Page 1

Release Notes Supporting
Cajun P220, P550, and P550R Switches
Software Release 4.0.1
November 1999
Part # 610-0120-061
Page 2

Release 4.0.1 Notes Supporting the Cajun P220, Cajun P550, and Cajun P550R Switches
© Copyright LUCENT TECHNOLOGIES 1999 ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
Printed in USA, November 1999
The products, specifications, and other technical information regarding the products contained in this document are subject to
change without notice. All information in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable, but is presented without warranty
of any kind, express or implied, and users must take full responsibility for their application of any products specified in this
document. Lucent disclaims responsibility for errors which may appear in this document, and it reserves the right, in its sole
discretion and without notice, to make substitutions and modifications in the products and practices described in this document.
Lucent, Cajun, CajunDocs, OpenTrunk, P550, P220 and CajunView are trademarks of Lucent Technologies.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows NT, Windows 95, Windows 98, and Internet Explorer are trademarks or registered trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation in the U.S. and/or other countries.
OpenView is a trademark of Hewlett Packard Company.
Netscape and Netscape Navigator are registered trademarks of Netscape Communications Corporation in the United States and
other countries.
3Com is a registered trademark and PACE is a trademark of 3Com or its subsidiaries.
Adobe is a registered trademark of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
Bay Networks and System 5000 are registered trademarks of Nortel Networks.
Cisco Catalyst 5000 is a registered trademark of Cisco Systems Incorporated.
ALL OTHER TRADEMARKS MENTIONED IN THIS DOCUMENT ARE PROPERTY OF THEIR RESPECTIVE OWNERS.
Page 3
Chapter 1 Read Me First
This section of the Release Notes Supporting the Cajun P220 and Cajun P550 family of switches
contains information that is crucial to know before proceeding to install or use the Cajun switch.
Please review the following release notes before continuing to the Overview section.
CAUTION: Release 4.0.1 embedded software requires a MINIMUM of 16 MB DRAM
(Dynamic Random Access Memory) to run on a Cajun P550 Layer 2
supervisor module. BEFORE upgrading, ensure that the switch meets this
16 MB DRAM requirement. A memory upgrade is not required for a Cajun
P550 Layer 3 supervisor module, or the Cajun P220.
CAUTION: Release 4.0.1 introduces a new ASCII configuration file format that replaces
the traditional binary (*.cfg) files used to store and restore saved
configurations. You must save your binary configuration before upgrading the
switch to Release 4.0.1 or rebooting the switch for the first time using Release
4.0.1. For information about saving your binary configuration, refer to the
“Installation” section of these release notes.
CAUTION: When making configuration changes to the switch, explicitly save changes by
copying the running configuration to the startup configuration to ensure that
the changes persist after the switch is restarted.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 3
Page 4

Chapter 2 Overview
This set of release notes supports the Cajun P220, Cajun P550, and Cajun P550R switches. For
detailed information about your product, refer the basic set of user documentation. These release
notes are intended to get you up and running as quickly as possible. The following topics are
covered:
• Read Me First
• Overview
• New Features
• Product Binaries
• Installation
• Problems and Workarounds
• Functional Restrictions
• Bug Fixes
• Additional Undocumented Commands
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 4
Page 5

Chapter 3 New Features
This section covers features specified for Release 4.0.1 of the Cajun P220, Cajun P550, and Cajun
P550R switches. All supporting documentation is available from the Lucent Technologies Web
site at HTTP://pubs.lucentctc.com.
The Cajun P550R switch, which supports Layer 3 technology, contains features that are not
available in the Layer 2 Releases of the switch.
The following new features are available in Release 4.0.1 through the Enhanced Command Line
Interface or the Web Agent:
• VTP eavesdropping (Cisco compatibility)
• LDAP Release 3 client necessary for RealNet Rules support
• Support for the following MIBs:
- Policy capabilities MIB (proprietary)
- RIP v1/v2 (RFC1724)
- OSPFv2 (RFC1850)
- IGMP – Internet Group Management Protocol MIB (draft-ietf-edmr-igmp-mib-
12.txt)
- IP Interface (proprietary)
- IP Forwarding/Route Table (RFC2096)
- IP ARP (RFC2011)
- DVMRP (draft)
- AppleTalk (RFC1243)
- IP Access List (proprietary)
- IPX Interfaces (proprietary)
• VRRP (Virtual Redundant Router Protocol, RFC 2338)
• Multiple configuration images – Multiple configuration files may be stored in NVRAM
and loaded into the switch at a later date
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 5
Page 6

