Page 1

Wireless-G Cable
Gateway
Use this guide to install the following product:
WCG200
User Guide
Page 2

COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS
Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered trademark or
trademark of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries. Copyright © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Other brands and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
FCC STATEMENT
This product has been tested and complies with the specifications for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used according to the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which is found by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to
try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment or devices
• Connect the equipment to an outlet other than the receiver's
• Consult a dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for assistance
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance
20cm between the radiator and your body.
INDUSTRY CANADA (CANADA)
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
The use of this device in a system operating either partially or completely outdoors may
require the user to obtain a license for the system according to the Canadian regulations.
EC DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY (EUROPE)
Linksys declares that the Wireless-G Cable Gateway conforms to the specifications listed below, following the provisions of the European R&TTE directive 1999/5/EC:
• EN 301 489-1, 301 489-17 General EMC requirements for Radio equipment.
• EN 609 50 Safety
• EN 300-328-1, EN 300-328-2 Technical requirements for Radio equipment.
Caution: This equipment is intended to be used in all EU and EFTA countries. Outdoor
use may be restricted to certain frequencies and/or may require a license for operation.
Contact local Authority for procedure to follow.
Note: Combinations of power levels and antennas resulting in a radiated power level of
above 100 mW equivalent isotropic radiated power (EIRP) are considered as not compliant with the above mentioned directive and are not allowed for use within the European
community and countries that have adopted the European R&TTE directive 1999/5/EC.
For more details on legal combinations of power levels and antennas, contact Linksys
Corporate Compliance.
• Linksys vakuuttaa täten että Wireless-G Cable Gateway conforms to the tyyppinen
laite on direktiivin 1999/5/EY oleellisten vaatimusten ja sitä koskevien näiden direktiivien muiden ehtojen mukainen.
• Linksys Group déclare la Wireless-G Cable Gateway conforms to the est conforme
aux conditions essentielles et aux dispositions relatives à la directive 1999/5/EC.
• Belgique:
Dans le cas d'une utilisation privée, à l'extérieur d'un bâtiment, au-dessus d'un
espace public, aucun enregistrement n'est nécessaire pour une distance de moins de
300m. Pour une distance supérieure à 300m un enregistrement auprès de l'IBPT est
requise. Pour une utilisation publique à l'extérieur de bâtiments, une licence de l'IBPT
est requise. Pour les enregistrements et licences, veuillez contacter l'IBPT.
• France:
2.4 GHz Bande : les canaux 10, 11, 12, 13 (2457, 2462, 2467, et 2472 MHz respectivement) sont complétement libres d'utilisation en France (en utilisation intérieur).
Pour ce qui est des autres canaux, ils peuvent être soumis à autorisation selon le
départment. L'utilisation en extérieur est soumis à autorisation préalable et très
restreint.
Vous pouvez contacter l'Autorité de Régulation des Télécommunications
(http://www.art-telecom.fr) pour de plus amples renseignements.
UG-WCG200-31021B-BW
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction 1
The Linksys Cable Gateway 1
Features 1
An Introduction to LANs and WANs 2
IP Addresses 2
Network Setup Overview 4
Chapter 2: Getting to Know the Cable Gateway 5
The Cable Gateway’s Back Panel Ports 5
The Reset Button 6
Rebooting the Cable Gateway 6
The Cable Gateway’s Front Panel LEDs 6
The USB Icon 8
USB Cabling 8
Chapter 3: Connecting the Cable Gateway 9
Overview 9
Ethernet Port Connection 9
USB Port Connection 11
Installing the USB Driver for Windows 98 13
Installing the USB Driver for Windows Millenium 15
Installing the USB Driver for Windows 2000 17
Installing the USB Driver for Windows XP 20
Chapter 4: Configuring the PCs 22
Overview 22
Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows Me 22
Windows 2000 24
Windows XP 26
Chapter 5: Using the Cable Gateway’s
Web-based Utility 28
Assessing the Web-Based Utility 28
The Setup Tab 29
The Wireless Tab 31
The Security Tabs 38
The Access Restriction Tabs 40
The Applications & Gaming Tabs 44
The Administration Tabs 48
The Status Tabs 57
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
D
Page 4

Chapter 1: Introduction
The Linksys Wireless-G Cable Gateway is the all-in-one solution for Internet connectivity in
your home. The Cable Modem function gives you a blazing fast connection to the Internet,
far faster than a dial-up, and without tying up your phone line.
Connect your computer to the Wireless-G Cable Gateway via USB, or take advantage of the
built-in 4-port 10/100 Ethernet Switch to jump start your home network. You can share f iles,
printers, hard drive space and other resources, or play head-to-head PC games. Connect four
PCs directly, or daisy-chain out to more hubs and switches to create as big a network as you
need. The built-in Wireless-G Access Point allows up to 32 wireless devices to connect to your
network at a blazing 54Mbps, without running cables through the house. It's also compatible
with Wireless-B devices, at 11Mbps. The Gateway's Router function ties it all together and
lets your whole network share that high-speed Internet connection.
To protect your data and privacy, the Wireless-G Cable Gateway features an advanced firewall
to keep Internet intruders and attackers out. Wireless transmissions can be protected by powerful data encryption. Safeguard your family with Parental Control features like Internet
Access Time Limits and Key Word Blocking. Conf iguration is a snap with any
web browser.
With the Linksys Wireless-G Cable Gateway at the heart of your home network, you're connected to the future.
• High-speed DOCSIS 2.0-ready Cable Modem gives you a fast, "Always On"
connection to the Internet
• Connect via USB, or use the built-in Router and 4-port Switch to jump start
your Ethernet network and share the Internet throughout your household
• Built-in Wireless-G (802.11g) Access Point also lets you connect without running wires
• Advanced firewall and security features protect your PCs, your data, and your
family
• Supports VPN Pass-Through for IPSec and PPTP Protocols
• Internal 4-Port Switch Dramatically Speeds Up Your Network
• DHCP Server Capability to Assign IP Addresses Automatically
1
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
The Linksys Cable Gateway
Features
F
Appendix A: Troubleshooting 54
Common Problems and Solutions 54
Frequently Asked Questions 55
Appendix B: Configuring Wireless Security in
Windows XP 59
Appendix C: Installing the TCP/IP Protocol 65
Appendix D: Finding the MAC Address and
IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter 67
Appendix E: Glossary 71
Appendix F: Specifications 82
Environmental 83
Appendix G: Warranty Information 84
Appendix H: Contact Information 85
Page 5
Dynamic IP Addresses
A dynamic IP address is automatically assigned to a device on the network,
such as PCs and print servers. These IP addresses are called “dynamic”
because they are only temporarily assigned to the PC or device. After a certain
time period, they expire and may change. If a PC logs onto the network (or the
Internet) and its dynamic IP address has expired, the DHCP server will assign
it a new dynamic IP address.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Servers
DHCP frees you from having to assign IP addresses manually every time a new
user is added to your network. PCs and other network devices using dynamic
IP addressing are assigned a new IP address by a DHCP server. The PC or net-
work device obtaining an IP address is called the DHCP client. By default, the
Cable Gateway’s WAN setting is DHCP client.
A DHCP server can either be a designated PC on the network or another network device, such as the Cable Gateway. By default, the Cable Gateway acts as
a DHCP server for your local network. If you already have a DHCP server running on your network, you must disable that DHCP server or the Cable
Gateway’s DHCP’s feature. If you run more than one DHCP server on your
network, you will experience network errors, such as conflicting IP addresses.
Note: Since the Cable Gateway is a device that connects two networks, it
needs two IP addresses—one for the LAN side, and one for the WAN side.
In this User Guide, you’ll see references to the “WAN IP address” and the
“LAN IP address.”
Since the Cable Gateway has firewall security, the only IP address on your
network that can be seen from the Internet is the Cable Gateway’s WAN IP
address.
32
Simply put, a router is a network device that connects two networks together.
The Cable Gateway has a built-in router that connects your Local Area
Network (LAN), which is the group of PCs in your home or off ice, to the
Wide Area Network (WAN), which is the Internet. The Cable Gateway
processes and regulates the data that travels between these two networks.
Think of the Cable Gateway as a network device with two sides: the first side is
made up of your private Local Area Network (LAN) of PCs. The other, public
side, is the Internet, or the Wide Area Network (WAN), outside of your home or
office.
The Cable Gateway’s firewall protects your network of PCs so users on the public, Internet side cannot “see” your PCs. This is how your local network
remains private. The Cable Gateway protects your network by inspecting the
first packet coming in through the WAN port before delivery to the final destination in the local network. The Cable Gateway inspects Internet port services
like the web server, ftp server, or other Internet applications, and, if allowed,
will forward the packet to the appropriate PC on the LAN side.
What’s an IP Address?
IP stands for Internet Protocol. Every device on an IP-based network, including
PCs, print servers, and routers, requires an IP address to identify its “location,”
or address, on the network. This applies to both the WAN and LAN connections.
There are two ways of assigning an IP address to your network devices.
Static IP Addresses
A static IP address is a fixed IP address that you assign manually to a PC or
other device on the network. Since a static IP address remains valid until you
disable it, static IP addressing ensures that the device assigned it will always
have that same IP address until you change it. Static IP addresses are commonly used with network devices such as server PCs or print servers.
An Introduction to LANs and WANs
IP Addresses
Note: Even if you assign a static IP address to a PC, other PCs can
still use DHCP’s dynamic IP addressing, as long as the static IP
address is not within the DHCP range of the LAN IP Address.
If the Cable Gateway’s DHCP feature fails to provide a dynamic IP
address, refer to “Appendix A: Troubleshooting.”
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
Page 6

