Page 1

Pub. 988-0151-461
www.lowrance.com
LMS-520C & LMS-525C DF
Fish-finding Sonar & Mapping GPS
Installation and Operation
Instructions
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 2

Copyright © 2006 Lowrance Electronics, Inc.
All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be copied, reproduced, republished, transmitted or distributed for any purpose, without prior written consent of
Lowrance. Any unauthorized commercial distribution of this
manual is strictly prohibited.
Lowrance
MapCreate™, FreedomMaps™ and NauticPath™ are trademarks of
LEI. Fishing Hot Spots
Inc. LakeMaster
marks of WayPoint Technologies, Inc. Navionics
trademark of Navionics, Inc. DURACELL
Duracell, Inc. RAYOVAC
ration. Energizer
®
is a registered trademark of Lowrance Electronics, Inc.
®
®
®
is a registered trademark of Fishing Hot Spots
and Pro Maps are trademarks or registered trade-
®
is a registered trademark of
and e
®
is a registered trademark of Rayovac Corpo-
®
2
are registered trademarks of Energizer Hold-
®
is a registered
ings, Inc.
Points of Interest Data in this unit are by infoUSA,
copyright © 2001-2006, All Rights Reserved. infoUSA is a
trademark of infoUSA, Inc.
Lowrance Electronics may find it necessary to change or end our policies, regulations and special offers at any time. We reserve the right to
do so without notice. All features and specifications subject to change
without notice. All screens in this manual are simulated. On the cover:
LMS-525CDF.
For free owner's manuals and the most current information on
this product, its operation and accessories,
visit our web site:
www.lowrance.com
Lowrance Electronics Inc.
12000 E. Skelly Dr.
Tulsa, OK USA 74128-2486
Printed in USA.
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 3

Table of Contents
Section 1: Read Me First! ......................................................... 1
Specifications: LMS-520c and LMS-525cDF.......................... 3
How to use this manual: typographical conventions ................ 10
Section 2: Installation............................................................. 13
Preparations ................................................................................ 13
Transducer Installation .............................................................. 13
Single-frequency transom installations ............................. 14
Dual-frequency transom installations ............................... 14
Single-frequency trolling motor installations ................... 14
Shoot-through hull installations ........................................ 14
Selecting a Transducer Location ............................................ 14
How low should you go? .......................................................... 16
Shoot-thru-hull vs. Transom Mounting ................................. 16
Transom Transducer Assembly And Mounting .................... 17
Trolling Motor Bracket Installation (single-frequency only) 23
Transducer Orientation and Fish Arches.............................. 23
Shoot-Thru-Hull Preparation ................................................. 24
Hulls with Flotation Materials........................................... 24
Testing Determines Best Location ......................................... 25
Shoot-thru-hull Installation ................................................... 27
Speed/Temperature Sensors ................................................. 28
Optional Speed Sensor Installation ....................................... 28
Power Connections ...................................................................... 30
Powering Your Display Unit ...................................................... 31
Power Diagram A ........................................................................ 32
Power Diagram B ........................................................................ 33
Powering a NMEA 2000 Network Bus ...................................... 33
GPS Antenna/Receiver Module .................................................. 34
Connecting to a NMEA 2000 Network ...................................... 35
NMEA 0183 Wiring (Data cable) ........................................... 36
Mounting the Unit: Bracket, In-Dash or Portable.................... 39
MMC or SD Card Memory Card Installation............................ 42
Other Accessories ........................................................................ 44
Cleaning Towel ........................................................................ 44
Face Cover ................................................................................... 45
Section 3: Basic Sonar Operation ........................................ 47
Keyboard ...................................................................................... 47
Power/lights on and off ............................................................... 48
Main Menu................................................................................... 48
Pages ............................................................................................ 50
Satellite Status Page............................................................... 50
Navigation Page ...................................................................... 51
i
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 4

Map Page ................................................................................. 51
Sonar Page ............................................................................... 52
Basic Sonar Quick Reference ............................................... 55
Sonar Operations ........................................................................ 56
Fish Symbols vs. Full Sonar Chart ........................................ 58
Section 4: Sonar Options........................................................ 61
ASP™ (Advanced Signal Processing) ......................................... 61
Alarms.......................................................................................... 62
Depth Alarms .......................................................................... 62
Zone Alarm .............................................................................. 63
Fish Alarm ............................................................................... 64
GPS Alarms ............................................................................. 65
NMEA 2000 Alarms .................................................................... 66
Calibrate Speed ........................................................................... 67
Chart Speed ................................................................................. 68
Colorline™ ................................................................................... 69
Depth Cursor ............................................................................... 70
Depth Range - Automatic ........................................................... 71
Depth Range - Manual................................................................ 71
Depth Range - Upper and Lower Limits ................................... 72
FasTrack™ ................................................................................... 73
Fish I.D.™ (Fish Symbols & Depths) ......................................... 74
FishTrack™.................................................................................. 76
Frequency (Change Transducer Frequency) ............................. 76
HyperScroll™............................................................................... 77
Log Sonar Chart Data................................................................. 78
Noise Rejection ............................................................................ 79
Overlay Data ............................................................................... 79
Ping Speed & HyperScroll™ ....................................................... 82
Reset Options............................................................................... 83
Reset Water Distance.................................................................. 84
Set Keel Offset............................................................................. 84
Sensitivity & Auto Sensitivity.................................................... 85
Automatic Sensitivity ............................................................. 86
Sonar Chart Mode ....................................................................... 87
Sonar Page & Sonar Chart Display Options ............................. 88
Full Sonar Chart ..................................................................... 88
Split Zoom Sonar Chart .......................................................... 89
Split Frequency Sonar Chart (LMS-525cDF only)................ 89
Digital Data/Chart .................................................................. 90
Customize Page Displays........................................................ 90
Flasher ..................................................................................... 92
Sonar with Custom Gauges ........................................................ 92
ii
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 5

Map with Sonar Split Screen.................................................. 94
Sonar Simulator .......................................................................... 95
Stop Chart.................................................................................... 97
Surface Clarity ............................................................................ 98
Transparency............................................................................... 99
Upper and Lower Limits........................................................... 100
Zoom & Zoom Bar...................................................................... 100
Zoom Pan ................................................................................... 100
Section 5: Sonar Troubleshooting ..................................... 101
Section 6: Basic GPS Operations ....................................... 105
Keyboard.................................................................................... 105
Power/lights on and off ............................................................. 106
Main Menu................................................................................. 106
Pages .......................................................................................... 108
Sonar Page ............................................................................. 108
Satellite Status Page............................................................. 108
Navigation Page .................................................................... 110
Map Page ............................................................................... 113
Map with Sonar ..................................................................... 117
Map with Custom Gauges..................................................... 118
Radar.......................................................................................... 119
Basic GPS Quick Reference ................................................ 121
Find Your Current Position...................................................... 122
Moving Around the Map: Zoom & Cursor Arrow Keys........... 122
Selecting Any Map Item with the Cursor................................ 123
Searching ................................................................................... 123
Set a Waypoint .......................................................................... 125
Navigate To a Waypoint ........................................................... 127
Set Man Overboard (MOB) Waypoint...................................... 127
Navigate Back to MOB Waypoint ............................................ 128
Navigate to Cursor Position on Map........................................ 128
Navigate to a Point of Interest ................................................. 130
Creating and Saving a Trail ..................................................... 130
Displaying a Saved Trail .......................................................... 132
Navigating Trails ...................................................................... 133
Visual Trailing....................................................................... 133
Navigate a Trail .................................................................... 133
Navigate a Back Trail (backtrack) ....................................... 135
Transfer Custom Maps and GPS Data Files ........................... 136
Cancel Navigation ..................................................................... 138
Section 7: Advanced GPS Operations.............................. 139
Find Distance from different Locations ................................... 139
Find Distance from Point to Point ........................................... 139
iii
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 6

Icons ........................................................................................... 140
Create Icon on Map ............................................................... 140
Create Icon at Current Position ........................................... 140
Delete an Icon ........................................................................ 140
Navigate to an Icon ............................................................... 141
Routes ........................................................................................ 141
Create and Save a Route ...................................................... 142
Delete a Route ....................................................................... 144
Edit a Route Name ................................................................ 145
Edit Route Waypoints ........................................................... 145
Navigate a Route ................................................................... 146
Navigate a Route in Reverse ................................................ 146
Trails .......................................................................................... 147
Delete a Trail ......................................................................... 147
Edit a Trail Name ................................................................. 148
Edit a Trail Color .................................................................. 148
Edit a Trail Pattern............................................................... 148
Utilities ...................................................................................... 149
Alarm Clock ........................................................................... 149
Sun/Moon Rise & Set Calculator.......................................... 149
Trip Calculator ...................................................................... 149
Trip Down Timer ................................................................... 149
Trip Up Timer........................................................................ 149
Waypoints .................................................................................. 149
Edit a Waypoint..................................................................... 150
Selecting a Waypoint ............................................................ 150
Create Waypoint by Entering a Position ......................... 151
Set a Waypoint by Average Position .................................... 152
Set a Waypoint by Projecting a Position.............................. 152
Section 8: System & GPS Setup Options .......................... 153
Alarms........................................................................................ 153
Auto Satellite Search ................................................................ 154
Check MMC Files and Storage Space...................................... 155
Communications Port Configuration ....................................... 155
Configure NMEA....................................................................... 156
Coordinate System Selection.................................................... 156
Map Fix ...................................................................................... 158
Customize Page Displays.......................................................... 159
GPS Simulator........................................................................... 160
Hide GPS Feature ..................................................................... 162
Initialize GPS ............................................................................ 162
Map Auto Zoom ......................................................................... 163
Map Data ................................................................................... 163
iv
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 7

Map Datum Selection................................................................ 165
Map Detail Category Selection................................................. 166
Map Orientation........................................................................ 166
NauticPath™ USA Marine Charts........................................... 168
Nautical Chart Notes ............................................................ 168
Port Information.................................................................... 169
Tidal Current Information.................................................... 170
Tide Information ................................................................... 172
Navionics® Charts ..................................................................... 173
Overlay Data ............................................................................. 174
Pop-up Help ............................................................................... 178
Reset Options............................................................................. 179
Screen Contrast and Brightness .............................................. 180
Set Language ............................................................................. 181
Set Local Time ........................................................................... 181
Show WAAS Alarm ................................................................... 182
Software Version Information .................................................. 183
Sounds and Alarm Sound Styles .............................................. 184
Track Smoothing ....................................................................... 185
Trail Options.............................................................................. 185
Update Trail Option.............................................................. 186
Trail Visible/Invisible and Other Trail Options.................. 188
Transparency............................................................................. 188
Units of Measure ....................................................................... 189
Section 9: Searching.............................................................. 193
Find Streets ............................................................................... 194
Find Any Item Selected by Map Cursor .................................. 195
Find Interstate Highway Exits ................................................ 195
Find Map Places or Points of Interest (POI) ........................... 198
Find Streets or Intersections.................................................... 200
Find Waypoints ......................................................................... 203
Section 10: NMEA 2000 Device Configuration................ 207
NMEA 2000 Menu..................................................................... 207
Bus Setup................................................................................... 207
Engine & Tank Configuration.................................................. 208
Tank Select ........................................................................ 209
Tank Size ........................................................................... 209
Set Configuration button .................................................. 209
Device Configuration Menu.................................................. 210
Device Information and Device Data ................................... 210
Fuel Management Menu........................................................... 211
Tank Location .................................................................... 211
Fuel Added ......................................................................... 211
v
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 8

Add Fuel............................................................................. 212
Fill Tank............................................................................. 212
Adding Fuel to Tank ............................................................. 212
Engine Operations................................................................. 212
Engine Select ..................................................................... 212
NMEA 2000 Alarms .................................................................. 213
Waypoint Sharing ..................................................................... 214
Backlight Synchronization ....................................................... 214
Configuring EP Sensors............................................................ 215
EP-35 Temperature Configuration ...................................... 215
Advanced Options menu ....................................................... 216
Instance.............................................................................. 216
Restore Defaults ................................................................ 216
EP-10 Fuel Flow Configuration............................................ 216
Advanced Options menu ....................................................... 217
Instance.............................................................................. 217
Restore Defaults ................................................................ 217
To restore default settings: ............................................... 218
EP-15 Fluid Level Configuration ......................................... 218
Advanced Options menu ....................................................... 220
Instance.............................................................................. 220
Restore Defaults ................................................................ 220
Suzuki Engine Interface Configuration............................... 221
Advanced Options menu ....................................................... 222
Instance.............................................................................. 222
Restore Defaults ................................................................ 222
Calibrating EP Sensors............................................................. 223
EP-10 Fuel Flow Calibration................................................ 223
EP-15 Fluid Level Calibration ............................................. 224
2-Point Calibration............................................................ 224
3-Point Calibration............................................................ 225
5-Point Calibration............................................................ 226
Fuel Flow Calibration in a Suzuki Engine Interface.......... 227
Engine Trim Calibration....................................................... 228
Reset Trim Calibration ......................................................... 229
Bennett Trim Tabs Calibration ............................................ 229
Section 11: Supplemental Material ................................... 231
vi
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 9

NOTICE!
The storage and operation temperature range for your unit is from -20
degrees to +167 degrees Fahrenheit (-28 degrees to +75 degrees Celsius). Extended storage or operation in temperatures higher or lower
than specified will damage the liquid crystal display in your unit. This
type of damage is not covered by the warranty. For more information,
contact the factory's Customer Service Department; phone numbers are
listed on the last page of the manual.
A CAREFUL NAVIGATOR NEVER RELIES ON ONLY ONE METHOD
TO OBTAIN POSITION INFORMATION.
When showing navigation data to a position (waypoint), a GPS unit will show
the shortest, most direct path to the waypoint. It provides navigation data to the
waypoint regardless of obstructions. Therefore, the prudent navigator will not
only take advantage of all available navigation tools when traveling to a waypoint, but will also visually check to make sure a clear, safe path to the waypoint
is always available.
When a GPS unit is used in a vehicle, the vehicle operator is solely responsible for operating the vehicle in a safe manner. Vehicle operators
must maintain full surveillance of all pertinent driving, boating or flying
conditions at all times. An accident or collision resulting in damage to
property, personal injury or death could occur if the operator of a GPSequipped vehicle fails to pay full attention to travel conditions and vehicle operation while the vehicle is in motion.
WARNING!
CAUTION
WARNING!
vii
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 10

Notes
viii
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 11

Section 1: Read Me First!
How this manual can get you out on the road, fast!
Welcome to the exciting world of digital sonar and GPS! We know
you're anxious to begin navigating and finding fish, but we have a favor
to ask. Before you grab the unit and begin installing it, please give us a
moment or two to explain how our manual can help you get the best
performance from your compact, wide-screen, combination fish finder
and mapping GPS receiver.
First, we want to thank you for buying a Lowrance sonar/GPS unit.
Whether you're a first time user or a professional fisherman, you'll discover that your unit is easy to use, yet capable of handling demanding
navigation and sonar tasks. When you team your unit with our custom
mapping software MapCreate™, you have an incredible combination.
You won't find another combination GPS and sonar unit with this
much power and this many features for this price!
Our goal for this book is to get you on the water fast, with a minimum
of fuss. Like you, we'd rather spend more time boating or fishing and
less time reading the manual!
So, we designed our book so that you don't have to read the whole thing
from front to back for the information you want. At the start (or end) of
each segment, we'll tell you what content is coming up next. If it's a
concept you're already familiar with, we'll show you how and where to
skip ahead for the next important topic. We've also made it easy to look
up any tips you may need from time to time. Here's how:
The manual is organized into 10 sections. This first section is an introduction to the LMS-520c and LMS-525cDF, sonar and GPS. It tells you
the basics you need to know before you can make the unit look around
and tell you where you are, or look below the surface to find some fish.
Section 2 will help you install your unit, the transducer and the GPS
antenna module. We'll show you how to get the MultiMedia Card
(MMC) correctly installed inside the unit. We'll also tell you about some
of the available accessories.
Section 3 covers Basic Sonar Operation. It will show you how easy it is
to run your sonar, right out of the box. This section features a one-page
Sonar Quick Reference. (If you've already jumped ahead and fig-
ured out how to install the unit yourself, and you just can't wait
any longer, turn to the Quick Reference on page 55 and head
for the water!)
1
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 12

After you've gained some experience with your sonar, you'll want to
check out Section 4, which discusses more advanced Sonar Options and
Other Features.
When you come to a sonar menu command on your unit’s screen, you can
look it up in the manual by skimming over the table of contents, just flipping through Section 3 or scanning through the sonar options in Section 4.
If you're having difficulty with your sonar, you can find an answer to
the most common problems in Section 5, Sonar Troubleshooting.
The manual switches from sonar to navigation in Section 6, which introduces you to Basic GPS Operations. This section features a one-
page GPS Quick Reference on page 121.
Section 6 contains short, easy-to-scan GPS lessons that follow one another in chronological order. They're all you'll need to know to find your
way on the water quickly.
After you've learned the basics (or if you already have some GPS experience), you may want to try out some of the unit’s many advanced
navigation features. That brings us to Section 7, Advanced GPS Opera-
tions. This section contains the rest of your unit’s GPS command functions, organized in alphabetical order.
When you come to a GPS menu command on the screen, you can look it
up in the manual by skimming over the table of contents, just flipping
through Section 6 or scanning through the command portion of Section
7.
Your unit is ready to use right out of the box, but you can fine tune and
customize it's operation with dozens of options. Since sonar is the unit's
key feature, we put the main sonar options in Section 4. Some options,
such as screen brightness settings, affect both sonar and GPS operations. We describe how to use those common options along with GPS
options in Section 8, System Setup and GPS Setup Options. Section 8 is
organized in alphabetical order.
In Section 9, we go into more detail on one of the unit’s most remarkable
GPS capabilities — Searching. We'll introduce a search example in the
Basic GPS Operation section, but there are so many map items you can
search for, we had to give this function it's own section in the manual! For
example, did you know your unit can look up business phone numbers,
functioning as a virtual Yellow Pages? We’ll show you how in Section 9.
Finally, in Section 10, we offer Supplemental Material, including a list
of the GPS datums used, warranties and customer service information.
2
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 13

