Page 1

ROTOSCAN RS4
Safety Laser Scanners
e reserve the right to
EN 2011/03 - 607144
W
make technical changes
SAFE IMPLEMENTATION AND OPERATION
Original operating instructions
Page 2

© 2011
Leuze electronic GmbH + Co. KG
In der Braike 1
D-73277 Owen - Teck / Germany
Phone: +49 7021 573-0
Fax: +49 7021 573-199
http://www.leuze.com
info@leuze.de
Version 8.6
Page 3

Contents
1 About this document..................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.1 Other applicable documents .........................................................................................................................................6
1.2 Used symbols and signal words ...................................................................................................................................6
2 Safety............................................................................................................................................................................ 7
2.1 Proper use .................................................................................................................................................................... 7
2.2 Appropriately qualified person ......................................................................................................................................7
2.3 Responsibility for safety................................................................................................................................................ 7
2.4 Laser.............................................................................................................................................................................8
2.5 Handling the safety sensor ...........................................................................................................................................8
2.6 Usage limits .................................................................................................................................................................. 8
2.7 Guarantee the availability of the safety sensor.............................................................................................................9
2.8 Providing the company operating the machine with information................................................................................... 9
2.9 Exemption of liability ................................................................................................................................................... 10
3 Device description ......................................................................................................................................................11
3.1 Device overview.......................................................................................................................................................... 12
3.2 Display elements ........................................................................................................................................................12
3.3 Mounting system (option) ...........................................................................................................................................14
3.4 ConfigPlug (option).....................................................................................................................................................14
4 Functions .................................................................................................................................................................... 15
4.1 Start/restart interlock................................................................................................................................................... 15
4.1.1 Start interlock..............................................................................................................................................................15
4.1.2 Restart interlock.......................................................................................................................................................... 15
4.2 Start test .....................................................................................................................................................................15
4.3 Automatic start/restart.................................................................................................................................................15
4.3.1 Automatic start............................................................................................................................................................15
4.3.2 Automatic restart......................................................................................................................................................... 16
4.4 Dust suppression ........................................................................................................................................................ 16
4.5 Field pair switchover ................................................................................................................................................... 16
4.6 Reference boundary monitoring .................................................................................................................................17
4.7 MotionMonitoring ........................................................................................................................................................ 17
5 Applications ................................................................................................................................................................19
5.1 Stationary danger zone guarding................................................................................................................................ 19
5.2 Stationary point of operation guarding........................................................................................................................20
5.3 Stationary access guarding ........................................................................................................................................ 21
5.4 Mobile danger zone guarding .....................................................................................................................................22
5.5 Mobile side guarding................................................................................................................................................... 23
6 Mounting .....................................................................................................................................................................24
6.1 Basic infos ..................................................................................................................................................................24
6.2 Basic infos on the protective field dimensioning .........................................................................................................25
6.2.1 Handling unmonitored areas....................................................................................................................................... 25
6.2.2 Protective field setup with adjacent safety sensors .................................................................................................... 26
6.3 Stationary danger zone guarding................................................................................................................................ 28
6.3.1 Beam level height ....................................................................................................................................................... 29
6.3.2 Safety distance "S" ..................................................................................................................................................... 29
6.3.3 Additional distance "C" because of the possibility of reaching over............................................................................ 30
6.3.4 Machine response times, stopping time ..................................................................................................................... 30
6.3.5 Application-conditional additional distances for safety distance "S" ........................................................................... 31
6.3.6 Minimum distance "D" to the protective field contour..................................................................................................31
6.4 Stationary point of operation guarding........................................................................................................................32
6.4.1 Safety distance "S" ..................................................................................................................................................... 33
6.4.2 Additional distance C ..................................................................................................................................................33
6.4.3 Machine response times, stopping time ..................................................................................................................... 33
6.4.4 Protective field and reference boundary ..................................................................................................................... 34
6.5 Stationary access guarding ........................................................................................................................................ 34
6.5.1 Safety distance "S" .................................................................................................................................................... 35
6.5.2 Machine response times, stopping time ..................................................................................................................... 35
Leuze electronic RS4 3
Page 4

Contents
6.5.3 Protective field contour and reference boundary........................................................................................................36
6.6 Mobile danger zone guarding on DTSs ...................................................................................................................... 36
6.6.1 Basic requirements.....................................................................................................................................................37
6.6.2 Minimum distance D ................................................................................................................................................... 37
6.6.3 Protective field dimensions ........................................................................................................................................39
6.6.4 Test mode for MotionMonitoring................................................................................................................................. 39
6.7 Mobile side guarding on DTSs.................................................................................................................................... 40
7 Technical data ............................................................................................................................................................ 41
7.1 Safety.......................................................................................................................................................................... 41
7.2 Optics.......................................................................................................................................................................... 41
7.3 Protective field ............................................................................................................................................................42
7.4 Warning field............................................................................................................................................................... 42
7.5 Measured data............................................................................................................................................................ 42
7.6 Electrical power supply .............................................................................................................................................. 43
7.7 Software...................................................................................................................................................................... 44
7.8 Ambient conditions ..................................................................................................................................................... 44
7.9 Dimensions, weight..................................................................................................................................................... 45
8 Electrical connection...................................................................................................................................................47
8.1 Electrical power supply...............................................................................................................................................47
8.2 Interfaces .................................................................................................................................................................... 47
8.2.1 X1 plug interface assignment ..................................................................................................................................... 48
8.2.2 Interface assignment, plug X2 .................................................................................................................................... 49
8.3 Assemble cables......................................................................................................................................................... 50
8.4 Integrating the safety sensor into machine control system.........................................................................................51
8.4.1 Downstream safety circuit with start/restart interlock, contactor monitoring, without field pair switchover ................. 51
8.4.2 Programmable logic controller (PLC) with corresponding safety level and field pair switchover................................ 51
9 Parameters ................................................................................................................................................................. 53
9.1 Administrative parameters..........................................................................................................................................53
9.1.1 Safety Laser Scanner name ....................................................................................................................................... 53
9.1.2 Description..................................................................................................................................................................53
9.1.3 Start segment output ..................................................................................................................................................53
9.1.4 Stop segment output................................................................................................................................................... 53
9.1.5 Output resolution ........................................................................................................................................................53
9.1.6 Serial interface baud rate............................................................................................................................................ 54
9.1.7 Alarm incident............................................................................................................................................................. 54
9.1.8 Precalculated measured values output....................................................................................................................... 54
9.1.9 2nd measured value calculation segment .................................................................................................................. 54
9.1.10 3rd measured value calculation segment ................................................................................................................... 54
9.2 Safety-relevant parameters ........................................................................................................................................55
9.2.1 Application .................................................................................................................................................................. 55
9.2.2 Response times..........................................................................................................................................................55
9.2.3 Dust suppression ........................................................................................................................................................55
9.2.4 Applicable field pair selection with scanner start ........................................................................................................56
9.2.5 Permitted field pair switchovers ..................................................................................................................................56
9.3 Field pair .....................................................................................................................................................................56
9.3.1 Protective field/description .......................................................................................................................................... 56
9.3.2 Warning field/description ............................................................................................................................................ 56
9.4 MotionMonitoring ........................................................................................................................................................ 56
9.4.1 Vehicle width............................................................................................................................................................... 56
9.4.2 Protective field side additional distance......................................................................................................................56
9.4.3 Laser scanner installation point .................................................................................................................................. 57
9.4.4 Warning field prerun time............................................................................................................................................ 57
9.4.5 Vehicle response time ................................................................................................................................................ 57
9.4.6 Brake wear and tear additional distance..................................................................................................................... 57
9.4.7 Ambient influences additional distance....................................................................................................................... 57
9.4.8 Speed with PF ............................................................................................................................................................58
9.4.9 Braking distance with PF ............................................................................................................................................58
9.4.10 Standstill monitoring ................................................................................................................................................... 58
9.4.11 Creep and reverse ...................................................................................................................................................... 58
Leuze electronic RS4 4
Page 5

Contents
10 Setting the device into service .................................................................................................................................... 59
10.1 Before first start-up ..................................................................................................................................................... 59
10.2 Switching on ............................................................................................................................................................... 59
10.3 Shutting down .............................................................................................................................................................59
10.4 Restart ........................................................................................................................................................................ 59
10.5 Starting up the replacement device ............................................................................................................................ 60
10.6 Starting up a safety sensor with the MotionMonitoring function.................................................................................61
11 Testing ........................................................................................................................................................................ 66
11.1 Testing before first start-up and after machine modification....................................................................................... 66
11.2 Regular test by an appropriately qualified person ...................................................................................................... 67
11.3 Daily functions test...................................................................................................................................................... 67
12 Maintenance ............................................................................................................................................................... 69
12.1 Clean the front screen ................................................................................................................................................69
12.2 Clean scatter screens.................................................................................................................................................70
13 Diagnostics and removing errors ................................................................................................................................ 71
13.1 What to do in case of failure? ..................................................................................................................................... 71
13.2 Operating displays of the LEDs .................................................................................................................................. 71
13.3 LED warning and error displays.................................................................................................................................. 72
13.4 Diagnostics codes.......................................................................................................................................................73
14 Repairs .......................................................................................................................................................................78
14.1 Change the front screen .............................................................................................................................................78
15 Disposing .................................................................................................................................................................... 81
16 Service........................................................................................................................................................................ 82
17 Accessories ................................................................................................................................................................83
17.1 Accessories to choose from........................................................................................................................................ 83
Leuze electronic RS4 5
Page 6
1 About this document
1.1 Other applicable documents
The information on the safety sensor is distributed over several documents to make working with the documents easier. You will find the documents and programs for the safety sensor in the following table:
About this document
Purpose and target group of the document Document/software
title
Software for users of the machine* for safety sensor
diagnostics if a fault occurs and for machine design
engineers* for configuring the safety sensor
Notes for the machine design engineer* Safe implementation
Notes for the machine design engineer* for configuring the safety sensor (Software RS4soft instructions)
Additional information on ROTOSCAN RS4/AS-i Additional information
Additional information on ROTOSCAN RS4/
PROFIsafe
* identifies the product that the safety sensor is installed in.
** You can download the current version of the software and all documents as PDF on the Internet at:
http://www.leuze.com/rotoscan
RS4soft Included with the product
and operation
(this document)
Safe parametering Art. no. 607143**
for the ROTOSCAN
RS4-4 connecting and
operating instructions
Additional information
for the ROTOSCAN
RS4-4 Laser Scanner
connecting and operating instructions
Source
delivery on CD-ROM**
Art. no. 607144**
Included with the product
delivery on CD-ROM
Included with the product
delivery on CD-ROM
Art. no. 607060**
Included with the product
delivery on CD-ROM
Art. no. 605054**
Included with the product
delivery on CD-ROM
1.2 Used symbols and signal words
Table 1.1: Warning symbols and signal words
Symbol for dangers
NOTICE Signal word for property damage
Indicates dangers that could damage the safety sensor if the measures for preventing
danger are not implemented.
CAUTION Signal word for minor injury
Indicates dangers that could slightly injure you if the measures for preventing danger are
not implemented.
WARNING Signal word for serious injury
Indicates dangers that could seriously or fatally injure you if the measures for preventing
danger are not implemented.
DANGER Signal word for life-threatening danger
Indicates dangers that could seriously or fatally injure you if the measures for preventing
danger are not implemented.
Table 1.2: Other symbols
Symbol for tips
Texts with this symbol provide you with further information on handling the safety sensor.
ª
Symbols for action steps
Text passages with this symbol instruct you to perform actions.
Leuze electronic RS4 6
Page 7

2 Safety
If the safety sensor is not selected and used correctly, severe accidents may result.
ª Carefully follow all notices regarding the safety sensor.
ª Make certain that all other people also know and observe the notices that apply to them.
The documents are part of the product. Non-observance presents a high risk to personal health and life.
ª Observe the documents on the CD ROM included with the product.
Alternatively you can also download the current documents on the Internet.
Internet: http://www.leuze.com/rotoscan
For an overview of other applicable documents (see chapter 1.1 „Other applicable documents“).
ª Read and observe the documents that apply for your activities in full before you work with the safety
sensor.
Safety
WARNING
Print out the relevant text parts to make reading and handling the documents easier.
2.1 Proper use
The safety sensor is used to protect people in danger zones or at points of operation on machines and to
protect objects and machine parts against the dangers of collision.
The safety sensor may only be used after it has been put into operation in accordance with the applicable
instructions, relevant rules and regulations on occupational health and safety at work and the recognized
safety-related rules and regulations have been placed on the machine by an appropriately qualified
person.
The safety sensor must be integrated into the machine's electrical control system in such a way that an
activation of the safety function safely stops or interrupts the dangerous process before a person can be
endangered.
If the machine does not allow the dangerous movement to be stopped at all times, you may not install the
safety sensor. Do not use the safety sensor, for example, together with a press with form-locking coupling.
2.2 Appropriately qualified person
Appropriately qualified is a person that,
• has acquired adequate knowledge and skills with regard to operating the machine, the configuration
and diagnostics software and testing the safety sensor through training and practical experience and
has proven their capabilities in practice,
• and is so well versed in the applicable rules and regulations on occupational health and safety at
work and the recognized safety-related rules and regulations that he/she can evaluate the safety of
the machine,
• and has been instructed in the machine's operation and safety rules and regulations,
• and has read and understood the respective applicable instructions for the safety sensor and the
machine's operating instructions,
• and has been charged by the respective person responsible for the machine's safety with the testing
of the safety sensor.
2.3 Responsibility for safety
The responsibility for the safety-assured use of the safety sensor and compliance with the regulations and
directives that apply in the country of use lies with the machine's manufacturer and company operating the
machine.
Leuze electronic RS4 7
Page 8
The manufacturer of the machine is responsible for:
• The safe design and construction of the machine.
• The safe implementation of the safety sensor.
• The provision of all relevant information to the operator company.
• Compliance with all regulations and directives for safely putting the machine into operation.
The operating company is responsible for:
• Instructing the operating staff.
• Maintaining the safe operation of the machine.
• Compliance with all occupational health and safety at work regulations and directives.
Passwords
Improperly set parameters on the safety sensor can cause serious accidents. The configuration of the
safety sensor is therefore protected by passwords.
ª Ensure that the passwords are kept locked away by the security officer.
ª The people responsible for the machine's safety must ensure that the appropriately qualified person can
properly perform the tests and work on the machine and the safety sensor in accordance with their
intended use.
2.4 Laser
The safety sensor corresponds with laser class 1. Additional activities for shielding the laser beams are
not required (safe for eyes).
Safety
ª Observe the applicable legal and local regulations for operating laser equipment.
2.5 Handling the safety sensor
ª Observe the permissible environmental conditions for storage and operation.
Front screen and scatter screens
The safety sensor's front screen and scatter screens must be clean, free of damage and properly installed.
ª Avoid touching the front screen and scatter screens.
ª Clean dirty screens immediately (according to these instructions).
ª Have damaged screens replaced immediately (according to these instructions).
Screwed-on cables
Improper handling can damage the safety sensor and result in safety-relevant signals not being sent. The
safety sensor's IP type of protection is only guaranteed with screwed-on plug cover caps.
ª Only operate, transport and store the safety sensor with screwed-on control cable (X1) and PC cable
(X2) or dummy plug (X2).
2.6 Usage limits
Laser Klasse 1
Laser Class 1
Laser de Classe 1
Only on closed rooms
The safety sensor is not suitable for use outdoors or under conditions with significant temperature
fluctuations. Humidity, condensation and other weather influences can impair the safety function.
ª Only use the safety sensor in closed rooms.
ª Observe all technical data and ambient conditions.
Industrial use only
The safety sensor is not suitable for residential areas, because it can cause radio interferences.
ª Only use the safety sensor in industrial environments.
Leuze electronic RS4 8
Page 9

Safety
Not on vehicles with combustion engines
The safety sensor is not suitable for use on vehicles with combustion engines, because alternators
or ignition systems can cause EMC disturbances.
ª Only use the safety sensor on vehicles without a combustion engine.
No changes on the safety sensor
The construction of the safety sensor may not be changed, because the protective function can no longer
be guaranteed if the safety sensor is changed. Manipulating the safety sensor also voids all warranty
claims against the manufacturer of the safety sensor.
Service life T
Values PL and PFH
according to ISO 13849-1: 2006
M
of the safety sensor refer to a service life TM of 20 years.
d
Repairs or the exchange of parts subject to wear and tear do not extend the service life.
Protective function limits
The safety sensor does not protect against:
• Projected (thrown out) parts
• Splashing/spraying liquids
• Gases and vapors
• Radiation
2.7 Guarantee the availability of the safety sensor
Vapors, smoke, dust, particles
Vapors, smoke, dust and all particles visible in the air can cause the machine to switch off unintentionally.
This can mislead the user into bypassing the safety devices.
ª Do not use the safety sensor in environments in which heavy vapors, smoke, dust or other visible par-
ticles occur at the beam level.
No stray light
Light sources can impair availability. Interfering light sources are:
• Infrared light
• Fluorescent light
• Strobe light
ª Ensure that there are no interfering light sources at beam level.
ª Prevent reflective surfaces at beam level.
ª Where applicable, take additional protective field distances into account.
ª Implement all additional measures to ensure that any special use of any effected beam types does not
impair the safety sensor's operation.
No obstructions in the protective field
ª Do not bring any additional window materials into the area monitored by the safety sensor.
2.8 Providing the company operating the machine with information
The machine manufacturer must inform the company operating the machine in detail and comprehensibly
about all activities that are required for the safety-assured operation of the machine with the safety sensor.
This also includes the forwarding of information from these instructions that the operating company
requires.
The type and content of the information may not, however, result in any questionable safety-related actions
by the user.
Where required, safety key, special tools and passwords should be maintained under the control of one or
more responsible or authorized people.
Leuze electronic RS4 9
Page 10

