Page 1

Instant Wireless®Series
Use this guide to install:
WET11
User Guide
Wireless Ethernet
Bridge
Page 2

COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS
Copyright © 2002 Linksys, All Rights Reserved. Instant Wireless, Linksys, and the
Linksys logo are registered trademarks of Linksys Group, Inc. Microsoft, Windows, and
the Windows logo are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. All other trademarks and brand names are the property of their respective proprietors.
LIMITED WARRANTY
Linksys guarantees that every Wireless Ethernet Bridge will be free from physical defects
in material and workmanship for one year from the date of purchase, when used within
the limits set forth in the Specifications section of this User Guide. If the product proves
defective during this warranty period, call Linksys Technical Support in order to obtain a
Return Authorization Number. BE SURE TO HAVE YOUR PROOF OF PURCHASE AND A
BARCODE FROM THE PRODUCT’S PACKAGING ON HAND WHEN CALLING. RETURN
REQUESTS CANNOT BE PROCESSED WITHOUT PROOF OF PURCHASE. When returning a product, mark the Return Authorization Number clearly on the outside of the package and include a copy of your original proof of purchase. All customers located outside of the United States of America and Canada shall be held responsible for shipping
and handling charges.
IN NO EVENT SHALL LINKSYS’S LIABILITY EXCEED THE PRICE PAID FOR THE PRODUCT FROM DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE USE OF THE PRODUCT, ITS ACCOMPANYING SOFTWARE, OR ITS DOCUMENTATION. LINKSYS DOES NOT OFFER REFUNDS FOR ANY
PRODUCT. Linksys makes no warranty or representation, expressed, implied, or statutory, with respect to its products or the contents or use of this documentation and all
accompanying software, and specifically disclaims its quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for any particular purpose. Linksys reserves the right to revise or
update its products, software, or documentation without obligation to notify any individual or entity. Please direct all inquiries to:
Linksys P.O. Box 18558, Irvine, CA 92623.
FCC STATEMENT
This Wireless Ethernet Bridge has been tested and complies with the specifications for a
Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used according to the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However , there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception,
which is found by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment or devices
• Connect the equipment to an outlet other than the receiver’s
• Consult a dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for assistance
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance
20cm between the radiator and your body.
UG-WET11-110502D JL
INDUSTRY CANADA (CANADA)
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
The use of this device in a system operating either partially or completely outdoors may require
the user to obtain a license for the system according to the Canadian regulations.
EC DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY (EUROPE)
Linksys Group declares that the Instant Wireless Series products included in the Instant
Wireless Series conform to the specifications listed below, following the provisions of the
EMC Directive 89/336/EEC and Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC:
• ETS 300-826, 301 489-1 General EMC requirements for Radio equipment.
• EN 609 50 Safety
• ETS 300-328-2 Technical requirements for Radio equipment.
Note: This equipment is intended to be used in all EU and EFTA countries. Outdoor use
may be restricted to certain frequencies and/or may require a license for operation. For
more details, contact Linksys Corporate Compliance.
Note: Combinations of power levels and antennas resulting in a radiated power level of
above 100 mW are considered as not compliant with the above mentioned directive and
are not allowed for use within the European community and countries that have adopted
the European R&TTE directive 1999/5/EC and/or the CEPT recommendation Rec 70.03.
For more details on legal combinations of power levels and antennas, contact Linksys
Corporate Compliance.
• Linksys Group vakuuttaa täten että Instant Wireless IEEE 802.11 PC Card tyyppinen
laite on direktiivin 1999/5/EY, direktiivin 89/336/EEC ja direktiivin 73/23/EEC oleellisten vaatimusten ja sitä koskevien näiden direktiivien muiden ehtojen mukainen.
• Linksys Group déclare que la carte PC Instant Wireless IEEE 802.11 est conforme
aux conditions essentielles et aux dispositions relatives à la directive 1999/5/EC, la
directive 89/336/EEC, et à la directive 73/23/EEC.
• Belgique B L’utilisation en extérieur est autorisé sur le canal 11 (2462 MHz), 12 (2467
MHz), et 13 (2472 MHz).
Dans le cas d’une utilisation privée, à l’extérieur d’un bâtiment, au-dessus d’un
espace public, aucun enregistrement n’est nécessaire pour une distance de moins
de 300m. Pour une distance supérieure à 300m un enregistrement auprès de l’IBPT
est requise. Pour une utilisation publique à l’extérieur de bâtiments, une licence de
l’IBPT est requise. Pour les enregistrements et licences, veuillez contacter l’IBPT.
• France F: Bande de fréquence restreinte: seuls les canaux 10, 11, 12, 13 (2457,
2462, 2467, et 2472 MHz respectivement) doivent être utilisés en France. Toute utilisation, qu'elle soit intérieure ou extérieure, est soumise à autorisation. Vous pouvez
contacter l'Autorité de Régulation des Télécommuniations (http://www.art-telecom.fr)
pour la procédure à suivre.
• France F: Restricted frequency band: only channels 10, 11, 12, 13 (2457, 2462,
2467, and 2472 MHz respectively) may be used in France. License required for
every indoor and outdoor installations. Please contact ART for procedure to follow.
• Deutschland D: Anmeldung im Outdoor-Bereich notwending, aber nicht genehmigungspflichtig. Bitte mit Händler die Vorgehensweise abstimmen.
• Germany D: License required for outdoor installations. Check with reseller for procedure to follow.
• Italia I: E' necessaria la concessione ministeriale anche per l'uso interno. Verificare
con i rivenditori la procedura da seguire. L'uso per installazione in esterni non e' permessa.
• Italy I: License required for indoor use. Use with outdoor installations not allowed.
• the Netherlands NL License required for outdoor installations. Check with reseller for
procedure to follow.
• Nederlands NL Licentie verplicht voor gebruik met buitenantennes. Neem contact op
met verkoper voor juiste procedure.
Page 3

