Page 1

1
Linksys WRT54G / WRT54GS
Magical transformations to a useful piece of equipment
or a Brick
By:
Sysmin – ISSAP, CISSP, NSA-IAM
and
Quigon – ISSAP, CISSP, NSA-IAM
Th e Ha c k er Pi mps
www.hackerpimps.com
OR
Page 2

2
About This Document
■
This document is not complete or current. Please
visit our site for the most current version.
www.hackerpimps.com/docs.html
Thank You,
The Hacker Pimps
Page 3

3
WARNING!! WARNING!! WARNING!!
■
Modifying your firmware will void your warranty.
■
It's not like you would have done anything with it
anyway.
■
There is a possibility that you may brick your
WRT.
■
Isn't that half of the fun?
■
Idea? Hmm... Buying the buyer protection plan
from Best Buy might work. Don't think they even
check them.
Page 4

4
WRT54G / WRT54GS At A Glance
■
WRT54G
➔
200Mhz MIPS
processor
➔
4MB of flash memory
➔
16MB of RAM
■
WRT54GS
➔
200Mhz MIPS
Processor
➔
8MB of flash memory
➔
32MB of RAM
➔
Default has speed
booster crap
Page 5

5
Custom Antenna Options
■
Directional or Omni-directional
■
RP-TNC connectors
Page 6

6
Custom Antenna Options
■
Coax Cable – What length? Type? Hmm... Just
check out http://www.ocarc.ca/coax.htm
■
Now you and your neighbors can share
bandwidth.
Page 7

7
Exterior Equipment
■
Some of this stuff may seem like a no-brainer
but...
➔
Make sure all devices that use electricity are protected
in a weatherproof enclosure.
➔
Use weatherproof fittings when available.
➔
Provide some sort of lighting protection.
➔
Use drip loops for connectors and building
penetrations.
Page 8

8
A Few Firmware Options
■
Original Linksys Firmware
■
www.linksys.com
■
OpenWRT
■
www.openwrt.org
■
Sveasoft
■
www.sveasoft.com
■
Batbox
■
www.batbox.org
■
WiFiBox
■
www.sourceforge.net/projects/wifi-box
■
Google for more.
Page 9

