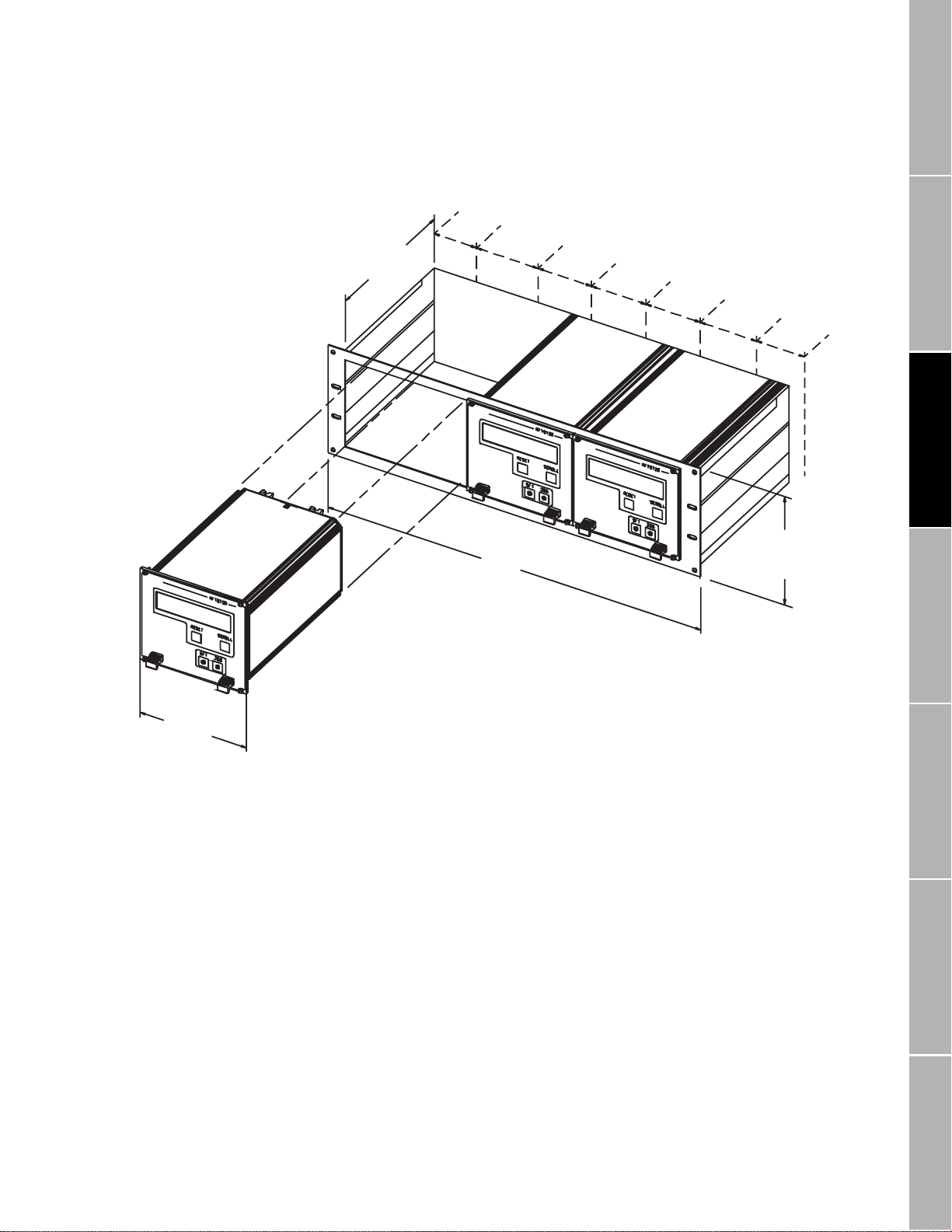
Transmitter Mounting
Figure 3-2. Rack-mount connector locations
Dimensions in
1 TE ≈ 5.08 mm
inches
(mm)
8 13/32
(213.5)
0TE
6TE – CN1
19
(483)
19TE – CN2
34TE – CN1
47TE – CN2
62TE – CN1
5 3/64
(128.4)
3HE
75TE – CN2
84TE
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
5 37/64
(141.7)
28TE
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
13
Page 24
continued
Transmitter Mounting
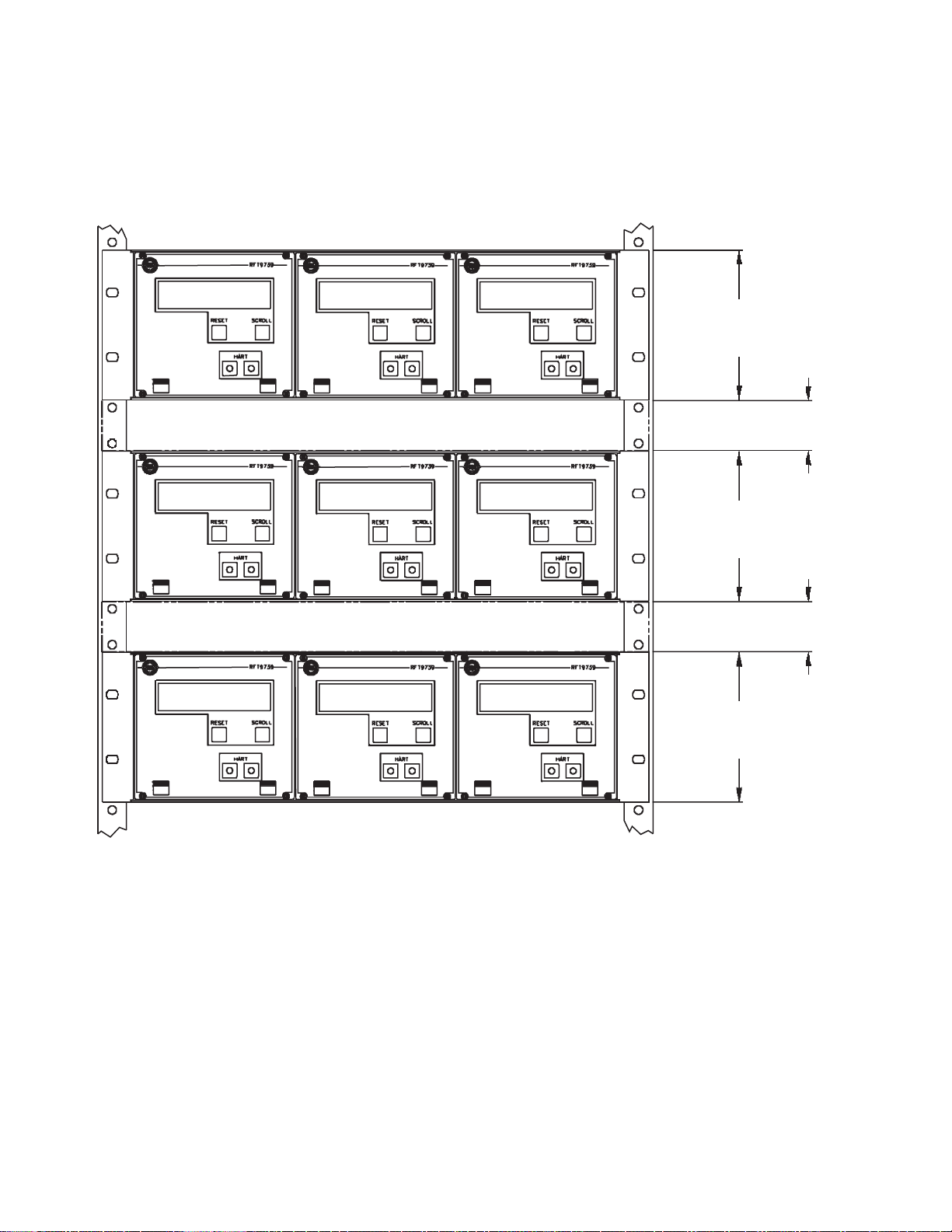
Figure 3-3. Space requirements for proper ventilation
Dimensions in
inches
(mm)
5 3/64
(128.4)
3HE
5 3/64
(128.4)
3HE
1 22/32
(42.8)
1HE
1 22/32
(42.8)
1HE
When installing multiple transm i t te rs in a sin gl e rack, 15 watts of forced-air co ol i ng, per transm i t te r, is
required. Maintain sufficient air flow to keep the ambient temperature be l ow 122 °F ( 50° C ).
5 3/64
(128.4)
3HE
14
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 25
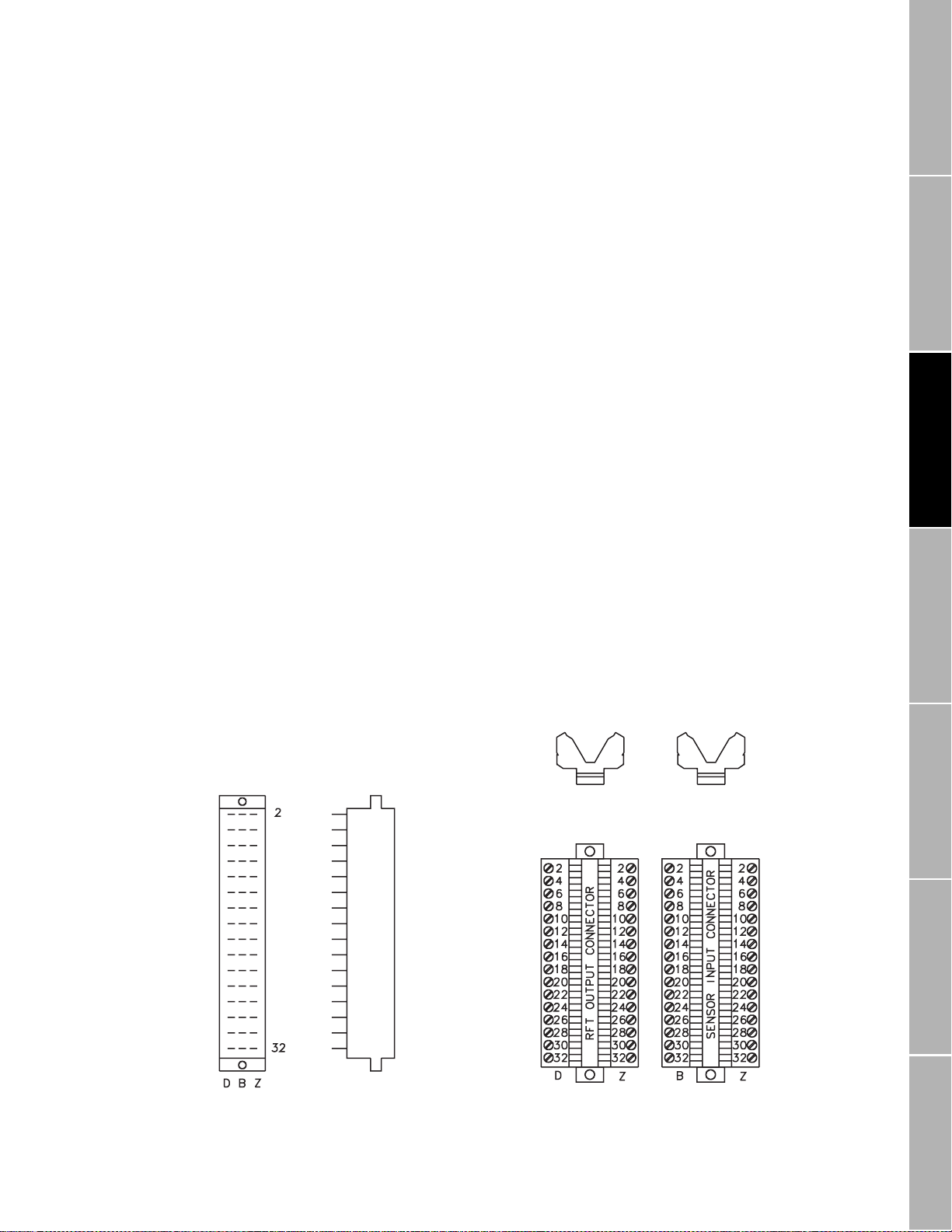
Transmitter Mounting
continued
3.2 Connectors
The back panel of the transmitter housing has two 32-pin connectors,
labeled CN1 and CN2, and a 2-pin connector, labeled CN3. Mating
terminal strips, shipped with the transmitter, plug into the connectors.
The detachable terminal strips enable wiring to remain connected when
the transmitter is removed from the rack.
• AC power-supply wiring connects to CN3
• DC power-supply wiring connects to CN2
• Sensor wiring connects to CN1
• Output wiring connects to CN2
Connectors CN1 and CN2 are available in two types, illustrated in
Figure 3-4
, page 15.
• The standard rectangular configuration accommodates fast-on (wire-
pin) or soldered connections.
• The optional Y-shaped connectors have screw terminals, which
accommodate wires as large as 14 AWG (2.5 mm²).
• For fast-on/solder connectors, on connector CN1, pin row D is not
used; on connector CN2, pin row B is not used.
Connectors CN1 and CN2 meet DIN standard 41612, Model F (male).
• The positions of connectors CN1 and CN2 in a 19" rack are indicated in
Figure 3-2
•See
, page 13.
Chapter 4
, page 17, for power-supply and sensor wiring
instructions.
Chapter 5
•See
, page 25, for output wiring instructions.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Figure 3-4. Types of connectors
Fast-on/solder
connecter
CN1 or CN2
Front Side
Y-Type
connector
CN2 CN1
Top
Front
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
15
Page 26

