
VHF APCO P25 TRANSCEIVER
TK-5710(B
TK-5710H(B
SERVICE MANUAL
TK-5710(B) with KCH-14
Cabinet (Lower)
(A01-2162-22)
Cabinet (Upper)
(A01-2161-22)
)
)
2005-5 PRINTED IN JAPAN
©
B51-8727-00 (S) 618
Use this service manual
together with the
KCH-14/15 service manual
(B51-8728-00).
KCH-14
(Front panel kit)
TK-5710H(B)
Cabinet (Upper)
(A01-2163-21)
CONTENTS
GENERAL .............................................................. 2
SYSTEM SET-UP .................................................. 4
REALIGNMENT ..................................................... 5
INSTALLATION ................................................... 11
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR .............................. 20
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION ...................................... 25
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA .................................. 33
COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION .......................... 35
PARTS LIST ......................................................... 37
EXPLODED VIEW................................................ 50
PACKING ............................................................. 52
ADJUSTMENT .................................................... 54
TERMINAL FUNCTION ....................................... 70
Cabinet (Lower)
(A01-2164-21)
PC BOARD
FINAL UNIT (X45-3750-10) : TK-5710 (B) ...... 74
FINAL UNIT (X45-3760-10) : TK-5710H (B) ... 76
CONTROL UNIT (X53-4120-10) ..................... 80
TX-RX UNIT (X57-7030-10) ............................ 84
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ...................................... 88
INTERCONNECTION DIAGRAM ...................... 104
BLOCK DIAGRAM ............................................. 106
LEVEL DIAGRAM .............................................. 110
OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES
KCH-14 / KCH-15 / KES-6 ............................ 111
SPECIFICATIONS ............................. BACK COVER
This product uses Lead Free solder

TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
)
GENERAL
INTRODUCTION
SCOPE OF THIS MANUAL
This manual is intended for use by experienced technicians familiar with similar types of commercial grade communications equipment. It contains all required service information for the equipment and is current as of this publication date. Changes which may occur after publication are
covered by either Service Bulletins or Manual Revisions,
which are issued as required.
ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS
When ordering replacement parts or equipment information, the full part identification number should be included.
This applies to all parts : components, kits, and chassis. If
the part number is not known, include the chassis or kit
number of which it is a part and a sufficient description of
the required component, for proper identification.
PERSONAL SAFETY
The following precautions are recommended for personal
safety :
•DONOT transmit if someone is within two feet (0.6
meter) of the antenna.
•DONOT transmit until all RF connectors are secure and
any open connectors are properly terminated.
• SHUT OFF this equipment when near electrical blasting
caps or while in an explosive atmosphere.
• All equipment should be properly grounded before
power-up for safe operation.
• This equipment should be serviced by only qualified
technicians.
PRE-INSTALLATION CONSIDERATIONS
1. UNPACKING
Unpack the radio from its shipping container and check
for accessory items. If any item is missing, please contact
KENWOOD immediately.
2. LICENSING REQUIREMENTS
Federal regulations require a station license for each
radio installation (mobile or base) be obtained by the
equipment owner. The licensee is responsible for ensuring
transmitter power, frequency, and deviation are within the
limits permitted by the station license.
Transmitter adjustments may be performed only by a
licensed technician holding an FCC first, second or general
class commercial radiotelephone operator’s license. There
is no license required to install or operate the radio.
3. PRE-INSTALLATION CHECKOUT
3-1. Introduction
Each radio is adjusted and tested before shipment.
However, it is recommended that receiver and transmitter
operation be checked for proper operation before
installation.
3-2. Testing
The radio should be tested complete with all cabling and
accessories as they will be connected in the final installation. Transmitter frequency, deviation, and power output
should be checked, as should receiver sensitivity, squelch
operation, and audio output. Signaling equipment operation
should be verified.
4. PLANNING THE INSTALLATION
4-1. General
Inspect the vehicle and determine how and where the
radio antenna and accessories will be mounted.
Plan cable runs for protection against pinching or crushing wiring, and radio installation to prevent overheating.
4-2. Antenna
The favored location for an antenna is in the center of a
large, flat conductive area, usually at the roof center. The
trunk lid is preferred, bond the trunk lid and vehicle chassis
using ground straps to ensure the lid is at chassis ground.
2

GENERAL
4-3. Radio
The universal mount bracket allows the radio to be
mounted in a variety of ways. Be sure the mounting surface
is adequate to support the radio’s weight. Allow sufficient
space around the radio for air cooling. Position the radio
close enough to the vehicle operator to permit easy access
to the controls when driving.
4-4. DC Power and wiring
1. This radio may be installed in negative ground electrical
systems only. Reverse polarity will cause the cable fuse
to blow. Check the vehicle ground polarity before
installation to prevent wasted time and effort.
2. Connect the positive power lead directly to the vehicle
battery positive terminal. Connecting the Positive lead to
any other positive voltage source in the vehicle is not
recommended.
3. Connect the ground lead directly to the battery negative
terminal.
4. The cable provided with the radio is sufficient to handle
the maximum radio current demand. If the cable must be
extended, be sure the additional wire is sufficient for the
current to be carried and length of the added lead.
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
)
5.
INSTALLATION PLANNING – CONTROL STATIONS
5-1. Antenna system
Control station. The antenna system selection depends
on many factors and is beyond the scope of this manual.
Your KENWOOD dealer can help you select an antenna
system that will best serve your particular needs.
5-2. Radio location
Select a convenient location for your control station radio
which is as close as practical to the antenna cable entry
point. Secondly, use your system’s power supply (which
supplies the voltage and current required for your system).
Make sure sufficient air can flow around the radio and
power supply to allow adequate cooling.
SERVICE
This radio is designed for easy servicing. Refer to the
schematic diagrams, printed circuit board views, and
alignment procedures contained in this manual.
NOTE
You must use KPG-95D version 2.00 or later for this
transceiver. KPG-95D version 1.XX does not work
properly.
3
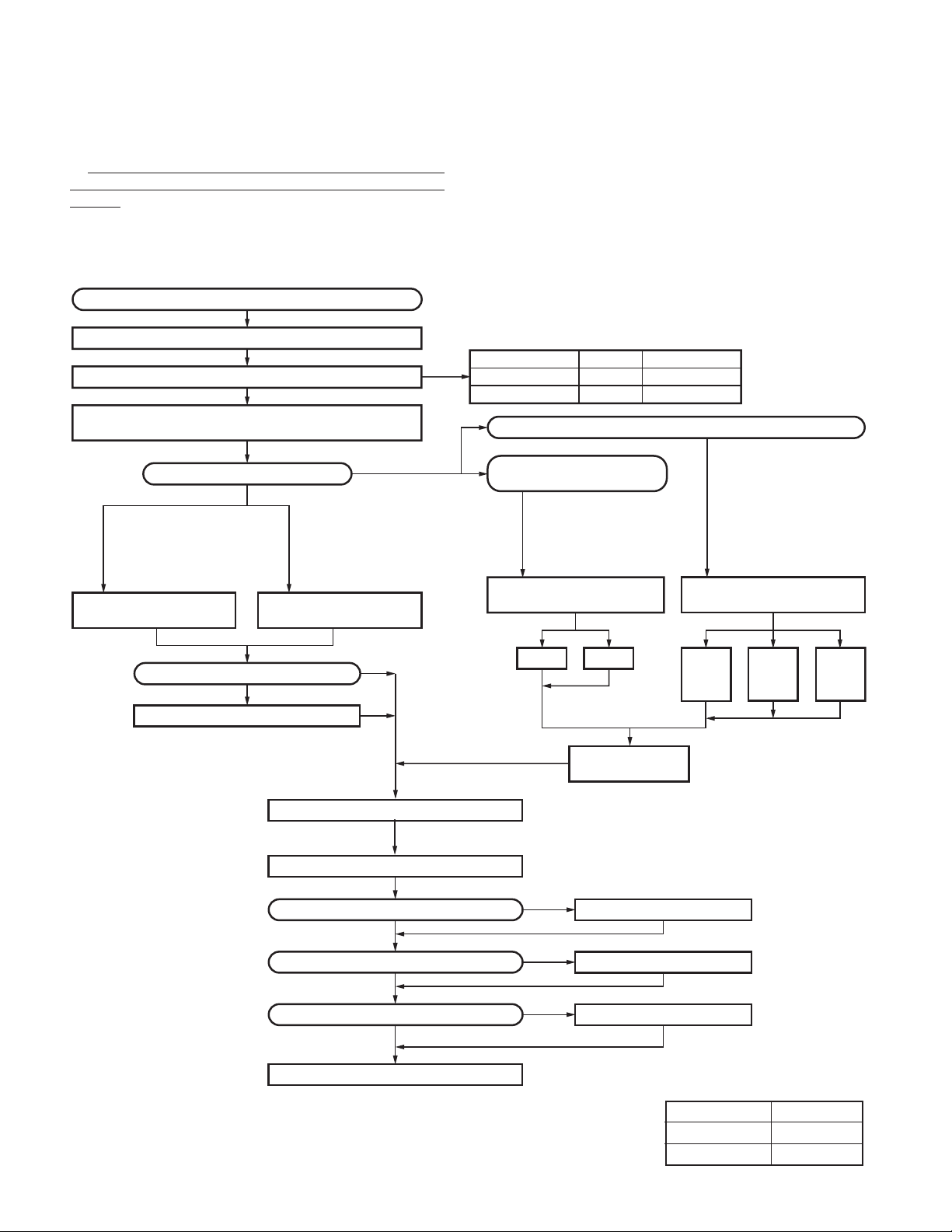
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
SYSTEM SET-UP
Before Reading About System Set-up
The TK-5710(B)/5710H(B) is a transceiver main unit
(without a panel or speaker) that you complete by adding
options.
The options are classified into three types according to
operation and function.
Merchandise received
License and frequency allocated by FCC
Choose the type of transceiver
TK-5710(B) or TK-5710H(B) is complete by combining
options with only the transceiver body (without panel)
Are you using the remote kit?
See page 11
Please refer to the
KCH-14/15 service manual
(B51-8728-00) for serving
information, such as circuit
diagram, parts list and etc.
KCH-14 (Basic model)
Front panel kit
Are you using the printed keytops?
See page 11
Supplied accessory keytops
NO
See page 11
Please refer to the
KCH-14/15 service manual
(B51-8728-00) for serving
information, such as circuit
diagram, parts list and etc.
KCH-15 (Full-featured
model) Front panel kit
YES
YES
NO
)
1. Install the front panel kit (controller) directly on a radio to
operate it. (Form : Radio + KCH-14/15)
2. Remotely control one radio with one controller. (Form
: Radio + KRK-5 + KCH-14/15 + KCT-22M/M2/M3)
3. Remotely control one radio with two controllers. (Form
: Radio + KRK-6DH + KCH-14/15 (two) + KCT-22M/M2/
M3 (two))
Frequency range
136~174MHz
136~174MHz 110W TK-5710H(B) K
Are you using one radio
with one controller?
See page 12
YES
Please refer to the
KRK-5/6DH service manual
(B51-8445-20) for serving
information, such as circuit
diagram, parts list and etc.
Single control head remote kit
KCH-14 KCH-15
RF power
50W TK-5710(B) K
Are you using one radio with two controllers?
KRK-5
(Option) (Option)
Type
YES
See page 14
Please refer to the
KRK-5/6DH service manual
(B51-8445-20) for serving
information, such as circuit
diagram, parts list and etc.
oror or
+
KRK-6DH
KCH-14
+
KCH-15
Dual control head remote kit
KCH-14
KCH-14
KCH-15
KCH-15
+
See pages 13 and 14
See page 16
(Option)
See page 17
(Option)
(Option)
Desk top microphone KMC-9B
Transceiver programming
KCT-23 DC cable
Are you using the voice guide & storage unit?
NO
Are you using the external speaker?
NO
Are you using the keypad microphone?
NO
Delivery
KCT-22M/M2/M3
Control cable
See page 5
A personal computer (IBM PC or compatible), programming
interface (KPG-43), and programming software (KPG-95D) are
required for programming. (The frequency and signaling data
are programmed for the transceiver.)
KCT-23 M,M3 : TK-5710(B), KCT-23 M2,M4 : TK-5710H(B)
YES
YES
YES
VGS-1
KES-5 or KES-6
KMC-28
Service manual parts No. list
Model Parts No.
KRK-5/6DH B51-8445-20
KCH-14/15 B51-8728-00
4
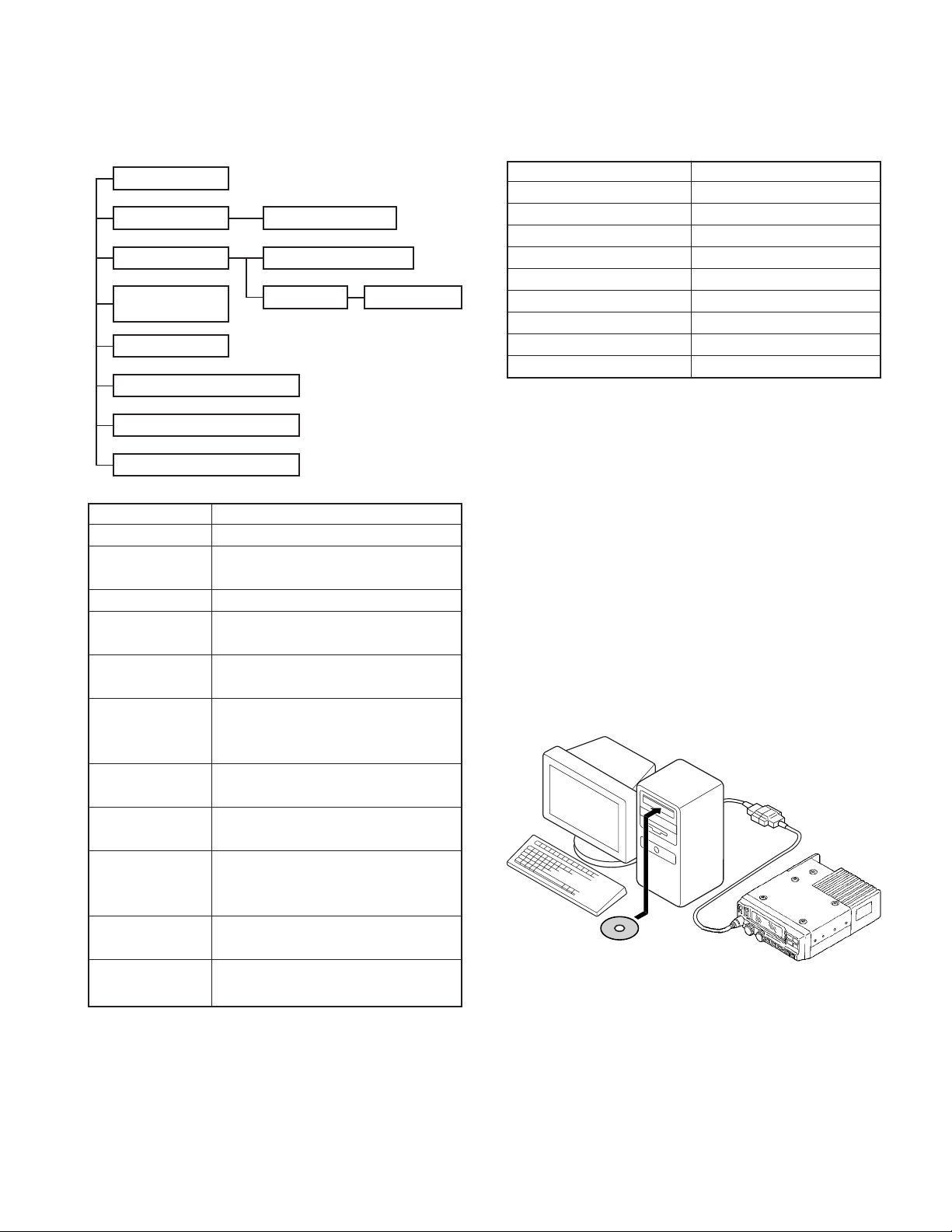
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
REALIGNMENT
1. Modes 2. How to Enter Each Mode
User mode
Panel test mode
PC mode
Firmware
programming mode
Clone mode
Self programming mode
Panel tuning mode
Data programming mode
PC test mode
PC tuning mode
User mode Power ON
Panel test mode [PF1] + Power ON
PC mode Received commands from PC
Panel tuning mode [Panel test mode] + [GRP^]
Firmware programming mode [PF2] + Power ON
Clone mode [PF5] + Power ON
Self programming mode [GRP^] + Power ON
Firmware version information [PF3] + Power ON
Clock adjustment mode [PF4] + Power ON
Mode Operation
)
Firmware version information
Clock adjustment mode
Mode Function
User mode For normal use.
Panel test mode Used by the dealer to check the fundamen-
tal characteristics.
Panel tuning mode
PC mode Used for communication between the
Data programming Used to read and write frequency data and
mode other features to and from the transceiver.
PC test mode Used to check the transceiver using the PC.
Firmware Used when changing the main program of
programming mode the flash memory.
Clone mode Used to transfer programming data from
Self programming You can program the frequency,
mode signaling and other functions using only the
Firmware version Used to confirm the internal firmware
information version.
Clock adjustment Used by the dealer to adjust date and time.
mode
Used by the dealer to tune the transceiver.
transceiver and PC (IBM compatible).
This feature is included in the FPU.
See panel tuning.
one transceiver to another.
transceiver.
3. Panel Test Mode
Setting method refer to ADJUSTMENT.
4. Panel Tuning Mode
Setting method refer to ADJUSTMENT.
5. PC Mode
5-1. Preface
The transceiver is programmed by using a personal computer, programming interface (KPG-43) and programming
software (KPG-95D).
The programming software can be used with an IBM PC
or compatible. Figure 1 shows the setup of an IBM PC for
programming.
IBM-PC
KPG-43
KPG-95D
Fig. 1
5-2. Connection procedure
1. Connect the transceiver to the personal computer with
the interface cable.
2. When the POWER switch on, user mode can be entered
immediately. When PC sends command the transceiver
enter PC mode, and “PROGRAM” is displayed on the
LCD.
When data transmitting from transceiver, the red LED is
lights.
5
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
)
REALIGNMENT
When data receiving to transceiver, the green LED is
lights.
Note:
The data stored in the personal computer must match
"Model Name and Market Code", when it is written into
the EEPROM and flash memory.
5-3. KPG-43 description
(PC programming interface cable: Option)
The KPG-43 is required to interface the transceiver to the
computer. It has a circuit in its D-sub connector (25-pin) case
that converts the RS-232C logic level to the TTL level.
The KPG-43 connects the microphone jack of the transceiver to the computers RS-232C serial port.
5-4. Programming software KPG-95D description
The KPG-95D is the programming software for the transceiver supplied on a CD-ROM. This software runs under MSWindows 98, ME, Windows 2000 or XP on an IBM-PC or
compatible machine.
The data can be input to or read from the transceiver and
edited on the screen. The programmed or edited data can be
printed out. It is also possible to tune the transceiver.
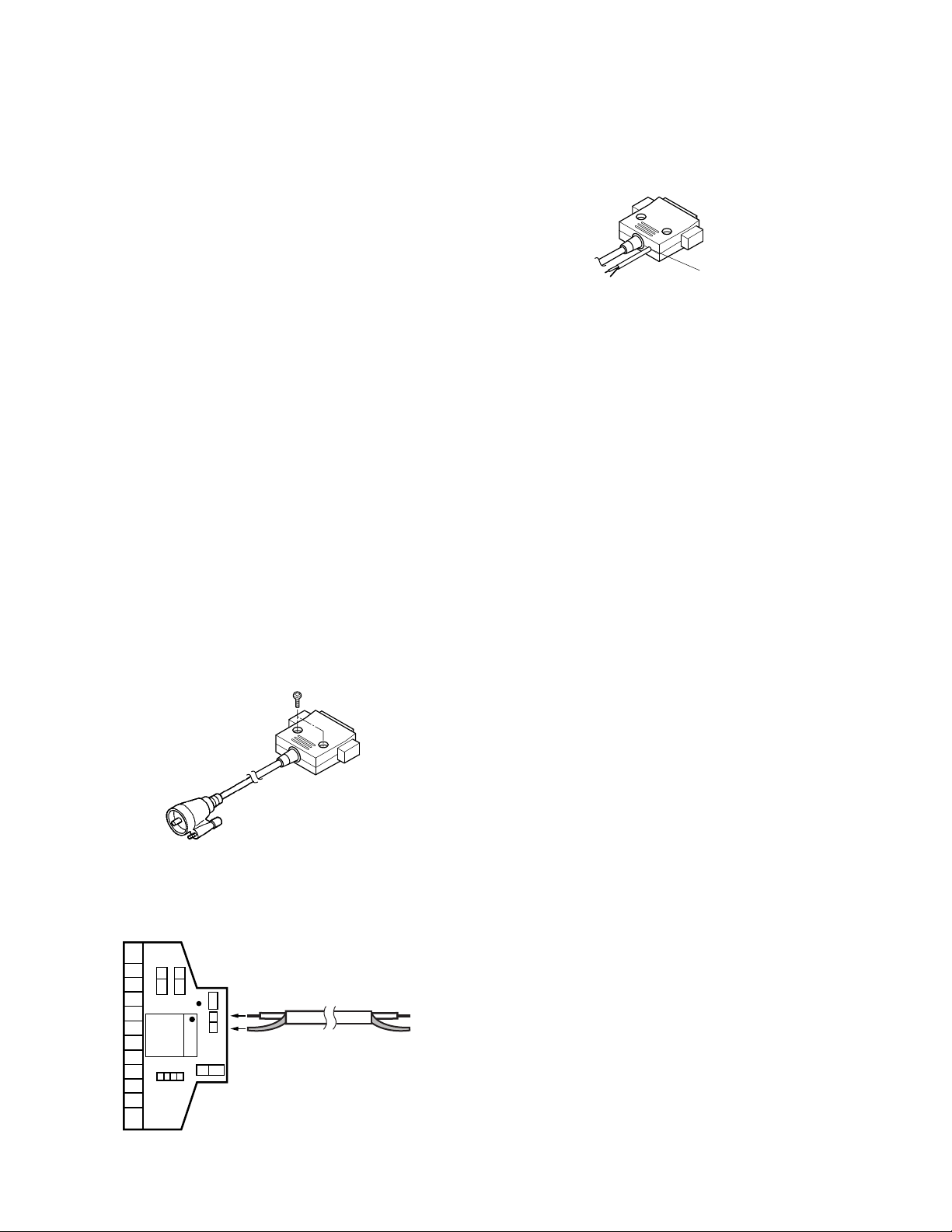
6. PC Tuning Mode
When making adjustment while in PC tuning mode,
modify the KPG-43 programming interface cable as described below.