9
Our Two Favorites
■
OpenWRT and Sveasoft
■
Why?
➔
Sveasoft is extremely easy to use and offers instant
results.
➔
OpenWRT has software packages and allows for
much flexibility.
■
The rest of the presentation will focus on these
two firmware options.
Page 10
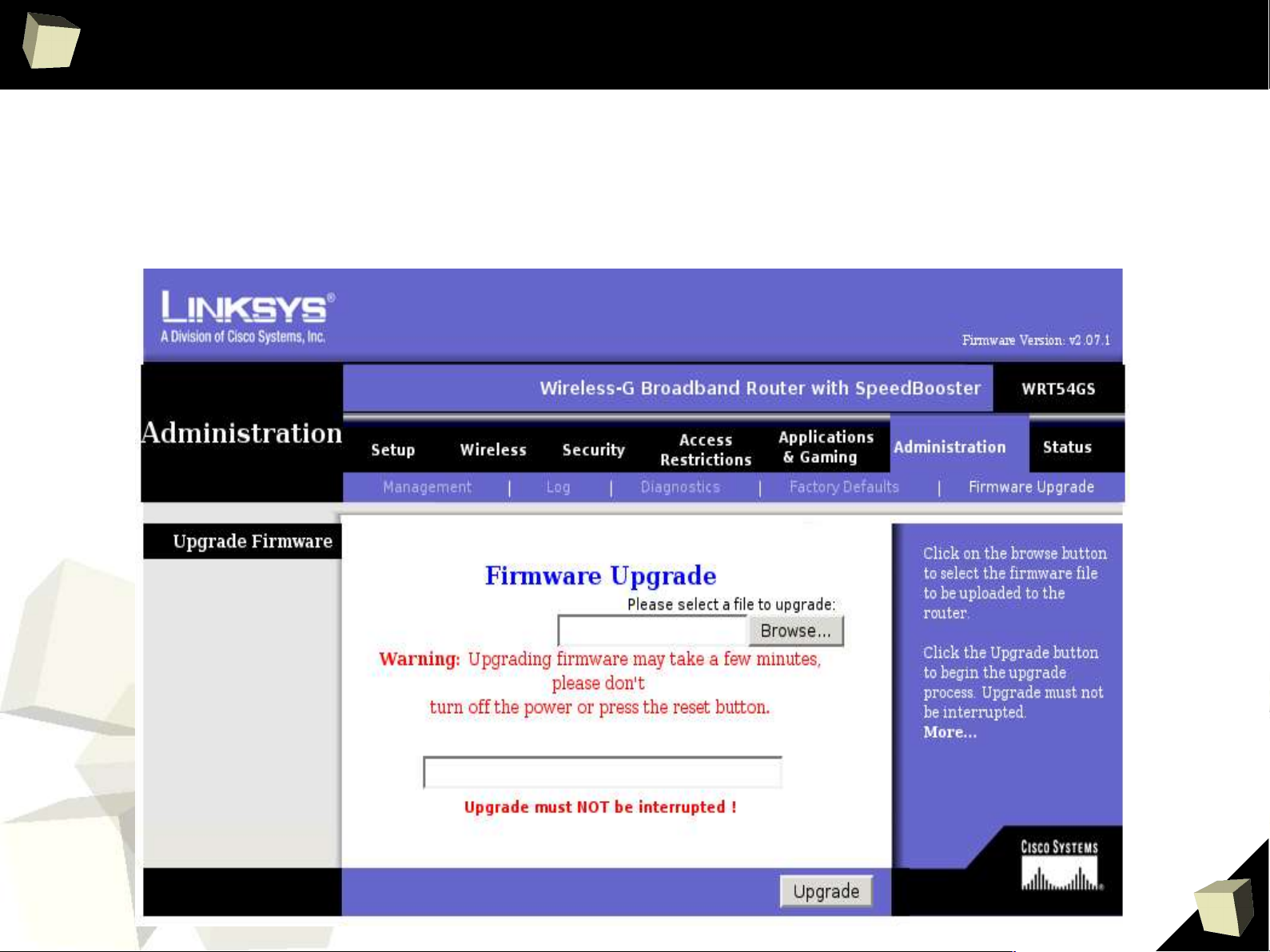
10
Installing New Firmware
■
The easiest way to upgrade firmware on Linksys
and Sveasoft.
Page 11

11
Setting OpenWRT NVRAM Variables
■
Showing NVRAM Values
nvram show
■
Searching NVRAM Values
nvram show | grep <string>
■
Setting NVRAM Values
nvram set <variable>=<value>
■
Don't forget to commit
nvram commit
■
Sometimes after committing a reboot is necessary
Page 12

12
OpenWRT and Ipkg
■
Works similar to Apt
■
Repositories are set up in /etc/ipkg.conf
■
ipkg update #Updates package list
■
ipkg install <pkgname> #Install certain package
■
ipkg remove <pkgname> #Removes package
Page 13

13
Funky Time Issue
■
OpenWRT Ain't Got The Time!
■
Discovered after some frustration
■
The output of the date command displays the year
as Jan 1st 2000 every time the access point is
power cycled
■
This causes problems for anything that is
dependent on date and time. Your digital
certificates may not be valid for another 5 years or
so.
■
This can cause problems with OpenVPN w/Digital
certificates and 802.1x
Page 14

14
Funky Time Issue Fix
■
Use the date command:
■
date <mmddhhmmccyy>
■
example: date 121813452004
■
More of a permanent fix by using ntpclient on boot.
■
install ntpclient via ipkg
■
Add the following to your rcS:
■
ntpclient -h pool.ntp.org -l -s &
Page 15

