Page 1

CP383
16 Channel Digital Input and
16 Channel Digital Output
CompactPCI Controller
Manual ID: 27784, Rev. Index 01
8 March, 2004
27784.01.VC.040308/162541
P R E L I M I N A R Y
The product described in this manual is
in compliance with all applied CE standards.
Page 2
Preface CP383
Revision History
Publication Title:
ID Number: 27784
Rev.
Index
01 Initial Issue 8 Mar, 2004
CP383 16 Channel Digital Input and 16 Channel Digital Output
CompactPCI Controller
Brief Description of Changes Date of Issue
Imprint
Kontron Modular Computers GmbH may be contacted via the following:
MAILING ADDRESS TELEPHONE AND E-MAIL
Kontron Modular Computers GmbH +49 (0) 800-SALESKONTRON
Sudetenstraße 7 sales@kontron.com
D - 87600 Kaufbeuren Germany
For further information about other Kontron Modular Computers products, please visit our
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Internet web site: www.kontron.com
Copyright
Copyright © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH. All rights reserved. This manual may
not be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated or converted to any electronic or machinereadable form in whole or in part without prior written approval of Kontron Modular Computers.
GmbH.
Disclaimer:
Kontron Modular Computers GmbH rejects any liability for the correctness and
completeness of this manual as well as its suitability for any particular purpose.
Page ii © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162541
Page 3
CP383 Preface
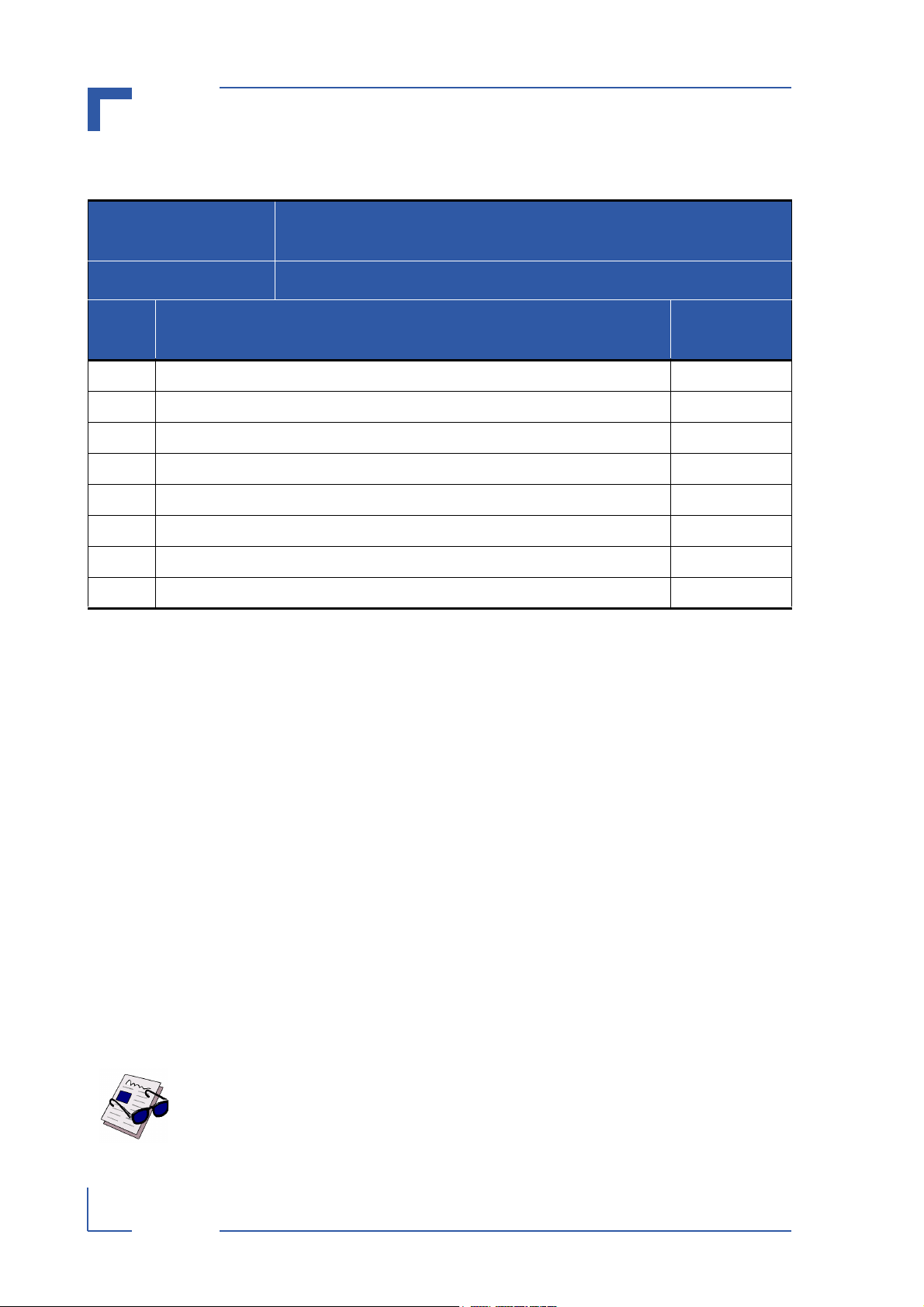
Table of Contents
Revision History .........................................................................................................ii
Imprint ........................................................................................................................ii
Copyright ....................................................................................................................ii
Table of Contents ...................................................................................................... iii
List of Tables ............................................................................................................ vii
List of Figures ...........................................................................................................ix
Proprietary Note ........................................................................................................xi
Trademarks ...............................................................................................................xi
Environmental Protection Statement .........................................................................xi
Explanation of Symbols ........................................................................................... xii
For Your Safety ....................................................................................................... xiii
High Voltage Safety Instructions ......................................................................... xiii
Special Handling and Unpacking Instructions .................................................... xiii
General Instructions on Usage ............................................................................... xiv
Two Year Warranty ...................................................................................................xv
Chapter
1. Introduction .................................................................................................. 1 - 3
1.1 System Overview .................................................................................... 1 - 3
1.2 Product Overview .................................................................................... 1 - 4
1.3 Board Overview ....................................................................................... 1 - 5
1.3.1 Board Introduction .......................................................................... 1 - 5
1.3.2 Board Specific Information .............................................................. 1 - 6
1.4 System Relevant Information .................................................................. 1 - 7
1.4.1 System Configuration ..................................................................... 1 - 7
1.4.2 Driver Software ............................................................................... 1 - 7
1.5 Board Diagrams ...................................................................................... 1 - 8
1.5.1 System Level Interfacing ................................................................ 1 - 8
1.5.2 Front Panel ..................................................................................... 1 - 9
1.5.3 Board Layout .................................................................................. 1 - 9
1.6 Technical Specifications
1
....................................................................... 1 - 10
P R E L I M I N A R Y
1.7 Software Support ................................................................................... 1 - 12
1.8 Applied Standards ................................................................................. 1 - 12
27784.01.VC.040308/162541
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page iii
Page 4

Preface CP383
1.9 Related Publications ......................................................................................1 - 13
Chapter
2. Functional Description .................................................................................2 - 3
2.1 General Information .................................................................................2 - 3
2.2 Board Level Interfacing Diagram .............................................................2 - 3
2.3 Digital Input Signal Conditioning ..............................................................2 - 5
2.4 Digital Output Signal Conditioning ...........................................................2 - 5
2.5 Optoisolation ............................................................................................2 - 5
2.6 DIO ProComm Controller .........................................................................2 - 5
2.7 System Interfaces ....................................................................................2 - 5
2.7.1 Digital Input and Output Interface ....................................................2 - 6
2.7.2 CPCI Interface and Pinout ..............................................................2 - 8
2.8 CapROM EEPROM .................................................................................2 - 9
2.9 Monitor and Control (M/C) .......................................................................2 - 9
2.10 Software ...................................................................................................2 - 9
2
Chapter
3. Installation ....................................................................................................3 - 3
3.1 Hardware Installation ...............................................................................3 - 3
P R E L I M I N A R Y
3.1.1 Safety Requirements .......................................................................3 - 3
3.1.2 Installation Procedures ....................................................................3 - 4
3.1.3 Removal Procedures .......................................................................3 - 5
3.2 Software Installation ................................................................................3 - 5
Chapter
4. Configuration ................................................................................................4 - 3
4.1 Jumper Settings .......................................................................................4 - 3
4.2 Digital Input Signal Requirements ...........................................................4 - 3
3
4
Page iv © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162541
Page 5
CP383 Preface
4.2.1 Channels ......................................................................................... 4 - 3
4.2.2 Signal Characteristics ..................................................................... 4 - 3
4.2.3 Channel Configuration .................................................................... 4 - 4
4.3 Digital Output Signal Properties .............................................................. 4 - 5
4.3.1 Channels ......................................................................................... 4 - 5
4.3.2 Connection of External Supply ....................................................... 4 - 5
4.3.3 Channel Connection ....................................................................... 4 - 6
4.3.4 Connection of Inductive Loads ....................................................... 4 - 7
4.4 Programming Interface ............................................................................ 4 - 8
4.4.1 Access Control Logic (Address Decoder) ....................................... 4 - 8
4.4.2 Reading Input Data ......................................................................... 4 - 9
4.4.3 Debouncing Inputs ........................................................................ 4 - 10
4.4.4 Detecting Input Events .................................................................. 4 - 11
4.4.5 Latching on Input Events .............................................................. 4 - 12
4.4.6 Comparing Input Patterns ............................................................. 4 - 12
4.4.7 Writing Output Data ..................................................................... 4 - 13
4.4.8 Hardware Debug/Test Registers ................................................... 4 - 14
4.4.9 Generating Interrupts .................................................................... 4 - 14
4.4.10 Programming the Board Capability ROM ..................................... 4 - 16
Chapter
5. Power Consumption .................................................................................... 5 - 3
5.1 System Power ......................................................................................... 5 - 3
5.1.1 CP383 Baseboard .......................................................................... 5 - 3
5.1.2 Backplane ....................................................................................... 5 - 4
5.1.3 Power Supply Units ........................................................................ 5 - 4
5
P R E L I M I N A R Y
5.2 Power Consumption Table ...................................................................... 5 - 6
Chapter
6. System Considerations ................................................................................ 6 - 3
6.1 Introduction ............................................................................................. 6 - 3
27784.01.VC.040308/162541
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page v
6
Page 6

Preface CP383
6.2 General ....................................................................................................6 - 3
6.3 Shielding ..................................................................................................6 - 3
6.4 Debouncing for Digital Inputs ...................................................................6 - 3
6.5 Process-Side Signal Conditioning for Digital Inputs ................................6 - 4
6.6 External Power Supply for Digital Outputs ...............................................6 - 4
6.7 Cable Interfacing ......................................................................................6 - 4
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page vi © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162541
Page 7