16
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 27
4 Power-Supply and Sensor
Wiring
4.1 General guidelines
WARNING
Failure to comply with requirements for
intrinsic safety if the sensor is installed in a hazardou s
area could result in an explosion.
Sensor wiring is intrinsically safe.
• Install the transmitter in a non-hazardous area.
• For intrinsically safe sensor inst allations, use this
document with Micro Motion UL or CSA installation
instructions.
• For hazardous area installations in Europe, refer to
standard EN 60079-14 if nation al standards do not apply.
• Terminal blocks may be unplugged from the transmitter back panel for
easier installation of wiring.
• Install cable and wiring to meet local code requirements.
• A switch may be installed in the power-supply line. For compliance with
low-voltage directive 73/23/EEC, a switch in close proximity to the
transmitter is required for AC-powered transmitters.
• Do not install AC power cable or unfiltered DC power cable in the same
conduit or cable tray as sensor cable or output wires.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
4.2 Power supply and grounding
Incorrect vol tage, or install ation with po wer s upply on,
will cause transmitter damage or failure.
• Match power-supply voltage with voltage indicated on
transmitter back panel. See
• Turn off power before installing transmitter.
Power-supply options
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
• The transmitter is configured at the factory for a 110/115 or
220/230 VAC pow er supply. A label in the upper corner on the
transmitter's back panel indicates the configured power-supply voltage.
See
• Any RFT9739 rack-mount transmitter can accept a DC power supply,
whether or not the back panel indicates the transmitter has been
configured for AC power.
• To change power-supply voltage from the configured voltage, see
Section 4.3
Figure 4-1
, page 21.
CAUTION
, page 18.
Figure 4-1
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
, page 18.
17
Page 28
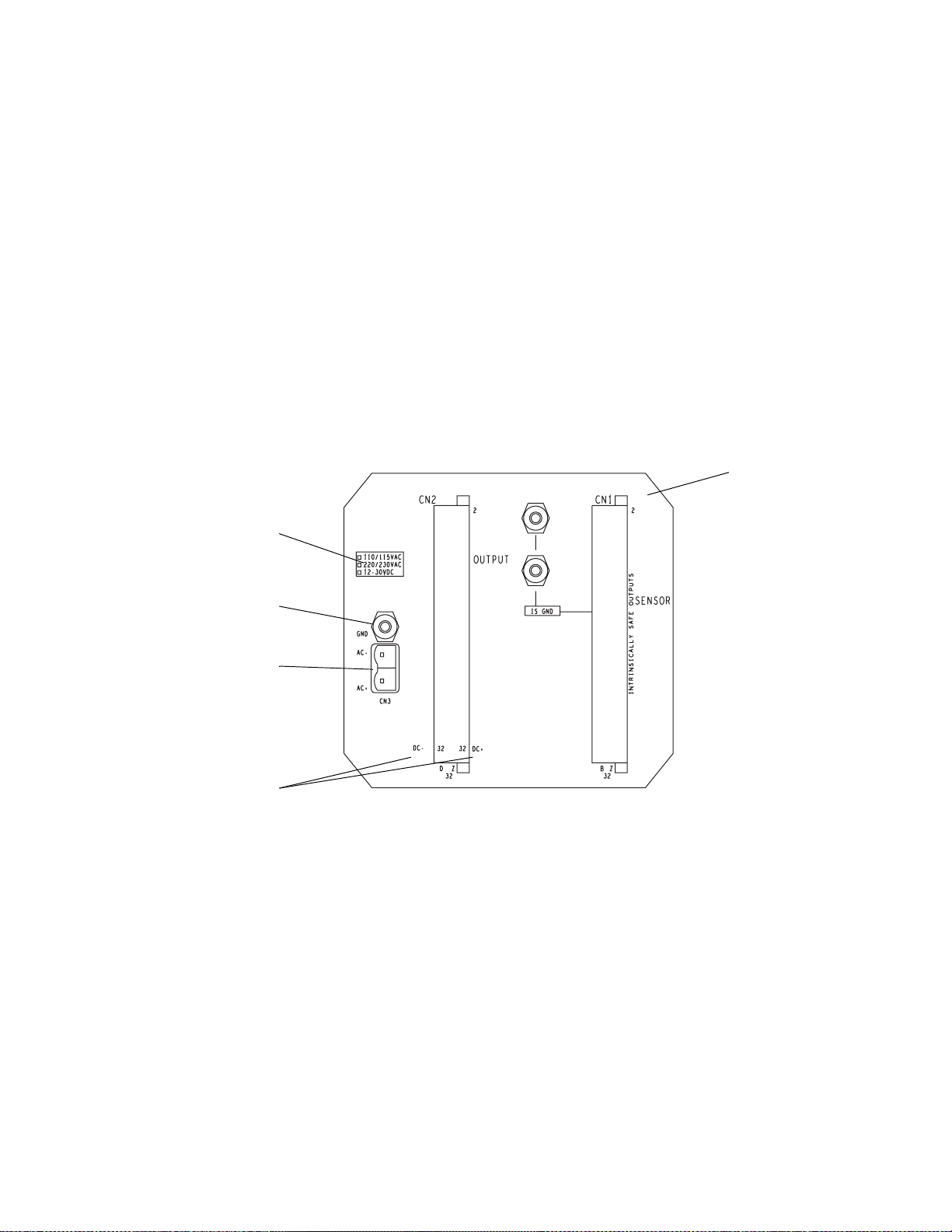
Power-Supply and Sensor Wiring
continued
Power-supply wiring
Some European applications require installation of AC power-supply
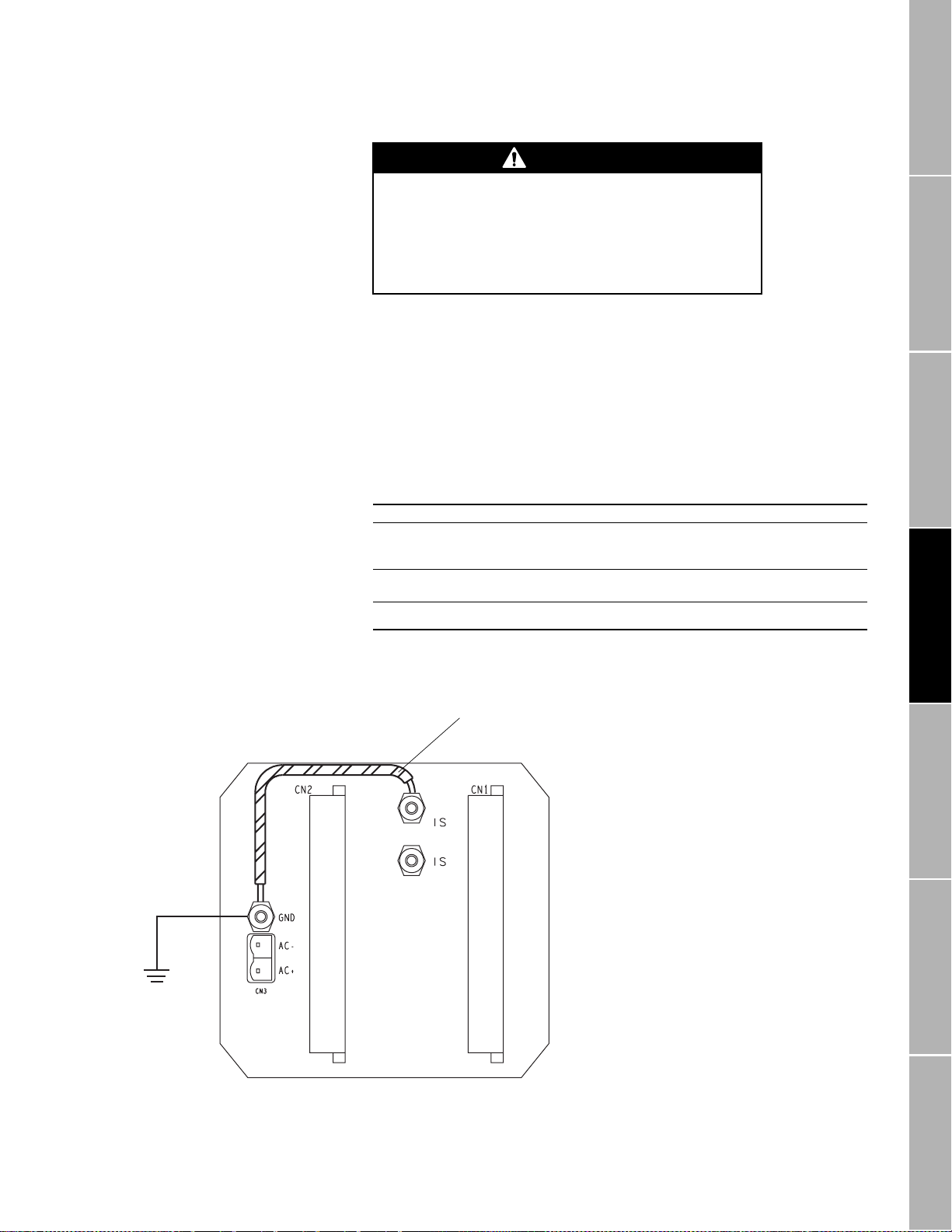
wiring to connector CN2, terminals D2 (AC+), D6 (AC–), and Z2 (GND).
In Europe, before making AC power-supply wiring connections at
CN2,
Europe, phone +31 (0) 318 549 443.
To install power-supply wiring, refer to
steps:
1. Match power-supply voltage to voltage indicated on the label in the
upper corner of the transmitter back panel.
2. Connect AC power-supply wiring at connector CN3 and the ground
lug directly above connector CN3; or connect DC power-supply wiring
at connector CN2, to terminals Z32 (DC+) and D32 (DC–).
3. Ground the transmitter as instructed below.
Figure 4-1. Power-supply wiring terminals
Power-supply
voltage label
AC power
ground
contact the Micro Motion Customer Service Department. In
Figure 4-1
and follow these
RFT9739
back panel
AC power -supply
DC power-supply
terminals
terminals
18
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 29
Power-Supply and Sensor Wiring
continued
Grounding
Table 4-1.
Selecting the proper
grounding scheme
CAUTION
Failure to comply with requirements for intrinsic
safety if the sensor is installed in a hazardous area
could result in an explosion.
The transmitter must be properly grounded. Follow the
instructions below to gr ound the transmitter.
To ensure proper grounding:
• If the sensor installation must comply with UL or CSA standards, refer
to the instructions in one of the following Micro Motion documents:
-
UL-D-IS Installation Instructions
-
CSA-D-IS Installation Instructions
• To determine which grounding instructions to use, refer to
Condition Figure Page
Sensor is installed in a non-hazardous area 4-2a 19
Sensor is installed in hazardous area,
plant does
installations in Europe onl y
Sensor is installed in a hazardous area,
any area except Europe
Plant uses a separate, high-integri t y, I.S. ground scheme 4-2c 20
have a separate intrinsically safe ground system ,
not
Table 4-1
4-2a 19
4-2b 20
.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Figure 4-2a. Grounding detail — typical
Earth
ground
Ground wire
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
If national standards are no t in effect, adhe re
to these guidelines for grounding:
• Use copper wire, 14 AWG (2.5 mm²) or
larger wire size.
• Keep all ground leads as short as pos si ble,
less than 1 ohm impedan ce.
• A factory-installed ground wire, connecting
the I.S. ground and power-supply ground
terminals , must remain in place.
• Connect power-supply ground direc tly to
earth.
• For hazardous area installation in Europ e,
use standard EN 60079 -1 4 as a guideline.
• To achieve potential equalization and comply
with CENELEC standards for hazardous
area installations in Eur ope, co nnect powerground terminal to the appropriate ground
terminals within the hazardous area, using a
potential equalizing line.
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
19
Page 30
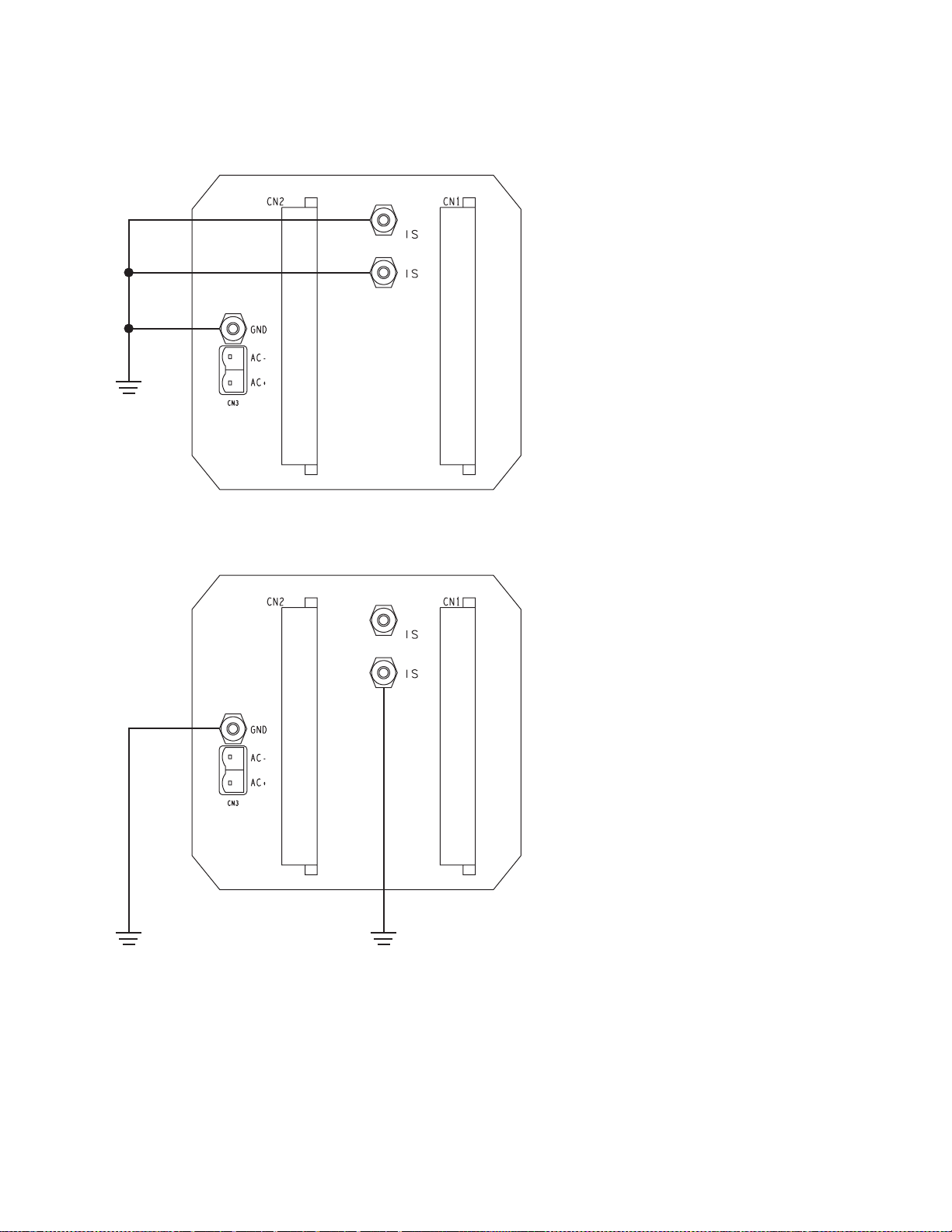
continued
Power-Supply and Sensor Wiring
Figure 4-2b. Grounding detail — hazardous-area sensor installations
Earth
ground
If national standards are no t in effect, adhe re
to these guidelines for grounding:
• Use copper wire, 14 AWG (2.5 mm²) or
larger wire size.
• Keep all ground leads as short as pos si ble,
less than 1 ohm impedan ce.
• Connect I.S. grounds and power-supply
ground directly to earth.
Figure 4-2c. Grounding detail — high-integrity I.S. installations
Earth
ground
High integrity
I.S. ground
If national standards are no t in effect, adhe re
to these guidelines for grounding:
• Use copper wire, 14 AWG (2.5 mm²) or
larger wire size.
• Keep all ground leads as short as pos si ble,
less than 1 ohm impedan ce.
• A factory-installed ground wire, connecting
the I.S. ground and power-supply ground
terminals, must be removed.
• Connect ground lead from power-supply
ground terminal directly to earth ground.
• To achieve potential equalization, connect
the I.S. ground terminal to the ap propriate
ground terminals w i thi n th e hazardous area,
using a potential equalizing line.
• I.S. ground wire must not be routed with
other wires.
20
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 31

Power-Supply and Sensor Wiring
continued
Fuses
4.3 Changing power-supply voltage
Fuses for the power-supply input are located inside the transmitter
housing on the power board. The transmitter has two fuses: one for an
AC power supply and one for a DC power supply.
• The AC power supply uses a UL/CSA 250mA/250V, time-lag, 5x20mm.
• The DC power supply uses a UL/CSA 2A/125V, time-lag, 5x20mm.
To access the AC-power fuse, remove the top cover. To access the
DC-power fuse, remove the bottom cover. Locate the power board. The
locations of the fuses on the board are indicated in
Figure 4-3
, page 21.
A switch labeled S1, located inside the transmitter on the power board
Figure 4-3
(see
), allows the AC power-supply voltage to be changed.
When switching from AC to DC power:
1. Remove the AC power wiring.
2. Properly install the DC wiring.
When switching AC voltage, or when switching from DC to AC
power:
1. Turn off power, then detach the existing power-supply wiring.
2. Remove the transmitter top cover.
3. Locate the power board. The location of switch S1 is indicated in
Figure 4-3
.
4. Set switch S1 to the appropriate position (115V or 230V), then
replace the top cover on the housing.
5. Mark the newly configured voltage on the label on the transmitter
back panel.
6. Properly install the new wiring.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Figure 4-3. Fuses and power-select switch
Power board
Switch S1 for AC
power-supply voltage
250 mA/250 V fuse
for AC power supply
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
2 amp/125 V fuse for
DC power supply
21
Page 32

