Page 1

Ninja 250R
Motorcycle
Service Manual
Page 2

Page 3

Quick Reference Guide
General Information 1 j
Periodic Maintenance 2 j
Fuel System 3 j
Cooling System 4 j
Engine Top End 5 j
Clutch 6 j
Engine Lubrication System 7 j
Engine Removal/Installation 8 j
This quick reference guide will assist
you in locating a desired topic or procedure.
•Bend the pages back to match the
black tab of the desired chapter number with the black tab on the edge at
each table of contents page.
•Refer to the sectional table of contents
for the exact pages to locate the specific topic required.
Crankshaft/Transmission 9 j
Wheels/Tires 10 j
Final Drive 11 j
Brakes 12 j
Suspension 13 j
Steering 14 j
Frame 15 j
Electrical System 16 j
Appendix 17 j
Page 4

Page 5

Ninja 250R
Motorcycle
Service Manual
All rights reserved. No parts of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or
transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic mechanical photocopying, recording or otherwise,
without the prior written permission of Quality Assurance Division/Consumer Products & Machinery
Company/Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., Japan.
No liability can be accepted for any inaccuracies or omissions in this publication, although every possible
care has been taken to make it as complete and accurate as possible.
The right is reserved to make changes at any time without prior notice and without incurring an obligation
to make such changes to products manufactured previously. See your Motorcycle dealer for the latest
information on product improvements incorporated after this publication.
All information contained in this publication is based on the latest product information available at the time
of publication. Illustrations and photographs in this publication are intended for reference use only and may
not depict actual model component parts.
© 2007 Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. First Edition (1): Nov. 15, 2007 (M)
Page 6
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
A ampere(s) lb pound(s)
ABDC after bottom dead center m meter(s)
AC alternating current min minute(s)
ATDC after top dead center N newton(s)
BBDC before bottom dead center Pa pascal(s)
BDC
BTDC before top dead center psi pound(s) per square inch
°C degree(s) Celsius r revolution
DC direct current rpm revolution(s) per minute
F farad(s) TDC top dead center
°F degree(s) Fahrenheit TIR total indicator reading
ft foot, feet
g gram(s) W watt(s)
h hour(s) Ω ohm(s)
L liter(s)
bottom dead center
PS
V
horsepower
volt(s)
COUNTRY AND AREA CODES
AT Austria
AU Australia MY Malaysia
CA Canada US United States
CAL California
CH Switzerland PH Phi
DE Germany WVTA Whole Vehicle Type Approval
FR France
GB
ID Indonesia
United Kingdom
lippines
Page 7

EMISSION CONTROL INFORMATION
To protect the environment in which we all live, Kawasaki has incorporated crankcase emission (1) and exhaust emission (2) control systems in compliance with applicable regulations of
the United States Environmental Protection Agency and California Air Resources Board. Additionally, Kawasaki has incorporated an evaporative emission control system (3) in compliance
with applicable regulations of the California Air Resources Board on vehicles sold in California
only.
1. Crankcase Emission Control System
This system eliminates the release of crankcase vapors into the atmosphere. Instead, the vapors
are routed through an oil separator to the inlet side of the engine. While the engine is operating,
the vapors are drawn into combustion chamber, where they are burned along with the fuel and air
supplied by the fuel injection system.
2. Exhaust Emission Control System
This system reduces the amount of pollutants discharged into the atmosphere by the exhaust
of this motorcycle. The fuel, ignition, and exhaust systems of this motorcycle have been carefully
designed and constructed to ensure an efficient engine with low exhaust pollutant levels.
The exhaust system of this model motorcycle manufactured primarily for sale in California in-
cludes a catalytic converter system.
3. Evaporative Emission Control System
Vapors caused by fuel evaporation in the fuel system are not vented into the atmosphere. In-
stead, fuel vapors are routed into the running engine to be burned, or stored in a canister when
the engine is stopped. Liquid fuel is caught by a vapor separator and returned to the fuel tank.
The Clean Air Act, which is the Federal law covering motor vehicle pollution, contains what is
commonly referred to as the Act’s “tampering provisions”.
“Sec. 203(a) The following acts and the causing thereof are prohibited...
(3)(A) for any person to remove or render inoperative any device or element of design installed
on or in a motor vehicle or motor vehicle engine in compliance with regulations under this
title prior to its sale and delivery to the ultimate purchaser, or for any manufacturer or dealer
knowingly to remove or render inoperative any such device or element of design after such
sale and delivery to the ultimate purchaser.
(3)(B) for any person engaged in the business of repairing, servicing, selling, leasing, or trading
motor vehicles or motor vehicle engines, or who operates a fleet of motor vehicles knowingly to remove or render inoperative any device or element of design installed on or in a
motor vehicle or motor vehicle engine in compliance with regulations under this title following its sale and delivery to the ultimate purchaser...”
NOTE
The phrase “remo ve or render inoperative any device or element of design” has been generally
○
interpreted as follows.
1. Tampering does not include the temporary removal or rendering inoperative of devices or elements of design in order to perform maintenance.
2. Tampering could include.
a.Maladjustment of vehicle components such that the emission standards are ex-
ceeded.
b.Use of replacement p arts or accessories which adversely affect the performance
or durability of the motorcycle.
c.Addition of components or accessories that result in the vehicle exceeding the stan-
dards.
d.Permanently removing, disconnecting, or rendering inoperative any component or
element of design of the emission control systems.
WE RECOMMEND THAT ALL DEALERS OBSERVE THESE PROVISIONS OF FEDERAL LAW,
THE VIOLATION OF WHICH IS PUNISHABLE BY CIVIL PENALTIES NOT EXCEEDING $10
000 PER VIOLATION.
Page 8

TAMPERING WITH NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM PROHIBITED
Federal law prohibits the following acts or the causing thereof. (1) The removal or rendering
inoperative by any person other than for purposes of maintenance, repair, or replacement, of any
device or element of design incorporated into any new vehicle for the purpose of noise control
prior to its sale or delivery to the ultimate purchaser or while it is in use, or (2) the use of the
vehicle after such device or element of design has been removed or rendered inoperative by
any person.
Among those acts presumed to constitute tampering are the acts listed below.
Replacement of the original exhaust system or muffler with a component not in compliance
•
with Federal regulations.
Removal of the muffler(s) or any internal portion of the muffler(s).
•
Removal of the air box or air box cover.
•
Modifications to the muffler(s) or air inlet system by cutting, drilling, or other means if such
•
modifications result in increased noise levels.
Page 9

Foreword
This manual is designed primarily for use by
trained mechanics in a properly equipped shop.
However, it contains enough detail and basic information to make it useful to the owner who desires to perform his own basic maintenance and
repair work. A basic knowledge of mechanics,
the proper use of tools, and workshop procedures must be understood in order to carry out
maintenance and repair satisfactorily. Whenever the owner has insufficient experience or
doubts his ability to do the work, all adjustments, maintenance, and repair should be carried out only by qualified mechanics.
In order to perform the work efficiently and
to avoid costly mistakes, read the text, thoroughly familiarize yourself with the procedures
before starting work, and then do the work carefully in a clean area. Whenever special tools or
equipment are specified, do not use makeshift
tools or equipment. Precision measurements
can only be made if the proper instruments are
used, and the use of substitute tools may adversely affect safe operation.
For the duration of the warranty period,
we recommend that all repairs and scheduled
maintenance be performed in accordance with
this service manual. Any owner maintenance or
repair procedure not performed in accordance
with this manual may void the warranty.
To get the longest life out of your vehicle:
Follow the Periodic Maintenance Chart in the
•
Service Manual.
Be alert for problems and non-scheduled
•
maintenance.
Use proper tools and genuine Kawasaki Mo-
•
torcycle parts. Special tools, gauges, and
testers that are necessary when servicing
Kawasaki motorcycles are introduced by the
Service Manual. Genuine parts provided as
spare parts are listed in the Parts Catalog.
Follow the procedures in this manual care-
•
fully. Don’t take shortcuts.
Remember to keep complete records of main-
•
tenance and repair with dates and any new
parts installed.
How to Use This Manual
In this manual, the product is divided into its
major systems and these systems make up the
manual’s chapters.
The Quick Reference Guide shows you all
of the product’s system and assists in locating
their chapters. Each chapter in turn has its own
comprehensive Table of Contents.
For example, if you want ignition coil information, use the Quick Reference Guide to locate
the Electrical System chapter. Then, use the
Table of Contents on the first page of the chapter to find the ignition coil section.
Whenever you see these WARNING and
CAUTION symbols, heed their instructions!
Always follow safe operating and maintenance
practices.
WARNING
This warning symbol identifies special
instructions or procedures which, if not
correctly followed, could result in per-
sonal injury, or loss of life.
CAUTION
This caution symbol identifies special
instructions or procedures which, if not
strictly observed, could result in dam-
age to or destruction of equipment.
This manual contains four more symbols (in
addition to WARNING and CAUTION) which will
help you distinguish different types of information.
NOTE
This note symbol indicates points of par-
○
ticular interest for more efficient and con-
venient operation.
Indicates a procedural step or work to be
•
done.
Indicates a procedural sub-step or how to do
○
the work of the procedural step it follows. It
also precedes the text of a NOTE.
Indicates a conditional step or what action to
take based on the results of the test or inspec-
tion in the procedural step or sub-step it fol-
lows.
In most chapters an exploded view illustration
of the system components follows the Table of
Contents. In these illustrations you will find the
instructions indicating which parts require specified tightening torque, oil, grease or a locking
agent during assembly.
Page 10

