
Introduction of engine OM 471 and
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
exhaust aftertreatment
Introduction into Service Manual

Mercedes>Benz Service
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Introduction of engine OM 471 and
exhaust aftertreatment
Technical status
01.09.2011
Daimler AG . Technical Information and Workshop Equipment(GSP/OI)
D$70546 Stuttgart

Information and copyright
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Product portfolio
You can also find comprehensive information about our
complete product portfolio on our Internet portal:
Link: http://aftersales.mercedes>benz.com
Questions and suggestions
If you have any questions or suggestions concerning this product, please write
to us.
E>Mail: customer.support@daimler.com
Telefax: +49>(0)18 05/0 10>79 78
or alternatively
Address: Daimler AG
GSP/OIS,
HPC R822, W002
D>70546 Stuttgart
(Germany)
©
2011 by Daimler AG
This document, including all its parts, is protected by copyright.
Any further processing or use requires the previous written consent of
Daimler AG, Department GSP/OIS, HPC R822, W002, D>70546 Stuttgart.
This applies in particular to reproduction, distribution, alteration, translation,
microfilming and storage and/or processing in electronic systems, including
databases and online services.
Image no. of title image: W00.01>1015>00
Order no. of this publication: 6517 1260 02 > HLI 000 000 02 82
09/11

SN00.00>W>0001>01HD Preface
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Preface
The intention behind this brochure is to introduce you to the new
6>cylinder inline diesel engine OM 471 along with the new
exhaust aftertreatment system (EATS).
This brochure is intended for the technical personnel entrusted
with the maintenance and repair of Mercedes>Benz trucks.
The content of this brochure is split up into:
•
as>built configuration descriptions
•
function descriptions
•
component descriptions
All the data listed in this brochure correspond with the technical
status as per September 2011.
Any changes or supplements hereto will be published in the
Workshop Information System (WIS) only.
Additional documents for the OM 471 engine and the EATS, such
as maintenance and repair instructions or wiring diagrams are
also available in the Workshop Information System (WIS).
Mercedes>Benz
W‘rth plant, GSP/TTM
September 2011
i
Introduction of engine OM 471 and exhaust aftertreatment > 09/2011 >
1
Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
SN00.00>W>0110HA
ENGINES 471.9
Overview of as>built configuration and function descriptions 2.8.11
Overview of new features
Engine OM!471
Technical data of diesel engine OM 471
As>built configuration
descriptions
Cylinder head cover, as>built configuration
Cylinder head, as>built configuration
Cylinder head gasket, as>built configuration
Crankcase as>built configuration
Connecting rod, as>built configuration
Piston, as>built configuration
Crankshaft, as>built configuration
Valve control; as>built configuration
Gear drive, as>built configuration
Camshaft, as>built configuration
Belt drive, as>built configuration
Page 10
Page 11
Page 12
Page 13
Page 18
Page 19
Page 21
Page 22
Page 23
Page 24
Page 29
Page 31
Page 32
Function descriptions
Crankcase ventilation system function
Charging, function
Engine management, function
Engine management, overall network
Engine management, behavior in the event
of malfunctions
Start procedure, function
Idle speed control, function
Working speed control, function
Driving, function
Engine shutoff procedure, function
Determination of the engine speed and
crankshaft angle, function
Determination of the compression stroke at
cylinder 1, function
Page 34
Page 35
Page 37
Page 39
Page 40
Page 42
Page 44
Page 46
Page 48
Page 50
Page 53
Page 54
2
Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Determination of coolant temperature,
function
Determination of air mass, function
Determination of the fuel temperature,
function
Function of the specified engine torque
calculation
Engine brake, function
Exhaust gas recirculation, function
Exhaust aftertreatment, function Vehicles with code (M5R) Engine version
EEV and vehicles with code (M5Y) Engine
version Euro V
Vehicles with code (M5Z) Engine version
Euro VI
Exhaust aftertreatment, overall network
Engine oil circuit, function
Engine oil circuit, diagram
Page 55
Page 56
Page 57
Page 58
Page 60
Page 66
Page 68
Page 73
Page 79
Page 80
Page 82
Coolant circuit, function
Coolant circuit, diagram
Engine cooling thermal management,
function
Engine cooling thermal management,
overall network
Fuel supply, function
Fuel low pressure circuit function Vehicles with code (M5R) Engine version
Fuel high pressure circuit function
i Only in vehicles with code (M7T)
Coolant pump, controlled.
EEV and vehicles with code (M5Y) Engine
version Euro V
Vehicles with code (M5Z) Engine version
Euro VI
Component descriptions
Central gateway control unit (CGW),
component description
A2
Page 83
Page 86
Page 87
Page 90
Page 91
Page 93
Page 96
Page 100
Page 101
i
Introduction of engine OM 471 and exhaust aftertreatment > 09/2011 >
3
Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Component description drive control (CPC)
control unit
Component description for engine
management (MCM) control unit
Electronic Brake Control control unit (EBS),
component description
Parameterizable special module (PSM)
control unit component description
Battery disconnect switch control unit,
component description
Radiator shutters, component description A54, A55
A3
A4
A10b, A10c
A22
A33
i Only in vehicles with one of the
following codes:
•
Code (E5T) ADR model class EX/II,
including AT
•
Code (E5U) ADR model class EX/III,
including EX/II and AT
•
Code (E5V) ADR model class FL,
including EX/II, EX/III and AT
•
Code (E5X) ADR model class AT
•
Code (E5Z) Accessories, ADR
•
Code (E9D) Preinstallation, for bipolar
battery disconnect switch
•
Code (E9E) ADR preinstallation, without
chassis shielding
Page 102
Page 103
Page 105
Page 106
Page 107
Page 109
i Only in vehicles with code (M7K)
Radiator shutters.
EATU output NOx sensor, component
description
Pump module, component description A58, M25
Exhaust aftertreatment (ACM) control unit,
component description
AdBlue metering device, component
description
EATU input NOx sensor, component
description
A57, A57 b1
Vehicles with code (M5R) Engine version
EEV and vehicles with code (M5Y) Engine
version Euro V
Vehicles with code (M5Z) Engine version
Euro VI
A60
Vehicles with code (M5R) Engine version
EEV and vehicles with code (M5Y) Engine
version Euro V
Vehicles with code (M5Z) Engine version
Euro VI
A67
A70, A70 b1
Vehicles with code (M5R) Engine version
EEV and vehicles with code (M5Y) Engine
version Euro V
Page 110
Page 112
Page 115
Page 117
Page 119
Page 121
Page 123
4
Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Auxiliary heater heating unit, component
description
Auxiliary heater coolant circulation pump,
component description
Travel and speed sensor, component
description
Exhaust pressure sensor upstream of diesel
oxidation catalytic converter, component
description
Exhaust pressure sensor downstream of
diesel particulate filter, component
description
Component description for accelerator
pedal sensor
Exhaust temperature sensor upstream of
diesel oxidation catalytic converter,
component description
Exhaust temperature sensor downstream of
diesel oxidation catalytic converter, top,
component description
Exhaust temperature sensor downstream of
diesel oxidation catalytic converter, bottom,
component description
Exhaust temperature sensor downstream of
diesel particulate filter, component
description
Exhaust temperature sensor upstream of
SCR catalytic converter, component
description
Exhaust temperature sensor downstream of
SCR catalytic converter, component
description
Vehicles with code (M5Z) Engine version
Euro VI
A901
i Only in vehicles with code (D6M)
Auxiliary water heater, cab or code (D6N)
Auxiliary water heater, cab and electric
motor.
A901 M2
i Only in vehicles with code (D6M)
Auxiliary water heater, cab or code (D6N)
Auxiliary water heater, cab and electric
motor.
B18
B37
i Only for vehicles with code (M5Z)
Engine version Euro VI.
B38
i Only for vehicles with code (M5Z)
Engine version Euro VI.
B44
B67
i Only for vehicles with code (M5Z)
Engine version Euro VI.
B68
i Only for vehicles with code (M5Z)
Engine version Euro VI.
B69
i Only for vehicles with code (M5Z)
Engine version Euro VI.
B70
i Only for vehicles with code (M5Z)
Engine version Euro VI.
B72
i Only in vehicles with code (M5R) Engine
version EEV and in vehicles with code
(M5Y) Engine version Euro V.
B73
Vehicles with code (M5R) Engine version
EEV and vehicles with code (M5Y) Engine
version Euro V
Page 125
Page 128
Page 130
Page 131
Page 132
Page 133
Page 134
Page 135
Page 136
Page 137
Page 138
Page 139
Page 140
i
Introduction of engine OM 471 and exhaust aftertreatment > 09/2011 >
5
Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
AdBlue fill level sensor/temperature sensor,
component description
Coolant pressure control sensor, component
description
Component description for crankshaft
position sensor
Component description for camshaft
position sensor
Component description for fuel
temperature sensor
Oil pressure sensor, description of
components
Component description for engine oil fill
level sensor
Component description for exhaust coolant
temperature sensor
Component description for intake coolant
temperature sensor
Charge air pressure and temperature sensor
in charge air pipe, component description
Turbine wheel rpm sensor, component
description
Component description for temperature
sensor downstream of air filter
Charge air temperature sensor in charge air
housing, component description
Exhaust gas recirculation differential
pressure sensor, component description
Component description for rail pressure
sensor
Diesel fuel metering device, component
description
Fuel filter module pressure sensor,
component description
Vehicles with code (M5Z) Engine version
Euro VI
B74
B87
i Only in vehicles with code (B3H)
Secondary water retarder.
B600
B601
B602
B604
B605
B606
B607
B608
B610
i Only for vehicles with code (M5Z)
Engine version Euro VI.
B611
i Only for vehicles with code (M5Z)
Engine version Euro VI.
B617
B621
B622
B625, B626, Y628, Y629
i Only for vehicles with code (M5Z)
Engine version Euro VI.
B638
Page 141
Page 142
Page 144
Page 145
Page 146
Page 147
Page 148
Page 149
Page 150
Page 151
Page 152
Page 153
Page 154
Page 155
Page 156
Page 157
Page 158
Page 159
6
Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Component description for coolant pump B640, Y631
i Only in vehicles with code (M7T)
Coolant pump, controlled.
No component description was created for
vehicles with a rigid coolant pump.
Residual heat pump, component description M20
i Only in vehicles with code (D6I)
Residual heat utilization.
Tachograph (TCO) component description P1
Electronic ignition lock (EIS), component
description
EMERGENCY OFF switch, component
description
EMERGENCY OFF switch frame, component
description
Engine start and engine stop button,
component description
Heating shutoff valve, component
description
Coolant pressure control solenoid valve,
component description
S1
S30
i Only in vehicles with one of the
following codes:
•
Code (E5T) ADR model class EX/II,
including AT
•
Code (E5U) ADR model class EX/III,
including EX/II and AT
•
Code (E5V) ADR model class FL,
including EX/II, EX/III and AT
•
Code (E5X) ADR model class AT
•
Code (E5Z) Accessories, ADR
•
Code (E9D) Preinstallation, for bipolar
battery disconnect switch
•
Code (E9E) ADR preinstallation, without
chassis shielding
S31
i Only in vehicles with one of the
following codes:
•
Code (E5T) ADR model class EX/II,
including AT
•
Code (E5U) ADR model class EX/III,
including EX/II and AT
•
Code (E5V) ADR model class FL,
including EX/II, EX/III and AT
•
Code (E5X) ADR model class AT
•
Code (E5Z) Accessories, ADR
•
Code (E9D) Preinstallation, for bipolar
battery disconnect switch
•
Code (E9E) ADR preinstallation, without
chassis shielding
S600
Y49
Y53
i Only in vehicles with code (B3H)
Secondary water retarder.
