Page 1

Training Manual
Mazda BT-50
NMT-009
Page 2

No part of this hardcopy may be reproduced in any form without prior permission of
Mazda Motor Europe GmbH.
The illustrations, technical information, data and descriptive text in this issue, to the best of our
knowledge, were correct at the time of going to print.
No liability can be accepted for any inaccuracies or omissions in this publication, although every
possible care has been taken to make it as complete and accurate as possible.
© 2006
Mazda Motor Europe GmbH
Training Services
Page 3

Table of Contents
General Information ..........................................................................00-1
Product Concept....................................................................................................00-1
Vehicle Identification Number................................................................................00-7
Engine Identification Number ................................................................................00-8
Other Vehicle Information Labels..........................................................................00-9
Model Plate..................................................................................................... 00-9
Tyre Pressure Label.......................................................................................00-9
Technical Data.....................................................................................................00-10
Jacking and Lifting...............................................................................................00-11
Towing.................................................................................................................00-12
Scheduled Maintenance Table............................................................................00-13
Remarks.......................................................................................................00-15
WL-C Engine......................................................................................01-1
Engine Performance Curve...................................................................................01-1
Overview................................................................................................................01-2
Mechanical..................................................................................................................01-3
Features ................................................................................................................01-3
Specifications ........................................................................................................01-3
Piston.....................................................................................................................01-4
Cylinder Head........................................................................................................01-5
Parts Location................................................................................................. 01-5
Valve Gear......................................................................................................01-7
Valve-Clearance Adjustment..........................................................................01-8
Camshaft Pulleys............................................................................................01-8
Timing Belt Auto Tensioner............................................................................01-9
Engine Timing............................................................................................... 01-10
Lubrication System..................................................................................................01-11
Features ..............................................................................................................01-11
Specifications ......................................................................................................01-11
Parts Location......................................................................................................01-12
System Overview.................................................................................................01-13
Oil Filter...............................................................................................................01-14
Cooling System ........................................................................................................01-15
Features ..............................................................................................................01-15
Specifications ......................................................................................................01-15
Parts Location......................................................................................................01-16
System Overview.................................................................................................01-17
Intake-Air System.....................................................................................................01-18
Features ..............................................................................................................01-18
Parts Location......................................................................................................01-19
System Overview.................................................................................................01-20
MAF Sensor.........................................................................................................01-21
MAF Learning Function.......................................................................................01-21
MAF Data Reset..................................................................................................01-21
MAP Sensor / IAT Sensor No.1...........................................................................01-21
Variable Geometry Turbocharger........................................................................01-22
Intake Manifold....................................................................................................01-23
Variable Swirl Control Shutter Valves...........................................................01-24
Vacuum Chamber................................................................................................01-24
Service Training BT-50
Page 4

Table of Contents
Fuel System ..............................................................................................................01-25
Features ..............................................................................................................01-25
Specifications ......................................................................................................01-25
Parts Location......................................................................................................01-26
System Overview.................................................................................................01-28
High-Pressure Pump...........................................................................................01-29
Common Rail.......................................................................................................01-29
Fuel Injectors.......................................................................................................01-30
Exhaust System........................................................................................................01-31
Features ..............................................................................................................01-31
Parts Location......................................................................................................01-31
Warm up system..................................................................................................01-32
Wiring Diagram.............................................................................................01-32
Exhaust Shutter Valve Solenoid Valve.........................................................01-33
Exhaust Shutter Valve Unit...........................................................................01-33
Operating Conditions....................................................................................01-33
Emission System ......................................................................................................01-34
Features ..............................................................................................................01-34
Parts Location......................................................................................................01-34
System Overview.................................................................................................01-36
EGR Solenoid Valve............................................................................................01-37
EGR Control........................................................................................................01-37
Intake Shutter Valve............................................................................................01-38
Charging and Starting System................................................................................01-39
Parts Location......................................................................................................01-39
Control System.........................................................................................................01-40
Features ..............................................................................................................01-40
Specifications ......................................................................................................01-40
Parts Location......................................................................................................01-41
System Overview.................................................................................................01-42
Block Diagram.....................................................................................................01-44
Relationship Chart...............................................................................................01-45
Crankshaft Position Sensor.................................................................................01-46
Camshaft Position Sensor...................................................................................01-47
Powertrain Control Module..................................................................................01-48
Features .......................................................................................................01-48
A/C Cut-Off Control ......................................................................................01-49
Glow Plug Relay...........................................................................................01-50
On-Board Diagnostic System..............................................................................01-51
Features .......................................................................................................01-51
Malfunction Indicator Lamp ..........................................................................01-51
Self Test .......................................................................................................01-51
PID Monitor..........................................................................................................01-52
Simulation Test....................................................................................................01-53
Maintenance and Repair .....................................................................................01-54
MAF Sensor Learning Function....................................................................01-54
Replacing the MAF Sensor...........................................................................01-54
PCM Replacement .......................................................................................01-55
Service Training BT-50
Page 5

Table of Contents
Suspension........................................................................................02-1
Features ................................................................................................................02-1
Specifications ........................................................................................................02-1
Parts Location........................................................................................................02-2
Front Suspension 2WD ..................................................................................02-2
Front Suspension 4WD ..................................................................................02-2
Rear Suspension............................................................................................02-3
Wheels and Tyres.......................................................................................................02-4
Specifications ........................................................................................................02-5
Driveline / Axle...................................................................................03-1
Features ................................................................................................................03-1
Specifications ........................................................................................................03-1
RFW System .........................................................................................................03-2
Parts Location................................................................................................. 03-2
System Overview............................................................................................03-3
On-Board Diagnostic System.........................................................................03-4
Transmission.....................................................................................05-1
Clutch ..........................................................................................................................05-1
Features ................................................................................................................05-1
Specifications ........................................................................................................05-1
Parts Location........................................................................................................05-2
Clutch Master Cylinder..........................................................................................05-3
Dual Mass Flywheel ..............................................................................................05-4
S15M(X)-D Manual Transmission ..............................................................................05-5
Features ................................................................................................................05-5
Specifications ........................................................................................................05-6
Overview................................................................................................................05-7
Power Flow............................................................................................................05-8
Shift Mechanism..................................................................................................05-10
Shift Mechanism Unit....................................................................................05-11
th
5
/ Reverse Gear Mechanism.....................................................................05-12
Reverse Gear Lockout Mechanism..............................................................05-14
HVAC ..................................................................................................07-1
Basic System..............................................................................................................07-1
Features ................................................................................................................07-1
Specifications ........................................................................................................07-1
Parts Location........................................................................................................07-2
Refrigerant System................................................................................................07-3
Control System...........................................................................................................07-4
Features ................................................................................................................07-4
Parts Location........................................................................................................07-4
Wiring Diagram......................................................................................................07-5
Climate Control Unit ..............................................................................................07-6
Service Training BT-50
Page 6

Table of Contents
Restraints...........................................................................................08-1
Airbag System ............................................................................................................08-1
Features ................................................................................................................08-1
Parts Location........................................................................................................08-2
Wiring Diagram......................................................................................................08-3
SAS Control Module..............................................................................................08-4
Side Airbag Sensors..............................................................................................08-5
Side Airbags..........................................................................................................08-5
Seat Belt Pretensioners.........................................................................................08-6
On-Board Diagnostic System................................................................................08-7
Features .........................................................................................................08-7
Self Test .........................................................................................................08-7
PID Monitor.....................................................................................................08-8
Body & Accessories..........................................................................09-1
Body Panels................................................................................................................ 09-1
Cabin.....................................................................................................................09-1
Ladder Frame........................................................................................................09-2
Cargo Box..............................................................................................................09-3
Anti-Corrosion Measures.......................................................................................09-3
Glass/Windows/Mirrors..............................................................................................09-4
Security and Locks.....................................................................................................09-5
Features ................................................................................................................09-5
Theft Deterrent System .........................................................................................09-5
Wiring Diagram...............................................................................................09-6
Exterior Trim...............................................................................................................09-7
Features ................................................................................................................09-7
Parts Location........................................................................................................09-7
Front and Rear Bumper.........................................................................................09-8
Interior Trim ................................................................................................................09-9
Features ................................................................................................................09-9
Parts Location........................................................................................................09-9
Lighting System........................................................................................................09-10
Features ..............................................................................................................09-10
Parts Location......................................................................................................09-10
Front Combination Light...............................................................................09-10
Rear Combination Light................................................................................09-11
Overview..............................................................................................................09-12
Daytime Running Light........................................................................................09-12
Wiring Diagram....................................................................................................09-13
Wiper / Washer System ............................................................................................09-14
Features ..............................................................................................................09-14
Parts Location......................................................................................................09-14
Wiring Diagram....................................................................................................09-15
Service Training BT-50
Page 7

Table of Contents
Audio System............................................................................................................09-16
Features ..............................................................................................................09-16
Specifications ......................................................................................................09-16
Audio Unit.....................................................................................................09-16
Speakers ......................................................................................................09-16
Parts Location......................................................................................................09-17
System Overview.................................................................................................09-18
On-Board Diagnostic System..............................................................................09-20
Self-Test Function ........................................................................................09-20
Diagnostic Assist Function ...........................................................................09-20
Power Systems.........................................................................................................09-21
Parts Location......................................................................................................09-21
Instrumentation / Driver Information System ........................................................09-22
Features ..............................................................................................................09-22
Specifications ......................................................................................................09-22
Instrument Cluster Overview...............................................................................09-23
Key Reminder Warning Alarm.............................................................................09-24
Input / Output Check Mode..................................................................................09-24
Control System.........................................................................................................09-25
Features ..............................................................................................................09-25
Data Link Connector............................................................................................09-25
Wiring Diagram....................................................................................................09-26
Service Training BT-50
Page 8

Table of Contents
Notes:
Service Training BT-50
Page 9

General Information
General Information
Product Concept
• The new Mazda BT-50 supersedes the B-Series, Mazda’s present pick-up truck. The
aim of the BT-50 development team was to create a new pickup model in line with the
current model range delivering Mazda’s Zoom-Zoom spirit in its individual and distinctive
way.
• The BT-50 has inherited the tough and reliable commercial truck performance of the BSeries. Simultaneously it presents a new fresh body styling and technologies that
customers enjoy on passenger cars and also demand more and more for pick-up trucks.
• The BT-50 is offered with RWD (Rear Wheel Drive) layout as 2WD or as manually
activated part-time 4WD.
BT-50_00001
Service Training BT-50 00-1
Page 10

General Information
• Plane body panels without the formerly used swage lines and other new styling elements
contribute to a more brawny, but clear and modern overall styling impression.
BT-50_00002
BT-50_00022
00-2 Service Training BT-50
Page 11

General Information
• The design and material quality of the interior has been improved and now reminds more
of a passenger car than of a pick-up truck.
BT-50_00003
• Beside the clearly arranged instrument panel the completely new T-shaped dashboard
contains a centre stack panel incorporating the latest modular audio system and the
climate control panel, both with easy to operate control elements.
BT-50_00004
Service Training BT-50 00-3
Page 12

General Information
• New features of the powertrain, such as the 16-valve DOHC-diesel engine with common
rail direct injection and Euro 4 emission standard, the dual-mass flywheel or the 5-speed
transmission S15M(X)-D contribute to a driving performance and emission output that
are comparable to passenger cars.
• The noise level emitted by the engine has been significantly reduced by the common rail
injection system and additionally dampened by broad use of insulation materials.
BT-50_00005
00-4 Service Training BT-50
Page 13

