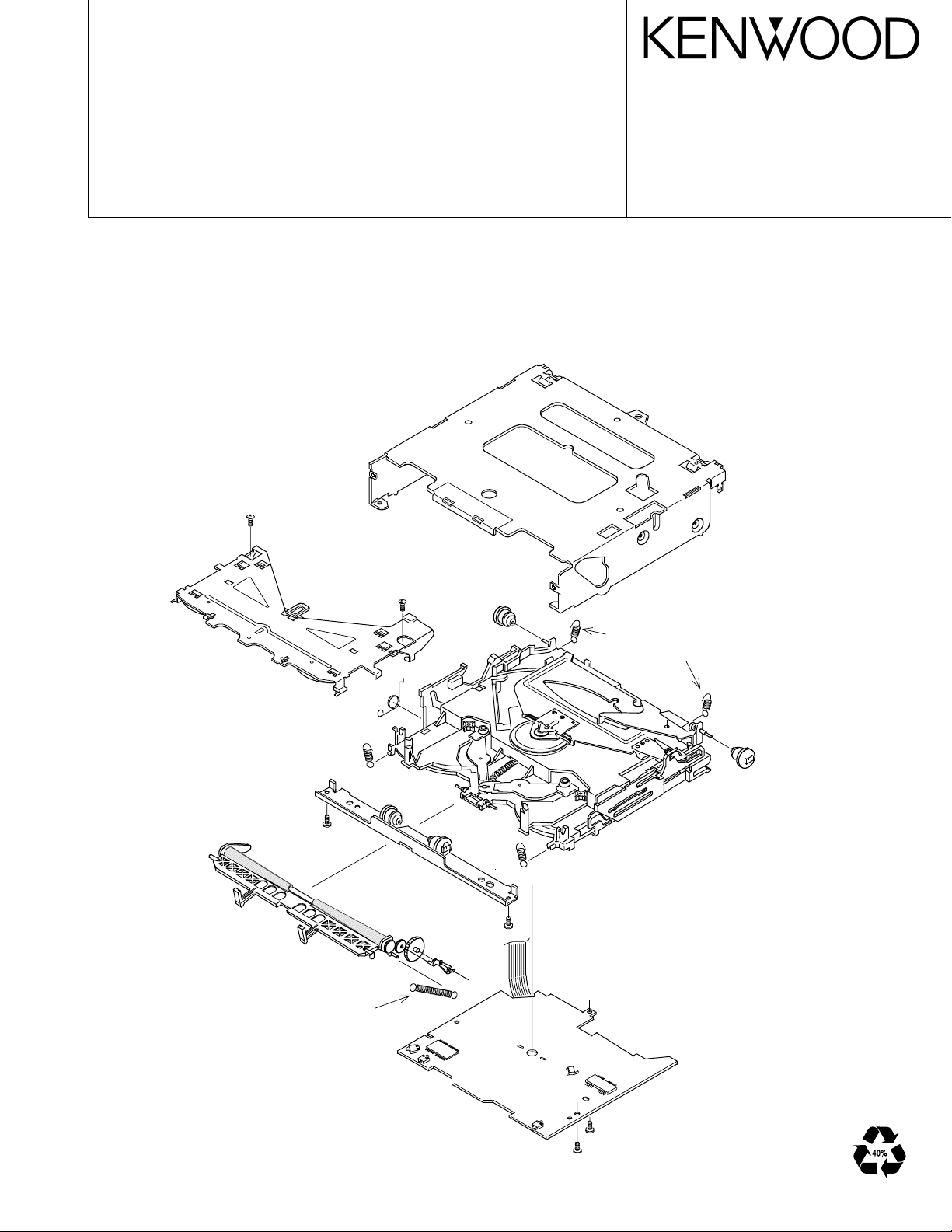
CD MECHANISM ASSY
X92-4470-0x
SERVICE MANUAL
DESCRIPTION MECHANISM
X92-4470-00 (DXM-6500W)
X92-4470-01 (DXM-6501W)
X92-4470-02 (DXM-6502W)
X92-4470-03 (DXM-6503W)
CONSTRUCTION OF MAJOR PARTS
© 2002-1 PRINTED IN JAPAN
B51-7899-00 (N) 3412
outer-chassis
disc guide assy
damper bracket
roller lever assy
dumper (X4)
floating spring (X4)
traverse chassis assy
roller spring
Mecha PCB
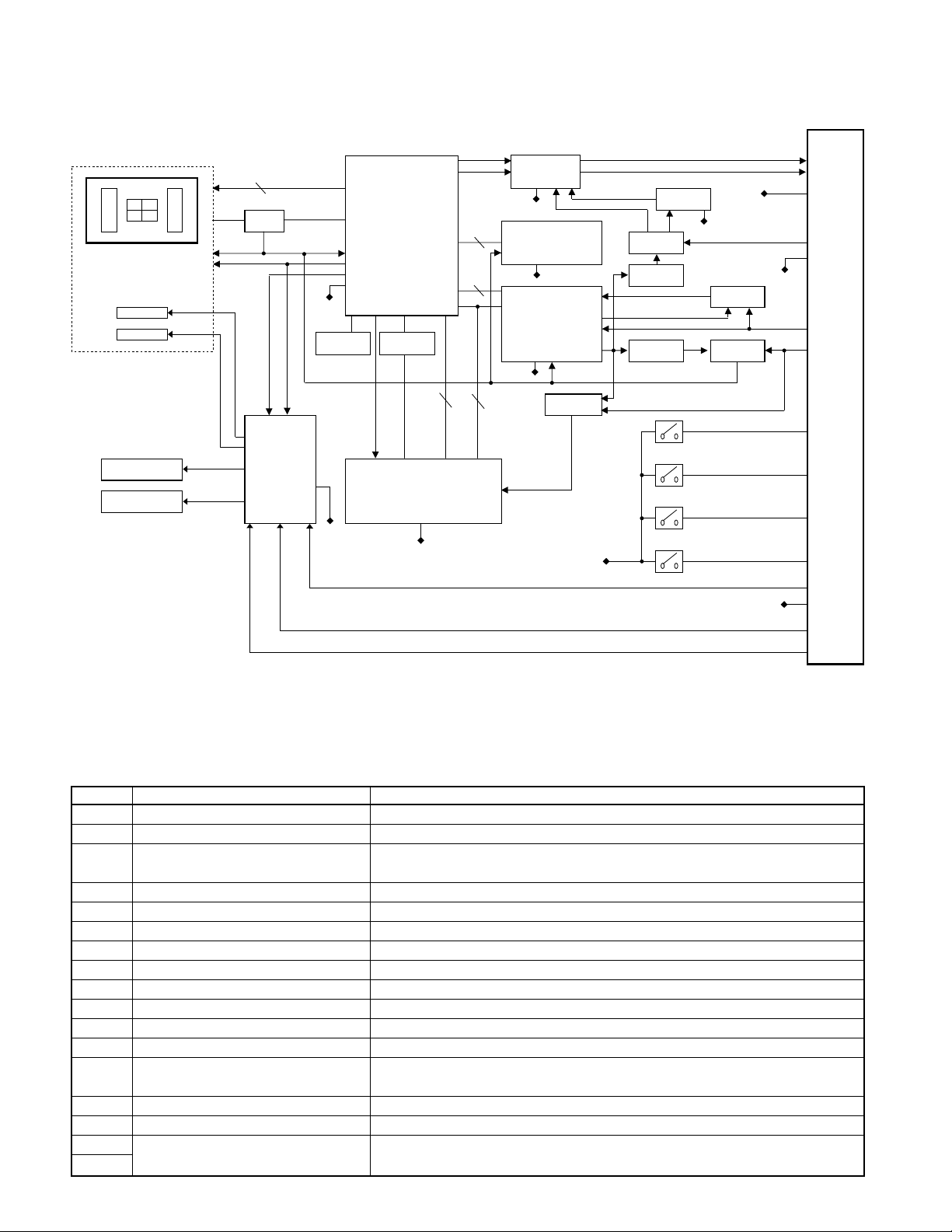
X92-4470-0x
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Pick-Up
B
A
E
C
D
Tr Coil
Fo Coil
Spindle Motor
Loading & Sled
Motor
A.GND
SW
0-01 Only
Mother Board
R-ch
L-ch
A.GND
A.+8V
D.GND
Bu.+5V
D4.7VD3.3VReg
Loe/Lim SW
8Eje SW
12Eje SW
S7.5V
S.GND
IC10
7
F
Q2
APC
IC4
Motor Driver
D.GND
X2
Clock
16.93MHz
16.93MHz
S.GND
1Chip IC
Servo Processor
RF Amp
MP3 Decorder
Vref
IC8
+
+
X3
Clock
24.57MHz
WMA Decorder
D.GND
9
IC12
LPF
A.GND
IC11
30
9
16
DRAM
D.GND
IC5 Q1 D.GND
/PON
µ-Com
D.GND
IC3
2.5V Reg
D.GND Los SW
IC6
A3.3 Reg
Q4
8V SW
Q5
SW
SW5V
Q3 IC2
SWPON
S3
S4
S2
S1
COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION
●CD PLAYER UNIT (X32-5220-0x)
Ref.No. Application/Function Operation/Condition/Compatibility
IC2 D3.3V AVR Power supply for the pickup, IC5, IC8-10 and IC11
IC3 D2.5V AVR Power supply for IC8
IC4 4CH BTL driver
IC5 Mecha. control MI-COM.
