Page 1

Page 2

You are the owner of our latest
This unit has been carefully engineered and manufactured to rigid quality Standards,
and should give you satisfactory and dependable Operation for many years.
We suggest that you read this instruction manual carefully from cover to cover to insure
the maximum Performance and trouble-free Operation of your new model TS-780.
Save the shipping box and
remote Operation, maintenance, or Service.
product
packing
the new TS-780 Duo Band Transceiver.
in the event your unit needs to be transported for
CONTENTS
SPECIFICATIONS
1. FEATURES ................................................................................................
2. BEFORE USING
3. CONTROLS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
4. PRELIMINARY..
OPERATING
5.
6. OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES
7.
TROUBLESHOOTING
BLOCK DIAGRAM.. ..........................................................................................
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
§
BOTTOM INTERNAL VIEWS.....................................................................
TOP
.............................................................................................
..........................................................................................
.............................................................
..........................................................................................
INSTRUCTIONS
.................................................................................
.................................................................................... .24
.......................................................................
.......................................................................... .2
2
3
4
5
9
.1 1
1
.22
.23
.27
Page 3
i
I
;
~-RH*n,,c,--,~~,~,,-,“~,~,,“,~,“~,”~,,,,,-”--”,“~-,“~,~,,.,~,,~,~~~--~~~-,“~~,.,“,,““,,,-‘”H(*~
TS-780 SPECIFICATIONS
i
:
i
GENERAL
Frequency Range.. .....................................
Mode ........................................................ SSB (USB, LSB), CW, FM
Antenna impedance ..................................
Voltage Requirements ................................
Power Consumption
Backup current (Battery)
Semiconductor Complement.. ..................... ..Transistors:
Dimensions.. .............................................
Weight.. ................................................... .lO.l kg (22.2
.................................... Receive (no Signal): 45 Watts (220 V AC), 1.2 A (13.8 V DC)
............................
.144.0~
430.0 ~ 440.0 MHz
..5 0 9 (144 MHz, 430 MHz)
..22 0 V AC,
13.8 V
Transmit: 130 Watts (220 V AC), 5 A (1 3.8 V DC)
..Les s than 10
FETs: 35
ICs:
Diodes: 195
.290
(1 1
146.0 MHz
50/60.
Hz
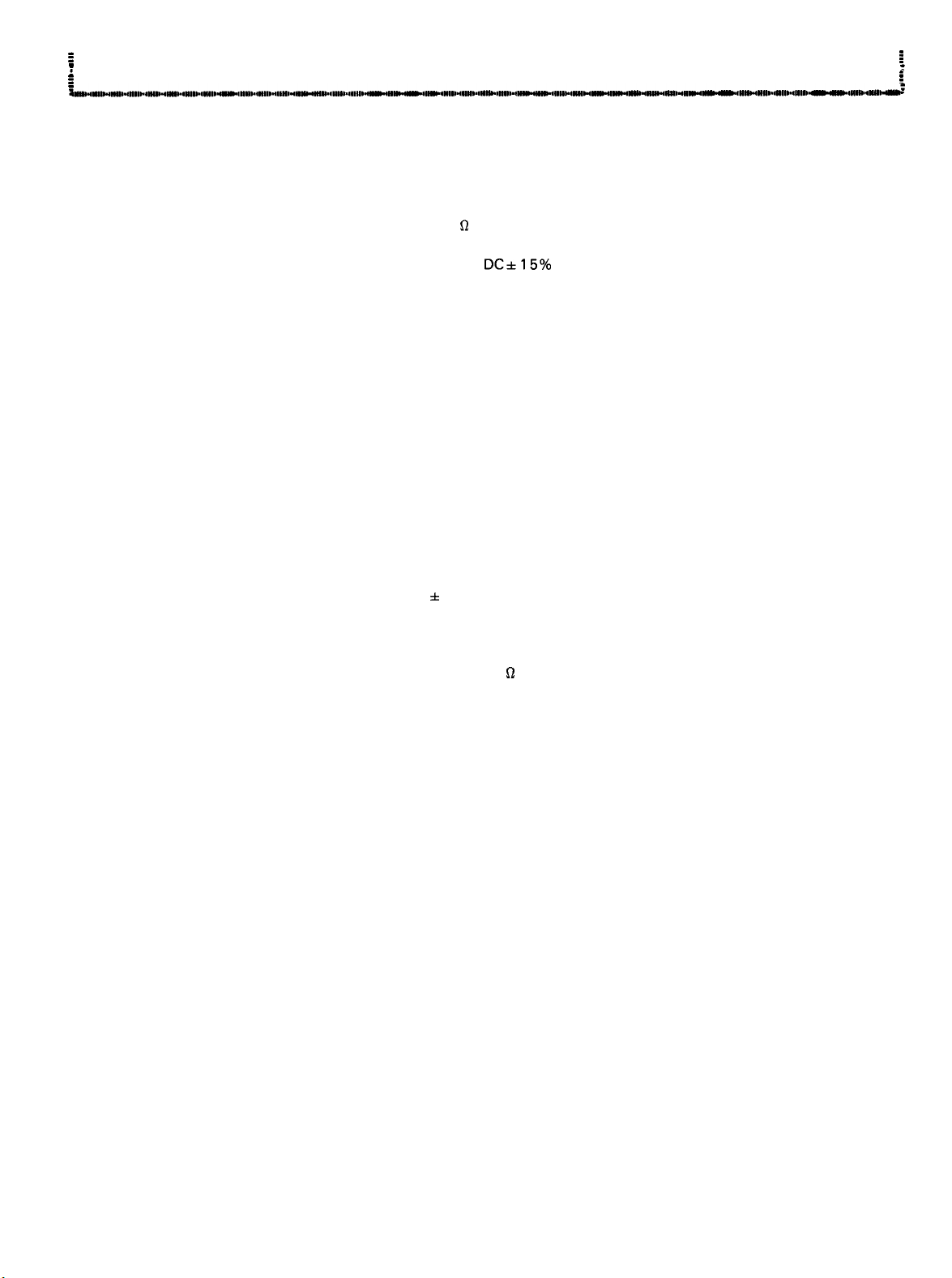
DC&l5%
yA
149
41
(W) x 124 (H) x 322 (D) mm
“-7/16)x (4”.7/8)x (12”-5/8)
Ibs)
TRANSMITTER SECTION
RF Power Output
Modulation ............................................... .SSB:
Maximum frequency deviation (FM) ...............f 5 kHz
Carrier Suppression ..................................... Better than 40 dB
Unwanted Sideband Suppression .................. .Better than 40 dB
Spurious Radiation .................................... ..Bette r than- 60 dB
Microphone
AF Response of Transmitter (SSB)
Repeater Frequency Shift-............................. 600 kHz or + 600 kHz
RPT Tone Frequency
........................................
Impedance
...............................
...................................1 7 50 Hz
................
SSB, CW, FM: 10 Watts
FM (LOW): Approx. 1 watt
Balanced modulation
FM: Variable reactance frequency shift
,500 ~
600
Q
.400~
2600 Hz (- 9 dB)
(144.0~
-7.6 MHz or - 1.6 MHz (430.0-440.0 MHz)
146.0 MHz)
RECEIVER SECTION
Receiver
Intermediate Frequency .............................. .l st: 30.865 MHz
Squelch Sensitivity.. ...................................
Audio Output ............................................
Receiver
Circuit and ratings are subject to Change without notice for improvement.
Sensitivity
Selectivity
....................................
.................................... .SSB, CW: 2.2 kHz (-6 dB)
.SSB, CW:
FM: 1 yV for 30 dB (S + N)/N
2nd: 10.695 MHz
3rd: 455 kHz (FM only)
.O. 1
6 yV (At threshold)
.2.0
Watts (with less than
FM: 14 kHz (-6 dB)
0.2 yV for 10 dB (S + N)/N
0.2 yV for 12 dB SINAD
4.8 kHz
30 kHz (- 60 dB)
10% distortion) into an 8 ohm load
(-60
dB)
2
Page 4