Page 11

GENERAL INFORMATION 1-1
General Information
Table of Contents
Before Servicing ..................................................................................................................... 1-2
Model Identification................................................................................................................. 1-7
General Specifications............................................................................................................ 1-8
Unit Conversion Table ............................................................................................................ 1-11
1
Page 12
1-2 GENERAL INFORMATION
Before Servicing
Before starting to perform an inspection service or carry out a disassembly and reassembly operation on a motorcycle, read the precautions given below. To facilitate actual operations, notes, illustrations, photographs, cautions, and detailed descriptions have been included in each chapter wherever
necessary. This section explains the items that require particular attention during the removal and
reinstallation or disassembly and reassembly of general parts.
Especially note the following.
Battery Ground
Before completing any service on the motorcycle, disconnect the battery cables from the battery to prevent the engine from accidentally turning over. Disconnect the ground
cable (–) first and then the positive (+). When completed
with the service, first connect the positive (+) cable to the
positive (+) terminal of the battery then the negative (–) cable to the negative terminal.
Edges of Parts
Lift large or heavy parts wearing gloves to prevent injury
from possible sharp edges on the parts.
Solvent
Use a high-flush point solvent when cleaning parts. High
-flush point solvent should be used according to directions
of the solvent manufacturer.
Cleaning vehicle before disassembly
Clean the vehicle thoroughly before disassembly. Dirt or
other foreign materials entering into sealed areas during vehicle disassembly can cause excessive wear and decrease
performance of the vehicle.
Page 13
Before Servicing
Arrangement and Cleaning of Removed Parts
Disassembled parts are easy to confuse. Arrange the
parts according to the order the parts were disassembled
and clean the parts in order prior to assembly.
Storage of Remov ed Parts
After all the parts including subassembly parts have been
cleaned, store the parts in a clean area. Put a clean cloth
or plastic sheet over the parts to protect from any foreign
materials that may collect before re-assembly.
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-3
Inspection
Reuse of worn or damaged parts may lead to serious accident. Visually inspect removed parts for corrosion, discoloration, or other damage. Refer to the appropriate sections
of this manual for service limits on individual parts. Replace
the parts if any damage has been found or if the part is beyond its service limit.
Replacement Parts
Replacement Parts must be KAWASAKI genuine or
recommended by KAWASAKI. Gaskets, O-rings, oil seals,
grease seals, circlips or cotter pins must be replaced with
new ones whenever disassembled.
Assembly Order
In most cases assembly order is the reverse of disassembly, however, if assembly order is provided in this Service
Manual, follow the procedures given.
Page 14
1-4 GENERAL INFORMATION
Before Servicing
Tightening Sequence
Generally, when installing a part with several bolts, nuts,
or screws, start them all in their holes and tighten them to
a snug fit. Then tighten them according to the specified sequence to prevent case warpage or deformation which can
lead to malfunction. Conversely when loosening the bolts,
nuts, or screws, first loosen all of them by about a quarter turn and then remove them. If the specified tightening
sequence is not indicated, tighten the fasteners alternating
diagonally.
Tightening Torque
Incorrect torque applied to a bolt, nut, or screw may
lead to serious damage. Tighten fasteners to the specified
torque using a good quality torque wrench.
Force
Use common sense during disassembly and assembly,
excessive force can cause expensive or hard to repair damage. When necessary, remove screws that have a non
-permanent locking agent applied using an impact driver.
Use a plastic-faced mallet whenever tapping is necessary.
Gasket, O-ring
Hardening, shrinkage, or damage of both gaskets and
O-rings after disassembly can reduce sealing performance.
Remove the old gaskets and clean the sealing surfaces
thoroughly so that no gasket material or other material remains. Install the new gaskets and replace the used O-rings
when re-assembling
Liquid Gasket, Non-permanent Locking Agent
For applications that require Liquid Gasket or a
Non-permanent Locking Agent, clean the surfaces so
that no oil residue remains before applying liquid gasket or
non-permanent locking agent. Do not apply them excessively. Excessive application can clog oil passages and
cause serious damage.
Page 15
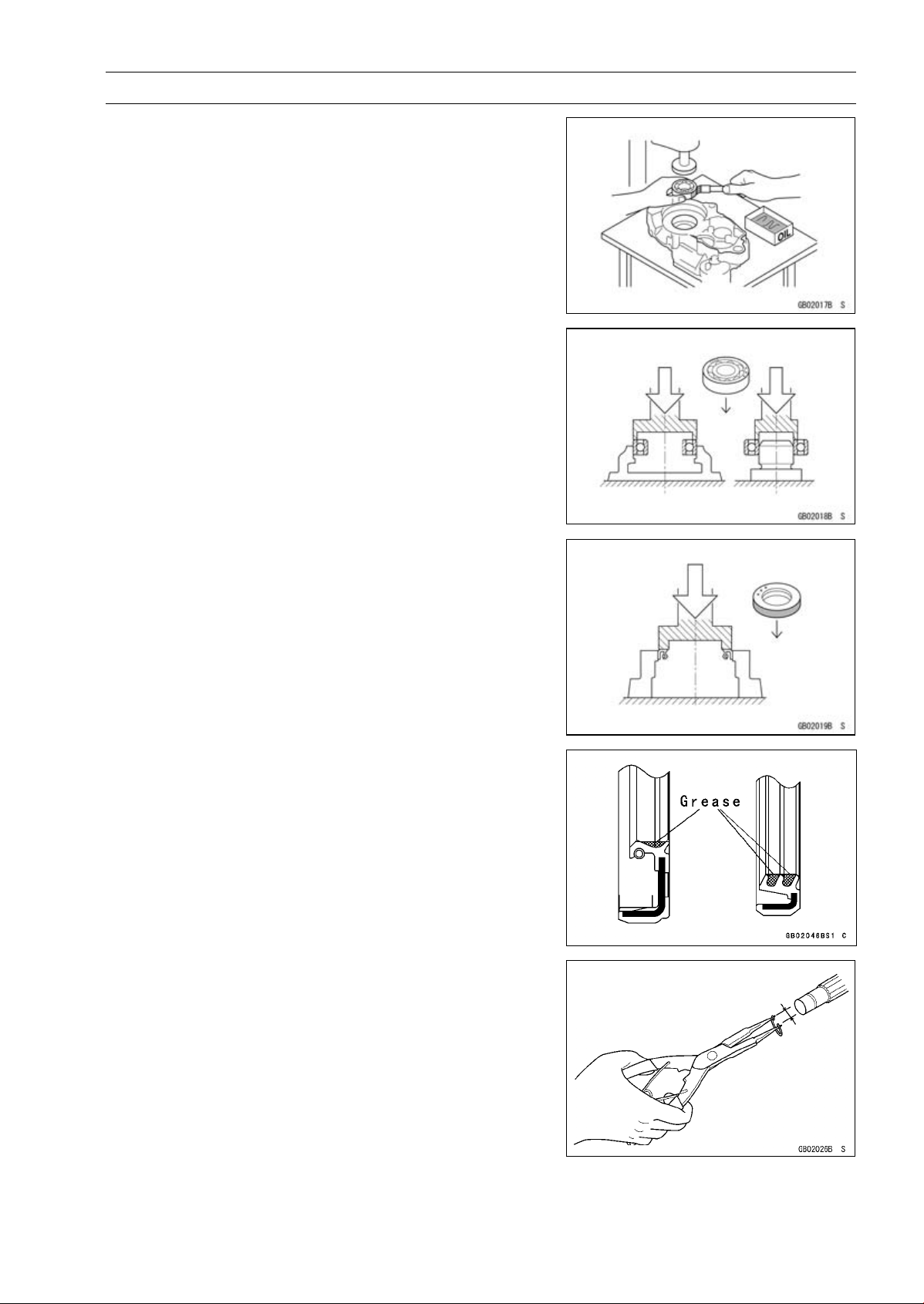
Before Servicing
Press
For items such as bearings or oil seals that must be
pressed into place, apply small amount of oil to the contact area. Be sure to maintain proper alignment and use
smooth movements when installing.
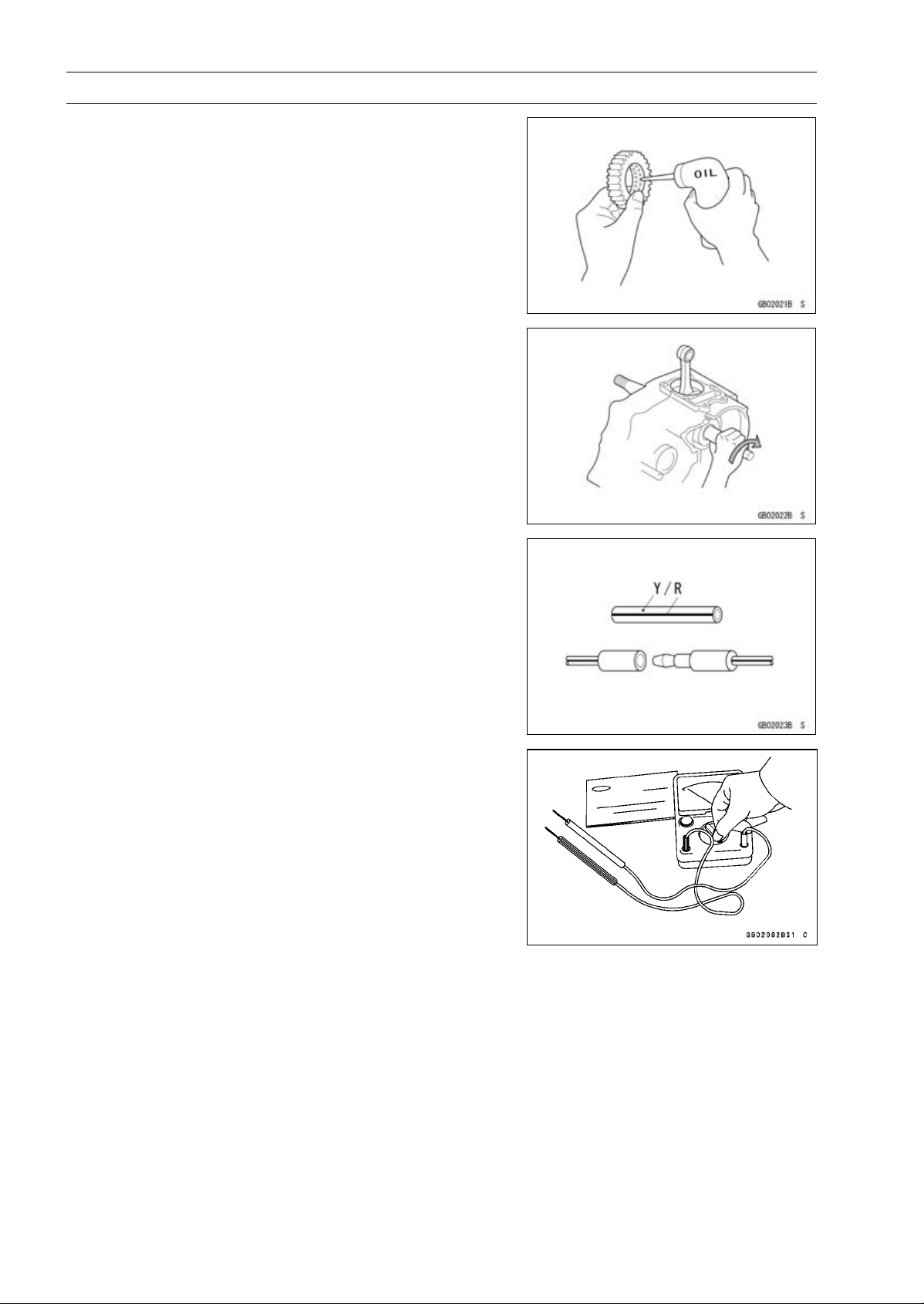
Ball Bearing and Needle Bearing
Do not remove pressed ball or needle unless removal is
absolutely necessary. Replace with new ones whenever
removed. Press bearings with the manufacturer and size
marks facing out. Press the bearing into place by putting
pressure on the correct bearing race as shown.
Pressing the incorrect race can cause pressure between
the i nner and outer race and result in bearing damage.
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-5
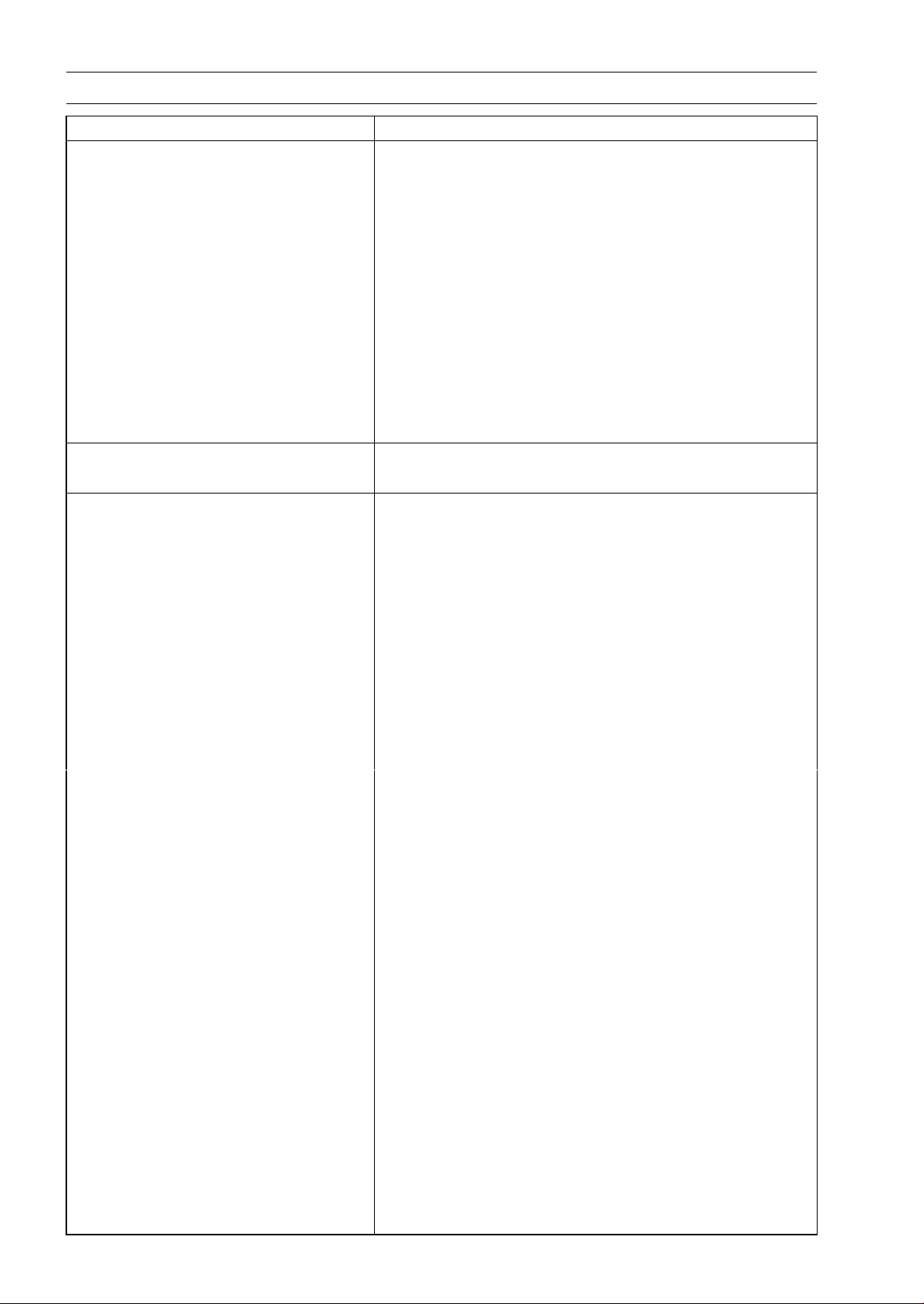
Oil Seal, Grease Seal
Do not remove pressed oil or grease seals unless removal
is necessary. Replace with new ones whenever removed.
Press new oil seals with manufacture and size marks facing
out. Make sure the seal is aligned properly when installing.
Apply specified grease to the lip of seal before installing
the seal.
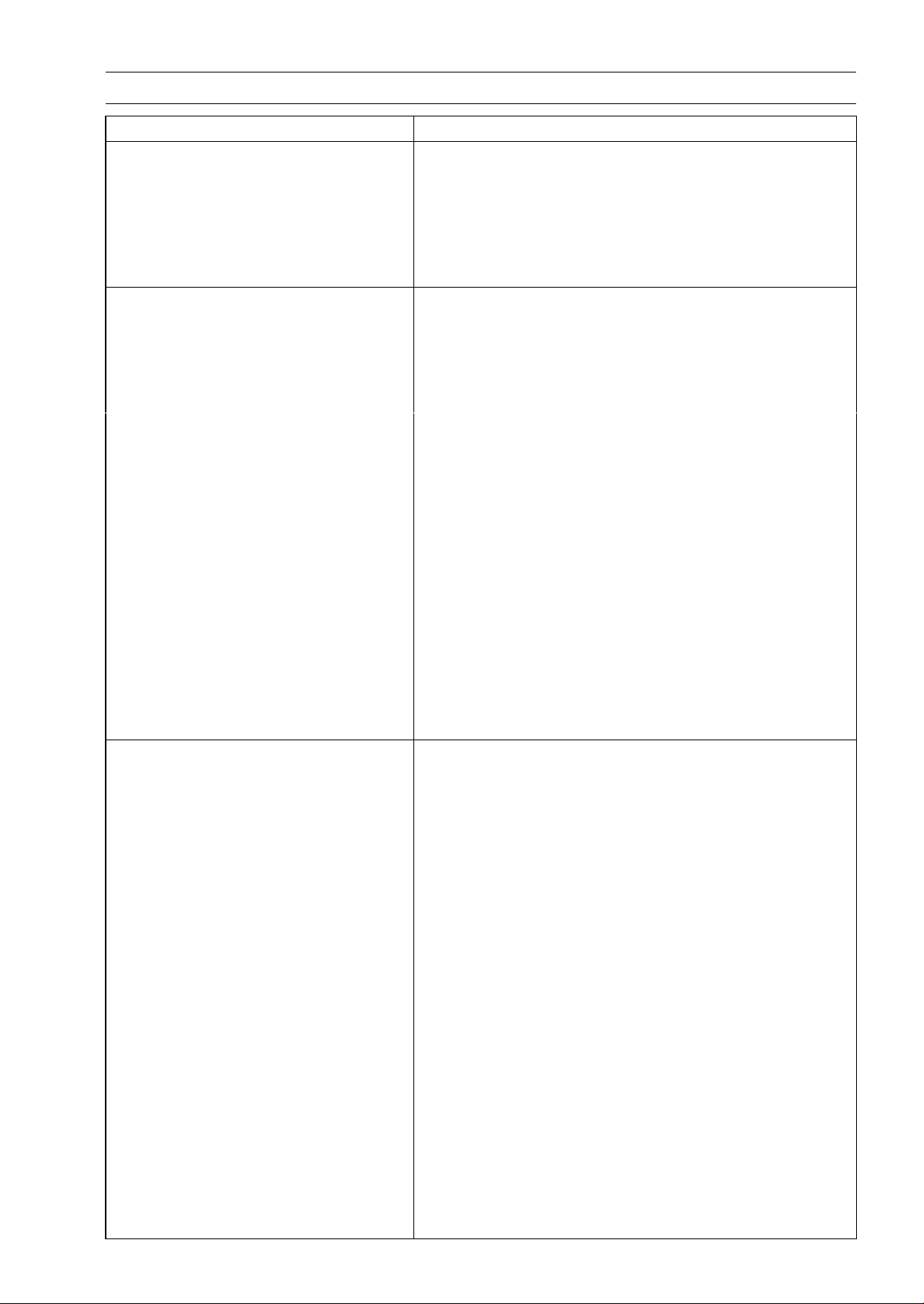
Circlips, Cotter Pins
Replace the circlips or cotter pins that were removed with
new ones. Take care not to open the clip excessively when
installing to prevent deformation.
Page 16
1-6 GENERAL INFORMATION
Before Servicing
Lubrication
It is important to lubricate rotating or sliding parts during
assembly to minimize wear during initial operation. Lubrication points are called out throughout this manual, apply
the specific oil or grease as specified.
Direction of Engine Rotation
When rotating the crankshaft by hand, the free play
amount of rotating direction will affect the adjustment. Rotate the crankshaft to positive direction (clockwise viewed
from output side).
Electrical Wires
A two-color wire is identified first by the primary color and
then the stripe color. Unless instructed otherwise, electrical
wires must be connected to those of the same color.
Instrument
Use a meter that has enough accuracy for an accurate
measurement. Read the manufacture’s instructions thoroughly before using the meter. Incorrect values may lead
to improper adjustments.
Page 17