15
Editing the IPTables Firewall
■
Rename the link in the /etc/init.d directory so it
doesn't start and so you can import the file from
ROM
■
Then copy the file from ROM
■
cp /rom/etc/init.d/S45firewall /etc/init.d/S45firewall
■
Edit the S45firewall file until your heart is content
■
vi S45firewall
Page 16

16
Certificate Warning!!!!
Franks and Beans!!!!
■
Warren Says: Never use default certificates that
come with anything. Create your own CA.
Page 17

17
Setting up a Certificate Authority
■
Creating your own CA can be fun!
■
OpenSSL
www.openssl.org
■
Compile or install using your favorite package
manager.
■
This is important because many of the auth types
and VPNs require Digital Certificates.
Page 18

18
Creating a Self Signed CA
■
Using the Perl Script CA.pl to create the CA.
perl CA.pl -newca
■
Sometimes it chokes and you need to finish the
job by creating the “serial” file yourself in the
directory that houses the CA information.
echo '01' >serial
touch index.txt
■
Ta da! You have a new CA.
Page 19

19
Create and Sign Request
■
Create a new certificate request
perl CA.pl -newreq
■
Sign a req
perl CA.pl -sign
■
To revoke a cert
openssl -revoke <newcert.pem>
■
Create Diffie Hellman Parameters
openssl dhparam -out dh1024.pem 1024
Page 20

20
VPNs and Tunneling
■
OpenVPN
➔
http://openvpn.sourceforge.net
■
Openswan
➔
http://www.openswan.org
■
SSH tunneling
Page 21

21
OpenVPN
■
http://openvpn.sourceforge.net
■
Uses UDP
■
Good for NAT'ed hosts
■
Uses SSL
■
Fairly easy to configure
■
Using an OpenVPN server can also help protect
your Internet connection when away from home
Page 22

22
OpenVPN Server Configuration
■
port specifies the port the server will run on
port 5000
■
dev tun or dev tap specifies the type of interface
dev tun
■
TLS Parameters for use of digital certificates
ca /path/to/cert #Root CA Cert
cert /path/to/cert #Cert for OpenVPN
key /path/to/key #Key for OpenVPN
dh /path/to/dh1024.pem #Diffie Hellman params
■
Guess what this option does.
mode server
Page 23

23
OpenVPN Server Configuration
■
push #Pushes options to clients,
it is usually used to push routing options.
■
cipher #The cipher used
■
redirect gateway local #Sets VPN as Default GW
■
verb #Sets the verbosity level
Page 24

24
OpenVPN Client Configuration
■
dev tun or dev tap specifies the type of interface
dev tun
■
remote specifies the server and port
remote 192.168.1.1 5000
tls-client #specifies machine as client
■
TLS parameters
ca /path/to/cert #Root CA Cert
cert /path/to/cert #Cert for OpenVPN
key /path/to/key #Key for OpenVPN
■
verb #sets the verbosity level
Page 25

25
OpenVPN Client Configuration
■
Cipher determines the cipher
cipher AES-128-CBC
■
redirect-gateway local #redirects traffic
■
pull #pulls settings from the server
Page 26

26
Fun with SSH
■
What's Required:
➔
ipkg install dropbear
➔
Dropbear is a stripped down version of OpenSSH
originally written to run on a 386 laptop with 4MB.
➔
Provides most OpenSSH capabilities
➔
Client and server
➔
Secure copy (SCP)
➔
Port forwarding
➔
Encrypted traffic
➔
Uses most of the same syntax as OpenSSH
Page 27

27
Fun with SSH
■
What you can do with it:
➔
Say you have a Squid server doing caching on your
internal network.
➔
You're on a public (possibly hostile) network.
➔
ssh root@wrtexternal.net -C -L
3128:ipofsquidbox:3128
➔
Now set your web browser's proxy settings to
127.0.0.1 port 3389.
➔
Your traffic will now be fully encrypted (and
compressed) until it gets to a “safe zone” (your home
network).
Page 28