• IPX Multinetting
• ASCII text configuration files with upload/download
• Redundant backplane support for Cajun P550R switches
• SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol)
• AppleTalk Routing
• Hexadecimal addressing – subnet masks may be represented by a hexadecimal value
• Access lists
- Source and destination IP address wildcarding and TCP/UDP ranges
- TCP established connection filtering
• Configuration scripting via command line execution
Additional Undocumented Features
Features in this section are not documented in the released product documentation.
BOOTP/DHCP Relay Gateway
You can Enable or Disable the BOOTP/DHCP Relay Gateway from the Enhanced CLI in Interface
mode using the command '[no] ip bootp-dhcp gateway'. From the Cajun Switch Web
Agent, this setting is located in the IP Interfaces dialog box. To open the IP Interfaces dialog box,
in the IP Configuration section of the Web Agent, click Interfaces. The default for this parameter
is Disable.
This parameter affects how the router chooses a source interface for the reception of BOOTP/
DHCP requests received on a VLAN, as this source interface determines the value that is inserted
by the router into the giaddr field and designates the IP subnet pool that the DHCP server uses
to assign an address.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 6
Page 7
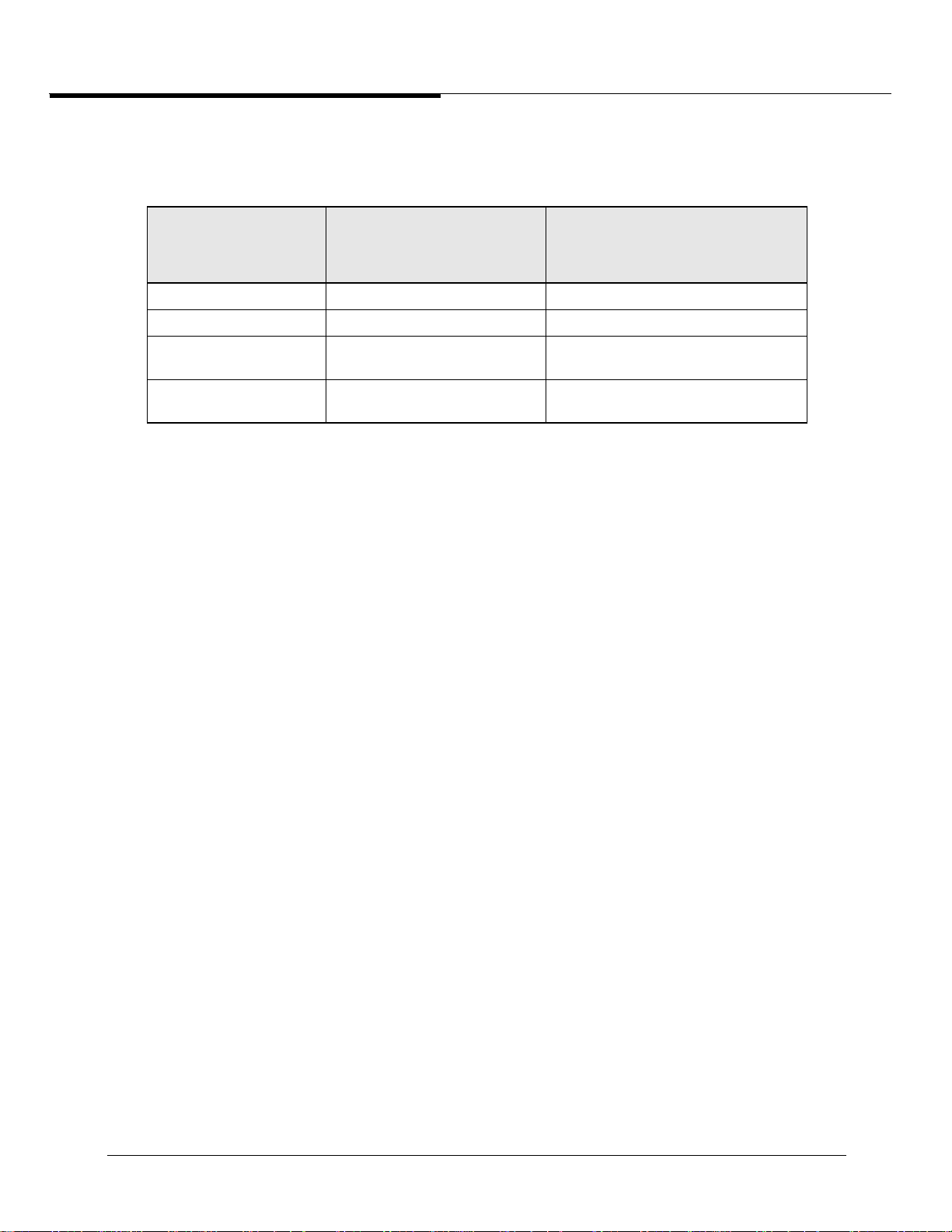
The source interface is determined as follows:
Table 1-1: Source Interface Determination: BOOTP/DHCP Relay Gateway
Number of
Interfaces on
VLAN
1 N/A The interface itself.
1 0 The first UP interface found.
1 1 Preferred interface if UP; otherwise, first
1 1 First preferred UP interface found;
Number of Interfaces
with Parameter
Enabled
Source Interface
UP interface found.
otherwise, first UP interface found.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 7
Page 8
Chapter 4 Product Binaries
The following table shows the binary files that contain embedded software for the Release 4.0.1
Cajun P220, Cajun P550, and Cajun P550R switches.
Table 1-2: Product Binary Files
Type of Switch Binary File
Cajun P220 m2200_v4.0.1.bin
Cajun P550 m5500_v4.0.1.bin
Cajun P550R m5500r_v4.0.1.bin
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 8
Page 9

Chapter 5 Installation
CAUTION: Release 4.0.1 embedded software requires a MINIMUM of 16 MB DRAM
(Dynamic Random Access Memory) to run on a Cajun P550 Layer 2
supervisor module. BEFORE upgrading, ensure that the switch meets this
16 MB DRAM requirement. A memory upgrade is not required for a Cajun
P550 Layer 3 supervisor module, or the Cajun P220.
NOTE: Release 4.0.1 introduces a new ASCII configuration file format that replaces the
traditional binary (*.cfg) files used to store and restore saved configurations. Before
upgrading the switch to Release 4.0.1, review the Installation section of these release
notes.
The following memory upgrade kits are available through your local sales representative:
Table 1-3: Module Descriptions
Description Model Number
16 MB Memory
Upgrade Kit
M5500-MEM16
32 MB Memory
Upgrade Kit
Use the following procedure to upgrade from Release 3.1 to Release 4.0.1 of the Cajun P220,
Cajun P550, or Cajun P550R switch. For more detailed installation procedures, refer to the Cajun
P550/P220 Switch Installation Guide.
M5500-MEM32
Downgrading to a Previous Release
1. In the CLI Configuration section of the Web Agent, click Config File Management.
In the Configuration File Management dialog box, save your Release 4.0.1 Running
Configuration (running.txt) to a TFTP server for potential later use.
2. From the Release 4.0.1 Enhanced CLI, clean the current configuration by issuing the
nvram init command.
3. Configure the switch to select the APP that contains the previous code release.
4. Reset the switch.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 9
Page 10

5. Use the CLI setup command to configure the switch.
6. Restore the binary configuration files of the release (3.1 or previous) you want to
restore. These configuration files do not reflect any changes you made to the
running configuration while using Release 4.0.1.
Problem: Release 4.0.1 of the Cajun switch contains new range-checking procedures
that may be reasonably more restrictive than those of previous releases.
Workaround: If you have a parameter in 3.1 that is outside the 4.0 range, it will be
noted in the Script Log File. After the second reboot the switch, check the Script Log File
to find out if any errors occurred as the script executed. To check the Script Log File, click
Script Log File in the CLI Configuration section of the Web Agent. If errors were
found, scroll up to find the particular error message. If you prefer to use the Enhanced
CLI, at the system prompt, type: show file logfile.txt.
NOTES:
• Some of the associated CLI command incorrectly list “Multilayer” and “3Com”.
These are not supported by the Cajun P550 48-Port 10/100 Media Module (M5548E100TC).
• In Release 4.0.1 of the Cajun switch, the Web Agent provides a new set of dialog
boxes in which you can:
- View startup and running configuration files
- View script execution log files
- Copy and manage configuration files
Ensure that you copy configuration files to a TFTP server or other storage location using
the Configuration File Management dialog box.
Upgrading from Release 3.1 or Previous Releases
Use the following procedure to upgrade the switch from Release 3.1 to Release 4.0.1.
NOTE: The Cajun switch does not support a direct upgrade to Release 4.0.1 from
releases prior to Release 3.0. If your switch runs a release prior to 3.0, upgrade the
switch to Release 3.0 or 3.1. Then, use the following procedure to upgrade the switch
from Release 3.0 or 3.1 to Release 4.0.1.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 10
Page 11

7. Save your Release 3.1 binary configuration file:
a. In the Memory Subsystems section of the Web Agent, click TFTP Update.
b. In the TFTP Server IP Address field, enter the IP address of the TFTP server to
which you will upload the 3.1 binary configuration file.
c. In the Filename field, specify the destination path and filename of the
configuration file. This is the TFTP server path.
d. In the TFTP Target Section pull-down menu, select Save Configuration
(binary).
e. Click the Update button.
f. Click the Status button. View the Transfer Completed message in the System
Status frame of the TFTP Update dialog box.
8. In the Memory Subsystems section of the Web Agent, click TFTP Update. In the
TFTP Update dialog box, download V4.0 onto your switch (into either APP1 or APP2).
9. Configure the switch to choose the appropriate APP (that contains V4.0 code) at the
next reboot.
10. Reset the switch to load the V4.0 image.
11. Refresh your Web browser window.
12. Verify the existence of the startup.txt file in NVRAM: in the CLI Configuration
section of the Web Agent, click Startup Config.
NOTE: The script log file (a new feature of Release 4.0.1) records the output of scripts
executed on the system, including the startup.txt file. Upon initial upgrade to Release
4.0.1, the script is generated but not run, and output is not initially recorded in the file.
13. In the CLI Configuration section of the Web Agent, click Script Log File. Scroll to
the bottom of the Script Log File to find out if any errors occurred as the script
executed. If errors were found, scroll up to find the particular error message.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 11
Page 12