Instant Wireless®Series
Chapter 1:Introduction
r
The versatile Wireless Ethernet Bridge can make any wired Ethernet-equipped
device a part of your wireless network. At home, use the Wireless Ethernet
Bridge to connect to game consoles, set-top boxes, or computers into your
wireless network to share your high-speed network connection. In the office,
convert your Ethernet-wired printer , scanner , camera, notebook, or desktop into
a wireless networked device.
It’s completely driver-free, so it works on any platform and under any operating system! Since there are no drivers to load, setup is a snap—just plug it into
your device and configure the network settings through your web browser.
You can also use the Wireless Ether net Bridge as a kind of “cable-less cable”
to connect remote areas together. Maybe Shipping is all the way across the
warehouse from Receiving. Or maybe you want to set up a home office in your
detached garage. With a Wireless Ethernet Bridge in the garage, and another
one (or a Wireless Access Point) in the house, you’re connected—with no
cabling hassle.
• An All-in-One Wireless Solution for Any Ethernet-Ready Network Device
• Interoperable with 802.11b (DSSS) 2.4GHz-Compliant Equipment
• No Additional Drivers Are Needed
• Up to 11 Mbps High-Speed Transfer Rate
• Dynamically Shifts between 11, 5.5, 2, and 1Mbps for Maximum
Adaptability
• Suppor ts up to 50 Remote Clients
• Assurance of Constant Connection via Direct Sequence Spread Spectr um
(DSSS)
• Conveniently Eliminates Cables and Network Wires Used by Network
Devices
• Equipped with One Standard 10Base-T Interface for Connection with Any
Ethernet-Ready Networked Resource
• Capable of up to 128-Bit WEP Encryption
• Setup Wizard for Easy Installation
• Free Technical Support—24 Hours a Day, 7 Days a Week, Toll-Free US
Calls
• 1-Year Limited War ranty
Wireless Ethernet Bridge
The Wireless Ethernet Bridge
Features
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction 1
The Wireless Ethernet Bridge 1
Features 1
Chapter 2: Getting to Know the Wireless Ethernet
Bridge 2
The Wireless Ethernet Bridge’s Back Panel 2
The Wireless Ethernet Bridge’s Front Panel LEDs 3
Chapter 3: Planning Your Wireless Network 4
Network Topology 4
Roaming 4
Ad-Hoc versus Infrastructure Mode 5
Chapter 4: Connecting the Wireless Ethernet
Bridge 7
Chapter 5: Setting Up the Wireless Ethernet
Bridge 8
Chapter 6: Using the Wireless Ethernet Bridge
Web-based Utility 16
Overview 16
Starting the Web-based Utility 16
Setup 18
Password 24
Status 25
Help 27
Appendix A: Troubleshooting 29
Common Problems and Solutions 29
Frequently Asked Questions 30
Appendix B: Glossary 34
Appendix C: Specifications 39
Environmental 40
Appendix D: Warranty Information 41
Appendix E: Contact Information 42
1
Page 4

Instant Wireless®Series
Wireless Ethernet Bridge
Chapter 2: Getting to Know the
Wireless Ethernet Bridge
The.W
Reset The Reset button resets the Bridge to its factory default set-
X-II
LAN The LAN port is where you will connect your Ethernet net-
ireless.Ethernet.Bridge's
F
igur
tings.
The X-II selection switch offers a choice between two settings. Use the X setting if you are connecting the Bridge to a
network card or other Ethernet device. Use the II setting if
you are connecting the Bridge to a hub or switch.
work cable.
..B
ack.Panel
e
2-
1
The.W
P
PWR Green. The PWR LED will light up when
DIAG Green. The DIAG LED will light up when
LAN Green. The LAN LED will be lit steadily
WLAN Green. The WLAN LED indicates the status
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter
ireless.Ethernet.Bridge's
anel
.LED
s
the Bridge is powered on.
there is a connection error. Re-establish the
connection to eliminate the error.
when the Bridge is connected to the LAN.
The LED will blink when there is LAN traffic.
of the link to the wireless local area network
(WLAN). The WLAN LED will be lit
steadily when the Bridge is connected to the
WLAN. The LED will blink when there is
WLAN traffic.
..F
ront
F
igur
e
2-
2
Power The Power port is where you will connect your power.
2
Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party responsible
for compliance could void the user authority to operate the equipment.
3
Page 5