CP383 Preface
List of Tables
1-2 System Relevant Information ................................................................... 1 - 7
1-3 CP383 Main Specifications .................................................................... 1 - 10
1-4 CP383 Digital Input Specifications ......................................................... 1 - 11
1-5 CP383 Digital Output Specifications ...................................................... 1 - 11
1-6 Applied Standards .................................................................................. 1 - 12
1-7 Related Publications .............................................................................. 1 - 13
2-1 Pinout of the Digital Input and Output Interface Connector CON2 .......... 2 - 7
2-2 Pinout of the CPCI Connector CON1 (J1) ............................................... 2 - 8
2-3 Digital Input Function Modes of the CP383 ............................................. 2 - 9
4-1 Backend Register Address Map .............................................................. 4 - 8
4-2 Input Data Register .................................................................................. 4 - 9
4-3 Transparent Input Data Register .............................................................. 4 - 9
4-4 Input Control Register ............................................................................ 4 - 10
4-5 Programmable Input Sample Rates ....................................................... 4 - 10
4-6 Input Event Mask Register ..................................................................... 4 - 11
4-7 Input Event Polarity Register ................................................................. 4 - 11
4-8 Input Status Register .............................................................................. 4 - 11
4-9 Input Latch-on-Event Register ............................................................... 4 - 12
4-10 Input Pattern Mask Register .................................................................. 4 - 12
4-11 Input Pattern Compare Register ............................................................ 4 - 12
4-12 Output Data Register ............................................................................. 4 - 13
4-13 Output Control Register ......................................................................... 4 - 13
4-14 Output Status Register ........................................................................... 4 - 13
4-15 Hardware Debug Register ..................................................................... 4 - 14
4-16 Hardware Status Register ...................................................................... 4 - 14
4-17 General Interrupt Enable Register ......................................................... 4 - 15
P R E L I M I N A R Y
4-18 General Interrupt Pending Register ....................................................... 4 - 15
4-19 Output Status Register ........................................................................... 4 - 15
4-20 Input IRQ Register ................................................................................. 4 - 15
4-21 ROM Command Register ....................................................................... 4 - 16
4-22 ROM Control Register ............................................................................ 4 - 16
4-23 Opcodes and Commands ...................................................................... 4 - 17
27784.01.VC.040308/162541
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page vii
Page 8

Preface CP383
4-24 ROM Status Register .............................................................................. 4 - 17
4-25 ROM Data Register ................................................................................ 4 - 17
5-1 Maximum Input Power Voltage Limits ...................................................... 5 - 3
5-2 DC Input Voltage Ranges ......................................................................... 5 - 3
5-3 Input Voltage Characteristics .................................................................... 5 - 5
4-4 Power Consumption Table ....................................................................... 5 - 6
5-1 Debouncing Periods ................................................................................. 6 - 4
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page viii © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162541
Page 9

CP383 Preface
List of Figures
1-1 CP383 System Level Interfacing Diagram ............................................... 1 - 8
1-2 CP383 Front Panel .................................................................................. 1 - 9
1-3 CP383 Board (Front View) ....................................................................... 1 - 9
2-1 CP383 Board Level Interfacing ................................................................ 2 - 4
2-2 Pin Layout of the Digital Input and Output Interface Connector CON2
2-3 CPCI Connector CON1 (J1)
4-1 Voltage Ranges ........................................................................................ 4 - 3
4-2 Input Channel Schematic ......................................................................... 4 - 4
4-3 Input Configuration (Example for Channel 0) ........................................... 4 - 4
4-4 Configuration Diagram for All Input Channels .......................................... 4 - 5
4-5 Digital Output Connection for One Cluster ............................................... 4 - 6
4-6 Digital Output Circuit for One Channel ..................................................... 4 - 6
4-7 External Reset Connection for One Cluster ........................................... 4 - 7
5-1 Start-Up Ramp of the CP3-SVE180 AC Power Supply ............................ 5 - 4
............................................................................ 2 - 8
. 2 - 6
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page ix
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 10

Preface CP383
This page has been intentionally left blank.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page x © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
Page 11

CP383 Preface
Proprietary Note
This document contains information proprietary to Kontron Modular Computers GmbH. It may
not be copied or transmitted by any means, disclosed to others, or stored in any retrieval
system or media without the prior written consent of Kontron Modular Computers GmbH or one
of its authorized agents.
The information contained in this document is, to the best of our knowledge, entirely correct.
However, Kontron Modular Computers GmbH cannot accept liability for any inaccuracies or the
consequences thereof, or for any liability arising from the use or application of any circuit,
product, or example shown in this document.
Kontron Modular Computers GmbH reserves the right to change, modify, or improve this
document or the product described herein, as seen fit by Kontron Modular Computers GmbH
without further notice.
Trademarks
Kontron Modular Computers GmbH, the PEP logo and, if occurring in this manual, “CXM” are
trademarks owned by Kontron Modular Computers GmbH, Kaufbeuren (Germany). In addition,
this document may include names, company logos and trademarks, which are registered trademarks and, therefore, proprietary to their respective owners.
Environmental Protection Statement
This product has been manufactured to satisfy environmental protection requirements where
possible. Many of the components used (structural parts, printed circuit boards, connectors,
batteries, etc.) are capable of being recycled.
Final disposition of this product after its service life must be accomplished in accordance with
applicable country, state, or local laws or regulations.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page xi
Page 12

Preface CP383
Explanation of Symbols
CE Conformity
This symbol indicates that the product described in this manual is in
compliance with all applied CE standards. Please refer also to the
section “Applied Standards” in this manual.
Caution, Electric Shock!
This symbol and title warn of hazards due to electrical shocks (> 60V)
when touching products or parts of them. Failure to observe the precautions indicated and/or prescribed by the law may endanger your
life/health and/or result in damage to your material.
Please refer also to the section “High Voltage Safety Instructions” on
the following page.
Warning, ESD Sensitive Device!
This symbol and title inform that electronic boards and their components are sensitive to static electricity. Therefore, care must be taken
during all handling operations and inspections of this product, in
order to ensure product integrity at all times.
Please read also the section “Special Handling and Unpacking
Instructions” on the following page.
Warning!
This symbol and title emphasize points which, if not fully understood
and taken into consideration by the reader, may endanger your health
and/or result in damage to your material.
Note ...
This symbol and title emphasize aspects the reader should read
P R E L I M I N A R Y
through carefully for his or her own advantage.
Page xii © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
Page 13
CP383 Preface
For Your Safety
Your new Kontron product was developed and tested carefully to provide all features necessary
to ensure its compliance with electrical safety requirements. It was also designed for a long
fault-free life. However, the life expectancy of your product can be drastically reduced by
improper treatment during unpacking and installation. Therefore, in the interest of your own
safety and of the correct operation of your new Kontron product, you are requested to conform
with the following guidelines.
High Voltage Safety Instructions
Warning!
All operations on this device must be carried out by sufficiently skilled
personnel only.
Caution, Electric Shock!
Before installing your new Kontron product into a system always
ensure that your mains power is switched off. This applies also to the
installation of piggybacks.
Serious electrical shock hazards can exist during all installation,
repair and maintenance operations with this product. Therefore,
always unplug the power cable and any other cables which provide
external voltages before performing work.
Special Handling and Unpacking Instructions
ESD Sensitive Device!
Electronic boards and their components are sensitive to static electricity. Therefore, care must be taken during all handling operations
and inspections of this product, in order to ensure product integrity at
all times.
Do not handle this product out of its protective enclosure while it is not used for operational
purposes unless it is otherwise protected.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Whenever possible, unpack or pack this product only at EOS/ESD safe work stations. Where
a safe work station is not guaranteed, it is important for the user to be electrically discharged
before touching the product with his/her hands or tools. This is most easily done by touching a
metal part of your system housing.
It is particularly important to observe standard anti-static precautions when changing piggybacks, ROM devices, jumper settings etc. If the product contains batteries for RTC or memory
backup, ensure that the board is not placed on conductive surfaces, including anti-static plastics or sponges. They can cause short circuits and damage the batteries or conductive circuits
on the board.
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page xiii
Page 14

Preface CP383
General Instructions on Usage
In order to maintain Kontron’s product warranty, this product must not be altered or modified in
any way. Changes or modifications to the device, which are not explicitly approved by Kontron
Modular Computers GmbH and described in this manual or received from Kontron’s Technical
Support as a special handling instruction, will void your warranty.
This device should only be installed in or connected to systems that fulfill all necessary
technical and specific environmental requirements. This applies also to the operational
temperature range of the specific board version, which must not be exceeded. If batteries are
present, their temperature restrictions must be taken into account.
In performing all necessary installation and application operations, please follow only the
instructions supplied by the present manual.
Keep all the original packaging material for future storage or warranty shipments. If it is
necessary to store or ship the board, please re-pack it as nearly as possible in the manner in
which it was delivered.
Special care is necessary when handling or unpacking the product. Please consult the special
handling and unpacking instruction on the previous page of this manual.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page xiv © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
Page 15

CP383 Preface
Two Year Warranty
Kontron Modular Computers GmbH grants the original purchaser of Kontron’s products a TWO
YEAR
LIMITED HARDWARE WARRANTY as described in the following. However, no other warranties
that may be granted or implied by anyone on behalf of Kontron are valid unless the consumer
has the express written consent of Kontron Modular Computers GmbH.
Kontron Modular Computers GmbH warrants their own products, excluding software, to be free
from manufacturing and material defects for a period of 24 consecutive months from the date
of purchase. This warranty is not transferable nor extendible to cover any other users or longterm storage of the product. It does not cover products which have been modified, altered or
repaired by any other party than Kontron Modular Computers GmbH or their authorized agents.
Furthermore, any product which has been, or is suspected of being damaged as a result of negligence, improper use, incorrect handling, servicing or maintenance, or which has been damaged as a result of excessive current/voltage or temperature, or which has had its serial
number(s), any other markings or parts thereof altered, defaced or removed will also be excluded from this warranty.
If the customer’s eligibility for warranty has not been voided, in the event of any claim, he may
return the product at the earliest possible convenience to the original place of purchase, together with a copy of the original document of purchase, a full description of the application the
product is used on and a description of the defect. Pack the product in such a way as to ensure
safe transportation (see our safety instructions).
Kontron provides for repair or replacement of any part, assembly or sub-assembly at their own
discretion, or to refund the original cost of purchase, if appropriate. In the event of repair, refunding or replacement of any part, the ownership of the removed or replaced parts reverts to
Kontron Modular Computers GmbH, and the remaining part of the original guarantee, or any
new guarantee to cover the repaired or replaced items, will be transferred to cover the new or
repaired items. Any extensions to the original guarantee are considered gestures of goodwill,
and will be defined in the “Repair Report” issued by Kontron with the repaired or replaced item.
Kontron Modular Computers GmbH will not accept liability for any further claims resulting
directly or indirectly from any warranty claim, other than the above specified repair,
replacement or refunding. In particular, all claims for damage to any system or process in which
the product was employed, or any loss incurred as a result of the product not functioning at any
given time, are excluded. The extent of Kontron Modular Computers GmbH liability to the
customer shall not exceed the original purchase price of the item for which the claim exists.
Kontron Modular Computers GmbH issues no warranty or representation, either explicit or
implicit, with respect to its products’ reliability, fitness, quality, marketability or ability to fulfil any
particular application or purpose. As a result, the products are sold “as is,” and the responsibility
to ensure their suitability for any given task remains that of the purchaser. In no event will
Kontron be liable for direct, indirect or consequential damages resulting from the use of our
hardware or software products, or documentation, even if Kontron were advised of the
possibility of such claims prior to the purchase of the product or during any period since the
date of its purchase.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Please remember that no Kontron Modular Computers GmbH employee, dealer or agent is
authorized to make any modification or addition to the above specified terms, either verbally or
in any other form, written or electronically transmitted, without the company’s consent.
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page xv
Page 16