5
Chapter 2: Getting to Know the
Cable Gateway
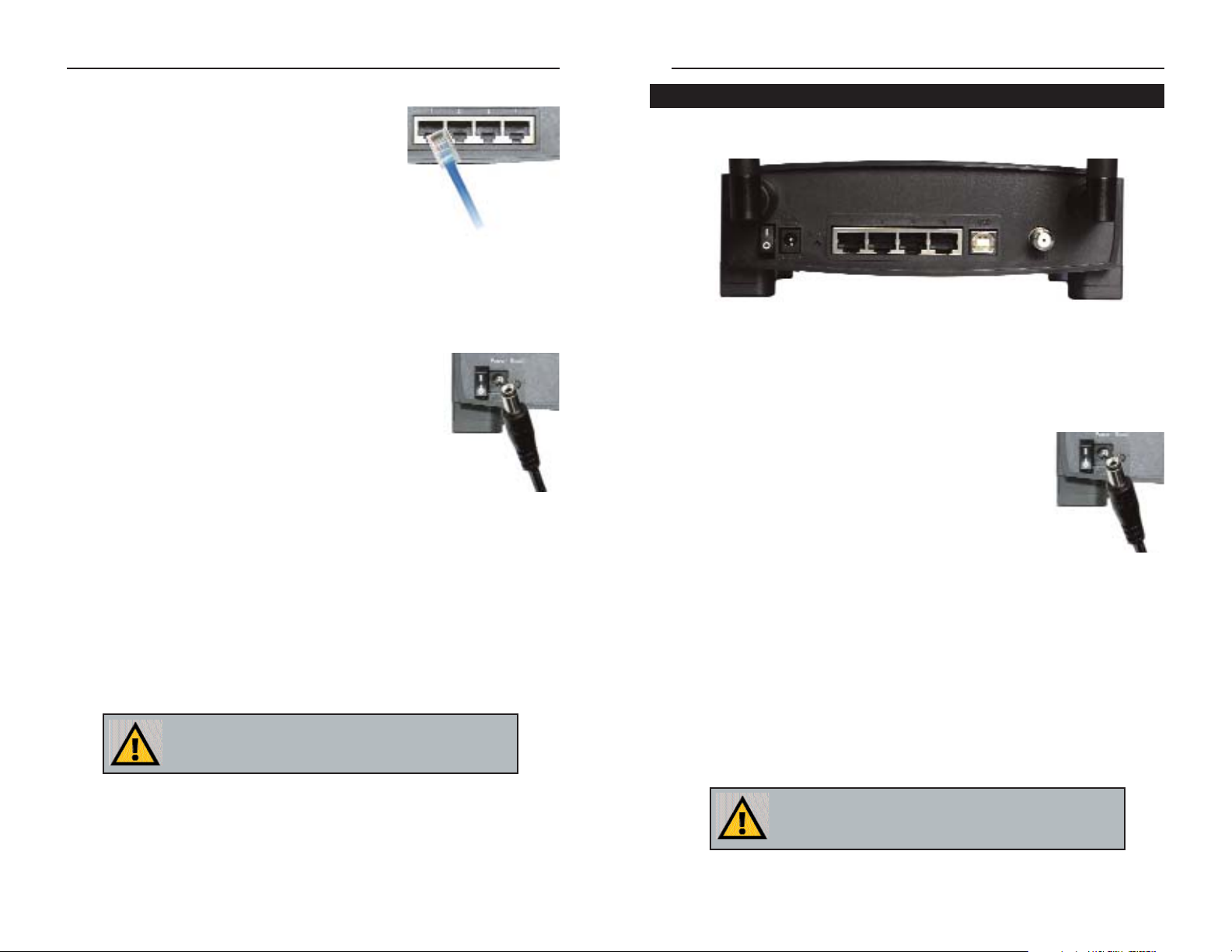
The Cable Gateway’s ports are located on the back panel of the Cable Gateway,
as shown in Figure 2-1.
On/Off Switch This switch is used for turning the Cable Gateway
on and off.
Power The Power port is where you will connect the power
adapter.
Reset Press this button to restore the Cable Gateway to it
factory default settings.
USB This is where you can use a USB cable to connect a
Windows-based to the Cable Gateway.
Ports 1-4 These four ports are used to connect network
devices, such as PCs, print servers, and remote hard
drives to your local area network (LAN).
Cable The Cable port is where you will connect your coax-
ial Cable line.
The Cable Gateway’s Back Panel Ports
Figure 2-1
This user guide covers the basic steps for setting up a network with the Cable
Gateway. After going through the Chapter 2: Getting to Know the Cable
Gateway, proceed through the following chapters:
• Chapter 3: Connecting the Cable Gateway
This chapter instructs you on how to connect the coaxial Cable line to the
Cable Gateway and connect the PC(s) to the Cable Gateway.
• Chapter 4: Configuring the PCs
This chapter instructs you on how to configure your PC(s) for a DHCP connection, if the network settings are not already set to DHCP.
• Chapter 5: Using the Cable Gateway’s Web-based Utility
This chapter explains how to configure the Cable Gateway for wireless networking using your web browser and the Cable Gateway’s web-based utility.
When you’re finished with the basic steps, you are ready to connect to the
Internet through your new network. An example of such a network is shown in
Figure 1-1.
4
Network Setup Overview
Notebook with
Ethernet Adapter
Wireless-G
Cable Gateway
LAN
PC with
Ethernet Adapter
WAN
Figure 1-1
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
Page 7
76
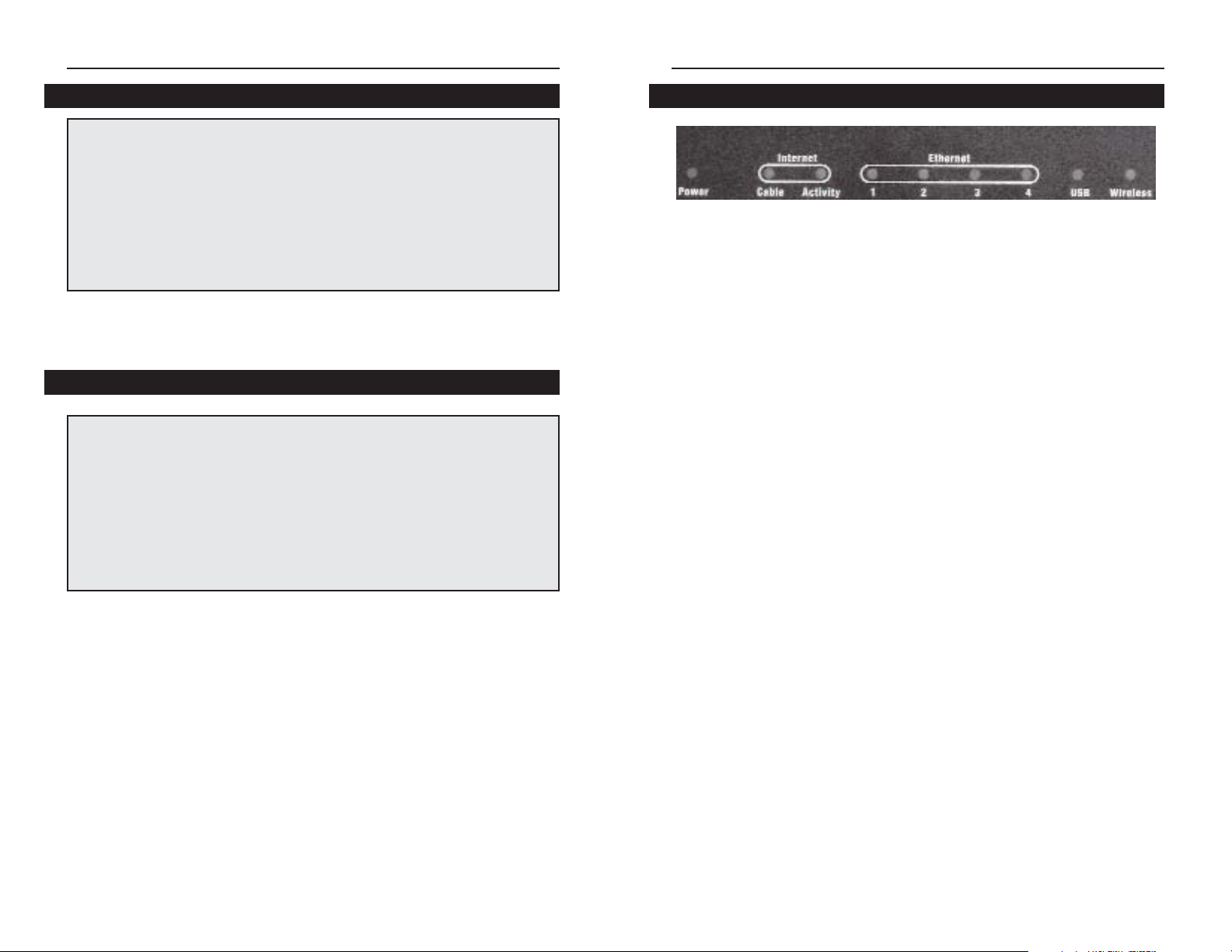
Power Green or red. The Green Power LED is solid when the
Cable Gateway is powered on. If the LED lights up red,
there is an error.
Internet - Cable Green. The Green LED will go through a series of
flashes as the Cable Gateway goes through its startup
and registration process. It will remain solid when
registration is complete and the Cable Gateway is
operational.
Internet -Activity Green. This LED flashes when data is being sent or
received through the cable Gateway interface.
Ethernet-1-4 Green or red. Ethernet 1-4 LED serves multiple pur-
poses. If the LED is solid green, the Cable Gateway is
successfully connected to a device through the corresponding port (1, 2, 3, or 4). If the LED is flashing
green, the Cable Gateway is actively sending or receiving data over that port. If the LED lights up red, there
is a collision.
USB Green or red. The LED is solid green when a PC is
connected to the Cable Gateway via USB, and drivers
are installed. If the LED flashes red, the cable is connected, but the driver isn’t loaded.
Wireless Green or red. The LED flashes green during wireless
activity. If the LED flashes red, there is an error condition.
Proceed to “Chapter 3: Connecting the Cable Gateway.”
The Cable Gateway’s Front Panel LEDs
Figure 2-2
Pressing the Reset Button and holding it in for a few seconds will clear all of
the Cable Gateway’s data and restore the factory defaults. This should be done
only if you are experiencing networking problems and have exhausted all of
the other troubleshooting options. By resetting the Cable Gateway, you run the
risk of creating conflicts between your PCs’ actual IP Addresses and what the
Cable Gateway thinks the IP Addresses of the PCs should be. You may be
forced to reboot each network PC.
The Reset Button
You should only reboot the Cable Gateway after all other troubleshooting
methods have been exhausted but before calling Linksys Technical Support.
There are two ways to reboot the Cable Gateway:
1) Turn the Cable Gateway’s power off for a few seconds and power it back on
again.
2) Unplug the Cable Gateway’s power adapter and plug it back in again.
Rebooting the Cable Gateway may cause conflicts with IP Addresses.
Rebooting the Cable Gateway
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
Page 8