General Information
• Other well-proven components, which are adopted from the B-Series as e.g. the chassis
with the ladder frame and the suspension, are refined by major or minor changes in
material, form, and/or dimension.
BT-50_00006
• The supplemental restraint system is now enhanced by combined head / side airbags as
used on the MX-5 (NC).
BT-50_00007
Service Training BT-50 00-5
Page 14
General Information
• The BT-50 is basically offered in three different body versions:
– REG (REGular) Cabin, available in 2WD or 4WD layout
BT-50_00008
– RAP (Rear Access Panel) Cabin (marketing name is ‘Freestyle Cab’), available in
4WD layout
– DBL (DouBLe) Cabin, available in 4WD layout
BT-50_00009
BT-50_00010
00-6 Service Training BT-50
Page 15
General Information
y
Vehicle Identification Number
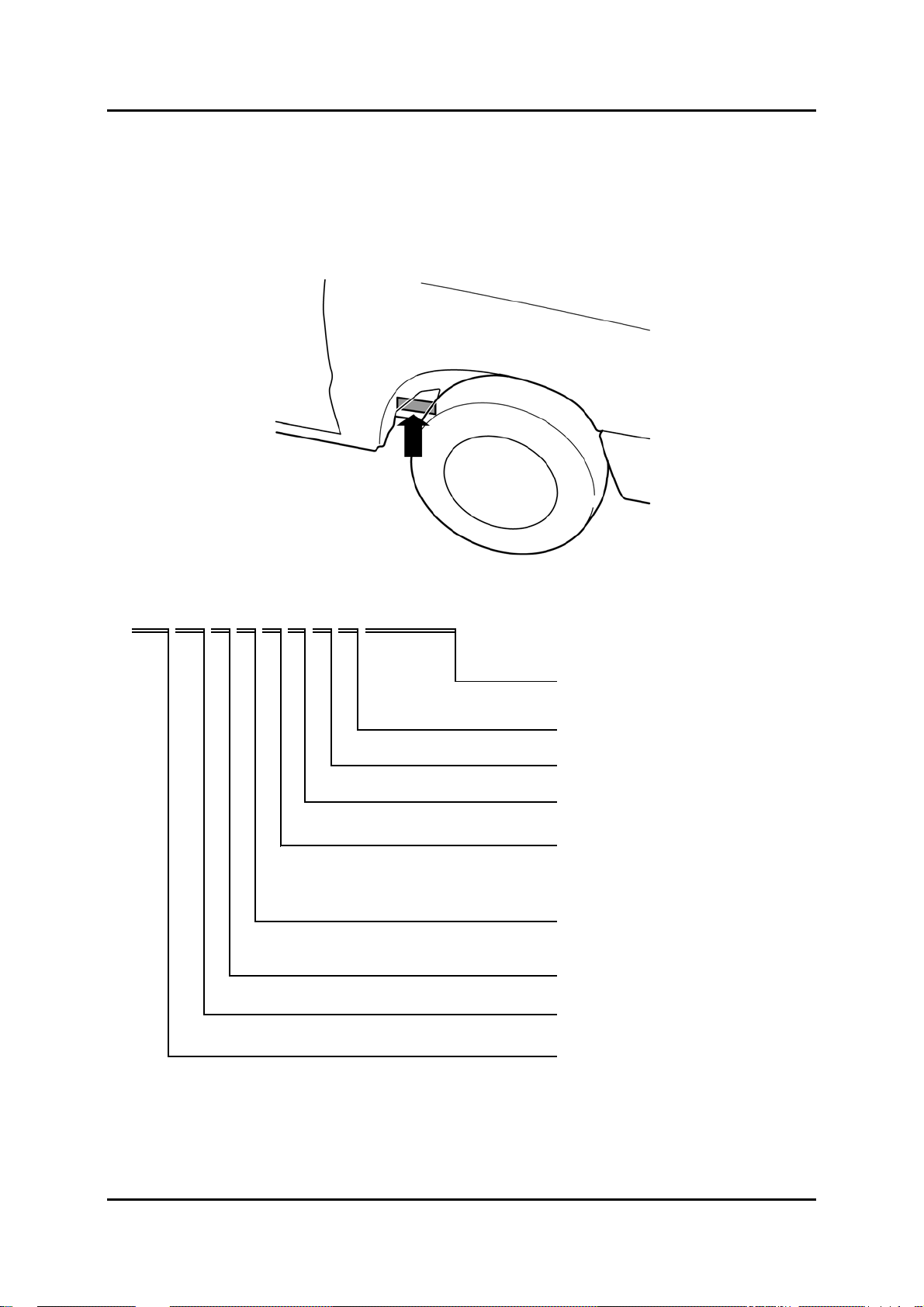
• The VIN is located on the outside of the right chassis member (visible from the right front
wheel arch). The model code of the BT-50 has remained ‘UN’, while the serial number
starts at 600,001.
JMZ UN 1 A 1 2 0 W 6 0 0 0 0 1
Serial No.
Plant
Dumm
Transmission
Engine Type
Body style
Drive axle
Vehicle type UN = Mazda BT-50
W= Auto Alliance Thailand
0
2 = 5 speed MTX
1 = WL-C (2.5 L)
B = REG cab (A)*
F = DBL cab (E)*
2 = RAP cab (1)*
1 = 2WD
8 = 4WD
BT-50_00011
World manufacturer indication JMZ = European (L.H.D., U.K.)
* without cargo box
BT-50_T00001
Service Training BT-50 00-7
Page 16
General Information
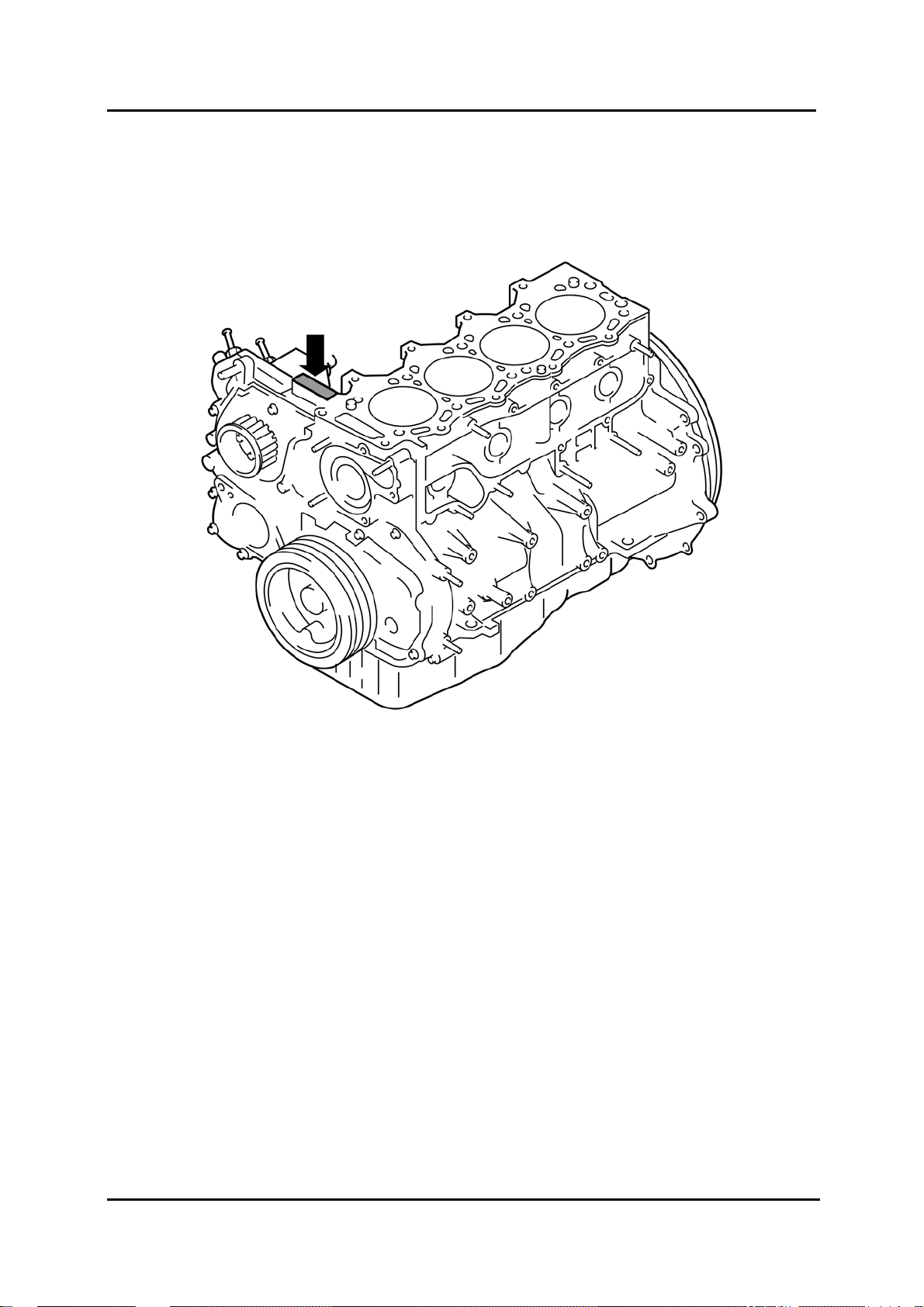
Engine Identification Number
• The engine identification number of the WL-C engine is located on the timing gear-side
of the cylinder block.
BT-50_00012
00-8 Service Training BT-50
Page 17
General Information
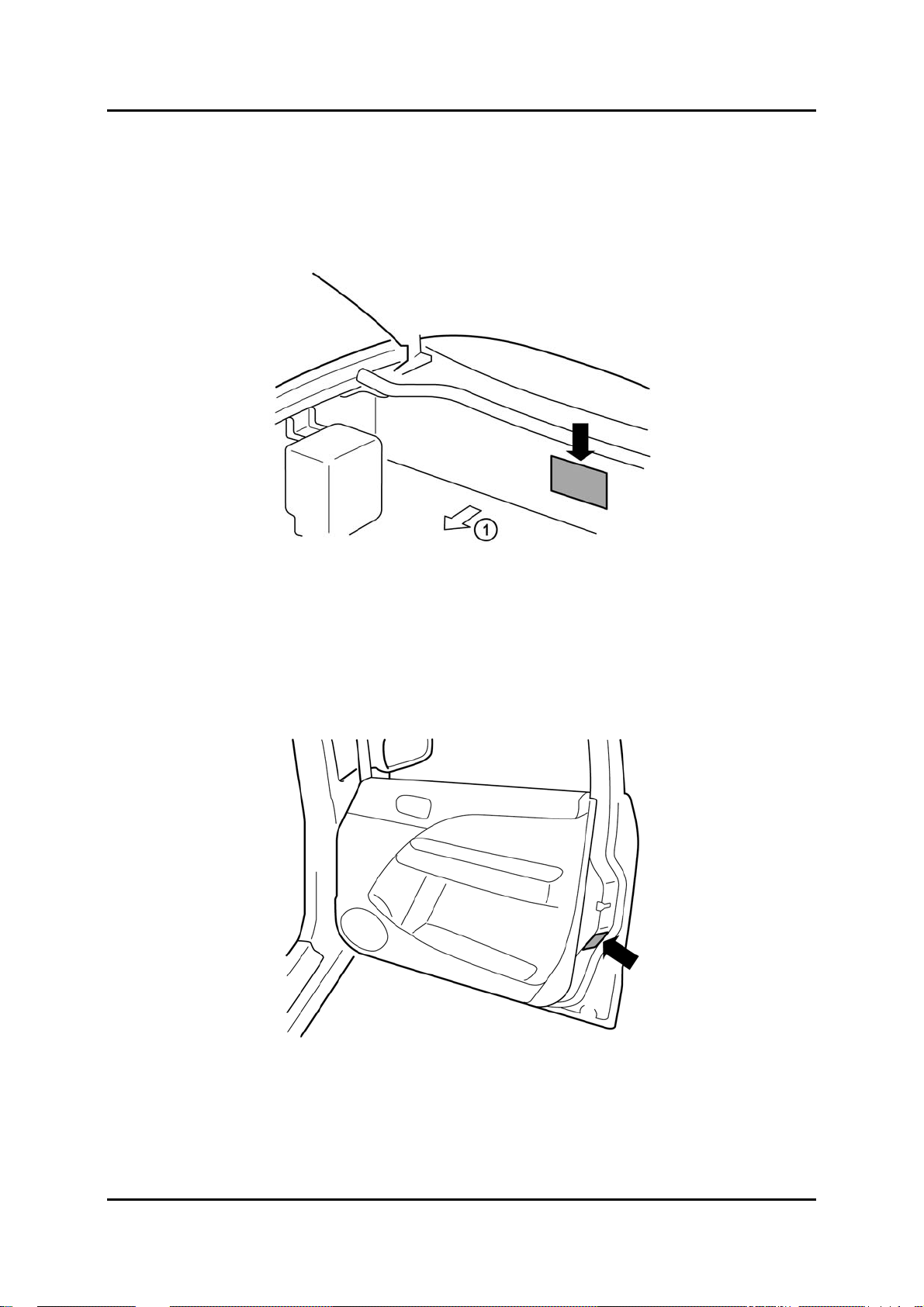
Other Vehicle Information Labels
Model Plate
• The model plate is located on the right side of the bulkhead in the engine compartment.
1 Driving direction
Tyre Pressure Label
• The tyre pressure label is located on the driver’s door as shown below.
BT-50_00013
BT-50_00014
Service Training BT-50 00-9
Page 18
General Information
(
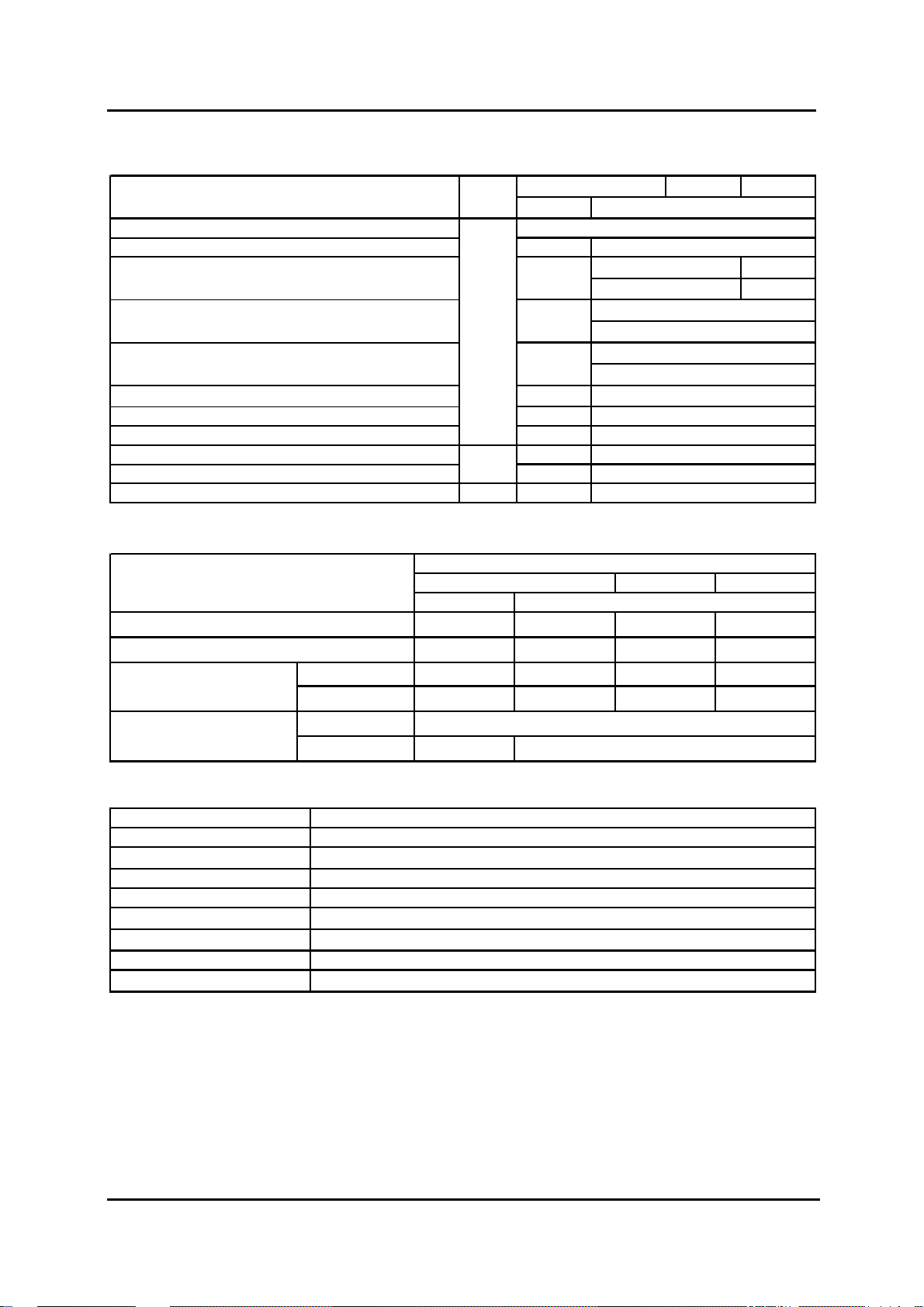
Technical Data
Item Unit
2WD
Overall length (w/o rear step bumper)
Overall width (AWD models with Overfenders) 1,715
Overall height (unladen) 1,620
Front track
mm
1,445
1,450Rear track
REG
1,745
1,750 *
RAP DBL
4WD
5,075
1,805
*1
2
1,445
1,495
1,440
1,470
Wheelbase 2,985
Ground clearance (unladen) 181
Maximum fording depth 300
Angle of approach (unladen) 24 32
Angle of departure (unladen) 26 27
°
Minimum turning circle (wall-to-wall) m 12
*1
P235/75R15 *2 245/70R16
3,000
207
450
12.6
Maximum Weight (kg)
Curb weight
Gross vehicle weight
Gross axle weight
Max.trailing load
Item
2WD
1,587 1,798 1,886 1,895
2,795 3,010 3,080 3,030
Front 1,170 1,430 1,430 1,430
Rear 1,860 1,850 1,850 1,850
unbraked
braked 1,600
REG
RAP DBL
4WD
750
3,000
*1
1,755
1,760 *
*1
*2
*1
*2
BT-50_T00002
2
BT-50_T00004
Item 2.5 MZR-CD (WL-C) Engine
Engine type Inline 4 Cyl., DOHC 16-valve, Turbocharged w.Intercooler
Displacement
2,499 cm
3
Bore x stroke 93 x 92 mm
Compression ratio 18.0 : 1
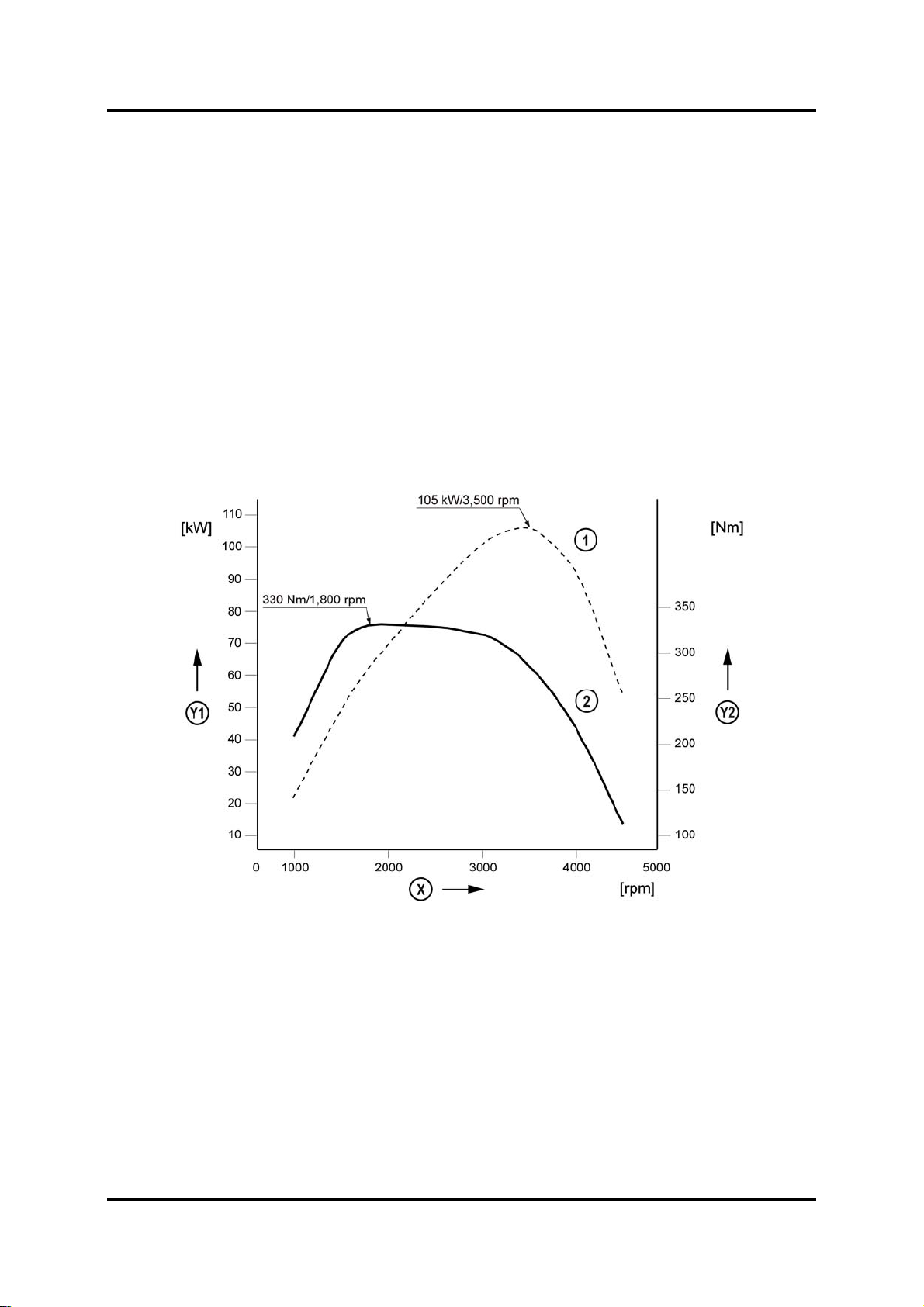
Max. power
Max. torque
105 kW
143 PS) at 3,500 min
330 Nm at 1,800 min
-1
-1
Emission standard Euro 4
Transmission 5-speed manual (S15M(X)-D)
BT-50_T00005
00-10 Service Training BT-50
Page 19