Specifications: LMS-520c and LMS-525cDF
General
Display: ............................5.0" (12.7 cm) diagonal high contrast color
Film SuperTwist LCD; programmable to
viewing preference.
Resolution: ......................480 pixel x 480 pixel resolution; 230,400 to-
tal pixels.
Backlighting: ..................Incandescent backlit screen with multiple
lighting levels; backlit keypad.
Input power: ...................10 to 15 volts DC.
Case size: .........................5.4" H x 6.9" W x 3.4" D (13.8 x 17.6 x 8.6
cm); sealed and waterproof; suitable for saltwater use.
MMC slots:.......................One with waterproof door (SD card compati-
ble).
Recording: ........................ GPS uses MMC & SD cards for recording trip
details and displaying charts or custom maps.
Sonar uses them to record and save sonar
chart logs.
Back-up memory:...........Built-in memory stores sonar records and
GPS data for decades. User settings are
stored when unit is turned off.
Languages: ......................10; menu languages selectable by user.
Sonar
Frequency: ......................LMS-525cDF: 50/200 kHz.
LMS-520c: 200 kHz.
®
Transducers: .....................A dual-frequency Skimmer
transducer with
built-in temperature sensor is packed with the
LMS-525cDF. It has 35°/12° cone angles. A
single-frequency Skimmer transducer with
built-in temperature sensor is packed with the
LMS-520c. It has a 20° cone angle. Transduc-
ers operate at speeds up to 70 mph (61 kts).
Transmitter:....................3,000 watts peak-to-peak/375 watts RMS.
3
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 14

Sonar sounding
depth capability:............LMS-525cDF: 2,500 feet/762 meters.
LMS-520c: 1,000 feet/305 meters.
(Actual capability depends on transducer
configuration and installation, bottom composition and water conditions. All sonar
units typically read deeper in fresh water
than in salt water.)
Depth display: ................ Continuous display.
Graph recording: ........... Up to 1 GB on one MMC (or SD) card
Audible alarms:..............Deep/shallow/fish/zone.
Automatic ranging: .......Yes, with instant screen updates.
Auto bottom track: ........Yes
Zoom bottom track:....... Yes.
Split-screen zoom: .........Yes.
Surface water temp: .....Yes, built into transducer.
Speed/distance log: .......Yes, with optional speed sensor (sensor in-
cluded with LMS-525cDF.)
GPS
Receiver/antenna:............External; LGC-2000 12 parallel channel
NMEA 2000-ready GPS/WAAS receiver/antenna.
Background map: ..........Built-in custom, detailed Lowrance map.
Contains: enhanced detail of continental U.S.
and Hawaii. Includes more than 60,000 nav
aids and 10,000 wrecks/obstructions in
coastal and Great Lakes waters. Metro areas, selected major streets/highways and interstate exit services details included.
™
Custom mapping:...........MapCreate
software optional; optional plug
and play LEI FreedomMaps™ offer the same
high-detail without the computer work of
MapCreate. Other plug and play mapping
options include IMS™ Fishing Hot Spots
LEI NauticPaths™ charts and Navionics
charts.
4
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
®
,
®
Page 15

Mapping memory: ...........Up to 1 GB on one MMC (or SD) card.
Position updates:...........Every second.
Position points: .............. 1,000 waypoints; 1,000 event marker icons.
Audible alarms:..............Arrival/off-course/anchor.
Graphic symbols for
waypoints or event
marker icons:..................63.
Routes: .............................100; up to 100 waypoints per route.
Plot Trails:.......................10 savable; up to 9,999 points per trail.
Zoom range: .................... 39 ranges; 0.02 to 4,000 miles.
NOTE:
The above memory capacities refer only the unit’s on-board memory.
The amount of GPS or sonar data you can record and save for recall
later is only limited by the number of MMC cards you have.
How Lowrance Sonar Works
Sonar has been around since the 1940s, so if you already know how it
works, skip down to read about the relatively new technology of GPS.
But, if you've never owned a sonar fish finder, this segment will tell you
the under water basics.
Sonar is an abbreviation for SO
ogy developed during World War II for tracking enemy submarines.
(Lowrance developed the world's first transistorized sportfishing sonar in
1957.) A sonar consists of a transmitter, transducer, receiver and display. In simple terms, here's how it finds the bottom, or the fish:
The transmitter emits an electrical impulse, which the transducer converts into a sound wave and sends into the water. (The sound frequency
can't be heard by humans or fish.) The sound wave strikes an object
(fish, structure, bottom) and bounces back to the transducer, which
converts the sound back into an electrical signal.
The receiver amplifies this return signal, or echo, and sends it to the
display, where an image of the object appears on the scrolling sonar
chart. The sonar's microprocessor calculates the time lapse between the
transmitted signal and echo return to determine the distance to the
object. The whole process repeats itself several times each second.
Your unit can record a log of the sonar signals that scroll across the
screen and save them to the MMC memory card. (These recordings are
und NAvigation and Ranging, a technol-
5
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 16

also called sonar charts or sonar graphs.) You can replay this sonar log
in the unit using the Sonar Simulator function, or play it back on a personal computer using our free Sonar Viewer. The viewer is available for
download from the Lowrance web site, www.lowrance.com.
You can save several different sonar log files, erase 'em and record new
ones, over and over again. The size of your sonar recordings is only limited by the free space available on your MMC.
How Lowrance GPS Works
You'll navigate faster and easier if you understand how your unit scans
the sky to tell you where you are on the earth — and, where you're going. First, think of your unit as a small but powerful computer. (But
don't worry — we made the unit easy to use, so you don't need to be a
computer expert to find your way!) It includes a keypad and a screen
with menus so you can tell it what to do. The screen also lets the unit
show your location on a moving map, as well as point the way to your
destination.
This gimbal-mounted unit uses an external antenna/receiver module,
which makes the whole system work something like your car radio. But
instead of your favorite dance tunes, this receiver tunes in to a couple
of dozen GPS satellites circling the earth. (It will also listen in to the
WAAS satellites in orbit, but more about that in the upcoming segment
introducing you to GPS and WAAS.)
Your unit listens to signals from as many satellites as it can "see"
above the horizon, eliminates the weakest signals, then computes its
location in relation to those satellites. Once the unit figures its latitude
and longitude, it plots that position on the moving map shown on the
screen. The whole process takes place several times a second!
The performance doesn't stop there. Stored in the permanent memory
of each unit is a basic background map of the entire world. We lock it in
here at the factory — you can't change or erase this map.
The background map is suitable for many navigation chores, but for
maximum accuracy and much more detail, you need our optional mapmaking software, MapCreate™. Some unit features — such as searching for businesses and addresses — won't work without a custom MapCreate map.
There is so much detail in our background map (and even more in
MapCreate) that we'll describe their contents and differences in Section
6, Basic GPS Operations, on page 105.
Another portion of the unit’s onboard memory is devoted to recording
GPS navigation information, which includes waypoints, event marker
6
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 17

icons, trails and routes. This lets you look back the way you came.
Think of this data storage like the hard drive memory in a computer or
a tape in a cassette tape recorder. You can save several different GPS
data files, erase 'em and record new ones, over and over again. These
GPS Data Files (file format *.usr) can be shared between, not only the
LMS-520c and LMS-525cDF, but other Lowrance GPS units and even
personal computers.
Your unit has one more thing in common with a personal computer.
Just as computers have a floppy disk drive for storing and exchanging
files, the unit has a slot for an MMC (MultiMedia Card) or SDC (Secure
Digital card) flash memory card. These solid-state memory devices are
about the size of a postage stamp, but can hold data ranging from 8 MB
to 1 GB. (Compare that to a floppy disk's 1.44 MB capacity!) Your unit
uses all that MMC space for two key GPS purposes. (The MMC is also
used to record sonar logs.)
First, you can backup your onboard GPS Data Files by copying them to
the MMC. Since the MMC is removable (like a floppy disk or a cassette
tape), you can store these GPS Data Files on a personal computer
equipped with an MMC card reader. (Or store them on a pocketful of
MMCs, if you don't have a computer.) Our MapCreate mapping software
can save, edit or create its own GPS Data Files, which can be copied to
the MMC and then loaded from the MMC into unit’s memory. (NOTE:
No matter where they come from, GPS Data Files must be loaded from
the MMC into memory before your unit can use them.)
The other key GPS use for MMCs is storage of special high-detail, custom maps, which you can produce on your computer with our MapCreate software. These MapCreate custom maps contain much greater detail than the basic background map. These Custom Map Files (file
format *.lcm) not only may be shared between the LMS-520c and
525cDF, but also with other Lowrance GPS and sonar/GPS units as
well as personal computers. (For example, the exact same MMC, custom map files and GPS data files can be used interchangeably between
your gimbal-mounted unit and the hand-held iFINDER™ GPS receiver.)
Your unit automatically reads Custom Map Files directly from the
MMC or SDC. To use a custom map, all you need to do is slide an MMC
containing a map into the unit.
Introduction to GPS and WAAS
Well, now you know the basics of how your unit does its work. You
might be ready to jump ahead to Section 2, Installation & Accessories,
7
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 18
on page 13, so you can mount your unit and plug in the power. Or you
might want to see how our text formatting makes the manual tutorials
easy to skim. If that's the case, move on to "How to Use This Manual"
on page 10. But, if you want to understand the current state of satellite
navigation, look over this segment describing how GPS and its new
companion WAAS work together to get you where you're going.
The Global Positioning System (GPS) was launched July 17, 1995 by
the United States Department of Defense. It was designed as a 24hour-a-day, 365-days-a-year, all weather global navigation system for
the armed forces of the U.S. and its allies. Civilian use was also available at first, but it was less accurate because the military scrambled
the signal somewhat, using a process called Selective Availability (SA.)
GPS proved so useful for civilian navigation that the federal government discontinued SA on May 2, 2000, after the military developed
other methods to deny GPS service to enemy forces. Reliable accuracy
for civilian users jumped from 100 meters (330 feet) under SA to the
present level of 10 to 20 meters (about 30 to 60 feet.)
Twenty-four satellites orbit 10,900 nautical miles above the Earth, passing overhead twice daily. A series of ground stations (with precisely surveyed locations) controls the satellites and monitors their exact locations
in the sky. Each satellite broadcasts a low-power signal that identifies
the satellite and its position above the earth. Three of these satellites are
spares, unused until needed. The rest virtually guarantee that at least
four satellites are in view nearly anywhere on Earth at all times.
A minimum of three satellites are required to determine a 2D fix.
The system requires signal reception from three satellites in order to
determine a position. This is called a 2D fix. It takes four satellites to
determine both position and elevation (your height above sea level —
also called altitude.) This is called a 3D fix.
8
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 19

Remember, the unit must have a clear view of the satellites in order to
receive their signals. Unlike radio or television signals, GPS works at
very high frequencies. These signals can be easily blocked by trees,
buildings, an automobile roof, even your body.
Like most GPS receivers, the unit doesn’t have a compass or any other
navigation aid built inside. It relies solely on the signals from the satellites to calculate a position. Speed, direction of travel, and distance are
all calculated from position information. Therefore, in order it to determine direction of travel, you must be moving and the faster, the better. This is not to say that it won’t work at walking or trolling speeds —
it will. There will simply be more "wandering" of the data shown on the
display.
GPS alone is plenty accurate for route navigation, but the U.S. Federal
Aviation Administration has special aircraft navigation needs that go
beyond basic GPS. So, the FAA has developed a program to boost GPS
performance with its Wide Area Augmentation System, or WAAS. The
FAA commissioned the system on July 11, 2003.
WAAS is designed to increase GPS accuracy to within 7.6 meters vertically
and horizontally, but it consistently delivers accuracies within 1-2 meters
horizontal and 2-3 meters vertical, according to the FAA. It does this by
broadcasting correction signals on GPS frequencies. Your unit automatically receives both GPS and WAAS signals.
However, there are some fringe areas of the U.S., including parts of
Alaska that do not yet receive robust WAAS coverage. Continued WAAS
development is planned to extend WAAS coverage in the years to come.
WAAS boosts the accuracy of land GPS navigation, but the system is
designed for aircraft. The satellites are in a fixed orbit around the
Equator, so they appear very low in the sky to someone on the ground
in North America. Aircraft and vessels on open water can get consistently good WAAS reception, but terrain, foliage or even large man-made
structures can sometimes block the WAAS signal from ground receivers.
You'll find that using your GPS receiver is both easy and amazingly
accurate. It’s easily the most accurate method of electronic navigation
available to the general public today. Remember, however, that this
receiver is only a tool. Always have another method of navigation available, such as a map or chart and a compass.
Also remember that this unit will always show navigation information
in the shortest line from your present position to a waypoint, regardless
9
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 20

of terrain! It only calculates position, it can’t know what’s between you
and your destination, for example. It’s up to you to safely navigate
around obstacles, no matter how you’re using this product.
How to use this manual: typographical conventions
Many instructions are listed as numbered steps. The keypad and arrow
"keystrokes" appear as boldface type. So, if you're in a real hurry (or
just need a reminder), you can skim the instructions and pick out what
menu command to use by finding the boldface command text. The following paragraphs explain how to interpret the text formatting for
those commands and other instructions:
Arrow Keys
The arrow keys control the movement of dotted cross-hair lines on your
mapping screen called the cursor. The arrow keys also control a horizontal line depth cursor on the sonar screen. The arrow keys help you
move around the menus so you can execute different commands. They
are represented by symbols like these, which denote the down arrow
key, the up arrow, the left arrow and the right arrow: ↓ ↑ ← →.
10
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 21

Keyboard
The other keys perform a variety of functions. When the text refers to a
key to press, the key is shown in bold, sans serif type. For example, the
"Enter/Icons" key is shown as
ENT and the "Menu" key is shown as MENU.
Menu Commands
A menu command or a menu option will appear in small capital letters, in
a bold sans serif type like this:
ROUTE PLANNING. These indicate that you
are to select this command or option from a menu or take an action of
some kind with the menu item. Text that you may need to enter or file
names you need to select are show in italic type, such as trail name.
Instructions = Menu Sequences
Most functions you perform with your unit are described as a sequence
of key strokes and selecting menu commands. We've written them in a
condensed manner for quick and easy reading.
For example, instructions for navigating a trail would look like this:
1. From the Map Page, press
2. Press ↓ to Trail 1|
ENT|→|↓ to NAVIG ATE|ENT.
MENU|MENU|↓ to MY TRAILS|ENT.
3. You are asked to wait while it converts the trail into a route.
4. The wait message disappears and the unit begins showing
navigation information along the trail.
Translated into complete English, step 1 above would mean: "Start on
the Map Page. Press the Menu key twice. Next, repeatedly press (or
press and hold) the down arrow key to scroll down the menu and select
(highlight) the My Trails menu command. Finally, press the Enter key."
Step 2 would mean: "Press the down arrow key repeatedly to scroll to
the trail named Trail 1, and press Enter. Next, press the right arrow
key and then the down arrow key to highlight the Navigate command,
then press Enter."
11
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 22

Notes
12
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 23

Section 2: Installation
Preparations
You can install the sonar and GPS systems in some other order if you
prefer, but we recommend this installation sequence:
Caution:
You should read over this entire installation section before drilling any holes in your vehicle or vessel!
1. Determine the approximate location for the sonar/GPS unit, so you
can plan how and where to route the cables for the antenna, transducer
and power. This will help you make sure you have enough cable length
for the desired configuration.
2. Determine the approximate location for the transducer and its cable
route.
3. Determine the approximate location for the GPS antenna module
and its cable route.
4. Determine the location of your battery or other power connection,
along with the power cable route.
5. Install the transducer and route the transducer cable to the sonar/GPS unit.
6. Install the GPS antenna and route the antenna cable to the sonar/GPS unit.
7. Install the power cable and route it to the sonar/GPS unit.
8. Mount the sonar/GPS unit to the bracket.
Transducer Installation
®
These instructions will help you install your Skimmer
transom, on a trolling motor or inside a hull. These instructions cover
both single- and dual-frequency Skimmer transducers. Please read all
instructions before proceeding with any installation.
The smaller single-frequency Skimmers typically use a one-piece,
stainless steel mounting bracket. The larger dual-frequency Skimmers
typically use a two-piece, plastic mounting bracket. The trolling motor
mount uses a one-piece plastic bracket with an adjustable strap.
These are all "kick-up" mounting brackets. They help prevent damage
if the transducer strikes an object while the boat is moving. If the
transducer does "kick-up," the bracket can easily be pushed back into
place without tools.
13
transducer on a
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 24