Preface CP383
This page has been intentionally left blank.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page xvi © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
Page 17

CP383 Introduction
Chapter 1
1
Introduction
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 1 - 1
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 18

Introduction CP383
This page has been intentionally left blank.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 1 - 2 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
Page 19

CP383 Introduction
1. Introduction
1.1 System Overview
The CompactPCI board described in this manual operates with the PCI bus architecture to support additional I/O and memory-mapped devices as required by various industrial applications.
For detailed information concerning the CompactPCI standard, please consult the complete
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) and CompactPCI Specifications. For further information regarding these standards and their use, visit the home page of the PCI Industrial Comput-
er Manufacturers Group (PICMG).
Many system relevant CompactPCI features that are specific to Kontron Modular Computers
CompactPCI systems may be found described in the Kontron CompactPCI System Manual.
Please refer to the section “Related Publications” at the end of this chapter for the relevant ordering information.
The CompactPCI System Manual includes the following information:
• Common information that is applicable to all system components, such as safety information, warranty conditions, standard connector pinouts etc.
• All the information necessary to combine Kontron’s racks, boards, backplanes, power
supply units and peripheral devices in a customized CompactPCI system, as well as configuration examples.
• Data on rack dimensions and configurations as well as information on mechanical and
electrical rack characteristics.
• Information on the distinctive features of Kontron CompactPCI boards, such as functionality, hot swap capability. In addition, an overview is given for all existing Kontron CompactPCI boards with links to the relating data sheets.
• Generic information on the Kontron CompactPCI backplanes, such as the slot assignment, PCB form factor, distinctive features, clocks, power supply connectors and signalling environment, as well as an overview of the Kontron CompactPCI standard backplane
family.
• Generic information on the Kontron CompactPCI power supply units, such as the input/
output characteristics, redundant operation and distinctive features, as well as an overview of the Kontron CompactPCI standard power supply unit family.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 1 - 3
Page 20

Introduction CP383
1.2 Product Overview
The CP383 Digital Input and Digital Output Controller is part of a comprehensive concept to
provide CompactPCI system integrators with a complete range of CompactPCI I/O products
which include the functions of analog input, analog output, digital input, and digital output implemented as separate individual boards. This concept ensures a maximum degree of system
design flexibility thus allowing efficient and effective usage of available resources.
As an enhancement to this concept, the CP383 combination board has been designed to implement digital input and digital output functions on one board. The CP383 is a 3U / 4HP CompactPCI board which provides 32 channels that are organized into 3 separate clusters, one
cluster consisting of 16 channels for digital input, and two clusters consisting of 8 channels
each for digital output.
The basic functions of this board are on the one hand to provide interfacing to the application
(process), perform D/D signal conversions, and to make raw digitized data available for further
processing via the 16 input channels, and on the other hand to provide a large number of automatically controlled, flexible digital outputs within a ruggedized board equipped with features
for electrical protection, such as overtemperature thermal shutdown, and overcurrent and undervoltage protection via the output channels. Each of the two digital output clusters can be
configured for its own external supply voltage as required.
The major components involved in these processes are the front end (process side) signal conditioning (digital input and digital output), the High Side Driver (HSD) switches (digital output),
and the Digital Input and Output Process and Communications (DIO ProComm) Controller
which is realized in a field-programmable gate array (FPGA). The DIO ProComm Controller is
designed to provide effective and efficient control of the digital input and output processes as
well as interfacing to the CPCI system controller.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 1 - 4 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
Page 21
CP383 Introduction
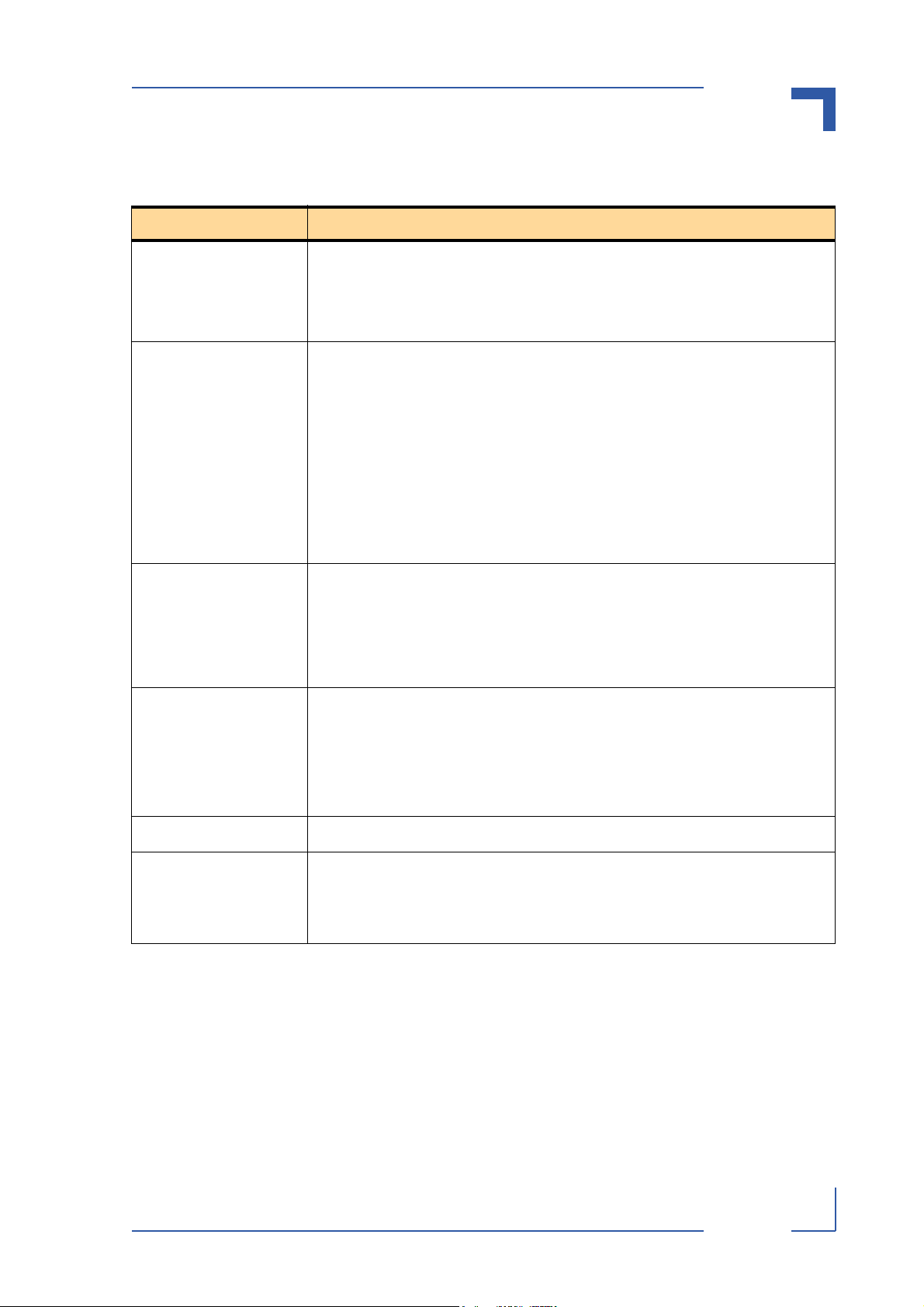
The following table provides a quick overview of the CP383 board.
Table 1-1: CP383 Product Overview
CP383 FEATURES DESCRIPTION
Digital Input and Output
Board
Digital Input Channel • Input Signals: Voltage range:low: -3V to +5V
Digital Output Channels 16 digital output channels in 2 independent clusters of 8 channels each. Each clus-
External Interfaces 2 external interfaces, the digital input and output interface connector CON2 on the
• CompactPCI: 3U, 4HP
• 33 MHz system clock
• 32-bit address and data bus
• Designed for Plug and Play
• Complies with the CPCI specification
high: +11V to +30 V (+24V standard)
Maximum current: 5 mA
• Channel Isolation: The input channels are isolated from the system side and do
not share common GND or VCC.
• Output Data: A maximum of 16 measured digital values
Interrupt messages (optional)
Programmable registers (read/ write, compare, event and
latch)
• Debouncing: Range of settings available: 33 MHz, 128 kHz, 32 kHz, 8 kHz,
2 kHz, 500 Hz, 125 Hz, 31 Hz (30 ns default)
ter may be set to operate at different voltages for different loads within the prescribed output voltage limits. The output is realized via the HSD switches.
The output channels are isolated from the system side and share common GND and
VCC within the clusters. The two output clusters are galvanically isolated from each
other.
front panel and a single CompactPCI connector at the rear.
The digital input and output interface connector supports up to 16 digital input and
16 digital output channels. The connector pins are subdivided into 3 clusters or
groups.
The CompactPCI connector is the standard CPCI type connector for CON1.
Indicators One green LED (Run) and one red LED (Fail), which are user configurable
Temperature Range The board is qualified to operate over a wide range of temperatures as follows:
1.3 Board Overview
1.3.1 Board Introduction
The CP383 is a digital input and digital output board which provides 32 channels grouped into
one digital input cluster consisting of 16 channels and two digital output clusters consisting of
8 channels each.
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 1 - 5
P R E L I M I N A R Y
• Operational: 0ºC to +60ºC Standard
-40ºC to +85ºC E2
• Storage: -55ºC to +125ºC
Page 22