1. Remove the two screws from the plug cover, then lift the
cover from the plug.
3. Create a hole in the casing (as shown in the illustration)
then fit the cable into the hole. Replace the cover and
secure it using the two screws.
MIC
ME
Cable
Create a hole
7. Firmware Programming Mode
7-1. Preface
Flash memory is mounted on the transceiver. This allows
the transceiver to be upgraded when new features are released in the future. (For details on how to obtain the firmware, contact Customer Service.)
7-2. Connection procedure
Connect the transceiver to the personal computer (IBM
PC or compatible) with the interface cable (KPG-43). (Connection is the same as in the PC Mode.)
7-3. Programming
1. Start up the firmware programming software (Fpro.exe).
2. Set the communications speed (normally, 115200 bps)
and communications port in the configuration item.
3. Set the firmware to be updated by File name item.
4. Press and hold the [PF2] key while turning the transceiver
power ON. Then, the orange LED on the transceiver lights
and “PROG 115200” is displayed.
5. Check the connection between the transceiver and the
personal computer, and make sure that the transceiver is
in the Program mode.
6. Press “write” button in the window. When the transceiver starts to receive data, the [PG] display is blinking.
7. If writing ends successfully, the checksum is calculated
and a result is displayed.
8. If you want to continue programming other transceivers,
repeat steps 4 to 7.
2. Solder the lead wire onto the MIC tab on the PCB, and
the ground wire onto the ME tab.
++
C5
C4
Q1
MIC
MAX232C
ME
TRD
MAXIM
GND
SB
IC1
6
C7
+
Note:
This mode cannot be entered if the Firmware Programming mode is set to Disable in the Programming software.
7-4. Baud rate change
1. If you press the [PF4] key while "PROG 115200" is displayed, the display changes to "PROG 57600" (The LED
blinks orange). If you press the [PF4] key again while
"PROG 57600" is displayed, the display changes to "PROG
19200" (The LED blinks green) to indicate that the write
speed is low speed (19200 bps). If you press the [PF4] key
again while "PROG 19200" is displayed, the display returns
to "PROG 115200" (The LED lights orange).
2. If you press the [PF5] key while "PROG 115200" is displayed, the checksum is calculated, and a result is displayed. If you press the [PF5] key again while the
checksum is displayed, "PROG 115200" is redisplayed.
Note: Normally, write in the high-speed mode.
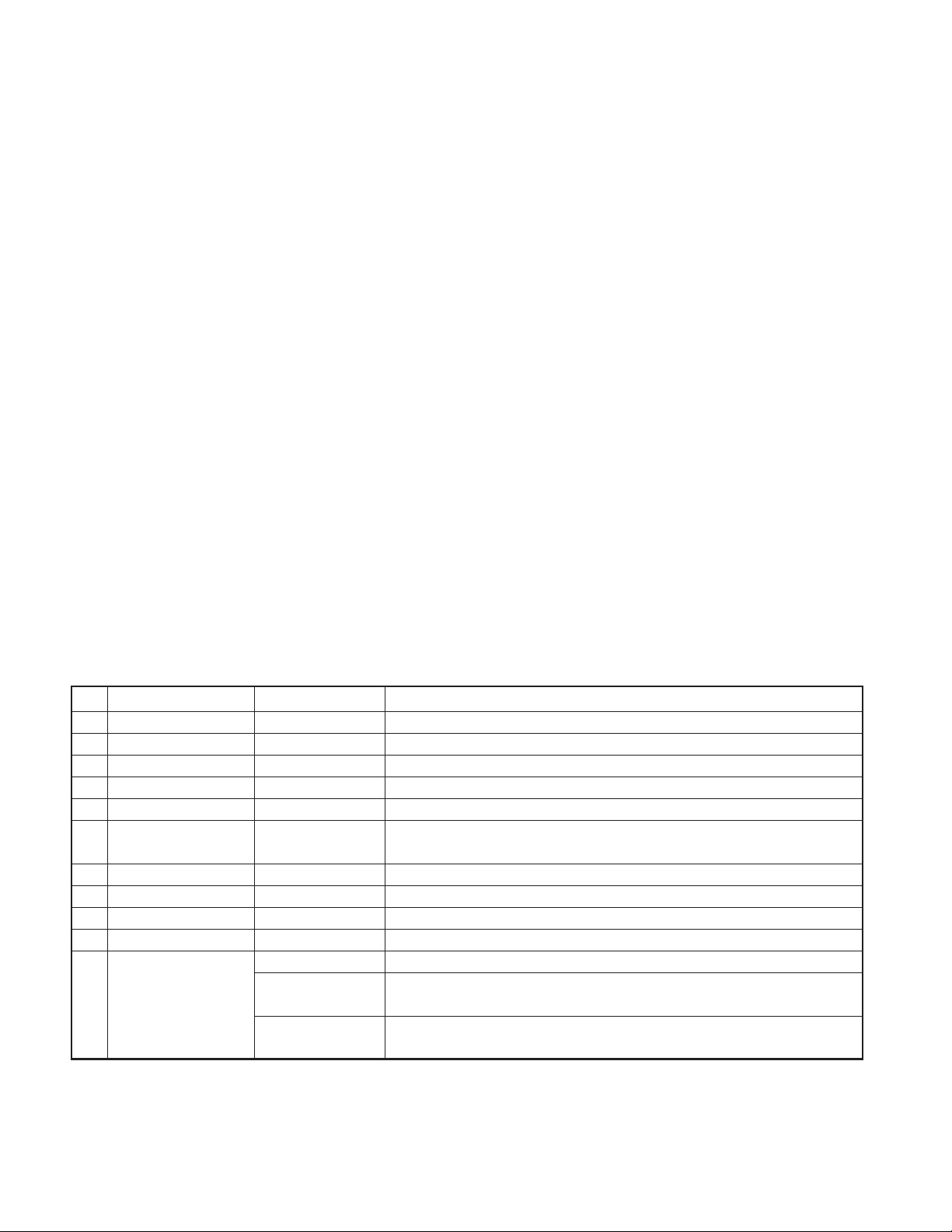
REALIGNMENT
[PF5]+Power ON
Is Read password
set?
“CLONE LOCK”
is displayed.
Ye s
Ye s
[PF2]
No
No
Enter the password and then
press the [PF2] key or [*] key
on the microphone.
Start the clone function
“CLONE MODE” is displayed.
Is password
correct?
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
)
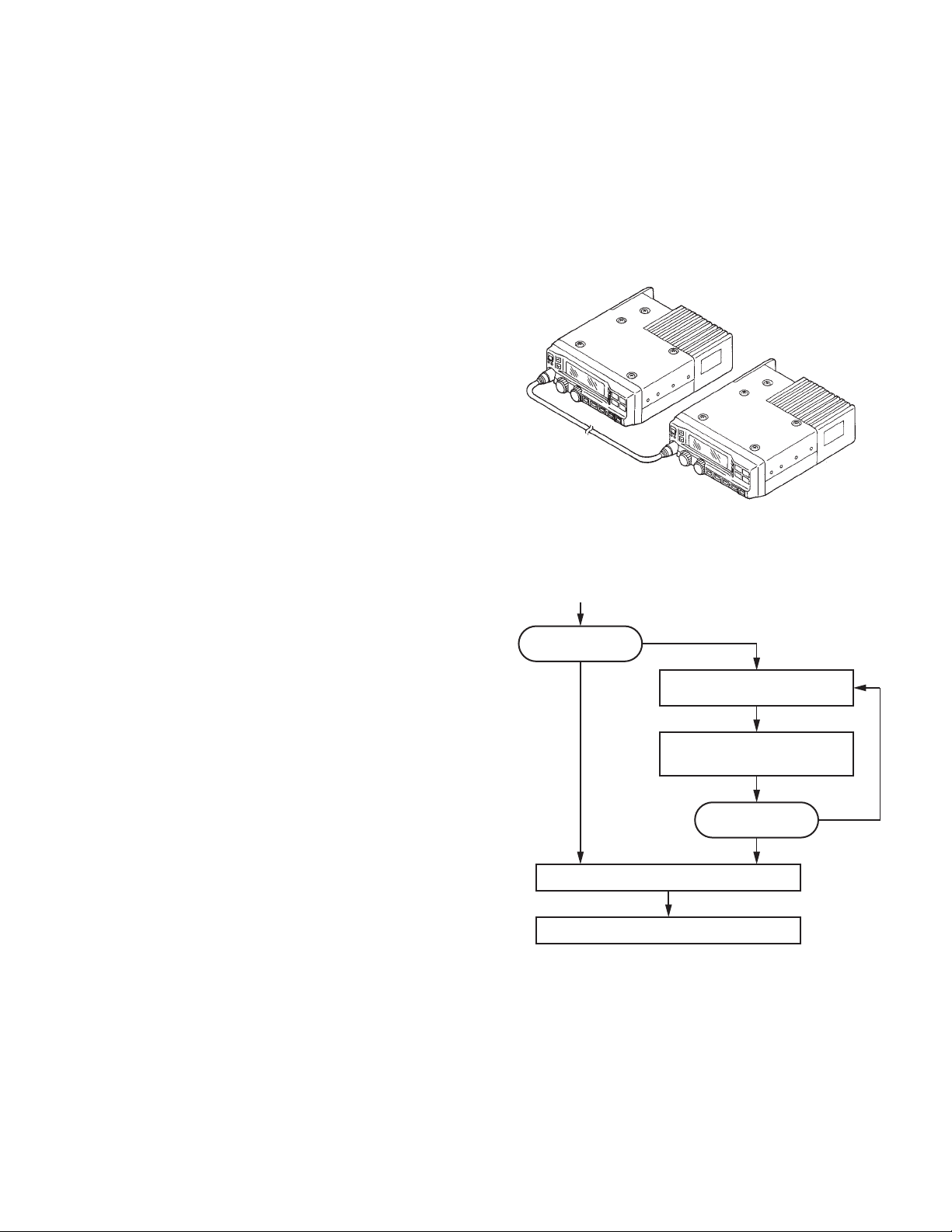
8. Clone Mode
ceiver to another by connecting them via their microphone
jacks. The operation is as follows (the transmit transceiver is
the master and the receive transceiver is a slave).
• Tuning data
• Embedded message with password
• Model name data
• ESN (Electronic Serial Number) data
1. Press and hold the [PF5] key while turning the transceiver
2. When you enter the correct password, and “CLONE
3.
• How to enter the read authorization password using
• How to enter the read authorization password using
4. Power ON the slave transceiver.
5. Connect the cloning cable (part No. E30-3370-05) to the
6. Press the [PF2] key on the master while the master dis-
7. The other slave can be continuously cloned. When the
Programming data can be transferred from one trans-
The following data cannot be cloned.
power ON. If the Read authorization password is set to
the transceiver, the transceiver displays “CLONE LOCK”.
If the password is not set, the transceiver displays
“CLONE MODE”.
MODE” is displayed, the transceiver can be used as the
cloning master. The following describes how to enter the
read authorization password.
the microphone keypad;
If one of keys 0 to 9 is pressed while "CLONE LOCK" is
displayed, the pressed number is displayed on the LCD.
Each press of the key shifts the display in order to the left.
If you press the [#] key, the least digit of the password is
deleted.
When you enter the password and press the [✳] key,
“CLONE MODE” is displayed if the entered password is
correct. If the password is incorrect, “CLONE LOCK” is
redisplayed.
the [Selector] knob;
If the [Selector] knob is rotated while "CLONE LOCK" is
displayed, the number (0 to 9) flashes on the LCD. When
you press the [GRP^] key, the currently selected number
is determined. If you press the [PF3] key, the least digit of
the password is deleted. If you press the [PF2] key after
entering the password in this procedure, “CLONE
MODE” is displayed if the entered password is correct. If
the password is incorrect, “CLONE LOCK” is redisplayed.
microphone jacks on the master and slave.
plays “CLONE MODE”. The data of the master is sent to
the slave. While the slave is receiving the data, “PROGRAM” is displayed. When cloning of data is completed,
the master displays “END”, and the slave automatically
operates in the User mode. The slave can then be operated by the same program as the master.
[PF2] key on the master is pressed while the master displays “END”, the master displays “CLONE MODE”.
Carry out the operation in step 4 to 6.
Notes:
• Cannot be cloned if the overwrite password is pro-
grammed to the slave.
• "Model Name and Market Code", "Head Configuration" and
"Head Type" must be same to clone the transceiver. However, it may be unable to clone the transceiver depending
on the enhanced features settings.
(Refer to the FPU for the enhanced features details.)
Cloning cable
(Part No. E30-3370-05)
Fig. 2
●
Flow Chart (Master transceiver)
7
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
)
REALIGNMENT
9. Self Programming Mode
Write mode for frequency data and signaling etc. To be
used ONLY by the authorized service person maintaining the
user's equipment. After programming, reset the FPU to the
"Self- Programming" disabled mode. Transceivers CANNOT
be delivered to the end-user in the self-programming mode.
The following setup items in the channels programmed by
the FPU can be changed using the self-programming mode.
The addition of new channel and the deletion of channel that
has already been programmed by the FPU cannot be
performed using the self-programming mode.
• RX Frequency
• TX Frequency
• Channel Type
• TX Mode (When the channel type is selected "MIXED".)
• Channel Spacing
• RX Signaling
• TX Signaling
• RX NAC
• TX NAC
• Talkgroup List No.
Note:
The personality will be also changed when the above-
mentioned items is changed. (Refer to the FPU for the
personality details.)
9-1. Enter to the self programming mode
Press and hold the [GRP^] key while turning the transceiver power ON. Ignoring whether the Read authorization
password is set or not, "PASSWORD" appears.
If the Read authorization password is not set to the transceiver, "SELF PG MODE" is displayed on the LCD when the
[PF2] key is pressed while "PASSWORD" is displayed.
If the password is set to the transceiver, "SELF PG MODE"
is displayed on the LCD when you enter the correct password while "PASSWORD" is displayed.
For the password input method, see "8.Clone Mode”
step 3 described on page 7.
Note :
This mode (self programming mode) cannot be set when
it has been disabled with the FPU.
9-2. Data writing
If the [PF4] key is pressed while Zone/Channel mode is
displayed, new data is written into memory. "WRITING" is
displayed while the transceiver is writing data.
The setup items for self programming mode are as follows.
No. Setup item Display Remarks
1 Select Zone/Channel ∗∗ - ∗∗∗ Zone : 1~50, Channel : 1~250
2 RX Frequency 1∗∗. ∗∗∗∗∗ MHz Receive frequency
3 TX Frequency 1 ∗∗.∗∗∗∗∗ MHz Transmit frequency
4 Channel Type TYPE ANALOG/APCO/MIXED
5 TX Mode MODE ANALOG/APCO
6 Channel Spacing SPACE
7 RX Signaling RX-SIG Receive QT/DQT
8 TX Signaling TX-SIG Transmit QT/DQT
9 RX NAC RX-NAC ∗∗∗ 000~FFF (Hexadecimal) Note:"F7F" cannot be set.
10 TX NAC TX-NAC ∗∗∗ 000~FFF (Hexadecimal) Note:"F7E" and "F7F"cannot be set.
11
Talkgroup List No.
None When you do not want to set the Talkgroup list number to the transceiver.
∗∗∗
∗∗∗∗∗∗∗∗∗∗∗∗
25.0kHz/12.5kHz (When the Channel type is selected "ANALOG" or "MIXED".)
APCO 12.5kHz/12.5kHz (When the Channel type is selected "APCO".)
Talkgroup list number (1~250)
(When the Talkgroup list name is not set to the transceiver.)
Talkgroup list name (12 digits)
(When the Talkgroup list name is set to the transceiver.)
8
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
REALIGNMENT
Key operation
• Normal mode
Item
Key
[PF1] Unused
[PF2] Go to the next item
[PF3] Zone/ Channel 2.5kHz/ 5kHz/ 6. 25kHz/
[PF4] Data
[PF5] Unused
[Selector] Zone/ Channel 1step
[GRP
[GRP
MIC keypad
([0] to [9]) input mode input mode
MIC keypad
([*])
MIC keypad Delete the least digit from
([#]) Unused the current number Unused
MIC PTT [PTT] + [2] : "A"
Zone- Channel RX Frequency TX Frequency Channel Type TX Mode
ANALOG/ APCO/ ANALOG/ APCO/ Channel Spacing
switching 7.5kHz/ 1MHz MIXED switching switching switching the current number Unused
step switching switching
Writing switching switching
up/ down up/ down up/ down in the specified digit up/ down
] Zone/ Channel 1step
up up up up
] Zone/ Channel 1step
down down down down
Unused
Unused
Go to the MIC keypad
On/ Off
Unused
Unused
Unused
Unused
Unused
Unused
Channel Spacing
Unused
RX Signaling TX Signaling RX NAC TX NAC TG List No.
1step/ Standard Delete the least digit from
(Press and hold to delete all numbers.)
QT/ DQT( N)/ DQT( I)/ OFF
Signaling
Signaling Determine the least digit TG List number
Signaling
Go to the MIC keypad
Increment/ Decrement a number
Add a digit to the current number
(Press and hold to delete all numbers.)
Unused
Unused
[PTT] + [5] : "B"
[PTT] + [8] : "C"
[PTT] + [0] : "D"
[PTT] + [#] : "E"
[PTT] + [*] : "F"
TG List number
TG List number
Unused
Unused
)
• MIC keypad input mode
Item
Key
[PF1] Cancel the MIC keypad input mode
[PF2] Cancel the MIC keypad input mode
[PF3] Delete the least digit from the current number
[PF4] Unused On/ Off QT/ DQT( N)/ DQT( I)/ OFF
[PF5] Unused
[Selector] Unused
[GRP ] Unused
[GRP ] Unused
MIC keypad Add a digit to the current number
([0] to [9]) (Return to the normal mode automatically if all digit are entered.)
MIC keypad Cancel the MIC keypad input mode
([*]) (Return to the normal mode)
MIC keypad Delete the least digit from the current number
([#]) (Press and hold to delete all numbers.)