Read these instructions carefully before attempting the installation.
Determine which of the mounting positions is right for your boat. Re-
member, the transducer installation is the most critical part of
a sonar installation.
NOTE:
The following installation types also call for these recommended
tools and required supplies that you must provide (supplies listed
here are not included):
Single-frequency transom installations
Tools include: two adjustable wrenches, drill, #29 (0.136") drill bit, flathead screwdriver. Supplies: high quality, marine grade above- or belowwaterline sealant/adhesive compound.
Dual-frequency transom installations
Tools: two adjustable wrenches, drill, #20 (0.161") drill bit, flat-head
screwdriver. Supplies: four, 1" long, #12 stainless steel slotted wood
screws, high quality, marine grade above- or below-waterline sealant/adhesive compound.
Single-frequency trolling motor installations
Tools: two adjustable wrenches, flat-head screwdriver. Supplies: plastic
cable ties.
Shoot-through hull installations
Tools: these will vary depending on your hull's composition. Consult your
boat dealer or manufacturer. Other tools are a wooden craft stick or
similar tool for stirring and applying epoxy, and a paper plate or piece
of cardboard to mix the epoxy on. Supplies: rubbing alcohol, 100 grit
sandpaper, specially formulated epoxy adhesive available from LEI (see
ordering information on the inside back cover). A sandwich hull also
requires polyester resin.
Selecting a Transducer Location
1. The location must be in the water at all times, at all operating speeds.
2. The transducer must be placed in a location that has a smooth flow
of water at all times. If the transducer is not placed in a smooth flow
of water, interference caused by bubbles and turbulence will show on
the sonar's display in the form of random lines or dots whenever the
boat is moving.
NOTE:
Some aluminum boats with strakes or ribs on the outside of the
hull create large amounts of turbulence at high speed. These boats
typically have large outboard motors capable of propelling the boat
14
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 25
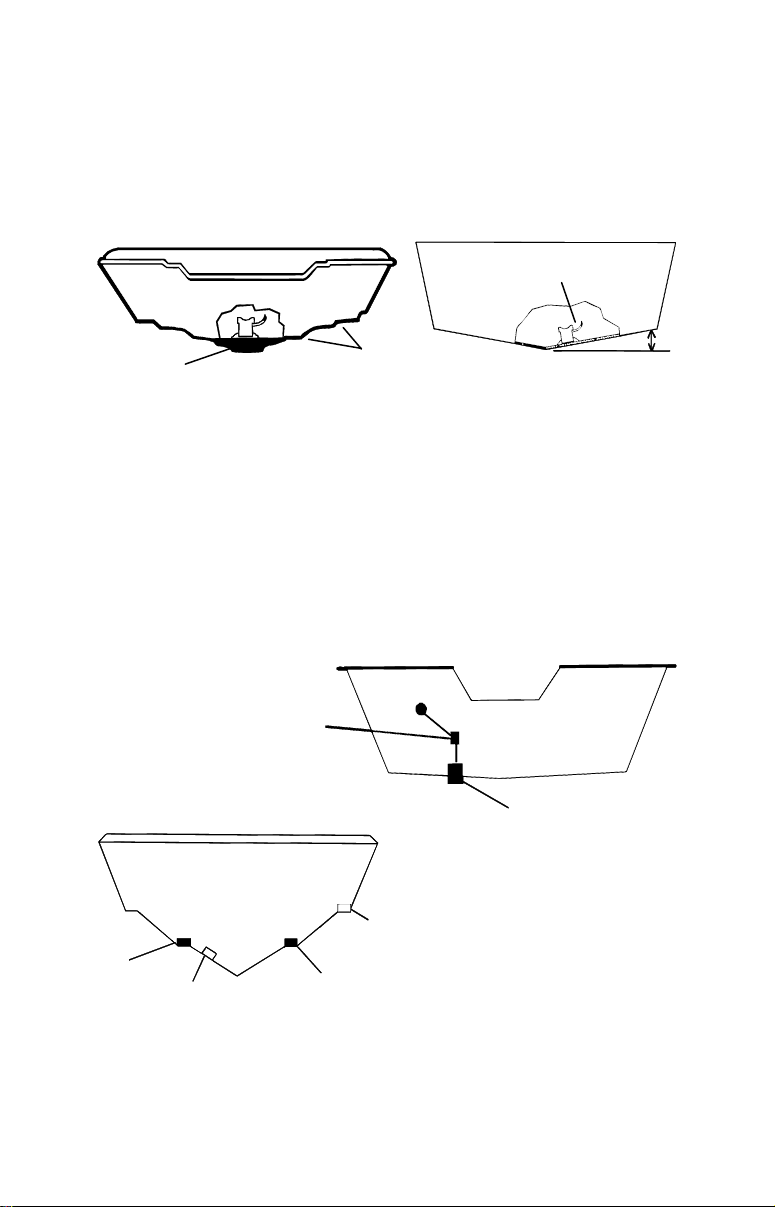
at speeds faster than 35 mph. Typically, a good transom location on
p
aluminum boats is between the ribs closest to the engine.
3. The transducer should be installed with its face pointing straight
down, if possible. For shoot-thru applications: Many popular fishing
boat hulls have a flat keel pad that offers a good mounting surface. On
vee hulls, try to place the transducer where the deadrise is 10° or less.
Deadrise less than 10°
Left, vee pad hull; right, vee hull. A pod style transducer is shown
Pad
here, but the principle is the same for Skimmers inside a hull.
Strakes
4. If the transducer is mounted on the transom, make sure it doesn't
interfere with the trailer or hauling of the boat. Also, don't mount it
closer than approximately one foot from the engine's lower unit. This
will prevent cavitation (bubble) interference with propeller operation.
5. If possible, route the transducer cable away from other wiring on the
boat. Electrical noise from engine wiring, bilge pumps and aerators
can be displayed on the sonar's screen. Use caution when routing the
transducer cable around these wires.
CAUTION: Clamp the transducer cable to transom near
the transducer. This will help
revent the transducer from
entering the boat if it is
knocked off at high speed.
Good location
Poor location
Good
location
Poor angle
Good and poor transducer locations.
Good location
15
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 26
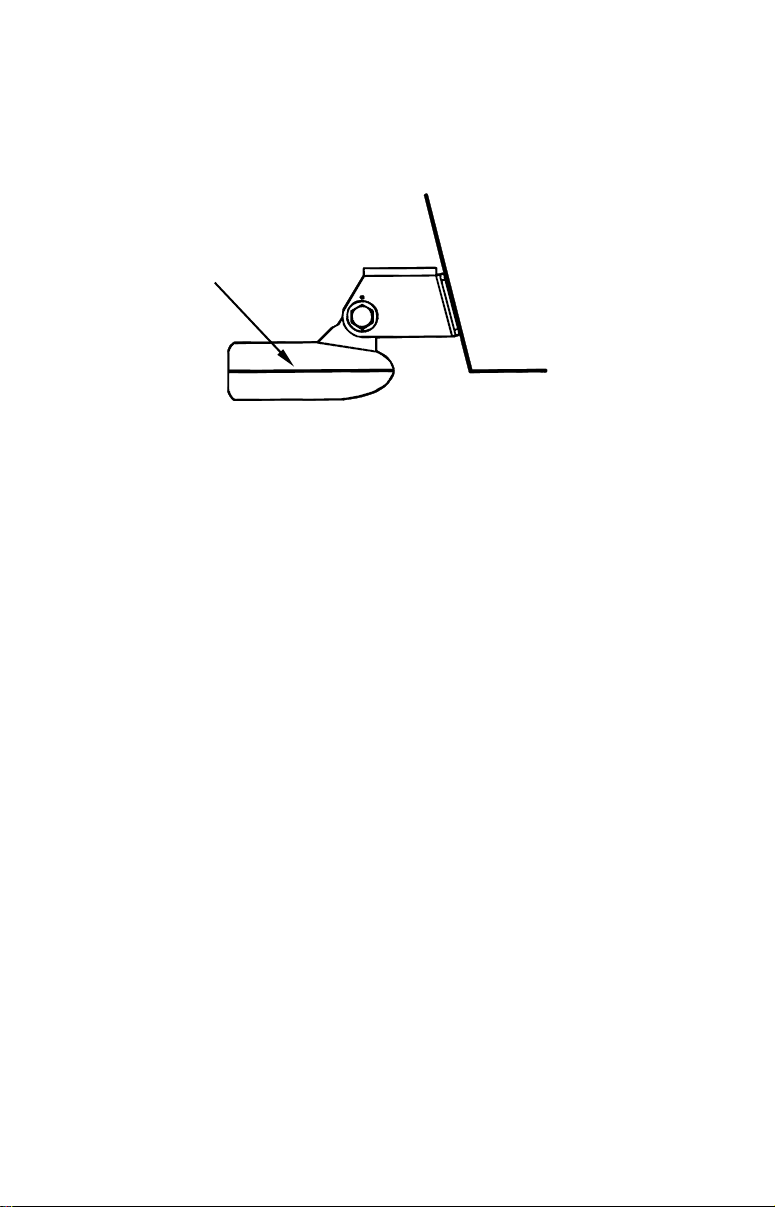
How low should you go?
For most situations, you should install your Skimmer transducer so
that its centerline is level with the bottom of the boat hull.
This will usually give you the best combination of smooth water flow
and protection from bangs and bumps.
Transducer
centerline
Align transducer centerline with hull bottom.
Transom
Hull bottom
However, there are times when you may need to adjust the transducer
slightly higher or lower. (The slots in the mounting brackets allow you
to loosen the screws and slide the transducer up or down.) If you frequently lose bottom signal lock while running at high speed, the transducer may be coming out of the water as you cross waves or wakes.
Move the transducer a little lower to help prevent this.
If you cruise or fish around lots of structure and cover, your transducer
may be frequently kicking up from object strikes. If you wish, you may
move the transducer a little higher for more protection.
There are two extremes you should avoid. Never let the edge of the
mounting bracket extend below the bottom of the hull. Never let the
bottom – the face – of the transducer rise above the bottom of the hull.
Shoot-thru-hull vs. Transom Mounting
In a shoot-thru-hull installation, the transducer is bonded to the inside
of the hull with epoxy. The sonar "ping" signal actually passes through
the hull and into the water. This differs from a bolt-thru-hull installation (often called simply "thru-hull"). In that case, a hole is cut in the
hull and a specially designed transducer is mounted through the hull
with a threaded shaft and nut. This puts the transducer in direct contact with the water.
Typically, shoot-thru-hull installations give excellent high speed operation and good to excellent depth capability. There is no possibility of
transducer damage from floating objects, as there is with a transommounted transducer. A transducer mounted inside the hull can't be
knocked off when docking or loading on a trailer.
16
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 27

However, the shoot-thru-hull installation does have its drawbacks.
First, some loss of sensitivity does occur, even on the best hulls. This
varies from hull to hull, even from different installations on the same
hull. This is caused by differences in hull lay-up and construction.
Second, the transducer angle cannot be adjusted for the best fish
arches on your sonar display. (This is not an issue for flasher-style
sonars.) Lack of angle adjustment can be particularly troublesome on
hulls that sit with the bow high when at rest or at slow trolling speeds.
Third, a transducer CAN NOT shoot through wood and metal hulls.
Those hulls require either a transom mount or a thru-hull installation.
Fourth, if your Skimmer transducer has a built in temp sensor, it will
only show the temperature of the bilge, not the water surface temp.
Follow the testing procedures listed in the shoot-thru-hull installation
section at the end of this lesson to determine if you can satisfactorily
shoot through the hull.
Transom Transducer Assembly And Mounting
The best way to install these transducers is to loosely assemble all of the
parts first, place the transducer's bracket against the transom and see if
you can move the transducer so that it's parallel with the ground.
The following instructions sometimes vary depending on the mounting
bracket that came with your transducer. Single-frequency Skimmers
come with a one-piece stainless steel bracket, while dual-frequency
Skimmers come with a two-piece plastic mounting bracket. Use the set of
instructions that fits your model.
1. Assembling the bracket.
A. One-piece bracket: Press the two small plastic ratchets into the
sides of the metal bracket as shown in the following illustration. Notice
there are letters molded into each ratchet. Place each ratchet into the
bracket with the letter "A" aligned with the dot stamped into the metal
bracket. This position sets the transducer's coarse angle adjustment for a
14° transom. Most outboard and stern-drive transoms have a 14° angle.
Dot
Align plastic ratchets in bracket.
17
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 28
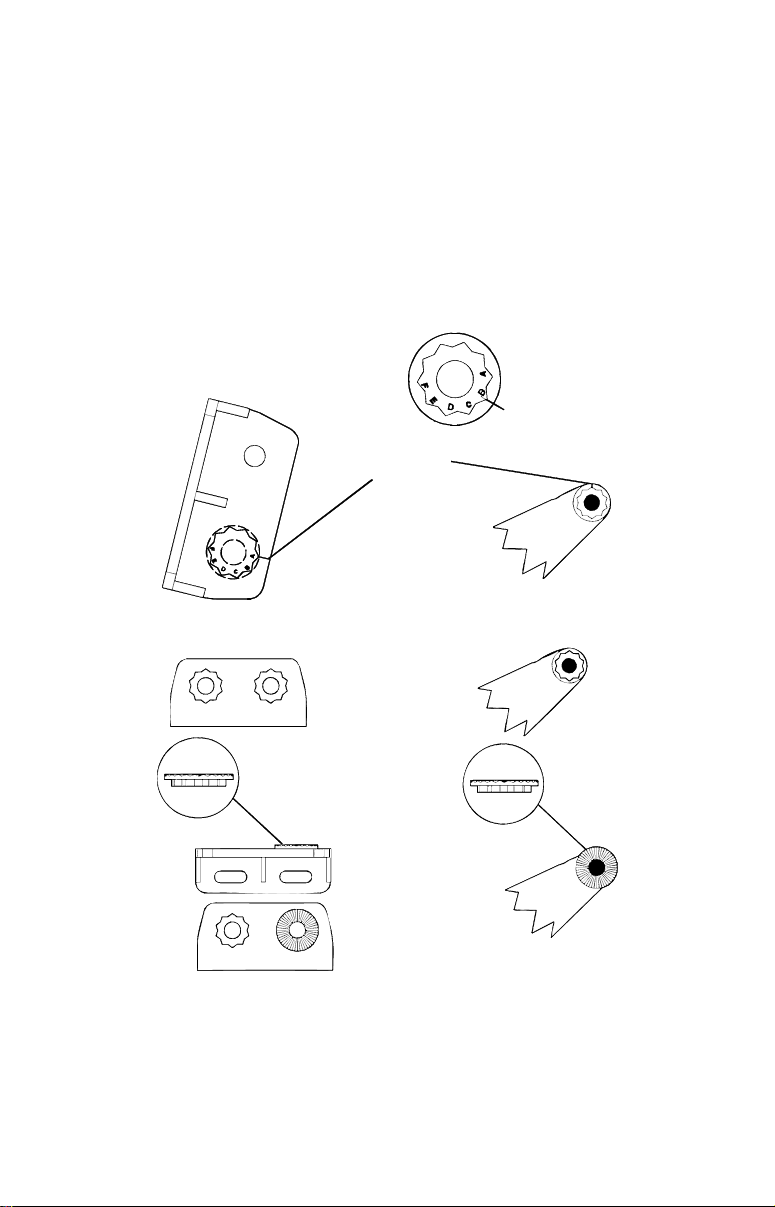
B. Two-piece bracket: Locate the four plastic ratchets in the trans-
Alig
r
ducer's hardware package. Press two ratchets into the sides of the plastic bracket and two on either side of the transducer as shown in the following illustrations. Notice there are letters molded into each ratchet.
Place the ratchets into the bracket with the letter "A" aligned with the
alignment mark molded into the bracket. Place the ratchets onto the
transducer with the letter "A" aligned with the 12 o'clock position on
the transducer stem. These positions set the transducer's coarse angle
adjustment for a 14° transom. Most outboard and stern-drive transoms
have a 14° angle.
nment letters
Alignment
positions
Transduce
Transducer bracket
Transducer
bracket
Insert and align ratchets.
Transducer
Ratchet
Ratchet
Add ratchets to bracket and transducer.
2. Aligning the transducer on the transom.
A. One-piece bracket: Slide the transducer between the two ratch-
ets. Temporarily slide the bolt though the transducer assembly and
18
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 29
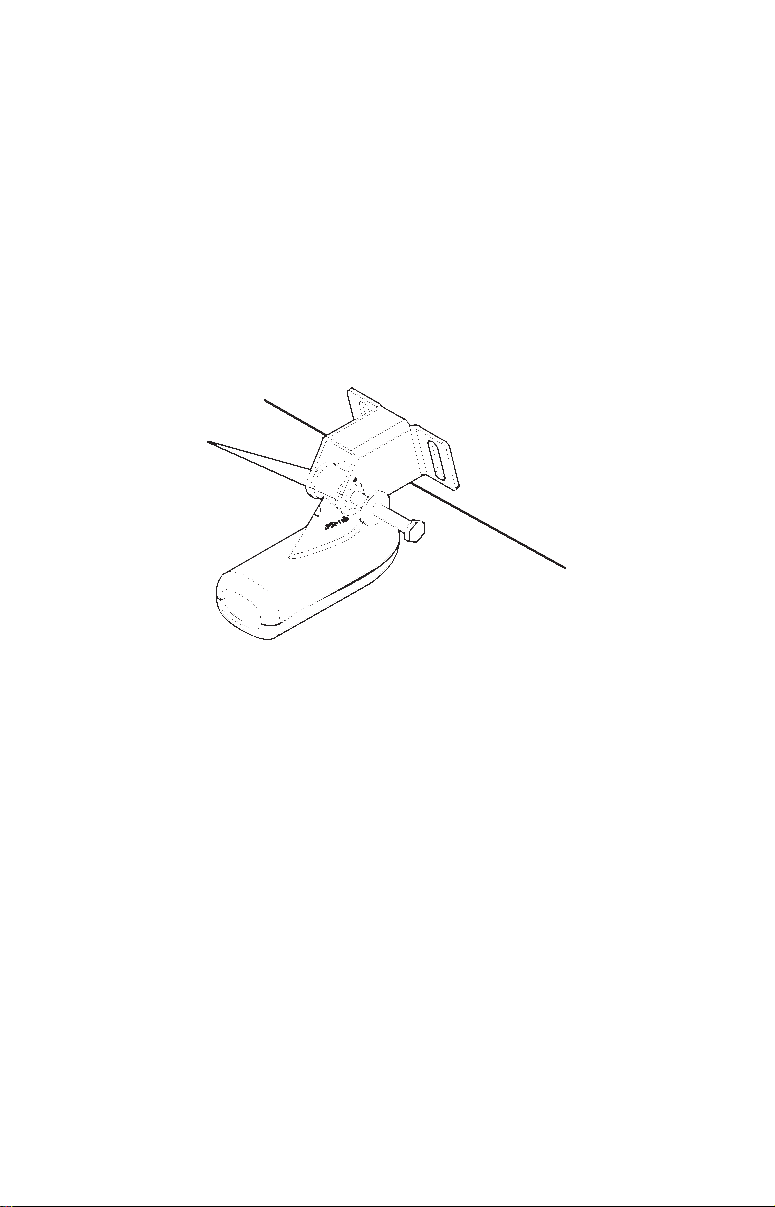
hold it against the transom. Looking at the transducer from the side,
check to see if it will adjust so that its face is parallel to the ground.
If it does, then the "A" position is correct for your hull.
If the transducer's face isn't parallel with the ground, remove the
transducer and ratchets from the bracket.
Place the ratchets into the holes in the bracket with the letter "B"
aligned with the dot stamped in the bracket.
Reassemble the transducer and bracket and place them against the
transom. Again, check to see if you can move the transducer so it's
parallel with the ground. If you can, then go to step 3A. If it doesn't,
repeat step 2A, but use a different alignment letter until you can
place the transducer on the transom correctly.
Ratchets
Insert bolt and check transducer position on transom.
B. Two-piece bracket: Assemble the transducer and bracket as shown
in the following figure. Temporarily slide the bolt though the transducer
assembly but don't tighten the nut at this time. Hold the assembled
transducer and bracket against the transom. Looking at the transducer
from the side, check to see if it will adjust so that its face is parallel to
the ground. If it does, then the "A" positions are correct for your hull.
If the transducer's face isn't parallel with the ground, remove and
disassemble the transducer and ratchets. Place the ratchets into the
bracket holes with the letter "B" aligned with the bracket alignment
mark. Place them on the transducer aligned with the 12 o'clock position on the transducer stem.
Reassemble the transducer and bracket and place them against the
transom. Again, check to see if you can move the transducer so it's
parallel with the ground. If you can, then go to step 3B. If it doesn't,
repeat step 2B, but use a different alignment letter until you can
place the transducer on the transom correctly.
19
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 30
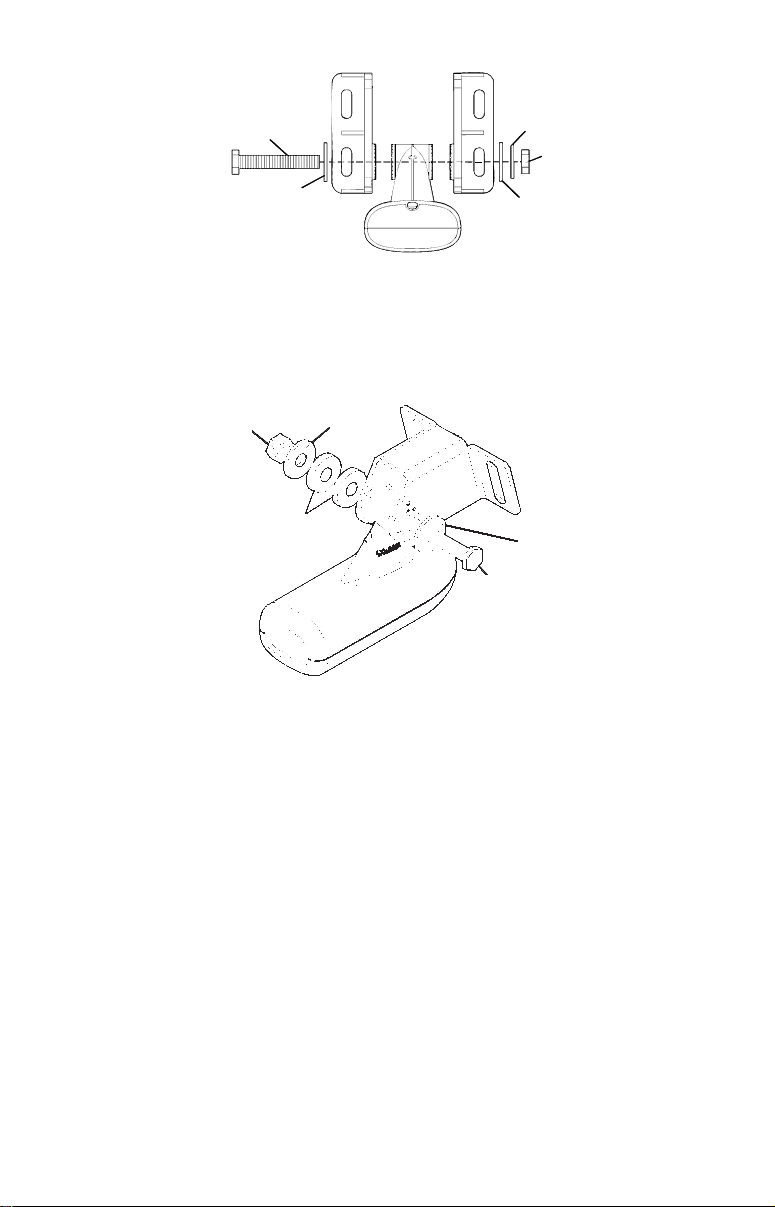
r
r
Bolt
Lock washe
Nut
Flat washer
Flat washe
Assemble transducer and bracket.
3. Assembling the transducer.
A. One-piece bracket: Once you determine the correct position for
the ratchets, assemble the transducer as shown in the following figure. Don't tighten the lock nut at this time.
Metal
Nut
Rubber
washers
washer
Metal washer
Bolt
Assemble transducer and bracket.
B. Two-piece bracket: Once you determine the correct position for
the ratchets, assemble the transducer as shown in the figure in step
2B. Don't tighten the lock nut at this time.
4. Drilling mounting holes.
Hold the transducer and bracket assembly against the transom. The
transducer should be roughly parallel to the ground. The transducer's centerline should be in line with the bottom of the hull. Don't
let the bracket extend below the hull!
Mark the center of each slot for the mounting screw pilot holes. You
will drill one hole in the center of each slot.
Drill the holes. For the one-piece bracket, use the #29 bit (for the #10
screws). For the two-piece bracket, use the #20 bit (for the #12 screws).
20
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 31

