Page 1

Model 7001 Switch System
Quick Reference Guide
A GREATER MEASURE OF CONFIDENCE
Page 2

Model 7001 Switch System
Quick Reference Guide
1992, Keithley Instruments, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Cleveland, Ohio, U.S.A.
Document Number: 7001-903-01 Rev. A
Page 3

Table of Contents
Safety Precautions.......................................................1
Introduction ................................................................ 5
Operation Summary....................................................6
Menu Structures.........................................................11
Default Conditions....................................................16
Error and Status Messages ......................................... 19
IEEE-488.2 Common Commands and Queries........... 25
SCPI Command Subsystems ...................................... 27
Page 4

Safety Precautions
The following safety precautions should be observed before
using this product and any associated instrumentation. Although some instruments and accessories would normally be
used with non-hazardous voltages, there are situations where
hazardous conditions may be present.
This product is intended for use by qualified personnel who
recognize shock hazards and are familiar with the safety precautions required to avoid possible injury. Read the operating information carefully before using the product.
The types of product users are:
Responsible body
the use and maintenance of equipment, for ensuring that the
equipment is operated within its specifications and operating
limits, and for ensuring that operators are adequately trained.
Operators
must be trained in electrical safety procedures and proper use
of the instrument. They must be protected from electric shock
and contact with hazardous live circuits.
Maintenance personnel
product to keep it operating, for example, setting the line
voltage or replacing consumable materials. Maintenance
procedures are described in the manual. The procedures explicitly state if the operator may perform them. Otherwise,
they should be performed only by service personnel.
Service personnel
perform safe installations and repairs of products. Only
properly trained service personnel may perform installation
and service procedures.
Keithley products are designed for use with electrical signals
that are rated Installation Category I and Installation Category II, as described in the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Standard IEC 60664. Most measurement,
control, and data I/O signals are Installation Category I and
must not be directly connected to mains voltage or to voltage
sources with high transient over-voltages. Installation Category II connections require protection for high transient
is the individual or group responsible for
use the product for its intended function. They
perform routine procedures on the
are trained to work on live circuits, and
1
Page 5

over-voltages often associated with local AC mains connections. The user should assume all measurement, control, and
data I/O connections are for connection to Category I sources
unless otherwise marked or described in the Manual.
Exercise extreme caution when a shock hazard is present.
Lethal voltage may be present on cable connector jacks or
test fixtures. The American National Standards Institute
(ANSI) states that a shock hazard exists when voltage lev els
greater than 30V RMS, 42.4V peak, or 60VDC are present.
A good safety practice is to expect that hazardous voltage
is present in any unknown circuit before measuring.
Users of this product must be protected from electric shock
at all times. The responsible body must ensure that users are
prevented access and/or insulated from every connection
point. In some cases, connections must be exposed to potential human contact. Product users in these circumstances
must be trained to protect themselves from the risk of electric
shock. If the circuit is capable of operating at or above 1000
volts,
no conductive part of the circuit may be exposed.
Do not connect switching cards directly to unlimited power
circuits. They are intended to be used with impedance limited sources. NEVER connect switching cards directly to AC
mains. When connecting sources to switching cards, install
protective devices to limit fault current and voltage to the
card.
Before operating an instrument, make sure the line cord is
connected to a properly grounded power receptacle. Inspect
the connecting cables, test leads, and jumpers for possible
wear, cracks, or breaks before each use.
When installing equipment where access to the main power
cord is restricted, such as rack mounting, a separate main input power disconnect device must be provided, in close proximity to the equipment and within easy reach of the operator.
For maximum safety , do not touch the product, test cables, or
any other instruments while power is applied to the circuit
under test. ALWAYS remove power from the entire test system and discharge any capacitors before: connecting or disconnecting cables or jumpers, installing or removing
2
Page 6
switching cards, or making internal changes, such as installing or removing jumpers.
Do not touch any object that could provide a current path to
the common side of the circuit under test or power line
(earth) ground. Always make measurements with dry hands
while standing on a dry, insulated surface capable of withstanding the voltage being measured.
The instrument and accessories must be used in accordance
with its specifications and operating instructions or the safety
of the equipment may be impaired.
Do not exceed the maximum signal levels of the instruments
and accessories, as defined in the specifications and operating information, and as shown on the instrument or test fixture panels, or switching card.
When fuses are used in a product, replace with same type and
rating for continued protection against fire hazard.
Chassis connections must only be used as shield connections
for measuring circuits, NOT as safety earth ground connections.
If you are using a test fixture, keep the lid closed while power
is applied to the device under test. Safe operation requires the
use of a lid interlock.
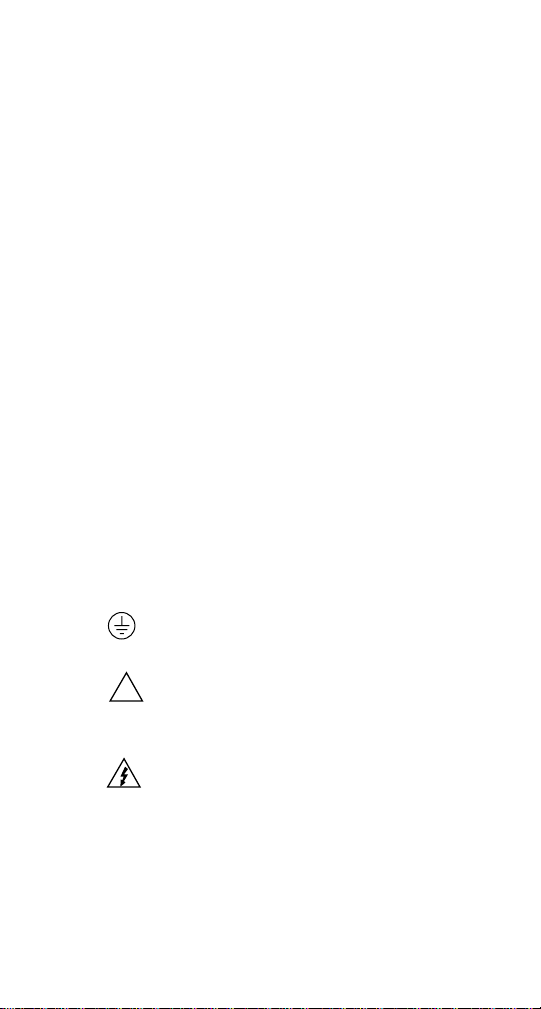
If a screw is present, connect it to safety earth ground
using the wire recommended in the user documentation.
!
The symbol on an instrument indicates that the user
should refer to the operating instructions located in the manual.
The symbol on an instrument shows that it can source
or measure 1000 volts or more, including the combined effect of normal and common mode voltages. Use standard
safety precautions to avoid personal contact with these voltages.
The
WARNING
might result in personal injury or death. Always read the as-
heading in a manual explains dangers that
3
Page 7