Model Identification
EX250J8F Left Side View (United States and Canada)
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-7
EX250J8F Right Side View (United States and Canada)
Frame Number Engine Number
Page 18
1-8 GENERAL INFORMATION
General Specifications
Items EX250J8F
Dimensions
Overall Length 2 085 mm (82.1 in.)
Overall Width 715 mm (28.1 in.)
Overall Height 1 110 mm (43.7 in.)
Wheelbase 1 400 mm (55.1 in.)
Road Clearance 130 mm (5.1 in.)
Seat Height 775 mm (30.5 in.)
Dry Mass 152 kg, (335 lb)
Curb Mass:
Front
Rear
Fuel Tank Capacity 18.0 L (4.8 US gal)
Performance
Minimum Turning Radius 2.7 m (8.9 ft)
Engine
Type
Cooling System
Bore And Stroke 62.0× 41.2 mm (2.5 × 1.6 in.)
Displacement 249 cm³ (15.2 cu in.)
Compression Ratio 11 . 6
Maximum Horsepower 23.4 kW (31.8 PS) @11 000 r/min (rpm),
Maximum Torque 22.0 N·m (2.24 kg·m, 16.2 ft·lb) @9 500 r/min (rpm),
Carburetion System Carburetor, Keihin CVK 30× 2
Starting System Electric starter
Ignition System Battery and coil (transistorized)
Timing Advance Electronically advanced
Ignition Timing From 10° BTDC @1 300 r/min (rpm)
Spark Plug NGK CR8E or ND U24ESR-N
Cylinder Numbering Method Left to Right, 1-2
Firing Order
Valve Timing:
Inlet
Open 36° BTDC
Close 56° ABDC
Duration 272°
Exhaust
Open 61° BBDC
Close 31° ATDC
Duration 272°
82 kg (181 lb)
87 kg (192 lb)
4-stroke, DOHC, 2-cylinder
Liquid-cooled
35° BTDC @4 000 r/min (rpm)
1-2
Page 19
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-9
General Specifications
Items EX250J8F
Lubrication System Forced ubrication (wet sump)
Engine Oil:
Grade API SE, SF or SG
API SH, SJ or SL with JASO MA
Viscosity
Capacity 1.7 L (1.80 US qt)
Drive Train
Primary Reduction System:
Type Gear
Reduction Tatio 3.087 (71/23)
Clutch Type
Transmission:
Type 6-speed, constant mesh, return shift
Gear Ratios:
1st 2.600 (39/15)
2nd 1.789 (34/19)
3rd
4th
5th
6th 0.893 (25/28)
Final Drive System:
Type Chain drive
Reduction Ratio 3.214 (45/14) (AU) 3.071 (43/14)
Overall Drive Ratio 8.859 @Top gear (AU) 8.466 @Top gear
Frame
Type Tubular, diamond
Caster (Rake Angle) 26°
Trail 82 mm (3.2 in.)
Front Wheel:
Tire Type Tubeless
Tire Size 100/70-17M/C 54H
Rim Size 17 × 2.75
Rear Wheel:
Tire Type Tubeless
Tire Size 130/70-17M/C 62H
Rim Size 17 × 3.50
Front suspension:
Type Telescopic fork
Wheel Travel 120 mm (4.7 in.)
Rear Suspension:
Type Swingarm (uni-trak)
Wheel Travel 130 mm (5.1 in.)
SAE10W-40
Wet multi disc
1.409 (31/22)
1.160 (29/25)
1.000 (27/27)
Page 20
1-10 GENERAL INFORMATION
General Specifications
Items EX250J8F
Brake Type:
Front Single disc
Rear Single disc
Electrical Equipment
Battery 12 V 6 Ah
Headlight:
Type Semi-sealed beam
Bulb:
High
Low
Tail/brake Light 12 V 5/21 W
Alternator:
Type Three-phase AC
Rated Output 19 A @5 000 r/min (rpm), 14 V
12 V 55 W + 55 W (quartz-halogen)
12 V 55 W (quartz-halogen)
Specifications are subject to change without notice, and may not apply to every country.
AU: Austral
ia Model
Page 21
Unit Conversion Table
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-11
Prefixes for Units:
Prefix Symbol Power
mega M × 1 000 000
kilo k ×1000
centi c ×0.01
milli m × 0.001
micro µ × 0.000001
Units of Mass:
kg ×2.205=lb
g × 0.03527 = oz
Units of Volume:
L × 0.2642 = gal (US)
L × 0.2200 = gal (imp)
L × 1.057 = qt (US)
L × 0.8799 = qt (imp)
L×2.113=
L × 1.816 =
mL × 0.03381 = oz (US)
mL × 0.02816 = oz (imp)
mL × 0.06102 = cu in
pint (US)
pint (imp)
Units of Length:
km × 0.6214 = mile
m × 3.281 = ft
mm × 0.03937 = in
Units of Torque:
N·m × 0.1020 = kgf·m
N·m × 0.7376 =
N·m × 8.851 = in·lb
kgf·m × 9.807 = N·m
kgf·m × 7.233 = ft·lb
kgf·m × 86.80 = in·lb
ft·lb
Units of Pressure:
kPa × 0.01020 =
kPa × 0.1450 = psi
kPa × 0.7501 = cm Hg
kgf/cm² × 98.07 = kPa
kgf/cm² × 14.22 = psi
cmHg×1.333=kPa
kgf/cm²
Units of Force:
N × 0.1020 = kg
N × 0.2248 = lb
kg ×9.807=N
kg ×2.205=lb
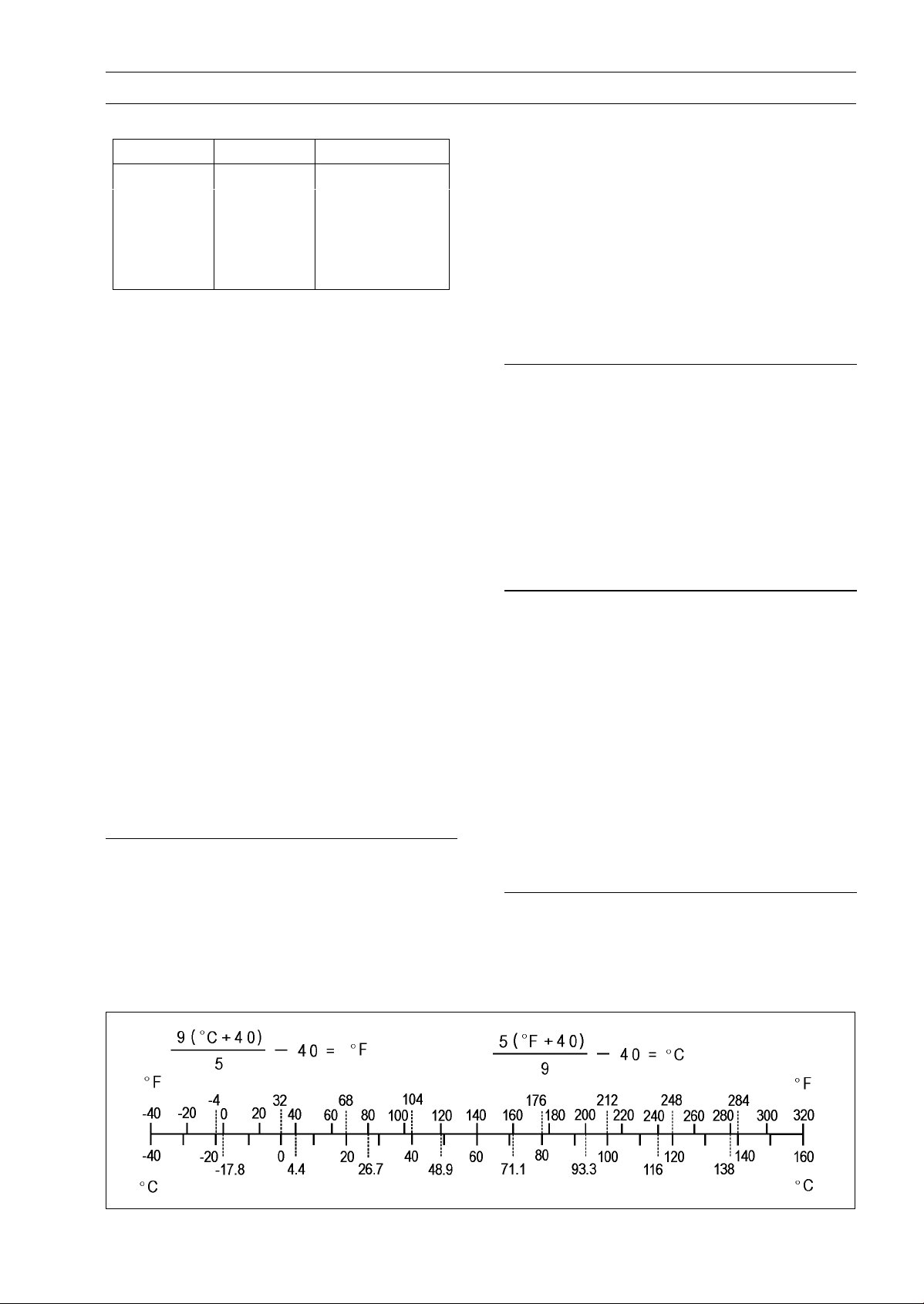
Units of Temperature:
Units of Speed:
km/h
× 0.6214 = mph
Units of Power:
kW ×1.360=PS
kW ×1.341=HP
PS × 0.7355 = kW
PS × 0.9863 = HP
Page 22

Page 23

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-1
Periodic Maintenance
Table of Contents
Periodic Maintenance Chart ................................................................................................... 2-3
Torque and Locking Agent...................................................................................................... 2-6
Specifications ......................................................................................................................... 2-11
Special Tools .......................................................................................................................... 2-13
Periodic Maintenance Procedures.......................................................................................... 2-14
Fuel System ......................................................................................................................... 2-14
Air Cleaner Element Cleaning........................................................................................... 2-14
Air Cleaner Element Installation........................................................................................ 2-15
Throttle Control System Inspection................................................................................... 2-15
Choke Operation Inspection ............................................................................................. 2-17
Engine Vacuum Synchronization Inspection..................................................................... 2-17
Idle Speed Inspection ....................................................................................................... 2-18
Idle Speed Adjustment...................................................................................................... 2-18
Fuel Hose Inspection (fuel leak, damage, installation condition) ...................................... 2-19
Evaporative Emission Control System (California Model) ................................................... 2-19
Evaporative Emission Control System Inspection ............................................................ 2-19
Cooling System.................................................................................................................... 2-20
Coolant Level Inspection................................................................................................... 2-20
Radiator Hose Damage and Installation Condition Inspection.......................................... 2-21
Coolant Filter Cleaning (Australia Model) ......................................................................... 2-21
Air Suction System .............................................................................................................. 2-21
Air Suction System Damage Inspection............................................................................ 2-21
Engine Top End ................................................................................................................... 2-22
Valve Clearance Inspection .............................................................................................. 2-22
Valve Clearance Adjustment............................................................................................. 2-23
Clutch................................................................................................................................... 2-26
Clutch Operation Inspection.............................................................................................. 2-26
Wheels/Tires........................................................................................................................ 2-27
Air Pressure Inspection..................................................................................................... 2-27
Wheel/Tire Damage Inspection......................................................................................... 2-27
Tire Tread Wear, Abnormal Wear Inspection .................................................................... 2-27
Wheel Bearing Damage Inspection .................................................................................. 2-28
Drive Train ........................................................................................................................... 2-29
Drive Chain Lubrication Condition Inspection ................................................................... 2-29
Drive Chain Slack Inspection ............................................................................................ 2-29
Drive Chain Slack Adjustment .......................................................................................... 2-30
Wheel Alignment Inspection ............................................................................................. 2-31
Drive Chain Wear Inspection ............................................................................................ 2-31
Chain Guide Inspection..................................................................................................... 2-32
Brake System ...................................................................................................................... 2-32
Brake Fluid Leak (Brake Hose and Pipe) Inspection ........................................................ 2-32
Brake Hose and Pipe Damage and Installation Condition Inspection............................... 2-32
Brake Operation Inspection .............................................................................................. 2-32
Brake Fluid Level Inspection............................................................................................. 2-33
Brake Pad Wear Inspection .............................................................................................. 2-33
Brake Light Switch Operation Inspection .......................................................................... 2-34
Suspensions ........................................................................................................................ 2-34
Front Forks/Rear Shock Absorber Operation Inspection .................................................. 2-34
Front Fork Oil Leak Inspection .......................................................................................... 2-35
Rear Shock Absorber Oil Leak Inspection ........................................................................ 2-35
2
Page 24

