Page 1

CURRENT INFORMATION SUMMARY May 2005 • CIS-254
Using the KODAK Negative Film Processing
Cartridges FC1 and FC2
The KODAK Negative Film Processing Cartridges FC1
and FC2 and KODAK Rinse Tablets are designed for use
in FUJI FP363SC and FP563SC Film Processors using
process cycle CN-16S. The FC1 and FC2 cartridges are
drop-in cartridges that provide convenience and ease of
use. The FC1 cartridge will process 200 rolls of 135-24
film; the FC2 cartridge will process 1000 rolls of 135-24
film.
The cartridges and tablets are part of Kodak’s systems
approach that enables users of other manufacturers’
minilabs to provide customers with high-quality film
processing in Kodak chemicals.
KODAK Negative Film Processing
Cartridge FC1 and Shipping Corrugate
KODAK Negative Film Processing
Cartridge FC2 and Shipping Corrugate
©Eastman Kodak Company, 2005
Page 2
OBTAINING THE CHEMICALS
Preparing Fresh Working Tank Solutions
Catalog numbers are as follows:
Product
KODAK Negative Film
Processing Cartridge
FC1
KODAK Negative Film
Processing Cartridge
FC2
KODAK Rinse Tablets* 4 191 3110
KODAK Negative Film
FC Tank Developer
KODAK Negative Film
FC Tank Bleach
KODAK Negative Film
FC Tank Fixer
KODAK Negative Film
FC Tank Rinse
*Used in water reservoir on processor
Min/Mult
Order Qty
2 801 7519
2 867 2701
1 833 9723
1 107 2024
1 813 4421
3 872 4791
CAT Number
SAFE HANDLING OF PHOTOGRAPHIC
CHEMICALS
Handle all chemicals carefully. When you mix solutions,
wear goggles or a face shield, a protective rubber apron,
and protective gloves made with neoprene or nitrile
rubber. Clean protective clothing after use to remove any
chemical residue that can cause contamination. For more
information about potential health hazards and safe
handling of specific Kodak chemicals, see the label and
the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for the chemical.
Consult the MSDS for regional contact information.
MSDS copies are available at the Kodak website at
www.kodak.com/go/photochemicals.
CONVERTING TO THE KODAK
NEGATIVE FILM PROCESSING
CARTRIDGES
Use the following Kodak chemicals to prepare fresh
working tank solutions:
Developer Tank (N1)
Use KODAK Negative Film FC Tank Developer
CAT No. 833 9723. Each kit makes 5.2 litres. Two kits
are required for the FP363SC processor. Three kits are
required for the FP563SC processor. Follow the directions
in the following table:
Step
1
2
3
4
FP363SC
Processor
Mix 2 bottles of
developer Part A
with 2 litres of water
in mixing bottle. Add
solution to processor
developer (N1) tank.
Mix 2 bottles of
developer Part B
with 2 litres of water
in mixing bottle. Add
solution to processor
developer (N1) tank.
Mix 2 bottles of
developer Part C
with 2 litres of water
in mixing bottle. Add
processor developer
(N1) tank.
Position tank level
gauge on processor
developer (N1) rack.
Add water to N1
level mark (about
2.3 litres).
FP563SC
Processor
Add 4 litres of water
to processor
developer (N1) tank.
Then mix 3 bottles of
developer Part A
with 2 litres of water
in mixing bottle. Add
solution to processor
developer (N1) tank.
Mix 3 bottles of
developer Part B
with 2 litres of water
in mixing bottle. Add
processor developer
(N1) tank.
Mix 3 bottles of
developer Part C
with 2 litres of water
in mixing bottle. Add
processor developer
(N1) tank.
Position tank level
gauge on processor
developer (N1) rack.
Add water to N1
level mark (about
2.4 litres).