Power-Supply and Sensor Wiring
continued
4.4 Sensor wiring
Cable connections to
sensor and transmitter
The instructions in this section explain how to connect a fully prepared
Micro Motion flowmeter cable to the RFT9739 and a sensor. The sensor
can be a Micro Motion ELITE, F-Series, Model D, DL, or DT sensor.
• The procedure for preparing Micro Motion flowmeter cable and cable
glands is described in the instructions that are shipped with the cable.
• Install cable and wiring to meet local code requirements.
• Use Micro Motion color-coded cable.
• Total length of cable from the sensor to the transmitter must not exceed
1000 feet (300 meters).
CAUTION
Improper installation of cable or conduit could cause
inaccurate measurements or flowmeter failure.
Keep cable away from devices such as transformers,
motors, and power lines, which produce large magnetic
fields.
CAUTION
Failure to seal sensor junction box could cause a
short circuit, which w ould result i n measureme nt error
or flowmeter failure.
To reduce risk of condensation or excessive moisture in
the sensor junction box:
• Seal all conduit openings.
• Install drip legs in conduit or cable.
• Fully tighten junction box cover.
The wiring procedure is the same for the sensor and transmitter. Refer to
the wiring diagrams on pages 23 through 24, and follow these steps:
1. Insert the stripped ends of the individual wires into the terminal
blocks. No bare wires should remain exposed.
• At the sensor, connect wiring inside the sensor junction box.
• At the transmitter, connect wiring to the transmitter's intrinsically
safe sensor terminals for sensor wiring, as numbered in
Table 4-2
,
page 23. The transmitter terminal block can be unplugged for easier
connection of wiring.
2. Locate the wires by color as indicated in
Table 4-2
, page 23.
3. Tighten the screws to hold the wires in place.
4. Tightly close the sensor junction-box cover. On an ELITE sensor
junction box, tighten all four cover screws.
22
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 33

Power-Supply and Sensor Wiring
continued
Table 4-2.
Terminal designations
Figure 4-4. Wiring to ELITE sensors
ELITE® sensor
terminals
Green
White
Violet
Yellow
Orange
Brown
Blue
Gray
Red
Clip drain wire back
Clip drain wire back
Clip drain wire back
Clip drain wire back
Brown
Green
White
Orange
Violet
Yellow
Wire
color
Sensor
terminal
Transmitter
terminal Function
Black* No connection CN1-Z4 Drain wires*
Brown 1 CN1-Z2 Drive +
Red 2 CN1-B2 Drive –
Orange 3 CN1-B6 Temperature –
Yell ow 4 CN1-B4 Temperature return
Green 5 CN1-Z8 Left pickoff +
Blue 6 CN1-Z10 Right pickoff +
Violet 7 CN1-Z6 Temperature +
Gray 8 CN1-B10 Right pickoff –
White 9 CN1-B8 Left pickoff –
*Combined drain wires from brown/red, green/white, and gray/blue pairs, and
yellow/orange/violet triplet. Th ese should be clipped back at the sensor en d.
Red
Yellow
White
Gray
RFT9739
terminals
B2
B4
B6
B8
B10
Flowmeter
cable
Maximum cable length 1000 ft. (300 m)
Red
Blue
Gray
Prepare cable in accordance with the
instructions that are shipped with the cable
Black
(Drains from all
wire sets)
Brown
Red
Green
White
Blue
Gray
Orange
Violet
Yellow
Orange
Brown
Z2
Black (Drains)
Z4
Violet
Z6
Green
Z8
Blue
Z10
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
Figure 4-5. Wiring to F-Series, Model D and DL sensors
F-Series, Model D
or DL sensor
terminals
Brown
Red
Orange
Yellow
Green
Blue
Violet
Gray
White
Clip drain wire back
Clip drain wire back
Clip drain wire back
Clip drain wire back
Maximum cable length 1000 ft. (300 m)
Brown
Red
Green
White
Blue
Gray
Orange
Violet
Yellow
instructions that are shipped with the cable
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
Flowmeter
cable
Prepare cable in accordance with the
Black
(Drains from all
wire sets)
Brown
Red
Green
White
Blue
Gray
Orange
Violet
Yellow
Red
Yellow
Orange
White
Gray
RFT9739
terminals
B2
B4
B6
B8
B10
Brown
Z2
Black (Drains)
Z4
Violet
Z6
Green
Z8
Blue
Z10
23
Page 34

continued
Power-Supply and Sensor Wiring
Figure 4-6. Wiring to Model DT sensors
Model DT
sensor terminals
User-supplied*
metal junction box
with terminal block
Brown
Red
Orange
Yellow
Green
Blue
Violet
Gray
White
Earth
ground
Sensor wire number
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Flowmeter
cable
Maximum cable length 1000 ft. (300 m)
Brown
Clip drain wire back
Clip drain wire back
Clip drain wire back
Clip drain wire back
*In Europe, the DT-sensor junction box is supplied by the factory.
Red
Green
White
Blue
Gray
Orange
Violet
Yellow
Prepare cable in accordance with the
instructions that are shipped with the cable
Black
(Drains from all
wire sets)
Brown
Red
Green
White
Blue
Gray
Orange
Violet
Yellow
Red
Yellow
Orange
White
Gray
RFT9739
terminals
B2
B4
B6
B8
B10
Brown
Z2
Black (Drains)
Z4
Violet
Z6
Green
Z8
Blue
Z10
24
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 35

5 Output Wiring
5.1 General guidelines
WARNING
Failure to comply with requirements for
intrinsic safety if the sensor is installed in a hazardou s
area could result in an explosion.
Output wiring is not intrinsically safe.
• Keep output wiring separated from power-supply wiring
and intrinsically safe sensor wiring.
• Follow all output wiring instructions to ensure the
transmitter and any connected devices will operate
correctly.
Output wiring connects to the terminals on connector CN2. Connector
CN2 is not intrinsically safe.
describe terminal designations on connector CN2, which can be
unplugged from the transmitter housing for easier installation of wiring.
• To avoid possible electrical interference, do not install output wiring in
the same conduit or cable tray as power-supply wiring or intrinsically
safe sensor wiring.
• Use individually shielded pairs of 22 AWG (0.3 mm²) or larger wires for
connections between the transmitter and any peripheral device.
• Connect shields of twisted-pairs to terminals CN2-Z4 and/or CN2-D4.
• To comply with CENELEC standards for hazardous area installations in
Europe, nonintrinsically-safe connections between the RFT9739 and
other devices may
less than or equal to 250 V.
only
Figure 5-1
be made to devices that maintain a voltage
and
Table 5-1
, page 26,
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
5.2 Maximum wire length
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
Currently, there is no system for accurately estimating the maximum
length of wire between the RFT9739 and a connected peripheral device.
Most applications will be able to use wire lengths up to 500 feet for
22 AWG wire (150 meters for 0.3 mm² wire), 50 feet for 28 AWG wire
(15 meters for 0.1 mm² wire), between the transmitter and any
peripheral device. However, these distances are estimates only.
Prior to commissioning the transmitter, a loop-test is recommended as a
means for determining whether or not output signals are being received
correctly at the receiving device.
25
Page 36

Output Wiring
Figure 5-1.
Output terminals
continued
Table 5-1. Output wiring terminal designations
CN2 terminal
number Function
D4, Z2 and Z4 Grounds Z6 DC power to pressure or DP transmitter
D10 and D12 Optocoupler output Z10 and D26 Dual-channel (quadrature) frequency
D14 and Z14 Signal gr ound
D16 and D14 Scroll inhibit Z12 and D26 Dua l -c hannel (quadrature) frequency
D18 and D14 Zero inhibit
D20 and D26 Remote zero input Z16 and Z14 Tube period output
D22 and Z22 RS-485 I/O Z18 and Z14 T em perature output
D24 and D26 F requency/pulse output Z20 mA input from pressure or DP transmitter
D28 and Z28 Secondary variable (SV) mA output Z24 and D26 Control output
D30 and Z30 Primary variable (PV) mA output Z26 Frequency output, DC supply voltage
D32 and Z32 DC power-supply input
CN2 terminal
number Function
output, channel A
output, channel B
26
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 37

Output Wiring
continued
5.3 Primary and secondary
mA outputs
The RFT9739 primary and secondary mA output signals can be
independently configured, and can represent flow, density, temperature,
event 1 or event 2. With a pressure transmitter, the primary and
secondary mA output signals can also represent pressure. For
information on configuring mA outputs for events, see any of the
following manuals or AMS on-line help:
Using the HART Communicator with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using ProLink Software with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using Modbus Protocol with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
The mA outputs can produce a user-selected 0-20 or 4-20 mA current.
(See "Milliamp output scaling," page 9.)
• When configured to produce 4-20 mA current, the mA output loop can
supply loop-powered process indicators.
For transmitters with software version 3.8 or higher,
•
when
configured to produce 4-20 mA current, the mA outputs are compliant
with the NAMUR NE43 standard. (All RFT9739 transmitters shipped
after November 1999 have software version 3.8 or higher.)
CAUTION
Milliamp output range has changed.
When configured for 4-20 mA, milliamp outputs will not
output live signals between 2.0 and 3.8 mA, or between
20.5 and 22 mA.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
In compliance with the NAMUR NE43 standard:
• 4-20 mA outputs will produce a live signal from 3.8 to 20.5 mA.
• 4-20 mA outputs will not produce a signal between 2.0 and 3.8 mA, or
• 4-20 mA output performance is illustrated in
Figure 5-2. 4-20 mA output performance
Downscale
fault indication level
Systems that rely on milliamp output signals in the ranges
listed above might not perform as expected. For RFT9739
transmitters shipped after November 1999, outputs will
saturate at 3.8 and 20.5 mA, unlike previous versions of
these instruments.
Reconfigure systems as necessary.
between 20.5 and 22 mA.
Figure 5-2
Upscale
fault indication level
Operating range (live si gnal)
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
.
2 3.8 2220.5
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
Output, mA
27
Page 38

Output Wiring
continued
Use RFT9739 terminals CN2-D30 and CN2-Z30 for the primary mA
output. Use terminals CN2-D28 and CN2-Z28 for the secondary mA
output. See
Figure 5-3
.
• Primary and secondary mA output loops are isolated and floating.
Additional grounding will result in optimum performance, and optimum
HART communication on the primary mA output. Ensure that mA
output loops are grounded properly, either at the transmitter end, or at
the external device.
• The maximum allowable length for mA signal wiring is determined by
measuring resistance over the signal wires and through the receiver
device. Total loop resistance must not exceed 1000 ohms.
• The primary mA output must be set to the 4-20 mA mode for the
Bell 202 physical layer. The Bell 202 layer will not work with the primary
mA output configured as a 0-20 mA output.
• The mA output is active and cannot be converted to passive.
Figure 5-3.
Primary and secondary
mA output wiring
RFT9739
output terminals
PV = Primary variable
SV = Secondary variable
PV+ (signal line)
PV– (return )
SV+ (signal line)
SV– (return )
28
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 39

Output Wiring
continued
Connections for HART®
communication devices
Figure 5-4
ProLink PC-Interface adaptor, or an AMS modem to the RFT9739 for
illustrates how to connect a HART Communicator, the
digital communication over the primary mA output. For information about
using the HART Communicator or ProLink program, see the appropriate
instruction manual. For information about using AMS software, see the
AMS on-line help.
Figure 5-4. HART® Communicator, ProLink® PC-Interface, and AMS modem connections
Rack-mount
RFT9739
HART socket
(same circuit as
PV terminals)
HART
Communicator,
ProLink PCI,
or AMS modem
R1
(Note 1)
PV+
HART socket or
PV terminals
PV–
R3
(Note 3)
R2
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
DCS or PLC
with internal
resistor
(Note 2)
1. If necessary, add resistance in the loop by installing resistor R1. SMART FAMILY® devices require a minimum loop
resistance of 250 ohms. Loop resistance must not exceed 1000 ohms, regardless of the communication setup.
CAUTION
Connecting a HART device to the RFT9739 primary variable milliamp output loop could cause transmitter
output error.
If the primary variable (PV) analog output is being used for flow control, connecting a HART device to the output
loop could cause the transmitter 4-20 mA output to change, which would affect flow control devices.
Set control devices for manual operation before connecting a HART device to the RFT9 739 primary variable
milliamp output loop.
2. The DCS or PLC must be configured for an active milliamp signal.
3. Resistor R3 is required if the DCS or PLC does not have an internal resistor.
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
29
Page 40

Output Wiring
continued
5.4 Frequency outputs
Frequency/pulse output
The RFT9739 frequency outputs include a frequency/pulse output, a
dual-channel phase-shifted frequency output for custody transfer
applications, and an optocoupler output.
• The frequency output loops are isolated and floating from other circuits
except the control output and external-zero input circuits. Ensure that
frequency output loops are grounded properly, either at the transmitter
end, or at the external device.
• The frequency output circuit uses a 2.2 kohm resistor tied to a 15-volt
source that limits the current to 7 mA. The output circuit is rated to
30 VDC, with 0.1 ampere maximum sinking capability, when used in
open collector mode. Open collector mode is described on page 33.
• The output is a nominal +15 V or +30 V square wave, unloaded. See
"Setting voltage level for VDE output requirements," page 37.
• Output impedance is 2.2 kohm.
• For use with receivers other than Micro Motion peripheral devices,
check the instruction manual for the receiver to make sure its inputvoltage and electrical-current ratings match the RFT9739 ratings.
The frequency/pulse output represents the flow rate, independent of the
primary and secondary mA outputs. The frequency/pulse output can be
used with all Micro Motion peripheral devices except the DMS Density
Monitoring System and the PI 4-20 Process Indicator, which do not have
frequency inputs.
The RFT9739 frequency/pulse output can be configured to provide any
one of the following:
• Mass flow rate
• Volume flow rate
• Mass flow total
• Volume flow total
Mass flow total and volume flow total are not available with some
RFT9739 transmitters shipped prior to 1998.
Use RFT9739 terminals CN2-D24 and CN2-D26 for the frequency/pulse
output. T erminal D26 serves as a common return for the frequency/pulse
output, dual-channel frequency output, control output, and remote zero
input. See
Figure 5-5
, page 31.
30
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 41

Output Wiring
PLC
or
pulse counter
FREQ+ (signal line)
RETURN (ground)
RFT9739
output terminals
PLC
or
pulse counter
1 to 3 kohm
resistor
FREQ+ (signal line)
RETURN (ground)
RFT9739
output terminals
continued
Default configuration
Figure 5-5.
Frequency/pulse output
wiring
When the RFT9739 is shipped from the factory, the frequency/pulse
output is internally powered by an isolated 15-volt source via a 2.2 kohm
pull-up resistor. This internal current is limited to approximately 7 mA.
Figure 5-5
See
.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Configuration for increased current
Figure 5-6.
Frequency/pulse output
wiring for increased
current
In some applications, it might be necessary to increase the current in the
frequency/pulse output circuit. See
Section 5.2
, page 25. For increased
current to the circuit, add a 1 to 3 kohm resistor across terminals
CN2-Z26 and CN2-D24, as illustrated in
Figure 5-6
.
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
31
Page 42

Output Wiring
continued
Configuration for constant current
Applications with high capacitance loading will benefit by wiring the
frequency/pulse output circuit to maintain a constant current source of
50 mA for any load between 0 and 220 ohms. This configuration renders
the control output circuit inoperable, and could affect the optocoupler
and dual-channel frequency outputs.
For constant current, add a jumper across terminals CN2-Z26 and
CN-D24, and a 100 to 250 ohm resistor at the PLC or pulse-counter end
of the cable, as illustrated in
Figure 5-7
.
CAUTION
Adding a jumper across terminals CN2-Z26 and
CN2-D24 renders the control output circuit inoperable.
Do not attempt to use the control output circuit after you
add a jumper across terminals CN2-Z26 and CN2-D24.
The control output can be reconfigured to function properly, independent
of this frequency/pulse wiring procedure. See "Control output in open
collector mode," page 41.
The optocoupler and dual-channel frequency outputs could be affected
by configuring the frequency/pulse output for constant current as
described above. To reduce this risk, use a 250 ohm resistor, as
indicated in
Figure 5-7
.
Figure 5-7.
Frequency/pulse output
wiring for constant current
RFT9739
output terminals
FREQ+ (signal line)
100 to 250 ohm resistor
(see note)
RETURN (ground)
To use the dual-channel frequency output or the optocoupl er out put
with this configuration, use o nly a 250 ohm resistor.
PLC
pulse counter
or
32
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 43