2-2 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Rocker Arm Operation Inspection..................................................................................... 2-35
Tie-Rod Operation Inspection ........................................................................................... 2-35
Swingarm Pivot Lubrication .............................................................................................. 2-36
Steering System ..................................................................................................................2-36
Steering Play Inspection ................................................................................................... 2-36
Steering Play Adjustment.................................................................................................. 2-36
Steering Stem Bearing Lubrication ................................................................................... 2-37
Electrical System ................................................................................................................. 2-37
Lights and Switches Operation Inspection........................................................................ 2-37
Headlight Aiming Inspection ............................................................................................. 2-39
Sidestand Switch Operation Inspection ............................................................................ 2-40
Engine Stop Switch Operation Inspection......................................................................... 2-41
Others.................................................................................................................................. 2-42
Chassis Parts Lubrication ................................................................................................. 2-42
Bolts, Nuts and Fasteners Tightness Inspection............................................................... 2-43
Replacement Parts .............................................................................................................. 2-44
Air Cleaner Element Replacement.................................................................................... 2-44
Fuel Hose Replacement ................................................................................................... 2-44
Coolant Change ................................................................................................................ 2-44
Radiator Hose and O-ring Replacement ........................................................................... 2-46
Engine Oil Change............................................................................................................ 2-47
Oil Filter Replacement ...................................................................................................... 2-47
Brake Hose and Pipe Replacement .................................................................................. 2-48
Brake Fluid Change .......................................................................................................... 2-48
Master Cylinder Rubber Parts Replacement .................................................................... 2-50
Caliper Rubber Parts Replacement .................................................................................. 2-51
Spark Plug Replacement .................................................................................................. 2-52
Page 25
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-3
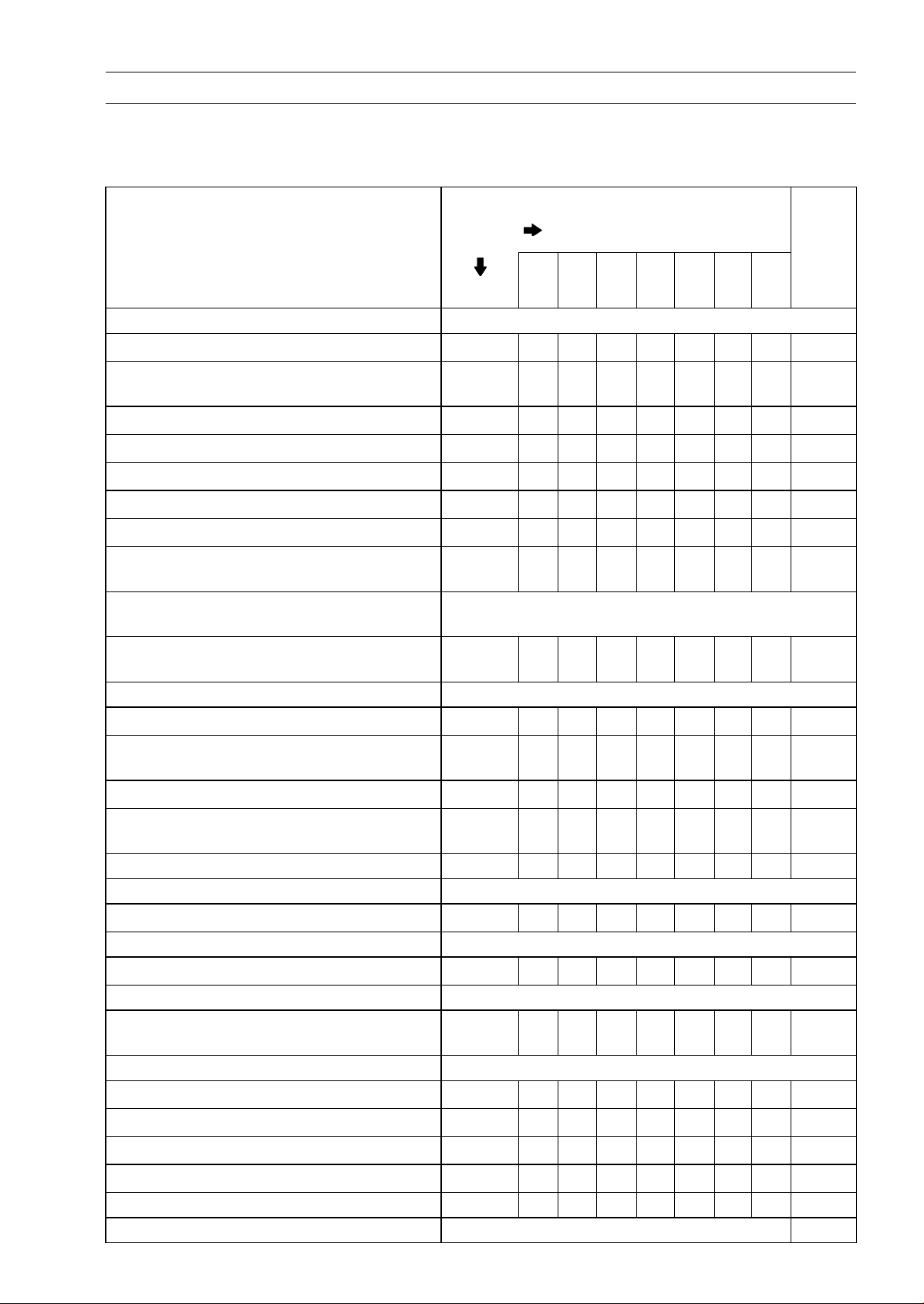
Periodic Maintenance Chart
The scheduled maintenance must be done in accordance with this chart to keep the motorcycle in
good running condition.The initial maintenance is vitally important and must not be neglected.
Periodic Inspection
FREQUENCY Whichever
comes
first
1 6 12 18 24 30 36
INSPECTION Every (0.6) (4) (7.5) (12) (15) (20) (24)
Fuel System
* ODOMETER READING
× 1 000 km
(× 1 000 mile)
See
Page
Air cleaner element - clean
Throttle control system (play, smooth
return, no drag) - inspect
Choke operation - inspect year
Engine vacuum synchronization - inspect
Idle speed - inspect
Fuel leak (fuel hose and pipe) - inspect year
Fuel hose and pipe damage - inspect year
Fuel hose and pipe installation condition inspect
Evaporative Emission Control System
(CAL)
Evaporative emission control system
function - inspect
Cooling System
Coolant level - inspect
Coolant leak (radiator hose and pipe) inspect
Radiator hose damage - inspect year
Radiator hose installation condition inspect
Coolant filter - clean year
Air Suction System
year
year
year
year
• • •
• • • •
• • • •
• • •
• • • •
• • • •
• • • •
• • • •
• • • • • • •
• • • •
• • • •
• • • •
• • • •
2-14
2-15
2-17
2-17
2-18
2-19
2-19
2-19
2-19
2-20
2-21
2-21
2-21
Air suction system damage - inspect
Engine Top End
Valve clearance - inspect
Clutch
Clutch operation (play, disengagement,
engagement) - inspect
Wheels and Tires
Tire air pressure - inspect year
Wheel/tire damage - inspect
Tire tread wear, abnormal wear - inspect
Wheel bearing damage - inspect year
Drive Train
Drive chain lubrication condition - inspect # Every 600 km (400 mile) 2-29
• • • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
2-21
2-22
2-26
2-27
2-27
2-27
2-28
Page 26
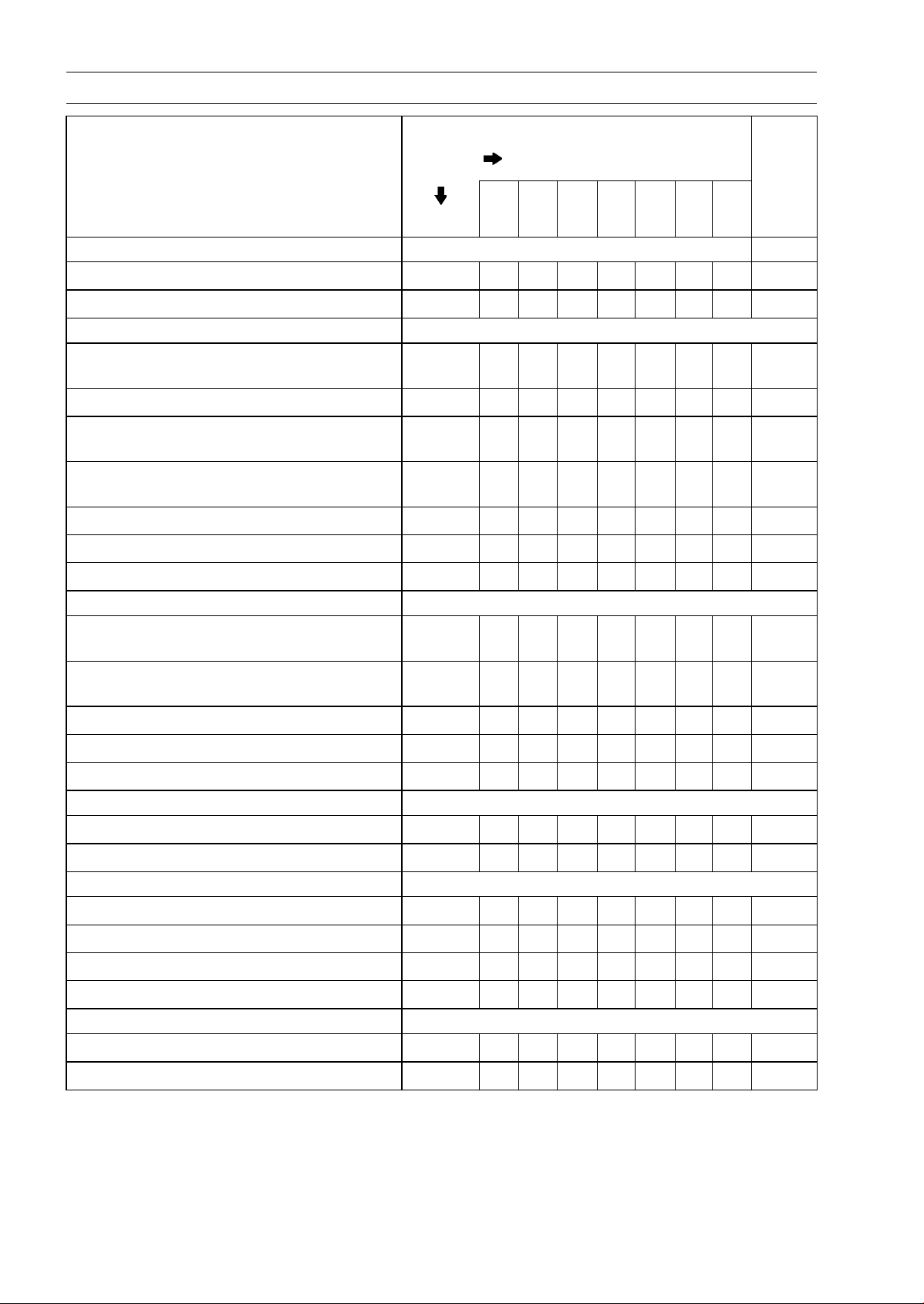
2-4 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Chart
FREQUENCY Whichever
comes
first
1 6 12 18 24 30 36
INSPECTION Every (0.6) (4) (7.5) (12) (15) (20) (24)
Drive chain slack - inspect # Every 1 000 km (600 mile) 2-29
Drive chain wear - inspect #
Drive chain guide wear - inspect
Brake System
Brake fluid leak (brake hose and pipe) inspect
Brake hose and pipe damage - inspect year
Brake hose and pipe installation condition
- inspect
Brake operation (effectiveness, play, no
drag) - inspect
Brake fluid level - in
Brake pad wear - inspect #
Brake light switch operation - inspect
Suspensions
Front forks/rear shock absorber operation
(damping and smoot
Front forks/rear shock absorber oil leak inspect
spect
h stroke) - inspect
year
year
year
6 months
year
• • • • • • •
• • • • • • •
• • • • • • •
• • • • • • •
• • • • • • •
• • • • • • •
* ODOMETER READING
× 1 000 km
(× 1 000 mile)
• • •
• • •
• • • • • •
• • •
• • •
See
Page
2-31
2-32
2-32
2-32
2-32
2-32
2-33
2-33
2-34
2-34
2-35
Rocker arm operation - inspect
Tie-rods operation - inspect
Swingarm pivot - lu
Steering System
Steering play - inspect year
Steering stem bearings - lubricate
Electrical System
Lights and switches operation - inspect year
Headlight aiming - inspect year
Sidestand switch operation - inspect year
Engine stop switch operation - inspect year
Others
Chassis parts - lubricate year
Bolts and nuts tightness - inspect
#: Service more frequently when operating in severe conditions; dusty, wet, muddy, high speed or
frequent starting/stopping.
*: For higher odometer readings, repeat at the frequency interval established here.
bricate
• • • •
2years
• • • •
• • •
• • •
•
•
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
• • •
2-35
2-35
2-36
2-36
2-37
2-37
2-39
2-40
2-41
2-42
2-43
Page 27
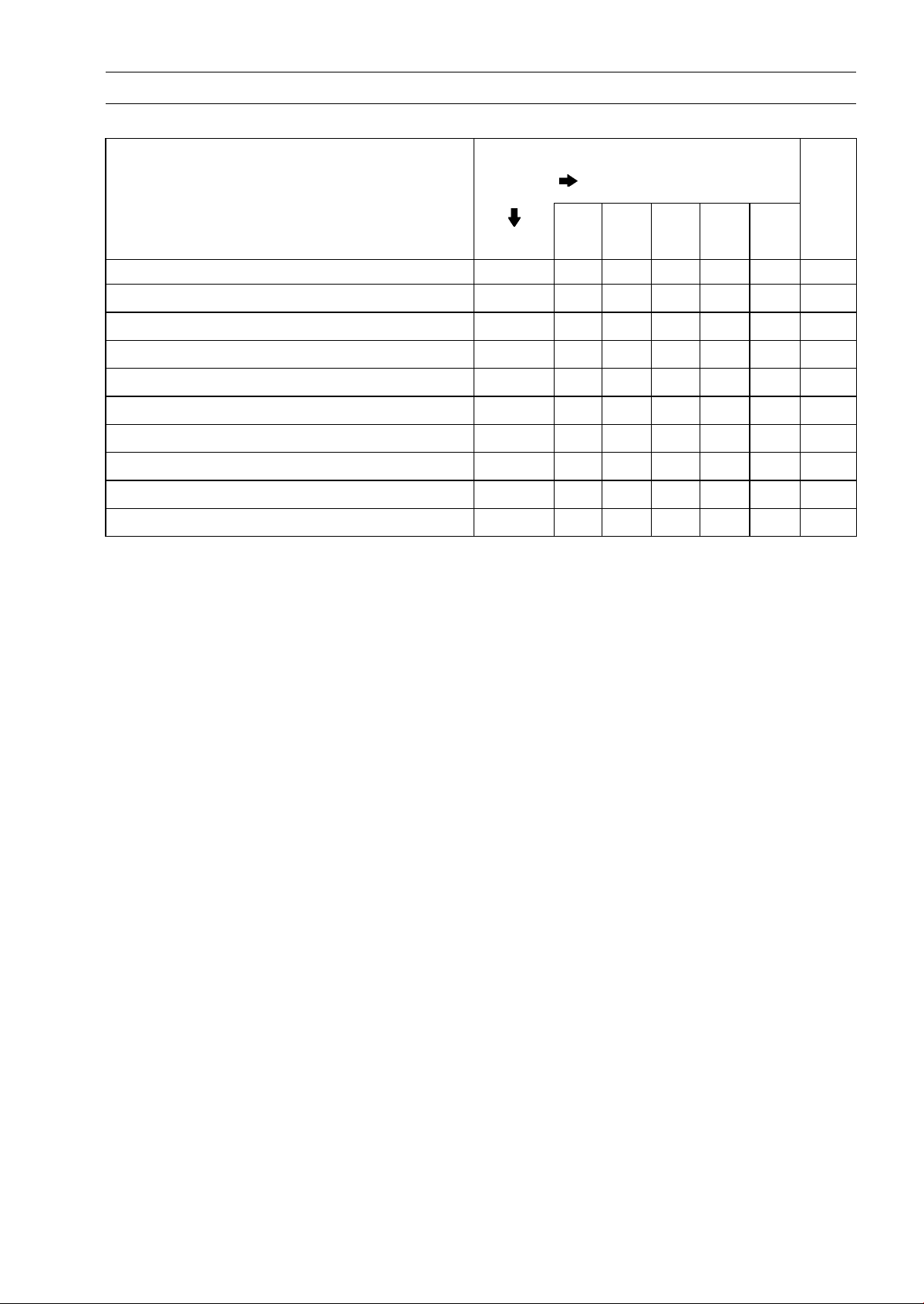
Periodic Maintenance Chart
Periodic Replacement Parts
FREQUENCY
Whichever
comes
first
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-5
* ODOMETER READING
× 1 000 km
(× 1 000 mile)
1 12 24 36 48
See
Page
CHANGE/REPLACE ITEM
Air cleaner element #
Fuel hose 4 years
Coolant 3 years
Radiator hose and O-ring 3 years
Engine oil #
Oil filter year
Brake hose and pipe 4 years
Brake fluid 2 years
Rubber parts of master cylinder and caliper 4 years
Spark plug
#: Service more frequently when operating in severe conditions; dusty, wet, muddy, high speed or
frequent starting/stopping.
*: For higher odometer readings, repeat at the frequency interval established here.
Every
2 years 2-44
(0.6) (7.5) (15) (24) (30)
•
•
•
year
• • • • •
• • • • •
•
• •
•
• • • •
2-44
2-44
2-46
2-47
2-47
2-48
2-48
2-50
2-52
Page 28
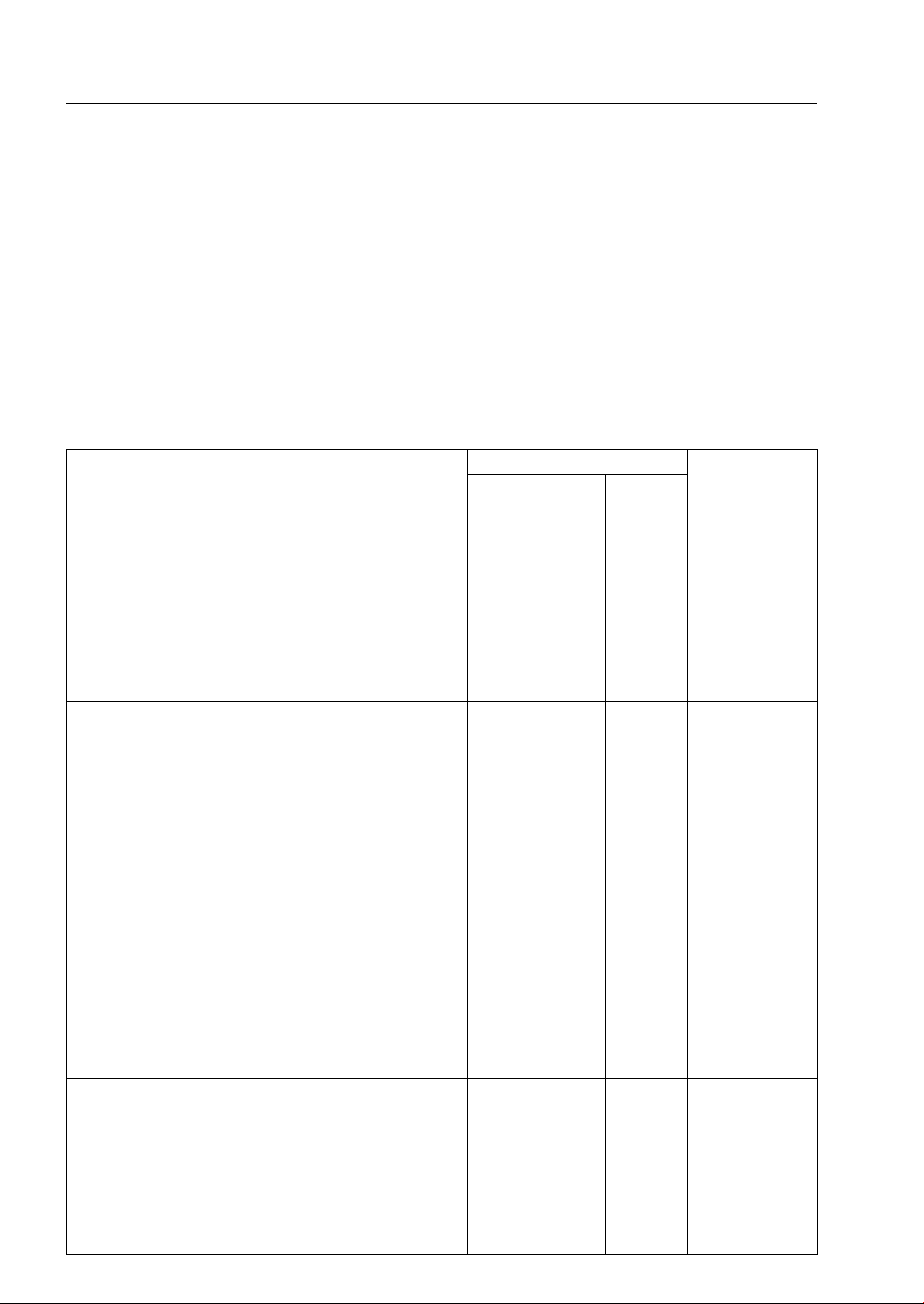
2-6 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Torque and Locking Agent
Use a torque wrench to tighten bolts and nuts to their specified torque values. If too little torque is
applied, the bolts and nuts could loosen and fall out. If too much torque is applied, the threads could
be sheared off.
To tighten a bolt or a nut, or to check their torque, loosen the bolt or nut one-half turn before tightening it to the specified torque.
Letters used in the “Remarks” column mean:
EO: Apply engine oil.
G: Apply grease.
L: Apply a non-permanent locking agent to the threads.
M: Apply molybdenum disulfide grease.
MO: Apply molybdenum disulfide oil solution.
R: Replacement Parts
S: Tighten the fasteners following the specified sequence.
Si: Apply silicone grease.
SS: Apply silicone sealant.
Fastener
Fuel System
Fuel Tap Mounting B
Fuel Gauge Mounting Bolts 6.9 0.7 61 in·lb
Air Cleaner Housing Cap Bolts 2.5 0.25 22 in·lb
Air Cleaner Housing Screws 1.15 0.12 10 in·lb
Air Cleaner Housing Mounting Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Air Cleaner Housing Clamp Screws 2.0 0.2 18 in·lb
Separate Bracket Bolt 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Cooling System
Water Temperature Switch 7.5 0.76 66 in·lb SS
Thermostat Cover Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Thermostat Housing Mounting Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Radiator Fan Switch 23.5 2.4 17
Radiator Bolt
Radiator Cap Bracket Bolt 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Water Pipe Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Water Hose Clamp Screws 1.5 0.15 13 in·lb
Drain Bolt 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Water Pump Cover Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Water Pump Bol
Reserve Tank Cap – – – Hand-Tighten
Reserve Tank Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Reserve Tank Bracket Bolt 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Engine Top End
Cylinder Head Cover Bolts
Camshaft Spro
Chain Tensioner Cap Bolt 5.0 0.5 44 in·lb
Air Suction Cover Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Vacuum Switch Valve Bracket Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Rear Camshaft Chain Guide Bolt-Lower 17 1.7 13
s
olts
ts
cket Bolts
N·m kgf·m ft·lb
2.5 0.25 22 in·lb
9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
15 1.5 11 L
Torque
Remarks
Page 29
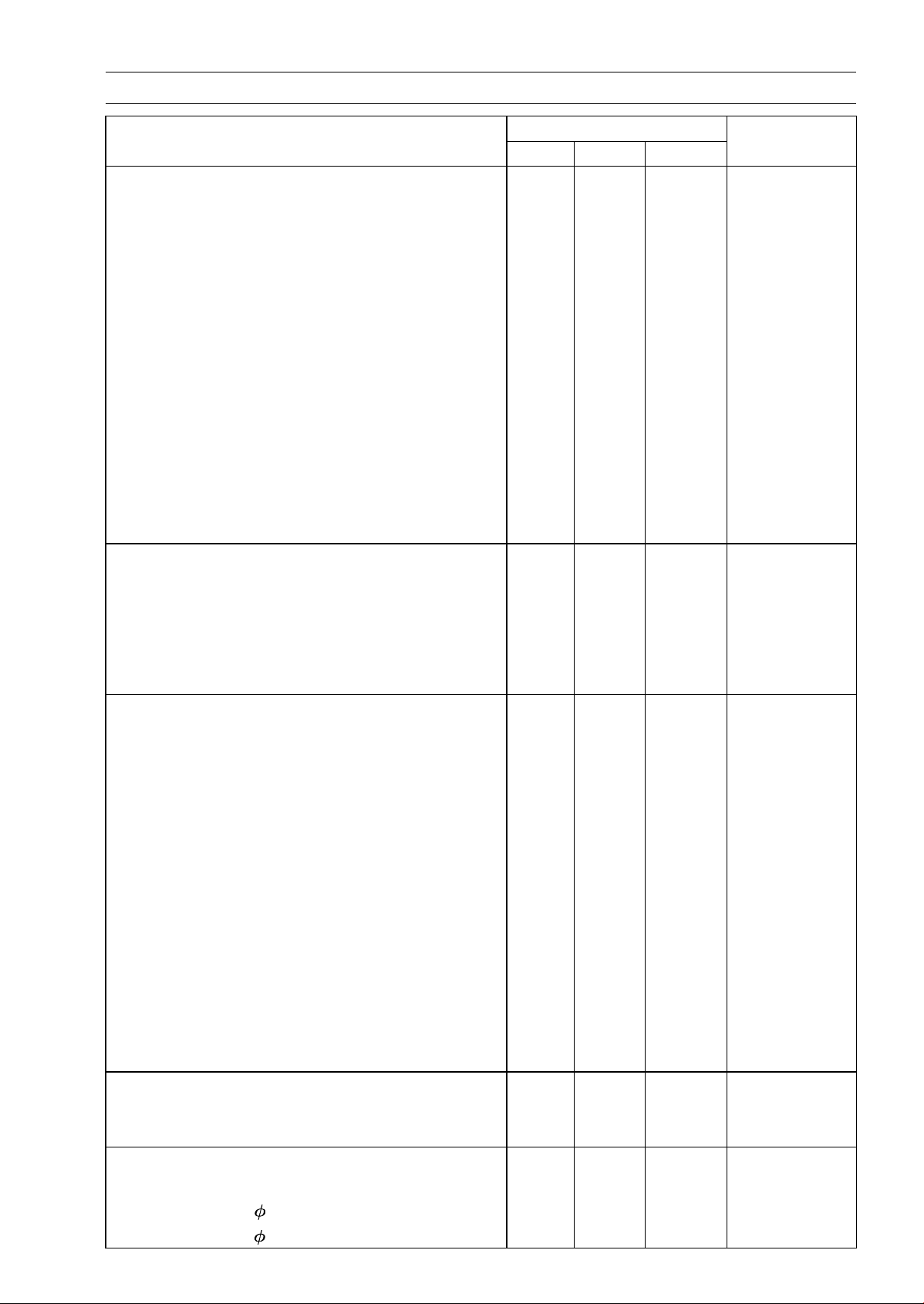
Torque and Locking Agent
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-7
Fastener
Chain Tensioner Mounting Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Camshaft Cap Bolts 12 1.2 106 in·lb S
Camshaft Cap Bolts 12 1.2 106 in·lb S
Cylinder Head Bolt (M6) 12 1.2 106 in·lb MO, S
Cylinder Head Bolts (M8) 24.5 2.5 18 MO, S
Water Passage Plugs 20 2.0 15 L
Carburetor Holder Clamp Screws 2.0 0.2 18 in·lb
Water Drain Bolt 5.9 0.6 52 in·lb
Muffler Body Rear Cover Bolts
Muffler Body Mounting Bolt 30 3.1 22
Muffler Body Clamp Bolt 17 1.7 13
Muffler Cover Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Muffler Cover Clamp Screw 6.9 0.70 61 in·lb
Exhaust Pipe Mounting Bolt 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Exhaust Pipe Holder Nuts 12 1.2 104 in·lb
Clutch
Clutch Lever Holder Clamp Bolts 8.8 0.9 78 in·lb
Clutch Spring Bolts 8.8 0.9 78 in·lb
Clutch Hub Nut
Oil Filler Plug
Clutch Cover Bolts
Engine Lubrication System
Oil Hose Banjo Bolts 19.6 2.0 14.5
Oil Pressure Relief Valve 15 1.5 11 L
Crankcase Oil Passage Plug 15 1.5 11
Oil Passage Plugs for Oil Pump 20 2.0 15 L
Oil Pipe Banjo Bolts 12 1.2 104 in·lb
Oil Drain Bolt 19.6 2.0 14.5
Oil Pressure Switch 15 1.5 11 SS
Oil Pressure Switch Terminal Bolt 1.5 0.15 13 in·lb
Oil Filter Mounting Bolts
Oil Breather Mounting Bolts
Oil Pump Mounting Bolts
Oil Screen Cover Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Plug 19.6 2.0 14.5
Breather Bolt 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Engine Removal/Installation
Engine Mounting Bracket Bolts and Nuts 64 6.5 47
Engine Mounting Nuts 64 6.5 47
Crankshaft/Transmission
Oil Breather Mounting Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb L
Crankcase Bolts 6 12 1.2 104 in·lb
Crankcase Bolts 8 (L = 90)
N·m kgf·m ft·lb
9.8 1.0 87 in·lb L
132 13.5 97.4
– – – Hand-Tighten
9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
19.6 2.0 14.5
9.8 1.0 87 in·lb L
9.8 1.0 87 in·lb L
24 2.4 18
Torque
Remarks
MO, S
Page 30
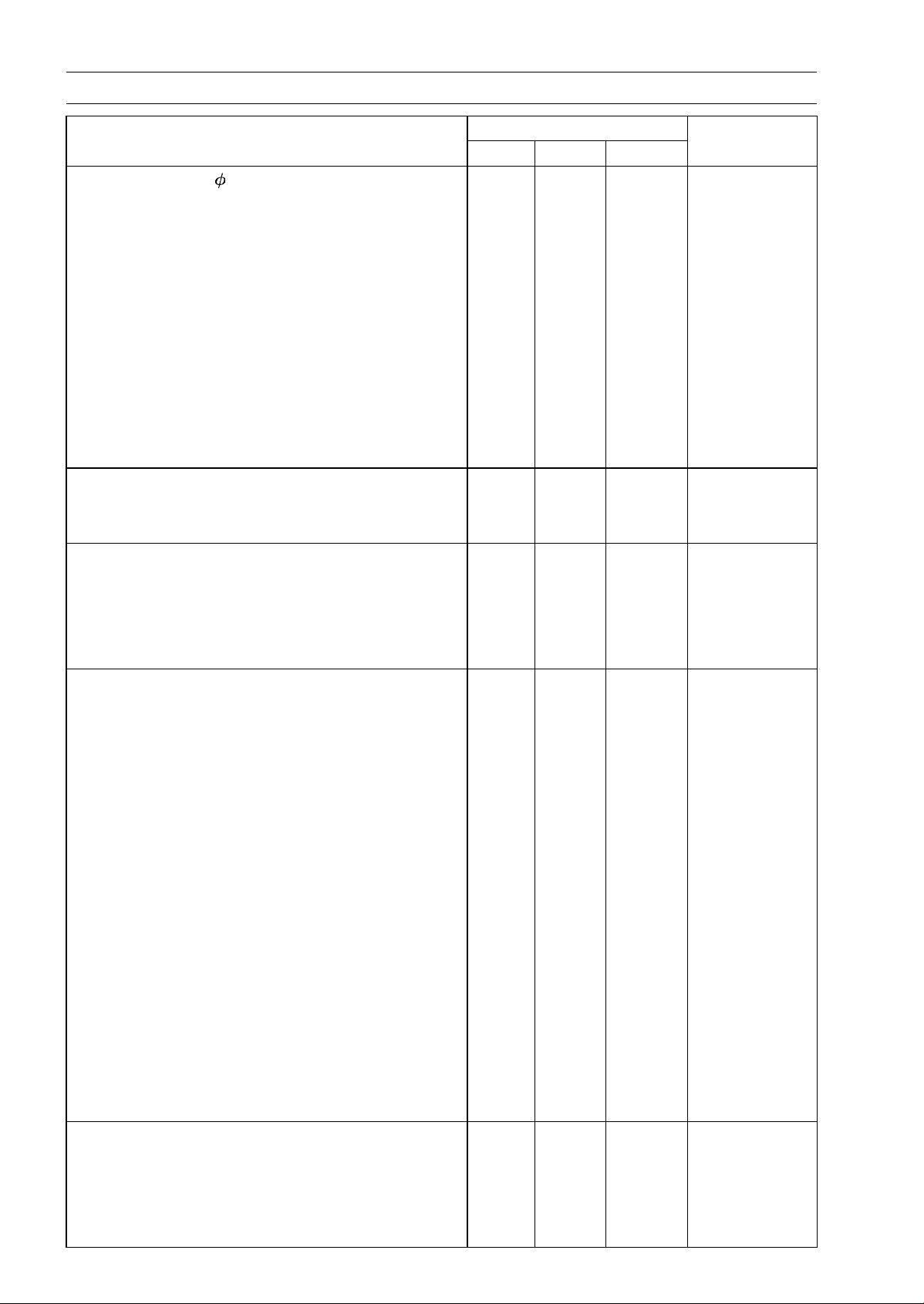
2-8 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Torque and Locking Agent
Fastener
Crankcase Bolts 8(L=73) 19 1.9 14 MO, S
Starter Motor Clutch Bolts
Connecting Rod Big End Cap Nuts
Shift Drum Bearing Hol
Shift Drum Pin Plate Bolt 9.0 0.9 80 in·lb L
Neutral Switch 15 1.5 11
External Shift Mechanism Return Spring Pin 19.6 2.0 14.5 L
Shift Drum Positioning Bolt 24.5 2.5 18
Shift Lever Link Bolt 12 1.2 104 in·lb
Front Tie-Rod Locknut (Left-Hand Threads) 7.0 0.7 62 in·lb
Rear Tie-Rod Locknut (Right-Hand Threads) 7.0 0.7 62 in·lb
Shift Pedal Mounting Bolt 25 2.5 18
Wheels/Tires
Front Axle Nut 88 9.0 65
Rear Axle Nut 98 10.0 72
Final Drive
Engine Sprocket Cover Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Engine Sprocket Nut 127 13 94 MO
Rear Sprocket Nuts 59 6.0 44
Rear Sprocket Studs
Brakes
Brake Lever Pivot
Bleed Valve 5.5 0.55 49 in·lb
Front Master Cylinder Clamp Bolts 8.8 0.9 78 in·lb S
Brake Disc Mounting Bolts 27 2.8 20 L
Brake Hose Banjo Bolts 25 2.5 18
Front Caliper Mounting Bolts
Front Brake Ligh
Brake Lever Pivot Bolt 1.0 0.1 9in·lb
Front Reservoir Cap Screws 1.5 0.15 13 in·lb
Reservoir Mounting Bolt 6.9 0.7 61 in·lb
Bleed Valve 5.5 0.55 49 in·lb
Brake Pedal Pivot Bolt 8.8 0.9 78 in·lb L
Push Rod Locknut 18 1.8 13
Brake Disc Mounting Bolts 27 2.8 20 L
Brake Hose Banjo Bolts 25 2.5 18
Rear Master Cylinder Mounting Bolts 25 2.5 18
Rear Caliper Mounting Bolts 25 2.5 18
Suspension
Front Fork Clamp Bolts (Upper) 21 2.1 15
Front Fork Top Plugs 23 2.3 16.5
Front Fork Clamp Bolts (Lower) 30 3.1 22
Front Fork Bottom Allen Bolts 20 2.0 15 L
tSwitchScrew
der Bolt
Bolt Locknut
N·m kgf·m ft·lb
34.3 3.5 25 L
27.5 2.8 20
12 1.2 104 in·lb L
– – – L
5.9 0.6 52 in·lb
25 2.5 18
1.0 0.1 9in·lb
Torque
Remarks
MO
Page 31