Page 160
Page 162
Page 163
Page 164
Page 165
Page 166
Page 167
Page 168
Page 169
i
Introduction of engine OM 471 and exhaust aftertreatment > 09/2011 >
7
Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Component description for fuel injectors Y608. to Y613
Component description for the
electromagnetic viscous coupling
Component description for exhaust gas
recirculation controller
Component description for engine brake
solenoid valve
AdBlue“ heater coolant solenoid valve,
component description
Component description for boost pressure
regulator
Component description for quantity control
valve
Oil separator component description
Component description for fuel system high
pressure pump
Pressure limiting valve, component
description
Component description for turbocharger
Component description for exhaust gas
recirculation cooler
Component description for AdBlue tank
Component description for oil pump
Oil/coolant module, component description
Oil thermostat, component description
Component description for oil/water heat
exchanger
Component description for coolant
thermostat
Retarder, component description i Only in vehicles with code (B3H)
Component description for fuel pump
Component description for fuel cooler
Component description for fuel filter
module
Diesel oxidation catalytic converter,
component description
Component description for SCR catalytic
converter
Exhaust aftertreatment unit, component
description
Y616, Y616 b1
Y621
Y624, Y625
Y627
Y636
Y642
Secondary water retarder.
i Only for vehicles with code (M5Z)
Engine version Euro VI.
Vehicles with code (M5R) Engine version
EEV and vehicles with code (M5Y) Engine
version Euro V
Vehicles with code (M5Z) Engine version
Euro VI
Vehicles with code (M5R) Engine version
EEV and vehicles with code (M5Y) Engine
version Euro V
Page 170
Page 174
Page 176
Page 178
Page 180
Page 181
Page 182
Page 183
Page 184
Page 185
Page 186
Page 187
Page 188
Page 189
Page 191
Page 193
Page 194
Page 195
Page 197
Page 203
Page 204
Page 205
Page 208
Page 209
Page 211
Page 213
8
Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Diesel particulate filter of exhaust
aftertreatment unit, component description
Nozzle unit for DPF regeneration,
component description
Heating system heat exchanger, component
description
Vehicles with code (M5Z) Engine version
Euro VI
i Only for vehicles with code (M5Z)
Engine version Euro VI.
i Only for vehicles with code (M5Z)
Engine version Euro VI.
Page 215
Page 218
Page 220
Page 221
i
Introduction of engine OM 471 and exhaust aftertreatment > 09/2011 >
9
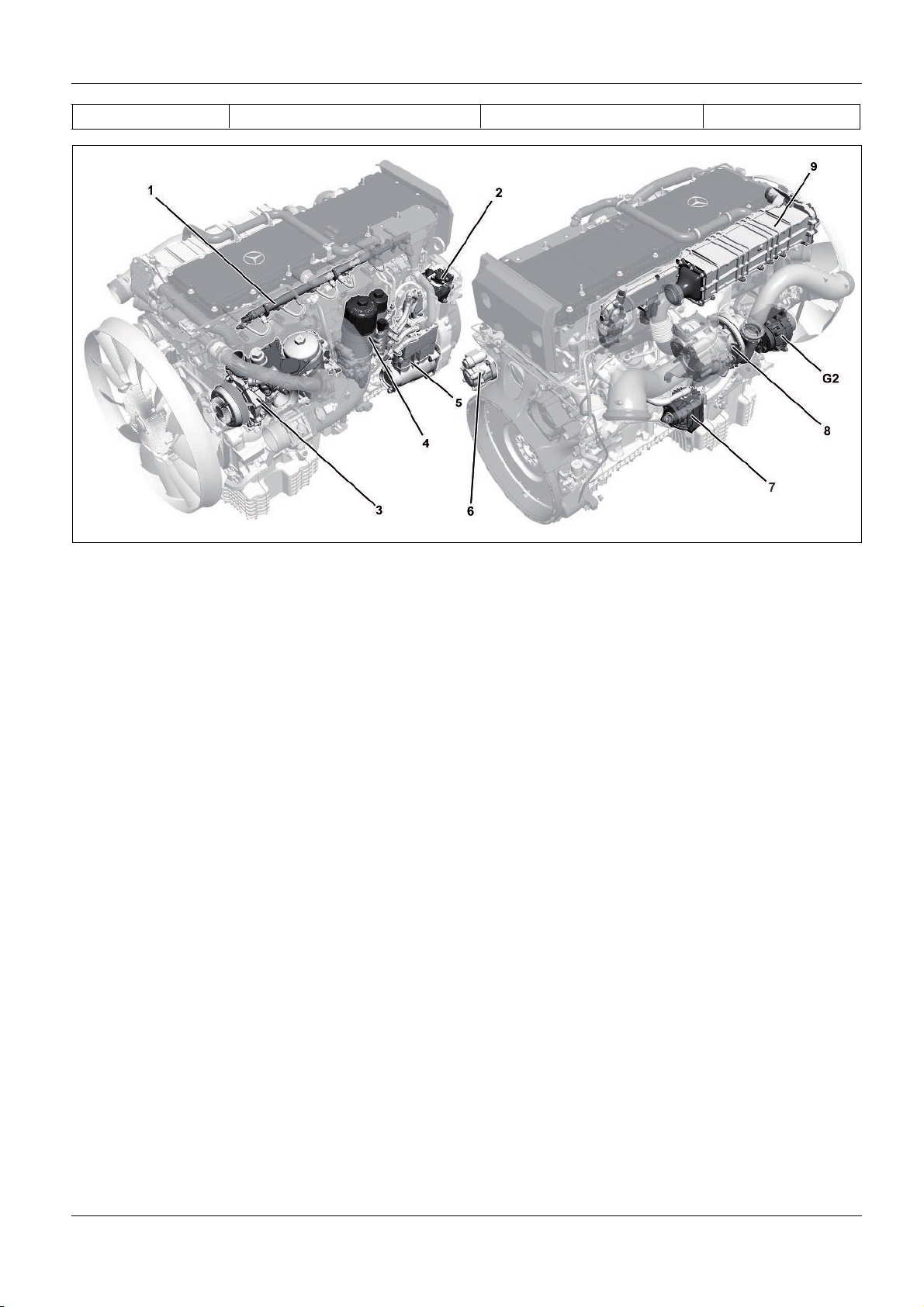
Engine
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
SN00.00>W>0002>04H Engine OM!471
1 Amplified Pressure Common>Rail
System (APCRS)
2 Diesel fuel>metering device (for
regeneration of diesel particulate
filter (DPF))
3 Oil/coolant module
The engine OM 471 is the first 6>cylinder inline engine with two
overhead camshafts to be used in a Mercedes>Benz commercial
vehicle.
Both camshafts are driven by a gear drive which is located at the
output side of the engine. The position of this drive gear makes a
major contribution to reducing noise emission.
The extremely compact design of the engine is based on the
optimized cylinder liner concept in which the overhead seat is
located at the bottom in the crankcase > this design measure
allows the gap between the cylinders to be reduced considerably.
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
The positive properties of the new engine have been made
possible by a variety of new technical developments:
•
The new injection system, the amplified pressure common
rail system (APCRS) (1), is the first common rail system to be
used in Mercedes>Benz commercial vehicles that minimizes
the quantity of fuel required for combustion. The advantage
of this system lies in the fact that the rail and high>pressure
lines have a relatively low pressure of 900 bar, and the fuel
pressure required for injecting into the injector is generated,
which has a particularly positive effect on material loads and
therefore on component longevity.
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
4 Fuel filter module
5 Compressor
6 Power steering pump
7 Oil separator for crankcase
ventilation system
8 Turbocharger
W01.10>1090>09
9 Cooled and regulated exhaust gas
recirculation (AGR)
G2 Generator
The OM 471 engine is available in four output stages between 310
and 375 kW.
Advantages of new 6>cylinder inline engine:
•
Lower fuel consumption in relation to high output
•
Smooth running characteristics, whereby only four
counterweights are required on the crankshaft
•
Excellent application capability for the various emissions
standards
•
Implementation of particularly high combustion pressures of
up to 230 bar
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
•
The completely redesigned engine brake system has an even
higher braking power.
•
The cooled and regulated exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) (9)
and the diesel particulate filter (DPF) as well as the modified
oil separator of the crankcase ventilation system (7) ensure
that tomorrow's emissions regulations can also be met.
•
The regulated coolant pump installed in the oil/coolant
module (3), which has already been installed in Actros
vehicles, also contributes to fuel economy.
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
i With each maintenance and repair work to the engine as well
as to the ancillary assemblies and detachable parts comes the
danger of property damage caused by soiling and foreign bodies.
The high pressure diesel injection system, the intake system and
the oil circuit, in particular, are at risk here.
10
To avoid any damage, when conducting repair work not only the
specified special tools must be used along with observance of the
WIS repair instructions, but in addition to this special care must be
given to cleanliness at the workbay.
Additional information is available in the document
AH00.00>N>5000>01H.
Technical data
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
SN00.00>W>0002>05H Technical data of diesel engine OM 471
General information
OM 471
Displacement (l) 12,8
No. of cylinders 6 (in line)
Valve control DOHC
Valve number for each cylinder
(intake/exhaust)
Idle speed (rpm) 560
Compression ratio (f) 17,3
Stroke (mm) 156
Stroke:bore ratio 1,18
Weight (kg) approx. 1200
Power categories
Output (kW) 310 330 350 375
Output (horsepower) 421 449 476 510
Torque (Nm) 2100 2200 2300 2500
2/2
OM 471 with
code M3A
OM 471 with
code M3B
OM 471 with
code M3C
OM 471 with
code M3D
Piston
OM 471
Diameter (mm) 132
Overall height (mm) 113
Compression height (mm) 75
Shank length 71,65
Piston pin
OM 471
Inside diameter (mm) 23.5
Outside diameter (mm) 58
Length (mm) 88
Fuel system
OM 471
Rail pressure, max. (bar) 900
Crankshaft bearing
OM 471
Diameter (mm) 114
Width (mm) 36
Connecting rod
OM 471
Length (mm) 268
Connecting rod bearing
OM 471
Diameter (mm) 95
Width (mm) 36,4
Crankcase, cylinder liner (wet)
OM 471
Cylinder diameter (mm) 132
Cylinder distance (mm) 165
i
Introduction of engine OM 471 and exhaust aftertreatment > 09/2011 >
11

As>built configurations
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
GF01.20>W>0801H
ENGINES 471.9
1 Cylinder head cover
2 Prefilter
3 Elastomer element
4 Elastomer seal
x Direction of travel
Cylinder head cover, as>built configuration 1.7.11
The cylinder head cover (1) consists of plastic and, on the one
hand, prevents ingress of water and foreign objects into the valve
assembly. On the other hand it seals the camshaft case to the
outside using an elastomer seal (4) and prevents escape of the
engine oil used to lubricate the valve assembly.