Chapter 6 Problems and Workarounds
The following problems and workarounds generally apply to all Cajun switches unless expressly
specified.
Cajun 48-Port 10/100 Media Module
Problem: Due to the positioning of the Cajun P550 48-Port Media Module (M5548E100TC) as a high-density desktop connectivity module, the following functionality is not
supported:
• Multi-layer and 3Com trunk mode
• Link aggregation (hunt groups)
• Port mirroring
• 3Com mapping table selection
• Flow control setting of "Enable with Aggressive Backoff"
• PACE priority mode
• Spanning tree mode (disabled by factory default; enabled in other cases)
• Port statistics: intra-BCM5308 unicast frames not reflected
Additionally, flow control and rate limiting available only on a per-module basis
Workarounds:
• If link aggregation is required over a 10/100TX Link, use a Cajun P550 20-port
Module (M5520-100TX) or a Cajun P550 Layer 3 12-port Copper Module (M5512R100TX).
• If a port is inadvertently configured to use Multilayer tagging, reconfigure the port to
use either Clear or IEEE 802.1Q tagging. To reconfigure the port from the Enhanced
CLI, enter the following command at the system prompt:
set port trunking-format {<mod-num>|<mod-port-range>}[...[,]{<modnum>|<mod-port-range>}] { clear | ieee-802.1Q}
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 12
Page 13

If a port is inadvertently configured to use 3Com tagging, use the following procedure:
1. Reconfigure the port to use either Clear or IEEE 802.1Q tagging.
2. Copy (Save) the Running-Config to the Startup-Config.
3. Reboot the switch.
NOTES:
• 3Com VLT Tagging is not supported but can be enabled on the Cajun P550 48-port
Media Module’s (M5548E-100TC) internal switch ports by using the Web or CLI
management interface.
• The Cajun P550 48-port Media Module (M5548E-100TC) has been optimized for
desktop connections. Spanning Tree topology change convergence time can be
lengthy. This could lead to loss of connectivity and/or wrongful flow of data.
Command Line Interface
The command "set vlan <vlan-id> <port>" is used to bind additional ports to a VLAN if
trunking is enabled on that port. To set the port default VLAN for a port, use "set port vlan
{<mod-num>|<mod-port-range>}[...[,]{<mod-num>|<mod-port-range>}] <vlan-id>".
Cajun DocServer
NOTE: Release notes for the Cajun DocServer incorrectly excludes mention of the P550
platform. Both the Cajun P550 and P220 platforms are supported.
DVRMP
NOTE: The Cajun P550R Switch may lose a small number of DVMRP neighbor-toneighbor probe messages which may cause multicast routing instability under heavy
loads.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 13
Page 14

Front Panel Display
Problem: The 'lastlink' application on the front panel display does not work on the
Cajun P220FE or P220G.
Workaround: Currently, no workaround is available.
Hardware
Frames Transmitted with CRC Errors
For the Cajun P550 20-port Module, Model M5520-100TX (P/N 311-0020-000: Revision Level
A or B), and the Cajun P550 12-port Module, Model M5512R-100TX, a temperature sensitivity
problem has been found when operating at 10Mbps. This sensitivity will result in the port
transmitting frames with CRC errors. These frames, since they have CRC errors, are then
dropped by the receiving station. Note that this problem only occurs at 10Mbps. 100Mbps
operation is not affected.
Software Release v1.0.17 (or later) has implemented a new configuration that disables the
power saving mode of the Phy chip. Disabling the power saving mode has the effect of moving
the operational temperature of the part past the problem range. Testing this software
configuration is 100% successful in resolving the error.
The software configuration command is only available from the CLI. It is saved in NVRAM.
Users should only disable the power saving mode for ports that are experiencing this problem.
Disabling the power saving mode for parts that are operating at a lower temperature than the
problem range may accidentally raise the temperature into the problem range. In legacy-cli
mode, use the following command to disable the power saving mode for ports:
Cajun> port set DisablePowerSave <slot>.<port> on
NOTE: To enter legacy mode, type legacy-cli at the command prompt. To return to
the Enhanced CLI from legacy mode, type exit at the command prompt.
Hot Swap Modules
Hot swapping modules may cause SEPROM and SMAC panic messages to appear in the event
log. These messages are for informational purposes only and should be ignored.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 14
Page 15

Loopback Tests
Loopback tests on ports may fail when there is traffic present on the link at start-up.
M5520-TX Loopback Tests During Cold Start
Occasionally M5520-TX (P/N M5520-100TX) boards with a Quality Phy will fail loopback tests
when the board initially is started. The problem corrects itself as the board warms up.
M5520-TX Auto-negotiation with Xircom Adapter Cards
M5520-TX (P/N M5520-100TX) boards manufactured with a Quality Phy do not autonegotiate
with Xircom brand adapter cards. If you are having this problem, disable auto-negotiation on
the affected ports, and set the port speed and duplex state manually.
Oversized Packets
Oversized packets are not counted in itemized statistics if the packet size is between 1519 and
1548 bytes.
Short Cables May Cause Auto-negotiation Problems
You may experience difficulties with auto-negotiation between some releases of the 10/
100Base-TX Module (M5510-100FX, M5520-100TX, M5510R-100FX, M5512R-100TX) and
adapter cards using physical interfaces manufactured by National Semiconductor. The symptom
is loss of connectivity. You can address this problem by either disabling auto-negotiation, or
using a patch cable longer that 5 meters. Use the following Enhanced Command Line Interface
command in legacy mode to correct the situation:
Cajun> port set NationalPhyMode <slot>.<port> enable
NOTE: To enter legacy mode, type legacy-cli at the command prompt. To return to
the Enhanced CLI from legacy mode, type exit at the command prompt.
NOTE: The factory default for ports now sets the National Phy mode to enabled.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 15
Page 16