IC6 A3.3V AVR Power supply for DAC, LPF operational reference voltage
IC7 Level shifting (3.3V→5V) Buffer and logic level conversion from IC10 to IC5
IC8 WMA decoder
IC9 Clock buffer for WMA
IC10 RF amplifier+CD DSP+MP3 decoder
IC11 4M bit DRAM For data buffer
IC12 Low pass filter 2nd low pass filter for audio signals
IC13 Schmitt trigger for WMA
Q1 SW5V SW
Q2 APC LD power control
Q3 D3.3V SW When PON (10pin) goes Hi, Q3 is turned on, and IC2 is working.
Q4
Q5 and IC12.
A.8V SW
Focusing coil, tracking coil, spindle motor and sled motor driv er, disc loading and
eject operation.
When PON (11pin) goes Lo, Q1 is turned on, and SW5V is supplied to IC7 and
AVREF (73PIN).
When PON (10pin) goes Hi, Q4 and Q5 are turned on, and A.8V is supplied to IC6
Lo/Ej
Motor
2
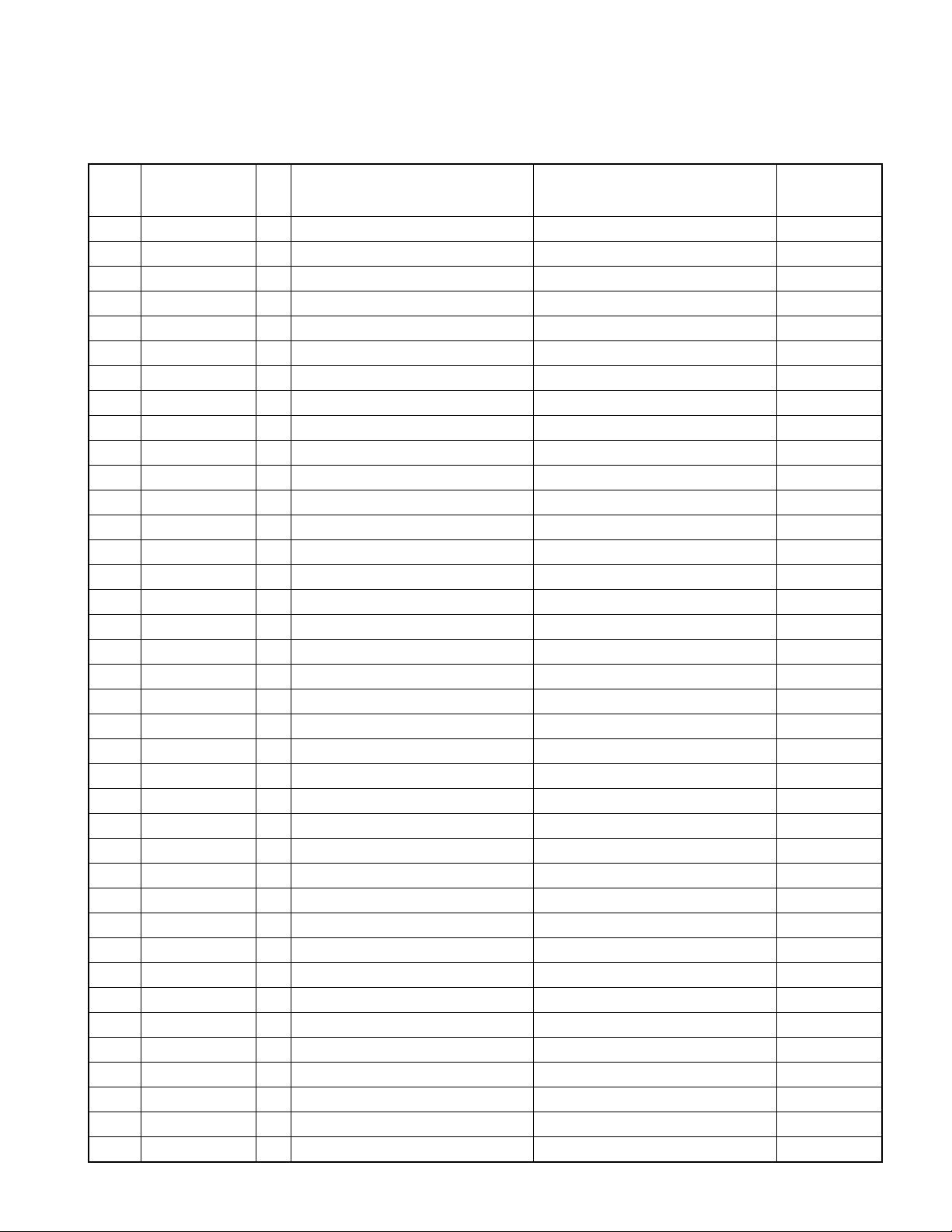
X92-4470-0x
MICROCOMPUTER’S TERMINAL DESCRIPTION
MECHANISM MICROCOMPUTER (IC5 : X32)
processing
Pin Name I/O Purpose Processing operation description description in
STBY
1~5 NC O Not use Low fixation Low
6 VDD - 5V potential
7 GND - GND potential
8,9 NC O Not use Low fixation Low
10 PON O Power ON/OFF control H : ON L : OFF Low
11 /PON O Power ON/OFF control H : OFF L : ON High
12 LOE/LIM_SW I Down limit SW detection L : inside circumference detection Hi-Z