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
5
Instant Wireless®Series
4
Unlike wired networks, wireless networks have two different modes in which
they may be set up: Infrastructure and Ad-Hoc. Choosing between these two
modes depends on whether or not the wireless network needs to share data or
peripherals with a wired network or not.
If the computers on the wireless network need to be accessible by a wired network or need to share a peripheral, such as a printer, with the wired network
computers, the wireless network should be set up in the Infrastructure mode.
The basis of Infrastructure mode centers around an access point, which serves
as the main point of communications in a wireless network (see Figure 3-1).
Access points transmit data to PCs equipped with wireless network card, which
can roam within a certain radial range of the access point. Multiple access
points can be arranged to work in succession to extend the roaming range, and
can be set up to communicate with your Ethernet hardware as well.
Ad-Hoc versus Infrastructure Mode
Figure 3-1
Chapter 3: Planning You r
Wireless Network
Network Topology
A wireless LAN is exactly like a regular LAN, except that each network device
in the LAN uses a Wireless Ethernet Bridge to connect to the network without
using wires. Computers in a wireless LAN must be configured to share the
same radio channel.
The Wireless Ethernet Bridge provides LAN access for wireless network
devices. An integrated wireless and wired LAN is called an Infrastructure configuration. A group of Wireless Ethernet Bridge users and an access point compose a Basic Service Set (BSS). Each PC equipped with an Wireless Ethernet
Bridge in a BSS can talk to any computer in a wired LAN infrastructure via the
Bridge.
An infrastructure configuration extends the accessibility of a Wireless Ethernet
Bridge to a wired LAN, and doubles the effective wireless transmission range
for two Wireless Ethernet Bridge PCs. Since the access point is able to forward
data within its BSS, the effective transmission range in an infrastructure LAN
is doubled.
The use of a unique ID in a Basic Service Set is essential.
The Wireless LAN infrastructure conf iguration is appropriate for enterprisescale wireless access to a central database, or as a wireless application for
mobile users.
Infrastructure mode also supports roaming capabilities for mobile users. More
than one BSS can be configured as an Extended Ser vice Set (ESS). This continuous network allows users to roam freely within an ESS. All Wireless
Ethernet Bridge PCs within one Extended Service Set must be configured with
the same SSID.
Selecting a feasible radio channel and optimum access point position is recommended. Proper access point positioning combined with a clear radio signal
will greatly enhance performance.
Network Topology
Roaming
Page 6
Wireless Ethernet Bridge
7
Instant Wireless®Series
If the wireless network is relatively
small and needs to share resources
only with the other computers on the
wireless network, then the Ad-Hoc
mode can be used. Ad-Hoc mode
allows computers equipped with
wireless transmitters and receivers to
communicate directly with each
other, eliminating the need for an
access point. The drawback of this
mode is that in Ad-Hoc mode, wireless-equipped computers are not able
to communicate with computers on a
wired network. And, of course, communication between the wireless-equipped computers is limited by the distance and
interference directly between them.
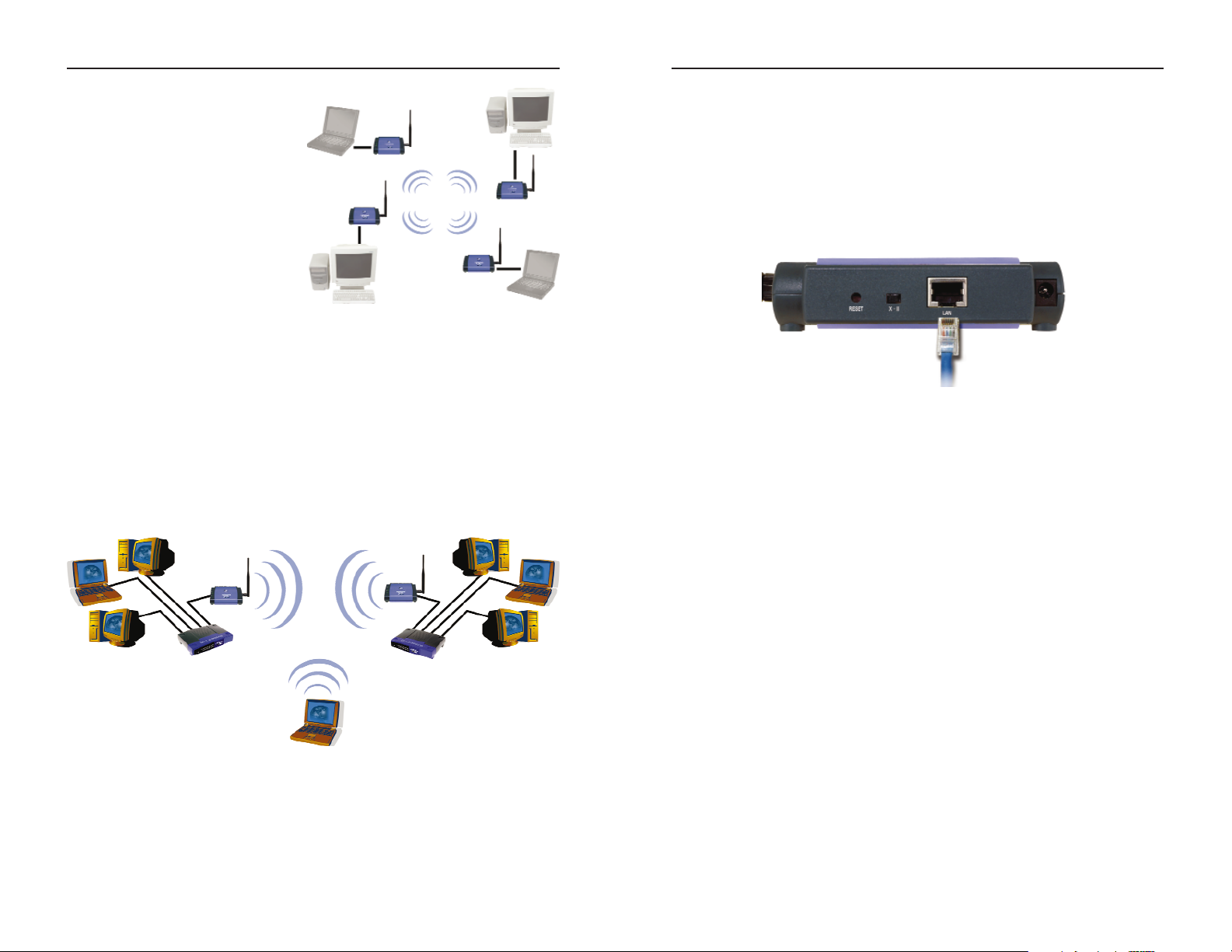
Figure 3-2 shows a typical scenario of four Wireless Ethernet Bridges in ad-hoc
mode. Figure 3-3 shows a typical wireless bridging scenario using two Wireless
Ethernet Bridges. Each wireless network is connected to a Wireless Ether net
Bridge through a switch. A separate notebook computer is equipped with a
wireless PC card and can communicate with both wireless networks as long as
it has the same SSID and channel as both wireless networks.
6
Chapter 4: Connecting the
Wireless Ethernet Bridge
1. Plug the included Ethernet network cable into the LAN port on the back
panel of the Bridge.
2. The X-II selection switch offers a choice between two settings. Slide the
X-II selection switch to the X position if you are connecting the Bridge to a
network card or other Ethernet device. Slide the X-IIselection switch to the
II position if you are connecting the Bridge to a hub or switch.
3. Plug the other end of the Ethernet network cable into the RJ-45 port on the
PC you wish to use to configure the Bridge.
4. Plug the supplied power cable into the Power port on the back panel of the
Bridge. Then plug the other end into an electrical outlet.
5. Proceed to the next section, “Chapter 5: Setting Up the Wireless Ether net
Bridge.”
6. After configuration, unplug the Ether net network cable from the PC, and
plug it into the RJ-45 port on the Ethernet-ready network device you wish
to add to the wireless network.
The hardware installation is complete.
Figure 4-1
Figure 3-3
Figure 3-2
Page 7

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
2. The screen shown in Figure 5-2 shows the two ways to configure the Bridge
using this Setup Wizard. Optimally, you should perform this setup through
a PC on your wired network. You can also set up the Bridge through one of
the PCs on your wireless network. Click the Next button to continue or the
Exit button to exit the Setup Wizard.
3. The screen shown in Figure 5-3 displays a list of Wireless Ethernet Bridges
on your network, along with the status information for each Bridge. (If you
have only one Bridge on your network, it will be the only one displayed.)
Select the Bridge you are currently installing by clicking its name in the
Selection box. Write down the IP address of the Wireless Ethernet Bridge,
so you can use it to access the Web-based Utility later. Click the Yes button
to continue or the Exit button to exit the Setup Wizard.
9
Instant Wireless®Series
8
Figure 5-2
Figure 5-3
Chapter 5: Setting Up the
Wireless Ethernet Bridge
Now that you’ve connected the Wireless Ethernet Bridge to your wired network, you are ready to set it up. The Setup Wizard will guide you through all
the steps necessary.
1. Insert the Setup Wizard CD-ROM into your PC’s CD-ROM drive. The
Setup Utility should run automatically, and the screen in Figure 5-1 should
appear. If it does not, click the Start button and choose Run. In the f ield
that appears, enter D:\setup.exe (if “D” is the letter of your CD-ROM
drive).
Click the Setup button to continue using the Setup Wizard. Click the User
Guide button to open the pdf version of this User Guide. Click the Linksys
Web button to access the Linksys website using an active Internet connec-
tion. Click the Exit button to exit the Setup Wizard.
Figure 5-1
Page 8