General Information
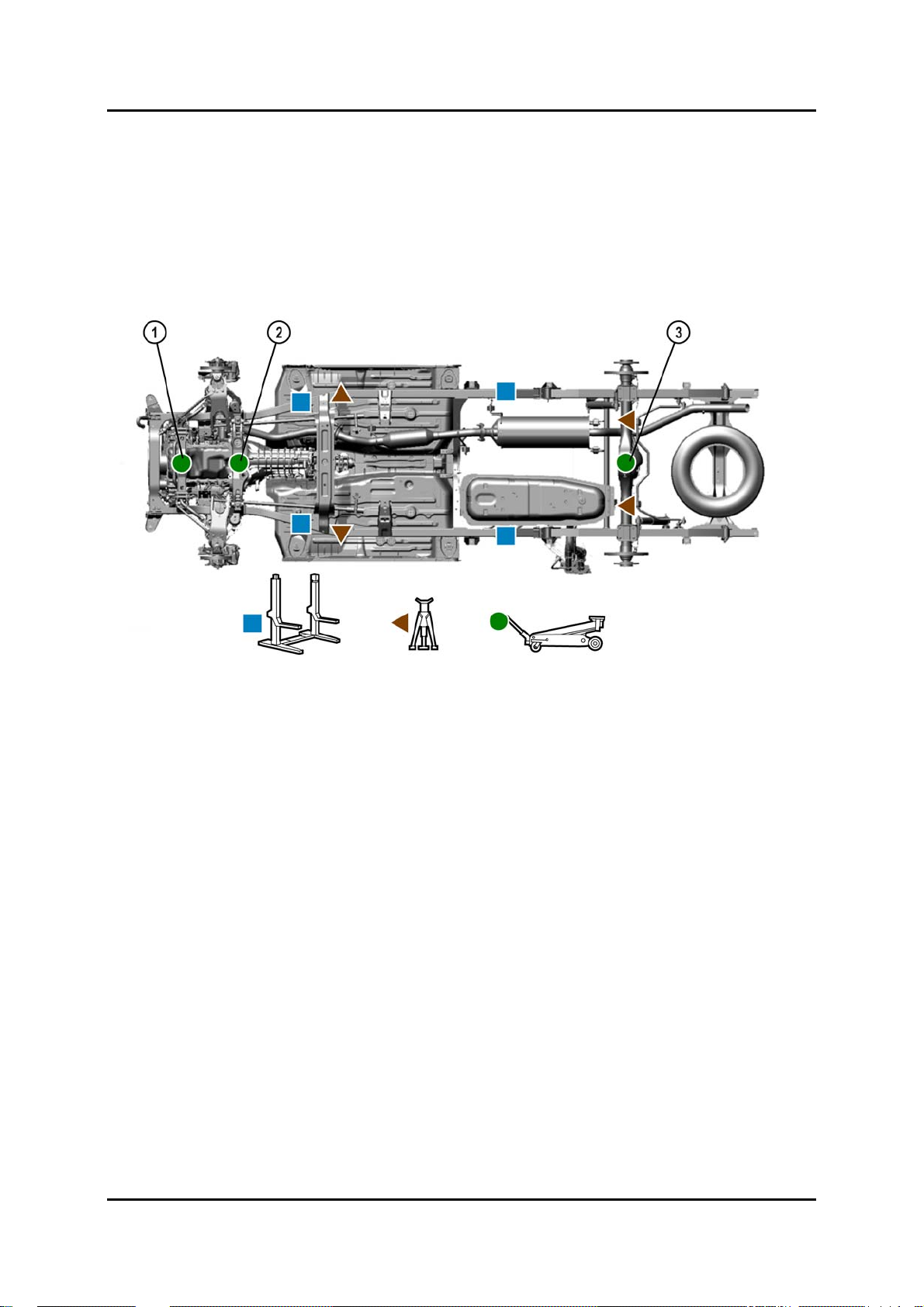
Jacking and Lifting
• The front of the vehicle can be lifted with a jack near the centre of the front
crossmember.
NOTE: The jacking point on the front axle for the 2WD is different to the 4WD model.
1 only 2WD 3 2WD and 4WD
2 only 4WD
BT-50_00023
Service Training BT-50 00-11
Page 20
General Information
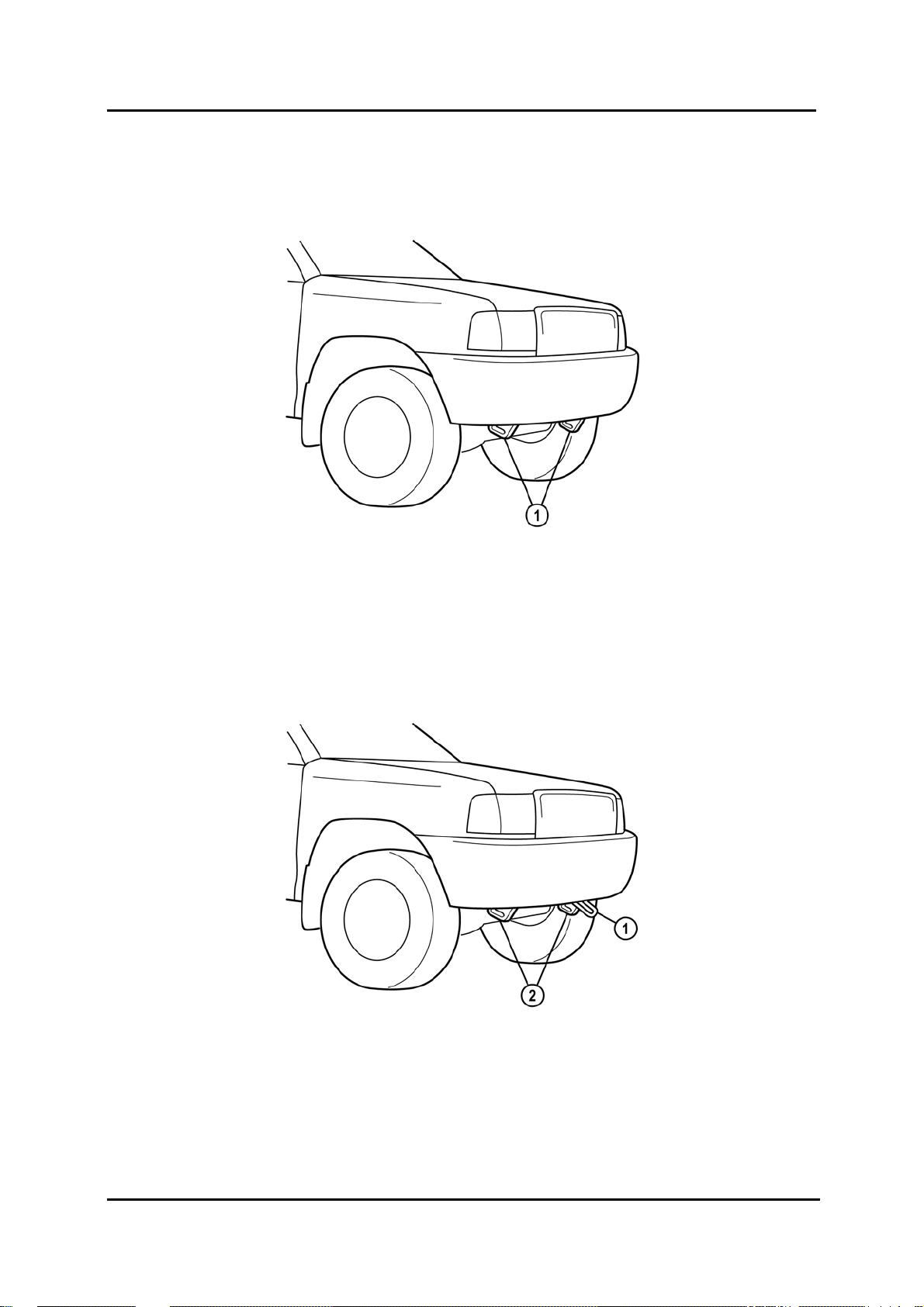
Towing
• The towing hooks on the 2WD model are different from the 4WD model.
2WD
1 Towing hooks
• The 4WD model has two tie-down hooks that may not be used for towing. The towing
hook is located on the left side.
BT-50_00020
4WD
1 Towing hook 2
Tie-down hooks
BT-50_00021
00-12 Service Training BT-50
Page 21
General Information
y
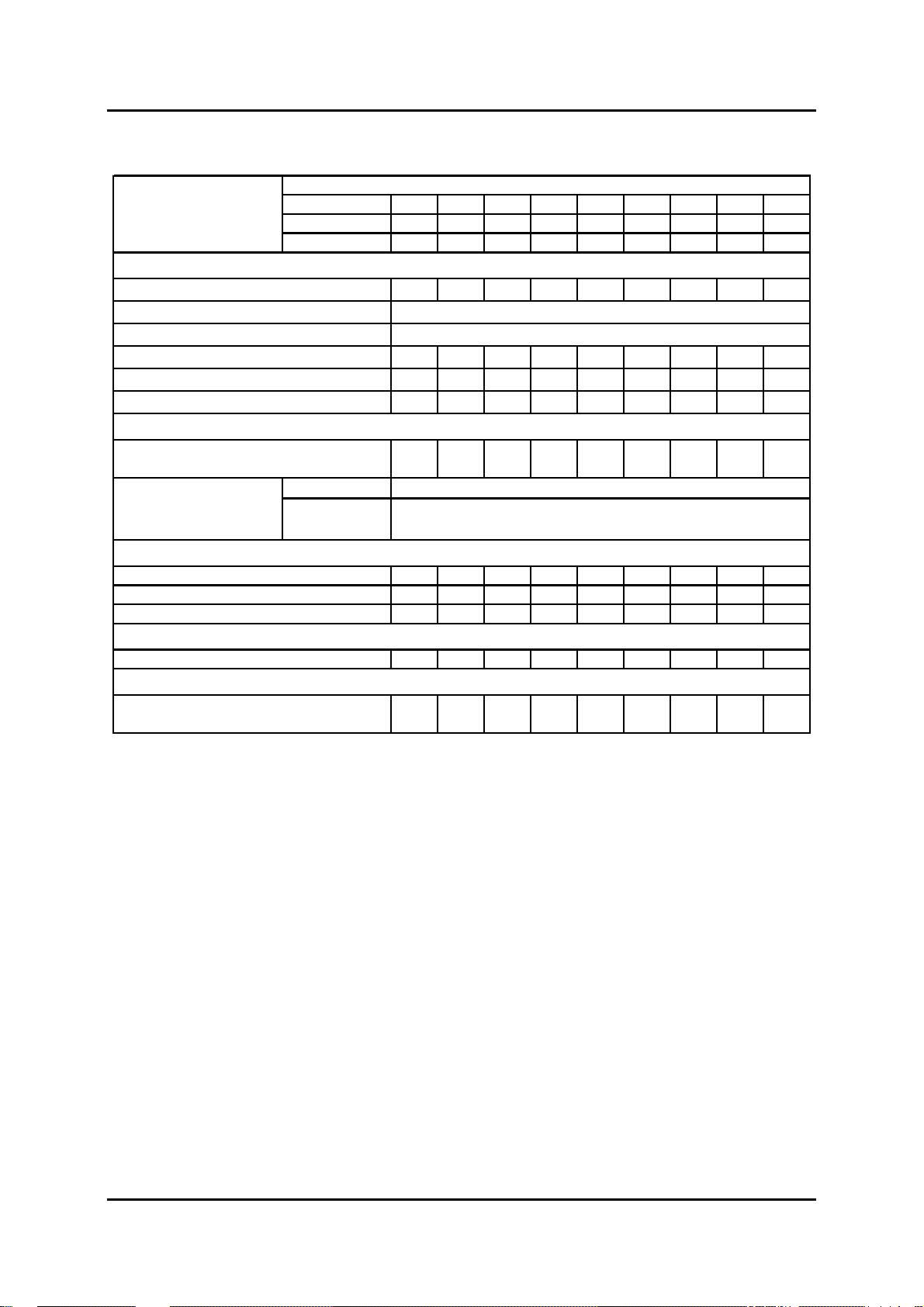
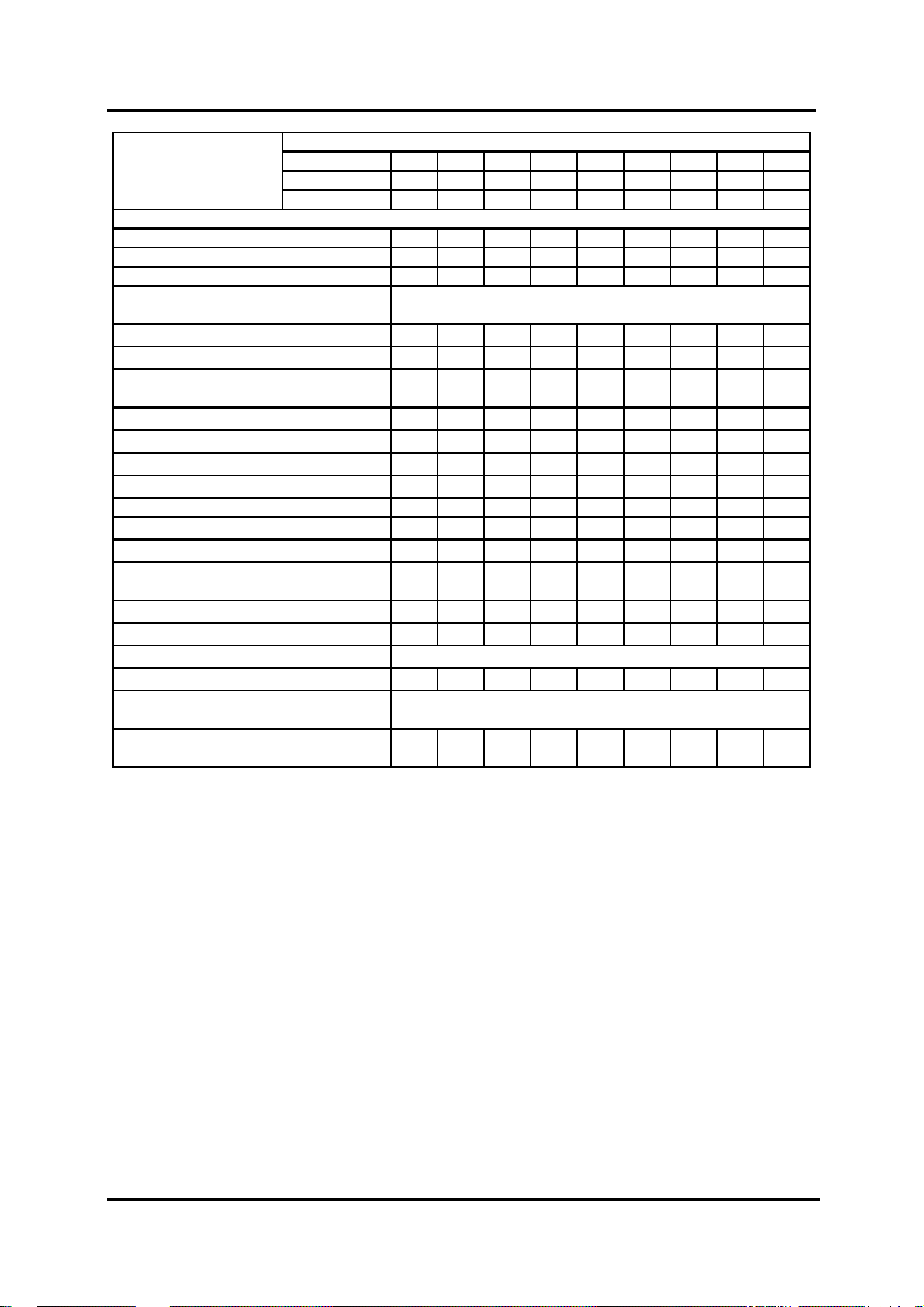
Scheduled Maintenance Table
Number of months or kilometers (miles), whichever comes first
Maintenance Interval
ENGINE
Engine valve clearance
Engine timing belt
Engine timing belt auto tensioner*
Engine oil
Engine oil filter
Drive belts
*2
*1
*2
*3
COOLING SYSTEM
Cooling system (including coolant level
adjustment)
Engine coolant
FUEL SYSTEM
Air cleaner element
Fuel filter
Fuel lines and hoses
*5
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
Air intake system
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
Months 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96 108
x1000 km 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180
x1000 miles 12.5 25 37.5 50 62.5 75 87.5 100 112.5
1
FL22 t
pe
Others
II
Replace every 120,000 km (75,000 miles)
Replace every 120,000 km (75,000 miles)
RRRRRRRRR
RRRRRRRRR
IIIIIIIII
IIII
*4
Replace every 200,000 km (125,000 miles) or 11 years
Replace first at 100,000 km (62,500 miles) or 4 years;
after that every 2 years
CCRCCRCCR
RRRR
IIIIIIIII
IIIIIIIII
Battery electrolyte level and specific gravity
IIIIIIIII
BT-50_T00006
Service Training BT-50 00-13
Page 22
General Information
Number of months or kilometers (miles), whichever comes first
Maintenance Interval
CHASSIS and BODY
Brake lines, hoses and connections
Brake fluid
Parking brake
*6
Months 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96 108
x1000 km 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180
x1000 miles 12.5 25 37.5 50 62.5 75 87.5 100 112.5
IIII
RRRR
IIIIIIIII
Brake booster and hoses
Disc brakes
Drum brakes
Power steering fluid, lines, hoses and
connections
Steering operation and linkages
Manual transmission oil
Rear differential oil (2WD)
Front and rear differential oil (4WD)
Transfer oil (4x4) I I R I I
Drive shaft dust boots (4WD)
Propeller shaft joints (4WD)
Front and rear suspension and ball joints
Front wheel bearing grease (2WD)
Wheel bearing axial play
Exhaust system and heat shields
Bolts and nuts on chassis and body
Body condition (for rust, corrosion and
perforation)
Tyres (including spare tyre ) with inflation
pressure adjustment
*7
*7
*8
IIIIIIIII
IIIIIIIII
RIRIRIRIR
IIIIIIIII
IIIIIIIII
TTTTTTTTT
IIIIIIIII
Inspect every 200,000 km (125,000 miles)
IIII
IIII
IIRI
IRIR
IIII
LLLL
RRRR
Inspect every 80,000 km (50,000 miles) or 5 years
Inspect annually
I
BT-50_T00007
Chart symbols
I
: Inspect: Inspect and clean, repair, adjust, or replace if necessary.
R
: Replace
T
: Tighten
L
: Lubricate
C
: Clean
00-14 Service Training BT-50
Page 23