MIC PTT Unused
RX Frequency TX Frequency RX Signaling TX Signaling
(Return to the normal mode)
(Return to the normal mode)
(Press and hold to delete all numbers.)
switching switching
9
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
●
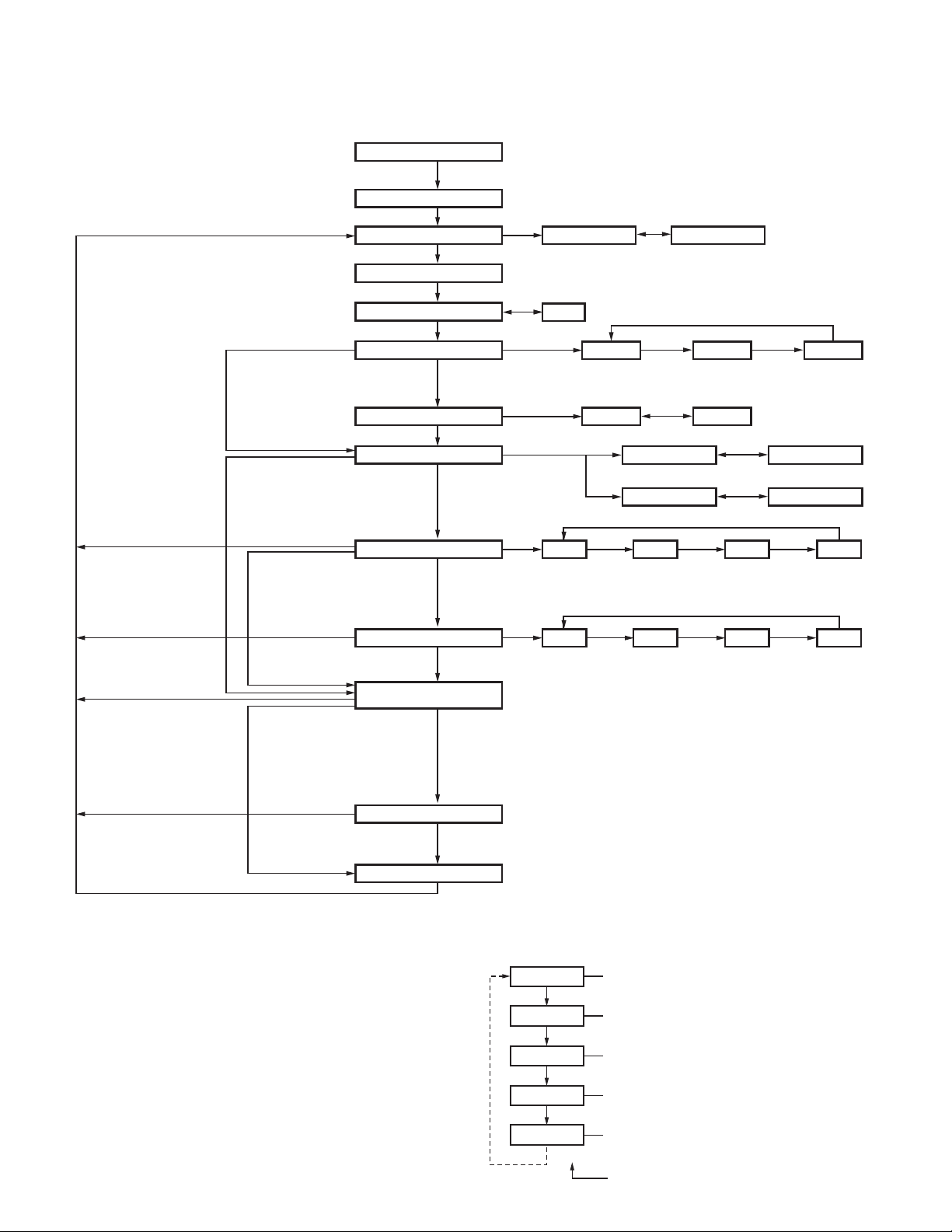
Self programming mode flow chart
] + Power ON
[GRP
^
[PF2]
[TX Frequency] : "OFF"
or
[Channel Type] : "ANALOG" or "APCO"
[PF2]
[Channel Type] : "APCO"
)
REALIGNMENT
Input Password
Read authorization password entry (6 digits)
[PF2]
Self programming mode
[PF2]
Zone/Channel
[PF2]
RX Frequency
[PF2]
TX Frequency
Channel Type
TX Mode
Channel Spacing
[PF4]
[PF2]
[PF2]
[TX Frequency] : Other than "OFF"
[Channel Type] : "MIXED"
[PF2]
[PF2]
[Channel Type] :
"ANALOG" or "MIXED"
Zone selection
When the [PF4] key is pressed,
new data is written into memory.
OFF
ANALOG
*1
*2
[PF3]
Channel selection
[PF3]
[PF3]
*1 [Channel Type] : "ANALOG" or "MIXED"
APCO 12.5kHz
*2 [Channel Type] : "APCO"
[PF3]
APCO
APCOANALOG
[PF3]
[PF3]
[PF3]
[PF4]
MIXED
12.5kHz25.0kHz
12.5kHz
[PF2]
[TX Frequency] : "OFF"
[Channel Type] : "ANALOG"
[PF2]
[Channel Type] : "ANALOG"
[PF2]
[TX Frequency] : "OFF"
Ta lkgroup ID List Amount : 0
or
[TX Frequency] : Other than "OFF"
[Channel Type] : "MIXED"
[TX Mode] : "ANALOG"
Ta lkgroup ID List Amount : 0
[PF2]
Ta lkgroup ID List Amount : 0
[PF2]
[TX Frequency] : "OFF"
[Channel Type] : "APCO" or "MIXED"
or
[TX Frequency] : Other than "OFF"
[Channel Type] : "MIXED"
[TX Mode] : "APCO"
[PF2]
[TX Frequency] : "OFF"
Ta lkgroup ID List Amount must not be 0.
or
[TX Frequency] : Other than "OFF"
[Channel Type] : "MIXED"
[TX Mode] : "ANALOG"
Ta lkgroup ID List Amount must not be 0.
10. Firmware Information Mode
Press and hold the [PF3] key while turning the transceiver
power ON and then keep pressing and holding the [PF3] key,
the firmware version information appears on the LCD.
11. Clock Adjustment Mode
11-1. Flow chart of operation
10
RX Signaling
TX Signaling
RX NAC
TX NAC
Talkgroup List No.
[PF2]
OFF QT
[PF2]
[TX Frequency] : Other than "OFF"
[Channel Type] : "ANALOG" or "MIXED"
[TX Mode] : "ANALOG"
[PF2]
[Channel Type] : "MIXED"
[PF2]
[TX Frequency] : Other than "OFF"
[Channel Type] : "APCO" or "MIXED"
If [Channel Type] is set to "MIXED",
[TX Mode] must be set to "APCO".
[PF2]
[Channel Type] : "APCO" or "MIXED"
Ta lkgroup ID List Amount must not be 0.
[PF4] + Power ON
YEAR
MONTH
DAY
HOUR
MINUTE
[PF4] [PF4] [PF4]
OFF QT DQT N
[PF4]
[Selector] or [GRP^] and [GRP ]
[PF2]
[Selector] or [GRP^] and [GRP ]
[PF2]
[Selector] or [GRP^] and [GRP ]
[PF2]
[Selector] or [GRP^] and [GRP ]
[PF2]
[Selector] or [GRP^] and [GRP ]
[PF2]
Completion
[PF4]
[PF4]
DQT N
^
^
^
^
^
[PF4]
DQT I
DQT I
INSTALLATION
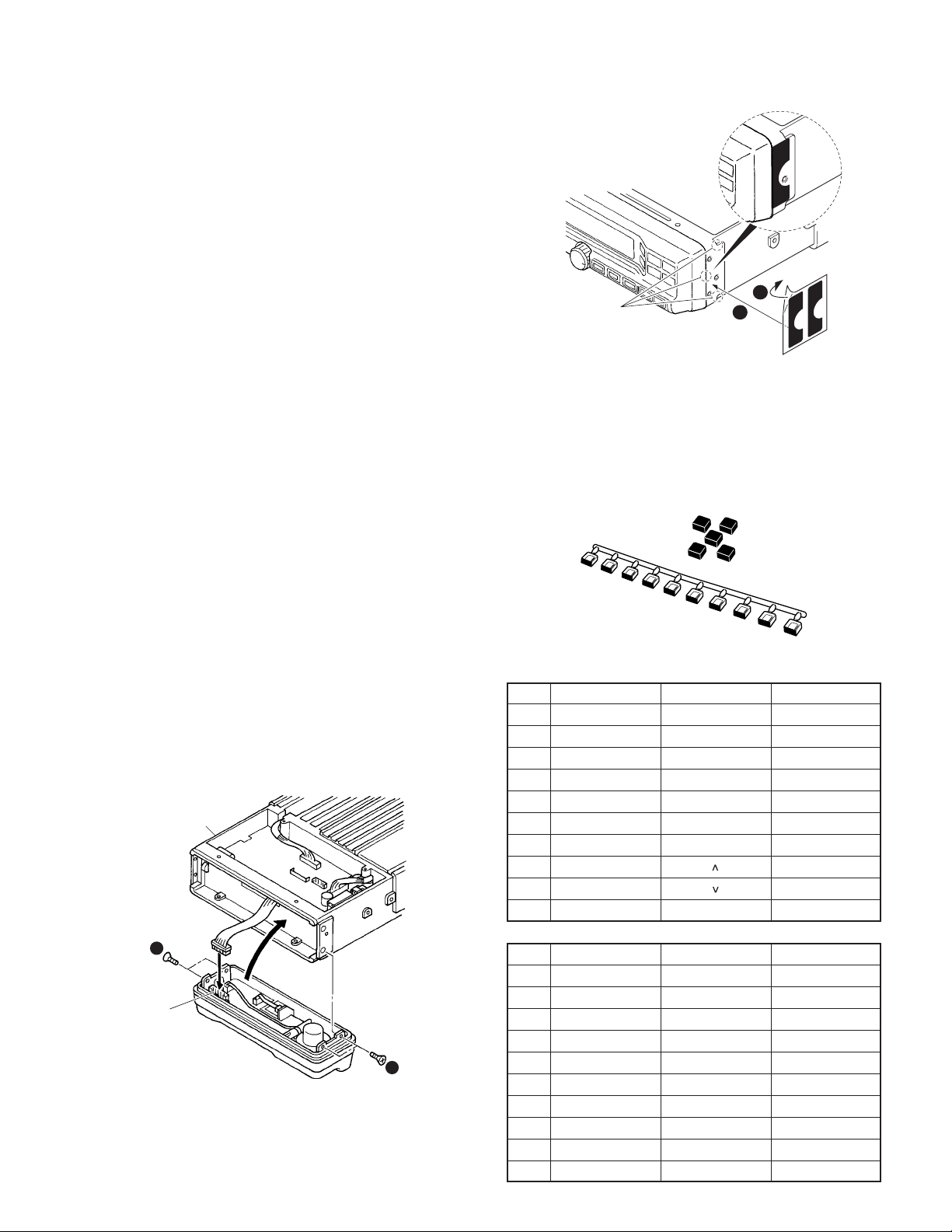
1. Front Panel Kit (KCH-14/15:Option)
1-1. Installing the KCH-14/15 front panel kit to the
transceiver
1. Remove the upper case and lower case of the transceiver.
2. Insert the lead wire with connector (W700) of the control
unit (X53-412) into the connector (CN1) of the KCH-14 or
KCH-15.
3. Install the KCH-14 or KCH-15 on the transceiver using the
four screws (z) supplied with the front panel kit.
Note:
Take care that the lead wire with connector (W700) is not
caught when fitting the KCH-14 or KCH-15 on the
transceiver. (You can install the panel upside down if
necessary to install the transceiver.)
4. Affixing the sheet (G11-4379-04) for the waterproof
(Fig.1-1-2).
(1) Remove the covering paper of the sheet (x).
(2) Affix the sheet while taking note of the position of the
three parts as shown in Fig.1-1-2 (c).
Firmly affix the sheet to the chassis by pushing the
double-coated tape with your fingers.
(3) Repeat step (2) to affix the sheet to the other side of
chassis.
Note:
The sheet cannot be reused. Affix a new sheet when you
removed the sheet.
5. Reassemble the upper case and lower case. (Refer to
page 24)
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
Affix the sheet while
taking note of the position
of the three parts.
Fig. 1-1-2
1-2. Installing the accessory keytops to the front
panel kit
When a function is set by the programming software
(KPG-95D), the key legend can be changed by inserting the
accessory keytops into PF1 to PF9 of the KCH-15 (PF1 to
PF5:KCH-14). The accessory contains 60 keytops as shown
the table below.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Fig. 1-2
2
3
8
9
10
)
Note:
Take care that the sheet (G11-4379-04) is not peeled off
when installing the upper / lower case.
6. Connect the short plug to the accessory connector (9-pin)
on the rear of the transceiver.
Transceiver
W700
1
CN1
KCH-14 or
KCH-15
1
Fig. 1-1-1
No. K29-5276-03 K29-5277-03 K29-5305-03
1AN RCL CH1
2 D/A RPT CH2
3 DIM SCN CH3
4HA SP CH4
5HC SPM CH5
6ICSQAUX A
7 MON TA AUX B
8 OPT AUX C
9 OST EMG
10 PA No printing ■
No. K29-9353-13 K29-9354-03 K29-9356-03
1 2TN GPS PAG
2AD STS SIT
3AR TAC SRC
4 CLK TON No printing
5 FNC RES No printing
6 PBK IDV No printing
7 SCP KDL No printing
8 SEC TGR No printing
9 SEL No printing No printing
10 SES No printing No printing
11
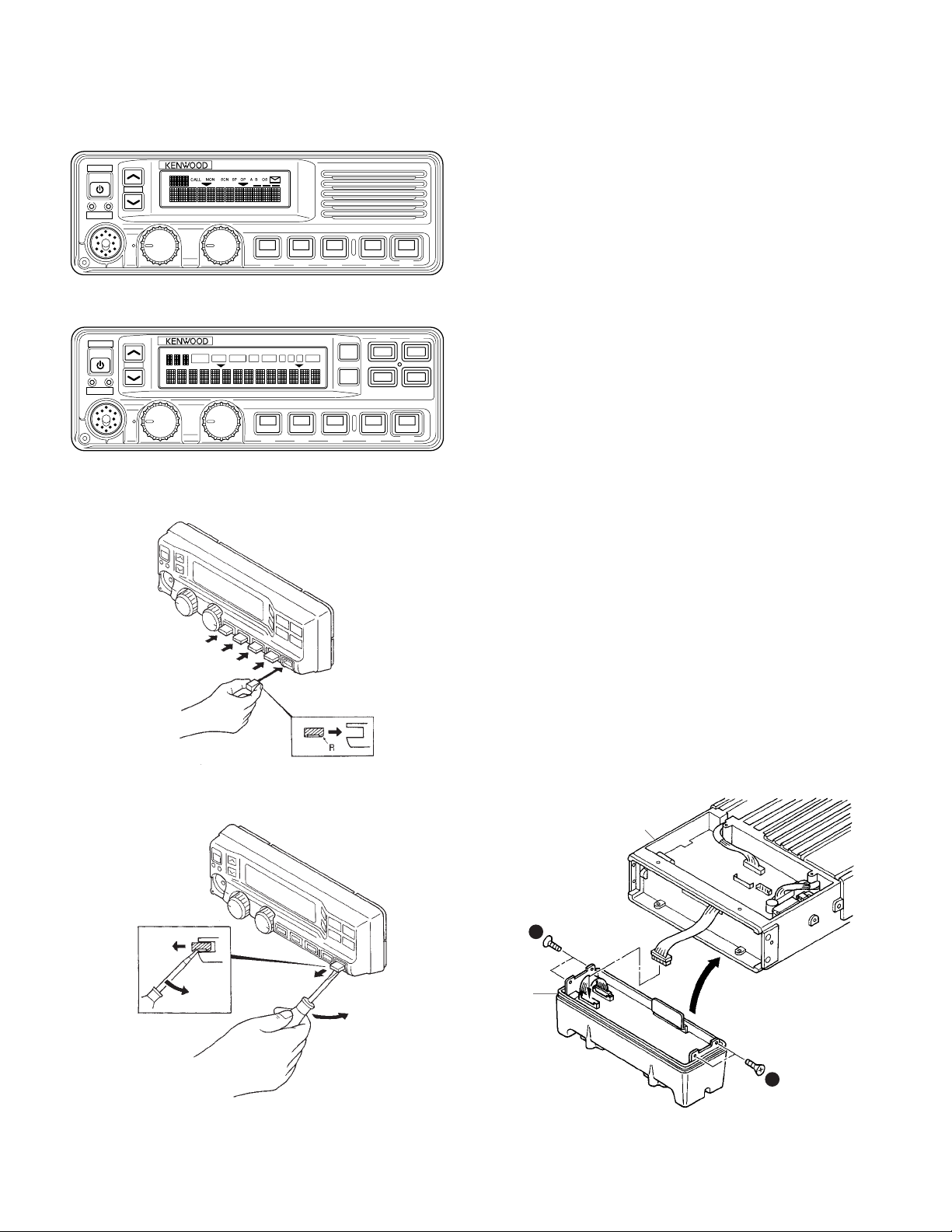
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
)
INSTALLATION
KCH-14
POWER
TX
BUSY
KCH-15
POWER
BUSY
TX
2. Remote kit (KRK-5:Option)
The KRK-5 remote kit is used to remotely operate the
GRP
VOL
GRP
VOL
CALL
CH
PF1 PF2 PF3 PF4 PF5
SCAN OPT OSTA B CMON
SP
CH
PF1 PF2 PF3 PF4 PF5
MON
PF7PF6
SCN
PF9PF8
Fig. 1-3
transceiver. The KRK-5 is connected to the KCH-14 or KCH15 with an optional KCT-22M (8 feet), KCT-22M2 (17 feet),
or KCT-22M3 (25 feet) control cable.
2-1. Installing the KRK-5 main panel onto the
transceiver
1. Remove the upper case and lower case of the transceiver.
2. Insert the lead wire with connector (W700) of the control
unit (X53-412) into the connector (CN4) of the KRK-5.
3. Install the KRK-5 main panel on the transceiver using four
screws (z).
Note:
Take care that the lead wire with connector (W700) is not
caught when fitting the KRK-5 main panel on the
transceiver.
4. Affixing the sheet (G11-4379-04) for the waterproof
(Fig.2-1-2).
(1) Remove the covering paper of the sheet (x).
(2) Affix the sheet while taking note of the position of the
three parts as shown in Fig.2-1-2 (c).
Firmly affix the sheet to the chassis by pushing the
double-coated tape with your fingers.
(3) Repeat step (2) to affix the sheet to the other side of
chassis.
Fig. 1-4 Keytop insertion
Note:
The sheet cannot be reused. Affix a new sheet when you
removed the sheet.
5. Reassemble the upper case and lower case of the transceiver. (Refer to page 24)
Note:
Take care that the sheet (G11-4379-04) is not peeled off
when installing the upper / lower case.
Tra nsceiver
1
Packing
KRK-5 main panel
W700
CN4
1
12
Fig. 1-5 Keytop removal
Fig. 2-1-1
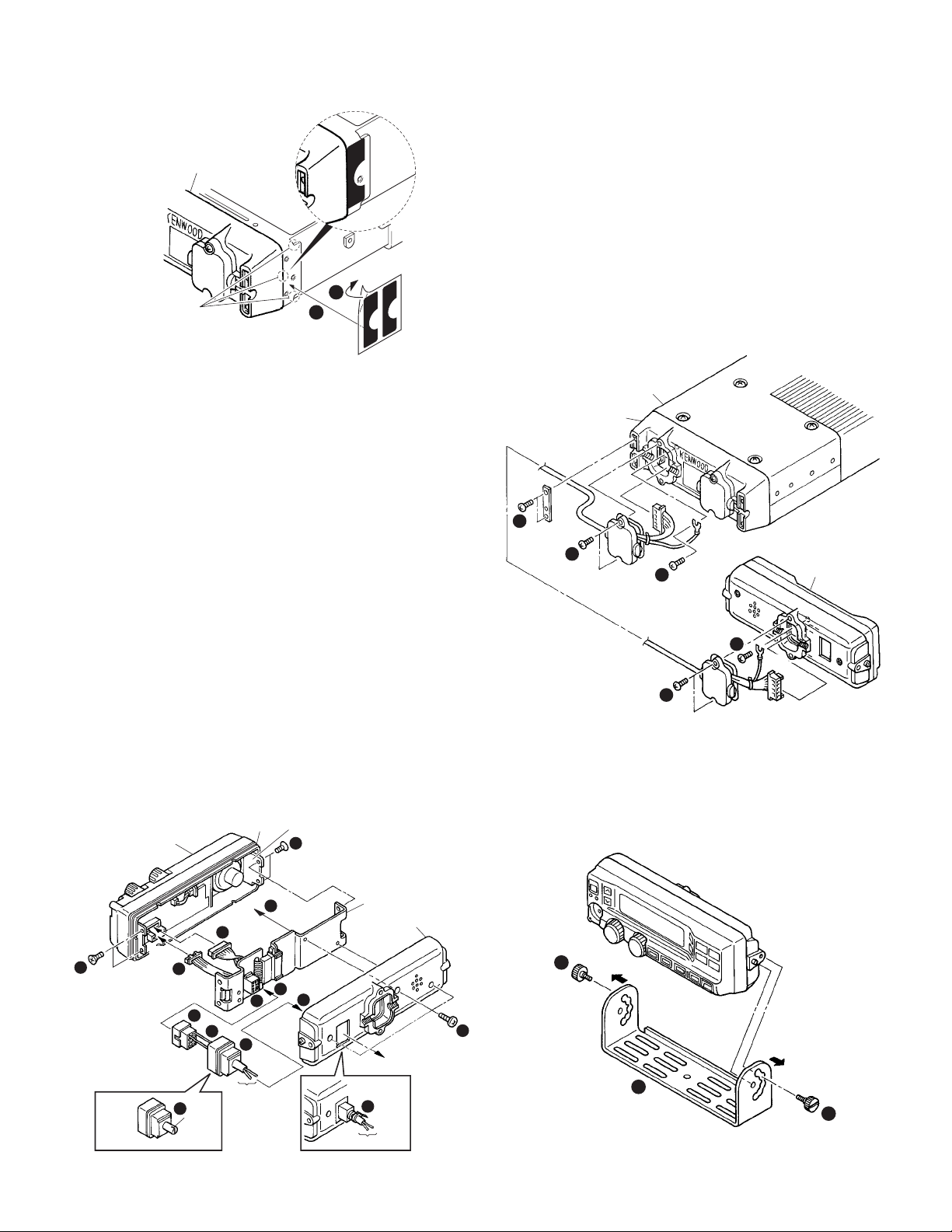
KRK-5 main panel
Affix the sheet while
taking note of the position
of the three parts.