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
6. The Basic Settings screen will now appear. Enter your wireless network’s
SSID, and select the Channel at which the network broadcasts its wireless
signal. Enter a unique Bridge Name for the Bridge. Then click the Ne xt button to continue or the Back button to return to the previous screen.
• SSID - The SSID is the unique name shared among all points in a wireless
network. The SSID must be identical for all points in the wireless network.
It is case-sensitive and must not exceed 32 alphanumeric characters, which
may be any keyboard character (do not use any spaces). Make sure this setting is the same for all points in your wireless network.
• Channel - Select the appropriate channel from the list provided to correspond with your network settings, betw een 1 and 11 (in North America). All
points in your wireless network must use the same channel in order to function correctly.
• Bridge Name - You may assign any name to the Bridge. Unique, memo-
rable names are helpful, especially if you are using multiple bridges on the
same network.
11
Instant Wireless®Series
4. For security purposes, you will be asked for your user name and password
in order to access the Bridge. In lowercase letters, enter admin in the
Password field (later you can change the password through the Web-based
Utility). Click the Yes button to continue or the No button to retur n to the
previous screen.
5. The screen shown in Figure 5-5 shows a choice of two wireless modes.
Click the Infrastructure Mode radio button if you want your wireless
computers to network with computers on your wired network using a wireless access point. Click the Ad-Hoc Mode radio button if you want multiple wireless computers to network directly with each other. Do not use the
Ad-Hoc mode if you want to network your wireless computers with computers on your wired network. Click the Next button to continue or the
Back button to return to the previous screen.
10
Figure 5-6
Figure 5-4
Figure 5-5
Page 9

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
8. The Security Settings screen, shown in Figure 5-8, appears next. Set the
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) encryption for your wireless network by
selecting a WEP configuration method.
• WEP (Disabled/64-bit WEP/128-bit WEP) - In order to utilize WEP
encryption, select 64-bit or 128-bit WEP from the drop-down menu. If y ou
do not want to use WEP encryption, keep the default setting, Disab led. The
Bridge’s WEP encryption is unique to Linksys and may conflict with other
manufacturers’WEP encryption.
If you select 64-bit or 128-bit WEP, you can create a WEP key automatically or manually. Go to step 9a to generate a WEP key automatically. Go
to step 9b to create a WEP key manually.
9a. Enter a passphrase.
• Passphrase - This is the code used when logging a wireless device onto the
wireless network. The passphrase is case-sensitive and should not be longer
than 16 alphanumeric characters. Based upon the passphrase created by
you, WEP key settings are automatically generated. This passphrase is only
compatible with other Linksys wireless products.
Click the Next button to continue or the Back button to return to the previous screen. Then on the WEP Key Settings screen, you will see the automatically generated WEP key. Click the Next button, and proceed to step 10.
13
Instant Wireless®Series
7. The IP Settings screen will appear next, shown in Figure 5-7. If your net-
work has a DHCP server, click the radio button next to Automatically
obtain an IP address (DHCP). Click the Next button to continue or the
Back button to return to the previous screen. Then proceed to step 8.
If your network does not have a DHCP server, click the radio button beside
Set IP conf iguration manually to select this option. Enter an IP Address,
IP Mask, and Gateway appropriate to your network. You must specify an IP
address on this screen. If you are unsure about the IP Mask and Gateway, it
is better to leave these two fields blank. Click the Next button to continue or
the Back button to retur n to the previous screen. Then proceed to step 8.
• IP Address - This IP address must be unique to y our network. Because this
is a private IP address, there is no need to purchase a separate IP address
from your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
• IP Mask - The Bridge’s IP Mask (also known as Subnet Mask) must be the
same as your Ethernet (wired) network.
• Gateway - Enter the IP address of your network’s Gateway here.
12
Figure 5-8
Figure 5-7
Page 10

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
11. The conf iguration using the Setup Wizard is complete. To conf igure any
other Bridges on your network, run this Setup Wizard again. To exit the
Setup Wizard, click the Exit button.
The Wireless Ethernet Bridge is now successfully set up for your network.
After you have reset the Bridge, unplug the Ethernet network cable from the
PC, and plug it into the RJ-45 port of the Ethernet-ready network device you
wish to add to the wireless network.
For more advanced configuration, keep the Bridge plugged into the PC,
and proceed to “Chapter 6: Using the Wireless Ethernet Bridge Web-
based Utility.”
15
Instant Wireless®Series
9b. Leave the Passphrase field blank, and click the Next button to continue or
the Back button to return to the previous screen.
If you selected 64-bit WEP, you will see Figure 5-9 (you will see a similar
screen if you choose 128-bit WEP). Enter a WEP key. If you are using 64bit WEP encryption, then the key must consist of exactly 10 hexadecimal
characters in length. If you are using 128-bit WEP encryption, then the key
must consist of exactly 26 hexadecimal characters in length. Valid hexadecimal characters are “0”-“9” and “A”-“F”. Then click the Next button,
and proceed to step 10.
10. Review your settings. Write down the Bridge’s IP Address if you want to
configure advanced settings through the Bridge’s Web-based Utility. Click
the Yes button to save these settings. Click the Back button to make
changes. Click the Exit button to exit the Setup Wizard.
14
Figure 5-11
Important: To activate the new settings, reset the Bridge. Turn off
the Bridge, and wait a few seconds. Then power on the Bridge.
Figure 5-9
Figure 5-10
Page 11

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
2. The Setup screen of the Bridge’s Utility will appear.
The Utility provides a convenient, web browser-based way to alter the
Bridge’s settings. It offers four main tabs:
• Setup - This screen enables you to configure the IP address and wireless
settings.
• Password - Use this tab to change the password or reset all settings to fac-
tory defaults.
• Status - This screen displays the Bridge’s current settings.
• Help - This screen provides explanations of various configuration settings
and links to online technical support resources.
17
Instant Wireless®Series
Chapter 6:Using the Wireless
Ethernet Bridge Web-based
Utility
The Bridge is designed to function properly after configuration using the Setup
Wizard. However, if you would like to change these settings or make more
advanced configuration changes, use your web browser and the Wireless
Ethernet Bridge Web-based Utility. This chapter explains how to use the Utility.
1. Open your web browser, and enter the IP address of the Wireless Ethernet
Bridge (the default is 192.168.1.225). Press the Enter key, and the screen
shown in Figure 6-1 will appear. In lowercase letters, enter admin in the
Password field (the default password is admin). Click the OK button. Y ou
can set a new password on the Password screen later.
16
Figure 6-2
Starting the Web-based Utility
Overview
Figure 6-1
Page 12