Intelligent Multicasting
Problem: Intelligent Multicasting can block protocols to non-multicast routers. If you
have enabled Intelligent Multicasting and configured a VLAN attached to one or more
non-multicast routers or multicast-capable endstations, Intelligent Multicasting will
configure router ports where multicast-enabled routers reside. These multicast router
ports are necessary to allow all multicast packets to the adjacent multicast routers. Nonmulticast enabled routers will not be considered router ports, and will not receive
multicast traffic for which an Intelligent Multicast session was created. The problem can
arise when multiple IP multicast addresses map to the same multicast MAC address,
resulting in protocol packets not being sent to the adjacent non-multicast enabled
routers.
EXAMPLE:
The unicast routing protocol in use on all connected routers is OSPF, and all ports are on
the same VLAN. An endstation joins the IP multicast group 226.128.0.5 on port 1. The
MAC address for the group is 01:00:5E:00:00:05. IGMP snooping creates a session for
this MAC address, with port 1 as the client port. There is a non-multicast OSPF router
attached to port 2. OSPF uses the IP multicast link-scoped group 224.0.0.5, which also
maps to a MAC address of 01:00:5E:00:00:05. Because port 2 is not a router port, and it
is not part of the 01:00:5E:00:00:05 session, the switch will only pass OSPF messages out
port 1.
Other protocols, such as the Service Location Protocol (RFC 2608), use 224.0.1.22 and
224.0.1.35, which can be blocked by endstations joining sessions that map to the same
MAC address.
Workaround: Make certain that all ports connected to a router are configured as router
ports to ensure that all router-to-router messages will not be blocked. If other nonrouter protocols such as the Server Location service are in use, create static sessions as
needed. Also, do not create static sessions that will conflict with the protocols in use on
your network. For a complete list of internet multicast addresses recognized by the
IANA, go to http://www.isi.edu/in-notes/iana/assignments/multicast-addresses.
NOTE: By default, the default “Rate Limiting” state for 10/100 Megabit ports is
Enabled, and multicast traffic is rate-limited (to 20%) on 10/100 Megabit ports. When
transmitted from these ports, multicast traffic is rate-limited unless Intelligent
Multicasting is enabled. If Intelligent Multicasting is enabled, the multicast traffic for
which the Intelligent Multicast session was created will not be subject to rate limiting
unless the rate limiting state is set to Enabled (all multicast included). If you do not
want to enable rate limiting of multicast traffic on a port, either 1)Enable Intelligent
Multicasting, or 2) Disable Rate-limiting on the port.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 16
Page 17

OSPF
Problem: Upgrading the switch from a Release 3.1 or other previous release to Release
4.0.1 may cause the loss of your virtual link configuration.
Workaround: After upgrading and resetting the switch, view your running
configuration to ensure that virtual links are intact. (To view your running
configuration, click Running Config in the CLI Configuration section of the Web
Agent.) If the virtual link configuration is lost, reconfigure the virtual links.
NOTES:
• When the Cajun P550 first boots up as an ABR or ASBR, it may send an ASBR
advertisement for itself. This advertisement is later flushed by the system.
• When changing the OSPF Router ID, the Cajun P550R does not immediately flush
the advertisements with the original Router ID. Instead these advertisements will be
flushed when they are aged from the database.
• When a virtual link is created on the Cajun P550R router, the router cannot detect if
the remote router is an ABR to area 0.0.0.0.
• There may be a loss of Web connectivity for about 10 seconds during LSA updates in
a large OSPF network.
Piggyback Ports
NOTE: If a router port for intelligent multicasting is mirrored with a piggyback port, the
piggyback port is listed instead of the router port.
RMON
NOTE: On Gigabit Ethernet port, under heavy utilization, 30 minute RMON stats always
show utilization as 0.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 17
Page 18

SNMP
NOTES:
• Cold start traps cannot be transmitted out of inband interfaces when Spanning Tree
is enabled.
• ipAddrTable does not display inactive interfaces (VLANs). An inactive interface
occurs when there are no active ports on a VLAN.
• You cannot have more than 10 SNMP community strings per switch.
Spanning Tree
NOTES:
• The Cajun P550 48-port Media Module (M5548E-100TC) supports Spanning Tree
for each group of eight ports at the internal switch port. Spanning Tree functionality
is disabled by default. If per-port STP is required, it is recommended that you use a
Cajun P550 20-port Module (M5520-100TX) or Cajun P550 Layer 3 12-port Copper
Module (M5512R-100TX).
• Release 4.0.1 does not allow modification of the Spanning Tree and Fast Start
features on the CPU switch port. When you modify all switch ports, the Spanning
Tree and Fast Start features will be not be applied for the CPU switch port and the
corresponding status line does not display.
• Spanning tree convergence may take longer than 30 seconds in complex networks
after a topology change
Problem: When IEEE 802.1D spanning tree is used with hunt groups, the non-flood
ports are shown as forwarding, even if the hunt group is blocked.
Workaround: The flood port of the hunt group shows the actual state of the spanning
tree. View the flood port to see the actual state of the spanning tree.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 18
Page 19

PPP and Telnet
NOTES:
• A Telnet session to the serial port via PPP may time out during attempts to transfer
large files, such as executable images, to a TFTP server over the same link. However,
the file transfer is not terminated. An in-progress TFTP file transfer continues and
ends only after the file transfer is completed.
• File transfer via TFTP over PPP links may terminate before completion if the dialin
PC is used TFTP server.
• A new baud rate may take effect before the current PPP connection is terminated if
the relevant baud rate change command is entered more than once resulting in
termination of PPP connection. This requires re-establishment of a PPP connection.
Time Zones
Problem: The System Clock may be incorrect after an upgrade to 4.0.
Workaround: Check the System Clock and reset it, if necessary. For information about
resetting the System Clock, refer to the Cajun P550/P220 Switch Operations Guide.
Problem: To support SNTP, the internal clock was changed from local time to GMT. The
System Clock is now displayed by converting the internal representation (GMT) to local
time by accounting for time-zone and summer-time hour configurations.
An upgrade routine has been added that changes the System Clock for all switches
running 3.0 or higher, given the following assumptions:
• The switch is running Release 3.x,
• The time-zone is set properly in the 3.x image, and
• The time-zone defined supports the North American Daylight Savings Time rules.
If any of these assumptions are false, the System Clock will be incorrect.
Workaround: Check the System Clock and reset it, if necessary. For information about
resetting the System Clock, refer to the Cajun P550/P220 Switch Operations Guide.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 19
Page 20

VLAN Issues
NOTE: If the Switch Port attribute Automatic VLAN Creation is set to Enabled, the
Allow Learning attribute must also be set to Enabled.
Configuring VLANs
NOTES:
• In certain large configurations, the switch powers up very slowly.
• If you set a port’s VLAN trunking mode to Clear, make sure not to change the VLAN
Binding Type from the default value: Static.
• If you are using both the VLAN auto-learning feature and the Binding Type Bind to
Received or Bind to All, make sure that you set the binding type before you set
Auto-learn to enable or else the port may not be automatically added to the VLAN.
Duplicate VLAN Error Message
NOTE: When you add a VLAN and then refresh your browser page, you may receive an
error message stating that the VLAN name is already in use.
IEEE 802.1Q Packets
Problem: When a tagged IEEE 802.1Q packet arrives on a port that is “bind-to-all” and
the VLAN does not exist on the switch, the packet is forwarded on to the VLAN assigned
to the port default VLAN for that port.
Workaround: To prevent unintended forwarding of unknown VLAN traffic to the port
default VLAN, configure the port default VLAN to the “discard” VLAN. However, please
note that automatic VLAN creation will not work if the port default VLAN is the
“discard” VLAN, because the switch does not learn for this VLAN.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 20
Page 21