Torque and Locking Agent
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-9
Fastener
Rocker Arm Pivot Nut 59 6.0 44
Tie-Rod Nuts 59 6.0 44
Rear Shock Absorber Mounting Nuts 59 6.0 44
Swingarm Pivot Nut 98 10.0 72
Steering
Steering Stem Nut 4.9 0.5 43 in·lb
Handlebar Holder Mounting Bolts 25 2.5 18
Steering Stem Head Bolt 44 4.5 32
Front Fork Clamp Bolts (Upper) 20 2.0 15
Front Fork Clamp Bolts (Lower) 30 3.1 22
Frame
Sidestand Nut 44 4.5 32
Front Footpeg Bracket Mounting Bolts 25 2.5 18
Rear Footpeg Bracket Mounting Bolts 25 2.5 18
Sidestand Switch Bolt 8.8 0.90 78 in·lb L
Windshield Mounting Screws 0.42 0.043 3.7 in·lb
Electrical System
Tail/Brake Light Mounting Bolts 5.9 0.6 52 in·lb
Plugs on Alternator Cover
Alternator Cover Bolts
Alternator Rotor Bolt 68.6 7.0 51
Alternator Stator Bolts 12 1.2 104 in·lb
Regulator/Rectifier Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Starter Motor Clutch Bolts 34.3 3.5 25 L
Crankshaft Sensor Screws
Ignition Coil Bolts
Spark Plugs
Starter Motor Terminal Locknut 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Starter Motor Assembly Bolts 3.5 0.36 31 in·lb
Starter Motor Mounting Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
Starter Relay Terminal Nut 5.0 0.5 44 in·lb
Oil Pressure Switch 15 1.5 11 SS
Neutral Switch 15 1.5 11
N·m kgf·m ft·lb
– – – Hand-Tighten
9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
3.0 0.30 27 in·lb
– – – see text
13 1.3 11 5 i n · lb
Torque
Remarks
Page 32