2.9 Exemption of liability
Leuze electronic GmbH + Co. KG is not liable in the following cases:
• safety sensor is not used as intended
• safety notices are not adhered to
• reasonably foreseeable misuse is not taken into account
• mounting and electrical connection are not properly performed
• proper function is not tested, see chapter 11 „Testing“
• changes (e.g., constructional, electrical) are made to the safety sensor.
Safety
Leuze electronic RS4 10
Page 11
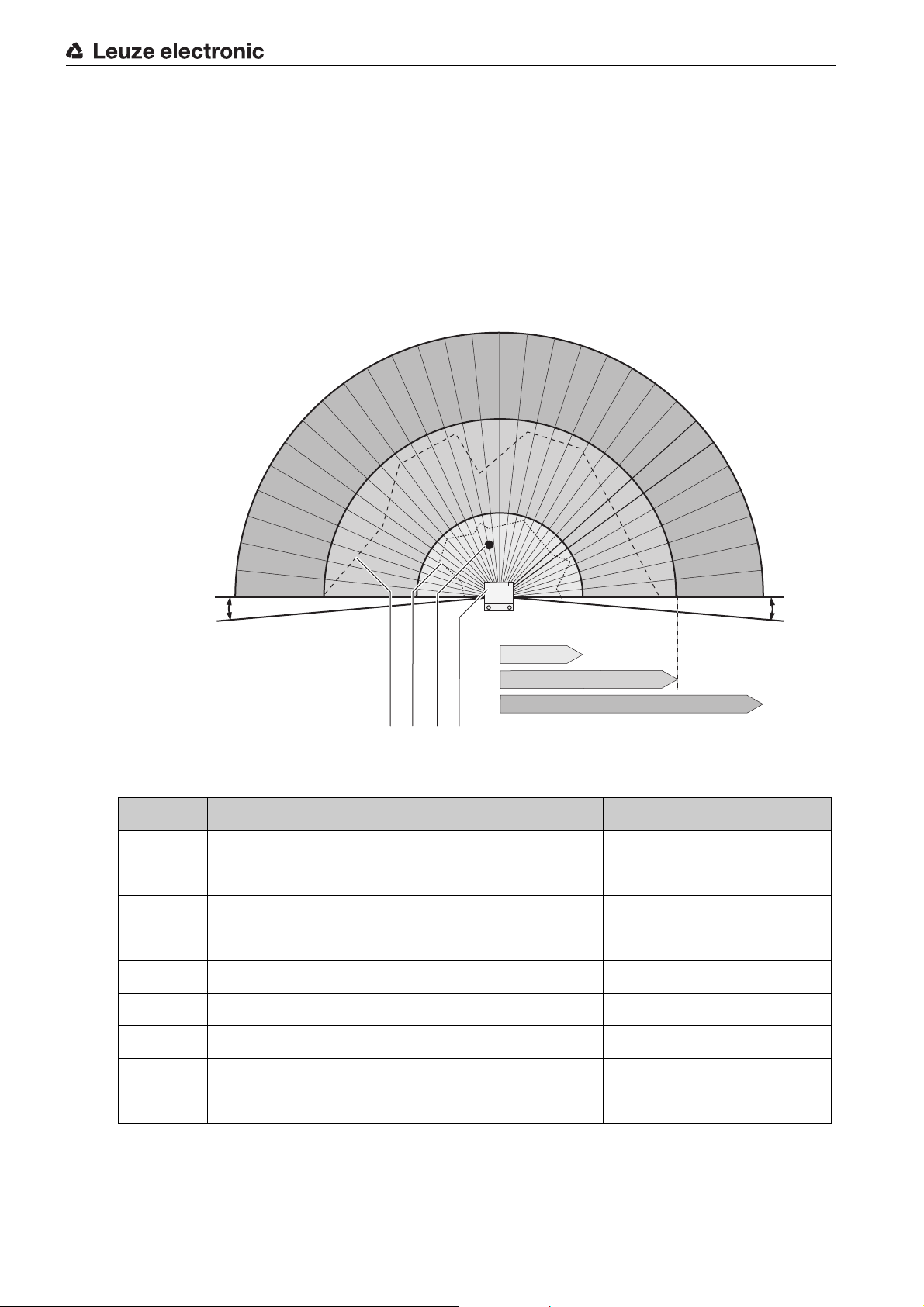
3 Device description
1
1
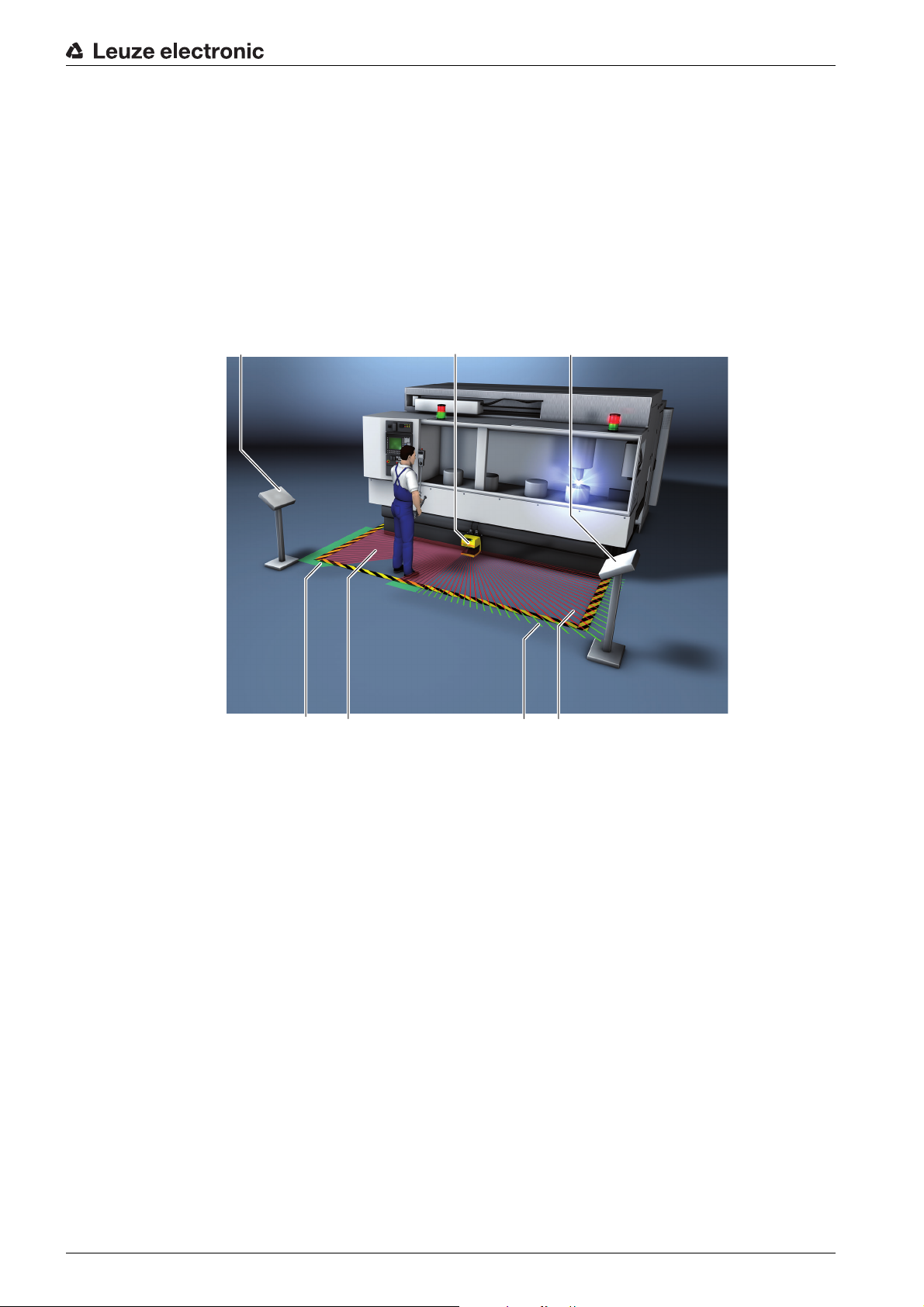
The ROTOSCAN RS4 safety sensor is an optical, two-dimensional measuring Safety Laser Scanner.
The safety sensor transmits periodic light pulses via a rotating deflection unit. The light pulses are reflected
by obstructions, e.g. people, and received by the safety sensor again and analyzed. The safety sensor
calculates the precise position of the obstruction from the light travel time and the angle of the deflection
unit at that time. If the obstruction is within a predefined area, the protective field, the safety sensor
performs a safety-related switching function. It switches the safety-related switching outputs off.
Only when the protective field is free again does the safety sensor reset the safety-related switching function, either automatically or following confirmation, depending on the operating mode.
The safety sensor can even detect people when they are wearing very dark clothes, which have a very
weak diffuse reflectance.
Device description
d
SF
WF
a
1 2
Figure 3.1: Safety sensor detection ranges
Pos. Description Comment
1 Configured warning field Example
2 Configured protective field Example
3 Object (person) in the protective field Example
4 Safety sensor
a Maximum measurement value logging 50 m
d Configurable protective and warning field extension -5°
e Configurable protective and warning field extension +5°
43
e
Leuze electronic RS4 11
PF Maximum protective field
WF Maximum warning field
Page 12
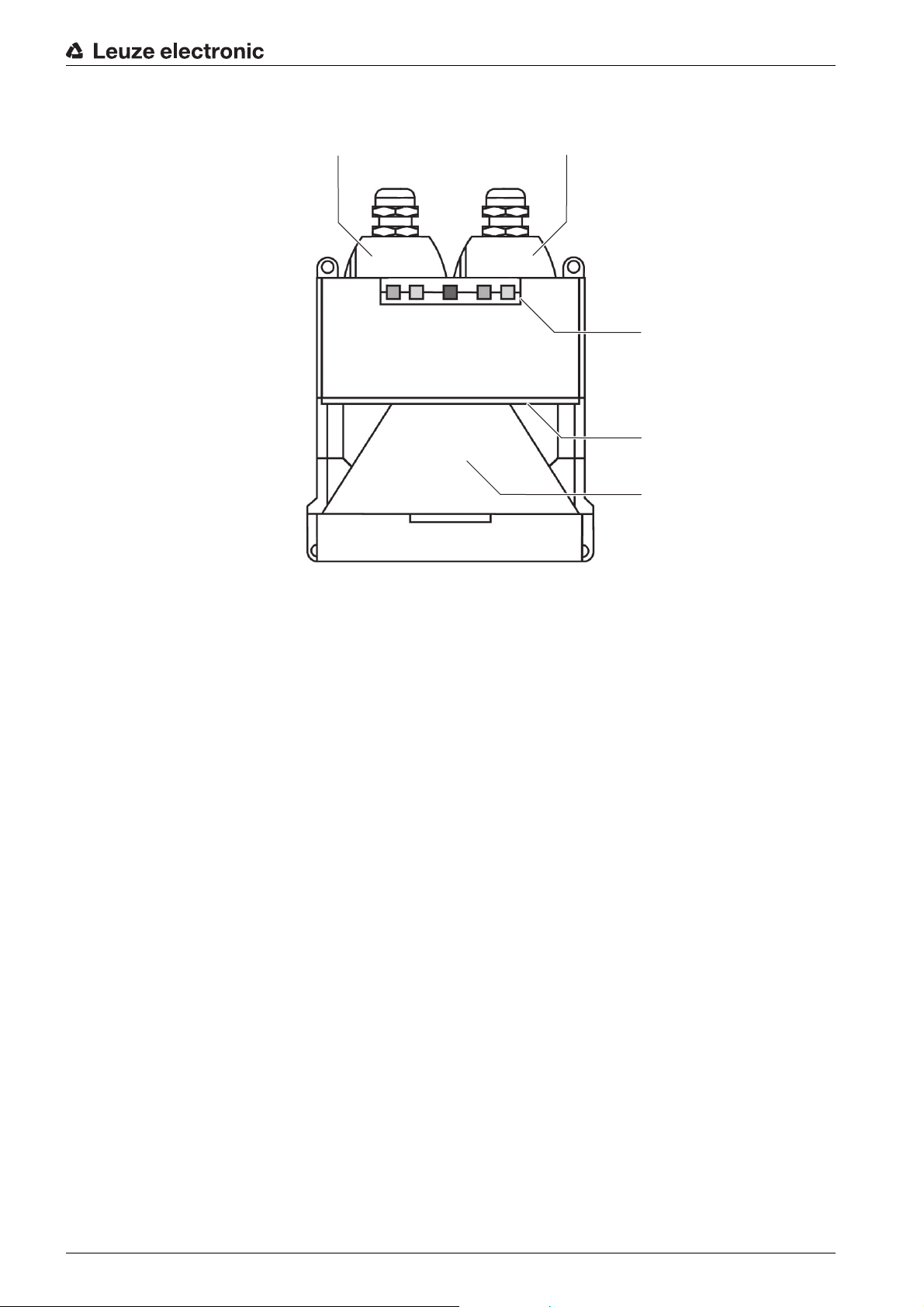
3.1 Device overview
2
4
5
3
1
Device description
1
1 X1 interface for controlling the machine, with protective cap
2 X2 interfaces for PC/laptop, with protective cap
3 Status display
4 Scatter screens
5 Front screen
Figure 3.2: Safety sensor overview
2
2
3
4
5
3.2 Display elements
Status display
Five LEDs on the front show the safety sensor's status
Leuze electronic RS4 12
Page 13
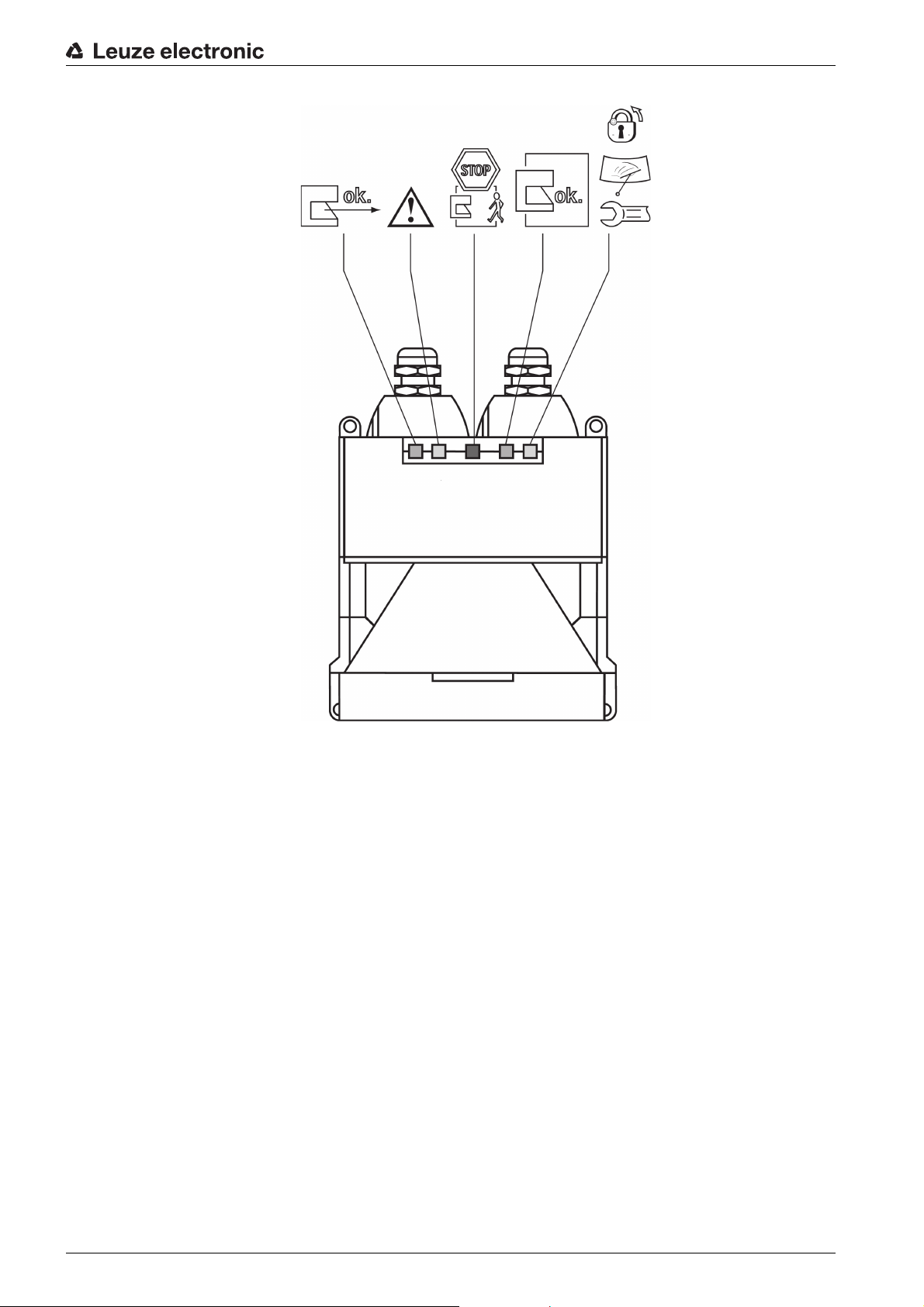
Device description
Figure 3.3: Status displays
1
3
52
4
Leuze electronic RS4 13
Page 14
Table 3.1: Meaning of the LEDs
ok.
STOP
ok.
LED Meaning
1, green Lights Sensor function is active; the active protective field is free.
Flashes with 2 Hz Fault on the field pair control inputs.
Flashes with 4 Hz MotionMonitoring has detected a fault.
2, yellow Lights Active warning field is seized.
Flashes with 2 Hz Front screen is dirty.
Flashes with 4 Hz ConfigPlug configuration is not compatible with the safety
sensor.
3, red Lights Safety-related switching outputs (OSSD 1 and 2) are
switched off.
4, green Lights Safety-related switching outputs (OSSD 1 and 2) are
switched on.
Device description
5, yellow Lights Start/restart interlock locked.
Flashes with 2 Hz Front screen is dirty.
Flashes with 4 Hz Fault
3.3 Mounting system (option)
The mounting system makes it easier to install and align the safety sensor. The mounting system is available as an accessory (see chapter 17.1 „Accessories to choose from“).
3.4 ConfigPlug (option)
The ConfigPlug makes it easier to swap out the safety sensor. It saves the configuration when the PC is
configured and automatically transfers it with the device swap-out to the replacement device. The ConfigPlug is available as an accessory (see chapter 17.1 „Accessories to choose from“).
Leuze electronic RS4 14
Page 15

