Lenovo ThinkStation P520, ThinkStation P520C Power Configurator [en, ar, bg, cs, da, de, el, es, es, fi, fr, he, hr, hu, it, ja, ko, nb, nl, pl, pt, pt, ro, ru, sh, sk, sl, sv, th, tr, uk, zc, zh]

LENOVO THINKSTATION
P520 AND P520C POWER
CONFIGURATOR

2
Contents
OVERVIEW
SECTION 1 – KEY ARCHITECTURAL CHANGES
SECTION 2 – POWER RATINGS FOR KEY SYSTEM COMPONENTS
SECTION 3 – P520 POWER CONFIGURATIONS
SECTION 4 – P520C POWER CONFIGURATIONS
SECTION 5 – APPENDIX
SECTION 6 – DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY

3
Overview
With the introduction of the ThinkStation P520 and P520c platforms, there are
changes in the way each system accommodates total power and power delivered
to devices within the system as compared to their predecessor platforms. The
purpose of this document is to highlight those changes such that users can make
informed decisions regarding which power supply to configure in the system and
which add-in cards can be officially supported.

4
Section 1 – Key Architectural Changes
There are some key architectural changes that have been made to the overall
power design of the P520 platform. In the predecessor P500 and P510 platforms,
the power supply had two methods to deliver power to the components within the
system:
• A printed circuit board (PCB) “edge” style connector that provided
power to the motherboard
• A cable connection that allowed for power to be distributed to add in
cards, such as auxiliary power for GPUs.
With the P520, all power is now delivered to the system in a single connection via
the PCB edge connector. Instead of using a separate cable connection for
auxiliary powered devices, power for those devices is now cabled directly off the
motherboard.
This becomes particularly advantageous when considering the upgradability of the
P520 power supply. For previous P5XX platforms, upgrading the power supply to
one with higher wattage sometimes also meant upgrading the auxiliary power
cabling associated with that supply. This was a bit of a daunting task as the
auxiliary cabling was routed underneath the motherboard requiring technicians to
disassemble a large portion of the system to fully upgrade the power supply and
cabling. With this new design, upgrading a power supply is as simple as installing
the new power supply unit, and attaching any auxiliary power cable updates
directly to the top of the motherboard. No system disassembly/reassembly is
necessary. Figure 1 below shows the basis of this new design.
P520c utilizes a more traditional approach to powering system components since
it supports a single capacity design. All onboard components and add-in cards
are powered through direct cable connections from the power supply.
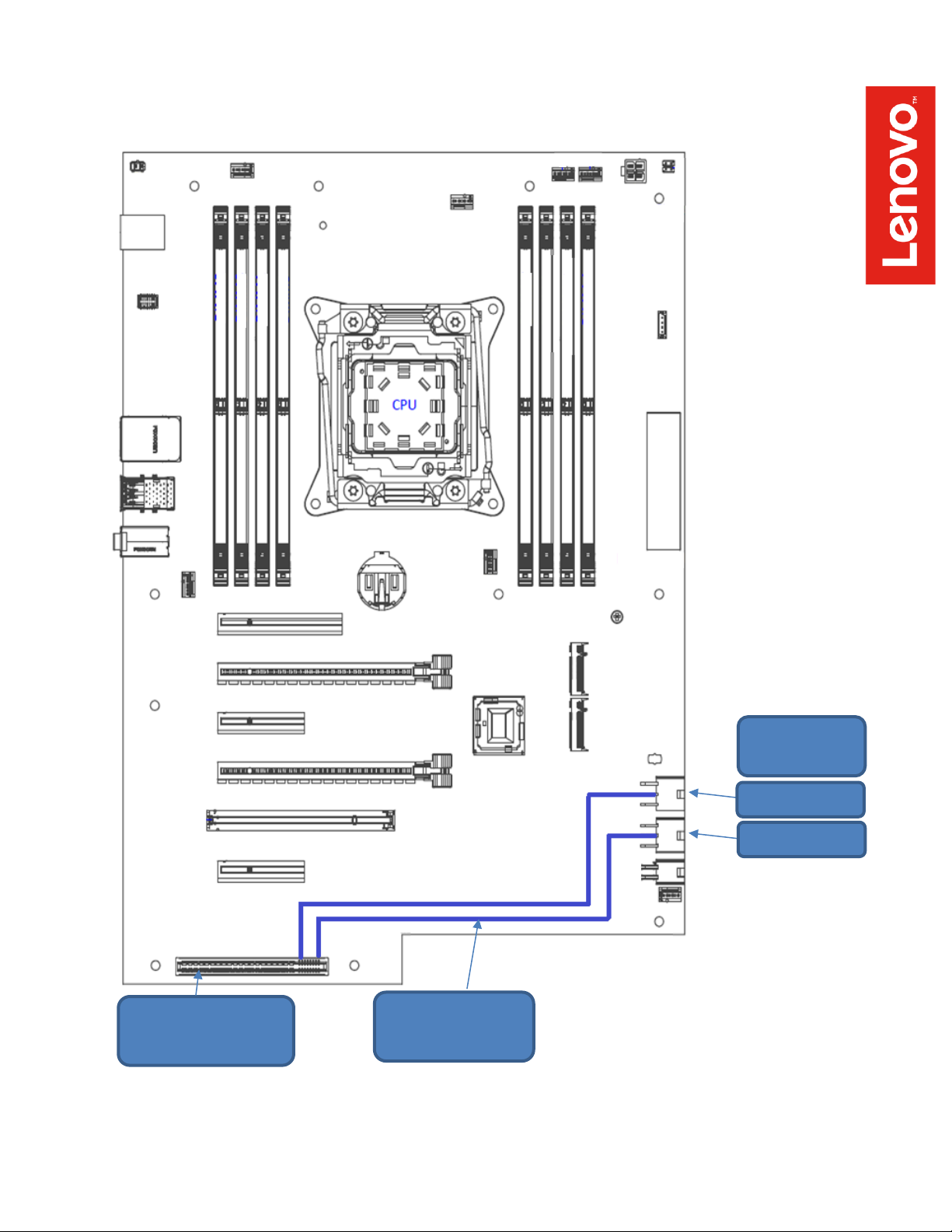
5
Figure 1 – P520 Power Design
Power Supply
Edge Connector
Aux Power
Connectors
Onboard Power
Routing
GPU_PWR1
GPU_PWR2