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
• MAC Address - The MAC Address of the Bridge is displayed here.
LAN
• Device Name - You may assign any name to the Bridge. Unique, memo-
rable names are helpful, especially if you are using multiple bridges on the
same wireless network.
• IP Address - If the Bridge will obtain an IP address automatically from a
DHCP server, such as a router, then select Obtain an IP address auto-
matically (DHCP). If you are assigning the Bridge a static IP address, then
select Use the following IP settings, and enter an IP Address, Subnet
Mask, and Gateway address in the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway
fields.
Wireless
• SSID - The SSID is the network name shared among all devices in a wire-
less network. The SSID must be identical for all devices in the wireless network. It is case-sensitive and must not exceed 32 alphanumeric characters,
which may be any keyboard character (do not use any spaces). Make sure
this setting is the same for all devices in your wireless network. For added
security, Linksys recommends that you change the default SSID (linksys)
to a name of your choice.
• Network Type - Choose a wireless operating mode for the Bridge. Click
the Infrastructure radio button if you want your wireless-equipped device
to communicate with computers and other devices on your wired network
using a wireless access point. Click the Ad Hoc radio button if you want
multiple wireless-equipped devices to communicate directly with each
other.
If you chose Ad Hoc mode, then select the cor rect operating channel for
your network using the Ad Hoc Wireless Channel drop-down menu. The
channel you choose should match the channel set on the other devices in
your wireless network.
• WEP - To enable WEP encryption, click the Enable radio button. To
increase wireless network security, using WEP encryption is strongly recommended. Then click the WEP Settings button to configure the WEP settings. To disable WEP encryption, keep the default setting, Disable.
19
Instant Wireless®Series
The Setup screen lets you conf igure the wired and wireless network settings
for the Bridge.
• Firmware Version - The version number of the Bridge’s fir mware is dis-
played here. Fir mware should be upgraded from the Help screen ONLY if
you experience problems with the Bridge.
18
Note: You may have to refresh this page to see any new settings.
Setup
Figure 6-3
Page 13

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
• Passphrase - Instead of manually entering WEP keys, you can enter a
Passphrase. This Passphrase is used to generate one or more WEP keys. It
is case-sensitive and should not be longer than 16 alphanumeric characters.
(The Passphrase function is compatible with Linksys wireless products
only. If you want to communicate with non-Linksys wireless products, you
will need to enter your WEP key(s) manually on the non-Linksys wireless
products.) After you enter the Passphrase, click the Generate Keys button
to create WEP key(s).
• Default Key - Select which WEP key (1-4) will be used when the Bridge
sends data. Make sure the other wireless-equipped devices are using the
same key.
• Keys 1-4 - If you are not using a Passphrase, then you can enter one or more
WEP keys manually.
Next to the Key 1 field, select the type of WEP encryption you wish to use
from the drop-down menu. If you want to use 64-bit WEP encryption, then
select 64 bits 10 hex digits. If you want to use 128-bit WEP encryption,
then select 128 bits 26 hex digits.
In each key field, manually enter a set of values. (Do not leave a key field
blank, and do not enter all zeroes. These are not v alid ke y v alues.) If you are
using 64-bit WEP encryption, then each key must consist of exactly 10
hexadecimal characters in length. If you are using 128-bit WEP encryption,
then each key must consist of exactly 26 hexadecimal characters in length.
Valid hexadecimal characters are “0”-“9” and “A”-“F”.
• Authentication Type - To use Open System authentication, keep the default
setting, Open System. To use Shared Key authentication, select the Shar ed
Key radio button. If you want the Bridge to use both authentication types,
select the Both radio button. For Open System authentication, the sender
and the recipient do NOT use a WEP key for authentication. For Shared Key
authentication, the sender and recipient use a WEP key for authentication.
Click the Apply button to save your changes. If your page doesn’t automatically refresh itself, then click the Refresh button of your web browser. Click
the Cancel button to cancel your changes. Click the Help button for additional on-screen information.
21
Instant Wireless®Series
An acronym for Wired Equivalent Privacy, WEP is an encryption method
used to protect your wireless data communications. WEP uses 64-bit or
128-bit keys to pro vide access control to y our netw ork and encryption security for every data transmission. To decode a data transmission, each device
in a network must use an identical WEP key. Higher encryption levels offer
higher levels of security, but due to the complexity of the encryption, they
may decrease network perfor mance.
• Advanced Wireless Settings - To conf igure advanced wireless settings,
such as Transmit Rate, AP Density, and Encryption Filter, click the
Advanced W ireless Settings button.
Click the Apply button to save your changes. If your page doesn’t automatically refresh itself, then click the Refresh button of your web browser. Click
the Cancel button to cancel your changes. Click the Help button for additional on-screen information.
WEP Settings
Use the WEP Settings screen to conf igure the Passphrase or WEP key settings
for your device, as well as the Authentication Type.
20
Figure 6-4
Note: You may have to refresh this page to see any new settings.
Page 14

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
• AP Density - This enables you to specify how many access points are near
the Bridge. Use this feature to reduce channel overlap and interference.
(This setting is available only for a Bridge set to infrastructure mode.)
Low: 1-2 nearby access points
Medium: 3-4 nearby access points
High: 5 or more nearby access points
• Encryption Filter - If you want the Bridge to ignore unencrypted data
transmissions, click the Enabled radio button. If you want the Bridge to
accept unencrypted data transmissions, keep the default setting, Disabled.
Click the Apply button to save your changes. If your page doesn’t automatically refresh itself, then click the Refresh button of your web browser. Click
the Cancel button to cancel your changes. Click the Help button for additional on-screen information.
23
Instant Wireless®Series
Advanced Wireless Settings
Use the Advanced Wir eless Settings screen to conf igure the Transmit Rate, AP
Density, and Encr yption Filter settings.
• Regulatory Domain - The Bridge’s Regulatory Domain is displayed here.
• Transmit Rate - The rate of data transmission should be set depending on
the speed of your wireless network. You can select a specif ic transmission
speed (1, 2, 1 or 2, 5.5, or 11Mbps), or keep the default setting, Automatic,
to have the Bridge automatically adjust the transfer speed for optimal performance and enable the Auto-Fallback feature. Auto-Fallback will negotiate the best possible connection speed between the Bridge and another
wireless-equipped device.
22
Figure 6-5
Note: If you enable the Encryption Filter, you must also configure
and enable WEP encryption.
Note: You may have to refresh this page to see any new settings.
Page 15

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
25
Instant Wireless®Series
The Password screen lets you change the Bridge’s Passw ord and restore the fac-
tory default settings.
• Admin Password - It is strongly recommended that you change the factory default password of the Bridge, which is admin. All users who try to
access the Bridge’s Web-based Utility will be prompted for the Bridge’s
Password. The new Password must not exceed 12 characters in length and
must not include any spaces. Enter the new Password a second time to confir m it.
• Restore Factory Defaults - Click the Yes radio button to reset all configuration settings to their default values. If you do not want to restore the factory defaults, then keep the default setting, No.
To save your changes, click the Apply button. Click the Cancel button to cancel your changes. Click the Help button for additional on-screen information.
24
The Status screen displayed the Bridge’s cur rent status and settings. All information is read-only.
• Device Name - The name you ha ve assigned to the Bridge is displa y ed here.
• Firmware Version - The version number of the Bridge’s fir mware is dis-
played here. F irmware should onl y be upgraded from the Help screen if you
experience problems with the Bridge.
• MAC Address - The MAC Address of the Bridge is displayed here.
Figure 6-6
Note: Any settings you ha ve sa v ed will be lost w hen the default settings are restored.
Figure 6-7
Password Status
Page 16