2-10 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Torque and Locking Agent
The table below, relating tightening torque to thread diameter, lists the basic torque for the bolts and
nuts. Use this table for only the bolts and nuts which do not require a specific torque value. All of the
values are for use with dry solvent-cleaned threads.
Basic Torque for General Fasteners
Threads Torque
dia. (mm)
5 3.4 ∼ 4.9 0.35 ∼ 0.50 30 ∼ 43 in·lb
6 5.9 ∼ 7.8 0.60 ∼ 0.80 52 ∼ 69 in·lb
8 14 ∼19 1.4 ∼1.9 10.0 ∼ 13.5
10 25 ∼ 34 2.6 ∼ 3.5 19.0 ∼ 25
12 44 ∼ 61 4.5 ∼ 6.2 33 ∼ 45
14 73 ∼ 98 7.4 ∼ 10.0 54 ∼ 72
16 115 ∼ 155 11.5 ∼ 16.0 83 ∼ 11 5
18 165 ∼ 225 17.0 ∼ 23.0 125 ∼ 165
20 225 ∼ 325 23 ∼ 33 165 ∼ 240
N·m
kgf·m ft·lb
Page 33

PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-11
Specifications
Item Standard Service Limit
Fuel System
Throttle Grip Free Play 2 ∼ 3 mm (0.08 ∼ 0.12 in.) –––
Idle Speed 1 300 ±50 r/min (rpm) –––
Carburetor Synchronization Vacuum
Air Cleaner Element Polyurethane foam –––
Cooling System
Coolant:
Type (Recommended) Permanent type antifreeze –––
Color Green –––
Mixed Ratio Soft water 50%, coolant 50% –––
Freezing Point –35°C (–31°F) –––
Capacity 1.5L(1.59USqt)
Engine Top End
Valve Clearance:
Inlet
Exhaust
Clutch
Clutch Lever Free Play 2 ∼ 3 mm (0.08 ∼ 0.12 in.) –––
Engine Lubrication System
Engine Oil:
Grade API SE, SF or SG
Viscosity SAE 10W-40 –––
Capacity 1.3 L (1.4 US qt) (when filter is not removed)
Level Between upper and lower level lines (Wait 2 ∼
Wheels/Tires
Tread Depth:
Front:
BRIDGESTONE 4.6 mm (0.181 in.) 1 mm (0.04 in.)
DUNLOP 4.5 mm (0.177 in.)
Rear:
BRIDGESTONE 7.0 mm (0.276 in.)
DUNLOP 7.4 mm (0.291 in.)
Air pressure: (when Cold)
Front Up to 170 kg (375 lb) load: 200 kPa (2.0
Rear
Less than 2.7 kpa (2 cmHg) difference
between two carburetors
0.15 ∼ 0.24 mm (0.0059 ∼ 0.0094 in.)
0.22 ∼ 0.29 mm (0.0087 ∼ 0.0114 in.)
API SH, SJ or SL with JASO MA
1.6 L (1.7 US qt) (when filter is removed)
3 minutes after idling or running)
kgf/cm², 28 psi)
Up to 170 kg (375 lb) load: 225 kPa (2.25
kgf/cm², 32 psi)
–––
–––
–––
–––
–––
–––
–––
2 mm (0.08 in.) up to
130 km/h (80 mph)
3 mm (0.12 in.) over
130 km/h (80 mph)
–––
–––
Final Drive
Drive Chain Slack 20 ∼ 30 mm (0.8 ∼ 1.2 in.) –––
Page 34

2-12 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Specifications
Item Standard Service Limit
Brakes
Brake Fluid:
Grade DOT4 –––
Brake Pad Lining
Thickness:
Brake Light Timing: –––
Front Pulled ON
Rear ON after 10 mm (0.39 in.) of pedal travel
Electrical System
Type
4.5 mm (0.18 in.) 1 mm (0.04 in.)
CR8E, U24ESR-N
–––
Page 35

Special Tools
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-13
Steering Stem Nut Wrench:
57001-1100
Vacuum Gauge KEK-55-5:
57001-1369
Filler Cap Driver:
57001-1454
Page 36

2-14 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Fuel System
Air Cleaner Element Cleaning
Remove:
•
Right Side Cover (see Side Cover Removal in the Frame
chapter)
Air Cleaner Cap Bolts [A]
Air Cleaner Cap [B]
Pull out the air cleaner element [A].
•
Separate the plastic holders [A].
•
WARNING
If dirt or dust is allowed to pass through into the carburetors, the butterfly valves may become stuck,
possibly causing an accident.
CAUTION
If dirt gets through into the engine, excessive engine wear and possibly engine damage will occur.
Page 37

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
WARNING
Clean the element in a well-ventilated area, and
make sure that there are no sparks or flame anywhere near the working area.
Because of the danger of highly flammable liquids,
do not use gasoline or a low-flash point solvent to
clean the element.
Clean the element [A] in a bath of high-flash point solvent,
•
and then dry it with compressed air or by shaking it.
After cleaning, saturate a clean, lint-free towel with SE,
•
SF, or SG class SAE 30 oil and apply the oil to the element
by tapping the element outside with the towel.
Visually check the element for tears or breaks.
•
If the element has any tears or breaks, replace the ele-
•
ment.
Air Cleaner Element Installation
Install the removed parts in reverse of removal.
•
Torque the air cleaner cap bolts.
•
Torque - Air Cleaner Cap Bolts: 2.5 N·m (0.25 kgf·m, 22
in·lb)
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-15
Throttle Control System Inspection
Check that the throttle grip moves smoothly from full open
•
to close [A], and the throttle closes quickly and completely
by the return spring in all steering positions.
If the throttle grip doesn’t return properly, check the throttle cable routing, grip free play, and cable damage. Then
lubricate the throttle cable.
Check the throttle grip free play [A].
•
If the free play is i ncorrect, adjust the throttle cable.
Throttle Grip Free Play
Standard: 2 ∼ 3 mm (0.08 ∼ 0.12 in.)
Page 38

2-16 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Loosen the locknut [A], and screw accelerator cable ad-
•
juster [B] in completely so as to give the throttle grip plenty
of play.
Turn the accelerator cable adjuster until 2 ∼ 3 mm (0.08 ∼
•
0.12 in.) of throttle grip play is obtained.
Tighten the locknut.
•
If the throttle cables can not be adjusted by using the cable adjuster at the upper end of the throttle cable, use the
cable adjusters at the lower ends of the throttle cables.
Remove:
•
Side Cover (see Side Cover Removal in the Frame chapter)
Right Lower Fairing (see Lower Fairing Removal in the
Frame chapter)
To make service easy, unscrew the reserver tank bolts
•
and remove the reserver tank with hoses
Turn out both upper nuts [A] and turn in both lower nuts [B]
•
as far as they will go so as to give the throttle grip plenty
of play.
With the throttle grip completely closed, turn out the lower
•
nut and turn in the upper nut of the decelerator cable [C]
until the inner cable just becomes tight.
Turn out the lower nut and turn in the upper nut of the
•
accelerator cable [D] until the correct free play is obtained.
Check that the throttle linkage lever [A] stops against the
•
idle adjusting screw [B] with the throttle grip closed.
Page 39

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Choke Operation Inspection
Remove:
•
Front Seat (see Front Seat Removal in the Frame chapter)
Fuel Tank (see Fuel Tank Removal)
Side Covers (see Side Cover Removal in the Frame
chapter)
Lower Fairings (see Lower Fairing Removal in the Frame
chapter)
Fuel Tank (see Fuel Tank Removal)
Push the choke lever [A] back all the way to its released
•
position.
Check choke cable free play [B].
•
Determine the amount of choke cable play at the choke
○
lever.
If the free play is incorrect, adjust the choke cable.
Choke Cable Free Play
Standard: 2 ∼ 3 mm (0.08 ∼ 0.12 in.)
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-17
Push the choke lever back all the way to its released po-
•
sition.
Pull the choke lever until the starter plunger lever [A] at the
•
carburetor touches the starter plunger [B]; the amount of
choke lever travel is the amount of choke cable play.
Loosen the locknut [A], and turn the adjuster [B] until the
•
cable has the proper amount of free play.
Tighten the locknut securely.
•
Engine Vacuum Synchronization Inspection
Situate the motorcycle using the center stand so that it is
•
perpendicular to the ground.
Remove the fuel tank, and connect the sub-fuel tank to
•
supply the fuel.
Remove the right lower fairing.
•
Warm up the engine.
•
Check the idle speed and adjust if necessary.
•
Pull the vacuum hoses off, and attach vacuum gauge [A]
•
to the vacuum hose fittings on the carburetors.
Special Tool - Vacuum Gauge KEK-55-5: 57001-1369
Page 40