sociated information very carefully before performing the
indicated procedure.
CAUTION
The
heading in a manual explains hazards that
could damage the instrument. Such damage may invalidate
the warranty.
Instrumentation and accessories shall not be connected to
humans.
Before performing any maintenance, disconnect the line
cord and all test cables.
To maintain protection from electric shock and fire, replacement components in mains circuits, including the power
transformer, test leads, and input jacks, must be purchased
from Keithley Instruments. Standard fuses, with applicable
national safety approvals, may be used if the rating and type
are the same. Other components that are not safety related
may be purchased from other suppliers as long as they are
equivalent to the original component. (Note that selected
parts should be purchased only through Keithley Instruments
to maintain accuracy and functionality of the product.) If you
are unsure about the applicability of a replacement component, call a Keithley Instruments office for information.
T o clean an instrument, use a damp cloth or mild, water based
cleaner. Clean the exterior of the instrument only. Do not apply cleaner directly to the instrument or allow liquids to enter
or spill on the instrument. Products that consist of a circuit
board with no case or chassis (e.g., data acquisition board for
installation into a computer) should never require cleaning if
handled according to instructions. If the board becomes contaminated and operation is affected, the board should be returned to the factory for proper cleaning/servicing.
All Keithley product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of Keithley Instruments, Inc.
Other brand and product names are trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective holders.
4
Page 8

Introduction
This quick reference guide includes summary information on front panel and IEEE-488 operation for the
Model 7001 Switch System. For detailed information,
consult the Model 7001 Instruction Manual.
5
Page 9

Operation Summary
Channel List and Scan List
A Channel List specifies the channels to be closed or
opened, and a Scan List specifies the channels to be
scanned. Each channel in the list is made up of either a
two integer CHANNEL number (for non-matrix type
cards) or a three integer CHANNEL number (for matrix
type cards). Examples:
1!2 = Slot 1, Channel 2
2!4 = Slot 2, Channel 4
1!2!3 = Slot 1, Row 2, Column 3
2!3!6 = Slot 2, Row 3, Column 6
Front panel operation
A Channel List is created with the SELECT CHANNELS
prompt displayed, and a Scan List is created with the
SCAN CHANNELS prompt displayed. The SCAN LIST
key toggles the display between the Channel List and
the Scan List.
Channels are entered into a Channel List and Scan List
using the keypad. The following examples demonstrate
proper format.
SELECT CHANNELS 1!1, 1!5-1!10, 2!1!1, M1,
SCAN CHANNELS 1!10-1!1, 2!1!3, M1,
Each entry is separated by a comma (,) which is inserted
by pressing the right cursor key ( ) or the ENTER key.
Notice that a comma is also used to terminate the list. A
channel range is specified by separating the range limits
6
Page 10

with a hyphen (-). The M1 entry represents a channel
pattern that is stored in memory (see STORE and
RECALL).
Edit keys A list can also be modified by using the edit
keys; DELETE and INSERT. A channel entry can be
deleted by placing the cursor on the desired entry and
pressing DELETE. To insert an entry, press INSERT
(INSERTING ENTRY displayed), place the cursor at the
appropriate location, and key in the new entry. Make
sure to insert a comma after keying in the channel entry.
When finished, press INSERT again to cancel the insert
function.
IEEE-488 bus operation
Over the bus, the Channel List is included with the
commands that are used to close or open channels. See
Closing and Opening Channels. The Scan List is created
using the :SCAN command. The following example
demonstrates proper format:
:SCAN (@ 1!10:1!1, 2!1!3, M1)
Note that range limits are separated by a colon (:), and
the last channel entry in the list is not terminated with a
comma.
Closing and Opening Channels
Front panel operation
Channels specified in the Channel List are closed by
pressing the CLOSE key. Channels specified in the
Channel List are opened by pressing the OPEN key.
7
Page 11