Output Wiring
continued
Configuration for open collector mode
The RFT9739 provides current to the frequency/pulse output circuit. In
applications where this current must be permanently suspended, and for
receiving devices that require input voltage higher than approximately
10 volts, the frequency/pulse output circuit can be used in open collector
mode.
To configure the output for open collector mode, a resistor must be
clipped as described below.
This procedure will permanently alter the
transmitter and cannot be reversed.
• Clip resistor R5 and add an external DC power supply and a pull-up
resistor. See
Figure 5-8
, page 34.
• The pull-up resistor must be of sufficient value to limit loop current to
less than 0.1 ampere, depending on the total loop resistance at the
transmitter.
• To prevent damage to the optocoupler and dual-channel frequency
output circuits, the external voltage must not exceed 15 V.
• Resistor R5 is located on the inside of the RFT9739 back panel.
CAUTION
Clipping resistor R5 will eliminate the internal voltage
source from the transmitter.
After clipping resistor R5, an external power supply is
required to use the transmitter’s frequency/pulse output.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Before permanently altering any equipment, contact the
Micro Motion Customer Service:
• In the U.S.A., phone 1-800-522-6277, 24 hours
• Outside the U.S.A., phone 303-530-8400, 24 hours
• In Europe, phone +31 (0) 318 549 443
• In Asia, phone 65-770-8155
To access resistor R5, refer to
Figure 5-9
, page 34, and follow these
steps:
1. Remove the bottom cover of the transmitter housing.
2. Remove the back panel, and carefully pull it loose from the power
board and the control board.
3. Locate and clip resistor R5 on the inside of the RFT9739 back panel.
Figure 5-10
See
, page 35.
4. Reinstall the bottom cover.
5. Reinstall the back panel, carefully aligning the connector pins with the
connectors on the power board and the control board.
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
33
Page 44

Output Wiring
Figure 5-8.
Frequency/pulse output
wiring for open collector
mode
continued
RFT9739
output terminals
DC
power
supply
Resistor
(See note)
Figure 5-9.
RFT9739 back panel
FREQ+ (signal lin e )
RETURN (ground)
Resistor must be of sufficient value to limit loop current to
less than 0.1 ampe re, depending on total loop resistance.
Back pane l
PLC
or
pulse counter
34
Bottom cover
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 45

continued
Output Wiring
Figure 5-10. Resistor R5 on inside of back panel
Inside of back panel
Resistor R5
Sensor Wiring
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
Pow er-Supply and
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
35
Page 46

Output Wiring
continued
Dual-channel frequency output
The transmitter has a dual-channel, phase-shifted frequency output for
custody transfer applications. The dual-channel frequency is derived
from the frequency/pulse output, and represents the same flow rate as
the frequency/pulse output. Each dual-channel frequency is always half
the value of the frequency/pulse output. For example, if the
frequency/pulse output is 4,000 Hz, each dual-channel output is
2,000 Hz. The phase shift between channels is 90 degrees.
Use RFT9739 terminals CN2-Z10, CN2-Z12, and CN2-D26 for the dualchannel frequency output. Terminal D26 serves as a common return for
the dual-channel frequency output, frequency/pulse output, control
output, and remote zero input. See
Figure 5-11. Dual-channel frequency output wiring
RFT9739
output terminals
GND (ground)
FREQ+A (Channel A signal line )
90°
Figure 5-11
.
FREQ+B (Channel B signal line)
RETURN (ground)
Host receiver
Example: Petrocount/IMS
Clip shield at
host receiver end
36
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 47

Output Wiring
Back pane l
Bottom cover
Power board
continued
Setting voltage level for
VDE output requirements
Figure 5-12.
RFT9739 back panel and
power board
To set the voltage level to 30 volts to meet VDE requirements for the
frequency/pulse output and dual-channel frequency output:
1. Remove the bottom cover of the transmitter housing.
2. Remove the back panel, and carefully pull it loose from the power
board and the control board. See
Figure 5-12
.
3. Locate jumper J10 on the power board, which is illustrated in
Figure 5-13
panel, whic h is illustrated in
, page 38. Locate jumper JP1 on the inside of the back
Figure 5-14
, page 38.
4. Both jumpers are labeled to show a position for standard 15 volt
operation (STD) and 30 V operation (VDE) to meet VDE output
requirements. Set both jumpers to the same position.
• With the jumper on the center pin and the pin labeled VDE, the
output is set for 30 volts. Set the output to the VDE position to meet
VDE output requirements.
• With the jumper on the center pin and the pin labeled STD, the
output is set for 15 volts. Unless the output must meet VDE
requirements, set the output to the STD position.
5. Reinstall the bottom cover.
6. Reinstall the back panel, carefully aligning the connector pins with the
connectors on the power board and the control board.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
37
Page 48

continued
Output Wiring
Figure 5-13. Jumper J10 on power board
Power board
Jumper
J10
Figure 5-14. Jumper JP1 on inside of back panel
Inside of back panel
Area of
detail
Detail of
back panel
Jumper
JP1
38
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 49

Output Wiring
continued
Optocoupler output
Figure 5-15. Optocoupler output wiring
RFT9739
output terminals
GND (ground)
The transmitter has an externally powered passive optocoupler output in
addition to the frequency/pulse and dual-channel frequency outputs.
The optocoupler output is derived from the primary frequency output,
and represents the same flow rate variable as the frequency/pulse
output.
Use RFT9739 terminals CN2-D10, CN2-D12, and CN2-D4 for the
optocoupler output.
Figure 5-15
•
illustrates the wiring connection from the optocoupler
output to an auxiliary device.
• Signal voltage is 0-2 VDC low, 16-30 VDC high, with a 0.01 ampere
maximum sinking capability.
Host receiver
Clip shield at
host receiver end
Example: PLC
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
OPTOCOUPLER– (emitter)
OPTOCOUPLER+ (collector)
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
39
Page 50

Output Wiring
continued
5.5 Control output
The control output can indicate flow direction, transmitter zeroing in
progress, faults, event 1 or event 2. For information on configuring the
control output for events, see any of the following manuals or AMS
on-line help:
Using the HART Communicator with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using ProLink Software with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using Modbus Protocol with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Use RFT9739 terminals CN2-Z24 and CN2-D26 for the control output.
Terminal D26 serves as a common return for the control output,
frequency/pulse output, dual-channel frequency output, and remote zero
input. See
Figure 5-16
.
• When configured to indicate flow direction, the output is high
(+15 VDC) when indicating forward flow , and low (0 VDC) when
indicating reverse flow.
• When configured to indicate transmitter zeroing in progress, the output
is low (0 VDC) when zeroing is in progress and high (+15 VDC) at all
other times.
• When configured to indicate faults, the output is low (0 VDC) when a
fault condition exists and high (+15 VDC) during normal operation.
• When configured to indicate event 1 or event 2, the output switches ON
(0 VDC) or OFF (+15 VDC) when the flow rate, flow total, density,
temperature, or pressure of the process fluid achieves a programmed
setpoint.
• The output circuit is rated to 30 VDC, with 0.1 ampere maximum
sinking capability, when used in open collector mode. Open collector
mode is described on page 41.
• Transmitter output is nominal 0 or +15 VDC, unloaded.
• Output impedance is 2.2 kohm.
40
Figure 5-16.
Control output wiring
RFT9739
output terminals
CONTROL (signal line)
RETURN (ground)
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 51

Output Wiring
continued
Control output in open collector mode
The RFT9739 provides current to the control output circuit. In
applications where this current must be permanently suspended, and for
receiving devices that require input voltage higher than approximately
10 volts, the control output circuit can be used in open collector mode.
If the frequency/pulse output is configured for constant current (see
"Configuration for open collector mode," page 33), the control output is
rendered inoperable. To reconfigure the control output to function
properly, independent of this frequency/pulse output configuration, the
control output circuit can be configured for open collector mode.
To configure the control output for open collector mode, a resistor must
be clipped as described below.
This procedure will permanently alter
the transmitter and cannot be reversed.
• Clip resistor R4 and add an external DC power supply and a pull-up
resistor. See
Figure 5-17
, page 42.
• The pull-up resistor must be of sufficient value to limit loop current to
less than 0.1 ampere, depending on the total loop resistance at the
transmitter.
• To prevent damage to the optocoupler and dual-channel frequency
output circuits, the external voltage must not exceed 15 V.
• Resistor R4 is located on the inside of the RFT9739 back panel.
CAUTION
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Clipping resistor R4 will eliminate the internal voltage
source from the transmitter.
After clipping resistor R4 an external power supply is
required to use the transmitter’s control output.
Before permanently altering any equipment, contact the
Micro Motion Customer Service:
• In the U.S.A., phone 1-800-522-6277, 24 hours
• Outside the U.S.A., phone 303-530-8400, 24 hours
• In Europe, phone +31 (0) 318 549 443
• In Asia, phone 65-770-8155
To access resistor R4, refer to
Figure 5-18
, page 42, and follow these
steps:
1. Remove the bottom cover of the transmitter housing.
2. Remove the back panel, and carefully pull it loose from the power
board and the control board.
3. Locate and clip resistor R4 on the inside of the RFT9739 back panel.
Figure 5-19
See
, page 43.
4. Reinstall the bottom cover.
5. Reinstall the back panel, carefully aligning the connector pins with the
connectors on the power board and the control board.
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
41
Page 52

Output Wiring
Figure 5-17.
Control output wiring for
open collector mode
continued
RFT9739
output terminals
DC
power
supply
Resistor
(See note)
CONTROL
(signal line)
RETURN (ground)
Resistor must be of suffici ent value to limit loop current to
less than 0.1 ampere, depending on total loop resistance.
Receiving
device
Figure 5-18.
RFT9739 back panel
Back pane l
42
Bottom cover
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 53

continued
Output Wiring
Figure 5-19. Location of resistor R4 on inside of back panel
Inside of back panel
Resistor R4
Sensor Wiring
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
Pow er-Supply and
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
43
Page 54

Output Wiring
continued
5.6 Peripheral device wiring
Table 5-2.
Peripheral wiring
diagrams
Figure 5-20. Wiring to DMS
RFT9739
output terminals
The wiring diagrams listed in
Table 5-2
illustrate connections from the
transmitter to Micro Motion peripheral devices.
Micro Motion peripheral device Figure Page
DMS Density Monitoring System 5-20 44
DRT Digital Rate Totalizer with LED display 5-21a 45
DRT Digital Rate Totalizer with LCD display 5-21b 45
FMS-3 Flow Monitoring System with LED display 5-22a 46
FMS-3 Flow Monitoring System with LCD display 5-22b 46
NFC Net Flow Computer 5-23 4 7
NOC Net Oil Computer with AC power supply 5-24a 48
NOC Net Oil Computer with DC power supply 5-24b 48
Model 3300 Discrete Controller with screw/solder terminals 5-25a 49
Model 3300 Discrete Controller with I/O cable 5-25b 49
Model 3350 Discrete Co nt ro ller 5-26 50
DMS
terminals
Note 1
1. Clip shields at this end.
2. This wire not terminated.
Note 2
Note 2
Note 1
Earth
ground
44
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 55

continued
Output Wiring
Figure 5-21a. Wiring to DRT with LED
RFT9739
output terminals
Clip shields
at this end
Earth
ground
DRT LED
terminals
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Figure 5-21b. Wiring to DRT with LCD
RFT9739
output terminals
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
DRT LCD
terminals
Clip shields
at this end
Earth
ground
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
45
Page 56

continued
Output Wiring
Figure 5-22a. Wiring to FMS-3 with LED
RFT9739
output terminals
FMS-3 LED
terminals
Clip shields
at this end
Earth
ground
Figure 5-22b. Wiring to FMS-3 with LCD
RFT9739
output terminals
FMS-3 LCD
terminals
Clip shields
at this end
Earth
ground
46
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 57

continued
Output Wiring
Figure 5-23. Wiring to NFC
RFT9739
output terminals
NFC
terminals
Note 1
Note 2
1. Clip shields at this end.
2. This wire not ter m inat ed.
Note 2
Note 1
Note 1
Earth
ground
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
47
Page 58

continued
Output Wiring
Figure 5-24a. Wiring to AC-powered NOC
RFT9739
output terminals
1. Clip shields at this end.
2. This wire not ter m inat ed.
Note 2
Note 1
NOC
terminals
Note 1
Note 2
Earth
ground
Note 1
Figure 5-24b. Wiring to DC-powered NOC
RFT9739
output terminals
Note 2
1. Clip shields at this end.
2. This wire not terminated.
Note 1
NOC
terminals
Note 1
Note 2
Note 1
48
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 59

continued
Output Wiring
Figure 5-25a. Wiring to Model 3300 with screw-type or solder-tail terminals
RFT9739
output terminals
Clip shields at this end
Figure 5-25b. Wiring to Model 3300 with I/O cable
RFT9739
output terminals
Model 3300
terminals
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Clip shields at this end
Model 3300
terminals
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
49
Page 60

continued
Output Wiring
Figure 5-26. Wiring to Model 3350
RFT9739
output terminals
Clip shields at this end
Model 3350
terminals
50
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 61

Output Wiring
continued
5.7 Pressure transmitter wiring
CAUTION
Failure to comply with requirements for
intrinsic safety if the sensor is installed in a hazardou s
area could result in an explosion.
Pressure transmitter wiring is not intrinsically safe.
Keep pressure transmitter wiring separated from
intrinsically safe sensor wiring, power-supply wiring, and
any other intrinsically safe wiring.
The RFT9739 accepts pressure input signals from a pressure
transmitter for pressure compensation.
• If a pressure transmitter connected to a host controller measures
gauge pressure at the sensor input, the RFT9739 can compensate for
the pressure effect on the sensor. Pressure compensation is required
only for the sensor models listed in
• Instructions for wiring the RFT9739 to a pressure transmitter are
provided below. Instructions for configuring the RFT9739 for pressure
compensation are provided in the following instruction manuals and in
the AMS on-line help:
-
Using the HART Communicator with Micro Motion Transmitters
-
Using ProLink Software with Micro Motion Transmitters
-
Using Modbus Protocol with Micro Motion Transmitters
Table 5-3
.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Table 5-3.
Sensors affected by
pressure
The RFT9739 pressure input terminals (CN2-Z6 and CN2-Z20) are
intended for use with a pressure transmitter, and should not be
connected to a control system.
If the RFT9739 is configured for pressure compensation, flowmeter
measurement will not be compensated for pressure during a pressure
input failure. If the signal from the pressure transmitter fails, both of the
following occur:
• The RFT9739 continues to operate in non-fault mode.
• A "Pressure Input Failure" message appears on the transmitter display,
a HART Communicator with the latest memory module, ProLink
software version 2.4 or higher, or AMS software.
ELITE F-Series Model D and DL
CMF025 (density only)
CMF050 (density only)
CMF100
CMF200
CMF300
CMF400
F025 (density only)
F050
F100
F200
D300 standard model
D300 Tefzel
D600
DL100
DL200
®
model
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
51
Page 62

continued
Output Wiring
If the pressure transmitter requires a power supply less than or
equal to 11.75 V ,
the RFT9739 can power the pressure transmitter. Use
RFT9739 terminals CN2-Z6 and CN2-Z20. Terminal Z6 (P) is the power
output to the pressure transmitter, and terminal Z20 (S) is the signal
input to the RFT9739, as shown in
If the pressure transmitter requires a power supply greater than
11.75 V,
or if other loop devices are required, an external source can
power the pressure transmitter. Use RFT9739 terminals CN2-Z20 and
CN2-D14 or CN2-Z14. Terminal Z20 (S) is the signal input to the
RFT9739, and terminal D14 or Z14 (SIGNAL GND) is the return, as
shown in
Figure 5-27b
If digital communication between the pressure transmitter and the
RFT9739 is required,
use primary variable terminals CN2-Z30 (PV+)
and CN2-D30 (PV–), as shown in
Figure 5-27a. Wiring to pressure transmitter — analog output
WARNING: Pressure transmitter wiring is
not intrinsically safe
, page 53.
Figure 5-27a
Figure 5-27c
.
, page 53.
RFT9739
output terminals
Pressure
transmitter
52
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 63

continued
Output Wiring
Figure 5-27b. Wiring to pressure transmitter — external power, analog input
WARNING: Pressure transmitter wiring is
not intrinsically safe
Power
supply
24 VDC 4-20 mA
Optional
loop device(s)
RFT9739
output terminals
Terminal CN2-D14 must be connected directly to the
negative (–) termina l of the external power supply.
Pressure
transmitter
Figure 5-27c. Wiring to pressure transmitter — digital communications
WARNING: Pressure transmitter wiring is
not intrinsically safe
RFT9739
output terminals
Pressure transmitte r
SMART only (1150 or 3051)
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
250 ohm ±5%,
0.5 w
250 ohm ±5%,
0.5 w
24 VDC
Power
supply
53
Page 64

