LINKSYS WAP54GPE User Manual

z
2.4
GH
802.11g
Wireless-G
Model No.
Exterior Access Point
WIRELESS
WAP54GPE
User Guide

Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
Copyright and Trademarks
Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered trademark or trademark of Cisco
Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries. Copyright © 2006 Cisco Systems,
Inc. All rights reserved. Other brands and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective holders.
WARNING:This product contains chemicals, including lead,
known to the State of California to cause cancer, and birth defects
or other reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling.
How to Use this User Guide
The user guide to the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point has been designed to make understanding
networking with the Access Point easier than ever. Look for the following items when reading this User
Guide:
This checkmark means there is a note of interest and is something you should
pay special attention to while using the Access Point.
This exclamation point means there is a caution or warning and is something that
could damage your property or the Access Point.
This question mark provides you with a reminder about something you might
need to do while using the Access Point.
In addition to these symbols, there are definitions for technical terms that are presented like this:
Also, each figure (diagram, screenshot, or other image) is provided with a figure number and description,
like this:
Figure numbers and descriptions can also be found in the “List of Figures” section.
WAP54GPE-UG-61026 v1.1 DF
word: definition.
Figure 0-1: Sample Figure Description

Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction 1
Welcome 1
What’s in this User Guide? 2
Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network 4
Network Topology 4
Roaming 4
Network Layout 4
Example of a Simple Wireless Network 5
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point 6
The LEDs 6
The Ports 7
The Reset Button and Ground 8
The Antenna Pattern 9
Chapter 4: Connecting the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point 12
Overview 12
Hardware Installation 12
Chapter 5: Setting Up the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point 14
Overview 14
Accessing the Utility 14
Navigating the Utility 15
Chapter 6: Configuring the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point 17
The Setup Tab 17
The Setup - Time Tab 18
The Wireless - Basic Wireless Settings Tab 19
The Wireless - Wireless Security Tab 21
The Wireless - Wireless Connection Control Tab 26
The Wireless - Advanced Wireless Settings Tab 27
The AP Mode Tab 29
The Administration - Management Tab 32
The Administration - Log Tab 34
The Administration - Factory Default Tab 36
The Administration - Firmware Upgrade Tab 36

Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
The Administration - Reboot Tab 37
The Administration - Config Management Tab 38
The Status - Local Network Tab 39
The Status - Wireless Tab 40
The Status - System Performance Tab 41
Appendix A: Troubleshooting 43
Frequently Asked Questions 43
Appendix B: Wireless Security 47
Security Precautions 47
Security Threats Facing Wireless Networks 47
Appendix C: Upgrading Firmware 50
Appendix D: Windows Help 51
Appendix E: Glossary 52
Appendix F: Specifications 57
Appendix G: Warranty Information 59
Appendix H: Regulatory Information 60
Appendix I: Contact Information 66

Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
List of Figures
Figure 2-1: Example of a Simple Wireless Network 5
Figure 3-1: Front Panel 6
Figure 3-2: Bottom Panel 7
Figure 3-3: Top Panel 7
Figure 3-4: Back Panel 8
Figure 3-5: Internal Antenna Pattern (Horizontal Plane) 9
Figure 3-6: Radio Coverage of the Access Point to Client Devices 10
Figure 3-7: Access Point to Access Point (bridging) Radio Coverage 11
Figure 4-1: Mark the Locations of the Two Wall-Mount Slots 12
Figure 4-2: Attach the Mounting Plate 12
Figure 4-3: Ground the Access Point 13
Figure 4-4: Attach the Access Point to the Wall 13
Figure 5-1: Login Screen 14
Figure 6-1: Setup - Static IP Address 17
Figure 6-2: Setup - Automatic Configuration - DHCP 18
Figure 6-3: Setup - Time 18
Figure 6-4: Wireless - Basic Wireless Settings 19
Figure 6-5: Wireless - Wireless Security (Disabled) 21
Figure 6-6: Wireless - Wireless Security (WPA-Personal) 21
Figure 6-7: Wireless - Wireless Security (WPA2-Personal) 22
Figure 6-8: Wireless - Wireless Security (WPA2-Personal Mixed) 22
Figure 6-9: Wireless - Wireless Security (WPA-Enterprise) 23
Figure 6-10: Wireless - Wireless Security (WPA2-Enterprise) 23
Figure 6-11: Wireless - Wireless Security (WPA2 - Enterprise Mixed) 24
Figure 6-12: Wireless Security - RADIUS 25
Figure 6-13: Wireless Settings - WEP 25
Figure 6-14: Wireless - Wireless Connection Control 26
Figure 6-1: Select MAC Address from Client Association Table 26

Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
Figure 6-15: Wireless - Advanced Wireless 27
Figure 6-16: AP Mode 29
Figure 6-17: Wireless Repeater 30
Figure 6-18: Site Survey 31
Figure 6-19: Administration - Management 32
Figure 6-20: The Administration - Log 34
Figure 6-21: Administration - Factory Default 36
Figure 6-22: Administration - Firmware Upgrade 36
Figure 6-23: Administration - Reboot 37
Figure 6-24: Administration - Config Management 38
Figure 6-25: Status - Local Network 39
Figure 6-26: Status - Wireless 40
Figure 6-27: Status - System Performance 41
Figure C-1: Firmware Upgrade 50

Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
Chapter 1: Introduction
Welcome
Thank you for choosing the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point. This Access Point will allow you to network
wirelessly better than ever.
How does the Access Point do all of this? An access point allows for greater range and mobility within your
wireless network while also allowing you to connect the wireless network to a wired environment. In fact,
the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point can support communications on up to eight wireless networks, using
Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) technology.
The Wireless-G Exterior Access Point also offers the convenience of Power over Ethernet (PoE) capability,
so it can receive data and power over a single Ethernet network cable. And with the advantage of its weatherresistant housing, you can mount the Access Point outside to extend your wireless networking range and
mobility to the outdoors. You can even connect wired networks in two different buildings, by using two
Access Points set to Wireless Bridge mode.
But what does all of this mean?
Networks are useful tools for sharing computer resources. You can access one printer from different
computers and access data located on another computer's hard drive. Networks are even used for playing
multiplayer video games. So, networks are not only useful in homes and offices, they can also be fun.
PCs on a wired network create a LAN, or Local Area Network. They are connected with Ethernet cables,
which is why the network is called "wired".
PCs equipped with wireless client cards or adapters can communicate without cumbersome cables. By
sharing the same wireless settings, within their transmission radius, they form a wireless network. This is
sometimes called a WLAN, or Wireless Local Area Network. The Access Point bridges wireless networks of
both 802.11g and 802.11b standards and wired networks.
Use the instructions in this Guide to help you connect the Access Point, set it up, and configure it to bridge
your different networks. These instructions should be all you need to get the most out of the Access Point.
access point: a device that allows wireless-equipped
computers and other devices to communicate with each
other and with devices on a wired network. Also used to
expand the range of a wireless network.
network: a series of computers or devices connected
together.
lan (local area network): the computers and networking
devices that make up your local network.
poe (power over ethernet): a technology enabling an
Ethernet network cable to deliver both data and power.
ethernet: network protocol defined in IEEE 802.3
standard that specifies how data is placed on and
retrieved from a common transmission medium.
adapter: a device that adds network functionality to your
PC.
802.11g: a wireless networking standard that specifies a
maximum data transfer rate of 54Mbps, an operating
frequency of 2.4GHz, and backward compatibility with
802.11b devices.
Chapter 1: Introduction
Welcome
802.11b: a wir eless networking standard that specifies a
maximum data transfer rate of 11Mbps and an operating
frequency of 2.4GHz.
1

Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
What’s in this User Guide?
This user guide covers the steps for setting up and using the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point.
• Chapter 1: Introduction
This chapter describes the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point’s applications and this User Guide.
• Chapter 2: Planning your Wireless Network
This chapter describes the basics of wireless networking.
• Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
This chapter describes the physical features of the Access Point.
• Chapter 4: Connecting the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
This chapter instructs you on how to connect the Access Point to your network.
• Chapter 5: Setting up the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
This chapter explains how to perform basic setting changes through the Web-based Utility.
• Chapter 6: Configuring the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
This chapter provides a reference for the available configuration through the Web-based Utility.
• Appendix A: Troubleshooting
This appendix describes some frequently asked questions regarding installation and use of the WirelessG Exterior Access Point.
• Appendix B: Wireless Security
This appendix explains the risks of wireless networking and some solutions to reduce the risks.
• Appendix C: Upgrading Firmware
This appendix instructs you on how to upgrade the Access Point’s firmware.
• Appendix D: Windows Help.
This appendix describes some of the ways Windows can help you with wireless networking.
• Appendix E: Glossary
This appendix gives a brief glossary of terms frequently used in networking.
• Appendix F: Specifications
This appendix provides the Access Point’s technical specifications.
Chapter 1: Introduction
What’s in this User Guide?
2

Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
• Appendix G: W arr anty Information
This appendix supplies the Access Point’s warranty information.
• Appendix H: Regulatory Information
This appendix supplies the Access Point’s regulatory information.
• Appendix I: Contact Information
This appendix provides contact information for a variety of Linksys resources, including Technical
Support.
Chapter 1: Introduction
What’s in this User Guide?
3

Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network
Network Topology
A wireless network is a group of computers, each equipped with one or more wireless adapters. Computers
in a wireless network must be configured to share the same radio channel to talk to each other. Several PCs
equipped with wireless cards or adapters can communicate with each other to form an ad-hoc network
without the use of an access point.
Linksys wireless adapters also provide access to a wired network when using an access point, such as the
Wireless-G Exterior Access Point, or wireless router. An integrated wireless and wired network is called an
infrastructure network. Each wireless PC in an infrastructure network can talk to any computer in a wired or
wireless network via the access point or wireless router.
An infrastructure configuration extends the accessibility of a wireless PC to a wired network, and may
double the effective wireless transmission range for two wireless adapter PCs. Since an access point is able
to forward data within a network, the effective transmission range in an infrastructure network may be
doubled (depending on antenna characteristics).
ad-hoc: a group of wireless devices communicating
directly with each other (peer-to-peer) without the use of
an access point.
infrastructure: a wireless network that is bridged to a
wired network via an access point.
Roaming
Infrastructure mode also supports roaming capabilities for mobile users. Roaming means that you can move
your wireless PC within your network and the access points will pick up the wireless PC's signal, providing
that they both share the same wireless channel and SSID.
Before you consider roaming, choose a feasible radio channel and optimum access poi nt position. Proper
access point positioning combined with a clear radio signal will greatly enhance performance.
Note that Spanning Tree Protocol should be disabled on the switches connecting to the APs to allow roaming
to work without disruption.
Network Layout
The Wireless-G Exterior Access Point has been designed for use with 802.11g and 802.11b products. The
Access Point is compatible with 802.11g and 802.11b adapters, such as the Notebook Adapters for your
laptop computers, PCI Adapters for your desktop PCs, and USB Adapters for when you want to enjoy USB
connectivity. These wireless products can also communicate with a 802.11g or 802.11b Wireless PrintServer.
Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network
Network Topology
roaming: the ability to take a wireless device from one
access point's range to another without losing the
connection.
ssid: your wireless network's name
4
Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
T o link your wired network with your wireless network, connect the Access Point’s Ethernet network port to
any switch or router with Power over Ethernet (PoE)—or a PoE injector, such as the Linksys WAPPOE or
WAPPOE12. Note that 12 VDC on WAPPOE12 is for the splitter output. Both PoE Injectors provide 48
VDC power output.
With these and many other Linksys products, your networking options are limitless. Go to the Linksys
website at www.linksys.com for more information about wireless products.
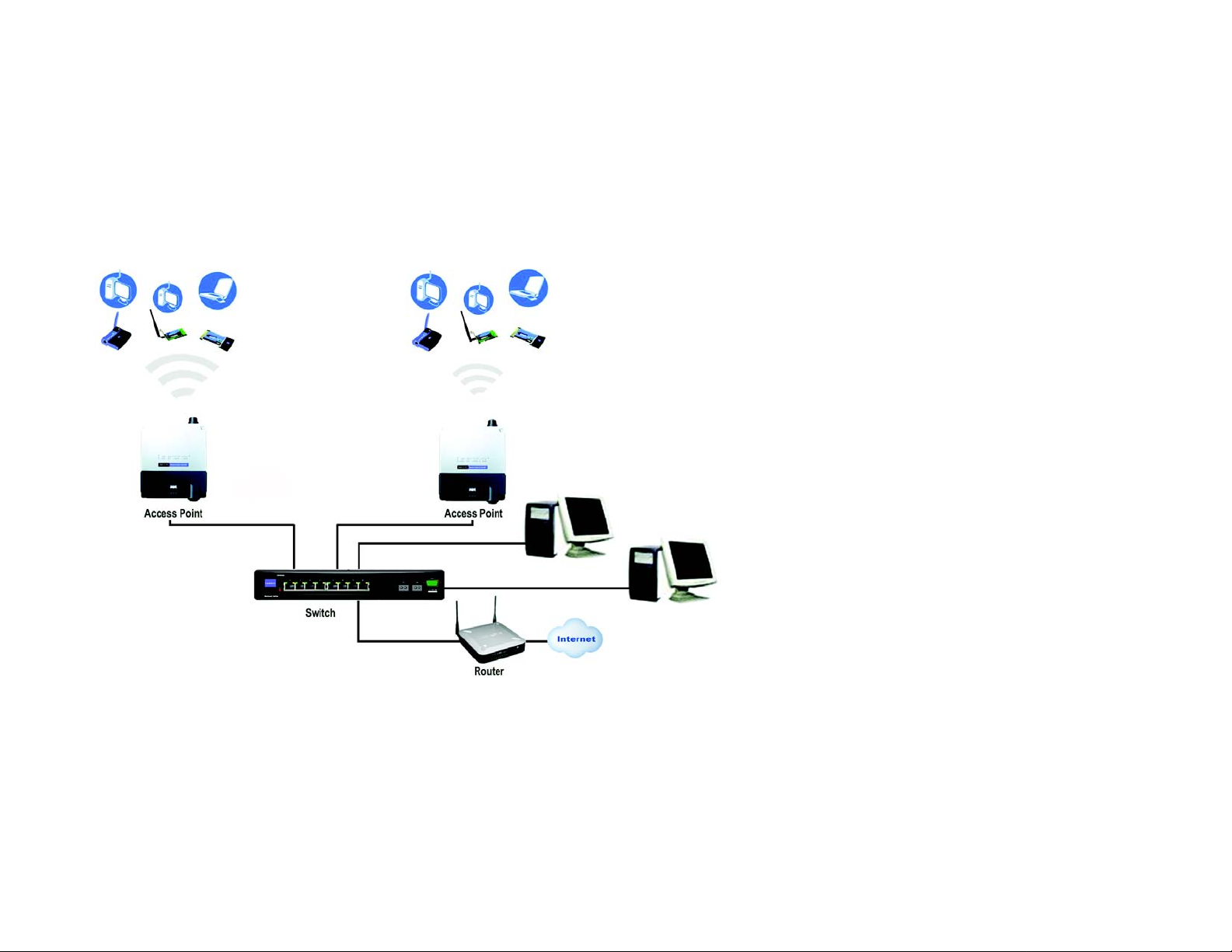
Example of a Simple Wireless Network
Figure 2-1: Example of a Simple Wireless Network
The above diagram shows a typical infrastructure wireless network setup. The Wireless Access Points are
connecting to a Linksys switch that provides power to the Access Points. Each Access Point can connect
multiple wireless devices to the network. This network will provide connectivity among wireless network
devices and PCs that have a wired connection to the switch.
Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network
Example of a Simple Wireless Network
5

Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
The switch then can connect to a router that can connect to an ISP to reach global Internet.
Chapter 2: Planning Your Wireless Network
Example of a Simple Wireless Network
6

Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
The LEDs
The Access Point's LEDs, where information about network activity is displayed, are located on the front
panel.
Figure 3-1: Fr ont Panel
Power Green. The power LED lights up when the Access Point is powered on.
Wired Green. The Wired LED lights up when the Access Point is successfully connected to a
device through the Ethernet network port. If the Wired LED is flashing, the Access Point is
actively sending to or receiving data from one of the devices over the Ethernet network
port.
Wireless Green. The Wireless LED lights up when the Access Point is successfully connected to a
wireless device. If the Wireless LED is flashing, the Access Point is actively sending to or
receiving data from a wireless device.
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
The LEDs
6

Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
The Ports
The Access Point's Ethernet network port is located on the bottom panel and the antenna port is located on
the top panel.
Figure 3-2: Bottom Panel
Ethernet The Ethernet network port connects to Ethernet network devices, such as a switch or router
that supports Power over Ethernet (PoE).
port: the connection point on a computer
or networking device used for plugging in
cables or adapters
Figure 3-3: Top Panel
Antenna The Access Point has a built-in, 9dBi directional antenna. It also has a reverse polarity
female N-type antenna port for an optional, high-gain external antenna such as the
HGA9N. The internal antenna will be disabled automatically when an external antenna is
connected.
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
The Ports
7

Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
The Reset Button and Ground
The Access Point's Reset button and ground are located on the back panel.
Reset But-
ton
Ground
Figure 3-4: Back Panel
Reset Button There are two ways to Reset the Access Point's factory defaults. Either press the Reset
button, for approximately ten seconds, or restore the defaults using the Access Point's
Web-based Utility.
Ground Before you mount the Access Point, you must ground the Access Point (to a large piece of
metal) as a precaution against electric shock.
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
The Reset Button and Ground
IMPORTANT:Resetting the Access Point
will erase all of your settings (including
wireless security, IP address, and power
output) and replace them with the factory
defaults. Do not reset the Access Point if
you want to retain these settings.
8
Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
The Antenna Pattern
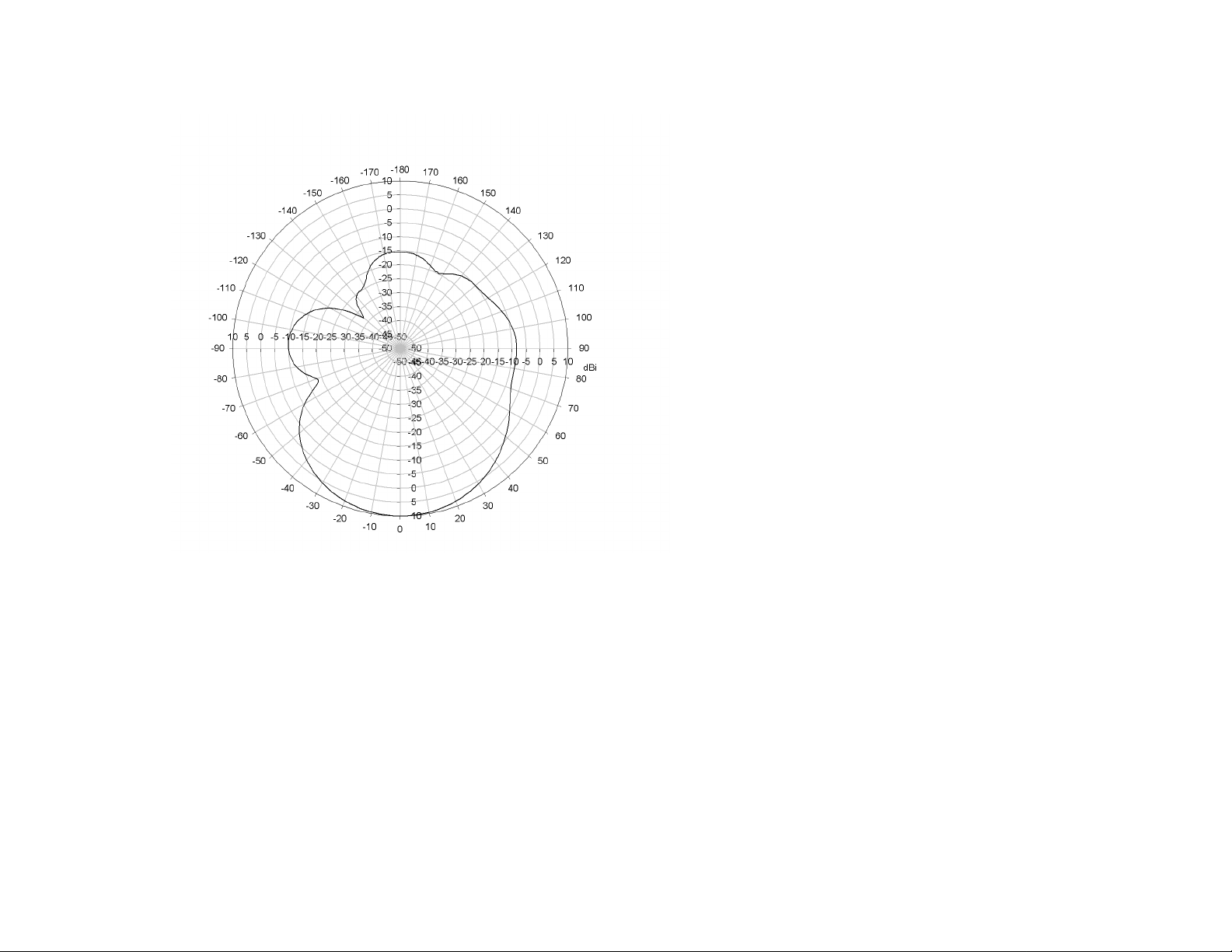
Figure 3-5: Internal Antenna Pattern (Horizontal Plane)
The above diagram shows the antenna pattern of the built-in directional antenna on the horizontal plane. The
power of the wireless signal is most strong on the direction perpendicular to the front surface (with Linksys
logo) of the Access Point. The peak gain of this antenna is 9dBi. The 3dB beamwidth is 47 degrees.
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
The Antenna Pattern
9
Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
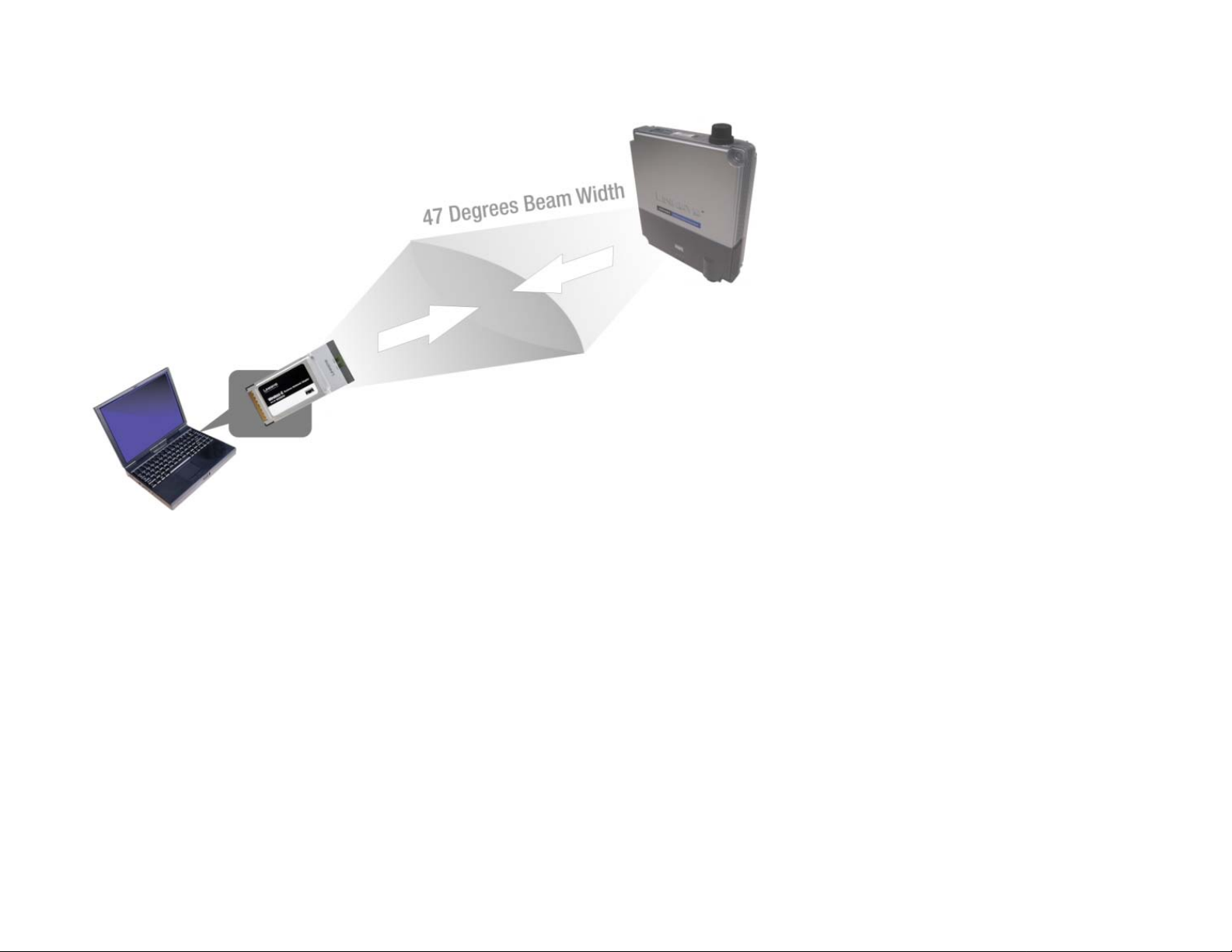
Figure 3-6: Radio Coverage of the Access Point to Client Devices
When using the Access Point to connect client devices, adjust it so the client devices are on the same
horizontal plane as the Access Point and within a 3dB angle of 47 degrees. This will ensure the strongest
signal and maximum reach.
If the Access Point is used inside a building, put it in a corner of the building for maximum coverage.
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
The Antenna Pattern
10
Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
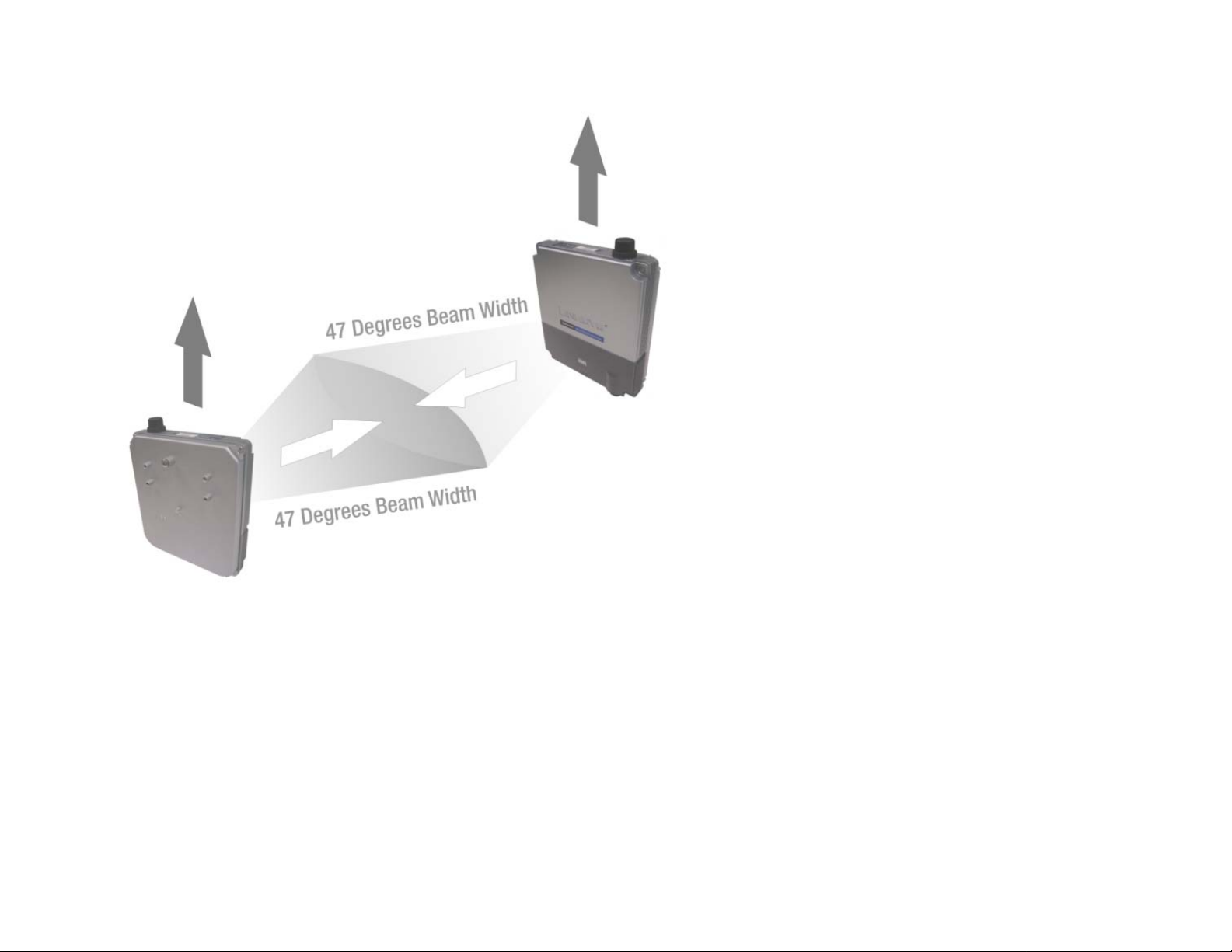
Figure 3-7: Access Point to Access Point (bridging) Radio Coverage
If the Access Point is used as a bridge or repeater, adjust the Access Points to face each other to ensure the
strongest signal and maximum reach.
Make sure that the orientation of the two Directional Antennas is the same. The radio wave is polarized so a
90 degree rotation will result in no received power.
Due to its directional characteristics, the internal antenna is ideal for point-to-point bridge mode or the spoke