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
The Help screen offers links to all of the help information for the Web-based
Utility’s screens and the Bridge’s online technical support resources. All information is read-only.
• Linksys Website - Click the Linksys W ebsite link to visit Linksys’s web-
site, www.linksys.com (available if you have an active Internet connection).
27
Instant Wireless®Series
LAN Settings
• IP Address - The Bridge’s IP Address is displayed here.
• Subnet Mask - The Bridge’s Subnet Mask is displayed here.
• Gateway - The Gateway address for the Bridge is displayed here.
LAN Statistics
• Ethernet TX - The number of packets transmitted to the Ethernet network
is displayed here.
• Ethernet RX - The number of packets received from the Ethernet network
is displayed here.
• Wireless TX - The number of packets transmitted to the wireless network
is displayed here.
• Wireless RX - The number of packets received from the wireless network
is displayed here.
Wireless Settings
• SSID - The Bridge’s SSID is displayed here.
• Network T ype - The Bridge’s mode is displayed here.
• Channel - The Bridge’s channel setting is displayed here.
• WEP - The status of the Bridge’s WEP encryption is displayed here.
Click the Refresh button to obtain the most up-to-date settings and statistics.
Click the Help button for additional on-screen information.
26
Figure 6-8
Help
Page 17

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
29
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
This section provides solutions to potential problems re garding the installation and
operation of the W ireless Ethernet Bridge. If you can’t find an answ er here, check
the Linksys website at www.linksys.com.
1. I can’t connect to the access point.
Open the Web-based Utility. On the Setup tab, perform the following steps:
• Verify that the operating mode is set to Infrastructure mode.
• Make sure that the SSID is the same as the SSID of the access point.
• On the WEP Settings screen, make sure that all of the WEP settings are
the same as the WEP settings of the access point.
2. I don’t know how to change the Bridge’s IP address.
You have two ways to change the Bridge’s IP address.
• Open the Web-based Utility. On the Setup screen, click the Use the follow-
ing IP settings radio button, and change the IP address there.
• If you encounter problems, power the Bridge off and on again, or push the
Reset button. Then try to change the IP address again.
3. The Bridge-enabled PC won’t communicate with a wireless-enabled PC or
printer.
Perform the following steps:
• Check that the wireless-enabled PC or printer is on the same wireless net-
work as the PC using the Bridge.
• Make sure that the SSID and operating mode are the same for all devices
connected to the same wireless network.
• If the wireless LAN settings are okay, make sure that all the devices are
on the same IP network.
4. The Web-based Utility doesn’t detect the Bridge.
Make sure that the Ethernet cable is properly connected and that the LAN
LED is lit. If the LED is not lit, change the position of the X-II selection
switch on the Bridge’s rear panel. Use the X setting if you are connecting
the Bridge to a network card or other Ethernet device. Use the II setting if
you are connecting the Bridge to a hub or switch.
Common Problems and Solutions
Instant Wireless®Series
• Online Manual in PDF Format - Click the Online manual in PDF format to view this User Guide on-screen. It is in Adobe Acrobat Portable
Document File (.pdf) format, so you will need the free Adobe Acrobat
Reader to view the pdf. If you do not have the Reader, click the Adobe
Website link to download it.
• Adobe Website (to obtain a PDF reader if required) - If you need to
download the Adobe Acrobat Reader to view the User Guide pdf, then click
the Adobe Website link.
28
Page 18

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
31
Instant Wireless®Series
5. The Web-based Utility won’t open.
Make sure that you have a LAN card (also known as a network adapter)
installed on the PC so you can use the Web-based Utility.
6. The Web-based Utility does not recognize my password.
The password is case-sensitive. Make sure you are using the correct case(s)
when entering the password.
If you forget your password, you can push the Bridge’s Reset button. This
will reset the password to the default setting; however, all other Bridge settings will be reset to the factory defaults as well. To use the default settings,
leave the User Name field blank, and enter admin in the Password field.
7. After I make changes through the Web-based Utility,the new settings aren’t displayed on-screen.
Click the Refreshbutton of your web bro wser. If the new settings aren’t displayed, then unplug the power adapter from the Bridge. Plug the power
adapter back in, and then click the Refresh button again.
What is the IEEE 802.11b standard?
It is one of the IEEE standards for wireless networks. The 802.11b standard
allows wireless networking hardware from different manufacturers to communicate, provided that the hardware complies with the 802.11b standard. The
802.11b standard states a maximum data transfer rate of 11Mbps and an oper-
ating frequency of 2.4GHz.
What IEEE 802.11b features are supported?
The product supports the following IEEE 802.11 functions:
• CSMA/CA plus Acknowledge protocol
• Multi-Channel Roaming
• Automatic Rate Selection
• RTS/CTS feature
• Fragmentation
• Power Management
Can I run an application from a remote computer over the wireless network?
This will depend on whether or not the application is designed to be used over
a network. Consult the application’s user guide to determine if it supports operation over a network.
30
Can I play multiplayer games with other users of the wireless network?
Yes, as long as the game suppor ts multiple players over a LAN. Refer to the
game’s user guide for more information.
What is ad-hoc mode?
When a wireless network is set to ad-hoc mode, the wireless-equipped computers are configured to communicate directly with each other. The ad-hoc
wireless network will not communicate with any wired network.
What is infrastructure mode?
When a wireless network is set to infrastructure mode, the wireless network is
configured to communicate with a wired network through a wireless access
point.
What is roaming?
Roaming is the ability of a portable computer user to communicate continuously while mo ving freel y throughout an area greater than that co vered b y a single wireless network access point. Before using the roaming function, the
workstation must make sure that it is the same channel number as the wireless
network access point of the dedicated coverage area.
To achieve true seamless connectivity, the wireless LAN must incorporate a
number of different functions. Each node and wireless network access point,
for example, must always acknowledge receipt of each message. Each node
must maintain contact with the wireless network even when not actually transmitting data. Achieving these functions simultaneously requires a dynamic RF
networking technology that links wireless network access points and nodes. In
such a system, the user’s end node undertakes a search for the best possible
access to the system. First, it ev aluates such factors as signal strength and quality, as well as the message load currently being carried by each wireless network access point and the distance of each wireless network access point to the
wired backbone. Based on that information, the node next selects the right
wireless network access point and registers its address. Communications
between end node and host computer can then be transmitted up and down the
backbone.
As the user moves on, the end node’s RF transmitter regularly checks the system to determine whether it is in touch with the original wireless network
access point or whether it should seek a new one. When a node no longer
receives acknowledgment from its original wireless network access point, it
undertakes a new search. Upon finding a new wireless network access point, it
then re-registers, and the communication process continues.
Frequently Asked Questions
Page 19