Output Wiring
continued
5.8 Remote-zero switch
Figure 5-28.
Wiring to remote-zero
switch
The transmitter can be zeroed from a remote switch. If the transmitter
display indicates flow rate, this contact will zero the flowmeter. If the
transmitter display indicates flow total, this contact will reset the flow
total.
Section 6.4
•
Section 6.5
•
, page 65, describes the flowmeter zeroing procedure.
, page 67, describes the totalizer reset procedure.
The switch must be a momentary-type contact, normally open, close to
zero, and must carry 1 mA of current in the closed position. The open
circuit voltage is 5 VDC.
Use terminals CN2-D20 and CN2-D26 for the remote switch. Terminal
D26 serves as a common return for the external-switch input,
frequency/pulse output, dual-channel frequency output, and control
output. See
Remote
switch
Figure 5-28
.
RFT9739
output terminals
ZERO+ (signal line)
RETURN (ground)
54
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 65

Output Wiring
continued
5.9 RS-485 multidrop network
The RFT9739 can be configured to communicate for any one of the
following options:
• HART protocol over the RS-485 standard
• HART protocol over the Bell 202 standard
• Modbus protocol over the RS-485 standard
• Modbus protocol over the RS-485 standard and HART protocol over
the Bell 202 standard
For communications configuration instructions, see "Communication
configuration mode," page 61. For Bell 202 network wiring, see
Section 5.10
, page 56.
Multiple transmitters can participate in an RS-485 multidrop network that
uses HART or Modbus protocol.
• Under HART protocol, an almost unlimited number of transmitters can
participate in the network. Each transmitter must have a unique tag
name. If polling addresses are used, up to 16 transmitters can have
unique polling addresses from 0 to 15.
• Under Modbus protocol, up to 15 transmitters can participate in the
network. Each transmitter must have a unique polling address from
1to 15.
To connect the transmitter to an RS-485 network, use transmitter
terminals CN2-Z22 and CN2-D22.
Figure 5-29
, page 56, shows how to
connect one RFT9739 or multiple RFT9739 transmitters to a host
controller for RS-485 serial communication.
• Install twisted-pair, shielded cable, consisting of 24-gauge (0.3 mm²) or
larger wire, between the RFT9739 and an RS-485 communication
device. Maximum cable length is 4000 feet (1200 meters).
• Some installations require a 120-ohm, ½-watt resistor at each end of
the network cable to reduce electrical reflections.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
For information on communication protocol requirements for
implementing an RS-485 network, phone the Micro Motion Customer
Service Depa rtment:
• In the U.S.A., phone 1-800-522-6277, 24 hours
• Outside the U.S.A., phone 303-530-8400, 24 hours
• In Europe, phone +31 (0) 318 549 443
• In Asia, phone 65-770-8155
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
55
Page 66

continued
Output Wiring
Figure 5-29. RS-485 wiring
One RFT9739 and
a host controller
Host
controller
Multiple RFT9739s and
a host controller
Host
controller
A
See note
B
A
See note See note
B
See note
Z22
D22
Z22
D22
RFT9739
RFT9739
Z22 D22
RFT9739
For long-distance communication, or if noise from an external source interferes with the
signal, install 120-ohm ½-watt resistors across terminals of both end devices.
5.10 Bell 202 multidrop network
The RFT9739 can be configured to communicate for any one of the
following options:
Z22 D22
RFT9739
• HART protocol over the RS-485 standard
• HART protocol over the Bell 202 standard
• Modbus protocol over the RS-485 standard
• Modbus protocol over the RS-485 standard and HART protocol over
the Bell 202 standard
For communications configuration instructions, see "Communication
configuration mode," page 61. For RS-485 network wiring, see
Section 5.9
, page 55.
Devices in a Bell 202 multidrop network communicate by sending and
receiving signals to and from one another. HART protocol supports up to
15 transmitters in a Bell 202 multidrop network. The actual maximum
number depends upon the type of transmitters, the method of
installation, and other external factors. Other Rosemount SMART
FAMILY transmitters can also participate in a HART-compatible network.
• A Bell 202 multidrop network uses twisted-pair wire, and allows only
digital communication. Digital communication requires a sample rate of
2 to 31 seconds at 1200 baud.
• A HART Communicator or other HART-compatible control system can
communicate with any device in the network over the same 2-wire pair.
56
Using multiple transmitters in a HART-compatible network requires
assigning a unique address from 1 to 15 to each transmitter.
• Assigning an address of 1 to 15 to the transmitter causes the primary
mA output to remain at a constant 4 mA level.
• The primary mA output must produce a 4-20 mA current for the Bell
202 physical layer . The Bell 202 lay er will not work with the primary mA
output configured as a 0-20 mA output when the current output is
0mA.
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 67

continued
Output Wiring
To connect the transmitter to a Bell 202 network, use RFT9739 terminals
CN2-Z30 and CN2-D30. See
• SMART FAMILY devices require a minimum loop resistance of
250 ohms. Loop resistance must not exceed 1000 ohms.
• Connect the mA outputs from each transmitter together so they
terminate at a common load resistor, with at least 250 ohms
impedance, installed in series.
Figure 5-30. Typical HART® network wiring
Figure 5-30
.
HART
Communicator,
ProLink PCI,
or AMS modem
250 ohm
load
4-20mA
IFT9701
RFT9739
field-mount
PV+17PV–
18
4-20mA
R-Series
RFT9739
rack-mount
PV+
PV–
CN2-
CN2-
Z30
D30
SMART
FAMILY
transmitter
DC source required for
other HART 4-20mA
passive transmitters
SMART
FAMILY
transmitter
24
DC
For optim um HART communication, mak e s ure the
output loop is single-point grounded to instrument
grade ground.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
57
Page 68

Output Wiring
continued
5.11 Security wiring
Figure 5-31.
Inhibit-switch wiring
Security wiring enables the use of remote (keyed) switches to disable
the front-panel Scroll and Reset buttons.
Scroll inhibit
To install a remote (key) switch that disables the front-panel Scroll
button, connect a signal line to terminal CN2-D16 (SCROLL INH) and a
ground wire to terminal CN2-D14 (SIGNAL GND). See
Figure 5-31
.
Reset inhibit
To install a remote (key) switch that disables the front-panel Reset
button, connect a signal line to terminal CN2-D18 (ZERO INH) and a
ground wire to terminal CN2-D14 (SIGNAL GND). See
Reset inhibit
switch
Scroll inhibit
switch
SIGNAL GND (return)
Figure 5-31
RFT9739
output
terminals
.
ZERO INH (signal line)
SCROLL INH (signal line)
58
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 69

6 Startup
6.1 Initialization
After wiring has been connected, power can be supplied to the
transmitter. During initialization, the transmitter performs a selfdiagnostic test and produces the following series of displays,
sequentially:
1. All pixels on
2. All pixels off
3. Al l eig hts
4. All pixels off
5. Copyright notification
For DC-powered transmitter s
must pro vi de a mini mu m of 2 amperes of inrush curre nt at a mi nim um of
12 volts at the transmitter's power input terminals. If the startup voltage
is pulled below 12 VDC, the transmitter could remain in the startup loop
indefinitely .
After the self-test is complete, one of 10 possible process variable
screens, such as the one depicted below, displays:
If the flowmeter is operating properly, the blinking "Msg" (message)
indicator appears in the bottom right corner of the screen to indicate
power has been cycled.
• To clear the "Msg" indicator, repeatedly press the Scroll button until the
display reads "Sensor OK *POWER / RESET*".
• To clear the message, press the Scroll button.
, at startup, the transmitter power source
INV:
GRAMS:
38450.5
Msg
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
If the message does not clear, or if error messages appear, refer to
Section 7.4
error messages.
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
, page 73, which provides an overview of diagnostic and
59
Page 70

Startup
continued
6.2 Using the display
Process variables mode
Table 6-1.
Display screens
The RFT9739 display enables the user to:
• View process variables, flow totals and inventory levels, and status
messages (see page 60)
• Set communication parameters (see page 61)
• Zero the flowmeter (see page 65)
• Reset the transmitter's flow totalizers (see page 67)
Use the Scroll and Reset buttons to operate the display.
After power to the transmitter is turned off and on, or "cycled," the
transmitter is in the process variables mode. The first screen that
appears is the last process variable that was viewed before power was
cycled. In the process variables mode, each screen indicates the value
and measurement unit for a process variable.
As the user scrolls through the process variable screens, they appear in
the order listed in
Screen Process variable
1 M a ss flow rate (RATE)
2 Volume flow rate (RATE)
3 Density (DENS)
4 Temperature (TEMP)
5 Mass total
6 Volume total
7 Mass inventory
8 Volume inventory
9 Differential pr essure or
10 Configuration event register
11 Calibration event register
12 Display test
13 Message (if any) – –
[1]
While read in g to tal (TOT) or i n ventory (INV) screen s, use the unit of mea sur e i n th e
lower left corner to dist ingui sh between mass and volume.
[2]
Screen appears only wh en transmitter is configured to indicate pressure.
[3]
Screen appears only wh en transmitter is configured for security m ode 8. See
Section 2.3
, page 5, for information about se curity modes.
Table 6-1
[1]
[1]
gauge pressure
[3]
.
Abbreviation in
upper left corner of screen
(TOT)
[1]
[1]
[2]
[3]
(TOT)
(INV)
(INV)
(DP) or
(P)
[3]
(CONFIG REG)
(CALIBRATE REG)
(DISPLAY TEST)
60
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 71

Startup
continued
When displaying total (TOT) or inventory (INV) screens, display
resolution is 10 places, including the decimal point. The position of the
decimal point is fixed, and depends on the flow calibration factor and
units of measure. If totalizers exceed the maximum display capability,
the display reads "*********". Clear the message with the Reset knob.
If a message exists, the blinking "Msg" (message) indicator appears in
the bottom right corner of each screen, indicating any of the following
conditions:
• Power to the transmitter has been cycled.
• The flowmeter has been zeroed.
• An error condition exists.
To read a message, scroll past all process variable screens to the
message screen (see
Table 6-1
, page 60). Uncorrected status
conditions remain in the message que ue. Other messa ges are clear e d
when the Scroll button is used to scroll past the message screen to the
flow rate screen.
If power to the transmitter has been cycled and the transmitter is
operating properly, the message reads "Sensor OK *POWER /
RESET*".
For more information about messages, refer to
Section 7.4
, page 73.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Communication configuration mode
Switch 5 on the transmitter control board allows the user to select the
standard communication configuration or establish a user-defined
configuration. See
Section 2.3
, page 5, and "Communication settings",
page 9. The communication configuration mode allows the user to
configure the transmitter's digital communication output using the
display and the Scroll and Reset buttons.
• If switch 5 is in the USER-DEFINED position, enter the communication
configuration mode from any process variable screen by pressing and
holding the Scroll button and the Reset button at the same time. In the
communication configuration mode, the text "M1", "M2", and "M3" will
appear in the upper left corner of the screen.
• For RFT9739 software versions 3.6 and later, if switch 5 is in the STD
COM position, an error message will be displayed if an attempt is made
to change the communication configuration using the Scroll and Reset
buttons.
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
61
Page 72

Startup
continued
M1 — Baud rate
To set the baud rate:
1. Press and release the Scroll button to view each baud rate option.
Choose from 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, or 38400 baud.
2. Press and hold the Reset button to select the displayed baud rate.
Release the Reset button when the display stops flashing.
3. When the selected baud rate flashes again, press and release the
Reset button to move to the M2 screen.
M2 — S=Stop bits, P=Parity
To set the stop bits and parity:
1. Press and release the Scroll button to view each stop bit (S) option.
Choose 1 stop bit or 2 stop bits.
2. Press and hold the Reset button to select the displayed stop bit.
Release the Reset button when the display stops flashing.
3. When the selected stop bit flashes again, press and release the
Reset button to move to the parity (P) options.
4. Press and release the Scroll button to view each parity (P) option.
Choose from odd parity (O), even parity (E), or no parity (N). HART
protocol requires odd parity; Modbus protocol requires odd parity,
even parity, or no parity, depending on the host controller.
5. Press and hold the Reset button to select the displayed parity.
Release the Reset button when the display stops flashing.
6. When the selected parity flashes again, press the Reset button to
move to the M3 screen.
62
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 73

Startup
continued
M3 — Data bits and protocol
The M3 screen enables selection of 7-bit or 8-bit mode for Modbus
protocol, or 8-bit mode for HART protocol.
• The HART protocol can use either the Bell 202 or RS-485 physical
layer.
• Using HART protocol over the primary mA output requires the Bell 202
physical layer.
CAUTION
Changing the protocol will cause the transmitter to
restart, which could result in switching of flow loop
control devices.
Set control devices for manual operation before changing
the communications protocol.
To set the data bits and protocol:
1. Press and release the Scroll button to view each data bits (D) option.
Choose from 7 data bits or 8 data bits. HART protocol requires 8 data
bits; Modbus protocol requires 7 data bits for ASCII mode or 8 data
bits for RTU mode.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
2. Press and hold the Reset button to select the displayed data bits.
Release the Reset button when the display stops flashing.
3. When the selected data bits flashes again, press and release the
Reset button to move to the protocol and physical layer options.
4. Press and release the Scroll button to view each protocol/physical
layer option. Choose from the following:
• HART protocol over the Bell 202 physical layer (HART/202)
• HART protocol over the RS-485 physical layer (HART/485)
• Modbus protocol over the RS-485 physical layer (Modbus/485)
• Modbus protocol over the RS-485 physical layer and HART protocol
over the Bell 202 physical layer (Modbus/202)
5. Press and hold the Reset button to select the displayed
protocol/physical layer. Release the Reset button when the display
stops flashing.
6. When the selected protocol/physical layer flashes again, press and
release the Reset button to restart the transmitter. If the
protocol/physical layer was not changed, the transmitter will not
restart, and the display will return to the process variable screen.
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
63
Page 74