side of point-to-multipoint bridge mode. It is recommended to use an external omni-directional antenna (e.g.
HGA9N) for repeater mode applications.
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
The Antenna Pattern
11
Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
Chapter 4: Connecting the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
hardware: the physical aspect of
Overview
This chapter explains how to mount and connect the Access Point.
Depending on your application, you might want to set up the IP address of the device first before mo unting
the device. Refer to "Chapter 5: Setting Up the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point".
Hardware Installation
1. Locate an optimum location on a wall for the Access Point. Refer to the antenna pattern in "Chapter 3:
Getting to Know the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point" to adjust the angle of the Access Point for your
application.
computers, telecommunications, and
other information technology devices.
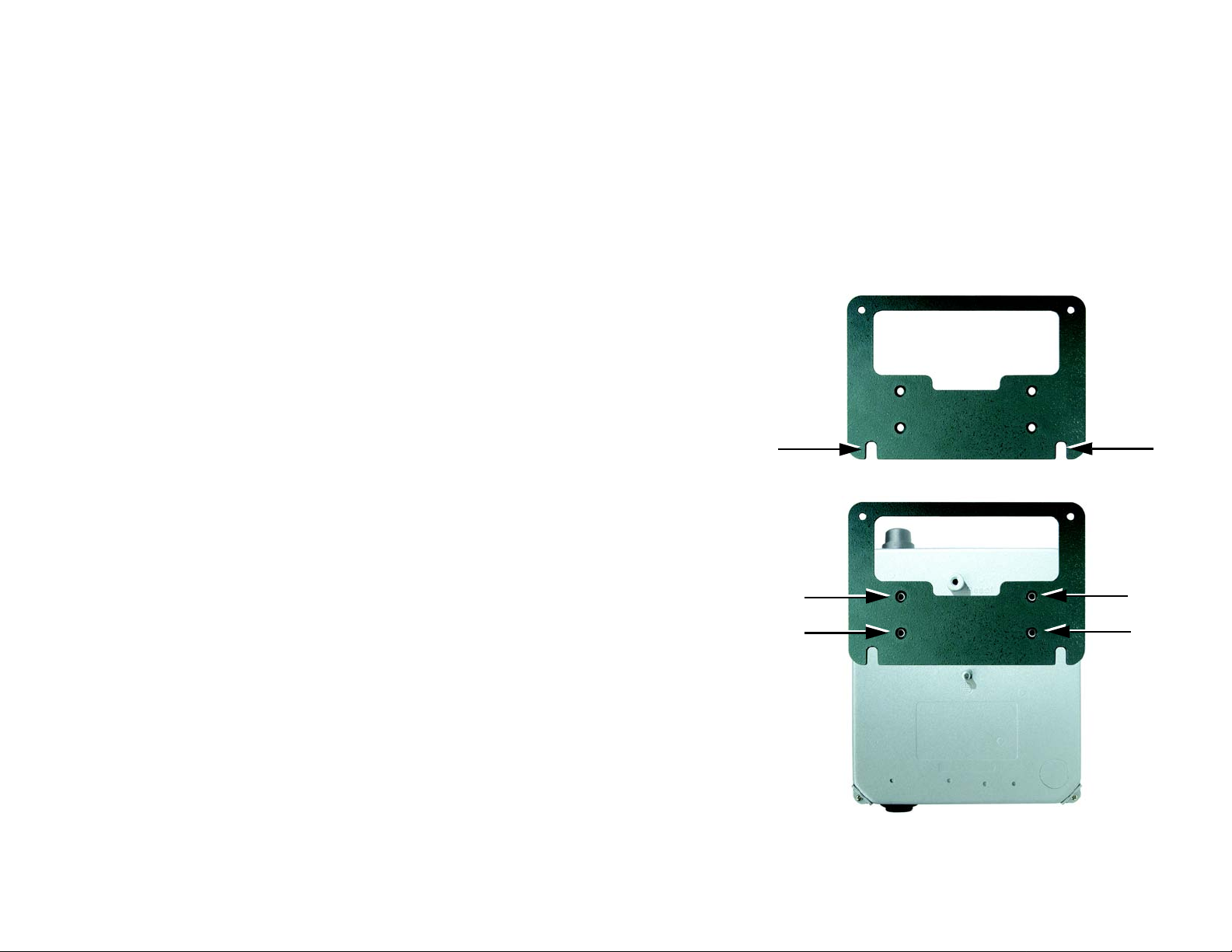
2. Using the mounting plate as a template, mark the locations of the two wall-mount slots that are on the
bottom of the mounting plate. Then, install a screw into each location.
3. Use four screws (included with the Access Point) to attach the mounting plate to the back panel of the
Access Point.
4. Connect the included Category 5e Ethernet network cable to the Ethernet network port of the Access
Point. Then, screw the connector cap tightly onto the port, so the Access Point has a water-resistant seal.
5. If you want to connect an optional, high-gain external antenna, unscrew the cap that protects the Type-N
antenna port, then, connect your antenna cable to this port.
Chapter 4: Connecting the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
Overview
Figure 4-1: Mark the Locations of the Two Wall-Mount
Slots
12
Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
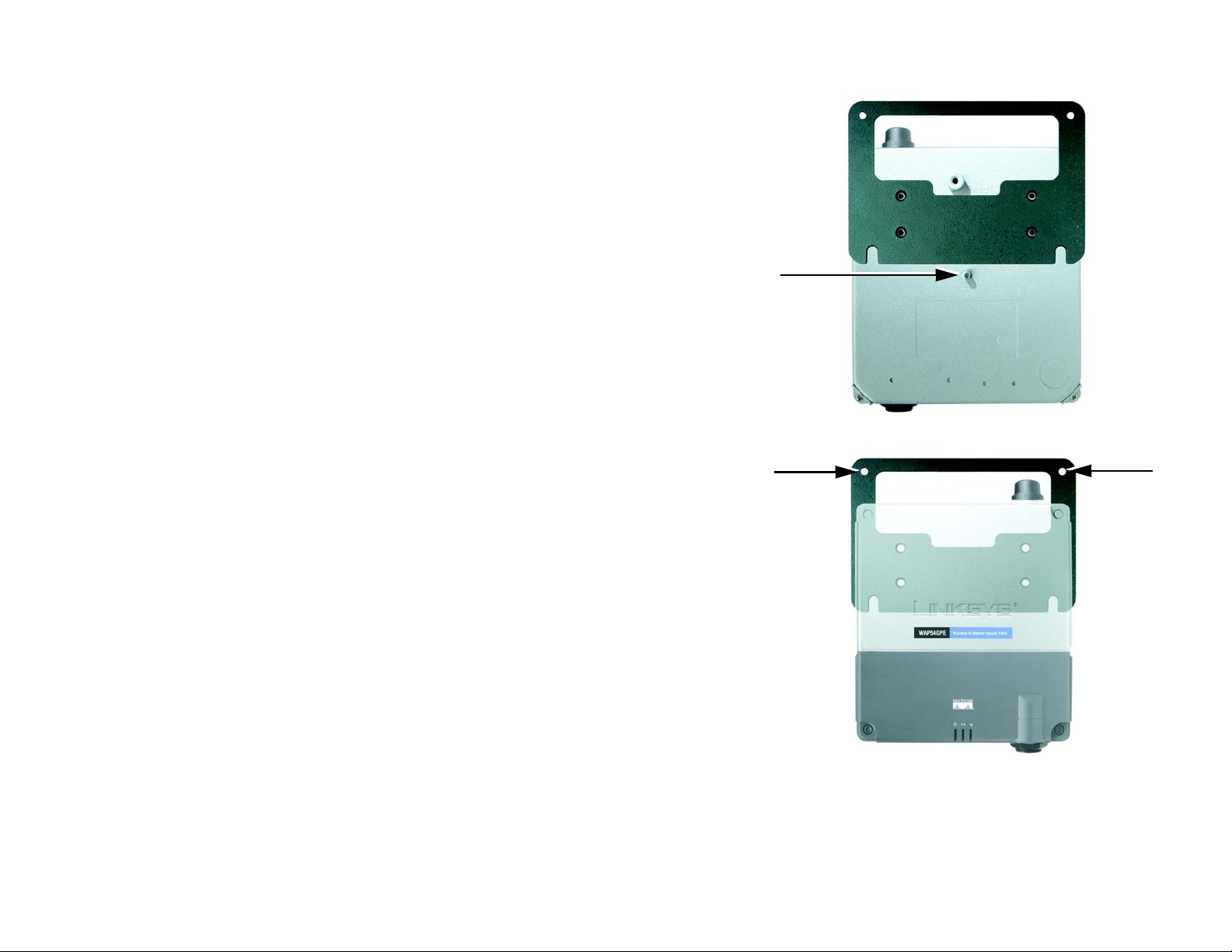
6. Make sure that you properly ground the Access Point.
7. Line up the Access Point’s wall-mount slots with the two screws on the wall. Then, slide the Access
Point down so that the screws fit snugly in the slots.
8. Attach a screw (not included) in each of the two holes on the top of the mounting plate so that the Access
Point is securely mounted to the wall.
9. Connect the other end of the Ethernet network cable to a switch, router, or other device that supports
Power over Ethernet. The Access Point will then be connected to your wired network.