4 Functions
The functions of the safety sensor must be matched to the respective application and its safety requirements. You can activate, deactivate and adjust functions with parameters (list of all parameters of the
safety sensor see chapter 9 „Parameters“). You configure the functions with the help of the RS4soft configuration and diagnostics software.
4.1 Start/restart interlock
The start/restart interlock has two functions:
• Start interlock
• Restart interlock
Using start/restart interlock
ª In addition to the safety sensor you must also install the start/restart button. The machine operator starts
the machine with this start/restart button.
ª Position the start/restart button outside the danger zone so that it cannot be activated from the protective
fields and danger zones. The operator must be able to see all danger zones from this position.
ª Identify the zone to be released on the start/restart button so that its meaning is clear and easy to under-
stand.
ª Ensure that nobody is in the danger zone before pressing the start/restart button.
Functions
4.1.1 Start interlock
The start interlock function prevents the machine from starting automatically after switching on or after the
power supply returns.
The machine only starts when you press the start/restart button.
4.1.2 Restart interlock
The restart interlock prevents the machine from starting automatically, as soon as the protective field is
free again. The restart interlock function always includes the start interlock function.
The machine only starts again when you press the start/restart button.
4.2 Start test
The start test function compels the operator to interrupt the protective field once after the safety sensor
start, e.g. with a test rod. Only then can the machine be started.
Using the start test
If you combine the start test with the automatic restart function, the start test serves as an automatic start/
restart signal.
4.3 Automatic start/restart
The machine starts automatically as soon as the machine is switched on or the supply voltage returns and
when the protective field is free again.
Using automatic start/restart
You can use the automatic start/restart function under the following conditions.
• The automatic start/restart function is taken over by a downstream safety-related component of the
machine control system.
or
• It is not possible to walk behind or go around the effective protective field.
ª Allow for an optical and/or acoustic start warning.
4.3.1 Automatic start
The automatic start function starts the machine automatically as soon as the supply voltage is present.
Leuze electronic RS4 15
Page 16
4.3.2 Automatic restart
The automatic restart function starts the machine automatically as soon as the protective field is free again.
4.4 Dust suppression
The dust suppression function increases the availability of the safety sensor when small particles are in
the air, e.g. material chips or insects.
Only deactivate the dust suppression function when, in addition to people, the safety sensor must also
detect extremely fast and small objects in your application.
If you use the safety sensor for the mobile danger zone guarding of DTSs, you must select the speed range
of your vehicle to optimize dust suppression.
4.5 Field pair switchover
The safety sensor has four or eight field pairs. Switchover between the field pairs is possible at all times,
provided the operating situation allows this.
During the switchover process the safety sensor monitors the field pair activated before the changeover
until a new one has been clearly activated. Use the field pair switchover when the danger zones vary
depending on the activity of the machine or the operating status, e.g. driverless transportation system
(DTSs), to control the protective field switchover for straight and curved stretches.
If the rules for field pair switchover are not complied with, the safety sensor signals a fault and the machine
stops.
Functions
Using field pair switchover
You can configure and switch over the field pairs according to the different requirements. The switchover
is performed via the corresponding control inputs on the X1 interface.
The precepts for the switchover depend on the amount of the selected field pairs and their numbers. The
activated field pair must correspond with the respective operating mode. The time of the switchover must
correspond with the machine's risk assessment. You must take the braking distances, response times and
machine stopping times, e.g. influenced by overlapping protective fields, into account.
If these rules are not complied with, the safety sensor goes to a fault status within 40 ms. The green LED
1 flashes with 2 Hz.
The following rules apply for switching over four field pairs:
• First the control unit must switch to a new field pair before it switches of the previous one.
• The switchover must be made within 1 sec. Both field pairs are monitored during the switchover
time.
• All field pairs must never be deactivated during the switchover.
• The switchover process performed by the control system must agree with the safety sensor's configuration. This configuration is specified with the configuration and diagnostics software.
Table 4.1: Connection of control inputs FP1 to FP4 with activation of field pairs 1 to 4.
Field pair Control input Description
FP1 FP2 FP3 FP4
1 1000Field pair 1 is active
2 0100Field pair 2 is active
3 0010Field pair 3 is active
4 0001Field pair 4 is active
The following rules apply for switching over eight field pairs:
• The switchover must be made within 40 ms, i.e. after 40 ms an input connection must be valid and
stable. The old field pair is monitored during the switchover time. The new field pair is monitored after
max. 80 ms.
• The switchover process performed by the control system must agree with the safety sensor's configuration. This configuration is specified with the configuration and diagnostics software.
Leuze electronic RS4 16
Page 17
Functions
Table 4.2: Connection of control inputs FP1 to FP4 with activation of field pairs 1 to 8.
Field pair Control input Description
FP1 FP2 FP3 FP4
1 1000Field pair 1 is active
2 0100Field pair 2 is active
3 0010Field pair 3 is active
4 0001Field pair 4 is active
5 1110Field pair 5 is active
6 1101Field pair 6 is active
7 1011Field pair 7 is active
8 0111Field pair 8 is active
WARNING
Field pair switchover to field pair 8 deactivates the monitoring function
No field pair is now monitored; the safety outputs (OSSDs) remain constantly active.
ª Never start the safety sensor with field pair 8.
ª Only use field pair 8 when there is no danger for people present, e.g. with vehicles in creep and
reverse, in the area of loading or park positions or during machine cycles with which there is no danger
for the operating staff.
4.6 Reference boundary monitoring
The reference boundary monitoring function prevents unintentional misalignment and deliberate manipulation of the safety sensor. If a protective field contains an area with reference boundary, the safety sensor
not only monitors interruptions of the protective field, it also monitors the concurrence of the measured
area contour with the set reference boundary. If the measurement values of the area contour deviate from
the defined reference boundary by more than the tolerance zone, i.e., if no object is detected in the area
with reference boundary, the safety sensor switches off and the safety-related switching outputs (OSSDs)
switch to off. The reference boundary function is set together with the definition of the protective field
boundaries.
4.7 MotionMonitoring
The MotionMonitoring function assists you during the configuration of the safety sensor for the mobile
danger zone guarding application for side-tracking skates and, during travel operation of the side-tracking
skate, monitors whether the control has selected the correct protective field for the given operating situation.
Using its internal measurement values, the safety sensor calculates the current speed of the side-tracking
skate and compares this value with the speed configured in the speed matrix of the safety sensor for the
protective field. This control function of MotionMonitoring leads to the following behavior:
• If the speed is higher than the speed given for the protective field, the safety sensor corrects by one
protective field upwards. If a second correction is required with an even faster speed, the safety sensor stops the side-tracking skate.
• If the maximum speed is exceeded, the safety sensor stops the side-tracking skate immediately.
Two further functions are integrated into the MotionMonitoring function, which are assigned to the two field
pairs, 7 and 8:
• Further travel blocking – field pair 7
• Creep and reverse – field pair 8
Leuze electronic RS4 17
Page 18

Functions
Further travel blocking
The further travel blocking function prevents the side-tracking skated from moving as long as field pair 7
is active. The safety sensor switches the safety-related switching outputs in field pair 7 off. The sidetracking skate can start to move again when the control switches to another protective field.
Creep and reverse
A safety sensor is mounted in both directions when a side-tracking skate travels forwards and backwards.
The creep and reverse function deactivates the safety sensor that is positioned opposing the current travel
direction. This safety sensor only monitors the speed and direction of movement: no protective field and
no warning field is monitored; the safety-related switching outputs remain set to ON. The maximum speed
with a creep speed is 100 mm/s. If the side-tracking skate moves faster than 100 mm/s, the safety sensor
switches the safety-related switching outputs off and stops the side-tracking skate. The creep function is
used as the side-tracking skate approaches the minimum distance to loading and unloading stations.
Using MotionMonitoring
Requirements for using the MotionMonitoring function:
• Side-tracking skate (AGV) with linear movement
• Transportation path length max. 50 m
• Transportation path restricted at both ends by a wall or boundary
Pedestrian traffic on the transportation path is possible because it is included in the calculations by
the safety sensor
• Side-tracking skate speed 6 m/s
• Only one side-tracking skate per path
ª Enter the speed levels of the AGV and the braking distance with maximum speed in the speed matrix
with the configuration.
The software interpolates the missing braking distances and automatically defines the protective and
warning fields.
During the initial start up, the configuration and diagnostic software displays the calculated measurement
values for speed and distance and a speed monitoring status display in a separate dialog field.
Notices on starting up a safety sensor with the MotionMonitoring function (see chapter 10 „Setting the
device into service“).
Function sequence
The protective field activated by the vehicle control— specified by protective field contour and travel
speed— is monitored by the safety sensor for protective field violation and excess travel speed!
The following steps describe the principle operating procedure of the MotionMonitoring function:
• Via 4 standard outputs, the vehicle control activates the protective field that is adapted to the operating system on the control inputs of the safety sensor:
• small protective field for slow travel
• medium protective field for moderate travel
• large protective field for fast travel
• PF8 for reverse travel
• The safety sensor monitors this protective field and switches off in the event of a violation.
• While the protective field is free, the safety sensor ascertains the current travel speed and travel
direction.
• The travel speed and travel direction are compared with the values configured in the speed matrix.
• If in agreement, i.e., the measured speed is smaller than the configured value, the system functions
correctly and the safety sensor activates alarm output 2.
• If the measured speed is greater than the configured value, the safety sensor assumes that a fault
has occurred in the system and deactivates alarm output 2.
Faults lead to two escalation levels:
• The protective field is corrected for a short time (5 s) while the next larger is automatically moni-
tored by the safety sensor.
• If the speed increases further or if the maximum speed is exceeded, the safety sensor switches off
the safety-related switching outputs; an entry appears in the diagnostics list.
Leuze electronic RS4 18
Page 19
5 Applications
3
4
3
3
The following chapters essentially describe the safety sensor's usage possibilities. To safely configure and
mount the safety sensor for the respective application (see chapter 6 „Mounting“).
5.1 Stationary danger zone guarding
Stationary danger zone guarding enables a very spacious protection of people on machines that are to
remain as accessible as much as possible. The safety sensor is applied as a stop-activating and presencedetecting protective device. The safety sensor's protective field is set up horizontally in front of the machine
or system's point of operation.
You can also use the stationary danger zone guarding if you do have to guard areas under the machine
or at the rear that are not visible.
Applications
1
4
6
1 EMERGENCY STOP command device and start/restart button
2 Safety sensor
3 Protective field 2, activated
4 Protective field 1, deactivated
5 Warning field 2, activated
6 Warning field 1, deactivated
2
5
1
3
Figure 5.1: Stationary danger zone guarding with two alternating work areas
Leuze electronic RS4 19
Page 20

5.2 Stationary point of operation guarding
3
4
3
3
Hand and arm protection are always required when people must work at the point of operation. The safety
sensor is applied as a stop-activating and presence-detecting protective device. The safety sensor's
protective field is set up vertically in front of the machine or system's point of operation. With small protective field dimensions the safety sensor provides the correspondingly required high resolution level. A sufficient safety distance to the point of operation ensures the finger protection.
Applications
5
3
1 Safety sensor
2 Reference boundaries of both protective fields
3 EMERGENCY STOP command device and start/restart button
4 Protective field 1, activated
5 Protective field 2, deactivated
1
4
2
3
Figure 5.2: Stationary point of operation guarding with protective field switchover
Leuze electronic RS4 20
Page 21

5.3 Stationary access guarding
4
3
3
Stationary access guarding protects people that step into a danger zone. The vertically aligned protective
field of the safety sensor detects the passage of a person. A side post and the floor serve as reference
boundary for monitoring the position of the protective field. In contrast to danger zone guarding, the safety
sensor no longer registers a person in the danger zone after the passage. This is why the start/restart inter-
lock function is vital for access guarding.
Applications
1
3
1 Safety sensor
2 Reference boundary of the protective field
3 EMERGENCY STOP command device and start/restart button
4 Protective field
Figure 5.3: Stationary access guarding
4
2
Leuze electronic RS4 21
Page 22