9
Chapter 3: Connecting the Cable
Gateway
You will connect the Cable Gateway to your Cable service’s coaxial cable line
and to the computers in your home or business. With the Cable Gateway, you
can use a standard Ethernet connection or connect via USB. For Ethernet connection continue with the Ethernet Cable Connection section. For USB connection, go to the next section, USB Cable Connection.
First, make sure that all the devices that you’ll be working with are powered
down, including your PCs and the Cable Gateway.
1. Connect the coaxial
cable that is provided
by your cable service
provider to the Cable
port that is on the
back of the Cable
Gateway, as shown in
Figure 3-1.
2. Connect one end of an Ethernet cable to your PC’s Ethernet adapter, as shown
in Figure 3-2.
Note: If your PC’s Ethernet adapter is not set up, please refer to the Ethernet
adapter’s user guide for more information.
Figure 3-1
Figure 3-2
The USB icon, shown in Figure 2-3, marks a USB port on a PC or device.
The Cable Gateway comes with one USB cable. Connect one end of the USB
cable to the Cable Gateway. Connect the other end to a computer’s USB port.
The picture shows two USB ports as they might appear on
your computer. Note the two USB icons marking the
ports.
8
The USB Icon
Figure 2-3
USB Cabling
Figure 5-2
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
Overview
Ethernet Port Connection
Page 9
First, make sure that all the devices that you’ll be working with are powered
down, including your PCs and the Cable Gateway.
1. Connect the coaxial cable that is provided by your cable service provider to
the Cable port that is on the back of the Cable Gateway, as shown in Figure
3-4.
2. Connect one end of a USB cable to your PC’s USB port and connect the other
end of the USB cable to the USB port on the back of the Cable Gateway, as
shown in Figure 3-4.
3. Connect the power adapter to the Cable Gateway, as
shown in Figure 3-5. Plug the other end of the power
adapter into the electrical outlet, preferably a surge protector.
4. Turn on the Cable Gateway. Then, turn on your PC.
5. During the boot up process, your computer should recognize the device and
ask for driver installation.
6. Next, you will need to install the USB Driver. Continue to the section for
your operating system. Return to step 7 after the driver installation.
7. Contact your Cable ISP to activate your account. Your Cable ISP will need
what is called a MAC Address for the cable modem capability of your Cable
Gateway in order to set up your account. The 12-digit MAC address is printed on a bar code label on the bottom of the Cable Gateway. Once you have
given them this number, your ISP should be able to activate your account.
Go
to “Chapter 4: Configuring the PCs.”
11
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
10
3. Connect the other end of the cable to one of the LAN ports on the back of the
Cable Gateway, as shown in Figure 3-3.
Make sure there is an Ethernet cable connected from the Cable Gateway to every
PC that you want on your local network. If you are connecting more than four
PCs to the Cable Gateway via Ethernet, you will also need to connect a hub or
switch to the Cable Gateway.
4. Connect the power adapter to the Cable Gateway,
as shown in Figure 3-4. Plug the other end of the
power adapter into the electrical outlet, preferably
a surge protector.
5. Turn on the Cable Gateway.
6. Contact your Cable ISP to activate your account. Your Cable ISP will need
what is called a MAC Address for the cable modem capability of your Cable
Gateway in order to set up your account. The 12-digit modem MAC
address is printed on a bar code label on the bottom of the Cable Gateway.
Once you have given them this number, your Cable ISP should be able to
activate your account.
7. Then, turn on the first PC that you want to use to configure the Cable
Gateway.
Go to “Chapter 4: Configuring the PCs.”
Figure 3-3
Figure 3-4
USB Port Connection
Figure 3-4
Figure 3-5
Important: Make sure to contact your ISP with your
MAC Address to activate your account.
Important: Make sure to contact your ISP with your
MAC Address to activate your account.
Page 10
3. Select CD-ROM drive as the only location where Windows will search
for the driver software and click the Next button.
4. Windows will notify you that it has identified the appropriate driver and is
ready to install it. Click the Next button.
13
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
1. When the Add New Hardware Wizard window appears, insert the Setup CD
into your CD-ROM drive and click Next.
2. Select Search for the best driver for your device and click the Next but-
ton.
12
Installing the USB Driver for Windows 98
Figure 3-1
Figure 3-2
Figure 3-3
Figure 3-4
Page 11
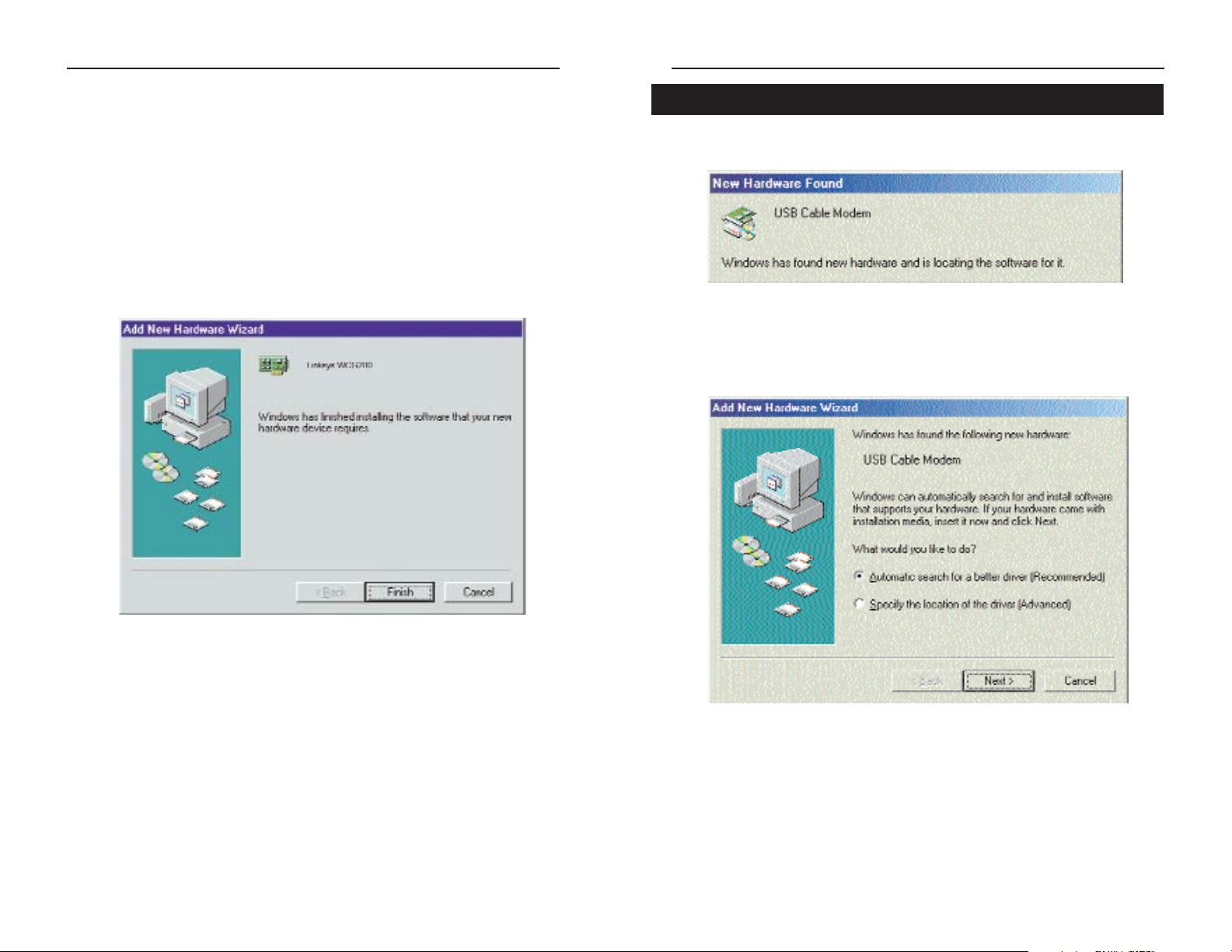
1. Start up your PC in Windows Millennium. Windows will detect new hardware connected to your PC.
2. Insert the Setup CD into your CD-ROM drive. When Windows asks you
for the location of the best driver, select Automatic search for a better
driver (Recommended) and click the Next button.
3. Windows will begin installing the driver for the modem. At this point, the
installation may require files from your Windows Millennium CD-ROM. If
prompted, insert your Windows Millennium CD-ROM into your CD-ROM
drive and enter d:\win9x in the box that appears (where “d” is the letter of
your CD-ROM drive). If you were not supplied with a Windows CD-ROM,
your Windows files may have been placed on your hard drive by your computer manufacturer. While the location of these files may vary,
15
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
5. Windows will begin installing the driver for the modem. At this point, the
installation may require files from your Windows 98 CD-ROM. If prompted, insert your Windows 98 CD-ROM into your CD-ROM drive and enter
d:\win98 in the box that appears (where “d” is the letter of your CD-ROM
drive). If you were not supplied with a Windows 98 CD-ROM, your
Windows files may have been placed on your hard drive by your computer
manufacturer. While the location of these files may vary, many manufacturers use c:\windows\options\cabs as the path. Try entering this path into
the box. If no files are found, check your computer’s documentation or contact your computer manufacturer for more information.
6. After Windows has completed installing this driver, click Finish.
7. When asked if you want to restart your PC, remove all diskettes and CDROMs from the PC and click Ye s . If Windows does not ask you to restart
your PC, click the Start button, choose Shut Down, choose Restart, then
click Ye s .
The Windows 98 driver installation is complete. Return to the section on
the USB Port Connection to finish the setup.
14
Figure 3-5
Installing the USB Driver for Windows Millennium
Figure 3-6
Figure 3-7
Page 12
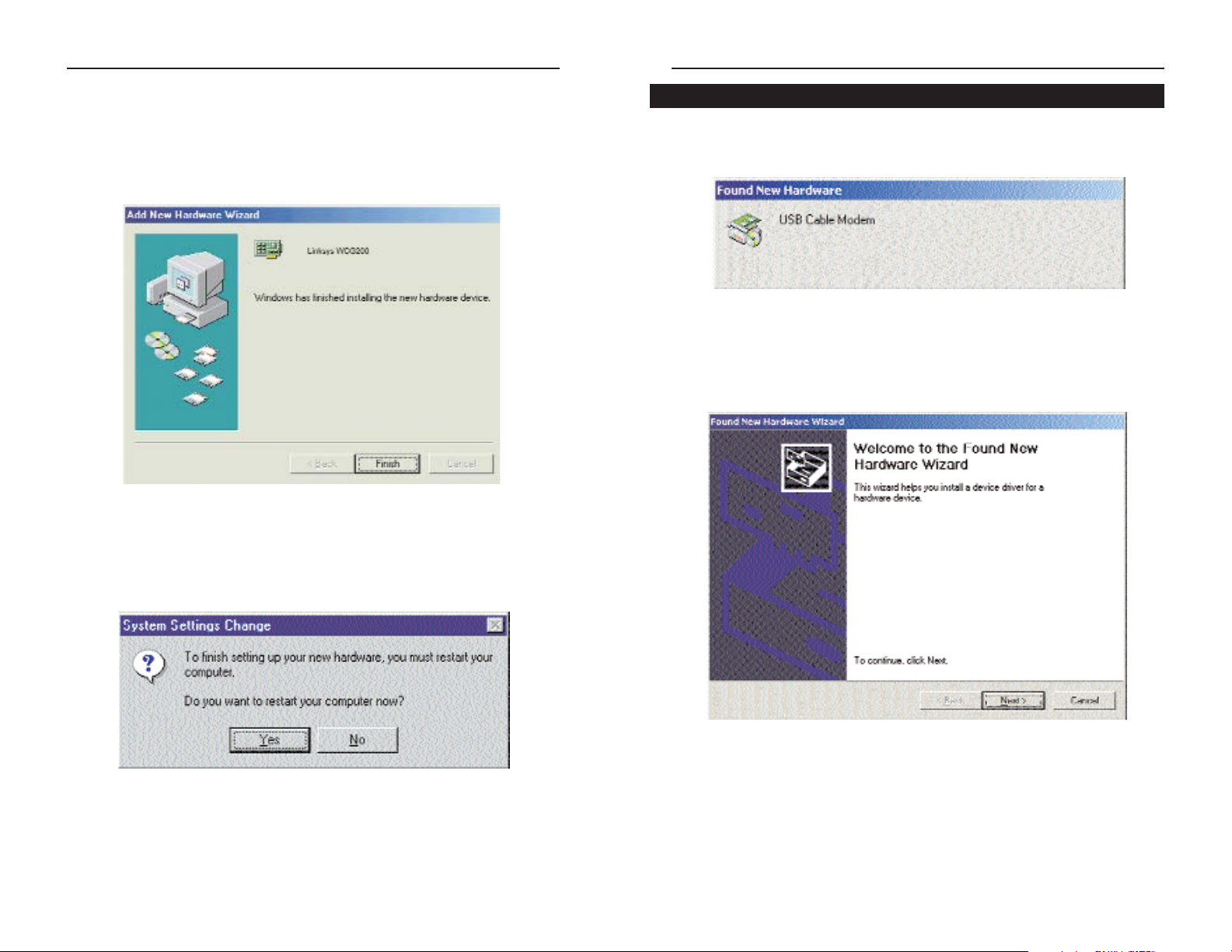
1. Start up your PC. Windows will notify you that it has detected new hardware. Insert the Setup CD into the CD-ROM drive.
2. When the Found New Hardware Wizard screen appears to confirm that
the USB Modem has been identified by your PC, make sure the Setup CD
is in the CD-ROM drive and click Next.
17
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
many manufacturers use c:\windows\options\install as the path. Try
entering this path into the box. If no files are found, check your computer’s documentation or contact your computer manufacturer for more information.
4. When Windows finishes installing the driver, click Finish.
5. When asked if you want to restart your PC, remove all diskettes and CDROMs from the PC and click Ye s . If Windows does not ask you to restart
your PC, click the Start button, choose Shut Down, choose Restart, then
click Ye s .
The Windows Millennium driver installation is complete. Return to the
section on the USB Port Connection to finish the setup.
16
Figure 3-8
Figure 3-9
Installing the USB Driver for Windows 2000
Figure 3-10
Figure 3-11
Page 13
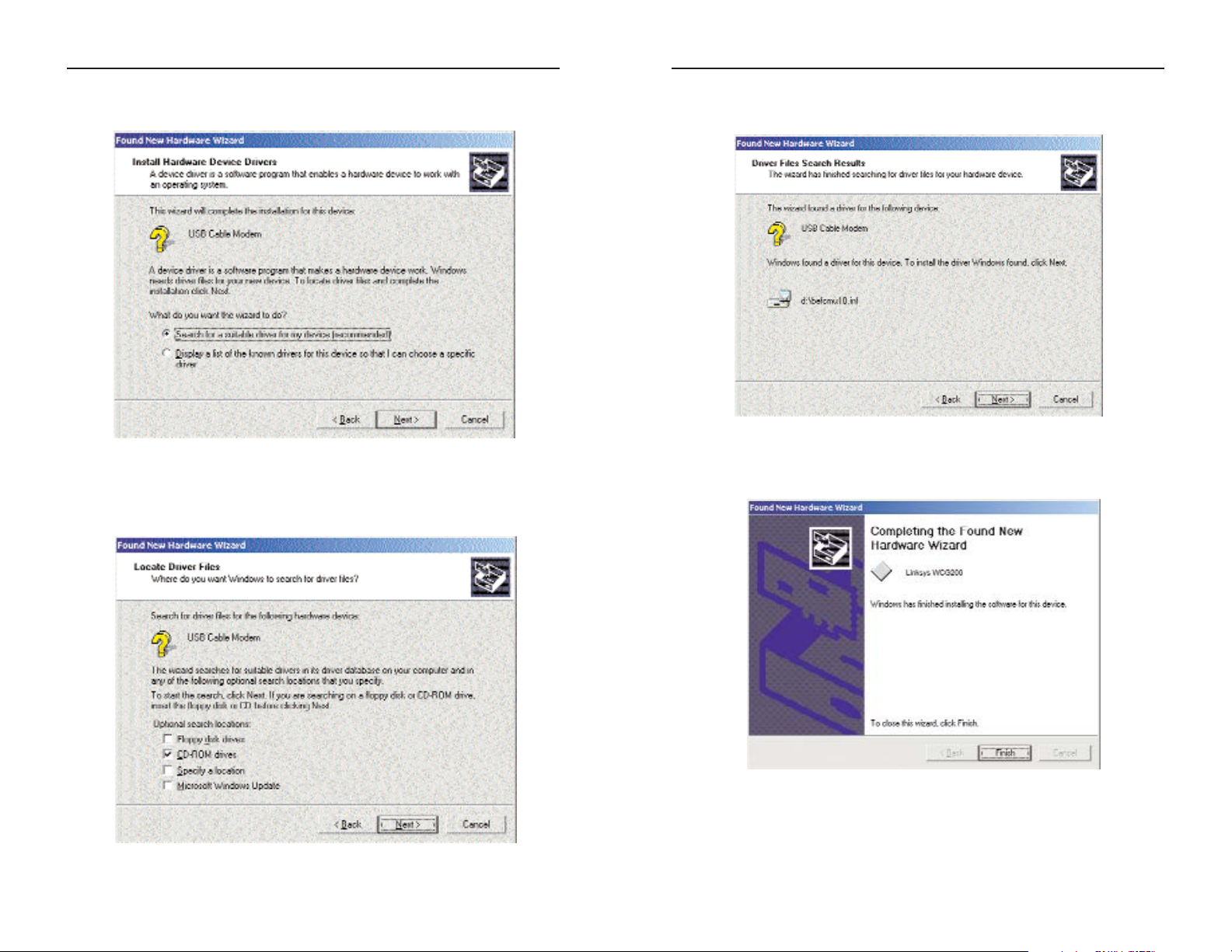
5. Windows will notify you that it has located the appropriate driver and is
ready to install it. Click the Next button.
6. When Windows has completed installing the driver, click Finish.
The Windows 2000 driver installation is complete. Return to the section
on the USB Port Connection to finish the setup.
19
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
3. Select Search for a suitable driver for my device and click the Next but-
ton.
4. Windows will now search for the driver software. Select only CD-ROM
drives and click the Next button.
18
Figure 3-12
Figure 3-13
Figure 3-14
Figure 3-15
Page 14
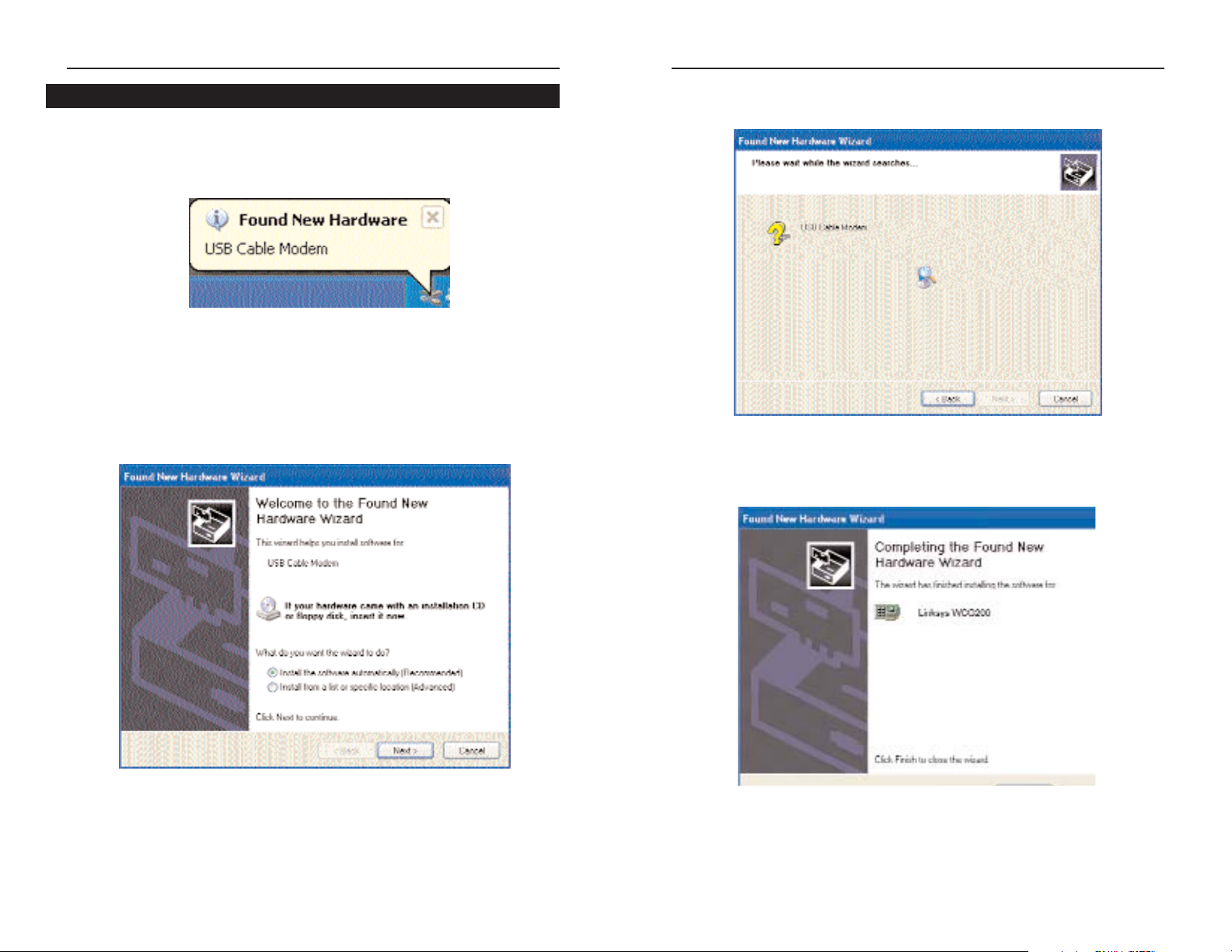
3. Windows will now search for the driver software. Click the Next button.
4. When Windows has completed installing the driver, click Finish.
The Windows XP driver installation is complete. Return to the section
on the USB Port Connection to finish the setup.
21
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
1. Start up your PC. Windows will notify you that it has detected new hardware. Insert the Setup CD into the CD-ROM drive.
2. When the Found New Hardware Wizard screen appears to confirm that the
USB Modem has been identified by your PC, make sure that the Setup CD
is in the CD-ROM drive and click Next.
20
Installing the USB Driver for Windows XP
Figure 3-18
Figure 3-19
Figure 3-16
Figure 3-17
Page 15
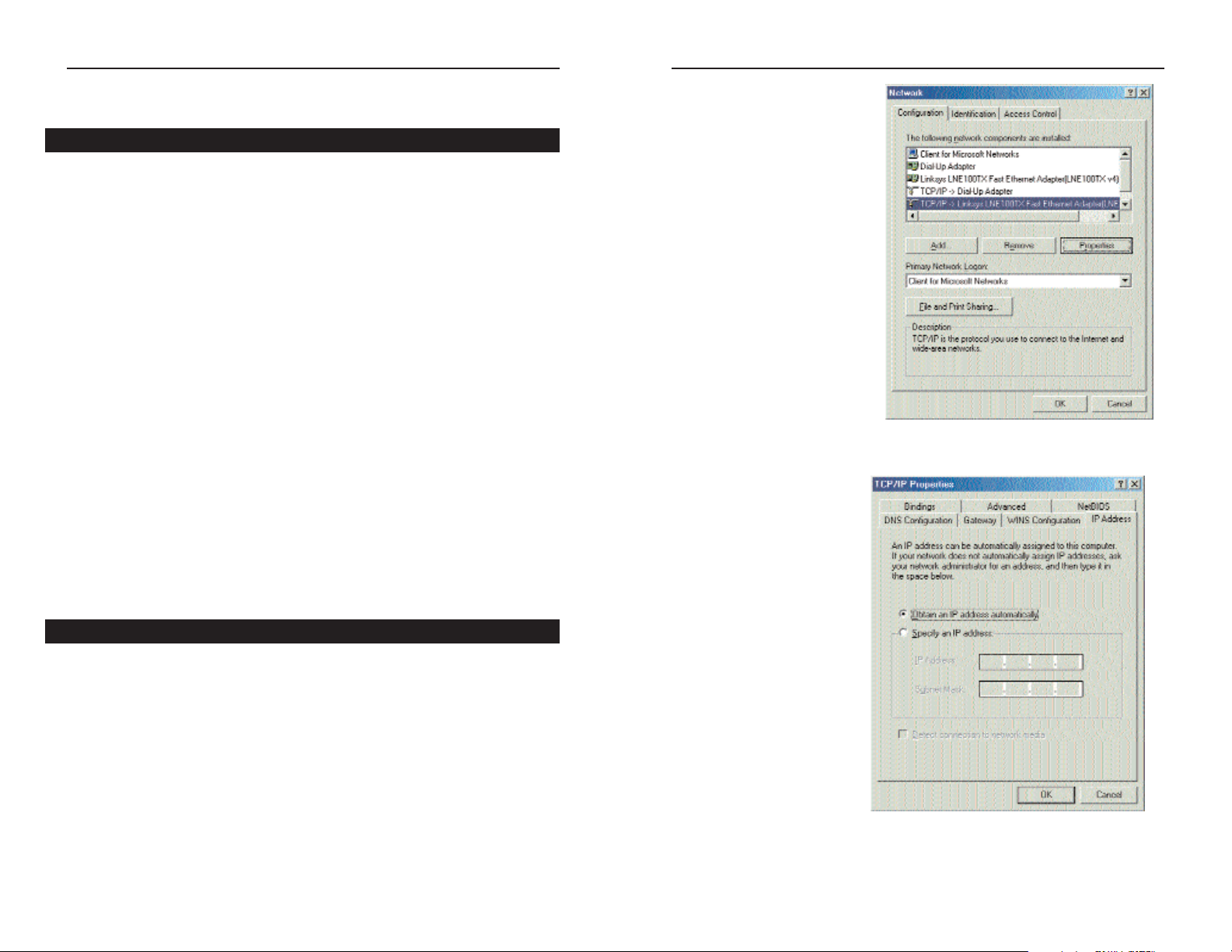
2. On the Configuration tab,
select the TCP/IP line for
the applicable Ethernet
adapter, as shown in Figure
4-1. Do not choose a
TCP/IP entry whose name
mentions DUN, PPPoE,
VPN, or AOL. If the word
TCP/IP appears by itself,
select that line. (If there is
no TCP/IP line listed, refer
to “Appendix C: Installing
the TCP/IP Protocol” or
your Ethernet adapter’s
documentation to install
TCP/IP now.) Click the
Properties button.
3. Click the IP Address
tab. Select Obtain an
IP address automatically, as shown in
Figure 4-2.
23
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
Chapter 4: Configuring the PCs
The instructions in this chapter will help you configure each of your computers to be able to communicate with the Cable Gateway.
To do this, you need to configure your PC’s network settings to obtain an IP (or
TCP/IP) address automatically (called DHCP). Computers use IP addresses to
communicate with each other across a local network or the Internet.
You will need to know which operating system your computer is running, such
as Windows 95, 98, Me, 2000, or XP. One way to find out which operating system you have is by clicking the Start button and selecting the Settings option.
Then, open the Control Panel, and double-click the System icon. The screen
that appears should display your operating system.
You may need to configure each computer you are connecting to the Cable
Gateway.
The next few pages show you, step by step, how to conf igure your network settings based on the type of Windows operating system you are using.
If your operating system is not referenced here, refer to your operating system’s
documentation.
Once you've configured your computers, continue to “Chapter 5: Using the
Cable Gateway’s Web-based Utility.”
1. Go to the Network screen. Do this by clicking the Start button, selecting
Settings and opening the Control Panel. From there, double-click the
Network icon.
22
Figure 4-2
Figure 4-1
Overview
Windows 95, 98, and Me
Page 16

4. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), as shown in Figure 4-4, and click the
Properties button.
5. Select Obtain an IP address automatically, as shown in Figure 4-5. Once
the new window appears, click the OK button. Click the OK button again
to complete the PC configuration.
6. Restart your computer.
Go to “Chapter 5: Using the Cable Gateway’s Web-based Utility.”
25
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
4. Now click the Gateway tab to ensure that the Installed Gateway field is left
blank. Click the OK button.
5. Click the OK button again. Windows may ask you for the original
Windows installation disk or additional files. Supply them by pointing to
the correct file location, e.g., D:\win98, D:\win9x,
c:\windows\options\cabs, etc. (if “D” is the letter of your CD-ROM drive).
6. Windows may ask you to restart your PC. Click the Ye s button. If Windows
does not ask you to restart, restart your computer anyway.
Go to “Chapter 5: Using the Cable Gateway’s Web-based Utility.”
1. Go to the Network screen by clicking the Start button. Click Settings and
then Control Panel. From there, double-click the Network and Dial-up
Connections icon.
2. Select the Local Area Connection icon for the applicable Ethernet adapter
(usually it is the first Local Area Connection listed). Do not choose a
TCP/IP entry whose name mentions DUN, PPPoE, VPN, or AOL. Doubleclick the Local Area Connection.
3. The Local Area
Connection
Status screen will
appear, as shown
in Figure 4-3.
Click the
Properties button.
24
Figure 4-4
Figure 4-5
Windows 2000
Figure 4-3
Page 17

4. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and click the Properties button.
5. Select Obtain an IP address automatically. Once the new window
appears, click the OK button. Click the OK button again (or the Close but-
ton if any settings were changed) to complete the PC configuration.
6. Restart your computer.
Go to “Chapter 5: Using the Cable Gateway’s Web-based Utility”.
27
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
The following instructions assume you are running Windows XP with the
default interface. If you are using the Classic interface (where the icons and
menus look like previous Windows versions), please follow the instructions for
Windows 2000.
1. Open the Network screen. To do this, click the Start button and select the
Control Panel. From there, click the Network and Internet Connections
icon, followed by the Network Connections icon.
2. Select the Local Area Connection icon for the applicable Ethernet adapter
(usually it is the first Local Area Connection listed). Double-click the
Local Area Connection and click the Properties button.
3. The Local Area Connection Status screen will appear. Click the Properties
button.
26
Figure 4-7
Figure 4-8
Windows XP
Figure 4-6
Page 18

29
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
28
The Setup
The first screen that appears is the Setup tab. This tab allows you to change the
Router's general settings. Change these settings as described here and click the
Save Settings button to save your changes or Cancel Changes to cancel your
changes.
Internet Setup
Internet Connection Type. The Router supports two connection types: Obtain
IP Address Automatically (DHCP) (the default connection type), and Set Static
IP Manually. Select the type that is supported by your ISP.
IP Address. This is the Router’s IP address, when seen from the WAN, or the
Internet. Your ISP will provide you with the IP Address you need to specify
here.
Subnet Mask. This is the Router’s Subnet Mask, as seen by external users on
the Internet (including your ISP). Your ISP will provide you with the Subnet
Mask.
Default Gateway. Your ISP will provide you with the Default Gateway
Address, which is the ISP server’s IP address.
The Setup Tab
Figure 5-3
Chapter 5: Using the Cable
Gateway’s Web-based Utility
For your convenience, an administrative utility has been programmed into the
Cable Gateway. From this browser-based utility, you can view the Cable
Gateway’s current status and, when wireless functions are enabled, administer
the wireless settings. This chapter explains all of the functions in this utility.
1. Open your web browser, and
enter 192.168.0.1 into the web
browser’s Address field, as
shown in Figure 5-1. Then,
press the Enter key.
2. An Enter Network Password
window, similar to that shown
in Figure 5-2, appears. Leave
the User Name field empty,
and enter admin (the default
password) in lowercase letters
in the Password field. Then,
click the OK button. Don’t
check the box next Remember
my password,, because you
should change the password
for better network security.
There are seven main tabs: Setup, Wireless, Security, Access Restrictions,
Applications & Gaming, Administration, and Status. Additional tabs are available after you click the main tabs.
Accessing the Web-Based Utility
Figure 5-2
Figure 5-1
Important: Some functions may be changed or
removed depending on your Internet Service
Provider.
Page 19

Basic Wireless Settings
Wireless Network. If you want to disable wireless networking, select Disable.
Wireless Network Name. Enter the Wireless Network Name (SSID) into the
field. The SSID is the network name shared among all devices in a wireless network. The SSID must be identical for all devices in the wireless network. It is
case-sensitive and must not exceed 32 alphanumeric characters, which may be
any keyboard character. Linksys recommends that you change the default SSID
(linksys) to a unique name of your choice.
Wireless Channel. Select the appropriate channel from the list provided to correspond with your network settings, between 1 and 11 (in North America). All
devices in your wireless network must use the same channel in order to function correctly.
Wireless Network Type. If you have Wireless-G and 802.11b devices in your
network, then keep the default setting, Mixed. If you have only Wireless-G
devices, select G-Only. If you want to disable wireless networking, select
Disable.
Current Encryption method will be listed.
To save your changes on this page, click the Save Settings button. To cancel
any unsaved changes on this page, click the Cancel Changes button.
31
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
Primary DNS. (Required) and Secondary DNS (Optional). Your ISP will provide you with at least one DNS (Domain Name System) Server IP Address.
Optional Settings (required by some ISPs)
Host Name and Domain Name. These fields allow you to supply a host and
domain name for the Router. Some ISPs require these names as identification.
You may have to check with your ISP to see if your broadband Internet service
has been configured with a host and domain name. In most cases, leaving these
fields blank will work.
Network Setup
Gateway IP. The values for the Router’s Local IP Address is shown here. In
most cases, keeping the default value will work.
Local IP Address The default value is 192.168.0.1.
Network Address Server Settings (DHCP) A Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP) server automatically assigns an IP address to each PC on
your network for you. Unless you already have one, it is highly recommended
that you leave the Router enabled as a DHCP server.
Local DHCP Server. DHCP is already enabled by factory default. If you
already have a DHCP server on your network, set the Router’s DHCP option to
Disable. If you disable DHCP, remember to assign a static IP address to the
Router.
Start IP Address. Enter a value for the DHCP server to start with when issuing IP addresses. This value must be 192.168.0.2 or greater, because the default
IP address for the Router is 192.168.0.1.
Number of Address (Optional). Enter the maximum number of PCs that you
want the DHCP server to assign IP addresses to. This number cannot be greater
than 253. In order to determine the DHCP IP Address range, add the starting
IP address (e.g., 10) to the number of DHCP users. By default, as shown in
Figure 5-3, add 10 to 245 and subtract 1, and the range is 192.168.0.1o to
192.168.0.254.
DHCP Address Range. The range of DHCP addresses is displayed here.
Time Setting. This is where you set the time for your Router. You can set it manually or automatically.
To save your changes on this page, click the Save Settings button. To cancel
any unsaved changes on this page, click the Cancel Changes button.
30
The Wireless Tab
Figure 5-4
Page 20