Note that the OPEN ALL key will open all channels,
including those not specified in the Channel List.
IEEE-488 bus operation
Over the bus, the :CLOSe and :OPEN commands are
used to control channels. Note that the Channel List is
included with the following examples:
:CLOSe (@ 1!1, 1!5:1!10, 2!1!1, M1)
:OPEN (@ 1!1, 1!5:1!10, 2!1!1, M1)
Note that a colon (:) is used to separate range limits, and
a comma is not used to terminate the list. The following
command is analogous to the front panel OPEN ALL key
and will simply open all channels:
:OPEN ALL
Scanning Channels
Channels are scanned in the order that they are presented in the Scan List.
Front panel operation
To perform a scan, first program the controlling aspects
of the scan (see T able 2), and then press STEP to take the
Model 7001 out of the idle state (ARM indicator on).
Regardless of how the scan is configured, the STEP key
is always active allowing you to manually step through
the scan.
8
Page 12

The scan can be terminated at any time by pressing the
OPEN ALL key. All closed channels will open and the
Model 7001 will return to the idle state (ARM indicator
off).
IEEE-488 operation
Over the bus, a scan is configured using the :TRIGger
subsystem commands.
Send the following command to take the Model 7001
out of the idle state and begin a scan:
:INITiate
The scan can be terminated by sending the following
command:
:ABORt
All closed channels will open and the Model 7001 will
return to the idle state.
Store and Recall
Up to 100 channel patterns can be stored in memory. A
channel pattern is simply a displayed pattern of open
and closed channels.
Front panel operation
1. Close the desired channels.
2. Press STORE and enter the desired memory location (1 to 100).
3. Press ENTER.
9
Page 13

To recall a channel pattern from memory:
1. Press RECALL and enter the memory location of the
stored channel pattern.
2. Press ENTER. The channel status display will immediately update to reflect the recalled channel pattern.
Another way to recall a channel pattern is to include a
memory location (e.g. M36) in a Channel List and/or
Scan List. In a Channel List, when CLOSE is pressed, the
closed channels in the specified channel pattern will
close, and when OPEN is pressed, the channels will
open. In a Scan List, when the memory location is
scanned, the channel status display will update to
reflect the specified channel pattern. The closed channels in the channel pattern will remain closed unless a
different channel pattern is scanned.
IEEE-488 bus operation
Over the IEEE-488 bus, the :SAVe and :RECall commands are used to save (store) and recall channel patterns. The following examples demonstrate proper
format:
:MEMory:SAVe M36
:MEMory:RECall M36
As in front panel operation, a memory location can be
included in the Channel List and/or Scan List.
10
Page 14

Menu Structures
The desired menu is displayed by pressing the appropriate key; MENU, SCAN CONFIGURA TION or CARD
CONFIGURA TION. Once in a menu structure, place
the cursor ( and keys) on the desired selection and
press ENTER. Use the keypad to enter parameters. Use
the EXIT key to back out of the menu structure and disable the menu.
Table 1: MAIN MENU structure
Menu item Description
SAVESETUP
SAVE
RESTORE
PWRON
FACTORY DEFAULT
USER SETUP
RESET
GPIB
ADDRESS
STATUS
DIGITAL-I/O
OUTPUT-STATUS
OUTPUT-POLARITY
INPUT-STATUS
Setup Menu:
Save setup at a memory location
(up to 10).
Return 7001 to setup stored at a
memory location.
Power-on Menu:
Power-on to factory default
setup conditions.
Power-on to setup stored at a
memory location.
Return 7001 to original power
on setup.
GPIB Setup Menu:
Check/change IEEE-488 address.
Display IEEE-488 status byte.
Digital I/O Menu:
Check/change states of digital
output channels.
Check/change polarity of digital
output port.
Read digital input channel.
11
Page 15

Table 1: MAIN MENU structure (Cont.)
Menu item Description
TEST
BUILT-IN TESTS
AUTO
MANUAL
DISPLAY TESTS
KEYS
Self-Test Menu:
Test Digital Board:
Run all tests automatically
Select tests to run
Test Display Board:
Verify operation of front panel
keys
PATTERNS
LANGUAGE
ENGLISH
GERMAN
FRENCH
GENERAL
SERIAL #
Verify operation of display
Choose Language:
Display messages in English.
Display messages in German.
Display messages in French.
General Menu:
Displays serial number, SCPI ver-
sion, and software revision.
STATUS-MESSAGES
Enables/disables status message
mode.
Table 2: CONFIGURE SCAN menu structure
Menu item Description
CHAN-CONTROL
CHANNEL-SPACING
TIMER
EXTERNAL
GPIB
MANUAL
TRIGLINK
Configure Channel Layer:
Select channel spacing:
Use a timer to select each chan-
nel in the scan.
Use an external trigger to select
each channel.
Use a bus trigger to select each
channel.
Use STEP key to select each
channel.
Use a Trigger Link trigger to
select each channel.
12
Page 16