5.4 Mobile danger zone guarding
4
3
3
Mobile danger zone guarding protects people that are located in the transportation path of an automated
guided vehicle. The distance between the protective field front edge and the vehicle front must be greater
than the stopping distance of the vehicle with selected speed and maximum load. A safe control system
selects speed-dependent protective fields and can activate side horizontal protective fields for curved
stretches.
Applications
3
4
1 Protective field 1 for forward travel, activated
2 Warning field 1 for forward travel, activated
3 Protective field 2 for curved stretch, left, deactivated
4 Protective field 3 for curved stretch, right, deactivated
Figure 5.4: Mobile danger zone guarding
1
2
Leuze electronic RS4 22
Page 23
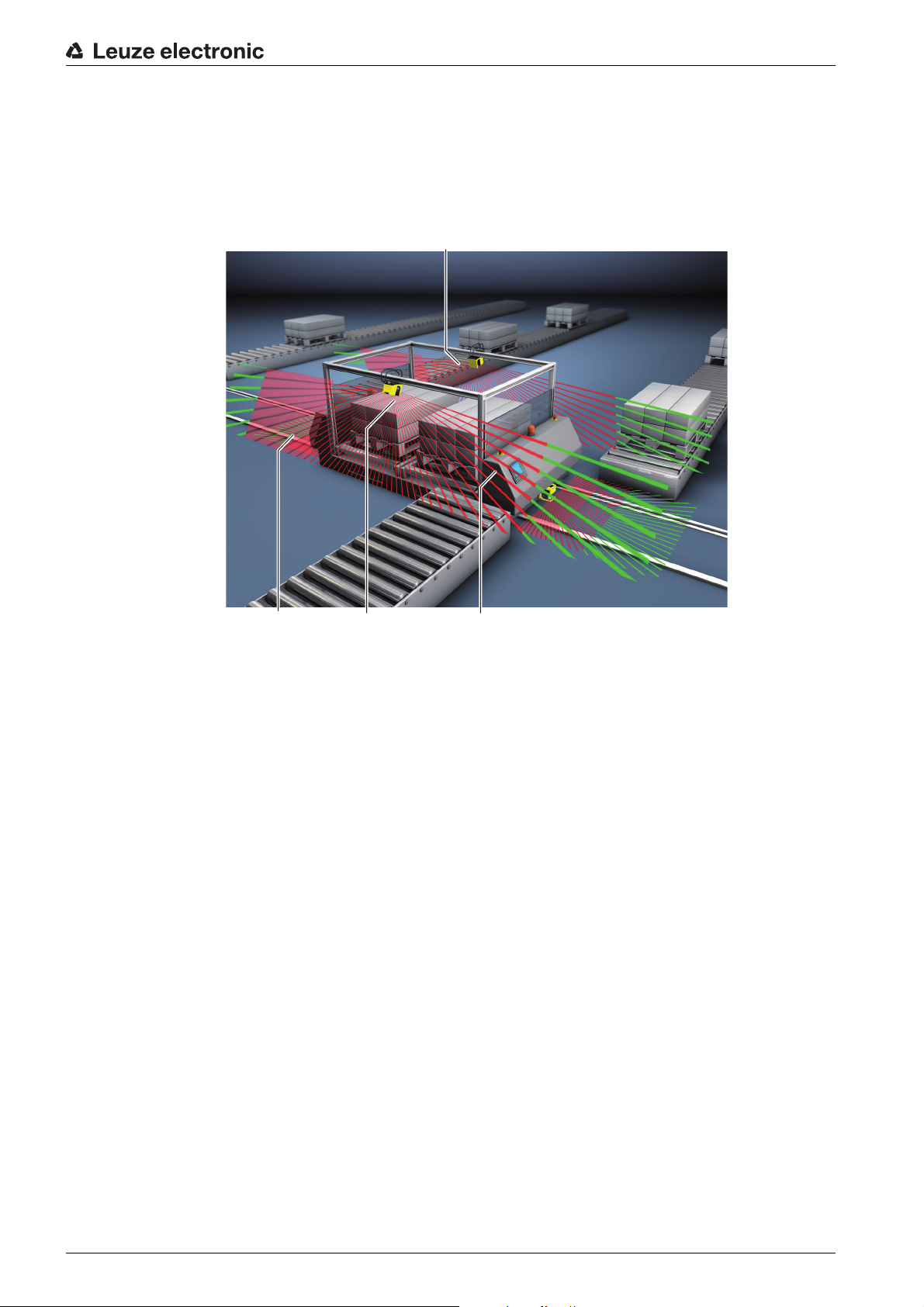
5.5 Mobile side guarding
4
3
3
Mobile side guarding protects people and objects that are located on the vehicles path. This application is
used when very low arranged conveyor lanes do not permit an unobstructed passage of horizontal, lateral
overlaying protective fields. The safety sensors are positioned laterally and the protective fields are
arranged vertically, at a slight tilt. The position of the front edges of the side protective fields is oriented
here on the position of the front edge of the horizontal protective field.
Applications
4
2
1 Protective field and warning field pair for forward travel, activated
2 Protective field and warning field pair for reverse travel, deactivated
3 Protective field and warning field pair for side guarding, right, activated
4 Protective field and warning field pair for side guarding, left, activated
3
1
Figure 5.5: Mobile side guarding on side-tracking skates
Leuze electronic RS4 23
Page 24
6 Mounting
6.1 Basic infos
The safety sensor's protective function is only guaranteed when the device arrangement, configuration,
protective field dimensioning and installation are coordinated with the respective application.
The installation work must only be performed by an appropriately qualified person in compliance with the
applicable standards and these instructions. The installation must be thoroughly inspected on completion.
ª You must observe and comply with the respective relevant machine-specific standards and regulations.
Basic procedure
ª Select the appropriate device type for the application.
Application Device type Resolution Configuration and installa-
Mounting
tion notes
Stationary danger zone safeguarding RS4-x
RS4-xE
Stationary point of operation guarding RS4-xE 30-40 mm see chapter 6.4 „Stationary
Stationary access guarding RS4-xE 150 mm see chapter 6.5 „Stationary
Mobile danger zone guarding on DTSs RS4-x
RS4-xM
Mobile side guarding on DTSs RS4-x 150 mm see chapter 6.7 „Mobile side
ª Determine the installation point.
ª Determine whether you are going to install the safety sensor with or without the mounting system.
ª During mounting, use the four supplied M5 screws or four similar screws with a diameter of 5 mm, and
make certain that the mounting elements or mounting construction supports at least four times the
weight of the device with or without mounting system.
ª Determine the size of the protective field on the basis of the point of installation, the calculated safety
distances and additional distances.
ª Determine the start/restart operating mode required for the application.
ª If you are using start/restart interlock, determine the position for the start/restart button.
ª Determine the conditions for the field pair switchover, if required.
ª Configure the safety sensor with the configuration and diagnostics software.
Many safety-relevant parameters are preset in the configuration and diagnostics software. Use these
preset values where possible.
ª Create a record document for the device configuration and protective field dimensioning. The document
must be signed by the person responsible for the configuration.
Include this document with the machine documentation.
ª Install protective enclosures or safety bars if the safety sensor is in an exposed position.
ª If there is a risk that the safety sensor will be used as a climbing aid, install a suitable physical cover
over the safety sensor.
Ensure that machine parts, protective grids or covers do not impair the safety sensor's field of vision.
50-70 mm see chapter 6.3 „Stationary
danger zone guarding“
point of operation guarding“
access guarding“
70 mm see chapter 6.6 „Mobile dan-
ger zone guarding on DTSs“
guarding on DTSs“
Leuze electronic RS4 24
Page 25
6.2 Basic infos on the protective field dimensioning
ª Dimension the protective field big enough that the safety sensor's switch-off signal can stop the danger-
ous movement in good time.
If several protective fields are selected with field switchover, this condition applies for all protective
fields.
Protective fields with a radius of less than 200 mm (safety sensor close range) are not permitted and
are therefore preset as minimum contour.
ª If you cannot sufficiently dimension a protective field, use additional protective measures, e.g. protec-
tive grids.
ª Ensure that the protective field cannot be walked behind in the direction of the danger zone.
ª Observe all delay times, e.g. safety sensor response times, control element response times, braking
times or machine or AGV stopping times.
ª Take changed delay times, which, for example, can be caused by reducing the braking force, into
account.
ª Observe shadowing effects, e.g. surfaces and areas behind static objects. People in the shadows of
these objects will not be detected by the safety sensor.
ª Observe the lateral tolerance when dimensioning the protective fields (see chapter 7 „Technical data“).
ª Do not use cone-shaped protective field contours, as these do not guarantee any protective effect.
ª Take the additional distances required for the application into account.
Mounting
6.2.1 Handling unmonitored areas
There is an area behind the safety sensor that the safety sensor does not monitor. Unmonitored areas can
also materialize, e.g. if you install a safety sensor on a rounded off vehicle front.
It must not be possible to walk behind unmonitored areas.
1 Safety sensor
2 Protective field
3 Unmonitored area
Figure 6.1: Protective field shape – unmonitored areas
ª Prevent access to an unmonitored area with screens.
ª Prevent walking behind by countersinking the safety sensor into the machine contour.
2
1
3
Leuze electronic RS4 25
Page 26
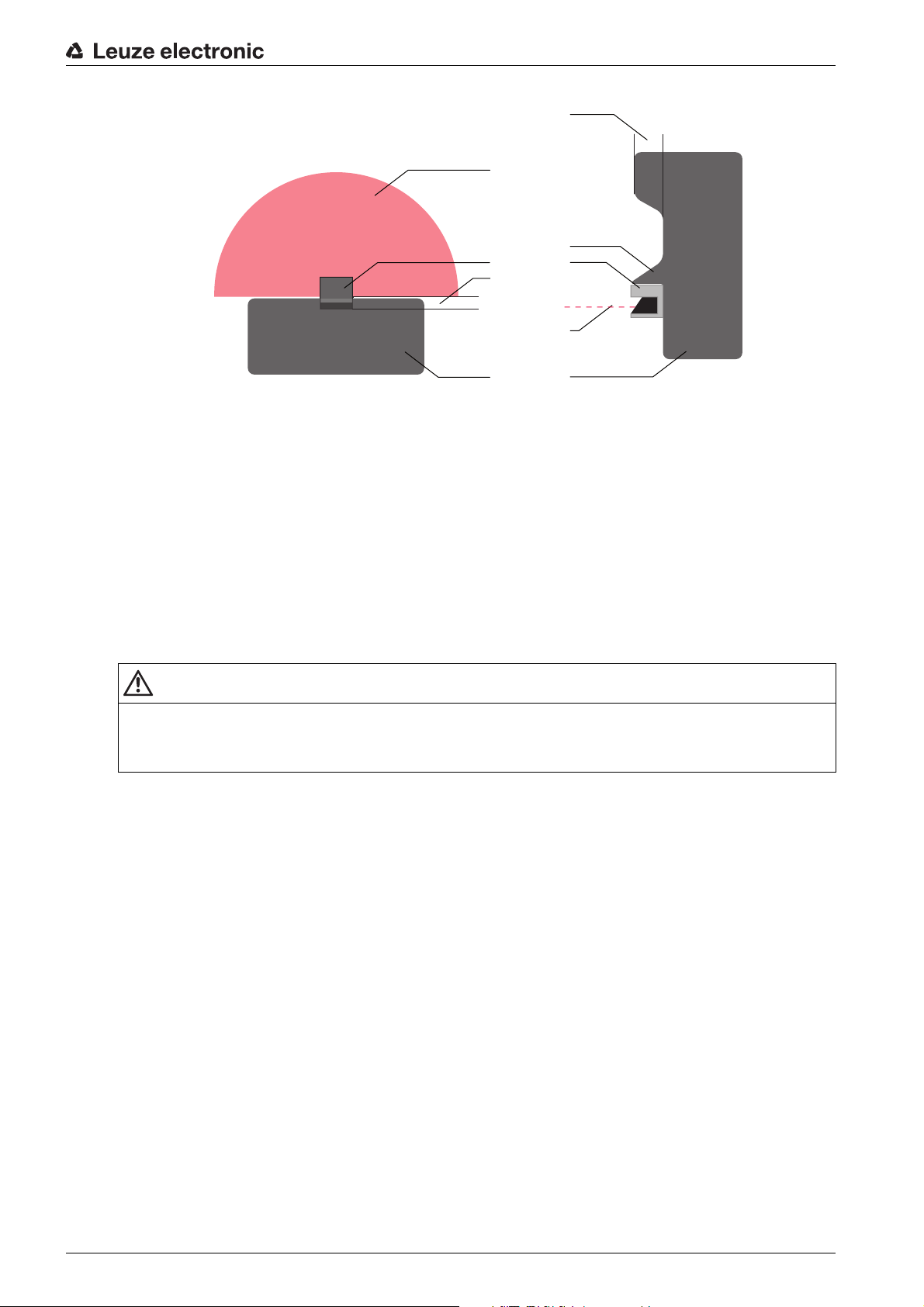
Mounting
1
2
5
3
1
3
2
1 Countersinking into the machine contour
2 Protective field
3 Safety sensor
4 Machine
5 Physical cover
Figure 6.2: Stepping behind protection by countersinking into the machine contour
ª Use a physical cover set at an angle over the safety sensor if you expect that the safety sensor will be
used as a climbing aid or standing surface.
6.2.2 Protective field setup with adjacent safety sensors
The safety sensor has been developed in a way that prevents several safety sensors from interfering with
one another as much as possible. Several adjacent safety sensors can, however, cause the response time
to increase if the fields overlap.
WARNING
The response time extends with reciprocal influencing of adjacent safety sensors.
ª If you do not plan for any measures against reciprocal influencing, take a response time extension of
40 ms into account with the safety distance calculation.
ª Plan for shielding with stationary applications.
The shielding must be at least as high as the safety sensor's front screen and flush with the front housing
edge.
If you plan for a shielding that is still within the countersinking in the machine contour, the resolution of
the protective fields must not be impaired at any accessible points.
You require the reciprocal shielding with both horizontal and vertical alignment of the protective fields.
4
4
Leuze electronic RS4 26
Page 27

Mounting
3
1
2
4
5
4
1
2
1 Point of operation
2 Safety sensor
3 Machine with countersinking for Sensor installation
4 Protective fields
5 Shielding
Figure 6.3: Shielding prevents reciprocal influencing of safety sensors set up beside one another.
ª Install the safety sensors off-set on the height.
100 mm
Figure 6.4: Height offset installation, parallel alignment
ª Install the safety sensors with crossed alignment.
Figure 6.5: Installation beside one another, without height offset, crossed alignment
Leuze electronic RS4 27
Page 28

Figure 6.6: Opposing installation, without height offset, crossed alignment
6.3 Stationary danger zone guarding
Mounting
Figure 6.7: Safety sensor activates the stop and, with protective field with rear area protection, performs
a presence-detecting function
Procedure
ª Determine the height of the beam level.
ª Calculate the necessary safety distance and determine the required additional distances for your appli-
cation.
ª Define the protective field boundaries and the warning field boundaries if required.
ª Configure the protective field so that the safety-related switching outputs are switched off from every
accessible point with sufficient minimum distance "D".
ª Mark the protective field boundaries on the floor.
You can easily test the safety sensor along this marking.
Leuze electronic RS4 28
Page 29

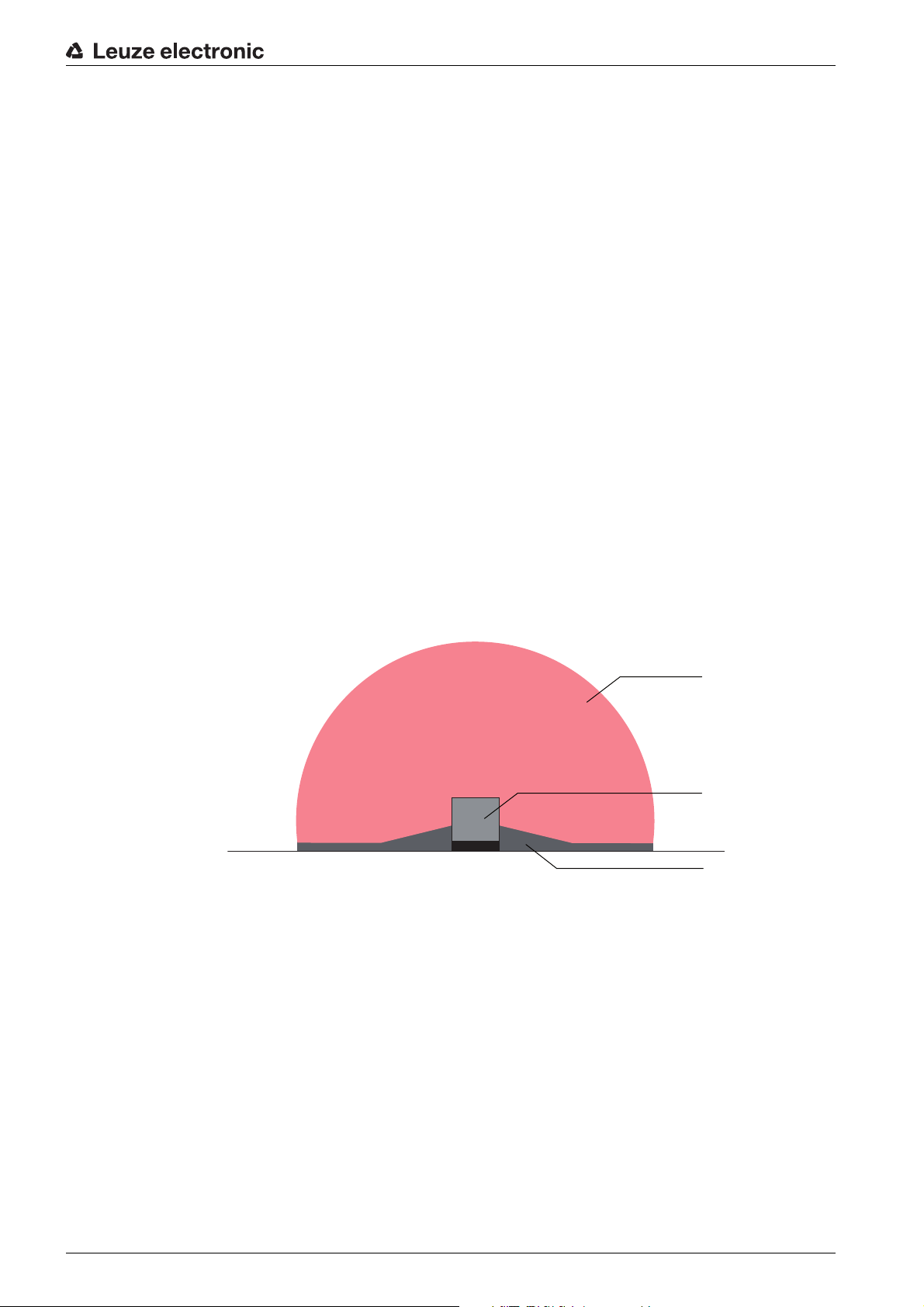
6.3.1 Beam level height
The minimum height of the beam level depends on the safety sensor resolution. To detect a human leg a
resolution of 50 mm is required at ankle height, and 70 mm at calf height (300 mm off the floor).
Mounting
Figure 6.8: Beam level close to the floor – 50 mm
resolution is required
H
Lowest permissible beam height from the standing surface level in mm
MIN
d Safety sensor resolution in mm
H
= 1000 mm
MAX
6.3.2 Safety distance "S"
The B standard, ISO 13855/EN999 specifies the general formula for the safety distance as follows:
Figure 6.9: Beam level at 300 mm – 70 mm reso-
lution is required
S Safety distance in mm
K Approach speed in mm/s
For parallel approach on a horizontally arranged protective field: 1600 mm/s
T
Safety sensor response time in s
1
T
Safety interface device response time in s, if used
2
T
Machine stopping time plus addition for deterioration in s
3
C Additional distance because of the possibility of reaching over in mm
Leuze electronic RS4 29
Page 30

6.3.3 Additional distance "C" because of the possibility of reaching over
You prevent reaching the point of operation by reaching over with the additional distance "C":
H Beam level height above the floor in mm
C
= 850 mm
MIN
H
= 1000 mm
MAX
Mounting
C
C
H
Figure 6.10: Beam level H = 300 mm,
C = 1080 mm
6.3.4 Machine response times, stopping time
The safety sensor's rotary mirror rotates on its own axis every 40 ms. One revolution is a scan. At least
two consecutive scans must be interrupted so that the safety-related switching outputs switch off. The
safety sensor's minimum response time is therefore 80 ms.
If you want to increase the safety sensor's availability in an environment with fine particles, increase the
number of interrupted scans after which the safety-related switching outputs switch off. With each additional scan the response time T
increases by 40 ms. With K = 1600 mm/s the safety distance increases
1
by 64 mm per additional scan.
ª Select a response time T1 of at least 120 ms or higher.
ª If you use a safety interface device, take the response time T2 from the safety interface device's techni-
cal data.
ª Determine the machine/system's stopping time T3.
If data is not available, you can commission Leuze electronic to perform measurements (see chapter 16
„Service“).
ª If an increase in the stopping time within the regular test periods is to be expected, take an additional
value into account for the machine's stopping time
H
Figure 6.11: Beam level H = 875 mm to 1000 mm,
C = 850 mm
T3.
Leuze electronic RS4 30
Page 31

6.3.5 Application-conditional additional distances for safety distance "S"
The protective field boundaries must be defined so that the calculated safety distance "S" to the point of
operation, extended by the additional distances, is complied with everywhere. Where this is not possible
or does not make sense, you can use hard guards as supplementary measures.
1
D
2
R
G
S
S
D
S
D
1 Routing machine with free space for sensor protective field in the area under the machine table
2 Safety sensor
3 Protective field contour
4 Warning field contour
S Calculated safety distance S
D Minimum distance "D" (= safety distance S + additional distance Z
R
Greater protective field radius without additional distances, measured from the rotation axis of the
G
rotary mirror
Figure 6.12: Defining the protective field contour for a stationary, horizontal protective field
+ if required, Z
SM
Mounting
3
4
)
REFL
ª Define the limits of the protective field using the safety distance "S" without an additional distance.
ª Determine the biggest protective field radius RG for this protective field.
The biggest protective field radius determines the additional distance ZSM for the system-conditional
measurement error, by which the protective field contour must be enlarged.
The position of the rotary mirror's center point with regard to the housing is provided by the dimensional
drawing (see fig. 7.1).
Table 6.1: Additional distance Z
for the protective field contour because of measurement error
SM
Biggest protective field radius RG without additional
distances
< 3.5 m 83 mm
u 3.5 m 100 mm
ª Avoid retro-reflectors at the beam level behind the protective field boundary. If this is not possible, add
another additional distance Z
of 100 mm.
REFL
6.3.6 Minimum distance "D" to the protective field contour
The minimum distance "D" is the distance between point of operation and protective field contour.
Additional distance
Z
SM
D Minimum distance between point of operation and protective field contour in mm
Z
Additional distance for system-conditional measurement error
SM
Z
Additional distance with retro-reflectors
REFL
ª If the protective field runs up against fixed boundaries, such as walls or machine frames, take a coun-
tersinking into the machine contour of at least the size of the necessary additional distance ZSM, and Z
REFL
where required, into account. With the protective field contour under these conditions, stay about 50 mm
away from the machine surface.
Leuze electronic RS4 31
Page 32

ª If the protective field runs up against hard guards, ensure that the protective field ends under instead
of in front of the hard guards. The width of the lower post must correspond with the size of the required
additional distances.
ª If all dangers in the fenced off area are covered by the safety sensor and the height of the beam level
is 300
mm, you can raise the bottom edge of the hard guards from 200 mm to 350 mm. The protective
field reaching to under the hard guards takes over the protective function of preventing an adult from
crawling under in this case.
ª Prevent obstructions within the calculated protective field boundaries. If this is not possible, implement
protective measures so that the point of operation cannot be reached from out of the shadow of the
obstruction.
6.4 Stationary point of operation guarding
Mounting
1
2
1 Safety sensor
2 Reference boundary
Figure 6.13: The safety sensor takes over the stop-activating and presence-detecting function if walking
behind the protective field is not possible.
The following resolutions are required:
• Detection of an adult's hand: 30 mm
• Arm detection: 40 mm
The required finger protection is ensured here by an additional distance "C", which depends on the
resolution, in addition to the safety distance.
Procedure
ª Calculate the necessary safety distance and determine the required additional distances for your appli-
cation.
ª In the configuration and diagnostics software, select the hand protection or arm protection presetting.
The protective field boundaries are automatically restricted as a result to the values listed in the technical data.
ª Specify the protective field boundaries and define the areas that monitor the position of the protective
field as reference boundary.
Leuze electronic RS4 32
Page 33