General Information
Remarks
• Refer below for a description of items marked with * in the maintenance chart.
– *1: Replacement of the engine timing belt and auto tensioner is required at every
120,000 km (75,000 miles). Failure to replace the timing belt and the auto tensioner
may result in damage to the engine.
– *2: If the vehicle is operated primarily under any of the following conditions, replace
the engine oil and oil filter more often than the recommended intervals.
a) Driving in dusty conditions
b) Extended periods of idling or low speed driving
c) Driving for long periods in cold temperatures or driving regularly at short
distance (less than 8 km/ 5 miles) only
*
–
3: Also inspect and adjust the power steering and air conditioner drive belts, if
installed.
*
–
4: Use FL22 type coolant in vehicles with the inscription ‘FL22’ on the radiator cap
itself or the surrounding area. Use FL22 when replacing the coolant.
*
–
5: If the vehicle is operated in very dusty or sandy areas, clean the air cleaner
element at every 10,000 km (6,250 miles) or 6 months. Replace the air cleaner
element at every 30,000 km (18,750 miles) or 18 months.
*
–
6: If the brakes are used extensively (for example, continuous hard driving or
mountain driving) or if the vehicle is operated in extremely humid climates, replace
the brake fluid annually.
*
–
7: If the vehicle is operated primarily under any of the following conditions, inspect
the disc brakes and drum brakes more often than the recommended intervals.
a) Driving on bumpy roads, gravel roads, snowy roads or unpaved roads
b) Driving uphill and downhill frequently
c) Repeated short-distance driving
*
–
8: If the vehicle is operated primarily under any of the following conditions, replace
the front wheel bearing grease at every 20,000 km (12,500 miles) or 12 months.
a) Driving in dusty conditions
b) Driving in rough, muddy or snow-melted conditions
c) Towing a trailer
Service Training BT-50 00-15
Page 24