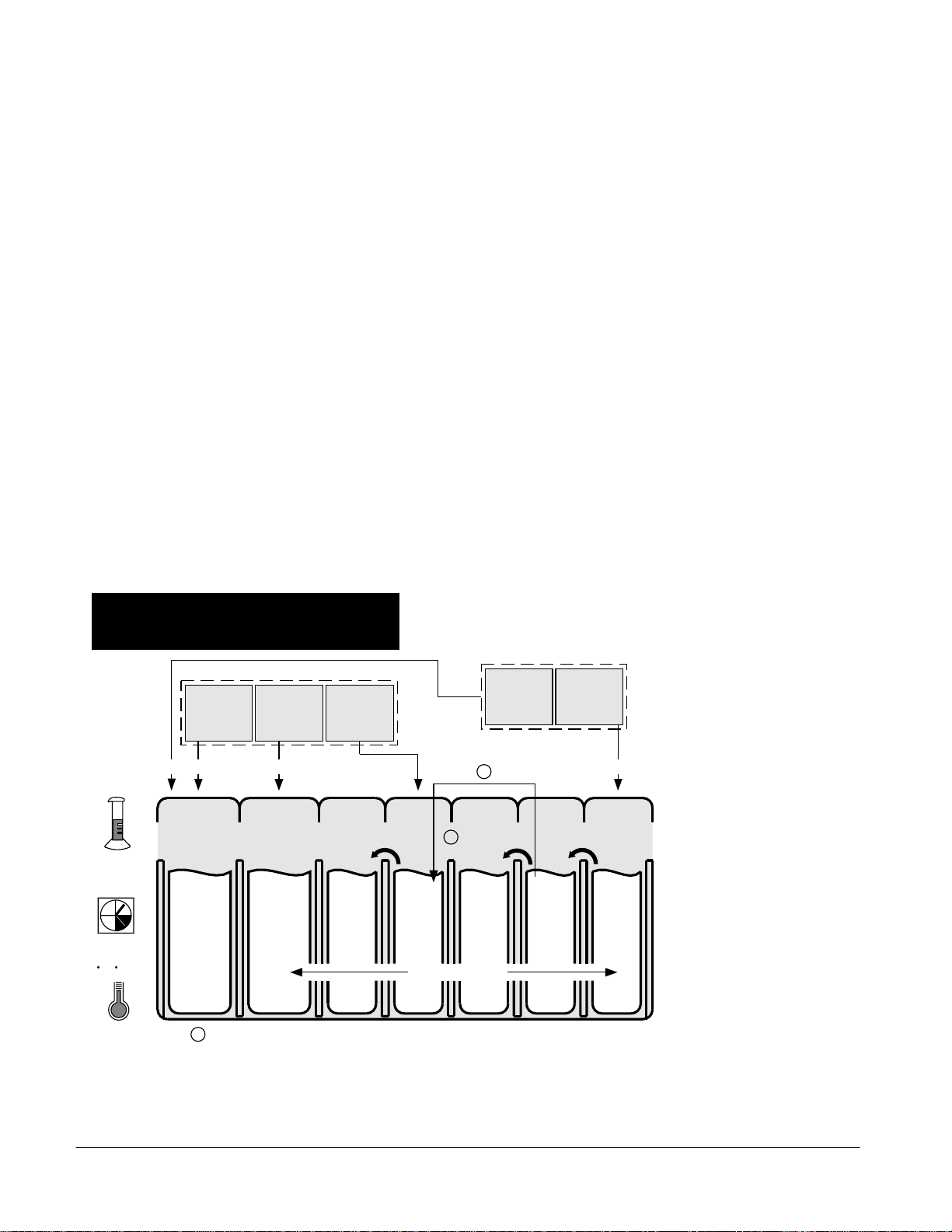
No processor adjustments are required to use KODAK
Negative Film Processing Cartridges FC1 and FC2. These
cartridges are designed to mix and replenish on top of
existing solution. Use the same processor settings that you
use with your current chemical cartridge. Standard
conditions are shown in Figure 1 on page 3.