Transom
Transom
Position transducer mount on transom and mark mounting holes.
Side view shown, left, and seen from above at right.
5. Attaching transducer to transom.
A. One-piece bracket: Remove the transducer from the bracket and
re-assemble it with the cable passing through the bracket over the
bolt as shown in the following figures.
For single-frequency Skimmer, route cable over bolt and through
bracket. Side view shown, left, and seen from above at right.
Both bracket types: Attach the transducer to the transom. Slide the
transducer up or down until it's aligned properly with the bottom of
the hull as shown in the preceding and following figures. Tighten the
bracket's mounting screws, sealing them with the sealant.
Adjust the transducer so that it's parallel to the ground and tighten
the nut until it touches the outer washer, then add 1/4 turn. Don't
over tighten the lock nut! If you do, the transducer won't "kick-up" if
it strikes an object in the water.
21
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 32

Bottom
of
hull
Flat-bottom hull Deep-"vee" hull
Align transducer centerline with hull bottom and attach transducer to
transom. Rear view of dual-frequency Skimmer shown.
6. Route the transducer cable through or over the transom to the sonar
unit. Make sure to leave some slack in the cable at the transducer. If
possible, route the transducer cable away from other wiring on the
boat. Electrical noise from the engine's wiring, bilge pumps, VHF radio
wires and cables, and aerators can be picked up by the sonar. Use caution when routing the transducer cable around these wires.
WARNING:
Clamp the transducer cable to the transom close to the
transducer. This can prevent the transducer from entering the boat if it is knocked off at high speed.
If you need to drill a hole in the transom to pass the connector through,
the required hole size be 1".
Caution:
If you drill a hole in the transom for the cable, make sure it is
located above the waterline. After installation, be sure to seal the
hole with the same marine grade above- or below-waterline sealant used for the mounting screws.
7. Make a test run to determine the results. If the bottom is lost at
high speed, or if noise appears on the display, try sliding the transducer bracket down. This puts the transducer deeper into the water,
hopefully below the turbulence causing the noise. Don't allow the
transducer bracket to go below the bottom of the hull!
22
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 33

Trolling Motor Bracket Installation
r
(single-frequency only)
1. Attach the optional TMB-S bracket to the transducer as shown in the
following figure, using the hardware supplied with the transducer.
(Note: The internal tooth washer is supplied with the TMB-S.)
TMB-S bracket
Bolt
Internal tooth washer
Nut
Flat washe
Attach motor mounting bracket to transducer.
2. Slide the adjustable strap supplied with the TMB-S through the slot
in the transducer bracket and wrap it around the trolling motor. Position the transducer to aim straight down when the motor is in the
water. Tighten the strap securely.
3. Route the transducer cable alongside the trolling motor shaft. Use
plastic ties (not included) to attach the transducer cable to the trolling motor shaft. Make sure there is enough slack in the cable for the
motor to turn freely. Route the cable to the sonar unit and the transducer is ready for use.
Transducer mounted on trolling motor, side view.
Transducer Orientation and Fish Arches
If you do not get good fish arches on your display, it could be because
the transducer is not parallel with the ground when the boat is at rest
in the water or at slow trolling speeds.
23
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 34

Partial fish arches
Transducer aimed
too far back
Full fish arch
Proper transducer angle
Transducer angles and their effects on fish arches.
Transducer aimed
too far forward
If the arch slopes up – but not back down – then the front of the transducer is too high and needs to be lowered. If only the back half of the
arch is printed, then the nose of the transducer is angled too far down
and needs to be raised.
NOTE:
Periodically wash the transducer's face with soap and water to remove any oil film. Oil and dirt on the face will reduce the sensitivity or may even prevent operation.
Shoot-Thru-Hull Preparation
Hulls with Flotation Materials
The transducer installation inside a fiberglass hull must be in an area
that does not have air bubbles in the resin or separated fiberglass layers. The sonar signal must pass through solid fiberglass. A successful
transducer installation can be made on hulls with flotation materials
(such as plywood, balsa wood or foam) between layers of fiberglass if
the material is removed from the chosen area. See the following figure.
24
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 35

WARNING:
Do not remove any material from your inner hull unless
you know the hull's composition. Careless grinding or
cutting on your hull can result in damage that could
sink your boat. Contact your boat dealer or manufacturer to confirm your hull specifications.
Fill with
Fill with resin
Flotation material
Inner hull
Epoxy to hull first
Epoxy the transducer to a solid portion of the hull.
Outer hull
For example, some (but not all) manufacturers use a layer of fiberglass,
then a core of balsa wood, finishing with an outer layer of fiberglass.
Removing the inner layer of fiberglass and the balsa wood core exposes
the outer layer of fiberglass. The transducer can then be epoxied directly to the outer layer of fiberglass. After the epoxy cures for 24
hours, fill the remaining space with polyester resin. When the job is
finished, the hull is watertight and structurally sound. Remember, the
sonar signal must pass through solid fiberglass. Any air bubbles in the
fiberglass or the epoxy will reduce or eliminate the sonar signals.
Testing Determines Best Location
Ideally, the shoot-thru transducer should be installed as close to the
transom as possible, close to the centerline. This will give you the best
performance during high speed maneuvers.
Transducer location
(high speed)
Transducer location
(trolling speed)
Shoot-thru-hull transducer locations for
high speed or trolling speed operation.
25
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 36

To choose the proper location for shoot-thru-hull mounting, follow these
testing procedures: (You may need a helper to complete these steps.)
1. Anchor the boat in about 30 feet of water. Add a little water to the sump
of the boat. Plug the transducer into the sonar unit, turn it on, then
hold the transducer over the side of the boat in the water. Adjust the
sensitivity and range controls until a second bottom echo is seen on the
display. (You'll need to turn off Auto Sensitivity, Auto Depth Range and
ASP™. Try a range setting that is two to three times the water depth.
The harder (more rocky) the bottom, the easier it will be to get a second
bottom signal.) Don't touch the controls once they've been set.
True bottom
Second bottom
Manual range setting
Example of a second bottom signal. Unit is in 30 feet of water, with
range set at 80 feet and sensitivity set at 87 percent.
2. Next, take the transducer out of the water and place it in the water in
the sump of the boat, face down. (The transducer face is shown in the
figure on the following page.) Notice how the signal strength decreases.
The second bottom signal will probably disappear and the bottom signal intensity will likely decrease.
3. Now move the transducer around to find the best location with the
strongest possible bottom signal. If you find a spot with an acceptable
bottom signal, mark the location and move on to step 4.
If you can't get an acceptable bottom signal, try turning up the sensitivity by three or five keystrokes and then move the transducer around
once more. If you find a spot that works, mark it and move on to step 4.
If you have to turn up sensitivity by more than five keystrokes to get a
good signal, the transducer should be mounted on the outside of the
hull. This is especially true if you have to turn sensitivity all the way
up to get a decent bottom signal.
26
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 37

4. Most people can get good results by following steps 1 through 3, so this
step is optional. If you want to make an extra effort to be absolutely
sure that your selected location will work under all conditions, make a
test run with the boat on plane and observe the bottom signal. You'll
need to figure some way to prop the transducer into position while you
make your test run. (A brick or two might be sufficient to hold it in
place.)
5. When you're satisfied with a location, mark it and proceed with
the installation.
Shoot-thru-hull Installation
If you are installing the transducer on a hull with floatation material
sandwiched within the hull, refer to the text "Hulls With Flotation Materials" beginning on page 24.
1. Make sure the area is clean, dry and free of oil or grease, then sand
both the inside surface of the hull and the face of the transducer with
100 grit sandpaper. The sanded hull area should be about 1-1/2 times
the diameter of the transducer. The surface of the hull must be flat
so the entire transducer face is in contact with the hull prior to bonding. After sanding, clean the hull and transducer with rubbing alcohol to remove any sanding debris.
Spread epoxy here
Sand this surface
(unit's face)
Orient the Skimmer
with the nose facing
the bow of the boat.
To bow
Epoxy transducer to hull.
27
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 38

WARNING:
Use only the epoxy available from LEI. It has been formulated to work with these installation procedures.
Other epoxy types may be too thin or may not cure to
the right consistency for optimum transducer performance.
2. The epoxy consists of the epoxy itself and a hardener. Remove the
two compounds from the package and place them on the paper plate.
Thoroughly stir the two compounds together until the mixture has a
uniform color and consistency. Do not mix too fast or bubbles will
form in the epoxy. After mixing, you have 20 minutes to complete the
installation before the epoxy becomes unworkable.
Spread a thin layer of epoxy (about 1/16" or 1.5 mm thick) on the face
of the transducer as shown in the previous figure. Make sure there
are no air pockets in the epoxy layer! Then, apply the remaining epoxy to the sanded area on the hull.
3. Press the transducer into the epoxy, twisting and turning it to force
any air bubbles out from under the transducer face. Stop pressing
when you bottom out on the hull. When you're finished, the face of
the transducer should be parallel with the hull, with a minimum
amount of epoxy between the hull and transducer.
4. Apply a weight, such as a brick, to hold the transducer in place while
the epoxy cures. Be careful not to bump the transducer while the epoxy is wet. Leave the weight in place for a minimum of three hours.
Allow the epoxy to cure for 24 hours before moving the boat.
5. After the epoxy has cured, route the cable to the sonar unit and it's
ready to use.
Speed/Temperature Sensors
Optional Speed Sensor Installation
All the units in this series can display speed and distance traveled, but
only the LMS-525cDF comes packed with a speed sensor. If you wish to
purchase an optional additional sensor for your unit, refer to the accessory ordering information inside the back cover of this manual. The
following instructions describe how to install the speed sensor.
Recommended tools for this job include: drill, 7/8" drill bit, 1/8" drill bit
for pilot holes, screwdriver. Required supplies for this job include: four
#8 stainless steel wood screws (3/4" long), high quality, marine grade
above- or below-waterline sealant.
28
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 39

First find a location on the boat's transom where the water flow is
smoothest. Don't mount the sensor behind strakes or ribs. These will
disturb the water flow to the speed sensor. Make sure the sensor will
remain in the water when the boat is on plane. Also make sure the location doesn't interfere with the boat's trailer. Typically, the sensor is
mounted about one foot to the side of the transom's centerline.
Once you've determined the proper location for the unit, place the sensor on the transom. The bottom of the bracket should be flush with the
hull's bottom. Using the sensor as a template, mark the hull for the
screws' pilot holes. Drill four 1/8" holes, one in each end of the slots.
Mount the sensor to the hull using #8 stainless steel wood screws (not
included). Use a high quality, marine grade above- or below-waterline
sealant to seal the screws. Make sure the sensor is flush with the bottom of the hull and tighten the screws.
Good location
Stern view showing good location for mounting sensor on transom.
Transom
Bottom of hull
Speed sensor mounting configuration:
side view (left) and rear view (right.)
Bottom of hull
If the base of the transom has a radius, fill the gap between the transom and the sensor with the sealant. This will help ensure a smooth
water flow.
Route the sensor's cable through or over the transom to the sonar unit.
If you need to drill a hole in the transom to pass the connector through,
the required hole size is 7/8".
29
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 40

CAUTION:
If you drill a hole in the transom for the cable, make sure it is
located above the waterline. After installation, be sure to seal the
hole with the same marine grade above- or below-waterline sealant used for the screws.
The sensor is now ready for use. Connect the sensor to the sonar socket
on the back of your unit and connect the transducer to the speed sensor's socket. If you have any questions concerning the installation of
the sensor, please contact your local boat dealer.
Power Connections
Your unit comes with a power/data cable that splits into three
branches, each with several exposed wires.
The thicker three-wire cable (white, red and black) is the power supply
for your display unit. This cable has no label.
The thinner branch with three wires (red, black and shield) is the
power cable for a NMEA 2000 network. It is labeled "NMEA 2000
POWER."
The branch with four wires (blue, yellow, orange, and shield) is a data
cable, labeled "RS-232 COMM." It supports a serial communication
port. This allows your unit to exchange NMEA 0183 data with another
device, such as an autopilot, DSC marine radio or computer.
Display unit power wires:
white, red and black
To unit
NMEA 2000 power wires:
red, black and shield
Data cable wires:
blue, yellow, orange,
and shield
The Power/Data cable for this unit.
NOTE:
There are two basic power connection options, which are shown in
the following two diagrams. Read the following instructions
carefully to determine which power connection applies to
your unit. Depending on your configuration, you may not use all of
these wires.
30
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 41