Chapter 7 Functional Restrictions
This section provides information on all of the functional restrictions of the Release 4.0.1 switch
software. The functional restrictions are documented alphabetically by functional area (for
example, VLANs, DVMRP, IP).
Hardware
Gigabit Ports Do Not Perform Auto-negotiation
Cajun Gigabit Ethernet ports operate at 1 Gbps, full duplex and have been widely tested for
interoperability with other devices. Currently, these ports do not support auto-negotiation. If you
connect a Cajun gigabit port to a device that supports auto-negotiation, you must disable autonegotiation on the non-Cajun device to ensure proper operation.
Hot Swapping Modules
If your switch supports a large configuration file, such as the startup.txt file, inserting and
configuring a new module while the switch is operational may cause console and telnet CLI
sessions to pause momentarily.
Link Status
When a large number of VLANs or endstations are on a hunt group, it may take several seconds
for the link status LED to change upon failure.
Ping
Unable to Ping the Inband Interface on a Layer 2 device. This problem does not occur with Layer
3 devices or with the Out of Band Interface.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 21
Page 22

Redundant Controller Support
In the event that the redundant switch controller fails, the switch will reset itself.
Auto-Negotiation
Some network cards do not auto-negotiate correctly with older releases of the 10/100TX
modules. This is evidenced by the reception of CRC errors on the mirror port. To avoid this
situation, disable auto-negotiation and manually configure the speed and duplex of the mirror
port and network card.
Spanning Tree
IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree
IEEE 802.1D spanning tree does not work with 3Com tags.
Web Configuration
The Disable Spanning Tree option available from the “spanning tree> vlan> port” the Cajun
Switch Web Agent disables the port. To disable Spanning Tree mode for the port, use the
“Modules and Ports > Switch Ports” Web page. When disabling the Spanning Tree for a port,
BPDUs received on that port are ignored and BPDUs are not generated by the switch for that
port. The port will move directly into the forwarding state from the disabled state. The port does
not trigger a topology detection change.
Setting the Spanning Tree Mode
When the Spanning Tree mode is set to IEEE 802.1D, BPDUs are sent out ports in Clear (nontrunked) format even if the port has a trunking format (3Com, IEEE 802.1Q, or Dual-Layer)
defined.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 22
Page 23

For ports that have a 3Com trunking format, the receiving end of the trunked port attempts to
interpret the clear BPDUs as trunked packets. Consequently, these BPDUs are discarded at the
receiving end. For Spanning Tree to function properly with 3Com trunked ports, the Spanning
Tree mode should be set to per-VLAN. In per-VLAN Spanning Tree, there is one instance of
Spanning Tree for each VLAN and the BPDUs are tagged with the VLAN ID, ensuring they are
interpreted correctly on the receiving end.
NOTE: Although this restriction does not apply to ports that use IEEE 802.1Q or MultiLayer trunking modes, it is still recommended that you set Spanning Tree to per-VLAN
when using trunked ports. This prevents an entire link from being blocked when there is
a loop in one VLAN.
TFTP
File Naming Standard for Embedded NVRAM File System
NOTE: All NVRAM files must use an 8.3 format for file names.
When downloading code to the NVRAM file system, use standard 8.3 file naming conventions
(the default download file names do not use this convention).
TFTP Download Status Delay
It takes a few seconds before the Status button on the TFTP Download screen returns accurate
information.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 23
Page 24

Chapter 8 Bug Fixes
The following bugs issued in Release 3.1 were fixed in Release 4.0.1.
• Switch crashes with a large number of OSPF LSA’s (over 3000) on the L3 Switch.
This has only occurred for one very large customer network and can be easily
identified by the crash log submitted to technical support.
• Secondary IP Addresses on L3 switch do no display the correct index value via SNMP.
• You cannot specify a subdirectory when TFTP saving a configuration.
• The DHCP Proxy agent on the L3 Switch does not forward a NACK response from a
DHCP server.
• Hung HTTP Processes can cause a loss of TCP Connectivity over time.
• The L2 Fault Tolerant switch may fail over to a Redundant Controller under heavy
sustained traffic loads. If a subsequent incorrect failure is detected on the second
Controller, networking problems could occur.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 24
Page 25

Chapter 9 Additional Undocumented
Commands
The following sections list and describe commands that are not included in the Cajun P550/P220
Switch Command Line Reference Guide for Release 4.0.1.
NOTE: Refer to the Lucent online documentation web site at HTTP://pubs.lucentctc.com,
for an updated release of the Cajun P550/P220 Switch Command Line Reference Guide that has
been updated after the release date.
Buffering Commands
Table1-4 shows new and changed buffering commands added to Release 4.0.1.
Table 1-4: Buffering Commands
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
set buffering
fabric-port
<fabric-port-spec>
[routing]
{input|output} agetimer {160-to320|640-to-1280}
set buffering
fabric-port
<fabric-port-spec>
[routing]
{input|output}
hipri-alloc
{10|20|30|40|50}
set buffering
fabric-port
<fabric-port-spec>
[routing]
{input|output}
hipri-service-ratio
{3-to-1|99-to-1|
999-to-1|9999-to-1}
N/A
N/A
N/A
<fabric-port-spec> – fabric port specifier -
#/#, #/FORE, #/#-#/# on P550/P550R,
CPU,G1,G2,G3,G4,G5,G6,G7,A1 on P220G
CPU,G1,A1,1-12,13-24 on P220.
The switch must be rebooted in order for
changes to this parameter to become effective.
<fabric-port-spec> – fabric port specifier
(#/#, #/FORE, #/#-#/# on P550/P550R)
(CPU,G1,
G2,G3,G4,G5,G6,G7,A1 on P220G)
(CPU,G1,A1,1-12,13-24 on P220).
<fabric-port-spec> – fabric port specifier
- #/#, #/FORE, #/#-#/# on P550/R550R. CPU,
G1, G2, G3, G4, G5, G6, G7, A1 on P220G.
CPU, G1, A1, 1-12, 13-24 on P220.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 25
Page 26