33
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
Wireless Security
Wireless SSID Broadcast. When wireless clients survey the local area for
wireless networks to associate with, they will detect the SSID broadcast by the
Router. To broadcast the Router's SSID, keep the default setting, Enabled. If
you do not want to broadcast the Router's SSID, then select Disabled.
Wireless Encryption Level. An acronym for Wired Equivalent Privacy, WEP
is an encryption method used to protect your wireless data communications.
WEP uses 64-bit or 128-bit keys to provide access control to your network and
encryption security for every data transmission. To decode data transmissions,
all devices-Wireless-G and 802.11b-in a network must use an identical WEP
key. Higher encryption levels offer higher levels of security, but due to the
complexity of the encryption, they may decrease network performance. If you
select 64-Bit Encryption, you will see the screen in Figure 5-6. If you select
128-Bit Encryption, you will see the screen in Figure 5-7. If you don’t want to
use WEP security, select No Encryption.
To save your changes on this page, click the Save Settings button. To cancel
any unsaved changes on this page, click the Cancel Changes button.
32
64-Bit Encryption
Default Key. Select which WEP key (1-4) will be used when the Router sends
data. Make sure the receiving device is using the same key.
Passphrase for Keys. Instead of manually entering WEP keys, you can enter a
Passphrase. This Passphrase is used to generate one or more WEP keys. It is
case-sensitive and should not be longer than 16 alphanumeric characters. (This
Passphrase function is compatible with Linksys wireless products only. If you
want to communicate with non-Linksys wireless products, enter the WEP key
manually on the non-Linksys wireless products.) After you enter the
Passphrase, click the Generate button to create WEP keys.
Wireless WEP Keys 1-4. WEP keys enable you to create an encryption scheme
for wireless LAN transmissions. If you are not using a Passphrase, then manually enter a set of values. (Do not leave a key field blank, and do not enter all
zeroes. These are not valid key values.)
For 64-bit WEP encryption, the key must be exactly 10 hexadecimal characters
in length.
When finished making your changes on this tab, click the Save Settings button
to save these changes, or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your
changes.
Figure 5-6
Figure 5-5
Page 21

35
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
128-Bit Encryption
Default Key. Select which WEP key (1-4) will be used when the Router sends
data. Make sure the receiving device is using the same key.
Passphrase for Keys. Instead of manually entering WEP keys, you can enter a
Passphrase. This Passphrase is used to generate one or more WEP keys. It is
case-sensitive and should not be longer than 16 alphanumeric characters. (This
Passphrase function is compatible with Linksys wireless products only. If you
want to communicate with non-Linksys wireless products, enter the WEP key
manually on the non-Linksys wireless products.) After you enter the
Passphrase, click the Generate button to create WEP keys.
Wireless WEP Keys 1-4. WEP keys enable you to create an encryption scheme
for wireless LAN transmissions. If you are not using a Passphrase, then manually enter a set of values. (Do not leave a key field blank, and do not enter all
zeroes. These are not valid key values.)
For 128-bit WEP encryption, the key must be exactly 26 hexadecimal characters in length. Valid hexadecimal characters are “0”-“9” and “A”-“F”.
When finished making your changes on this tab, click the Save Settings button
to save these changes, or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your
changes.
34
Wireless Network Access
Wireless Network Access. If this function is enabled, only the computers on
the list will be allowed access to the wireless network. To add a computer to the
network, click Enabled to enable the function. Then, enter the MAC address in
the fields, and click the Select MAC Address From Networked Computers
button, and the screen in Figure 5-9 will appear.
Select the MAC Address from the list, and click the Add button. Click the
Refresh button if you want to refresh the screen. Click the Close button to
return to the previous screen.
When finished making your changes on this tab, click the Save Settings button
to save these changes, or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your
changes.
Figure 5-8
Figure 5-9
Figure 5-7
Page 22

the next DTIM with a DTIM Interval value. Its clients hear the beacons and
awaken to receive the broadcast and multicast messages.
Fragmentation Threshold. This value should remain at its default setting of
2346. The range is 256-2346 bytes. It specifies the maximum size for a packet
before data is fragmented into multiple packets. If you experience a high packet error rate, you may slightly decrease the Fragmentation Threshold. Setting
the Fragmentation Threshold too low may result in poor network performance.
Only minor modifications of this value are recommended.
RTS Threshold. This value should remain at its default setting of 2347. The
range is 0-2347 bytes. Should you encounter inconsistent data flow, only minor
modifications are recommended. If a network packet is smaller than the preset
RTS threshold size, the RTS/CTS mechanism will not be enabled. The Router
sends Request to Send (RTS) frames to a particular receiving station and negotiates the sending of a data frame. After receiving an RTS, the wireless station
responds with a Clear to Send (CTS) frame to acknowledge the right to begin
transmission.
Authentication Type. The default is set to Open System or Shared Key,
which allows either Open System or Shared Key authentication to be used. For
Open System authentication, the sender and the recipient do NOT use a WEP
key for authentication. For Shared Key authentication, the sender and recipient
use a WEP key for authentication. If you want to use only Shared Key authentication, then select Shared Key.
When finished making your changes on this tab, click the Save Settings button
to save these changes, or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your
changes.
37
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
Advanced Wireless Settings
Advanced Wireless
On this screen you can access the Advanced Wireless features of Basic Data
Rates, Control Tx Rates, Beacon Interval, DTIM Interval, Fragmentation
Threshold, RTS Threshold, and Authentication Type. Note - these adveance settings typically do not need to be modified.
Basic Data Rates. Select Min or All from the drop-down menu for rate.
Control Tx Rates. Select Min or All from the drop-down menu for the trans-
mission rate. All will negotiate the best possible connection speed between the
Router and a wireless client.
Beacon Interval. The default value is 100. Enter a value between 1 and 65,535
milliseconds. The Beacon Interval value indicates the frequency interval of the
beacon. A beacon is a packet broadcast by the Router to synchronize the wireless network.
DTIM Interval The default value is 3. This value, between 1 and 255 milliseconds, indicates the interval of the Delivery Traffic Indication Message
(DTIM). A DTIM field is a countdown field informing clients of the next
window for listening to broadcast and multicast messages. When the Router
has buffered broadcast or multicast messages for associated clients, it sends
36
Figure 5-10
Page 23

39
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
Firewall
When you click the Security tab, you will see the Firewall screen (see Figure
5-11). This screen contains Filters and Block WAN Requests. Filters block
specific internal users from accessing the Internet and block anonymous
Internet requests and/or multicasting.
Firewall Protection. To add Firewall Protection, click Enabled. If you do not
want Firewall Protection, click Disabled.
Filter Proxy. Use of WAN proxy servers may compromise the Router's security. Denying Filter Proxy will disable access to any WAN proxy servers. To
enable proxy filtering, click Enabled.
Filter Cookies. A cookie is data stored on your PC and used by Internet sites
when you interact with them. To enable cookie filtering, click Enabled.
Filter Java Applets. Java is a programming language for websites. If you
deny Java Applets, you run the risk of not having access to Internet sites created using this programming language. To enable Java Applet filtering, click
Enabled.
Filter ActiveX. ActiveX is a programming language for websites. If you deny
ActiveX, you run the risk of not having access to Internet sites created using
this programming language. To enable ActiveX filtering, click Enabled.
38
Filter Multicast. Multicasting allows for multiple transmissions to specific
recipients at the same time. If multicasting is permitted, then the Router will
allow IP multicast packets to be forwarded to the appropriate computers.
Select Enable to filter multicasting, or Disable to disable this feature.
Block Anonymous Internet Requests. This keeps your network from being
“pinged” or detected and reinforces your network security by hiding your network ports, so it is more difficult for intruders to work their way into your
network. Select Enable to block anonymous Internet requests, or Disable to
allow anonymous Internet requests.
When finished making your changes on this tab, click the Save Settings button to save these changes, or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your
changes.
VPN Passthrough
Virtual Private Networking (VPN) is a security measure that creates a secure
connection between two remote locations by using specific settings. The
VPN Passthrough screen, shown in Figure 5-12, allows you to configure your
VPN settings to make your network more secure.
IPSec Passthrough. Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is a suite of protocols
used to implement secure exchange of packets at the IP layer. To allow IPSec
Passthrough, click the Enabled button. To disable IPSec Passthrough, click
the Disabled button.
PPTP Passthrough. Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol Passthrough is the
method used to enable VPN sessions to a Windows NT 4.0 or 2000 server. To
allow PPTP Passthrough, click the Enabled button. To disable PPTP
Passthrough, click the Disabled button.
When finished making your changes on this tab, click the Save Settings button to save these changes, or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your
changes.
Figure 5-12
Figure 5-11
The Security Tabs
Page 24

Website Blocking
Keyword Blocking. To block a keyword, click Enable. Enter a keyword in the
New Keyword field, then clickAdd. To remove a keyword from being blocked,
select the keyword from the Keyword List, then click Remove.
Website Blocking. To block a website, click Enable. Then click Deny
Websites in List. Enter the website address in the New Website field, then
click Add. To remove a website from being blocked, select Allow Websites in
List, select the website from the Website List, then click Remove.
Scheduling. Select Always block or Block from and select a range of time and
days.
Timed Access
This screen is used to add or remove access from a computer on your network
by days and time.
Add/Remove a Host. Click Enabled. To select a specific computer that you
want to block or allow access, click Select MAC Address from Networked
Computers, and the screen in Figure 5-15 will appear.
41
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
The Access Restrictions tabs, shown in Figure 5-13, allow you allows you to
block or allow specific kinds of Internet usage.
40
Figure 5-14
The Access Restrictions Tabs
Figure 5-13
Page 25

43
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
Select the MAC Address from the list, click the Select button , and click the
Add button. Click the Refresh button if you want to refresh the screen. Click
the Close button to return to the previous screen. When you return to the Timed
Access screen, the MAC Address will appear in the f ields. Select a filter from
the drop-down list, if desired, then click either the Add button, or the Remove
button, as appropriate.
Day to Block. You can select Everyday or specified days to block or allow.
Time to Block. You can select All day, or a range of time.
42
Filter Internet Traffic
This screen is used to filter Internet traffic by IP Address Range or by Port
Range.
Filtering Rules. You can filter by IP Address Range or Port Range.
IP Address Range
To set up a filter using IP addresses, enter the range of IP addresses you wish
to filter in the Start and End fields. Users who have filtered IP addresses will
not be able to access the Internet at all. If you only want to filter one IP address
instead of a range of IP addresses, enter the same value into both fields. For
instance, if you wish to filter the PC with the IP address of 192.168.0.5, enter
5 into both fields on one line: 192.168.0.5 ~ 192.168.0.5.
Port Range
To filter users by network port number, select the protocol you want to filter,
TCP, UDP, or Both, in the Protocol drop-down box. Enter the port numbers
you want to filter in the Start and End fields. Users connected to the Router
will no longer be able to access any port number listed there.
When finished making your changes on this tab, click the Save Settings button to save these changes, or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your
changes.
Figure 5-16
Figure 5-15
Page 26

Port Range Forwarding
Port Range. To add a server using Port Range Forwarding, complete the fol-
lowing fields:
Application. Enter the name of the application.
Start and End. Enter the number or range of external ports(s) used by the serv-
er or Internet application. Check with the Internet application software documentation for more information.
Protocol. Select the protocol TCP or UDP, or select Both.
IP Address. Enter the IP address of the server that you want the Internet users
to be able to access. To find the IP address, go to “Appendix D: Finding the
MAC Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter.”
Enabled. Check the Enabled box to enable the services you have defined. Port
Range Forwarding will not function if the Enabled button is left unchecked.
This is disabled (unchecked) by default.
When finished making your changes on this tab, click the Save Settings button
to save these changes, or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your
changes.
45
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
When you click the Applications & Gaming tab, you will see the Port Range
Forwarding screen (see Figure 5-17). Port Range Forwarding sets up public
services on your network, such as web servers, ftp servers, e-mail servers, or
other specialized Internet applications. (Specialized Internet applications are
any applications that use Internet access to perform functions such as videoconferencing or online gaming. Some Internet applications may not require any
forwarding.) When users send this type of request to your network via the
Internet, the Router will forward those requests to the appropriate PC.
Before using Forwarding, you should assign a static IP address to the designated PC.
If you need to forward all ports to one PC, click the DMZ tab.
44
Figure 5-18
The Applications & Gaming Tabs
Figure 5-17
Page 27

DMZ
The DMZ screen allows one local user to be exposed to the Internet for use of
a special-purpose service such as Internet gaming and videoconferencing.
Whereas Port Range Forwarding can only forward a maximum of 10 ranges of
ports, DMZ hosting forwards all the ports for one PC at the same time.
DMZ. To use this feature, select Enable. To disable DMZ hosting, select
Disable.
DMZ Host IP Address. To expose one PC, enter the computer’s IP address. To
get the IP address of a computer, refer to “Appendix D: Finding the MAC
Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter.”
When finished making your changes on this tab, click the Save Settings button
to save these changes, or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your
changes.
47
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
46
Figure 5-20
Port Triggering
The Port Triggering screen allows the Router to watch outgoing data for spe-
cific port numbers. The IP address of the computer that sends the matching
data is remembered by the Router, so that when the requested data returns
through the Router, the data is pulled back to the proper computer by way of IP
address and port mapping rules.
Port Triggering
Application Enter the application name of the trigger.
Triggered Range For each application, list the triggered port number range.
Check with the Internet application documentation for the port number(s)
needed.
Start Port Enter the starting port number of the Triggered Range.
End Port Enter the ending port number of the Triggered Range.
When finished making your changes on this tab, click the Save Settings button
to save these changes, or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your
changes.
Figure 5-19
Page 28