Fig. 2-1-2
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
)
INSTALLATION
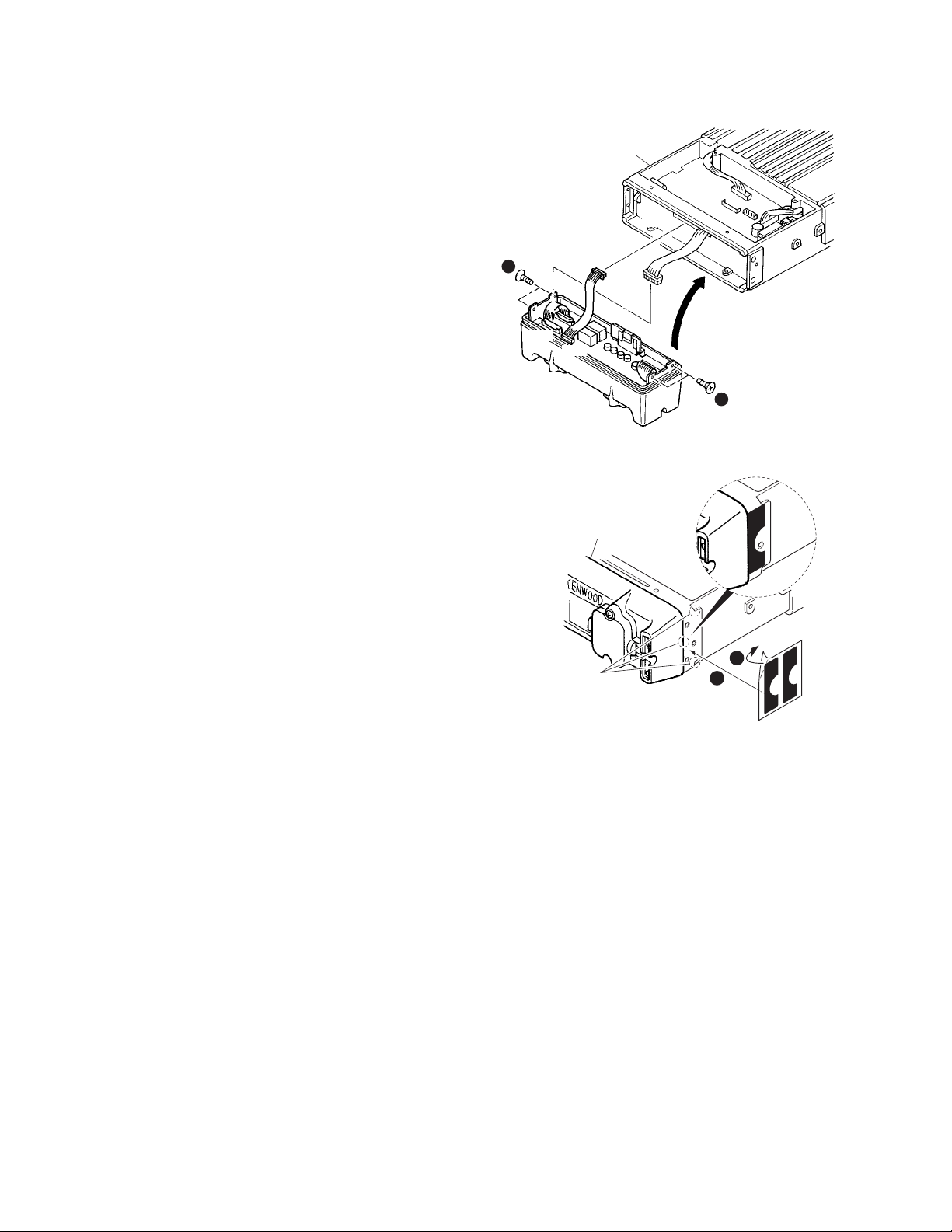
2-3. Control cable (KCT-22) connection (Fig. 2-3)
1. Insert one connector of the control cable to the
transceiver (with KRK-5) and the other to the display.
Connect the cable to the GND terminal with the screw
(z) supplied with the control cable.
2. Secure the one connector of the control cable to the KRK-
5 main panel with two screws (x) according to the
installation condition of the transceiver. Secure the
control cable to the KRK-5 main panel with the cable
2
3
fitting (J21-4354-04) and two screws (c) supplied with
the KRK-5.
3. Secure the other connector of the control cable to the
display with two screws (v) in the same way.
2-2. Installing the KRK-5 rear panel onto the front
panel kit
The following steps apply to both the KCH-14 and
KCH-15.
1. Remove three screws (z) on the KRK-5 rear panel, then
remove the KRK-5 sub panel.
2. Insert the lead wire with connector (W102) of the KRK-5
into the connector (CN1) of the front panel kit (x).
3. Insert the lead wire with connector (W103) of the KRK-5
into the connector (CN3) of the front panel kit (c).
4. Make a slight cut in the end of the rubber cap (v).
5. Slide the lead wire of the connector wiring (b) through
the slit in the rubber cap (n).
6. Insert the rubber cap into the hole of the KRK-5 rear panel
(m).
7. Insert the connector (,) to the ACC connector (.) on the
KRK-5 sub panel as shown by the arrow (/).
8. Install the KRK-5 sub panel onto the sub panel of the front
panel kit (Ω).
9. Install the KRK-5 sub panel to the sub panel of the front
panel kit using four screws (≈).
10.
Reinstall the KRK-5 rear panel using three screws
removed in step 1.
11.Use a wire band to secure the lead wire at the end of the
rubber cap (ç).
Front panel kit
(Example : KCH-14)
Packing
Sub panel
12
Transceiver
KRK-5 main panel
3
Cable
fitting
2
Control cable
KCT-22
GND
1
1
4
Display
GND
Fig. 2-3
2-4. Display installation (Fig. 2-4)
1. Install the display with the angle bracket (J29-0648-03)
(z) and two screws (N08-0526-04) (x) supplied with the
KRK-5.
12
Rubber
cap
CN1
CN3
3
W103
1
Make
4
a cut
11
2
W102
10
7
5
9
6
IGN,
GND etc.
8
3
KRK-5 sub panel
KRK-5 rear panel
Lead wire
13
IGN,GND etc.
2
1
1
Angle
bracket
2
Fig. 2-4
Fig. 2-2
13
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
)
INSTALLATION
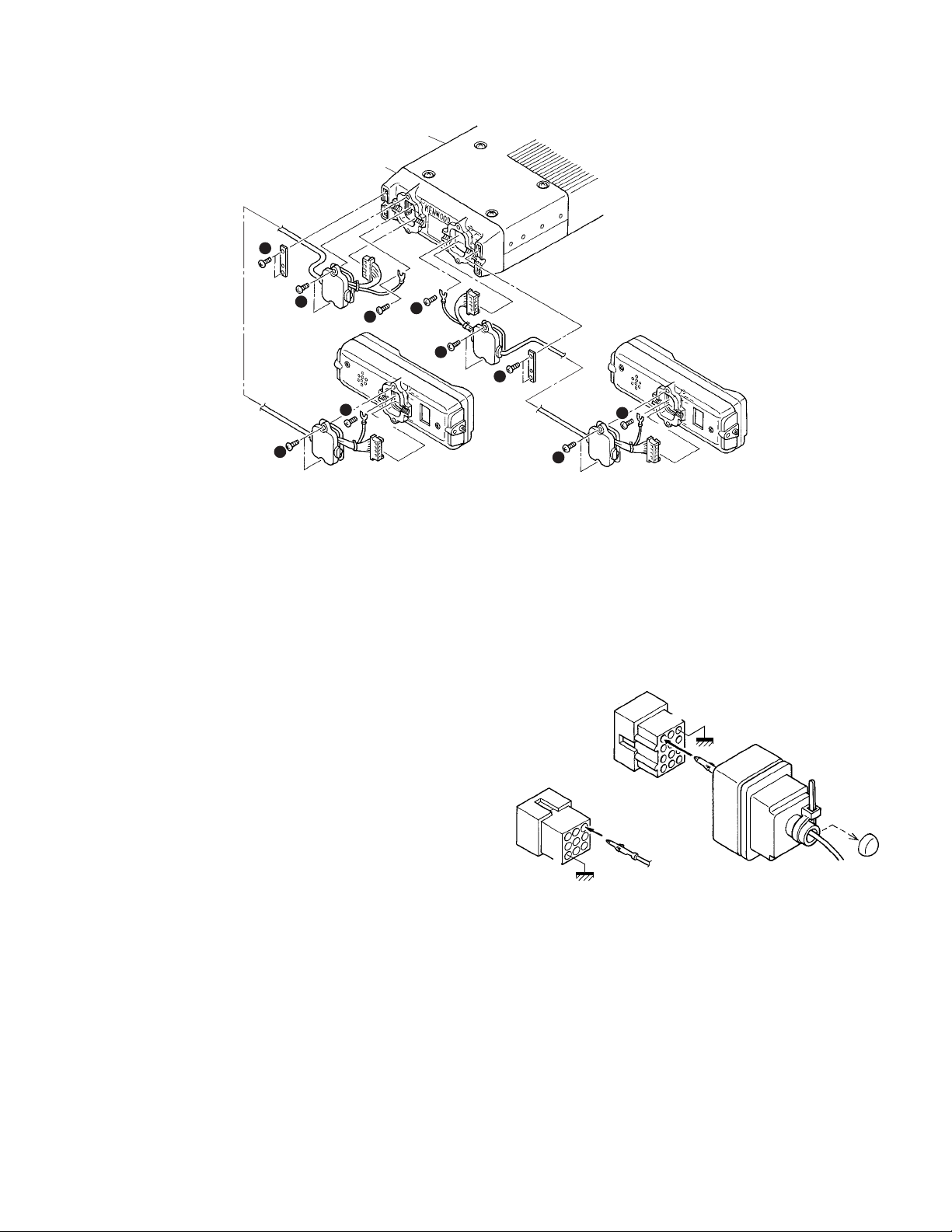
3. Dual Control Head Remote Kit (KRK-6DH:Option)
The KRK-6DH remote kit connects two displays (two
KCH-14s or KCH-15s) to the transceiver. The KRK-6DH is
connected to the KCH-14s or KCH-15s with two optional
control cables. There are three version of the control cable :
KCT-22M (8 feet), KCT-22M2 (17 feet), and KCT-22M3 (25
feet).
3-1. Installing the KRK-6DH main panel onto the
transceiver
1. Remove the upper case and lower case of the trans-
ceiver.
2. Insert the lead wire with connector (W700) of the control
unit (X53-412) into the connector (CN4) of the KRK-6DH.
Insert the lead wire with connector (W104) of the KRK-
6DH into the connector (CN724) of the transceiver.
3. Install the KRK-6DH main panel on the transceiver using
four screws (z).
Note:
Take care that the lead wire with connector (W700) is not
caught when fitting the KRK-6DH main panel on the
transceiver.
4. Affixing the sheet (G11-4379-04) for the waterproof
(Fig.3-1-2).
(1) Remove the covering paper of the sheet (x).
(2) Affix the sheet while taking note of the position of the
three parts as shown in Fig.3-1-2 (c).
Firmly affix the sheet to the chassis by pushing the
double-coated tape with your fingers.
(3) Repeat step (2) to affix the sheet to the other side of
chassis.
Note:
The sheet cannot be reused. Affix a new sheet when you
removed the sheet.
5. Reassemble the upper case and lower case of the
transceiver. (Refer to page 24)
Note:
Take care that the sheet (G11-4379-04) is not peeled off
when installing the upper / lower case.
14
Transceiver
CN724
1
W104
CN4
CN5
KRK-6DH
main panel
W700
1
Fig. 3-1-1
KRK-6DH main panel
Affix the sheet while
taking note of the position
of the three parts.
2
3
Fig. 3-1-2
3-2. Installing two KRK-6DH rear panels onto two
front panel kits
Install each KRK-6DH rear panel onto each front panel kit
as same as "2-2.Install the KRK-5 rear panel onto the front
panel kit" described on page 13.
3-3. Control cable (KCT-22) connection (Fig. 3-2)
1. Use two control cables. Insert one connector of the one
control cable to the transceiver (with KRK-6DH) and the
other to the display 1.
Insert one connector of the other control cable to the
transceiver (with KRK-6DH) and the other to the display 2.
Connect each cable to the GND terminal with the screws
(z) supplied with each control cable.
2. Secure the one connector of each control cable to the
KRK-6DH main panel with two screws (x) according to
the installation condition of the transceiver. Pass the
control cables through the grooves at both ends of the
KRK-6DH main panel and secure the control cables to the
KRK-6DH with the cable fitting (J21-4354-04) and two
screws (c) supplied with the KRK-6DH.
3. Secure the other connectors of the control cables to the
display 1 and display 2 with two screws (v) in the same
way.
3
Cable
fitting
2
Display 1
KRK-6DH
main panel
1
INSTALLATION
Transceiver
GND
GND
1
2
Cable
fitting
3
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
Display 2
)
KCT-22
Control cable
4
1
GND
4. Ignition Sense Cable (KCT-18:Option)
The KCT-18 is an optional cable to use the following
functions:
• Ignition function
The ignition function allows you to turn the transceiver's
power on and off with the ignition key of your car. When you
are driving with the ignition key on, the horn alert function is
disabled.
• Timed power-off function
The timed power-off function turns the transceiver's
power off the time specified with the programming
software (KPG-95D) after the ignition key is turned off.
When you are driving with the ignition key on, the horn alert
function is disabled.
The ignition sense function and the timed power-off
function can be used at the same time.
4-1. Connecting the KCT-18 cable to the transceiver
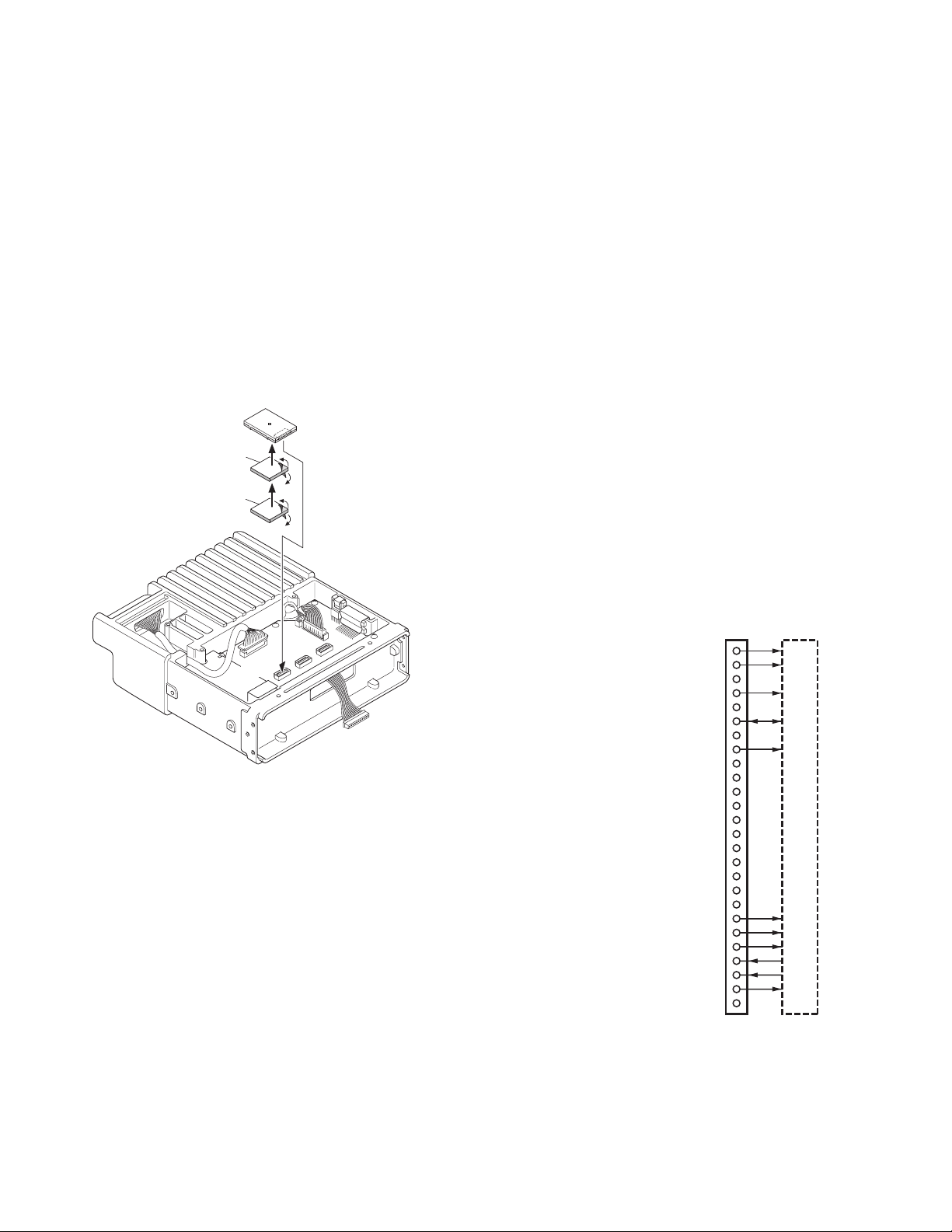
1. Remove the short plug from the accessory connector (9-
pin) on the rear of the transceiver.
2. Insert the KCT-18 lead terminal into pin 1 (IGN) of the
short plug (9-pin).
3. Connect the short plug to the accessory connector (9-pin)
on the rear of the transceiver.
Note: You must setup using the KPG-95D.
KCT-22
Control cable
Fig. 3-2
1
GND
4
3. Connect the square plug and rubber cap to the accessory
connector (12-pin) on the rear of the control head, then
clamp the bottom of the rubber cap with the supplied tie
wrap.
Note: You must setup using the KPG-95D.
Square plug
(12-pin)
3
7
9
Short plug
(9-pin)
1
3
KCT-18
1
12
10
Rubber cap
Tie wrap
Cut
KCT-18
Fig. 4-1 Fig. 4-2
4-2. Connecting the KCT-18 cable to the KRK-5/
6DH remote kit
1. Remove the square plug from the accessory connector
(12-pin) on the rear of the control head.
2. Cut off the end of the rubber cap (accessory), insert the
KCT-18 lead terminal into the rubber cap, and insert it into
pin 1 (IGN) of the square plug.
15
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
)
INSTALLATION
5. Voice Guide & Storage Unit (VGS-1: Option)
5-1. Installing the VGS-1 unit in the transceiver
1. Remove the upper case and upper packing of the
transceiver.
2. Attach two cushions to the VGS-1 as shown in figure.
Note:
Be sure not to cover the VGS-1 connector (CN1) with the
cushion.
3. Insert the VGS-1 connector (CN1) into the control unit
connector (CN744).
Note: You must setup using the KPG-95D.
VGS-1
Cushion
(G13-1992-04)
21 x 21 x 2.5mm
Cushion
(G13-1974-04)
21 x 21 x 1.0mm
CN1
6. Voice Scrambler Board Connection
1. Remove the upper case and upper packing of the
transceiver.
2. Two kinds of the scrambler board are available, and the
following describes the each installation method.
• How to install the scrambler board (Connector
connection type)
(1) Attach two cushions to the scrambler board as shown
in Fig.7-2.
Note:
Be sure not to cover the scrambler board connector
with the cushion.
(2) Insert the scrambler board into the control unit
connector (CN771).
• How to install the scrambler board (Lead wire
connection type)
(1) Attach the cushion to the scrambler board as shown
in Fig.7-2.
(2) Solder each lead wire of the scrambler board to a
necessary location of each landing on the component
side of the control unit.
Note: You must setup using the KPG-95D.
CN744
Fig. 5
Component side of the Control unit
CN771 / Solder land
BC1 (Scrambler code output 1)
BC2 (Scrambler code output 2)
LOK (No connection)
PTOS (PTT output)
NC (No connection)
ECHO (Echo PTT)
NC (No connection)
BC4 (Scrambler code output 4)
E (GND)
E (GND)
NC (No connection)
NC (No connection)
E (GND)
5C (5V)
NC (No connection)
NC (No connection)
NC (No connection)
NC (No connection)
NC (No connection)
AC (Scrambler control signal output)
TXO (MIC signal output)
RXEO (Audio signal output)
RXEI (Audio signal input)
STXI (MIC signal input)
BC3 (Scrambler code output 3)
8C (8V)
Fig. 6
1
Voice scrambler board
26
16
INSTALLATION
Extracting tool
(11-03-0002)
Jumper lead
(a)
(b)
Barbs
Crimp terminal
Short plug
(E37-0733-05)
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
)
7. ANI Board Connection
1. Remove the upper case and upper packing of the
transceiver.