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
33
Instant Wireless®Series
32
What is WEP?
WEP is Wired Equivalent Privacy, a data privacy mechanism based on a 40/64
bit shared key algorithm, as described in the IEEE 802.11 standard.
Can Instant Wirelessproducts support file and printer sharing?
Instant Wireless products perform the same function as LAN products.
Therefore, Instant Wireless products can work with NetWare, Windows
NT/2000, or other LAN operating systems to support printer or f ile sharing.
What is ISM band?
The FCC and their counterparts outside of the U.S. have set aside bandwidth
for unlicensed use in the ISM (Industrial, Scientific and Medical) band.
Spectrum in the vicinity of 2.4 GHz, in particular, is being made available
worldwide. This presents a tr uly revolutionary opportunity to place convenient
high speed wireless capabilities in the hands of users around the globe.
What is Spread Spectrum?
Spread Spectrum technology is a wideband radio frequency technique developed by the military for use in reliable, secure, mission-critical communications systems. It is designed to trade off bandwidth efficiency for reliability,
integrity, and security. In other words, more bandwidth is consumed than in the
case of narrowband transmission, but the trade-off produces a signal that is, in
effect, louder and thus easier to detect, provided that the receiver knows the
parameters of the spread-spectrum signal being broadcast. If a receiver is not
tuned to the right frequency, a spread-spectrum signal looks like backg round
noise. There are two main alternatives, Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
(DSSS) and Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS).
What is DSSS? What is FHSS? And what are their differences?
Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) uses a narrowband carrier that
changes frequency in a pattern that is known to both transmitter and receiver.
Properly synchronized, the net effect is to maintain a single logical channel. To
an unintended receiver, FHSS appears to be short-duration impulse noise.
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) generates a redundant bit pattern for
each bit to be transmitted. This bit pattern is called a chip (or chipping code).
The longer the chip, the greater the probability that the original data can be
recovered. Even if one or more bits in the chip are damaged during transmission, statistical techniques embedded in the radio can recover the original data
without the need for retransmission. To an unintended receiver, DSSS appears
as low power wideband noise and is rejected (ignored) by most narrowband
receivers.
Would the information be intercepted while transmitting on air?
Instant Wireless products feature two-fold protection in security. On the hardware side, as with Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum technology, it has the
inherent security feature of scrambling. On the software side, Instant Wireless
products offer the encryption function (WEP) to enhance security and access
control. Users can set it up depending upon their needs.
Page 20

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
35
Instant Wireless®Series
34
DNS - The Domain Name System (DNS) is the way that Internet domain
names are located and translated into Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. A
domain name is a meaningful and easy-to-remember “handle” for an Internet
address.
DSSS (Direct-Sequence Spread Spectrum) - DSSS generates a redundant bit
pattern for all transmitted data. This bit pattern is called a chip (or chipping
code). Even if one or more bits in the chip are damaged during transmission,
statistical techniques embedded in the receiver can recover the original data
without the need for retransmission. To an unintended receiver, DSSS appears
as low power wideband noise and is rejected (ignored) by most narrowband
receivers. However, to an intended receiver (i.e. another wireless LAN endpoint), the DSSS signal is recognized as the only valid signal, and interference
is inherently rejected (ignored).
Dynamic IP Address - An IP address that is automatically assigned to a client
station in a TCP/IP network, typically by a DHCP server. Network devices that
serve multiple users, such as servers and printers, are usually assigned static IP
addresses.
ESS (Extended Service Set) - A set of more than two or more BSSs (multiple
access points) forming a single network.
FHSS (Frequency Hopping Spread Spectr um) - FHSS continuously changes
(hops) the carrier frequency of a conventional carrier several times per second
according to a pseudo-random set of channels. Because a fixed frequency is not
used, and only the transmitter and receiver know the hop patterns, interception
of FHSS is extremely difficult.
Firmware - Code that is written onto read-only memory (ROM) or prog rammable read-only memory (PROM). Once firmware has been written onto the
ROM or PROM, it is retained even when the device is turned off.
IEEE - The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. The IEEE
describes itself as “the world's largest technical professional society—promoting the development and application of electrotechnology and allied sciences
for the benefit of humanity, the advancement of the profession, and the wellbeing of our members.”
The IEEE fosters the development of standards that often become national and
international standards. The organization publishes a number of journals, has
many local chapters, and has several lar ge societies in special areas, such as the
IEEE Computer Society.
Appendix B: Glossary
802.11b - One of the IEEE standards for wireless networking hardware.
Products that adhere to a specific IEEE standard will work with each other,
even if they are manufactured by different companies. The 802.11b standard
specifies a maximum data transfer rate of 11Mbps, an operating frequency of
2.4GHz, and WEP encryption for security. 802.11b networks are also referred
to as Wi-Fi networks.
Ad-hoc Network - An ad-hoc network is a group of computers, each with a
wireless adapter, connected as an independent 802.11 wireless LAN. Ad-hoc
wireless computers operate on a peer-to-peer basis, communicating directly
with each other without the use of an access point. Ad-hoc mode is also
referred to as an Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS) or as peer-to-peer
mode, and is useful at a departmental scale or SOHO operation.
Default Gateway - The router used to forward all traffic that is not addressed
to a station within the local subnet.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - A protocol that lets network
administrators centrally manage and automate the assignment of Internet
Protocol (IP) addresses in an organization's network. Using the Internet's set of
protocol (TCP/IP), each machine that can connect to the Internet needs a
unique IP address. When an organization sets up its computer users with a connection to the Internet, an IP address must be assigned to each machine.
Without DHCP, the IP address must be entered manually at each computer and,
if computers move to another location in another part of the network, a new IP
address must be entered. DHCP lets a network administrator supervise and distribute IP addresses from a central point and automatically sends a new IP
address when a computer is plugged into a different place in the network.
DHCP uses the concept of a “lease” or amount of time that a given IP address
will be valid for a computer. The lease time can vary depending on how long a
user is likely to require the Internet connection at a particular location. It’s especially useful in education and other environments where users change frequently. Using very short leases, DHCP can dynamically reconfigure networks
in which there are more computers than there are available IP addresses.
DHCP supports static addresses for computers containing Web servers that
need a permanent IP address.
Page 21