Diagnostics
This screen allows you to run a Ping Test to determine if an IP Address is
online.
Ping Test
Ping Target. Enter the IP Address that you want to ping in the field.
No. of Pings. Enter the number of times that you want to ping.
Ping Size. Enter the size of the ping to send.
Ping Interval. Enter the Ping Interval in Milliseconds.
Ping Timeout. Enter the Timeout in Milliseconds.
Click the Start Test button to start the Ping Test. Click the Abort Test button
to stop the test.
Click the Refresh button to refresh the screen and view the test results. Click
the Clear Result button to remove the results from the test that are displayed
in the window.
49
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
48
Figure 5-22
The Administration tabs contain Security, Diagnostics, and Advanced
Administration screens.
Security
Security. To change your password, enter the Gateway Password in the (Enter
New Password) field, then re-enter it in the (Re-enter To Confirm) field.
Reporting
E-mail Alerts. Click Enable to allow alerts.
Your Email Address. Enter the E-mail adress that the alerts will be sent to.
Your SMTP Server Name. Enter the name of your SMTP server in the field.
Logs
The log with the description, count, last occurrence, target, and source of the
alert can be viewed here. To send the E-mail Log, click the E-mail Log button.
To clear the log, click the Clear Log button.
When finished making your changes on this tab, click the Save Settings button
to save these changes, or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your
changes.
Figure 5-21
The Administration Tabs
Page 29

51
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
Advanced
The Advanced screen allows you to restore the Router’s configuration to its factory default settings, and to enable routing and NAT.
Advanced Administration
Restore Factory Defaults. To clear all of the Gateway’s settings and reset
them to its factory defaults, click Ye s .
Routing and NAT. Click Disable to disable all NAT and routing functions of
the Cable Gateway, and allow only the cable modem function. The IP address
of the device will change to 192.168.100.1.
When finished making your changes on this tab, click the Save Settings button
to save these changes, or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your
changes.
50
When you click the Status tab, you will see the Gateway screen (see Figure 6-
30). It displays information about the Gateway and its settings.
Information
Standard Specification Compliant. The specification is displayed here.
Hardware Version. The current hardware version is displayed here.
Sofware Version. The current software version is displayed here.
Cable Modem MAC Address. The MAC Address of the cable modem is dis-
played here.
Cable Modem Serial Number. The serial number of the cable modem is displayed here.
CM certificate. The installation status of the CM certificate is displayed here.
The Status Tabs
Note: The information provided and buttons available may vary
depending on the Gateway’s settings.
Figure 5-24
Figure 5-23
Note: Do not restore the factory defaults unless you are having difficulties with the Gateway and have exhausted all other troubleshooting
measures. Once the Gateway is reset, you will have to re-enter all of
your configuration settings.
Page 30

53
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
52
Startup Procedure. The status and comments for Acquire Downstream
Channel, Connectivity State, Boot State, and Security are displayed.
Downstream Channel. The status of the downstream channel items of Lock
Status, Modulation, Channel ID, Sybol rate, Downstream Power, and SNR, are
displayed.
Upstream Channel. The status of the upstream channel items of Lock Status,
Modulation, Channel ID, Sybol rate, and Upstream Power, are displayed.
Local Network
DHCP Clients. The DHCP clients of your network are listed. Select the client,
then click the Release button to remove the client from the lease. The current
system time is displayed below.
Figure 5-26
Status
System Up Time. This indicates how long the Gateway has been active.
Network Access. Thsi indicates whether access to the network has been
achieved.
WAN IP Address. This indicates the IP Address that is assigned to the cablemodem.
WAN DHCP IP Address Lease. This indicates how long the lease is.
WAN DHCP IP Expires. This indicates when the lease expires.
Connect
The status of the Gateway’s connections are displayed on this screen.
Figure 5-25
Page 31

4. The Cable Link LED will not go solid.
• Verify that the coaxial cable is firmly plugged into the Cable Gateway’s
cable port, with the other end plugged directly into the Cable wall jack.
• Verify that your Cable account is active.
• Verify that your cable ISP has been given the correct MAC Address for
the cable modem function.
5. I can’t access the Internet from the Cable Gateway.
• Check if both ends of the network cable and power adapter are properly
connected. Check if the status LEDs on the front panel are functioning
properly.
• If using Windows 95, 98 or Me, check the TCP/IP setup on the client side.
Run winipcfg by clicking on the Start button, selecting Run, and typing
winipcfg in the Run field. Press Enter. The PC should have an IP address
of 192.168.0.xxx (“xxx” is from 2 to 254.). The Subnet Mask is
255.255.255.0; the default gateway IP should be the Cable Gateway’s IP
Address, and check that the DNS is correct.
• Check the same setup values in the Cable Gateway’s Summary page.
6. When I enter a URL or IP address, I get a time out error.
• Check to see if your other PCs work. If they do, verify that your PC’s IP
settings are correct (IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, and
DNS)
• If the PCs are configured correctly, but still not working, check the Cable
Gateway. Make sure that it is connected and ON. Connect to it and check
its settings. (If you cannot connect to it, check the LAN and power connections.)
• If the Cable Gateway is configured correctly, check your Internet connection to see that it is working correctly.
• Manually configure the TCP/IP with a DNS address provided by your ISP.
What is the maximum number of IP addresses that the Cable Gateway will sup-
port? The Cable Gateway will support up to 253 IP addresses.
Does the Cable Gateway support IPSec Pass-Through? Yes, it is a feature built
into the Cable Gateway.
Does the Cable Gateway support IPX or AppleTalk? No. TCP/IP is the only proto-
col standard for the Internet and has become the global standard for communications. IPX, a NetWare communications protocol used only to route messages from one node to another, and AppleTalk, a communications protocol
used on Apple and Macintosh networks, can be used for LAN to LAN connections, but those protocols cannot connect from WAN to LAN.
55
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
54
Frequently Asked Questions
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
This section provides possible solutions to problems regarding the Cable
Gateway’s installation and operation. If your situation is described here, the
problem should be solved by applying the corresponding solution. If you can’t
find an answer here, check the Linksys website at www.linksys.com.
1. The Cable Gateway is not working.
• Verify that the Power cord and other network cables are plugged in.
• Check the LAN and Cable Modem - Cable LEDs on the Cable Gateway’s
front and verify that they are lit appropriately.
• Check the settings on your PC.
• Check the Cable Gateway’s settings.
• Verify that your cable ISP has been given the correct MAC Address for
the cable modem function.
2. I can’t connect to the Cable Gateway.
• Verify that the Cable Gateway is properly installed; LAN connections are
OK, and it is powered ON.
• Make sure that your PC and the Cable Gateway are on the same network
segment. If you are not sure, initiate the DHCP function, and let the PC
get the IP address automatically.
• Make sure that your PC is using an IP address within the default range of
192.168.0.2 to 192.168.0.254 and thus compatible with the Cable
Gateway default IP Address of 192.168.0.1
• Also, the Subnet Mask should be set to 255.255.255.0 to match the Cable
Gateway. For the Cable Gateway, you can check these settings by using
Control Panel-Network to check the Properties for the TCP/IP protocol.
3. The Diag LED stays lit when it shouldn’t.
• The Diag LED lights up when the device is first powered up. The system
will boot up itself and check for proper operation. After finishing the
checking procedure, the LED turns off to show the system is working
fine. If the LED remains lit after this time, the device is not working properly. Contact your cable provider if this problem persists.
Common Problems and Solutions
Page 32

57
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
56
How do I get
Half-Life: Team Fortress
to work with the Cable Gateway? The default
client port for Half-Life is 27005. The computers on your LAN need to have
“+clientport 2700x” added to the HL shortcut command line; the x would be
6, 7, 8, and on up. This lets multiple computers connect to the same server.
One problem: Version 1.0.1.6 won’t let multiple computers with the same CD
key connect at the same time, even if on the same LAN (not a problem with
1.0.1.3). As far as hosting games, the HL server does not need to be in the
DMZ. Just forward port 27015 to the local IP address of the server computer.
The web page hangs; downloads are corrupt, or nothing but junk characters are
being displayed on the screen. What do I need to do? Force your Ethernet
adapter to 10Mbps or half duplex mode, and turn off the “Auto-negotiate”
feature of your Ethernet adapter as a temporary measure. (Please look at the
Network Control Panel in your Ethernet adapter’s Advanced Properties tab.)
Make sure that your proxy setting is disabled in the browser. Check our website at www.linksys.com for more information.
If all else fails in the installation, what can I do? Reset the Cable Gateway by
holding down the reset button until the Diag LED fully turns on and off.
Will the Cable Gateway function in a Macintosh environment? Yes, but the Cable
Gateway’s setup pages are accessible only through Internet Explorer v4.0 or
Netscape Navigator v4.0 or higher for Macintosh. NOTE: Linksys does not
provide technical support for Macintosh computers.
With which type of firewall is the Cable Gateway equipped? The Cable Gateway
uses NAT and TCP/IP port inspections. It also has SPI (Stateful Packet
Inspection).
I am not able to access the Cable Gateway’s web configuration screen. What can
I do? You may have to remove the proxy settings on your Internet browser,
e.g., Netscape Navigator or Internet Explorer. Or remove the dial-up settings
on your browser. Check with your browser documentation.
What is DMZ? Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) allows one IP address (computer) to
be exposed to the Internet. Some applications require multiple TCP/IP ports
to be open. It is recommended that you set your computer with a static IP if
you want to use DMZ.
If DMZ is used, does the exposed user share the public IP with the Cable Gateway?
No.
What is Network Address Translation and what is it used for? Network Address
Translation (NAT) translates multiple IP addresses on the private LAN to one
public address that is sent out to the Internet. This adds a level of security
since the address of a PC connected to the private LAN is never transmitted
on the Internet. Furthermore, NAT allows the Cable Gateway to be used with
low cost Internet accounts, when only one TCP/IP address is provided by the
ISP. The user may have many private addresses behind this single address provided by the ISP.
Does the Cable Gateway support any operating system other than Windows 95, 98,
Me, NT, 2000, or XP? Yes, but Linksys does not, at this time, provide technical
support for setup, configuration or troubleshooting of any non-Windows
operating systems. USB features are only supported by Windows 98, Me,
2000, and XP.
Does the Cable Gateway support ICQ send file? Yes, with the following fix: click
ICQ menu -> preference -> connections tab->, and check I am behind a
firewall or proxy. Then set the f irewall time-out to 80 seconds in the firewall
setting. The Internet user can then send a file to a user behind the Cable
Gateway.
How do I get KaZaA to work with the Cable Gateway? KaZaA is fully compatible
with the Cable Gateway, but you must make sure that, during installation, you
select “no idea” when asked about your firewall selection. Set your proxy settings to “No Proxy Server” in your File>Preferences.
I set up an Unreal Tournament Server, but others on the LAN cannot join. What do
I need to do? If you have a dedicated Unreal Tournament server running, you
need to create a static IP for each of the LAN computers and forward ports
7777, 7778, 7779, 7780, 7781, and 27900 to the IP address of the server. You
can also use a port forwarding range of 7777 ~ 27900. If you want to use the
UT Server Admin, forward another port (8080 usually works well but is used
for remote admin. You may have to disable this.), and then in the
[UWeb.WebServer] section of the server.ini file, set the ListenPort to 8080 (to
match the mapped port above) and ServerName to the IP assigned to the
Cable Gateway from your ISP.
Can multiple gamers on the LAN get on one game server and play simultaneously
with just one public IP address? It depends on which network game or what
kind of game server you are using. For example, Unreal Tournament supports
multi-login with one public IP.
Page 33

59
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
58
Appendix B: Configuring Wireless
Security in Windows XP
An acronym for Wired Equivalent Privacy, WEP is an encryption scheme used
to protect your wireless data communications. WEP uses a combination of 64bit or 128-bit keys to provide access control to your network and encryption
security for every data transmission. To decode a data transmission, each point
in a network must use an identical 64-bit or 128-bit key. Higher encryption levels mean higher levels of security, but due to the complexity of the encryption,
they may mean decreased network performance.
You may also have heard the term “40-bit” used in conjunction with WEP
Encryption. This is simply another term for 64-bit WEP encryption. This level
of WEP encryption has been called 40-bit because it uses a 40-bit secret key
along with a 24-bit Initialization Vector (40 + 24 = 64). Wireless vendors may
use either name. Linksys uses the term “64-bit” when referring to this level of
encryption.
If possible, make sure your wireless network is functioning before attempting
to configure WEP.
A 128-bit WEP encrypted wireless network will NOT communicate with a 64bit WEP encrypted wireless network. Therefore, make sure that all of your
wireless devices are using the same encryption level. All wireless devices complying with the 802.11b or 802.11g standard will support 64-bit WEP.
Configure WEP in the Wireless Setup section of “Chapter 5: Using the
Gateway’s Web-based Utility.” Go to Features Setup tab. Click on Wireless,
then Setup. Use the WEP Key in the Key 1 field to configure WEP in Windows
XP.
Note: WEP Encryption is an additional data security measure and
not essential for Gateway operation.
Does the Cable Gateway pass PPTP packets or actively route PPTP sessions? The
Cable Gateway allows PPTP packets to pass through.
Is the Cable Gateway cross-platform compatible? Any platform that supports
Ethernet and TCP/IP is compatible with the Cable Gateway.
How many ports can be simultaneously forwarded? Theoretically, the Cable
Gateway can establish 520 sessions at the same time, but you can only forward 10 ranges of ports.
Does the Cable Gateway replace a modem? Is there a cable modem in the Cable
Gateway? Yes. The Cable Gateway has an integrated cable modem, so this
product will replace your current cable modem.
What are the Cable Gateway’s advanced features? The Cable Gateway’s
advanced features include Filters, Forwarding, and DMZ host.
How do I get mIRC to work with the Cable Gateway? Set port forwarding to 113
for the computer on which you are using mIRC. If you are experiencing difficulty after setting the port forwarding, try changing the Direct Client-toClient (DCC) settings to a range from 1024 to 1030 on the DCC option and
Forwarding page of the Web-based Setup Utility.
If your questions are not addressed here, refer to the contact information
on the last page of this manual, or online at support.linksys.com.
Page 34