General Information
Notes:
00-16 Service Training BT-50
Page 25
Engine WL-C Engine
WL-C Engine
• The BT-50 is offered with the 2.5 L common rail diesel engine, which has the
identification code WL-C.
• The design and operation of the WL-C engine are essentially carried over from that of
the B-Series with WLT-3 engine, except for the new features described in the respective
sections.
NOTE: Further information can be found in the Training Manual of the ‘B-Series’ (NMT-005)
and in ‘Basic Diesel Engine Management’ (CT-L2005) and ‘Advanced Diesel Engine
Management’ (CT-L3004).
Engine Performance Curve
BT-50_01001
X Engine speed 1 Power curve
Y1 Engine power 2 Torque curve
Y2 Engine torque
Service Training BT-50 01-1
Page 26

WL-C Engine Engine
Overview
BT-50_01002
01-2 Service Training BT-50
Page 27
WL-C Engine Mechanical
Mechanical
Features
• The mechanical system of the WL-C engine has the following new features:
– Pistons with integrated combustion chamber
– Coated piston skirt
– Reduced compression ratio
– Newly constructed aluminium alloy cylinder head
– Double overhead camshafts (driven by a timing belt)
– Four valves per cylinder
– Adjustable roller-type rocker arms
– Timing belt auto tensioner
Specifications
Item
Type
Cylinder arrangement and number
Combustion chamber
Valve system
Displacement
Bore x stroke
Compression ratio
Compression pressure
IN
Valve timing
EX
Valve clearance
(engine cold)
IN mm 0.10-0.16
EX mm 0.17-0.23
Specification
WL-C
Diesel 4-stroke
Inline, 4-cylinder
Direct injection
DOHC, timing gear and belt driven, 16 valves
ml 2,499
mm 93.0 x 92.0
18.0:1
kPa 2,942 (standard) 2,648 (minimum)
Open BTDC (°) 10
Close ABDC (°) 30
Open BBDC (°) 40
Close ATDC (°) 8
BT-50_T01001
Service Training BT-50 01-3
Page 28
Mechanical WL-C Engine
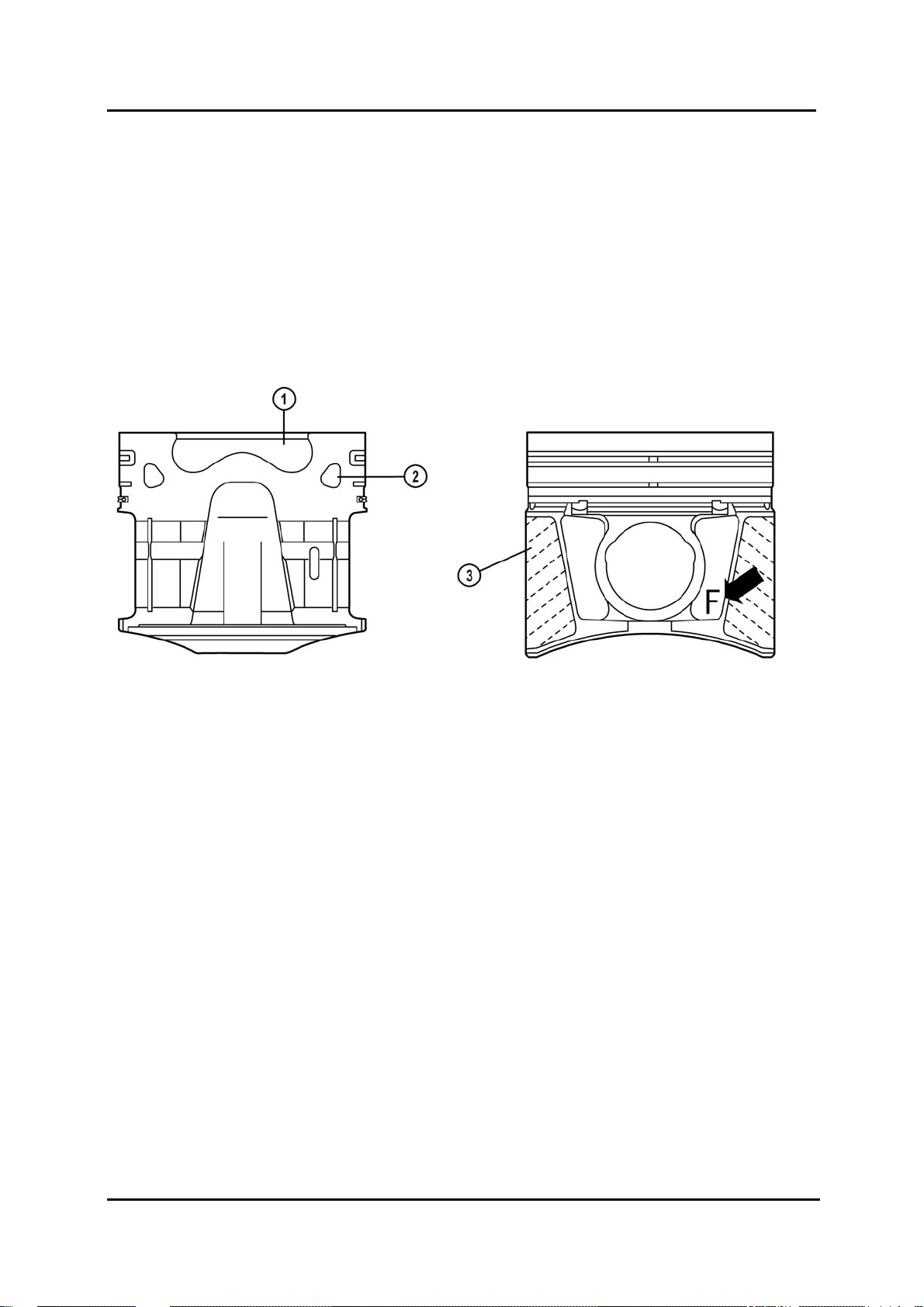
Piston
• In accordance with the adoption of the common rail injection system, the piston head
shape now incorporates the combustion chamber. Due to the modified piston shape the
compression ratio is reduced from 21.6: 1 on the WLT-3 engine to 18.0: 1.
• A reduction of the internal friction and hence of the engine’s mechanical loss has been
achieved by coating of the piston skirt area.
NOTE: The piston side marked with ‘F’ must be installed towards the timing gear-side of the
engine.
BT-50_01006
1 Combustion chamber 3 Piston skirt coating
2 Cooling oil channel
NOTE: Oversize bearings for the crankshaft and connecting rods, as well as oversize
pistons are available in various dimensions (refer to Engine W/M).
01-4 Service Training BT-50
Page 29
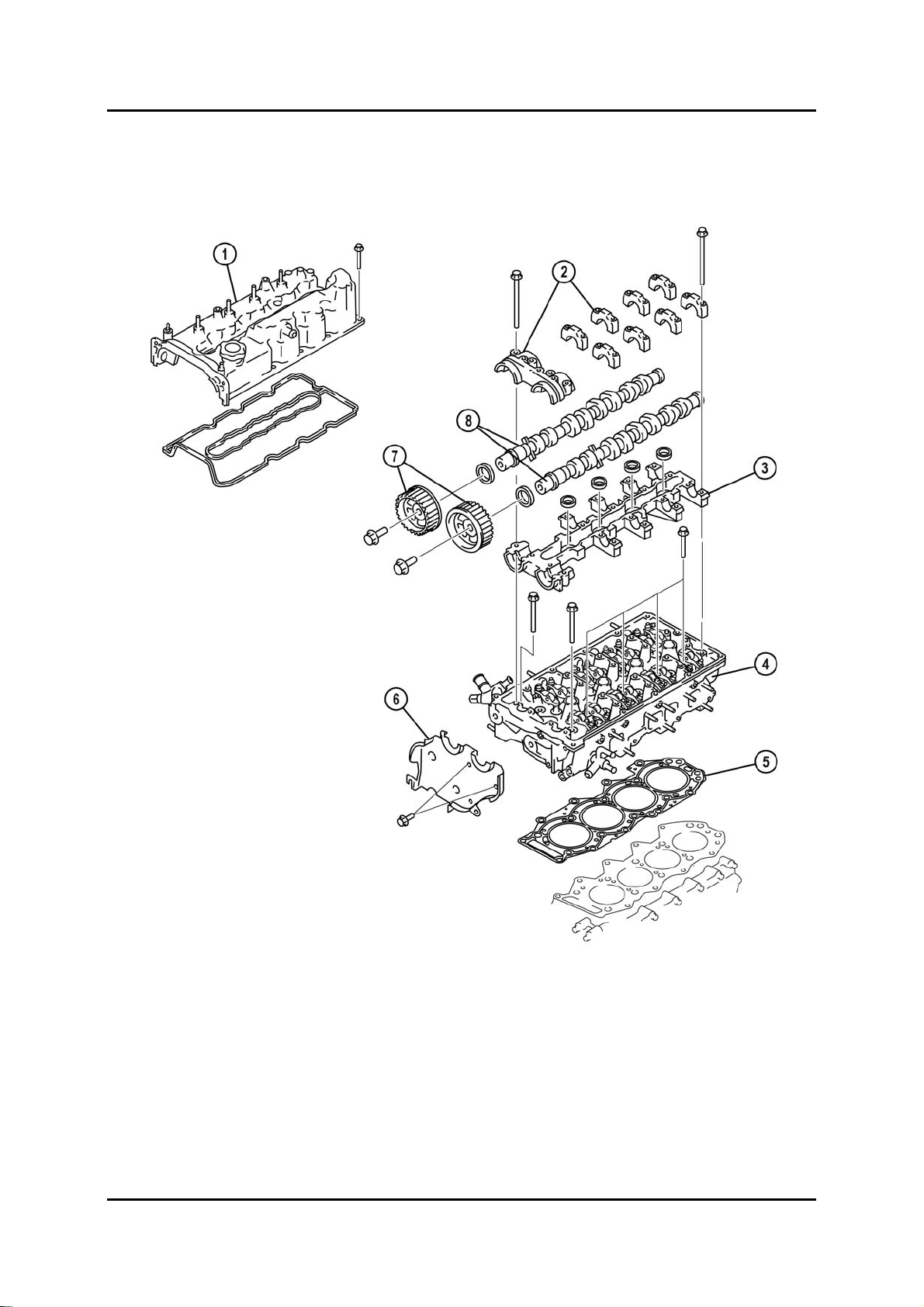
WL-C Engine Mechanical
Cylinder Head
Parts Location
BT-50_01007
1 Cylinder head cover 5 Cylinder head gasket
2 Upper camshaft bearing caps 6 Seal plate
3 Lower camshaft bearing case with
injector sealing rings
4 Cylinder head 8 Camshaft
7 Camshaft pulley
Service Training BT-50 01-5
Page 30
Mechanical WL-C Engine
• The cylinder head and the full floating cylinder head cover are made of aluminium alloy.
• The steel laminated cylinder head gasket is available in three different thicknesses
depending on the piston protrusion. The gasket is marked respectively (refer to Engine
W/M).
• The camshafts are supported in a separate bearing case, which is available as a
separate spare part.
• For lubrication of the cam lobes, bearings / journals and rocker arms, the camshafts are
hollow and have oil bores at each lubricating point.
BT-50_01008
A Exhaust camshaft 3 Oil passage
B Intake camshaft 4 Location of cylinder no.1
1 Thrust force bearing boss 5 Hexagonal shaped surface
2 Oil bore
NOTE: The cylinder head surface must not be machined. If necessary, the cylinder head
must be replaced (refer to Engine W/M).
01-6 Service Training BT-50
Page 31

WL-C Engine Mechanical
Valve Gear
• The valve gear comprises helical gears and a timing belt
• The timing belt drives two camshafts and is adjusted by an auto tensioner.
• Adjustable roller type rocker arms have been adopted to lower the friction between
camshaft lobe and rocker arm, reducing the engine’s mechanical loss.
BT-50_01009
1
Camshaft
2 Camshaft 6 Timing belt auto tensioner
3 Rocker arm 7 Timing belt
4 Balancer shaft
pulley
5
Helical
gear
NOTE: The construction of the helical gears and their adjustment procedure is identical to
that of the WLT-3 engine (refer to the engine W/M).
Service Training BT-50 01-7
Page 32

Mechanical WL-C Engine
Valve-Clearance Adjustment
• The valve clearance is measured between roller and cam lobe.
CAUTION: For loosening the locknut of the adjusting screw the cam lobe must push down
the rocker arm firmly as shown in the figure below. Otherwise the claw of the
rocker arm might be damaged.
BT-50_01010
1 Cam lobe 4 Rocker arm
2 Adjusting screw 5 Claw
3 Locknut 6 Roller
Camshaft Pulleys
• The camshaft pulleys for intake and exhaust camshaft are identical. They are positioned
on the camshaft with pins and have to be installed as shown in the figure below.
BT-50_01011
1 Intake side camshaft pulley 3 Exhaust side camshaft pulley
2 Pin
01-8 Service Training BT-50
Page 33

WL-C Engine Mechanical
Timing Belt Auto Tensioner
• A timing belt auto tensioner has been adopted to maintain timing belt tension constant.
The timing belt tension is released by turning the auto tensioner counterclockwise with
the aid of an Allen wrench (with max. 39 Nm apply force). The turned back tensioner is
secured by inserting a fixing pin with 6 mm diameter into the appropriate bore (No. 3 in
figure below).
BT-50_01055
1 Apply force (max. 39 Nm) 3 Hole for fixing pin
2 Mounting bolts (C+B)
BT-50_01014
1 Rod 4 Spring
2 Seal 5 Oil
3 Plunger 6 Ball
NOTE: In case air has entered the pressure chamber of the auto tensioner, it must be bled
using a certain procedure (refer to W/M).
Service Training BT-50 01-9
Page 34

Mechanical WL-C Engine
Engine Timing
• When replacing the timing belt the timing marks must be positioned as shown in the
figure below.
1 Intake camshaft pulley 3 Timing mark
2 Exhaust camshaft pulley 4 High-pressure pump pulley
BT-50_01013
01-10 Service Training BT-50
Page 35

WL-C Engine Lubrication System
Lubrication System
Features
• The lubrication system of the WL-C engine has the following new features:
– Plastic oil strainer with resin filter
– Spin-on type oil filter with full-flow paper element
– Double layer oil pan with additional oil baffle
Specifications
Item
Type
Specification
WL-C
Force-fed type
Oil pressure (reference values)
[after warm up]
Type
Oil pump
Oil cooler Water-cooled
Oil cooler bypass valve opening
pressure
Oil filter
Oil capacity
(approx.
quantity)
Grade
Viscosity (SAE)
Remarks
Relief valve
opening pressure
(reference value)
Type
Type
Bypass pressure kPa 80-120
Total (dry engine) 8.0
Oil replacement 6.8
Oil and oil filter
replacement
(at idle) kPa 100-330
(at 2,500 rpm)
kPa
kPa 580-700
kPa 164-200
Full-flow paper element, spin-on type
L
API CF or ACEA B1/B3/B5
e.g. Mazda genuine Dexelia oil
410-570
Gear type
5W-30
7.0
BT-50_T01003
Service Training BT-50 01-11
Page 36

Lubrication System WL-C Engine
Parts Location
BT-50_01044
1 Oil jet valve 7 Oil cooler and oil filter body component
2 Oil pressure switch 8 Oil pan
3 Oil dipstick 9 Oil drain plug
4 Oil cooler 10 Oil strainer
5 Oil filter body 11 Oil outlet pipe
6 Oil filter 12 Oil pump
01-12 Service Training BT-50
Page 37

WL-C Engine Lubrication System
System Overview
1 Oil pressure switch 12 Main bearing
2 Vacuum pump 13 Crankshaft
3 Turbocharger 14 Connecting rod bearing
4 Timing gears 15 Oil pump
5 Oil Strainer 16 Piston
6 Oil filter 17 Oil jet valve
7 Oil cooler 18 Oil pan
8 Oil cooler and oil filter body component 19 Oil passage
9 Camshaft 20 Oil relief passage
10 Orifice 21 Oil bypass passage
11 Balancer shaft
BT-50_01015
Service Training BT-50 01-13
Page 38

Lubrication System WL-C Engine
Oil Filter
• The spin-on type oil filter consists of one full flow element. The bypass element that has
been additionally used on the filter WLT-3 engine has been dropped.
1 Full-flow paper element
BT-50_01017
01-14 Service Training BT-50
Page 39