13 8EjE_SW I Not use Low fixation Hi-Z
14 LOS_SW I Not use Low fixation Hi-Z
15 12EjE_SW I Not use Low fixation Hi-Z
16,17 NC O Not use Low fixation Low
18 IC/Vpp - Writing voltage (FLUSH) 19 MUTE_L O Lch audio mute control L : mute ON H : mute OFF Low
20 MUTE_R O Rch audio mute control L : mute ON H : mute OFF Low
21~25 NC O Not use Low fixation Low
26 EFLG I WMA error detection H : error L : not error Out-Low
27 WAIT I Weight control signal detection Out-Low
28 FOK I Focus condition detection H : Focus OK L : Focus NG Out-Low
29,30 NC O Not use Low fixation Low
31 RESET I Reset detection H : normal L : reset Hi-Z
32 XT1 I Not use Hi-Z
33 XT2 - Not use 34 REGC 35 X2 36 X1 I Hi-Z
37 Vss - GND potential
38 VDD - 5V potential
39 NC O NC Output stop Low
40 WRL O Multiplexer WRITE signal _LBEN : 61002 (not use) _WRL : 63760 Out-Low
41 NC O Not use Low fixation Low
42 R/W O Multiplexer _R/W signal _R/W : 61002 _WRH : 63760 (not use) Out-Low
43 DSTB,RD O Multiplexer DSTB or RD signal _DSTB : 61002 _RD : 63760 Out-Low
44 ASTB O Multiplexer ASTB signal Out-Low
45,46 NC O Not use Low fixation Low
47~54 AD0~7 I/O Multiplexer address/data Out-Low
55 BVdd - Power supply for bus inter face