A prefilter (2) is integrated in the cylinder head cover (1). The
prefilter (2) ensures that the engine oil which is swirled by the
valve assembly and mixes with the blow>by gases is roughly
separated before the blow>by gases are passed on to the oil
separator for the crankcase ventilation system.
W01.20>1046>76
For acoustic decoupling of the cylinder head cover (1) an
elastomer element (3) is inserted in all through holes which serve
to attach the cylinder head cover (1) to the camshaft case. The
elastomer elements (3) reduce noise emissions and possible
damage which can occur due to vibrations.
12

As>built configurations
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
GF01.30>W>0800H
Cylinder head, as>built configuration 1.7.11
ENGINES 471.9
The engine OM 471 has a one>piece cylinder head.
There are two intake valves and two exhaust valves for each
cylinder in the cylinder head. The narrow engine design means
that overall a symmetrical location of the valves can ensue. This
symmetrical valve pattern is optimum for the combustion.
Tightening procedure for cylinder head
bolts
1 > 38 Cylinder head bolt (M15¥2) 40 Bolt (M10)39 Bolt (M10)
Cylinder head bolts
In order to ensure that the correct bolts are used when installing
the cylinder head, on each bolt head there is an embossing which
provides information on the thread strength of the respective
cylinder head bolt.
The cylinder head bolts have the M15 2 thread and therefore have
the embossing "15".
All the cylinder head bolts must be tightened in four stages as per
a set tightening pattern. The tightening torques and the
tightening angle can be obtained from the repair instructions.
W01.30>1105>78
As the cylinder head bolts elongate due to assembly, the shank
length for each bolt which has already been used once must be
measured before it is reassembled.
The relevant bolt must be replaced when the permissible shank
length is exceeded.
i The cylinder head bolts are no longer assembled when the
valve assembly is mounted. The valve assembly must be removed
before dismantling the cylinder head.
i
Introduction of engine OM 471 and exhaust aftertreatment > 09/2011 >
13
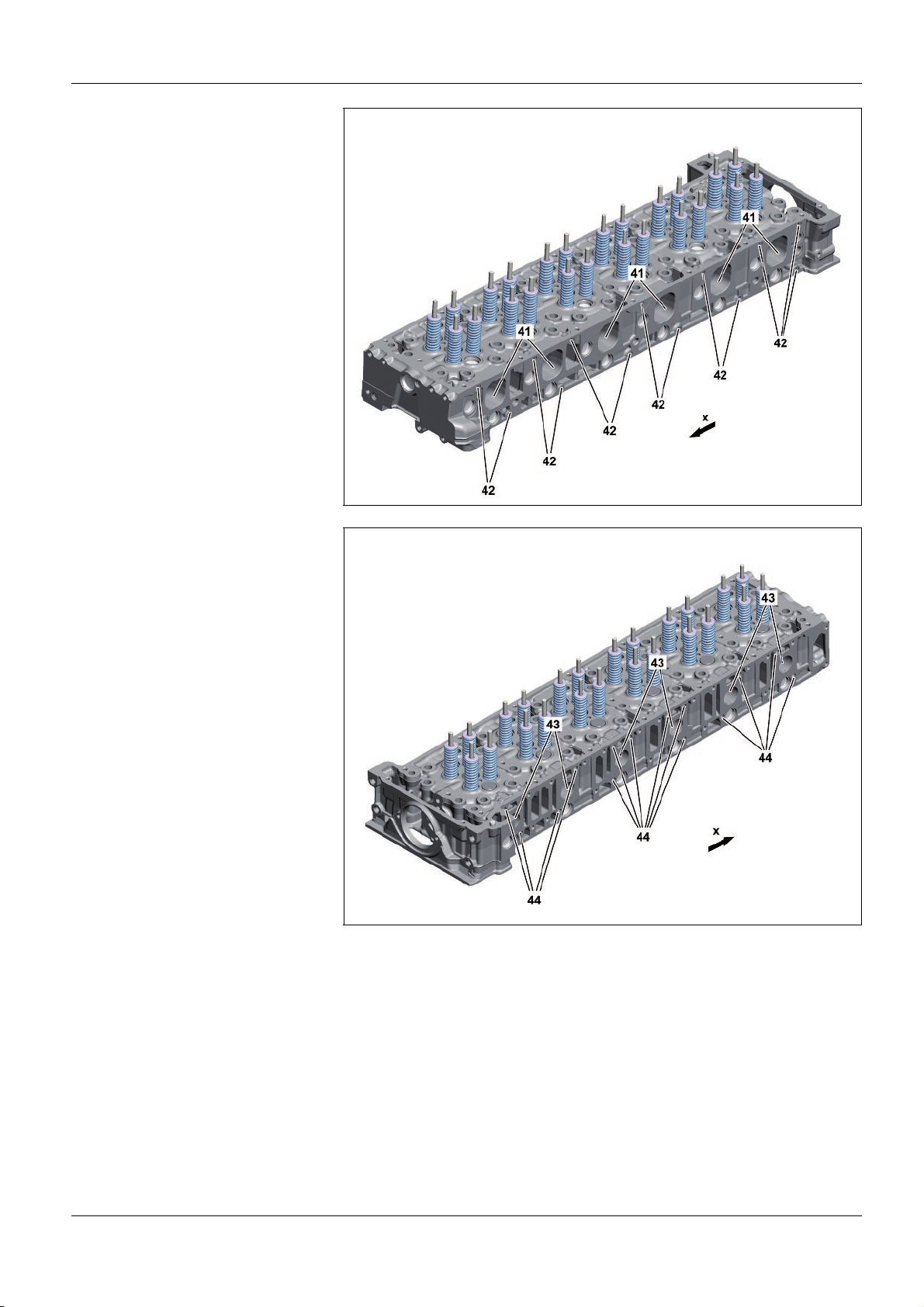
As>built configurations
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
41 Intake ports
42 Threaded holes for the charge air