WL-C Engine Cooling System
p
Cooling System
Features
• The cooling system of the WL-C engine has the following new features:
– Longlife engine coolant FL-22
– Asymmetric positioned radiator fan blades for noise reduction (thermo-modulated
fan-type)
Specifications
Item
Type Water-cooled, forced circulation
Coolant capacity (approx. quantity)
Water pump Type Centrifugal, V-belt driven
Type Wax, bottom-bypass
Thermostat
Radiator Type Corrugated fin
Cooling system
ca
Cooling fan
Opening temperature °C 80-84
Full-open temperature °C 95
Full-open lift mm 8.5 or more
Cap valve opening pressure kPa 93.2-122.6
Type Thermo-modulation type
Number of blades 9
Outer diameter mm 450
L
Specification
WL-C
Without heater: 8.8
With heater: 9.4
BT-50_T01005
Service Training BT-50 01-15
Page 40

Cooling System WL-C Engine
Parts Location
1 Radiator cowling 5 Cooling fan
2 Water pump pulley 6 Coolant reserve tank
3 Thermostat 7 Radiator
4 Water pump 8 Cooling system cap
NOTE: To bleed the cooling system follow the instructions of the W/M.
BT-50_01045
01-16 Service Training BT-50
Page 41

WL-C Engine Cooling System
System Overview
1 Coolant reserve tank 7 Heater
2 EGR cooler 8 Water pump
3 Cylinder head 9 Thermostat
4 Turbocharger 10 Radiator
5 Cylinder block 11 Coolant flow direction
6 Oil cooler
BT-50_01018
Service Training BT-50 01-17
Page 42

Intake-Air System WL-C Engine
Intake-Air System
Features
• The intake-air system of the WL-C engine has the following new features:
– Newly designed air cleaner housing with dry filter element
– MAF (Mass Air Flow) sensor with integrated IAT (Intake Air Temperature) sensor
– VGT (Variable Geometry Turbocharger) with VBC (Variable Boost Control)
1)
no.2 *
system *
and MAF learning function
1)
– Enlarged charge-air cooler made of aluminium alloy
– Newly designed intake manifold with VSC (Variable Swirl Control) system *
– Vacuum chamber to reduce vacuum fluctuations
– MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure) sensor with integrated IAT sensor no. 1
*1) Similar to Mazda6 pre F/L (2.0 MZR-CD)
1)
01-18 Service Training BT-50
Page 43

WL-C Engine Intake-Air System
Parts Location
BT-50_01021
1 Glow plug 9 Fresh-air duct
2 VGT 10 Glow plug cord
3 Check valve 11 Charge-air cooler
4 VBC solenoid valve 12 VSC solenoid valve
5 Vacuum chamber 13 Glow plug relay
6 VBC vacuum actuator 14 MAP / IAT no.1 sensor
7 Air cleaner 15 VSC vacuum actuator
8 MAF / IAT no.2 sensor 16 Intake manifold
Service Training BT-50 01-19
Page 44

Intake-Air System WL-C Engine
System Overview
1 Charge-air cooler 10 Glow plug
2 Check valve 11 Vacuum pump
3 Vacuum chamber 12 VSC vacuum actuator
4 VBC solenoid valve 13 VSC solenoid valve
5 MAF / IAT no.2 sensor 14 VSC shutter valves
6 Air cleaner 15 MAP / IAT no.1 sensor
7 VGT 16 Intake manifold
8 VBC vacuum actuator 17 To PCM
9 Guide blades
BT-50_01020
01-20 Service Training BT-50
Page 45

WL-C Engine Intake-Air System
MAF Sensor
• The MAF sensor with integrated IAT sensor no.2 is installed on the air filter.
MAF Learning Function
• The MAF learning function is used to compensate any deterioration of the MAF sensor. It
should be carried out at each service interval by means of M-MDS (refer to chapter
‘Maintenance and Repair’).
MAF Data Reset
• When the MAF sensor is replaced the adaptation values in the PCM must be reset by
means of M-MDS (refer to chapter ‘Maintenance and Repair’).
MAP Sensor / IAT Sensor No.1
• The MAP sensor incorporates IAT sensor no.1 and is installed on the intake manifold.
1 Boost sensor 3 PCM
2 IAT sensor no.1
BT-50_01052
Service Training BT-50 01-21
Page 46

Intake-Air System WL-C Engine
Variable Geometry Turbocharger
• The BT-50 uses a VGT, which controls the boost pressure by adjusting guide blades.
The operation is similar to that of the VGT used on the Mazda6 (2.0 MZR-CD).
1 VBC vacuum actuator 3 Exhaust-gas flow
2 Intake-air flow
BT-50_01046
01-22 Service Training BT-50
Page 47

WL-C Engine Intake-Air System
Intake Manifold
• The intake manifold features two helical intake ports per cylinder for optimal swirl of
intake air. The 2
nd
and 3rd cylinder share a common secondary intake port to minimise
the required space.
1 Secondary intake port 4 VSC vacuum actuator
2 Primary intake port 5 Intake manifold
3 VSC shutter valves
BT-50_01024
BT-50_01023
Service Training BT-50 01-23
Page 48

Intake-Air System WL-C Engine
Variable Swirl Control Shutter Valves
• The BT-50 uses VSC shutter valves, which reduce the exhaust emissions at low engine
speeds. The operation is similar to that of the VSC shutter valves used on the Mazda6
pre F/L with 2.0 MZR-CD engine. The VSC shutter valves are located in the secondary
intake ports.
• The VSC shutter valves are operated from idle speed to 2,300 rpm.
Vacuum Chamber
• The vacuum chamber reduces vacuum fluctuations in the vacuum supply line for the
VBC and EGR solenoid valve.
1 To vacuum pump 3 Vacuum chamber
2 To VBC solenoid valve 4 To EGR solenoid valve
BT-50_01025
01-24 Service Training BT-50
Page 49

WL-C Engine Fuel System
Fuel System
Features
• The fuel system of the WL-C engine has the following new features:
– High-pressure pump incorporating gear-type feed pump with overflow valve, three
element-type radial piston pump, fuel metering valve, and fuel temperature sensor
– Common rail with fuel pressure sensor and pressure limiter valve *
– Solenoid valve-type fuel injectors with injector correction factors, directly controlled
by the PCM *
1)
2)
– Multiple fuel injection (up to two pilot injections, but no post injections)
– Check valve in the fuel return line to prevent fuel from flowing back to the injectors
1)
Similar to Mazda3 (1.6 MZ-CD)
*
2)
*
Similar to Mazda6 (2.0 MZR-CD)
Specifications
Item
High-pressure pump
Rail Pressure MPa
LFuel tank capacity
Specification
Bosch CP3S3
at idle Max.
32 160
2WD 4WD
63 70
BT-50_T01012
*1)
Service Training BT-50 01-25
Page 50

Fuel System WL-C Engine
Parts Location
BT-50_01027
1 Fuel gauge sender unit 3 Vehicles with cargo box
2 Fuel tank (4WD) 4 Vehicles without cargo box
01-26 Service Training BT-50
Page 51

WL-C Engine Fuel System
BT-50_01028
1 Check valve in fuel return line 6 Sedimentor switch
2 Fuel injectors 7 Fuel filter (incl. fuel warmer for cold regions)
3 Fuel pressure sensor 8 Common rail
4 High-pressure pump 9 Pressure limiter valve
5 Fuel metering valve
Service Training BT-50 01-27
Page 52

Fuel System WL-C Engine
System Overview
1 Pressure limiter valve 8 High-pressure pump
2 Check valve 9 Fuel filter
3 Fuel injector 10 Sedimentor switch
4 Common rail 11 Fuel tank
5 Fuel pressure sensor 12 To PCM
6 Fuel metering valve 13 Fuel flow
7 Fuel temperature sensor
BT-50_01029
01-28 Service Training BT-50
Page 53

WL-C Engine Fuel System
High-Pressure Pump
• The BT-50 uses the high-pressure pump (CP3S3) with three pumping elements offset by
120°. The operation is similar to the high-pressure pump (CP3.2) used on the Mazda3
(1.6 MZ-CD), which is also manufactured by Bosch.
1 Fuel return 4 High-pressure pump
2 Fuel high-pressure from fuel filter 5 Fuel metering valve
3 Fuel temperature sensor 6 Gear-type feed pump
BT-50_01030
Common Rail
• The common rail is equipped with a fuel pressure sensor and a pressure limiter valve,
which are not available as separate spare parts. In case of a malfunction on these
components the common rail must be replaced as a unit.
1 Connection (fuel injector side) 4 Common rail
2 Fuel pressure sensor 5 Pressure limiter valve
3 Connection (high-pressure pump side)
NOTE: The high-pressure pipes can be re-used up to five times after removing.
BT-50_01031
Service Training BT-50 01-29
Page 54

Fuel System WL-C Engine
Fuel Injectors
• The WL-C engine uses solenoid valve-type fuel injectors, which are directly controlled by
the PCM. The operation is similar to the Mazda3 (1.6 MZ-CD).
• The fuel injectors are mounted with brackets to the cylinder head.
• When a fuel injector has to be replaced the eight-digit injector correction factor must be
programmed into the PCM by means of M-MDS (refer to the chapter ‘Maintenance and
Repair’).
BT-50_01048
1 Return fuel flow (to fuel tank) 7 Valve control plunger
2 Fuel flow (from common rail) 8 Nozzle needle
3 Injector head 9 Valve ball
4 Injector classification code (A0 for the
WL-C engine)
5 Injector correction factor 11 Solenoid valve coil
6 Fuel injector
10 Orifice plate
NOTE: The injector sealing rings located in the lower camshaft bearing case have to be
replaced at each removal of the injectors.
01-30 Service Training BT-50
Page 55

WL-C Engine Exhaust System
Exhaust System
Features
• The exhaust system has the following new features:
– Modified exhaust manifold
– Warm up system with exhaust shutter valve (if equipped)
Parts Location
1 Exhaust manifold 6 Warm up switch
2 Joint pipe 7 With exhaust shutter valve
3 Oxidation catalytic converter 8 Front pipe
4 Main silencer 9 VGT
5 Tail pipe
BT-50_01034
Service Training BT-50 01-31
Page 56

Exhaust System Engine
Warm-Up System
• Since the common-rail diesel engines do not provide enough residual heat for the
heating system of the vehicle, a warm-up system has been adopted to heat up the
passenger compartment quickly at low ambient temperatures. It consists of:
– Warm-up switch
– PCM
– Exhaust shutter valve solenoid valve
– Exhaust shutter valve vacuum actuator
– Exhaust shutter valve
• When the driver pushes the warm-up switch the PCM energizes the exhaust shutter
valve solenoid valve. Thereby vacuum is applied to the exhaust shutter valve vacuum
actuator, which closes the exhaust shutter valve in the front pipe of the exhaust system.
Due to the closed shutter valve the exhaust gas backpressure raises, accelerating
engine warming-up and thus quickly providing warm engine coolant for the heating
system.
Wiring Diagram
1 PCM 3 Exhaust shutter valve solenoid valve
2 Warm up switch
BT-50_01054
01-32 Service Training BT-50
Page 57

WL-C Engine Exhaust System
Exhaust Shutter Valve Solenoid Valve
• The exhaust shutter valve solenoid valve (ON/OFF-type) is located above the vacuum
chamber in the engine compartment.
Exhaust Shutter Valve Unit
• The exhaust shutter valve unit consists of exhaust shutter valve, exhaust flange, transfer
lever, stop screw, actuation rod, and vacuum actuator.
1 Transfer lever 5 Exhaust flange
2 Actuation rod 6 Pivot
3 Exhaust shutter valve vacuum actuator 7 Exhaust shutter valve
4 Stop screw
Operating Conditions
• The warm-up system operates when all of the following conditions are met:
– Warm-up switch pushed
– ECT below 77 °C
– IAT (no.2) below 13 °C
– Engine speed below 1,370 rpm.
BT-50_01053
Service Training BT-50 01-33
Page 58

Emission System WL-C Engine
Emission System
Features
• The emission system of the WL-C engine has the following features:
– One EGR solenoid valve to control EGR valve position instead of two solenoid
valves as used on the B-series
*1)
– EGR control solenoid valve for quick EGR cut-off
– EGR valve position sensor
– Enlarged EGR cooler
– Three-step ISV (Intake Shutter Valve) with vacuum actuator *
– ISV solenoid valve (half) and ISV solenoid valve (full) *
2)
2)
– Oxidation catalytic converter
1)
Similar to Mazda2 pre F/L (1.4 MZ CD)
*
2)
*
Similar to Mazda6 pre F/L (2.0 MZR CD)
Parts Location
BT-50_01032
1 Rollover valves 4 Evaporative chamber
2 Vehicles with cargo box 5 Check valve (two-way)
3 Vehicles without cargo box
01-34 Service Training BT-50
Page 59

WL-C Engine Emission System
BT-50_01033
1 Oxidation catalytic converter 6 EGR control solenoid valve
2 EGR cooler 7 ISV solenoid valve (full)
3 EGR solenoid valve 8 ISV solenoid valve (half)
4 MAF sensor 9 EGR valve
5 ISV 10 Air filter
Service Training BT-50 01-35
Page 60

Emission System WL-C Engine
System Overview
BT-50_01035
1 Air filter 9 EGR solenoid valve
2 ISV 10 EGR control solenoid valve
3 EGR valve position sensor 11 Fuel tank
4 EGR valve 12 Rollover valves
5 MAF sensor 13 Check valve (two-way) (without cargo box)
6 Oxidation catalytic converter 14 Evaporative chamber (without cargo box)
7 ISV solenoid valve (full) 15 To PCM
8 ISV solenoid valve (half)
01-36 Service Training BT-50
Page 61

WL-C Engine Emission System
EGR Solenoid Valve
A To EGR valve 1 EGR solenoid valve
B To vacuum chamber
BT-50_01047
EGR Control
• The PCM controls the position of the EGR valve by means of the EGR solenoid valve
(via duty signal) and the EGR control solenoid valve (via ON/OFF signal).
– When EGR is desired the PCM controls the EGR solenoid valve with a large duty
ratio and energizes the EGR control solenoid valve, so that vacuum is applied to the
EGR vacuum actuator. Due to this the EGR valve opens and exhaust gas is
recirculated.
– When less or no EGR is desired the PCM controls the EGR solenoid valve with a
small duty ratio and energizes the EGR control solenoid valve, so that the vacuum
applied to the EGR vacuum actuator is reduced by a ventilation passage. Due to this
the spring-loaded EGR valve closes and less or no exhaust gas is recirculated.
– When the EGR should be cut off (e.g. during acceleration) the PCM de-energizes the
EGR control solenoid valve, so that the EGR vacuum actuator is ventilated
irrespective of the control by the EGR solenoid valve. Due to this the EGR valve
closes quickly and EGR is stopped.
Service Training BT-50 01-37
Page 62