Introduction CP383
1.3.1.1 Board Introduction - Digital Input
The digital input cluster consists of 16 input channels. The source of the digital inputs must be
a voltage generator. The board accepts only differential voltages up to a maximum of +30V. The
input current is limited to 5 mA over the specified input voltage range.
Input signal processing begins with the presentation of the signal to the front panel connector.
Signal conditioning prior to the signal reaching the DIO ProComm Controller includes: overvoltage protection, ESD, low-pass filtering, inverse polarity protection, defined low and high ranges, current limitation, optoisolation and buffering.
After signal conditioning, all parallel digital data is routed to the DIO ProComm Controller,
where the control and status registers are set.
The DIO ProComm Controller controls the interface with the CompactPCI bus and the dedicated software.
Input signal types and ranges are as follows:
• Edge frequency:
• Maximum 10 kHz
• Voltage Ranges:
• High range: +11V to +30V (+24V nominal)
• Low range: -3V to +5V
• Channel isolation
• The input channels are isolated from the system side and do not share common GND
or VCC.
• Differential input
Output data
The following outputs are routed from the DIO ProComm Controller to the CompactPCI bus:
• Input data for all channels as a 32-bit value (each bit from 0 - 15 represents the status of
• Flag set information from the control and status registers
• Interrupts
P R E L I M I N A R Y
1.3.1.2 Board Introduction - Digital Output
The two digital output clusters consist of 8 output channels each. The digital output requests
from the system controller are processed accordingly by the DIO ProComm Controller and are
then routed to the HSD switches, which in turn perform output signal conditioning using the external supply voltage as the power source.
An external reset input is provided to simultaneously switch off all the outputs per cluster and
sets all the HSD switches to open. Each cluster has its own separate reset signal input.
:
the respective input channel)
This reset can be used by the application to keep the inputs low after a fault condition.
1.3.2 Board Specific Information
Specific board components involved in the digital output process:
• One front panel connector (62-pin, female, D-sub type)
Page 1 - 6 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
Page 23
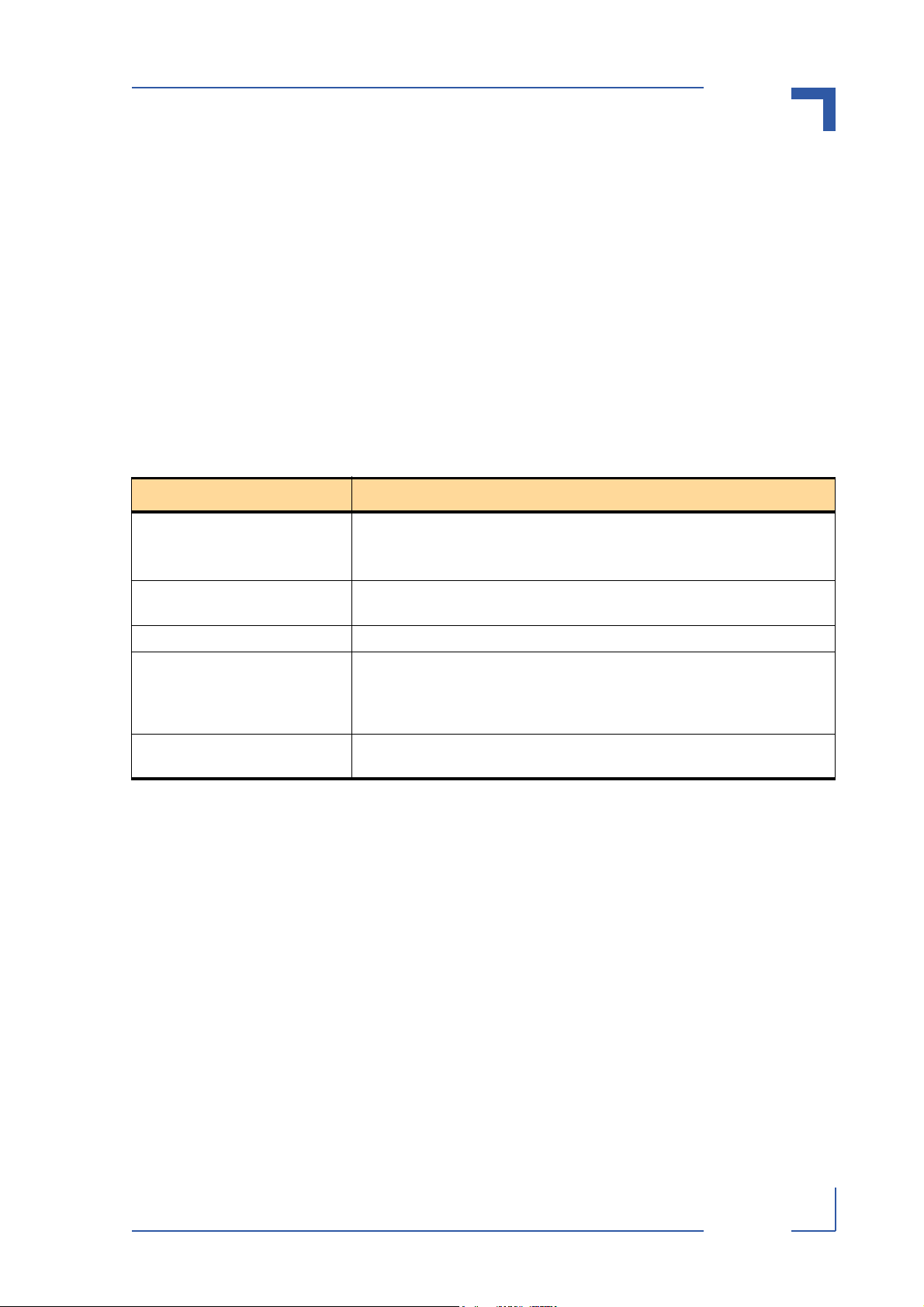
CP383 Introduction
• 16 channels of input signal conditioning
• 16 channels of output signal conditioning: 4 HSD switches (4 channels per switch,
2 switches per cluster)
• Optoisolation for each input and output channel from the system side
• One FPGA (the DIO ProComm Controller)
• One CompactPCI bus connector (CON1, board to backplane, 132-pin, female, six row)
• One EEPROM (CapROM)
1.4 System Relevant Information
The following system relevant information is general in nature but should still be considered
when developing applications using the CP383.
Table 1-2: System Relevant Information
SUBJECT INFORMATION
System Configuration The CP383 operates with a system clock frequency of 33 MHz.
The number of CP383s which can be installed in any one system depends
solely on the number of carrier interfaces available.
Master/ Slave Functionality The CP383 functions only as a slave. As such it requires a System Master for
servicing.
System Controller The CP383 cannot function as a system controller.
Digital Inputs Digital inputs to the CP383 must be conform to the inputs specifications set
forth in this manual for the CP383. In most cases, some form of signal conditioning will be required on the process side prior to a signal being presented
to the CP383.
Digital Outputs The voltage source for the digital outputs of CP383 must conform with the
specifications set forth in this manual.
1.4.1 System Configuration
When implementing applications, precautions must be taken to ensure that the input signals
presented to the CP383 comply with the specifications set forth in this manual. For this reason
it will be necessary for most applications to provide signal conditioning prior to presenting the
digital inputs to the CP383.
The external supply voltage (VCC) used as the output voltage on the CP383, must be within
the specified supply voltage range. In addition, it should be a DC supply with good ripple and
noise characteristics. Please refer to chapters 4 and 5 for further information.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
1.4.2 Driver Software
The CP383 is supplied with appropriate driver software which provides software interfacing
with the System Master.
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 1 - 7
Page 24

Introduction CP383
1.5 Board Diagrams
The following diagrams illustrate board functionality and component layout.
1.5.1 System Level Interfacing
Figure 1-1: CP383 System Level Interfacing Diagram
CompactPCI System
System Master
CPCI BUS
Digital Input
and Output
System
CP383
1
P R E L I M I N A R Y
digital
input
16 max
1
digital
input
digital
output
16 max
n
CP383
digital
input
16 max
1
digital
input
digital
output
16 max
digital
output
1
1
digital
output
Page 1 - 8 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
Page 25

CP383 Introduction
1.5.2 Front Panel
Figure 1-2: CP383 Front Panel
CP 383
RUN FAIL
A green “Run” LED and a red “Fail” LED have been placed on the
front panel, to cater for the most likely use of these LEDs. However,
they are user configurable and may be employed for user defined
purposes.
1.5.3 Board Layout
Figure 1-3: CP383 Board (Front View)
LED1
Digital Input Signal Conditioning
Channels 0 ... 15
C
O
N
2
Digital Output Signal Conditioning
Switch
Digital Output Signal Conditioning
Switch Switch
DIGIN Cluster
Switch
DIGOUT A Cluster
DIGOUT B Cluster
Channels
A0 ... A7
Channels
B0 ... B7
O
P
T
O
O
P
T
O
O
P
T
O
O
P
T
O
O
P
T
O
O
P
T
O
O
P
T
O
O
P
T
O
OPTO
CON3
210
19
DIO
ProComm
Controller
CapROM
P R E L I M I N A R Y
25
C
O
N
1
1
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 1 - 9
Page 26

Introduction CP383
1.6 Technical Specifications
Table 1-3: CP383 Main Specifications
GROUP/
INTERFACE
DIO ProComm
Controller and
Related
Peripheral
Memory
CompactPCI
Interface
(See note at foot
of table)
Digital Input and
Output Interface
TYPE DESCRIPTION
FPGA Logic Device Provides CompactPCI interfacing and IO control logic
CapROM 4 kbit (512 byte) EEPROM
Realized on 132-pin,
female, six row connector (standard CPCI type
connector for CON1)
Software Driver Information
PCI Interface VI/O voltage is neither relevant nor used
Master/ Slave Functionality
One 62-pin, female,
three row, D-sub connector
Bus Width: 32-bit, Bus Speed: 33 MHz
64 kB memory space, non-prefetchable
Utilizes interrupt line INTA
PCI Header:
Device ID: 0x5555
Vendor ID: 0x1556
Class Code: 0x110000
Subsystem Device ID: 0x0120
Subsystem Vendor ID: 0x1518
Only slave functionality provided
Supports up to 16 digital input channels and 16 digital output
channels
Indicators Front Panel LEDs One green and one red LED to indicate operational status
Form Factor 3U, 4HP
Mechanical Conforms with IEEE 1101.1
System Power Con-
P R E L I M I N A R Y
General
sumption
Temperature Range Operational: 0ºC to +60ºC Standard
Climatic Humidity 93 % RH at 40°C, non-condensing (acc. to IEC 60068-2-78)
Dimensions 100 mm x 160 mm single height Eurocard
Board Weight 170 grams
only + 3.3V: maximum 600 mW (all IO channels activated)
Storage: -55ºC to +125ºC
Note ...
The Device ID and Vendor ID refer to the chip manufacturer. In the Class Code
value given, “11” relates to the data acquisition and signal processing controllers and “0000” relates to the DPIO modules. Subsystem Device ID and Subsystem Vendor ID are defined by Kontron.
-40ºC to +85ºC E2
Page 1 - 10 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
Page 27

CP383 Introduction
Table 1-4: CP383 Digital Input Specifications
TYPE DESCRIPTION
Input Voltage Range Low: -3V to +5V
High: +11V to +30V
Channels 16 channels isolated from the system side. They do not share common GND
or VCC.
Channel Connections 2 pins per channel; differential input
Input Filter (edge frequency) 10 kHz
Input Protection 8 kV ESD
Isolation 2 kV process to system
Input Impedance Minimum: 1.5 k ohm
Maximum: 6 k ohm at 30V
Table 1-5: CP383 Digital Output Specifications
TYPE DESCRIPTION
Output Voltage Range Low state: =< +1.5 V
High state: > +8.0 V and < +35 V
Current per channel: max. 0.5 A
Leakage current: 20 µA
Channels 16 channels grouped into two clusters of eight channels each
Common GND and VCC for each output cluster
The output channels are isolated from the system side and share common
GND and VCC within the clusters. The two output clusters are galvanically isolated from each other.
Channel Connections 1 pin per channel, single-ended
External Reset All digital output channels of a cluster can be collectively switched low by
using one of the following methods:
• externally via the EXTRESET signal
• internally on request from the application via the DIO ProComm
Controller
This results in all outputs being kept switched low irrespective of the input
data for these channels.
External Voltage (VCC) +9.5 V to +35 V
Switch “On” Resistance R
Max. Output Frequency 2.5 kHz
System Switching Delay Time T
ds,on
= 4 µs, T
d,on
= 1.8 ohm
d,off
= 90 µs
P R E L I M I N A R Y
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 1 - 11
Page 28