Table 1-4: Buffering Commands (Continued)
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
set buffering
fabric-port
<fabric-port-spec>
[routing]
{input|output} prithreshold {1|
2|3|4|5 |6|7|allframes-normalpriority}
set buffering port
<mod-port-spec>
output age-timer
{21|42|84|
168|336|672|1340}
set buffering port
<mod-port-spec>
output hipri-alloc
{10|20| 30 |40|50}
set buffering port
<mod-port-spec>
output hipriservice-ratio {1to-1|3-to-1|7-to1|15-to-1| 31-to1|63-to-1|127-to1|255-to-1|511-to1| 1023-to-1|2047to-1| 4095-to1|8191-to-1| 16383to-1|32767-to-1}
N/A
set buffering port
<mod-swport-spec>
output age-timer
{21|
42|84|168|336|672|
1340}
set buffering port
<mod-swport-spec>
output hipri-alloc
{10 |20|30|40|50}
set buffering port
<mod-swport-spec>
output hipriservice-ratio {1to-1|3-to-1 |7-to1|15-to-1| 31-to1|63-to-1| 127-to1|255-to-1| 511-to1|1023-to-1| 2047to-1|4095-to-1|
8191-to-1|16383-to1| 32767-to-1}
<fabric-port-spec> – fabric port specifier
- (#/#, #/FORE, #/#-#/# on P550/P550R)
(CPU,G1,G2,
G3,G4,G5,G6,G7,A1 on P220G) (CPU,G1,A1,112,13-24 on P220).
Default: 168
<mod-swport-spec> – switch port specifier
- (#/# on P550/P550R) (A1...A4 on P220G)
(A1...A4, 1...24 on P220).
The switch must be rebooted in order for
changes to this parameter to become effective.
Default: 20
<mod-swport-spec> - switch port specifier -
(#/# on P550/P550R) (A1...A4 on P220G)
(A1...A4, 1...24 on P220).
Default: 1023-to-1
<mod-swport-spec> - switch port specifier -
(#/# on P550/P550R) (A1...A4 on P220G)
(A1...A4, 1...24 on P220).
set buffering port
<mod-port-spec>
output prithreshold
{1|2|3|4|5|6|7|
all-frames-normalpriority}
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 26
set buffering port
<mod-swport-spec>
output prithreshold
{1|2|3|4|5|6|7|
all-frames-normalpriority}
Default: 4
<mod-swport-spec> – switch port
specifier - (#/# on P550/P550R) (A1...A4 on
P220G) (A1...A4, 1...24 on P220).
Page 27

Table 1-4: Buffering Commands (Continued)
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
show buffering
fabric-port
[<fabric-port-spec>
[...,<fabric-portspec>]]
show buffering port
[<mod-port-spec>
[…,<mod-portspec>]]
N/A <fabric-port-spec> – fabric port specifier - (#/
#, #/FORE, #/#-#/# on P550)
(CPU,G1,G2,G3,G4,G5,G6,G7,A1 on P220G)
(CPU,G1,A1,1-12,13-24 on P220).
show buffering port
[<mod-swport-spec>
[…,<mod-swportspec>]
<mod-swport-spec> – switch port specifier (#/# on P550/P550R) (A1...A4 on P220G)
(A1...A4, 1...24 on P220).
DVMRP Commands
Table1-5 shows new and changed DVMRP Commands in Release 4.0.1:
Table 1-5: DVMRP Commands
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
To Enable:
ip dvmrp interface
type {broadcast|
nonEncapsulatedTunnel|
IPIPTunnel}
N/A A tunnel endpoint address must be set
before a DVMRP interface is configured to be a tunnel. Use the [no] ip
dvmrp remote-tunnel-address
<IP-address> command to set the
tunnel endpoint address.
To Disable:
[no] ip dvmrp
interface type
To Enable:
ip multicast ttlthreshold <ttl-thresh>
To Disable:
[no] ip multicast ttlthreshold
show ip dvmrp
forwarding cache
To Enable:
ip multicast ttlthreshold {0,127,255}
To Disable:
no ip multicast ttlthreshold
N/A System Supported: P550R
{0,127,255} – The TTL (time-to-live)
threshold.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 27
Page 28

IGMP Commands
Table1-6 shows new and changed IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol MIB, draft-ietfedmr-igmp-mib-12.txt) commands in Release 4.0.1:
Table 1-6: IGMP Commands
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
To Enable:
ip igmp process-leaves
To Disable:
[no] ip igmp processleaves
To Enable:
ip igmp process-leaves
{0,1}
To Disable:
[no] ip igmp processleaves
• 1 – Enables the processing of leave
requests on an interface.
• 0 – Disables the processing of leave
requests on an interface.
Use the no form of this command to
set the command back to the default,
which is 1 enabled.
To Enable:
ip igmp querier
To Disable:
[no] ip igmp querier
N/A show ip igmp interface Display IGMP multicast-related infor-
To Enable:
ip igmp querier {0,1}
To Disable:
[no] ip igmp querier
• 1 – The interface is a group querier
on the interface.
• 0 – The interface is not a group
querier on the interface.
Use the no form to set the command
back to its default, which is 0 not
group membership querier.
This command is for IGMP release 1
only.
mation for all IGMP interfaces.
Command Mode: User
System Supported: P550R
IP Commands
Table1-7 shows new and changed IP Commands in Release 4.0.1:
Table 1-7: IP Commands
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
To Enable:
arp <ip-address>
<hardware-address>
N/A
System Supported: P550R
To Disable:
[no] arp <ip-address>
<hardware-address>
clear ip route
{<network> [<mask>] *}
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 28
N/A System Supported: P550R
Page 29

Table 1-7: IP Commands (Continued)
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
N/A clear tcp all Clear all TCP connections that aren't
N/A clear tcp local <ip-
address> <tcp-port>
remote <ip-address>
<tcp-port>
N/A To Enable:
ip bootp-dhcp gateway
To Disable:
[no} ip bootp-dhcp
gateway
ip max-arp-entries
<value>
ip max-route-entries
<value>
To Enable:
ip redirects
To Disable:
[no] ip redirects
ip telnet inactivityperiod <timeout>
N/A show arp [<ip
To Enable:
N/A
To Disable:
[no] ip max-arp-entries
To Enable:
N/A
To Disable:
[no] ip max-routeentries
N/A The default state is enabled, unless
To Enable:
N/A
To Disable:
[no] ip telnet
inactivity-period
addr>][<ifname>][static]
in the listening state.
Command Mode: Configuration
Clear the TCP connection specified by
the local IP address and port and
remote IP address and port.
Command Mode: Configuration
Enable or disable the designation of
this interface as the preferred receiver
of BOOTP/DHCP requests received on
a VLAN.
This is useful with multinetted interfaces. If no multinetted interface has
this parameter set to Enabled or is not
UP, the router chooses an interface to
receive the BOOTP/DHCP request.
Command Mode: Interface
System Supported: P550R
The no form of this command restores
the maximum number of ARP cache
entries to the default, which is 16384.
System Supported: P550R
The no form of this command restores
the maximum number of routes to the
default which, is 16384.
System Supported: P550R
VRRP is configured.
System Supported: P550R
Use the no form of this command to
restore the default, which is 900 sec-
onds, or 15 minutes.
System Supported: P550R
Display the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache.
This command is equivalent to the
show ip arp command.
• ip-addr – the IP address.
• if-name – the interface name.
• static – displays static arp
information.
Command Mode: User
System Supported: P550R
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 29
Page 30

Table 1-7: IP Commands (Continued)
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
show ip arp [static] show ip arp [<ip-addr>]
[<if-name>] [static]
show ip interface
[<interface-name>]
show ip traffic N/A System Supported: P550R
show udp statistics N/A System Supported: P550R
N/A System Supported: P550R
This command is equivalent to the
show arp command.
• ip-addr – the IP address.
• if-name – the interface name.
System Supported: P550R
IPX Commands
Table1-8 shows new and changed IPX Commands in Release 4.0.1:
Table 1-8: IPX Commands
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
N/A To Enable:
ipx max-route-entries
<max-route-entries>
To Disable:
[no] ipx max-routeentries
Specify the maximum number of IPX
routes in the route table. Use the no
form of the command to return to the
default value of 2048.
If the maximum number of routes is
decreased, the switch must be rebooted for the value to take effect. If the
value is increased, the change occurs
immediately.
<max-route-entries> – the maximum number of routes that can
appear in the IPX route table. The
value must be in the range 1 to 10240.
The value you enter is rounded up to
the nearest multiple of 256.
Command Mode: Configuration
System Supported: P550R
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 30
Page 31