6
Section 2 – Power Ratings for Key System
Components
In order to fully understand the power capabilities of the ThinkStation P520 and
P520c platforms, it’s important to understand the defined power ratings for the
various internal components used within the system. Figure 2 below describes
the power ratings for the various CPUs supported on the P520 and P520c.
Figure 2 - CPU Power Ratings
CPU Name
(Xeon Skylake-W)
CPU Power
Additional CPU Information
W-2102
120W
2.9GHz, 4 cores, DDR4-2400
W-2104
120W
3.2GHz, 4 cores, DDR4-2400
W-2123
120W
3.6GHz, 4 cores, DDR4-2666, Turbo, Hyper-threading
W-2125
120W
4.0GHz, 4 cores, DDR4-2666, Turbo, Hyper-threading
W-2133
140W
3.6GHz, 6 cores, DDR4-2666, Turbo, Hyper-threading
W-2135
140W
3.7GHz, 6 cores, DDR4-2666, Turbo, Hyper-threading
W-2145
140W
3.7Ghz, 8 cores, DDR4-2666, Turbo, Hyper-threading
W-2155
140W
3.3GHz, 10 cores, DDR4-2666, Turbo, Hyper-threading
W-2195
140W
2.3GHz, 18 cores, DDR4-2666, Turbo, Hyper-threading
CPU Name
(Xeon Cascade Lake-W)
CPU
Power
Additional CPU Information
W-2223
120W
3.6GHz, 4 cores, DDR4-2933, Turbo, Hyper-threading
W-2225
105W
4.1GHz, 4 cores, DDR4-2933, Turbo, Hyper-threading
W-2235
130W
3.8GHz, 4 cores, DDR4-2933, Turbo, Hyper-threading
W-2245
155W
3.9GHz, 8 cores, DDR4-2933, Turbo, Hyper-threading
W-2255
165W
3.7GHz, 10 cores, DDR4-2933, Turbo, Hyper-threading
W-2265
165W
3.5GHz,12 cores, DDR4-2933, Turbo, Hyper-threading
W-2275
165W
3.3Ghz, 14 cores, DDR4-2933, Turbo, Hyper-threading
W-2295
165W
3.0GHz, 18 cores, DDR4-2666, Turbo, Hyper-threading
 Loading...
Loading...