2 Using the KODAK Negative Film Processing Cartridges FC1 and FC2 • CIS-254
Page 3
Bleach Tank (N2)
Use KODAK Negative Film FC Tank Bleach,
CAT No. 107 2024. Each kit makes 3.6 litres of tank
bleach solution. One kit is required to prepare the bleach
tank in either the FP363SC processor or the FP563SC
processor. Add the contents of 1 bottle to the empty
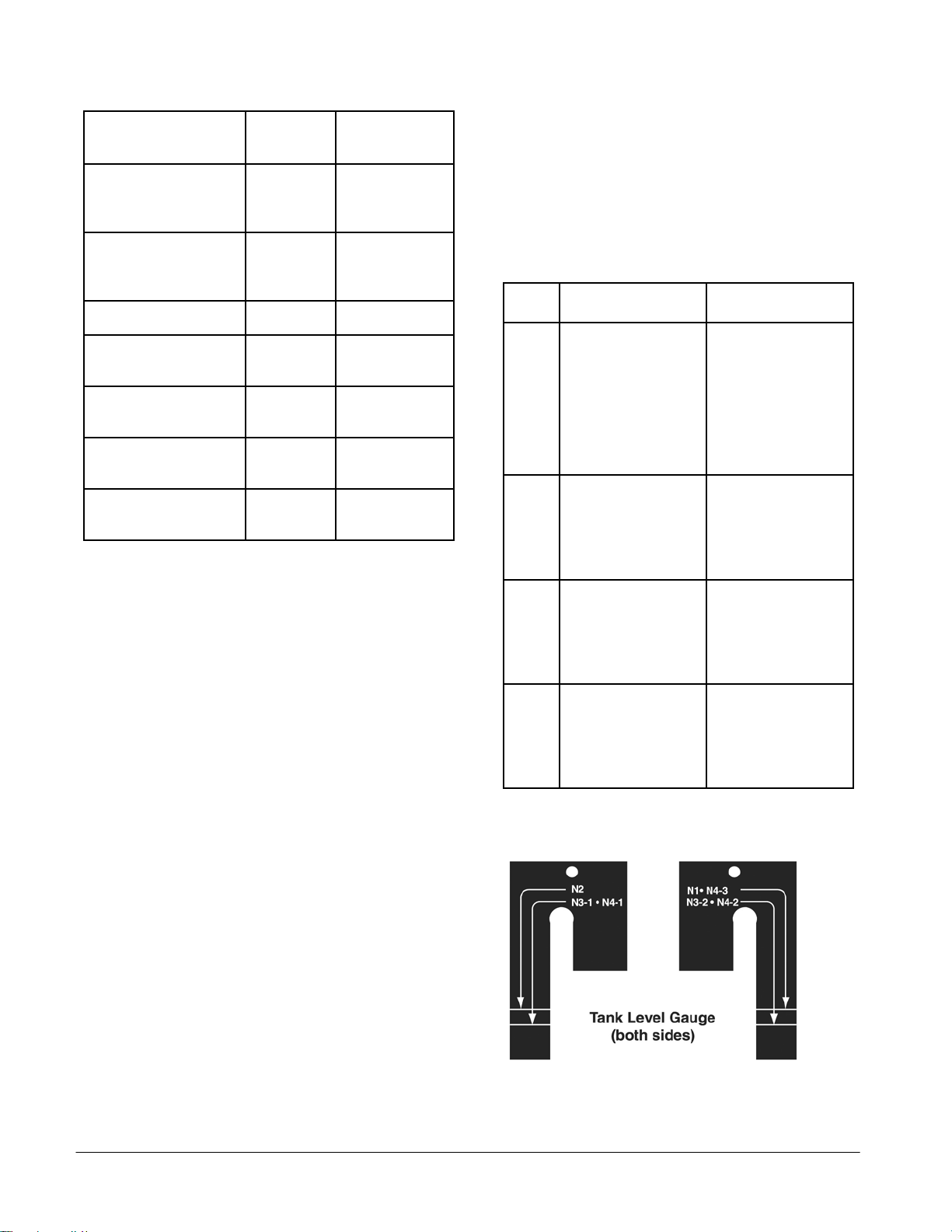
bleach (N2) tank. Position the tank level gauge on the
bleach (N2) tank rack, and add water to the N2 level mark
on the gauge. For faster warm-up, use water close to
operating temperature (31 to 41˚C [88 to 106˚F]).
Fixer Tanks (N3-1 & N3-2)
Use KODAK Negative Film FC Tank Fixer,
CAT No. 813 4421. Each kit makes 3.6 litres of tank fixer
solution. One kit is required to prepare each fixer tank in
either the FP363SC processor or the FP563SC processor
(two tanks per machine). Add the contents of 1 bottle to
each empty tank (N3-1 and/or N3-2). Position the tank
level gauge on the fix tank rack (N3-1 or N3-2), and add
water to the N3-1 or N3-2 level mark on the gauge. For
faster warm up, use water close to operating temperature
(31 to 41˚C [88 to 106˚F]).