Introduction CP383
Table 1-5: CP383 Digital Output Specifications (Continued)
TYPE DESCRIPTION
Signal Output
Overcurrent Protection
Undervoltage Protection for
external power supply
Overtemperature If the case temperature of the High Side Driver switches exceeds 150°C, the
Isolation 2 kV process to system
For output currents of greater than 0.8 A, the output will be switched to a failure mode: square wave signal with a maximum current amplitude of 0.4A and
an on/off time (t
This type of system failure indication is made available to the DIO ProComm
Controller.
For the voltage source (EXTVCC) <= +8.5V, the outputs are switched off.
This type of system failure indication is made available to the DIO ProComm
Controller.
outputs are switched off.
This type of system failure indication is made available to the DIO ProComm
Controller.
on, toff
) of 100 µs.
1.7 Software Support
The CP383 is supplied with appropriate driver software which provides software interfacing to
the System Master. The CP383 supports Windows XP
VxWorks
and Linux.
, Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000,
1.8 Applied Standards
The Kontron Modular Computers’ CompactPCI systems comply with the requirements of the
following standards:
Table 1-6: Applied Standards
TYPE STANDARD
Emission EN50081-1
P R E L I M I N A R Y
ENVIRONMENTAL TESTS
CE
MECHANICAL Mechanical Dimensions IEEE 1101.1
Immunity, Industrial Environment EN61000-6-2
Immunity, IT Equipment EN55024
Electrical Safety EN60950
Vibration, Sinusoidal IEC60068-2-6
Random Vibration, Broadband IEC60068-2-64 (3U boards)
Permanent Shock IEC60068-2-29
Single Shock IEC60068-2-27
Climatic Humidity IEC60068-2-78
Page 1 - 12 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
Page 29

CP383 Introduction
1.9 Related Publications
Table 1-7: Related Publications
ISSUED BY DOCUMENT
CompactPCI
Systems
CP383
PICMG CompactPCI Specification, V. 2.0, Rev. 3.0
Kontron Modular Computers CompactPCI Systems Manual (ID 19953)
ST Microelectronics L6376 0.5A High-Side Driver Quad Intelligent Power
Switch
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 1 - 13
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 30

Introduction CP383
This page has been intentionally left blank.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 1 - 14 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162542
Page 31

CP383 Functional Description
Chapter 1
2
Functional Description
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 2 - 1
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 32

Functional Description CP383
This page has been intentionally left blank.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 2 - 2 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
Page 33

CP383 Functional Description
2. Functional Description
The following chapters present more detailed, board level information about the CP383 Digital
Input and Digital Output Controller whereby the board components and their basic functionality
are discussed in general.
2.1 General Information
The CP383 is comprised basically of the following:
• Digital input signal conditioning
• Digital output signal conditioning (High Side Driver switches), common GND and VCC for
each output cluster
• Optocouplers
• DIO ProComm Controller
• Controls digital inputs and outputs
• Provides interfacing to the CompactPCI bus
• System interfaces for:
• Front panel
• 16 channels of digital input and 16 channels of digital output
• External supply connection for each digital output cluster
• External hardware reset for each digital output cluster
• One 62-pin, female, 3-pin row, D-sub connector (CON2)
• CompactPCI bus
• 132-pin, female, 6-pin row connector (CON1)
• CompactPCI specification
• Onboard memory: Capability EEPROM (CapROM)
• Monitor and Control
• Two operational status LEDs for user-defined purposes
• External reset
• Output failure indicators
• Software
2.2 Board Level Interfacing Diagram
The following figure demonstrates the interfacing structure between the internal processing
modules of the CP383 and other major CP383 system components. Where CP383 system elements have common interfacing they are grouped into a block. Interfacing common to only
one element of a block is indicated with a direct connecting line. The interfacing lines are shown
in white where they are onboard and in black for board external interfacing.
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 2 - 3
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 34

Functional Description CP383
Figure 2-1: CP383 Board Level Interfacing
CP383 Digital Input and
Digital Output Controller
CPCI Interface
DIO ProComm Controller
Optoisolation
DIGOUT A
CLUSTER
Signal
Cond.
HSD SWITCH
DIGOUT B
CLUSTER
Signal
Cond.
HSD SWITCH
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Outputs
0 ... 7
Outputs
8 ... 15
DIGIN
CLUSTER
Signal
Cond.
Inputs
0 ... 15
Reset &
Supply Voltage
Digital Output
Page 2 - 4 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
Reset &
Supply Voltage
Digital In put
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
Page 35

CP383 Functional Description
2.3 Digital Input Signal Conditioning
The digital input signal conditioning consists of the following:
• Overvoltage protection
• Low-pass signal filtering
• Current limitation
• Inverse polarity protection
• Input signal high-low determination
• Output signal stabilization buffering
2.4 Digital Output Signal Conditioning
The major element of the digital output signal conditioning is the HSD switches which are able
to drive inductive, capacitive or resistive loads. Diagnostic information for the System Master
and extensive use of electrical protection are among their main characteristics.
The HSD switch (type L6376 manufactured by SGS THOMSON) is a QUAD intelligent power
switch which adapts the digital output signals to the prevailing voltage and current levels, and
also provides corresponding mechanisms to protect against undervoltage, overcurrent and
overtemperature.
The output voltage level is adapted to the external supply voltage for high level and for low level
output voltage respectively via the integrated FET transistor output stage within the HSD
switch. The HSD switch implements a clamp diode for inductive load driving. The voltage
source for the CP383 front end is implemented using an external voltage source (nominal
+24V, also in the range +9.5V to +35V).
The input signals to the HSD switches are derived from the system side, directly from the outputs of the optocoupler devices.
2.5 Optoisolation
The process side is galvanically isolated from the system side. The process side of the board
is separated from the system side by a bank of optocouplers which serve to protect the system
side from any excess voltages or voltage spikes.
2.6 DIO ProComm Controller
The DIO ProComm Controller is responsible for supervising and controlling the digital acquisition and the digital data output process, and maintaining communication with the CompactPCI
System Master. Applications address the CP383 through its software driver interface within the
System Master whereby the controller accepts requests from the driver and executes them accordingly. Digital data from the signal conditioning is processed through the DIO ProComm
Controller and then made available to the System Master. Digital data from the System Master
is processed through the DIO ProComm Controller and then routed to the HSD switches.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
2.7 System Interfaces
The CP383 provides interfacing capability for the following system elements:
• Front panel connector
• CompactPCI bus
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 2 - 5
Page 36

Functional Description CP383
Digital inputs, digital outputs, external voltage, and external reset are routed via the CON2 connector. Interfacing to the CompactPCI bus is accomplished via the CON1 connector. Test and
program development is supported by the CON3 connector.
External supply for each output cluster:
The connection for the external supply (+24V DC [9.5V to 35V] for each output cluster) is realized by reserved/defined pins within each output cluster at the front panel connector CON2.
Note ...
In addition to supplying the current for the logic parts of the power switches
which are linked to the digital outputs, the external voltage supplies also have to
supply the current for the 8 digital output loads per cluster.
External reset for each output cluster:
The digital outputs will be brought to zero output level on power-up. In addition to the reset by
software, the reset lines (one per each output cluster) are routed to the front panel.
2.7.1 Digital Input and Output Interface
The digital input and output interface is routed through the CON2 connector. The following figure and table indicate the pin layout and pinout of this connector.
Figure 2-2: Pin Layout of the Digital Input and Output Interface Connector CON2
0+
0-
1+
1-
2+
2-
3+
3-
4+
4-
CP 383
RUN FAIL
P R E L I M I N A R Y
KEY
= GND
R = Reset
+ = VCC
Note:
Each cluster has its own
external reset and external
supply voltage (VCC and GND).
They are not connected with each other
on the CP383.
Pin 43
5-
7+
8-
10+
11+
11-
13+
14+
14-
0
3
6
0
3
6
Pin 22
5+
6+
6-
7-
8+
9+
9-
10-
12+
12-
13-
15+
15-
1
2
4
5
7
+
+
+
R
1
2
4
5
7
+
+
+
R
DIGIN
CLUSTER
DIGOUT A
CLUSTER
DIGOUT B
CLUSTER
Pin 1
Page 2 - 6 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
Page 37

CP383 Functional Description
Table 2-1: Pinout of the Digital Input and Output Interface Connector CON2
CLUSTER PIN SIGNAL PIN SIGNAL PIN SIGNAL
42 DIN0- 21 DIN0+
62 DIN1+ 41 DIN2+ 20 DIN1-
61 DIN2- 40 DIN3- 19 DIN3+
60 DIN4+ 39 DIN5+ 18 DIN4-
59 DIN5- 38 DIN6- 17 DIN6+
DIGIN
DIGOUT A
DIGOUT B
58 DIN7+ 37 DIN8+ 16 DIN7-
57 DIN8- 36 DIN9- 15 DIN9+
56 DIN10+ 35 DIN11+ 14 DIN10-
55 DIN11- 34 DIN12- 13 DIN12+
54 DIN13+ 33 DIN14+ 12 DIN13-
53 DIN14 - 32 DIN15- 11 DIN15+
52 DOUT_A0 31 DOUT_A2 10 DOUT_A1
51 DOUT_A3 30 DOUT_A5 9 DOUT_A4
50 DOUT_A6 29 EXTVCC_A 8 DOUT_A7
49 EXTVCC_A 28 EXTVCC_A 7 EXTVCC_A
48 EXTGND_A 27 EXTRESET_A 6 EXTGND_A
47 DOUT_B0 26 DOUT_B2 5 DOUT_B1
46 DOUT_B3 25 DOUT_B5 4 DOUT_B4
45 DOUT_B6 24 EXTVCC_B 3 DOUT_B7
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 2 - 7
44 EXTVCC_B 23 EXTVCC_B 2 EXTVCC_B
43 EXTGND_B 22 EXTRESET_B 1 EXTGND_B
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 38

Functional Description CP383
2.7.2 CPCI Interface and Pinout
The CPCI interface is based on the specification PICMG 2.0 R 3.0, 10/1/99. The following figure and table indicate the pin layout and pinout of the CPCI connector, CON1 (J1).
Figure 2-3: CPCI Connector
CON1 (J1)
F EDCBA
25
CON1
1
Table 2-2: Pinout of the CPCI Connector CON1 (J1)
PIN ROW
PIN
A B C D E F
1NCNCNCNCNCGND
2NCNCNCTDOTDIGND
3 INTA# NC NC NC NC GND
4 NC GND NC NC NC GND
5NCNCRSTGNDNCGND
6 NC GND 3.3V CLK AD[31] GND
7 AD[30] AD[29] AD[28] GND AD[27] GND
8 AD[26] GND NC AD[25] AD[24] GND
9 C/BE[3] IDSEL AD[23] GND AD[22] GND
10 AD[21] GND 3.3V AD[20] AD[19] GND
11 AD[18] AD[17] AD[16] GND C/BE[2] GND
12-14 Key Area
15 3.3V FRAME# IRDY# GND TRDY# GND
16 DEVSEL# GND NC STOP# LOCK# GND
17 3.3V NC NC GND PERR# GND
18 SERR# GND 3.3V PAR C/BE[1] GND
19 3.3V AD[15] AD[14] GND AD[13] GND
P R E L I M I N A R Y
20 AD[12] GND NC AD[11] AD[10] GND
21 3.3V AD[9] AD[8] M66EN C/BE[0] GND
22 AD[7] GND 3.3V AD[6] AD[5] GND
23 3.3V AD[4] AD[3] NC AD[2] GND
24 AD[1] NC NC AD[0] NC GND
25 NC NC NC 3.3V NC GND
Page 2 - 8 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
Page 39