6.4.1 Safety distance "S"
The B standard, ISO 13855/EN999 specifies the general formula for the safety distance as follows:
S Safety distance in mm
K Approach speed in mm/s
For normal approach on a vertically arranged protective field: 2000 mm/s
T
Safety sensor response time in s
1
T
Safety interface device response time in s, if used
2
T
Machine stopping time plus addition for deterioration in s
3
C Additional distance in mm because of possible penetration into the protective field before the stop
function activates
Mounting
Depending on the calculated value of the safety distance, you must proceed differently with the result:
ª If S is e 500 mm, use the calculated result.
ª If S is > 500 mm, calculate the safety distance again with the approach speed K = 1600 mm/s.
If S is therefore u 500 mm, use this value.
If S is therefore S < 500 mm, use at least S = 500 mm.
6.4.2 Additional distance C
With a resolution less than 14 mm, a finger or the flat of a hand can penetrate a stretch into the protective
field without the stop function activating. You must therefore include an additional distance "C".
d Safety sensor resolution (30 mm and 40 mm)
For 30 mm resolution the additional distance C = 128 mm; for 40 mm resolution C = 208 mm.
6.4.3 Machine response times, stopping time
The safety sensor's rotary mirror rotates on its own axis every 40 ms. One revolution is a scan. With each
additional scan the response time T
increases by 40 ms. With K = 2000 mm/s approach speed this corre-
1
sponds with an increase in the safety distance of 80 mm per additional scan. With K = 1600 mm/s it is
64 mm.
ª Select a response time T1 of at least 80 ms or higher.
ª If you use a safety interface device, take the response time T2 from the safety interface device's techni-
cal data.
ª Determine the machine/system's stopping time T3.
If data is not available, you can commission Leuze electronic to perform measurements (see chapter 16
„Service“).
ª If an increase in the stopping time within the regular test periods is to be expected, take an additional
value into account for the machine's stopping time
T3.
Leuze electronic RS4 33
Page 34

6.4.4 Protective field and reference boundary
With a vertical protective field, you must define at least two sides of the protective field contour as reference boundary in accordance with IEC/EN 61496-3. The objective is to monitor the position of the protective field with regard to its marginal area. If the arrangement misaligns and the distance of the safety sensor
to the reference surface changes as a result, switch the safety-related switching outputs off.
1
Mounting
e
3
4
S
1 Physical frame for reference boundary
2 Reference boundary, must cover at least two sides of the protective field
3 Safety sensor
4 Distance "e" between the reference boundary frame and machine opening, recommended: e u
150 mm
5 Machine opening contour
Figure 6.14: Define the protective field and reference boundary, stationary point of operation guarding,
vertical protective field
6.5 Stationary access guarding
5
2
e
1
1
2
3
4
1 EMERGENCY STOP command device and start/restart button
2 Safety sensor
3 Protective field, left conveyor line, activated
4 Reference boundary of the protective field
5 Protective field, right conveyor line, deactivated
Figure 6.15: Stationary access guarding, vertical protective field
5
1
Leuze electronic RS4 34
Page 35

Mounting
The picture shows an input and output station with conveyor lanes in a danger zone. In this case three
different protective fields are used:
• "Left conveyor lane" protective field
• "Right conveyor lane" protective field
• "Both conveyor lanes" protective field
The safety-set machine control system ensures the switchover between the protective fields.
You may only change over protective fields when additional measures prevent the passage through the
respective inactive protective field. This can, for example, be the dimensions of a loaded palette, which
makes it impossible to enter the danger zone during the switchover.
The vertical protective field of the access guarding only detects people during passage through. After the
passage a start/restart interlock must ensure that the dangerous movement does not start again automatically.
Safety sensors with a > 40 mm resolution are suitable for finger, hand and arm detection! The
required protection for these body parts must be ensured with an additional distance C = 850 mm
in addition to the safety distance. This distance is equivalent to average arm length.
Procedure
ª Select the start/restart interlock function.
ª Attach the start/restart button.
ª Install an optical and/or acoustic start warning with the corresponding risk.
ª Calculate the required safety distance.
ª Specify the protective field boundaries and define the areas that monitor the position of the protective
field as reference boundary.
6.5.1 Safety distance "S"
The B standard, ISO 13855/EN999 specifies the general formula for the safety distance as follows:
S Safety distance in mm
K Approach speed in mm/s
For access guarding with vertical protective field: 1600 mm/s
T
Safety sensor response time in s
1
Maximal 0.080 s
T
Safety interface device response time in s, if used
2
T
Machine stopping time plus addition for deterioration in s
3
C Additional distance in mm
With safety sensors with > 40 mm resolution at least 850 mm
6.5.2 Machine response times, stopping time
The safety sensor's rotary mirror rotates on its own axis every 40 ms. One revolution is a scan. An object
must be detected in at least two consecutive scans so that the safety-related switching outputs switch off.
The safety sensor's minimum response time is therefore 80 ms.
If you want to increase the safety sensor's availability in an environment with fine particles, increase the
number of interrupted scans after which the safety-related switching outputs switch off. With each additional scan the response time T
increases by 40 ms. With K = 1600 mm/s the safety distance increases
1
by 64 mm per additional scan.
Leuze electronic RS4 35
Page 36

ª Select a response time T1 = 80 ms.
Never define a value higher than 80 ms for T1 for access guarding or passage controls. With higher values it can happen that a person might not be detected when passing through the protective field with
an approach speed of 1600 mm/s.
If you select the access guarding presetting in the configuration and diagnostics software, T
ically set to 80 ms.
ª If you use a safety interface device, take the response time T2 from the safety interface device's techni-
cal data.
ª Determine the machine/system's stopping time T3.
If data is not available, you can commission Leuze electronic to perform measurements (see chapter 16
„Service“).
ª If an increase in the stopping time within the regular test periods is to be expected, take an additional
value into account for the machine's stopping time
6.5.3 Protective field contour and reference boundary
With a vertical protective field you must define at least two sides of the protective field contour as reference
boundary in accordance with IEC/EN 61496-3. The objective is to monitor the position of the protective
field with regard to its marginal area. If the arrangement misaligns and the distance of the safety sensor to
the reference changes as a result, switch the safety-related switching outputs off.
T3.
Mounting
is automat-
1
1
2
3
1 Protective field contour PF1, guards the "left conveyor lane"
2 Safety sensor
3 Reference boundary of PF1, left frame and floor
4 Protective field contour PF2, guards "both conveyor lanes"
5 Reference boundary of PF2, right frame and floor
4
5
Figure 6.16: Define the protective field and reference boundaries, stationary access guarding, vertical
protective field
ª In the configuration and diagnostics software select the access guarding presetting before configuring
the protective fields. The software consequently requests a reference boundary on at least two sides of
the protective field.
ª When defining the protective field ensure that there are no gaps bigger than 150 mm.
ª When defining the protective field boundaries, specify the sectors that monitor the position of the pro-
tective field as reference boundary.
6.6 Mobile danger zone guarding on DTSs
Danger zone guarding protects people and objects that are in rooms in which vehicles move in, e. g. automated guided vehicle systems (DTSs).
WARNING
Danger of injury because of insufficient vehicle stopping distance
ª The company operating the machine must use organizational measures to prevent people from enter-
ing the protective field of the vehicle from the sides or being able to move towards an approaching vehicle.
Leuze electronic RS4 36
Page 37

Procedure
ª Only install the safety sensor on the front of the vehicle.
If you must also guard the reverse travel, you must also install a safety sensor on the rear of the vehicle.
ª Select 70 mm resolution.
ª Do not set the height higher than 200 mm above the floor.
A person lying on the floor can therefore be safely detected. This is required by the C standard, EN 1525
"Safety of industrial trucks – Driverless trucks and their systems".
ª Set the protective field length so that the response time until braking and the braking distance, including
factors for wear and tear and floor conditions, and any necessary additional distances are taken into
account.
6.6.1 Basic requirements
ª Only use the safety sensor on vehicles with electrical drive and electrically influenced drive and braking
devices.
ª Mount the safety sensor on the vehicle so that there are no unmonitored areas u 70 mm between the
protective field and vehicle front.
6.6.2 Minimum distance D
The horizontally arranged protective field protects people and objects that are in the vehicle's path and are
detected by the front edge of the protective field.
Mounting
200
V · (T +T )
max
1
2
D · L · L
D
A
D
2
1
B
Z
GES
Figure 6.17: Mobile danger zone guarding, required minimum distance D calculation
ª Configure an upstream warning field that reduces the vehicle's speed.
A full brake with a subsequent interruption of the protective field is then executed moderately and is less
demanding on the vehicle's drives.
ª Dimension the minimum distance D for the maximum speed as if the speed reduction initiated by the
warning field had not happened.
Only when the protective field is interrupted do the safety-related switching outputs switch off and safely
brake the vehicle.
Leuze electronic RS4 37
Page 38

Mounting
Stopping distance D
Stopping distance in mm
D
A
v
Maximum vehicle speed in mm/s
max
T
Safety sensor response time in s
1
T
AGV response time in s
2
D
Braking distance with v
B
L
Factor for brake wear and tear
1
L
Factor for problematic floor conditions, e.g. dirt, wet conditions
2
A
and maximum vehicle load in mm
max
Additional distances Z
Total of the required additional distances
Z
Ges
Z
Additional distance for system-conditional measurement error, see (see table 6.1)
SM
Z
Additional distance required with lack of floor space HF in mm
F
Z
Additional distance required with retro-reflectors beyond the protective field boundaries
REFL
Z
= 100 mm
REFL
The additional distance Z
sensor mirror's rotary axis to the protective field boundary without Z
is always required. Its size depends on the biggest radius RG from the safety
SM
. The position of the rotary mirror axis
Ges
depends on the installation situation.
The additional distance Z
is required if the vehicle does not have enough free floor space HF and there
F
is therefore no space under the vehicle or the safety sensor for the tips of the feet. You determine the additional distance Z
Figure 6.18: Diagram for determining the additional distance Z
If wheels are mounted near the side wall, always add an additional distance Z
according to the following diagram:
F
Z
F
H
F
120
100
H
F
80
60
40
20
Z
40
80
60
20
with lack of floor space H
F
100
120
140
u 150 mm.
F
160
F
F
Leuze electronic RS4 38
Page 39

Minimum distance D
D Minimum vehicle front distance (danger) to the protective field front edge in mm
D
Stopping distance in mm
A
Z
Total required additional distances
Ges
6.6.3 Protective field dimensions
Mounting
GES
Z
L
F
R
G
R
F
D Minimum distance, vehicle front (danger) to protective field front edge
Stopping distance
D
A
Total required additional distances to the front and for both sides
Z
Ges
F
Distance, safety sensor center to the left vehicle edge
L
Distance, safety sensor center to the right vehicle edge
F
R
Biggest radius in the protective field Z
R
G
Figure 6.19: Mobile danger zone guarding, dimensions for horizontal protective field
ª Arrange the protective field symmetrically with reference to the vehicle width, even if the safety sensor
is not arranged centered.
ª Take the required free space for overlaying side protective fields under the conveyor lanes along the
transportation path into account.
ª If you have to expect angle deviations of the vehicle during the travel, plan an additional tolerance range
to guarantee undisturbed travel operation.
6.6.4 Test mode for MotionMonitoring
You require a special test mode to be able to check the MotionMonitoring function with the daily function
check.
Configure this test mode in the control system as follows:
• Control system selects protective field 1
• Control system moves vehicle with speed for protective field 2
Alarm output 2 must signal that the speed will be exceeded.
GES
Z
D
A
D
for determining the additional distance ZSM
GES
Z
GES
Leuze electronic RS4 39
Page 40

6.7 Mobile side guarding on DTSs
WARNING
Danger of injury because of insufficient vehicle stopping distance
ª The company operating the machine must use organizational measures to ensure that people cannot
enter the vehicle's protective field from the side.
ª For mobile vertical protective fields use a resolution of at least 150 mm.
ª Position the protective field edges in the travel direction in accordance with the front protective field edge
of the horizontal protective field (
ª Ensure that the response time of all components of the switch-off circuit are the same or balance the
response times with different protective field dimensioning.
ª Set the vertical protective fields at a slight angle so that the lower protective field edges protrude over
the vehicle width by the amount of the additional distances, Z
figure 6.17).
see chapter 6.6.3 „Protective field dimensions“).
, ZF and Z
SM
where required (see
REFL
Mounting
Leuze electronic RS4 40
Page 41

7 Technical data
7.1 Safety
Type in accordance with IEC/EN/UL 61496 Type 3
Technical data
Safety Integrity Level SIL (IEC/EN 61508) SILCL
(IEC 62061)
Performance Level (PL) in accordance with
ISO 13849-1: 2006
Category in accordance with ISO 13849-1 Cat. 3
Average probability of a failure to danger per hour
(PFH
Service life T
Certifications
7.2 Optics
Laser protection class in acc. with EN 60825-1 Class 1
Wavelengths 905 nm
Repetition frequency 25 kHz
SIL2
PL d
-7
1.5 x 10
)
d
M
20 years
1/h
Scan rate 25 scans/s, equal to 40 ms/scan
Scanning angle Max. 190°
Angle resolution 0.36°
Lateral tolerance without mounting system ± 0.18° (with reference to the housing rear
panel)
Lateral tolerance with mounting system ± 0.22° (with reference to the housing rear
panel)
Leuze electronic RS4 41
Page 42

7.3 Protective field
Technical data
Variant
Number of field pairs 4 8 4 8 8
Reference boundary can be selected x x – x x
Protective field range
At 30 mm resolution – – – 1.60 m 1.60 m
At 40 mm resolution – – – 2.20 m 2.20 m
At 50 mm resolution – – – 2.80 m 2.80 m
At 70 mm resolution 2.15 m 2.15 m 4.00 m 4.00 m 6.25 m
At 150 mm resolution 2.15 m 2.15 m 4.00 m 4.00 m 6.25 m
Minimum range that can be set 200 mm
Detection range of the test object from the housing
edge
Diffuse reflectance PF minimum 1.8 %
7.4 Warning field
RS4-2E RS4-2M RS4-4 RS4-4E
RS4-4M
The detection capability is restricted in the 0 mm
to 50 mm range to increase availability.
RS4-6E
RS4-6M
Number of field pairs see chapter 7.3 „Protective field“
Warning field range 0 - 15 m
Object size 150 mm x 150 mm
Diffuse reflectance WF minimum Min. 20 %
7.5 Measured data
Measurement range 0 - 50 m
Diffuse reflectance 20 %
Radial resolution 5 mm
Lateral resolution 0.36°
Leuze electronic RS4 42
Page 43

7.6 Electrical power supply
Voltage supply 24 V DC (+20 % / -30 %) Power supply in acc.
Overcurrent protection Via 1.6 A fuse melting fuse in the cabinet
Current consumption Approx. 420 mA (use power supply with 2.5 A)
Power consumption 10 W with 24 V plus output load
Overvoltage protection Overvoltage protection with safe limit stop
Protective earth conductor Connection not permitted
Interface X1 connector plug SUB-D15
Interface X2 connector plug SUB-D9
Inputs
Start/restart +24 V opto-decoupled, dynamically monitored
Technical data
with IEC 742 with safe supply isolation and
compensation with voltage dips of up to 20 ms
in acc. with EN 61496-1.
Field pair switchover Selection of 4 or 8 field pairs via 4 control lines,
+24 V opto-decoupled, dynamically monitored,
logical 1 = field pair activated
Signal definition:
High/logical 1 16 - 30 V
Low/logical 0 < 3 V
Safety outputs
OSSD transistor safety-related switching outputs 2 safe PNP semiconductor outputs
Short circuit-proof, cross-circuit monitored
Minimum Typical Maximum
Switching voltage high active U
- 3.2 V
B
Switching voltage low 2.0 V
Switching current 250 mA
Cut-off frequency f
Load capacity C
load
g
1 kHz
100 nF
Cable length between safety sensor and load with
gauge 0.5 mm
2
Permitted wire gauge 0.5 mm
2
50 m
Test pulse width 100 PV
Test pulse distance 5 ms
Leuze electronic RS4 43
Page 44

Technical data
Interfaces
Data interface X2 RS 232 (max 10 m),
RS 422 (twisted pair, max. 50 m)
AS-Interface safety at work Optional: All variants RS4-xxx/A1,
except RS4-2E
PROFIBUS DP PROFIsafe Optional: All variants RS4-xxx/P1,
except RS4-2E
Control outputs
Warning field/dirt/fault 2 x PNP transistor outputs, configurable
Max. switching current 100 mA
Alarm high active U
Alarm low inactive < 2.0 V
Permissible cable length with 0.5 mm
7.7 Software
Configuration and diagnostics software RS4soft under Windows 95/98/2000/NT/XP
7.8 Ambient conditions
Protection rating IP 65 in acc. with IEC 60529
Safety class II
Ambient temperature, operation 0 to + 50 °C
Ambient temperature, storage -20 to +60 °C
Humidity DIN 40040, table 10, code letter E (reasonably
Interference rejection In acc. with DIN EN 61496-1 (type 4), Also in
- 4 V
B
2
50 m, shielded, only connect shield in the cabinet with PE
dry)
acc. with DIN 40839-1/3 test pulses 1, 2, 3a, 3b
and 5
Vibration stress over 3 axes In acc. with IEC 60068 part 2-6, 10-150 Hz
max 5 G
Permanent shock over 3 axes In acc. with IEC 60068 part 2-29, 10 G, 16 ms
Disposal Specialist disposal required
Leuze electronic RS4 44
Page 45

7.9 Dimensions, weight
Housing Aluminum diecast, plastic
Technical data
Standard version dimensions (ensure free space for
plug with fixing and cable)
140 x 155 x 135 (W x H x D) in mm
Details (see fig. 7.1)
Standard version weight Approx. 2 kg
Distance, beam level center to the bottom housing
48.75 mm
edge
Distance, bottom housing edge to the rotary mirror
67 mm
axis
122.3
R2.6
b
88
61.1
38.5
C
a
ca.195
143.8
170
141
R
a
b
148
77.8
R2.6
C
Laser Klasse 1
Laser Class 1
Laser de Classe 1
Complies with IEC 60825-1:2001, 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11
except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50 dated June 24, 2007
130
R Bending radius of the connected cable
a Rotary mirror axis
bBeam level
A Interface X1 for connection with the control system
B Interface X2 for connection with PC or laptop
All dimensions in mm.
Figure 7.1: ROTOSCAN RS4 dimensions
48.7
21
5
B
A
132
135
64
140
Leuze electronic RS4 45
Page 46

Mounting system (option)
Technical data
56.6
23
90
51.5
74.4
155.4
9
157.5
166.3
192
All dimensions in mm.
Figure 7.2: Mounting system dimensions
9°
Leuze electronic RS4 46
Page 47