Table 2: CONFIGURE SCAN menu structure (Cont.)
Menu item Description
ASYNCHRONOUS
SEMI-SYNCHRONOUS
IMMEDIATE
HOLD
NUMBER-OF-CHANS
USE-SCANLIST-LENGTH
CHAN-COUNT
INFINITE
ENTER-CHAN-COUNT
CONTROL
SOURCE
ACCEPTOR
SCAN-CONTROL
SCAN-SPACING
TIMER
EXTERNAL
GPIB
MANUAL
TRIGLINK
IMMEDIATE
HOLD
NUMBER-OF-SCANS
INFINITE
ENTER-SCAN-COUNT
Use separate lines for In/Out
triggers.
Use same line for In/Out trig-
gers.
Use to scan channels immedi-
ately.
Use to hold up the scan in the
channel layer.
Define number of channels to
scan:
Count = number of channel
entries in scan list.
User defined count:
Repeat channel scanning
indefinitely.
Count = user defined value (1
to 9999)
Select trigger control mode:
Enable the Source Bypass.
Disable the Source Bypass.
Configure Scan Layer:
Select scan spacing:
Use the timer to control scan
spacing.
Use external triggers to control
scan spacing.
Use bus triggers to control scan
spacing.
Use STEP key to control scan
spacing.
Use Trigger Link triggers to con-
trol scan spacing.
Use to pass operation immedi-
ately into the channel layer.
Use to hold up the scan in the
scan layer.
Define number of scans to be per-
formed:
Repeat scan indefinitely.
Count = user defined value (1 to
9999).
13
Page 17

Table 2: CONFIGURE SCAN menu structure (Cont.)
Menu item Description
CONTROL
SOURCE
ACCEPTOR
ARM-CONTROL
ARM SPACING
MANUAL
IMMEDIATE
GPIB
EXTERNAL
TRIGLINK
HOLD
ARM-COUNT
INFINITE
ENTER-ARM-COUNT
TRIGGER-CONTROL
SOURCE
ACCEPTOR
CHAN-RESTRICTIONS
SINGLE-CHAN
RESTRICTED-CHANNELS
Select trigger control mode:
Enable Source Bypass.
Disable Source Bypass.
Configure Arm Layer:
Select arm spacing control:
Use STEP key to arm scanner.
Use to arm scanner immediately.
Use a bus trigger to arm scanner.
Use an external trigger to arm
scanner.
Use a Trigger Link trigger to arm
scanner.
Use to hold up the scan in the
arm layer.
Define number of times to arm
scanner:
Continuously re-arm scanner.
User defined count value (1 to
9999).
Select trigger control mode:
Enable Source Bypass.
Disable Source Bypass.
Define channel restrictions:
Enable/disable Single Channel
Mode.
Specify channels that cannot be
closed.
14
Page 18

Table 3: CARD CONFIG MENU structure
Menu item Description
TYPE
SLOT-1
SLOT-2
#-OF-POLES
SLOT-1
SLOT-2
CARD-PAIR Enable or disable Card Pair.
DELAY
SLOT-1
SLOT-2
READ-I/O-CARD Identify I/O Cards.
Set Card Type:
Assign model number to card in slot 1.
Assign model number to card in slot 2.
Select # Of Poles:
Select pole mode for card in slot 1.
Select pole mode for card in slot 2.
Set Delay For:
Set delay for card in slot 1.
Set delay for card in slot 2.
15
Page 19

Default Conditions
Table 4: Factory default and RESET
Item Factory default RESET
Channel status All open All open
Channel list Cleared No change
Scan list Cleared No change
GPIB address 7 No change
Digital I/O output
level
Language English No change
Status messages Off Off
# of poles 2-pole (both slots) No change
Card pair Off Off
Delay 0 sec 0 sec
Channel spacing Manual (STEP key) Manual (STEP key)
Number of channels Scan list length Scan list length
Channel trigger con-
trol
Scan spacing Immediate Immediate
Number of scans Infinite Infinite
Scan trigger control Acceptor Acceptor
Arm spacing Immediate Immediate
Arm count 1 1
Arm trigger control Acceptor Acceptor
Single channel Off Off
Restricted channels None No change
High High
Source Source
Note: “No change” indicates that RESET does not affect the currently set condition.
16
Page 20