CP383 Functional Description
2.8 CapROM EEPROM
The CapROM is a 4 kbit (512 byte) EEPROM which provides the capability to store board control relevant information to allow software configuration of the CP383.
2.9 Monitor and Control (M/C)
Various monitor and control functions are available for the operation of the CP383. The front
panel of the board is equipped with two LEDs for user-defined purposes. One green (RUN) and
one red (FAIL) have been placed on the front panel in anticipation of their most likely use. However they are freely programmable, the indicators being selected by the System Master (access
to the hardware debug register (hdr)).
The following table describes the digital input function modes of the CP383.
Table 2-3: Digital Input Function Modes of the CP383
MODE DESCRIPTION
Event hit The CP383 monitors the input ports and detects any change in their state:
- Whenever individual input channels are enabled they are monitored.
- The direction of the change-of-state may be set.
- A status register reports the detected events.
Latch hit In addition to standard event detection (i.e. event-hit) there is a latch mode exten-
sion. This mode is used in the event that it is necessary to capture the inputs when
a defined event has occurred.
Compare hit It is possible to detect a complete input pattern automatically. The input vector is
continuously compared with the content of the mask register. Single inputs may also
be individually masked out.
The system failure indicators regarding undervoltage, overcurrent and overtemperature are
made available to the DIO ProComm Controller, and are automatically reset by the HSD switches once the condition has been corrected and the output returns to normal mode.
An input signal Halt/Reset is available to set an inactive state for each individual output cluster
and also to shut down each individual output cluster during operation as necessary.
2.10 Software
Driver software is available for the System Master application software.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 2 - 9
Page 40

Functional Description CP383
This page has been intentionally left blank.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 2 - 10 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
Page 41

CP383 Installation
Chapter 1
3
Installation
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 3 - 1
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 42

Installation CP383
This page has been intentionally left blank.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 3 - 2 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
Page 43

CP383 Installation
3. Installation
The CP383 has been designed for easy installation. However, the following standard precautions, installation procedures, and general information must be observed to ensure proper installation and to preclude damage to the board or injury to personnel.
3.1 Hardware Installation
The product described in this manual can be installed in any available 3U slot of a CompactPCI
system except for the system master slot.
3.1.1 Safety Requirements
The board must be securely fastened to the chassis using the two front panel retaining screws
located at the top and bottom of the board to ensure proper grounding and to avoid loosening
caused by vibration or shock.
In addition, the following electrical hazard precautions must be observed.
Caution, Electric Shock Hazard!
Ensure that the system main power is removed prior to installing or removing
this board. Ensure that there are no other external voltages or signals being
applied to this board or other boards within the system. Failure to comply with
the above could endanger your life or health and may cause damage to this
board or other system components including process-side signal conditioning
equipment.
ESD Equipment!
This Kontron board contains electrostatically sensitive devices. Please
observe the following precautions to avoid damage to your board:
Discharge your clothing before touching the assembly. Tools must be discharged before use.
Do not touch any onboard components, connector pins, or board conductive
circuits.
If working at an anti-static workbench with professional discharging equipment, ensure compliance with its usage when handling this product.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 3 - 3
Page 44

Installation CP383
3.1.2 Installation Procedures
To install the board proceed as follows:
1. Ensure that the safety requirements indicated above are observed.
Warning!
Failure to comply with the instruction below may cause damage to the
board or result in improper system operation. Please refer to chapters
4 and 5 for configuration information.
2. Ensure that the board is properly configured for operation before installing.
Note ...
Care must be taken when applying the procedures below to ensure
that when the board is inserted it is not damaged through contact with
other boards in the system.
3. To install the board perform the following:
1. Prior to installation of the board disengage the insertion/extraction handle by first unlocking the handle and pressing it down.
2. Insert the board into an appropriate slot, and, using the insertion/ extraction handle,
ensure that it is properly seated in the backplane. (Front panel is flush with the rack
front; the insertion/extraction handle is locked.)
4. Fasten the front panel retaining screws.
5. Connect external interfacing cables to the board as required.
6. Ensure that the interfacing cables are properly secured.
Warning!
Proper and safe operation of the CP383 Digital Input and Digital Output
Controller depends on the correct configuration of the external voltage and
loads. System integrators must ensure that all voltages presented to the CP383
comply with the specifications set forth in this manual.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Failure to comply with the above may cause damage to the board or result in
improper system operation. Please refer to chapters 4 and 5 for configuration
information.
Page 3 - 4 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
Page 45

CP383 Installation
3.1.3 Removal Procedures
To remove the board proceed as follows:
1. Ensure that the safety requirements indicated above are observed.
Warning!
Care must be taken when applying the procedures below to
ensure that when the board is removed it is not damaged
through contact with other boards in the system.
2. Disconnect any interfacing cables that may be connected to the board.
3. Loosen both of the front panel retaining screws.
4. To remove the board from the backplane perform the following:
1. Unlock the insertion/extraction handle by pressing down on the grey locking mechanism in the middle of the handle. (This should be achievable with a minimum of force.
If necessary lift the handle up slightly while pressing down on the grey locking mechanism.)
2. Disengage the board from the backplane by pressing down on the insertion/extraction
handle and pull the board out of the slot ensuring that the board does not make contact
with adjacent boards. (If the handle does not move, it is not unlocked. Repeat the unlocking procedure above and try again. Do not use force!)
3.2 Software Installation
Installation of the CP383 driver software is a function of the application operating system. For
further information refer to the appropriate software documentation.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 3 - 5
Page 46

Installation CP383
This page has been intentionally left blank.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 3 - 6 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
Page 47

CP383 Configuration
Chapter 1
4
Configuration
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 4 - 1
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 48

Configuration CP383
This page has been intentionally left blank.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 4 - 2 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
Page 49

CP383 Configuration
4. Configuration
This chapter provides information for configuring the CP383 board for operation.
4.1 Jumper Settings
The CP383 does not have any jumpers which require configuring.
4.2 Digital Input Signal Requirements
In addition to the input signal type and its range, which have been specified in table 1-4, system
integrators must be aware of certain input configuration requirements for the CP383. The following paragraphs provide information regarding individual connection configuration requirements.
4.2.1 Channels
The CON2 connector of the CP383 provides two input pins per channel. This allows each channel to be configured separately as required. This is illustrated in figure 2-2, which shows the
front panel connector pinout, with the 16 input channels shown starting at the top of the connector with channel 0 (DIGIN cluster).
The following sections address the basic requirements.
4.2.2 Signal Characteristics
The signals are differential and the specified voltage ranges illustrated in the following figure
should be observed.
Figure 4-1: Voltage Ranges
+30V Maximum
+24V
standard
HIGH
HIGH
+11V
INDETERMINATE ZONE
+5V
is > +11V
P R E L I M I N A R Y
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 4 - 3
LOW
LOW is < +5V
-3V
Page 50

Configuration CP383
4.2.3 Channel Configuration
The following figure illustrates the typical schematic of an input channel.
Figure 4-2: Input Channel Schematic
System Input Cluster
to system
Signals require to be connected: plus to plus, minus to ground as shown in figure 4-3 below.
Figure 4-3: Input Configuration (Example for Channel 0)
D
JFET
G
S
CP383
+
Voltage
Source
V
DIGIN0+
Pin21
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Signal
Input
DIGIN0Pin42
CON2
Page 4 - 4 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
Page 51

CP383 Configuration
Figure 4-4: Configuration Diagram for All Input Channels
Digital Sensors
CON2
Ch 0
+
V
Ch n
Ch 15
CP383
4.3 Digital Output Signal Properties
In addition to the output signal type and its range, which have been specified in table 1-5, system integrators must be aware of certain output configuration requirements for the CP383. The
following paragraphs provide some information regarding individual connection configuration
requirements.
4.3.1 Channels
The CON2 connector of the CP383 provides only one output pin per channel. This is illustrated
in figure 2-2, which shows the front panel connector pinout with the 16 output channels shown
starting at the middle of the connector with channel 0 (DIGOUT A cluster).
The following sections address the basic requirements.
4.3.2 Connection of External Supply
The CP383 requires an external voltage for operation.
The input connection for this voltage is realized via the 62-pin front panel connector CON2. The
pinout of this connector is provided in table 2-1.
The two clusters have split supply planes, so that it is possible to provide each cluster (DIGOUT
A and DIGOUT B clusters) with a separate voltage, with different voltage values within the defined range (see also table 1-1)..
P R E L I M I N A R Y
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 4 - 5
Note ...
Each channel has a maximum current of 0.5 A. In situations where many channels are carrying a high current, separate, larger gauge cables for the external
power supply should be used.
Page 52

Configuration CP383
4.3.3 Channel Connection
The following diagrams illustrate the external connection of the CP383 to the application.
Figure 4-5: Digital Output Connection for One Cluster
Supply Voltage
External
VCC
External GND
Figure 4-6: Digital Output Circuit for One Channel
+
V
LOAD
LOAD
CON2
CON2
0
1
7
External VCC
Ch 0
Ch 1
Ch 7
EXTGND
CP383
Supply Voltage
P R E L I M I N A R Y
External
VCC
External GND
+
V
0
LOAD
External VCC
Rds, on
Ch 0
EXTGND
CP383
Page 4 - 6 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
Page 53

CP383 Configuration
Figure 4-7: External Reset Connection for One Cluster
CON2
Supply Voltage
Ch 0
0
External
VCC
External GND
Note ...
The voltage source for each cluster is an external supply (in the range +9.5V to
+35V DC). Therefore the GND reference for the digital output is the ground
potential of this external voltage supply.
Note ...
Individual outputs should not be cascaded as it cannot be guaranteed that
power sharing will be proportional, due to the transistor characteristics of each
HSD switch.
+
V
LOAD
LOAD
7
R
Ch 7
Reset
EXTGND
CP383
4.3.4 Connection of Inductive Loads
The outputs have internal clamping diodes for each channel, which are able to demagnetize
inductive loads.
The limitation is the peak power dissipation of the digital outputs at the front end. Where there
are large loads or if there is the possibility that additional loads require demagnetization simultaneously, external demagnetization circuits are required.
There are two possible topologies for the demagnetization versus ground or versus supply voltage.
27784.01.VC.040308/162543
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 4 - 7
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Note ..
For more detailed information about the external demagnetization circuits,
please refer to the L6376 data sheet referenced under chapter 1.8 Related Publications.
Page 54