2. In the “Control Panel” window, click the Network and Internet
Connections icon.
3. Click on the Network Connections icon.
4. The “Network Connections” window will appear. Under LAN or HighSpeed Internet you will see all Network cards that are installed and operating in your computer. Double-click the Wireless Network Connection
icon associated with your wireless adapter.
If the “Wireless Network Connection Status” window appears, continue to
the next step.
61
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
The following steps will help you enable WEP and enter the encryption key
manually for your wireless PC cards, in order to enable your Windows XP system to communicate with the Gateway wirelessly.
These steps assume that you are running Windows XP in the default mode.
Be sure you have the WEP Key generated in the Gateway, shown in the Key 1
field.
1. Click the Start button and go to the Control Panel.
60
Figure B-2
Figure B-3
Figure B-1
Page 35

63
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
62
6. When the “Wireless Network Connection Properties” window appears,
click the Wireless Networks Ta b.
7. If the appropriate wireless network, specified by the Gateway’s SSID, is
displayed in the “Preferred networks” section, double-click it and continue
to the next step.
Otherwise, click on the appropriate wireless network, specified by the
Gateway’s SSID, in the “Available networks” section. Then, click the
Configure button.
Figure B-6
Figure B-7
If a “Connect to Wireless Network” window appears, in the Available
Networks section, click the desired wireless network, specified by the
Gateway’s SSID. Then, double-click the Wireless Network Connection
icon.
5. When the “Wireless Network Connection Status” window appears, click the
Properties button.
Figure B-4
Figure B-5
Page 36

Appendix C: Installing the TCP/IP
Protocol
Follow these instructions to install the TCP/IP protocol on one of your PCs only
after a network card has been successfully installed inside the PC. These
instructions are for Windows 95, Windows 98, and Windows Me. For TCP/IP
setup under Windows NT, 2000, and XP, see your Windows manual.
1. Click the Start button. Choose Settings and then Control Panel.
2. Double-click on the Network icon to bring up your Network window.
Select the Configuration tab.
3. Click the Add button.
4. Double-click on Protocol.
5. Highlight Microsoft under the list of manufacturers.
65
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
64
Figure C-1
8. The “Wireless Network Properties” window will appear.
Click the check box for the Data encryption (WEP enabled) option.
Remove the check from the Network Authentication (Shared mode) and
The key is provided for me automatically fields.
In the "Network key" field, enter the exact Key (all 10 or 26 digits, depending on the level of encryption) generated by the Gateway.
Verify that the “Key format” field displays “Hexadecimal digits” and that
the “Key length” field displays either “40 bits (10 digits)” or “104 bits (26
digits)”. If this is not displayed, you have entered the key incorrectly.
Click the OK button to save the settings. Click on OK buttons until you
get back to the “Wireless Network Connection Status” window. Close any
open windows to get back to the Windows XP desktop.
Close any applications and reboot your PC. After reboot, WEP configuration
is complete and you should be able to connect wirelessly to the Gateway.
Figure B-8
Page 37

67
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
6. Find and double-click TCP/IP in the list to the right (see Figure C-2).
7. After a few seconds, the main Network window will appear. The TCP/IP
Protocol should now be listed.
8. Click the OK button. Windows may ask for original Windows installation
files. Supply them as needed, e.g., c:\windows\options\cabs, D:\win98,
D:\win95.
9. Windows will ask you to restart the PC. Click the Ye s button.
The TCP/IP installation is now complete.
66
Appendix D: Finding the MAC
Address and IP Address for Your
Ethernet Adapter
This section describes how to find the MAC address for your Ethernet adapter
to do either MAC Filtering for the Gateway and ISP. You can also find the IP
address of your computer’s Ethernet adapter. The IP address is used for f iltering. Follow the steps in this appendix to f ind the MAC address or IP address
for your adapter in Windows 95, 98, Me, NT, 2000, and XP.
For Windows 95, 98, and Me:
1. Click on Start and Run. In the Open field, enter winipcfg. Then press the
Enter key or the OK button.
2. When the IP Conf iguration window appears, select the Ethernet adapter
you are using to connect to the Gateway via a CAT 5 Ethernet cable.
Figure D-1
Figure D-2
Figure C-2
Figure C-3
Page 38

69
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
68
2. In the command prompt, enter ipconfig /all. Then press the Enter key.
3. Write down the Physical Address as shown on your computer screen; it is
the MAC address for your Ethernet adapter. This will appear as a series of
letters and numbers.
The MAC address/Physical Address is what you will use for MAC
Filtering.
The example in Figure D-5 shows the IP address of your Ethernet adapter
as 192.168.1.100. Your computer may show something different.
Figure D-5
Note: The MAC address is also called the Physical
Address.
3. Write down the Adapter Address as shown on your computer screen (see
Figure D-3). This is the MAC address for your Ethernet adapter and will
be shown as a series of numbers and letters.
The MAC address/Adapter Address is what you will use for MAC
Filtering.
The example in Figure D-3 shows the IP address of your Ethernet adapter
as 192.168.1.100. Your computer may show something different.
For Windows NT, 2000, and XP:
The following steps show an alternative way of obtaining the MAC address and
IP address for your Ethernet adapter.
1. Click on Start and Run. In the Open field, enter cmd. Press the Enter key
or click the OK button.
Figure D-4
Note: The MAC address is also called the Adapter
Address.
Figure D-3
Page 39

Appendix E: Glossary
10BaseT - An Ethernet standard that uses twisted wire pairs.
100BaseTX - IEEE physical layer specification for 100 Mbps over two pairs of
Category 5 UTP or STP wire.
802.11b - One of the IEEE standards for wireless networking hardware.
Products that adhere to a specific IEEE standard will work with each other,
even if they are manufactured by different companies. The 802.11b standard
specifies a maximum data transfer rate of 11Mbps, an operating frequency of
2.4GHz, and WEP encryption for security. 802.11b networks are also referred
to as Wi-Fi networks.
Adapter - Printed circuit board that plugs into a PC to add to capabilities or
connectivity to a PC. In a networked environment, a network interface card
(NIC) is the typical adapter that allows the PC or server to connect to the
intranet and/or Internet.
Auto-negotiate - To automatically determine the correct settings. The term is
often used with communications and networking. For example, Ethernet
10/100 cards, hubs and switches can determine the highest speed of the node
they are connected to and adjust their transmission rate accordingly.
Beacon Interval - A beacon is a packet broadcast by the Access Point to keep
the network synchronized. A beacon includes the wireless LAN service area,
the AP address, the Broadcast destination addresses, a time stamp, Delivery
Traffic Indicator Maps, and the Traffic Indicator Message (TIM).
Bit - A binary digit. The value - 0 or 1-used in the binary numbering system.
Also, the smallest form of data.
Boot - To cause the computer to start executing instructions. Personal computers contain built-in instructions in a ROM chip that are automatically executed
on startup. These instructions search for the operating system, load it and pass
control to it.
71
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
70
When entering the information using the Router’s web-based utility, you will
type the 12-digit MAC address in this format, XXXXXXXXXXXX without
the hyphens for MAC Filtering.
Figure D-6
Page 40

DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - A protocol that lets network
administrators manage centrally and automate the assignment of Internet
Protocol (IP) addresses in an organization's network. Using the Internet's set of
protocol (TCP/IP), each machine that can connect to the Internet needs a
unique IP address. When an organization sets up its computer users with a connection to the Internet, an IP address must be assigned to each machine.
Without DHCP, the IP address must be entered manually at each computer and,
if computers move to another location in another part of the network, a new IP
address must be entered. DHCP lets a network administrator supervise and distribute IP addresses from a central point and automatically sends a new IP
address when a computer is plugged into a different place in the network.
DHCP uses the concept of a "lease" or amount of time that a given IP address
will be valid for a computer. The lease time can vary depending on how long a
user is likely to require the Internet connection at a particular location. It's especially useful in education and other environments where users change frequently. Using very short leases, DHCP can dynamically reconfigure networks
in which there are more computers than there are available IP addresses.
DHCP supports static addresses for computers containing Web servers that
need a permanent IP address.
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) - Allows one IP address (or computer) to be
exposed to the Internet. Some applications require multiple TCP/IP ports to be
open. It is recommended that you set your computer with a static IP address if
you want to use DMZ Hosting.
DNS - The domain name system (DNS) is the way that Internet domain name
are located and translated into Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. A domain name
is a meaningful and easy-to-remember "handle" for an Internet address.
Domain - A subnetwork comprised of a group of clients and servers under the
control of one security database. Dividing LANs into domains improves performance and security.
Download - To receive a file transmitted over a network. In a communications
session, download means receive, upload means transmit.
73
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
Broadband - A data-transmission scheme in which multiple signals share the
bandwidth of a medium. This allows the transmission of voice, data and video
signals over a single medium. Cable television uses broadband techniques to
deliver dozens of channels over one cable.
Browser - A browser is an application program that provides a way to look at
and interact with all the information on the World Wide Web or PC. The word
"browser" seems to have originated prior to the Web as a generic term for user
interfaces that let you browse text files online.
Buffer - A buffer is a shared or assigned memory area used by hardware
devices or program processes that operate at different speeds or with different
sets of priorities. The buffer allows each device or process to operate without
being held up by the other. In order for a buffer to be effective, the size of the
buffer and the algorithms for moving data into and out of the buffer need to be
considered by the buffer designer. Like a cache, a buffer is a "midpoint holding
place" but exists not so much to accelerate the speed of an activity as to support the coordination of separate activities.
Cable Modem - A device that connects a computer to the cable television network, which in turn connects to the Internet. Once connected, cable modem
users have a continuous connection to the Internet. Cable modems feature
asymmetric transfer rates: around 36 Mbps downstream (from the Internet to
the computer), and from 200 Kbps to 2 Mbps upstream (from the computer to
the Internet).
Category 5 - ANSI/EIA (American National Standards Institute/Electronic
Industries Association) Standard 568 is one of several standards that specify
"categories" (the singular is commonly referred to as "CAT") of twisted pair
cabling systems (wires, junctions, and connectors) in terms of the data rates
that they can sustain. CAT 5 cable has a maximum throughput of 100 Mbps and
is usually utilized for 100BaseTX networks.
Default Gateway - The routing device used to forward all traffic that is not
addressed to a station within the local subnet.
Denial of Service - A protocol that directs the network to no longer respond to
requests that might arise as the result of a Denial of Service attack.
Denial of Service Attack - An assault on a network that floods it with so many
additional requests that regular traffic is either slowed or completely interrupted.
72
Page 41

FTP (File Transfer Protocol) - A protocol used to transfer files over a TCP/IP
network (Internet, UNIX, etc.). For example, after developing the HTML pages
for a Web site on a local machine, they are typically uploaded to the Web server using FTP.
FTP includes functions to log onto the network, list directories and copy f iles.
It can also convert between the ASCII and EBCDIC character codes. FTP operations can be performed by typing commands at a command prompt or via an
FTP utility running under a graphical interface such as Windows. FTP transfers
can also be initiated from within a Web browser by entering the URL preceded
with ftp://.
Unlike e-mail programs in which graphics and program files have to be
"attached," FTP is designed to handle binary files directly and does not add the
overhead of encoding and decoding the data.
Full Duplex - The ability of a device or line to transmit data simultaneously in
both directions.
Gateway - A device that interconnects networks with different, incompatible
communications protocols.
Half Duplex - Data transmission that can occur in two directions over a single
line, but only one direction at a time.
Hardware - Hardware is the physical aspect of computers, telecommunications, and other information technology devices. The term arose as a way to distinguish the "box" and the electronic circuitry and components of a computer
from the program you put in it to make it do things. The program came to be
known as the software.
Hub - The device that serves as the central location for attaching wires from
workstations. Can be passive, where there is no amplification of the signals; or
active, where the hubs are used like repeaters to provide an extension of the
cable that connects to a workstation.
ICQ - A conferencing program for the Internet that provides interactive chat,
e-mail and file transfer and can alert you when someone on your predefined list
has also come online.
IEEE (The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) - The IEEE
describes itself as "the world's largest technical professional society, promoting
75
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message) - A DTIM field is a countdown
field informing clients of the next window for listening to broadcast and multicast messages. When the AP has buffered broadcast or multicast messages for
associated clients, it sends the next DTIM with a DTIM Interval value. AP
Clients hear the beacons and awaken to receive the broadcast and multicast
messages.
Dynamic IP Address - An IP address that is automatically assigned to a client
station in a TCP/IP network, typically by a DHCP server. Network devices that
serve multiple users, such as servers and printers, are usually assigned static IP
addresses.
Encryption - A security method that applies a specific algorithm to data in
order to alter the data's appearance and prevent other devices from reading the
information.
Ethernet - IEEE standard network protocol that specifies how data is placed
on and retrieved from a common transmission medium. Has a transfer rate of
10 Mbps. Forms the underlying transport vehicle used by several upper-level
protocols, including TCP/IP and XNS.
Firewall - A firewall is a set of related programs, located at a network gateway
server, that protects the resources of a network from users from other networks.
(The term also implies the security policy that is used with the programs.) An
enterprise with an intranet that allows its workers access to the wider Internet
installs a firewall to prevent outsiders from accessing its own private data
resources and for controlling what outside resources to which its own users
have access.
Basically, a firewall, working closely with a router, examines each network
packet to determine whether to forward it toward its destination.
Firmware - Code that is written onto read-only memory (ROM) or programmable read-only memory (PROM). Once firmware has been written onto the
ROM or PROM, it is retained even when the device is turned off.
Fragmentation - Breaking a packet into smaller units when transmitting over
a network medium that cannot support the original size of the packet.
74
Page 42