8 Electrical connection
ST
OP
o
k.
o
k
.
3
4
1
2
The safety sensor may only be connected and integrated into the machine's control system by an appropriately qualified person.
ª Observe the safety notes (see chapter 2 „Safety“) and technical data (see chapter 7 „Technical data“).
ª Ensure that the voltage supply and all connected input and output current circuits have safe mains iso-
lation in acc. with IEC 742.
The safety-related switching output is redundantly configured.
ª Basically you always connect both safety-related switching outputs (OSSDs) with the machine's switch-
off circuit so that they are both separately fully effective for switching off the dangerous movement (
chapter 8.4 „Integrating the safety sensor into machine control system“).
You may not use the alarm outputs for switching safety-relevant signals.
8.1 Electrical power supply
see chapter 7.6 „Electrical power supply“
8.2 Interfaces
The safety sensor has two interfaces:
• Interface X1 for connection with the control system
• Interface X2 for connection with PC or laptop
Electrical connection
see
Interface Type Function
X1 SUB-D15
• Power supply
• Switching lines and signal lines
X2 SUB-D9 Configuration interface and data interface:
• Parameter configuration
• Protective field definition and warning field definition
• Data transfer and measured value transfer
• Diagnostics
1
2
3
4
1 X1 plug
2 X2 plug
3 X2 cable for connection with PC/laptop
4 Protective housing, if no PC/laptop connected
Figure 8.1: Safety sensor interfaces
The plug housings are included with delivery. A protective housing is also included for the X2 interface.
The protective housing protects interface X2 if no PC is connected.
Screw the plug and protective housing on tight to prevent dust and moisture from penetrating.
Leuze electronic RS4 47
Page 48

The protective housing consists of:
• Housing with seal ring and fixing bolts
• M16 cable gland with dummy plugs
• Plug with solder connection
8.2.1 X1 plug interface assignment
Electrical connection
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
Figure 8.2: X1 plug interface assignment
PIN Color code Signal Description
1 black GND Supply voltage earth
2 blue Restart Input, safety sensor reset and start/restart button connection
3red U
B
supply voltage
4 orange FP 1 Control input for activating field pair 1
5 Yellow Alarm 1 Semiconductor output with switch-off with:
• Warning field interruption
• Warning message, e.g. "Front screen slightly dirty"
• Fault message, e.g. "Front screen very dirty"
• Internal fault
You can combine the functions.
6 green FP 2 Control input for activating field pair 2
7 violet FP 3 Control input for activating field pair 3
8 gray FP 4 Control input for activating field pair 4
9 n.c. NC Do not assign
10 n.c. NC Do not assign
11 white OSSD 1 Semiconductor output channel 1, switch-off with protective field inter-
ruption
12 White/black OSSD 2 Semiconductor output channel 2, switch-off with protective field inter-
ruption
13 n.c. NC Do not assign
14 White/
NC Do not assign
brown
15 brown Alarm 2 Semiconductor output with switch-off with:
• Warning field interruption
• Warning message, e.g. "Front screen slightly dirty"
• Fault message, e.g. "Front screen very dirty"
• Internal fault
You can combine the functions.
Leuze electronic RS4 48
Page 49

8.2.2 Interface assignment, plug X2
Plug X2 as RS 232 port
Figure 8.3: Plug X2 interface assignment as RS 232 port
PIN Signal Description
1 --- Reserved
2 TxD Data communication, send
3 RxD Data communication, receive
4 --- Reserved
5 GND/shield Ground/shield
Electrical connection
1
6
2
3
4
5
7
8
9
6 RS 232 Reserved
7 NC Do not assign
8 NC Do not assign
9 Reserved Reserved for test purposes
Plug X2 as RS 422 port
1
6
2
7
3
8
4
9
5
Figure 8.4: Plug X2 interface assignment as RS 422 port
PIN Signal Description
1 Tx+ Data communication, send
2 Tx- Data communication, send
3 Rx- Data communication, receive
4 Rx+ Data communication, receive
5 GND/shield Ground/shield
6 RS 422 Selection as interface RS 422 via jumper to pin 5
7 NC Do not assign
8 NC Do not assign
9 Reserved Reserved for test purposes
Leuze electronic RS4 49
Page 50

8.3 Assemble cables
You can either use the plug housing included with delivery and assemble the cables yourself, or you can
use already assembled cables (see chapter 17 „Accessories“).
Control cables with ConfigPlug integrated in the plug, for example, are available as accessories. ConfigPlug saves the configuration and transfers this automatically to the safety sensor.
Only use shielded cables.
Electrical connection
a
3
35
b
3
35
aSocket X1
b Connector X2
The cable glands permit cable diameters of 6.5 to 10.5 mm.
Assemble X1 cable
Table 8.1: X1 cable requirements
Plug SUB-D, 15-pin
Socket SUB-D, 15-pin
Wire gauge Min. 0.5 mm
2
Cable external diameter 6.5 mm to 10 mm
Cable length Max. 50 m
Assemble X2 cable
Table 8.2: X2 cable requirements
Plug SUB-D, 9-pin
Socket SUB-D, 9-pin
Wire gauge Min. 0.2 mm
2
or 24 AWG
Cable external diameter 6.5 mm to 10 mm
Cable length RS 232: Max. 10 m
RS 422: Max. 50 m, data lines 1 and 2 plus 3 and 4 twisted
pair
Leuze electronic RS4 50
Page 51

Electrical connection
E
V
V
8.4 Integrating the safety sensor into machine control system
The following examples show options for integrating the safety sensor into the machine control system.
As soon as you have connected the operating voltage and activated a protective field the safety sensor is
ready for operation.
8.4.1 Downstream safety circuit with start/restart interlock, contactor monitoring, without field pair switchover
+24V
1
-A1
0V
PE
-W1
-X1
-X1
-W1
2
412
32
2
3 1211109
4 14 15
1
FP 1
+24V
Restart
ROTOSCAN RS4-4
0V
1
Alarm
SH1
8117
65
n.c.
FP 4
FP 3
FP 2
RxD+
TxD+
TxD-
-X2
1
2 9
n.c.
RxD-
4 53
OSSD1
Shield
13
n.c.n.c.
OSSD2
n.c.
n.c.
RS232/422
6 7 8
2
8
Alarm
1159
156
reserved
1
2
S22 S12 S31 S33 S34 S35
A1
-A3
X1
X2
9
+24V
MSI-SR4
0V
A2
Var. B
2 AOPD-
1 AOPD+
2 AOPD+
-K3
Var. A
-K4
-K3 -K4
IV-0
-K3
-K4
RES-0
L+ L+
1
1
2
2
13 23 41
RES-I
14 24 42
*
A1
-K3
A2
A1
-K4
A2
L- L-
33
34
*
Figure 8.5: Wiring example with external start/restart interlock and contactor monitoring, without field
pair switch
+24
0
P
* Release circuits for the dangerous movement: Integrate these contacts into the control system so that
the dangerous state is removed when the contact is open.
Applications in acc. with category 3 or 4 in acc. with ISO 13849-1 require a two-channel integration (see
var. A).
Variant B shows a single-channel integration.
The monitoring of the downstream contactors K1 and K2 (contactor monitoring, EDM) is implemented in
this connection example with the integration of the rest contacts K1 and K2.
8.4.2 Programmable logic controller (PLC) with corresponding safety level and field pair switchover
The safety level corresponds with at least category 3 in acc. with ISO 13849-1.
Leuze electronic RS4 51
Page 52

Electrical connection
4
+24V
-A1
0V
PE
1,6 A
-W1
2
-X1
Res ta r t
ROTO SCAN RS4 - 4
0V
1
-X1
-W1
1
2
412
32 678 155
3 1211109
4 14 15
FP 1
+24V
Alar m 1
SH1
8
7
65
FP 4
FP 3
FP 2
TxD+
TxD-
1
2 9
-X2
11
13
1
n.c.
n.c.
OSSD2
OSSD
RS232/422
Sh ie ldRxD -
RxD +
6 7 8
4 53
8115
n.c.n.c.
X1
Alar m 2
9
156
X2
reserved
n.c.
n.c.
9
-A2
V
I/O
+24
0V
Saf e t y
St an d ar d
inputs
Saf e t y PLC
Saf e t y
outpu ts
+2
0V
PE
Figure 8.6: Example of a connection with a safe PLC with corresponding safety level (min. category 3,
ISO 13849-1) and field pair switchover.
Leuze electronic RS4 52
Page 53

9 Parameters
You enter all parameters for the safety sensor's configuration in the software (see "Safe parametering"
instructions).
The safety sensor is configured at the factory with the maximum protective field and activated start/restart
interlock. Configure the safety sensor according to your application.
9.1 Administrative parameters
9.1.1 Safety Laser Scanner name
The Safety Laser Scanner name parameter unambiguously names the safety sensor.
Settings
• Max. 20 characters
• No default value.
9.1.2 Description
The Description parameter contains further information for clearly assigning the safety sensor. You can,
for example, provide the safety sensor's precise point of use.
Settings
Parameters
• Max. 100 characters
• No default value.
9.1.3 Start segment output
The Start segment output parameter names the segment of the measured contour that will be shown first.
Settings
• Settable value: 0 to 528
• Default value: 0
For showing 180° use the value 14 as start segment.
For showing 190° use the value 0 as start segment.
9.1.4 Stop segment output
The Stop segment output parameter names the segment of the measured contour that will be shown last.
Settings
• Settable value: 0 to 528
• Default value: 528
For showing 180° use the value 514 as stop segment.
For showing 190° use the value 528 as stop segment.
9.1.5 Output resolution
The Output resolution parameter provides the number of measured values per section shown. The respective smallest measured values are connected with one another with the display on the monitor.
Settings
• Settable value: 1 to 8
• Default value: 4
If you want a detailed contour display, enter 1. If you want a smoothed out and quicker updated contour
display, enter 8.
Leuze electronic RS4 53
Page 54

9.1.6 Serial interface baud rate
The Serial interface baud rate parameter provides the transfer rate between the safety sensor and the PC.
Settings
• Settable value: 9600 to 115200 baud
• Default value: 57600 baud
The set value must agree with the PC's transfer rate.
9.1.7 Alarm incident
The Alarm incident parameter provides the incident at which the safety sensor will switch off alarm outputs
Alarm 1 and Alarm 2.
Settings
•Device warning
• Warning field interrupted
• Device warning or warning field interrupted
•None
• Default value: Warning field interrupted
Parameters
9.1.8 Precalculated measured values output
The Precalculated measured values output parameter determines whether the safety sensor will issue the
distance measured value and the speed precalculated from it via the serial interface.
Settings
•Activated
• Deactivated
• Default value: Deactivated
The first segment is always 90° (straight). You can provide two more segments for the measured
value calculation.
9.1.9 2nd measured value calculation segment
The 2nd measured value calculation segment parameter provides the second segment, for which the
distance and precalculated speed will be issued.
Settings
•0-528
• Default value: 14
9.1.10 3rd measured value calculation segment
The 3rd measured value calculation segment parameter provides the third segment, for which the distance
and precalculated speed will be issued.
Settings
•0-528
• Default value: 514
Leuze electronic RS4 54
Page 55

9.2 Safety-relevant parameters
9.2.1 Application
The Application parameter provides the usage scenario that the safety sensor will be configured for.
Settings
You can select from the following applications. Depending on the set application, the parameters "Resolution" and "Start/restart interlock" are preset:
Selectable application Resolution Start/restart interlock
Danger zone guarding 70 mm Activated
Leg detection 50 mm Activated
AGV 70 mm Deactivated,
MotionMonitoring 70 mm Deactivated,
Passage control 150 mm Activated
Parameters
restart automatic with 2000 ms delay
restart automatic with 2000 ms delay
Arm protection 40 mm Activated
Hand protection 30 mm Activated
Body protection 150 mm Activated
Freely selectable Presettings 70 mm Activated
Default value: Danger zone guarding
9.2.2 Response times
The Response times parameter provides the time until the safety sensor switches off the OSSD 1 and
OSSD 2 safety-related switching outputs or the alarm output with warning and protective field interruptions.
You provide two response times:
• PF response time: Time until the safety sensor switches off the OSSD 1 and OSSD 2 safety-related
switching outputs.
• WF response time: Time until the safety sensor switches off the alarm output.
Settings
• Multiple of 40 ms, in the 80 ms-640 ms range
• Default values:
• PF response time: 80 ms
• WF response time: 80 ms
9.2.3 Dust suppression
The dust suppression parameter indicates whether or not the dust suppression function is activated.
Settings:
•Activated
• Deactivated
• Default value: Activated
Vehicle speed: The Vehicle speed parameter specifies the range for the maximum speed of your
driverless transportation system. Settings:up to 1500 mm/s up to 2500 mm/s up to 4000 mm/s
faster than 4000 mm/s Default value: faster than 4000 mm/s
Leuze electronic RS4 55
Page 56

9.2.4 Applicable field pair selection with scanner start
The Applicable field pair selection with scanner start parameter indicates which field pair may be active
when the safety sensor starts.
Settings
You select the applicable field pairs in a matrix:
• x: Field pair allowed with start
• Empty field: Field pair forbidden with start
• Default values: Field pairs 1, 2, 3 and 4 allowed
9.2.5 Permitted field pair switchovers
The Permitted field pair switchovers parameter indicates the switchover from field pair to field pair that is
permitted and in which sequence. With forbidden switchover sequences the safety sensor stops the
machine.
Settings
You select the permitted field pair switchovers in a matrix:
• x: Field pair switchover permitted
• Empty field: Field pair switchover forbidden
• Default values: No field pair switchover allowed
Parameters
9.3 Field pair
9.3.1 Protective field/description
The Description parameter names the protective field.
Settings
• Max. 20 characters
• Default values: PF1 to PF4
9.3.2 Warning field/description
The Description parameter names the warning field.
Settings
• Max. 20 characters
• Default values: WF 1 to WF 4
9.4 MotionMonitoring
9.4.1 Vehicle width
The Vehicle width, left and Vehicle width, right parameters provide the width of the vehicle from the rotary
mirror axis of the safety sensor to the vehicle side.
Settings
• 100 mm-6000 mm
• Default value: 100 mm
The total of the Vehicle width, left and Vehicle width, right values must be at least the overall vehicle width.
9.4.2 Protective field side additional distance
The Protective field side additional distance parameter provides the safety distance between a vehicle side
and the protective field.
Use a protective field side additional distance if people can approach the vehicle from the side.
Leuze electronic RS4 56
Page 57

Settings
• 25 mm-6000 mm
• Default value: 100 mm
9.4.3 Laser scanner installation point
The Laser scanner installation point parameter provides the point at which the safety sensor is installed
on the vehicle front.
The software calculates the rear limit of the protective fields and warning fields on the basis of the setting.
Settings
• Countersunk
• Without mounting system
• With mounting system
• Default value: With mounting system
9.4.4 Warning field prerun time
The Warning field prerun time parameter provides the amount of time between the interruption of the
warning field and the interruption of the protective field, regardless of the speed of the respective protective
field.
The software calculates the warning field size with the warning field prerun time, depending on the protective field size.
Parameters
Settings
• 1 ms-5000 ms
• Default value: 1500 ms.
9.4.5 Vehicle response time
The Vehicle response time parameter provides the time from switching off the safety sensor until the
braking starts.
It is the combined response times of all components of the switch-off circuit, e.g. safety modules, safety
relays.
Settings
• 10 ms-640 ms
• Default value: 300 ms.
9.4.6 Brake wear and tear additional distance
The Brake wear and tear additional distance parameter provides the factor by which the braking distance
is extended by wear and tear components, which are integrated into the braking process.
Settings
• 0 %-100 %
• Default value: 10 %
9.4.7 Ambient influences additional distance
The Ambient influences additional distance parameter provides the factor by which the braking distance
is extended by ambient influences, e.g. by wet conditions or dust on the path covering.
Settings
• 0 %-100 %
• Default value: 10 %
Leuze electronic RS4 57
Page 58

9.4.8 Speed with PF
The Speed with PF x parameter provides the maximum speed that the vehicle reaches with this protective
field.
Settings
• Maximum value: 8000 mm/s
If you specify the Speed with PF x parameter for multiple protective fields, the difference between the
protective fields must be at least 100 mm/s. From the Speed with PF x and Braking distance with PF x
parameters, the software calculates the required protective field lengths and the braking deceleration.
9.4.9 Braking distance with PF
The Braking distance with PF x parameter provides the braking distance that the vehicle requires to come
to a standstill with maximum speed with this protective field.
Settings
• Maximum value: Scanner range in mm
Provide the parameter for the protective field in which the vehicle has the highest maximum speed. The
software interpolates all other braking distances.
9.4.10 Standstill monitoring
Parameters
The Standstill monitoring parameter indicates whether or not further travel blocking in the MotionMonitoring function is activated.
Settings
•Activated
• Deactivated
• Default value: Deactivated
9.4.11 Creep and reverse
The Creep and reverse parameter indicates whether creep and reverse is activated in the MotionMonitoring function.
Settings
•Activated
• Deactivated
• Default value: Deactivated
Leuze electronic RS4 58
Page 59

10 Setting the device into service
10.1 Before first start-up
In accordance with IEC TS62046 and national regulations, such as EU Directive 89/655 EEC, for
example, tests are prescribed in the following situations:
• Before first start-up
• Following machine modifications
• After long machine standstill
• After a safety sensor upgrade or reconfiguration
10.2 Switching on
Prerequisites:
• You have configured the safety sensor with the configuration and diagnostics software and transferred the configuration to the safety sensor.
• Interface X1 of the safety sensor is connected to the control or safety relay.
• Protective housing is mounted on interface X2.
CAUTION
Danger of injury with unpredictable machine behavior with first start-up.
ª Ensure that nobody is in the machine's danger zone.
Setting the device into service
ª Start the machine.
ª Press the start/restart button if the start interlock function is activated.
or
If the start test function is activated, interrupt the protective field and release it again. The machine then
starts automatically.
10.3 Shutting down
Shut the machine with the safety sensor down temporarily
When you shut down the machine with the safety sensor temporarily, you do not have to observe any more
steps. The safety sensor saves the configuration and starts again with the switch-on with this configuration.
Shut down safety sensor and remove from machine
When you shut down the safety sensor and store it away for a later use, you must reset the safety sensor
to the factory settings.
ª Reset the safety sensor to the factory settings (see instructions, "Safe parametering").
10.4 Restart
Restarting the machine with the safety sensor
If you have only shut down the system with the safety sensor temporarily and are restarting the system
without any changes, you can restart the safety sensor with the configuration that applied with the shutdown. The configuration remains saved in the safety sensor.
ª Perform a function check (see chapter 11.3 „Daily functions test“).
Start up machine with safety sensor after modification or reconfiguration.
If you have performed significant changes on the machine or have reconfigured the safety sensor, the
safety sensor must be checked as with the first start-up.
ª Test the safety sensor (see chapter 11.1 „Testing before first start-up and after machine modification“).
Leuze electronic RS4 59
Page 60