SECTION 1. FEATURES
1. 144/430
transceiver.
0 8 bit microprocessor controlled VFO and full variety of
auxiliary functions.
0 FM circuitry based on KENWOOD’s advanced
technology and outstanding SSB quality.
0 Buit-in VOX.
0 Buit-in side tone and CW circuitry capable of semi-
break-in Operation.
0 Adoption of power module in the transmitter final Stage
for dependable Operation on both bands.
2. Built-in digital display that indicates operating frequency
in all modes.
0 Digital display equipped with easy-to-read green
Phosphor tubes.
0 7-digit digital display that directly reads down to
100 Hz.
0 Frequency indicator that reads out carrier positions
when mode of Operation is changed.
0 Two VFO’s (A and BI are built into the transmitter for
more enjoyable Operation such as “Cross-frequency”
Operation.
0 Buit-in 1 0-channel memory circuit stores operating fre-
quencies and bands. Two channels (CH9 and CH10)
can be called out by using CALL channel switch.
0 Easy-to-read display indicated 2 VFO’s ( R, b ), memory
channels ( 1
0 Display function that clears frequency below 1 kHz in
FM-CH.
3. Dependable electrical and mechanical functions
0 VFO frequencies are switchable in 2 Speeds, SLOW (in
12.5 kHz, FM-CH) and FAST (in 5 kHz, FM-CH).
0 VFO knob equipped with variable torque mechanism.
0 Pushbutton band select switched (UP and DOWN) that
shift up and shift down frequency between 144 MHz
and 440 MHz in 12 bands at 1 MHz intervals.
0 Wide band design for both transmitter and receiver that
eliminates the need for tuning the RF circuits.
0 Panel layout based on human engineering.
0 Full variety of indicating functions to check operating
conditions (OFFSET, ON AIR, BUSY, F.LOCK, RIT,
F.STEP).
0 Amplified type AGC and ALC circuits that maintain
receive and transmit Outputs at constant
distortion.
MHz, all mode (FM, SSB (USB, LSB), CW)
-~8 )
and priority channels ( c and c
level
)
without
4. A multitude of auxiliary functions for more enjoyable
Operation.
0 The use of RAM memory System enables any given fre-
quencies to be stored in or cleared. (IO memory chan-
nels).
0 Built-in back-up battery holder to keep data stored at all
times.
0 Built-in memory
and 430 MHz.
0 RIT circuit function on VFO, memory channels and
priority channels.
0 Adoption of frequency lock circuit.
0 A repeater shift circuit is provided, and the shift width
on the 144 MHz band is - 600 kHz or + 600 kHz, and
that on the 430 MHz band is - 7.6 MHz or - 1.6 MHz,
which may be selected as required. The tone frequency
is 1,750 kHz. In the event of off band, the digital
display goes out and transmission is halted.
0 KENWOOD’s unique noise blanker (NB) circuit to
eliminate pulse type noise.
0 Four-function meter serves as S meter, RF meter, ALC
meter and Center meter.
0 RF power HIGH/LOW selecting function provides conve-
nience in transmission with
0 Auxiliary (AUX) socket.
5. Designed for fixed and mobile Station Services.
0 ACIDC 2-way power Operation.
0 Equipped with a grip for carrying convenience.
0 Sufficient AF output power (2.5
0 Built-in large sized speaker (7.5 cm). External speaker
connecting
jack.
scan
for selection between 144 MHz
local
stations in FM.
W/4
9).
3
Page 5
2-l. ACCESSORIES
The following accessory items are included with the
unit.
Instruction manual ......................... .l copy
Fuse 2A (AC)
............................... .2 pieces
2-2. OPERATING LOCATION
As with any solid state equipment, the TS-780 should
be kept from extremes of heat and humidity. Choose an
operating location that is dry and cool, and avoid operating
the unit in direct sunlight.
7A (DC) ............................... .2 pieces
Foot (with screws) ......................... .2 pieces
Speaker plug ................................. .l piece
DIN
plug
....................................... .l piece
AC power cord
DC power cord
.............................. .l piece
.............................. .l piece
Microphone .................................. .l piece
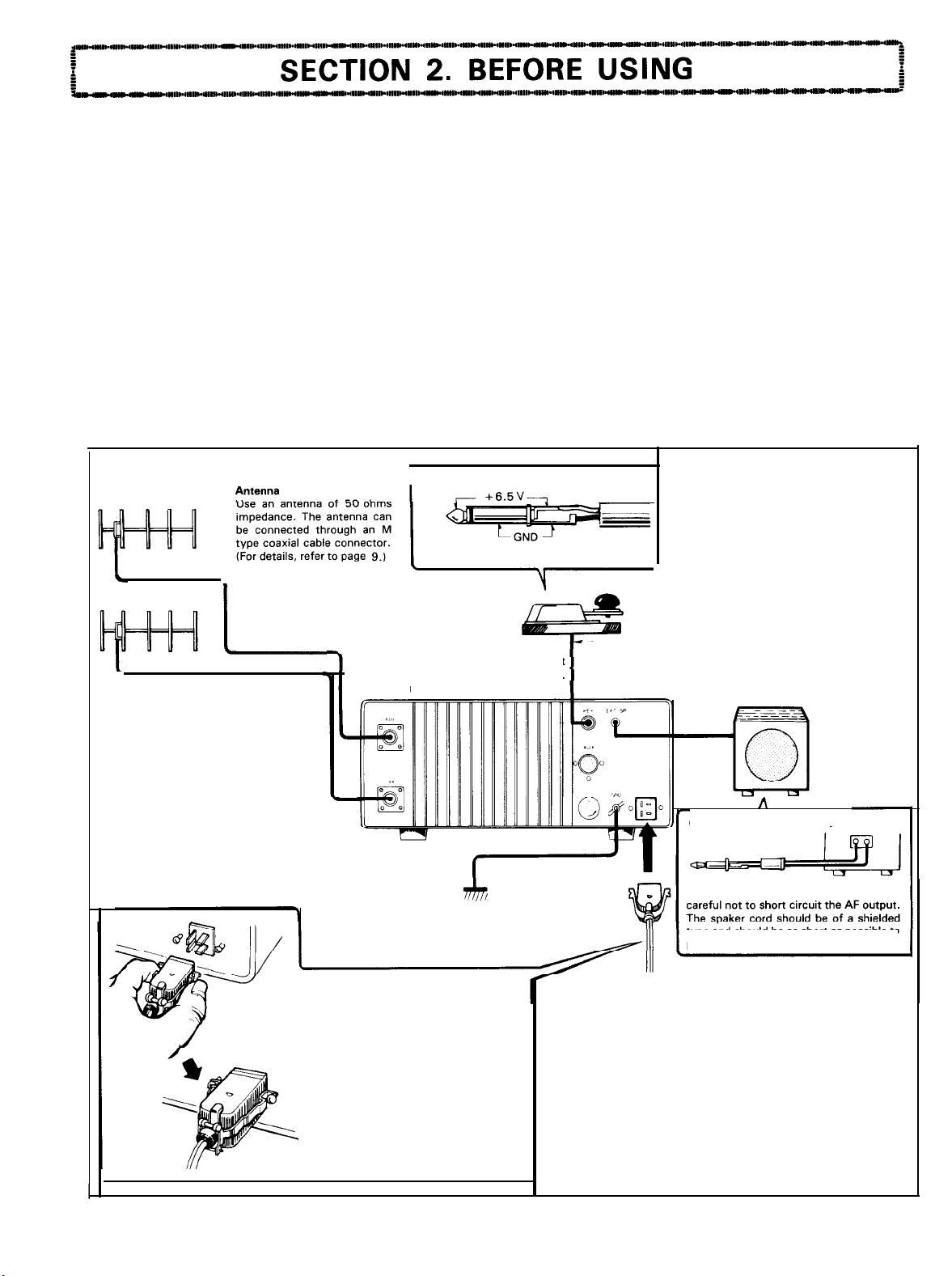
2-3. CABLING FOR ANTENNA, POWER SUPPLY AND OTHERS
430 MHz
144 MHz
I
Check for correct
Connection of electric key
L-
.
Key
For CW Operation, connect
the key through a phone plug.
Use shielded cable.
polarity
Extemal speaker
A speaker is included in the unit. If you
wish to use an extemal speaker, connect
it by using the supplied speaker plug. A
communication-use (lowlhigh cut typel
speaker rated at 4-B ohms is recommended. The Option speaker (SP-71) is
designed to perfectly match the characteristics of the TS-780. Plugging in an
external
speaker will automatically
disconnect the built-in speaker. DO not
connect the speaker to the PHONES jack,
as this jack has a level adjusting resistor.
1
Ground
To prevent electric shock, TVI and BCI,
select a good grounding location: Connect the unit to the ground using a heavy
earth
line
and an appropriate earthing rod.
The earth
ble
line
should be as short as possi-
Power supply connection
The power cord has a 4P
ing tab. When connecting the
squeeze the locking tab to ensure that it
properly fits in place. To disconnect the
Cord, squeeze the locking tab again until
if is released from the locked Position.
plug
with a lock-
Cord,
Extemal speaker
SP-71
A
Connection of speaker plug
When connecting an extemal speaker, be
type and should be as short as possible to
prevent RF from being induced.
Power supply
The unit is designed to operate on AC
ching between AC and DC is accomplished by replacing the power cord
(DC power cord is optional.) When connecting the power
to observe the following Points:
1. Turn off the power switch and set the standby switch to REC position.
2. When replacing the power
(or
battery) with care.
Failure to observe the above procedure might result in electric shock or
darnage to the
unit.
Cord,
(220
V) or DC (13.8 V). Swit-
Cord,
be sure
disconnect it from the AC supply
Page 6
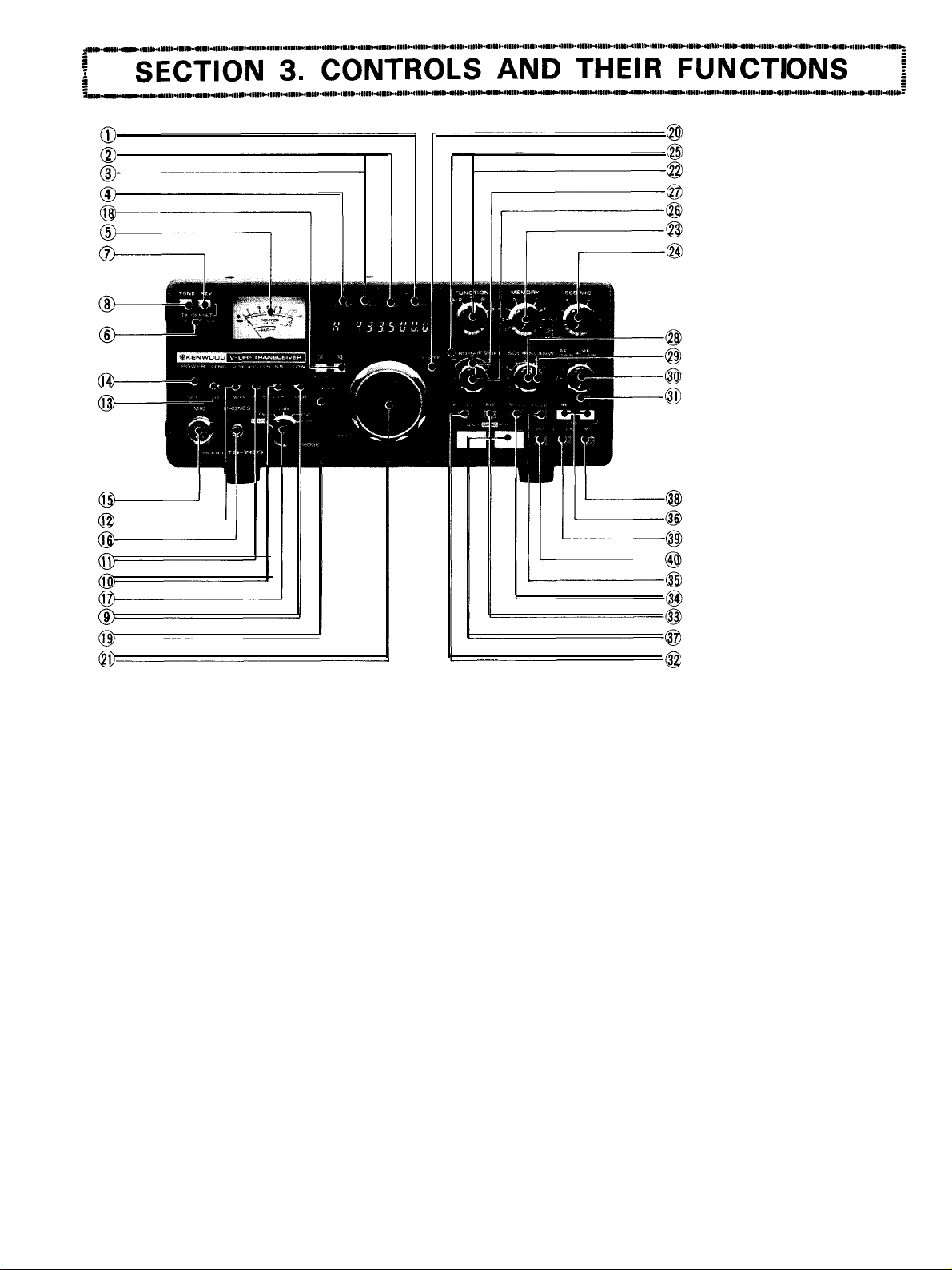
F. LOCK Indicator
2
BUSY Indicator
3
ON AIR Indicator
4
OFFSET Indicator
5
Meter
6
TX-OFFSET Switch
7
REV (Reverse) Switch
8
TONE Switch
9
LOW POWER Switch
NB
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
(noise
Meter Switch
VOX Switch
Standby Switch
POWER Switch
MIC Connector
PHONES Jack
MODE Switch
PRIO.
TIGHT Level
F. STEP Indicator
Tuning Knob
FUNCTION Switch
MEMORY Selector
SSB MIC
RIT Indicator
RIT Control
IF SHIFT Knob
SQUELCH Control
SCAN-W
AF GAIN Control
RF GAIN Control
F. STEP Switch
RIT Switch
SCAN Switch
HOLD
M. S Switch
BAND Switch
M (Memory) Switch
F. LOCK Switch
M.
Switch
blanker) Switch
M Switch
R
(Memory
Recall)
3-l. FRONT PANEL
1
F. LOCK Indicator
This indicator will light when the LOCK switch is turned ON
(VFO frequency is locked).
2 BUSY Indicator
This indicator lights when the squelch is open in FM or.FM-
CH receive mode, allowing the Operator to check whether
the other Station is transmitting.
3 ON AIR Indicator
This indicator will light during transmission.
4 OFFSET Indicator
This indicator lights when the TX OFFSET switch is set to
the D - A or D - B Position for repeater Operation.
5 Meter
This meter has four functions,
the meter select switch.
RFIS:
The meter serves as “S” meter indicating the
strength of received
from 1 to 10 (FM), or 1 to 9,
9+40
dB (SSB
each
being selected by using
Signal
on a scale graduated
9+20
CW).
dB and
During transmission, the meter indicates RF
output.
ALC/CEN: In FM receive mode (MODE switch in FM, FM-
CH position), the meter functions as a Center
meter. Turn the VFO knob to your desired
receive
Signal
until the meter pointer is
centered.
In other operating mode (SSB,
CW),
the meter
indicates the transmitter ALC voltage. In SSB
Operation, adjust the MIC gain control so that
the meter pointer deflects within the ALC zone
on the scale. In CW Operation,
adjust
the CAR.
L knob.
6 TX-OFFSET Switch
This switch is used to shift the TX frequency from the RX
frequency for repeater Operation. After the repeater operation, it should be set to the SIMP Position; the TX frequency will coincide with the RX frequency. In case of Off-band,
the frequency is not shifted and the transceiver is set in
simplex mode.
5
Page 7
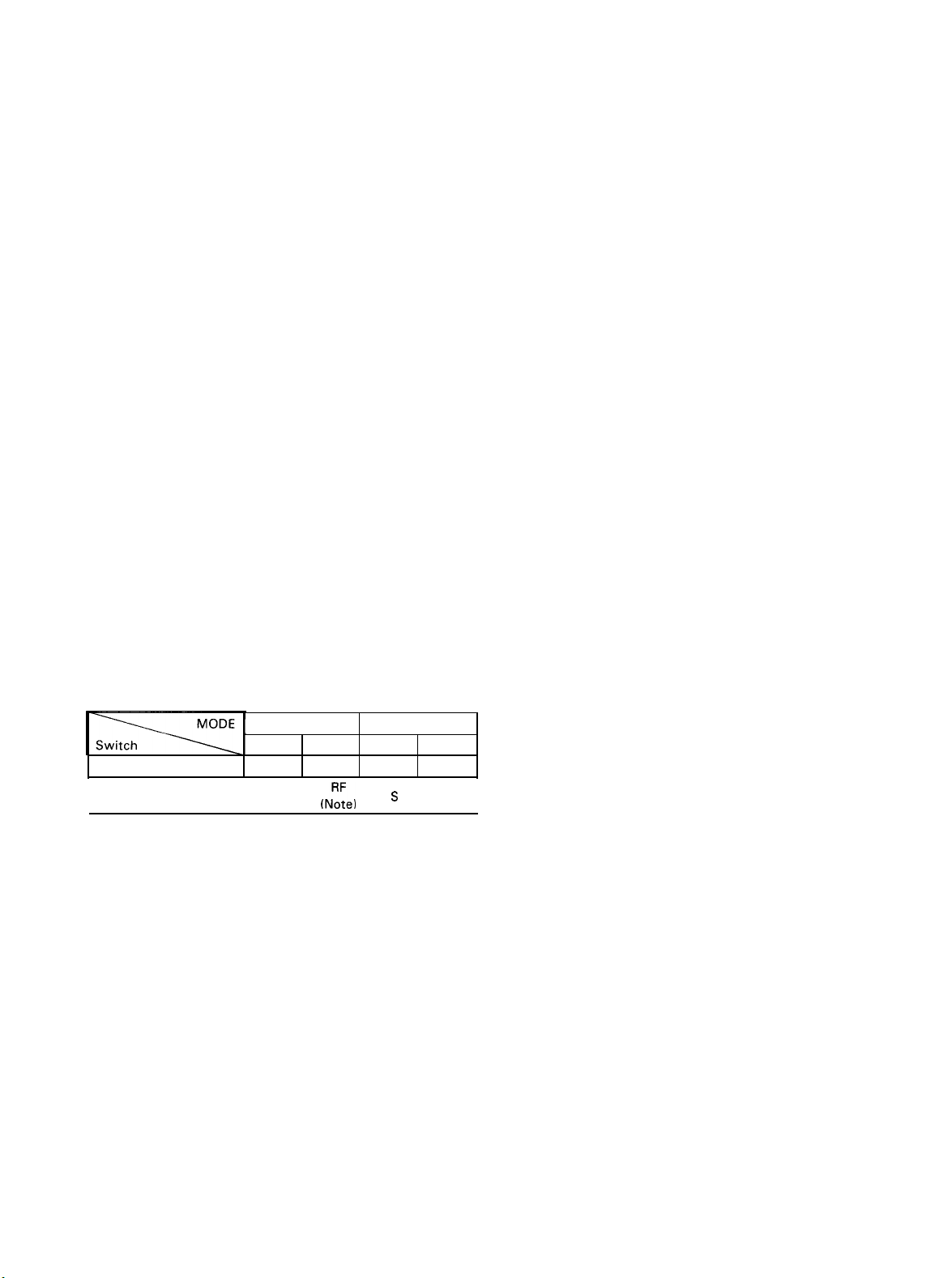
7 REV (Reverse) Switch
This switch is used to check repeater input
depressing the switch, the TX and RX frequencies are
reversed. To reverse the frequencies once again, set the
transceiver in transmit mode while holding the switch in
the depressed Position.
8 TONE Switch
Tone oscillator switch which makes 1750 Hz FM wave
when pressed in FM mode only.
9 LOW POWER Switch
Set this switch to LOW Position and the FM transmit output is reduced to about 1 Watt. Use the switch for FM
mode only. (This switch has no effect on SSB and CW
mode.)
10 NB (noise blanker) Switch
Use this switch during SSB or CW Operation to reduce
pulse ignition type noise from automobiles, etc. This is very
useful when receiving weak Signals.
(This switch will not function in FM mode.)
Signal.
By
16 PHONES Jack
This headphone
8-l 6 ohms impedance. Connect KENWOOD headphones
HS-4, 5 or 6 available as an optional accessory.
A stereo headphones may also be connected.
17 MODE Switch
In FM-CH mode, the VFO frequency is switched in
20/10
kHz Steps.
In FM, LSB, USB or CW mode, the VFO frequency is swit-
ched in
18 PRIO. M Switch
Depress the PRIO. M
channel 9CH. Depres the [IO] switch to
These memory channels are preset to 145.000.0 and
433.000.0, respectively, but can be set to any desired frequencies.
19 TIGHT lever
This lever is used to increase the torque of the VFO dial
knob so that the knob can not be rotated by external shock.
20/200
jack
allows use of a set of headphones of
Hz Steps.
191
switch to
call
out the memory
call
out the 1 OCH.
11 Meter switch
By using this switch, the meter functions as an S meter,
ALC meter or CEN (Center) meter.
Note: When the switch is set to the ALC/CEN Position
during FM transmission, the meter functions as an
RF meter but the meter pointer deflection will be
slightly deviated.
Meter functions
FM
RX
RF/S
I
ALC/CEN
12 VOX Switch
This switch is used for voice operated transmission on FM
or SSB, or semi-break-in Operation on CW (set to VOX posi-
tion). lt is also used in combination with the standby switch
or microphone PTT switch (set to MAN position).
13 Standby Switch
Set this switch to the down Position for reception, and to
the up Position for transmission. By pressing the
microphone PTT switch, the unit automatically shifts from
reception to transmission.
14 POWER Switch
The power to the unit is turned ON by setting the power
switch to the up Position, and turned OFF at the down
tion.
15 MIC Connector
Connector for microphone up/down input and PTT circuit.
S
I
CEN
TX
RF
/ OlZel / ’ / ALC
SSB/CW
RX
S
TX
RF
posi-
20 F. STEP Indicator
This indicator will light when the F. STEP switch (32) is
ON.
21 Tuning Knob
Turn this knob to select
22 FUNCTION Switch
This function switch
transceive functions. Normally It should be set to the
or “B” Position.
A-R: For VFO A Operation during reception and for VFO B
Operation during transmission.
I
A: For VFO A Operation.
8: For VFO B Operation.
8-R: For VFO B Operation during reception, and for VFO A
Operation during transmission.
23 MEMORY Selector
This switch selects any of the memory channels l-l OCH.
Use the switch when frequencies are stored in the memory
channels or the stored frequencies are called out in the ON
Position of the RM switch.
The channels
nels [9] and [IO]. These channels are preset to
145.000.0 MHz and 433.000.0 MHz, respectively.
24 SSB MIC
This control adjusts the gain of the microphone amplifier
during SSB Operation. Adjust it so that the ALC meter does
not deflect beyond the ALC Zone.
25 RIT Indicator
This indicator will light when the RIT switch (33) is ON.
(9)
and ( IO] are common to the priority chan-
your desired frequency.
selects one of the following
“A”
6
Page 8
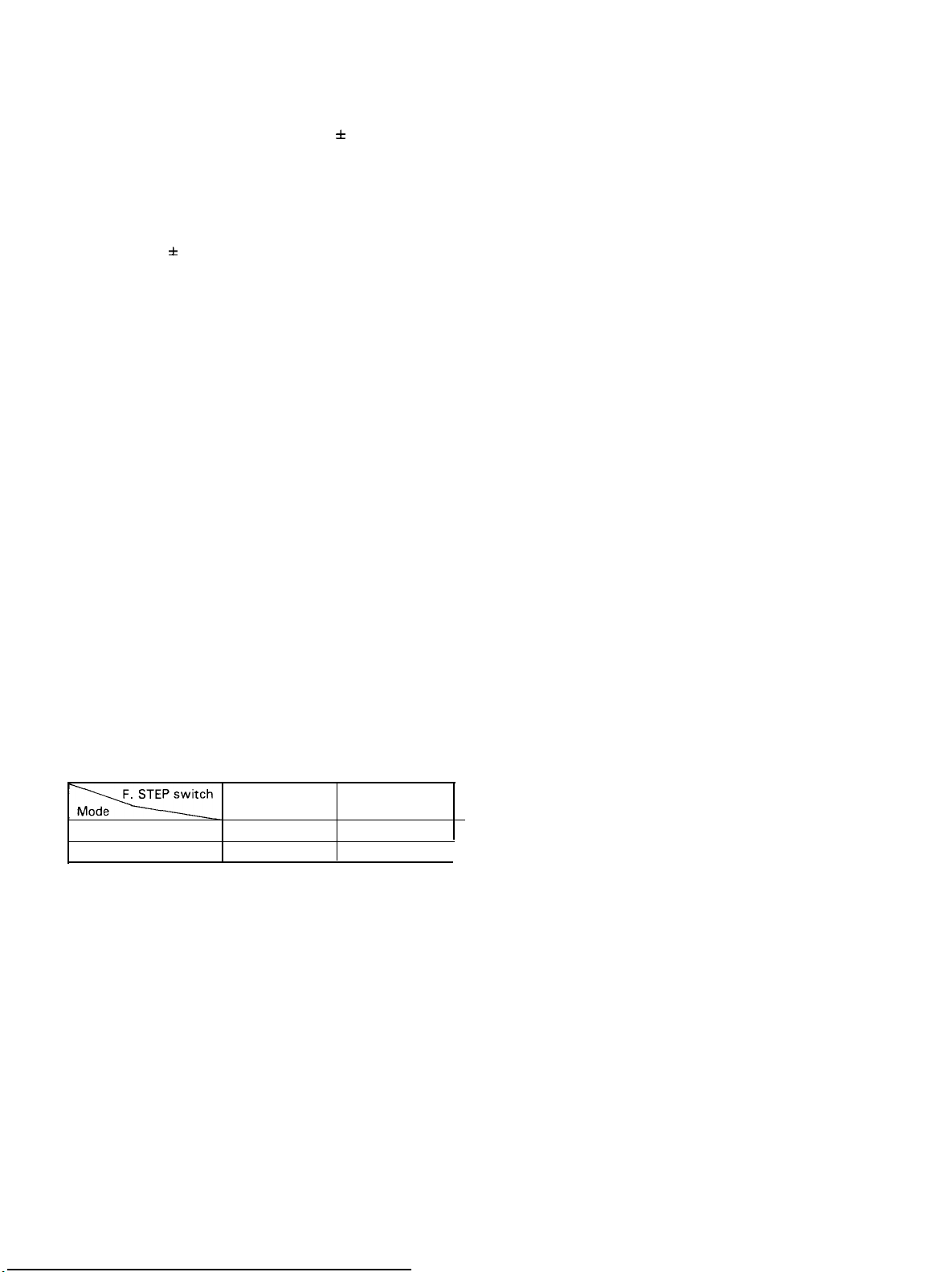
26 RIT Control 36 M. S Switch
With the RIT switch ON, the RIT knob allows the Operator
to vary the receive frequency by about f 1.5 kHz without
affecting the transmit frequency. The Center Position “0”
is RIT-OFF.
27 IF SHIFT Knob
By using this control, the IF crystal filter Center frequency
can be shifted + 1 kHz, allowing adjustment of tone quality, or eliminating interference from adjacent frequencies.
For normal Operation, this control should be set to the
Center “0” Position (detent).
28 SQUELCH Control
Turning this control clockwise during FM mode will
activate the squelch circuit.
29 SCAN-W
This switch is used to select the
and 10 MHz).
30 AF GAIN Control
This control adjusts the gain of the receiver audio amplifier.
Clockwise rotation will increase the output
31 RF GAIN Control
For adjusting the RF amplifier gain of the receiver. The gain
is minimum at the extreme counterclockwise Position. Normally, this control is set in its extreme clockwise Position.
scan
width (0.5, 1, 3, 5
level
This switch selects and scans the frequency stored in the
memory channel.
by setting the transceiver in transmit mode.
37 BAND Switch
For selecting the band
to be operated. By pressing the UP switch, the frequency is
stepped up band by band. When the DOWN switch is
pressed, the frequency is stepped down band by band. In
either case, the band is switched in 1 MHz Steps.
38 M (Memory) Switch
This switch is used to store the desired frequency in the
memory channel.
When the switch is depressed, an oscillation Sound is
heard, indicating that the frequency is stored in the
memory channel.
39 F. LOCK Switch
This switch
switch ON, the VFO frequency remains unchanged even
when the tuning knob, BAND switch or MIC UP/DOWN
switch is manipulated. This feature is useful when
operating the transceiver on the same frequency for many
hours, or when it is used for mobile Operation.
The RIT switch can be used even in the ON Position of the
F. LOCK switch. The F. LOCK indicator will light when the
F. LOCK switch is ON.
locks
Scan
is released by the HOLD switch or
(144-145
the operating frequency of VFO. With the
MHz or
430-439
MHz)
32 F. STEP Switch
By using this switch, the VFO frequency is varied at a slow
or fast
can be checked on the F. STEP indicator.
33 RIT Switch
This push switch turns the RIT (Receiver Increment Tuning)
circuit ON and OFF. With the switch depressed, the circuit
is activated and the RIT indicator is illuminated. The RIT circuit is turned OFF when the switch is out.
34 SCAN Switch
This switch turns ON and OFF the VFO
VFO frequency is scanned at the
F. STEP switch. The switch is also used for re-scanning of
M. S (memory scan) or for scanning at busy stop.
35 HOLD
This switch is used to stop
Speed
as shown below. The operating conditions
SSB.CW,FM
FM - CH
F. STEP
OFF ON
20 Hz 200 Hz
12.5 kHz 5 kHz
scan
circuit. The
Speed
selected by the
scan
Operation.
40 M. R (Memory Recalll Switch
Memory channel is called out when this switch is turned
ON. For the channels in which frequencies are not stored,
the corresponding channel numbers are indicated.
3-2. REAR PANEL
1
430 MHz ANT (antenna) Connector IN type)
For connection of the 430 MHz band antenna.
1
2 144 MHz ANT (antenna) Connector (M type)
For connection of the 144 MHz band antenna.
3 Heat Sink
Dissipates heat from the final Stage transistors and power
supply transistors.
4 CW KEY Jack
This
jack
is used for operating the transceiver in CW mode.
Connect a telegraph key using a 2P plug.
5 SP (Extemal Speaker) Jack
Connect an external speaker of 4-8 ohms impedance using
the supplied plug.
7
Page 9
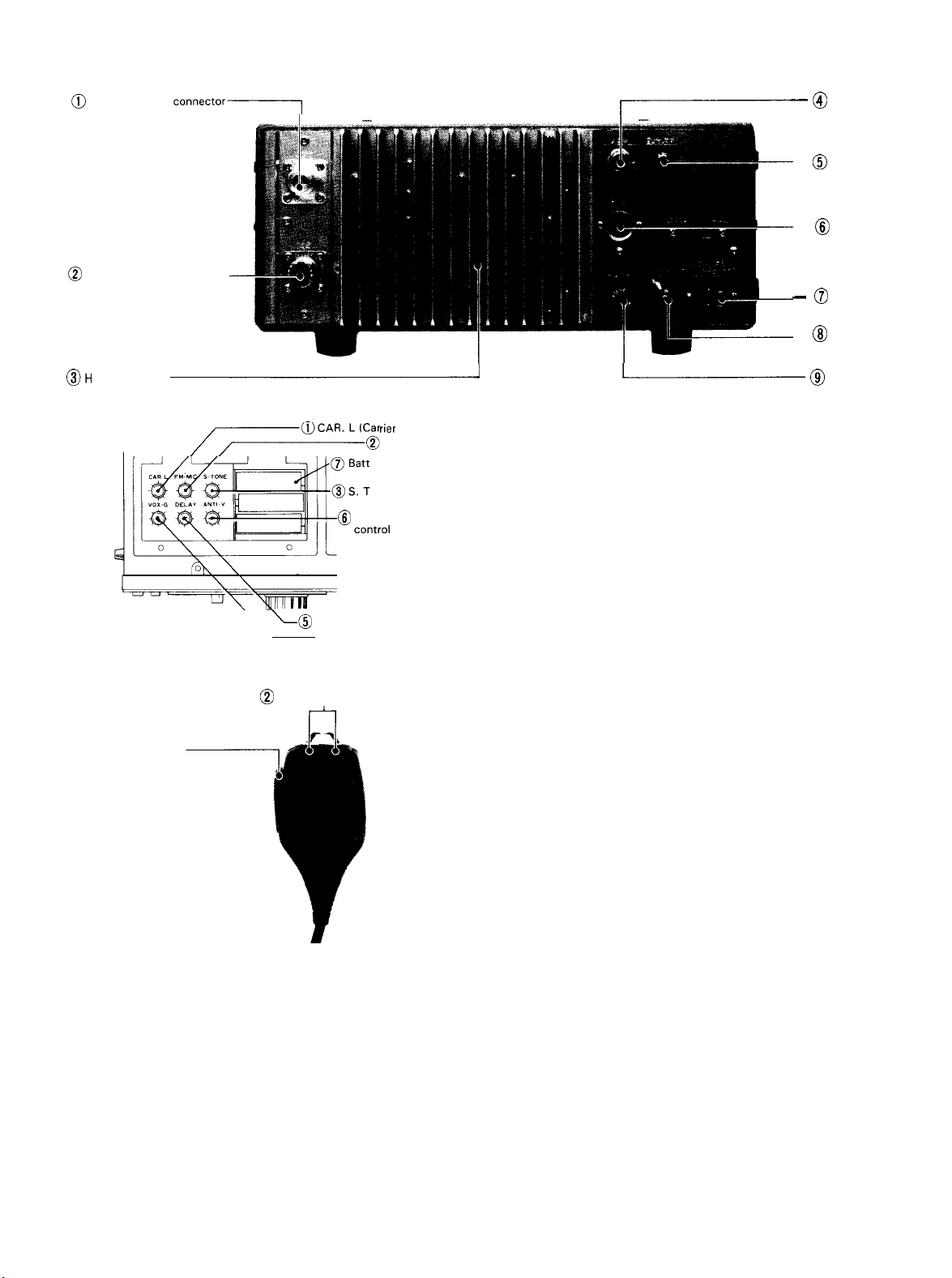
@
430 MHz ANT
connectorpI
7
@ CW KEY jack
- @
SP jack
- @
AUX socket
144 MHz ANT
0
eat sink
OH
@PTT Switch
-
connector-
10
DELAY (DELAY TIME) control
@VOX-G (VOX GAIN) control
@
UP-DOWN Switch
rier level) control
FM.MIC control
ery case for backup
ONE (Side tonel
@
ANTI-V (ANTI VOX)
- @
Power connector
- @
GND terminal
u
@ Fuse holder
9 Fuse Holder
A 2A fuse. When it blows, check the
Cause
and replace
with the spare supplied.
3-3. INTERNAL VIEW
1
CAR. L (Carrier Level) Control
This control adjusts the carrier level in CW mode. lt does
not function in other modes. Use the control within
ALC zone.
2 FM-MIC Control
This control adjusts the sensitivity of the microphone dur-
ing FM transmission.
3 SIDE TONE Control
This control adjusts the monitoring level of side tone during
CW Operation.
the
6 AUX socket
This connector is used for controlling a linear amplifier,
etc., or for external standby. For connection, use the supplied 7P plug (DIN
7
Power Connector (AC and DC)
type).
For connection of the supplied AC power cord or the
specified DC power cord (DC 13.8 V).
8 GND (earth) Terminal
For connection of an earth lead.
4 VOX-G Control
This control adjusts the sensitivity of the VOX controlled
Operation.
5 DELAY (Delay Time) Control
This control adjusts the VOX time constant. Adjust it
according to the
Speed
of Speech.
6 ANTI-V (ANTI VOX) Control
This control is used to adjust the VOX System so that it is
not tripped by Sound from the speaker.
7 Back-up Battery Case
Load battery into the case to back-up memory channels.
Battery will last for about 1 year.
3-4 MICROPHONE
1
PTT Switch
Press-to-talk switch for transmission.
2 UP-DOWN Switch
This switch is used to shift the VFO frequency up or down.
8
Page 10
4-
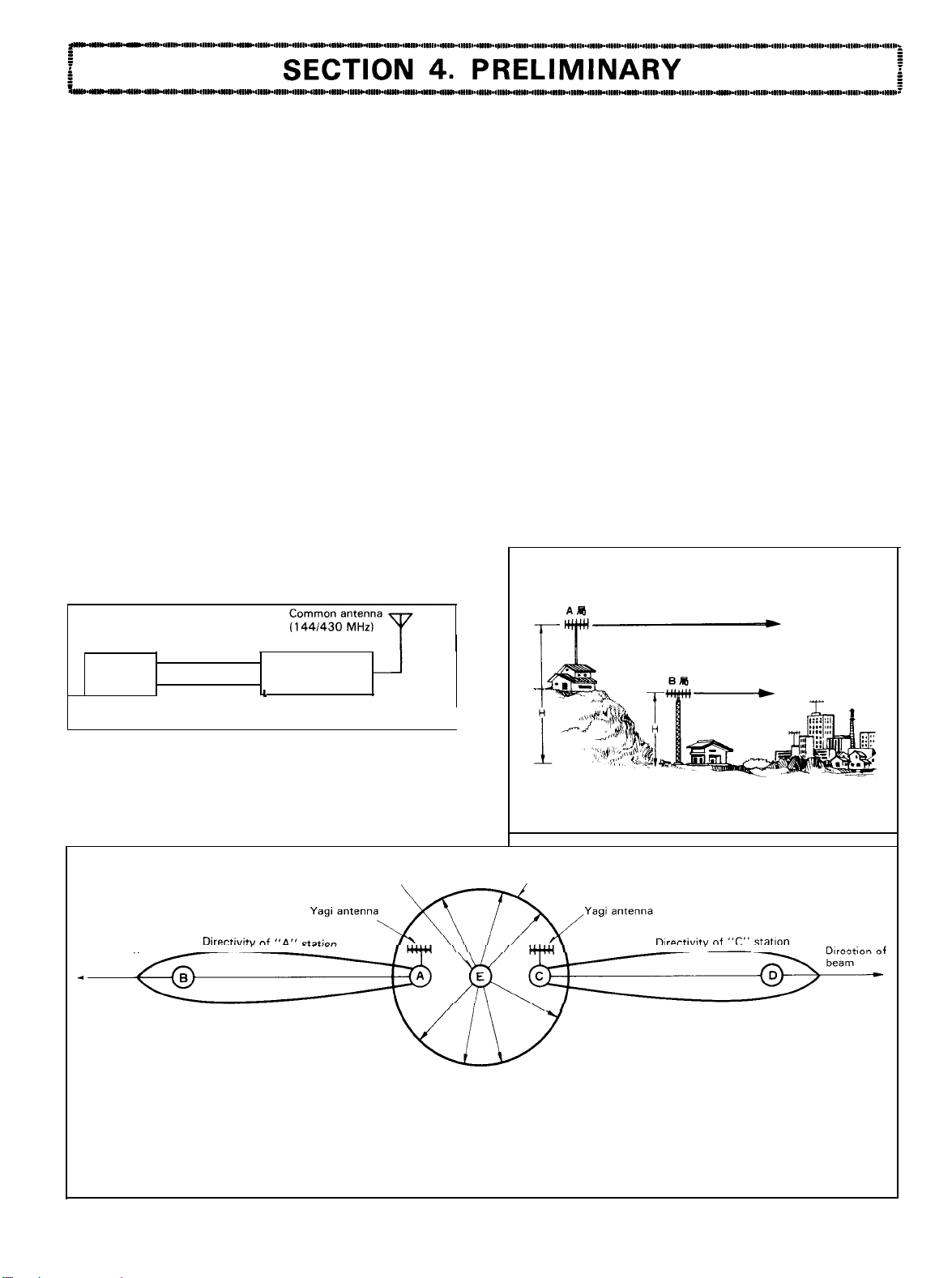
1. ANTENNA
The Performance of the transceiver depends upon the
type of antenna to be used. To ensure the maximum perfor-
mance of the TS-780, select a suitable antenna and adjust
it for the best condition.
Common Antenna for
144/430
MHz Operation
The TS-780 is designed so that two different transmit
Outputs (144 and 430 MHz) are supplied to individual
antennas. Use of individual antennas is recommanded as it
simplifies the antenna matching and minimizes the loss
cuased by antenna. However, if it is desired to use a com-
mon antenna, available from market, because of installa-
tion conditions, etc.,
it should be properly adjusted and
connected by carefully following the instruction manual
furnished with the antenna. An example of connection of a
common antenna is illustrated in Fig. 4.
Notes:
1. A common antenna should be connected through a
dividing filter (some types of common antenna have
built-in dividing filter).
2. An antenna selector (up to 430 MHz) may be used in
lieu of a dividing filter.
3. Never attempt to connect a common antenna without
using a dividing filter.
Antennas for fixed Station Operation should be installed
observing the following three conditions:
l Selection of Antenna
Choose an antenna suitable for the purpose of use,
budget and installation location.
In general, a beam antenna such as Yagi antenna is
suitable for Operation with DX stations or a specific station, and a ground plane omnidirectional antenna for
Operation with
local
stations. In the case of Yagi antennas, use of a stacked type antenna as shown in Fig. 5
will provide excellent directivity and RF gain.
l Installation Location
For satisfactory DX Operation, the antenna should be in-
stalled as high as possible. An example of a good
tion for the installation of antenna is on a hill such as
loca-
illustrated in Fig. 6, “A” Station.
Installing as antenna in such a high location allows
reception of many stations; however, this often creates
a possibility of radio interference. Therefore, it is recommended that a stacked type directional Yagi antenna be
used for satisfactory DX Operation.
The “A” Station on the
tion than the
“B”
hill
provides better transceive opera-
Station if the same type of antenna is used.
144 MHz cable
TS-780
430 MHz cable
Dividing filter
L
Antenna
cable
Fig. 4 Connection of Common Antenna
Type of Antenna
Choose a proper antenna according to whether it is used
for fixed Station or mobile Station Operation. For fixed station Operation, a Yagi antenna (directional type) or a ground
plane antenna (omnidirectional type) is recommended.
Ground plane antenna (omnidirectional)
Directlon of
beam
*
.
“A”
and “C” stations are transmitting with the same
frequency, while
the Signal. In this case, radio interference is very little.
However, if “E” Station is transmitting with the Same
freauencv and “A” and “C” stations are receivinq the
Signal, interference will possibly occur.
“B”
and “D” stations are receiving
Fig. 5 Antenna Directivity
(The
Pattern Shows an Ideal condition. In practice, this pat-
tern becomes complex because it is influenced by surroun-
ding buildings and geographical features.)
I
Fig. 6 Good Location for Antenna Installation
Directivity of “E” Station
In areas crowded
mended that a beam antenna be used. as it
eliminates interference when those stations are
transmltting with the Same frequencv.
with
many stations. it is recom-
Page 11
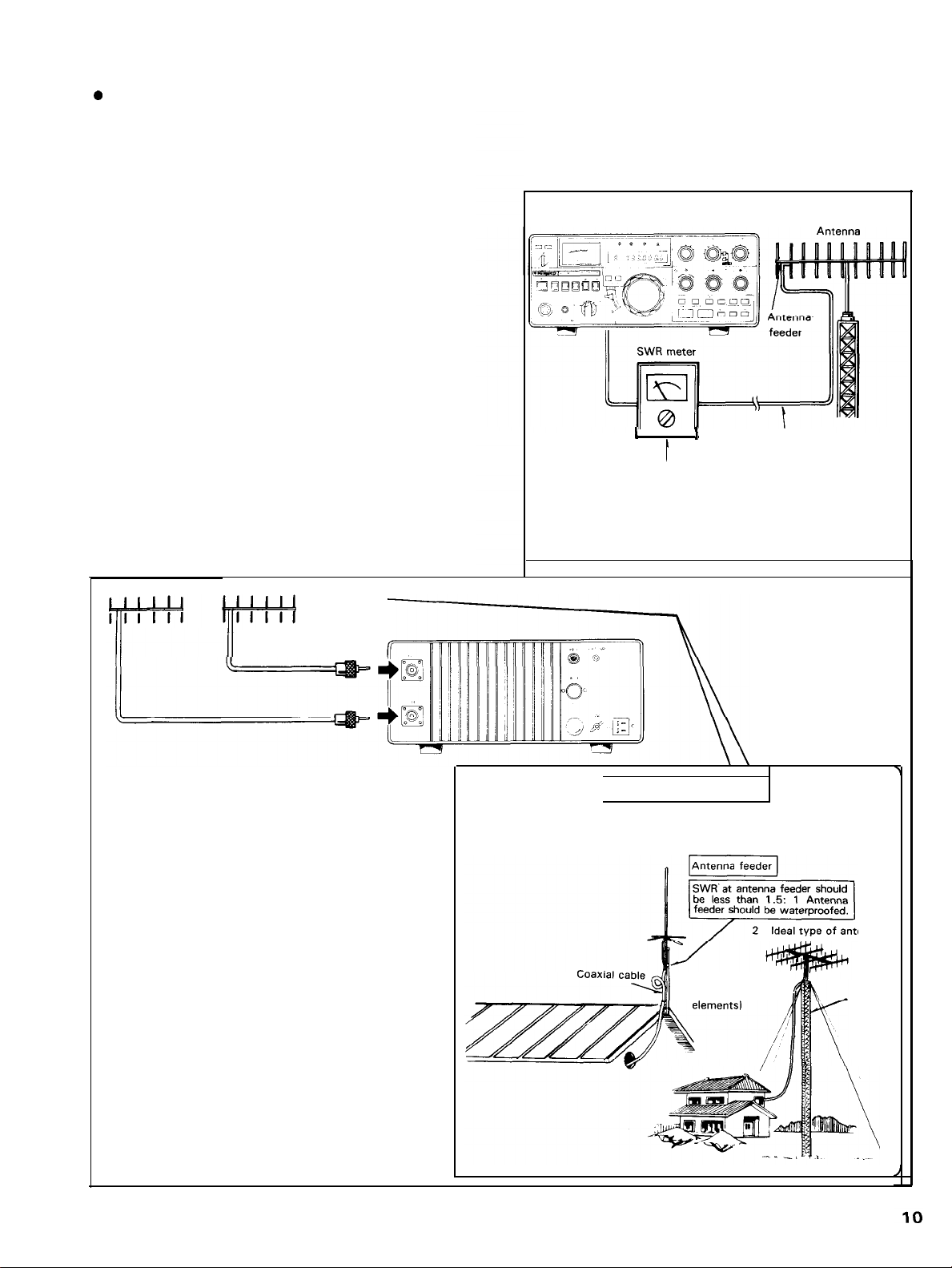
0 Adjustment (SWR)
Your antenna must be connected to a 50 ohms coaxial
cable, since the antenna impedance of the TS-780 is
50 Ohms. Also, the antenna must be adjusted to
50 ohms impedance. This adjustment is called impedance matthing.
Proper impedance matthing is accomplished by checking SWR (VSWR: Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) using a
SWR meter. Ideal SWR is 1: 1.
The SWR meter should be connected between the
antenna feeder and the antenna terminal at the rear of
the transceiver, whichever is more convenient. Note
that the reading of SWR meter varies somewhat depending on the location of connection because of the loss in
the antenna cable. This is particularly noticeable when
the antenna cable is more than 10 m long.
An antenna System which
Shows
a standing wave ratio
of less than 1 .5 will insure satisfactory transceive
Operation.
4-2. COAXIAL CABLE
For satisfactory transceive Operation, coaxial cable
must be used. When the transceiver is used for fixed sta-
tion Service, the coaxial cable becomes relatively long, so
low loss (large sized) coaxial cable of the shortest possible
length should be used, as the loss of coaxial cable cannot
be neglected when operating in high frequency bands, particularly in 144 MHz or higher bands.
When the coaxial cable needs to be extended more than
10 m, use one of larger size such as RG8/U or UR67.
I
’t ’
Whan SWR meter is connected as shown above. the actual
SWR at the antenna feeder is higher than 1.5 because of the
loss of the coaxial cable
1
Coaxial cable
Fig. 7 Adjustment of Antenna System
Antenna feeder
ANT terminal
8. Antenna installation
1 Ground plane
antenna
4-row horizontal
Stack (4 parallel
enna
Tower
Fig. 8
Page 12
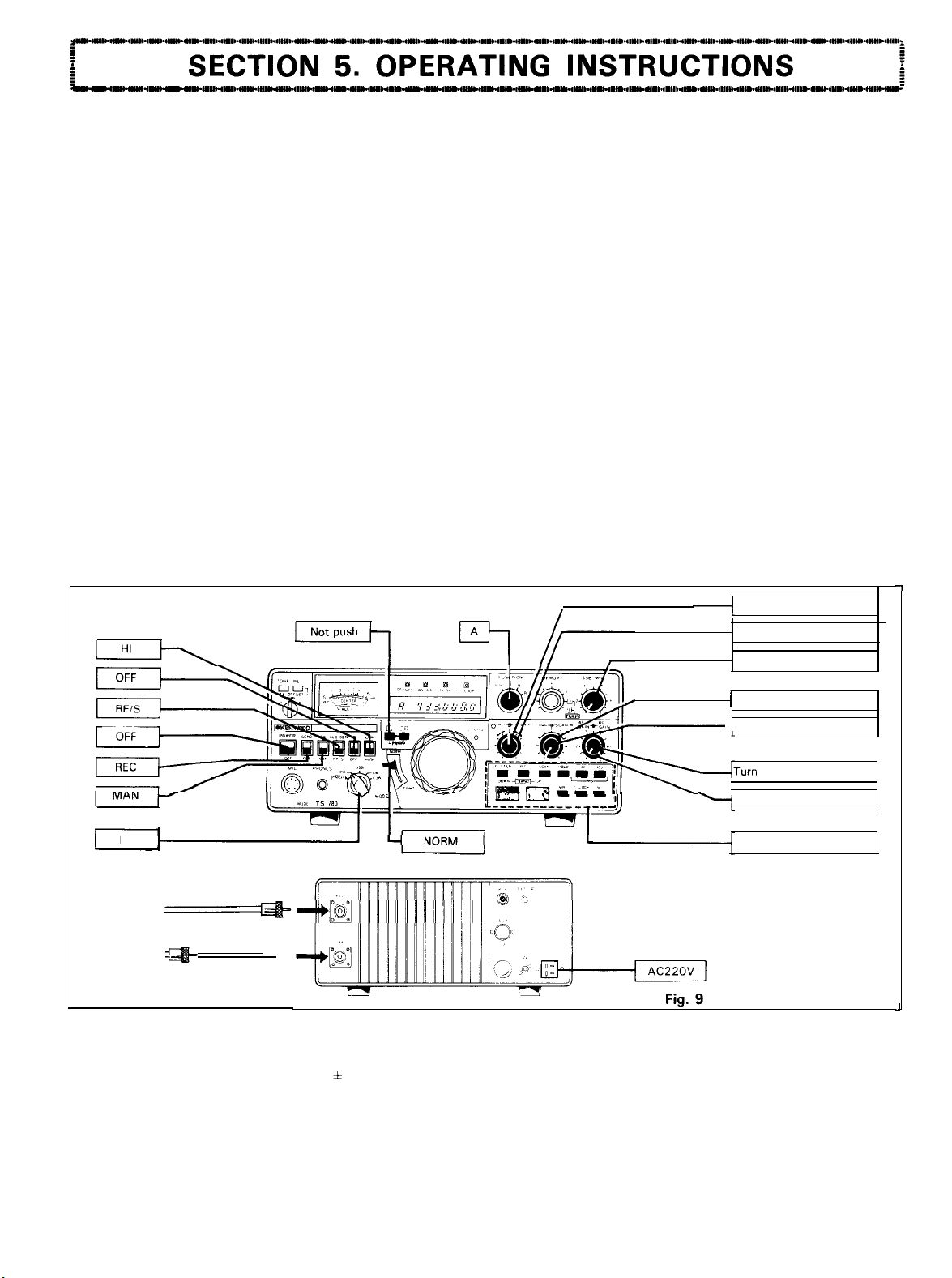
5-l. OPERATING MODES
The TS-780 can be operated in the following modes by
using the MODE switch.
CW - Transmission and reception of Morse
FM - Transmission and reception of FM
USB - Upper side band transmission and reception (A3j).
USB is normally used on 144 and 430 MHz bands.
LSB - Lower side band transmission and reception (A3j).
Signals
Signals (F3).
(Al ).
5-2. FM MODE
Reception
Set the knobs and switches as shown in Fig. 9, then
proceed as follows: When the shift switch is at SIMP (in
simplex Operation), the mode switches FM-A and FM-B
operate in the same way so either of which may be used.
(Refer to 5-l 4).
1.
Turn the POWER switch ON. The meter and diqital
display are illuminated to indicate the power is on. The
digital display indicates 144.000 MHz and VFO A.
Select your operating frequency band by pressing the
DOWN (or UP) BAND switch. The frequency is shifted
band bv band at
each
oress of the DOWN (or
.~
UP)
I
A
T
switch. When either switch is pressed for 0.5 second or
longer, the frequency is shifted about 0.5 second intervals.
2. Turn the AF GAIN control clockwise and noise or
will be heard from the speaker. Adjust the control for
suitable
(To
sent, turn the SQL control.)
3. Turn the VFO dial slowly until the
clearly while observing the “S” meter deflection.
4. Set the meter switch to ALC/CEN and turn the VFO dial
until the meter is centered while receiving the
the other Station. When the meter pointer indicates the
Center Position, it means that the transmit frequency
has tuned to the receive frequency. Set the meter
switch to RF/S. Since the IF band is wide in FM mode, a
slight deviation of frequency does not affect the recep-
tion. In transmitting Operation, however, the other Party
may be using a fixed channel, so it is advisable to set the
meter in the Center Position (Zero-in) by adjusting the
VFO dial knob.
*
level.
eliminate the noise which is heard when
Signal
is heard most
Zero-in means that your transmit frequency coincides
precisely with the receive frequency.
“0”
(center position)
“0”
(Center position)
Turn fully counterclockwise
Signal
Signal
Signal
is ab-
of
-l
FM
To 430 MHz ANTENNA
To 144 MHz ANTENNA
Use of RIT Switch
The RIT (Receiver incremental Tuning) switch is used to
shift the receive frequency by about f 1.5 kHz without
affecting the transmit frequency (the indication of digital
display remains unchanged).
When the receive frequency is offset, turn on the RIT
switch (the RIT indicator will light) and turn the RIT control
so that the transceiver is tuned in the frequency.
Note that the receive frequency is offset from the
~
1
,fCfully counterclockwise
Turn fully counterclockwise
iw\Turn
&ZA
transmit frequency when the RIT switch is turned on, so
the switch must be set to OFF after QSO.
Use of RF GAIN Control
This is used to adjust the
ly, leave it fully clockwise. for a very strong incoming
Signal,
turn it counterclockwise. If there is a strong
the vicinity of your operating frequency, lower the RF gain
to reduce intermodulation interference.
\
receiver
fullycounterclockwise
Turn fully clockwise
OFF
Pre-setting for Reception
RF Stage gain. Normal-
Signal
in
i
11
Page 13
Use of SQUELCH control
This control is used to eliminate noise when
sent. Turn the control slowly until noise disappears. When
the control is properly adjusted, only the receive
heard from the speaker. This control is also used according
to the strength of input
Transmission
Notes:
1.
Before transmitting, perform all the necessary pro-
cedures for Optimum reception. Make sure that the frequency you have selected does not interfere with other
stations.
2. Check to make sure that the antenna connected is of the
proper type. Use of an improper antenna will result not
only in insufficient power but also in TV1 and BC1 .
DO not attempt to operate the transceiver without connecting antenna as it will
transceiver.
Signal
during mobile Operation.
Cause
Signal
is ab-
Signal
is
darnage to the
Use of LOW POWER Switch
This switch is used to reduce transmit power during
Operation with a local Station, thus preventing interference
to other stations. lt is also effective to reduce the power
consumption.
Set the switch to the up Position and the transmit power
is reduced to about 1 Watt.
The transmit power is indicated on the RF meter. Since
the indication on the RF meter depends on the installation
condition of antenna, it will not indicate the exact output
power. If the meter indicates “8” at the rated power, then
the reading of the meter will be “1” or “2” when the LOW
POWER switch is turned on.
Note:
The LOW POWER switch is used in FM mode only.
5-3.
Reception
than LSB. As far as the operating technique is concerned,
there is no
in” technique in SSB mode required a little experience.
described in section on “FM Mode”, except that the MODE
switch should in USB Position.
SSB Mode
On VHF bands, USB is traditionally more often used
differente
For SSB Operation, set the knobs and switches as
between two. Generally, the “zero-
Fig. 10 Transmission
Set the controls referring to Fig. 9. For transmission, use
the following procedure:
1. Set the MODE switch to FM and the STANDBY switch
to SEND (when the PTT switch is pressed,
transmitted at the REC Position of the standby switch).
Check to see that the RF meter is working and the ON
AIR indicator is lit. Set the STANDBY switch to REC.
2. Adjust the microphone gain by turning the FM MIC control. Normally, Optimum gain is obtained in the Center
Position of the knob. If required, turn the control
counterclockwise to reduce the gain.
Center Dosition
Fig. 11 MIC GAIN Adjustment
Signal
is
Fig. 12 Transmission in SSB Mode
1
After the settings have been completed, proceed as
follows:
1. Turn the POWER switch ON and adjust the AF GAIN
knob for suitable loudness.
2. Turn the VFO tuning knob slowly to receive SSB Signal.
First set the VFO knob a few kHz lower than the receive
frequency (turn the knob counterclockwise) and you will
hear a high pitched tone such as is heard from a
magnetic recording tape set in the fast-forward mode.
Turn the knob clockwise for higher frequency and the
Sound will become clearer. Set the knob in such a position where the Sound is heard most clearly (this is the
Zero-in Point).
12
Page 14
Note:
The Zero-in Point can be easily located because the Sound
loses its clarity suddenly when the frequency
Passes
away
from the Zero-in Point. If a clear Sound cannot be heard by
following the above procedure, it may be an indication that
the
Signal
is LSB. Set the MODE switch to LSB Position. In
this case, the setting of the VFO knob should be made in
reverse
Order.
Transmission
1. Set the MODE switch to USB and the meter switch to
ALC/CEN.
Other controls remain the same as outlined in
section on “FM Mode”.
2. Adjust the microphone gain. This adjustment should be
made with the standby switch set to SEND or the
microphone PTT switch depressed.
Next, speak into the microphone and adjust the SSB
Mic gain control on the front Panel, making sure that the
ALC meter does not deflect beyond the ALC zone.
After completion of the above adjustment, set the meter
switch to RF.
Note:
Periodically check the ALC meter deflection. lf, due to
heat, etc.,
there iS a Change in deflection, reset the
meter to within the ALC Zone.
Discrimination between SSB and FM
1. Use of S meter
If
the S meter is steady (meter pointer almost Stops), the
incoming
Signal
is FM; otherwise, it is SSB.
2. Use of MODE switch
If
a clear
switch, the
Signal
is heard at the FM Position of the MODE
Signal
is FM. The Sound in SSB mode is not
heard at this Position.
Use of RIT Switch
For detailed information, refer to section on “FM
Mode”. In SSB mode, if the receive frequency has drifted,
set the RIT switch to ON and adjust the RIT knob, as in the
case
of FM mode.
When the RIT switch is ON, the receive frequency is
off-
set from the transmit frequency, so it is necessary to turn
the switch off when tuning to another frequency.
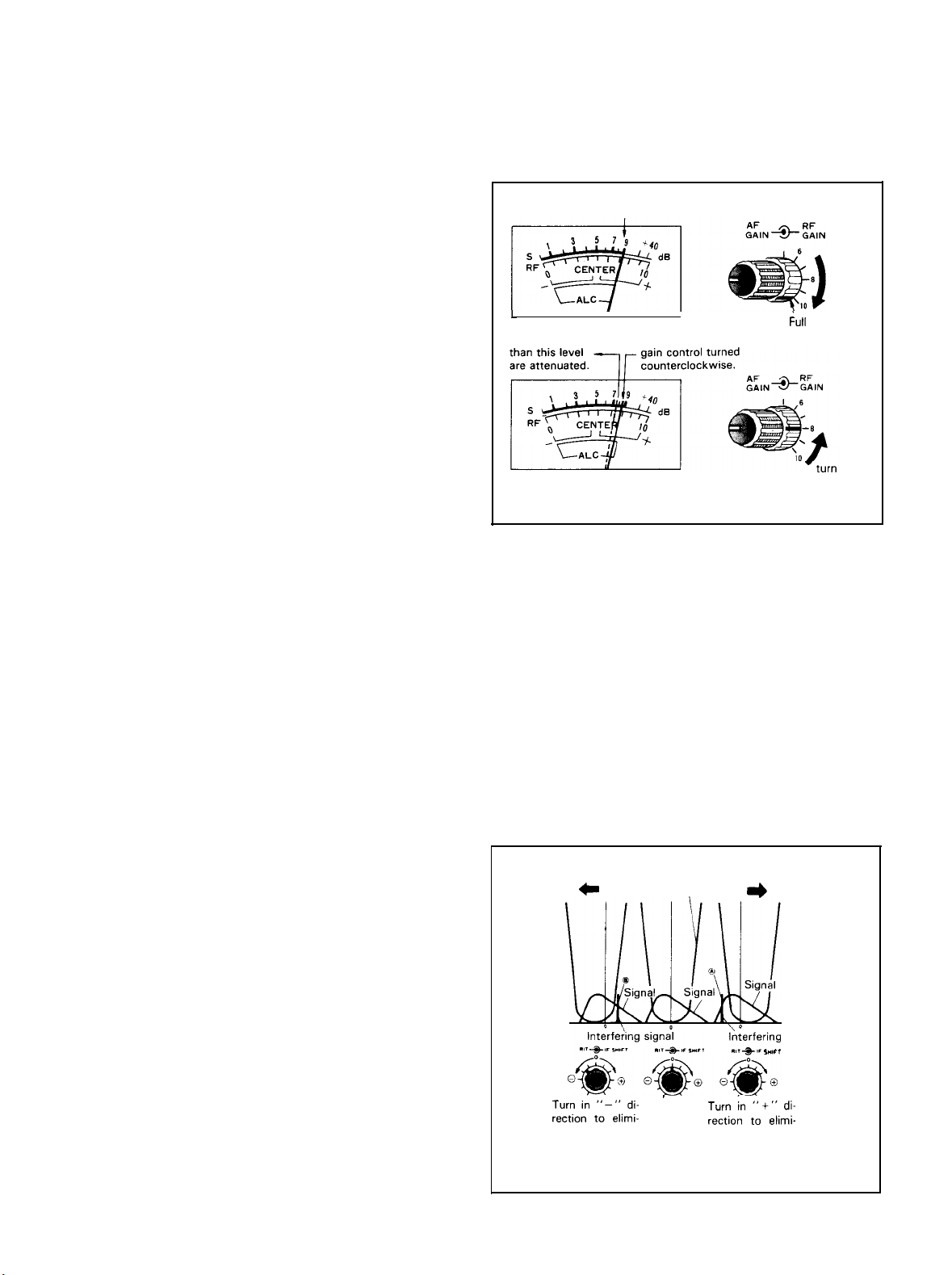
The secret of reading accurate
Signal
strength is to turn
the RF GAIN control counterclockwise so that it is a little
lower than the
Signal level
read on the S meter at the full
clockwise Position, as shown in Fig. 13.
Maximum S meter reading
of an incoming signal.
Signals
I
weaker
I
Meter deflection
with RF GAIN
hl
clockwise
Position
counterclockwise.
Fig. 13 RF GAIN Control Setting
5-4 IF SHIFT Control
The IF SHIFT control is used to shift the passband of the
IF filter without changing receive frequency. By turning this
control in either direction, the IF passband is shifted as
shown in Fig. 14.
The IF SHIFT is effective in eliminating interference
when the receive
during Operation in both SSB and CW modes.
Turning the control in
terference from low frequency
frequency component in the
Turning the control in ” - ” direction will eliminate interference from high frequency
component is
Turned in “- ”
direction
Signal
cut
off accordingly.
IF
filter passband direction
c
characteristic
is superimposed on nearby
“+”
direction will eliminate in-
Signal.
In this way, the low
Signal
is
cut
off.
Signal.
The high frequency
Turned in ” + ”
*
Signals
Use of NB (noise blanker) Switch
The NB switch is used to suppress pulse noise such as
ignition noise generated by car engine.
Use of RF GAIN Control
For detailed information, refer to section on “FM
Mode”. Normally, this control should be left in full
clockwise position. When a very strong incoming
present, turn it counterclockwise. The noise
the receive
Signal level
is attenuated for clear reception.
level
Signal
below
If the RF GAIN is reduced excessively in SSB or CW
mode, the S meter deflection will increase irrespective of
incoming
Signal
strength. This is due to the circuit
characteristics and is not an indication of trouble.
13
is
Teupo;
,-;;,;;;
nate interference
from
Signal
B
Fig. 14 IF SHIFT Control
I2erfering Signal
‘,‘+d I”WI
“n
;,+;;,v:
nate tnterference
from Signal A
Page 15
5-5 CW Mode
Reception
Set the controls and switches as outlined in section on
“FM Mode”, except that the MODE switch should be set
to CW. For reception, proceed as follows:
1. Turn the POWER switch ON and adjust the AF GAIN
control for suitable volume.
2. Turn the VFO knob slowly for the desired receive
so that a 800 Hz beat is heard. In this way, the frequen-
cy of your Station will coincide (Zero-in) with the frequency of your party’s Station.
Similarly, if your Party
response to your
cy has coincided with your frequency.
Note:
The 800 Hz beat can be checked by using a frequency
counter.
calls
back with a 800 Hz beat in
call,
it means that the party’s frequen-
Transmission
Adjustments of the transmitter for CW Operation are
basically the same as for FM Operation. The transceiver will
be ready for use when adjusted in FM mode provided that
the frequencies are the Same.
For transmission, set the controls and switches as
outlined in section on “FM Mode”, except that the MODE
switch should be set to CW and the meter switch to
ALC/CEN. Connect your key to the KEY
Panel.
1.
Check to ensure that the MODE switch is set to CW. Set
the standby switch to SEND and the ON AIR indicator
will light. Under this condition, press the key down and
the ALC meter should deflect. Set the standby switch
back to REC Position.
Note:
If
the key is not connected, the ALC meter will deflect
when the standby switch is set to SEND.
2. Adjust the CAR LEVEL control
With the standby switch in the SEND Position, adjust
the control so that the ALC meter deflects within the
ALC zone when the key is pressed down.
Then, release the key. Set the standby switch back to
REC Position and the meter switch to RF/S Position.
Note:
If there is a Change in ALC meter deflection, reset in the
Same
manner as in the SSB mode.
3. Adjust the side tone
The TS-780 has a built-in side tone circuit for monitoring your station’s CW
just the side tone volume, open the top cover and turn
the SIDE TONE control for desired level.
This adjustment should be made in receive mode with
the key pressed down (standby switch in REC position),
since, in so doing, the side tone circuit is activated.
Signal
during transmission. To ad-
jack
Signal
on the rear
Use of RIT
For detailed information, refer to section on “FM
Mode”. Use the RIT switch when your party’s frequency
has deviated from 800 Hz or you wish to transmit with a
different beat frequency.
Use of NB
Refer to section on “SSB Mode”.
Switch
Switch
Use of RF GAIN Knob
Refer to section on “SSB Mode”.
Use of IF SHIFT Control
By using the IF SHIFT in conjunction with the RIT, tone
quality can be adjusted.
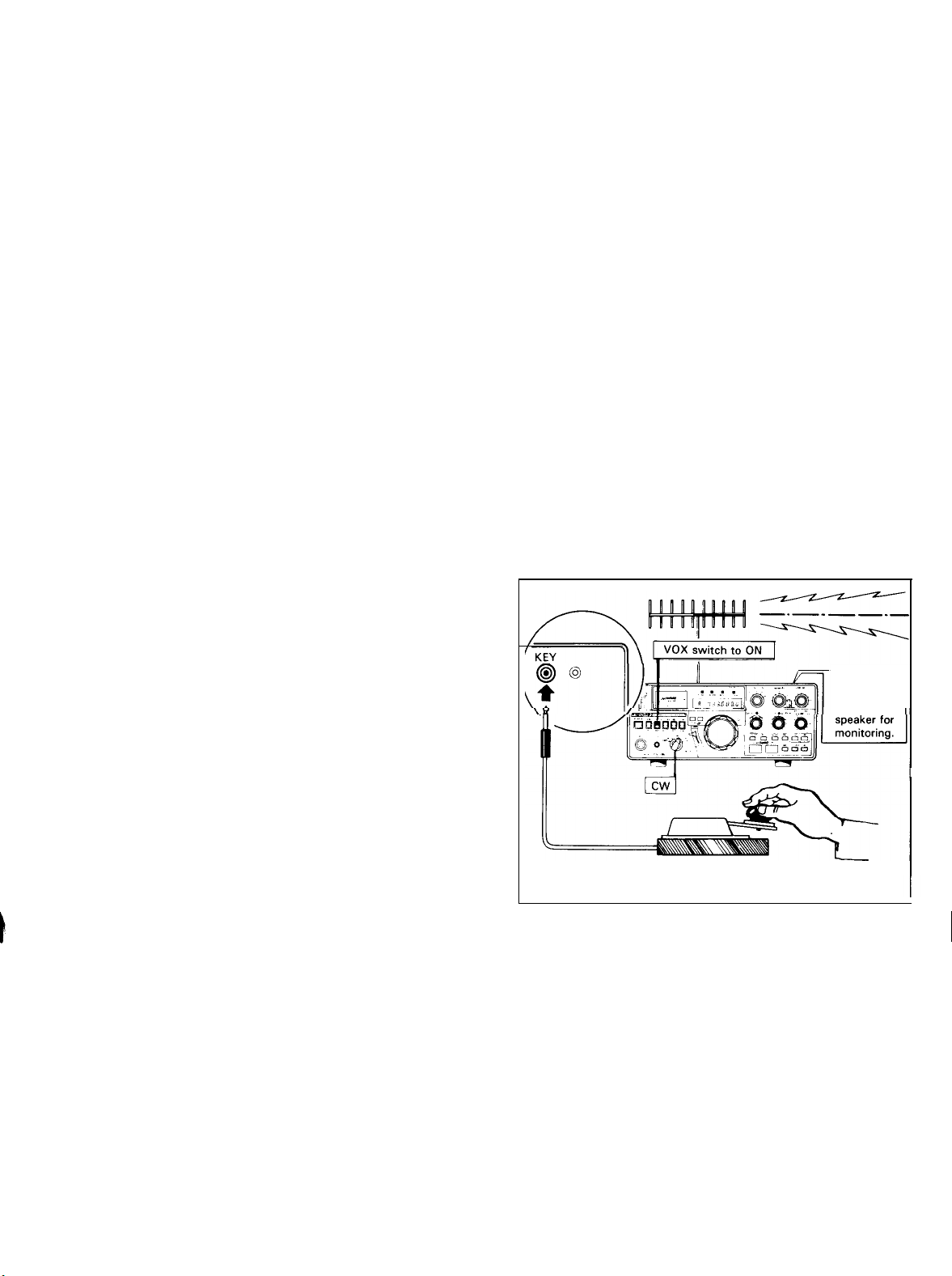
Semi-Break-In Operation
The TS-780 is capable of semi-break-in Operation, in ad-
dition to the usual CW Operation with the standby switch.
The semi-break-in uses the side tone to activate the VOX
circuit which switches to transmit when the key is pressed
down and to receive when it isreleased. For semi-break-in
Operation, set the MODE switch to CW and the VOX
switch to ON. Other operating procedures are the same as
for the usual VOX Operation (Refer to 5-6).
Side tone
is heard
from
---l
Fig. 15 Semi-break-in Operation
14
Page 16
5-6 VOX OPERATION
The VOX is an automatic switching System that switches the transceiver to transmit and receive while speaking
into the microphone. This is mainly used in SSB mode.
With the VOX switch set to ON, the transceiver is
automatically switched to transmit mode when you speak
into the microphone and to receive mode when you stop
talking. For VOX Operation, the standby switch should be
set to REC.
Control Settings
1.
Adjustment of VOX GAIN Control
With the standby switch set to REC, place the VOX
switch in the VOX (ON) Position.
First turn the VOX GAIN control clockwise and adjust it
so that the transceiver is switched to transmit mode
when you speak into the microphone with normal voice.
Turn the control further clockwise and the gain is
increased allowing the transceiver to be switched to
transmit mode with a lower
excessive VOX gain results in misoperation by ambient
noise.
The condition of VOX Operation can be checked through
the speaker. When any Sound is heard from the speaker,
it means that the transceiver is in receive mode; otherwise, it is in transmit mode. In transmit mode, the ON
AIR indicator Comes on and, in receive mode, the light of
indicator goes off.
2. Adjustment of ANTI VOX GAIN Control
This control is located on top of the case (sec page 9)
and is used to prevent the VOX circuit from being
misoperated by the Sound of speaker.
Adjust the VOX GAIN control as directed in item (1)
above. Then, adjust the AF GAIN control for suitable
volume while receiving
Hold the microphone
adjust the ANTI VOX GAIN control until speaker Sound
will not activate the VOX circuit.
the control in clockwise direction will Cause the ANTI
VOX circuit to operate, resulting in failure of the
transceiver to be switched to transmit mode.
3. Adjustment of VOX DELAY Control
This control is used to hold the transmitter on after VOX
Operation. If the hold time is too short, the TS-780
returns to receive whenever you pause speaking. If too
long, the TS-780 will not return to receive after speaking. Adjust the control so that the transceiver holds proper transmitting time when you speak at normal Speed.
This control is also effective for CW semi-break-in
Operation.
During CW Operation, do notturn the control excessively
in clockwise direction, as it takes a long time until the
transceiver returns to receive when the key is released;
making it impossible to perform smooth semi-break-in
Operation.
20~
level
of voice. However,
Signals
from a Station.
30 cm from the speaker and
Excessive
turning of
Note:
If the VOX switch is left ON, the TS-780 will momentarily transmit when the POWER switch is turned on.
After VOX Operation, set the VOX switch to OFF.
5-7 READING THE FREQUENCIES
The TS-780 digital display indicates carrier positions in
all operating modes. Because of the use of a
the carrier Position remains the same when the MODE
switch is manipulated, thus the transmit and receive frequency can be directly read on the digital display, except
for CW reception where the frequency on the display is
higher by the beat frequency (800 Hz: see section on “CW
Mode”) than the transmit frequency.
Note:
The digital display does not indicate the frequency varied
by the RIT knob.
special
circuit,
5-8 BAND SWITCH (UP-DOWN)
The BAND switch consists of two pushbutton switches,
UP and DOWN. By pressing the UP switch, the frequency is
shifted up by 1 band and, by pressing the DOWN switch
the frequency is shifted down by 1 band. By holding either
switch down, the frequency is shifted continuously at 0.5
seconds intervals. As shown in the illustration below, the
BAND switch functions separately for the VFO A and B
(sec section 5- 9 on “Operation of 2 VFO’s). The BAND
switch uses feather-tauch pushbutton switches. A tone
pulse is heard whenever the switch is pressed.
5-9 DIGITAL VFO
The TS-780 VFO is designed so that the pulses
generated by rotating the VFO knob are counted by the
microprocessor to vary the frequency through PLL circuit.
The frequency is varied step by Step. The step interval is
20 Hz (SLOW) for CW and
(FAST) for fast-forward and FM Operation. Either step can
be selected by the S/F switch (sec section 5-12).
The adjustable range of the digital VFO is shown in
Table
1.
F.STEP switch “OFF” F.STEP switch “ON”
144 MHz BAND
430 MHz BAND
Turning the VFO dial in either direction will shift the fre-
quency in endless mode between 144.000.00 and
145.999.98 In the 144 MHz band. The dial also functions
similarly in the 430 MHz band. Note that the upper limit of
the band varies according to the Position (ON/OFF) of the
F. STEP switch or mode.
144,000.00- 144,000.00-
430,000.00- 430,000.00-
SSB
Operation or 200 Hz
145,999.98 145.999.80
439.999.98 439.999.80
Table 1
I
15
Page 17