28
Fun with SSH
■
What you can do with it:
➔
SSH tunnelling can be done seamlessly with almost
any TCP based connection.
➔
Dropbear does NOT have IPv6 capability (yet).
➔
Connections aren't limited to your internal network.
➔
Things get a bit hairy using Windows XP as a client for
Terminal Services via SSH (but still can be done).
Page 29

29
802.1x
■
Better than standard WEP.
■
Can use your new Digital Certificates.
■
Can do dynamic key rotation.
■
Stronger authentication.
■
Can still use usernames / passwords if you want
(yuck!). Only this time with more security.
Page 30

30
802.1x Linux Client
■
www.open1x.org
■
Has extensive configuration options
■
Configurations are done through configuration files
■
Supports multiple authentication types including
EAP-TLS, PEAP, and LEAP
Page 31

31
802.1x Windows Client
■
Later versions of Windows have built-in support.
■
XP with SP2 has best support.
■
XP with SP1 has limited support.
■
2k has a a download with limited support.
Page 32

32
802.1x with TinyPEAP
■
The easiest way to do 802.1x with the WRT.
■
Works with Linksys and Sveasoft firmware.
■
Nice web interface for adding users and setting
preferences.
■
Set security mode to: Radius
■
Set the radius server address to the address of
the AP.
■
Radius port should be 1812
■
Shared key should be: password
■
set an initial WEP key
■
Add users though the GUI
Page 33

33
TinyPEAP
Page 34

34
IPv6
■
What's Required:
➔
ipkg install iproute2
➔
ipkg install radvd
➔
ipkg install kmod-ipv6
➔
IPRoute2 allows for easier configuration of IPv6 over
IPv4 tunnels.
➔
RADVD (Route Advertiser Daemon) broadcasts an
IPv6 prefix to the rest of your network
➔
kmod-ipv6 is the IPv6 kernel modules for connectivity
and firewalling.
Page 35

35
IPv6
■
Getting connected:
➔
We used Hurricane Electric as an IPv6 Tunnel Broker.
➔
http://www.tunnelbroker.net
➔
Allows for a static IPv6 over IPv4 tunnel and a /64 for
your internal network.
➔
Fairly easy to get it all working.
➔
Requires registration and a few hours for HE to set up
the tunnel.
Page 36

36
IPv6
■
Getting connected:
➔
Once HE establishes the tunnel, set up your end:
➔
ip tunnel add he.net mode sit remote 64.71.128.83 \ local
12.34.56.78 ttl 255
➔
ip link set he.net up
➔
ip addr add 2001:470:1F01:F00D::2F1/127 dev he.net
➔
ip route add ::/0 dev he.net
➔
ip -f inet6 addr
➔
You can also add these commands to /etc/init.d/rcS to
make them more permanent.
➔
ping6 www.kame.net to make sure you have
connectivity.
Page 37

37
IPv6
■
For the rest of your network:
➔
Set up your router advertiser:
➔
vi /etc/radvd.conf
➔
interface br0
{ AdvSendAdvert on;
MinRtrAdvInterval 3;
MaxRtrAdvInterval 10;
AdvHomeAgentFlag off;
prefix 2001:470:1F01:CAFE::/64
{ AdvOnLink on;
AdvAutonomous on;
AdvRouterAddr on;
};};
Page 38

38
IPv6
■
For the rest of your network:
➔
Assign one of the /64 IPv6 IPs to the br0 interface
➔
ip -6 addr add 2001:470:1F01:CAFE::1/64 dev br0
➔
Ensure IPv6 forwarding is enabled
➔
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv6/conf/all/forwarding
➔
Start RADVD
➔
radvd -m logfile -l /var/log/radvd.log
➔
These can also be added to /etc/init.d/rcS.
➔
You should now be able to ping6 www.kame.net from
IPv6 enabled clients.
Page 39