10.5 Starting up the replacement device
The replacement device and the device being replaced must agree as follows:
• Device type upward compatible in accordance with specification plate or with previous device with
greater range and greater scope of function.
• Installation position
•Alignment
Mount and align replacement device
ª Mount the replacement device at the previous safety sensor's position.
ª Align the safety sensor as with the previous safety sensor.
Transfer configuration to replacement device
You have two options for transferring the configuration to the replacement device:
• When using the ConfigPlug by attaching the ConfigPlug to the replacement device.
• With the configuration and diagnostics software
Transfer configuration with the PC
ª Connect the safety sensor's X2 interface with the PC.
ª Transfer the configuration to the replacement device (see also, "Safe parametering" instructions).
Setting the device into service
Use ConfigPlug
The ConfigPlug has a switch that determines the transfer direction of the configuration:
Switch setting Transfer direction
1 The ConfigPlug overwrites the safety sensor's configuration.
X The configuration saved in the ConfigPlug is overwritten.
ª Set the switch in the plug to position 1.
ª Attach the ConfigPlug to interface X1.
The ConfigPlug transfers the configuration to the safety sensor when the safety sensor is started. A brief
flashing of the two yellow LEDs 2 and 5 confirms the successful transfer of the configuration.
The replacement device is not compatible if the safety sensor displays a fault.
Test the replacement device
The replacement device test depends on whether you use the ConfigPlug or have transferred the configuration with the PC to the safety sensor.
ª If you have used the ConfigPlug, test the safety sensor using the checklist for the daily test.
or
If you have transferred the configuration with the PC, check the safety sensor in accordance with the
first start-up (see chapter 10.1 „Before first start-up“).
Leuze electronic RS4 60
Page 61

Setting the device into service
10.6 Starting up a safety sensor with the MotionMonitoring function
Prerequisite for starting up the safety sensor with the MotionMonitoring function is proper mounting (see
chapter 6.6 „Mobile danger zone guarding on DTSs“)!
ª Complete the checklist for the MotionMonitoring function.
You can find this at the end of this chapter.
ª Start the RS4soft configuration and diagnostics software and connect the PC to the safety sensor.
ª Create the configuration using the data entered in the checklist.
Observe the configuration notices in the following section!
ª Load the inspected configuration into the safety sensor.
ª Start up the entire system, consisting of vehicle and safety sensor.
ª Align the safety sensor; the measurement value display shown in the "Definition of protective fields"
view of the RS4soft configuration and diagnostics software is suitable for performing the alignment:
Place an object (cardboard box) measuring approx. 25 cm in width and 50 cm in height in the middle of
the transportation path approx. 1 m in front of the respective reference surface (end of the travel path)
(see figure 10.1).
Use the measurement value display to check that this object can be seen from all positions of the vehicle
to the end of the transportation path in the middle of the reference surface. This is the case if the object in
the middle of the arrow shown in the measurement value display can be seen and the reference surface
completely covers the corresponding width of the displayed arrow at every vehicle position and forms a
straight line in this area (see figure 10.1).
Leuze electronic RS4 61
Page 62

Setting the device into service
1
2
1
2
3
4
5
1 m
3
4
1
3
4
1 Reference surface (1000 mm x 250 mm @ 20 m; 1400 mm x 500 mm @ 45 m)
2Object
3 Transportation path
4 Safety sensor
5 Vehicle
Figure 10.1: Alignment of the safety sensor with subsequent assessment of the reference surface Motion-
Monitoring
ª Inspect the protective fields and warning fields of the safety sensor by examining the measurement val-
ue display shown:
Is the displayed measurement value line yellow all the way through?
Do the green LED1 and green LED4 of the safety sensor illuminate?
Does the red LED3 illuminate upon entry into the protective field and is the "Brake" function initiated in
the vehicle control?
ª Check the safety-related switching outputs and their subsequent function from the vehicle:
Does the green LED1 illuminate—and, 2 seconds later, green LED4—after exiting the protective field?
ª If you answered all of the questions with "yes", start up the vehicle and remove the object from the trans-
portation path!
ª Check the lateral extension (right and left) of the protective fields along the transportation path by mov-
ing the vehicle along the entire transportation path at medium speed
ª Check the quality of the reference surface along the transportation path by moving the vehicle along the
entire transportation path at medium speed. In the diagnostics window of the “Measurement value con
tour” view of the RS4soft configuration and diagnostics software, the value of the “Quality” variable in
segment
264 must always be greater than 80
-
Leuze electronic RS4 62
Page 63

Setting the device into service
ª Test the corresponding braking distances for all configured vehicle speeds by placing a cardboard box
in the transportation path:
Does the vehicle come to a stop in front of the cardboard box in each test?
ª Now switch to the normal process (planned operating procedure) and display the activities list in the
RS4soft configuration and diagnostics software.
ª Observe the MotionMonitoring status messages and make corrections if necessary:
To be expected are excessive speeds with a correction of the protective field and / or a drop of the “Quality” value to below 50; furthermore, brief protective field violations (green LED flickers) or warning field
violations are possible.
ª Check the measured speeds with those in the configuration.
ª Make corrections until the vehicle travels the entire distance without correction messages in the activi-
ties list.
ª Lastly, perform brake tests again with a cardboard box:
Does the vehicle stop in front of the cardboard box in all cases?
ª Save the configuration, print it out and archive the configuration with the protective fields in your vehicle
documentation.
Configuration notices:
ª Select the response time of the laser scanner between 160 ms and 200 ms.
ª Define a speed raster that is appropriate for the process:
The speed levels should be spaced at least 200 mm/s apart.
The process should also offer the option and time to switch between these speeds.
ª Select the switchover points in the configuration of the safety sensor 50 mm/s higher than in the vehicle
control– this increases the tolerance during the protective field switchover.
ª Defining the braking distance:
For mechanically or unregulated systems, measure the braking distances.
For electronic systems with consistent braking deceleration, enter the braking distance in such a way
that braking deceleration displayed in the speed matrix corresponds to that of the electronic braking system.
ª Activate and use field pairs 7 and 8:
Use field pair 7 while the vehicle is stopped or during load transfer; while vehicles are at a standstill,
persons may be present in the transportation path. At the end positions of the transportation path, the
availability of the safety sensor can be increased if persons are present for longer periods of time.
Use field pair 8 for travel in reverse.
Leuze electronic RS4 63
Page 64

Setting the device into service
Table 10.1: Checklist for using the safety sensor with the MotionMonitoring function
Prerequisites: fulfilled not fulfilled planned changes/ad-
ditions
1. Side-tracking skate with forward and backward
linear movement
2. Only one vehicle on the path, no vehicles traveling towards one another
3. Transportation path < 50 m
4. Transportation path terminated within just a few
meters of front and rear
• Wall or siding with the same width as vehicle serves as reference surface for the
measurement
• No requirements on the reference surface
(e.g., simple concrete wall, grey)
• Pillars, columns or wall projections in the
reference surface may affect the measurements and function
5. Speeds < 6 m/s
6. No storage spaces for pallets or parking spaces
for high-lift trucks within the transportation path
7. Within the transportation path—from reference
surface to reference surface—moderate traffic
of high-lift trucks (passages, storage/removal)
is possible at any time; frequent crossing of the
transportation path by individual persons is
completely ignored
Preparing the configuration fulfilled not fulfilled planned changes/ad-
ditions
1. Define the start-up / restart behavior. Automatic Start inter-
lock
2. Determine response times of the downstream
in ms
safety circuit of the side-tracking skate:
Time until the brake acts
3. Define the speed profile of the vehicle: at which
levels does the side-tracking skate travel at
which speeds?
Number of
protective
fields
4. Define the maximum speed. in mm/s
5. Determine the braking distance at maximum
speed-is the braking deceleration known?
6. Are other braking distances known at other
speed levels?
in mm
in mm
in mm
in mm
in mm
in mm
2
at v= _____ in mm/s
at v= _____ in mm/s
at v= _____ in mm/s
at v= _____ in mm/s
7. Define the installation conditions of the safety
sensor (mounting system?).
Leuze electronic RS4 64
Page 65

Setting the device into service
Preparing the configuration fulfilled not fulfilled planned changes/ad-
ditions
8. Determine the vehicle width and position of the
safety sensor.
Distance to right vehicle edge
Distance to left vehicle edge
in mm
in mm
9. Are the reverse / further travel blocking functions used?
10. Observe the allowances for brake wear and foot
protection / additional spacing at side.
11. Examine automatically created protective fields
and warning fields and correct as necessary!
PF8 / PF7
in %
Leuze electronic RS4 65
Page 66

11 Testing
11.1 Testing before first start-up and after machine modification
In accordance with IEC TS62046 and national regulations, such as EU Directive 89/655 EEC, for
example, tests are prescribed in the following situations:
• Before first start-up
• Following machine modifications
• After long machine standstill
• After a safety sensor upgrade or reconfiguration
WARNING
Danger of serious injury through unpredictable machine behavior with first start-up.
ª Ensure that nobody is in the machine's danger zone.
ª Check the effectiveness of the switch-off function in accordance with the following checklist in all of the
machine's operating modes along the defined protective field contour. With driverless transportation
systems(DTSs): Take the entire route into consideration.
ª Document all tests comprehensibly and print out the safety sensor's configuration incl. protective field
shapes for your documentation.
ª Instruct the operating staff before beginning the activity. The training is the responsibility of the operating
company.
ª Attach the instructions for daily testing on the machine so that they are clearly visible in the operating
staff's native language. You can print out the chapter "Daily function check" for this.
Testing
Leuze electronic offers the test before first start-up by an appropriately qualified person as a
safety inspection (see chapter 16 „Service“).
Checklist for testing the safety sensor before the machine's first startup.
Tester: Appropriately qualified person
This checklist serves as a reference for the machine manufacturer or supplier. It replaces neither the test
of the entire machine or system before the first start-up nor its regular tests by an appropriately qualified
person. This checklist contains minimum testing requirements. Depending on the application, other tests
may be necessary.
ª Store this checklist with the machine documents.
Items on the check list Yes No
Were all safety directives and standards relevant to this machine type observed?
Does the Declaration of Conformity of the machine include a listing of these documents?
Does the safety sensor satisfy the safety-related capability (PL, SIL, category) as
required by the risk assessment?
Circuit diagram: Are both safety-related switching outputs (OSSDs) integrated in the
downstream machine control acc. to the required safety category?
Circuit diagram: Are the switching elements controlled by the safety sensor, e.g. contactors with positive-guided contacts monitored by a feedback circuit (EDM)?
Does the electrical wiring match the circuit diagrams?
Have the required protective measures against electrical shock been effectively
implemented?
Leuze electronic RS4 66
Page 67

Testing
Items on the check list Yes No
Has the maximum stopping time of the machine been remeasured and recorded in
the machine documents?
Is the required safety distance (protective field of the safety sensor to the next point of
operation) maintained?
Are all points of operation of the machine accessible only through the protective field
of the safety sensor? Are all accessible safety devices, e.g. protective grids correctly
mounted and secured against manipulation?
Is an unprotected presence between the respectively activated protective field and
the point of operation safely ruled out or, for example, prevented by an additional
physical protective device?
Is the command device for triggering the start/restart interlock of the safety sensor or
the machine mounted in accordance with specifications?
Is the safety sensor correctly aligned (tilt angle) and are all fixing screws and plugs
tight?
Are safety sensor, connecting cable, plug, protection caps and command devices
undamaged and without any sign of manipulation?
Has the effectiveness of the protective function of all configured protective fields and
for all of the machine's operating modes been checked with a functions check?
Is the safety sensor effective during the entire dangerous movement of the machine?
Is the dangerous movement stopped when the safety sensor is disconnected from
the supply voltage, when the machine operating mode changes or when a change is
made to another protective device?
Are the instructions for the safety sensor's daily test mounted clearly visible for the
operating staff?
11.2 Regular test by an appropriately qualified person
Regular tests of the safe interaction of the safety sensor and the machine are used to reveal machine
changes or unauthorized changes, i.e., manipulations on the safety sensor. Test intervals are regulated
by country-specific regulations. IEC TS62046 recommends a regular test every 6 months.
ª Have all tests been performed by an appropriately qualified person.
ª Take the country-specific regulations and the times and periods they include into account.
Leuze electronic offers the test before first start-up by an appropriately qualified person as a
safety inspection (see chapter 16 „Service“).
11.3 Daily functions test
The safety sensor's switch-off function must be tested daily or at shift changes and with every change of
the machine operating mode in accordance with the following checklist in order to reveal any possible
damage or manipulations.
WARNING
Danger of serious injury through unpredictable machine behavior with the test.
ª Ensure that nobody is in the machine's danger zone.
Leuze electronic RS4 67
Page 68

Testing
WARNING
Machine operation may not continue if errors occur during the daily test
If you answer one of the checkpoints with no, the machine or the vehicle may no longer be operated.
ª Have the entire machine tested by an appropriately qualified person (see chapter 11.2 „Regular test
by an appropriately qualified person“).
Daily functions test checklist
Tester: Authorized operating personnel or instructed person
Items on the check list Yes No
Is the safety sensor correctly aligned (tilt angle) and are all fixing screws and plugs
tight?
Are safety sensor, connecting cable, plug, protection caps and command devices
undamaged and without any sign of manipulation?
Are all points of operation of the machine accessible only through the protective field
of the safety sensor? Are all additional protective devices correctly mounted, e.g.
protective grids?
ª Switch the machine on, wait approx. 20 s until the auto-test sequence has finished.
With an automatic restart: Do LED 1 and LED 4 light green?
With start interlock: Do LED 1, LED 3 and LED 5 light yellow?
ª Activate the safety sensor's command device (with start/restart interlock function) or
interrupt the protective field with a test instrument* (with start test function).
Do LED 1 and LED 4 light green?
Stationary applications:
ª Interrupt the selected protective field of the safety sensor with the test instrument*
with running operation.
Do LED 1 and 4 go off? Does LED 3 light red? Does the dangerous movement stop
immediately?
Mobile applications:
ª Interrupt the selected protective field of the safety sensor with the test instrument*
with moving vehicle.
Do LED 1 and 4 go off? Does LED 3 light red?
Does the vehicle stop within the limits defined in the configuration log?
ª Repeat the test described above at different points of the danger zone for all config-
ured protective fields.
Do the protective field boundaries with stationary applications agree with the floor
marking?
MotionMonitoring:
ª Start the test mode for MotionMonitoring on the control unit.
Does alarm output 2 signal that the speed is exceeded?
* Diameter of the test instrument in accordance with the safety sensor resolution of the configuration log
Leuze electronic RS4 68
Page 69

12 Maintenance
Clean the front screen and the scatter screens as required by the application-conditional load rating.
12.1 Clean the front screen
Use the RS4-Clean-Set consisting of special cleanser and cleaning cloths for cleaning the front screen
(see chapter 17 „Accessories“).
The procedure for cleaning depends on the kind of dirt.
Dirt Cleaning
Maintenance
Particles, loose, scouring
Particles, loose, non-scouring
Particles, sticking
Particles, statically charged
Particles/drops, smearing
Water drops
Oil drops
Fingerprints
Scratches
NOTICE
The wrong cleansers or clothes will damage the front screen
ª Do not use any scouring cleansers or scratching cloths.
ª Vacuum without touching or blow away softly, oil-free
ª Wipe free in one swipe with cleaning cloth
ª Vacuum without touching or blow away softly, oil-free
or
Wipe free in one swipe with cleaning cloth
ª Wet with cloth soaked in cleanser
ª Wipe free in one swipe with cleaning cloth
ª Vacuum without touching
ª Wipe free in one swipe with cleaning cloth soaked with cleanser
ª Wet with cloth soaked in cleanser
ª Wipe free in one swipe with cleaning cloth
ª Wipe free in one swipe with cleaning cloth
ª Wet with cloth soaked in cleanser
ª Wipe free in one swipe with cleaning cloth
ª Wet with cloth soaked in cleanser
ª Wipe free in one swipe with cleaning cloth
ª Change front screen (see chapter 14.1 „Change the front
screen“)
If the cleaning takes longer than four seconds, e.g. with fingerprints, the safety sensor displays
the fault of the front screen monitoring. After the cleaning you must then reset the safety sensor
with the start/restart button.
Leuze electronic RS4 69
Page 70

ª Soak cloth with cleanser.
ª Wipe front screen free in one swipe.
12.2 Clean scatter screens
ª Soak cloth with cleanser.
Maintenance
ª Wipe scatter screen free in one swipe.
Leuze electronic RS4 70
Page 71

13 Diagnostics and removing errors
13.1 What to do in case of failure?
The safety sensor has a three-level diagnostics concept to quickly remove errors. Proceed gradually in
steps to remove an error:
ª Read the safety sensor's status signaled by the LEDs and remove the errors with the specified mea-
sures.
ª Read out the diagnostics list with the configuration and diagnostics software and remove the errors with
the aid of the solution provided there.
ª Create the service file with the configuration and diagnostics software and send this service file for
remote diagnostics to Leuze.
13.2 Operating displays of the LEDs
LEDs Status Measure
1
green2yellow3red4green5yellow
Diagnostics and removing errors
00100
02 x (1)1 02 x (1)
0110–
1–101
10010
11010
• Boot process, configuration process
Safety-related switching outputs
are switched off.
• Boot process, configuration process
• Safety-related switching outputs
are switched off.
• Data comparison with ConfigPlug
• The active protective field is
seized.
• Safety-related switching outputs
are switched off.
• The active warning field is seized.
• The sensor function is active; the
active protective field is free.
• Safety-related switching outputs
are switched off.
• Start/restart interlock locked.
• The sensor function is active; the
active protective field is free.
• The active warning field is free.
• Safety-related switching outputs
are switched on.
• The sensor function is active; the
active protective field is free.
• The active warning field is seized.
• Safety-related switching outputs
are switched on.
ª Press the start-/
restart button.
Object is in the warning field.
ª Check the warning
field definition if
required.
0LED off
1 LED lights
– LED not relevant
Leuze electronic RS4 71
Page 72