Table 5: *RST and :SYSTem:PRESet
Command name *RST value
:INITiate
:CONTinuous
:ARM
:SEQuence[1]
:LAYer[1]
:COUNt
:SOURce
:TCONfigure
:DIRection
:ASYNchronous
:ILINe
:OLINe
:LAYer2
:COUNt
:DELay
:SOURce
:TIMer
:TCONfigure
:DIRection
:ASYNchronous
:ILINe
:OLINe
:TRIGger
:SEQuence1
:COUNt
:AUTO
:DELay
:SOURce
:TIMer
:TCONfigure
:PROTocol
:DIRection
:ASYNchronous
:ILINe
:OLINe
:SSYNchronous
:LINE
OFF
1
IMMediate
ACCeptor
1
2
1
0
IMMediate
0.001
ACCeptor
1
2
1
OFF
0
IMMediate
0.001
ASYNchronous
ACCeptor
1
2
1
:SYSTem:PRESet
value
OFF
1
IMMediate
ACCeptor
1
2
INFinite
0
IMMediate
0.001
ACCeptor
1
2
Scan list length
ON
0
MANual
0.001
ASYNchronous
SOURce
1
2
1
17
Page 21

Table 5: *RST and :SYSTem:PRESet (Cont.)
Command name *RST value
[:ROUTe]
:CONFigure
:SLOT[1]
:STIMe
:SLOT2
:STIMe
:CPAir
:SCHannel
:DISPlay
:SMESsage
0
0
OFF
OFF
OFF
:SYSTem:PRESet
value
0
0
OFF
OFF
OFF
18
Page 22

Error and Status Messages
Table 6: Error and status messages
Code number Description
+522
+521
+510
+173
+172
+171
+161
+101
0
-100
-101
-102
-103
-104
-105
-108
-109
-110
-111
-112
-113
-114
-120
-121
-123
-124
-128
EE = Error event
SE = Status event
“Slot 2 identification error” (EE)
“Slot1 identification error” (EE)
“Saved state error” (EE)
“Waiting in arm layer 2” (SE)
“Waiting in arm layer 1” (SE)
“Waiting in trigger Layer” (SE)
“Program running” (SE)
“Operation Complete” (SE)
“No error” (SE)
“Command Error” (EE)
“Invalid Character” (EE)
“Syntax Error” (EE)
“Invalid Separator” (EE)
“Data Type Error” (EE)
“GET not allowed” (EE)
“Parameter not allowed” (EE)
“Missing Parameter” (EE)
“Command Header Error” (EE)
“Command Header Separator Error” (EE)
“Program mnemonic too long” (EE)
“Undefined header” (EE)
“Header suffix out of range” (EE)
“Numeric data error” (EE)
“Invalid character in number” (EE)
“Exponent too large” (EE)
“Too many digits in number” (EE)
“Numeric data not allowed” (EE)
19
Page 23

Table 6: Error and status messages (Cont.)
Code number Description
-140
-141
-144
-148
-150
-151
-154
-158
-160
-161
-168
-170
-171
-178
-200
-201
-202
-210
-211
-212
-213
-214
-215
-220
-221
-222
-223
-224
-241
-260
-330 “Self Test failed” (EE)
EE = Error event
SE = Status event
“Character data error” (EE)
“Invalid character data” (EE)
“Character data too long” (EE)
“Character data not allowed” (EE)
“String data error” (EE)
“Invalid string data” (EE)
“String too long”
“String data not allowed” (EE)
“Block data error” (EE)
“Invalid block data” (EE)
“Block data not allowed” (EE)
“Expression error” (EE)
“Invalid expression” (EE)
“Expression data not allowed” (EE)
“Execution error” (EE)
“Invalid while in local” (EE)
“Settings lost due to rtl” (EE)
“Trigger error” (EE)
“Trigger ignored” (EE)
“Arm ignored” (EE)
“Init ignored” (EE)
“Trigger deadlock” (EE)
“Arm deadlock” (EE)
“Parameter Error” (EE)
“Settings conflict” (EE)
“Parameter data out of range” (EE)
“Too much data” (EE)
“Illegal parameter value” (EE)
“Hardware missing” (EE)
“Expression Error” (EE)
20
Page 24

Table 6: Error and status messages (Cont.)
Code number Description
-350
-410
-420
-430
-440
EE = Error event
SE = Status event
“Queue overflow” (EE)
“Query interrupted” (EE)
“Query unterminated” (EE)
“Query deadlocked” (EE)
“Query unterminated after indefinite
response” (EE)
21
Page 25

Standard Event
Status Register
(B0)
OPC
&
Standard Event
Status Enable
Register
(B0)
OPC
(B2) (B1)
QYE
(B3)
DDE
(B4)
EXE
(B5)
CME
(B6)
URQ
(B7)
PON
(B15-B8)
* ESR ?
PON = Power On
URQ = User Request
CME = Command Error
EXE = Execution Error
DDE = Device - Dependent Error
QYE = Query Error
OPC = Operation Complete
&
&
&
&
&
OR
Figure 1: Standard event status
&
To Event Summary
Bit (ESB) of
Status Bite
Register (See
Figure 3).
QYE
DDE
EXE
CME
URQ
PON
* ESE ?
* ESE
(B2) (B1)
(B3)
(B4)
(B5)
(B6)
(B7)
(B15-B8)
& = Logical AND
OR = Logical OR
22
Page 26