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
MAC Address - The MAC (Media Access Control) address is a unique number assigned by the manufacturer to any Ethernet networking device, such as a
network adapter, that allows the network to identify it at the hardware level.
mIRC - mIRC runs under Windows and provides a graphical interface for logging onto IRC servers and listing, joining, and leaving channels.
Network Mask - Also known as the “Subnet Mask.”
PCMCIA - The PCMCIA (Personal Computer Memory Card International
Association) is an industry group organized in 1989 to promote standards for a
credit card-size memory or I/O device that would fit into a personal computer,
usually a notebook or laptop computer.
Ping (Packet INternet Groper) - An Inter net utility used to deter mine whether
a particular IP address is online. It is used to test and debug a network by sending out a packet and waiting for a response.
RJ-45 - A connector similar to a telephone connector that holds up to eight
wires, used for connecting Ethernet devices.
Roaming - In an infrastructure mode wireless network, this refers to the ability to move out of one access point's range and into another and transparently
reassociate and reauthenticate to the new access point. This reassociation and
reauthentication should occur without user intervention and ideally without
interruption to network connectivity. A typical scenario would be a location
with multiple access points, where users can physically relocate from one area
to another and easily maintain connectivity.
SOHO (Small Office/Home Office) - Refers to any small office or home
office environment.
Static IP Address - A per manent IP address that is assigned to a node in a
TCP/IP network.
Subnet Mask - The method used for splitting IP networks into a series of subgroups, or subnets. The mask is a binary pattern that is matched up with the IP
address to turn part of the host ID address field into a field for subnets.
37
Instant Wireless®Series
IEEE 802.11b - One of the IEEE standards for wireless networks. The 802.11b
standard allows wireless networking hardware from different manufacturers to
communicate, provided that the hardware complies with the 802.11b standard.
The 802.11b standard states a maximum data transfer rate of 11Mbps and an
operating frequency of 2.4GHz.
Infrastructure Network - An infrastructure network is a group of computers
or other devices, each with a wireless adapter, connected as an 802.11 wireless
LAN. In infrastructure mode, the wireless devices communicate with each
other and to a wired network by first going through an access point. An infrastructure wireless network connected to a wired network is referred to as a
Basic Service Set (BSS). A set of two or more BSS in a single network is
referred to as an Extended Service Set (ESS). Infrastr ucture mode is useful at
a corporation scale, or when it is necessary to connect the wired and wireless
networks.
IP Address - In the most widely installed level of the Internet Protocol (IP)
today, an IP address is a 32-binary digit number that identif ies each sender or
receiver of information that is sent in packets across the Internet. When you
request an HTML page or send e-mail, the Internet Protocol part of TCP/IP
includes your IP address in the message (actually, in each of the packets if more
than one is required) and sends it to the IP address that is obtained by looking
up the domain name in the Uniform Resource Locator you requested or in the
e-mail address you're sending a note to. At the other end, the recipient can see
the IP address of the Web page requester or the e-mail sender and can respond
by sending another message using the IP address it received.
IPCONFIG - A utility that provides for querying, def ining and managing IP
addresses within a network. A commonly used utility, under Windows NT and
2000, for configuring networks with static IP addresses.
ISP - An ISP (Internet service provider) is a company that pro vides individuals
and companies access to the Internet and other related services such as website
building and virtual hosting.
LAN - A local area network (LAN) is a g roup of computers and associated
devices that share a common communications line and typically share the
resources of a single processor or server within a small geographic area (for
example, within an office building).
36
Page 22

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
Appendix C: Specifications
Standard IEEE 802.11b,IEEE 802.3
Channels 11 Channels (US,Canada)
13 Channels (Europe)
Ports One RJ-45 (10BaseT)
One Reverse SMA Antenna
Transmit 19 dBm
Receive Sensitivity -83 dBm (typical)
Modulation DSS,BPSK, QPSK, CCK
LEDs Power, LAN,WLAN, Diag
Network Protocol TCP/IP
39
Instant Wireless®Series
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) - A method (protocol) used along with
the IP (Internet Protocol) to send data in the form of message units (datagram)
between netw ork devices over a LAN or WAN. While IP takes care of handling
the actual delivery of the data (routing), TCP takes care of keeping track of the
individual units of data (called packets) that a message is divided into for efficient delivery over the network. TCP is known as a "connection oriented" protocol due to requiring the receiver of a packet to return an acknowledgment of
receipt to the sender of the packet resulting in transmission control.
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) - The basic com-
munication language or set of protocols for communications over a network
(developed specifically for the Internet). TCP/IP defines a suite or group of
protocols and not only TCP and IP.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) - A method (protocol) used along with the IP
(Internet Protocol) to send data in the form of message units (datagram)
between netw ork devices over a LAN or WAN. While IP takes care of handling
the actual delivery of the data (routing), UDP takes care of keeping track of the
individual units of data (called packets) that a message is divided into for efficient delivery over the network. UDP is known as a “connection-less” protocol
due to NOT requiring the receiver of a packet to retur n an acknowledgment of
receipt to the sender of the packet (as opposed to TCP).
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) - A data privacy mechanism based on a 64-
bit shared key algorithm, as described in the IEEE 802.11 standard.
WINIPCFG - Conf iguration utility based on the Win32 API for querying,
defining, and managing IP addresses within a network. A commonly used utility, under Windows 95, 98, and Millennium, for configuring networks with
static IP addresses.
WLAN - A group of computers and associated devices that communicate with
each other wirelessly. If set to infrastructure mode, the WLAN can communicate with a wired network through a wireless network access point.
38
Page 23

Wireless Ethernet Bridge
41
Instant Wireless®Series
Dimensions 4.94" x 3.70" x 1.22"
(125.5 mm x 94 mm x 31 mm)
Unit Weight 7.1 oz. (0.2 kg)
Power 5V DC
Certifications FCC Class B, CE Mark
Operating Temp. 32°F to 122°F (0°C to 50°C)
Storage Temp. -13°F to 158°F (-25°C to 70°C)
Operating Humidity 10% to 90%, Non-Condensing
Storage Humidity 10% to 90%, Non-Condensing
40
Appendix D:Warranty Information
BE SURE TO HAVE YOUR PROOF OF PURCHASE AND A BARCODE
FROM THE PRODUCT’S PACKAGING ON HAND WHEN CALLING.
RETURN REQUESTS CANNOT BE PROCESSED WITHOUT PROOF OF
PURCHASE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL LINKSYS’S LIABILITY EXCEED THE PRICE
PAID FOR THE PRODUCT FROM DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE
USE OF THE PRODUCT, ITS ACCOMPANYING SOFTWARE, OR ITS
DOCUMENTATION. LINKSYS DOES NOT OFFER REFUNDS FOR ANY
PRODUCT.
LINKSYS OFFERS CROSS SHIPMENTS, A FASTER PROCESS FOR PROCESSING AND RECEIVING YOUR REPLACEMENT. LINKSYS PAYS
FOR UPS GROUND ONLY. ALL CUSTOMERS LOCATED OUTSIDE OF
THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AND CANADA SHALL BE HELD
RESPONSIBLE FOR SHIPPING AND HANDLING CHARGES. PLEASE
CALL LINKSYS FOR MORE DETAILS.
Environmental
Page 24

Instant Wireless®Series
Appendix E: Contact Information
For help with the installation or operation of this product, contact Linksys
Technical Support at one of the phone numbers or Inter net addresses below.
Sales Information 800-546-5797 (LINKSYS)
Technical Support 800-326-7114
RMA Issues 949-271-5461
Fax 949-265-6655
E-mail support@linksys.com
Web http://www.linksys.com
FTP Site ftp.linksys.com
42
© Copyright 2002 Linksys,All Rights Reserved.
http://www.linksys.com
 Loading...
Loading...