The VFO Knob is of variable torque type. When the lever
at the left of the knob is set to NORM, the knob can be
rotated quickly because of the flywheel effect. When the
lever is set to TIGHT, the knob is given a heavy torque and
hence the knob will not rotate accidentally by external
shock. This feature is useful for fine tuning or mobile operation.
When the MODE switch is changed to or from FM-CH
Position, the operating frequency becomes as shown table
3.
5-10 OPERATION OF 2
The TS-780 has two VFO’s, A and B,
trolled by a microprocessor.
By using the FUNCTION switch, the desired VFO can be
selected. The use of two VFO’s also permits Operation with
their own frequencies
A-R or B-R Operation. The table below Shows the positions
of the FUNCTION switch and VFO’s selected.
The two VFO’s (A and BI can be operated in different
bands (for example, VFO A: 144 MHz, VFO B: 430 MHz;
or in the same band. They can also be used as a memory.
Examples:
1.
With your contact’s schedule frequency stored in VFO
B, you can operate VFO A until your contact Starts
transmitting.
2.
During FM Operation, you can locate a sub-channel and
shift the frequency for repeater Operation by the VFO
not in use.
FUNCTION
SWITCH
RECEPTION
VFOs
each
(Cross
channel Operation) such as
TRANSMISSION
Table 2
being con-
Frequency
displayed
Note 1:
* 1When the F. STEP switch is turned OFF, the frequency
will shift to the nearest 12.5 kHz step frequency
within the displayed frequency.
* 2 When the F. STEP switch is turned ON, the frequency
will shift the nearest 5 kHz step frequency within the
displayed frequency.
The 100 Hz digit disappears.
Note 2:
Table 3
mode, the frequency of VFO B is shifted in the same way.
In the SSB mode, the frequency bellow
be changed.
145.317.7
145.312.5
(NOTE: "1) (NOTE: '2)
Shows
the frequencies of VFO A. In the FM-CH
145.317.6 145.315.0 145.315
145.315
Table 3
145.315.0
10 kHz
Order
may
5-12 USE OF F. STEP SWITCH
This switch is used to Change the step of VFO frequency. By pressing the switch, the F. STEP LED will light. In
the SSB, CW or FM mode, this switch should be set to
OFF, except when the tuning knob is used. When the
switch is set to ON, the frequency on the 100 Hz
becomes even number and the frequency on the 10 kHz
Order
is cleared to “0”. The frequency remains the same
when the switch is set to OFF.
Order
5-11 USE OF FM-CH
With the MODE switch set to FM-CH Position, the VFO
Operation changes to
F. STEP switch, the channel frequency shifts up in
12.5 kHz Steps, and in the ON Position, in 5 kHz Steps.
433.000 433.005
433.0125 433.010
433.0250 433.015
433.0375 433.020
433.9875
click
type. In the OFF Position of the
433.995
Table 4
5-13 USE OF MEMORY
This switch is used to store the desired frequency in the
memory. The frequency is stored in the channels
by using the M switch and MEMORY selector. The stored
frequency is called out by pressing the MR switch to ON.
(1-1
0 ch)
16
Page 18