Caution:
All of the wires in the power/data cable have bare ends for easier installation. The bare ends on any unused wires could cause
an electrical short if left exposed. To prevent this, you should
cover the individual wire ends – either by capping them with
wire nuts, wrapping them with electrical tape or both. (You
should cut off the bare wire before taping off the ends.)
Powering Your Display Unit
The display unit works from a 12-volt DC battery system. Attach the
display power cable (with provided 3-amp fuse) to an accessory switch
or power bus. If this results in electrical interference, connect direct to
a battery but install an in-line switch on the cable.
Caution:
We strongly recommend that you shut off the power supply to the
power cable when the unit is not in use, especially in saltwater environments. When the unit is turned off but still connected to a
power supply, electrolysis can occur in the power cable plug. This
may result in corrosion of the plug body along with the electrical
contacts in the cable and the unit's power socket. Risk of electrolysis corrosion is even greater when the cable is unplugged from the
unit, but still connected to a power source.
We recommend you connect the power cable to the auxiliary power
switch included in most boat designs. If that results in electrical
interference, or if such a switch is not available, we recommend
connecting direct to the battery and installing an in-line switch.
This will let you shut off power to the power cable when the unit is
not in use. When you are not using the unit, you should always
shut off power to the power cable, especially when the power cable
is disconnected from the unit.
WARNING:
This product must be independently fused with the enclosed 3-amp fuse (or equivalent), even if you connect to
a fused accessory or power bus.
If a malfunction happens inside the unit, extensive damage can occur if the enclosed fuse is not used. As with all
electrical devices, this unit could be damaged to a point
that it is unrepairable and could even cause harm to the
user when not properly fused.
Failure to use a 3-amp fuse will void your warranty.
31
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 42

If possible, keep the power cable away from other boat wiring, especially
p
the engine's wires. This will provide the best isolation from electrical
noise. If the cable is not long enough, splice #18 gauge wire onto it.
The display power cable has three wires, white, red and black. Red is the
positive (+) lead, black is negative (–) or ground. The white wire is unused by your unit and should be capped. Make sure to attach the in-line
fuse holder to the red lead as close to the power source as possible.
For example, if you have to extend the power cable to the power bus or
battery, attach one end of the fuse holder directly to the power bus or
battery. This will protect both the unit and the power cable in the event
of a short.
This unit has reverse polarity protection. No damage will occur if the
power wires are reversed. However, the unit will not work until the
wires are attached correctly.
Power Diagram A
Mandatory
network
power-off
switch
White
(unused)
Shield
Black
3-amp fuse
Black
Red
12 volt DC
power source
Display Unit
Power Cable
Data Cable
To unit
NMEA 2000
Power Cable
3-amp fuse
Recommended
display unit
ower-off switch
Use this method if you are powering the display unit and a GPS mod-
ule or the display unit and a NMEA 2000 network. (Fuses may be dif-
ferent from those shown.).
The network and any NMEA 2000 devices, including the GPS
module, will not operate
unless the NMEA 2000 Power Cable is
connected to power. The NMEA 2000 power cable must be connected
32
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 43

to power even if your only NMEA 2000 device is the GPS module and it
is connected to the display unit's Network socket. (However, never
connect multiple power sources to a NMEA 2000 network. If you
have a network that is already powered, see diagram B on page 33.)
Power Diagram B
To unit
Red wire with
3-amp fuse
Display Unit
Power Cable
White wire
(unused)
All unused Data
or NMEA 2000
power wires
should be
capped with
wire nuts and
electrical tape
to prevent
shorts.
Data Cable
Use this method if you are only powering your display unit and are not
powering a NMEA 2000 network or any NMEA 2000 accessory device,
including a GPS module. (Fuse may be different from that shown.)
NMEA 2000 Power Cable
Recommended
power off switch
Black wire
12 volt DC
power source
The method in diagram B is also used when your display unit is connected to a NMEA 2000 network that is already connected to power.
(Never connect multiple power sources to a NMEA 2000 network.)
Powering a NMEA 2000 Network Bus
A NMEA 2000 bus must be connected to a power source to operate.
NMEA 2000 devices, including GPS modules, draw their power from
the network bus.
If you have a pre-existing NMEA 2000 network installation, it may already be connected to another power source. If you are not sure about a
network's power status, consult the boat manufacturer or dealer. If your
NMEA 2000 bus is already powered, you can ignore the NMEA 2000
Power cable and use the method shown in Power Diagram B above.
Never attach two power sources to a single NMEA 2000 bus.
33
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 44

If you do need to power your NMEA 2000 bus, attach the NMEA 2000
Power cable to an accessory switch as indicated in power diagram A on
page 32. The NMEA 2000 Power cable's red wire should be attached
(with provided 3-amp fuse) to the positive (+) terminal. The NMEA
2000 Power cable's black and shield wires should both be attached to
the negative (–) terminal.
WARNING:
The NMEA 2000 network bus is always on and constantly
drawing power. You must connect NMEA power to a
switched power source so you can turn off the network
when not in use. Failure to connect to and use a power
switch will drain your boat battery, which could stop
your boat's operation.
GPS Antenna/Receiver Module
The LMS-520c and LMS-525cDF packages include the LGC-3000 GPS
module. This device contains the unit's external antenna and receiver
for GPS and WAAS signals. The antenna/receiver module comes with a
15-foot extension cable. This module can be mounted on a flat surface
or pole, or an optional magnet is available for temporary mounting on
any ferrous surface.
You need to select an antenna installation location that has a clear, unobstructed view of the sky. After the module is installed, connect it to the
unit. The LGC-3000 can communicate with your GPS unit either directly
(using the supplied extension cable) or through a NMEA 2000 network.
LGC-3000 Module, bottom view (left) and top view (right).
NOTE
See the module’s instruction sheet, publication part number 9880154-651, for complete installation instructions.
34
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 45

To use the module in an automobile, you may achieve good results by
simply placing the external antenna on the top of the dash, at the base of
the windshield. A piece of the rubber non-skid shelf liner material available in recreational vehicle supply stores will help hold the antenna in
place. This may not work well if you have a cab-over design pickup truck
camper or motor home. If dashboard reception is poor, simply relocate
the antenna module elsewhere on the vehicle for a clearer view of the
sky.
Connecting to a NMEA 2000 Network
A network bus is an installed and operational network cable (backbone)
running the length of your boat, already connected to a power supply and
properly terminated. Such a bus provides network connection nodes at
various locations around your boat. The NMEA 2000 network is similar to
the telephone wiring in a house. If you pick up a phone in your living room,
you can hear someone talking into the phone in the bedroom.
Lowrance and LEI provide all the cables you will need to create a NMEA
2000 network. Lowrance provides T connectors and extension cables so
you can add devices along the backbone wherever you want. Once you
have a working network, every sensor added will come with its own T
connector for easy expansion.
The simplest NMEA 2000 network is a GPS or sonar/GPS display unit
with the LGC-3000, one double-T connector, two 120 ohm terminators
and any extension cables needed to connect them. The diagram below
details how to set up that type of network.
35
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 46

Network port
on display unit
Double T
Connector
120-ohm
terminator
Extension cable
LGC-3000
Extension cable
120-ohm
terminator
LGC-3000 and display unit as an expandable NMEA 2000 network.
The diagram has a double T connector with two 120-ohm terminators —
one at each end of the connector. It is easy to expand this network by removing a terminator from one end of the double T connector, then inserting a new T connector or extension cable between the double T connector
and terminator (See the NMEA 200 network general information document that came with your unit for more information).
NMEA 0183 Wiring
(Data cable)
To exchange NMEA 0183 data, this unit has one NMEA 0183 version
2.0 communication port. Com port one (Com-1) can be used to receive
NMEA format GPS data. The com port can also transmit NMEA format
GPS data to another device.
The four wires for the com port are combined with the Power Supply
cable and NMEA 2000 Power cable to form the power/data cable
(shown earlier). Com-1 uses the yellow wire to transmit, the orange
wire to receive and the shield wire for signal ground. Your unit does
not use the blue wire.
36
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 47

Y
To unit
Com-1
Orange (Receive)
Shield (Ground)
NMEA Transmit
Ground
GPS Receiver
Com-1 wiring to receive NMEA position information
from some other GPS receiver.
To Other
ellow (Transmit)
Com-1
To unit
Com-1 wiring to transmit NMEA position information
Shield (Ground)
to another NMEA-compatible device.
NMEA Receive
Ground
To Other
Device
37
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 48

(
)
SP-BL optional
speed sensor
Power/Data
socket
Sonar socket
LMS-525CDF (rear view)
Network
socket
Ethernet socket
future enhancement
Double T
connector
120 ohm
terminator
Data cable
NMEA 2000
Power cable
Transducer
LMS-520c and LMS-525cDF cable connections.
Display unit
power cable
LGC-3000
120 ohm
terminator
Extension cables
38
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 49

Mounting the Unit: Bracket, In-Dash or Portable
You can install your unit on the dash with the gimbal bracket. It can
also be installed in the dash or mounted on a portable power supply.
If you use the supplied bracket, you may be interested in the optional
R-A-M
bracket to a swivel mount, which can be used on the dash or overhead
mounting positions.
®
bracket mounting system. This converts the unit's gimbal
Optional R-A-M mounting system.
Bracket Installation
Mount the unit in any convenient location, provided there is clearance
behind it when it's tilted for the best viewing angle. You should also make
sure there is enough room behind it to attach the power, transducer and
GPS antenna/receiver module cables.
Holes in the bracket's base allow wood screw or through-bolt mounting.
You may need to place a piece of plywood on the back side of thin fiberglass panels to reinforce the panel and secure the mounting hardware.
39
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 50

Front
Install the gimbal bracket. Orient the bracket so the arms slope to-
ward the front of your unit.
Drill a 1-inch (25.4 mm) hole in the dash for the power, transducer and
antenna cables. The best location for this hole is immediately under the
gimbal bracket location. This way, the bracket can be installed so that
it covers the hole, holds the cables in position and results in a neat installation. Some customers, however, prefer to mount the bracket to the
side of the cable hole — it's a matter of personal preference.
23.4
173.9
[6.85]
[0.92]
72.9
[2.87]
137.9
[5.43]
Millimeter
[Inch]
Front view (left) and side view (right) showing dimensions of the LMS-
520c and LMS-525cDF sonar/GPS units mounted on gimbal bracket.
157.9
[6.22]
56.9
[2.24]
40
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 51

After drilling the hole, pass the transducer connector up through the
A
hole from under the dash, followed by antenna connector. Pass the
power cable's bare-wire end down though the hole from the top.
If you wish, you can fill in the hole around the cables with a good marine caulking compound. (Some marine dealers stock cable hole covers
to conceal the opening.) No matter what type of installation you prefer,
be sure to leave enough slack in the cables to allow tilting or swiveling
the unit. If you choose to fill in the hole, be sure to position the cables
against the rear edge of the hole as you apply the fill material.
Before positioning the bracket, be sure to hold the cables against the
rear edge of the hole. Slide the bracket over the hole and butt the rear
of the bracket base against the cables, thus pinning them in place
against the side of the hole. Fasten the bracket to the dash. Attach the
unit to the gimbal bracket using the gimbal knobs and washers.
In-Dash Installation
You can mount the unit in the dash with an optional FM-5 In-Dash
Adapter Kit. The kit includes mounting hardware, a template for cutting the hole and an instruction sheet, part 988-0147-43.
LWAYS VERIFY DIMENSIONS
In-dash mounting template for LMS-520c and LMS-525cDF sonar/GPS
units, showing dimensions.
NOTE: The figure above is not printed to scale. A scaled template (FM-
5 In-Dash Adapter Kit instructions) is available for free download from
our web site, www.lowrance.com.
146.5
[5.76]
Top
In-Dash
Template
Millimeters
[Inches]
R 7.9
[0.31]
113.5
[4.46]
41
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 52

Portable Installation
Like many Lowrance products, the unit is capable of portable operation
by using an optional portable power pack. The power pack, a magnetequipped antenna module and an optional portable transducer, expands the uses for your sonar/GPS unit. It makes it easy to transfer
your unit from a boat to a car, recreational vehicle, airplane or other
vehicle without mounting a second bracket. You can use it in your own
car or boat, then take it along when riding in a friend's vehicle.
The power pack can be used with eight "D" cell alkaline batteries or an
optional sealed, rechargeable battery. Visit our web site for a complete
listing of all the available portable power packs.
PPP-15 Portable Power Pack with transducer installed. Shown with
the X67C IceMachine™ .
MMC or SD Card Memory Card Installation
Your unit uses a MultiMedia Card to store information, such as sonar
logs, custom maps, waypoints, trails and other GPS data. It can also
use Secure Digital Cards (SD card) to store data.
NOTE:
Throughout this manual, we will use the term MMC, but just remember that your unit can use an MMC or SD card to store data.
42
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 53

Both of these solid-state flash memory devices are about the size of a
postage stamp. An SD card is slightly thicker than an MMC. As this
manual went to press, MMCs were available in storage capacities of 8
MB, 16 MB, 32 MB, 64 MB and 128 MB. SD cards were available with
capacities of 8 MB, 16 MB, 32 MB, 64 MB, 128 MB, 256 MB and 1 GB.
Additional MMC cards are available from LEI Extras; see ordering information inside the back cover of this manual. MMCs and SD cards
are also available at many camera and consumer electronics stores.
The MMC slot is located in a compartment on the front of the case. The
compartment door is located at the lower right corner. The following
figure shows a close-up with the door opened.
MMC groove for card removal
Thumb
screw
Insert card face up,
this way
Memory card compartment with a 16 MB MMC card installed.
To remove an MMC
1. Open the card compartment door by unscrewing the thumb screw.
The screw should only be finger tight. If it was over-tightened, use a
thumbnail, a coin or a screwdriver to open the door.
2. Just press a finger against the label of the MMC and drag it from the
slot.
3. Close the compartment door and fasten the thumb screw finger tight.
To add an MMC or SD Card
1. Open the card compartment door.
2. Grasp the bottom of the MMC and push the top of the card into the
slot. Once the card is started, use your fingernails to slide it the rest of
the way to the left, until it is firmly seated in the slot.
3. Close the compartment door and fasten the thumb screw finger tight.
43
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 54

Other Accessories
Cleaning Towel
A lint-free microfiber towel is included for cleaning the unit’s screen.
The towel is highly effective in clearing away water spots, smudges and
finger prints. Just wipe the screen with the dry towel — it's not necessary to moisten the towel with water. If the screen is badly soiled, you
may use water or common window or lens cleaners. However, DO NOT
use polishing compounds or any other abrasive product.
If you lose the towel or wear it out, you can replace it with a similar
microfiber cloth. These are often available where shop towels or automobile cleaning towels are sold.
Caution:
Cleaning fabrics other than the microfiber towel type may scratch
the screen. Polishing compounds or other abrasive cleaners will
scratch the screen. Damage caused by incorrect cleaning is not covered by the warranty. You may wash the towel if it becomes soiled
or loses its effectiveness, but do not use fabric softener. Fabric softener will ruin the towel’s cleaning capability.
LMS-520c and LMS-525cDF accessories include MMC cards, MMC
card readers and MapCreate™ mapping software for your computer.
MMC card readers are available in USB and parallel port versions.
Two switch boxes are available for this unit. The SB-7X transducer
switch box switches two transducers to one sonar unit. The SB-8X transducer switch box switches two sonar units to one transducer.
If these accessories are not available from your dealer, see the accessory ordering information on the inside back cover of this manual. Visit
our web site for a complete listing of all the available accessories.
MapCreate™ CD-ROM (left); MMC card reader for USB ports (right).
44
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 55

Now that you have your unit installed, move on to Section 3, Basic Sonar Operations. There, we'll present a series of step-by-step tutorials to
teach you the basics of how to operate your sonar.
NOTE:
When you first turn the unit on, the Map Page appears. If you'd
rather start learning about GPS operation first, turn over to Section 6, Basic GPS Operations.
Face Cover
Your unit comes with a white protective cover that snaps on and off the
front of the unit. This cover is intended for use when the vehicle is idle.
WARNING:
When the unit is mounted in an unprotected area, such
as an open boat cockpit, the protective face cover must
be removed when the vehicle is moving at high speed.
This includes towing a boat on a trailer at highway
speeds. Otherwise, wind blast can pop off the cover.
45
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 56

Notes
46
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 57

Section 3: Basic Sonar Operation
This section addresses the unit's most basic sonar operations. Before
you turn on the sonar unit, it's a good idea to learn about the different
keys, the Main Menu, the four Page screens and how they all work together. BUT, if you just can't wait to get on the water, turn to the onepage Quick Reference on page 55.
Keyboard
4
8
2
3
5
MMC slot access door
LMS-525cDF sonar/GPS unit, front view, showing map with sonar split
screen, keyboard and access door for the MMC slot.
9
7
6
1
1. PWR/LIGHT (Power & Light) – The PWR key turns the unit on and
off and activates the backlight.
2. PAGES – Pressing this and the ← → arrow keys switches the unit
between the four different page screens. (Satellite Status Page, Navigation Page, Map Page and Sonar Page.) Each page represents one of the
unit's major operation modes.
47
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 58