56 BVss - GND for bus inter face
57~64 AD8~15 I/O Multiplexer data/address Out-Low
3
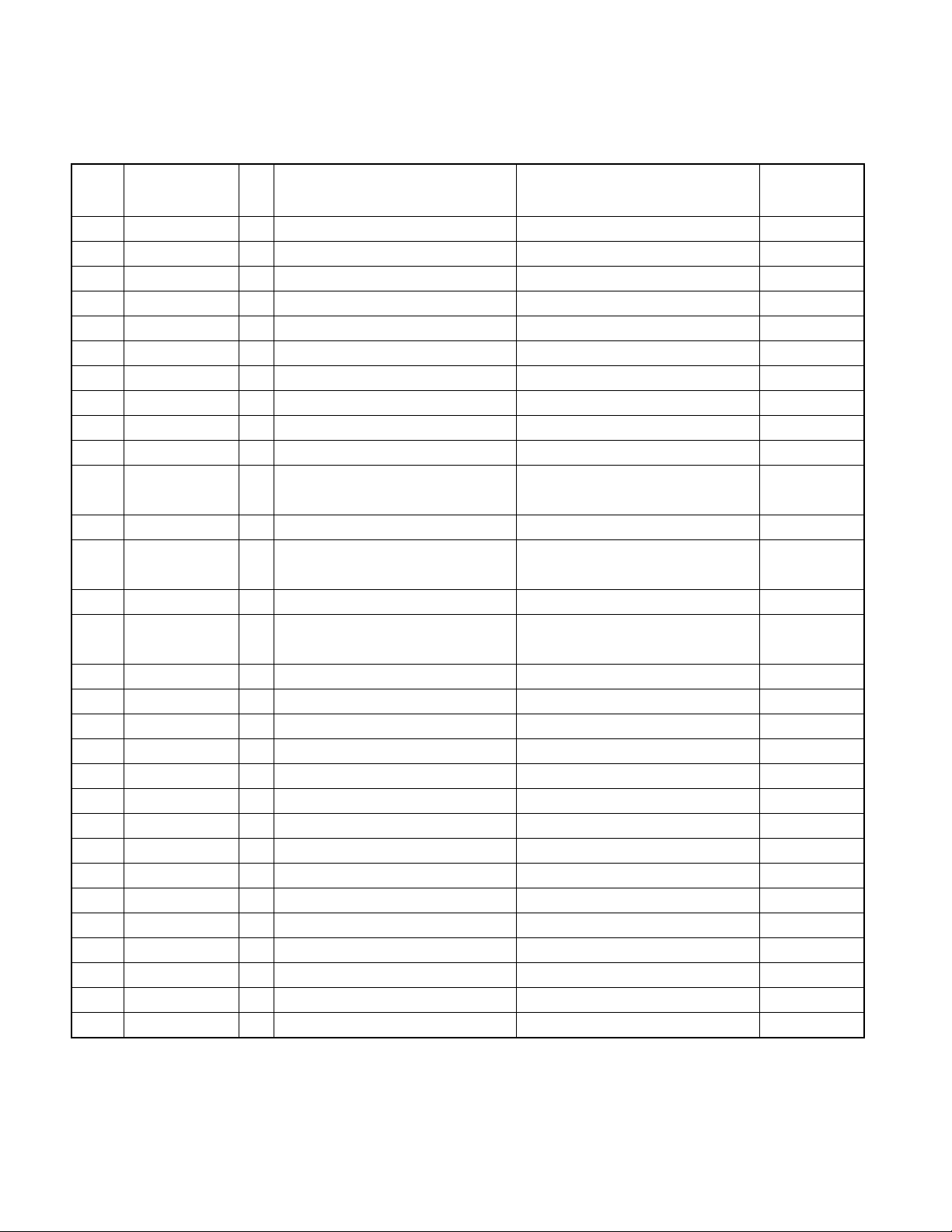
X92-4470-0x
MICROCOMPUTER’S TERMINAL DESCRIPTION
Pin Name I/O Purpose Processing operation description description in
65 /HCSB O Chip selection control H : OFF L : ON Low
66 /CS O Chip selection control H : OFF L : ON Low
67 DSP RESET O DSP reset control H : normal L : reset Low
68 REQ I data transmit request input Hi-Z
69 DBBWRDY0 I DBB00 register writing permit input Hi-Z
70 DBBRRDY0 I DBB00 register reading permit input Hi-Z
71 Avdd 72 Avss 73 Avref I A/D port standard voltage input
74~77 NC I Not use Low fixation Hi-Z
78 HOT I temperature shift detection
79 M-CONT I Not use Low fixation Hi-Z
80 WMA I WMA correspondence switching
81 NC I Not use Hi-Z
82 ASEL I Audio output polarity switching
83 DASC I Shock proof specification switching H : shock proof ON L : shock proof OFF Hi-Z
84 TEST2 I Test terminal 2 Hi-Z
85 TEST3 I Test terminal 3 Hi-Z
86 NC O Not use Low fixation Low
87 MSTOP I Standby return interrupt H : stop cancel L : stop Hi-Z (Low input)
88 INTSV I Interrupt from servo IC H : interrupt Hi-Z
89 FOGUP I Focus gain up interrupt H : Fo gain up L : normal Hi-Z