Startup
continued
6.3 Custody transfer event registers
Event registers are provided for security requirements for custody
transfer applications. When the transmitter is configured for security
mode 8 (see
Section 2.3
, page 5), the transmitter meets security
requirements for custody transfer described in National Institute of
Standards and Technology (NIST) Handbook 44.
Custody transfer event registers record one change for each change
"session." A change session begins when the transmitter is taken out of
security mode 8, and ends when security mode 8 is reentered. To begin
a change session, set switches 1, 2, and 3 to the OFF position. A
change session ends when switches 1, 2, and 3 are reset to the ON
position. After a change session ends, security event registers will
increase by one (1) if any of the parameters listed in
Table 6-2
have
been changed.
• Each register will increase up to 999, then roll over to zero.
• Custody transfer event registers cannot be reset.
View the security event registers using any of the following methods:
• With the RFT9739 display. If the transmitter has a display, event
registers can be viewed from the CONFIG REG and CALIBRATE REG
screens when the transmitter is configured for security mode 8.
• With ProLink software version 2.3 or higher. Refer to on-line help for
instructions.
• With AMS software. Refer to on-line help for instructions.
• With a HART Communicator.
• With a HART-compatible or Modbus-compatible master controller.
Table 6-2.
Parameters that affect
event registers
Configuration register
Mass flow cutoff
Flow damping
Volume flow cutoff
Flow direction
Primary m A scaling factors
Secondary mA scaling factors
Calibration regist er
Mass flow units
Volume flow units
Auto zero calibration
Density calibration
Flow calibration factor
Meter factors
Frequency output scaling factors
• Frequency
•Rate
Primary m A output trim
Secondary mA output trim
Primary m A output assignment
Secondar y m A out put assignment
Control output assignment
Master reset
Density calibration factors
• Density A and Density B
• K1, K2, an d FD
• Density temperature coef ficient
Pressure compensa tion factors
•Flow factor
• Density factor
• Flow calibration pressure
64
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 75

Startup
continued
6.4 Flowmeter zeroing
Zeroing procedure
CAUTION
Failure to zero the flowmeter at initial startup could
cause measurement error.
Zero the flowmeter before putting it in operation.
Flowmeter zeroing establishes flowmeter response to zero flow and sets
a baseline for flow measurement.
To zero the transmitter, follow these steps:
1. Prepare the flowmeter for zeroing:
a. Install the sensor according to the sensor instruction manual.
b. Apply power to the transmitter, then allow it to warm up for at least
30 minutes.
c. Ensure the transmitter is in a security mode that allows flowmeter
zeroing. See "Security modes", page 6.
d. Run the process fluid to be measured through the sensor until the
sensor temperature reading approximates the normal process
operating temperature.
2. Close the shutoff valve downstream from the sensor.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
3. Ensure zero flow through the sensor.
CAUTION
Flow through the sensor du ring flo wmeter zer oin g will
result in an inaccurate zero setting.
Make sure the sensor tubes are
flow through the sensor is
flowmeter zeroing.
completely
completely
4. Zero the transmitter in any of four ways:
• Press and hold the Reset button for at least ten seconds. (In the rate
screens, "RATE" appears in the upper left corner of the screen.)
• An external contact closure can be used for transmitter zeroing.
(Refer to
Section 5.8
, page 54, for wiring instructions). Close the
contact for at least ten seconds.
• Issue an auto zero command using a HART Communicator, a
HART-compatible or Modbus-compatible master controller, or the
ProLink program.
• Issue a "zero trim" command with the AMS program.
full and fluid
stopped during
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
65
Page 76

Startup
continued
During the zeroing procedure, the display reads "Sensor OK CAL IN
PROGRESS". The default zero time will range from 20 to 90 seconds,
depending on the sensor.
After flowmeter zeroing has been completed, the mass flow rate or
volume flow rate screen reappears, and the blinking "Msg" (message)
indicator appears in the lower right corner. To clear the message
indicator, scroll past the volume inventory screen to the message
screen, which should read "Sensor OK *ERROR CLEARED*".
Diagnosing zero failure
Additional information
about flowmeter zeroing
If zeroing fails, the blinking "Msg" (message) indicator appears. The
message screen will indicate the zero failure with a message such as
"*ZERO ERROR*", "*ZERO TOO HIGH*", or "*ZERO TOO LOW*". An
error condition could indicate:
• Flow of fluid during flowmeter zeroing
• Partially empty flow tubes
• An improperly mounted sensor
To clear a zeroing error, cycle power to the transmitter, ensure that the
sensor flow tubes are filled with fluid and flow is stopped, then re-zero
the flowmeter again.
Flowmeter zeroing can be disabled using the transmitter’s security
modes or with a remote (keyed) switch that disables the RFT9739 Reset
button.
Table 6-1
•
flowmeter zeroing. Refer to
describes how RFT9739 security modes 1 through 8 affect
Section 2. 3
, page 5, for more information
about security modes.
Section 5.11
•
, page 58, describes how to install keyed switches to
disable the front-panel Reset button.
The transmitter has a programmable zeroing time (number of
measurement cycles), and enables the user to set the standa rd
deviation limits. For more information, see any of the following instruction
manuals:
Using the HART Communicator with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using ProLink Software with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using Modbus Protocol with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Table 6-1. Effect of security modes on flowmeter zeroing
Per formed with
Reset button
HART or Modbus device
66
Mode
1
Mode
2
Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled
Mode
3
Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled
Mode
4
Mode
5
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Mode
6
Mode
7
Mode
8
Page 77

Startup
continued
6.5 Totalizer control
The transmitter's mass totalizer and volume totalizer can be started,
stopped, and reset using any of the following:
• A HART Communicator
• ProLink software version 2.4 or higher
• A Modbus device
•AMS software
In addition, the totalizer can be reset from the RFT9739 front panel.
WARNING
When the totalizers are stopped, the frequency/pulse
output is disabled.
If the frequency/pulse output is used for process control,
failure to set co ntrol devices for manual operation could
affect process control.
• Before stopping the totalizers, set process control
devices for manual operation.
• To enable the frequency/pulse output, restart the
totalizers.
Totalizer functions can be disabled using the transmitter’s security
modes or with a remote (keyed) switch.
Table 6-2
•
RFT9739 security modes 1 through 8. Refer to
more information about security modes.
Section 5.11
•
disable the front-panel Scroll and Reset buttons.
, page 68, lists the totalizer functions that are disabled with
Section 2.3
, page 5, for
, page 58, describes how to install keyed switches to
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Mass and volume totalizers cannot be reset independently. When one
totalizer is reset, the other is also reset. Resetting the totalizer has no
effect on the mass or volume inventory. To reset the transmitter's mass
totalizer and volume totalizer using the RFT9739 Scroll and Reset
buttons:
1. Use the Scroll button to view the process variable screens until either
totalizer screen appears. (In the totalizer screens, "TOT" appears in
the upper left corner.)
2. Hold the Reset button until the screen turns blank, then release.
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
67
Page 78

continued
Startup
Table 6-2. Effect of security modes on totalizer control
Flow
condition
No flow Scroll and Reset
With flow Scroll and Reset
Resetting the totalizer has no ef fect on the mass or volume inventory.
For more information about security modes, refer to
6.6 Process measurement
Performed
with
buttons
HART or Modbus
device
buttons
HART or Modbus
device
Mode
1
Mode
2
Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled
Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled
Mode
3
Disabled Disab led Disabled
Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled
Section 2.3
, page 5.
After flowmeter zeroing has been completed as described in
Section 6.4
, page 65, the flowmeter is ready for process measurement.
Mode
4
Mode
5
Mode
6
Mode
7
Mode
8
68
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 79

7 Troubleshooting
7.1 General guidelines
Troubleshooting a Micro Motion flowmeter is performed in two parts:
1. Tests of wiring integrity
2. Observation of the transmitter's diagnostic tools, which include
diagnostic messages and fault output levels.
CAUTION
During troublesho oting, the trans mitter could pr oduce
inaccurate flow signals.
Set control devices for manual operation while
troubleshooting the flowmeter.
Follow these general guidelines when troubleshooting a Micro Motion
flowmeter:
• Before beginning the diagnostic process, become familiar with this
instruction manual and with the instruction manual for the sensor.
• While troubleshooting a problem, leave the sensor in place, if possible.
Problems can result from the specific environment in which the sensor
operates.
• Check all signals under both flow and no-flow conditions. This
procedure will minimize the possibility of overlooking some causes or
symptoms.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Output Wiring Startup TroubleshootingBefore You Begin Getting Started Mounting
7.2 Transmitter diagnostic tools
Fault outputs
In some situations, troubleshooting requires use of the transmitter's
diagnostic tools, which include fault output levels and diagnostic
messages.
The RFT9739 has downscale and upscale fault outputs. (See "Milliamp
output scaling", page 9.) Fault output levels are listed in
Table 7-1
Table 7-1. Fault output levels
Output Operating condition Downscale Upscale
0-20 mA Alarm 0 mA 22 mA
EPROM, RAM, or RTI error; transmitter failure 0 mA 24 mA
4-20 mA Alarm 2 mA 22 mA
EPROM, RAM, or RTI error; transmitter failure 0 mA 24 mA
Frequency/pulse Alarm 0 Hz 15 kHz
EPROM, RAM, or RTI error; transmitter failure 0 Hz 19 kHz
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
.
69
Page 80

Troubleshooting
continued
Diagnostic messages
The transmitter provides diagnostic messages, which can be viewed on
the display of a HART Communicator, or in the Status window of the
ProLink software program. Messages are described in the following
instruction manuals, and in AMS on-line help:
Using the HART Communicator with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using ProLink Software with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using Modbus Protocol with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Use a HART Communicator with the latest memory module, a Modbus
host controller, or ProLink software version 2.3 or higher to view the
following parameters:
•Drive gain
• Tube frequency
• Left and right pickoff voltages
•"Live zero"
Many of the messages that can be read with a HART Communicator, the
ProLink program, or AMS software can be read from the transmitter
display. These messages are described in
Modbus host controllers use status bits as diagnostic messages.
In the event of a display readback failure, if the error does not clear itself
within 60 seconds, cycle power to the transmitter (turn power OFF, then
ON).
Section 7.4
, page 73.
7.3 Interrogation with a HART®
device
Connect a HART device to the communications socket on the transmitter
front panel (the socket is labeled "HART"), or use the ProLink program to
communicate with the transmitter.
• If the HART Communicator does not offer RFT9739 "Dev v4" as a
device description, the communicator memory module might need to
be upgraded.
• Use ProLink software version 2.3 or higher.
• Use AMS software.
• Contact the Micro Motion Customer Service Department to upgrade
your HART Communicator or ProLink program:
-
In the U.S.A., phone 1-800-522-6277
-
Outside the U.S.A., phone 303-530-8400
-
In Europe, phone +31 (0) 318 549 443
-
In Asia, phone 65-770-8155
Figure 7-1
the ProLink PC Interface adaptor, or AMS serial modem to the
RFT9739. For more information, see the HART Communicator or
ProLink software instruction manual, or AMS on-line help.
, page 71, explains how to connect a HART Communicator,
70
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 81

continued
Troubleshooting
Figure 7-1. HART® Communicator, ProLink® PC-Interface, and AMS modem connections
Rack-mount
RFT9739
HART socket
(same circuit as
PV terminals)
HART
Communicator,
ProLink PCI,
or AMS modem
R1
(Note 1)
PV+
HART socket or
PV terminals
PV–
R3
(Note 3)
R2
Before You Begin Getting Started Mounting
DCS or PLC
with internal
resistor
(Note 2)
1. If necessary, add resistance in the loop by installing resistor R1. SMART FAMILY® devices require a minimum loop
resistance of 250 ohms. Loop resistance must not exceed 1000 ohms, regardless of the communication setup.
CAUTION
Connecting a HART device to the RFT9739 primary variable milliamp output loop could cause transmitter
output error.
If the primary variable (PV) analog output is being used for flow control, connecting a HART device to the output
loop could cause the transmitter 4-20 mA output to change, which would affect flow control devices.
Set control devices for manual operation before connecting a HART device to the RFT9739 primary variable
milliamp output loop.
2. The DCS or PLC must be configured for an active milliamp signal.
3. Resistor R3 is required if the DCS or PLC does not have an internal resistor.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Output Wiring Startup Troubleshooting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
71
Page 82

Troubleshooting
continued
Fault detection indicates an interruption in the functional integrity of the
sensor and the transmitter, including the sensor pickoff coils, drive coil,
and RTD. Faults, such as a short or an open circuit, are detected by the
HART device.
The transmitter runs continuous self-diagnostics. If these diagnostics
reveal a f ailure, the HART de vice displays an error message. Self-testing
allows the transmitter to check its own circuitry.
The transmitter works with a Micro Motion flow sensor to provide flow
information. Therefore, many of the troubleshooting checks pertain only
to the sensor. However, a HART Communicator, the ProLink program,
and AMS software enable the user to perform other tests:
• Performing an
mA output test
forces the transmitter to produce a user-
specified current output of 0 to 22 mA.
• Performing a
frequency/pulse output test
forces the transmitter to
produce a user-specified frequency output between 0.1 and
15,000 Hz.
• Performing an
mA output trim
allows adjustment of the primary and
secondary mA outputs against a highly accurate external standard
such as a digital multimeter (DMM) or receiving device.
Perform mA trim and/or test procedures, if necessary, as described in
the HART Communicator or ProLink software instruction manuals, or in
AMS on-line help.
• If the transmitter is in security mode 8, mA output test, mA output trim,
and frequency/pulse output test procedures cannot be performed. For
more information, see "Security mode 8", page 7.
• If the transmitter is in fault condition, an mA output test cannot be
performed.
• If the transmitter is not properly connected to a sensor, or if the sensor
is in fault condition, an mA output test cannot be performed.
72
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 83

Troubleshooting
continued
Before You Begin Getting Started Mounting
7.4 Troubleshooting using the transmitter display
Not configured
Transmitter failure messages
Using the message screen, refer to the following sections to
troubleshoot:
• Overrange and sensor error messages
• Transm itte r failure messages
• Slug flow and output saturated messages
• Informational messages
After the user performs a master reset, the message display reads "NOT
CONFIGURED", indicating the flowmeter requires complete
characterization and reconfiguration. Use a HART Communicator or the
ProLink program to configure the transmitter. To perform a master reset,
Section 7.7
see
, page 79.
If a transmitter failure occurs, the display produces one of the following
messages:
• "Xmtr Failed"
• "(E)eprom Error "
• "RAM Error"
•"RTI Error"
If a transmitter failure occurs, contact the Micro Motion Customer
Service Depa rtment.
Table 7-2
describes transmitter failure messages.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
CAUTION
Transmitter failures are critical, and could cause
unintentional switching of process control devices.
The transmitter does not have any parts that are
serviceable by the us er. If a transmitter failure is in di cated,
phone the Micro Motion Customer Service Department:
• In the U.S.A., phone 1-800-522-6277, 24 hours
• Outside the U.S.A., phone 303-530-8400, 24 hours
• In Europe, phone +31 (0) 318 549 443
• In Asia, phone 65-770-8155
Table 7-2. Using transmitter failure messages
Message Condition
Xmtr Failed Tran sm i tte r ha rd ware failure Phone the Micro Motion Customer Service Department:
(E)EPROM error EPROM checksum failure
RAM Error RAM diagnostic failure
RTI Error Real-time interrupt failure
Corrective action
• In the U.S.A., phone 1-800-522-6277, 24 hours
• Outside the U.S.A., phone 303-530-8400, 24 hours
• In Europe, phone +31 (0) 318 549 443
• In Asia, phone 65-770-815 5
Output Wiring Startup Troubleshooting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
73
Page 84