Now that the hardware installation is complete, proceed to "Chapter 5: Setting Up the Wireless-G Exterior
Access Point," for directions on how to configure the Access Point.
Figure 4-2: Attach the Mounting Plate
Chapter 4: Connecting the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
Hardware Installation
Figure 4-3: Ground the Access Point
13
Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
Chapter 5: Setting Up the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
Overview
The Access Point has been designed to be functional right out of the box with the default settings. However,
if you'd like to change these settings, the Access Point can be configured through your web browser with the
Web-based Utility. This chapter explains how to use the Utility.
The Utility can be accessed via web browsers, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer or Mozilla Firefox
through the use of a computer that is networked with the Access Point.
For a basic network setup, most users only have to use the following screens of the Utility:
•Setup
On the Setup screen, enter your basic network settings (IP address) here.
• Management
Click the Administration tab and then select the Management screen. The Access Point’s default
password is admin. To secure the Access Point, change the AP Password from its default.
Most users will also customize their wireless settings:
• Wireless
On the Wireless screen, change default SSID under the Basic Wireless Settings Tab. Select the level of
security under the Wireless Security Tab.
Accessing the Utility
HAVE YOU:Enabled TCP/IP on your PCs?
PCs communicate over the network with this
protocol. Refer to “Appendix D: Windows
Help” for more information on TCP/IP.
tcp/ip: a set of protocols PCs use to
communicate over a network.
browser: an application that provides a way to
look at and interact with all the information on
the World Wide Web.
There are three ways to connect to your Access Point for the first time.
1. If you have a 48V Power Injector (e.g. Linksys WAPPOE), power up your Access Point first then
connect the cable on your Injector to your PC. Configure your PC to have static IP address on the same
subnet as the Access Point’s default IP address (192.168.1.245).
2. If you have a PoE switch (e.g. Linksys SRW224P), connect your Access Point and your PC to the same
LAN. Configure your PC to have the static IP address on the same subnet as the Access Point’s default IP
Chapter 5: Setting Up the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
Overview
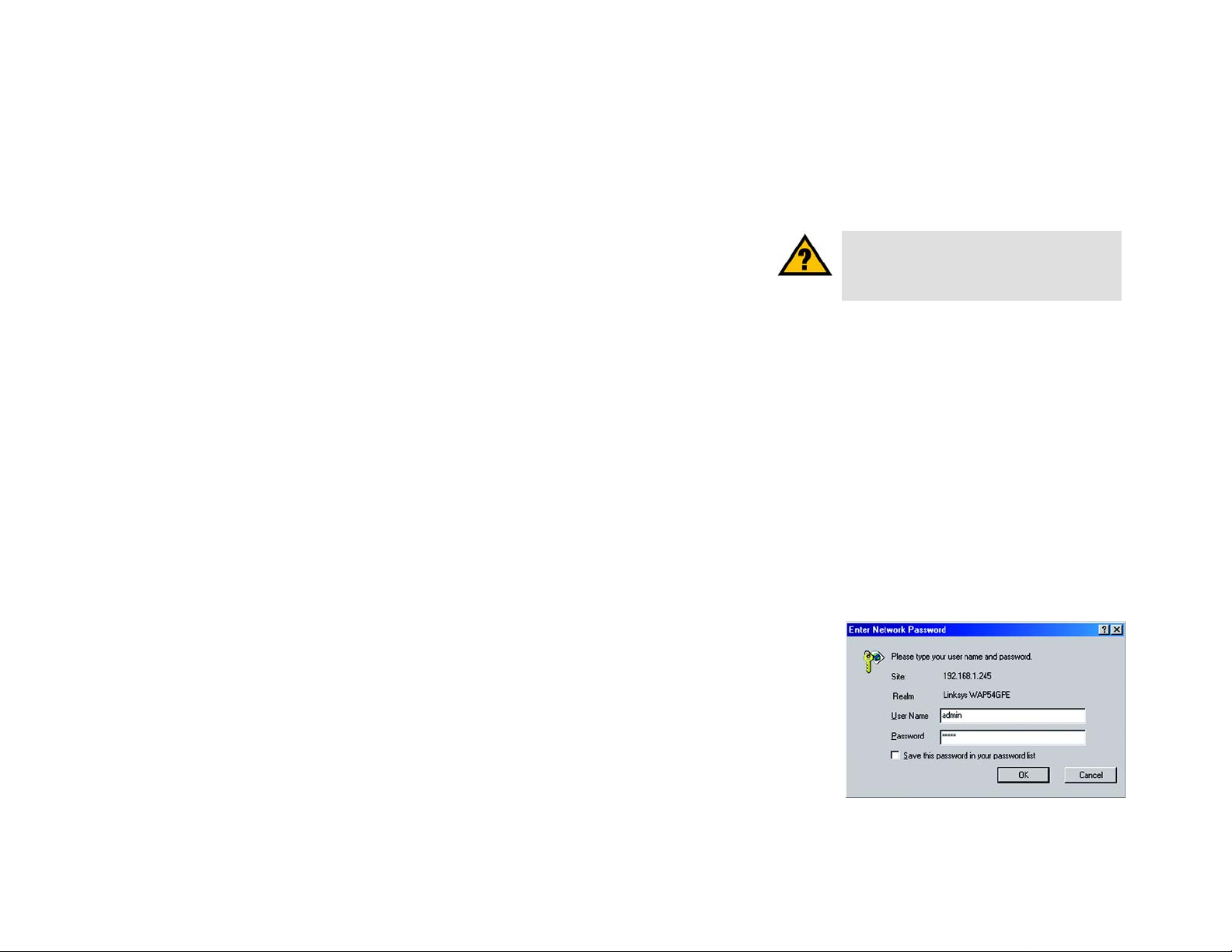
Figure 5-1: Login Screen
14

Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
address (192.168.1.245). Or if there is DHCP server connected to the switch, configure it to assign the IP
address in 192.168.1.0/24 subnet. Your PC will get an IP address in the subnet through the DHCP.
3. It is not recommended to use it this way, but you can connect your PC wirelessly to the Access Point
when the DHCP server is connected on the LAN side. It is not recommended because you can easily lose
your connection through configuration changes.
Launch your web browser, such as Internet Explorer or Mozilla Firefox and enter the Access Point’s default
IP address, 192.168.1.245, in the Address field. Press the Enter key.
Enter admin in the User Name field. The first time you open the Web-based Utility, use the default
password, admin. (You can set a new password from the Administration - Management tab.) Then click the
OK button.
After setting up the Access Point to use DHCP or manually configure a new IP address, move your Access
Point to the desired network. You will have to use the new IP address the next time you access the Webbased Utility.
Navigating the Utility
The Web-based Utility consists of the following five main tabs: Setup, Wireless, AP Mode, Administration,
and Status. Additional screens (sub tabs) will be available from most of the main tabs.
The following briefly describes the main & sub tabs of the Utility.
Setup
Enter the Host Name and IP Address settings on this screen.
Wireless
You will use the Wireless tabs to enter a variety of wireless settings for the Access Point.
• Basic Wireless Settings. Choose the wireless network mode (e.g. wireless-G), Virtual Local Area
Network (VLAN) settings, SSIDs, and transmit rates on this screen.
• Wireless Security. Use this screen to configure the Access Point’s security settings.
• Wireless Network Access. Use this screen to populate your Access List to permit or block certain MAC
address access to your wireless network.
Chapter 5: Setting Up the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
Navigating the Utility
15

Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
• Advanced Wireless Settings. Use this screen to configure the Access Point’s more advanced wireless
settings (e.g. Wireless Isolation, Output Power, etc.).
AP Mode
Use this screen to configure the Access Point operation mode with WDS (Wireless Distribution System).
Administration
You will use the Administration tabs to manage the Access Point.
• Management. This screen allows you to customize the password and Simple Network Management
Protocol (SNMP) settings.
• Log. Configure the Log settings for the Access Point on this screen.
• Factory Default. Use this screen to reset the Access Point to its factory default settings.
• Firmware Upgrade. Upgrade the Access Point’s firmware on this screen.
• Reboot. Use this screen to reboot the Access Point.
• Config Management. You can back up the configuration file for the Access Point, as well as save the
backup configuration file to the Access Point.
Status
You will be able to view status information for your local network, wireless networks, and network
performance.
• Local Network. This screen displays system information, including software & hardware version, MAC
address, and IP address on the LAN side of the Access Point.
snmp: the standard network management
protocol on the Internet.
firmware: the software image that runs on a
CPU inside a networking device.
• Wireless. This screen will display current information on the Access Point and its wireless networks.
• System Performance. This screen will display current information on the Access Point and its data
transmissions.
Chapter 5: Setting Up the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point
Navigating the Utility
16
 Loading...
Loading...