Operation Event
Condition Register
PTR Transition
NTR Filter
Operation Event
Status Register
Operation Event
Status Enable
Register
Set
Set
(B1)(B15 - B11) (B9) (B8) (B7) (B4) (B3) (B2) (B0)
Trig
Trig
(B5)
(1) (2)
Arm
Idle
(B6)
(B10)
Arm
Idle
(B1)(B15 - B11) (B9) (B8) (B7) (B4) (B3) (B2) (B0)
(B5)
(B6)
(B10)
Set
Trig
Arm
Idle
(B1)(B15 - B11) (B9) (B8) (B7) (B4) (B3) (B2) (B0)
(B5)
(B6)
(B10)
&
Figure 2: Operation event status
&
Set
(B1)(B15 - B11) (B9) (B8) (B7) (B4) (B3) (B2) (B0)
PTR = Positive Transition Filter
NTR = Negative Transition Filter
&
&
OR
To Operation
Summary Bit
(OSB) of Status
Byte Register.
Trig
Arm
Idle
(See Figure 5-11).
(B5)
(B6)
(B10)
& = Logical AND
OR = Logical OR
(1) From Trigger Event Register set (see Figure 5-5 in 7001 Instruction Manual).
(2) From Arm Event Register set (see Figure 5-5 in 7001 Instruction Manual).
Set = Settling
Idle = Idle
Trig = Waiting for Trigger
Arm = Waiting for Arm
23
Page 27

Status Byte
Register
Service Request
Enable Register
(B1) (B0)
(B2)
EAV
0
MSS
QSB
MAV
ESB
RQS
0
(B3)
(B4)
(B5)
(B6)
Status Summary Messages
(B7)
OSB
(B15 - B8)
* STB ?
Serial Poll
&
&
&
&
&
OR
(B1) (B0)
& = Logical AND
(B2)
EAV
(B3)
QSB
(B4)
MAV
(B5)
ESB
(B6)
(B7)
OSB
(B15 - B8)
OSB = Operation Summary Bit
* SRE ?
* SRE
Figure 3: Status byte and service request (SRQ)
OR = Logical OR
EAV = Error Available
ESB = Event Summary Bit
MAV = Message Available
QSB = Questionable Summary Bit
MSS = Master Summary Status (IEEE-488.2)
RQS = Request for Service (IEEE-488.1)
24
Page 28

IEEE-488.2 Common
Commands and Queries
Table 7: IEEE-488.2 common commands and queries
Mnemonic Name Description
*CLS Clear status Clears all event registers, and
Error Queue.
*ESE <n> Event status
enable command
*ESE? Event status enable
query
*ESR? Event status
register query
*IDN? Identification
query
*OPC Operation com-
plete command
*OPC? Operation com-
plete query
*OPT? Option identifica-
tion query
*RCL <n> Recall command Returns the 7001 to the setup
*RST Reset command Returns the 7001 to the *RST
Read Standard Event Status.
Read Standard Event Status
Register.
Read Standard Event Status
Register.
Read ID information.
Sets OPC bit in the Standard
Event Status Register after all
pending commands have
been executed.
Places an ASCII “1” into the
output queue when all pending commands have been
completed.
Read model number for each
slot.
stored in the designated
memory location (0 to 9).
default conditions.
25
Page 29

Table 7: IEEE-488.2 common commands and queries
(Cont.)
Mnemonic Name Description
*SAV <n> Save command Saves the current setup to the
designated memory location
(0 to 9).
*SRE <n> Service request
enable command
*SRE? Service request
enable query
*STB? Read status byte
query
*TRG Trigger command Issues a bus trigger.
*TST? Self-test query Performs a checksum test on
*WAI Wait-to-continue
command
Programs Service Request
Enable Register.
Read Service Request Enable
Register.
Read Status Byte Register.
ROM.
Wait until all previous com-
mands are executed.
26
Page 30

SCPI Command Subsystems
Table 8: DISPlay command summary
Command Description
:DISPlay
[ :WINDow[1]]
:TEXT
:DATA <a>
:STATe <b>
:STATe?
:WINDow2
:TEXT
:DATA <a>
:STATe <b>
:STATe?
:SMESsage <b> Enable (1 or ON) or disable (0 or OFF)
:SMESsage? Read state of status message display.
Path to locate message to top portion of
display
Path to control user text messages:
Define ASCII message “a” (up to 20
characters).
Enable (1 or ON) or disable (0 or
OFF) message.
Read state.
Path to locate message to bottom portion
of display:
Path to control user text messages:
Define ASCII message “a” (up to 32
characters).
Enable (1 or ON) or disable (0 or
OFF) message.
Read state.
status messages.
Table 9: OUTPut command summary
Command Description
:OUTPut
:TTLn
:LSENse AHIGh|
ALOW
:LSENse?
Path and command to specify output
line “n” (1-4):
Set polarity; active high (AHIG) or
active low (ALOW).
Read polarity.
27
Page 31