2-18 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Start the engine and let it idle to measure the carburetor
•
intake vacuum.
If the intake vacuum difference between the two cylinders
exceeds the limit, adjust the synchronization.
Engine Vacuum Synchronization
Less than 2.7 kPa (2 cmHg) difference between both
cylinders
Turn the adjusting screw [A] to synchronize the carbure-
•
tor.
If the carburetor synchronization cannot be obtained by
using the adjusting screw, check for dirt or blockage, and
then check the pilot screw settings.
Check the Carburetor Synchronization again.
•
NOTE
Do not turn the pilot screws carelessly during carburetor
○
synchronization. You may cause poor running at low
engine speed.
Idle Speed Inspection
Start the engine and warm it up thoroughly.
•
With the engine idling, turn the handlebar to both sides
•
[A].
If handlebar movement changes the idle speed, the
throttle cables may be improperly adjusted or incorrectly
routed or damaged. Be sure to correct any of these
conditions before riding ( see Throttle Control System
Inspection or Cable, Wire, and Hose Routing section in
the Appendix chapter).
WARNING
Operation with improperly adjusted, incorrectly
routed or damaged cables could result in an unsafe
riding condition.
Check idle speed.
•
If the idle speed is out of the specified range, adjust it.
Idle Speed
Standard: 1 300 ±50 r/min (rpm)
Idle Speed Adjustment
Start the engine and warm it up thoroughly.
•
Turn the adjusting screw [A] until the idle speed is correct.
•
Open and close the throttle a few times to make sure that
○
the idle speed is within the specified range. Readjust if
necessary.
Page 41
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
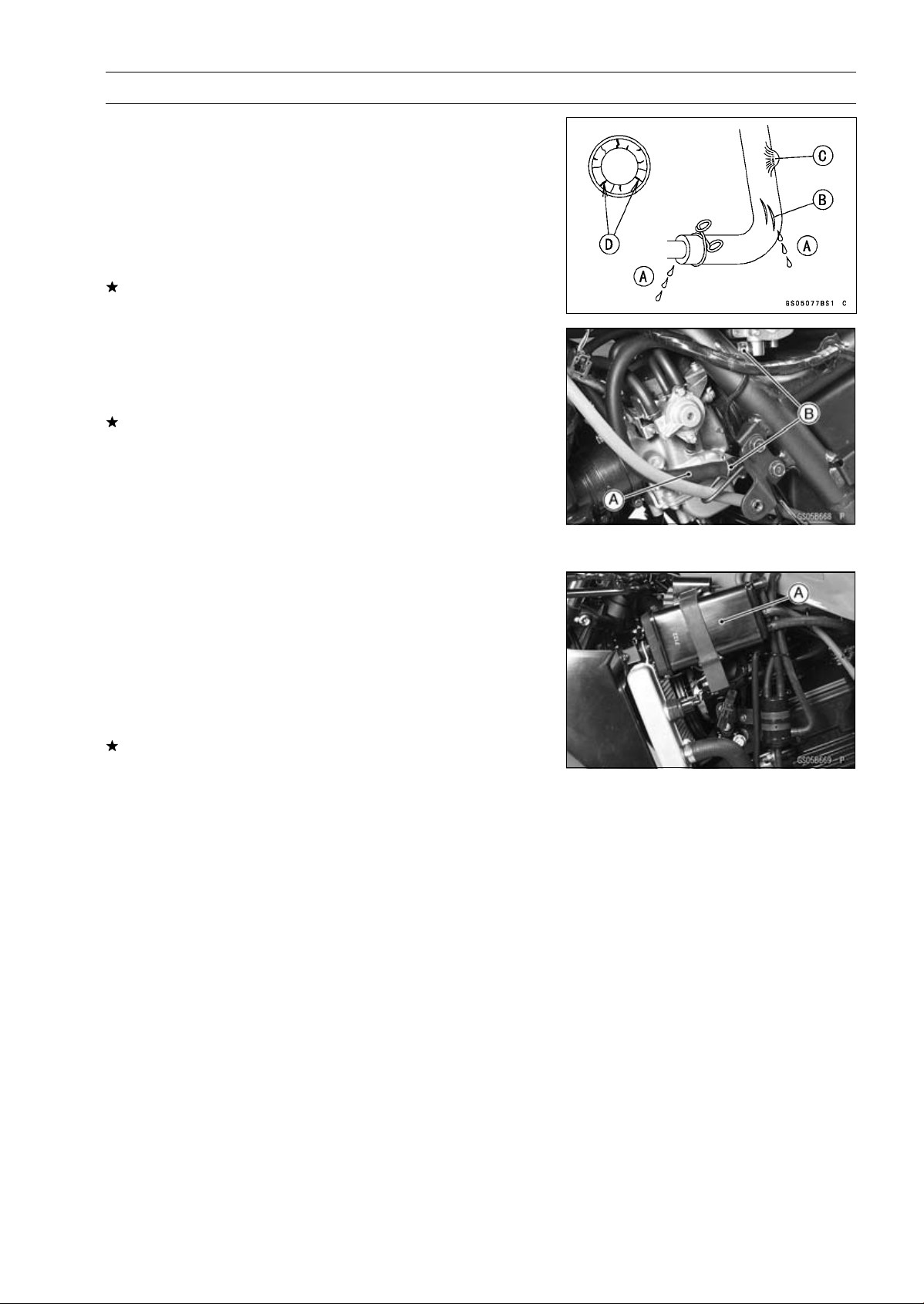
Fuel Hose Inspection (fuel leak, damage, installation condition)
The fuel hose is designed to be used throughout the mo-
○
torcycle’s life without any maintenance. However, if the
motorcycle is not properly handled, the high pressure inside the fuel line can cause fuel to leak [A] or the hose to
burst. Remove the fuel tank (see Fuel Tank Removal in
the Fuel System chapter) and check the fuel hose.
Replace the fuel hose if any fraying, cracks [B], bulges [C]
or ozone cracks [D] are noticed.
Check that the hose [A] are securely connected and
•
clamps [B] are tightened correctly.
Check that the hoses are routed according to Cable, Wire,
•
and Hose Routing section in the Appendix chapter.
Replace the hose if it has been sharply bent or kinked.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-19
Evaporative Emission Control System (California Model)
Evaporative Emission Control System Inspection
Inspect the canister as follows.
•
Remove:
○
Left Lower Fairing (see Lower Fairing Removal in the
Frame chapter)
Remove the canister [A], and disconnect the hoses from
○
the canister.
Visually inspect the canister for cracks or other damage.
○
If the canister has any cracks or bad damage, replace it
with a new one.
NOTE
The canister is designed to work well through the motor-
○
cycle’s life without any maintenance if it is used under
normal conditions.
Page 42

2-20 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Check the liquid/vapor separator as follows.
•
Remove:
○
Left Lower Fairing (see Lower Fairing Removal in the
Frame chapter)
Disconnect the hoses from the separator, and remove the
○
separator [B] from the motorcycle left side.
Visually inspect the separator for cracks and other dam-
○
age.
If the separator has any cracks or damage, replace it with
a new one.
To prevent the gasoline from flowing into or out of the
○
canister, hold the separator perpendicular to the ground.
Check the hoses of the evaporative emission control sys-
•
tem as follows.
Check that the hoses are s ecurely connected and clips
○
are in position.
Replace any kinked, deteriorated or damaged hoses.
○
Route the hoses according to Cable, Wire, and Hose
○
Routing section in the Appendix chapter.
When installing the hoses, avoid sharp bending, kinking,
○
flattening or twisting, and route the hoses with a minimum
of bending so that the emission flow will not be obstructed.
Cooling System
Coolant Level Inspection
NOTE
Check the level when the engine is cold (room or ambi-
○
ent temperature).
Check the coolant level in the reserve tank [A] with the
•
motorcycle held perpendicular (Do not use the sidestand).
If the coolant level is lower than the “L” level line [B], remove the right center fairing (see Center Fairing Removal
in the Frame chapter) and unscrew the reserve tank cap,
and add coolant to the “F” level line [C].
“L”: low
“F”: full
CAUTION
For refilling, add the specified mixture of coolant
and soft water. Adding water alone dilutes the
coolant and degrades its anticorrosion properties.
The diluted coolant can attack the aluminum engine parts. In an emergency, soft water alone can
be added. But the diluted coolant must be returned
to the correct mixture ratio within a few days.
If coolant must be added often or the reservoir tank
has run completely dry, there is probably leakage in
the cooling system. Check the system for leaks.
Coolant ruins painted surfaces. Immediately wash
away any coolant that spills on the frame, engine,
wheels or other painted parts.
Page 43

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Radiator Hose Damage and Installation Condition Inspection
The high pressure inside the radiator hose and pipe can
○
cause coolant to leak [A] or the hose to burst if the line is
not properly maintained.
Visually inspect the hoses for signs of deterioration.
•
Squeeze the hoses. A hose should not be hard and
brittle, nor should it be soft or swollen.
Replace the hose if any fraying, cracks [B] or bulges [C]
are noticed.
Check that the hoses are securely connected and clamps
•
are tightened correctly.
Torque - Radiator Hose Clamp Screws: 1.5 N·m (0.15 kgf·m,
13 in·lb)
Coolant Filter Cleaning (Australia Model)
Remove the fuel tank (see Fuel Tank Removal in the Fuel
•
System chapter).
Drain the coolant (see Coolant Change).
•
Remove the filter [A] from the water hoses [B] of carbure-
•
tor system.
Blow off dirt and sediment on the filter with compressed
•
air.
Filter Body [C]
Water Pipe [D]
Coolant Valve Assy [E]
Water Pump [F]
Carburetor [G]
Damper [H]
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-21
Air Suction System
Air Suction System Damage Inspection
Pull the v acuum switch valve hose [A] out of the air
•
cleaner.
Page 44
2-22 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Start the engine and run it at idle speed.
•
Plug [A] the vacuum switch valve hose end with your fin-
•
ger and feel vacuum pulsing in the hose.
If there is no vacuum pulsation, check the hose line for
leak. If there is no leak, check the vacuum switch valve
or air suction valve (see Engine Top End chapter).
Engine Top End
Valve Clearance Inspection
NOTE
Valve clearance must be checked and adjusted when
○
the engine is cold (room temperature).
Remove:
•
Cylinder Head Cover (see Cylinder Head Cover Removal in the Engine Top End chapter)
Left Lower Fairing (see Lower Fairing Removal in the
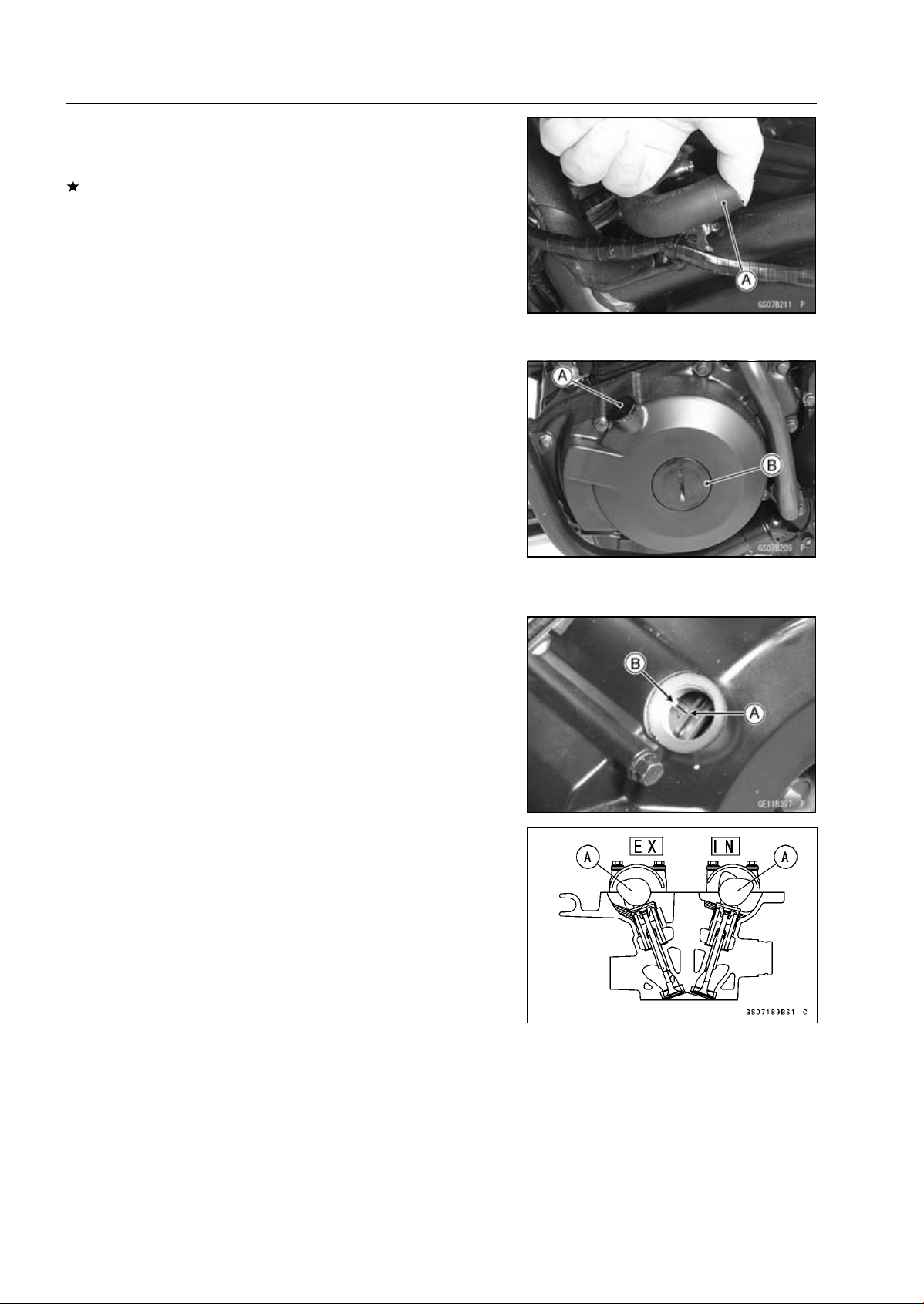
Frame chapter)
Unscrew the two plugs [A], [B] on the alternator cover.
•
Special Tool - Filler Cap Driver: 57001-1454
Check the valve clearance when the pistons are at TDC.
•
The pistons are numbered beginning with the engine left
○
side.
Using a wrench on the crankshaft rotation bolt, turn the
•
crankshaft clockwise until the "2/T" [A] mark on the timing
rotor is aligned with the projection [B] in the inspection
window on the alternator cover.
Measure the valve clearance of the valves for which the
○
cam [A] are turned away from each other.
Page 45

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Using the thickness gauge [A], measure the valve clear-
•
ance between cam and valve lifter.
Valve Cleara nce
Standard:
Exhaust
Inlet
Each piston has two inlet and two exhaust valves. Mea-
○
sure these two inlet or exhaust valves at the same crankshaft position.
Valve Clearance Measuring Position
#1 Piston TDC at End of Compression Stroke →
Inlet valve clearances of #1 piston, and
Exhaust valve clearances of #1 piston
0.22 ∼ 0.29 mm (0.0087 ∼ 0.0114 in.)
0.15 ∼ 0.24 mm (0.0059 ∼ 0.0094 in.)
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-23
NOTE
Check the valve clearance using this method only.
○
Checking the clearance at any other cam position may
result in improper valve clearance.
Valve Clearance Measuring Position
#2 Piston TDC at End of Compression Stroke →
Inlet valve clearances of #2 piston, and
Exhaust valve clearances of #2 piston
If the valve clearance is not with in the specified range,
first record the clearance, and adjust it.
Valve Clearance Adjustment
To change the valve clearance, remove the camshaft
•
chain tensioner, camshafts and valve lifters. Replace the
shim with one of a different thickness.
NOTE
Mark and record the locations of the valve lifters and
○
shims so that they can be reinstalled in their original
positions.
Page 46

2-24 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Clean the shim to remove any dust or oil.
•
Measure the thickness of the removed shim [A].
•
Select a new shim thickness calculation as follows.
•
a+b–c=d
[a] Present Shim Thickness
[b] Measured Valve Clearance
[c] Specified Valve Clearance (Mean Value = 0.255 mm
(Exhaust), 0.195 mm (Inlet))
[d] Replace Shim Thickness
Example (Inlet):
2.90 + 0.45 – 0.195 = 3.155 mm
Exchange the shim for the 3.175 size shim.
○
CAUTION
Don’t use the shims for another models. This could
cause wear of the valve stem end, and valve stem
damage.
Page 47