2. Attach the cushion to the ANI board as shown in Fig.7-2.
3. Solder each lead wire of the ANI board to a necessary
location of each landing on the component side of the
control unit.
Note: You must setup using the KPG-95D.
Component side of the Control unit
Solder land
BUSY (Channel busy signal output)
EMG (Emergency signal output)
TCONT (Speaker mute signal input)
AINH (MIC mute signal input)
AUX I/O (Emergency signal input)
3M double coated cushion
No.4008 (or No.4408)
25 x 25 mm
3M double coated cushion
No.4032 (or No.4432)
25 x 25 mm
AKEY (Key input)
NC (No connection)
NC (No connection)
NC (No connection)
PTOA (PTT output)
NC (No connection)
E (GND)
E (GND)
NC (No connection)
NC (No connection)
E (GND)
5C (5V)
STON (Side tone input)
ATXI (Data input)
NC (No connection)
NC (No connection)
NC (No connection)
NC (No connection)
NC (No connection)
NC (No connection)
8C (8V)
Fig. 7-1
ANI board
ANI board
Voice scrambler
board
(Connector type)
Voice scrambler
board
(Lead wire type)
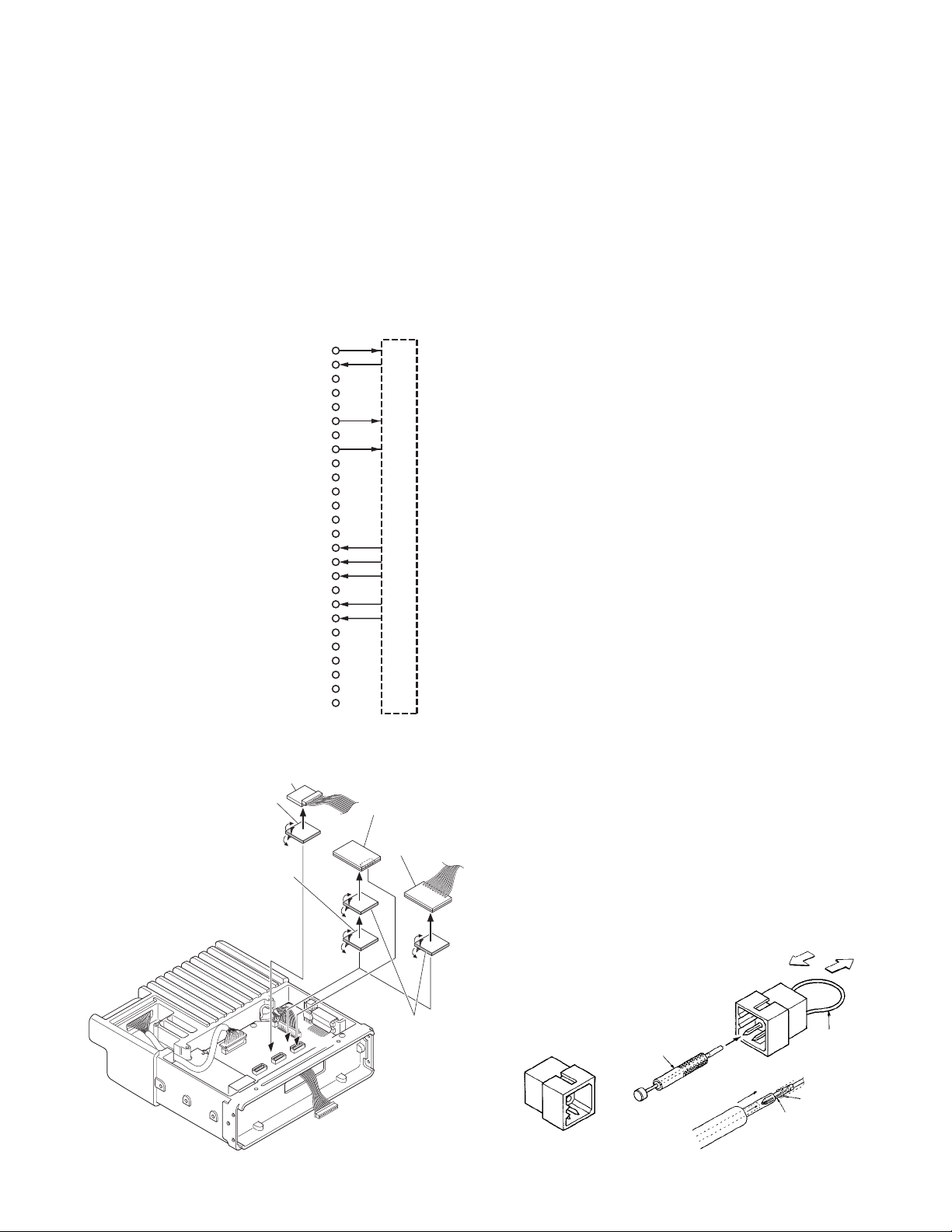
8. External Speaker (KES-5/6:Option)
The speaker output from the transceiver is as follows:
1. The KCH-14 has a built-in speaker (3W/8 ohms).
2. The KCH-15 does not have a built-in speaker.
3. The external speaker output from the accessory
connector (9-pin) on the rear of the transceiver is 13W/4
ohms. Use the KES-5 or KES-6.
4. The speaker output from the accessory connector (12pin) on the rear of the control head is 2W/4 ohms. If the
remote kit (KRK-5, KRK-6DH) is used, use the KES-5 or
KES-6.
Note :
Since the transceiver uses a BTL audio amplifier, do not
ground the speaker output pin.
8-1. Connecting the KES-5/6 external speaker to
the transceiver
• When taking the AF output from the accessory
connector (9-pin) on the rear of the transceiver
The following tools are required for changing the
connector.
Extracting tool
The following extracting tool is recommended :
Molex Inc. Order No. : 11-03-0002
1. Remove the short plug from the accessory connector (9pin) on the rear of the transceiver (Fig. 8-1-1).
Note : Save the jumper, which is required when the
transceiver is used without the external speaker.
2. Remove the terminals with the jumper from the
connector housing holes number 3 and 6 using the
extracting tool.
Removing the jumper lead (Fig. 8-1-2)
1) Insert the extracting tool (11-03-0002) into the
connector while pushing the jumper lead in the
direction of (a).
2) Push the extracting tool into collapse the barbs of the
crimp terminal.
3) Pull out the lead while continuing to push the
extracting tool in the direction (b).
3. Reinsert the terminal with the black and white stripe lead
into hole number 2, and the terminal with the black lead
into hole number 6 (Fig. 8-1-3).
4. Connect the short plug to the accessory connector (9-pin)
on the rear of the transceiver.
Fig. 7-2
CN771
3M double
coated cushion
No.4008
(or No.4408)
25 x 25 mm
Fig. 8-1-1 Fig. 8-1-2
17
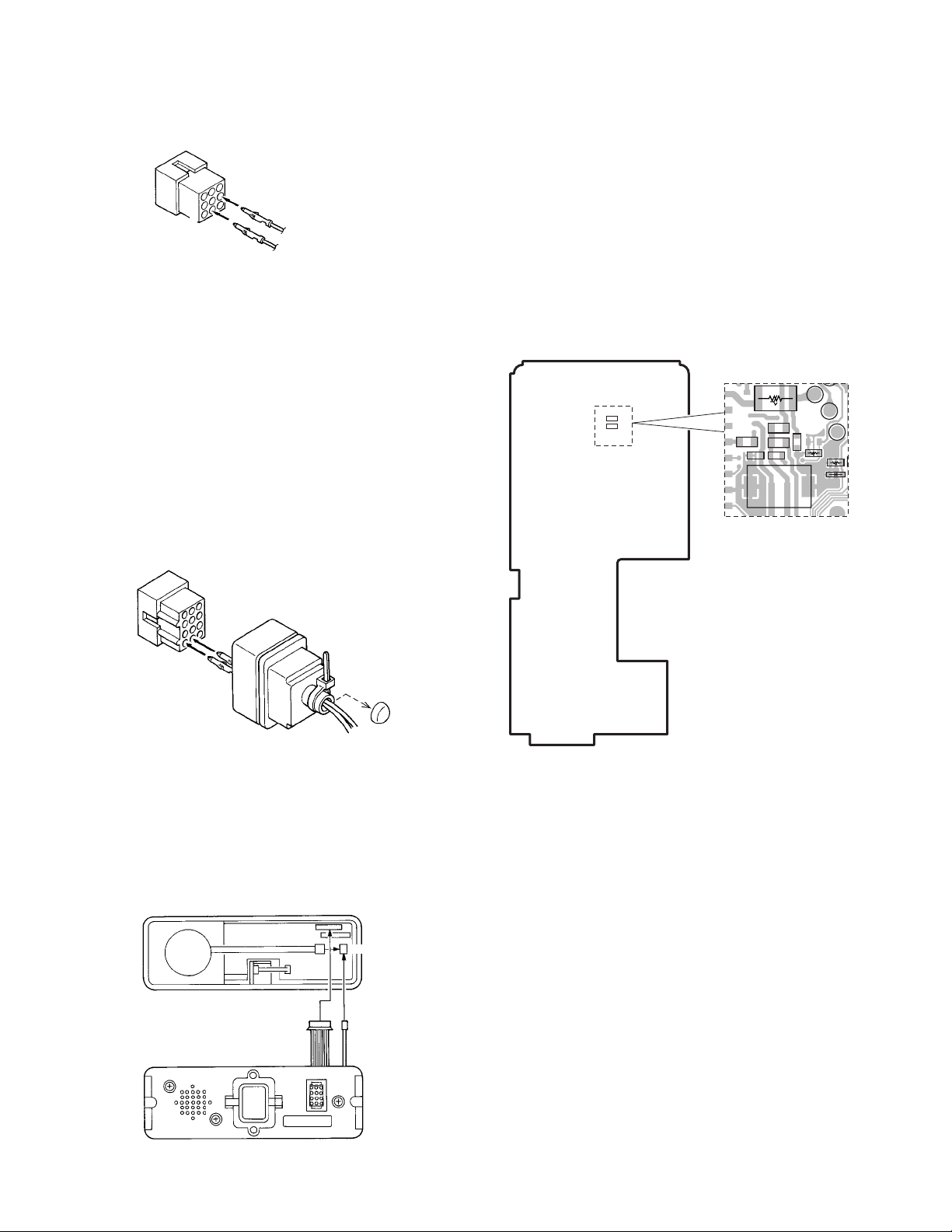
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
)
INSTALLATION
Short plug
(9-pin)
1
7
9
2
To KES-5 or KES-6
6
Black/White lead
Black lead
Fig. 8-1-3
8-2. Connecting the KES-5/6 external speaker to
the KRK-5/6DH remote kit
• When taking the AF output from the 12-pin
accessory connector on the rear of the control
head
• Modification of plug (12-pin)
1. Remove the square plug from the accessory connector
(12-pin) on the rear of the control head.
2. Cut off the end of the rubber cap, insert the KES-5/6
speaker cable into the cap, and insert it into pins 10 and
11 of the square plug.
3. Connect the square plug and rubber cap to the accessory
connector (12-pin) on the rear of the control head, then
clamp the bottom of the rubber cap with the supplied tie
wrap.
Square plug (12-Pin)
8-3. Modification to increase the audio output of
the control head
The speaker output can be increased to 13W by moving
jumper resistor (0 ohm) R74 to $R73 on the KCH-14 display
unit (X54-349 A/3). In this case, the KCH-14 internal speaker
cannot be used because the maximum input (3W) of the
internal speaker is exceeded. Therefore, use the KES-5 or
KES-6.
Note :
Even if the KRK-6DH is modified in this way, the audio
output of head 2 cannot be increased.
SB
ES2
$R73
R74
CN2
KCH-14
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-349 A/3)
Foil side view
NC
Rubber cap
11
10
Tie wrap
Cut
Speaker cable
(To KES-5 or KES-6)
Fig. 8-2-1
• If the KCH-14 is used
If the KES-5 or KES-6 is connected to the 12-pin
accessory connector, remove the internal speaker wire.
If the internal speaker is used, remove the wire
connected to pins 10 and 11 of the 12-pin accessory
connector.
SP
18
KCH-14
CN3
CN1
Rear of the control head
Fig. 8-2-2
CN2
Fig. 8-3
8-4. Use as public address speaker
1. Remove the short plug from the 9-pin accessory
connector on the rear of the transceiver. (Remove the
jumper lead as described in Section 8-1 on page 17.)
2. Insert the KES-5/6 speaker leads into pins 7 and 8 of the
short plug.
3. If you remove jumper shorting pins 3 and 6, the 20W PA
(public address) voice signal is output from pins 7 and 8.
(Only when the PA or SP switch is on.)
4. If you use the transceiver shorted with pins 3 and 6, the
internal speaker is available (when the KCH-14 is used).
The KCH-15 does not contain a speaker.
Note :
Relationship between accessory connector (9-pin) connection and speaker output.
When pins 3 and 6 are shorted ; The 3W internal speaker
is used (KCH-14 only).
When pins 3 and 6 are opened and is output from pins 7
and 8 ; The 20W external speaker is used.
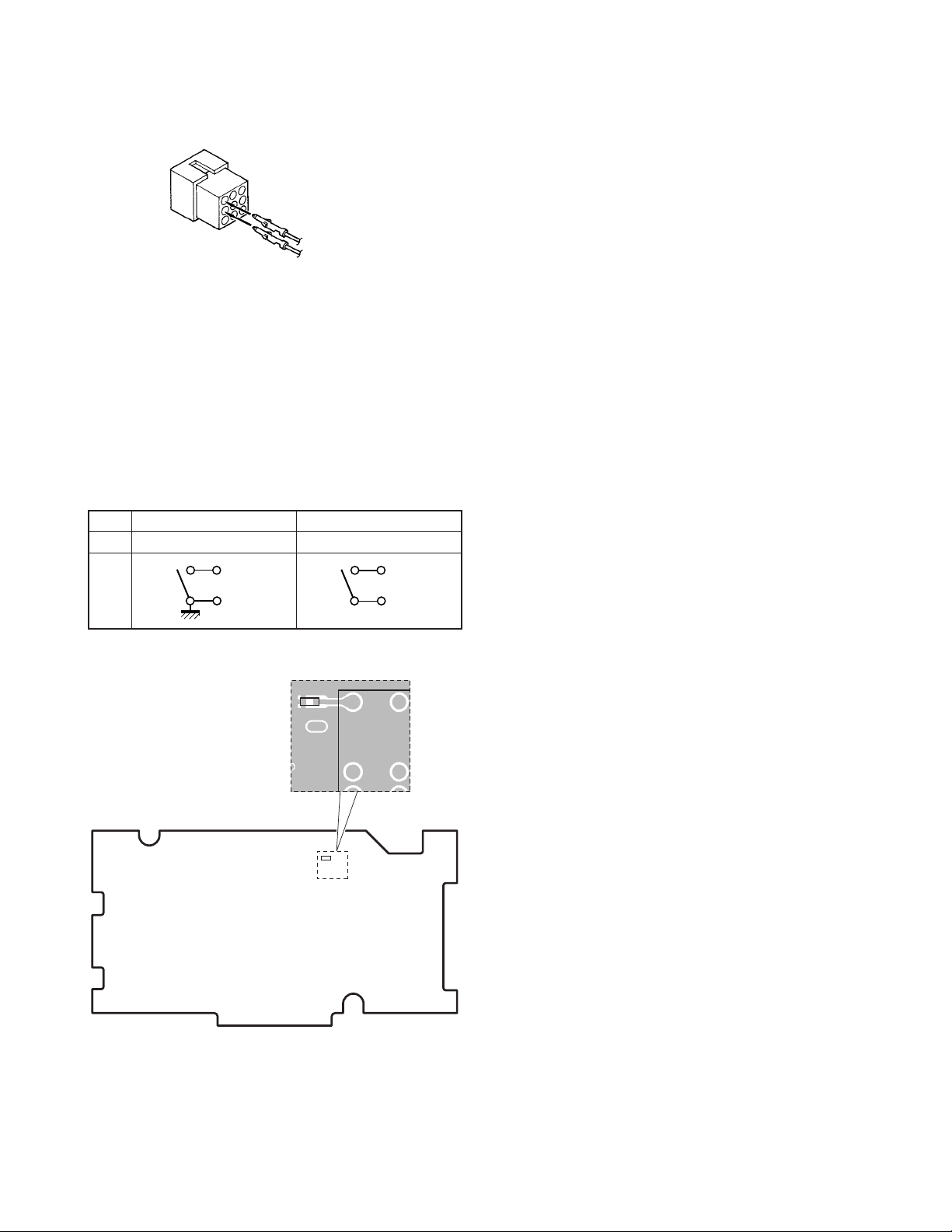
INSTALLATION
Short plug (9-pin)
7
8
Crimp terminal
(E23-0613-05)
Fig. 8-4
9. Horn Alert Function
The HR1 and HR2 pins of the accessory connector (9-pin)
on the rear of the transceiver are connected to the relay
(K700) and the maximum current is 1A.
1. Remove the upper case of the transceiver.
2. To make the HR2 pin, remove the jumper resistor (0 ohm)
R960 on the control unit (X53-412) as shown in Table 1.
3. Reassemble the PC board and the upper case.
To KES-5 or KES-6
Black lead
Black/White lead
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
)
Default Modification
R960 Present Absent
State
HR1
HR2
Table 1
R960
K700
CONTROL UNIT (X53-412)
Component side view
HR1
HR2
Fig. 9
19
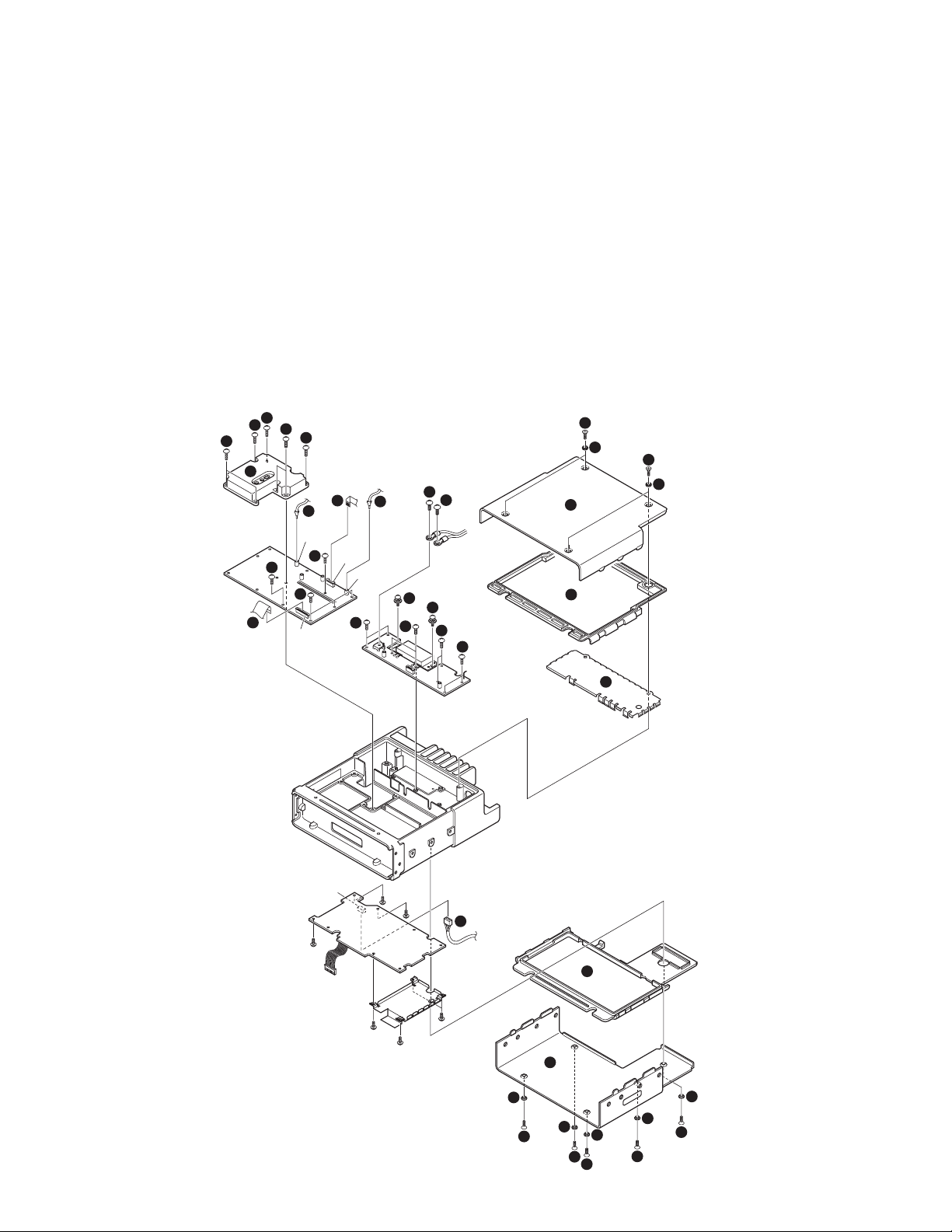
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR
Disassembly Procedure (TK-5710 (B))
■ Removing the upper/ lower case and shield cover
1. Remove the 9 screws z and 9 spacers x.
2. Remove the upper case c and lower case v.
3. Remove the upper packing b and lower packing n.
4. Remove the shield cover m.
■ Removing the TX-RX unit (X57-703)
1. Remove the 7 screws , holding the PLL shield cover.
2. Remove the PLL shield cover ..
3. Remove the coaxial cables from the two connectors
(CN150, CN200) of the TX-RX unit /.