Table 10: ROUTe command summary
Command Description
[:ROUTe]
:CLOSe <list>
:STATe?
:CLOSe? <list> Read state of specified channels
:OPEN <list>|ALL Open specified (or all) channels.
:OPEN? <list> Read state of specified channels
:SCAN <list>
:POINts?
:SCAN? Read scan list.
:FCHannels <list> Specifies channels that cannot
:FCHannels? Read forbidden channels.
:CONFigure:
:SCHannel <b>
:SCHannel?
:CPAir <b>
:CPAir?
:SLOT1
:CTYPE <type>
:CTYPE?
:POLE <n>
:POLE?
:STIMe <num>
:STIMe?
Close specified channels:
Read closed channels.
(1=closed, 0=open).
(1=open, 0=closed).
Specify scan list:
Read number of channels in
scan list.
be closed (forbidden).
Configuration command path:
Enable (1 or ON) or disable (0
or OFF) Single Channel.
Read Single Channel mode.
Enable (1 or ON) or disable (0
or OFF) Channel Pairing.
Read Channel Pairing.
Path to configure CARD 1:
Specify card type.
Read card type.
Select pole mode (1, 2 or 4).
Read pole mode.
Set relay settling time (0 to
99999.999 sec).
Read relay settling time.
28
Page 32

Table 10: ROUTe command summary (Cont.)
Command Description
[:ROUTe]
:CONFigure:
:SLOT2
:CTYPE <type>
:CTYPE?
:POLE <n>
:POLE?
:STIMe <num>
:STIMe?
:MEMory
:SAVE M<num>
:RECall M<num>
Path to configure CARD 2:
Specify card type.
Read card type.
Select pole mode (1, 2 or 4).
Read pole mode.
Set relay settling time (0 to
99999.999 sec).
Read relay settling time.
Path to program memory:
Saves channel pattern in mem-
ory (1-100).
Recalls channel pattern from
memory (1-100).
Table 11: SENSe command summary
Command Description
:SENSe[1]
:TTL1
:DATA?
Command path for input port.
Read digital input port.
29
Page 33

Table 12: SOURce command summary
Command Description
:SOURce Command path to program digital output
port bits:
:TTL1
[:LEVel] <b>
[:LEVel]?
:TTL2
[:LEVel] <b>
[:LEVel]?
:TTL3
[:LEVel] <b>
[:LEVel]?
:TTL4
[:LEVel] <b>
[:LEVel]?
Path to program Bit 1:
Set (1 or ON) or reset (0 or off).
Read Bit 1.
Path to program Bit 2:
Set (1 or ON) or reset (0 or off).
Read Bit 2.
Path to program Bit 3:
Set (1 or ON) or reset (0 or off).
Read Bit 3.
Path to program Bit 4:
Set (1 or ON) or reset (0 or off).
Read Bit 4.
Table 13: STATus command summary
Command Description
:STATus
:OPERation
[:EVENt]?
:CONDition?
:PTRansition <n>
:PTRansition?
:NTRansition <n>
:NTRansition?
:ENABle <n>
:ENABle?
:ARM
Path to control operation event
registers:
Read status register.
Read condition register.
Program positive transition reg-
ister (0 to 1122).
Read positive transition register.
Program negative transition reg-
ister (0 to 1122).
Read negative transition register.
Program enable register (0 to
1122).
Read enable register.
Path to control arm event regis-
ters:
30
Page 34

Table 13: STATus command summary (Cont.)
Command Description
:STATus
:OPERation
:ARM
[:EVENt]?
:CONDition?
:PTRansition <n>
:PTRansition?
:NTRansition <n>
:NTRansition?
:ENABle <n>
:ENABle?
:SEQuence
[:EVENt]?
:CONDition?
:PTRansition <n>
:PTRansition?
:NTRansition <n>
:NTRansition?
:ENABle <n>
:ENABle?
:TRIGger
[:EVENt]?
:CONDition?
:PTRansition <n>
:PTRansition?
Read status register.
Read condition register.
Program positive transition
register (0 or 2).
Read positive transition regis-
ter.
Program negative transition
register (0 or 2).
Read negative transition regis-
ter.
Program enable register (0 or
2).
Read enable register.
Path to control the sequence
event registers:
Read status register.
Read condition register.
Program positive transition
register (0 to 6).
Read positive transition reg-
ister.
Program negative transition
register (0 to 6).
Read negative transition
register.
Program enable register (0
to 6).
Read enable register.
Path to control trigger event
registers:
Read status register.
Read condition register.
Program positive transition
register (0 or 2).
Read positive transition reg-
ister.
31
Page 35

Table 13: STATus command summary (Cont.)
Command Description
:STATus
:OPERation
:ARM
:TRIGger
:NTRansition <n>
:NTRansition?
:ENABle <n>
:ENABle?
:PRESet Return status registers to default
:QUEue
[:NEXT]?
:ENABle <list>
Program negative transition
register (0 or 2).
Read negative transition
register.
Program enable register (0
or 2).
Read enable register.
states.
Path to access error queue:
Read most recent error message.
Specify error and status mes-
sages for queue.
Table 14: SYSTem command summary
Command Description
:SYSTem
:ERRor? Read Error/Status Queue.
:POSetup RST|
PRESet|SAV0|
SAV1|SAV2|SAV3|
SAV4|SAV5|SAV6|
SAV7|SAV8|SAV9
:POSetup? Read power-on setup.
:PRESet Return instrument to default condi-
Select Power-on setup.
tions.
32
Page 36