1 Select the desired frequen-
cy by the tuning knob.
2 Select the desired channel
by
the MEMORY selector to
store the frequency.
3 Depress the MR switch to
ensure that the selected
4 Depress the M switch and
memory.
Fig. 14 Use of MEMORY
5-14 USE OF SCAN SWITCH
With the SCAN switch ON, the FUNCTION (A,
flickers to indicate that the frequency is scanned.
FM-CH mode
1. Adjust the squelch sensitivity by the SQL VR and set the
Signal level
2. By setting the SCAN switch to ON, the channel is
shifted to the next one regardless whether a
present in the channel
the channel is not shifted).
3. Even when the channel is BUSY stopped, the function
keeps flickering.
4. When
SCAN Stops for about 1 seconds and Starts again.
FM mode
1.
Depress the SCAN switch continuously and the channel
is scanned at a high Speed. In BUSY stop, keep the
switch depressed to fast forward the
receiving band. In this way, the
smoothly.
2. Other operations are the same as in the FM-CH mode.
for BUSY stop.
(If
the switch is kept depressed,
Signal
is absent in the BUSY stop channel, the
Signal
scan
is restarted
Signal
is
beyond the
b)
Fig. 15 MEMORY Recall
L
The channels (9, 10) are for PRIO. M channels. In the
9 ch, 145.000.0 MHz is stored and, in the 10 ch,
433.000.0 MHz is stored. These frequencies can be
changed as desired. In this case, the PRIO. M channels (9,
IO) are also changed.
Note 1: The PRIO. M channels (9, IO) are the same as the
channels (9, IO) called out by the MR switch.
Note 2: When an empty channel is called out, only the
channel No. is indicated on the display.
Note 3: When the channels (9, IO) are called out by the
MR switch, the channel No. is indicated as"C, C
Note 4: When a frequency, stored in ON Position of
F. STEP switch, is called out, the F. STEP LED
will light.
Note 5: Frequency down to 10 Hz
frequency Change due to RIT is not stored.
Note 6: In the FM-CH mode, the frequencies on the 1 kHz-
10 Hz
Order
are stored as “0”. When called out,
the full frequency is indicated on the display.
Note 7: In repeater Operation, when a frequency is stored
during transmission, only the frequency which is
not shifted is stored.
Order
is stored, but the
Other modes
1.
Search Operation only; BUSY stop is not used.
Depress the HOLD switch or transmit
Signals.
The
scan
is released and the FUNCTION Stops flickering.
Use of SCAN W Switch
The SCAN W switch is used to adjust the
The
scan
width is changed according to the frequency at
the Start of scan. The following
Shows
the Operation of the
scan
width.
SCAN W switch in the FM-CH mode where the frequency
is scanned starting from 431.637.5 MHz.
SCAN
W
switch
0.5
430
r
I
3
431 431.5 432 433
l
il 1’
434 436
433.981.5
I
I III
440
‘!
5
IO
.__-------
430
__---
431
__----
____-_--
.637.5
-------
439.987.:
c
440
Fig. 16
17
Page 19

IO.5 MHz1
When the scan, starting from 431.637.5 MHz, reaches
the upper limit 431.987.5 MHz, it jumps down to the
lower limit 431.500.0 MHz where the
again. This action is repeated while holding 0.5 MHz
width.
(1
MHz]
When the
upper limit 431.987.5 MHz, it jumps down to the lower
limit 431 .OOO.O MHz and reaches 431.987.5 MHz again.
This action is repeated while holding 1 MHz width.
[3
MHz]
Similarly, when the
431.000.0 MHz to the upper limit 431.637.5 MHz, it
jumps down to the lower limit and reaches the upper limit
again. This action is repeated while holding 3 MHz width.
The lower limit is 431.637.5 MHz minus the frequency
on 100 kHz
one step lower than 434.000.0 MHz which is the lower
limit plus 3 MHz but the
[5
MHz1
The upper and lower limits are calculated in the same
manner as for 3 MHz width. The
the lower limit and the upper limit while holding 5 MHz
width.
[lO
MHz]
The
439.987.5 MHz and the lower limit 430.000.0 MHz
while holding 10 MHz width.
430 431
SCAN
.w
switch
j-----
Note 1: In the SCAN W Position 3, 5 or 10, the
Note 2: In these Position, the
Note 3: The
Note 4: The
scan
reaches from 431.637.5 MHz to the
scan reaches
Order,
and the upper limit is 433.987.5 MHz,
scan
Starts from 431.637.5 MHz.
scan
scan
is repeated between the upper limit
432
433 438 433
432.967.5
---------1
144 MHz band is repeated between the upper
limit 145.987.5 MHz and the lower limit
144.000.0 MHz.
scan
does not shift over the
144 and 430 MHz bands. For example, when the
SCAN W is 5 in 438.250.0 MHz, the
fected holding 5 MHz width.
scan
width should be calculated even in the
following
1)
When VFO (A, B) is switched.
2) When SCAN W switch is set to another posi-
3) When BAND switch is depressed.
SCAN switch is depressed for BUSY stop.
To Change the
released.
cases:
tion.
scan
width remains unchanged when the
scan
width, the
scan
is started
from the lower limit
is repeated between
I
I,
scan
in the
scan
is ef-
scan
should be
440
Note 5: The BAND switch can be used during
tion, but it does not function continuously when it
is kept depressed. This switch also functions even
when the F. LOCK switch is ON.
The
scan
is released when the PRIO. M, MR or MS switch is
set to ON.
scan
opera-
5-15 USE OF MS (MEMORY SCAN) SWITCH
When the 144 MS or 430 MS switch is set to ON, the
function (CH No.) flickers to indicate that the memory
channels (l-l 0 ch) can be scanned (the squelch threshold
should be set as in the case of VFO scan).
With the 144 MS switch ON, the memory channel for
144 MHz band can be scanned. With the 430 MS switch
ON, the memory channel for the 430 MHz band is scann-
ed. When both switches are ON, all the channels (both for
144 and 430 MHz bands) are scanned. To hold the scan,
use the procedure for VFO scan. To restart the scan, set
the SCAN switch to ON.
Note 1:
Note 2: When
Note 3: When all the channels are 144 MHz band and the
Note 4: Only memorized channels are scanned.
5-l 6 USE OF
quencies in the memory channels 9 or 10 can be recalled
with first priority. In the channel 9 and 10.
145.000.0 MHz and 433.000.0 MHz are preset respec-
tively, while any frequency can be memorized in
channel. Display of the PRIO. M channel is as follows:
c
Note: 1 The PRIO. M 9 is
Note: 2 The PRIO. M channel frequency is displayed to
5-17 BACKUP OF MEMORY CHANNEL
Scan
is not effected when the SCAN switch is
kept depressed.
scan
is held in the ON Position of both MS
switches, it can be restarted by setting either
switch to OFF or by pressing the CALL or MR
switch.
430 MS switch is set to ON, the function flickers
quickly and a oscillation Sound is heard continuously. This also occurs when all the channels
are 430 MHz band and the 144 MS switch is set
to ON.
PRIO.
M CHANNEL
With the PRIO. M 9 or 10 switch set to ON, stored fre-
each
:5;5,UfiQ,G
100 Hz digit.
or c
$r_r(J,fia2,U
Prior
to the PRIO. M 10.
FRE-
QUENCY
Any desired memory channel frequency can be stored in
the RAM (Random Access Memory) of the micro-
Computer. But the data (frequency) in the RAM is cleared
when the power switch is set to OFF. The transceiver has
its own built-in backup circuit to hold the data (frequency)
even when the power switch is OFF during both AC and DC
operations. By loading backup battery in the transceiver
battery case, the battery power is always supplied to the
backup circuit. In this way, the data is not. cleared
regardless of the Position of the power switch. The backup
18
Page 20

current is less than 10 PA and the battery lasts for about
one year. When the backup circuit is not used, the VFO frequency returns to 144.000.0 MHz in the OFF Position of
the power switch.
5-18 OPERATION ON EXTERNAL DC POWER
(MOBILE OPERATION)
The TS-780 also operates on external DC power
(DCI
3.8 V* 15%) for mobile Operation.
Installation
The method of mobile Operation is basically the same as
that of fixed Station Operation.
Select a suitable location for installation of the
transceiver. The installation location may vary depending
on the size and structure of car. The transceiver may be
placed
on the passenger’s seat; in this case, it should be
secured with the seat belt so that it will not drop off the
seat if the car Stops suddenly.
5-
19 REPEATER OPERATION
The TS-780 is capable of the following repeater operations on the bands of 144 MHz to 146 MHz and 430 MHz
to 440 MHz.
Frequency Shift
144 to 146 MHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-A
D-B
430 to 440 MHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .D-A
D-B
In the D-A Position, the transmitting frequency is
7.6 MHz lower than the receiving frequency. In the D-B
Position, the transmitting frequency is 1.6 MHz lower than
the receiving frequency.
If the transmitting frequency is outside of the amateur
band, the digital display goes out and no
transmitted.
-600 kHz
+ 600 kHz
-
7.6 MHz
-
1.6 MHz
Signals
will be
Mobile Antenna
Various types of mobile antennas are available for use
on 144 and 430 MHz bands. You can use a
wavelength whip antenna, ground plane antenna or 5/8
wavelength antenna.
Note:
Most roof mount antennas are designed so that the antenna base is earthed to the car body. Mount the antenna
securely referring to the instruction manual supplied with
the antenna.
DC Cable
When the transceiver is to be operated from DC power,
a DC power cable with an 7 A fuse should be used.
In DC Operation, please prepare a DC cable as Fig. 18.
DC power
Battary Capacity
During mobile Operation, the transceiver draws about
5 A of current, so a battery having about 35AH of capacity
is sufficient for proper transceiver Operation. However,
since the battery is given an additional load, it is advisable
to use the transceiver while the car engine is operating.
Note:
To insure safe driving of car, it is recommended that the
transceiver be operated in fixed channel mode.
Cord
Fig. 18 DC Cable
1/4
Operating Procedure:
1)
Turn the band switch to the Position representing the
operating frequency.
2) Set the TX-OFFSET switch to the appropriate Position.
The OFFSET indicator lights.
3) Turn the VFO dial to the desired receiving frequency,
and push the TONE switch. The built-in tone oscillator
circuit (1,750 Hz) operates to send the 1,750 Hzmodulated
TONE switch is a non-leck type so that, when the
switch is released, the tone oscillator Stops sending the
Signals.
The transmitting frequency is shifted 600 kHz down
from the receiving frequency on the band of 144 to
146 MHz at D-A Position; and 7.6 MHz or 1.6 MHz
down from the receiving frequency on the band of 430
to 440 MHz depending on the TX-OFFSET switch
tion. The shifted frequencies are digitally indicated.
If any of the shifted frequencies is outside of the
amateur band, the digital display goes out, and no
Signals
The REV switch is used to check repeater input Signal.
By depressing that switch, the TX and RX frequencies
are reversed.
In case of other shift repeaters, set the SHIFT switch to
SIMP, and the function switch to A-R or B-R.
For example, in case of a repeater Station with a shift of
+ 1 .6 MHz from 433 MHz, set the function switch to
the A-R Position, VFO-A to 433.0 MHz and VFO-B to
434.6 MHz.
Then the TS-780 receives 433.0 MHz and transmits
434.6 MHz Signals.
In a similar way, repeater operations of other shifts are
possible.
Signal
to operate a repeater Station. The
will be transmitted.
posi-
19
Page 21

5-20 OSCAR OPERATION
At present, two amateur radio communication satellites
(No. 7 and No. 8) are travelling along the
(No. 6 is not available because the battery power has been
exhausted). These satellites can be used as your repeater.
The TS-780 will function when used with the satellites as
follows.
[OSCAR No. 71
A mode: 2 m - 10 m . . . . . . . . . . Repeater up-link transmitter
B mode: 70 cm- 2 m.........Repeater up-link transmitter
or Repeater downlink receiver
[OSCAR No. 81
A mode: 2
J mode: 2 m- 70 cm.........Repeater up-link transmitter
[RADIO 1,2)
Table 5
plication of the TS-780 in 70 cm- 2 m repeater Operation
is illustrated in Fig. 19.
m~10
m
. . . . . . . . . . Repeater up-link transmitter
or
Repeater down-link receiver
2 m - 1 0 m . . . . . . . . Repeater up-link transmitter
Shows
the link frequencies. An example of ap-
Orbit
of the earth
OSCAR Operation with the TS-780 alone where the
FUNCTION switch is set to A-R and the VFO A is used as a
430 MHz band receiver and the VFO B as a 145 MHz band
transmitter, is not possible because the downlink
cannot be monitored.
In OSCAR Operation, it is imperative to use a separate
transmitter and receiver so that the downlink
received as shown in Fig. 19. lt is also necessary for you to
become acquainted with some special knowledges relative
to the
Orbit
tracking of satellite, usage of beacon waves,
operating manner, antenna installation, etc.
With
basic
knowledges, you will be able to enjoy
repeater communication through the amateur satellites
with little difficulty. Reference materials such asguide
books and instruction books are available from market.
Signal
Signal
can be
5-21 AUX SOCKET
This socket is used for connecting the suplied DIN con-
nector to supply the following voltages to external equip-
ment.
View from the rear Panel
Cross type
Yagi antenna
for DX QSO
Microphone
Up-link
frequency
Down-link
frequency
Beacon
frequency
*
B or J mode are received by LSB mode.
Transmit only
Fig. 19 Example of OSCAR Operation
OSCAR No. 7 OSCAR No. 8
OSCAR satellite
(A
mode)
Receive only
RADIO
No. 1, 2
(2m-10m
145.88
to
145.92
29.360
to
29.400
7 IbR
03
Cl
5
9’
Fig. 20 AUX Socket
Terminal
1 3 /
The AUX socket is used for connection to a linear
amplifier, receiver booster or external standy unit. When
using care should be taken so that
at the terminals 2, 4 and 5 will not exceed 10 mA, as
otherwise the transceiver may be damaged.
Symbol Application
NO.
1
2 E43 8 V DC 10 mA
NC
ELC
t
Open terminal
Extemal ALC input terminal
Transmitter operates when earthed.
Table 6
*
10
4
2
(430
MHz)
each
of the load currents
Table 5
20
Page 22

The following optional accessories are available with the
TS-780.
0 Communication Externat Speaker SP-7 1
This speaker provides clear,
high-Cut cone, best suited for communication use.
0 Communication Headphones HS-4
Specifically designed with consideration given to the shape
of ear pads, materials and weight to insure many hours of
fatigueless listening. The impedance is 8 Ohms.
0 High Class Communication Headphones HS-5
The most ideal headphones with “open air” type ear pads
to eliminate pressure to the
natural
tone. The open air type ear pads can be readily
replaced with the pressure type ones.
natural
tone with the use of a
head
and ears and to provide
,
0 Light-weight Communication Headphones HS-6
Specifically designed to reduce the weight and to improve
the tone quality.
0 Ham Clock HC-l 0
The HC-10 is a highly advanced world clock with dual
display which memorizes 10 world major cities and 2 additional regions.
0 De-Luxe Fixed Station Microphone MC-60/S8
Communication microphone with a piano-touch PTT
switch specifically designed for fixed Station Operation.
SP-7 1
HC-l 0
HS-4
HS-5
MC-60/S8
Page 23

jll,ll.llllll.(lllll.~,,,,,.,,,,,,.,,,,,,.,,,,,,.,,,,,,.,,,~,,,,,,.,,,,,,.~,,,,,.,,,,,,.,,,,,,.,,,,,,.~,,,,,.~,,,,,.,,,,,,.,,,,,,.,,,,,,.,,,,,,.,,,,,,.‘,,,,,.~,,,,,.,,,,,,.‘,,,,,.,“,,,.,
i
i
SECTION 7. TROUBLE SHOOTING
,111
I., w, I.,
,111
,.I
,111
I.,
,111 ,.I ,111
,.,,,,, ,.,
,111 I.4111,
,., ,u, I., ,,,,,.,
M,, m ,111
,.I
,111 I
.,,,w. I,,,,, *
,111,. ‘
,,,,,&
i
:
i
SYMPTOMS
No receiver noise from speaker in FM Squelch circuit is ON.
mode.
Transceiver is connected to antenna, but 1. Antenna connectors for 144 and
no Signal is received, while “S” meter
pointer remains deflected. correctly.
Even in the absence of Signal, “S” meter
pointer remains deflected.
SSB Signal is being received but speaker. Transceiver is set for opposite side band.
RIT control inoperative. RIT switch is OFF. Set RIT switch to ON (indication of digital
SSB receive Signal is in “high Cut” or “low
Cut”.
~--.
No transmit output (SSB).
No transmit output (CW). 1. Improper connection of KEY jack or
No side tone during CW Operation. S-TONE control in minimum Position. Turn the S-TONE control clockwise.
No FM modulation or insufficient modula- FM-MIC control in minimum Position.
tion.
--~-
VOX not operating. 1. VOX switch is OFF. 1. Set VOX switch to ON.
Sound Stops when dial is turned quickly in PLL unlock circuit is operating; this is normal and is not an indication of trouble.
F.STEP ON.
Channel scanned first is not clearly
indicated when MS switch is set to ON. MS switch to ON once again, or wait until the scan complets one cycle.
Scan does not continue when F.LOCK is
ON or BAND SW is depressed.
~-
UP/DOWN Speed is slow when dial is turn- The Speed is controlled by the dial.
ed during continued UP/DOWN of BAND.
RX
frequency which is not shifted is stored Unshifted RX frequency is stored during repeater Operation.
when TX frequency is stored during
repeater Operation.
When VFO A is 433.00 MHz and VFO B is Repeater Operation at A-R and B-R is complex. Use the A or B Position.
145.00 MHz during repeater Operation,
the display flickers (VFO A and B are indicated alternately) at function A-R TX
OFF SET
When the power switch is set to OFF and Set the power switch to ON more than 10 seconds after it has been set to OFF.
ON without using the backup circuit, VFO
and memory CH are not reset properly.
When their is a faulty indication.
” -”
or ” + ” and REV SW ON.
-
430 MHz bands are not connected
2. Squelch is ON. 2. Turn squelch control counterclockwise.
3. Microphone PTT switch is depressed. 3. Set PTT switch to receive Position.
RF GAIN control is set too low. Turn RF GAIN control fully clockwise.
Maladjustment of IF SHIFT. Set the control in the Center (detent)
1. Poor contact of MIC jack or plug. 1. Connect the microphone plug securely.
2. SSB MIC control in minimum Position. 2. Turn SSB MIC control clockwise.
poor contact of KEY.
2. CARL control in minimum Position. 2. Turn CAR.L control clockwise.
2. VOX GAIN control in minimum Position. 2. Turn VOX GAIN control clockwise.
When Signal is present in the first channel, the scan busy Stops (FM, FM-CH mode). Set
Scan Operation is effected even when F.LOCK is ON. The BAND UP/DOWN is possible
during scan Operation.
Set the power switch to OFF (when using the back-up function, this should be done after
removing the batteries), and reset it to ON after a few seconds. Check that the switch
has been correctly reset before inserting the batteries.
CAUSE
-
COUNTERMEASURE
Turn SQUELCH control counterclockwise.
1. Check antenna and connect correctly.
Set MODE switch to LSB or USB.
display remains the Same).
Position.
1. Connect the KEY securely.
Turn FM-MIC control clockwise.
22
Page 24

--
Bedienungsanleitung
für den
70cm/2m-FM/SSB/CW-
Transceiver
TS-780
-
@
KENWOOD
TS-780
Page 25

Inhaltsverzeichnis
Technische Daten
1. Besondere Eigenschaften .......................................
2. Betriebsvorbereitungen ..........................................
3.
Bedienungselemente und ihre Funktionen .............
4. Anschlüsse
5. Bedienungsanleitung
6. Lieferbares Zubehör
7. Fehlersuchtabelle ...................................................
Blockschaltbild
Gesamtschaltbild
Innenansichten
Die in Klammern stehenden Ziffern entsprechen den Seitenzahlen
des engl. Original-Handbuches
Frequenzbereiche . . . .
Betriebsarten. . . .
Frequenzdrift . . .
SENDETEIL
Hf-Ausgangsleistung. . . .
Frequenzabweichung . . .
Frequenzhub. . . . . .
Modulation . . . . . .
Seitenbandunterdrückung . .
Trägerunterdrückung . . .
Nebenwellenabstrahlung . .
Mikrofon-Impedanz . . .
........................................................
.............................................................
..............................................
..............................................
im Anhang des engl. Original-Handbuches
(INSTRUCTION
MANUAL)
Technische Daten
2 m: 144.000 - 146.000 MHz
70 cm: 430.000 - 440.000 MHz
. *
.
.
. * . . .
.
. .
.
.
.
.
. .
.
. .
.
.
.
.
. .
SSB (A3J). CW
?
1,5 kHz innerhalb der ersten Betriebsstunde nach 1 Minute
Einlaufzeit; danach L 500 Hz/30 Minuten.
Hl = 10 W, LOW = 1 W (nur bei FM),
.
bei SSB und CW stufenlos einstellbar
<+10x10-6
.
+5kHz
.
SSB: durch Balancemodulator
.
FM: Frequenzmodulation durch Reaktanzmodulator
>40 dB
>40 dB
Hl = < -60 dB, LOW = < -40 dB
500 - 600 Ohm
(A1 )
(2)
(3) 3
(4) 3
(5) 6
(9) 8
(11) 10
(21) 18
(22) 19
FM (F3)
2
EMPFANGSTEIL
Schaltungsart . . . .
Zwischenfrequenzen . . .
Eingangsempfindlichkeit .
Nebenwellenunterdrückung
Trennschärfe . . . .
SSB, CW . . . . . .
FM . . . . . .
Squelch-Empfindlichkeit .
Suchlauf-Empfindlichkeit .
Nf-Ausgangsleistung . .
ALLGEMEINES
Hf-Ausgangsimpedanz . .
Betriebsspannung . . .
Speicher-Dauerstromversorgung
Leistungsaufnahme . . . .
Stromverbrauch . . . . .
Betriebstemperatur . . . .
Abmessungen
Gewicht . . . . . . .
(BxHxT)
. . .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
*
.
. . . . . .
.
. .
.
. .
. . .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. . .
. . .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. 9 .
.
.
.
.
.
. .
SSB, CW: Doppelsuper
FM: Dreifachsuper
1.
Zf: 30,865 MHz, 2. Zf: 10,695 MHz
2. Zf: 455 kHz (nur bei FM-Empfang)
SSB, CW: 0.2 UV für 10 dB S/N
FM: 1.0 UV für 30 dB S/N
0,2 UV für 12 dB SINAD
.
60 dB
.
2,2
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
kHz/-6
14
kHz/-6
0,16 UV (Schwellwert)
0,2 UV (Schwellwert)
2 Watt an 8 Ohm
50 Ohm, Coax (1 PL-, 1 N-Norm-Anschluß)
Netzbetrieb: 220 V~ , 50-60 Hz
Batteriebetrieb: 13.8 V= (Minuspol an Masse)
durch drei 1,5 V-Mangan-Mignonzellen (Lebensdauer ca. 3 Jahre)
Netzbetrieb: TX max. 130 W
Batteriebetrieb: TX max. 5 A
Speicher-Dauerstromversorgung: 10 uA
-10
290x124x322mm
10,1 kg
dB, 4.8
dB, 30
C bis+50°C
kHz/-60
kHz/-60
RX max. 45 W (o. Signal)
RX max. 1,2 A (o. Signal)
dB
dB
Technische Änderungen ohne Vorankündigung jederzeit vorbehalten
Copyright @by Trio-Kenwood Inc., Tokio, Japan. Übersetzt durch Trio-Kenwood Communications GmbH, 6374 Steinbach, W. Germany mit
Genehmigung der Trio-Kenwood Inc. Nachdruck - auch auszugsweise - verboten. 1. Auflage,
2
.
April 1982 , Printed in W. Germany
Page 26

Einleitung
Sie sind nun stolzer Besitzer unseres neuesten 2 m/ 70 cm-Duoband-Transceivers, des Kenwood TS-780. Vor seiner Auslieferung mußte das
Gerät zahlreiche strenge Fertigungs- und Endkontrollen durchlaufen, um seinen hohen Leistungsstandard unter Beweis zu stellen. Lesen Sie
diese Bedienungsanleitung genau durch, bevor Sie Ihren neuen Transceiver erstmalig in Betrieb nehmen. Bei sachgemäßer Bedienung wird
.Ihnen der TS-780 jahrelang zuverlässige Dienste leisten.
Bitte verwahren Siedas gesamte Verpackungsmaterial sorgfältig auf, damit Sie das Gerät im Falle einer erforderlich werdenden Instandsetzung
bruchsicher verschicken können.
Verehrter Kunde,
infolge der unaufhaltsamen Preissteigerungen, die auch vor dem Druckgewerbe nicht haltmachen, haben wir uns entschlossen, die deutschsprachigen Bedienungsanleitungen für unsere Amateurfunkgeräte etwas zu vereinfachen. Dies betrifft in erster Linie die Beschriftungen innerhalb der zahlreichen Textabbildungen in dem englischen Instruction Manual, die nach erfolgter Übersetzung ins Deutsche an gleicher Stelle
wieder einmontiert werden müssen, Dieser Vorgang ist sehr zeitaufwendig und verursacht erhebliche Druckkosten, die wir auf keinen Fall an
unsere Kunden weitergeben wollen. Die Mehrzahl der Abbildungen in dem engl. Instruction Manual ist so klar und eindeutig, daß sie keiner
näheren Erläuterung bedürfen. Ist dies dennoch der Fall, finden Sie den entsprechenden Text in dieser Bedienungsanleitung unterhalb der
Abbildung in deutscher Übersetzung. Wir wollen Ihnen damit die Mühe ersparen, fortlaufend in der deutschen und englischen Bedienungsanleitung blättern und die entsprechenden Textstellen aufsuchen zu müssen und hoffen - Ihr Einverständnis vorausgesetzt - daß Ihnen die Umstellung auf das neue, noch etwas ungewohnte Format der Bedienungsanleitung leichtfallen wird.
Ihre
Trio-Kenwood Communications GmbH
Teil 1 - Besondere Eigenschaften
0
70 cm/2 m-Duoband-Transceiver für die Betriebsarten FM, SSB
1.
(USB, LSB) und CW
Weitgehende Automatisierung und Steuerung der VFOs sowie
0
nahezu aller anderen Funktionen durch 8 bit-Mikroprozessor.
0
FM-Teil in bewährter Kenwood-Schaltungskonzeption und her-
vorregende Qualität der SSB-Signale.
Eingebaute VOX-Steuerung
0
Semi-break-in-Betrieb in CW mit eingebautem Mithörton-
0
Generator.
0
Neuartige Leistungsverstärker-Module in der Sender-Endstufe
für beide Bänder.
Eindeutige Einstellung und Ablesung der jeweiligen Arbeits-
2.
frequenz in allen Betriebsarten durch Digitalanzeige
0
7-stellige Digitalanzeige mit einer Auflösung von + 100 Hz.
0
Digitale Anzeige der Trägerfrequenz bei Betriebsartenwechsel.
Digitalanzeige aus 7-Segment-Zifferelementen, durch hellgrüne
0
Phosphor-Leuchtschicht auch bei Sonnenlicht klar erkennbar.
0
Zwei Digital-VFOs (A & B) ermöglichen interessanten ,,Duplex”Betrieb auf beiden Bändern.
0
10 Memorykanäle zur Speicherung von Betriebsfrequenzen nach
eigener Wahl in beiden Bandbereichen, wobei die beiden Vorzugskanäle CH 9 und CH 10 durch Betätigung der PRIO.MSchalter sofort abgerufen werden können.
Digitale Anzeige des jeweils zugeschalteten VFOs
0
Memorykanäle (1 bis 8) und der Vorzugskanäle (c und c).
0
Automatische Abrundung der Betriebsfrequenz auf den nächstniedrigeren Kanal bei FM-Kanalraster-Betrieb (FM-CH).
3.
Zuverlässige mechanische und elektrische Funktionen:
0
VFO-Rasterschritte bei FM-Kanalbetrieb
Stufen einstellbar: Schnell (FAST) mit 12.5 kHz-Raster und
langsam (SLOW) mit 5 kHz-Raster.
0
Drehmoment des VFO-Abstimmknopfes durch zuschaltbare
Friktionsbremse einstellbar.
0
Drucktastengesteuerter Bandschalter mit manuellem Suchlauf
vorwärts und rückwärts in 1 MHz-lnkrementen innerhalb des
gesamten 2 m- und 70 cm-Bandes von 144 - 146 MHz, bzw.
430 - 440 MHz in zwölf einzelnen Bandabschnitten.
0
Bei Bandwechsel entfällt die Nachabstimmung der Hf-Kreise
durch die breitbandige Auslegung der Sender- und Empfänger-
schaltung.
0
Ergonomisch gestaltete Frontplatte mit funktionell richtiger
Anordnung der verschiedenen Regler und Schalter.
(FM-CH)
(A,
b), der
in zwei
LED-Leuchtanzeigen zur Überwachung aller wichtigen Funktionen wie Sender-Frequenzablage
AIR), belegte Kanäle
Empfänger-Feinverstimmung (RIT) und Frequenzraster
(F.STEP).
0
Stabile, verzerrungsfreie Sende- und Empfangssignale durch
AGC- und ALC-Verstärkungsregelungen.
4.
Vielseitige Betriebsmöglichkeiten und beispielloser Bedienungskomfort
0
Speicherung und Abruf beliebiger Frequenzen auf 10 RAM
Memorykanälen.
Eingebaute Batterie-Halterung für die Dauerstromversorgung
0
der Speicherschaltung.
0
Memory-Suchlauf im 2 m-Band zwischen 144 und 146 MHz
und im 70 cm-Band zwischen 430 und 440 MHz nach freier
Wahl.
0
Empfänger-Feinverstimmung
auch bei den Memory- und Vorzugskanälen wirksam ist.
0
Einschaltbare Sperre der Hauptabstimmung
0
Duplex-Betrieb über Umsetzer mit vorwählbarer Frequenzab-
lage (-600 kHz/SIMPLEX/+600 kHz) im 2 m-Band, bzw.
(-7,6 MHz/SIMPLEX/-1.6
1750 Hz-Ruftongenerator zum Auftasten von Umsetzern. Bei
überschreiten der Band-Grenzfrequenzen ertönt ein Warnsignal
und der Sender wird auf Simplex geschaltet.
0
Wirkungsvolle Ausblendung impulsförmiger Störsignale wie z.B.
Kfz-Zündfunkenstörungen durch die einzigartige KenwoodStöraustastung.
Vierfunktions-Instrument, das als S-Meter, Hf-Leistungsmesser,
0
ALC-Messer, sowie als FM-Kanalmittenanzeiger dient.
0
Sender-Endstufe auf 1 W (LOW) und 10 W (HIGH) Ausgangsleistung umschaltbar in FM, stufenlos einstellbar in SS8 und CW.
0
AUX-Buchse zum Anschluß von Zusatzgeräten.
5.
Für ortsfesten und Mobilbetrieb geeignet:
Wahlweiser Netzbetrieb mit 220/240
0
mit 12 V=.
0
Eingebauter Tragegriff zum bequemen Transport.
Erstaunliche Nf-Ausgangsleistung (2.5 Watt an 4 Ohm)
0
Klangvoller Einbaulautsprecher (Korb- D:7,5 cm) und Anschluß-
0
buchse für Zusatzlautsprecher.
(BUSY),
(OFFSET),
Abstimm-Sperre (F.LOCKj,
(RIT),
die bei beiden VFOs, sowie
MHz) im 70 cm-Band. Eingebauter
V~oder
Sendung (ON
(F.LOCK)
Batteriebetrieb
Teil 2 - Betriebsvorbereitung
2.1 Kontrolle des serienmäßigen Zubehörs
Im Versandkarton muß sich das folgende serienmäßige Zubehör
befinden:
Bedienungsanleitung, deutsch
Instruction Manual (B50-3957-00)
Glasrohr-Feinsicherung 2 A
Glasrohr-Feinsicherung 7 A
Fuß (mit Befestigungsschraube)
Lautsprecherstecker (mini-Klinkenstecker 3.5 mm 6) . . . . . . . . . . . 1 Stück
DIN-Stecker
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
(f.
Netzbetrieb)
(f.
Batteriebetrieb)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Stück
Stück
2 Stück
2 Stück
2 Stück
Stück
Stromversorgungskabel für Netzbetrieb ..,............................. 1 Stück
Stromversorgungskabel für Batteriebetrieb
Handmikrofon mit PTT- und Fernbedienungs-Suchlauftasten 1 Stück
2.2 Wahl das geeigneten Standortes
Wie alle transistorisierten Geräte ist auch der TS-780 hitze- und
feuchtigkeitsempfindlich. Wählen Sie daher einen trockenen und
kühlen Standort, an dem das Gerät weder direkter Sonneneinstrahlung noch übermäßiger Wärme durch Heizkörper, Kamine o.a. ausgesetzt ist.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1 Stück
3
Page 27