Table 1-8: IPX Commands (Continued)
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
N/A To Enable:
ipx max-service-entries
<max-service-entries>
To Disable:
[no] ipx max-serviceentries
N/A To Enable:
ipx ping-default
{novell|diagnostic}
To Disable:
[no] ipx ping-default
Specify the maximum number of IPX
services in the service table. Use the
no release of the command to return
to the default value of 2048.
If the maximum number of services is
decreased, the switch must be rebooted for the value to take effect. If the
value is increased, the change occurs
immediately.
<max-service-entries> – the
maximum number of IPX services that
can appear in the service table. The
value must be in the range 1 to 10240.
The value you enter is rounded up to
the nearest multiple of 256.
Command Mode: Configuration
System Supported: P550R
Set the type of IPX ping packet issued
by the router when the ipx ping
command is issued. Use the no form
of the command to return to the
default ping type; novell.
• novell – transmits standard
Novell pings.
• diagnostic – transmits diagnostic
request/response pings.
To Enable:
ipx type-20propagation
{both|inbound|outbound
|disabled}
To Disable:
[no] ipx type-20propagation
To Enable:
N/A
To Disable:
[no] ipx type-20propagation
{both|inbound|outbound|
disabled}
Command Mode: Configuration
System Supported: P550R
• both – The interface accepts and
forwards type 20 propagation
broadcast packets. This is the
default.
• inbound – The interface only
accepts type 20 broadcast packets.
• outbound – The interface only
forwards type 20 propagation
broadcast packets to other
network segments.
• disabled – The interface does not
accept or forward type 20
propagation broadcast packets.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 31
Page 32

LDAP Commands
Table1-9 shows new and changed LDAP commands in Release 4.0.1:
Table 1-9: LDAP Commands
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
ldap debug <debuglevel>
To Enable:
ldap producer-signal
<producer-signal>
To Disable:
[no] ldap producersignal <producersignal>
N/A Command removed from CLI.
N/A Command removed from CLI.
To Enable:
ldap search-base
<search-base-dn>
To Disable:
[no] ldap search-base
<search-base-dn>
To Enable:
ldap server primary
<ip-addr> [<port-num>]
To Disable:
[no] ldap server
primary <ip-addr>
[<port-num>]
To Enable:
ldap server secondary
<ip-addr> [<port-num>]
To Disable:
[no] ldap server
secondary <ip-addr>
[<port-num>]
To Enable:
N/A
To Disable:
[no] ldap search-base
To Enable:
N/A
To Disable:
[no] ldap server
primary
To Enable:
ldap server secondary
<ip-addr> [<port-num>]
To Disable:
[no] ldap server
secondary
Please note the change to the no form
of the command.
The default port is 389.
Please note the change to the no form
of the command.
The default IP address is 0.0.0.0.
Please note the change to the no form
of the command.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 32
Page 33

Logging Commands
Table1-10 shows new and changed logging commands in Release 4.0.1:
Table 1-10: Logging Commands
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
To Enable:
logging console
[{start|system|config|
temp|
resource|fan|service_p
ort|user_port|auth_fai
lure|
bridge_stat|switch_fab
ric|protocol}]
To Disable:
[no] logging console
[{start|system|config|
temp|
resource|fan|service_p
ort|user_port|auth_fai
lure|
bridge_stat|switch_fab
ric|protocol}]
To Enable:
logging history
[{start|system|config|
temp|
resource|fan|service_p
ort|user_port|auth_fai
lure|
bridge_stat|switch_fab
ric|protocol}]
To Enable:
N/A
To Disable:
[no] logging console
To Enable:
N/A
To Disable:
[no] logging history
Please note the change to the no form
of the command.
Please note the change to the no form
of the command.
To Disable:
[no] logging history
[{start|system|config|
temp|
resource|fan|service_p
ort|user_port|auth_fai
lure|
bridge_stat|switch_fab
ric|protocol}]
To Enable:
logging history size
{128|512|1024|2048
To Disable:
[no] logging history
size
{128|512|1024|2048}
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 33
To Enable:
N/A
To Disable:
[no] logging history
size
Please note the change to the no form
of the command.
Page 34

Table 1-10: Logging Commands (Continued)
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
To Enable:
logging shutdown size
{16|32|64|128}
To Disable:
[no] logging shutdown
size {16|32|64|128}
To Enable:
logging traps
[{start|system|config|
temp|resource|
fan|service_port|user_
port|auth_failure|
bridge_stat|switch_fab
ric|protocol}]
To Disable:
[no] logging traps
[{start|system|config|
temp|
resource|fan|service_p
ort|user_port|auth_fai
lure|
bridge_stat|switch_fab
ric|protocol}]
To Enable:
N/A
To Disable:
[no] logging shutdown
size
To Enable:
N/A
To Disable:
[no] logging traps
Please note the change to the no form
of the command.
Please note the change to the no form
of the command.
OSPF Commands
Table1-11 shows new and changed OSPF Commands in Release 4.0.1:
Table 1-11: OSPF Commands
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
To Enable:
ip ospf
authentication-key
<password>
To Disable:
[no] ip ospf
authentication-key
show ip ospf interface
[<interface-name>]
show ip ospf virtuallinks
N/A System Supported: P550R
N/A System Supported: P550R
N/A System Supported: P550R
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 34
Page 35

Policy Commands
Table1-12 shows new and changed Policy Commands in Release 4.0.1:
Table 1-12: Policy Commands
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
To Enable:
ip access-group
<access-list-name>
[default-action-deny]
To Disable:
[no] ip access-group
To Enable:
ip access-list
<access-list-name>
<access-list-index>
{permit|deny|fwd[1-8]}
{<source-ip-addr>
[<source-wildcard>]
|any|host <source-ipaddr>}
To Disable:
[no] ip access-list
<access-list-name>
[<access-list-index>]
N/A There is no default.
To Enable:
[ip] access-list
<access-list-name>
<access-list-index>
{permit|deny|fwd1-8}
<protocol-id>{<sourceip-addr> <sourcewildcard>|any|host
<source-ip-addr> }
[{lt|eq|gt|range}
<port> [<port>]]
{<dest-ip-addr> <destwildcard> | any | host
<dest-ip-addr> }
[{lt|eq|gt|range}
<port> [<port>]]
[established]
To Disable:
N/A
• <protocol-id> – name or
number of an IP protocol. It can be
one of the keywords eigrp, gre,
icmp, igmp, igrp, ip, ipinip, nos,
ospf, tcp, or udp, or an integer in
the range 0 to 255 representing an
IP protocol number. To match any
Internet protocol (including ICMP,
TCP, and UDP) use the keyword
ip.
• <dest-ip-addr> – number of
the network or host to which the
packet is being sent. Use a 32-bit
quantity in four-part, dotteddecimal format. Use the keyword
any as an abbreviation for a dest
and dest -wildcard of 0.0.0.0 and
255.255.255.255. Use "host <destip-addr>" as an abbreviation for a
destination with dest-wildcard of
0.0.0.0.
• <dest-wildcard> – wildcard
bits to be applied to the
destination. Use a 32-bit quantity
in four-part, dotted-decimal
format. Place ones in the bit
positions you want to ignore.
• operator – (Optional) Compares
source or destination ports.
Possible operands include: lt = less
than, gt =greater than, eq=equal,
neq =not equal, and range
=inclusive range.
If the operator is positioned after the
source and source-wildcard, it must
match the source port.
If the operator is positioned after the
destination and destination-wildcard,
it must match the destination port.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 35
Page 36