4. Remove the flat cables from the two connectors (CN600,
CN601) of the TX-RX unit Ω.
5. Remove the 5 screws ≈.
8
8
8
8
TX-RX
unit
9
11
8
11
10
CN150
12
12
CN601
CN200
12
16
CN600
)
■ Removing the Final unit (X45-375)
1. Remove the cables from the connector (CN702) of the
control unit ç.
2. Remove the 2 screws √ holding the power module.
3. Remove the solder of the power module with a solder
absorber.
4. Remove the 2 screws ∫ holding the + (positive) terminal
and - (negative) terminal of the power supply cable.
5. Remove the 8 screws ~ holding the final unit.
6. Remove the solder of the antenna receptacle with a
solder absorber.
1
2
15
10
15
14
14
16
16
16
4
6
1
2
20
CN702
Control
unit
Final unit
13
7
5
3
2
2
1
2
1
1
1
2
2
1
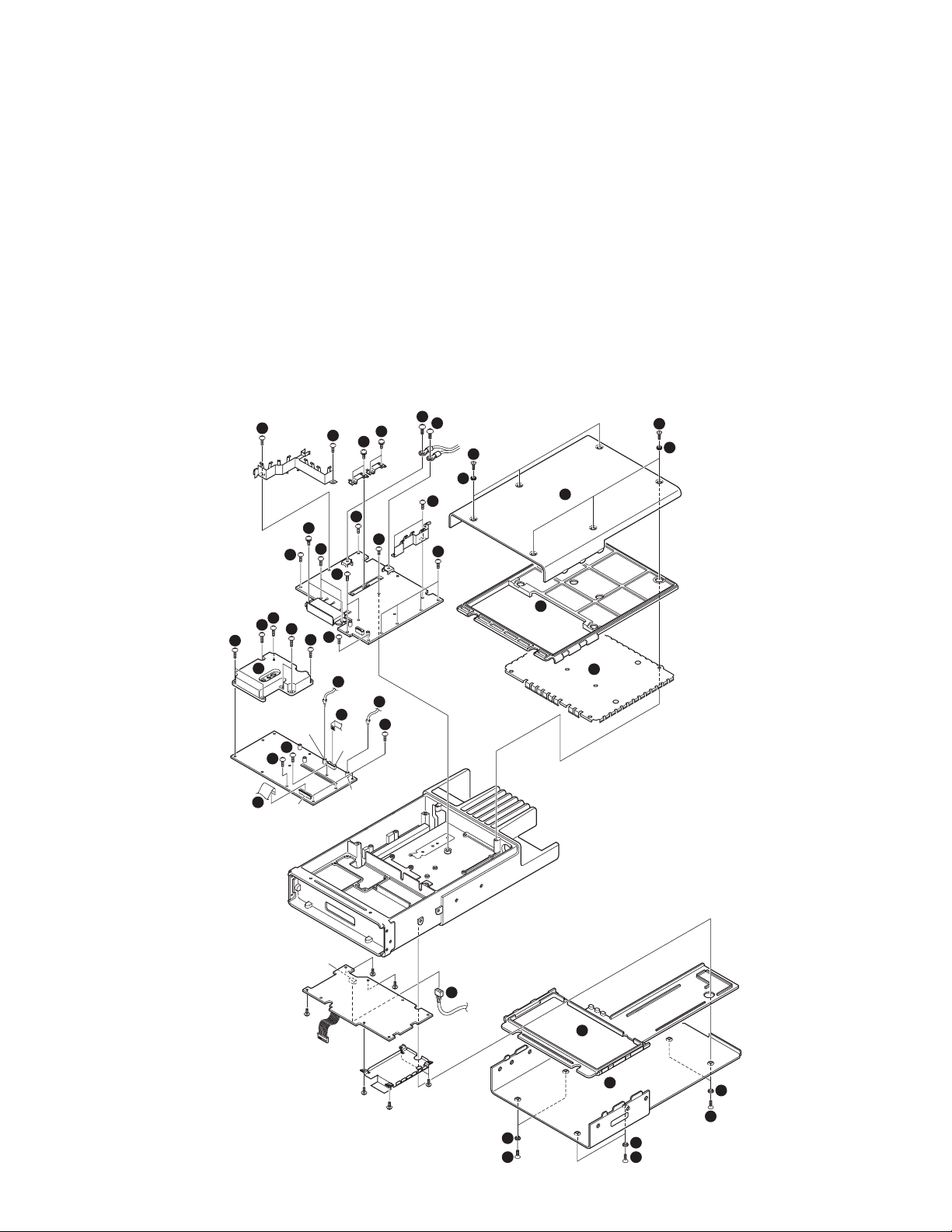
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR
Disassembly Procedure (TK-5710H (B))
■ Removing the upper/ lower case and shield cover
1. Remove the 12 screws z and 12 spacers x.
2. Remove the upper case c and lower case v.
3. Remove the upper packing b and lower packing n.
4. Remove the shield cover m.
■ Removing the TX-RX unit (X57-703)
1. Remove the 7 screws , holding the PLL shield cover.
2. Remove the PLL shield cover ..
3. Remove the coaxial cables from the two connectors
(CN152, CN200) of the TX-RX unit /.
4. Remove the flat cables from the two connectors (CN600,
CN601) of the TX-RX unit Ω.
5. Remove the 5 screws ≈.
16
17
17
14
17
17
15
15
17
17
17
16
17
17
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
)
■ Removing the Final unit (X45-376)
1. Remove the cables from the connector (CN702) of the
control unit ç.
2. Remove the 2 screws √ holding the power module.
3. Remove the solder of the power module with a solder
absorber.
4. Remove the 4 screws ∫ holding the two final transistors.
5. Remove the 2 screws ~ holding the + (positive) terminal
and - (negative) terminal of the power supply cable.
6. Remove the 16 screws µ holding the final unit.
7. Remove the solder of the antenna receptacle with a
solder absorber.
1
1
2
4
2
8
TX-RX
unit
8
8
8
17
8
9
12
12
11
CN600
10
11
CN152
CN601
CN200
CN702
10
12
Final unit
Control
unit
13
6
7
5
3
2
1 1
2
1
2
21
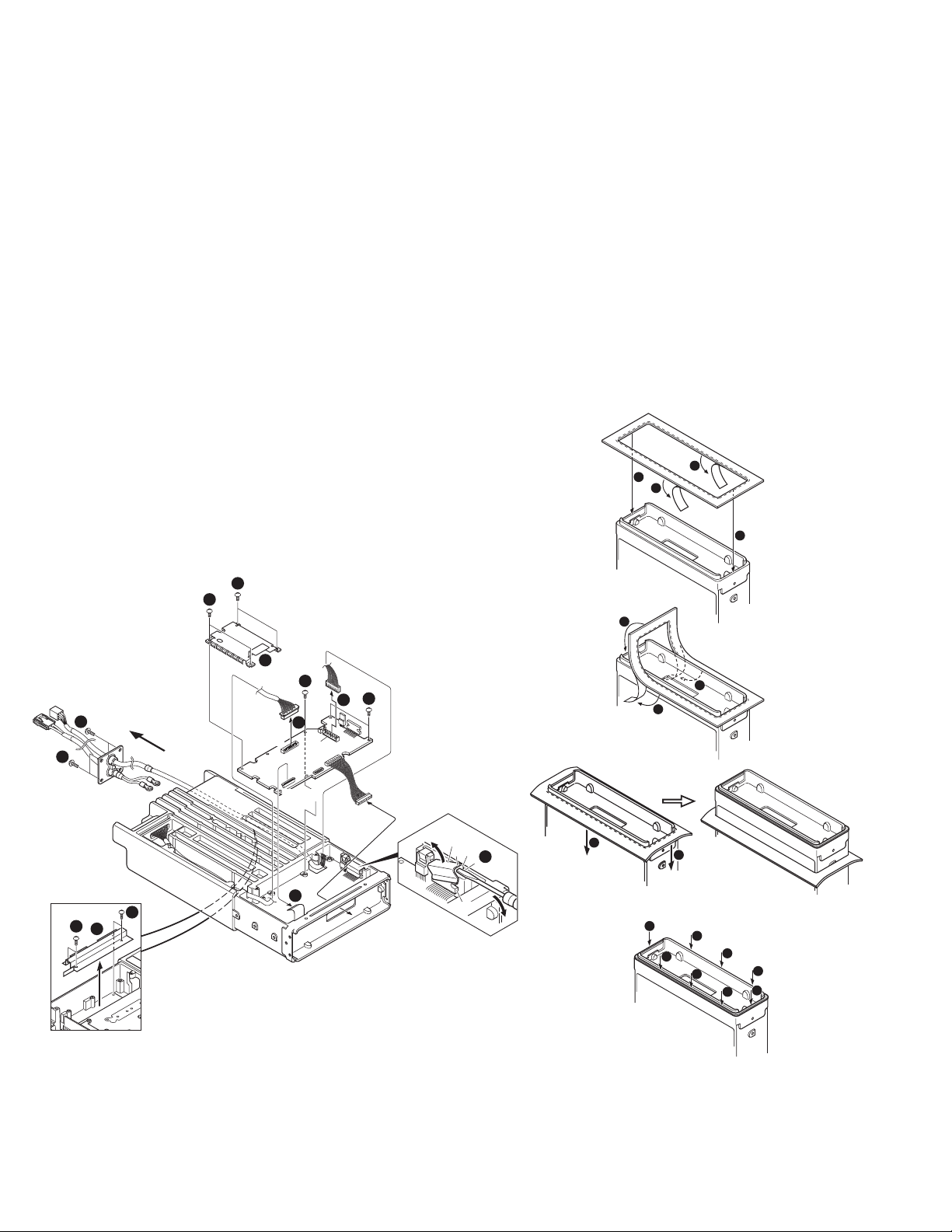
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
2
2
1
1
5
5
3
3
4
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR
)
Disassembly Procedure
(TK-5710 (B) / 5710H (B))
■ Removing the Control unit (X53-412)
1. Remove the 7 screws z.
2. Remove the shield plate x.
3. With a flat-head screwdriver, remove the 2 flat springs
holding the ICs (IC706, IC732) c.
4. Remove the flat cable from the connector (CN782) v.
5. Remove the cables from the two connectors (CN728,
CN783) b.
■ Removing the accessory cable and power supply
cable on the rear of the transceiver
1. Confirm the following contents.
• The screws holding the + (positive) terminal and -
(negative) terminal of the power supply cable is
removed.
• The cable from the connector (CN783) of the Control
unit is removed.
2. Remove the 4 screws n holding the shield plate, and
remove the shield plate m from the chassis (TK-5710H(B)
only).
3. Remove the 4 screws , on the rear of the transceiver.
4. Pull out the power supply cable and accessory cable.
1
1
Precautions for Reassembly
■ Affixing the sheet (G11-4381-04)
1. Remove the covering paper from one side of the sheet z.
2. Place the sheet on the front side of the chassis x, then
affix it to one side of the front chassis.
Firmly affix the sheet to the chassis by pushing the
double-coated tape with your fingers.
3. Remove the covering paper from other side of the sheet
c, then affix it to the other side of the front chassis v.
Firmly affix the sheet to the chassis by pushing the
double-coated tape with your fingers.
4. Push the sheet toward the rear of the chassis b, then cut
away any unnecessary parts of the sheet.
5. Firmly affix the sheet to the chassis by pushing the
double-coated tape with your fingers n.
8
8
6
7
6
2
CN728
1
5
CN782
4
CN783
1
5
Flat
spring
3
IC
22
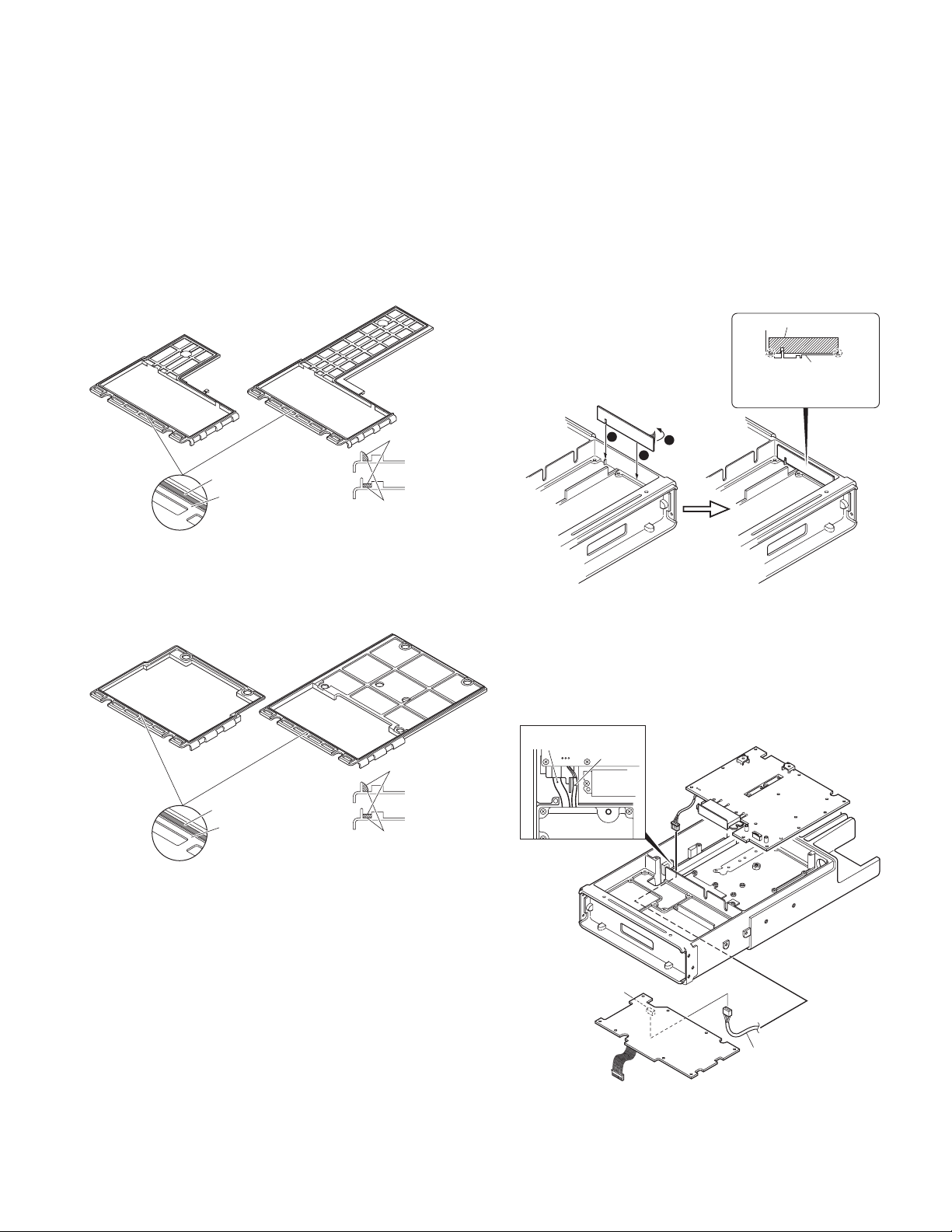
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
Control
unit
CN702
Final unit
W2
W2 terminal
cable
Accessory
cable
W2 terminal
cable
2
2
1
sheet
chassis side
Confirm that there is no
gap between the sheet and
the chassis side.
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR
)
■ Painting the lubricant (Part No.:490-0019-05) on
the groove of the case packing
Paint the lubricant to the position as shown in figure after
replacing or assembling the case packing.
Note :
To assure waterproofing, paint the lubricant on the
groove of the case packing.
• Case packing (Upper)
TK-5710(B)
Paint the lubricant (Part No.490-0019-05)
on the groove of the case packing.
TK-5710H(B)
lubricant
case packing
OK
NG
lubricant
groove of the
case packing
■ Affixing the sheet (G11-4378-04):TK-5710(B) only
1. Remove the covering paper of the sheet z.
2. Affix it to one side of chassis, so that the hollow of the
sheet fits the convex of the chassis x.
Note :
Affix it so as not to leave a gap between the sheet and
the chassis side.
3. Repeat step 2 to affix the sheet to the other side of
chassis.
• Case packing (Lower)
TK-5710(B)
TK-5710H(B)
lubricant
lubricant
case packing
Paint the lubricant (Part No.490-0019-05)
on the groove of the case packing.
OK
NG
groove of the
case packing
■ Align the cable connecting the W2 terminal:
TK-5710H(B) only
When you assemble the final unit, align the cable
connecting the W2 terminal as shown in figure, then
insert it into the connector (CN702) of the control unit.
23
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR
)
■ Procedures after installing the case packing to
the chassis
After installing the case packing to the chassis, confirm
that all corners of the upper / lower packing are securely
fitted to the chassis. Place are shown in the arrow in the
figure below.
• Case packing (Upper)
TK-5710H
TK-5710
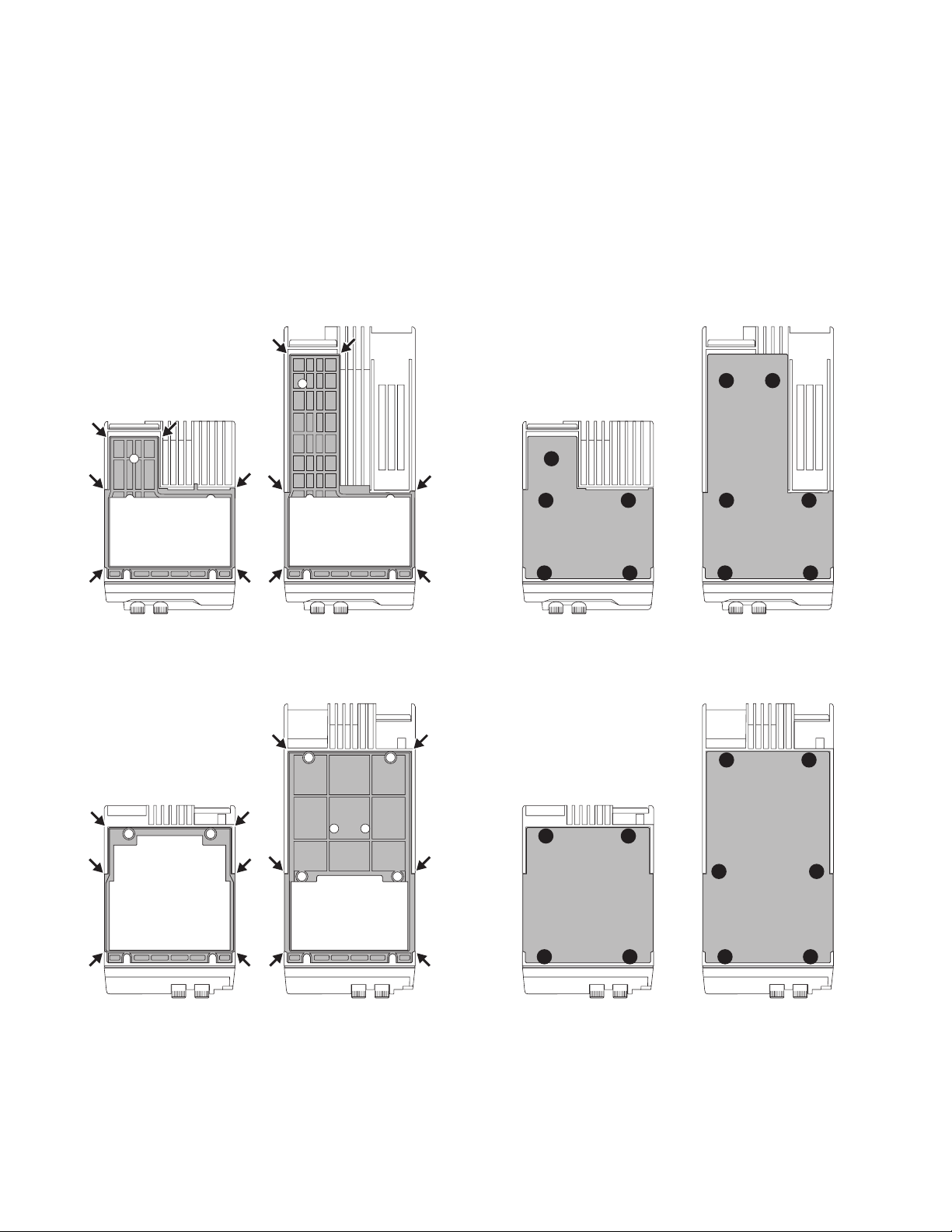
■ Sequence of tightening the screws for the
upper / lower case to the chassis
Install the upper / lower case to the chassis and tighten
the screws in the order shown in the figure below.