Figure 1
Stabilizer/Final Rinse Tanks (N4-1, N4-2, N4-3)
Use KODAK Negative Film FC Tank Rinse,
CAT No. 872 4791. The kit contains three bottles of
concentrate. Each bottle will make 1.9 litres of rinse tank
solution. One bottle is required to make a rinse tank
solution in each rinse tank of the FP363SC processor or
the FP563SC processor (three tanks per machine). Add
the contents of one bottle to each empty tank (N4-1, N4-2,
N4-3). Position the tank level gauge on the rinse tank
rack, and add water to the N4-1, N4-2 or N4-3 level mark
on the gauge (depending on which tank is being mixed.).
For faster warm up, use water close to operating
temperature (31 to 41˚C [88 to 106˚F]).
Water Reservoir
Use KODAK Rinse Tablets, CAT No. 191 3110. Add
tablet(s) into the loading port on top of the reservoir
before adding water. Use one tablet for every 4 litres of
water.
CN-16S
Replenishment
Rate
mL/135-24 roll
(mL/M)
Time
min:sec
Temperature
C ( F)
Process Cycle with
KODAK Negative Film
Cartridge Chemistry
FC1 Cartridge
Negative Film
Developer
Replenisher
N1-RA
15 (13.5)
N1 N2 N3-1 N3-2 N4-1 N4-2
3:05 0:50
+
_
38.0 0.2
+
_
(100.4
0.4)
1
The N4-2 Rinse is pumped into the N3-2 Fixer Tank to dilute the Fixer
Replenisher to specification.
Negative Film
Bleach
Replenisher
N2-R
to
0:70
Negative Film
Fixer
Replenisher
N3-R
0:50
to
0:70
0:50 0:30
to
0:70
35 - 41 (95 - 106)
1
Negative Film
Developer
Replenisher
1
FC2 Cartridge
N1-RB
RinseDeveloper FixerBleach Fixer Rinse
0:20
Negative Film
Rinse
Replenisher
N4-R
30 (27)7.5 (6.75)5 (4.5)
Rinse
N4-3
0:20
Dry
Using the KODAK Negative Film Processing Cartridges FC1 and FC2 • CIS-254 3
Page 4

USING KODAK CONTROL STRIPS,
PROCESS C-41, TO MONITOR THE
PROCESS
Use KODAK Control Strips, Process C-41, to monitor
process performance
Each time you process a control strip, position it in
the same location in the processor. Process a control strip
at these times:
• At the beginning of the day or shift, before processing
customer work
• At the end of the day or shift
Plotting Control-Strip Densities
Create a control chart by using the KODAK Process
Record Form Y-55 or similar graph paper. Your chart
should have the same format as the Process CN-16S
“Visual Process Control Guide” shown on page 8.
Tolerances and Limits for KODAK Control Strips,
Process C-41
Color-
Balance
Spread
Limit
Aim-Value
Adjust-
ment
Tolerance
Measure-
ment
D-min ±0.03 +0.03 +0.05 —
LD ±0.04 ±0.06 ±0.08 —
HD-LD ±0.03 ±0.07 ±0.09 0.09
Action
Limits
Control
Limits
C-41
9141
KODAK Control Strip,
Process C-41
CAT No. 180 3709
Yellow
D-max
HD
LD
D-min
Cutoff
Notch
D-maxb-Yb
±0.07 +0.10 +0.12 —
1. Before you begin to use a box of control strips,
remove the reference strip from the box, and store it at
room temperature.
2. Use a precision densitometer to measure the densities
in the center of the Yellow, HD, LD, and D-min
patches on the reference strip. Do not move the strip as
you make the density readings or you may affect the
precision and repeatability of the measurement. Use
transmission mode Status M.
3. To obtain the aim densities, apply the correction
factors to the densities read in Step 2. The correction
factors are found on a sheet packaged with the
control strips. Make sure you use the correction
factors for Process CN-16S. To obtain the HD-LD
aim value, subtract the adjusted LD value form the
adjusted HD value. To obtain the D-max
-Yb aim
b
value, subtract the adjusted blue density of the yellow
step from the adjusted blue density of the D-max
step. Use the Process CN-16S Reference Aims
Worksheet on page 9 to help calculate the aim
densities.