Table 1-12: Policy Commands (Continued)
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
N/A ip access-list -
Continued from previous
page
N/A show [ip] access-group Display the current IP access group.
show ip access-lists
[<access-list-name>]
show [ip] access-lists
[<access-list-name>]
The range operator requires two port
numbers. All other operators require
one port number.
• port – the decimal number or
name of a TCP or UDP port. A port
number is a number from 0 to
65535.
• established – for the TCP
protocol only. Indicates an
established connection. A match
occurs if the TCP datagram has the
ACK or RST bits set. The
nonmatching case is that of the
initial TCP datagram to form a
connection.
Command Mode: User
System Supported: P550R
The command description is
unchanged.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 36
Page 37

Port Commands
Table1-13 shows new and changed Port Commands in Release 4.0.1:
Table 1-13: Port Commands
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
N/A show ethernet counters
[{<mod-num>|<modswport-spec>}]
N/A show ethernet counters
<mod-swport-spec>
history <sampleinterval>
Display ethernet interface statistics.
• <mod-num> – specifies the chassis
module number of the switch
ports that are to have their
ethernet statistics displayed. (Valid
on 550 and 550R only)
• <mod-swport-spec> – specifies
a particular switch port whose
specific ethernet statistics are to be
displayed.
If no <mod-num> or <mod-swport-
spec> is specified then ethernet interface statistics is displayed for all ports
on all modules in the chassis.
If <mod-num> is specified then all
switch ports on that module have their
ethernet interface statistics displayed.
If <mod-swport-spec> is specified
that particular port's ethernet interface
statistics are displayed.
Command Mode: User
Display interface ethernet history sam-
ples.
• <mod-num> – specifies the chassis
module number of the switch
ports that are to have their
ethernet statistics displayed. (Valid
on Cajun P550 and P550R only)
• <mod-swport-spec> – specifies
a particular switch port whose
specific ethernet statistics are to be
displayed.
• <sample-interval> The
history sample interval.
If no <mod-num> or <mod-swport-
spec> is specified then ethernet interface statistics is displayed for all ports
on all modules in the chassis.
If <mod-num> is specified then all
switch ports on that module have their
ethernet interface statistics displayed.
If <mod-swport-spec> is specified
that particular port's ethernet interface
statistics are displayed.
Command Mode: User
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 37
Page 38

Table 1-13: Port Commands (Continued)
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
N/A show module counters
[<mod-num>]
N/A show port
physical[{<modnum>|<mod-portrange>}[...,{<modnum>|<mod-portrange>}]]
Display the aggregate switch port statistics for a specified module or all
modules on a Cajun P550 or P550R.
• mod-num – Specifies the number
of the module in the chassis for
which aggregate switch port
statistics are to be displayed. (Valid
on Cajun P550 and P550R only)
Command Mode: User
Display the physical port configuration
of the specified ports.
• mod-num
• mod-port-range
Command Mode: User
SNMP Commands
Table1-14 shows new and changed SNMP Commands in Release 4.0.1:
Table 1-14: SNMP Commands
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
N/A To Enable:
snmp-server location
<string>
To Disable:
[no] snmp-server
location <string>
Set the system location string. Use the
no form of this command to remove
the system location string.
<string> – the system location
string.
Switch IP Commands
Table1-15 shows new and changed Switch IP Commands in Release 4.0.1:
Table 1-15: Switch IP Commands
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
set ip route {default|
<dest-ip-addr> <mask>}
<gateway-ip-addr>
N/A Default: The CLI searches for the
matching interface as indicated by the
gateway IP address and installs the
default gateway on that interface.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 38
Page 39

Table 1-15: Switch IP Commands (Continued)
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
N/A set ip telnet
inactivity-period
<timeout>
Specifies how many seconds a telnet
session remains open with no activity.
Setting it to 0 disables the timer so that
sessions never close because of inactivity.
The default is 900 seconds or 15
minutes.
<timeout> – the timeout period, in
seconds.
Command Mode: Configuration
System Supported: P220, P550
System Commands
Table1-16 shows new and changed System Commands in Release 4.0.1:
Table 1-16: System Commands
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
To Enable:
ip http help server
<url> <directory>
To Disable:
[no] ip http help
server
reload N/A Command Mode: Privileged
To Enable:
ip http help server
{<url>|ip <ip-addr>}
<directory>
To Disable:
N/A
ip <ip-addr> – the IP address.
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 39
Page 40

UI Commands
Table1-17 shows new and changed UI Commands in Release 4.0.1:
Table 1-17: UI Commands
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
N/A ping <ip-addr> [<count>
[<delay> [<size>
[<timeout>[quiet]]]]]
Check host reachability and network
connectivity.
• <ip-addr> – IP Address of the
host to ping.
• <count> – the number of ping
attempts you want to perform
with this operation. The default
is 5.
• <delay> – the number of
milliseconds the switch waits
between generating pings. The
default is 1.
• <size> – the size of the packet
sent during a ping operation. The
default is 4.
• <timeout> – the number of
seconds to wait for an ICMP reply.
The default is 2.
• quiet – specify this parameter to
disable the display of the ping
operation in progress.
Command Mode: Privileged
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 40
Page 41

Table 1-17: UI Commands (Continued)
Old Command New Command New Definition/Argument
N/A ping ipx <ipx-
network.next-hop-node>
[<count> [<delay>
[<size>
[<timeout>[quiet]]]]]
Check the IPX host reachability and
network connectivity.
• <ipx-network.next-hop-
node> – the IPX Address of the
host to ping. IPX-network is a
hexadecimal number between 1
and 8 digits long, and next-hopnode form is aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff.
• <count> – the number of ping
attempts you want to perform
with this operation. The default is
1.
• <delay> – the number of
milliseconds the switch waits
between generating pings. The
default is 1.
• <size> – the size of the packet,
excluding the MAC, IPX and PING
headers, sent during a ping
operation. The default is 256.
• <timeout> – the number of
seconds to wait for a reply. The
default is 2.
• quiet – specify this parameter to
disable the display of the ping
operation in progress.
Command Mode: Privileged
System Supported: P550R
N/A show users Display a list of users who are cur-
rently logged into the switch.
Command Mode: User
Cajun P220, P550, P550R Switch Release Notes, Release 4.0.1 41
 Loading...
Loading...