• Upper case
TK-5710H
5 6
TK-5710
5
3
1 2
4
3
1 2
4
• Case packing (Lower)
TK-5710
TK-5710H
• Lower case
TK-5710
3 4
1 2
TK-5710H
5 6
3 4
1 2
24
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
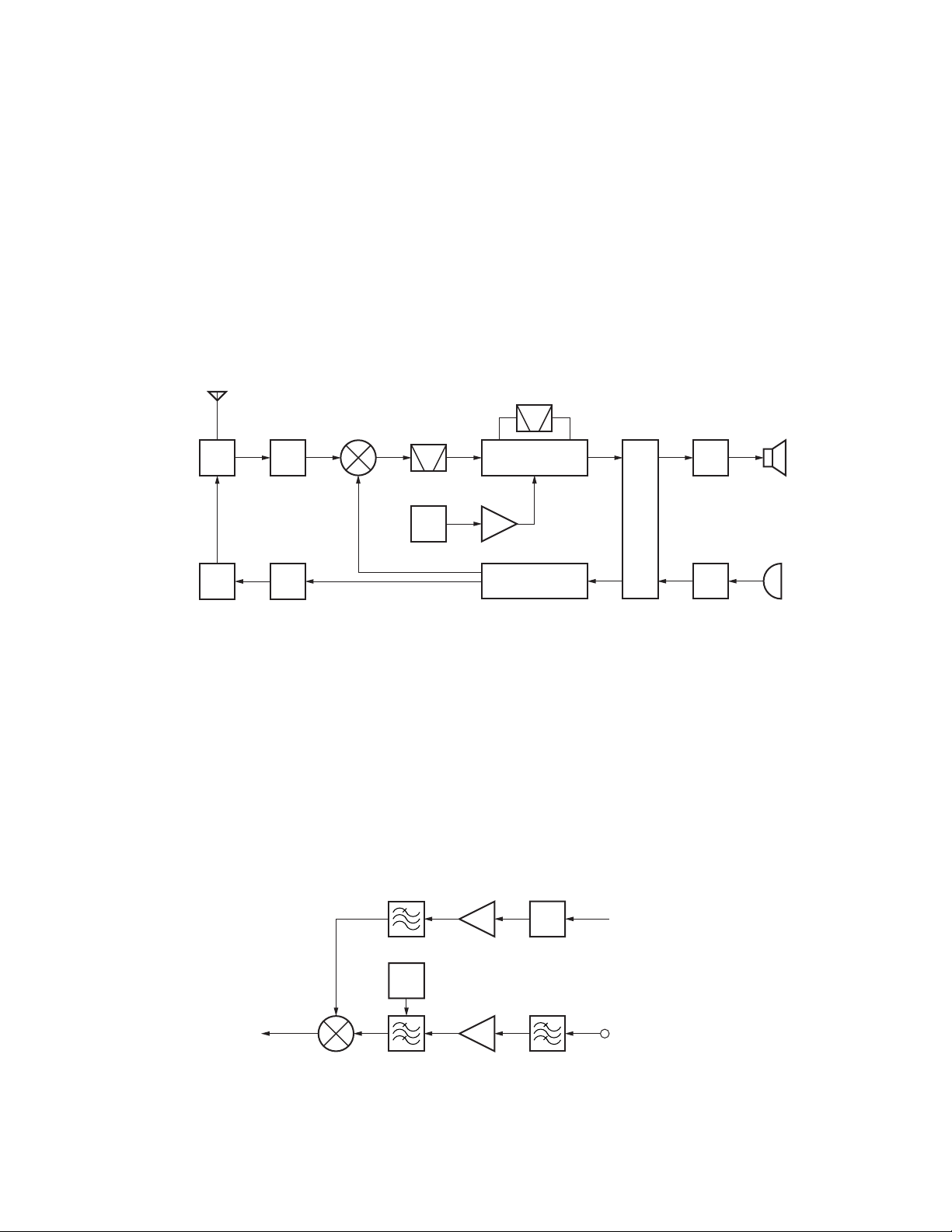
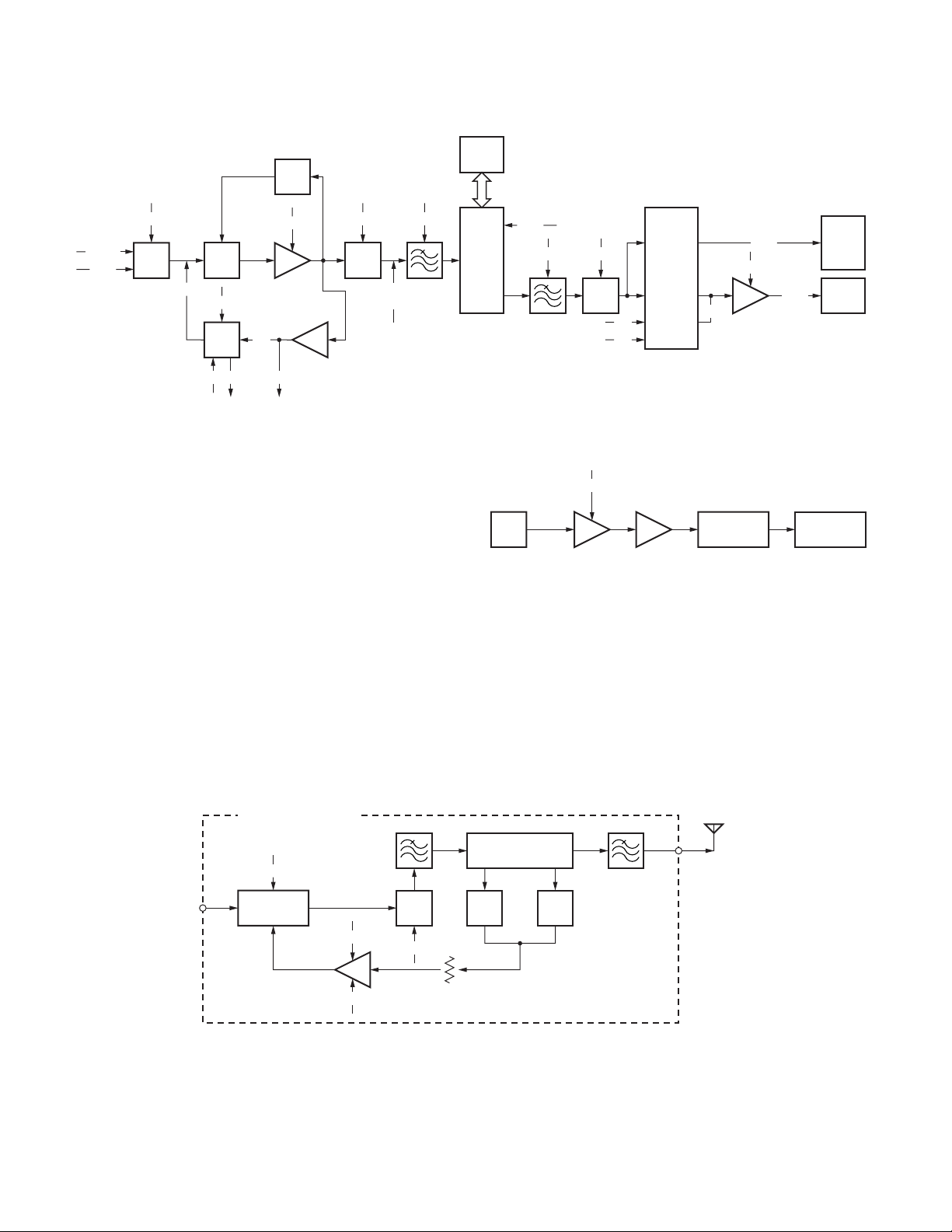
1. Overview
This transceiver is a VHF/FM/APCO portable transceiver
designed to operate in the frequency range of 136 to
174MHz.
2. Frequency Configuration
The receiver is a double-conversion superheterodyne
using first intermediate frequency (IF) of 49.95MHz and
second IF of 450kHz. Incoming signals from the antenna are
mixed with the local signal from the PLL circuit to produce
the first IF of 49.95MHz.
This is then mixed with the 50.4MHz second local
ANT
TX/RX : 136~174MHz
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
The unit consists of receiver, transmitter, phase-locked
loop (PLL) frequency synthesizer, base band parts, power
supply, and control circuits.
oscillator output to produce the 450kHz second IF. This
signal is detected to give the demodulated signal in the DSP.
The transmit signal frequency is generated by the PLL
VCO, and modulated by the signal from the DSP. It is then
amplified and fed to the antenna.
CF
450kHz
)
ANT
SW
PA
AMP
RF
AMP
TX
AMP
1st MIX
185.95~
223.95MHz
136~174MHz
MCF
49.95MHz
16.8MHz
VCXO
Fig. 1 Frequency configuration
3. Receiver System
3-1. Front-end RF Amplifier
The receive signal from the RX terminal (CN200) of the TXRX unit (X57-703) is amplified by a transistor (Q200) and
passes through the band-pass filter (L221, L222, L223) to
remove unwanted signal.
The signal passing through the band-pass filter goes into
the 1st mixer.
These band-pass filters are tuned to a desired frequency
by variable capacitance diode (D200, D201, D202).
A tuning voltage corresponding to the desired signal is
SP
IF AMP
x3
50.4MHz
MIX
FPGA
A/D
D/A
DSP
PLL
VCO
AF
AMP
MIC
MIC
AMP
applied to each variable capacitance diode to tune to the
receive frequency.
3-2. 1st Local
The 1st mixer uses double balanced mixer (A400).
The receive signal passing through the band-pass filter
(L221, L222, L223) and the 1st local signal generated by the
VCO, are mixed by the 1st mixer (A400) to produce a 1st IF
signal (49.95 MHz) (Upper heterodyne).
1st IF
49.95MHz
1st MIXER
A400
LPF
D200,D201,D202
VC
TUNE
BPF
L221,L222,L223
Local AMP
Q201
RF AMP
Q200
LNA
VCO
1st Local OSC
185.95~223.95MHz
RX terminal(CN200)
136~174MHz
Fig. 2 Front-end RF amplifier and 1st local
25
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
)
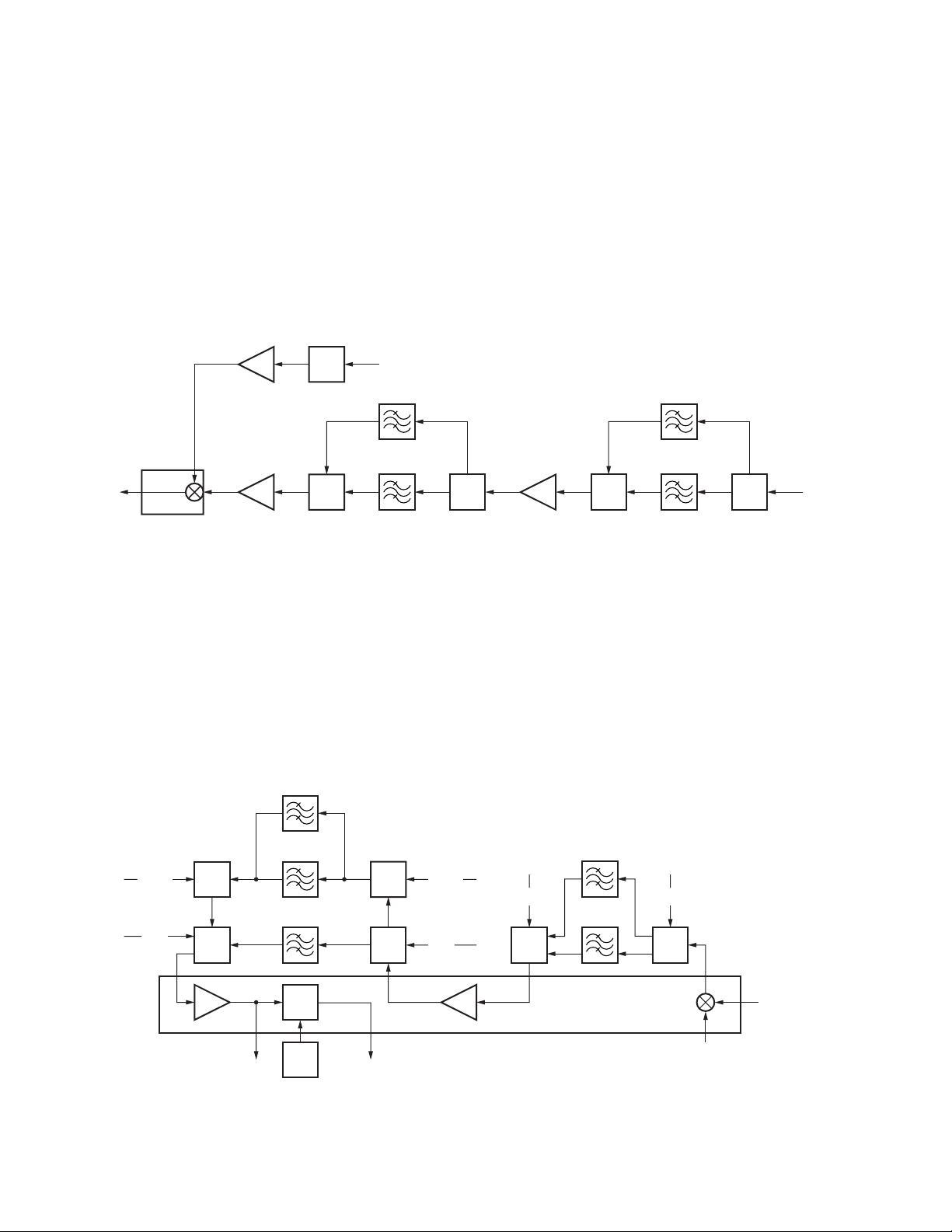
3-3. 1st IF
The 1st IF signal passes through the MCF (Monolithic
Crystal Filter) to remove unwanted signal.
The MCF has two paths (Wide band: XF200, Narrow band:
XF201), and these are controlled with the IF filter switch
(D205, D206, D207, D208, D209, D210, D211 and D212).
The signal passes through the MCF (XF200) when the
Wide band (D206, D208, D210 and D212 are ON) is selected.
The signal passes through the MCF (XF201) when the
Narrow band (D205, D207, D209 and D211 are ON) is
2nd IF
450kHz
IC212
FM IC
2nd Local
50.40MHz
Tripler
Q205
Q203 Q202
D211
D212
X200
VCXO
SW
16.8MHz
WIDE
XF200
NARROW
XF201
Fig. 3 1st IF and 2nd Local
3-5. 2nd IF
The 2nd IF signal passes through the ceramic filter to
remove unwanted signal.
The ceramic filter has three paths (Wide band: CF201 and
CF204, Narrow band: CF200 and CF203, APCO band: CF201
and CF202), and these are controlled with the multiplexers
(IC205, IC206, IC207, IC209, IC210 and IC211).
The control line is W/N1, W/N2 and VN.
The signal passes through the ceramic filters (CF201 and
CF204) when the Wide band (W/N1: high level, W/N2: high
D209
D210
selected.
The 1st IF signal passing through these MCFs is amplified
by the IF amplifier (Q203) and goes into the FM IC (IC212).
3-4. 2nd Local
The 1st IF signal (49.95 MHz) amplified by the IF amplifier
(Q203) and the 2nd local signal (50.4 MHz) generated by
tripling the reference oscillator frequency (16.8 MHz) of the
VCXO (X200) by Q205, are mixed in the FM IC (IC212) to
produce a 2nd IF signal (450 kHz) (Upper heterodyne).
WIDE
XF200
SW
D207
D208
SW
NARROW
XF201
level, VN: high level) is selected. The signal passes through
the ceramic filters (CF200 and CF203) when the Narrow band
(W/N1: low level, W/N2: low level, VN: high level) is selected.
The signal passes through the ceramic filters (CF201 and
CF202) when the APCO band (W/N1: high level, W/N2: low
level, VN: low level) is selected.
The APCO signal is A/D-converted by the FPGA IC (IC730)
and DSP IC (IC715), and is performed APCO demodulation.
The detected FM signal and the APCO signal are fed to the
CODEC IC (IC724) respectively.
D205
D206
SW
1st IF
49.95MHz
26
WIDE
CF204
NARROW
IC211
W/N 2 W/N 2
VN
SW
IC210
SW
CF203
APCO
CF202
DET
L232
DET
APCO FM
COIL
IC207
SW
SW
IC206
VN
Fig. 4 2nd IF
WIDE
CF201
W/N 1 W/N 1
IC209
SW
NARROW
CF200
IC212
FM IC
IC205
SW
2nd IF
450kHz
2nd Local OSC
50.4MHz
1st IF
49.95MHz
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
)
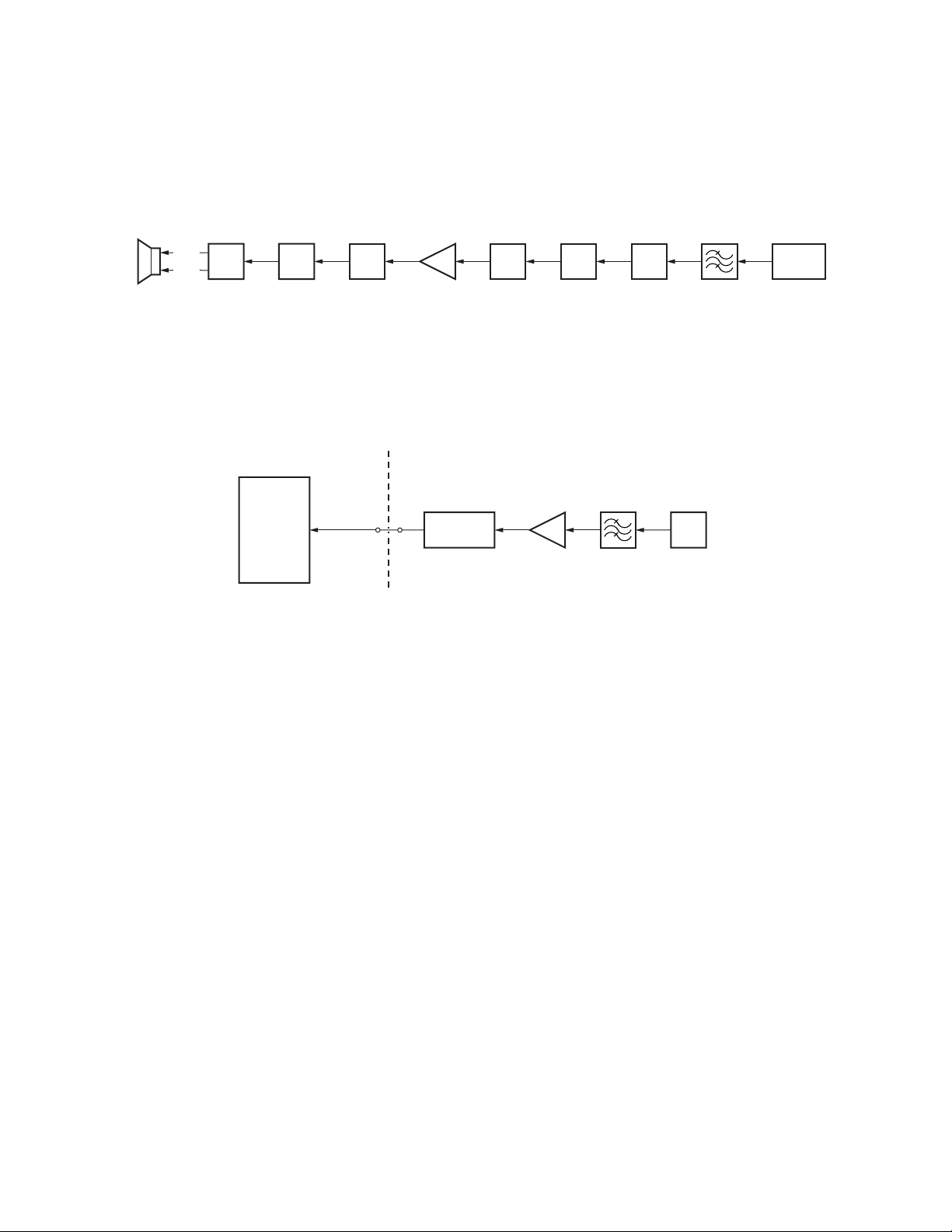
3-6. Audio Amplifier Circuit
The AF signal from the CODEC IC (IC724) passes through
the low-pass filter (IC729), analog switch (IC731) and
summing amplifier (IC742), and then it goes into the D/A
converter (IC738).