Troubleshooting
continued
Overrange and sensor error messages
Slug flow
If a sens or f a ilure occur s, if t he sen sor c ab le is f aul ty, or if meas ured flo w,
measured temperature, or measured density go outside the sensor
limits, the display produces one of the following messages:
• "Sensor Error"
• "Drive Overrng"
• "Input Overrange"
• "Temp Overrange"
• "Dens Overrng"
To interpret overrange and sensor error messages, use the transmitter
fault output levels, a digital multimeter (DMM) or other reference device,
and refer to
• Turn off power to the transmitter before unplugging terminal blocks.
• Unplug terminal blocks from the transmitter back panel to check
circuits.
Programmed slug flow limits enable transmitter outputs and the display
to indicate conditions such as slug flow (gas slugs in a liquid flow
stream). Such conditions adversely affect sensor performance by
causing erratic vibration of the flow tubes, which in turn causes the
transmitter to produce inaccurate flow signals.
If the user programs slug limits, a slug flow condition causes the
following to occur:
1. The message display reads "SLUG FLOW".
2. The frequency/pulse output goes to 0 Hz.
3. The mA outputs indicating the flow rate go to the level that represents
zero fl ow.
Table 7-3
, page 75, for corrective actions.
Output saturated messages
The flowmeter resumes normal operation when liquid fills the flow tubes
and density stabilizes within the programmed slug flow limits.
The user can also program a slug duration, from 0 to 60 seconds, into
the configuration of an RFT9739. If process density goes outside a slug
flow limit, flow outputs hold their last measured value for the period of
time established as the slug duration.
Table 7-4
typical corrective actions.
If an output variable exceeds its upper range limit, the display message
reads "Freq Overrange", "mA 1 Saturated" or "mA 2 Saturated". The
message can mean the output variable has exceeded appropriate limits
for the process, or can mean the user needs to change measurement
units.
Table 7-4
and lists typical corrective actions.
, page 75 summarizes possible slug flow errors and lists
, page 75 summarizes possible output saturated messages
74
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 85

continued
Troubleshooting
Table 7-3. Using overrange and sensor error messages
Instructions
1. Tur n off power to transmitter.
2. Unplug terminal blocks from transmitter back panel to check circuits.
Message Other symptoms Cause(s) Corrective action(s)
Drive Overrng or
Input Overrange
Sensor Error • Transmi t te r produces fault outputs
Drive Overrng or
Dens Overrng
Temp Overrange • Tran sm i t te r produces fault outputs
• Transm it te r pr oduces fault outputs
• At the transmitter, DMM indicates open or
short circu it f rom r ed wire to brown wire
• At the sensor, DMM indicates open or short
circuit from red wire to brown wire
• Transm it te r pr oduces fault outputs
• At the transmitter, DMM indicates open or
short circu it f rom gre en wi r e to w hi te wire
• At the sensor, DMM indicates open or short
circuit from green wire to wh ite wi re
• At the transmitter, DMM indicates open or
short circu it f rom blue wir e to gray wire
• At the sensor, DMM indicates open or short
circuit from blue wire to gray wire
Tran sm i t te r pr od uces fault outputs M oi sture in sensor case • Repl ace conduit and/or
Tran sm i t te r produces fault outputs • Inappropriate dens ity
• At the transmitter, DMM indicates open or
short circuit from yellow wire to orange wire
• At the sensor, DMM indicates open or short
circuit from yellow wire to orange wire
• Transm it te r pr oduces fault outputs
• At the transmitter, DMM indicates open or
short circuit from violet wire to yellow wire
• At the sensor, DMM indicates open or short
circuit from violet wire to yellow wire
• Flow rate outside
sensor limit
• Faulty cab l e
• Open or short drive
coil in sensor
• Flow rate outside
sensor limit
• Faulty cab l e
• Open or short l ef t
pickoff in sensor
• Faulty cab l e
• Open or short right
pickoff in sensor
factors
• Process density
> 5.0000 g/cc
• Severely erratic or
complete cessatio n of
flow tube vibration due
to gas slugs or solids
in process fluid
• Plugged flow tube
• Temperature outside
sensor limit
• Faulty cab l e
• Open or short l ead
length compensator
• Faulty cab l e
• Open or short RTD in
sensor
• Fill sensor with process fluid
• Bring flow rate wit hin sensor
limit
• Monitor flow rate
• If open or short at
transmitter , reconnect wiring
or repair cable
• If open or short at se nsor,
return sensor to Micro
Motion
• If open or short at
transmitter , reconnect wiring
or repair cable
• If open or short at se nsor,
return sensor to Micro
Motion
conduit seals
• Repair cable
• Return sensor to Micro
Motion
• Calibrate for density
• Correct density factors
• Monitor density
• Bring density within se nsor
limit
• Purge flow tubes with
steam, water, or purging
chemical
• Bring temperature within
sensor limit
• Monitor temperature
• If open or short at
transmitter , reconnect wiring
or repair cable
• If open or short at se nsor,
return sensor to Micro
Motion
Before You Begin Getting Started Mounting
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Output Wiring Startup Troubleshooting
Table 7-4. Using slug flow and output saturated messages
Message Condition Corrective action(s)
Slug flow • G as slugs causing process densi t y t o go below low slug flow limit
• Solids causing process density to go above high slug flow limit
Freq overrange Flow rate driving output from terminal s CN 2-D24 (FREQ) and
CN2-D26 (RETURN) to 0 or 15 kHz
mA 1 saturated Output from terminals CN2-Z30 (PV+) and CN2-D30
(PV–) equals 0, 3.8, or 20.5 m A
mA 2 saturated Output from terminals CN2-Z28 (SV+) and CN2-D28
(SV–) equals 0, 3.8, or 20.5 m A
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
• Monitor density
• En ter new slug flow limits
• Enter new slug duration
• Change flow measurement unit s
• Rescale frequency/pu l se ou t put
• Reduce flow rate
• Change value of variable at 20 mA
• Alter fluid process
75
Page 86

Troubleshooting
continued
Informational messages
Information messages are described below.
Table 7-5
, page 77,
summarizes informational messages and lists typical corrective actions.
Power Reset
indicates a power failure, brownout, or power cycle has
interrupted operation of the transmitter. The transmitter has a nonvolatile
memory, which remains intact despite power interruptions.
Cal in Progress
indicates flowmeter zeroing in progress or density
calibration in progress.
Zero Too Noisy
indicates mechanical noise has prevented the
transmitter from setting an accurate zero flow offset during transmitter
zeroing.
Zero Too High
Zero Too Low
or
indicates f low was not complet ely sh ut
off during sensor zeroing, so the transmitter has calculated a zero flow
offset that is too great to allow accurate flow measurement. Zero Too
Low indicates the zero flow offset is negative.
Burst Mode
indicates the user has configured the transmitter to send
data in burst mode while operating under HART protocol. In burst mode,
the transmitter bursts data at regular intervals.
mA 1 Fixed
mA 2 Fixed
or
indicates one of several conditions:
• The mA output trim or test was not completed. The output remains
fixed at the assigned level until the user completes the output trim or
test procedure.
• The user has assigned a polling address other than 0 to the transmitter
for Bell 202 communication. The output remains fixed at 4 mA until the
user assigns a polling address of 0 to the transmitter.
76
Event 1 On
Event 2 On
or
switches ON if an event tied to an RFT9739
output switches the output ON.
• With mass or volume total assigned to the event, the event switches
ON and OFF according to the low or high configuration of the alarm.
With a LOW alarm, the event switches ON when the user resets the
totalizer. With a HIGH alarm, the event switches OFF when the user
resets the totalizer.
• With flow, density, temperature, or pressure assigned to the event, the
event switches OFF or ON whenever the process variable crosses the
setpoint.
Security Breach
indicates the transmitter security mode has been
changed from security mode 8. Clear the message by reentering
security mode 8 or by performing a master reset.
Error Cleared
indicates a previous message has been cleared.
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 87

continued
Troubleshooting
Table 7-5. Using informational messages
Message Condition Corrective action(s)
Power Reset • Power failure
Cal in Progress • Flowmeter zeroing in progress
Zero Too Noisy Mechanical noise prevented accurate zero
Zero Too High
Zero Too Low
Burst Mode Transm it te r co nf i gur ed to send data in burst
mA 1 Fixed Communica tio n failure dur i ng test or trim of
mA 2 Fixed Communica tio n failure dur i ng test or trim of
Event 1 On Event (alarm) 1 is ON • If totalizer assigned:
Event 2 On Event (alarm) 2 is ON
Security Breach Security mode changed from mode 8 • Re-enter security mode 8
•Brownout
• Power cycl i ng
• Density calibration in progress
flow setting during auto zero
Flow not completely shut off during auto zero C om pletely shut off flow, then rezero
Moisture in sensor jun ct ion box caused zero
drift
mode under HART protocol
mA output from term i nals CN2-Z30 (PV+)
and CN2-D30 (PV–)
Polling address of 1 to 15 assigned to
RFT9739 for HART in Bell 202
output from termi n al s C N 2- Z28 (SV+) and
CN2-D28 (SV–)
Check accuracy of totalizers
• If Cal in Progress disappears, no action
• If Cal in Progress reappears after zeroing or
calibration is completed:
-
Check flowmeter cable
-
Eliminate noise, then rezero or recalibrate
Eliminate mechanical noi se, if possible, then rezero
Ensure interior of junction box is comp letely dry, then
rezero
Switch burst mode OFF
Complete trim or test
• Change polling address to zero (0 )
• Use RS-485 communication standard
Complete trim or test
-
Low alarm switches event ON at totalizer reset
-
High alarm switches event OFF at totalizer reset
• If other variable assigned, event switches ON/OFF
when variable crosses setpoi nt
• Perform master reset
Before You Begin Getting Started Mounting
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
7.5 Power supply
The transmitter is configured at the factory for a 110/115 VAC or
220/230 VAC pow er supply. All RFT9739 rack-mount transmitters can
accept a 12 to 30 VDC power supply, independent of the AC powersupply configuration.
• A label on the upper corner of the transmitter back panel indicates the
configured power-supply voltage.
• The AC power supply voltage configuration can be changed by the
user. See
Section 4.3
, page 21.
Check for specified power at the transmitter terminals.
• Wire DC power at connector CN2, to terminals Z32 (DC+) and
D32 (DC–).
• Wire AC power at connector CN3 and the ground lug above connector
CN3.
• Some European applications require installation of AC power-supply
wiring to connector CN2, terminals D2 (AC+), D6 (AC–), and
Z2 (GND).
connections at CN2,
In Europe, before making AC power-supply wiring
contact the Micro Motion Customer Service
Department. In Europe, phone +31 (0) 318 549 443.
• If the transmitter is wired for an AC power supply, ensure switch S1 on
the power board is in the appropriate position. See
Section 4.3
,
page 21.
• Check fuses. See "Fuses", page 21.
Output Wiring Startup Troubleshooting
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
77
Page 88

Troubleshooting
continued
7.6 Wiring
For transmitter wiring instructions, refer to
Chapter 5
, page 25. Wiring problems are often incorrectly diagnosed as
Chapter 4
, page 17, and
a faulty sensor. At initial startup of the transmitter, always check the
following:
1. Proper cable, and use of shielded pairs
2. Proper wire termination
a. Wires on correct terminals
b. Wires making good connections at transmitter terminals
c. Wires making good connections at the sensor terminals
d. Wires properly connected at any intermediate terminal junction,
such as the user-supplied junction box between a Model DT
sensor and transmitter.
If a fault condition is indicated, follow these instructions:
1. Disconnect the transmitter's power supply.
2. Unplug the terminal blocks from the transmitter back panel.
3. Use a digital multimeter (DMM) to measure resistance between wire
pairs at the transmitter terminals:
-
Drive coil, check terminals CN1-Z2 and CN1-B2 (brown/red)
-
Left pickoff coil, check terminals CN1-Z8 and CN1-B8
(green/white)
-
Right pickoff coil, check terminals CN1-Z10 and CN1-B10
(blue/gray)
-
RTD, check terminals CN1-Z6 and CN1-B4 (viol et/yellow)
4. If the measured resistance is outside the range listed in
Table 7-6
repeat the measurements at the sensor terminals.
5. Reinsert the terminal blocks and restore power to the transmitter.
6. Use the DMM to troubleshoot the flowmeter.
,
Table 7-6. Nominal resistance ranges for flowmeter circuits
Notes
• Temperature sensor value increases 0.38675 ohms per °C increase in temperature
• Nominal resistance values will vary 40% per 100°C. However, confirming an open coil or shortened coil is more important than any slight deviation from the resistance values presented below.
• Resistance across terminals 6 and 8 (right pickoff) should be within 10% of resistance across term inals 5 and 9 (left
pickoff).
• Resistance values depend on the sensor model and date of manufacture.
Circuit Wire colors
Drive coil Brown to red 1 to 2 CN1-Z2 to CN1-B2 8 to 2650
Left pickoff Green to white 5 to 9 CN1-Z8 to CN1-B8 15.9 to 300
Right pickoff Blue to gray 6 to 8 CN1-Z10 to CN1-B10 15.9 to 300
Temperature sensor Orange to viol et 3 to 7 CN1-B6 to CN 1- Z6 100 Ω at 0°C + 0.38675 Ω / °C
Lead length compensat or Yellow to violet 4 to 7 CN1-B4 to CN1-Z6 100 Ω at 0°C + 0.38675 Ω / °C
Sensor
terminals Transmitt er terminals Normal resistance ra nge
Ω
Ω
Ω
78
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 89

Troubleshooting
continued
Before You Begin Getting Started Mounting
7.7 Master reset
Use the switches on the transmitter control board to perform a master
reset (see
Figure 1-1
, page 2, for the location of the control board). A
master reset causes communication options to default to the setup used
by HART Communicators, causes all other configuration options to
return to their default values, and
requires complete characterization
and reconfiguration of the transmitter.
Table 7-7
, page 80, lists master reset defaults for characterization and
configuration variables.
CAUTION
All configuration data will be lost by performing a
master reset.
Before performing a master reset, phone the Mi cro Mot ion
Customer Service Department:
• In the U.S.A., phone 1-800-522-6277, 24 hours
• Outside the U.S.A., phone 303-530-8400, 24 hours
• In Europe, phone +31 (0) 318 549 443
• In Asia, phone 65-770-8155
To perform a master reset:
1. Note the position of switch 5.
2. Shut off power to the transmitter.
3. Set switches 1, 2, and 3 to the OFF position.
4. Set switches 4, 5, 6, and 10 to the ON position.
5. Restore power . Wait until the "Msg" indicator appears on the
transmitter display.
6. Set switches 4, 6, and 10 to the OFF position.
7. Return switch 5 to its original position.
8. Shut off power to the transmitter. Wait 30 seconds.
9. Restor e power.
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
Output Wiring Startup Troubleshooting
If switches are left in the ON position, another master reset will occur the
next time power to the transmitter is shut off and then restored.
an unintentional master reset,
position after performing a master reset.
After the user performs a master reset, the blinking "Msg" indicator
appears in the lower right corner of the display to indicate the presence
of a status message. If the user scrolls to the message screen, it reads
"NOT CONFIGURED", indicating the transmitter memory contains
default variables.
To characterize the sensor and configure the transmitter, use a HART
communicator, the ProLink program, or a Modbus host. For more
information, see
completed, the message display reads "Sensor OK *ERROR
CLEARED*", and the transmitter is ready for normal operation.
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
Section 2.2
T o avoid
set switches 4, 6, and 10 to the OFF
, page 4. After characterization is
79
Page 90

continued
Troubleshooting
Table 7-7. Default values after a master reset
Characterization variables
Default Default
Flow calibration factor 1.00005.13 Mass flow factor 1.0
Density Volume flow factor 1.0
Density A 0.0000 g/cc Density factor 1.0
K1 density constant 5000.00 Pressure
Density B 1.0000 g/cc Pressure polling No
K2 density constant 50000.00 Field device tag DP CELL!
Density temperature coeff i ci ent 4.44% p er 100° C Pressure input at 4 mA 0.00 psi
FD density constant 0.000 Pressure input at 20 mA 1000.00 psi
Temperature calibration factor 1.00000T0000.0 Pr ess ure correction for flow 0.00% per psi
Pressure correction for density 0.00 g/cc per psi
Flow calibration pressure 0.00 psi
Measurement units
Default Default
Mass flow unit g/sec Temperature unit °C
Volume flow unit l/sec Pressure unit psi
Density unit g/cc
Field device variables
Default Default
Mass flow cutoff 0.00 g/sec Low slug flow limit 0.0000 g/cc
Volume flow cutof f 0.0000 l/sec High slug flow limit 5.0000 g/cc
Flow direction Forward only Internal da m pi ng o n density 2.00 sec
Internal damp ing on flow 0.80 sec Internal da m pi ng on temperature 4.00 sec
Transmitter output variables
Default Default
Primary m A output variable Mass flow Frequency/pulse output variable Mass flow
Upper range value 160.00 g/ sec Frequenc y 10000.00 Hz
Lower range value –160.00 g/sec Rate 15000.00 g/sec
Added damping 0.00 sec Maximum pulse width 0.50 sec
Secondary mA output variable Temperature Control output Flow direction
Upper range value 450.00°C Slug duration 1.00 sec
Lower range value –240.00°C Polling address 0
Added damping 0.00 sec Burst mode Off
Device information
Default Default
Tran sm i t te r tag name
Description
Message
Date 01/
M. RESET
CONFIGURE XMTR
MASTER RESET
DATA DESTROYED
JAN
/1995
-
ALL
Sensor model Unknown
Sensor flow tube material Unknown
Sensor flange type Unknown
Sensor flow tube liner material None
Communication settings
Default with switch 5* set to STD COMM Default with switch 5* set to USER DEF
Stop bits and parity 1 stop bit, odd parity 1 stop bit, odd parity
Protocol, physical layer, baud rate HART Bell 202 on primary mA at 1200 baud,
HART on RS-485 at 1200 baud
and Modbus RTU on RS-485 at 9600 baud
* For informat i on a bout switches and switch settings, see
Section 2.3
, page 5.
80
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 91