manifold attachment
x Direction of travel
43 Exhaust ducts
44 Threaded holes for the charge air
manifold attachment
W01.30>1122>76
x Direction of travel
W01.30>1123>76
14
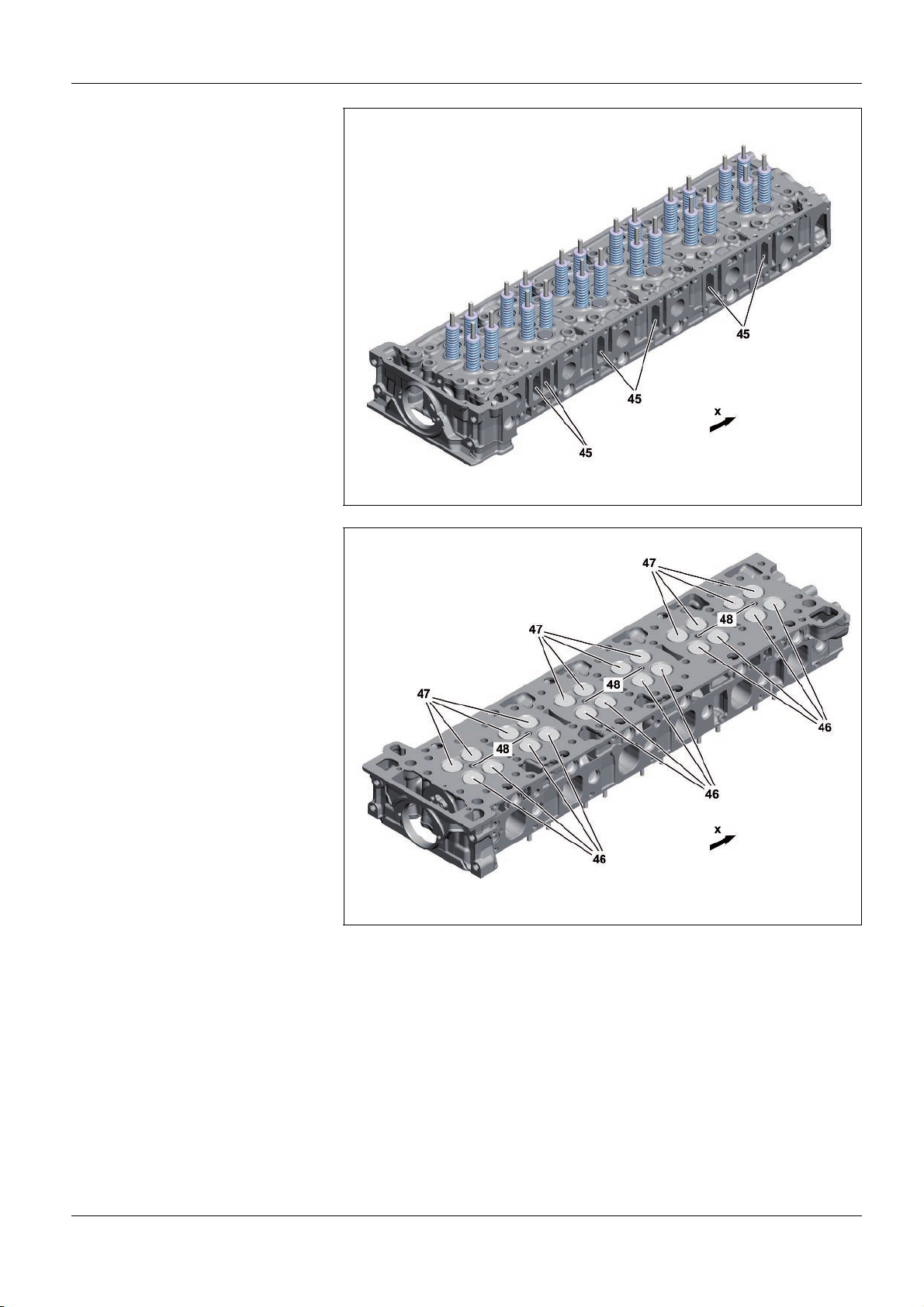
45 Connectors for coolant collector block
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
x Direction of travel
46 Inlet valves
47 Exhaust valves
48 Bores for the fuel injectors
As>built configurations
W01.30>1124>76
x Direction of travel
W01.30>1125>76
i
Introduction of engine OM 471 and exhaust aftertreatment > 09/2011 >
15
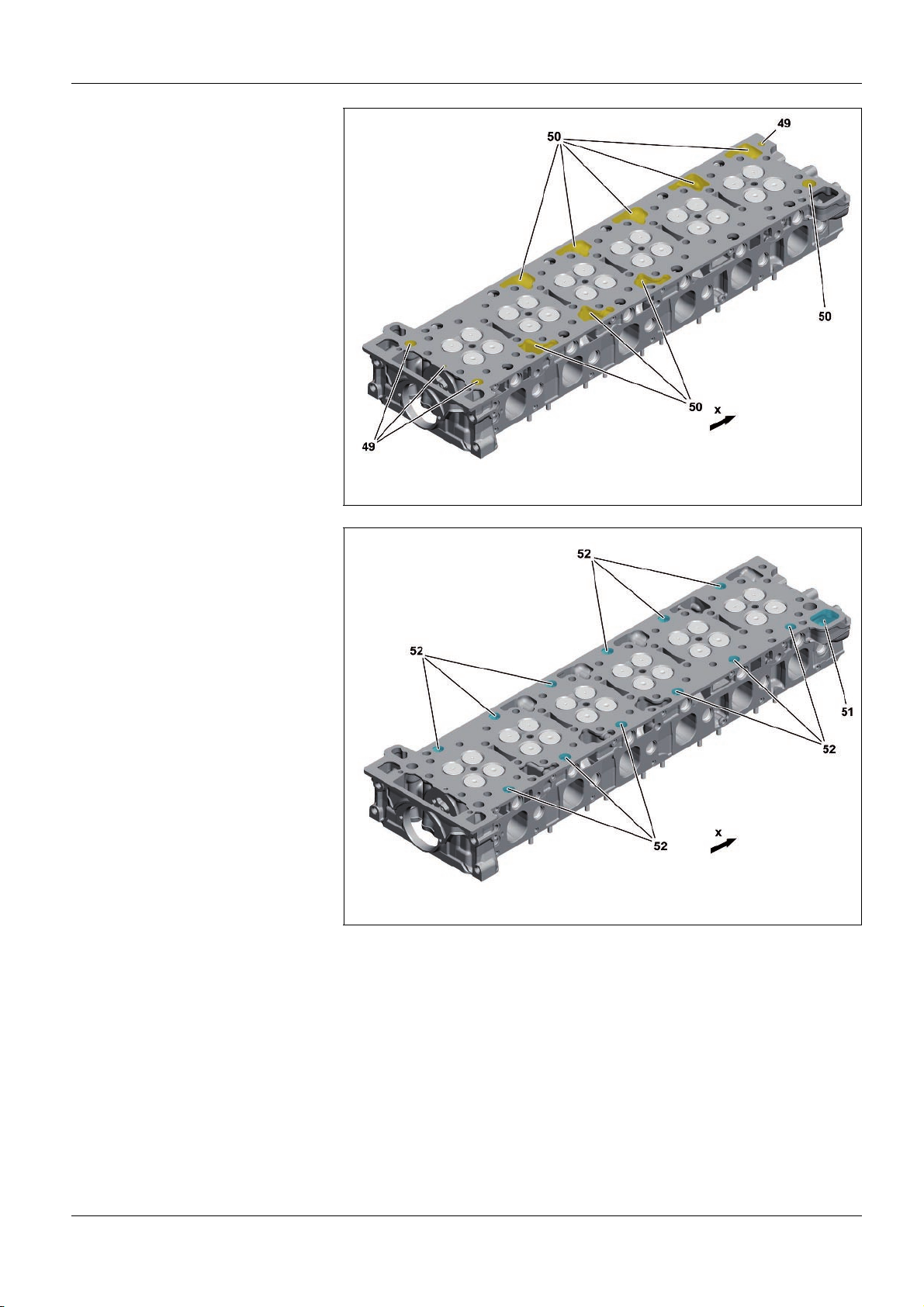
As>built configurations
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
49 OiI overflow holes from cylinder
crankcase to cylinder head
50 Oil return flow openings or oil return
flow holes from cylinder head to
cylinder crankcase
x Direction of travel
51 Coolant short>circuit channel from
cylinder head to cylinder crankcase
52 Coolant overflow holes from cylinder
crankcase to cylinder head
W01.30>1126>76
x Direction of travel
W01.30>1127>76
16
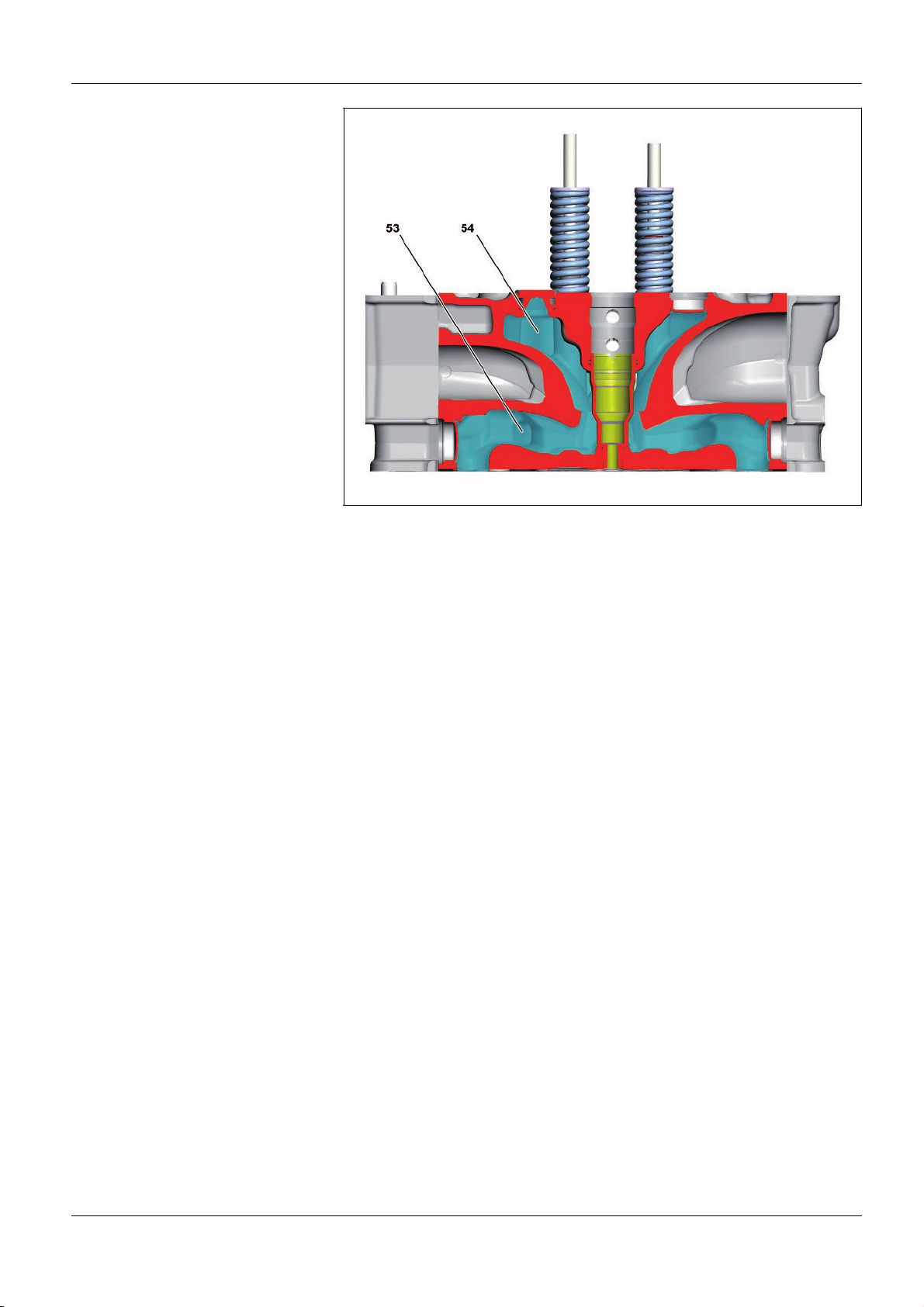
Cooling levers
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
53 Lower cooling level
54 Upper cooling level
Cooling
The cylinder head has a divided coolant jacket. This means that
the coolant, after it has flushed around the cylinders, flows into
the cylinder head on the inlet side and on the exhaust side. The
advantage is that the coolant first flushes around the fuel
injectors and valve seat rings in the lower cooling level (53) of the
cylinder head.
As>built configurations
W01.30>1128>76
After this the coolant flows into the upper cooling level (54) of the
cylinder head and cools the valve guides. The coolant is collected
there and directed outwards.
i
Introduction of engine OM 471 and exhaust aftertreatment > 09/2011 >
17
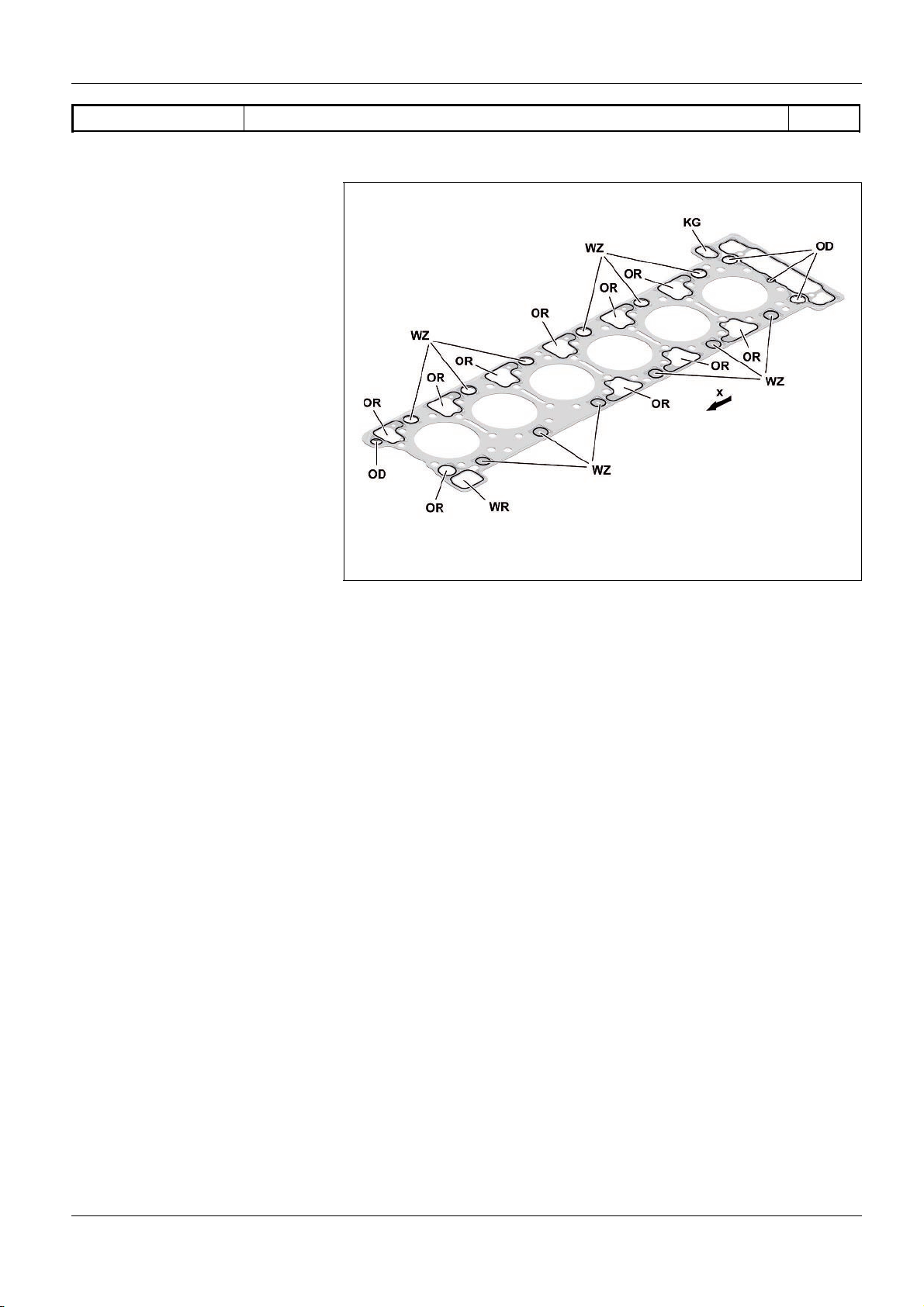
As>built configurations
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
GF01.30>W>0801H
Cylinder head gasket, as>built configuration 1.7.11
ENGINES 471.9
Upper side of the cylinder head seal
OD Engine oil feed openings
OR Engine oil return opening
WR Coolant bypass duct opening
WZ Coolant feed opening
KG Opening for the blow>by duct to the
crankcase ventilation system
x Direction of travel
The cylinder head gasket consists of a number of layers of stainless
steel.