LAN (local area network) - A group of computers and associated devices that
share a common communications line and typically share the resources of a
single processor or server within a small geographic area (for example, within
an office building).
MAC (Media Access Control) Address - A unique number assigned by the
manufacturer to any Ethernet networking device, such as a network adapter,
that allows the network to identify it at the hardware level.
Mbps (Megabits per second) - One million bits per second; unit of measure-
ment for data transmission.
mIRC - mIRC runs under Windows and provides a graphical interface for logging onto IRC servers and listing, joining and leaving channels.
Multicasting - Sending data to a group of nodes instead of a single destination.
Network - A system that transmits any combination of voice, video and/or data
between users.
NIC (Network Interface Card) - A board installed in a computer system, usu-
ally a PC, to provide network communication capabilities to and from that computer system. Also called an adapter.
Node - A network junction or connection point, typically a computer or work
station.
Notebook (PC) - A notebook computer is a battery-powered personal computer generally smaller than a briefcase that can easily be transported and conveniently used in temporary spaces such as on airplanes, in libraries, temporary
offices, and at meetings. A notebook computer, sometimes called a laptop computer, typically weighs less than five pounds and is three inches or less in thickness.
Packet - A unit of data routed between an origin and a destination in a network.
Packet Filtering - Discarding unwanted network traffic based on its originat-
ing address or range of addresses or its type (e-mail, file transfer, etc.).
PC Card - A credit-card sized removable module that contains memory, I/O,
or a hard disk.
77
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
76
the development and application of electrotechnology and allied sciences for
the benefit of humanity, the advancement of the profession, and the well-being
of our members."
The IEEE fosters the development of standards that often become national and
international standards. The organization publishes a number of journals, has
many local chapters, and several large societies in special areas, such as the
IEEE Computer Society.
IP (Internet Protocol) - The method or protocol by which data is sent from one
computer to another on the Internet. It is a standard set of rules, procedures, or
conventions relating to the format and timing of data transmission between two
computers that they must accept and use to be able to understand each other.
IP Address - In the most widely installed level of the Internet Protocol (IP)
today, an IP address is a 32-binary digit number that identifies each sender or
receiver of information that is sent in packet across the Internet. When you
request an H
TM
L page or send e-mail, the Internet Protocol part of TCP/IP
includes your IP address in the message (actually, in each of the packets if more
than one is required) and sends it to the IP address that is obtained by looking
up the domain name in the Uniform Resource Locator you requested or in the
e-mail address you're sending a note to. At the other end, the recipient can see
the IP address of the Web page requestor or the e-mail sender and can respond
by sending another message using the IP address it received.
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) - A suite of protocols used to implement
secure exchange of packets at the IP layer. IPSec supports two basic modes:
Transport and Tunnel. Transport encrypts the payload of each packet, leaving
the header untouched, while Tunnel mode encrypts both the header and the payload and is therefore more secure. IPSec must be supported on both transmitter and receiver and must share a public key. Tunnel mode is widely deployed
in VPNs (Virtual Private Networks).
IPX (Internetwork Packet EXchange) - A NetWare communications protocol
used to route messages from one node to another. IPX packets include network
addresses and can be routed from one network to another.
ISP (Internet Service Provider) - A company that provides individuals and
companies access to the Internet and other related services such as Web site
building and virtual hosting.
Page 43

SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection) - A firewall technology that monitors the state
of the transaction so that it can verify that the destination of an inbound packet matches the source of a previous outbound request. It examines not just the
headers of the packet, but also the contents, to determine more about the packet than just its source and destination information. It is called "stateful" because
verifies that the stated destination computer has previously requested the current communication. In this way, it verifies that all communications are initiated by the recipient computer and are taking place only with sources that are
known and trusted from previous interactions. In addition to being a more rigorous inspection, stateful packet inspection closes off ports until connection to
the specific port is requested. This allows an added layer of protection from the
threat of port scanning.
SSID (Service Set IDentifier) - A unique name shared among all points in a
wireless network. The SSID must be identical for each point in the wireless network and is case-sensitive.
Static IP Address - A permanent IP address that is assigned to a node in an IP
or a TCP/IP network.
STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) - Telephone wire that is wrapped in a metal
sheath to eliminate external interference.
Subnet Mask - The method used for splitting IP networks into a series of subgroups, or subnets. The mask is a binary pattern that is matched up with the IP
address to turn part of the host ID address field into a field for subnets.
Switch - 1. A data switch connects computing devices to host computers,
allowing a large number of devices to share a limited number of ports. 2. A
device for making, breaking, or changing the connections in an electrical circuit.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) - A method (protocol) used along with
the IP (Internet Protocol) to send data in the form of message units (datagram)
between network devices over a LAN or WAN. While IP takes care of handling
the actual delivery of the data (routing), TCP takes care of keeping track of the
individual units of data (called packets) that a message is divided into for eff icient delivery over the network. TCP is known as a "connection oriented" protocol due to requiring the receiver of a packet to return an acknowledgment of
receipt to the sender of the packet resulting in transmission control.
79
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
Port - A pathway into and out of the computer or a network device such as a
switch or router. For example, the serial and parallel ports on a personal computer are external sockets for plugging in communications lines, modems and
printers.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) - A protocol which allows the Point
to Point Protocol (PPP) to be tunneled through an IP network. PPTP does not
specify any changes to the PPP protocol but rather describes a "tunneling service" for carrying PPP (a tunneling service is any network service enabled by
tunneling protocols such as PPTP, L2F, L2TP, and IPSEC tunnel mode). One
example of a tunneling service is secure access from a remote small office network to a headquarters corporate intranet via a Virtual Private Network (VPN)
that traverses the Internet. However, tunneling services are not restricted to corporate environments and may also be used for personal (i.e., non-business)
applications.
RJ-11 (Registered Jack-11) - A telephone connector that holds up to six wires.
The RJ-11 the common connector used to plug a telephone into a wall.
RJ-45 (Registered Jack-45) - A connector similar to a telephone connector that
holds up to eight wires, used for connecting Ethernet devices.
Router - Protocol-dependent device that connects subnetworks together.
Routers are useful in breaking down a very large network into smaller subnetworks; they introduce longer delays and typically have much lower throughput
rates than bridges.
RTS (Request To Send) - An RS-232 signal sent from the transmitting station
to the receiving station requesting permission to transmit.
Server - Any computer whose function in a network is to provide user access
to files, printing, communications, and other services.
Software - Instructions for the computer. A series of instructions that performs
a particular task is called a "program." The two major categories of software are
"system software" and "application software." System software is made up of
control programs such as the operating system and database management system (DBMS). Application software is any program that processes data for the
user.
A common misconception is that software is data. It is not. Software tells the
hardware how to process the data.
78
Page 44

WA N (Wide Area Network)- A communications network that covers a rela-
tively large geographic area, consisting of two or more LANs. Broadband communication over the WAN is often through public networks such as the telephone (DSL) or cable systems, or through leased lines or satellites. In its most
basic definition, the Internet could be considered a WAN.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) - A data privacy mechanism based on a 64-
bit or 128-bit shared key algorithm, as described in the IEEE 802.11 standard.
WINIPCFG - Configuration utility based on the Win32 API for querying,
defining and managing IP addresses within a network. A commonly used utility for configuring networks with static IP addresses.
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) - A group of computers and associat-
ed devices that communicate with each other wirelessly.
81
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) - The basic com-
munication language or set of protocols for communications over a network
(developed specifically for the Internet). TCP/IP defines a suite or group of
protocols and not only TCP and IP.
Throughput - The amount of data moved successfully from one place to another in a given time period.
TX Rate - Transmission Rate.
Upgrade - To replace existing software or firmware with a newer version.
Upload - To transmit a file over a network. In a communications session,
upload means transmit, download means receive.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) - The address that defines the route to a file
on the Web or any other Internet facility. URLs are typed into the browser to
access Web pages, and URLs are embedded within the pages themselves to provide the hypertext links to other pages.
USB (Universal Serial Bus) - A "plug-and-play" interface between a comput-
er and peripherals, such as digital cameras, scanners, game controllers, speakers, keyboards, portable data storage, or printers. With USB, you can add a new
peripheral to your computer without having to add an adapter card or powering
down the computer. USB also supports hot-swapping, the addition or removal
of devices while the computer is running.
USB 1.1-compliant devices support data rates of 1.5Mbps (low-speed) and up
to 12Mbps (full-speed). USB 2.0-compliant devices are backward compatible
with earlier USB devices, and they support data rates of 1.5Mbps (low-speed),
12Mbps (full-speed), and up to 480Mbps (high-speed).
UTP - Unshielded twisted pair is the most common kind of copper telephone
wiring. Twisted pair is the ordinary copper wire that connects home and many
business computers to the telephone company. To reduce crosstalk or electromagnetic induction between pairs of wires, two insulated copper wires are
twisted around each other. Each signal on twisted pair requires both wires.
Since some telephone sets or desktop locations require multiple connections,
twisted pair is sometimes installed in two or more pairs, all within a single
cable.
80
Page 45

Dimensions: 7.32" x 2.48" x 6.08" (186 mm x 63 mm x 154.5 mm)
Unit Weight: 1.5 lb. (0.68 kg)
Power: 12VDC, 1A
Certifications: DOCSIS 1.1, DOCSIS 2.0, FCC Part 15B Class B, UL
1950, EN60950, CE EN 55022 Class B, VCCI, IC-03
Operating Temp.: 0ºC to 40ºC (32ºF to 104ºF)
Storage Temp.: -20°C-70°C (-4°F-158°F)
Operating Humidity: 20% to 90%, Non-Condensing
Storage Humidity: 20% to 90%, Non-Condensing
83
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
82
Environmental
Appendix F: Specifications
Model Number WCG200
Standards DOCSIS 1.0, DOCSIS 1.1, DOCSIS 2.0, IEEE 802.11g,
IEEE 802.11b.
Ports 4 RJ-45 10/100, 1 USB, 1 Female Coax F-Connector
Buttons Power ON/OFF switch, Reset
Cabling Type
Cable Coaxial
LAN UTP Category 5 or better
USB Type B USB
LEDs Power, Cable, Activity, Ethernet, USB, Wireless
Security WEP, MAC address filtering, SPI Firewall
Page 46

85
Wireless-G Cable Gateway
Appendix G: Warranty Information
LIMITED WARRANTY
Linksys warrants to You that, for a period of three years (the “Warranty Period”), your
Linksys Product will be substantially free of defects in materials and workmanship under
normal use. Your exclusive remedy and Linksys' entire liability under this warranty will be
for Linksys at its option to repair or replace the Product or refund Your purchase price less
any rebates. This limited warranty extends only to the original purchaser.
If the Product proves defective during the Warranty Period call Linksys Technical Support in
order to obtain a Return Authorization Number, if applicable. BE SURE TO HAVE YOUR
PROOF OF PURCHASE ON HAND WHEN CALLING. If You are requested to return the
Product, mark the Return Authorization Number clearly on the outside of the package and
include a copy of your original proof of purchase. RETURN REQUESTS CANNOT BE
PROCESSED WITHOUT PROOF OF PURCHASE. You are responsible for shipping
defective Products to Linksys. Linksys pays for UPS Ground shipping from Linksys back
to You only. Customers located outside of the United States of America and Canada are
responsible for all shipping and handling charges.
ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES AND CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY OR
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE LIMITED TO THE DURATION OF
THE WARRANTY PERIOD. ALL OTHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED CONDITIONS,
REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES, INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF NON-INFRINGEMENT, ARE DISCLAIMED. Some jurisdictions do not allow
limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts, so the above limitation may not apply to
You. This warranty gives You specific legal rights, and You may also have other rights which
vary by jurisdiction.
This warranty does not apply if the Product (a) has been altered, except by Linksys, (b) has
not been installed, operated, repaired, or maintained in accordance with instructions supplied
by Linksys, or (c) has been subjected to abnormal physical or electrical stress, misuse, negligence, or accident. In addition, due to the continual development of new techniques for
intruding upon and attacking networks, Linksys does not warrant that the Product will be
free of vulnerability to intrusion or attack.
TO THE EXTENT NOT PROHIBITED BY LAW, IN NO EVENT WILL LINKSYS BE
LIABLE FOR ANY LOST DATA, REVENUE OR PROFIT, OR FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, INCIDENTAL OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES, REGARDLESS
OF THE THEORY OF LIABILITY (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), ARISING OUT OF
OR RELATED TO THE USE OF OR INABILITY TO USE THE PRODUCT (INCLUDING ANY SOFTWARE), EVEN IF LINKSYS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN NO EVENT WILL LINKSYS’LIABILITY EXCEED
THE AMOUNT PAID BY YOU FOR THE PRODUCT. The foregoing limitations will
apply even if any warranty or remedy provided under this Agreement fails of its essential
purpose. Some jurisdictions do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the above limitation or exclusion may not apply to You.
Please direct all inquiries to: Linksys, P.O. Box 18558, Irvine, CA 92623.
84
Appendix H: Contact Information
For help with the installation or operation of the Cable Gateway, contact
Linksys Technical Support at one of the phone numbers or Internet addresses
below.
For help with the installation or operation of this product, contact Linksys
Technical Support at one of the phone numbers or Internet addresses below.
Sales Information 800-546-5797 (LINKSYS)
Technical Support 800-326-7114*
RMA (Return Merchandise
Authorization) Issues www.linksys.com (or call 949-271-5461)
Fax 949-265-6655
Email support@linksys.com
We b http://www.linksys.com
FTP Site ftp.linksys.com
* Before phoning Technical Support, try rebooting the Cable Gateway, as
shown in “Chapter 2: Getting to Know the Cable Gateway” under the heading “Rebooting the Cable Gateway”. Also, make sure that you have contacted your ISP with your MAC Address to activate your account, as shown in
“Chapter 3: Connecting the Cable Gateway.”
85
Page 47

© Copyright 2003 Linksys, All Rights Reserved.
www.linksys.com
 Loading...
Loading...