430 MHz
1
Antenna
0
Use an antenna of 50 ohms
impedance. The antenna can
be connected through an M
type coaxial cable connector.
(For
details, refer to page 9.)
Connection of electric ke
4
Externat speaker
0
A speaker is included in the unit.
wish to use
it by using the supplied speaker
communication-use (low/high
speaker rated at 4
mended. The
designed
cteristics of the TS-780. Plugging in an
external speaker will automatically
disconnect the built-in speaker. D
connect the speaker to the PHONES jack,
as this jack has a level adjusting resistor.
an external speaker, connect
-
8 ohms is recom-
Option
to
perfectly match the chara-
speaker (SP-7 1) is
cut
If
you
plug.
type)
O not
A
ble
location: Con-
It II il II /I !I II II
Power
supply connection
The power
ing
squeeze the
properly
Cord,
It IS
cord
tab. When connecting the
squeeze the
released from the locked
has a 4P plug with a lock-
locking
fits in place. To disconnect the
tab to ensure that it
locking
tab again until
position.
I I il
Cord,
External speaker
SP-71
II
I I
Connection of speaker plug
When connecting an external speaker, be
careful not to short circuit the AF output.
The spaker
type and should be as short as possible to
Pöwer supply
The unit is designed to operate on AC
ching
between AC and DC is accomplished by replacing the power
(DC power
to observe the following Points:
1. Turn off the power switch and set the standby switch to REC
2. When replacing the power
Failure to observe the above procedure might result in electric shock or
darnage to the
cord IS
optional.) When connecting the power
tion.
(or
battery) with care.
unit.
Cord,
A
I
JJ
cord
should be of a shielded
(220
VI or DC (13.8 V). Swit-
Cord.
be sure
posi-
disconnect It from the AC supply
I
cord
2.3 Anschluß der Antenne, der Stromversorgung und der Zusatzgeräte
1 Antenne
Zum Anschluß geeignet sind alle 50 Ohm-Antennen für das 2 m-,
bzw. 70 cm-Band mit Coax-Speiseleitung und Coax-Steckverbindern
der Typenreihe ,,PL” und ,,N". Näheres darüber in Abschnitt 4
(Anschlüsse).
”
2
Erde
Zur Gewährleistung der Berührungssicherheit, sowie zur Vermei-
dung von Fernseh- und Rundfunkstörungen sollte der Transceiver
unbedingt geerdet werden. Dazu die GND-Klemme über ein ausreichend starkes, isoliertes Kabel (Masseband) mit einer MetallrohrWasserleitung oder einem Erdungsspieß verbinden.
ACHTUNG! Gasleitungen dürfen auf keinen Fall zur Erdung benutzt werden. Die Erdleitung sollte so kurz wie möglich sein.
3 Morsetaste
Zum Anschluß geeignet sind normale, halbautomatische und elek-
tronische Tasten, die über eine abgeschirmte Leitung mit der Buchse
KEY an der Rückwand des TS-780 verbunden werden. Beim Anlöten des Klinkensteckers (6.3 mm 4) an das Anschlußkabel der
Taste auf die aus der Detailabbildung ersichtliche Polung achten.
4 Außenlautsprecher
Zur Verbesserung der Sprachverständlichkeit - insbesondere bei
SSB-Empfang - kann zusätzlich zum eingebauten Lautsprecher
noch ein Außenlautsprecher wie die Kenwood-Modelle SP-70 oder
SP-71 an den TS-780 angeschlossen werden. Ansonsten werden
Lautsprecher mit begrenztem Übertragungsbereich (400-2600 Hz)
und einer Impedanz von 4 - 8 Ohm empfohlen. Bei angeschlossenem
Außenlautsprecher ist der Einbaulautsprecher abgeschaltet. Den
Außenlautsprecher nicht an die Kopfhörerbuchse anschließen, da
sonst der Wiedergabepegel durch die eingebaute gehörrichtige
Lautstärkekorrektur zu gering ist.
I
5. Anschluß des Lautsprechersteckers
Den serienmäßig mitgelieferten 3,5 mm-Miniatur-Klinkenstecker
wie gezeigt an das Lautsprecherkabel anlöten, dabei aber unbedingt
Kurzschlüsse des Nf-Ausgangs vermeiden. Zur Verhinderung von
Hf-Einstreuungen und Rückkoppelungen sollte als Lautsprecherkabel eine möglichst kurze, abgeschirmte Leitung verwendet
werden.
6 Anschluß des Stromversorgungskabels
Am Ende des Stromversorgungskabels ist eine 4-polige SpezialKupplung mit Sicherungslaschen angebracht. Zum Anschluß die
Sicherungslaschen wie gezeigt etwas zusammendrücken und die
Kupplung bis zum Einrasten auf die Steckerstifte am Transceiver
schieben. Zum Lösen der Verbindung die Sicherungslaschen
wieder zusammendrücken und die Kupplung nach hinten abziehen.
7 Stromversorgung
Der TS-780 kann wahlweise mit Netzspannung (220 V~, 50-60
oder Gleichspannung (13,8
werden. Die Umschaltung von einer Stromart auf die andere erfolgt
automatisch durch die Kontaktbelegung der Spezialkupplung am
Ende des Stromversorgungskabels. Beim Anschluß des Kabels fol-
gende Punkte beachten:
1. Den POWER-Schalter in Stellung ,,OFF” und den
Schalter in Stellung ,,REC” bringen.
2. Beim Übergang von einer Stromart auf die andere, das Strom-
versorgungskabel vorher immer zuerst von der Spannungsquelle
(Netzsteckdose oder Batterie) trennen.
Nichtbeachtung kann zu gefährlichen elektrischen Schlägen oder
zu Schäden am Transceiver führen.
V),
z. B. aus einer Autobatterie betrieben
STANDBY-
Hz)
4
Page 28

Teil 3 - Bedienungsorgane und ihre Funktion
r
8
3.1 Frontplatte
1
Leuchtanzeige für Abstimmsperre 1 F. LOCK)
Diese Anzeige leuchtet, wenn sich der Schalter F.LOCK 39 auf
,,ON” befindet und die VFO-Frequenz verriegelt ist.
2 Leuchtanzeige für besetzte Kanäle (BUSY)
Diese Anzeige leuchtet, wenn bei geöffneter Rauschsperre
(SQUELCH) in den Betriebsarten FM und FM-CH eine Gegen-
station auf dem betreffenden Kanal empfangen wird, die ein
Trägersignal aussendet. Auf diese Weise kann jederzeit kontrolliert
werden, auf welchem Kanal Funkbetrieb herrscht.
3 Sender-Betriebsanzeige (ON AIR)
Diese Anzeige leuchtet während des Sendebetriebs.
4 Anzeige für Sender-Frequenzablage
Diese Anzeige leuchtet, wenn der Schalter TX OFFSET 6 auf
-
A oder D - B eingestellt ist, z. B. bei Umsetzer-Betrieb.
D
5 Meßinstrument (METER)
Dieses Zeigerinstrument hat vier verschiedene, am METER-Schalter
11 wählbare Funktionen:
RF/S:
ALC/CEN: Bei FM-Empfang d. h. in Stellung ,,FM”, bzw. ,,FM
Bei Empfangsbetrieb arbeitet das Instrument als SMeter und zeigt die relative Feldstärke des
bei FM-Betrieb auf der Teilskala ,,S" von 1 bis 10,
bei SSB- und CW-Betrieb auf der gleichen Skala
zwischen 1 und 9, zusätzlich noch 9 + 20 dB und
9 + 40
dB, an.
Bei Zurücknahme der Hf-Vorverstärkung (RF-Gain)
wird bei SSB/CW-Betrieb die Schwellwert-Spannung
angezeigt und es werden nur noch die Signale durchgelassen, die diese überschreiten.
Bei Sendebetrieb kann auf der Teilskala ,,RF” die
Hf-Ausgangsleistung abgelesen werden.
CH” des Betriebsartenschalters (MODE) 17 arbeitet
das Instrument als Kanalmitten-Anzeiger. Zur Scharfabstimmung bei FM Empfang den
knopf so einstellen, daß der Zeiger genau auf die
Markierung CENTER in Skalenmitte weist.
Bei SSB- und CW-Betrieb kann auf der Teilskala ,,ALC”
die ALC-Regelspannung des Senders abgelesen werden.
Dazu bei SSB-Betrieb den Regler MIC GAIN 24, bei
CW-Betrieb den Regler
der Oberseite des Gehäuses) so einstellen, daß der
Zeiger keinesfalls über den ALC-Skalenbereich ausschlägt.
(OFFSET)
VFO-Abstimm-
CAR.L.
(unter der Klappe auf
RX-Signals
6 Schalter für Sender-Frequenzablege
Mit diesem Schalter läßt sich bei Duplexbetrieb über Umsetzer die
Sendefrequenz gegenüber der Empfangsfrequenz nach oben oder
unten verlagern. Bei Simplex-Betrieb auf Direktkanälen muß der
Schalter in Stellung
dann mit gleicher Sende- und Empfangsfrequenz. Bei Überschreitung der oberen und unteren Bandgrenzen erfolgt keine Sender-
Frequenzablage und das Gerät schaltet automatisch auf die Betriebsart SIMPLEX um.
7 Frequenzablage-Umkehrschalter (REV)
Durch Betätigung dieses Schalters werden die Sende- und Empfangs-
frequenzen gegeneinander vertauscht, so daß die Eingabefrequenzen
der Umsetzer zur Kontrolle abgehört werden können (sog. ,,Unter-
band-Abfrage”). Um für eine Kurzmitteilung mit umgekehrter Fre-
quenzablage (Repeater
auf Sendebetrieb umschalten und dabei die REV-Taste im ge-
drückten Zustand festhalten. Siehe auch Kapitel 5-19.
8 Tonruftaste
Durch Betätigung dieser Taste wird der eingebaute 1750 Hz-Ruf-
tongenerator zum Auftasten von Umsetzern aktiviert.
9 Sendeleistungs-Umschalter (LOW POWER)
In Stellung ,,LOW” dieses Schalters wird die Sendeleistung bei
FM-Betrieb von 10 W auf 1 W reduziert. Diese Schalterstellung
ist jedoch nur bei FM-, nicht aber bei SSB- und CW-Betrieb wirk-
sam. Bei diesen beiden Betriebsarten ist die Sendeleistung durch
die Regler SSB MIC und
10 Schalter für Störaustastung (NOISE BLANKER)
Bei SSB- und CW-Betrieb läßt sich mit diesem Schalter die einge-
baute Störaustastung aktivieren, die impulsförmige Störsignale,
z. B. Kfz-Zündfunkenstörungen, wirksam ausblendet. Diese Stör-
austastung erweist sich besonders beim Empfang schwacher Signale
als sehr nützlich. Bei FM-Empfang ist sie jedoch unwirksam, da
hierbei die ,,Störaustastung” durch die AM-Unterdrückung der
Zf-Stufen automatisch gewährleistet ist.
11 Meßinstrumenten-Umschalter (METER
Durch entsprechende Einstellung dieses Schalters arbeitet das Meßinstrument als S-Meter, ALC-Regelspannungsmesser oder bei
Betrieb als Kanalmitten-Anzeiger.
HINWEIS:
Wird der Schalter bei FM-Sendebetrieb
arbeitet das Meßinstrument als Hf-Leistungsmesser, wobei der Zeigerausschlag etwas von der Norm abweicht.
L
(TONE)
,,SIMP”
reverse)
CAR.L
(TX
OFFSET)
gebracht werden. Der TS-780 arbeitet
arbeiten zu können, den TS-780
stufenlos einstellbar.
FM-
SWITCH)
FM-
auf
ALC/CEN
eingestellt,
5
Page 29

Funktionen des Meßinstruments
I
SCHALTERSTELLUNG
t
BETRIEBSART
FM
I
SSB/CW
-2
l
) siehe obigen Hinweis
12 Schalter für sprachgesteuerte Sende/EmpfangsumschaItung
(VOX)
Durch Betätigung dieses Schalters arbeitet der Transceiver bei SSB-
und FM-Betrieb mit sprachgesteuerter Sende/EmpfangsumschaItung,
bei CW-Betrieb im semi-break-in-Verfahren (dabei auf ,,VOX” einstellen). Die VOX-Steuerung ist auch in Verbindung mit dem
STANDBY-Schalter 13 und der PTT-Taste des Mikrofons wirksam
(dabei auf ,,MAN” einstellen).
13 Sende/Empfangsumschalter
Bei Empfangsbetrieb den Schalterknopf in die untere, bei Sende-
betrieb in die obere Stellung bringen. Durch Betätigung der PTTTaste am Mikrofon schaltet der Transceiver automatisch von
Empfangs- auf Sendebetrieb um.
14 Netzschalter (POWER)
Zum Einschalten des Transceivers den Schalterknopf in die obere
(ON), zum Ausschalten in die untere Stellung (OFF) bringen.
15 Mikrofonbuchse
Spezialbuchse zum Anschluß des serienmäßigen Handmikrofons
mit PTT- und
16 Kopfhörerbuchse (PHONES)
An diese Buchse können beliebige Kopfhörer mit einer Impedanz
-
von 4
die als Sonderzubehör angeboten werden.
oder 5 kHz-lnkrementen, bei FM-, SSB (USB/LSB)- und
trieb in 20 Hz- oder 200 Hz-lnkrementen je nach Stellung des
drücken. Diese beiden Vorzugskanäle sind werksseitig
eingestellt, jedoch lassen sich bei Bedarf auch andere Frequenzen
verändert und ein unbeabsichtigtes Verstellen verhindert.
gewünschte Betriebsfrequenz.
Schalterstellungen und -funktionen:
16 Ohm, - auch Stereo-Kopfhörer - angeschlossen werden.
Eingebaute Anpassungswiderstände sorgen für eine gehörrichtige
Lautstärkekorrektur des Wiedergabepegels. Besonders zu empfehlen sind die Kenwood-Amateurkopfhörer HS-4, HS-5 oder HS-6,
17 Betriebsartenschalter (MODE)
Mit diesem Schalter lassen sich die Betriebsarten und das
Frequenzraster einstellen und zwar bei FM CH-Betrieb in 12,5 kHz-
Rasterschalters
18 Schalter für Memory-Vorzugskanäle
Zum sofortigen Abrufen des Memorykanals 9 die Taste
Q, zum Abrufen des Memorykanals 10 die Taste
145.000.0 MHz (2 m-Band), bzw. 433.000.0 MHz (70 cm-Band)
in den Vorzugs-Memories
19 Drehmomentbremse
Mit diesem Hebel läßt sich die im VFO-Abstimmknopf eingebaute
Friktionsbremse zuschalten, die das Drehmoment des Knopfes
20 Leuchtanzeige für Frequenzrasterumschalter (F.STEP)
Diese Anzeige leuchtet in Stellung ,,ON” des Schalters für die
12,5/5
kHz bzw.
21 Abstimmknopf
Dieser Knopf dient zur manuellen Abstimmung des
22 VFO-Funktionsschalter
Mit diesem Schalter lassen sich die beiden
gewünschte Transceive-Betriebsart (Simplex oder Duplex) einstellen. Normalerweise soll dieser Schalter in Stellung
,,B’
gebracht werden (Simplex).
A-R
VFO A
VFO A
A
B
VFO B
B-R
VFO B
23 Memorykanal-Wahlschalter (MEMORY)
Mit diesem Schalter lassen sich die Festfrequenz-, bzw. Memorykanäle 1 bis 10 anwählen. Er dient sowohl zur Frequenzeingabe
beim Programmieren der Memorykanäle als auch in Stellung ON
des MR-Schalters 38 zum Abrufen der Memoryfrequenzen.
Bei den Memorykanälen CH 9 und CH 10 handelt es sich
bereits erwähnten Vorzugskanäle
den werksseitig programmierten Frequenzen von 145.00.0
2 m-Band, bzw. 433.000.0 MHz im 70 cm-Band.
im
(MIC)
Fernbedienungs-Suchlauftasten
(F.STEP).
20/200
arbeitet als Empfänger-, VFO B als Sender-VFO
arbeitet als Empfänger- und Sender-VFO, VFO B
auf Bereitschaft.
arbeitet als Empfänger- und Sender-VFO, VFO A
auf Bereitschaft.
arbeitet als Empfänger-, VFO A als Sender-VFO
(STANDBY)
(UP/DOWN)
(PRI0.M)
(PRI0.M)
(TIGHT/NORM)
Hz-Rasterumschaltung 32.
speichern.
(FUNCTION)
(PRIORITY
9 und 10
PRI0.M
VFOs
Digital-VFOs
CHANNELS) mit
VFO-
CW-Be-
PRI0.M
10
auf
auf die
auf die
,,A’
oder
um die
MHz
24 Mikrofon-Pegelregler (SSB MIC)
Mit diesem Regler läßt sich der Mikrofonverstärker bei SSB-Sendebetrieb auf den richtigen Pegel einstellen. Dieser Pegel bestimmt
direkt die Sendeleistung während der SSB-Aussendung. Dazu den
Knopf so weit im Uhrzeigersinn drehen, daß der Zeiger des Meßinstruments 5 nicht über das Ende des ALC-Skalenbereichs ausschlägt. Durch Reduzierung der Verstärkung ist somit eine stufenlose Regelung der Sendeleistung bei SSB möglich.
25 Leuchtanzeige für Empfänger-Feinverstimmung
Diese Anzeige leuchtet in Stellung ,,ON” des RIT-Schalters 33.
26 Regler für Empfänger-Feinabstimmung (RIT)
In Stellung ,,ON” des RIT-Schalters 33 läßt sich mit diesem Regler
die
+ 1,5
0 des Knopfes ist die Empfänger-Feinabstimmung unwirksam.
27 Regler für Zf-Shift
Mit diesem Regler läßt sich die Mittenfrequenz des Zf-Quarzfilters
zur Verbesserung der Klangqualität und zur Ausblendung von
Störsignalen bei Empfangsbetrieb um + 1 kHz verschieben. Unter
normalen Empfangsbedingungen sollte der Reglerknopf in die
rastende Mittelstellung (0) gebracht werden.
26 Regler für die Rauschsperre
Den Reglerknopf bei FM-Empfang soweit im Uhrzeigersinn
drehen, bis das Hintergrundrauschen während der Empfangspausen
gerade aussetzt.
29 Schalter für Suchlaufbegrenzung (SCAN
Mit diesem Schalter läßt sich der abzutastende Frequenzbereich
beim Suchlauf (SCAN) auf 500 kHz, 1, 3, 5 oder 10 MHz
grenzen.
30 Nf-Verstärkungsregler (AF
Mit diesem Regler läßt sich die Wiedergabelautstärke bei Empfangsbetrieb stufenlos einstellen. Durch Drehen des Reglerknopfes im
Uhrzeigersinn nimmt die Lautstärke zu, beim Drehen in entgegen-
gesetzter Richtung ab.
31 Hf-Verstärkungsregler (RF
Mit diesem Regler läßt sich die Hf-Verstärkung emfängerseitig
stufenlos einstellen. Am Linksanschlag des Reglers ist die Verstärkung am geringsten. Unter normalen Empfangsbedingungen
sollte der Regler im Uhrzeigersinn bis in die rechte Endstellung
gebracht werden.
32 Schalter für Frequenzrasterumschaltung (F.STEP)
Durch entsprechende Einstellung dieses Schalters ändern sich die
VFO-Freauenzen schrittweise langsam oder schnell. Die jeweilige
Schalterstellung ist an der Leuchtanzeige
33 Schalter für Empfänger-Feinabstimmung (RIT)
zeige 25. Die Feinabstimmung selbst erfolgt am RIT-Regler 26.
Zum Ausschalten der Feinabstimmung die Taste durch nochmaliges
Drücken auslösen.
34 Suchlaufschalter (SCAN)
Mit diesem Schalter wird der autom. VFO-Suchlauf ein- und ausge-
schaltet. Der Suchlauf erfolgt mit dem am Schalter F.STEP 32
eingestellten Frequenzraster. Dieser Schalter dient ebenfalls zur
auf einem belegten Kanal unterbrochen wird.
35 Suchlauf-Stopschalter (HOLD)
Durch Betätigung dieses Tastenschalters wird der Suchlauf beendet.
36 Schalter für Memory-Suchlauf (MS.) 144 oder 436
Durch Betätigung dieses Tastenschalters wird der Memory-Suchlauf
ausgelöst, der die in den Memorykanälen 1
quenzen in numerischer Reihenfolge abfragt. Der Memory-Suchlauf
kann entweder durch Drücken der HOLD-Taste 35 oder durch Um-
schalten des Transceivers auf Sendebetrieb beendet werden. Durch
Drücken eines oder beider Schalter werden entweder die 2 m-, die
70 cm- oder alle Kanäle abgesucht.
37 Bandumschalter (BAND)
Dieser Schalter dient zur Wahl des 2 m-Bandes (144 - 146 MHz)
und des 70 cm-Bandes (430
UP ändert sich die vorgewählte Bandfrequenz um jeweils 1 MHz
zum oberen, durch Drücken der Taste DOWN ebenfalls um jeweils
1 MHz zum unteren Bandende hin.
Empfangsfrequenz ohne Beeinflussung der Sendefrequenz um
kHz nach oben oder unten verschieben. In Mittenstellung
(IF SHIFT)
(SQUELCH)
W.)
ein-
GAIN)
GAIN)
F.STEP
20 erkennbar.
Schalterstellungen und -funktionen:
Durch Drücken der Taste bis zum Einrasten wird die EmpfängerFeinabstimmung (RIT) zugeschaltet. Dabei leuchtet die
Fortsetzung des Memory- oder des VFO-Suchlaufs, wenn dieser
-
10 gespeicherten Fre-
-
440 MHz). Durch Betätigung der Taste
RIT-An-
6
Page 30

38 Speicher-Eingabetaste (MEMORY)
Dieser Schalter dient zur Eingabe der Memorykanal-Frequenzen.
Bei Betätigung der Taste ertönt ein Pfeifton der anzeigt, daß die
betreffende Frequenz im zugehörigen Memorykanal eingelesen und
gespeichert ist.
39 Schalter für VFO-Frequenzverriegelung
(F.LOCK)
Mit diesem Schalter läßt sich die VFO-Frequenz bei Bedarf ver-
riegeln. In Stellung ON des Schalters ändert sich die VFO-Frequenz
selbst durch Betätigung des Abstimmknopfs, des BAND-Schalters
oder der Suchlauftasten
(UP/DOWN)
am Mikrofon nicht, was be-
quenz gearbeitet wird und auch bei Mobilbetrieb. Die Empfänger-
Feinabstimmung (RIT) ist jedoch bei verriegelter VFO-Frequenz,
also in Stellung ON des F.LOCK-Schalters, weiterhin wirksam. Bei
eingeschalteter VFO-Frequenzverriegelung leuchtet die Anzeige
F.LOCK 1.
40 Schalter für Memorykanal-Anzeige (M.R.)
Bei Betätigung dieses Schalters erscheinen auf der Digitalanzeige
die Nummern und Frequenzen der programmierten Memory-Kanäle in numerischer Reihenfolge. Bei nicht benutzten Memorykanälen wird nur die Ziffer, nicht aber die Frequenz angezeigt.
sonders dann von Vorteil ist, wenn längere Zeit mit gleicher Fre-
@
430 MHz ANT
MHz ANT c:onnector
144
0
connector
@
CW KEY jack
SP jack
AUX socket
(6
Power connector
@
Heat sink
3.2 Rückseite
1
Anschlußbuchse für 70 cm-Antenne (430)
Coaxbuchse Typ N zum Anschluß von 70 cm-Antennen.
2 Anschlußbuchse für 2 m-Antenne (144)
Coaxbuchse Typ SO-239 zum Anschluß von 2 m-Antennen
3 Kühlkörper
Dient zur Abfuhr der von den Transistoren der Senderendstufe und
des Netzteils erzeugten Wärme ins Freie.
4 Anschlußbuchse für Morsetaste (CW KEY)
6.3
mm-Klinkenbuchse zum Anschluß von Morsetasten bei CW-
Betrieb. Abbildung 2.3 zeigt, wie ein
2-poliger
PL-Klinkenstecker
an das abgeschirmte Anschlußkabel der Taste anzulöten ist.
5 Anschlußbuchse für Außenlautsprecher (SP)
3,5
mm-Miniatur-Klinkenschaltbuchse zum Anschluß eines Außen-
lautsprechers. Abbildung 2.3 zeigt, wie der mitgelieferte MiniaturKlinkenstecker an das abgeschirmte Lautsprecherkabel anzulöten
6 Anschlußbuchse für Zusatzgeräte
An diese Buchse können unter Verwendung des mitgelieferten
poligen DIN-Steckers Zusatzgeräte wie Linearendstufen, Empfangsvorverstärker, Decoder, Tonbandgeräte usw. angeschlossen
werden.
7 Steckverbinder für Stromversorgungskabel
4-poliger Steckverbinder zum Anschluß des serienmäßig mitge-
lieferten Netzkabels und des angegebenen Stromversorgungskabels
für Batteriebetrieb
8 Erdungsklemme
Flügelmutter zum Anschluß des Erdungskabels.
9 Sicherungshalter ( FUSE)
Mit Glasrohr-Feinsicherung 2 A trage. Beim Durchbrennen der
Sicherung ist zunächst die Ursache der Störungen zu beheben
und dann erst die mitgelieferte Ersatzsicherung einzusetzen.
ist.
3.3 Geräte-Oberseite
Die folgenden Bedienungselemente befinden sich auf der Oberseite
des Transcelver-Gehäuses und sind nach Öffnen der Abdeckklappe
zugänglich. Dazu erst die beiden Stöpsel im Deckel bis zum An-
schlag herausziehen.
1
Einstellregler für Trägerpegel
(CAR.L)
Dieser Regler dient zur Trägerpegel-Einstellung bei CW-Betrieb.
In allen anderen Betriebsarten ist er funktionslos. Den Regler so
einstellen, daß der Zeiger des Meßinstruments nicht über das Ende
des ALC-Skalenbereichs ausschlägt. Durch Reduzierung des Trä-
gerpegels ist eine stufenlose Regelung der Sendeleistung bei CW
möglich.
2 Mikrofon-Pegelregler
Mit diesem Regler läßt sich die Mikrofon-Eingangsempfindlichkeit
bei FM-Sendebetrieb einstellen. Der max. Frequenzhub ist auf
+-
3 Mithörton-Pegelregler (SIDE TONE)
Dieser Regler dient zur Einstellung der gewünschten Wiedergabe-
laustärke des Mithörtons bei CW-Sendebetrieb.
4 VOX-Empfindlichkeitsregler (VOX-G)
Mit diesem Regler läßt sich die Ansprechempfindlichkeit der
sprachgesteuerten Sende/EmpfangsumschaItung nach Bedarf ein-
0
CAR. L (Carrier level control
g
FM-MIC control
Battery case for backup
stellen.
5 VOX-Verzögerungsregler
Mit diesem Regler läßt sich die Zeitkonstante der VOX-Steuerung
einstellen. Den Regler so justieren, daß die VOX nicht nach jedem
gesprochenen Wort abfällt. Die optimale Einstellung ist je nach
S. TONE (Side tone)
(68
ANTI-V (ANTI VOX)
control
Sprechgeschwindigkeit durch Versuch zu ermitteln.
6 ANTI VOX-Regler
Diesen Regler so einstellen, daß die sprachgesteuerte
fangsumschaltung
sprechers (akustische Rückkopplung) ausgelöst wird.
7 Batteriefach
Dieses Fach dient zur Unterbringung von drei 1.5 V-Alkali-Man-
gan-Mignonzellen (Gr. ,,AA”) für die Dauerstromversorgung der
Memory-Kanäle. Beim Einsetzen der Batterien auf die aus der Abbildung ersichtliche Polung achten. Die
satzes betragt etwa 1 Jahr.
kHz begrenzt.
(VOX)
GND terminal
L
(13.8
(GND)
(AUX)
(AC/DC/POWER)
V=)
(FM-MIC)
(DELAY)
9,
Fuse
Sende/Emp
nicht durch die Schallwellen des Laut-
Lebensdauer des
Batterie-
holder
7-
7
Page 31