90 ZMUTE_R I 0bit mute detection H : mute ON L : mute OFF Hi-Z
91 ZMUTE_L I 0bit mute detection H : mute ON L : mute OFF Hi-Z
92 NC O Not use Low fixation Low
93 D-MUTE O Mute driver H : OFF L : ON Low
94 SYS_SDA I/O system microcomputer 12C data Hi-Z
95 NC O Not use Low fixation Low
96 SYS_SCL I/O system microcomputer 12C clock Hi-Z
97~100 NC O Not use Low fixation Low
Detection voltage 4V cancel
voltage 3.9V
H : DXM-6500 (correspond to WMA)
L : DXM-6400 (Don't correspond to WMA)
H : turning-over output
L : non- turning-over output
processing
STBY
Hi-Z
Hi-Z
Hi-Z
4
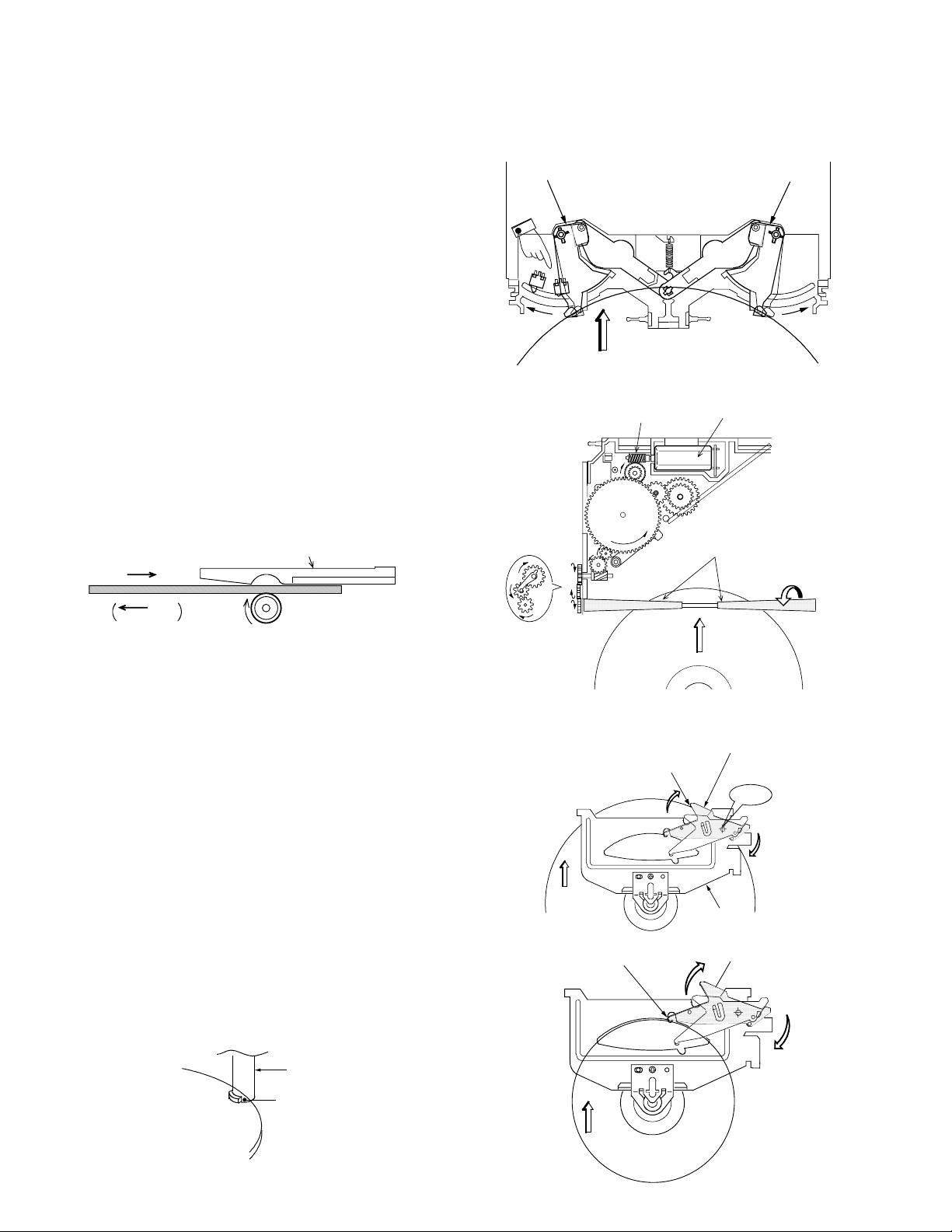
OPERATION DESCRIPTION
Center
of rotation
X92-4470-0x
[1] Disc Loading
(1) Turning the loading switch ON
1)When a disc is inserted, the disc arms open to the left and
right and the claw below disc arm (L) sets the loading switch
ON.
2)The above starts the motor rotation.
(2) Loading the disc
1) When the motor starts rotation, the worm gear also starts
to turn as shown in the figure.
2) The rotation force is transmitted to the gear train.
3)When the force is transmitted to the final gear, the rollers
rotate to pull in the disc.
Disc guide
Disc IN
Disc
Switch ON!
Disc arm(L) Disc arm(R)
Disc
Worm gear
Motor
Rubber rollers
Disc OUT