The cylinder head gasket at the engine oil feed openings (OD) and
at the coolant feed opening (WZ) is fitted with raised elastomer
elements through which the seal between the cylinder head and
the cylinder crankcase is improved.
W01.30>1120>06
18
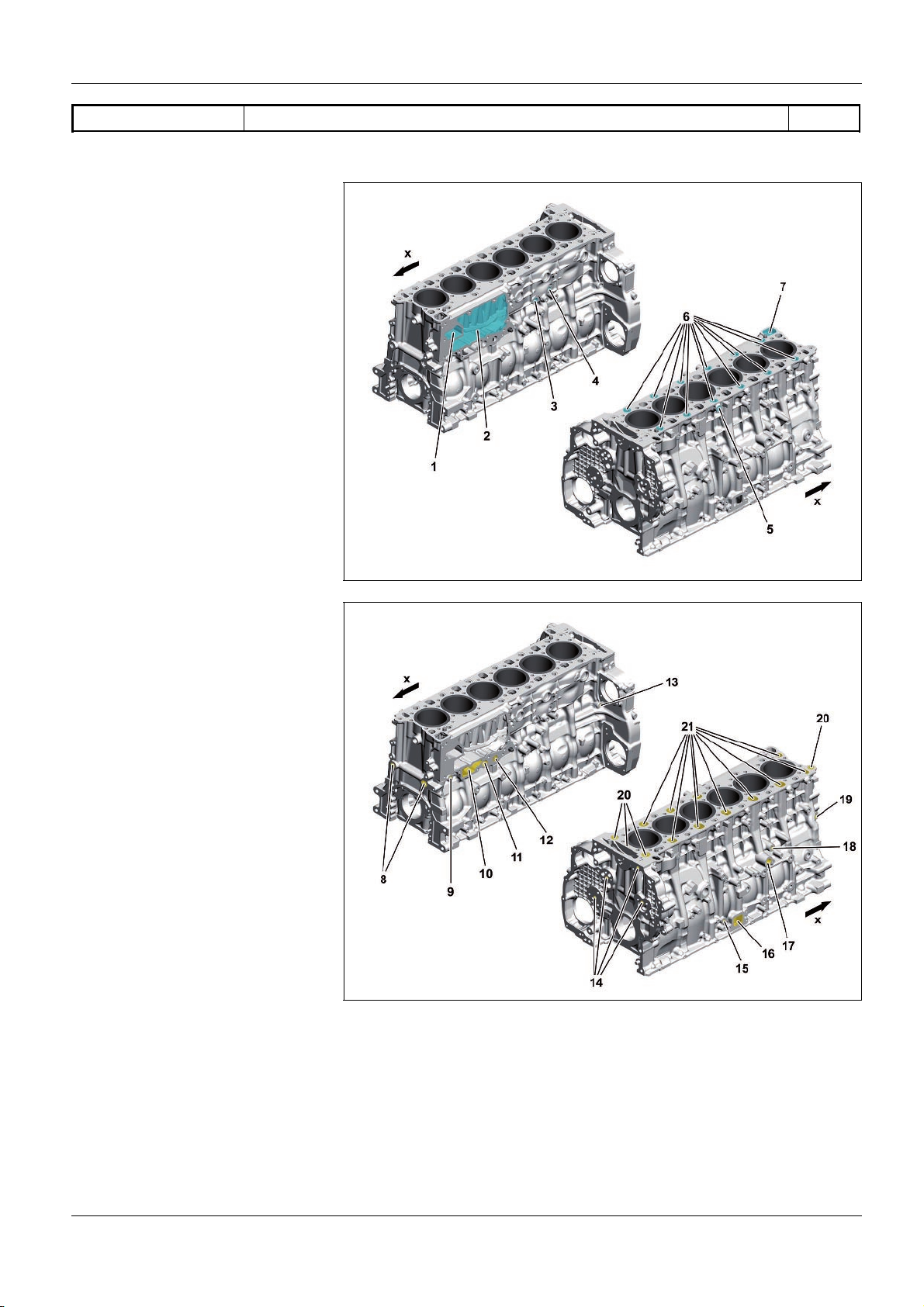
As>built configurations
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
GF01.40>W>0802H
Crankcase as>built configuration 1.7.11
ENGINES 471.9
Crankcase from above, shown with coolant
ducts
1 Coolant bypass duct
2 Recess for oil>water heat exchanger
3 Coolant connection for fuel cooler
4 Coolant connection for compressor
5 Coolant connection for exhaust gas
recirculation positioner
6 Coolant overflow holes to the cylinder
head
7 Coolant return from the cylinder head
x Direction of travel
Crankcase from above, shown with oil
ducts
8 Oil hole closed longitudinally
9 Connection for the oil pressure sensor
10 Oil return duct from oil filter (for
changing the oil filter)
11 Oil feed from oil/coolant module
(from oil filter) to crankcase
12 Oil feed from crankcase (from the oil
pump) to
oil/coolant module
13 Oil hole closed off laterally
14 Bores for oil supply to the gear drive
15 Connection for oil supply of the
centrifuge on the oil separator to the
crankcase ventilation system
16 Oil return duct from oil separator for
crankcase ventilation system
17 Oil return duct from turbocharger
18 Connection for oil supply to the
turbocharger
19 Oil hole closed off laterally
W01.40>1144>76
W01.40>1145>76
20 OiI overflow holes to the cylinder
head
21 Oil return ducts from cylinder head
x Direction of travel
i
Introduction of engine OM 471 and exhaust aftertreatment > 09/2011 >
19
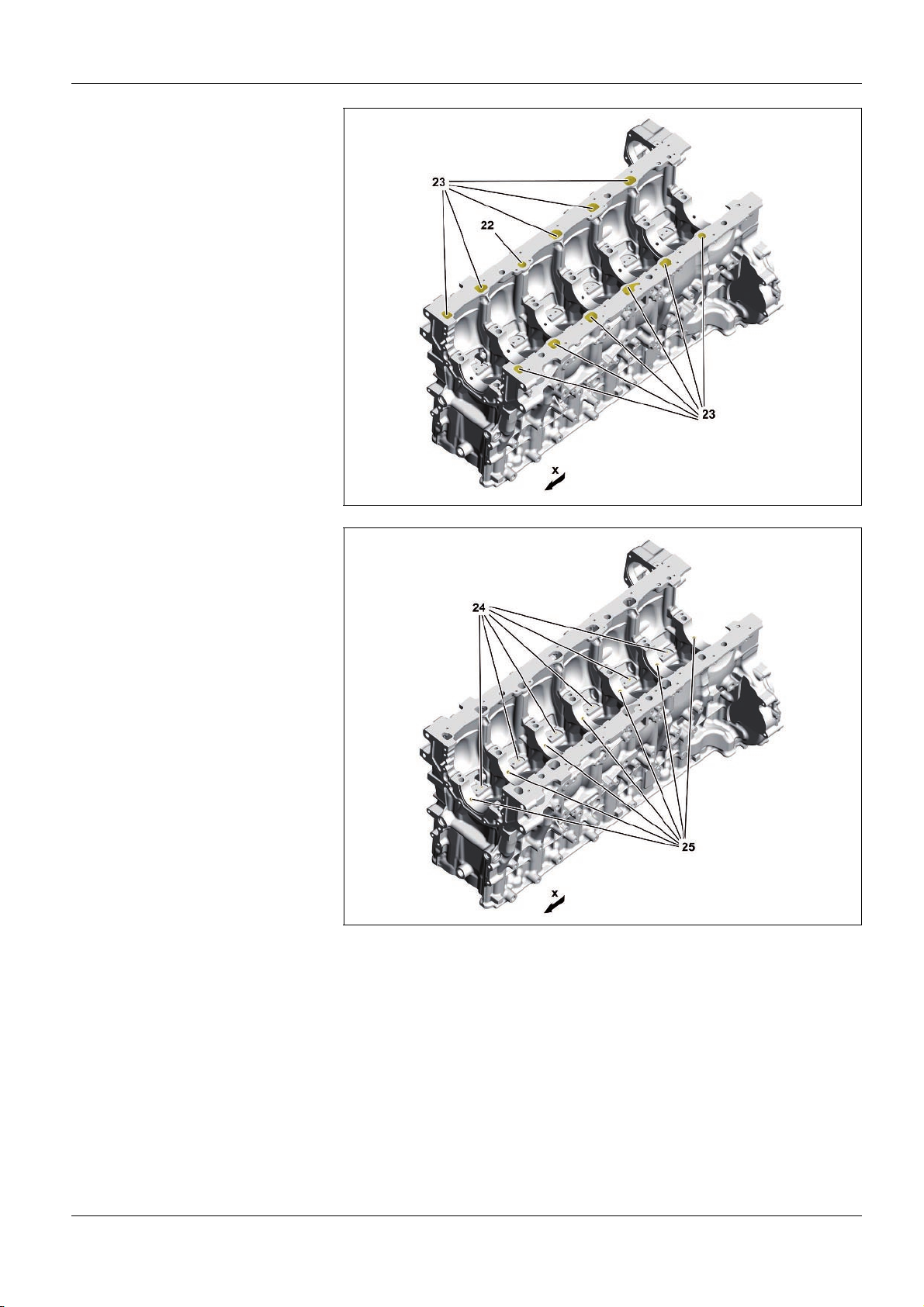
As>built configurations
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Crankcase from below, shown with oil
ducts
22 Oil return duct to oil/coolant module
23 Oil return ducts to oil pan
x Direction of travel
Crankcase from below, shown with oil
ducts
24 Bores for oil supply to the oil spray
nozzles
25 Bores for oil supply to the main
bearing, crankshaft and connecting
rod bearing
W01.40>1146>76
x Direction of travel
The crankcase consists of cast iron and is characterized by the
following features:
f a high rigidity and low noise emissions due to the vertical
and horizontal reinforcements, as well as due to the design
form of the oil return ducts
f a compact design due to the low distance from the cylinder
The crankcase also has 1.5 mm recesses at the sealing surface to
the cylinder head for all coolant overflow holes to the cylinder
head (6) and for all oil overflow holes to the cylinder head (20).