3.4 Mikrofon
1
Sprechtaste
Zur Sendung diese Taste drücken.
2 Fernbedienung- und Suchlauftasten
Diese Tasten dienen zur Auslösung des manuellen Suchlaufs vorwärts (UP) und rückwärts (DOWN) (Tasten gedrückt halten), zur
fernbedienten Abstimmung bzw. zum weiterschalten der FM-Ka-
näle (FM-CH) (Tasten nur kurz drücken).
(PTT)
(UP/DOWN)
Teil 4 - Einbau und Anschluß
@PTT
Switch
@
UP-DOWN Switch
4.1 Antennen
Die Leistung des Transceivers hängt weitgehend von der verwendeten Antenne ab. Aus diesem Grunde sollte für den TS-780 eine geeignete Antenne gewählt und optimal abgeglichen werden.
Bei Verwendung einer gemeinsamen Antenne für das 2 m- und
70 cm-Band:
Der TS-780 verfugt über zwei getrennte Antennenanschlüsse für das
2 m- und 70 cm-Band, so daß für jeden Bereich eine geeignete Antenne benutzt werden kann. Wir empfehlen grundsätzlich separate
Antennen für jedes der beiden Bänder, da hierdurch die Anpassung
wesentlich vereinfacht wird und die Dämpfungsverluste geringer
sind. Selbstverständlich sind auch die teilweise auf dem Zubehörmarkt angebotenen VHF/UHF-Kombiantennen verwendbar, wenn
aus irgendwelchen Gründen keine separaten Antennen gebaut wer-
Bei
den können.
gleich, vorschriftsmäßigen Anschluß und Entkopplung zu achten.
Befolgen Sie genau die Betriebs- und Anschlußanweisungen des
Antennenherstellers. Fig. 4 zeigt den Anschluß einer solchen Kombi-Antenne an den TS-780.
HINWEISE:
1.
Kombi-Antennen für das 2 m- und 70 cm-Band dürfen nur über
eine entsprechende Antennenweiche angeschlossen werden. Bei
einigen dieser Antennen ist die Weiche bereits eingebaut.
2.
Anstelle der Antennenweiche kann auch ein Coaxumschalter
(obere Grenzfrequenz 440 MHz) verwendet werden.
3.
Kombi-Antennen niemals ohne Weiche an den TS-780 anschließen.
Kombiantennen ist unbedingt auf exakten Ab-
Fig. 4
Anschluß einer Kombi-Antenne an den TS-780
Die Wahl einer geeigneten Antenne
Bei der Wahl der Antenne kommt es in erster Linie darauf an, ob
der Transceiver vorwiegend für ortsfesten oder Mobilbetrieb eingesetzt werden soll. Für ortsfesten Betrieb eignen sich Yagi-Antennen
mit ausgeprägter Richtwirkung oder Ground Plane-Rundstrahlantennen. Beim Bau von Antennen für ortsfesten Betrieb sind drei
wichtige Faktoren zu beachten:
o Eignung und Strahlungscharakteristik
Wählen Sie eine Antenne, deren Montage problemlos möglich ist
und keine rechtlichen oder andere Konsequenzen nach sich zieht,
denn nicht alle Wohnungsvermieter gestatten den Bau von Amateurfunkantennen. Auch die Kostenfrage spielt bei der Wahl der Antenne eine Rolle.
Für häufige DX-Verbindungen oder Funkverkehr mit bestimmten
Stationen empfehlen wir eine Mehrelement-Yagi-Antenne, während
für Orts-, Distriks- und Umsetzer-Funkverkehr meist schon eine
preisgünstige Ground Plane-Antenne ausreicht. Wegen ihrer ausge-
zeichneten Richtcharakteristik und ihres hohen Gewinns sind
Mehrelement-, Parabeam- und Kreuzyagi-Antennen besonders vorteilhaft. Fig. 5 zeigt die Richtcharakteristik und die Reichweite der
verschiedenen Antennentypen in Form eines Strahlungsdiagramms,
Fig. 8 ein Beispiel für eine sehr gute, universell verwandbare Antennenanlage.
o Antennenstandort
Um einwandfreie DX-Verbindungen gewährleisten zu können,
sollte die Antenne so hoch wie möglich installiert werden. Die
ideale Lösung wäre ein Antennenstandort auf einem Hügel, wie
auf Fig. 6
sierbar ist.
Eine andere Lösung ist die Antennenmontage auf einem möglichst
hohen Mast, also über dem Störnebel am Boden oder über der
Dachhaut eines Hauses. Da hierbei allerdings Empfangsstörungen
z. B. durch Überreichweiten oder naheliegende Sender unvermeidlich sind, sollte man einer mehrstöckigen Yagi-Antenne den Vorzug
geben und zur Verbesserung der Richtwirkung
lungsgebieten
o Stehwellenverhältnis
Da die Antennenimpedanz des TS-780 50 Ohm beträgt, muß der
Antennenanschluß über eine 50 Ohm Coax-Speiseleitung erfolgen.
Fig. 5 -Richtcharakteristik verschiedener Antennen
Dieses Strahlungsdiagramm zeigt Idealbedingungen. In der Praxis
ist es jedoch wegen der durch Gebäude und andere natürliche sowie künstliche Hindernisse (Berge, Hügel, Hochhäuser usw.) verursachten Mehrfachechos und Reflektionen der Signale weitaus
komplizierter.
Die Stationen
Signale werden von den Stationen ,,B” und “D” empfangen. In
diesem Fall sind die Empfangsstörungen relativ gering. Sie nehmen
jedoch stark zu, wenn auch die Station
sendet und die Stationen
In Ballungsgebieten, in denen viele Amateurstationen arbeiten,
wird eine Richtantenne (Beam) empfohlen, da hierdurch Störungen
vermieden werden können, wenn mehrere Stationen auf gleicher
Frequenz senden.
Ebenso muß die Antenne auf einen reellen Fußpunktwiderstand
von 50 Ohm abgestimmt werden. Anders ausgedrückt heißt das:
Die Antenne muß exakt an die Impedanz des TS-780
Ohm angeglichen werden. Man nennt diesen Vorgang daher auch
i
mpedanzanpessung.
Dies geschieht mit Hilfe eines Stehwellen-Meßgeräts. Das ideale
Stehwellenverhältnis
betragt 1.
Zur ,Messung wird das Stehwellenmeßgerät wie Fig. 7 zeigt zwischen
die Antennenbuchse des Transceivers und die Antennen-Coaxspeise-
leitung geschaltet. Je nach dem, an welchem Punkt der Speiseleitung das SWR-Meter eingefugt ist, kann die Anzeige etwas abweichen, was auf die Dämpfungsverluste im Antennenkabel zurückzuführen ist. Je kürzer die Entfernung zwischen SWR-Meter
und Antennenbuchse des Transceivers, umso genauer ist der Meßwert. Dies gilt besonders dann, wenn die Antennenspeiseleitung
länger als 10 m ist.
(A)
gezeigt, was allerdings nur in seltenen Fällen reali-
-
-
einen Antennenrotor verwenden.
(SWR)
,,A”
und ,,C” senden mit gleicher Frequenz. Deren
,,E”
,,A’
und
,,C”
das Signal empfangen.
-abgekürzt SWR
(Standing
vor allem in Bal-
mit gleicher Frequenz
-
also 50
Wave Ratio)
-
8
Page 32

Ground plane antenna (omnidirectionall
Directivity of “E” Station
0
@Directivity of
1 = Ground Plane-Rundstrahlantenne
2 = Yagi-Antenne
3 = Richtwirkung der Antennenanlage der Station
4 = Richtwirkung der Antennenanlage der Station
5 = Richtwirkung der Antennenanlage der Station
6 = Strahlungsrichtung der Antenne
selbst
bei Verwendung der gleichen Antennenart bietet die Statior
,A”
auf dem Hügel bessere Sende- und Empfangsmöglichkeiten als
die
Station ,,B’ mit hohem Antennenmast.
“A” Station
,,E’
,,A’
,,C”
Directivity of
I
“C”
station
Antenna
J
feeder
2
3
Coaxial cable
1
Antenna
Fig. 6 - Günstiger Antennenstandort
Ein einwandfreier Sende/Empfangsbetrieb ist nur bei Antennen
mit einem SWR von weniger als 1,5 gewährleistet.
f?-=l+
l$==H=H
ntennafeederzi
Fig. 8 - Antennenanschluß
1 =Ground Plane-Antenne
2 = Einspeisungspunkt
3 =Das SWR am Einspeisungspunkt darf nicht mehr als 1,5 be-
tragen. Außerdem muß der Einspeisungspunkt völlig wasser-
dicht sein.
4 =Coaxkabel
5 = Ideale Antenne
6 =4-fach gesteckte Yagi-Antenne
7 =Antennenmast
8 = Speiseleitung
9 =Antennenbuchse
4.2 Coaxkabel
Zur Vermeidung von Störeinstrahlungen und Leistungsverlusten
sollte nur dämpfungs- und kapazitätsarmes Coaxkabel als AntennenSpeiseleitung verwendet werden. Bei ortsfestem Betrieb des TS-780
wird diese Speiseleitung in der Regel recht lang ausfallen. Zur Ver-
meidung von Leistungsverlusten, vor allem in den Frequenzbereichen oberhalb von 144 MHz, wird Coaxkabel geringer Dämpfung
mit großem Querschnitt wie z. B.
neuere
dabei, die Länge der Speiseleitung auf ein Mindestmaß zu reduzie-
ren.
Für Speiseleitungen von mehr als 10 m Länge eignen sich auch
Coaxkabel der Typen RG-8U oder UR-67.
HFE-2/2
mit Folienabschirmung empfohlen. Wichtig ist
RG-218U, RG-219U
oder das
1 = Antenne
2 = Einspeisungspunkt
3 = Coaxkabel
4 = Stehwellen-Meßgerät (2 m- bzw. 70 cm-Typ)
Wird das Stehwellen-Meßgerät wie nebenstehend gezeigt, in die
Speiseleitung eingefügt liegt die Anzeige wegen der Dämpfungs
Verluste des Kabels meist über 1.5
0
Fig. 7 - Antennenanpassung
I
1 B. Antenna
4 Koaxial
1 Ground plane
cable
.
installation
antenna
~3~;q
feeder should
6 4-row
Q
c-4
horizontal
be waterproofed.
5
Ideal type of antenna
b
;,,,,
Page 33

Teil 5 - Bedienungsanleitung
5.1 Betriebsarten 5.2 Betriebsart FM
Der TS-780 läßt sich am MODE-Schalter auf folgende Betriebsarten
umschalten:
cw
FM
USB- Sendung und Empfang auf dem oberen Seitenband (A3j)
LSB- Sendung und Empfang auf dem unteren Seitenband
Sendung und Empfang von Morsesignalen
Sendung und Empfang von FM-Signalen (F3)
-
im 2 m-VHF-Bereich (144 MHz) und im 70 cm-UHFBereich (430 MHz)
(A3j) wird normalerweise nicht verwendet, außer in
Spezialfällen wie Transponder- oder Satelliten-Betrieb
(OSCAR, RADIO SPUTNIK)
nicht drücken
(A1)
Empfangsbetrieb
Die einzelnen Regler und Schalter gemäß Fig. 9 einsteilen, dann wie
folgt fortfahren: in Stellung SIMP (Simplex- bzw. DirektkanalTransceivebetrieb) arbeiten die FUNCTION-Schalterstellungen A
und B in gleicher Weise, so daß sowohl der VFO ,,A’ als auch VFO
,,B’ verwendet werden können. Siehe Abschnitt 5-l 4.
1. Den POWER-Schalter in Stellung ,,ON” bringen. Dabei leuchten
die Digital-Frequenzanzeige und die Skalenlampen des Meßinstru-
ments auf. Auf die Digitalanzeige erscheint die Frequenz von
144.000 MHz und der Buchstabe ,,A’ (= VFO
te Betriebsfrequenz durch Betätigung der BAND-Tasten UP (vor-
wärts)
oder DOWN (rückwärts) einstellen. Dabei nimmt die Fre-
quenz bei jedem Tastendruck um jeweils einen Bandabschnitt zu.
Wird die Taste länger als 0.5 Sekunden lang im gedrückten Zustand
festgehalten, ändert sich die Frequenz in Intervallen von jeweils
0,5 Sekunden.
,,A”).
Die gewünsch-
,,0” (Mittelstellung)
FM
-
70 cm-Antenne
-:c:z~
2 m-Antenne
a--t_
2. Den Regler AF GAIN langsam so weit im Uhrzeigersinn drehen,
bis ein Signal oder Hintergrundrauschen aus dem Lautsprecher zu
hören ist. Den Regler dann auf die gewünschte Wiedergabelautstärke
einstellen.
(Zum Ausblenden des Hintergrundrauschens bei Empfangspausen
den SQUELCH-Regler so weit im Uhrzeigersinn drehen, bis das
Rauschen eben aussetzt.
3. Die Scharfabstimmung am VFO-Abstimmknopf vornehmen und
diesen so einstellen, bis das Signal klar und deutlich zu empfangen
ist. Dabei die Anzeige des S-Meters beobachten.
4. Den METER-Schalter in Stellung
VFO-Abstimmknopf danach so einstellen, bis der Zeiger des Meßinstruments genau auf die Skalenmarke CENTER weist. Der Emp-
fangsteil ist dann genau auf die Kanalmitte (Diskriminator-Nulldurchgang) des Sendesignals der Gegenstation abgestimmt. Den
METER-Schalter nun in Stellung RF/S bringen. Da der TS-780 bei
FM-Empfang breitbandig arbeitet, bleiben geringfügige Frequenz-
schwankungen des RX-Signals ohne Auswirkung. Falls die Gegenstation jedoch auf einer Festfrequenz sendet, empfiehlt es sich, den
Transceiver auf Kanalmitte (Nulldurchgang) des Signals am VFO-
Drehknopf abzustimmen.
l
)
Unter ,,Nullabstimmung” versteht man die genaue überein-
Stimmung der Empfangsfrequenz mit der Sendefrequenz der
Gegenstation.
ALC/CEN
c
lL.Millii.
bringen und den
-
u?t
Linksanschlag
aus
,,0” (center position) = Mittelstellung
Turn fully counterclockwise = Linksanschlag
Turn fully clockwise = Rechtsanschlag
OFF = aus (Tasten nicht drücken)
Not push = nicht drücken
I---l
AC220V
1
Fig. 9 - Voreinstellungen für FM-Empfang
die Empfangsfrequenz dann durch entsprechende Einstellung des
RIT-Reglers ,,nachziehen”.
Es ist jedoch darauf zu achten, daß die Empfangsfrequenz bei gedrückter RIT-Taste nicht mehr mit der Sendefrequenz übereinstimmt. Daher den RIT-Schalter nach Beendigung des Funkverkehrs
mit der Gegenstation wieder in Stellung ,,OFF” (Taste ausgelöst)
bringen.
Der Hf-Verstärkungsregler (RF
Mit diesem Regler läßt sich die Hf-Verstärkung des Empfangsteils
stufenlos einstellen. Normalerweise sollte der Reglerknopf am rech-
ten Endanschlag
des ,,Zustopfeffekts” beim Empfang sehr starker Signale oder zur
Vermeidung von Intermodulationen durch Stationen, die auf benachbarten Frequenzen arbeiten, die Hf-Verstärkung durch Drehen
des RF GAIN-Reglers etwas verringern.
Die Rauschsperre
Mit diesem Regler läßt sich das störende Hintergrundrauschen bei
Empfangspausen ausblenden. Dazu den Reglerknopf langsam so
weit im Uhrzeigersinn drehen, bis das Rauschen eben aussetzt
(Ansprechschwelle). Bei sachgemäßer Einstellung der Rauschsperre
werden nur die reinen Empfangssignale über den Lautsprecher
wiedergegeben. Je nach Stärke des Eingangssignals kann die
Rauschsperre auch bei Mobilbetrieb verwendet werden.
(FULLY
(SQUELCH)
GAIN)
CLOCKWISE) stehen. Zur Vermeidung
Die Empfänger-Feinabstimmung
Mit der Empfänger-Feinabstimmung (RIT) läßt sich die Empfangsfrequenz ohne Änderung der Sendefrequenz um _t 1,5 kHz nach
oben und unten verschieben. Die Digital-Anzeige ändert sich dabei
jedoch nicht.
Bei Frequenzdrift des Sendesignals der Gegenstation zunächst den
RIT-Schalter betätigen, wobei die RIT-Anzeige aufleuchtet und
10
(RIT)
Sendebetrieb
Hinweise:
1.
Vor Aufnahme des Sendebetriebs sicherstellen, daß alle Maß-
nahmen für einen einwandfreien Empfang getroffen worden
sind. Vor allem darauf achten, daß durch die gewählte Betriebsfrequenz keine anderen Stationen gestört werden.
Page 34

auf die gewünschte
Lautstärke einstellen
Fig. 10 - Einstellung bei Sendebetrieb
Nochmals kontrollieren, ob die richtige Antenne für das ent-
2.
sprechende Band angeschlossen, bzw. zugeschaltet ist. Ungeeignete Antennen führen nicht nur zur Leistungsverminderung,
sondern verursachen auch Fernseh- (TVI) und Rundfunk-Emp-
fangsstörungen
ohne angeschlossene Antenne auf Sendebetrieb umschalten, da
dies zu schweren Schäden führen kann.
Die Regler und Schalter gemäß Fig. 9 einstellen. Zusätzlich sind
noch folgende Einstellungen erforderlich:
1. Den MODE-Schalter auf ,,FM” und den STANDBY-Schalter
auf ,,SEND” einstellen (In Stellung REC des STANDBY-Schal-
ters wird der Transceiver bei Betätigung der PTT-Taste am Mikrofon auf Sendebetrieb umgeschaltet). Die ON Al R-Anzeige
,leuchtet auf und am Meßinstrument kann die relative Sende-
leistung auf der RF-Teilskala abgelesen werden. Den
BY-Schalter wieder in Stellung ,,REC” bringen.
2. Den Regler FM MIC auf der Gehäuse-Oberseite, wie nebenstehend gezeigt, langsam im Uhrzeigersinn drehen. Die optimale
Mikrofonverstärkung wird gewöhnlich in Mittelstellung des Reglerknopfes erreicht. Falls erforderlich kann die Mikrofonver-
Stärkung durch Drehen des Reglerknopfes entgegengesetzt dem
Uhrzeigersinn verringert werden.
r
(BCI).
Den Transceiver unter keinen Umständen
Mittelstellung
STAND-
Fig. 12 - Einstellung des MODE-Schalters bei
SSB-Betrieb
MODE-Schalter ist in Stellung ,,USB” zu bringen, wie Fig. 12 zeigt.
Nach erfolgter Einstellung der Regler und Schalter wie folgt fort-
fahren:
1.
Den POWER-Schalter auf ,,ON” und den Regler AF GAIN auf
die gewünschte Wiedergabelautstärke einstellen.
2.
Den Transceiver am VFO-Drehknopf langsam so abstimmen,
bis ein SSB-Signal empfangen wird. Dazu den VFOzunächst
durch Drehen des Knopfes entgegengesetzt dem Uhrzeigersinn
auf eine Frequenz einstellen, die einige kHz unterhalb der
Empfangsfrequenz liegt, wobei ein hoher Summton zu hören
ist, ähnlich wie beim schnellen Vorlauf des Bandes bei einem
Spulen-Tonbandgerät. Wird der VFO-Knopf nun vorsichtig im
Uhrzeigersinn gedreht in Richtung höherer Frequenz, wird der
Empfang immer klarer. Den Knopf schließlich in die Stellung
bringen, in der das Signal mit größter Lautstärke und verzerrungsfrei ohne Überlagerungston zu hören ist (sog. ,,Nulldurch-
gang”).
Hinweis:
Der Nulldurchgangspunkt läßt sich leicht auffinden, da das Signal
plötzlich stark verzerrt klingt, wenn die Frequenz nach Durchlaufen des Punktes wieder zunimmt. Wird trotz genauer Befolgung
der obigen Anweisungen kein klarer Empfang erzielt, handelt es
sich wahrscheinlich um ein LSB-Signal von einem Transponder
oder Satelliten. Den MOSE-Schalter dann auf ,.LSB” einstellen
und die VFO-Abstimmung in entgegengesetzter Richtung - also
mit einer höheren Frequenz beginnend - vornehmen.
I
11 Einstellung der Mikrofonverstärkung
Der Sendeleistungsumschalter ( LOW POWER)
Mit diesem Schalter läßt sich die Sendeleistung - insbesondere bei
Orts-, Districts- und Umsetzer-QSOs und wann immer es möglich
ist - auf 1 Watt reduzieren, um Störungen anderer Stationen zu
vermeiden. Mit verringerter Sendeleistung ist selbstverständlich
auch der Stromverbrauch bei Mobilbetrieb, bzw. bei Batteriebetrieb bei Field Days oder anderen Freiluft-Contests erheblich nied-
riger.
Wird der Schalterknopf in die obere Stellung gebracht, geht die
Sendeleistung auf 1 Watt zurück.
Die Sendeleistung selbst kann auf der RF-Teilskala des Meßinstruments abgelesen werden. Der Zeigerausschlag des Instruments
ist jedoch weitgehend von der Art und Anpassung der verwendeten
Antenne abhängig, d. h. es wird nicht die exakte, sondern nur die
relative Sendeleistung angezeigt. Wird beispielsweise auf der RFTeilskala bei voller Sendeleistung ein Wert von ,,8” abgelesen, geht
die Anzeige beim Umschalten auf reduzierte Sendeleistung auf
bis ,,2” zurück.
Hinweis: Der Sendeleistungs-Umschalter LOW POWER ist nur bei
FM-Betrieb wirksam.
5.3 Einseitenbandbetrieb (SSB)
Empfangsbetrieb
Auf dem 2 m-Band
häufiger in der Betriebsart USB (oberes Seitenband) als in LSB
(unteres Seitenband) gearbeitet, obwohl die Betriebstechnik bei
beiden die gleiche ist. Der ,,Nullabgleich” bei SSB-Betrieb erfordert
jedoch eine gewisse Erfahrung.
Die Einstellung der einzelnen Regier und Schalter erfolgt in glei-
cher Weise wie unter ,,FM-Betrieb” beschrieben. Lediglich der
(VHF)
wird nach internationaler Übereinkunft
,,1“
Sendebetrieb
1. Den MODE-Schalter auf ,,USB” und den METER-Schalter auf
,,ALC/CEN” einstellen. Die Einstellung der übrigen Regler und
Schalter ist die gleiche wie unter ,,FM-Sendebetrieb” beschrieben.
2. Die Mikrofonverstärkung am Regler SSB MIC einstellen. Diese
Einstellung sollte entweder bei gedrückter PTT-Taste am Mikro-
fon oder in Stellung ,,SEND” des STANDBY-Schalters vorge-
nommen werden.
Dann das Mikrofon mit normaler Lautstärke besprechen und
dabei den Regler SSB MIC so einstellen, daß der Zeiger des
Meßinstruments nicht über das Ende der ALC-Teilskala aus-
schlägt. Eine Reduzierung der Sendeleistung ist durch Zurück-
regeln der SSB-Mikrofonverstärkung möglich.
Nach Durchführung dieser Einstellungen den METER-Schalter
wieder in Stellung ,,RF” bringen.
Unterscheidungsmerkmale von SSB- und FM-Signalen
1.
Durch Ablesen des S-Meters:
Falls das Meßinstrument eine konstante Anzeige liefert, d. h.
der Zeiger sich nicht bewegt, handelt es sich um ein FM-Signal,
sonst um SSB-Signale.
2. Durch Einstellung des MODE-Schalters:
Wird in Stellung ,,FM” des MODE-Schalters ein sauberes, klares
Signal empfangen, handelt es sich um ein FM-Signal. In dieser
Schalterstellung ist kein SSB-Signal zu hören.
Die Empfänger-Feinabstimmung (RIT)
Eine genaue Funktionsbeschreibung der Empfänger-Feinabstimmung (RIT) befindet sich im Abschnitt ,,FM-Betrieb” dieser Bedienungsanleitung. Falls bei SSB-Empfang die Frequenz der Ge-
genstation ,,driftet” kann die Empfangs-Frequenz nach Betätigung
des RIT-Schalters am RIT-Regler geringfügig nachgestimmt werden.
In Stellung ,,ON” des RIT-Schalters weichen Sende- und Empfangsfrequenz voneinander ab. Nach Ende des QSOs den
Schalter wieder in Stellung ,,OFF” und den RIT-Regler in Mittel-
stellung (,,O”) bringen.
RIT-
11
Page 35