Configuration CP383
4.4 Programming Interface
4.4.1 Access Control Logic (Address Decoder)
All the resources of the CP383 are mapped within the 64 kB PCI memory address space which
itself is set in the PCI configuration register BAR0. The port size of all local or backend registers
is 32-bit by default. The address map of the registers is as follows.
Table 4-1: Backend Register Address Map
BASE ADDRESS
SIZE FUNCTION
(BAR0)
+ 0x0000 4 kB COMMON BOARD REGISTER
0x0400 32 bit g_irq General Interrupt Enable Register
0x0800 32 bit hsr Hardware Status Register
0x0804 32 bit i_pen General Interrupt Pending Register
0x0C00 32 bit hdr Hardware Debug Register
+ 0x1000 4 kB CAPABILITY ROM, SERIAL EEPROM
0x1000 32 bit r_cmd Command Register
0x1400 32 bit r_ctl Control Register
0x1800 32 bit r_sta Status Regsiter
0x1C00 32 bit r_dat Data Register
+ 0x2000 4 kB DIGOUT A CLUSTER
0x2400 32 bit o_ctl_a Output Control Register
0x2800 32 bit o_sta_a Output Status Register
0x2C00 32 bit o_dat_a Output Data Register
+ 0x3000 4 kB DIGOUT B CLUSTER
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 4 - 8 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
0x3400 32 bit o_ctl_b Output Control Register
0x3800 32 bit o_sta_b Output Status Register
0x3C00 32 bit o_dat_b Output Data Register
+ 0x4000 4 kB DIGIN CLUSTER
0x4400 32 bit i_ctl Input Control Register
0x4408 32 bit i_irquen Input Irq Enable Register
0x440C 32 bit e_pol Input Event Polarity Register
0x4410 32 bit e_msk Input Event Mask Register
0x4414 32 bit e_len Input Latch-on Event Register
0x4418 32 bit c_cmp Input Pattern Compare Register
27784.01.VC.040308/162544
Page 55

CP383 Configuration
Table 4-1: Backend Register Address Map (Continued)
BASE ADDRESS
(BAR0)
0x441C 32 bit c_msk Input Pattern Mask Register
0x4800 32 bit i_event, Input Status Register
0x4C00 32 bit d_in, Input Data Register
0x4C04 32 bit input, Transparent Input Data
+ 0x5000 44 kB Reserved
SIZE FUNCTION
4.4.2 Reading Input Data
The input ports are made visible via the Input Data Register. This register reflects the inputs
after them having passed the digital programmable debouncer. An active input appears there
as a logical "1" whereas an open or inactive input port appears as a logical "0". The bit ordering
naturally corresponds with the numbering of the input ports at the connector.
Table 4-2: Input Data Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31-16 r 0 Reserved
15-0 r - Input (debounced)
Note ...
Where the enhanced features such as interrupts, pattern or event detection are
not required, only the input data register is relevant.
Table 4-3: Transparent Input Data Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31-16 r 0 Reserved
15-0 r - Input (transparent)
Note ...
In addition to the Input Data Register, there is a second non-latched input register (debouncer bypassed).
4.4.3 Debouncing Inputs
By default, all inputs are filtered through a passive analog low-pass filter placed immediately
behind the input connector. Additionally, the CP383 provides a programmable digital debouncer which is common for all inputs. The input ports are sampled at a programmable sample rate
which is derived from PCI bus clock. Two consecutive samples must be equal before being
stored in the input data register. By this means, bouncing and spikes on inputs can be filtered
out. For example, with a selected input sample rate of 500 Hz, input pulses which are shorter
than 2 ms are filtered out.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
27784.01.VC.040308/162544
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 4 - 9
Page 56

Configuration CP383
Table 4-4: Input Control Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31-8 R/W 0 RESERVED
7 r/w 0 Input enable
6 r/w 0 Event detect enable
5 r/w 0 Latch mode enable
4 r/w 0 Pattern detect enable
2-0 r/w 000 Debounce control deb [2 ... 0]
Note ...
The inputs are sampled through the debouncer after the Input Enable bit is set.
Additional features such as event and pattern detection and latch mode are also
enabled in the input control register, after being configured within the corresponding mode registers.
Table 4-5: Programmable Input Sample Rates
deb [2 ... 0]
000 1 33 MHz 30 ns
001 2^8 128 KHz 8 µs
010 2^10 32 KHz 32 µs
011 2^12 8 KHz 128 µs
100 2^14 2 KHz 0.5 ms
101 2^16 0.5 KHz 2 ms
110 2^18 125 Hz 8 ms
111 2^20 31 Hz 32 ms
P R E L I M I N A R Y
CLOCK
DIVIDER
Note ...
The clock divider default value is 1. In addition to the choice of debouncing filters, there is an analog filter implemented on the board with an edge frequency
at 10 kHz.
INPUT SAMPLE CLOCK
@ 33MHz PCI
INPUT SAMPLE PERIOD
@ 33MHz PCI
4.4.4 Detecting Input Events
Detecting events on input means that the CP383 hardware can supervise the input ports upon
their changing state and without being continuously polled. This mode is controlled by three
control registers. In the Input Event Mask Register, individual input events can be enabled
which should be monitored. In the Input Polarity Register the direction of the change-of-state
is set. Detected events are reported in the corresponding Input Event Status Register.
Table 4-6: Input Event Mask Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
Page 4 - 10 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162544
Page 57

CP383 Configuration
Table 4-6: Input Event Mask Register
31-16 r/w 0 Not used
15 - 0 r/w 1 Input event mask bits
Note ...
A set bit means that event detection is disabled for the corresponding input port.
Table 4-7: Input Event Polarity Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31-16 r/w 0 Not used
15 - 0 r/w 0 Input event polarity bits
Note ...
A bit setting of 0 bit means that an event is detected when the input port
changes from 0 to 1 whereas a setting of 1 means that an event is detected
when the input changes from 1 to 0.
Table 4-8: Input Status Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31 r/w 0 Input latch-on-event status flag
30 r/w 0 Input compare status flag
15 - 0 r/w 0 Input event status flags
Note ...
A set bit means that an event was detected on the corresponding input port.
Events must be cleared by writing a "1" to the corresponding input event flag.
Otherwise, consecutive events on the same input would no longer be detected.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
27784.01.VC.040308/162544
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 4 - 11
Page 58

Configuration CP383
4.4.5 Latching on Input Events
In addition to the standard event detection described above, there is a latch mode extension.
This mode is used in cases where it is necessary to capture the inputs when one of the defined
events occurs.
Table 4-9: Input Latch-on-Event Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31-16 r 0 Not used
15 – 0 r 0 Latch on event, enable bits to activate
Note ...
A set bit means that a detected event on the corresponding input is latched. If
all bits are enabled, all inputs are latched immediately. To switch back from latch
mode into active mode, all detected events and the input latch-on-event status
flag have to be reset by writing a "1" to the corresponding bits in the Input Status
Register.
4.4.6 Comparing Input Patterns
In addition to the Event Detection Mode, it is also possible to detect a complete input pattern
automatically. In this mode the input vector is continuously compared with the content of the
Input Pattern Compare Register. In the case of a match a flag is set within the Input Status Register. Single inputs can also be masked out individually in the Input Pattern Mask Register.
Table 4-10: Input Pattern Mask Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31-16 r/w 0 Not used
15 - 0 r/w 1 Input event mask bits
Note ...
A set bit means that the corresponding input is masked out for pattern recognition. There is no special enable for pattern recognition since it is switched off by
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Table 4-11: Input Pattern Compare Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31-16 r/w 0 Not used
15 - 0 r/w 1 Input pattern compare bits
default as long as all mask bits are set.
Note ...
This register stores the input compare data. A compare match is reported within
the Input Status Register (Bit 31). To reset a compare match, the status flag
must be reset by writing a "1" to it and also the match condition must cease.
Page 4 - 12 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162544
Page 59

CP383 Configuration
4.4.7 Writing Output Data
Table 4-12: Output Data Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31-8 r/w 0 Reserved
7-0 r/w 0 Data, 8-bit digit
Note ...
Output data is 8 bit (each cluster); this register is read/write enable.
Table 4-13: Output Control Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31-2 r/w 0 Reserved
1 r/w 0 irqen
0 r/w 1 Reset
Note ...
irqen is for diagnostic issuing an interrupt.
The reset bit should be set to 0 to activate a cluster.
Table 4-14: Output Status Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31 r 0 Fail
30 r 0 Diag
29-0 r 0 Reserved
Note ...
The Diag status flag is the diagnostic bit from the HSD switch; Fail is the latched
diag status flag.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
27784.01.VC.040308/162544
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 4 - 13
Page 60

Configuration CP383
4.4.8 Hardware Debug/Test Registers
These registers are for internal test and debug only. The Common Status Register contains
logic version and PCB version. The Common Debug Register is a read/write register without
any further functionality besides the front panel monitor and control LEDs.
Table 4-15: Hardware Debug Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31-2 r/w 0 Reserved
1r/w0 FAIL
0 r/w 0 RUN
Table 4-16: Hardware Status Register
BITS TYPE
31-16 r 0 Reserved
15-8 r 00 HW Version (PCB Index)
7-0 r 01 Logic Version
Note ...
The HW version starts with 0, the Logic version starts with 1. At each further
release it will be incremented by 1.
DEFAULT
*
FUNCTION
4.4.9 Generating Interrupts
For digital outputs, a detected fail flag set in the register can trigger an interrupt. For digital
inputs, a detected event or in other words any event flag set in the Input Status Register can
trigger an interrupt. Thus, any input can be enabled individually for interrupt generation.
Independent of the interrupt cause, a board interrupt is handled on the hardware level always
in the same way.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
After having set the input control registers where compare data and events are defined, interrupts can be enabled individually within the Input IRQ Enable Register. Within the interrupt service routine, interrupts should be handled as follows.
1. Check if the board is the cause of the interrupt (General Interrupt Pending is set).
2. If yes, check the reason for the interrupt by reading the fail flag in the output status register and by reading the digital input status register.
3. Reset the corresponding Flag by writing a "1" to a set status bit (fail) or to the Input Event
Flag.
4. Reset the board’s IRQ by resetting the General Interrupt Pending Bit by writing a "1" to
that status bit.
5. Return from Interrupt.
Page 4 - 14 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162544
Page 61

CP383 Configuration
Note ...
The board will continue issuing an interrupt until all interrupt sources are handled completely and no interrupt condition remains.
Table 4-17: General Interrupt Enable Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31 r/w 0 Board Interrupt Enable
30 - 0 r/w 0 Reserved
Note ...
A set bit means that the board’s interrupt is enabled.
Table 4-18: General Interrupt Pending Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31 r/w 0 Board Interrupt Pending
29 - 0 r/w 0 Reserved
Note ...
A set bit means that the board’s interrupt is pending. A board interrupt must be
cleared by writing a "1" to the corresponding output irqen event flag.
Table 4-19: Output Status Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31 r 0 Fail
30 r 0 Diag
29 - 0 r 0 Reserved
Table 4-20: Input IRQ Register
P R E L I M I N A R Y
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31 r/w 0 Not used
30 r/w 0 Input compare interrupt enable
29 - 0 r/w 0 Input event interrupt enable
27784.01.VC.040308/162544
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 4 - 15
Page 62