Troubleshooting
continued
Before You Begin Getting Started Mounting
7.8 Additional information about troubleshooting
7.9 Customer service
For more information about troubleshooting the RFT9739 transmitter,
see any of the following instruction manuals or AMS on-line help:
Using the HART Communicator with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using ProLink Software with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
Using Modbus Protocol with Micro Motion Transmitters
•
For technical assistance, phone the Micro Motion Customer Service
Department:
• In the U.S.A., phone 1-800-522-6277, 24 hours
• Outside the U.S.A., phone 303-530-8400, 24 hours
• In Europe, phone +31 (0) 318 549 443
• In Asia, phone 65-770-8155
Pow er-Supply and
Sensor Wiring
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
Output Wiring Startup Troubleshooting
81
Page 92

82
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 93

Appendix
A RFT9739 Specifications
Performance specifications
Sensor model Mass flow accuracy*
ELITE liquid ±0.10% ± [(zero stability / flow rate) x 100]% of rate
gas ±0.50% ± [(zero stability / flow rate) x 100]% of rate
F-Series liquid ±0.20% ± [(zero stability / flow rate) x 100]% of rate
gas ±0.70% ± [(zero stability / flow rate) x 100]% of rate
D (except DH38), DT and DL liquid ±0.15% ± [(zero stability / flow rate) x 100]% of rate
gas ±0.65% ± [(zero stability / flow rate) x 100]% of rate
DH38 liquid ±0.15% ± [(zero stability / flow rate) x 100]% of rate
gas ±0.50% ± [(zero stability / flow rate) x 100]% of rate
Sensor model Mass flow repeatability
ELITE liquid ±0.05% ± [½(zero stability / flow rate) x 100]% of rate
gas ±0.25% ± [(zero stability / flow rate) x 100]% of rate
F-Series liquid ±0.10% ± [½(zero stability / flow rate) x 100]% of rate
gas ±0.35% ± [(zero stability / flow rate) x 100]% of rate
D (except DH38), DT and DL liquid ±0.05% ± [½(zero stability / flow rate) x 100]% of rate
gas ±0.30% ± [(zero stability / flow rate) x 100]% of rate
DH38 liquid ±0.05% ± [½(zero stability / flow rate) x 100]% of rate
gas ±0.25% ± [(zero stability / flow rate) x 100]% of rate
Density ac cu racy Density repeatability
Sensor model
ELITE (except CMF010P) liquid only ±0.0005 ±0.5 ±0.0002 ±0.2
ELITE CMF010P liquid only ±0.002 ±2.0 ±0.001 ±1.0
F-Series liquid only ±0.002 ±2.0 ±0.0 01 ±1.0
D6, D12, D25, D40, DH100, DH150 liquid only ±0.002 ±2.0 ±0.001 ±1.0
DH6, DH12, DH38 liquid only ±0.004 ±4.0 ±0.002 ±2.0
D65, DL65, DT65, D100, DT100,
D150, DT150, DH300
D300, D600, DL100, DL200 liquid only ±0.0005 ±0.5 ±0.002 ±2.0
Sensor model Temperat ure accuracy Temperature repeatability
All sensors ±1°C ± 0.5% of reading in °C ±0 .02°C
liquid only ±0.001 ±1.0 ±0.0005 ±0 .5
g/cc kg/m
*
3
g/cc kg/m
3
* Flow accuracy includes the combined effects of repeatability, linearity, and hysteresis. All specifications for liquids are based on
reference conditions of water at 68 to 77°F (20 to 25°C) and 15 to 30 psig (1 to 2 bar), unless otherwise noted. For values of zero
stability, refer to product speci f ic at ions for each sensor.
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
83
Page 94

RFT9739 Specifications
Functional specifications
Output signals Analog
continued
Two independently configured analog outputs, designated as primary
and secondary, can represent mass or volumetric flow rate, density,
temperature, event 1 or event 2. With a pressure transmitter, can also
provide indication for pressure. Internally powered, can be selected as
4-20 mA or 0-20 mA current outputs. Outputs cannot be changed from
active to passive. Galvanically isolated to ±50 VDC, 1000 ohm load limit.
Out-of-range capability: 0-22 mA on 0-20 mA output; 3.8-20.5 mA on
4-20 mA output.
Milliamp (mA) output rangeability
Flow
Maximum span determined by sensor specifications.
Range limit determined by sensor maximum rate.
Minimum recommended span (% of nominal flow range):
ELITE sensors 2.5%
F-Series sensors 10%
D, DT, and DL sensors 10%
D300 and D600 sensors 5%
High-pressure (DH) sensors 20% typical
Density
Range limit 0 to 5 g/cc (0 to 5000 kg/m³)
Minimum span 0.05 g/cc (50 kg/m³)
Temperature
Range limit –400 to 842°F (–240 to 450°C)
Minimum span 36°F (20°C)
Frequency
One frequency/pulse output can be configured to indicate mass flow
rate, volumetric flow rate, mass total (inventory), or volume total
(inventory), independent of analog outputs. Internally powered, 0-15 V
square wave, unloaded; 2.2 kohm impedance at 15 V, galvanically
isolated to ±50 VDC. In open collector configuration: sinking capability,
0.1 amps in "on" condition (0 volt level), 30 VDC compliance in "off"
condition. Signal can be scaled up to 10,000 Hz. Out-of-range capability
to 15,000 Hz. Programmable pulse width for low frequencies.
Dual-channel frequency
Approved for custody transfer applications, a dual-channel frequency
output, referred to as frequency A and frequency B. Phase shift between
channels is 90 degrees. Output derived from the primary frequency, and
represents the same process variable as the frequency/pulse output, but
with half the frequency. All specifications match frequency/pulse output
except: Signal can be scaled up to 5,000 Hz; out-of-range capability to
7500 Hz. The output complies with VDE/VDI 2188 when jumper JP1 is
installed.
84
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 95

RFT9739 Specifications
continued
Optocoupler output
The optocoupler is an externally powered output. Signal voltage: low
level 0-2 VDC, high level 16-30 VDC. Maximum signal current 0.01 amp.
Maximum capacitive load 150 nF at 10 kHz. Output is derived from the
primary frequency, and represents the same process variable as the
frequency/pulse output. The output complies with VDE/VDI 2188.
Control
One control output can represent flow direction, fault alarm, zero in
progress, event 1 or event 2. Internally powered, digital level, 0 or 15 V,
2.2 kohm pull-up, galvanically isolated to ±50 VDC. In open collector
configuration: sinking capability, 0.1 amps in "on" condition (0 volt lev el),
30 VDC compliance in "off" condition.
Communication
Switch allows selection of preset or user-defined settings.
• Default preset-settings: HART protocol over Bell 202, on the primary
mA output, 1200 baud; Modbus protocol in RTU mode, on the RS-485
output, 9600 baud; 1 stop bit, odd parity.
• Default user-defined settings: HART protocol, on the RS-485 output,
1200 baud, 1 stop bit, odd parity.
Bell 202 signal is superimposed on primary variable mA output, and
available for host system interface. F requency 1.2 and 2.2 kHz,
amplitude 0.8 V peak-to-peak, 1200 baud. Requires 250 to 1000 ohms
load resistance.
RS-485 signal is a ±5 V square wave referenced to transmitter ground.
Baud rates between 1200 baud and 38.4 kilobaud can be selected.
Additional outputs Sensor frequency
For use with Micro Motion peripheral devices, 8 V peak-to-peak at
sensor natural frequency, referenced to sensor ground, 10 kohm output
impedance.
Sensor temperature
For use with Micro Motion peripheral devices, 5 mV/°C, referenced to
signal ground, 10 kohm output impedance.
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
85
Page 96

RFT9739 Specifications
continued
API gravity
API gravity references to 60°F (15°C). Uses correlation based on API
equation 2540 for Generalized Petroleum Products.
Accuracy of corrected density calculation relative to API-2540 from 0 to
300°F:
Process fluid g/cc kg/m
3
°API
Diesel, heater, and fuel oils ±0.0005 ±0.5 ±0.2
Jet fuels, kerosenes, and solvents ±0.002 ±2.0 ±0.5
Crude oils and JP4 ±0.004 ±4.0 ±1.0
Lube oils ±0.01 ±10 ±2.0
Gasoline and naphthenes ±0.02 ±20 ±5.0
Minimum 4-20 mA span: 10°API
Standard volume
Outputs standard volume at 60°F or 15°C for Generalized Petroleum
Products when °API is selected as density unit of measure. Accuracy of
standard volume measurements depends on accuracies of mass flow
rate, density, temperature and temperature-corrected °API calculation,
and can be estimated using the root mean square method. Standard
volume accuracy of ±0.5% of rate is typically attainable for Generalized
Petroleum Products such as fuel oils, jet fuels, and kerosenes.
Pressure compensation
The analog input can accept a signal from a pressure transmitter for
pressure compensation of flow and density. Range, 0-25 mA. Can be
used to power independent pressure or differential pressure transmitter.
Voltage sourcing capability, 15 V. Input impedance, 100 ohms.
Low-flow cutoff
Flow values below the low-flow cutoff cause digital and frequency
outputs to default to zero flow levels. Each mA output may be configured
for an additional low-flow cutoff.
Slug-flow limits
Transmitter senses density outside limits. Flow output remains at last
measured value, for a programmed time of 0 to 60 seconds, before
defaulting to zero flow.
Damping
Wide range of programmed filter time constants for damping on flow,
density, and temperature. Additional damping may be applied to mA
outputs.
Fault indication
Faults can be indicated by user-selected downscale (0-2 mA, 0 Hz) or
upscale (22-24 mA, 15-19 kHz) output lev els. The control output can
also be configured to indicate a fault condition at 0 V.
86
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 97

RFT9739 Specifications
continued
Output testing
Output testing can be conducted with a HART Communicator, the
ProLink program, a Modbus host, or AMS software.
Current source
Transmitter can produce a user-specified current between 0 and 22 mA
on a 0-20 mA output, or between 2 and 22 mA on a 4-20 mA output.
Frequency source
Transmitter can produce a user-specified frequency between 0.1 and
15,000 Hz.
Display
Display is a 2-line, 16-character, alphanumeric liquid crystal display
(LCD). Using the transmitter’s scroll function, the user can view flow rate,
density, temperature, mass and volume totals and inventory levels, and
status messages on the LCD . A reset button allows the user to reset the
transmitter’s flow totalizers and communication parameters, and perform
the flowmeter zeroing procedure.
Power-supply options
and fuses
110/115 VAC ± 25%, 48 to 62 Hz, 10 watts typical, 15 watts maximum,
fused with UL/CSA 250mA/250V, time-lag, 5x20mm.
220/230 VAC ± 25%, 48 to 62 Hz, 10 watts typical, 15 watts maximum,
fused with UL/CSA 250mA/250V, time-lag, 5x20mm.
All AC-powered RFT9739 transmitters comply with low-voltage directive
73/23/EEC per IEC 1010-1 with Amendment 2.
12 to 30 VDC, 7 watts typical, 14 watts maximum, fused with UL/CSA
2A/125V, medium-lag, 5x20mm. At startup, transmitter power source
must provide a minimum of 2 amperes of short-term current at a
minimum of 12 volts at the transmitter's power input terminals.
Environmental limits Ambient temperature limits
Operating: 32 to 122°F (0 to 50°C)
Storage: –4 to 158°F (–20 to 70°C)
Humidity limits
Meets SAMA PMC 31.1-1980
Vibration limits
Meets SAMA PMC 31.1-1980, Condition 1
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
87
Page 98

RFT9739 Specifications
Environmental effects EMI effect
continued
Rack-mount RFT9739 transmitters feature enhanced EMI immunity and
the requirements of the EMC directive 89/336/EEC per EN 50081-1
(January 1992) and EN 50082-2 (March 1995) when operated at
nominal rated flow measurement range. Enhanced EMI immunity is
required for transmitters installed in the European Community after
1 January 1996.
For specific EMC effects within the EC, the Technical EMC file may be
reviewed at Fisher-Rosemount Veenendaal.
All RFT9739 transmitters meet the requirements of SAMA PMC 33.1
(October 1978), Class 1, A, B, C (0.6% span) at nominal flow rate. All
RFT9739 transmitters meet the recommendations of ANSI/IEEE C62.41
(1991) for surge and EFT.
To meet the above specifications, the transmitter must be installed with
an approved Micro Motion sensor, and the sensor cable must be either
doubly shielded with full contact glands, or installed in continuous, fully
bonded metallic conduit. The transmitter and sensor must be directly
connected to a low-impedance (less than 1 ohm) earth ground.
Transmitter outputs must be run in standard twisted-pair, shielded
instrument wire.
Hazardous area classifications
Ambient temperature effect on transmitter
On mA outputs: ±0.005% of span/°C
On temperature output: ±0.01°C/°C
On mA input: ±0.01% of span/°C
When properly installed with an approved sensor, the RFT9739 rackmount transmitter can be installed in the following areas:
UL
Non-hazardous locations. Provides nonincendive sensor outputs for use
in Class I, Div. 2, Groups A, B, C, and D; or intrinsically safe sensor
outputs for use in Class I, Div. 1, Groups C and D, or Class II, Groups E,
F, and G.
CSA
Non-hazardous locations. Connections to sensor are intrinsically safe for
use in Class I, Div. 1, Groups C, D, and Class II, Groups E, F, and G.
CENELEC
Safe area only. Connections to sensor are intrinsically safe in
[EEx ib ] IIC areas.
88
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
Page 99

RFT9739 Specifications
continued
Physical specifications
Housing
19-inch rack, European standard DIN 41494: 128 mm (3HE) high x
142 mm (28TE) wide x 231.9 mm deep.
Electrical connections
Two connectors per DIN 41612, type F. Choose either fast-on (wire-pin)
solder connectors (standard) or Y-shaped screw-terminal connectors
(optional). Sensor connectors and output connectors are not
interchangeable.
Weight
4.4 lb (2.0 kg)
RFT9739 Rack-Moun t Transmitter Instruction Manu al
89
Page 100

90
RFT9739 Rack-Mount Transmitter Instruct ion M anual
 Loading...
Loading...