Note: If you are using an older code of control strip
that does not list correction factors for Process
CN-16S, apply the Process Factors listed in the
following table to the density readings after applying
the regular correction factors for Process C-41.
4 Using the KODAK Negative Film Processing Cartridges FC1 and FC2 • CIS-254
Page 5

Additional Process CN-16S
Adjustment Factors for Use with
Process C-41 Control Strips
Step R G B
Yellow 0.00 0.00 0.00
D-max 0.00 0.00 +0.07
HD +0.04 0.00 +0.07
LD 0.00 0.00 0.00
D-min 0.00 0.00 0.00
4. Process a control strip and measure the Yellow,
D-maxb-Y
HD, LD, and D-min patches.
b,
5. Calculate the variations from aim by subtracting the
aim densities from your control-strip densities. Plot
the variations on your control chart. Plot variations
that are higher than the corresponding aim values
(+ values) above the aim line. Plot variations that are
lower than the aim values (– values) below the aim
line.
If any of the variations from aim plots beyond the
action or control limits, process another control strip. If
the second control strip confirms the results of the first
strip, determine the cause of the problem. Using the
“Visual Process Control Guide” on page 8 provides a
good starting place. If the problem is not readily
correctable, contact Kodak Service and Support at
(866) 352-4367.
USING THE “VISUAL PROCESS
CONTROL GUIDE” AND KODAK
CONTROL STRIPS TO TROUBLESHOOT
PROCESS CN-16S
If your Process CN-16S control chart indicates an out-ofcontrol plot position, use the “Visual Process Control
Guide” as follows to troubleshoot the process and apply
corrective action.
First check for operational errors:
• Make sure the control-strip code matches the
reference-strip code.
• Calibrate the densitometer.
• Re-check the control-strip aims and verify the
correction factors.
• Verify the problem by processing a second control
strip.
• Determine if any recent processor maintenance could
have caused a problem.
• Verify that tank and replenisher solutions were mixed
correctly.
• Use an accurate thermometer to verify that the
developer temperature and other solution temperatures
are correct.
Match your plots to the “Visual Process Control
Guide” to identify the problem:
• Match your control plots to the examples given on the
“Visual Process Control Guide.” Compare only one
plot parameter at a time (D-max
, HD-LD, LD,
b-Yb
D-min). Note that the pattern of the red, green, and
blue plot deviations can be an indicator of different
problems.
• Write down the problems indicated by each parameter
for the plots that are out of control. Consider that you
may have more than one problem occurring at the
same time.
• Consider each potential cause of the out-of-control
condition, and verify the operational conditions of the
processor.
When you have determined the most likely cause(s)
of the out-of-control condition, take corrective action to
eliminate the cause, and use the prescriptions to eliminate
the symptom of the problem.
Corrective Action and Prescriptions
D-maxb – Yb:
This parameter monitors the performance of the bleach
solution for retained silver. A bleach solution that is
underreplenished or diluted will not efficiently bleach the
film, leaving retained silver in higher-density areas. If the
D-max
with the following test:
1. Immerse the processed control strip in the bleach tank,
and soak it for 7 minutes.
2. Remove the strip, rinse it thoroughly with water for
3 minutes, and dry it.
3. Re-read the strip, re-plot D-max
new plot to the earlier plot. If the new plot shows a
difference of -0.05 density unit or more (lower), it
confirms a bleaching problem. If there is no change or
less than a 0.05 change, the bleach is not a problem.