Configuration CP383
4.4.10 Programming the Board Capability ROM
The Board Capability ROM contains all the board data necessary to identify board, version, optional features, etc., and to setup the basic software. The BCR is implemented using a 4 kbit
serial EEPROM of the type Microchip 93LC66.
(The contents list of the BCR is not described here.)
The serial interface of the device has been realized in hardware resulting in a very simple register based programming interface with command, control, status and data registers. All protocol and serial timing specifications are resolved by hardware.
Programming of the BCR is undertaken as follows: The control word is written into the ROM
Control Register including command opcode and internal address. Then optional data (in case
of Write action) is written into the ROM Data Register. Command execution is started by setting
the Startbit in the ROM Command Register. Then Ready/Busy must be polled in the ROM Status Register. After reaching Ready status, the next command can be set up and data (in case
of Read action) can be fetched from the ROM Data Register.
Table 4-21: ROM Command Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31 r/w 0 Startbit
30-0 r/w 00 Reserved
Note ...
The Startbit will be automatically reset as soon as an action is completed.
Table 4-22: ROM Control Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31-19 r/w 0 Reserved
17-16 r/w 00 Opcode
P R E L I M I N A R Y
15-8 r/w 00 Reserved
8-0 r/w 00 Internal address (A8 ... A0)
Note ...
The commands READ, EWEN (Write Enable) and WRITE are sufficient for all
purposes.
Page 4 - 16 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162544
Page 63

CP383 Configuration
Table 4-23: Opcodes and Commands
OPCODE A8 ... A0 COMMAND
00 11xxxxxxx EWEN
10 xxxxxxxxx READ
01 xxxxxxxxx WRITE
Note ...
The EWEN (Erase and Write Enable) command must be executed once before
the first write.
Table 4-24: ROM Status Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31 r/w 0 Busy/Ready
30-0 r/w 00 Reserved
Note ...
As soon as the Startbit is set the Busy/Ready bit becomes active (Busy=1). It
remains set as long as the command is executed and is reset when command
execution is complete.
Table 4-25: ROM Data Register
BITS TYPE DEFAULT FUNCTION
31-8 r/w 0 Reserved
7-0 r/w 0 Data (for data read and write commands)
P R E L I M I N A R Y
27784.01.VC.040308/162544
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 4 - 17
Page 64

Configuration CP383
This page has been intentionally left blank.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 4 - 18 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162544
Page 65

CP383 Power Consumption
Chapter
5
Power Consumption
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 5 - 1
Page 66

Power Consumption CP383
This page was intentionally left blank.
Page 5 - 2 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
Page 67

CP383 Power Consumption
5. Power Consumption
5.1 System Power
The new Intel Pentium M processor family requires substantially more power than earlier Pentium lll processors, although less than the Pentium 4. This results in special requirements for
the power supply and the backplane. The considerations presented in the ensuing chapters
must be taken into account by system integrators when specifying the CP383 system environment.
5.1.1 CP383 Baseboard
The CP383 baseboard itself has been designed for optimal power input and distribution. Still it
is necessary to observe certain criteria essential for application stability and reliability.
In the table below, absolute maximum input voltage ratings are specified to ensure that the
CP383 is not damaged during operation. Power supplies to be used with the CP383 should be
carefully tested to ensure compliance with these ratings.
Table 5-1: Maximum Input Power Voltage Limits
SUPPLY VOLTAGE MAXIMUM PERMITTED VOLTAGE
+3.3 V +3.6 V
+5 V +5.5 V
+12 V +14.0 V
-12 V -14.0 V
The following table specifies the ranges for the different input power voltages within which the
board is functional. The CP383 is not guaranteed to function if the board is not operated within
the prescribed limits.
Table 5-2: DC Input Voltage Ranges
INPUT SUPPLY VOLTAGE ABSOLUTE RANGE
+3.3 V 3.2 V min. to 3.47 V max.
+5 V 4.85 V min. to 5.25 V max.
+12 V 11.4 V min. to 12.6 V max.
-12 V -11.4 V min. to -12.6 V max.
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 5 - 3
Page 68

Power Consumption CP383
5.1.2 Backplane
The backplane to be used with the CP383 must be adequately specified and must provide optimal power distribution for the +3.3 V power input.
5.1.3 Power Supply Units
The start-up behavior of CPCI and PCI (ATX) power supplies is critical for all new CPU boards.
These boards require a defined power of sequence and start-up behavior of the power supply.
The required behavior is described in the ATX (http://www.formfactors.org/FFDe-
tail.asp?FFID=1&CatID=2) and the CPCI (PICMG, http://www.picmgeu.org/) specification.
5.1.3.1 Start-Up Requirement
Power supplies must comply with the following in order to be used with the CP383.
• Beginning at 10% of the nominal output voltage, the voltage must rise within > 0.1 ms to
< 20 ms to the specified regulation range of the voltage. Typically: > 5 ms to < 15 ms.
• There must be a smooth and continuous ramp of each DC output voltage from 10% to
90% of the regulation band.
• The slope of the turn-on waveform shall be a positive, almost linear voltage increase and
have a value from 0 V to nominal Vout.
The following figure illustrates an example of the recommended start-up ramp of a CPCI power
supply for all Kontron boards delivered up to now.
Figure 5-1: Start-Up Ramp of the CP3-SVE180 AC Power Supply
5.1.3.2 Power-up Sequence
The +5 VDC output levels must always be equal to or higher than the +3.3 VDC output during
power-up and normal operation.
The time from +5 VDC until the output reaches its minimum in regulation level and from
+3.3 VDC until the output reaches its minimum in regulation level must be < 20 ms.
Page 5 - 4 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
Page 69

CP383 Power Consumption
5.1.3.3 Tolerance
The tolerance of the voltage lines is described in the CPCI specification (PICMG 2.0 R3.0).The
recommended measurement point for the voltage is the CPCI connector on the CPU board.
The following table provides information regarding the required characteristics for each board
input voltage.
Table 5-3: Input Voltage Characteristics
VO LTAGE NOMINAL VALUE TOLERANCE MAX. RIPPLE (p-p) REMARKS
5 V +5.0 VDC +5%/-3% 50 mV Not required
3.3 V +3.3 VDC +5%/-3% 50 mV Main voltage
+12 V +12 VDC +5%/-5% 240 mV Not required
-12 V -12 VDC +5%/-5% 240 mV Not required
VI/OPCI I/O voltage +3.3 VDC or +5 VDC +5%/-3% 50 mV Not required
GND Ground, not directly
connected to poten-
tial earth (PE)
The output voltage overshoot generated during the application (load changes) or during the
removal of the input voltage must be less than 5% of the nominal value. No voltage of reverse
polarity may be present on any output during turn-on or turn-off.
5.1.3.4 Regulation
The power supply shall be unconditionally stable under line, load, unload and transient load
conditions including capacitive loads. The operation of the power supply must be consistent
even without the minimum load on all output lines.
Note...
Non-industrial ATX PSUs require a greater minimum load than a single CP383
is capable of creating. When a PSU of this type is used, it will not power up
correctly and the CP383 may hang up. The solution is to use an industrial PSU
or to add more load to the system.
Note...
If the main power input is switched off, the 3.3V supply voltage will not go to 0V
instantly. It will take a couple of seconds until capacitors are discharged. If the
voltage rises again before it went below a certain level, the circuits may enter a
latch-up state where even a hard RESET will not help any more. The system
must be switched off for at least 3 seconds before it may be switched on again.
If problems still occur, turn off the main power for 30 seconds before turning it
on again.
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 5 - 5
Page 70

Power Consumption CP383
5.2 Power Consumption Table
The goal of this description is to provide a method to calculate the power consumption for the
CP383 baseboard and for additional configurations.
The power consumption table below indicates the voltage for the CP383 board. The value was
measured using an 8-slot passive CompactPCI backplane with the power supply. The operating systems used was Windows
25°C.
Table 4-4: Power Consumption Table
POWER CP383
5 V not recommended
3.3 V 600 mW
®
2000. All measurement were conducted at a temperature of
Page 5 - 6 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
Page 71

CP383 System Considerations
Chapter 1
6
System Considerations
27784.01.VC.040308/162549
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 6 - 1
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 72

System Considerations CP383
This page has been intentionally left blank.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Page 6 - 2 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162549
Page 73

CP383 System Considerations
6. System Considerations
6.1 Introduction
In addition to the basic specification requirements for the CP383 which have been addressed
in chapter 4, system integrators need to be aware of the overall system environment and the
application needs when designing the interfacing to the CP383. The following chapters address
a number of more apparent considerations which should be addressed, but certainly not all of
the possible situations which may be encountered. Many of the considerations presented here
are recommendations, but some are definite requirements if the CP383 is to successfully
achieve its purpose.
6.2 General
Considerations:
1. Care must be taken to ensure that proper grounding concepts are followed, and that the
integrity of the grounding system within the application be maintained.
2. Input wire routing should avoid proximity to high voltage or current sources.
3. Where possible input wiring length should be kept as short as possible.
6.3 Shielding
Considerations:
1. Input cable shielding in general is recommended.
2. The requirements for shielding can be seen primarily as a function of the system design
and environment, but empirical results must also be considered.
3. The CON2 connector has a metal housing which is connected to the CP383 shield and
is isolated from the system ground.
4. Ensure that if shielding is used that it is not in anyway connected to the system ground.
6.4 Debouncing for Digital Inputs
On the CP383 it is possible to select from a number of debouncing times, dependant on the
type of switches/sensors in use. For example, when using mechanical switches or relays to
switch the input, bouncing will always occur and therefore debouncing is necessary. A debounce period may be selected from a range of values available, accessible via software in the
register depending on the settle time. Where it is known that an application does not generate
bouncing problems, the debounce period may be set to the default value.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
27784.01.VC.040308/162549
ID 27784, Rev. 01 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH Page 6 - 3
Page 74

System Considerations CP383
Table 5-1: Debouncing Periods
CLOCK DIVIDER
1 (default value - see note below) 33 MHz 30 ns
2^8 128 kHz 8 µs
2^10 32 kHz 32 µs
2^12 8 kHz 128 µs
2^14 2 kHz 0.5 ms
2^16 0.5 kHz 2 ms
2^18 125 Hz 8 ms
2^20 31 Hz 32 ms
Note ...
The clock divider default value is 1. In addition to the choice of debouncing filters, there is an analog filter implemented on board with an edge frequency at
10 kHz.
INPUT SAMPLE CLOCK
@ 33 MHz PCI CLK
INPUT SAMPLE PERIOD
@ 33 MHz PCI CLK
6.5 Process-Side Signal Conditioning for Digital Inputs
Considerations:
1. Input signals presented to the CP383 must be within the ranges specified for signals in
table 1-4 or erroneous results will occur as well as possible damage to the CP383.
6.6 External Power Supply for Digital Outputs
Considerations:
1. Voltage sources presented to the CP383 must be within the ranges specified in table 1-5
or erroneous results will occur as well as possible damage to the CP383.
P R E L I M I N A R Y
2. In addition to supplying the current for the logic parts of the power switches which are
linked to the digital outputs, the external voltage supplies also have to supply the current
for the 8 digital output loads per cluster.
6.7 Cable Interfacing
Considerations:
1. No modification to the CP383 itself is permitted.
2. If necessary, cabling to the CP383 CON2 connector should be physically fixed to prevent
strain on the CON2 connector.
Warning!
Each channel has a maximum current of 0.5 A. In situations where many channels are carrying a high current, separate, larger gauge cables for the external
power supply should be used.
Page 6 - 4 © 2004 Kontron Modular Computers GmbH ID 27784, Rev. 01
27784.01.VC.040308/162549
 Loading...
Loading...