3. MENU – Press this key to show the menus and submenus, which
allow you to select a command or adjust a feature. This also accesses
search functions for streets, intersections, addresses and highway exits.
4. ARROW KEYS – These keys are used to navigate through the
menus, make menu selections, move the map and sonar chart cursors
and enter data.
5. ENT/ICONS (Enter & Icons) – This key allows you to save data, ac-
cept values or execute menu commands. It is also used to create event
marker icons.
6. EXIT – The Exit key lets you return to the previous screen, clear
data or close a menu.
7. WPT – (Waypoint) The Waypoint key is used to save and recall way-
points, search for waypoints and access the waypoint list. It also
launches the Point-of-Interest (POI) search menus and is involved in
some navigation functions.
8. ZOUT – (Zoom Out) – This key lets you zoom the screen out. On the
Sonar Page, it returns you to a full sonar chart display, showing the
entire water column from surface to bottom. On the Map Page, it lets
you see a larger geographic area on the map. Less detail is seen as you
zoom out.
9. ZIN – (Zoom In) – This key lets you zoom the screen in. On the Sonar
Page, this key enlarges fish signals and bottom detail. On the Map
Page, zooming in lets you see greater detail in a smaller geographic
area on the map.
Power/lights on and off
To turn on the unit, press PWR. As the unit powers up, the Map Page is
displayed first. To switch to the Sonar Page, press
and press
To turn on the backlight, press
light levels. Repeatedly pressing
settings and turn off the backlight.
Turn off the unit by pressing and holding the
ENT.
PWR again. The unit has three back-
PWR will cycle through the backlight
PAGES, select SONAR
PWR key for 3 seconds.
Main Menu
The unit has a Main Menu, which contains some function commands
and some setup option commands. The instructions in this section will
deal only with sonar functions, the basic commands that make the unit
show sonar signals on your screen. This sonar unit will work fine right
out of the box with the factory default settings.
48
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 59

You can access the Main Menu from any of the four Page screens by
pressing
display, press
MENU|MENU. To clear the menu screen and return to the page
EXIT.
Main Menu.
The Main Menu commands and their functions are:
Screen: changes the contrast or brightness of the display screen.
Sounds: enables or disables the sounds for key strokes and alarms and
sets the alarm style.
Transparency: adjusts the level of transparency for menus.
Alarms: turns sonar and GPS alarms on or off and changes alarm
thresholds.
Route Planning: used to plan, view or navigate a route.
My Trails: shows, creates and deletes plot trails. Also used to navigate
or backtrack a trail.
Cancel Navigation: turns off the various navigation commands. Used
to stop navigating after you have reached your destination waypoint,
Point of Interest or map cursor location; or after you reach the end of a
route or trail.
Sonar Setup: sets various sonar options.
GPS Setup: sets various GPS receiver options.
System Setup: sets general configuration options.
NMEA 2000: provides access to all NMEA 2000 network setup options,
including the configuration of devices on the network. For more information, see Section 10: NMEA 2000 Menu.
Sun/Moon Calculations: finds the rising and setting time of the sun
and the moon.
Trip Calculator: shows trip status and statistics.
49
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 60

Timers: controls the up timer, down timer and alarm clock settings.
Browse MMC Files: this allows you to view the installed MMC card
and the files it contains.
Pages
The unit has five Page displays that represent the four major operating
modes. They are the Satellite Status Page, the Navigation Page, the Map
Page and Sonar Page. They are accessed by pressing the
then using ← → to select a Page. (Clear the Pages Menu by pressing
EXIT.)
Pages Menu showing Sonar display options.
Satellite Status Page
The Satellite Status Page provides detailed information on the status
of the unit's satellite lock-on and position acquisition. To get to the Satellite Status Page: Press the
STATUS. (Clear the Pages Menu by pressing EXIT).
PAGES key, then use → or ← to select
This page represents a GPS function, so it is discussed in much greater
detail in Sec. 6.
No matter what Page you are on, a flashing current position indicator/question mark symbol and flashing GPS data displays indicate that
satellite lock has been lost and there is no position confirmed.
WARNING:
Do not begin navigating with this unit until the numbers
have stopped flashing!
PAGES key,
50
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 61

Satellite Status Page.
Navigation Page
This screen has a compass rose that not only shows your direction of
travel, but also the direction to a recalled waypoint. To get to the Navigation Page: Press
PAGES| → or ← to NAVIGATION|EXIT.
This page represents a GPS function, but also has a navigation with
sonar option, which will keep you updated on what is under your boat
as well as where you’re going.
Navigation page with Sonar (left). Navigation Page with digital data
(right).
Map Page
The Map Page screens show your course and track from a "bird's-eye"
view, on a moving map. By default, this unit shows the map with north
always at the top of the screen. The arrow in the center of the screen is
your present position. It points in the direction you're traveling.
51
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 62

Map Pages, showing position on Bull Shoals Lake, Arkansas. The full
map option (left). Map with sonar option (right).
Map Page is also the default screen that appears when you turn on the
unit. To get to the Map Page from another page: Press
to
MAP|EXIT.
PAGES| → or ←
You can display a split screen showing both the Map and Sonar pages
at the same time. This feature is discussed in Sec. 4, Sonar Options &
Other Features.
The Map Page represents a GPS function, so it is discussed in much
greater detail in Sec. 6.
Sonar Page
The Sonar Page displays the sonar chart. This is a "cross-section" view
of the water column beneath the boat. The chart moves across the
screen, displaying sonar signal echoes that represent fish, structure
and the bottom.
To get to the Sonar Page: Press the
lect
SONAR. (Clear the Pages Menu by pressing EXIT.) The Pages Menu
PAGES key, then use → or ← to se-
also offers five chart display options under the Sonar Page category. To
access them, press
PAGES|← or→ to SONAR|↓ to Option Name|EXIT.
The Sonar Page also has its own menu, which is used for some advanced
functions and for setting various options. (Sonar Options and other features are discussed in Sec. 4.) To Access the Sonar Page menu, from the
Sonar Page press
MENU.
52
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 63

Pages Menu (left) showing sonar chart display option commands.
Sonar Page in full sonar chart display mode (right).
Split Zoom page (left) and Split Frequency page (right).
Digital Data page (left) and Flasher page (right).
53
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 64

Digital data
overlay
(depth &
temperature)
Fish arches
Structure
Sonar Page Menu.
Surface signal
Surface clutter
Depth scale
In FasTrack, fish
arches show as
horizontal bars.
Zoom bar
Bottom signal
Sonar Page showing full sonar chart mode.
FasTrack
bar graph
You can customize how the Sonar Page displays its pictures and other
data in many ways.
We'll discuss all of those features and options in Sec. 4, but to show you
how easy this unit is to operate, the following page contains a simplified, 10-step quick reference that will cover most fish finding situations. The quick reference describes how your unit will operate with all
the sonar features in their automatic modes, which are set at the factory.
54
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 65

Basic Sonar Quick Reference
1. Depress the PWR key to turn on the unit.
2. Opening screen displays Map Page. Rotate through the four main
Page screens (Map Page, Satellite Status Page, Navigation Page, Sonar
Page) by pressing
Pages to display Sonar Page.
3. If GPS data is desired, wait while unit locates satellites and calculates
current position. When the unit acquires position, a tone sounds and a position acquired message appears.
4. With position acquired (if desired), head for your fishing grounds.
Your unit will automatically display digital depth and surface water
temperature in the top left corner of the screen.
The auto settings will track the bottom, displaying it in the lower portion of the screen. The full sonar chart will scroll from right to left,
showing you what's under the boat as you cruise across the water. You
can change the display by:
PAGES|← or → to select Page Name|EXIT. Switch
Zoom in to enlarge the chart for more detail: press
Zoom out to return to full chart mode: press
ZIN.
ZOUT.
5. Watch the display for the appearance of fish symbols (or arches, if
Fish I.D.™ is turned off). When you see fish symbols or arches, you've
found fish! Stop the boat and get your lure or bait into the water at the
depth indicated on the sonar chart.
6. Gauge the fish depth by visually comparing the fish symbols or
arches with the depth scale on the right side of the screen.
7. If you are drifting at a very low speed or anchored, you are not mov-
ing fast enough for a fish to return the tell-tale fish arch signal. As you
drift over a fish, or as a fish swims through the transducer's signal
cone, the fish echo will appear as a straight line suspended between the
surface and the bottom when Fish I.D. is turned off.
8. To turn off the unit, press and hold
PWR key for three seconds.
55
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 66

Sonar Operations
As you can see from the quick reference on the previous page, basic operation
is pretty easy, right out of the box. If you are a sonar novice, try operating the
unit with the factory defaults until you get a feel for how it's working.
As you're learning the basics, there is one setting you might want to tinker
with from time to time — Sensitivity.
Sensitivity controls the unit's ability to pick up echoes. If you want to see
more detail, try increasing the sensitivity, a little at a time. There are situations when too much clutter appears on the screen. Decreasing the sensitivity
can reduce the clutter and show the strongest fish echoes, if fish are present.
As you change the sensitivity setting, you can see the difference on the chart
as it scrolls.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
These figures show results of different sensitivity levels on the same loca-
tion. Fig. 1: Sensitivity at 88 percent, determined by Auto Sensitivity.
Typical of full auto mode. Fig. 2: Sensitivity set at 75 percent. Fig. 3: Sen-
sitivity set at 50 percent. Fig. 4: Sensitivity set at 100 percent.
56
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 67

You can change the sensitivity level whether you are in Auto Sensitivity
mode or Manual Sensitivity mode. The adjustment method works the
same in both modes, but it gives you slightly different results.
Adjusting sensitivity in Auto Sensitivity Mode is similar to manually adjusting a car's speed with the accelerator pedal while cruise control is on.
You can tell the car to run faster, but when you let off the gas the cruise
control automatically keeps you from running slower than the minimum
speed setting. In the unit, auto mode will let you increase sensitivity to
100 percent, but the unit will limit your minimum setting. This prevents
you from turning sensitivity down too low to allow automatic bottom
tracking. When you change the setting with auto turned on, the unit will
continue to track the bottom and make minor adjustments to the sensitivity level, with a bias toward the setting you selected.
Adjusting sensitivity in Manual Sensitivity Mode is similar to driving a
car without cruise control — you have complete manual control of the
car's speed. In the unit, manual mode allows you to set sensitivity at
100 percent (maximum) or zero percent (minimum.) Depending on water conditions, the bottom signal may completely disappear from the
screen when you reduce sensitivity to about 50 percent or less!
Try adjusting sensitivity in both auto and manual modes to see how
they work.
To adjust sensitivity:
1. Press
MENU|ENT.
2. The Sensitivity Control Bar appears. Press ↓ to decrease sensitivity;
press ↑ to increase sensitivity. When it's set at the desired level, press
EXIT. (When you reach the maximum or minimum limit, a tone sounds.)
Sonar Menu with Sensitivity command selected (left). The Sensitivity
Control Bar (right).
57
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 68

NOTE:
If you want to change the sensitivity in Manual Mode, first turn off
Auto Sensitivity: from the Sonar Page, press
TIVITY
|ENT|↑ to SENSITIVITY|ENT. Press ↓ or ↑ to pick a different sen-
sitivity setting. When it's set at the desired level, press
MENU|↓ to AUTO SENSI-
EXIT.
Important Tip:
While you are experimenting and learning, it's possible to scramble
the settings so that the sonar picture disappears from your screen.
If that happens, remember that it's easy to switch back to full
automatic operation by simply restoring the factory auto settings.
To Restore Factory Settings:
1. Press
2. The unit asks if you want to reset all the options. Press ← to
YES|ENT. All options are reset, and the unit reverts back to the Map
Page at the 4000 mile zoom range. (Any recorded sonar logs or GPS
data will be unchanged.)
Fish Symbols vs. Full Sonar Chart
You may have noticed in the quick reference that we used fish arches
in full sonar chart mode for our example, and not the popular Fish
I.D.™ fish symbol feature. Here's why.
Fish I.D. is an easier way for a sonar novice to recognize a fishy signal
return when he sees it. However, locating fish by symbol only has some
limitations.
Your sonar unit's microprocessor is remarkably powerful, but it can be
fooled. Some of the echoes calculated to be fish could be tree limbs or tur-
tles! To see what's under your boat in maximum detail
you turn off Fish I.D. and begin learning to interpret fish arches.
Fish I.D. is most handy when you're in another part of the boat or performing some task that prevents you from watching the sonar screen.
Then, you can turn on Fish I.D. and the audible fish alarm. When that
lunker swims under your boat, you'll hear it!
Fish I.D. can also be useful when you want to screen out some of the
sonar detail gathered by your unit. For example, in one case fisherman
in San Francisco Bay saw clouds of clutter in the water but no fish
arches. When a down rigger was pulled up, it brought up several small
jellyfish. The fisherman switched their sonar to Fish I.D., which
screened out the schools of jellyfish and clearly showed the game fish
there as fish symbols.
MENU|MENU|↓ to SYSTEM SETUP|ENT|↓ to RESET OPTIONS|ENT.
, we recommend
58
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 69

Other Free Training Aids
The sonar options section discusses Fish I.D., fish alarms and other
features in greater detail. If you or a friend has Internet access, you can
also learn more about interpreting what you see on your sonar screen.
Visit our web site, www.lowrance.com. Be sure to check out the free
Sonar Tutorial, which includes animated illustrations and more pictures of actual sonar returns, all described in detail. There's even a
"printer friendly" version of the tutorial available on our web site…it
makes a great supplement to this operation manual!
You can also download a free copy of our Sonar Viewer software. This
PC-based software application plays back any sonar chart log recorded
with a Lowrance sonar product. Features include:
• Adjustable range, zoom, sensitivity, color line, noise rejection,
surface clarity, etc. of the recorded file.
• Color interpretation of sonar signals can be user defined.
• Operates like a Windows Multimedia Player with forward, re-
verse, pause, fast forward, fast reverse, and scroll buttons.
• Adjustments update the entire record displayed.
• Can print in full color.
• Window can dynamically be sized on your monitor.
• Mouse cursor shows GPS position, depth and sounding number
anywhere on the visible record.
For the ultimate training aid, be sure to download the free emulator
software for your unit. Aside from being fun, this program can help you
learn both basic and advanced operations without burning boat fuel!
Lowrance is one of the first sonar manufacturers to provide this type of
training tool for customers.
This PC application simulates the actual sonar/GPS unit on your computer. You can run it from your computer keyboard or use your mouse
to press the virtual keys. Easy download and installation instructions
are available on our web site.
59
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 70

Free training emulator is available for your unit on our web site.
The emulator works exactly like your real sonar/GPS unit. Using the
Sonar Simulator and GPS Simulator features, it allows you to play
back sonar logs, run GPS routes and trails and create real waypoints
you can use in the field! You can even take snapshots of the Sonar
Chart and print them or e-mail them to friends.
60
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 71

Section 4: Sonar Options
ASP™ (Advanced Signal Processing)
The ASP™ feature is a noise rejection system built into the sonar unit
that constantly evaluates the effects of boat speed, water conditions
and interference. This automatic feature gives you the best display possible under most conditions.
The ASP feature is an effective tool in combating noise. In sonar terms,
noise is any undesired signal. It is caused by electrical and mechanical
sources such as bilge pumps, engine ignition systems and wiring, air
bubbles passing over the face of the transducer, even vibration from the
engine. In all cases, noise can produce unwanted marks on the display.
The ASP feature has four settings — Off, Low, Medium and High. If
you have high noise levels, try using the "High" ASP setting. However,
if you are having trouble with noise, we suggest that you take steps to
find the interference source and fix it, rather than continually using
the unit with the high ASP setting.
There are times when you may want to turn the ASP feature off. This
allows you to view all incoming echoes before they are processed by the
ASP feature.
Sonar Menu with Sonar Features highlighted (left). Sonar Features
menu (right) with Noise Rejection (ASP) set to default low setting.
To change the ASP level:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
2. Press ↓ to
3. Press ↓ or ↑ to select a setting, then press
4. To return to the previous page, press
NOISE REJECTION|ENT.
MENU|↓ to SONAR FEATURES|ENT.
ENT.
EXIT|EXIT.
61
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 72

Alarms
This unit has three different types of sonar alarms. The first is the Fish
Alarm. It sounds when the Fish I.D.™ feature determines that an echo
is a fish.
Another alarm is the Zone Alarm, which consists of a bar on the side of
the screen. Any echo on the chart that appears inside this bar triggers
this alarm.
The last alarm is the Depth Alarm, which has both a Shallow and a
Deep setting. Only the bottom signal will trigger this alarm. This is
useful as an anchor watch, a shallow water alert or for navigation.
Depth Alarms
The depth alarms sound a tone when the bottom signal goes shallower
than the shallow alarm's setting or deeper than the deep alarm's setting. For example, if you set the shallow alarm to 10 feet, the alarm
will sound a tone if the bottom signal is less than 10 feet. It will continue to sound until the bottom goes deeper than 10 feet.
The deep alarm works just the opposite. It sounds a warning tone if the
bottom depth goes deeper than the alarm's setting. Both depth alarms
work only off the digital bottom depth signals. No other targets will trip
these alarms. These alarms can be used at the same time or individually.
Main Menu with GPS Alarms selected (left). Sonar Alarms menu
(right).
To adjust and turn on the shallow alarm:
1. Press MENU|MENU|↓ to ALARMS|ENT|↓ to SONAR ALARMS|ENT.
2. Press → to
SHALLOW ALARM DEPTH|ENT.
62
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 73