See the “Visual Process Control Guide” for other
possible causes.
bleach tank solution with fresh solution made from the
KODAK Negative Film FC Tank Bleach, as described on
page 3. Also check the output of the bleach replenisher
pump and calibrate. Be sure that the bleach replenishment
rate is set correctly.
indicates a retained-silver problem, confirm it
b-Yb
, and compare the
b-Yb
If the test confirms a bleaching problem, replace the
Using the KODAK Negative Film Processing Cartridges FC1 and FC2 • CIS-254 5
Page 6

HD-LD (Contrast):
This parameter monitors developer activity. Contrast is
the primary indicator of developer agitation, oxidation,
concentration, or contamination. If the developer tank
solution is under-agitated, too dilute, or oxidized, the
plots will be low. If the developer tank solution is overconcentrated or contaminated, the plots will be high. If
the process is very out of control, i.e., by more than 0.15
density unit over or under aim, replace all of the
developer tank solution. If the developer is contaminated,
make sure you rinse the tank out thoroughly, and then
replace all of the developer tank solution. If the plots are
less than 0.15 density unit over or under aim, you can risk
a prescription.
Prescriptions:
• For high HD-LD plots:
Overconcentration: Dilute the developer with warm
water in an amount equal to 5 percent of the volume in
the developer tank. Repeat as necessary until the
process is in control.
• For low HD-LD plots:
Under concentrated (Diluted): Replace developer tank
with a tank mix of KODAK Negative Film FC Tank
Developer, use mixing instructions on page 2.
Under agitation: Call a service representative to fix the
agitation pump on the processor.
Oxidation: Check for air bubbles in the developer
tank, and call a service technician if bubbles are
visible. If oxidation is caused by low utilization, see
the corrective action in KODAK Publication No.
CIS-246, Operating Minilabs at Low Levels of
Utilization. This publication is available on the Kodak
website at www.kodak.com/go/photochemicals.
LD (speed):
This parameter monitors developer activity. Speed is the
primary indicator of problems with developer time,
temperature, and especially replenishment rate. For
development time that is too long, temperature that is too
high, or overreplenishment, the LD plots will be high. For
time that is too short, temperature that is too low, or
underreplenishment, the LD plots will be low. Check the
developer time and temperature, and adjust them to
specification. The developer time should be 3:05 ± 0:05;
the temperature should be 38 ± 0.2˚C.
If the plots are very out of control, i.e., by more than
0.12 density unit over or under aim, dump and replace all
of the developer tank solution. If the plots are less than
0.12 density over or under aim, you can risk a
prescription.
Prescriptions:
• For high LD plots:
Overreplenishment: Replace a portion of the developer
tank solution (5.2 litres) with one KODAK Negative
Film FC Tank Developer Kit. Check the replenishment
rate setting. Check the output of the developer
replenisher pump and calibrate. Lower the developer
replenishment rate by 10 percent or more if necessary.
• For low LD plots:
Underreplenishment: Replace a portion of the developer
tank (5.2 litres) with one KODAK Negative Film FC
Tank Developer Kit. Check the replenishment rate
setting, and check the pump output of the developer
replenisher pump and calibrate. Increase the developer
replenishment rate by 10 percent or more if necessary.
6 Using the KODAK Negative Film Processing Cartridges FC1 and FC2 • CIS-254
Page 7

D-min (Clear Area of Film):
This parameter may monitor developer, bleach, or fixer
problems. If a developer problem is indicated, see the
HD-LD or LD parameter for confirmation and corrective
action. If a bleach or fixer problem is indicated, see the
corrective action below:
Bleach (Stain):
Developer carryover into the bleach can form a staining
by-product that can elevate D-min, especially the green
D-min. This occurs when the bleach is underreplenished
or under-aerated.
Prescriptions:
• Replace the bleach tank solution with KODAK
Negative Film FC Tank Bleach. Refer to the directions
on page 3.
• Check the bleach aeration to make sure it is working
properly.
• Check the output of the bleach replenishment pump
and calibrate.
• Check the replenishment rate for bleach, and adjust to
the correct rate.
Fixer (Retained Silver Halide):
Retained silver halide is caused by an exhausted fixer
solution due to underreplenishment, dilution, or oxidation.
This is indicated by a high D-min, especially the red
D-min. To confirm retained silver halide, run this test:
1. Immerse the processed control strip in the fixer tank
and soak it for 7 minutes.
2. Remove the strip, rinse it thoroughly with water for
3 minutes, and dry it.
3. Re-read the strip and re-plot D-min. Compare the red
D-min to the earlier plot. If the new plot shows a
difference of at least 0.05 (lower), it confirms a fixer
problem. Replace both fixer tanks with KODAK
Negative Film FC Tank Fixer. Use directions on
page 3. Also, check the output of the fixer replenisher
pump and calibrate. Set the fixer replenishment rate to
the correct value.