These serve to receive the respective elastomer elements in the
cylinder head gasket.
W01.40>1147>76
The following major assemblies and components are located on
the crankcase:
Right>hand side
f Turbocharger
f Starter
f Oil separator for crankcase ventilation system
Left>hand side
f Oil/coolant module
f Engine management (MCM) control unit
f Fuel filter module
f Fuel high pressure pump
f Compressor, power steering pump
20

As>built configurations
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
GF03.10>W>0800H
Connecting rod, as>built configuration 1.7.11
ENGINES 471.9
1 Connecting rod
2 Connecting rod small end (small)
3 Connecting rod bushing
4 Connecting>rod shank
5 Connecting rod big end
6 Connecting rod bearing shells
7 Connecting rod bearing cap
8 Stretch bolt
The connecting rods are forged in steel and are characterized by
their high strength.
The connecting point between the connecting rod (1) and the
connecting rod bearing cap (7) is cracked. This has the advantages,
amongst other things, that one has no offset after screwing
together both parts and the connecting rod bearing cap (7)
cannot slip.
A connecting rod bushing (3) is pressed into a small connecting
rod small end (2).
W03.10>1119>76
i
Introduction of engine OM 471 and exhaust aftertreatment > 09/2011 >
21
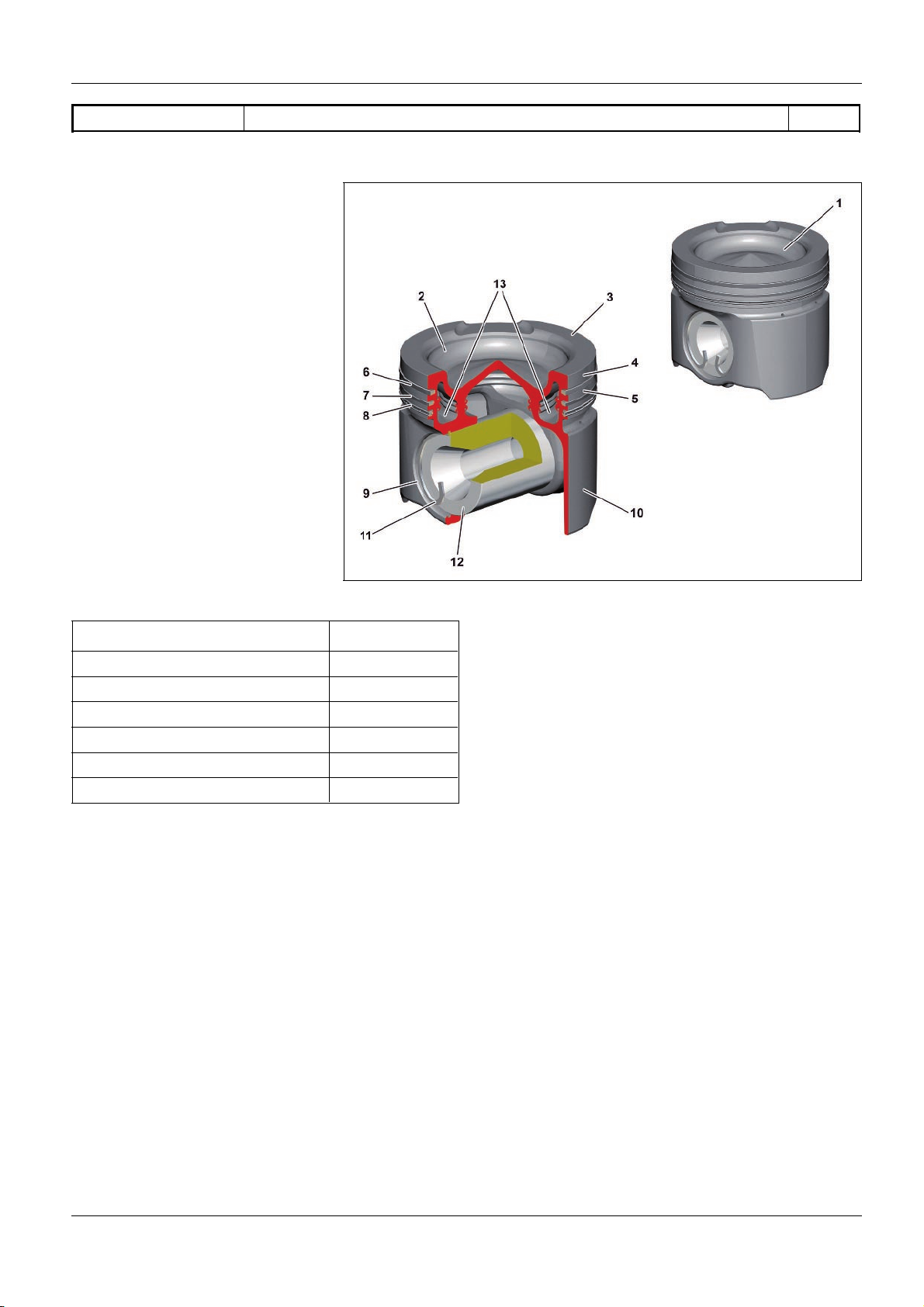
As>built configurations
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
GF03.10>W>0801H
ENGINE 471.9
1 Piston
2 Combustion recess
3 Piston crown
4 Top land
5 Piston ring zone
6 1st piston ring
7 2nd piston ring
8 Oil scraper ring
9 Bolt eye
10 Piston skirt
11 Piston bolt circlip
12 Piston pin
13 Cooling duct
Piston, as>built configuration 2.8.11
Feature
OM 471
Version Two piece
Material Steel
Weight (with spring steel sheet) 3,339 KG
Piston diameter 132 mm
Bolt diameter 58 mm
Surface friction optimized
Piston (1)
The piston (1) consists of a forged upper section and a forged
lower section, which are connected to each other by means of a
friction weld.
Piston crown (3)
The piston crown (3) is fitted with a combustion recess (2).
Through the combustion recess (2) the clearance volume is
partially transferred into the piston (1).
Top land (4)
The top land (4) protects the 1st piston ring (6) against excessively
heating during the combustion process.
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
W03.10>1124>76
Piston ring zone (5)
The 1st piston ring (6), the 2nd piston ring (7) and the oil scraper
ring (8) are located in the piston ring zone (5).
The 1st piston ring (6), the 2nd piston ring (7) take on the task of
fine sealing to the crankcase.
The oil scraper ring (8) wipes off excess oil on the cylinder wall and
leads the oil back into the oil pan.
Piston skirt (10)
The piston skirt (10) serves to guide the piston (1) into the cylinder
liner. It transfers the lateral forces to the cylinder wall.
Located in the piston skirt (10) is the bolt eye (9) which supports
the piston pin (12).
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
22
As>built configurations
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Cooling
The piston (1) is cooled via an oil spray nozzle for each cylinder
located in the crankcase.
The oil spray nozzle continuously sprays engine oil into an
injection opening in the cooling duct (13). Due to the coaxial spray
direction of the oil spray nozzle the greatest possible throughput
of engine oil is achieved in the cooling duct (13) and thus cooling
of the piston is improved significantly.
One further opening which is located on the opposite side serves
as a drain.
Additional bores in the cooling duct (13) serve to achieve better
lubrication of the piston pin (12) and the connecting rod bearing
bushing.
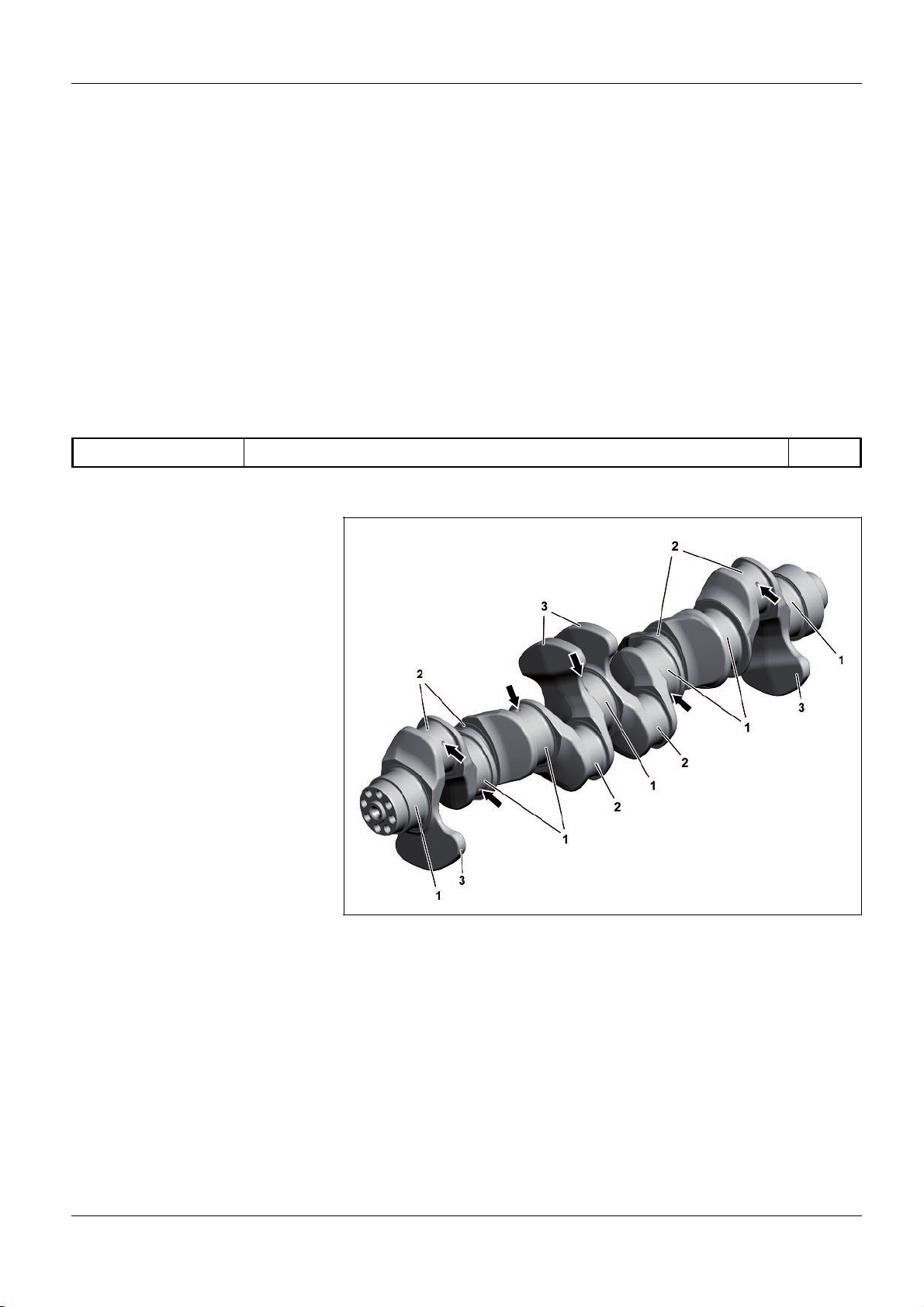
GF03.20>W>0800H
Crankshaft, as>built configuration 2.8.11
ENGINE 471.9
1 Crankshaft bearing journals
2 Connecting rod bearing journals
3 Counterweight
Protecting the contact surfaces
In order to protect the contact surfaces the friction, above all in
the startup phase of the engine, is reduced by the applied
protective coatings. This allows a longer working life and engine
damage is avoided by the emergency running characteristics
which result from the coating if the lubrication is faulty.