ES 1
ES 2
IC732
AF
AMP
IC727
SW
IC732
SW
Fig. 5 Audio amplifier circuit
3-7. Squelch Circuit
A noise component is output from the FM IC (IC212). The
desired noise signal is extracted by the band-pass filter, and
is amplified by the noise amplifier (Q208).
The output signal from the noise amplifier is rectified by
CONTROL UNIT (X53-412) TX-RX UNIT (X57-703)
IC703
CPU
ASQL
121
D203
RECTIFIER
The output signal from the D/A converter (IC738) passes
through the amplifier (IC739), audio mute switch (Q732) and
analog switch (IC727), and then it is amplified by the audio
amplifier (IC732).
IC738
DAC
D203 to produce a DC voltage, which is output from D203 as
squelch voltage.
of the CPU (IC703) and is compared with the reference
voltage preset in the CPU to control audio signal ON/OFF.
IC742
SUM
The squelch voltage goes into the ASQL terminal (pin 121)
NOISE AMP
Q208
IC731(1/2)
SW
IC724IC729(1/2)IC739
CODEC
IC212
FM IC
Fig. 6 Squelch circuit
4. Transmitter System
4-1. Audio Band Circuit
The audio band circuit of the transmitter system consists
of the following:
•Microphone mute switch (Q723)
• AGC (Automatic Gain Control) (Q715, Q716, IC719,
D727, D728)
• Scrambler board switch (Q720)
The microphone mute switch (Q723) cuts off audio
signals from the external microphone.
The AGC (Q715, Q716, IC719, D727, D728) is an
amplifier that reduces gain automatically by greatly
increasing the attenuation when the audio signal of a certain
level or higher is present. It controls the gain so that the
audio signal input to the CODEC IC (IC724) is not clipped.
If an optional scrambler board is installed, the switch
(Q720) adjusts the signal path so that the audio signal is fed
to the CODEC IC through the scrambler board.
The audio signal is fed to the CODEC IC (base band
circuit) through the above path.
4-2. Base Band Circuit
The base band circuit of the transmitter system consists
of the following:
• CODEC IC (IC724)
• DSP IC (IC715)
• LPF (Low-Pass Filter) (IC729)
• Summing amplifier (IC733)
• DAC (D/A Converter) (IC738)
• Amplifier (IC735)
The audio signal output from the base band circuit is
converted to digital data of a sampling frequency of 48 kHz
and a quantization resolution of 16 bits. This digital data is
sent to the DSP IC (IC715), and voice signals of 300 Hz or
lower and frequencies of 3 kHz or higher are cut off and an
audio range 300 Hz to 3 kHz is extracted.
The audio signal is then pre-emphasized in FM mode and
synthesized with the signals, such as QT and DQT, as
required, and is then output from the CODEC IC. In APCO
mode, the audio signal is converted to the C4FM base band
signal and output from the CODEC IC. The DTMF and MSK
base band signals are also generated by the DSP IC and
output by the CODEC IC.
LPF (IC729) removes quantization noise from the base
band signal output from the CODEC IC.
The summing amplifier (IC733) sets the base band signal
level to the DAC input range.
The DAC (IC738) assigns the base band signal to the VCO
(Q413, Q414, Q416) and VCXO (X400).
At this time, the level output according to the transmit
carrier is fine-adjusted according to the modulation method
of FM Wide, FM Narrow and APCO.
27
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
T/R
SW
D435
3dB
Attenuator
POWER
MODULE
Drive AMP
Q150
8T
Drive AMP
Q151
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
)
D727,D728
DET
MUTE
MIC
Q723
3.3A
SW
Q715
Q716
Ai
ATT
3.3A
SW
Ao TXO(SCR)Ai
IC719
(1/2)
IC720
Ao
5C
AGC
IC718
(1/2)
5C 5C
Q720
SW
STXI(SCR)
ATXI(ANI)
IC719
Fig. 7 Audio band and Base band circuit
4-3. Drive Amplifier Circuit (From T/R switch to
Power module)
The transmit signal passing through the T/R switch
(D435) is amplified by the two drive amplifiers (Q150,
Q151). The transmit signal from the drive amplifier (Q151)
passes through a 3dB attenuator and is fed to the power
module .
IC715
DSP
IC724
CODEC
3.3A
IC729
(2/2)
IC738
DAC
5C
5C
MCO
MCO
RST
VDD
FC
5C 5C
IC733
SUM
Fig. 8 Drive amplifier circuit
MO
8C
IC735(2/2)
MB
Q413,
Q414,
Q416
VCO
X400
VCXO
4-4. Final Amplifier Circuit (From Power module to
Antenna output): TK-5710 (B)
The transmit signal from the TX terminal (CN1) of the final
unit (X45-375) is amplified by the power module (IC2).
The signal amplified by the power module passes
through the antenna switch (D1, D12, D3 and D11), CM
coupler and low-pass filter, then it is fed to the antenna.
CM coupler is a line for detecting forward wave and
reflected wave.
Forward wave is detected by D5, and is converted into
FINAL UNIT (X45-375)
TX(CN1)
+B
IC2
POWER
MODULE
IC1
D1,D3,
D12,D11
8T
APC
PC
ANT
SW
8T VR1
Fig. 9 Final amplifier circuit: TK-5710 (B)
DC voltage. The converted DC voltage is fed to the APC
comparator (IC1), and is compared with the PC voltage, then
is output from the OUT-B terminal (pin 7) of IC1 as an APC
voltage. The APC voltage controls the gate voltage of the
power module (IC2), and keeps transmission output stable.
If an abnormal antenna load is connected, reflected wave
is detected by D6, and output voltage (DC voltage) is fed to
the APC comparator (IC1). The transmission output is
reduced more as this DC voltage rises.
ANT
D5
FWD
DET
CM
COUPLER
D6
REFL
DET
LPF
28
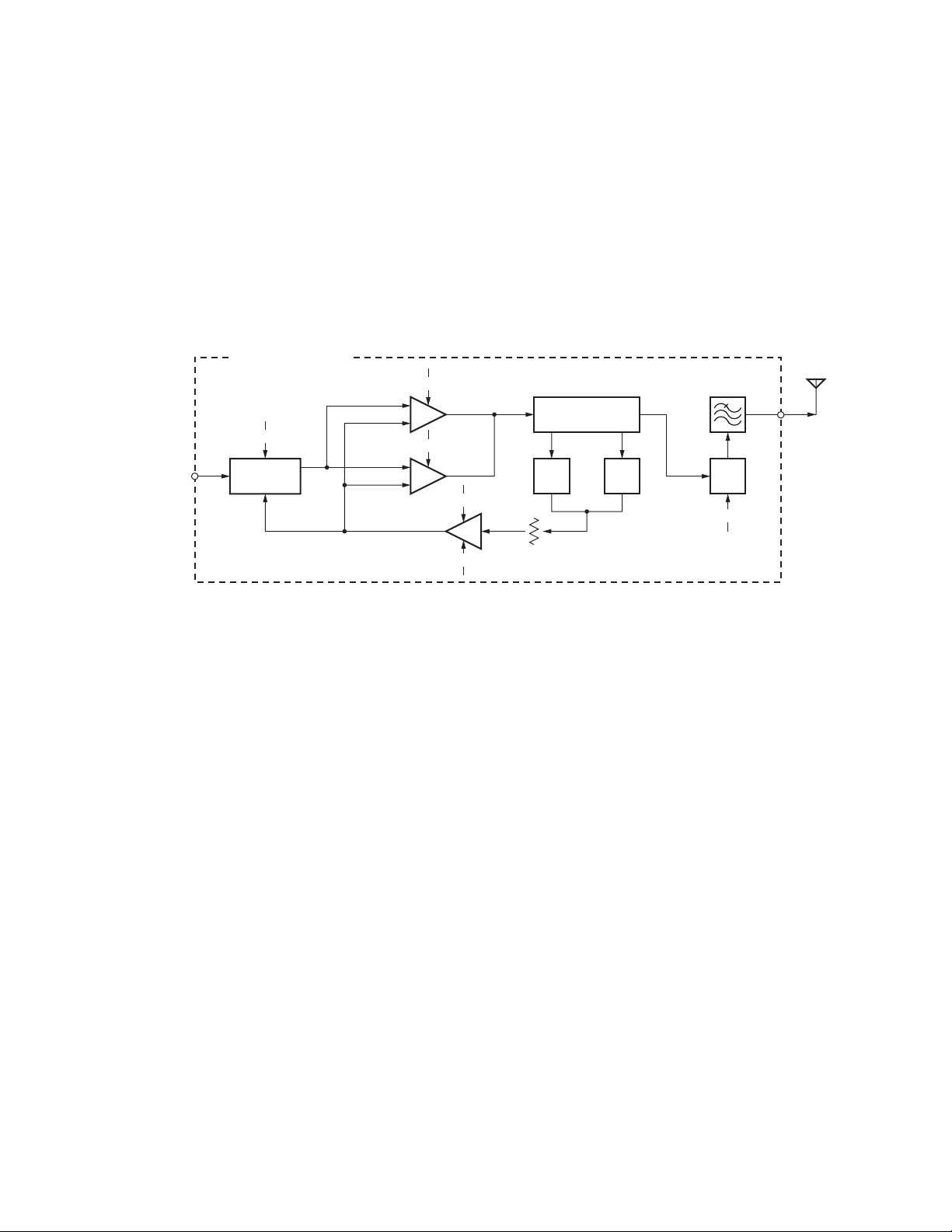
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
)
4-5. Final Amplifier Circuit (From Power module to
Antenna output): TK-5710H (B)
The transmit signal from the TX terminal (CN1) of the final
unit (X45-376) is amplified by the power module (IC1).
The signal amplified by the power module is divided into
two signal, and further is amplified by the final amplifier
(Q1,Q2). The each signal from Q1 and Q2 is combined.
The combined signal passes through the antenna switch
(D6, D8, D9), CM coupler and low-pass filter, then it is fed to
the antenna.
CM coupler is a line for detecting forward wave and
reflected wave.
FINAL UNIT (X45-376)
+B
Q1
+B
Q2
IC2
TX(CN1)
+B
IC1
POWER
MODULE
Final AMP
Final AMP
8T
APC
PC
Forward wave is detected by D3, and is converted into
DC voltage. The converted DC voltage is fed to the APC
comparator (IC2), and is compared with the PC voltage, then
is output from the OUT-B terminal (pin 7) of IC2 as an APC
voltage. The APC voltage controls the gate voltage of the
power module (IC1) and final amplifier (Q1,Q2), and keeps
transmission output stable.
If an abnormal antenna load is connected, reflected wave
is detected by D4, and output voltage (DC voltage) is fed to
the APC comparator (IC2). The transmission output is
reduced more as this DC voltage rises.
ANT
LPF
CM
COUPLER
D3
VR1
FWD
DET
D4
REFL
DET
D6
D8,D9
ANT
SW
8T
Fig. 10 Final amplifier circuit: TK-5710H (B)
4-6. Temperature Protection Circuit : TK-5710 (B)
To prevent thermal destruction of the power module
(IC2), this circuit reduces APC voltage when temperature of
the power module (IC2) rises.
The CPU (IC703) detects temperature with a thermistor
(TH1) and controls reference voltage to the APC circuit.
5. PLL Frequency Synthesizer
The PLL Frequency Synthesizer consists of the following
components:
• VCXO (X400)
• VCO (Q413, Q414,Q416)
• Rheostat IC (IC401)
• PLL IC (IC400)
• Local switch (D435, D436)
5-1. VCXO (X400)
VCXO (X400) generates a reference frequency of 16.8
MHz for the PLL frequency synthesizer. This reference
frequency is applied to pin 10 of the PLL IC (IC400).
The VCXO oscillation frequency is fine-adjusted by
controlling the voltage applied to pin 1 of the VCXO with DAC
(IC738). It is also controlled with pin 1 of the VCXO if the
output from VCXO is modulated.
4-7. Temperature Protection Circuit : TK-5710H (B)
To prevent thermal destruction of the power module
(IC1) and final amplifier (Q1,Q2), this circuit reduces APC
voltage when temperature of the power module (IC1) and
final amplifier (Q1,Q2) rises.
The CPU (IC703) detects temperature with the
thermistor (TH1,TH2) and controls reference voltage to the
APC circuit.
5-2. VCO
There is two RX VCOs (RX VCO 1, RX VCO 2) and a TX
VCO.
The RX VCO 1 (Q413) and RX VCO 2 (Q414) generate a 1st
local receive signal. The RX VCO 1 oscillation frequency is
185.95 to 204.9475 MHz and the RX VCO 2 oscillation
frequency is 204.95 to 223.95 MHz.
The TX VCO (Q416) generates a transmit carrier. The TX
VCO oscillation frequency is 136 to 174 MHz.
The VCO oscillation frequency is determined by two
systems of operation switching terminals "STR" and "VCO1/2"
and two systems of voltage control terminals "C/V" and
"ASSIST".
The operation switching terminals, "STR" and "VCO1/2",
are controlled by the control lines (STR, VCO1/2) output from
the CPU (IC703). When the STR logic is high and the VCO1/2
logic is high, the RX VCO 1 output a 1st local receive signal.
When the STR logic is high and the VCO1/2 logic is low, the
29
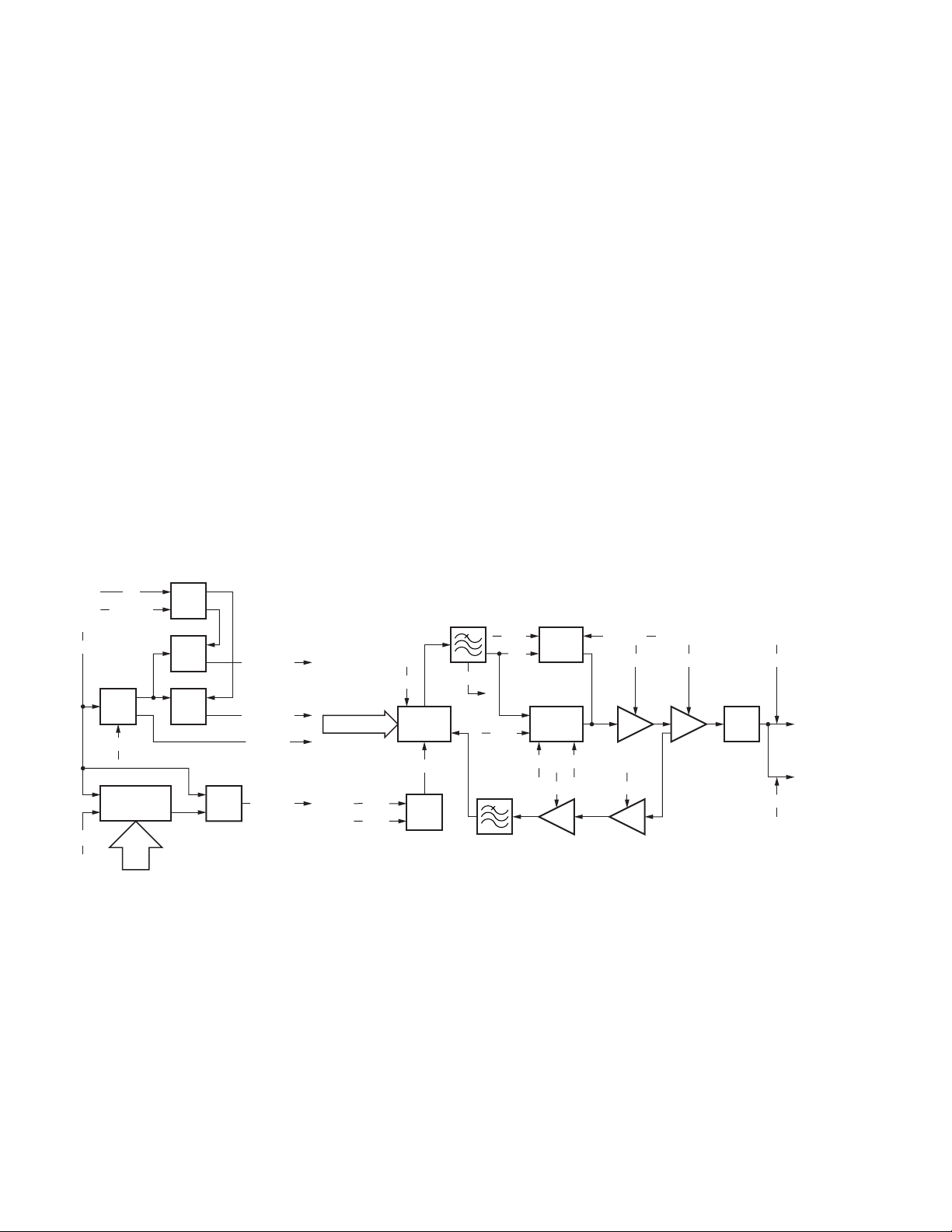
TK-5710(B)/5710H(B
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
)
RX VCO 2 output a 1st local receive signal. When the STR
logic is low, the TX VCO output a transmit carrier.
The voltage control terminals, "CV" and "ASSIST", are
controlled by the PLL IC (IC400) and rheostat IC (IC401) and
the output frequency changes continuously according to the
applied voltage. For the modulation input terminal, "MOD",
the output frequency changes according to the applied
voltage. This is used to modulate the VCO output. "MOD"
works only when " STR" is low.
5-3. Rheostat IC (IC401)
The rheostat IC (IC401) is connected to the VCO voltage
control terminal, "ASSIST", and quickly controls the VCO
oscillation frequency. However, its accuracy is low and the
VCO frequency cannot be matched accurately with the
desired transmit carrier or the 1st local receive signal.
The rheostat IC is controlled by the CPU (IC703) through
the 3-line "PCS", "DAT", "CLK" serial bus.
5-4. PLL IC (IC400)
PLL IC compares the differences in phases of the VCO
oscillation frequency and the VCXO reference frequency,
returns the difference to the VCO CV terminal and realizes
the "Phase Locked Loop" for the return control. This allows
the VCO oscillation frequency to accurately match (lock) the
desired frequency.
When the frequency is controlled by the PLL, the
frequency convergence time increases as the frequency
difference increases when the set frequency is changed. To
supplement this, the rheostat IC is used before control by the
PLL IC to bring the VCO oscillation frequency close to the
desired frequency. As a result, the VCO CV voltage does not
change and is always stable at approximately 2 V.
The desired frequency is set for the PLL IC by the CPU
(IC703) through the 3-line "EP", "DAT", "CLK" serial bus.
Whether the PLL IC is locked or not is monitored by the CPU
through the “UL” signal line. If the VCO is not the desired
frequency (unlock), the "UL" logic is low.
5-5. Local Switch (D435, D436)
The connection destination of the signal output from the
amplifier (Q419) is changed with the diode switch (D435) that
is controlled by the transmission power supply, 8T, and the
diode switch (D436) that is controlled by the receive power
supply, 8R.
If the 8T logic is high, it is connected to a transmit-side
pre-pre-drive amplifier (Q150). If the 8R logic is high, it passes
through the local amplifier (Q210) and then is connected to a
receive-side mixer (A400).
8CL
5C
5C
VCO 1/2
Q405
Q407
SW
STR
IC401 IC402
POTENTIO
METER
PCS
CLK
DAT
SW
Q409
SW
Q408
SW
VCO
TUNE
8CL
RX VCO 1
8CL
RX VCO 2
8CL
TX VCO
ASSIST
EP CLK DAT
3.3V
MB
5C
IC400
PLL
16.8MHz
X400
VCXO
Fig. 11 PLL block diagram
6. Control Circuit
The control circuit consists of CPU (IC703) and its peripheral circuits. It controls the TX-RX unit and transfers data to
the Control unit. IC703 mainly performs the following;
1) Switching between transmission and reception by PTT
signal input.
2) Reading system, zone, frequency, and program data from
the memory circuit.
3) Sending frequency program data to the PLL.
4) Controlling squelch on/off by the DC voltage from the
squelch circuit.
5) Controlling the audio mute circuit by decode data input.
Q413,Q414
ASSIST
T/R
SW
8T
pre-pre-drive
8R
8C
Buff
AMP
Q417
8CLASSIST
5C
RF AMP
Q418
Buff
AMP
Q419
8C
D435,D436
CV
MO
8CL
CV
RX
VCO1,2
Q416
TX
VCO
5C
DOUBLER
Q403
6-1. Memory Circuit
Memory circuit consists of the CPU (IC703) and a flash
memory (IC712). A flash memory has a capacity of 16M bits
and contains the transceiver control program for the CPU. It
also stores the data for transceiver channels and operating
parameter that are written by the FPU. This program can be
easily written from an external devices.
The EEPROM (IC701) stores the last channel data, the
scan on status, and other parameters.
■ Flash memory
Note : The flash memory (IC712) stores the data that is
AMP
(Q150)
Local
AMP
(Q201)
30
 Loading...
Loading...