Die Störaustastung (Noise Blanker)
Bei Mobilbetrieb in SSB und CW kann die Störaustastung
(NB) zur
Unterdrückung von Zündfunkenstörungen zugeschaltet werden.
Bei FM ist sie wegen der automatischen AM-Unterdrückung der
FM-ZF-Stufen außer Betrieb.
1T
urned In ” - ”
direction
c
2
IF
filter passband direction
characteristic
3Turned
*
i
In ” + ”
Der Hf-Verstärkungsregler (Fl F
GAIN)
Näheres über Funktion und Einstellung des Hf-Verstärkungsreglers
im Abschnitt ,,FM-Betrieb”. Normalerweise sollte dieser Regler
immer in Rechtsanschlag gebracht werden. Nur bei überstarken
Empfangssignalen den Reglerknopf zur Vermeidung von Über-
steuerungen etwas entgegengesetzt dem Uhrzeigersinn drehen. Dadurch wird der Rauschpegel des Empfangssignals zur Verbesserung
der Lesbarkeit auf einen Wert unterhalb des Nutzsignals abgesenkt.
Wird der Regler RF GAIN bei SSB- und CW-Betrieb zu weit entge-
gengesetzt dem Uhrzeigersinn gedreht, nimmt die Anzeige des
SMeters ohne Rücksicht auf die tatsächliche Stärke des RX-Signals
immer weiter zu. Dies beruht auf der Schaltung des Regelkreises
und des Meßwerks und ist kein Anzeichen irgendeiner Störung.
Hierbei wird die Schwellwert-Spannung mit angezeigt und nur noch
die Signale, die diese überschreiten, können empfangen werden.
Die richtige Einstellung der Hf-Verstärkung ist garnicht so schwer.
Ein Tip: den RF GAIN-Regler so weit entgegengesetzt dem Uhr-
zeigersinn drehen, bis das S-Meter einen etwas geringeren Zeigerausschlag liefert als im Rechtsanschlag des Reglerknopfes.
1M
aximum S meter reading
of an
Incoming Signal.
.
Signal Signal
4 lnterfering
.s r
-++ ,r ,“,,
5 Turn In “- ” di-
rection to elimi-
nate interference
from signal B
Signal
‘m’*wr”+,.
.,
I
6 T
rection to elimi-
nate Interference
from Signal A
0
4 lnterfering
.,,+#, ,cmm,l
urn In“+”
Signal
di
Fig. 14 - Wirkungsweise der Zf-Shift
1 = In Richtung auf das Minuszeichen drehen
2 = Zf-Durchlaßkurve (Bandpaß)
3 = In Richtung auf das Pluszeichen drehen
4 = Störträger
5 = Zum Ausblenden des Störträgers (Signal B) in Richtung auf das
Minuszeichen drehen.
6 = Zum Ausblenden des Störträgers (Signal A) in Richtung auf das
Pluszeichen drehen.
~
2
AF
‘,,N-8-%‘,
Full clockwise
Position
IO
f
5
turn
counter-
clockwise.
3s
ignals
weaker with RF GAIN
than this level
are
attenuated.
4Meter deflection
gain control turned
--T
counterclockwise.
dB
Fig. 13 - Einstellung des RF GAIN-Reglers
1 = maximale S-Meter-Anzeige beim Empfang eines Signals
2 = Regler am rechten Endanschlag
3 = Signale mit schwächerem als diesem Pegel werden abgeschwächt
4 = S-Meter-Anzeige bei Zurücknahme des RF GAIN-Reglers
5 = Langsam unter Beobachtung des S-Meters entgegengesetzt dem
Uhrzeigersinn drehen
5.4 Zf-Shift
Mit dem Regler IF SHIFT läßt sich die Durchlaßkurve (Bandpaß)
des Zf-Filters ohne Änderung der Empfangsfrequenz in beiden
Richtungen verschieben, wie Fig. 14 zeigt.
Mit Hilfe der I F SHI FT können dem Nutzsignal überlagerte Stör-
träger auf dicht benachbarten Frequenzen bei SSB- und CW-Empfang wirkungsvoll ausgeblendet werden. Durch Drehen des Reglerknopfes in Richtung auf das Pluszeichen (+) werden Störträger
unterhalb der Empfangsfrequenz, durch Drehen in Richtung auf
das Minuszeichen
geblendet, wie Fig. 14 zeigt.
5.5 Telegrafiebetrieb (CW)
Empfangsbetrieb
Die Regler und Schalter wie im Abschnitt ,,FM-Betrieb” beschrieben einstellen, lediglich den MODE-Schalter in Stellung ,,CW”
bringen. Dann wie folgt fortfahren:
1. Den POWER-Schalter in Stellung ,,ON” bringen und den Regler
AG GAIN auf die gewünschte Wiedergabelautstärke einstellen.
2.
Den VFO langsam auf die gewünschte Betriebsfrequenz abstimmen, bei dqen Erreichen ein 800 Hz Schwebungston zu hören
ist. Die Empfangsfrequenz stimmt dann genau mit der Sende-
(IF
SHIFT)
(-)
solche oberhalb der Empfangsfrequenz aus-
frequenz der Gegenstation überein (Nulldurchgang).
Oder anders ausgedrückt: Wenn Sie Ihren Partner mit genau
800 Hz hören, sobald er Ihren Ruf beantwortet, bedeutet das
automatisch, daß Ihre beiden Frequenzen exakt übereinstim-
men. Bei Übereinstimmung der eigenen Sendefrequenz mit der
Empfangsfrequenz der Gegenstation hört auch diese den gleichen
800 Hz-Schwebungston.
Hinweis:
Der 800 Hz-Schwebungston kann genauestens überprüft werden,
indem man einen NF-Frequenzzähler an den Lautsprecher an-
schließt und die entstehende 800 Hz-Anzeige durch Nachstimmen
konstant hält.
Sendebetrieb
Die Einstellung und Abstimmung des TS-780 ist bei CW-Sendebe-
trieb generell die gleiche wie beim an anderer Stelle beschriebenen
FM-Sendebetrieb.
Zum Senden die Regler und Schalter wie im Abschnitt ,,FM-Sendebetrieb” beschrieben einstellen, jedoch den MODE-Schalter auf
,,CW” und den METER-Schalter auf
,,ALC/CEN”
einstellen. Die
Morsetaste an die Buchse KEY an der Rückwand des Transceivers
anschließen.
1.
Nochmals überprüfen, ob der MODE-Schalter richtig auf ,,CW”
eingestellt worden ist. Dann den STANDBY-Schalter in Stel-
lung ,,SEND” bringen, wobei die ON AIR-Anzeige aufleuchtet.
Die Morsetaste drücken und im gedrückten Zustand festhalten.
Dabei auf die Anzeige des Meßinstruments im ALC-Skalenbe-
reich achten. Den STANDBY-Schalter wieder auf ,,REC” stellen.
Hinweis:
Bei nicht angeschlossener Morsetaste liefert das Meßinstrument
bereits beim Umschalten des STANDBY-Schalters auf ,,SEND”
eine Anzeige im ALC-Skalenbereich,
2. Den Träger-Pegelregler
(CAR
LEVEL) wie folgt einstellen:
Den STANDBY-Schalter in Stellung ,,SEND” bringen und den
Regler CAR LEVEL bei gedrückter Morsetaste so einstellen,
daß der Zeiger des Meßinstruments nicht über das Ende der
ALC-Teilskala auswandert. Die Taste loslassen, den
Schalter auf ,,REC” und den METER-Schalter auf
einstellen. Durch Zurücknahme des Trägerpegels mit dem
STANDBY-
,,RF/S”
CAR.L-
Regler kann die CW-Sendeleistung stufenlos reduziert werden.
3. Den Mithörton wie folgt einstellen: Der TS-780 ist mit einem
eingebauten Mithörton-Generator ausgerüstet, mit dem das eigene
CW-Signal während der Sendung kontrolliert werden kann. Zur
Regelung der Mithörton-Lautstärke, die Klappe auf der Gehäu-
se-Oberseite öffnen und den Regler SIDE TONE auf die ge-
wünschte Lautstärke einstellen.
Diese Einstellung sollte jedoch bei Empfangsbetrieb vorgenommen werden. Dazu den STANDBY-Schalter auf REC einstellen
12
Page 36

und die Morsetaste zum Aktivieren das Mithörton-Generators
drücken. Dieser läßt sich so auch als Morse-Übungsgerät verwenden.
Empfänger-Feinabstimmung
Nähere Einzelheiten darüber im Abschnitt ,,FM-Betrieb”. Den
(RIT)
RIT-
Die Funktion der VOX-Steuerung läßt sich über den eingebauten
Lautsprecher kontrollieren. Wird irgendein Geräusch oder Signal
über den Lautsprecher wiedergegeben, ist der TS-780 auf Empfangsbetrieb, sonst auf Sendebetrieb geschaltet. Bei Sendebetrieb leuch-
tet die ON Al R-Anzeige, bei Empfangsbetrieb bleibt sie dunkel.
Schalter in Stellung ,,ON” bringen und den RIT-Regler entsprechend nachstellen, wenn die Frequenz der Gegenstation unstabil ist,
d. h. von 800 Hz abweicht oder wenn mit einer abweichenden
Schwebungsfrequenz gesendet werden soll.
2. Einstellung des ANTI VOX-Reglers
Dieser Regler befindet sich auf der Gehäuse-Oberseite (siehe Kap.
3.3.6). Mit ihm läßt sich der Schwellwert so einstellen, daß die
sprachgesteuerte Sende/Empfangsumschaltung nicht durch die vom
Störaustastung
(NB)
Siehe Abschnitt ,,SSB-Betrieb”
Lautsprecher abgestrahlten Schallwellen versehentlich ausgelöst
wird.
Zunächst den Regler VOX GAIN wie unter (1) oben beschrieben
Hf-Verstärkungsregler (RF
GAIN)
Siehe Abschnitt ,,SSB-Betrieb”
und dann den Regler AF GAIN auf die normale Empfangslautstärke
einstellen.
Das Mikrofon etwa 20
Zf-Shift (I F SHI FT)
Die Tonqualität der CW-Signale kann durch entsprechende Einstel-
I
lung des Reglers
F SHI FT in Verbindung mit der Empfänger-Fein-
abstimmung (RIT) verbessert werden.
und den ANTI VOX-Regler dann so einstellen, daß die vom Laut-
sprecher abgestrahlten Schallwellen die VOX-Steuerung nicht mehr
aktivieren. Wird der ANTI VOX-Regler jedoch zu weit im Uhrzeigersinn gedreht, geht die Ansprechschwelle der VOX-Steuerung zurück,
so daß der Transceiver beim Besprechen des Mikrofons nicht mehr
Semi-break-in-Betrieb
von Empfangs- auf Sendebetrieb umschaltet.
Neben herkömmlichem CW-Betrieb mit manueller Sende/EmpfangsUmschaltung am STANDBY-Schalter ermöglicht der TS-780 auch
den sogenannten ,,Semi-break-in-Betrieb”. Bei dieser Betriebsart
aktiviert der Mithörton die VOX-Steuerung, die den Transceiver
beim Drücken der Morsetaste auf Sendung und beim Loslassen der
Taste auf Empfang umschaltet. Dazu den MODE-Schalter auf ,,CW”
und den VOX-Schalter in Stellung ,,VOX” bringen. Ansonsten unterscheidet sich der Semi-break-in-Betrieb nicht von der sprachgesteuerten Sende/Empfangsumschaltung, die im Abschnitt 5-6 eingehend beschrieben wird.
3. Einstellen der VOX-Abfallverzögerung (VOX
Mit diesem Regler wird die Einschaltdauer der VOX-Steuerung ein-
gestellt. Ist diese zu kurz, schaltet der Transceiver mitunter nach
jedem gesprochenen Wort oder nach kürzeren Sprechpausen wieder
von Sende- auf Empfangsbetrieb zurück, bei zu langer Einschaltdauer jedoch überhaupt nicht. Den Regler daher so einstellen, daß
nach den einzelnen Kurzen Sprechpausen, z. B. nach einem beende-
ten Satz nicht sofort von Sende- auf Empfangsbetrieb zurückgeschaltet wird. Diese Justierung sollte bei normalem Sprechtempo
und normaler Lautstärke durchgeführt werden. Die VOX-Abfall-
verzögerung ist auch bei Semi-break-in CW-Betrieb wirksam.
Bei CW-Betrieb sollte der Regler allerdings nicht zu weit im Uhr-
zeigersinn gedreht werden, da es sonst zu lange dauert, bis der Transceiver beim Loslassen der Morsetaste von Sende- auf Empfangsbetrieb umschaltet, so daß kein einwandfreier Semi-break-in-Betrieb
mehr gewährleistet ist.
-
30 cm vor dem Lautsprecher plazieren
DELAY)
Hinweis:
In Stellung ,,ON” des VOX-Schalters arbeitet der TS-780 nach dem
Einschalten kurzzeitig in der Betriebsart Sendung. Nach Beendi-
gung des Funkverkehrs mit sprachgesteuerter Sende/Empfangsum-
schaltung
5.7 Ablesen der Frequenzanzeige
Auf der Digitalanzeige des TS-780 lassen sich bei allen Betriebsarten
die Trägerfrequenzen ablesen. Aufgrund der besonderen Schaltung
ändert sich die Trägerfrequenz-Anzeige auch bei Betätigung des
MODE-Schalters nicht, das heißt: Sende- und Empfangsfrequenz
können direkt auf der Digitalanzeige abgelesen werden. Ausgenom-
men davon ist der CW-Empfang, wobei die Anzeige um 800 Hz
Fig. 15 - Semi break-in-Betrieb
1 = VOX-Schalter in Stellung ,,ON” bringen.
2 = Der Mithörton ist zur Kontrolle über den Lautsprecher mithör-
bar.
(Schwebungsfrequenz) höher ist als die Sendefrequenz. Siehe auch
Abschnitt ,,Telegrafiebetrieb (CW)“.
Hinweis:
Die Digitalanzeige ändert sich nicht bei Betätigung der Empfängerfeinabstimmung (RIT).
55 Sprachgesteuerte Sende/Empfangsumschaltung
(VOX)
Die VOX-Steuerung des TS-780 schaltet den Transceiver beim Be
sprechen des Mikrofons automatisch von Empfangs- auf Sendebetrieb um. Diese Sprachsteuerung wird vorwiegend bei SSB-Betrieb
eingesetzt.
In Stellung ,,VOX” des VOX-Schalters ist diese automatische Umschaltung aktiviert, die den Sender durch die beim Besprechen des
Mikrofons entstehenden Schallwellen (Sprachmodulation) aktiviert
und bei Sprechpausen den Transceiver wieder auf Empfang umschaltet. Der STANDBY-Schalter muß dabei in Stellung ,,REC”
gebracht werden.
5.8 Bandschalter
Die Bandumschaltung erfolgt mit den Bandschaltertasten BAND
UP/DOWN. Bei Betätigung der Taste UP springt die Frequenz in
Intervallen von jeweils einem Bandabschnitt
zum oberen Bandende hin, bei Betätigung der Taste DOWN eben-
falls in Intervallen von einem Bandabschnitt (1 MHz) rückwärts,
d. h. zum unteren Bandende hin. Werden die Tasten im gedrückten
Zustand festgehalten, springt die Frequenz in exakten 0.5 Sek.Intervallen um jeweils 1 MHz. Wie die nachstehende Tabelle zeigt,
arbeitet der BAND-Schalter nur auf einem VFO
VFO-B). Siehe auch Abschnitt 5-10 ,,Betrieb mit zwei VFOs”.
Bei den BAND-Tasten UP und DOWN handelt es sich um besonders
Einstellungen
1. Einstellung des VOX-Empfindlichkeitsreglers (VOX
GAIN)
leichtgängige Tipptasten, die auf leichtesten Fingerdruck reagieren
und bei deren Betätigung ein Kontrollton zu hören ist.
Den STANDBY-Schalter in Stellung ,,REC” und den VOX-Schalter
in Stellung ,,VOX” bringen.
Den Regler VOX GAIN dann langsam so weit im Uhrzeigersinn
drehen, bis der Transceiver beim Besprechen des Mikrofons mit
normaler Lautstärke auf Sendebetrieb umschaltet. Wird der Regler
noch weiter im Uhrzeigersinn gedreht, erfolgt die Umschaltung auf
Sendebetrieb schon bei relativ leiser Sprechweise. Allerdings besteht dann die Gefahr, daß die VOX-Steuerung auch auf Umgebungsgeräusche anspricht.
5.9 Digital-VFO
Die Abstimmung des TS-780 ist so ausgelegt, daß die bei Betätigung
des VFO-Drehknopfes erzeugten Impulse mit Hilfe eines Mikroprozessors gezählt und zur Frequenzaufbereitung in der
wendet werden. Die Frequenzänderung erfolgt schrittweise in 20
Hz-lnkrementen (langsam) oder in 200 Hz-lnkrementen (schnell)
bei CW-, SSB- und FM-Betrieb. Die Schrittfolge läßt sich am Schalter F.STEP einstellen. Siehe Abschnitt 5-12.
den VOX-Schalter wieder in Stellung ,,MAN” bringen.
(BAND UP/DOWN)
(1
MHz) vorwärts, d.h.
(VFO-A
oder
PLL-Stufe
ver-
13
Page 37

Tabelle 1 zeigt den Abstimmbereich des Digital-VFOs.
Band
2 m (144
MHz)
70 cm (430 MHz)
Stellung des Schalters F. STEP
,,OFF”
(aus)
144.000.00-145.999.98
430.000.00-439.999.98
,,ON”
144.000.00-145.999.80
430.000.00-439.999.80
(ein)
Wird der MODE-Schalter auf FM-CH eingestellt, ändern sich die
Betriebsfrequenzen wie in der nachstehenden Tabelle 3 gezeigt.
Stellung das
MODE-Schalters
SSB, CW, FM,bFM-CH CW, FM
FM-CH, b SSB,
Stellung des
OFF
Schalters F.STEP
OFF (aus).ON
(ein)
(aus) ,ON fein)
Tabelle 1
Durch Drehen des VFO-Abstimmknopfes in beiden Richtungen
Frequenz-
Anzeige
wird der TS-780 fortlaufend zwischen 144.000.09 und 145.999.98
im 2 m-Band durchgestimmt, desgleichen im 70 cm-8and zwischen
430.000.00 und 439.999.80 MHz, wobei die obere Grenzfrequenz
des jeweiligen Bandes von der Stellung
F.STEP abhängt.
(ON/OFF)
des Schalters
Tabelle 3
Das Drehmoment des VFO-Knopfes läßt sich verändern. Befindet
sich der Hebel links neben dem Drehknopf in Stellung ,,NORM”,
arbeitet die VFO-Abstimmung leichtgängig mit Schwungradeffekt
Hinweis 1:
l 11
und ermöglicht damit einen schnellen Frequenzwechsel. In Stellung
TIGHT des Hebels ist die eingebaute Friktionsbremse zugeschaltet.
Der Knopf läßt sich dann wesentlich schwerer betätigen, wodurch
l
ein versehentliches Verstellen insbesondere bei Mobilbetrieb ver-
mieden wird.
5.10 Betrieb mit zwei VFOs
Der TS-780 verfugt über zwei, durch Mikroprozessoren gesteuerte
A und 8.
VFOs,
Mit dem FUNCTION-Schalter kann wahlweise VFO-A oder VFO-8
zugeschaltet werden, wobei jeder mit eigener, separater Frequenz
arbeitet. Dadurch ist ein sogenannter Duplex-Betrieb mit unterschiedlichen Sende- und Empfangsfrequenzen möglich, wobei so-
Hinweis 2:
Tabelle 3 zeigt die Betriebsfrequenzen und zugehörige Digitalanzeige des VFO-A. Die Funktion des VFO-B ist genau die gleiche.
Bei SSB-Betrieb können sich die Frequenzen hinter der 10 kHz-
Stelle ändern.
wohl der VFO-A als auch VFO-8 als Empfänger bzw. Sender-VFO
eingesetzt werden kann. Die nachstehende Tabelle zeigt den Zusammenhang zwischen den Stellungen des
FUNCTION-Schalters
und dem Betrieb der beiden VFOs.
Es bieten sich u. a. folgende Betriebsmöglichkeiten: VFO-A arbeitet
im 2 m-Band, VFO-B hingegen im 70 cm-Band oder beide im glei-
VFOs
chen Band. Beide
können auch als zusätzliche Speicherplätze
benutzt werden.
5.12 Der Schalter F.STEP
Mit diesem Schalter läßt sich die Schrittfolge der VFO-Frequenzen
einstellen. Beim Drücken der Taste bis zum Einrasten leuchtet die
LED-Anzeige F.STEP auf. Falls die Abstimmung nicht am VFODrehknopf erfolgt, ist der Schalter in den Betriebsarten SSB, CW
oder FM auf OFF
Drücken auslösen. In Stellung ,,ON” des Schalters werden Fre-
quenzen unterhalb von 100 Hz auf den nächst niedrigen 200 Hz-
Beispiele:
1. Die mit der Gegenstation vereinbarte Betriebsfrequenz wird im
Wert abgerundet. In Stellung OFF des Schalters erfolgt keine
Frequenzänderung.
VFO-B gespeichert. Der Funkbetrieb kann jetzt mit dem VFO-A
fortgesetzt werden, bis die Gegenstation mit den Sendungen be-
ginnt.
2.
Bei FM-Betrieb kann mit dem VFO-A ein Ausweichkanal ge-
sucht werden, während VFO-B auf den Umsetzer eingestellt
bleibt. Ebenso kann auf diese Weise über Umsetzer gearbeitet
werden, die von der Norm (-600 kHz, -7.6 MHz,
abweichende Frequenzablagen (z. B.
+1,6
MHz oder
-1,6
-4,6
MHz)
MHz)
besitzen.
Tabelle 4
Stellung des
FUNCTION-
Schalters
A
B
A-R
B-R
Tabelle 2
Empfangs-VFO Sende-VFO
A
A
B B
A B
B
A
5.13 Die Speicherschaltung (MEMORY)
Die Memory-Taste (M) dient zur Eingabe der gewünschten Frequenzen in die insgesamt 10 Speicher des TS-780, die mit Drehschalter MEMORY angewählt werden können. Der Abruf der in
einem Memory gespeicherten Frequenz erfolgt durch Betätigung
der Taste MR (Memory
Bei den Kanälen 9 und 10 handelt es sich um die sogenannten
,,Vorzugskanäle”
sind und zwar Kanal 9 auf 145.000.0 MHz und Kanal 10 auf
433.000.0 MHz. Diese Frequenzen können jedoch bei Bedarf jederzeit geändert werden durch Eingabe abweichender Frequenzen.
145.317.7 145.317.6 145.315.0 145.315
145.312.5 145.310 145.315.0
*Hinweis 1
l
Hinw. 2
In Stellung ,,OFF” des Schalters F.STEP wird die Frequenz
auf der Digitalanzeige bis zum nächsten
12,5
kHz-Raster-
schritt abgerundet.
2)
In Stellung ,,ON” des Schalters F.STEP wird die Frequenz
auf der Digitalanzeige bis zum nächsten 5 kHz-Rasterschritt
abgerundet.
Die letzte Stelle der Digitalanzeige (100 Hz) wird dabei
ausgeblendet.
(aus)
einzustellen (Taste durch nochmaliges
Stellung des
Schalters F.STEP
OFF 20 Hz
ON
Stellung des MODE-Schalters
--
SSB,
t-
CW, FM FM-CH
12.5 kHz
200 Hz
5 kHz
Recall)
(PRIO.M),
die bereits werksseitig programmiert
5.11 FM-Kanalbetrieb (FM-CH)
In Stellung FM-CH das MODE-Schalters arbeiten die VFOs mit
vorgegebenem ,,Kanal”-raster und zwar in Stellung ,,OFF” des
Schalters F.STEP im
12,5
kHz-, in Stellung ,,ON” im 5 kHz-Kanal-
raster, wobei der Hauptabstimmknopf als ,,Kanalschalter” hör- und
fühlbar einrastet.
Hinweis 1:
Die Frequenzen der Vorzugskanäle
mit der Taste MR abgerufen werden.
Hinweis 2:
Bei Abruf eines Memory-Kanals, in dem keine Frequenz gespeichert
Beispiele:
433.000 433.005
433.0125
433.010
433.0250 433.015
433.0375 433.020
ist, erscheint auf der Digitalanzeige lediglich die Kanalnummr.
Hinweis 3:
Werden die Vorzugskanäle
Taste MR abgerufen, erscheint auf der Digitalanzeige anstelle der
Kanalnummer der Buchstabe
höhenversetzt und in digitaler Schreibweise, um auf die Vorzugs-
433.9875 433.995
kanäle aufmerksam zu machen,
14
PRI0.M
PRI0.M.
9 und 10 können auch
9 oder 10 durch Betätigen der
,,C’
(Kanal
9),
bzw. ,,C” (Kanal
10)
Page 38

r
1 Select the desired frequen-
cy by the tuning knob.
2 Select the desired channel
by the MEMORY selector to
store the frequency.
3 Depress the MR switch to
ensure that the selected
channel is not occupied. Occupied channels can be
cleared as necessary.
4 Depress the M switch and
an oscillation Sound
heard, indicattng that the
frequency is stored
memory.
In
the
@&i-
y--i
gjjj
0 co,og
c
IS
.@
~
F?&c
.;@
Fig. 15 - Eingabe von Frequenzen in die Memories
1 = Die gewünschte Frequenz am VFO-Drehknopf einstellen.
2 = Das zum Speichern dieser Frequenz vorgesehene Memory am
MEMORY-Drehschalter vorwählen.
3 = Zur Kontrolle, daß der betreffende Memorykanal nicht belegt
ist, kurz die Taste MR drücken. Eingegebene Frequenzen können bei Bedarf gelöscht werden.
4 = Die gewünschte Frequenz jetzt durch Drücken der M-Taste in
das Memory eingeben.
3.
Selbst wenn der Suchlauf auf einem belegten Kanal anhält,
flackert die FUNCTION-Leuchtanzeige weiter.
4.
Endet der Funkverkehr auf einem belegten Kanal
(BUSY),
wird
der Suchlauf nach einer Pause von 1 Sekunde automatisch fortgesetzt.
Betriebsart ,,FM”
1. Wird die SCAN-Taste im gedrückten Zustand festgehalten, arbeitet der Suchlauf kontinuierlich, d. h. ohne anzuhalten, mit
hoher Geschwindigkeit. Soll der Suchlauf nach dem Anhalten
auf einem belegten Kanal fortgesetzt werden, ist die
SCAN-
Taste abermals zu drücken.
2.
Die übrigen Funktionen des Suchlaufs sind die gleichen wie
beim FM-Kanalbetrieb (FM-CH).
Andere Betriebsarten
1. Nur normaler Suchlauf ohne Anhalten auf belegten Kanälen
(BUSY)
möglich. Zum Anhalten des Suchlaufs entweder die
HOLD-Taste drücken oder den Transceiver kurzzeitig auf Sendebetrieb umschalten. Nach Beendigung des Suchlaufs erlischt
die FUNCTION-Leuchtanzeige.
Suchlauf-Begrenzungsschalter (SCAN W)
Mit diesem Schalter kann die Untergrenze des Suchlaufbereichs
eingestellt und damit der Suchlauf selbst eingeschränkt werden.
Am folgenden Beispiel soll die Funktion der Suchlaufbegrenzung
(SCAN W) in der Betriebsart FM-CH (FM-Kanalbetrieb) bei einer
Anfangsfrequenz von 431.637.5 MHz im 70 cm-Band erläutert
werden.
1 Set to the channel from
which
the stored frequency
is called out.
2 Depress the MR switch.
~-~-~
SCAN
+W
switch
0.5
I
3
5
430 431
431.5 432
*-
$
---
__---
431
987
____-----
___---
433
5
433 987
*
w
__----
434 436
Fig. 16 - Abrufen gespeicherter Memory-Frequenzen
1 = Die Nummer des abzurufenden Memory-Kanals am Schalter
MEMORY einstellen.
2 = Zum Abruf der vorgewählten Kanalfrequenz die Taste MR
drücken.
A= Memory-Kanal-Nummer
Hinweis 4:
Wird eine in Stellung ,,ON” des Schalters F.STEP eingegebene
Memory-Frequenz abgerufen, leuchtet die LED-Anzeige
F.STEP
auf.
Hinweis 5:
Es können Frequenzen bis zu einer Genauigkeit (Auflösung) von
10 Hz eingegeben werden. Frequenzänderungen durch EmpfängerFeinverstimmung (RIT) werden jedoch nicht gespeichert. ser Vorgang wiederholt sich dann laufend mit einem auf
Hinweis 6: (500 kHz) beschränkten Suchlaufbereich.
Frequenzen von 1.0 kHz, bzw. 10 Hz werden bei der Betriebsart
FM-CH als ,,O” eingegeben. Beim Abruf erscheint jedoch die voll-
6-
ständige Frequenz
bzw. 7-stellig auf der Digitalanzeige.
Hinweis 7:
Wird beim Betrieb über Umsetzer eine Frequenz während des
Sendens eingegeben, wird nur die tatsächliche Empfangsfrequenz
ohne Ablage gespeichert.
10
430
431.637.5
Stellung des Schalters SCAN W
Stellung ,,0,5 MHz”
Der Suchlauf beginnt bei 431,637,5 MHz, endet bei 431,987,5 MHz
und springt auf die Untergrenze von 431.500.0 MHz zurück. Die-
Stellung
Der Suchlauf beginnt bei 431.637.5 MHz, endet bei
und springt auf die Untergrenze von 431 .OOO.O MHz zurück, um
dann wieder bis 431.987.5 MHz vorzulaufen. Der Vorgang wiederholt sich dann laufend mit einem auf 1 MHz beschränkten Such-
laufbereich.
,,1
MHz”
431.987.5MHz
5
435
987
c
439
0,5
440
5
987.5
440
MHz
5.14 Der Suchlaufschalter
In Stellung ,,ON” des Suchlaufschalters SCAN flackert die
TION-Leuchtanzeige
(SCAN)
(A, b)
als Funktionskontrolle des Suchlaufs.
FUNC-
Betriebsart ,,FM-CH” (FM-Kanalbetrieb)
1. Den SQUELCH-Regler so einsteilen, daß der Suchlauf auf be-
(BUSY)
legten Kanälen
eingehalten wird.
2. Wird der SCAN-Schalter in Stellung ON gebracht, schaltet der
Suchlauf automatisch auf den nächsten Kanal um, auch wenn
auf diesem kein Funkverkehr herrscht. (Bei dauernd gedrückter
Taste ändert sich die Frequenz nicht).
Stellung ,,3 MHz”
Der Suchlauf beginnt bei 431.637.5 MHz und endet bei 433.987.5
MHz als Obergrenze des Suchlaufbereichs, um dann wieder auf
431 .OOO.O MHz zurückzuspringen. Dieser Vorgang wiederholt sich
laufend in dem auf 3 MHz begrenzten Suchlaufbereich.
Stellung ,,5 MHz”
Die obere und untere Bandbegrenzung wird in der gleichen Weise
,,3
wie in Stellung
MHz” des SCAN-Schalters berechnet, wobei
eine Wiederholung des Suchlaufs mit einer Bandbreite von 5 MHz
zwischen den betreffenden Bandbegrenzungen erfolgt.
15
Page 39