The disc is pulled in or out when the rollers are pushed against
the disc guide.
Roller
[2] Operation of Slider (R)
(1) Activating the trigger arm
1) When the disc is pulled in by the rollers, the disc edge pushes
the trigger arm and rotates it.
2)When the disc is an 8cm disc, it is pulled upwards by the
tapering on the disc guide. The trigger arm is rotated when
the disc pushes the claw (section A) located before the trigger arm.
When the 8cm disc reaches the loading end position, the roller
areas supporting the disc decreases. To prevent the disc from
dropping in this case, the claw is provided with a projection f or
supporting the disc.
Claw (A)
Projection
Side view
Position pushed by the disc
Disc IN
Trigger arm
Clamper chassis
A
Trigger arm
Disc
8cm Disc
5
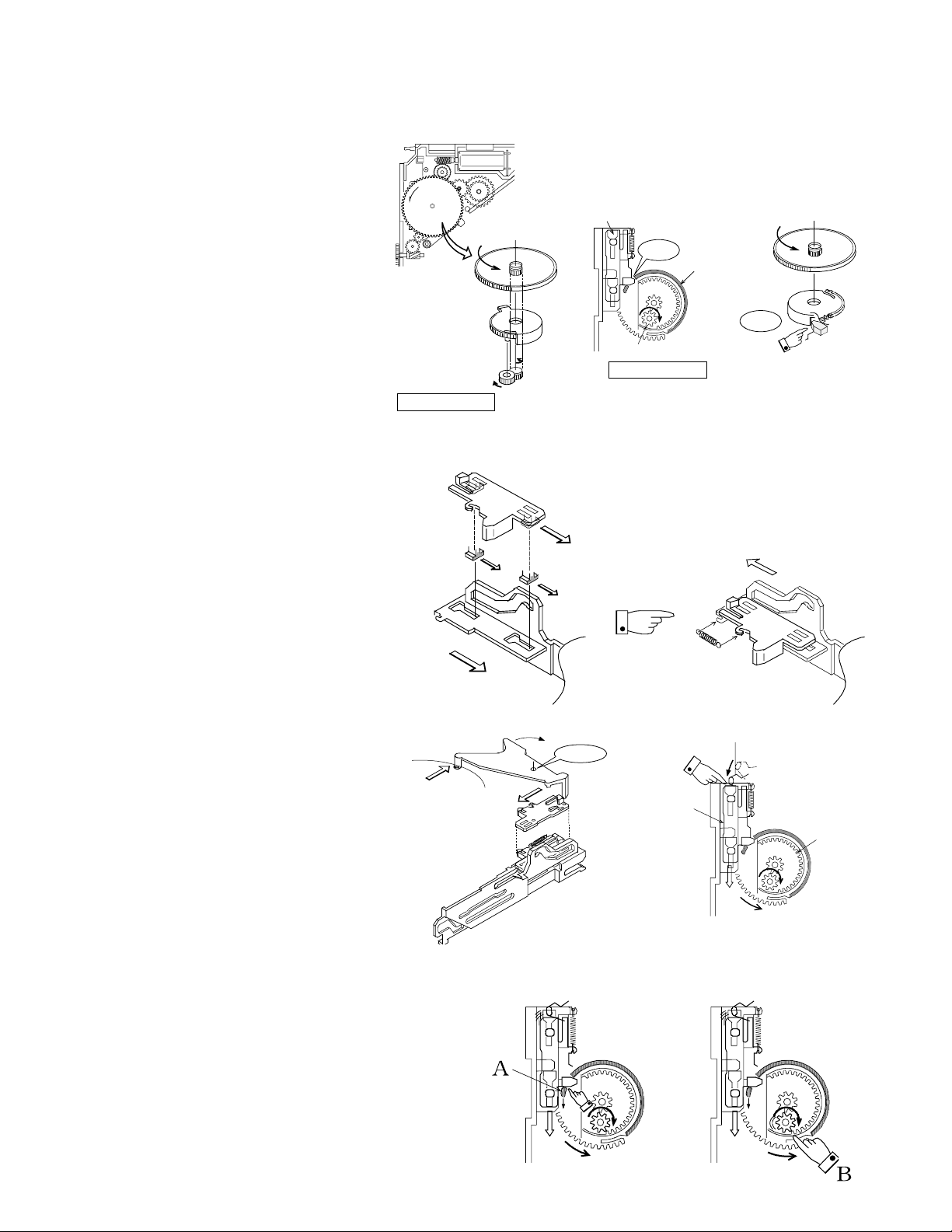
X92-4470-0x
Locked
Locked
Center
of rotation
(2)Basic construction (Initial position
of the planetary gear mechanism)
1)Even after the disc has been inserted, the
motor rotated and the gear train also rotated,
slider (R) does not start operation yet.This
is because the planetary gear mechanism
is used and the carrier gear is locked by the
slider mechanism. In this period, the planetary gear is in the loose condition.
2) When the sun gear is rotating and the carrier gear is locked, the planetary gear is running idle.
OPERATION DESCRIPTION
Slider (R)
Sun gear
Carrier
gear
Planetary gear
Planetary gear
Loose condition
Loose condition
Carrier gear's rib
(3) Basic construction (Construction of
the trigger slider and slider (R))
The trigger slider is assembled with slider (R)
and pushed in the direction of the arrow by
the force of a spring.
(4) Operation of slider (R)
1) Activating the trigger slider
When the trigger arm is rotated by the pressure of the disc, the trigger arm pushes the
trigger slider.
Slider (R)
Tigger arm
Disc
Trigger slider
Trigger slider
Trigger slider
Spring
Trigger arm
Gear teeth
on the traverse
chassis
Carrier gear
2) Rotating (engaging) the planetary gear
When the trigger slider is moved, it pushes down the wall
(section A) of the carrier gear. (Initial rotation of the carrier
gear)
This causes the planetary gear, which is attached on a pin
of the carrier gear, to move according to the rotation of the
carrier gear. When the planetary gear is meshed with a gear
tooth (section B) of the traverse chassis , the planetary gear
starts rotation.
The rotation of the planetary gears causes the carrier gear
to rotate.
6
 Loading...
Loading...