3. Press ↑ or ↓ to change the first number, then press → to move the
cursor to the next number and repeat until the depth is correct, then
press
ENT.
4. Press ← to
5. To turn off the alarm, press
NAR
ALARMS|ENT|ENT|EXIT|EXIT|EXIT.
SHALLOW ALARM ENABLED|ENT|EXIT|EXIT|EXIT.
MENU|MENU|↓ to ALARMS|ENT|↓ to SO-
To switch to a different depth setting, open the Sonar Alarms menu
and repeat the instructions in step 3 above.
To adjust and turn on the deep alarm:
1. Press MENU|MENU|↓ to ALARMS|ENT|↓ to SONAR ALARMS|ENT.
2. Press ↓ to
DEEP ALARM ENABLED|→ to DEEP ALARM DEPTH|ENT.
3. Press ↑ or ↓ to change the first number, then press → to move the
cursor to the next number and repeat until the depth is correct, then
ENT.
press
4. Press ← to
5. To turn off the alarm, press
ALARMS|ENT|↓ to DEEP ALARM ENABLED|ENT|EXIT|EXIT|EXIT.
NAR
DEEP ALARM ENABLED|ENT|EXIT|EXIT|EXIT.
MENU|MENU|↓ to ALARMS|ENT|↓ to SO-
To switch to a different depth setting, open the Sonar Alarms menu
and repeat the instructions in step 3 above.
Zone Alarm
The zone alarm is triggered when any echo passes inside the zone
alarm bar, shown on the right side of the screen.
To adjust and turn on the zone alarm:
1. Press MENU|MENU|↓ to ALARMS|ENT|↓ to SONAR ALARMS|ENT.
2. Press ↓ to
ZONE ALARM ENABLED|→ to ADJUST ZONE|ENT.
63
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 74

Sonar Alarms menu with Adjust Zone command selected (left).
Adjust Zone Alarm selection box with Upper selected (right).
3. To set the upper boundary for the Zone Alarm, use ← or→ to select
UPPER, then press ↑ or ↓ to move the top of the bar to the desired depth.
4. To set the lower boundary for the Zone Alarm, use ← or→ to select
LOWER, then press ↑ or ↓ to move the bottom of the bar to the desired
depth.
5. Press
EXIT|← to ZONE ALARM ENABLED|ENT|EXIT|EXIT|EXIT. Now, any
echo — fish, bottom, structure — within the zone alarm's depth range
will trigger the zone alarm.
6. To turn off the alarm, press
ALARMS|ENT|↓ to ZONE ALARM ENABLED|ENT|EXIT|EXIT|EXIT.
NAR
MENU|MENU|↓ to ALARMS|ENT|↓ to SO-
To switch to a different depth setting, open the Sonar Alarms menu
and repeat the instructions in steps 3 and 4 above.
Fish Alarm
Use the fish alarm for a distinctive audible alarm when fish or other
suspended objects are detected by the Fish I.D.™ feature (Fish I.D.
must be turned on for the Fish Alarm to work). A different tone sounds
for each fish symbol size shown on the display.
64
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 75

Sonar Alarms menu with Fish Alarm selected. The check box to the left
is blank, indicating the alarm is turned off.
To turn on fish alarm:
1. Press MENU|MENU|↓ to ALARMS|ENT|↓ to SONAR ALARMS|ENT.
2. Press ↓ to
3. To turn off the alarm, press
ALARMS|ENT|↓ to FISH ALARM|ENT|EXIT|EXIT|EXIT.
NAR
FISH ALARM|ENT|EXIT|EXIT|EXIT.
MENU|MENU|↓ to ALARMS|ENT|↓ to SO-
GPS Alarms
You can set an arrival alarm to flash a warning message and sound a
tone when you cross a preset distance from a waypoint. For example, if
you have the arrival alarm set to .1 mile, then the alarm will flash a
message when you come within .1 mile of the recalled waypoint.
GPS Alarm highlighted on Alarms menu (left). GPS Alarms menu
(right).
The off course alarm warns you when your track drifts too far to the
right or left of the course line to the waypoint. For example, if the
alarm is set to .1 mile, then the alarm flashes a message if you drift .1
miles to the right or left of the line to the waypoint.
65
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 76

The anchor alarm is triggered when you drift outside of a preset radius.
Using the .1 mile as an example, if you're anchored and the boat moves
more than .1 miles, a tone will sound and a message will appear.
1. To set an alarm, press
2. Use ↓ ↑ to select the desired category, then press
MENU|MENU|↓ to ALARMS|ENT|ENT.
ENT to turn on
(check) or turn off (uncheck) the desired Alarm Enabled box.
3. To change distance settings, use
then press →|
ENT to activate the distance dialog box. Press ↑ ↓ to
↓ ↑ to select the desired category,
change the first character, then press → to the next character and repeat until the distance is set.
4. When the adjustments are finished, return to the main page display
by repeatedly pressing
EXIT.
IMPORTANT ALARM NOTES
Anchor Alarm - The anchor alarm may be triggered even when
you're sitting still. This can happen when using a small (less than
.05 mile) anchor alarm range.
Arrival Alarm - If you set the arrival alarm's distance to a small
number and you run a route (see the Navigate Routes segment),
this unit may not show navigation data to the next waypoint, once
you arrive at the first one. You may not be able to come close
enough to the first waypoint to trip the arrival alarm.
NMEA 2000 Alarms
The NMEA 2000 Alarm can be set to monitor multiple EP-10 Fuel Flow
and EP-15 Fluid Level sensors. You can set a threshold for each alarm
in its corresponding Percent box. Thresholds give you control over
when the alarm will go off. You may want the alarm to go off when the
black water tank is filled to 75 percent of its capacity, likewise, you
may want to know when the fuel level falls below 30 percent of tank
capacity.
To get to the NMEA 2000 Alarms menu, press
ALARMS and press ENT. Choose NMEA 2000 ALARMS and press ENT.
1. With the Fluid Level Device window highlighted, press
↑ ↓ to select the device you want to monitor, then press
2. To enable the Full Alarm, highlight
ENT to turn on (check) the alarm. Press → to the Percent box and
press
ENT. Use the ↑ ↓ keys to select the first number, then press → to
press
FULL ALARM Enabled box and
move to the next number. When the desired percentage has been entered, press
ENT.
MENU|MENU, select
ENT and use
ENT.
66
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 77

NMEA 2000 Alarms highlighted on Alarms menu (left). NMEA 2000
Alarms menu (center). Alarm Status page (right).
3. To enable the Empty Alarm, highlight the EMPTY ALARM Enabled box
and press
press
ENT to turn on (check) the alarm. Press → to the Percent box and
ENT. Use the ↑ ↓ keys to select the first number, then press → to
move to the next number. When the desired percentage has been entered, press
ENT.
Tip
You do not have to set both the Full and Empty alarms. Choose
both Full and Empty alarms or activate them individually.
Calibrate Speed
The speed sensor can be calibrated to compensate for inaccuracies. Before you change the setting, first calculate the percentage that the
speed is off. You will enter this percentage in a moment.
If, for example, you figure the sensor is reading 10 percent faster than
actual speed, you will enter – 10 in the calibration window. If the sensor is reading 5 percent slower than true speed, you will enter + 5 in
the window.
Calibrate Water Speed highlighted on Sonar Setup menu (left). Cali-
brate Speed dialog box (right).
67
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 78

A good way to gauge your speed sensor's performance is to compare its
reading with the ground speed measured by your unit's GPS functions.
When you make a run to compare GPS ground speed to speed sensor
speed, perform your test in relatively calm water free of current, if possible. (Unless, of course, you are taking the speed of current into consideration when making your calculation.) After you have a correction
figure, here's how to enter it:
1. Press
SPEED|ENT.
MENU|MENU|↓ to SONAR SETUP|ENT|↓ to CALIBRATE WATER
2. Enter the number you calculated earlier: press ↑ or ↓ to change the
first character (+ or –), then press → to move the cursor to the next
number and repeat until the percentage is correct, then press
EXIT.
Chart Speed
The rate that echoes scroll across the screen is called the chart speed.
The default is maximum; we recommend that you leave the speed set
there for virtually all fishing conditions.
You, however, might consider experimenting with chart speed when
you are stationary or drifting very slowly. You may sometimes achieve
better images as you slow down the chart speed to match how fast you
are moving across the bottom.
If you are at anchor, ice fishing or fishing from a dock, experiment with
a chart speed around 50 percent. If you are drifting slowly, try a chart
speed around 75 percent. When you are stationary and a fish swims
through the sonar signal cone, the image appears on the screen as a
long line instead of a fish arch. Reducing the chart speed may result in
a shorter line that more closely resembles a regular fish return.
Sonar Page menu with Chart Speed command selected (left).
Chart Speed Control Bar (right).
68
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 79

If you do experiment with chart speed, remember to reset it to maximum when you resume trolling or moving across the water at higher
speed.
To change chart speed:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to CHART SPEED|ENT.
2. The Chart Speed Control Bar appears. Press ↓ to decrease chart
speed; press ↑ to increase chart speed.
3. When it's set at the desired level, press
EXIT.
Colorline™
Colorline lets you distinguish between strong and weak echoes. It
"paints" a brighter color on targets that are stronger than a preset
value. This allows you to tell the difference between a hard and soft
bottom. For example, a soft, muddy or weedy bottom returns a weaker
signal which is shown with a narrow, colored line (dark blue tinged
with red or a little yellow.) Since fish are among the weakest echoes,
they show up mostly as blue arches. A hard bottom or other relatively
hard target returns a strong signal which causes a wider brightly colored line (reddish yellow to bright yellow.)
If you have two signals of equal size, one with red to yellow color and
the other without, then the target with brighter color (yellow) is the
stronger signal. This helps distinguish weeds from trees on the bottom,
or fish from structure.
Colorline is adjustable. Experiment with your unit to find the ColorLine setting that's best for you.
Sonar Page menu with ColorLine command selected (left).
The Colorline control bar (right).
69
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 80

To adjust Colorline level:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to COLORLINE|ENT.
2. The ColorLine Control Bar appears. Press ↓ to decrease ColorLine;
press ↑ to increase ColorLine.
3. When it's set at the desired level, press
Thin or no ColorLine
EXIT.
Wider
ColorLine
A small amount of Colorline (left) is indicative of a soft bottom. A
wider patch of Colorline indicates a harder bottom (right).
Depth Cursor
The depth cursor consists of a horizontal line with a digital depth box
on the right side. The numbers inside the box show the depth of the
cursor.
Cursor line
Depth box
Sonar Page menu with Depth Cursor selected (left). Sonar chart with
active depth cursor (right). The cursor is set at 34.64 feet deep.
70
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 81

The cursor can be moved to any location on the screen, letting you pinpoint the depth of a target.
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to DEPTH CURSOR|ENT.
2. The depth cursor appears. Press ↓ to lower the cursor line; press ↑ to
raise the cursor line.
3. To clear the depth cursor, press
EXIT.
Depth Range - Automatic
When turned on for the first time, the bottom signal is automatically
placed in the lower half of the screen. This is called Auto Ranging and
is part of the automatic function. However, depending upon the bottom
depth and the current range, you can change the range to a different
depth.
Sonar Page menu with Depth Range selected (left). Depth Range Con-
trol Scale (right).
1. From the Sonar Page, press MENU|↓ to DEPTH RANGE|ENT.
2. The Depth Range Control Scale appears. Press ↑ or ↓ to select a dif-
ferent depth range. A blue bar highlights the selected range. The light
numbers cannot be selected.
3. When the new range is selected, press
EXIT to clear the menu.
Depth Range - Manual
You have complete control over the range when the unit is in the manual mode. There are 16 depth ranges, from 5 feet to 4,000 feet.
To switch to Manual Depth Range:
1. First, turn off automatic depth range. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to AUTO DEPTH RANGE|ENT.
2. Press ↑ to
DEPTH RANGE |ENT and the Depth Range Control Scale ap-
pears.
71
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 82

3. Press ↓ or ↑ to select a different depth range. A horizontal blue bar
highlights the selected range.
4. When the new range is selected, press
EXIT to clear the menu. Repeat
these steps to turn on Auto Depth Range.
NOTE:
The sonar's depth capability depends on the water, bottom conditions, transducer installation and other factors.
Depth Range - Upper and Lower Limits
Virtually any segment of the water column can be displayed by using
the upper and lower limit feature. This lets you pick the shallow and
deep depth range limits that are shown on the screen, provided there is
at least 10 feet between the upper and lower limit you select. For example, a range from 12 feet to 34 feet could be used.
Changing the upper and lower limits gives you far greater control over
the depth range. This feature lets you "zoom in" the display in almost
unlimited combinations. Nearly any segment of the water column, from
the surface to the bottom can be shown.
Sonar Page Menu with Upper and Lower Limits selected (left). Sonar
Chart Limits menu with Upper Limit selected (right).
To change the upper and lower limits:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to UPPER AND LOWER LIMITS|ENT.
The Sonar Chart Limits menu appears, with Upper Limit selected.
2. To set the upper limit, press
ENT. Press ↑ or ↓ to change the first
number, then press → to move the cursor to the next number and repeat until the depth is correct, then press
EXIT.
72
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 83

3. To set the lower limit, press ↓ to
LOWER LIMIT|ENT. Press ↑ ↓ to change
the first number, then press → to move the cursor to the next number
and repeat until the depth is correct, then press
Fish arches
Area
"zoomed"
EXIT repeatedly.
Normal display, in auto depth range mode (left). Display "zoomed" with
Upper and Lower Limits focusing on the portion of the water column
from 20 feet to 40 feet deep (right). In the "zoomed" image, note the target
definition at lower left, showing a fish holding just above the structure.
To turn off upper and lower limits:
From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to AUTO DEPTH RANGE|ENT|EXIT.
FasTrack™
This feature automatically converts all echoes to short horizontal lines
on the display's far right side. The graph on the rest of the screen continues to operate normally. FasTrack gives you a rapid update of conditions directly under the boat. This makes it useful for ice fishing, or
when you are fishing at anchor. When the boat is not moving, fish signals are long, drawn out lines on a normal chart display. FasTrack converts the graph to a vertical bar graph that, with practice, makes a useful addition to fishing at a stationary location.
73
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 84

Surface clutter
Structure
Bottom signal
Fish arches
In FasTrack, fish
arches show as
horizontal bars.
Sonar Page showing FasTrack.
FasTrack
bar graph
Fish I.D.™ (Fish Symbols & Depths)
The Fish I.D. feature identifies targets that meet certain conditions as
fish. The microcomputer analyzes all echoes and eliminates surface
clutter, thermoclines, and other signals that are undesirable. In most
instances, remaining targets are fish. The Fish I.D. feature displays
fish symbols on the screen in place of the actual fish echoes.
There are several fish symbol sizes. These are used to designate the
relative size between targets. In other words, Fish I.D. displays a small
fish symbol when it thinks a target is a small fish, a medium fish symbol on a larger target and so on.
The sonar's microcomputer is sophisticated, but it can be fooled. It can't
distinguish between fish and other suspended objects such as trotlines,
turtles, submerged floats, air bubbles, etc. Individual tree limbs extending outwards from a group of limbs is the hardest object for the
Fish I.D. feature to distinguish from fish.
You may see fish symbols on the screen when actually, there are no
fish. The reverse is also true. The illustrations on the next page show
how Fish I.D. can actually miss fish that are present.
Does that mean Fish I.D. is broken? No — the feature is simply interpreting sonar returns in a specific way to help take some of the work
out of reading the screen. Remember: Fish I.D. is one of the many tools
we provide so you can analyze your sonar returns for maximum fish
finding information. This and other features can help you successfully
"see" beneath the boat under varied water and fishing conditions. So,
practice with the unit in both the Fish I.D. mode and without to become
more familiar with the feature. The default for Fish I.D. is off.
74
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 85

Sonar Features menu with Fish I.D. Symbols selected on dual-
frequency menu (left); single-frequency menu (right). When the check
box to the left is checked, the feature is on.
Fig. 1 A
Fig. 1 B
Many fish
arches visible
Fewer fish
symbols visible
Fig. 2 A
Fish arches
above structure
Figures 1A and 2A show Sonar Page in normal chart mode (left). Figures
1B and 2B (right) show the same underwater scene with Fish I.D. turned
on. Note how arches are replaced with symbols.
Fig. 2 B
No fish shown
FasTrack graph
confirms fish
75
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 86

To turn the Fish I.D. feature on:
p
1. From the Sonar Page, press
2. Press → to
FISH SYMBOLS|ENT|EXIT|EXIT.
MENU|↓ to SONAR FEATURES|ENT.
To turn off Fish I.D., repeat the instructions in step 2.
FishTrack™
The FishTrack feature shows the depth of a fish symbol when it appears on the display. This lets you accurately gauge the depth of targets. This feature is available only when the Fish I.D. feature is on. The
default setting for FishTrack is off.
To turn on FishTrack:
(Note: These instructions will turn on FishTrack and Fish I.D. at the
same time.)
1. From the Sonar Page, press
2. Press →|then press ↓ to
MENU|↓ to SONAR FEATURES|ENT.
FISH DEPTHS|ENT|EXIT|EXIT.
To turn off FishTrack, repeat the instructions in step 1. Turning off
FishTrack in this manner will not turn off Fish I.D. symbols.
Symbols with
FishTrack de
ths
Sonar Features menu with Fish I.D. Depths selected on dual-frequency
menu (left). When the check box to the left is checked, the feature is on.
Sonar Page with Fish I.D. symbols and FishTrack depths turned on
(right).
Frequency (Change Transducer Frequency)
(LMS-525cDF only)
The LMS-525cDF transducer can operate at both 200 kHz and 50 kHz.
The 200 kHz frequency has a 12° cone angle and the 50 kHz frequency
has a 35° cone angle.
76
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 87