Emission System WL-C Engine
Intake Shutter Valve
• The WL-C engine uses a three-step ISV, which increases the EGR rate at low engine
speeds and prevents bucking movements of the engine during shut-off. The operation is
similar to the ISV used on the Mazda6 pre F/L (2.0 MZR-CD).
BT-50_01026
1 Fully opened at normal driving (for low
EGR rate or no EGR)
2 Fully closed when the engine is shut off 5 Second vacuum actuator operates
3 Slightly opened to create vacuum (for
high EGR rate)
4 First vacuum actuator operates for high
EGR rate and shortly when the engine is
shut off
shortly when the engine is shut off
NOTE: Function and operation of the ISV are as described for the Denso common rail
system in the course ‘Basic Diesel Engine Management’ (CT-L2005).
01-38 Service Training BT-50
Page 63

WL-C Engine Charging and Starting System
Charging and Starting System
• A modified generator has been adopted for the charging system, while the starting
system is identical to that used on the B-Series.
Specification
WL-C
BT-50_T01009
Battery
Generator
Starter
Parts Location
Item
Voltage (V) 12
Type and capacity
(5-hour rate)
Output (V-A) 12-70
Regulated voltage (V) 14.1-14.7
Self diagnosis function Equipped
Type Coaxial reduction
Output (kW) 2.2
(Ah) 95D31R (64)
BT-50_01039
1 Starter 3 Generator
2 Additional battery (for cold regions) 4 Main battery
Service Training BT-50 01-39
Page 64

Control System WL-C Engine
Control System
Features
• The control system of the WL-C engine has the following new features:
– CKP (CranKshaft Position) sensor located at the flywheel
– CMP (CaMshaft Position) sensor
– PCM (Powertrain Control Module) with extended control strategies
Specifications
Item
IAT sensor No.2 (built into MAF sensor) Thermistor
MAF sensor Hot-wire
IAT sensor No.1(built into MAP sensor) Thermistor
MAP sensor Piezoelectric element
ECT sensor Thermistor
CMP sensor Hall element type
CKP sensor Inductive type
APP sensor Potentiometer
EGR valve position sensor Potentiometer
BARO sensor (built into PCM) Piezoelectric element
Fuel temperature sensor Thermistor
Fuel pressure sensor Piezoelectric element
Neutral switch ON/OFF
CPP switch ON/OFF
Idle switch ON/OFF
Specification
WL-C
BT-50_T01006
01-40 Service Training BT-50
Page 65

WL-C Engine Control System
Parts Location
BT-50_01036
1 MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp) 13 CMP sensor
2 Glow indicator light 14 Fuel pressure sensor
3 APP sensor 15 High-pressure pump
4 Main relay 16 Fuel temperature sensor
5 Idle switch 17 Fuel metering valve
6 Brake switch 18 ECT sensor
7
DLC-2
8 CPP switch 20 Glow plug relay
9 A/C switch 21 A/C relay
10 DLC-1 22 EGR valve position sensor
11 Warm up switch 23 PCM (with built-in BARO sensor)
12 MAF sensor / IAT sensor no.2 24 CKP sensor
(Data Link Connector)
19 MAP sensor / IAT sensor no.1
Service Training BT-50 01-41
Page 66

Control System WL-C Engine
System Overview
BT-50_01037
01-42 Service Training BT-50
Page 67

WL-C Engine Control System
1 EGR valve position sensor 22 Idle switch
2 VBC solenoid valve 23 APP sensor
3 MAF sensor / IAT sensor no.2 24 Main relay
4 Exhaust shutter valve 25 Engine switch
5 Exhaust shutter solenoid valve 26 Neutral switch
6 Oxidation catalytic converter 27 A/C switch
7 CMP sensor 28 DLC-1 / DLC-2
8 ECT sensor 29 Vehicle speed signal
9 Fuel injectors 30 CAN Bus
10 CKP sensor 31 CPP switch
11 Glow plugs 32 A/C relay
12 VSC solenoid valve 33 BARO sensor
13 MAP sensor / IAT sensor no.1 34 PCM
14 Fuel pressure sensor 35 Glow plug relay
15 Fuel metering valve 36 MIL
16 Fuel temperature sensor 37 Glow indicator light
17 Sedimentor switch 38 Tachometer
18 ISV solenoid valve (full) 39 To PCM
19 ISV solenoid valve (half) 40 To glow plug relay
20 EGR solenoid valve 41 To IC (Instrument Cluster)
21 EGR control solenoid valve
Service Training BT-50 01-43
Page 68

Control System WL-C Engine
g
Block Diagram
Input
Battery
CPP switch
Neutral switch
APP sensor Fuel metering valve
Idle switch Fuel injectors
MAF sensor / IAT sensor no.2 VBC solenoid valve
ECT sensor VSC solenoid valve
Fuel temperature sensor EGR solenoid valve
BARO sensor EGR control solenoid valve
PCM Control
Strate
Idle speed control
Glow control
Variable boost
Variable swirl control
Fuel injection amount
Fuel injection timing
ies
control
control
control
Output
MAP sensor / IAT sensor no.1 ISV solenoid valves (half, full)
Fuel pressure sensor Glow indicator light
CMP sensor Glow plug relay
CKP sensor A/C relay
Vehicle speed signal Immobiliser module
A/C switch MIL
EGR valve position sensor
Immobiliser module
Warm up switch
Multiple fuel injection
control
Fuel pressure control
EGR control
A/C cut-off control
Immobiliser-related
information
OBD
Warm up system
control
Exhaust shutter solenoid
valve
BT-50_T01007
01-44 Service Training BT-50
Page 69

WL-C Engine Control System
Relationship Chart
x: Applicable
Control Item
Item
Idle speed control
Warm up system control
Glow control
Variable boost control
Variable swirl control
Fuel injection timing control
Multiple fuel injection control
Fuel pressure control
EGR control
A/C cut-off control
Immobiliser system
Input device
Battery x
CPP switch x x x x x
Neutral switch x x x x x
APP sensor x x xxxxxxx
Idle switch x
MAF sensor x xxxx
IAT sensor no.2 x xxxxx
IAT sensor no.1 x
ECT sensor xxxxxxxxxx
Fuel temperature sensor x x
BARO sensor xxxxxx
MAP sensor x
Fuel pressure sensor x x
CMP sensor x x x
CKP sensor x xxxxxxxx
Vehicle speed signal x x x
A/C switch x
EGR valve position sensor x
Warm up switch x x
Immobiliser-related information x
Output device
Fuel metering valve x x
Fuel injectors x x x x
VBC solenoid valve x
VSC solenoid valve x
EGR control solenoid valve x
ISV solenoid valve (half, full) x
Exhaust shutter solenoid valve x
Glow indicator light x
Glow plug relay x
A/C relay x
Immobiliser-related information x
BT-50_T01008
Service Training BT-50 01-45
Page 70

Control System WL-C Engine
Crankshaft Position Sensor
• The inductive type CKP sensor is located at the upper part of clutch housing. The pulse
wheel is installed to the primary mass of the flywheel, and has 58 projections with a
space of 6°crank angle between each projection. A space of 18° defines a determined
crankshaft position.
BT-50_01050
1 CKP sensor 3
2 Pulse wheel
NOTE: When the CKP signal fails during engine operation, the engine stalls and will not start
again.
Flywheel
01-46 Service Training BT-50
Page 71

WL-C Engine Control System
Camshaft Position Sensor
• The Hall-type CMP sensor is installed at the right front side of the cylinder head. A
projection on the intake camshaft pulley covers 26° camshaft rotation angle.
BT-50_01051
1 CMP sensor 4 Pulse wheel
2 PCM 5 Intake camshaft pulley
3 CPU 6 Gap (1,4 mm)
NOTE: When the CMP signal fails during engine operation, the engine continues to run and
will start again (with little extended cranking time) after it has been shut off.
Service Training BT-50 01-47
Page 72

Control System WL-C Engine
Powertrain Control Module
Features
• The PCM has the following new features:
– Programmable module
– Built in BARO sensor
– A/C (Air Conditioning) cut-off control
– Glow plug relay with feedback to PCM *
– Integrated RFW (Remote Free Wheel) control on versions with 4WD (refer to chapter
‘Driveline / Axle’)
– HS-CAN (High Speed Controller Area Network) connection to DLC-2 for
communication with M-MDS (refer to chapter ‘Body & Accessories’)
1)
Similar to Mazda6 (2.0 MZR CD)
*
• The PCM is mounted on the driver’s side in the passenger compartment at the lower Apillar. On vehicles with U.K. specification a cover with shear bolts secures the PCM.
1)
1 PCM 3 Connector
2 Bracket
BT-50_01040
01-48 Service Training BT-50
Page 73

WL-C Engine Control System
• The PCM has two connectors with 154 pins in total.
BT-50_01041
• Similar to other current modules the PCM now allows to carry out the following
programming functions by means of M-MDS:
– Programmable module installation (to replace PCM)
– Module reprogramming (to update software calibration)
– Programmable parameters (to input injector correction factors)
– As-build data (to update As-build data)
– Data reset (PCM and MAF sensor)
– MAF learning (to adapt MAF sensor condition to PCM)
NOTE: For replacement of the PCM certain procedures have to be followed (refer to the
chapter ‘Maintenance and Repair’).
A/C Cut-Off Control
• Under the following engine operating conditions the PCM turns the A/C relay off to
improve driveability:
– For a certain time when the accelerator-opening angle is 87.5 % or more.
– Permanently when ECT is above 113 °C until temperature falls below 110 °C.
Service Training BT-50 01-49
Page 74

Control System WL-C Engine
Glow Plug Relay
• The glow plug relay has a feedback line to the PCM to facilitate failure detection. The
PCM operates the glow plug relay for max. 120 s at an engine coolant temperature
below 32 °C.
1 From main relay 5 Glow plugs
2 Glow plug relay 6 Glow plug circuit fuse
3 PCM 7 From battery
4 Glow indicator light (IC)
BT-50_01038
01-50 Service Training BT-50
Page 75

WL-C Engine Control System
On-Board Diagnostic System
Features
• The OBD (On-Board Diagnostic) system has the following features:
– MIL
– Self test
– PID monitor
– Simulation test
Malfunction Indicator Lamp
• The MIL is located in the IC. It illuminates when emission related malfunction have been
detected by the OBD system. In this case a corresponding DTC is stored in the PCM.
The glow plug indicator light has no indication function for any detected malfunction as
on the B-series.
Self Test
• The self-test function allows reading out DTCs of the PCM. Therefore connect the MMDS to the DLC-2 of the vehicle and select the option ToolboxÆSelf TestÆModulesÆ
PCM ÆRetrieve CMDTCs.
• In addition the KOEO (Key On, Engine Off) self-test and the KOER (Key On, Engine
Running) self test can be performed. Therefore connect the M-MDS to the DLC-2 of the
vehicle and select the option ToolboxÆSelf TestÆModulesÆPCMÆKOEO/KOER On
Demand Self Test.
NOTE: The self-test function cannot be carried out by using DLC-1.
Service Training BT-50 01-51
Page 76

Control System WL-C Engine
A
A
A
PID Monitor
• The PID monitor function allows monitoring the PIDs of the PCM. Therefore connect the
M-MDS to the vehicle and select the option ToolboxÆDataloggerÆModulesÆPCM.
PID Definition Unit/Condition
AT
AC_REQ A/C request signal
CCS
APP Accelerator pedal position %
APP2 Accelerator pedal position sensor no.2
ARPMDES Target engine speed rpm
BARO Barometric pressure
BOO Brake switch OFF/ON
CPP Clutch pedal position switch OFF/ON
DTCCNT DTC count —
ECT Engine coolant temperature
EGRV2 EGR control solenoid valve OFF/ON
FIP_SCV Fuel metering valve A
FLT Fuel temperature °C
FRP Fuel rail pressure Pa
GP_LMP Glow indicator light OFF/ON
GPC Glow plug relay OFF/ON
IASV ISV solenoid valve (half) OFF/ON
IASV2 ISV solenoid valve (full) OFF/ON
IAT Intake air temperature (IAT sensor no.1)
INGEAR Load / no load condition OFF/ON
IVS Idle switch OFF Idle / Idle
LOAD Engine load %
Ambient air temperature °C
OFF/ON
/C relay
Accelerator pedal position sensor no.1APP1
High-pressure pump flow controlFIP_FL
OFF/ON
%
V
%
V
Pa
V
°C
V
A
%
°C
V
BT-50_T01010a
01-52 Service Training BT-50
Page 77

WL-C Engine Control System
PID Definition Unit/Condition
Mass airflowMAF
MAP Manifold absolute pressure
MIL Malfunction indicator lamp OFF/ON
MIL_DIS Distance travelled since the MIL was activated km
RPM Engine speed rpm
SEGRP DSD Desired EGR valve position %
SELTESTDTC Diagnostic trouble codes —
VBCV VBC solenoid valve %
VPWR Module supply voltage V
VSS Vehicle speed km/h
WARMSW Warm-up switch OFF/ON
WARMSOL Exhaust solenoid valve shutter valve OFF/ON
Simulation Test
• The simulation test function allows activating certain PIDs of the PCM. Therefore
connect the M-MDS to the vehicle and select the option ToolboxÆDataloggerÆ
ModulesÆPCM.
g/s
V
Pa
V
BT-50_T01010b
×: Applicable
—: Not applicable
PID Applicable component Unit/Condition
ACCS # A/C relay OFF/ON × x
EGRV2 # EGR control solenoid valve OFF/ON × x
GP_LMP # Glow indicator light OFF/ON × x
GPC # Glow plug relay OFF/ON × x
IASV # ISV solenoid valve (half) OFF/ON × x
IASV2 # ISV solenoid valve (full) OFF/ON × x
INJ_1 # Fuel injector no.1 OFF — ×
INJ_2 # Fuel injector no.2 OFF — ×
INJ_3 # Fuel injector no.3 OFF — ×
INJ_4 # Fuel injector no.4 OFF — ×
SEGRP # EGR solenoid valve % — x
VBCV #
VBC solenoid valve
%—
Test condition
KOEO KOER
BT-50_T01011
x
Service Training BT-50 01-53
Page 78