Table 14: SYSTem command summary
Command Description
:VERSion? Read revision level of the SCPI Stan-
dard.
Table 15: Trigger command summary
Command Description
:INITiate
[:IMMediate]
:CONTinuous <b>
:ABORt Reset trigger system and go to
Initiate one trigger (scan)
cycle.
Enable (1 or ON) or disable (0
or OFF) continuous initiation.
idle state.
33
Page 37

Table 15: Trigger command summary (Cont.)
Command Description
:ARM[:SEQuence[1]]
[:LAYer[1]]
:IMMediate
:COUNt <n>|
INFinite
:COUNt?
:SOURce HOLD|
IMMediate|
MANual|BUS|
TLINk|EXTernal
:SOURce?
:SIGNal
:TCONfigure
:DIRection
SOURce |
ACCeptor
:DIRection?
:ASYNchronous
:ILINe <n>
:ILINe?
:OLINe <n>
:OLINe?
Subsystem command path to
configure scan:
Path to program Arm Layer 1
(arm layer) of scan:
Loop around control source.
Program number of arms (1
to 9999, or INFinite).
Read arm count.
Select Arm Layer 1 control
source.
Read source.
Loop around control source.
Path to configure Triggers.
Enable (SOUR) or disable
(ACC) Bypass.
Read direction.
Path to configure asyn-
chronous Trigger Link:
Select input line (1 to 6).
Read input line.
Select output line (1 to
6).
Read output line.
34
Page 38

Table 15: Trigger command summary (Cont.)
Command Description
:ARM[:SEQuence[1]]
:LAYer2
:IMMediate
:COUNt <n>|
INFinite
:COUNt?
:DELay <num>
:DELay?
:SOURce HOLD|
IMMediate|
MANual|BUS|
TLINk|EXTernal
|TIMer
:SOURce?
:SIGNal
:TIMer <num>
:TIMer?
:TCONfigure
:DIRection
SOURce|
ACCeptor
:DIRection?
:ASYNchronous
:ILINe <n>
:ILINe?
:OLINe <n>
:OLINe?
Path to program Arm Layer 2
(scan layer) of scan:
Loop around control source.
Program number of scans (1
to 9999, or INFinite).
Read scan count.
Program delay (0 to
99999.999 sec)
Read delay.
Select Arm Layer 2 control
source.
Read source.
Bypass scan control source
one time only.
Set timer interval (0 to
99999.999 sec).
Read timer interval.
Path to configure Triggers:
Enable (SOUR) or disable
(ACC) Bypass.
Read direction.
Path to configure asyn-
chronous mode:
Select input line (1 to 6).
Read input line.
Select output line (1 to
6).
Read output line.
35
Page 39

Table 15: Trigger command summary (Cont.)
Command Description
:TRIGger
:IMMediate
:COUNt <n>|
INFinite
:AUTO ON|OFF
:COUNt?
:DELay <num>
:DELay?
:SOURce HOLD|
IMMediate|
MANual|BUS|
TLINk|EXTernal|
TIMer
:SOURce?
:SIGNal
:TIMer <num>
:TIMer?
:TCONfigure
:PROTocol
ASYNchronous|
SSYNchronous
:PROTocol?
:DIRection
SOURce|
ACCeptor
:DIRection?
:ASYNchronous
:ILINe <n>
:ILINe?
Path to program Trigger Layer
(channel layer) of scan:
Scan channels immediately.
(Loop around control
source.)
Program number of channels
(1 to 9999, or INFinite).
Enable (on) to use scan-
list-length.
Read channel count.
Program delay (0 to
99999.999 sec)
Read delay period.
Select Trigger Layer Control
Source.
Read source.
Bypass channel control
source one time only.
Set timer interval (0 to
99999.999 sec).
Read timer interval.
Path to configure Triggers:
Select protocol (asynchro-
nous or semi-synchro-
nous Trigger Link.)
Read protocol.
Enable (SOUR) or disable
(ACC) Bypass.
Read direction.
Path to configure asynchro-
nous Trigger Link mode:
Select input line (1 to 6).
Read input line.
36
Page 40

Table 15: Trigger command summary (Cont.)
Command Description
:TRIGger
:TCONFigure
:ASYNchronous
:OLINe <n>
:OLINe?
:SSYNchronous
:LINE <n>
:LINE?
Select output line (1 to 6).
Read output line.
Path to configure semi-
synchronous Trigger Link
mode:
Select trigger line (1 to 6).
Read trigger line.
37
Page 41

38
Page 42

Specifications are subject to change without notice.
All Keithley trademarks and trade names are the property of Keithley
Instruments, Inc. All other trademarks and trade names are the
property of their respective companies.
Keithley Instruments, Inc.
28775 Aurora Road • Cleveland, Ohio 44139 • 440-248-0400 • Fax: 440-248-6168
1-888-KEITHLEY (534-8453) www.keithley.com
© Copyright 2000 Keithley Instruments, Inc.
Printed in the U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...