The default frequency is 200 kHz, which is best for use in shallow water (about 300 feet or less). This frequency is the best choice for about
80 percent of the fresh and salt water sport fishing applications. When
you get into very deep salt water, 300 to 500 feet or deeper, the 50 kHz
frequency is the best choice.
The 200 kHz transducer will give you better detail and definition, but
less depth penetration. The 50 kHz transducer will give you greater
depth penetration, but a little less detail and less definition. (Remember,
all sonar units typically read deeper in fresh water than in salt water.)
There is a common exception to these rules of thumb. Some fishermen
on freshwater lakes (or the ocean) using downriggers like to see them
on the sonar. In many of those cases, you'll see a 50 kHz transducer
frequency in use because the wider cone angle lets them watch the bait.
Sonar Features menu with a frequency of 200 kHz selected.
To change the frequency setting to 50 kHz:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
2. Press →|then press ↓ to
3. Press
EXIT|EXIT to clear the menu.
MENU|↓ to SONAR FEATURES|ENT.
50 KHZ|ENT.
To change the frequency setting to 200 kHz:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
2. Press →|then press ↓ to
3. Press
EXIT|EXIT to clear the menu.
MENU|↓ to SONAR FEATURES|ENT.
200 KHZ|ENT.
HyperScroll™
See the entry on Ping Speed, which controls the HyperScroll feature.
77
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 88

Log Sonar Chart Data
If you have an MMC installed in the unit, the sonar data shown on the
screen can be saved to the MMC. This can be played back at any time
(to play a recorded sonar chart log, see the entry in this section for Sonar Simulator). If you have a personal computer and Internet access,
visit our web site, www.lowrance.com, and download the free Sonar
Viewer and the emulator for your unit. These programs will allow you
to replay sonar logs on your personal computer.
Sonar Page menu with the Log Sonar Chart Data selected (left). Sonar
Chart Logging menu (right) with the Start Logging selected. The menu
says the MMC has 5.42 MB of free space, which will record the scroll-
ing chart for 28 minutes and 44 seconds.
To record or log chart data:
1. Press
2. To record data using the default settings, press
MENU|↓ to LOG SONAR CHART DATA|ENT.
ENT. The menu clears
and the Sonar Page title bar shows the name of the file you are recording. Warning messages will appear as recording time begins to run
out.
NOTE:
You can change any of the settings by using the cursor arrows to
highlight different commands. Select
change the name. Select
CHART QUALITY if you want to lower the file
FILE NAME if you want to
quality and record for a longer period of time. After you've changed
the settings, select
START LOGGING and press ENT.
78
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 89

Noise Rejection
See the entry on Advanced Signal Processing in this section.
Overlay Data
On any Page display except Satellite Status, you can "float" or overlay
additional GPS or navigation data on the screen with the Overlay Data
command. For example, if you left your watch at home, you could display the local time on top of the map. Or, if you wanted to see details
about your route and trip, you could show your bearing, course, average
speed and trip distance.
The various data available from your unit are divided into categories in
the Overlay Data menu. These categories include GPS Data, Navigation, Trip Calculator, Time, Sonar Data and Miscellaneous Data.
You can select items from any of these categories for display, in any
combination — the category divisions are there only to help you sort
through the information.
Overlay Data highlighted on sonar menu (left). Overlay Data Shown
menu (right).
To overlay information on your screen:
1. Press
MENU|↓ to OVERLAY DATA|ENT.
2. If you currently have any overlay data on your screen, it will be
listed here. Select
(ENTER TO ADD) and press ENT. The data viewer shows
information categories with "+" or "–" symbols next to each category
name. A category with a "+" next to it is expandable, meaning its contents are hidden.
Selecting the category name and pressing
ENT will show the category's
contents, so you can choose items within it. An expanded category (one
with a "–" next to its name) can be collapsed to hide its contents. Just
select the category name and press
ENT.
79
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 90

Data Viewer menu (left). Sonar Data category expanded (right).
3. Expand any categories that might contain data you want to display.
Then press ↓ or ↑ to select a data option.
4. With the data option highlighted, press
ENT to check it (turn on) and
uncheck it (turn off). As you turn it on, the data will appear on top of
the screen. Every Page display has a maximum number of items you
can show using the Overlay Data command.
5. After the desired changes are made, press
EXIT|EXIT to return to the
page display.
Steering
arrow
Map Page showing boat cruising Puget Sound, Washington (left) with
Overlay Data turned on. This example shows Depth, Ground Speed
and the Steering Arrow. Note that the Steering Arrow always points
directly to the destination you are navigating toward. In this case, the
boater is headed on a northwesterly course of 275º. Since the helmsman is on course, the Steering Arrow is pointing straight ahead. If the
boat veered off course, the arrow would show which direction to steer
to get back on course. Sonar Page with Overlay Data turned on (right),
showing Depth, Ground Speed and the Track the boat is following.
80
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 91

To remove overlaid data:
1. While on the Page that shows the item or items you want to remove,
MENU|↓ to OVERLAY DATA|ENT.
press
2. You'll see a list of the overlay data currently displayed. Select the
item you want to remove from your display and press
ENT|ENT to re-
move the data. To remove another item, select the item and press
ENT|ENT.
3. When you have finished removing all the items you want from the
screen, press
EXIT to return to the page display.
NOTE
You can also remove data directly from the Data Viewer menu by unchecking the data option you would like to remove.
Overlay Data Shown with Water Temp selected (left). Remove button
highlighted (center). Water Temp has been removed from Overlay
Data Shown menu (right).
To move overlaid data:
You may find it useful to rearrange data that is floating in your display
window.
1. From one of the Map Pages, press
MENU|↓ to OVERLAY DATA|ENT.
2. You'll see a list of the overlay data currently displayed. Select the
item you want to move and press
ENT|→ to MOVE|ENT.
3. The data begins to flash on your screen. Use any combination of →,
←, ↑ and ↓ to move the data to a new location on the screen.
4. When satisfied, press
EXIT|EXIT.
NOTE:
The Customize command and the Overlay Data command both use
the same information categories. The difference between the two
commands is that Customize changes only the data boxes on a
81
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 92

screen, and Overlay Data changes only the information floating on
the screen without a box. See Customize Page Displays, on page 90,
for information on customizing data boxes.
To change displayed data font size:
1. From the Map or Sonar page, press MENU|↓ to OVERLAY DATA|ENT.
2. Press ↓ or ↑ to select Data Type,
five overlay options: Off, Small, Medium, Large and Enormous.
3. Select the desired setting. The selected data type will be displayed in
the new size. To change the font size for another Data Type, repeat
Steps 2 and 3. Press
NOTE:
Some data types can be displayed in only one font size. If that is the
case, the Data Size box will not be displayed for that data type.
EXIT to return to the sonar display.
then use ← → to scroll through the
Ping Speed & HyperScroll™
Ping Speed controls the rate at which the transmitter and transducer
broadcast sonar sound waves — pings — into the water. The unit has a
default ping speed of 50 percent. At normal boating speeds, this automatically provides enough return echoes to refresh the screen and
scroll the chart at maximum chart speed.
However, when you are running at high speeds, or just want the fastest
possible screen update, you may want to use the HyperScroll™ feature.
When you change the Ping Speed to any setting greater than 50 percent, the unit automatically enters HyperScroll mode.
These faster ping rates allow you to maintain a high-detail picture on
the screen, and the screen refresh rate and chart scroll speed can keep
pace with the boat as it moves quickly over the bottom terrain.
When using HyperScroll, you may also need to manually decrease the
sensitivity for optimum performance. Depending on water depth and
other conditions, HyperScroll may cause a second bottom echo to return
to the transducer during the next ping cycle, or sounding. This can result
in a large amount of clutter appearing on the screen. If this occurs, just
decrease the sensitivity to a level that eliminates the clutter. When you
turn HyperScroll off, you can return to your original sensitivity level.
82
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 93

Sonar Menu with Ping Speed selected (left).
Ping Speed Control Bar set to its default setting (right).
To change Ping Speed:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to PING SPEED|ENT.
2. The Ping Speed Control Bar appears. Press ↑ to increase ping speed;
press ↓ to decrease speed. When it's set at the desired level, press
EXIT.
To adjust Sensitivity:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|ENT.
2. The Sensitivity Control Bar appears. Press ↓ to decrease sensitivity;
press ↑ to increase sensitivity. When it's set at the desired level, press
EXIT. (When you reach the maximum or minimum limit, a tone sounds.)
To turn off HyperScroll:
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to PING SPEED|ENT.
2. The Ping Speed Control Bar appears. Press ↓ to decrease ping speed
to 50 percent. When it's set at the desired level, press
EXIT.
When you boost ping speed and switch into HyperScroll, the width of
the FasTrack bar graph display doubles in width at the right side of the
screen. This allows you to better see the virtually instantaneous sonar
returns, just as you would on a flasher sonar unit. For more information on FasTrack, see its entry in this section.
Reset Options
This command is used to reset all features, options and settings to their
original factory defaults. This is useful when you have changed several
settings and want to return the unit to basic automatic operation.
1. Press
2. Press ← to
MENU|MENU|↓ to SYSTEM SETUP|ENT|↓ to RESET OPTIONS|ENT.
YES|ENT.
83
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 94

3. All the menus are cleared and the unit reverts to the Map Page at
the 4000 mile zoom range, just as if you had turned it on for the first
time. All options have been returned to the factory settings.
System Setup menu with Reset Options selected (left). The Reset Op-
tions dialog box, with "Yes" selected (right).
NOTE:
Reset Options does not erase any waypoints, routes, plot trails, or
sonar logs.
Reset Water Distance
The sonar chart's Digital Data display option includes a box that shows
distance traveled, called Water Distance. This information is calculated
from an optional water speed sensor, not the GPS. The Water Distance
window can be reset to zero using the Reset Water Distance command.
Press
TANCE
MENU|MENU|↓ to SONAR SETUP|ENT|↓ to RESET WATER DIS-
|ENT. The menus are cleared and the water distance is reset to 0.00.
Set Keel Offset
This unit measures water depth from the face of the transducer. Since
the transducer is installed below the water surface, the distance displayed by the digital depth, chart depth scale, chart cursor or fish symbols is not the exact water depth. If the transducer is 1 foot below the
surface, and the screen shows the water depth as 30 feet, then the actual depth is 31 feet.
On sailboats or other large vessels with deep drafts, the distance between the transducer installation and the keel or lower engine unit can
be several feet. In those cases, an inexact depth reading could result in
grounding or striking underwater structure.
84
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 95

The Keel Offset feature eliminates the need for the navigator to mentally calculate how much water is under his keel.
Keel Offset lets you calibrate the digital depth, chart depth scale, chart
cursor depth and fish symbol depth displayed on the screen. To calibrate
the depth indicators, first measure the distance from the face of the
transducer to the lowest part of the boat. In this example, we will use 3.5
feet. This will entered as a negative 3.5 feet, which makes the depth indicators perform as if the transducer's lower in the water than it really is.
1. Press
OFFSET|ENT.
MENU|MENU|↓ to Sonar Setup ENT. Use ↓ to select SET KEEL
2. The Keel Offset dialog box appears. Press ↓ to change the plus (+)
sign to a minus (–) sign.
3. Press → to the first number, then press ↑ to change the number to 3
4. Press → to the second number, then press ↑ to change the number to
5, then press
EXIT. The depth indicators now accurately show the depth
of water beneath the keel.
NOTE:
If knowing the exact depth of water beneath the keel is less important, you can calibrate the depth indicators so that they show the actual water depth from surface to bottom. To do this, first measure the
distance from the face of the transducer up to the surface (the water
line on the boat). In this example, we will use 1.5 feet. This will be entered as a positive 1.5 feet, which makes the depth indicators perform
as if the transducer's higher in the water than it really is.
1. Press
OFFSET|ENT.
MENU|MENU|↓ to Sonar Setup ENT. Use ↓ to select SET KEEL
2. The Keel Offset dialog box appears with a plus (+) sign at the
front of the box.
3. Press → to the first number, then press ↑ to change the number
to 1.
4. Press → to the second number, them press ↑ to change the number to 5, then press
EXIT. The depth indicators now accurately show
the water depth from surface to bottom.
Sensitivity & Auto Sensitivity
The sensitivity controls the ability of the unit to pick up echoes. Sensitivity can be adjusted, because water conditions vary greatly. A low
sensitivity level (from zero to 50 percent) excludes much of the bottom
information, fish signals, and other target information.
85
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 96

High sensitivity levels let you see this detail, but it can also clutter the
screen with many undesired signals. Typically, the best sensitivity level
shows a good solid bottom signal with Colorline and some surface clutter.
Automatic Sensitivity
The default sensitivity mode is automatic. The unit bases the sensitivity level on water depth and conditions. When the unit is in the automatic mode, sensitivity is automatically adjusted to keep a solid bottom
signal displayed, plus a little more power. This gives it the capability to
show fish and other detail.
However, situations occur when it becomes necessary to increase or
decrease the sensitivity. This typically happens when you wish to see
more detail, so an increase in sensitivity is indicated. Or, wave action
and boat wakes can create enough tiny air bubbles to clutter much of
the water column. In that case, a decrease in sensitivity is indicated to
reduce some of the clutter.
The control bar used to adjust sensitivity up or down is the same
whether the unit is in the automatic or manual mode. In automatic you
can adjust sensitivity up to 100 percent but the unit will limit your
minimum setting. In auto, the unit will continue to make small adjustments, allowing for the setting you selected.
In manual mode, you have complete control over sensitivity, with the
ability to set it anywhere from zero to 100 percent. Once you select a
level in manual, the unit will continue to use that exact sensitivity setting until you change it or revert to auto mode.
To adjust sensitivity in auto mode:
1. Press
MENU|ENT.
2. The Sensitivity Control Bar appears. Press ↓ to decrease sensitivity;
press ↑ to increase sensitivity. When it's set at the desired level, press
EXIT. (When you reach the maximum or minimum limit, a tone sounds.)
86
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 97

Sonar Menu with Sensitivity selected (left). The Sensitivity Control
Bar (right).
To adjust sensitivity in manual mode:
1. First, turn off Auto Sensitivity: from the Sonar Page, press
to
AUTO SENSITIVITY|ENT.
2. Press ↑ to
SENSITIVITY|ENT and the Sensitivity Control Bar appears.
MENU|↓
Press ↓ or ↑ to pick a different sensitivity setting. When it's set at the
desired level, press
EXIT.
To turn Auto Sensitivity back on:
From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to AUTO SENSITIVITY|ENT|EXIT.
NOTE:
To return to the original factory setting for Auto Sensitivity, see the
entry in this section on Reset Options. If sensitivity is in manual
mode, the Reset Options command will switch back to Auto and reset the factory setting at the same time.
Tip:
For quicker sensitivity adjustments, try leaving the Sensitivity
Control Bar on the screen as the chart scrolls. You can see the
changes on the screen as you press the up or down arrows. This is
handy when there's a lot of clutter in the water, and you are matching the sensitivity to rapidly changing water conditions.
Sonar Chart Mode
The default color scheme for the sonar chart is the white background,
but we offer other variations to suit your viewing preferences. The
chart can be displayed in grayscale, reverse grayscale, blue background, white background, nightview, iceview, or bottom color tracking.
87
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 98

To change the chart mode color scheme:+
1. From the Sonar Page, press
MENU|↓ to SONAR FEATURES|ENT.
2. Press ↓ to
3. Press ↓ or ↑ to Mode Name|
4. Press
SONAR CHART MODE|ENT.
ENT.
EXIT|EXIT to return to the Sonar Page.
Sonar Page & Sonar Chart Display Options
The Pages Menu offers five chart display options for dual-frequency models and four options for single-frequency models. To access them, press
PAGES|← or→ to SONAR|↓ to Option Name|EXIT.
Pages Menu showing sonar chart display options.
Full Sonar Chart
This is the default mode used when the unit is turned on for the first
time or when it's reset to the factory defaults.
The bottom signal scrolls across the screen from right to left. Depth
scales on the right side of the screen aid in determining the depth of
targets. The line at the top of the screen represents the surface. The
bottom depth and surface temperature (if equipped with a temperature
sensor or a transducer with a temp sensor built in) show at the top left
corner of the screen.
The FasTrack™ display shows just to the right of the scale. This
changes all echoes into short horizontal bars, replicating a flasher sonar. The zoom bar on the far right shows the area that's zoomed when
the zoom is in use. (See the Zoom section for more information.)
88
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 99

Full Sonar Chart. The Overlay Data (depth and water temperature)
are both set to the small text size.
Split Zoom Sonar Chart
A split chart shows the underwater world from the surface to the bottom on the right side of the screen. The left side shows an enlarged version of the right side. The zoom range shows in the bottom left corner.
Split Zoom Sonar Chart. The left window is zoomed 2X in the first im-
age (left). The left window is zoomed 4X in the second image (right).
Split Frequency Sonar Chart
(LMS-525cDF only)
This page shows sonar data from the 50 kHz transducer on the left side
of the screen and data from the 200 kHz transducer on the right side.
All other functions and features are the same as the Full Chart page.
You can adjust the sensitivity in each window.
To adjust sensitivity in auto mode:
1. Press
MENU|ENT.
2. The unit asks which window (50kHz or 200kHz) you would like to
adjust. Press ← or→ to select the one you want |
ENT.
89
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
Page 100

3. The Sensitivity Control Bar appears. Press ↓ to decrease sensitivity;
press ↑ to increase sensitivity. When it's set at the desired level, press
EXIT. (When you reach the maximum or minimum limit, a tone sounds.)
The Split Frequency Sonar Chart page allows you to adjust
sensitivity separately for each window.
Digital Data/Chart
This mode shows the chart on the right side of the screen. The left side has
five digital data boxes containing: Water Depth; Water Speed (from an optional speed sensor); Water Distance (distance traveled or log, it also requires a speed sensor); Surface Water Temperature and Voltage.
Digital Data/Chart
Customize Page Displays
Every Page display option except Full Map (on the Map Page) has customizable data boxes to provide constant on-screen information.
The data available from your unit is divided into categories in the Data
Viewer menu. These categories include GPS Data, Navigation, Trip
90
www.Busse-Yachtshop.de email: info@busse-yachtshop.de
 Loading...
Loading...