Control System WL-C Engine
Maintenance and Repair
MAF Sensor Learning Function
• The MAF learning procedure by means of M-MDS must be carried out at every service
interval. During this procedure the MAF learning is performed at engine speeds of
750 min
PowertrainÆEngine ChecksÆLearning and follow the instructions.
• The MAF learning procedure can also be initiated manually via DLC-1. Therefore,
connect terminal TEN (Test ENgine) five times to ground within five seconds. The glow
indicator light is illuminated while MAF learning is performed and flashes five times after
the procedure is completed.
Replacing the MAF Sensor
• After replacing the MAF sensor certain procedures have to be performed in the following
order:
1. Perform MAF sensor data reset procedure to reset the adaptation values in the PCM
-1
, 1850 min-1, and 2500 min-1. To perform the procedure select ToolboxÆ
for the MAF sensor. Therefore, select the option ToolboxÆPowertrainÆData
ResetÆMAF sensor and follow the instructions.
2. Perform KOEO self-test procedure.
3. Turn the engine switch to the OFF position.
4. Wait for 5 s.
5. Start the engine.
6. Perform KOER self-test procedure.
7. Turn the engine switch to the off position.
NOTE: It is recommended to perform the MAF sensor learning function when a MAF data
reset has been carried out.
01-54 Service Training BT-50
Page 79

WL-C Engine Control System
PCM Replacement
• When the PCM has been replaced certain procedures have to be performed in the
following order:
1. Perform PCM configuration procedure.
2. Perform IMMOBILISER SYSTEM programming.
3. Perform PCM data reset procedure to reset all adaptation values in the PCM with the
aid of the M-MDS. Therefore, select the option ToolboxÆPowertrainÆData
ResetÆPCM and follow the instructions.
4. Perform After repair procedure.
5. Start the engine.
6. Turn the engine switch to the off position.
7. Turn the engine switch to the ON position (Engine off).
8. Perform KOEO self-test procedure.
9. Turn the engine switch to the off position.
10. Wait for 5 s.
11. Start the engine.
12. Perform KOER self-test procedure.
13. Turn the engine switch to the off position.
NOTE: For further information refer to the W/M.
NOTE: It is recommended to perform the MAF sensor learning function when a PCM data
reset has been carried out.
Service Training BT-50 01-55
Page 80

Control System WL-C Engine
Notes:
01-56 Service Training BT-50
Page 81

Suspension
Suspension
Features
• The front and rear suspension of the BT-50 have the following new features:
– Enlarged diameter and modified damper valve tuning of the double acting low
pressurised shock absorbers
– Enlarged diameter of the front stabiliser
– Extended leaf springs on the rear axle
– Modified wheel alignment values
Specifications
Item
Front suspension
Suspension type
Spring type
Stabilizer
Shock absorber type Cylindrical, double-acting
Front wheel
alignment
(Unloaded
condition*)
Rear suspension
Suspension type
Spring type
Shock absorber type Cylindrical, double-acting
Type
Diameter mm 27 28
Maximum steering
angle
Total toe-in mm 2-8 3-9
Camber angle (reference value)
Caster angle (reference value)
Steering axis inclination 8°25'
Inner 33°00'-37°00' 31°30'-35°30'
Outer 30°00'-35°00' 27°00'-32°00'
2WD 4WD
0°35' ±1°
1°56' ±1°
Specification
Double wishbone
Torsion bar spring
Torsion bar
RAP cab: 0°44' ±1°
DBL cab: 0°45' ±1°
RAP cab: 2°07' ±1°
DBL cab: 2°06' ±1°
RAP cab: 10°37'
DBL cab: 10°35'
Leaf spring
Semi elliptic leaf spring
* : Fuel tank full; engine cool ant and engi ne oi l at specified level, and spare tire, jack and tools in designated position.
BT-50_T02001
Service Training BT-50 02-1
Page 82

Suspension
Parts Location
Front Suspension 2WD
1 Front shock absorber 4 Lower arm
2 Torsion bar spring 5 Tension rod
3 Upper arm 6 Front stabiliser
Front Suspension 4WD
BT-50_02002
BT-50_02003
1 Shock absorber 4 Lower arm
2 Torsion bar spring 5 Front stabiliser
3 Upper arm
02-2 Service Training BT-50
Page 83

Suspension
Rear Suspension
BT-50_02004
1 4WD 3 Shock absorber
2 2WD 4 Leaf spring
Service Training BT-50 02-3
Page 84

Wheels and Tyres Suspension
Wheels and Tyres
• The wheels and tyres have the following new features:
– Modified wheel and tyre sizes
– Modified wheel offset
– New designs for 15- and 16-inch aluminium alloy wheels and 15-inch steel wheels.
1 15-inch standard steel rim (2WD) 3 15-inch aluminium alloy rim (2WD)
2 15-inch design steel rim (4WD) 4 16-inch aluminium alloy rim (4WD)
BT-50_02001
02-4 Service Training BT-50
Page 85

Suspension Wheels and Tyres
Specifications
Specification
Aluminium
alloy
88.2-117.6
1.5 max.
2.0 max.
15 x 61/2JJ 16 x 7J
139.7
Steel
235/75R15
109S
210
210 210
1.6
Aluminium
245/70R16
alloy
111S
210
Wheel
Tyre
Wheel
and
tyre
Item
Size
Offset
Pitch circle diameter
Material
Size
Front
Air
pressure
kPa
Rear
Remaining tread
Wheel nut tightening
torque
Wheel and tyre
runout mm
15 x 61/2J
mm 25 10
mm
Steel
215/70R15C 106/104S
Up to four
persons
Full load
Up to four
persons
Full load 290 270
mm
Nm
Radial
direction
Axial
direction
20
220
210
375
BT-50_T02002
Service Training BT-50 02-5
Page 86

Wheels and Tyres Suspension
Notes:
02-6 Service Training BT-50
Page 87

Driveline / Axle
A
Driveline / Axle
Features
• The driveline / axle of the BT-50 has the following new features:
– Modified transfer case due to increased engine torque and new transmission
– RFW control with OBD function integrated in PCM (separate RFW module has been
dropped)
NOTE: Further information can be found in the Training Manuals ‘B-Series’ (NMT-005) and
in ‘Manual transmission and 4WD’ (CT-L1002).
Specifications
Specification
Taper roller bearing
Taper roller bearing
Semi-floating
Banjo type
739
35.0
Hypoid gear
Straight bevel gear
8.9
API service GL-5
SAE 90
Hypoid gear
Straight bevel gear
8.00
3.727
bove -18°C: SAE 90
Below -18°C: SAE 80
BT-50_T03001
Drive type
Transmission type
Front axle
Bearing type
Rear axle
Bearing type
Support type
Casing
Length
Diameter
Rear differential
Reduction gear
Differential gear
Ring gear size
Final gear ratio
Front differential
Reduction gear
Differential gear
Ring gear size
Final gear ratio
Item
2WD 4WD
S15M-D S15MX-D
mm
mm
(Inch)
3.416 3.727
Grade
TypeDifferential oil
TypeDifferential oil
Viscosity
Capacity L 2.45 2.35
(Inch)
Grade API service GL-5
Viscosity
Capacity L 1.9
_
Service Training BT-50 03-1
Page 88

RFW System Driveline / Axle
RFW System
• The RFW system is controlled by the PCM. The input and output components are the
same as used for the B-Series with separate RFW control module.
Parts Location
BT-50_03001
1 RFW main switch 7 RFW vacuum actuator
2 Transfer neutral switch 8 Joint shaft component
3 4WD switch 9 Lock solenoid valve
4 One-way check valve 10 Free solenoid valve
5 RFW switch 11 PCM
6 RFW unit
03-2 Service Training BT-50
Page 89

Driveline / Axle RFW System
System Overview
1 4WD indicator light 11 One-way check valve
2 RFW indicator light 12 Lock solenoid valve
3 To battery 13 Free solenoid valve
4 Front differential 14 RFW main switch
Lock
5
6 Free 16 Vehicle battery
7 RFW vacuum actuator 17 Engine switch
8 RFW unit 18 Selector lever
9 RFW switch 19 4WD switch
10 To vacuum pump 20 Transfer neutral switch
15 PCM
BT-50_03002
Service Training BT-50 03-3
Page 90

RFW System Driveline / Axle
On-Board Diagnostic System
• Detected malfunctions are stored as 4-digit DTCs in the PCM memory and can be
retrieved by means of M-MDS.
DTC Table
DTC Malfunction
P1812 RFW lock solenoid valve circuit failure
P1813 RFW lock solenoid valve open circuit
P1814 RFW lock solenoid valve circuit/short to battery
P1815 RFW lock solenoid valve circuit/short to ground
P1878 RFW free solenoid valve circuit failure
P1879 RFW free solenoid valve open circuit
P1880 RFW free solenoid valve circuit/short to battery
P1885 RFW free solenoid valve circuit/short to ground
BT-50_T03002
Simulation Test
• A simulation test has been adopted to check the function of certain output components
by means of M-MDS.
PID Applicable component
4WDMODE_L #
HUBLOCK #
HUBLOCK_L #
NTFLAMP #
Condition
4WD indicator light OFF/ON
RFW lock solenoid valve OFF/ON
RFW free solenoid valve OFF/ON
RFW indicator light OFF/ON
Test condition
Engine switch at
ON
BT-50_T03003
NOTE: Further diagnosis is supported by the symptom troubleshooting section in the W/M.
03-4 Service Training BT-50
Page 91

Transmission Clutch
Clutch
Features
• The clutch system of the BT-50 has the following new features:
– Clutch master cylinder with one-way valve and pulsation damper
– Dual mass flywheel
Specifications
Item
Manual transmission type
Clutch control
Clutch cove r
Clutch disc
Clutch pedal
Clutch master cylinder inner diameter
Clutch release cylinder inner diameter
Clutch fluid type
Spring type
Set load
Outer diameter mm 250
Inner diameter mm 155
Type
Pedal ratio
Full stroke mm
Specification
S15M-D, S15MX-D
Hydraulic
Diaphragm
N
mm 15.87
mm 22.23
SAE J1703, FMVSS 116 DOT-3
10,100
Suspended
5.2
152
BT-50_T05001
Service Training BT-50 05-1
Page 92

Clutch Transmission
Parts Location
BT-50_05013
1 Dual-mass flywheel 5 Clutch release cylinder
2 Clutch disc 6 Clutch release collar
3 Clutch cover 7 Clutch pedal
4 Clutch release fork 8 Clutch master cylinder
05-2 Service Training BT-50
Page 93

Transmission Clutch
Clutch Master Cylinder
• The one-way valve prevents harsh clutch engagement by a throttle, which prevents too
quick back flowing of the fluid when the clutch is engaged thus ensuring smooth driving
off.
• The pulsation damper reduces pressure fluctuations in the hydraulic line during clutch
operation, minimizing operation noise and vibration transmission to the clutch pedal.
1 One-way valve 2 Pulsation damper
BT-50_05001
Service Training BT-50 05-3
Page 94

Clutch Transmission
Dual Mass Flywheel
• The dual mass flywheel compensates torque fluctuations thus reducing rattle noises of
the transmission gears.
1 Torsional-vibration damping spring 3 Primary flywheel
2 Secondary flywheel
BT-50_05014
05-4 Service Training BT-50
Page 95

Transmission S15M(X)-D Manual Transmission
S15M(X)-D Manual Transmission
• Due to the increased engine torque the newly developed three-shaft 5-speed manual
transmission S15M-D has been adopted for the 2WD version, while the S15MX-D
transmission with an additional transfer case has been adopted for the 4WD version.
• Except for the transfer case the construction and operation of both transmissions are
basically the same. They have superseded the R15M(X)-D transmission used on the BSeries.
Features
• Construction and operation of the S15M(X)-D transmission are quite similar to the P66MD transmission introduced on the MX-5 (NC). It has the following features:
– Triple-cone synchroniser mechanism for the 1
– Double-cone synchroniser mechanism for the 3
– Single-cone synchroniser mechanism for 4
– Integrated shift mechanism unit comprising shift rods and forks, detent balls, and pin-
type interlock mechanism
st
and 2nd gear
rd
gear
th
, 5th and reverse gear
– Cam-type reverse lockout mechanism
Service Training BT-50 05-5
Page 96

S15M(X)-D Manual Transmission Transmission
A
A
A
Specifications
Item
Transmission type
Transmission/Transfer control
Shift assist
1GR
2GR
Gear ratio
Transmission case oil
Shift control case oil
[S15M-D]
Transfer ratio
Transfer case oil
[S15MX-D]
3GR
4GR
5GR
Reverse
Type
Capacity
(approx.quantity)
Type Manual Transmission fluid type
Capacity
(approx.quantity)
High
Low
Type
Capacity
(approx.quantity)
Specification
S15M-D, S15MX-D
Floor-shift
Synchromesh
3.905
2.248
1.491
1.000
0.800
3.391
Manual Transmission fluid type
L3.55
ml 220-260
1.000
2.020
Manual Transmission fluid type
L1.85
BT-50_T05002
05-6 Service Training BT-50
Page 97

Transmission S15M(X)-D Manual Transmission
Overview
BT-50_05002
A Extension housing (S15M-D) 5 Reverse idler gear
B Transfer case (S15MX-D) 6 Reverse gear
1 Output shaft 7 5
rd
2 3
3 2
4 1
gear 8 Counter shaft
nd
gear 9 Input shaft
st
gear
th
gear
Service Training BT-50 05-7
Page 98

S15M(X)-D Manual Transmission Transmission
Power Flow
BT-50_05003
1st Gear
2nd Gear
3rd Gear
BT-50_05004
BT-50_05005
05-8 Service Training BT-50
Page 99

Transmission S15M(X)-D Manual Transmission
BT-50_05006
4th Gear
5th Gear
Reverse Gear
BT-50_05007
BT-50_05008
Service Training BT-50 05-9
Page 100

S15M(X)-D Manual Transmission Transmission
Shift Mechanism
• Most of the shift mechanism components are accommodated in the shift mechanism
unit. Due to its five speed layout the S15M(X)-D transmission requires four shift rods in
total (three in the shift mechanism unit and one in the transmission housing).
1 Section A-A 3 Control rod
2 Shift mechanism unit 4 Shift rod
BT-50_05009
05-10 Service Training BT-50
 Loading...
Loading...