Arrows Oil holes
The crankshaft is mounted in the crankcase with 7 crankshaft
bearing journals (1).
Counterweights (3) are forged onto the webs to avoid vibrations
arising.
The crankshaft bearing journals (1) and the connecting rod
journals (2) are inductively hardened and ground in the surface
layer.
W03.20>1216>06
There are oil holes (arrows) on the crankshaft bearing journals (1)
and on the connecting rod journal (2) over which the crankshaft
bearing and connecting rod bearing are lubricated.
i
Introduction of engine OM 471 and exhaust aftertreatment > 09/2011 >
23
As>built configurations
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
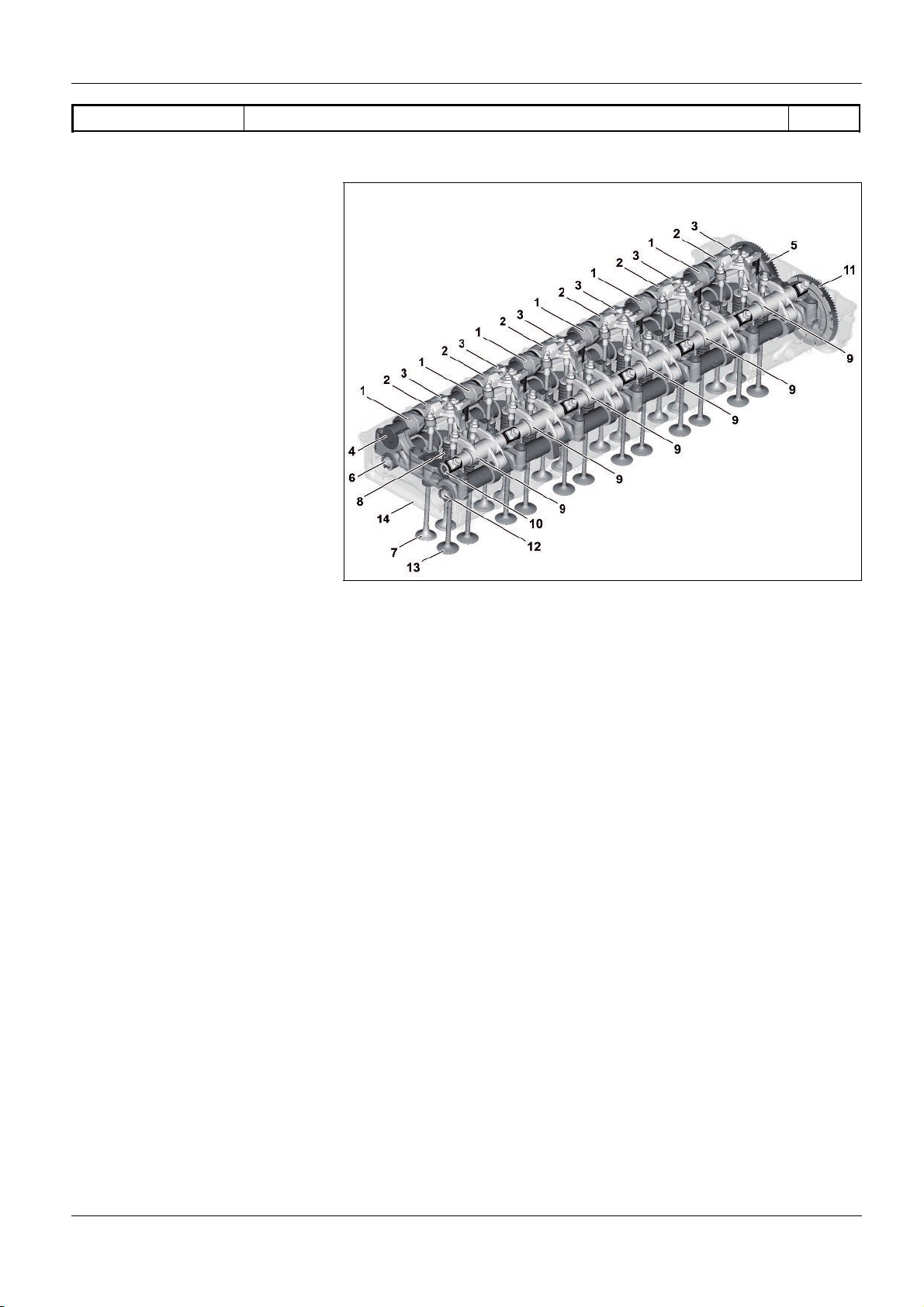
GF05.00>W>0800H
Valve control; as>built configuration 1.7.11
ENGINES 471.9
Valve control overall
1 Exhaust rocker arm
2 Exhaust rocker arm with
hydroelement
3 Brake rocker arm
4 Exhaust rocker arm spindle
5 Drive gear for exhaust camshaft
6 Exhaust camshaft
7 Outlet valve
8 Valve spring
9 Intake rocker arm
10 Intake rocker arm spindle
11 Drive gear for intake camshaft
12 Intake camshaft
13 Inlet valve
14 Camshaft frame
The gas exchange system in the combustion chambers is
controlled via the valve control.
Components of the valve control include:
•
Two upper recumbent camshafts > the intake camshaft (12)
and the exhaust camshaft (6), which are driven by the gear
drive via the pinion gear drive for the intake camshaft (11) or
via the pinion gear drive for the exhaust camshaft (5)
•
Two rocker arm spindles > the intake rocker arm spindle (10)
and the exhaust rocker arm spindle (4) on which the intake
rocker arm (9) or exhaust rocker arm (1), the exhaust rocker
arm with hydroelement (2) as well as the brake rocker arm
(3) are mounted
•
Two exhaust valves (7) and two intake valves (13) per
cylinder which are located symmetrically and pressed onto
their seat via the valve springs (8) if they are not actuated by
the corresponding rocker arm.
W05.00>1033>06
24
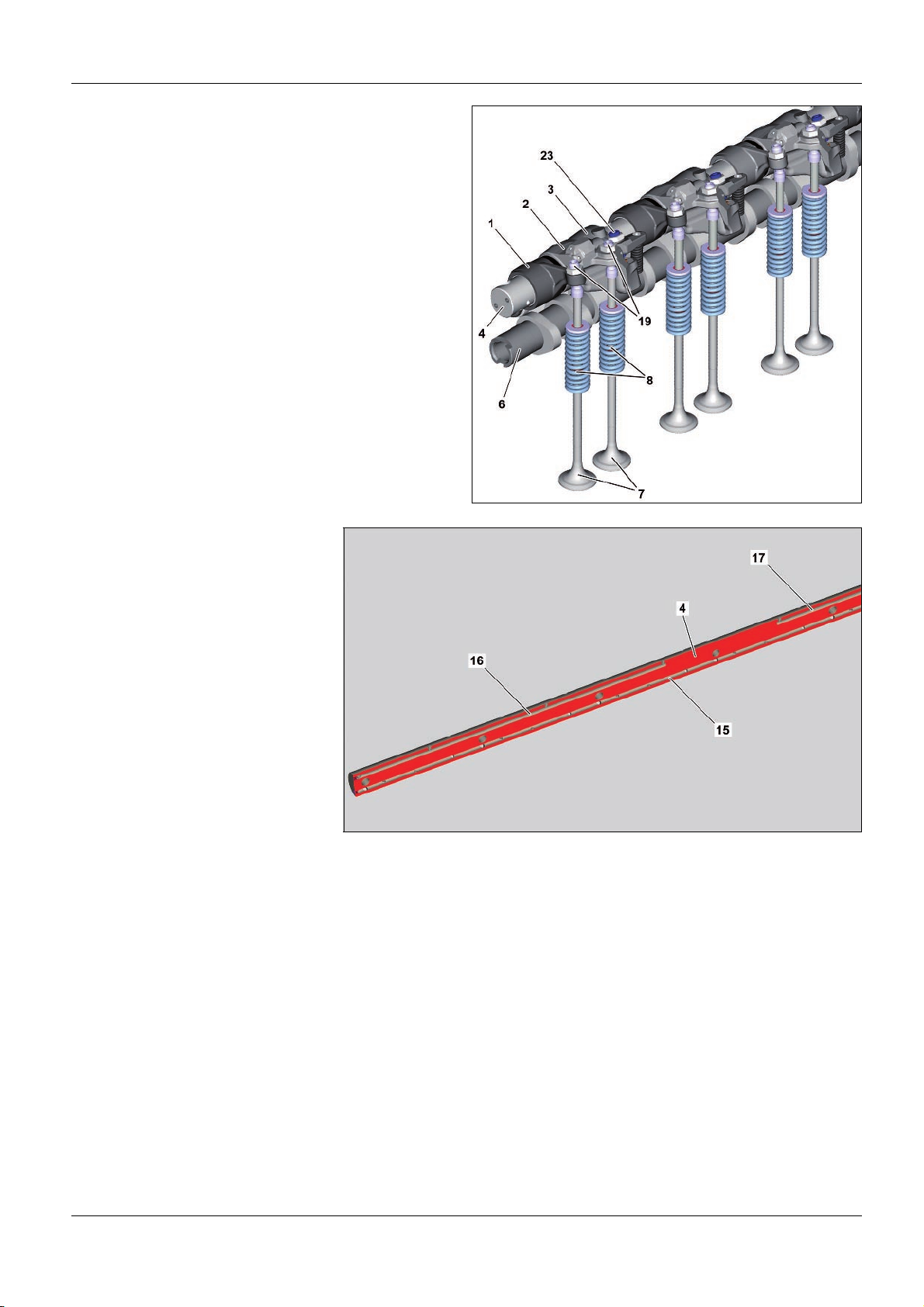
Valve control on the exhaust side
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
1 Exhaust rocker arm
2 Exhaust rocker arm with hydroelement
3 Brake rocker arm
4 Exhaust rocker arm spindle
6 Exhaust camshaft
7 Exhaust valves
8 Valve springs
19 Adjusting elements for adjusting the valve clearance
23 Adjusting element for engine brake
Design of the exhaust rocker arm spindle
(4)
4 Exhaust rocker arm spindle
15 Lubricating oil duct
16 Oil duct for cylinders 1 and 3
17 Oil duct for cylinders 4 and 6
As>built configurations
W05.00>1034>82
i
Introduction of engine OM 471 and exhaust aftertreatment > 09/2011 >
W05.00>1035>75
25
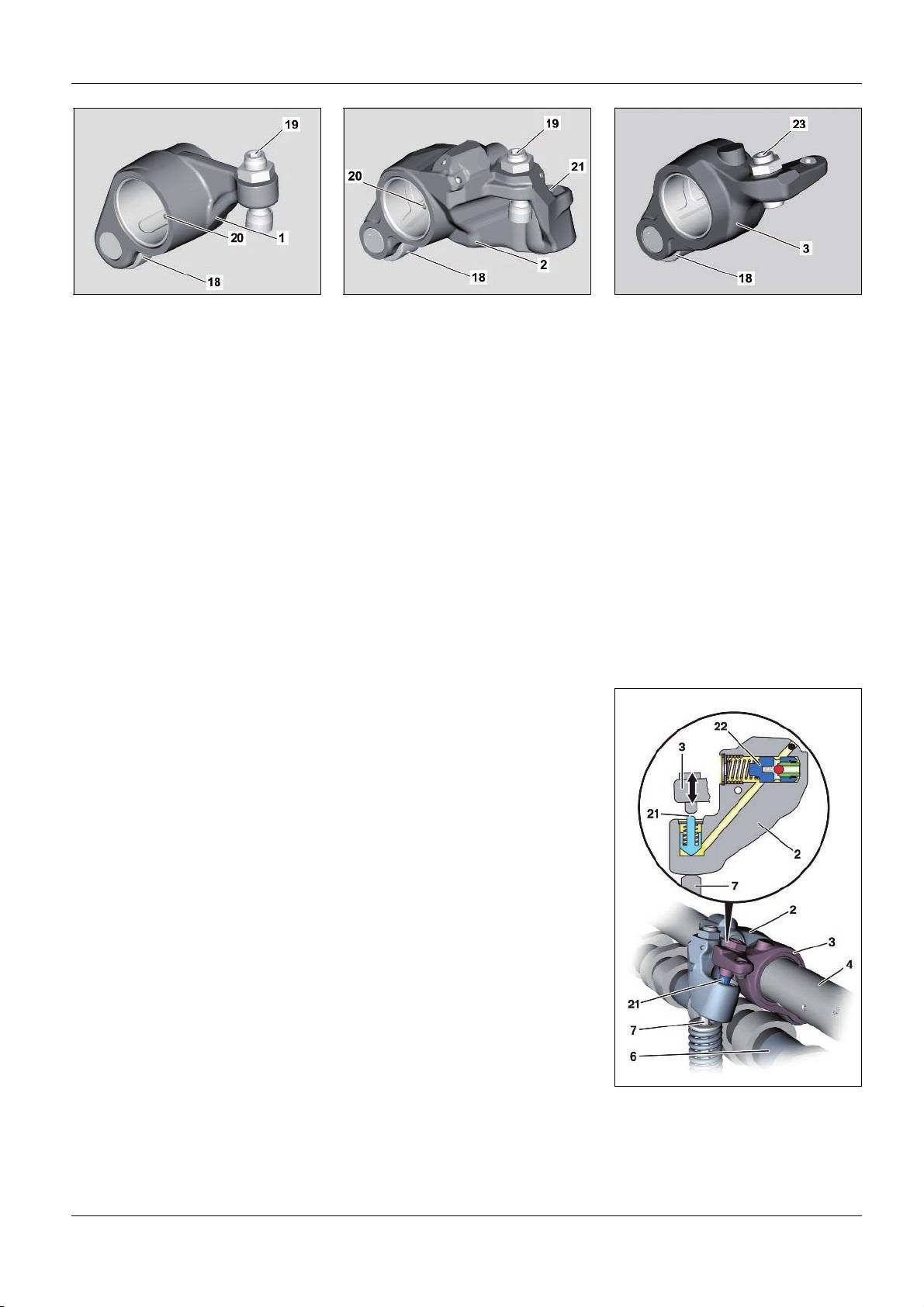
As>built configurations
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
W05.00>1036>01 W05.00>1037>01 W05.00>1038>01
Design of the rocker arm
1 Exhaust rocker arm
18 Rocker arm roller
19 Adjusting element for adjusting the
valve clearance
20 Oil inlet hole
2 Exhaust rocker arm with
hydroelement
18 Rocker arm roller
19 Adjusting element for adjusting the
valve clearance
20 Oil inlet hole
21 Piston
3 Brake rocker arm
18 Rocker arm roller
23 Adjusting element for engine brake
The valve control of the exhaust side is characterized by the fact
that every cylinder has three rocker arms > one exhaust rocker arm