39
Community Networking
■
Using the WRT as a wireless client.
■
Using WDS (Wireless Distribution System).
■
Creating a Phat network in your neighborhood
because sharing your Internet connection is fun
for everyone.
■
Do some prior planning and have an objective for
your community network.
■
Doesn't matter if you want to share Internet
access or files, planning goes a long way.
■
Know what type of antennas you need to use.
Page 40

40
Community Networking
■
Be mindful of obstructions in the fresnel zone.
■
Metal can be a very bad thing.
Page 41

41
WRT as a Wireless Client
■
Allows you to connect to another access point
using wireless.
■
No need to configure main access point.
■
Must be configured with the same SSID.
■
Must be configured with on the same channel.
Page 42

42
Using WDS in Sveasoft
■
Setup through the GUI
■
Easy to configure
■
Can still use the wireless interface even though it
is meshing.
■
Enter MAC addresses of other AP's wireless
interfaces into the WDS config page
Page 43

43
WDS and Sveasoft
Page 44

44
WDS in Sveasoft
■
Set the scope, hand out DHCP, and be the
gateway on one AP.
■
Set up this AP as the gateway on other APs.
■
Turn off DHCP on other APs.
Page 45

45
Hotspots and Authentication
■
NoCat
➔
http://nocat.net
■
Chillispot
➔
http://www.chillispot.org
Page 46

46
Cross Compiling Applications
■
Easy way to get a cross compiler up and running:
➔
Requires a Debian based distro
➔
From http://skaya.enix.org/wiki/ToolChain
➔
apt-get install toolchain-source toolchain-source-gdb
toolchain-source-newlib
➔
tpkg-make mipsel-linux
➔
cd binutils-mips-linux-*/ ; debuild -us -uc
➔
su -
➔
debi
➔
TPKG_SERVER=ftp://ftp.us.debian.org tpkg-install-libc
mipsel-linux
➔
go to the gcc-mips-linux-* dir
➔
debuild -us -uc
➔
debi
➔
A lot easier than it sounds
Page 47

47
Cross Compiling Applications
■
Not so easy ways
➔
Compile from source (good luck!!!)
➔
Use CrossTool
➔
Cross compiler build scripts from
http://www.kegel.com/crosstool/
➔
Has issues with BASH 3.xx
➔
I've never gotten a compiler up and running these ways
➔
To make an app from source (from ToolChain slide):
➔
CC=mipsel-linux-gcc CFLAGS=” -s --static” ./configure \ --
host=mipsel
➔
make
Page 48

48
Cross Compiling Applications
■
Issues with compiling
➔
AKA -- My limited knowledge with embedded
development and cross compilers
➔
Linux uses GLibC for C Libraries
➔
OpenWRT uses uCLibC
➔
much more stripped down and compact C Library
➔
Binaries compiled with GLibC must be statically
compiled (hence the --static)
➔
They end up being huge (even after the symbols get
stripped...-s)
➔
We're working on it
➔
Trying to use the Tool Chain that actually builds OpenWRT
Page 49

49
Customizing OpenWRT
■
2 Config scripts to know about (for now)
➔
/buildroot/sources/openwrt/busybox/busybox.config
➔
Busybox is a command line interface used in embedded
systems (many POSIX tools in an >200kb package if
configured properly).
➔
There are some tools you might want that aren't compiled in
by default (e.g. mkswap, swapon, swapoff).
➔
/buildroot/sources/openwrt/kernel/linux.config
➔
Standard .config file from the 2.4.20 kernel
➔
for more flexibility, enabling and disabling modules you
need/don't need.
➔
BE VERY CAREFUL DOING THIS. You could end up
with a firmware that bricks your WRT.
➔
Don't say we didn't warn you.
Page 50