430 431 432 433 438 439 440
5.16 Die Vorzugskanäle
Die in den Vorzugskanälen
(PRI0.M.)
PRI0.M
9 und 10 gespeicherten Fre-
quenzen werden ,,bevorzugt”, d. h. direkt abgerufen, wenn man
;i
die zugehörigen Schalter
PRI0.M
9 oder 10 in Stellung ,,ON”
bringt. Werksseitig sind die beiden Kanäle bereits vorprogrammiert
und zwar Kanal 9 mit einer Frequenz von 145.000.0 MHz und Kanal 10 mit einer Frequenz von 433.000.0 MHz, wobei beide Kanäle
bei Bedarf auch mit anderen Frequenzen belegt werden können.
Stellung ,,10 MHz”
Die Frequenzen der beiden Vorzugskanäle werden wie folgt ange
zeigt:
In dieser Stellung erfolgt der Suchlauf mit der vollen Bandbreite
von 10 MHz zwischen der Untergrenze von 430900.0 MHz und
der Obergrenze von 439.997.5 MHz.
Hinweis 1:
In den Stellungen ,,3, 5 und 10” (MHz) des SCAN W-Schalters wird
der Suchlauf im 2 m-Band (144 MHz) zwischen der Untergrenze
Hinweis 1:
Beim Abruf der Vorzugskanäle hat Kanal 9 stets den Vorrang vor
Kanal 10.
Hinweis 2:
Die Digital-Frequenzanzeige der Vorzugskanäle
(PRI0.M)
erfolgt
mit einer Auf Iösung von 100 Hz.
von 144.000.0 MHz und der Obergrenze von 145.987.5 MHz fort-
laufend wiederholt, da die Bandbreite dieses Bereichs nur 2 MHz
betragt.
Hinweis 2:
In den vorgenannten Stellungen des SCAN-Schalters ist der Such-
lauf auf die tatsächliche Breite des betreffenden Bandes begrenzt,
d. h. der Suchlauf erfolgt nur innerhalb des jeweiligen Bandes bis
zur oberen Bandgrenze und springt nicht von einem Band in das
nächste weiter.
Hinweis 3:
Die Bandbegrenzung des Suchlaufs läßt sich auch unter den folgenden Betriebsbedingungen berechnen:
1)
wenn der VFO-A (oder
2)
wenn der Schalter SCAN W in eine andere Stellung gebracht
VFO-B)
zugeschaltet ist.
wird.
3)
Wenn eine der BAND-Tasten betätigt wird.
Hinweis 4:
Die Suchlaufbegrenzung ändert sich nicht, wenn die Suchlauftaste
SCAN betätigt wird und der Suchlauf beim Erreichen eines belegten
Kanals (BUSY) endet. Zur Änderung der Suchlaufbegrenzung muß
5.17 Dauerstromversorgung für die Memory-Kanäle
Der Direktzugriffspeicher (RAM) des Mikroprozessors ermöglicht
das Einlesen jeder beliebigen Frequenz im 2 m- und 70 cm-Band.
Normalerweise wurden jedoch die gespeicherten Informationen
beim Ausschalten des Transceivers sofort gelöscht. Um dies zu vermeiden, wurde der TS-780 mit einer Dauerstromversorgung für die
zehn Memory-Kanäle ausgerüstet, die von der jeweiligen Spannungsquelle, also Netz oder Kfz-Batterie unabhängig ist und damit eine
Speicherhaltung bei ausgeschaltetem Gerät garantiert. Diese Dauerstromversorgung besteht aus drei Trockenbatterien (1,5 V-AlkaliMangan-Mignonzellen), die in einem besonderen Batteriefach unter
dem Gehäusedeckel untergebracht sind. Wegen der geringen Stromaufnahme der Speicher von lediglich 10 uA, erreichen die Batterien
eine durchschnittliche Lebensdauer von einem Jahr. Sind keine
Batterien zur Dauerstromversorgung der Memory-Kanäle eingesetzt,
geht die VFO-Frequenz sofort auf 144.000.0 MHz zurück, wenn der
Netzschalter (POWER) des Gerätes auf ,,OFF” gestellt wird. Ebenso werden die Vorzugskanäle (PRI0.M) 9 und 10 auf 145.000.0
bzw. 433.000.0 MHz zurückgesetzt.
der Suchlauf durch Auslösung der HOLD-Taste abgeschaltet werden.
Hinweis 5:
Die BAND-Tasten lassen sich auch während
des
Suchlaufs betätigen,
wobei die Bandbereichs-Fortschaltung allerdings nicht kontinuier-
5.18 Mobilbetrieb mit externer Stromversorgung
Bei Mobilbetrieb arbeitet der TS-780 mit einer
13.8
V+-
15%.
Gleichspannung
von
lich erfolgt, solange eine der BAND-Tasten im gedrückten Zustand
festgehalten wird. Die BAND-Umschaltung ist auch bei zugeschalteter Frequenzrastung wirksam, d. h, wann sich der Schalter F.
LOCK in Stellung ,,ON” befindet.
Mobil-Einbau
Der Mobilbetrieb des TS-780 unterscheidet sich nur unwesentlich
vom ortsfesten Betrieb.
Die für den Mobileinbau geeignete Stelle im Kraftfahrzeug hängt im
Der Suchlauf wird bei Betätigung der Tasten
PRI0.M.
MR oder MS
sofort abgebrochen.
5.15 Der Memory-Suchlauf (MEMORY SCAN)
Werden die Tastenschalter 144 MS oder 430 MS in Stellung ,,ON”
gebracht, flackert die FUNCTION-Leuchtanzeige (Kanal-Nr.). Dies
bedeutet, daß die Memory-Suchlaufschaltung (MEMORY SCAN)
aktiviert ist und die Memory-Kanäle I-IO in numerischer Reihenfolge abgefragt werden. Die SQUELCH-Ansprechschwelle wird dazu in der gleichen Weise wie beim VFO-Suchlauf eingestellt.
wesentlichen von dessen Bauart und den bestehenden Platzverhältnissen ab. Bei größeren Fahrzeugen kann der Einbau evtl. unter
dem Instrumentenbrett auf der Baifahrerseite oder auf der Mittel-
konsole vorgenommen werden, bei kleineren empfiehlt es sich, den
Transceiver mit dem Anschnallgurt auf dem Beifahrersitz selbst zu
befestigen, damit er beim plötzlichen Bremsen nicht herunterfallen
kann. Auf jeden Fall ist darauf zu achten, daß weder der Fahrer,
noch der Beifahrer behindert werden und der Transceiver so einzubauen ist, daß bei Notbremsungen usw. Verletzungen der Insassen
ausgeschlossen sind.
In Stellung ,,ON” das Schalters 144 MS werden nur die Memory-
Kanäle im 2 m-Band, in Stellung ,,ON” des Schalters 430 MS nur
die Memory-Kanäle im 70 cm-Band in numerischer Reihenfolge
abgefragt. Es können auch die Memory-Kanäle beider Bänder ab-
l
gefragt werden, wozu die Schalter 144 MS und 430 MS gleich-
zeitig in Stellung ,,ON” zu bringen sind. Das Abschalten des
Me-
Mobilantennen
Als Mobilantenne eignen sich fast alle vom Fachhandel angebotenen Typen für das 2 m- und 70 cm-Band. Besonders zu empfehlen
sind
1/4&
oder
5/8
A-Stabantennen, sowie Ground Plane-Anten-
nen.
mory-Suchlaufs erfolgt wie oben für den VFO-Suchlauf beschrie-
ben. Zur Fortsetzung des Suchlaufs die SCAN-Taste betätigen.
Hinweis:
Bei Antennen für Dachmontage ist auf einwandfreie Erdung des
Hinweis 1:
Wird die SCAN-Taste im gedrückten Zustand festgehalten, erfolgt
kein Suchlauf.
Antennenfußes zu achten, der galvanisch mit dem Chassis des Fahr-
zeugs (Masse) zu verbinden ist. Nähere Einzelheiten sind den Montageanweisungen des Antennen-Herstellers zu entnehmen.
Hinweis 2:
Wird der Suchlauf angehalten, wenn beide MS-Schalter auf ,,ON”
eingestellt sind, kann er fortgesetzt werden, indem man entweder
einen der beiden MS-Schalter in Stellung ,,OFF” bringt (Taste aus-
lösen), die PRIO.M.-Taste oder die MR-Taste betätigt.
Hinweis 3:
Werden die Memory-Kanäle ausschließlich für Frequenzen im 2 m-
Band (144 MHz) benutzt und der Schalter 430 MS in Stellung
,,ON” gebracht, blinkt die FUNCTION-Leuchtanzeige sehr schnell,
während gleichzeitig ein Dauer-Warnton zu hören ist. Das gleiche
ist der Fall, wenn die Memory-Kanäle ausschließlich für Frequenzen
im 70 cm-Band (430 MHz) verwendet werden und der Schalter
144 MS auf ,,ON” eingestellt ist.
Hinweis 4:
Beim Memory-Suchlauf werden nur diejenigen Memory-Kanäle
abgefragt, in denen Frequenzen gespeichert sind.
Stromversorgungskabel
Zum Mobilbetrieb des TS-780 ist ein Stromversorgungskabel der auf
Fig. 18 gezeigten Art erforderlich. In die rote (Plus-) Ader muß un-
bedingt eine 7 A-Sicherung eingefugt werden.
Stromverbrauch
Bei Mobilbetrieb beträgt die maximale Stromaufnahme des TS-780
ca. 5 A, so daß die Kapazität der Fahrzeugbatterie mindestens 35 Ah
betragen sollte, um einen einwandfreien Betrieb zu gewährleisten.
Sind andere Stromverbraucher wie Scheinwerfer, Wagenheizung
usw. zugeschaltet, sollte der Transceiver wegen des erhöhten Strom-
verbrauchs nur bei laufendem Motor betrieben werden, um die
Fahrzeugbatterie nicht übermäßig zu belasten. Wir empfehlen den
Einbau eines Spannungsmessers zur Überwachung der Bordspannung.
16
Page 40

~-1
FUSE Holder
Fig. 18
-
Stromversorgungskabel für Mobilbetrieb
1=Stromversorgungskabel
2 = rote Ader (+)
3 = schwarze Ader
4 = Sicherungshalter mit 7A-Sicherung
5 =
Steckverbinder
Hinweis:
Im Interesse der Verkehrssicherheit sollte der TS-780 bei Mobilbe-
trieb nur auf Festfrequenzen (Memory oder FM-CH) benutzt
werden.
5.19 Duplex-Betrieb über Umsetzer
Bei Duplex-Betrieb über Umsetzer arbeitet der TS-780 mit folgenden
Frequenzablagen im 2 m-, bzw. 70 cm-Band:
Bandbereich
(-)
Stellung des
Schalters
TX OFFSET
Frequenzablage
Der TS-780 arbeitet dann mit einer Empfangsfrequenz von 433
MHz und einer Sendefrequenz von 434.6 MHz.
Auf
ähnliche
möglich, deren Frequenzablage nicht der üblichen Norm entspricht
z. B. im Ausland.
15.20 Funkbetrieb über OSCAR-Amateurfunksatelliten
Gegenwärtig befinden sich zwei OSCAR-Amateurfunksatelliten,
OSCAR 7 und OSCAR 8 und zwei RADIO-Satelliten sowjetischer
Funkamateure
nicht mehr funktionstüchtig, da seine Batterien erschöpft sind.
Die genannten Satelliten dienen unter anderem als Umsetzer für
den Amateurfunk-Betrieb.
Auch mit dem TS-780 ist eine Funkbetrieb über Amateur-Satelliten
wie nachstehend beschrieben möglich:
OSCAR Nr. 7
Betriebsart A
Betriebsart B Eingabefrequenzen
OSCAR Nr. 8
Betriebsart A
Betriebsart J Eingabefrequenzen
RADIO 1, 2
Tabelle 5 zeigt die Ein- und Ausgabefrequenzen, die in Fachkreisen
auch UP LINK- bzw. DOWN-LINK-Frequenzen genannt werden,
während Fig. 19 den typischen Betriebsablauf über Satelliten im
70 cm- und 2 m-Band zeigt.
Betriebsart
Weise ist ein Duplex-Betrieb über andere Umsetzer
(RS
1.2) auf einer Erdumlaufbahn. OSCAR 6 ist
oder
oder
Eingabefrequenzen
Ausgabefrequenzen (Empfang)
Eingabefrequenzen
Ausgabefrequenzen (Empfang)
Eingabefrequenzen
OSCAR No. 7 OSCAR No. 8 RADIO
A
B
2 m - 10 m
70 cm - 2 m (Senden)
2 m - 10 m (Senden)
2 m - 70 cm (Senden)
2 m - 10 m (Senden)
A
J
[Senden)
No. 1.2
430 - 440 MHz D-A
D-B
Hinweis:
Im 70 cm-Band ist die Sendefrequenz in Stellung ,,D-A” des Schal-
ters TX OFFSET
1,6
MHz niedriger als die Empfangsfrequenz.
Liegt die Sendefrequenz außerhalb der zulässigen 2 m- bzw. 70 cm-
Amateurbänder, ertönt ein Warnsignal und der Sender wird auto-
matisch auf Simplex geschaltet.
Einstellung der Regler und Schalter bei Betrieb über Umsetzer
1) Die gewünschte Betriebsfrequenz durch Betätigung der BANDTasten UP oder DOWN einstellen.
2)
Den Schalter TX OFFSET auf die entsprechende Frequenzab-
lage einstellen, wobei die OFFSET-Anzeige aufleuchtet.
3) Die Empfangsfrequenz auf der VFO-Skala einstellen, dann die
Ruftontaste (TONE) drücken. Dadurch wird der eingebaute
Ruftongenerator aktiviert, der ein dem Träger überlagertes
1750 Hz-Signal zum Auftasten des Umsetzers erzeugt. Bei der
TONE-Taste handelt es sich um einen Moment-Taster, der den
Ruftongenerator beim Loslassen sofort wieder ausschaltet.
In Stellung ,,D-A” des Schalters TX OFFSET liegt die Sendefrequenz
im 2 m-Band (144-146 MHz) 600 kHz unterhalb der Empfangsfrequenz, im 70 cm-Band in Stellung ,,D-A” 7.6 MHz, in Stellung
,,D-B”
1,6
Frequenzablage kann auf der Digitalanzeige abgelesen werden.
Liegt die Sendefrequenz bei zugeschalteter Frequenzablage außer-
halb der zulässigen Amateur-Bandbereiche, ertönt ein Warnsignal
und der Sender wird automatisch auf Simplex geschaltet.
Mit dem REV-Schalter lassen sich Sende- und Empfangsfrequenz
gegeneinander vertauschen, d. h. die Sendefrequenz befindet sich
dann anstelle der Empfangsfrequenz und umgekehrt,
Möglichkeit besteht, die Umsetzer-Eingabefrequenzen abzuhören
bzw. eine Kurzmitteilung durchzugeben, daß auf einer Direktfrequenz gearbeitet werden kann. Bei Umsetzern mit abweichender
Frequenzablage den TX-OFFSET-Schalter auf ,,SIMP” und den
FUNCTION-Schalter auf ,,A-R” oder ,,B-R” einstellen und die
Ablage mit beiden VFOs einstellen.
Beispiele:
Zum Betrieb über einen 70 cm-Umsetzer, dessen Frequenzablage
1,6
MHz oberhalb der Eingabe von 433 MHz liegt, den FUNCTIONSchalter auf ,,A-R” einstellen, VFO-A auf 433 MHz und VFO-B
auf 434.6 MHz abstimmen.
7,6
MHz niedriger, in Stellung ,,D-B” jedoch nur
MHz unterhalb der Empfangsfrequenz. Die jeweilige
- 7.6
- 1,6
wodurch
MHz
MHz
die
Eingabe
Ausgabe
Bakenfreq.
Hinweis:
In den Betriebsarten B und J wird das Signal im unteren Seitenband
(LSB) empfangen.
Wird der TS-780 in Stellung ,,A-R” des FUNCTION-Schalters,
VFO-A als Empfangs-VFO im 430 MHz Band und VFO-B als
Sender-VFO im 145 MHz-Band eingesetzt, ist kein Funkbetrieb
über OSCAR-Satelliten möglich, da das Ausgabesignal im 29 MHz-
Band nicht empfangen werden kann.
Zum Betrieb über OSCAR-Satelliten ist daher unbedingt ein zusätzlicher Kurzwellen-Empfänger z. B. der Kenwood R 1000 oder
oder Transceiver, z. B. der Kenwood TS-830, erforderlich, um das
DOWN LINK-Signal (Ausgabe) im 29 MHz-, bzw. 10 m-Band empfangen zu können, wie Fig. 19 zeigt. Außerdem sollte man über die
grundlegenden Kenntnisse der Betriebstechnik bei Satelliten-Ama-
teurfunk wie z. B. Berechnung der Umlaufbahnen, Bakenfrequenzen,
Spezialantennen mit Nachführmöglichkeit usw. verfügen.
Sind diese Kenntnisse vorhanden, steht einem Sende/Empfangsbetrieb über OSCAR-Satelliten nichts mehr im Wege. Fachliteratur
über dieses Spezialgebiet wird vom Fachhandel angeboten. Außerdem berichten Amateurfunk-Fachzeitschriften regelmäßig über den
Satellitenfunk.
5.21 Die Anschlußbuchse für Zusatzgeräte
Fig. 20 und Tabelle 6 zeigen die Beschaltung der 7-poligen DIN-
Buchse AUX an der Rückwand des
satzgeräte wie Linear-Endstufen, Empfangsvorverstärker, Tonbandgeräte, Decoder oder externe Sende/EmpfangsumschaIter (Standby-
Relais) angeschlossen werden. Dabei ist unbedingt darauf zu achten, daß die Kontakte 2, 4 und 5 höchstens mit 10 mA belastet
werden dürfen, da es sonst zu Schäden am Transceiver kommen
kann. Ein
Zubehör des TS-780.
145.85 432.125 145.85 145.9 145.88
to
145.95 432.175 145.95to146.0 145092
29.40 145.975 29.40 435.1 29.360
to to to
29.50 145.925 29.60 435.2 29.400
29.502 145.972 29.402 435.097 29.400
(AUX)
Transceivers,
7-poliger
DIN-Stecker befindet sich im serienmäßigen
an die solche Zu-
to
to
R
600
17
Page 41

1
'Cross type
Y
‘,
von der Rückwand aus gesehen
Microphone
6
Fig. 19
-
8Transmit
only
9R
eceive only
Typischer Transceive-Betrieb über OSCAR-Satellit
1 = Mehrelement-Yagiantenne für DX-Verbindungen
2 = Kreuzdipol-Antenne für Orts-QSOs3 = Eingabe (145 MHz-Band)
4 = OSCAR-Satellit (Betriebsart A)
5 = Ausgabe (29 MHz-Band)
6 = Mikrofon
7 = Morsetaste
8 = TS-780 (nur für Sendebetrieb)
9 = TS-830 oder TS-530 (nur für Empfangsbetrieb)
10 = Lautsprecher
Fig. 19 - Zusatzbuchse
Die Kontakte 1 und 6 sind ab Werk nicht beschaltet, so daß sie
wahlweise z. B. an den Ausgang des NF-Verstärkers, den Mikrofonverstärker-Eingang (zum Anschluß eines AFSK-Encoder-Decoders
für Funkfernschreibbetrieb oder eines Notruf-Auswerters) oder an
andere Punkte der Schaltung gelegt werden können.
Kontakt Bezeichnung Zweck
Nr.
(AUX)
Tabelle 6
.‘f-- NC nicht beschaltet
2
3 ELC Eingang für externes
4 14c
5
,ld
7 SS
E43 8 V, 10 mA, (430 MHz)
ALC-Steuersignal
8 V, 10 mA, (144 MHz)
9T
NC
9V, 10mA
(bei Sendebetrieb)
nicht beschaltet
externer RX / TX-Umschalter.
Sender wird durch Kurzschließen
nach Masse aktiviert.
Teil 6
Für den TS-780 ist folgendes empfehlenswerte Sonderzubehör.er.
hältlich:
Stationslautsprecher SP-70 und SP-71
0
Formschöne, klangvolle 8 Ohm-Lautsprecher, in Design und
Farbgebung zum TS-780 passend. Das Spezial-Konussystem
mit Hochtonbedämpfung verbessert die Verständlichkeit der
Empfangssignale vor allem bei SSB-Betrieb ganz wesentlich.
Amateur-Kopfhörer HS-4
0
Preisgünstiger, leichter und gequem zu tragender Kopfhörer
mit 8 Ohm-System. Allseitig geschlossene Muscheln mit ringförmigen, weichen Kissen. Verstellbarer, gepolsterter Kopfbügel.
Amateur-Luxuskopfhörer HS-5
0
Ein Kopfhörer in HiFi-Qualität mit hervorragenden Wiedergabe-
eigenschaften. Rückseitig offene 8 Ohm-Systeme mit Polyester-
Membran und auswechselbaren Ohrmuscheln garantieren stun-
denlanges, ermüdungsfreies Tragen.
0 Amateur- Leichtkopfhörer HS-6
Eine Entwicklung der Kenwood HiFi-Abteilung. Ausgezeichnete Klangqualität und extrem geringes Gewicht sind die besonderen Merkmale dieses Kopfhörers mit weichen Schaumgummikissen und verstellbarem Kopfbügel.
Digital-Weltzeituhr HC-10
0
Ein Schmuckstück für jeden Raum. 6-stellige Digitalanzeige der
Ortszeit, Datumsanzeige
und 10 fest programmierte Weltzeitzonen der wichtigsten
Regionen. Optische Datumsgrenzenanzeige. Eingebaute Stoppuhr
zur Kontrolle der Funkverkehrs-Dauer mit eingebautem Speicher.
Hohe Ganggenauigkeit. Bitte Sonderprospekt anfordern.
(Monat/Tag),
-
Lieferbares Sonderzubehör
sowie zwei frei wählbare
HS-5 MC-60/S8
0 Stationsmikrofon MC-60/S8
Formschönes Tischmikrofon mit umschaltbarer Impedanz
(600 Ohm / 50 kOhm), leichtgängige PTT-Taste mit Verriegelung. Coiled cord-Anschlußkabel mit Spezialstecker. Und jetzt
ganz neu: eingebaute Fernbedienungs-Suchlauf-Tasten UPI
DOWN.
18
HS-6
HC-10
Page 42

Festgestellte Störung Mögliche Ursache
Abhilfe
Keine Wiedergabe über den Lautsprecher
Trotz angeschlossener Antenne und
Meter-Anzeige kein Empfang möglich
S-Meter liefert auch ohne Eingangssignal
eine Anzeige
Kein SSB-Empfang möglich
Empfänger-Feinverstimmung (RIT)
arbeitet nicht
Ungenugende Klangqualität der SSBEmpfangssignale
Kein SSB-Sendebetrieb möglich
Kein CW-Sendebetrieb möglich
S-
SQUELCH-Regler steht am Rechtsanschlag
1. Antennen für das 2 m- und 70 cm-Band
sind vertauscht oder falsch angeschlossen
worden.
2. SQUELCH-Regler am rechten Endanschlag Uhrzeigersinn drehen.
3. PTT-Taste am Mikrofon ist gedrückt
oder verriegelt
Regler RF GAIN unsachgemäß eingestellt
Transceiver ist auf das andere Seitenband
eingestellt.
RIT-Schalter befindet sich in Stellung
,,OFF”
Regler I F SH I FT unsachgemäß eingestellt
1. Mikrofon unsachgemäß angeschlossen
2. Regler SSB MIC steht am linken
Endanschlag
1.
Morsetaste unsachgemäß angeschlossen
oder Kontakte defekt.
2. Regler
schlag
CAR.L
steht im linken Endan-
SQUELCH-Regler entgegengesetzt dem Uhr-
zeigersinn drehen
1.
Antennen, Koaxkabel und Antennenan-
Schlüsse überprüfen
2. SQUELCH-Regler entgegengesetzt dem
3. PTT-Taste loslassen oder entriegeln.
RF GAIN-Regler bis zum Anschlag im Uhr-
zeigersinn drehen
MODE-Schalter in die richtige Stellung
(USB oder LSB) bringen.
RIT-Schalter in Stellung ,,ON” bringen
RIT-Anzeige muß dabei aufleuchten
Regler IF SHIFT in die rastende Mittel-
Stellung bringen
1. Mikrofonanschluß und Kontakte des
Steckers überprüfen
2. Regler SSB MIC im Uhrzeigersinn drehen
(
ALC-Anzeige beachten!)
1.
Anschluß der Morsetaste und des
Klinkensteckers überprüfen
2. Regler
CAR.L
(ALC-Anzeige beachten!)
im Uhrzeigersinn drehen
F;eikMithörton bei CW-Sendebetrieb
Keine oder unzureichende Modulation
der FM-Sendesignale (Kein Hub!)
VOX-Steuerung arbeitet nicht 1. VOX-Schalter befindet sich in Stellung
Keine Wiedergabe wenn der
stimmknopf in Stellung ON des Schalters
F.STEP
schnell gedreht wird
Keine genaue Anzeige des ersten Kanals
bei Memory-Suchlauf (MS)
Keine Fortsetzung des Suchlaufs in Stellung ON des Schalters F.LOCK oder bei
gedrückter BAND-Taste
Zu geringe Schaltgeschwindigkeit wenn
die VFO-Abstimmung bei gedrückter
BAND-Taste UP oder DOWN bedient
wird
VFO-Ab-
Regler S.TONE befindet sich am linken
Endanschlag
Regler FM-MIC steht am linken Endan-
schlag
OFF
2. Regler VOX GAIN steht am linken
Endanschlag
PLL-Schaltung ist ausgerastet. Das ist normal und kein Anzeigen einer Störung.
Bei Funkverkehr auf dem ersten Memorykanal wird der Suchlauf dort in den Betriebsarten
FM oder FM-CH unterbrochen. Den Schalter MS wieder in Stellung ON bringen oder warten,
bis der Suchlauf von vorn beginnt.
Der Suchlauf ist auch in Stellung ON des Schalters F.LOCK aktiviert. Außerdem kann
während des Suchlaufs die Bandumschaltung vorwärts/rückwärts (BAND
bedient werden.
Die Schaltgeschwindigkeit wird durch die VFO-Abstimmung beeinflußt
Regler S.TONE im Uhrzeigersinn drehen
Regler FM-MIC im Uhrzeigersinn drehen
1.
VOX-Schalter in Stellung ON bringen
2. Regler VOX GAIN im Uhrzeigersinn
drehen
UP/DOWN)
Empfangsfrequenz wird anstelle der
Sendefrequenz mit Frequenzablage bei
Betrieb über Umsetzer gespeichert
Arbeitet VFO-A bei Betrieb über Umsetzer auf 144 MHz und VFO-B auf 430
MHz, flackert die Anzeige in Stellung
A-R des FUNCTION-Schalters, Stellung
,,+” oder
und Stellung ON des Schalters REV
Wird der Transceiver ohne DauerstromVersorgung der Memories aus- und
kurz danach wieder eingeschaltet,
ändern sich die VFO- und die MemoryChannel-Frequenzen und werden nicht
korrekt zurückgesetzt
,,-”
des Schalters TX OFFSET
Nur die Empfangsfrequenz wird bei Transceivebetrieb über Umsetzer ohne Ablage
gespeichert
Funkbetrieb über Umsetzer in Stellung A-R oder B-R des FUNCTION-Schalters ist sehr
kompliziert. Den FUNCTION-Schalter daher besser auf ,,A” oder ,,B” einstellen.
Transceiver frühestens 10 Sekunden nach dem Ausschalten wieder einschalten, damit sich
die Anzeigeschaltung stabilisieren kann.
Page 43

Trio-Kenwood Communications GmbH,Industriestr.8a,8374Steinbach/Taunus,West-Germany,Tel.:08171
-75035,Telex:410817triod
Page 44

Page 45

Page 46

Page 47

Page 48

Page 49

Page 50

Page 51

Page 52

TOP & BOTTOM INTERNAL VIEWS
AVR unit
(X43-1420-00)
Control unit
(X53-1240-61)
PLL
unit
(X50-1770-00)
TX unit
(X56-1420-00)
144 MHz final
(X60-1 180-51)
(Under)
430 MHz final unit ass’y
(X60-1 180.00)
unit
ass’y
27
IF
unit
(X48-1350-61)
430 HET unit
(X50-1790-00)
RF unit
(X44-1470-00)
 Loading...
Loading...