13.3 LED warning and error displays
LEDs Status Measure
1
green2yellow3red4green5yellow
Diagnostics and removing errors
1001(1)
0 (1) 1 0 ((1))
0 ((1)) 1 0 ((1))
(1) 0 1 0 ((1))
((1)) 0 1 0 ((1))
0010((1))
• The sensor function is
active; the active protective
field is free.
• The active warning field is
free.
• Safety-related switching outputs are switched on.
• Front screen is dirty.
• Device fault
• Safety-related switching outputs are switched off.
• Front screen is dirty.
• Device fault
• Safety-related switching outputs are switched off.
• ConfigPlug configuration is
not compatible with the
safety sensor; the configuration cannot be transferred.
• Device fault
• Safety-related switching outputs are switched off.
• Errors on the field pair control inputs
• Device fault
• Safety-related switching outputs are switched off.
• MotionMonitoring has
detected a fault: Vehicle
movement does not agree
with the active field pair.
• Device fault
• Safety-related switching outputs are switched off.
ª Clean the front screen as
soon as possible.
Device still works.
ª Clean the front screen.
ª Start the safety sensor
again.
ª Replace the safety sensor.
The safety sensor type
must correspond with the
ConfigPlug's configuration.
ª Check the field pair swi-
tchover, switchover
sequences and switchover
times.
At least one field pair must
always be active.
ª For the precise error
cause, read out the diagnostics list with the software.
ª Check the vehicle's speed
and travel direction.
ª Check the control system's
field pair switchover
ª Wait 5 seconds.
The safety sensor performs a reboot.
ª If the reboot is not suc-
cessful, read out the diagnostics list with the software.
0LED off
1 LED lights
(1) LED flashes with 2 Hz
((1)) LED flashes with 4 Hz
– LED not relevant
Leuze electronic RS4 72
Page 73

13.4 Diagnostics codes
You can create a diagnostics list with the software. The incidents that occurred during the safety sensor
operation are listed in this diagnostics list. Each incident is given with place and number. The meaning of
the incidents is shown in the following table.
Place Number Meaning Measure
Diagnostics and removing errors
102 2 Data transfer error on interface X2.
103 2 Data transfer error on interface X2.
104 2 Data transfer error on interface X2.
105 6 Function, access, command not
allowed with currently selected authorization level.
201 4 Interface X2 time specifications not
complied with, last message overwritten.
302 2 Interface X2 time specifications not
complied with, send data not acknowledged.
306 5 Previous message not completely
issued, interface X2 time specifications
not complied with.
801 2 Error memory cannot be read, internal
defect.
ª Check the interface parameters and
start the transfer again.
ª Check the interface parameters and
start the transfer again.
ª Check the interface parameters and
start the transfer again.
ª Change the authorization level and
start the transfer again.
ª Check the interface parameters and
start the transfer again.
ª Check the interface parameters and
start the transfer again.
ª Check the interface parameters and
start the transfer again.
ª If reset is not successful, contact cus-
tomer service.
805 6 Error memory cannot be transferred,
transfer error on interface X2.
1002 1 Motor does not reach the nominal
speed after start, internal defect.
1002 2 Motor speed not constant after start,
internal defect.
1003 1 Motor does not reach the nominal
speed after start, internal defect.
1003 2 Motor speed not constant after start,
internal defect.
1003 3 Motor speed not constant after start,
time exceeded.
1110 4 Safety-related switching outputs
(OSSDs) cannot be switched, short-circuit with 0 V DC or +24 V DC.
1110 5 Safety-related switching outputs
(OSSDs) cannot be switched, short-circuit between OSSD1 and OSSD2.
1110 6 Safety-related switching outputs
(OSSDs) cannot be switched, short-circuit with 0 V DC or +24 V DC.
ª Check the interface parameters and
start the transfer again.
ª If reset is not successful, contact cus-
tomer service.
ª If reset is not successful, contact cus-
tomer service.
ª If reset is not successful, contact cus-
tomer service.
ª If reset is not successful, contact cus-
tomer service.
ª If reset is not successful, contact cus-
tomer service.
ª Check the connection/wiring of the
OSSDs.
ª Check the connection/wiring of the
OSSDs.
ª Check the connection/wiring of the
OSSDs.
Leuze electronic RS4 73
Page 74

Diagnostics and removing errors
Place Number Meaning Measure
1111 7 Short-circuit between safety-related
switching outputs OSSD1 and OSSD2
1111 8 Short-circuit of one safety-related
switching output (OSSD) with 0 V DC.
1111 9 Short-circuit of one safety-related
switching output (OSSD) with
+24 V DC.
1606 4 Angle error detected, poss. rotation of
the sensor housing; switch-off and reset
followed.
1607 5 Angle error detected, poss. rotation of
the sensor housing; switch-off and reset
followed.
1608 8 Motor speed not constant during opera-
tion, poss. rotation of the sensor housing.
1608 9 Motor speed not constant during opera-
tion, poss. rotation of the sensor housing.
ª Check the connection/wiring of the
OSSDs.
ª Check the connection/wiring of the
OSSDs.
ª Check the connection/wiring of the
OSSDs.
ª If reset is not successful, contact cus-
tomer service.
ª If reset is not successful, contact cus-
tomer service.
ª If reset is not successful, contact cus-
tomer service.
ª If reset is not successful, contact cus-
tomer service.
1608 10 Motor speed not constant during opera-
tion, poss. rotation of the sensor housing.
1705 1 Signal of a light beam safety device of
the window monitoring below the bottom limit, dirty front screen.
1705 2 Signal of a light beam safety device of
the window monitoring above the upper
limit, oil/grease on the front screen
1906 1 Safety-related switching outputs
(OSSDs) cannot be switched, internal
or external short-circuit.
1906 2 Safety-related switching outputs
(OSSDs) cannot be switched, internal
or external short-circuit.
1906 5 Read back error on the safety-related
switching outputs (OSSDs), internal or
external short-circuit.
1906 6 Error on the laser's switch-off path,
switch-off because of eye safety, internal defect
ª If reset is not successful, contact cus-
tomer service.
ª Clean the front screen (see
chapter 12.1 „Clean the front screen“).
ª Clean the front screen (see
chapter 12.1 „Clean the front screen“).
ª Check the connection/wiring of the
OSSDs. If reset is not successful, contact customer service.
ª Check the connection/wiring of the
OSSDs. If reset is not successful, contact customer service.
ª Check the connection/wiring of the
OSSDs. If reset is not successful, contact customer service.
ª If reset is not successful, contact cus-
tomer service.
1907 4 Angle error detected, poss. rotation of
the sensor housing; switch-off and reset
ª If reset is not successful, contact cus-
tomer service.
followed.
1907 7 Angle error detected, poss. rotation of
the sensor housing; switch-off and reset
ª If reset is not successful, contact cus-
tomer service.
followed.
Leuze electronic RS4 74
Page 75

Diagnostics and removing errors
Place Number Meaning Measure
2002 12 The configuration data displayed for the
check was not acknowledged for too
long.
2007 18 Date of the protective field currently
being transferred is older than the date
saved in the safety sensor.
2017 19 Data transfer error with ConfigPlug
2017 23 The connected safety sensor does not
support the configuration file in the ConfigPlug.
2017 24 The connected safety sensor does not
support the configuration file in the ConfigPlug.
2017 26 Date of the configuration currently being
transferred is older than the date saved
in the safety sensor.
2018 42 MotionMonitoring, error with the speed
matrix transfer.
2018 43 MotionMonitoring, error with the speed
matrix transfer.
ª Start the transfer again.
ª Update the PC's date and time setting.
ª Replace the ConfigPlug or the com-
plete cable with plug.
ª Change the safety sensor, observe
the device type.
ª Change the safety sensor, observe
the device type.
ª Update the PC's date and time setting.
ª Start the configuration transfer again.
ª Start the configuration transfer again.
2018 44 MotionMonitoring, the right side of a
protective field does not match the predefined vehicle width.
2018 45 MotionMonitoring, a protective field
length does not match the predefined
braking distance of the vehicle.
2018 46 MotionMonitoring, the left side of a pro-
tective field does not match the predefined vehicle width.
2018 50 MotionMonitoring, the left side of a pro-
tective field does not match the predefined vehicle width.
2201 5 Number of measurements in the scan is
too small because of motor rotation
speed error or internal fuse is defect.
2302 1 Error occurred while scanner was start-
ing.
2401 13 Reference measurement failed, dust in
the device, as the plug housing or
dummy cap not screwed.
ª Check all parameters in the wizard,
calculate the protective fields again
and start the transfer again.
ª Check all parameters in the wizard,
calculate the protective fields again
and start the transfer again.
ª Check all parameters in the wizard,
calculate the protective fields again
and start the transfer again.
ª Check all parameters in the wizard,
calculate the protective fields again
and start the transfer again.
ª If reset is not successful, contact cus-
tomer service.
Sequential error.
ª Screw the plugs of interfaces X1 and
X2.
2401 10 Reference measurement failed; glare
Safety sensor performs reset.
from another light source (905 nm) or
rotation speed error.
2401 41 Reference measurement failed; glare
Safety sensor performs reset.
from another light source (905 nm) or
rotation speed error.
Leuze electronic RS4 75
Page 76

Diagnostics and removing errors
Place Number Meaning Measure
2402 10 Reference measurement failed; glare
from another light source (905 nm) or
rotation speed error.
2402 41/42 Reference measurement failed; glare
from another light source (905 nm) or
rotation speed error.
2701 1 Invalid diagnostics command received,
software not compatible with firmware.
2702 3 Invalid diagnostics value requested,
software not compatible with firmware.
2800 2 2 field pair control inputs activated lon-
ger than 1 s.
2800 3 The protective field switchover per-
formed does not comply with the specifications programmed in the safety
sensor.
2800 4 More then 2 protective fields are acti-
vated during operation.
2800 6 Unusable or defective control voltage
for the protective field activation.
Safety sensor performs reset.
Safety sensor performs reset.
ª Use a newer version of the configura-
tion and diagnostics software.
ª Use a newer version of the configura-
tion and diagnostics software.
ª Check the switchover times of the con-
trol inputs FP - FP4.
ª Check the activation of the protective
fields in the program wizard.
ª Check the activation of the control
inputs FP1-FP4.
ª Check the activation of the control
inputs FP1-FP4.
2800 8 No protective field activated. Can occur
during operation and switching off the
device.
2801 1 Error while testing the inputs for the pro-
tective field switchover, internal defect.
2802 3 The protective field activation per-
formed does not comply with the specifications programmed in the safety
sensor.
2802 4 More than 2 protective fields selected
when starting the safety sensor.
2802 6 Unusable or defective control voltage
for the protective field activation.
2802 8 No protective field activated during the
safety sensor start.
2804 3 The protective field activation per-
formed does not comply with the specifications programmed in the safety
sensor.
ª If detected during running operation,
check the activation of the control
inputs FP1-FP4.
ª Contact the customer service.
ª Check the activation of the protective
fields in the program wizard.
ª Only activate one of the control inputs
FP1-FP4.
ª Check the activation of the control
inputs FP1-FP4.
ª Activate one of the control inputs FP1-
FP4.
ª Check the activation of the protective
fields in the program wizard.
2804 4 No protective field clearly selected.
ª Check the activation of the control
inputs FP1-FP4.
2804 6 Unusable or defective control voltage
for the protective field activation.
3016 11 Confirmed single password entered
ª Check the switchover times of the con-
trol inputs FP1 - FP4.
ª Repeat the password entry.
wrong.
Leuze electronic RS4 76
Page 77

Diagnostics and removing errors
Place Number Meaning Measure
3203 6 Safety sensor has optical glare caused
by another device.
3203 7 Safety sensor has optical glare caused
by another device.
3402 2 MotionMonitor, field pair activated
wrong several times. Speed exceeding
can no longer be corrected.
3402 3 MotionMonitor, speed very much
exceeded. Exceeding cannot be corrected.
3402 10 MotionMonitor, maximum speed
exceeded or wrong field pair activation.
Cannot be corrected.
3403 7 MotionMonitor, activated field pair was
not released in the configuration.
3403 12 MotionMonitor, error on the field pair
control inputs. Activated protective field
not defined.
3406 8 MotionMonitor, further travel blocking
cannot switch off the safety-related
switching outputs (OSSDs).
ª Switch off the supply voltage and start
the safety sensor again.
ª Switch off the supply voltage and start
the safety sensor again.
ª Check the activation of the protective
fields in the speed matrix and the
speed the vehicle moved at.
ª Check the activation of the protective
fields in the speed matrix and the
speed the vehicle moved at.
ª Check the activation of the protective
fields in the speed matrix and the
speed the vehicle moved at.
ª Check the activation of the protective
fields in the speed matrix and the program wizard.
ª Check the activation of the creep and
further travel blocking functions.
ª Check the connection/wiring of the
OSSDs.
Leuze electronic RS4 77
Page 78

14 Repairs
14.1 Change the front screen
If the front screen is scratched you must change it.
Only an instructed and appropriately trained person may change the front screen.
It is changed in two steps:
• Change front screen
• Calibrating the front screen
Change the front screen
NOTICE
Safety sensor defect function caused by dirt
ª Perform all work in the most dust-free environment possible.
Do not touch any of the parts inside the device.
Remove all fingerprints on the front screen.
ª Remove the safety sensor from the machine.
ª Place the safety sensor on an even base.
ª Loosen the four Allen screws on the rear of the housing.
ª Carefully pull the two housing parts apart.
Repairs
ª Loosen the screws of the fixing plates.
ª Remove the fixing plates.
ª Push the old front screen backwards out of the housing.
Leuze electronic RS4 78
Page 79

Repairs
2
ª Hold the new front screen on the sides and carefully place it in the correct position.
Ensure that the rubber seal sits correctly in the slot provided for this in the housing and is not damaged.
ª Check that there is no gap of light between the front screen and the housing.
ª Fix the front screen with the fixing plates.
You support screwing the fixing plates with a little pressure on the furthest outside edge of the front
sc
reen.
ª Check the safety sensor components, e.g. mirror, optics, housing parts for dust and blow the safety
s
ensor down as required with a light, oil-free stream of compressed air.
ª Carefully put the two housing parts back together.
The two retaining bolts must slide into the rubber sleeves provided for this.
111
2
1 Retaining bolts
2 Rubber sleeves
ª Carefully tighten the Allen screws on the housing rear by alternating between them.
ª Remove any fingerprints on the front screen.
Leuze electronic RS4 79
Page 80

Calibrating the front screen
Prerequisites:
• The new front screen is correctly mounted.
• Front screen is clean and scratch-free.
• Ambient temperature: 20 °C-25 °C
CAUTION
Faulty calibration caused by dirty or scratched front screen
ª Only calibrate front screens that are as good as new and clean again
ª Connect interface X1 with the control system.
ª Connect interface X2 with the PC.
ª Calibrate the front screen using the software, see "Safe parametering" instructions.
Repairs
Leuze electronic RS4 80
Page 81

15 Disposing
Dispose of safety sensors that can no longer be used according to all applicable specifications and regulations.
Disposing
Leuze electronic RS4 81
Page 82

16 Service
Leuze electronic provides the following services:
• Safety-related start-up and configuration (incl. safety inspection)
• Safety inspection incl. stopping distance measurements
• Instructions on "Laser Scanner Competence"
Our Customer Service and technical hotline will be only too happy to help you at all times:
• Tel: +49 8141 5350-111
• E-mail: service.schuetzen@leuze.de
Service
Leuze electronic RS4 82
Page 83

17 Accessories
Special accessories are also available for the safety sensor. These are optimally harmonized with the
safety sensor.
17.1 Accessories to choose from
Part No. Article Description Length, construc-
Mounting accessories
50033346 RS4-MS RS4 mounting system
50035814 RS4-Adap-P RS4 scanner adapter plate
Start-up
97005003 RS4-COB-24 RS4 configuration and test device,
Connection system
Accessories
tion design
24 V DC
548520 CB-D15E-5000S-11GF RS4 control cable with ConfigPlug,
scanner-side assembled
548521 CB-D15E-10000S-11GF RS4 control cable with ConfigPlug,
scanner-side assembled
548522 CB-D15E-25000S-11GF RS4 control cable with ConfigPlug,
scanner-side assembled
548523 CB-D15E-50000S-11GF RS4 control cable with ConfigPlug,
scanner-side assembled
548530 CB-D15E-10000S-11WF RS4 control cable with ConfigPlug,
scanner-side assembled
50035863 CB-D9-3000-5GF/GM RS4 PC cable, RS232, assembled at
both sides
50035865 CB-D9-5000-5GF/GM RS4 PC cable, RS232, assembled at
both sides
50035867 CB-D9-10000-5GF/GM RS4 PC cable, RS232, assembled at
both sides
520083 AC-D15E-GF ConfigPlug for all RS4, straight, with-
out cable, for automatic configuration
with device swap-out
5 m, straight / open
end
10 m, straight / open
end
25 m, straight / open
end
50 m, straight / open
end
10 m, angled / open
end
3 m
5 m
10 m
50035735 RS4-MG-X1-Set RS4 plug, socket, 15 pins, for X1
interface
50035768 RS4-MG-X2-Set RS4 plug, socket, 9 pins, for X2 inter-
face
426266 RS4-MGS-X1-Set RS4 plug, socket, 15 pins, for X1
interface, cable routing to the rear
426265 RS4-MGS-X2-Set RS4 plug, socket, 9 pins, for X2 inter-
face, cable routing to the rear
Leuze electronic RS4 83
Page 84

Accessories
Part No. Article Description Length, construc-
tion design
Cleaning fluid
430400 RS4-Clean-Set1 RS4 cleaning liquid for plastic,
150 ml, cleaning cloths, 25 pieces,
soft, fuzz-free
430410 RS4-clean-Set2 RS4 cleaning liquid for plastic,
1,000 ml, cleaning cloths, 100
pieces, soft, fuzz-free
Leuze electronic RS4 84
Page 85

Accessories
You can download this EC Declaration of Conformity as a PDF from:
http://www.leuze.com/rotoscan
Leuze electronic RS4 85
 Loading...
Loading...