50
Mod The #@&$ Out Of It!
WrtZilla
Yes, this is a functional WRT
Page 51

51
Recon and Attacks
Stage II:
Recon and Attacks
Page 52

52
Drive-by Upload
■
Remember why it is so important to change your
defaults?
Page 53

53
FuxorWRT by THP
“Don't Enter us, We'll enter you!”
Page 54

54
THP Customized Firmware
■
FuxorWRT
➔
Hacker Pimps' Customized OpenWRT firmware
➔
Includes (out of the box):
➔
most kernel modules embedded into the firmware
➔
smbmount & smbclient
➔
nbtscan
➔
aircrack
➔
NFS client/NFS Swap
➔
IPv6 stack (with Router Advertiser)
➔
THC-Hydra
➔
Lutz (tiny port scanner similar to NMAP)
➔
hping2
➔
stunnel
➔
Misc. exploits for computers behind the WRT54G(S)
➔
Suggestions?
Page 55

55
More Fuxor
■
FuxorWRT Build
➔
Customized linux.config
➔
Customized busybox.config
➔
Several cross compiled tools and apps
➔
copied into /opt/build_mipsel/root
➔
Re-running “make” in your buildroot dir adds new
programs and Kernel/BusyBox mods
➔
Custom /opt/build_mipsel/root/etc/banner
Page 56

56
Netcat
■
Using netcat as a port scanner.
➔
nc -v -z <host> <port range>
■
Using netcat to connect to ports and banner grab.
➔
nc <host> <port>
■
Using Lutz
➔
-sC Connect() Scan. Default for nonroot users
➔
* -sS SYN-Stealth Scan. Default for r00t
➔
* -sF,-sX,-sN FIN,Xmas,NULL-Scan instead of SYN
➔
Many other options
Page 57

57
More Attacks
■
What can be done with FuxorWRT?
➔
Discover hosts
➔
Port scan
➔
Scan for shares
➔
Transfer data
➔
Mount shares
➔
Crack WEP
➔
Exploit
Page 58

58
When Firmware Goes Bad
Stage III:
When Firmware Goes Bad
Page 59

59
When Firmware Goes Bad
■
To avoid certain problems make sure that you turn
boot wait on.
nvram set boot_wait=on
■
Something else to try
➔
Set the computer up to ping 192.168.1.1
➔
Remove cover and short out pins 15 and 16 on the
nvram chip
➔
Apply power
➔
Once the ping is working tftp the image to the wrt
➔
tftp 192.168.1.1
➔
tftp> binary
➔
tftp> rexmt 1
➔
tftp> trace
➔
tftp> put <imagefile>
Page 60

60
When Firmware Goes Bad
■
Hold in the reset button
■
Pray to the gods of firmware and offer up a
sacrifice. Maybe an old telephone or something?
Page 61

61
Uses For Brick
7 Uses for a Bricked WRT
Page 62

62
The WRT Purse
See Demo
Extras Needed: 1 short piece of Cat5
1 long piece of Cat5
Page 63

63
The WRT Soccer Ball
Page 64

64
The WRT Plastic Surgeon
Who could possibly
know more about
plastic surgery?
Page 65

65
The WRT Rap Star
Fo Shizzle
Page 66

66
The WRT Lawn Sprinkler
Page 67

67
The WRT Pleasure Device
Extras Needed: 1 Midget
1 Kazoo
Page 68

68
Thank You
■
We would like to thank the developers of the
various projects and communities that make them
great. Your work is greatly appreciated.
Page 69

69
Useful Links
■
www.openwrt.org
■
www.sveasoft.com
■
http://openvpn.sourceforge.net
■
http://www.openswan.org
■
http://voidmain.is-a-geek.net:81/redhat/wrt54g_revival.html
■
www.openssl.org
■
http://www.neonbox.org/nanobox
Page 70

70
Any Questions?
■
Sysmin Sys73m47ic
Nathan Hamiel – ISSAP, CISSP, NSA-IAM
sysmin@neohaxor.org
■
Quigon
Gene Cronk – ISSAP, CISSP, NSA-IAM
gene@hacktek.com
Th e Ha c k er Pi mps
www.hackerpimps.com
 Loading...
Loading...