If there is no change or less than a 0.05 change, the
fixer is not a problem. See the “Visual Process Control
Guide” for other possible causes.
MANAGING EMPTY CARTRIDGES
In most regions, it should be possible to participate in a
local community recycling program. Check with program
authorities to determine if these packaging materials are
eligible for local recycling. If they are accepted,
disassemble the package and place the bottles and
corrugated material in your recycling bin. Follow all
material preparation instructions from the recycler. See
KODAK Publication No. CIS-148, Recycling KODAK
Photochemical Containers, for more information on
preparing the empty bottles for recycling. CIS-148 and
other publications on waste management are available on
the Kodak website at www.kodak.com/go/KES. If local
recycling is not an option, dispose of the empty bottles
and the package with your normal solid waste.
SILVER RECOVERY
Publications on silver management that include
recommendations and descriptions of silver-recovery
options are available in the Silver Management section of
the Kodak Environmental Services Publications Center at
www.kodak.com/go/KES.
Using the KODAK Negative Film Processing Cartridges FC1 and FC2 • CIS-254 7
Page 8

Figure 2
Process
CN-16S Visual Process Control Guide
.25
D-maxB - Y
B
(+ 0.10 & 0.12)
Bleach
Activity
- retained silver
HD-LD
(+/- 0.07 & 0.09)
Developer
Activity
- concentration
- contamination
- oxidation
- agitation
.20
.15
.10
.05
+
-
.05
.10
.15
.20
.25
.25
.20
.15
.10
.05
+
-
.05
.10
.15
.20
.25
Retained Silver
+ Bleach is dilute or
underreplenished
0
+
Over concentrated, if
0
trend
- Underconcentrated,
if trend
- Oxidized, if trend
- Agitation, if rapid
loss
Relative Height of
R
B
G
arrows is an indicator of
control-strip performance
leading to the cause
indicated in text box
+ Contamination, if sudden
+ Possibly frozen reference
LD
(+/- 0.06 & 0.08)
Developer
Activity
- time/temp
- replenishment
D-min
(+ 0.03 & 0.05)
Developer
- overconcentration
- overreplenishment
Bleach
- stain
.15
.10
.05
+
-
.05
.10
.15
.05
+
-
.05
0
0
DATES
+ Developer
temperature too high
or dev time too long
- Developer
temperature too low
or time too short
+ Weak Fixer,
Developer
contamination
or light fog
+Developer
Replenishment too
high (trend)
- Developer
Replenishment too
low (trend)
+ Developer
overreplenished
or over concentrated
Leuco Cyan Dye
Bleach very
dilute or Fixer
underreplenished
(trend)
+ Bleach stain from
too much Developer
carry-over, no
aeration or
underreplenishment
Fixer Activity
- retained silver halide
F002_1271EC
8 Using the KODAK Negative Film Processing Cartridges FC1 and FC2 • CIS-254
PROCESS:
MACHINE:
EASTMAN KODAK COMPANY, Rochester, NY 14650
Page 9

Process CN-16S
Reference Aims Worksheet
Date: Code:
D-maxb Density Readings
Control Strip Correction Factor
Corrected D-max
Yellowb Density Reading
Red Green Blue
Control Strip Correction Factor
Corrected Yellowb
AIM
b-Yb
D-max
HD Density Readings
Control Strip Correction Factors
Corrected HD
LD Density Readings
Control Strip Correction Factors
AIM
LD
AIM
HD-LD
D-min Density Readings
Control Strip Correction Factors
AIM
D-min
Using the KODAK Negative Film Processing Cartridges FC1 and FC2 • CIS-254 9
Page 10

Note: The contents of this publication are subject to change. To be sure you have the
most up-to-date publication, check www.kodak.com/go/photochemicals; select
Technical Information to find Current Information Summaries.
EASTMAN KODAK COMPANY • ROCHESTER, NY 14650
Using KODAK Negative Film Processing
Cartridges FC1 and FC2
KODAK Publication No. CIS-254 Kodak is a trademark.
Digital & Film Imaging Systems
Minor Revision 5-05
 Loading...
Loading...