(1), one exhaust rocker arm with hydroelement (2) and one brake
rocker arm (3).
All rocker arms are fitted with a rocker arm roller (18). Use of
rocker arm rollers (18) means that wear between the respective
actuation cams of the exhaust camshaft (6) and the corresponding
rocker arm is reduced. The noise emission of the valve assembly is
also reduced.
Exhaust valve control for a deactivated engine brake
2 Exhaust rocker arm with hydroelement
3 Brake rocker arm
4 Exhaust rocker arm spindle
6 Exhaust camshaft
7 Outlet valve
21 Piston
22 Check valve
Rotational movement of the camshaft is converted into linear travel by the exhaust cam on
the exhaust camshaft (6) and transferred to the associated exhaust rocker arm on the
exhaust rocker arm spindle (4). The exhaust rocker arms steer the linear travel in turn onto
the respective exhaust valves (7) which are opened and then closed again by the valve
springs.
Because the pistons (21) are pressed by a spring to their lower limit stop when the engine
brake is deactivated, no contact takes place between the brake rocker arms (3) and the
exhaust rocker arms with hydroelement (2) and the brake rocker arms (3) run in idle. This
serves to prevent any unnecessary piston (21) motion and therefore any unnecessary wear.
The exhaust rocker arm (1) and exhaust rocker arm with
hydroelement (2) are each equipped with an adjusting element
for adjusting the valve clearance (19). The clearance between the
brake rocker arm (3) and exhaust rocker arm with hydroelement
(2) is set using the adjusting element for the engine brake (23).
The exhaust rocker arm (1), exhaust rocker arm with
hydroelement (2) and brake rocker arm (3) are mounted rotatable
on the exhaust rocker arm spindle (4).
The exhaust rocker arm spindle (4) is made out of solid material
due to the higher loads in the engine brake system and is fitted
with oil ducts > a lubricating oil duct (15) and two oil ducts for
operation of the engine brake.
26
W05.00>1024>73
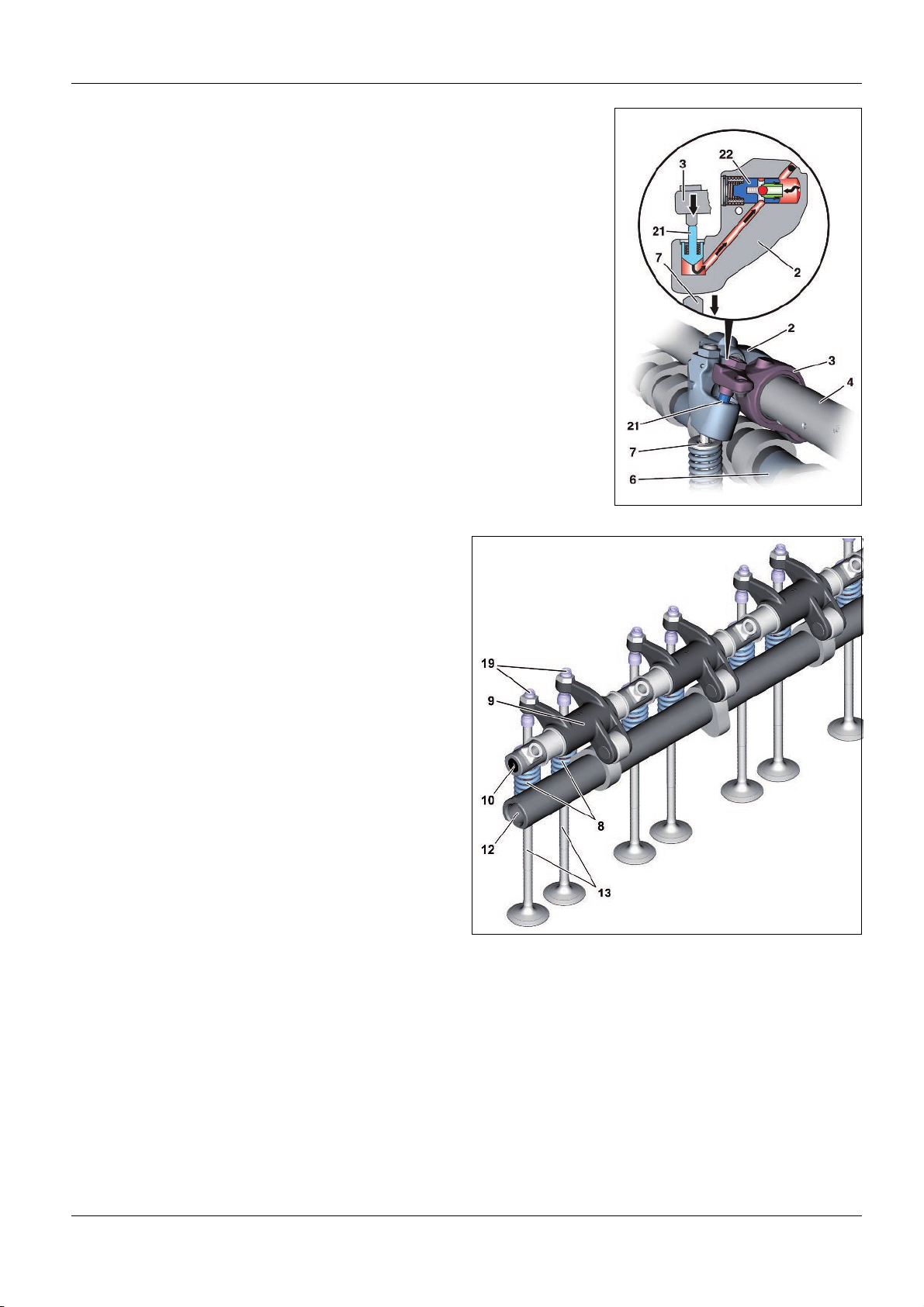
Exhaust valve control for an activated engine brake
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
2 Exhaust rocker arm with hydroelement
3 Brake rocker arm
4 Exhaust rocker arm spindle
6 Exhaust camshaft
7 Outlet valve
21 Piston
22 Check valve
When in engine brake operation up to six exhaust valves (7), one per cylinder are opened as
follows, according to the engine brake stage, by the brake cam of the exhaust camshaft (6):
The corresponding exhaust rocker arms with hydroelement (2) have oil pressure applied to
them in engine brake operation via the oil inlet hole (20). If the corresponding brake rocker
arm (3) now presses on the piston (21), the check valve (22) is closed by the increased oil
pressure. Depressurization is prevented and the downward movement of the respective
brake rocker arm (3) is transmitted by the piston (21) onto the associated exhaust rocker arm
with hydroelement (2) which opens the respective exhaust valve (7).
As>built configurations
W05.00>1025>73
Valve control on the inlet side
8 Valve springs
9 Intake rocker arm
10 Intake rocker arm spindle
12 Intake camshaft
13 Inlet valves
19 Adjusting elements for adjusting the valve clearance
W05.00>1039>82
i
Introduction of engine OM 471 and exhaust aftertreatment > 09/2011 >
27
 Loading...
Loading...