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Adjustment Shims
Thickness Part Number Mark
2.50 92180-1014 50
2.55 92180-1016
2.60 92180-1018 60
2.65 92180-1020 65
2.675 92180-1174 68
2.70 92180-1022 70
2.725 92180-1175 73
2.75 92180-1024
2.775 92180-1176 78
2.80 92180-1026 80
2.825 92180-1177 83
2.85 92180-1028 85
2.875 92180-1178 88
2.90 92180-1030 90
2.925 92180-1179 93
2.95 92180-1032 95
2.975 92180-1180 98
3.00 92180-1034 00
3.025 92180-1181 03
3.05 92180-1036 05
3.075 92180-1182 08
3.10 92180-1038 10
3.125 92180-1183 13
3.15 92180-1040 15
3.175 92180-1184 18
3.20 92180-1042 20
3.25 92180-1044 25
3.30 92180-1046 30
3.35 92180-1048 35
3.40 92180-1050 40
3.45 92180-1052 45
3.50 92180-1054 50
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-25
55
75
Page 48

2-26 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Clutch
Clutch Operation Inspection
Pull the clutch lever just enough to take up the free play
•
[A].
Measure the gap between the lever and the lever holder.
•
If the gap is too wide, the clutch may not release fully. If
the gap is too narrow, the clutch may not engage fully. In
either case, adjust it.
Clutch Lever Free Play
Standard: 2 ∼ 3 mm (0.08 ∼ 0.12 in.)
WARNING
To avoid a serious burn, never touch the engine or
exhaust pipe during clutch adjustment.
Turn the adjuster [B] so that 5 ∼ 6 mm (0.20 ∼ 0.24 in.) [A]
•
of threads are visible.
Remove the right lower fairing (see Lower Fairing Re-
•
moval in the Frame chapter).
Slide the dust cover [A] from the clutch cable lower end
•
out of place.
Loosen both adjusting nuts [B] at the clutch cover as far
•
as they will go.
Pull the clutch outer cable [C] tight and tighten the adjust-
•
ing nuts against the bracket [D].
Slip the rubber dust cover back onto place.
•
Turn the adjuster at the clutch lever until the free play is
•
correct.
WARNING
Be sure that the outer cable end at the clutch lever
is fully seated in the adjuster at the clutch lever, or
it could slip into place later, creating enough cable
play to prevent clutch disengagement.
After the adjustment, start the engine and check that the
•
clutch does not slip and that it releases properly.
Page 49

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Wheels/Tires
Air Pressure Inspection
Remove the air valve cap.
•
Measure the tire air pressure with an air pressure gauge
•
[A] when the tires are cold (that is, when the motorcycle
has not been ridden more than a mile during the past 3
hours).
Install the air valve cap.
•
Adjust the tire air pressure according to the specifications
if necessary.
Air P ressure (when Cold)
Front:
Rear:
Wheel/Tire Damage Inspection
Remove any imbedded stones [A] or other foreign parti-
•
cles [B] from tread.
Visually inspect the tire for cracks and cuts, and replace
•
the tire if necessary. Swelling or high spots indicate internal damage, requiring tire replacement.
Visually inspect the wheel for cracks, cuts and dents dam-
•
age.
If any damage is found, replace the wheel if necessary.
Upto170kg(375lb)
200kPa(2.00kgf/cm²,28psi)
Upto170kg(375lb)
225kPa(2.25kgf/cm²,32psi)
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-27
Tire Tread Wear, Abnormal Wear Inspection
As the tire tread wears down, the tire becomes more susceptible to puncture and failure. An accepted estimate is
that 90% of all tire failures occur during the last 10% of tread
life (90% worn). So it is false economy and unsafe to use
the tires until they are bald.
Measure the tread depth at the center of the tread with a
•
depth gauge [A]. Since the tire may wear unevenly, take
measurement at several places.
If any measurement is less than the service limit, replace
the tire (see Tire Removal/Installation in the Wheels/Tires
chapter).
Page 50

2-28 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Tread Depth
Standard:
Front:
BRIDGESTONE 4.6 mm (0.181 in.)
DUNLOP 4.5 mm (0.177 in.)
Rear:
BRIDGESTONE 7.0 mm (0.276 in.)
DUNLOP 7.4 mm (0.291 in.)
Service Limit:
Front
Rear
To ensure safe handling and stability, use only the
recommended standard tires for replacement, inflated to the standard pressure.
1 mm (0.04 in.)
2 mm (0.08 in.)
(Upto130km/h(80mph))
3 mm (0.12 in.)
(Over 130 km/h (80 mph))
WARNING
NOTE
Most countries may have their own regulations a mini-
○
mum tire tread depth: be sure to follow them.
Check and balance the wheel when a tire is replaced
○
with a new one.
Wheel Bearing Damag e Inspection
Raise the front wheel off the ground with jack (see Front
•
Wheel Removal in the Wheels/Tires chapter).
Turn the handlebar all the way to the right or left.
•
Inspect the roughness of the front wheel bearing by push-
•
ing and pulling [A] the wheel.
Spin [B] the front wheel lightly, and check for smoothly
•
turn, roughness, binding or noise.
If roughness, binding or noise is found, remove the front
wheel and inspect the wheel bearing (see Front Wheel
Removal, Hub Bearing Inspection in the Wheels/Tires
chapter).
Raise the rear wheel off the ground with stand (see Rear
•
Wheel Removal in the Wheels/Tires chapter).
Inspect the roughness of the rear wheel bearing by push-
•
ing and pulling [A] the wheel.
Spin [B] the rear wheel lightly, and check for smoothly
•
turn, roughness, binding or noise.
If roughness, binding or noise is found, remove the rear
wheel and inspect the wheel bearing (see Rear Wheel Removal, Hub Bearing Inspection in the Wheels/Tires chapter) and coupling (see Coupling Bearing Inspection in the
Final Drive chapter).
Page 51

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Drive Train
Drive Chain Lubrication Condition Inspection
If a special lubricant is not available, a heavy oil such as
•
SAE 90 is preferred to a lighter oil because it will stay on
the chain longer and provide better lubrication.
If the c hain appears especially dirty, clean it before lubri-
•
cation.
CAUTION
The O-rings between the side plates seal in the lu-
bricant between the pin and the bushing. To avoid
damaging the O-rings and resultant loss of lubri-
cant, observe the following rules.
Use only kerosene or diesel oil for cleaning an O
-ring drive chain. Any other cleaning solution such
as gasoline or trichloroethylene will cause deterio-
ration and swelling of the O-ring. Immediately blow
the chain dry with compressed air after cleaning.
Complete cleaning and drying the chain within 10
minutes.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-29
Apply oil to the sides of the rollers so that oil will penetrate
•
to the rollers and bushings. Apply the oil to the O-rings so
that the O-rings will be coated with oil.
Wipe off any excess oil.
•
Oil Applied Areas [A]
O-rings [B]
Drive Chain Slack Inspection
NOTE
Check the slack with the motorcycle setting on its side-
○
stand.
Clean the chain if it is dirty, and lubricate it if it appears
○
dry.
Check the wheel alignment (see Wheel Alignment Inspec-
•
tion).
Rotate the rear wheel to find the position where the chain
•
is tightest.
Measure the vertical movement (chain slack) [A] midway
•
between the sprockets.
If the chain slack exceeds the standard, adjust it.
Chain Slack
Standard: 20 ∼ 30 mm (0.8 ∼ 1.2 in.)
Page 52

2-30 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Drive Chain Slack Adjustment
Remove the cotter pin [A], and loosen the axle nut [B].
•
Loosen the both chain adjuster locknuts [C].
•
If the chain is too loose, turn in the left and right chain
adjuster nuts [D] evenly.
If the chain is too tight, turn out the left and right chain
adjuster nuts evenly, and kick the wheel forward.
Turn both chain adjuster nuts evenly until the drive chain
•
has the correct amount of slack. To keep the chain
and wheel properly aligned, the notch [E] on the left
wheel alignment indicator [F] should align with the same
swingarm mark or position [G] that the right indicator
notch aligns with.
WARNING
Misalignment of the wheel will result in abnormal
wear and may result in an unsafe riding condition.
Tighten both chain adjuster locknuts securely.
•
Tighten the axle nut.
•
Torque - Rear Axle Nut: 98 N·m (10.0 kgf·m, 72 ft·lb)
Turn the wheel, measure the chain slack again at the tight-
•
est position, and readjust if necessary.
Insert a new cotter pin [A].
•
NOTE
When inserting the cotter pin, if the slots in the nut do
○
not align with the cotter pin hole in the axle, tighten the
nut clockwise [B] up to next alignment.
It should be within 30°.
○
Loosen once and tighten again when the slot goes past
○
the nearest hole.
Bend the cotter pin [A] over the nut [B].
•
WARNING
If the rear axle nut is not securely tightened or the
cotter pin is not installed, an unsafe riding condition may result.
Page 53

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Wheel Alignment Inspection
Check that the notch [A] on the right wheel alignment indi-
•
cator [B] aligns with the same swingarm mark or position
[C] that the left alignment indicator notch aligns with.
If they do not, adjust the chain slack and align the wheel
alignment (see Drive Chain Slack Adjustment).
NOTE
Wheel alignment can be also checked using the
○
straightedge or string method.
WARNING
Misalignment of the wheel will result in abnormal
wear, and may result in an unsafe riding condition.
Drive Chain Wear Inspection
Remove:
•
Chain Cover (see Swingarm Removal in the Suspension
chapter)
Rotate the rear wheel to inspect the drive chain for dam-
•
aged rollers, and loose pins and links.
If there is any irregularity, replace the drive chain.
Lubricate the drive chain if it appears dry.
Stretch the chain taut by hanging a 98 N (10 kg, 20 lb)
•
weight [A] on the chain.
Measure the length of 20 links [B] on the straight part [C] of
•
the chain from the pin center of the 1st pin to the pin center
of the 21st pin. Since the chain may wear unevenly, take
measurements at several places.
If any measurements exceed the service limit, replace the
chain. Also, replace the front and rear sprockets when the
drive chain is replaced.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-31
Drive Chain 20-link Length
Standard: 317.5 ∼ 318.1 mm (12.50 ∼ 12.52 in.)
Service Limit: 323 mm (12.72 in.)
WARNING
If the drive chain wear exceeds the service limit, re-
place the chain or an unsafe riding condition may
result. A chain that breaks or jumps off the sprock-
ets could snag on the engine sprocket or lock the
rear wheel, severely damaging the motorcycle and
causing it to go out of control.
For safely, use only the standard chain. It is an end-
less type and should not be cut for installation.
Standard Chain
Make: ENUMA
Typ e :
Link: 106 links
EK520SR-O
2
Page 54

2-32 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Chain Guide Inspection
Remove:
•
Swingarm (see Swingarm Removal in the Suspension
chapter)
Visually inspect the chain guide [A].
•
Replace the chain guide if it shows any signs of abnormal
wear or damage.
Brake System
Brake Fluid Leak (Brake Hose and Pipe) Inspection
Apply the brake lever or pedal and inspect the brake fluid
•
leak from the brake hoses [A], fittings [B] and pipes [C].
If the brake fluid leaked from any position, inspect or replace the problem part.
Brake Hose and P ipe Damage and Installation Condition Inspection
Inspect the brake hoses, fittings and pipes for deteriora-
•
tion, cracks and signs of leakage.
The high pressure inside the brake line can cause fluid to
○
leak [A] or the hose to burst if the line is not properly maintained. Bend and twist the rubber hose while examining
it.
Replace the hose and pipe if any crack [B], bulge [C] or
leakage is noticed.
Tighten any brake hose banjo bolts and brake pipe joint
nuts.
Torque - Brake Hose Banjo B olts: 25 N·m (2.5 kgf·m, 18
ft·lb)
Inspect the brake hose routing.
•
If any brake hose routing is incorrect, route the brake hose
according to Cable, Wire, and Hose Routing section in the
Appendix chapter.
Brake Operation Inspection
Inspect the operation of the front and rear brake by run-
•
ning the vehicle on the dry road.
If the brake operation is insufficiency, inspect the brake
system.
WARNING
When inspecting by running the vehicle, note a
surrounding traffic situation enough in the place of
safety.
Page 55

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Brake Fluid Level Inspection
Check that the brake fluid level in the front brake reservoir
•
[A] is above the lower level line [B].
NOTE
Hold the reservoir horizontal by turning the handlebar
○
when checking brake fluid level.
If the fluid level is lower than the lower level line, fill the
reservoir to the upper level line [C] in the reservoir.
Check that the brake fluid level in the rear brake reservoir
•
[A] is above the lower level line [B].
If the fluid level is lower than the lower level line, fill the
reservoir to the upper level line [C].
WARNING
Change the brake fluid in the brake line completely
if the brake fluid must be refilled but the type and
brand of the brake fluid that is already in the reser-
voir are unidentified. After changing the fluid, use
only the same type and brand of fluid thereafter.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-33
Recommended Disc Brake Fluid
Grade: DOT4
Follow the procedure below to install the rear brake fluid
•
reservoir cap correctly.
First, tighten the rear brake fluid reservoir cap [B] clock-
○
wise [C] by hand until slight resistance is felt indicating
that the cap is seated on the reservoir body, then tighten
the cap an additional 1/6 turn [D] while holding the brake
fluid reservoir body [A].
Brake Pad Wear Inspection
Check the lining thickness [A] of the pads in each caliper.
•
If the lining thickness of either pad is less than the service
limit [B], replace both pads in the caliper as a set.
Pad Lining Thickness
Standard: 4.5 mm (0.18 in.)
Service Limit: 1 mm (0.04 in.)
Page 56

2-34 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Brake Light Switch Operation Inspection
Turn on the ignition switch.
•
The brake light [A] should go on when the brake lever is
•
applied or after the brake pedal is depressed about 10
mm (0.39 in.).
If it does not, adjust the brake light switch.
Disconnect the connector [A].
•
Turn the brake light switch to adjust the switch.
•
Connect the connector.
•
If it does not go on, inspect or replace the following items.
Battery (see Charging Condition Inspection in the Electrical System chapter)
Brake Light (see Tail/Brake Light Removal in the Electrical System chapter)
Main Fuse 30 A and Taillight Fuse 10 A (see Fuse Inspection in the Electrical System chapter)
Front Brake Light Switch [A] (see Switch Inspection in
the Electrical System chapter)
Rear Brake Light Switch (see Switch Inspection in the
Electrical System chapter)
Harness (see Wiring Inspection in the Electrical System
chapter)
Suspensions
Front Forks/Rear Shock Absorber Operation Inspection
Pump the forks down and up [A] 4 or 5 times, and inspect
•
the smooth stroke.
If the forks do not smoothly or noise is found, inspect the
fork oil level or fork clamps (see Front Fork Oil Change in
the Suspension chapter).
Page 57

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Pump the seat down and up [A] 4 or 5 times, and inspect
•
the smooth stroke.
If the shock absorber does not smoothly stroke or noise
is found, inspect the oil leak (see Rear Shock Absorber
Oil Leak Inspection).
Front Fork Oil Leak Inspection
Visually inspect the front forks [A] for oil leakage.
•
Replace or repair any defective parts, if necessary.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-35
Rear Shock Absorber Oil Leak Inspection
Visually inspect the shock absorber [A] for oil leakage.
•
If the oil leakage is found on it, replace the shock absorber
with a new one.
Rocker Arm Operation Inspection
Pump the seat down and up 4 or 5 times, and inspect the
•
smooth stroke.
If the rocker arm [A] does not smoothly stroke or noise
is found, inspect the fasteners and bushings (see Rocker
Arm/Tie-Rod Bushing, Sleeve Inspection in the Suspen-
sion chapter).
Tie-Rod Operation Inspection
Pump the seat down and up 4 or 5 times, and inspect the
•
smooth stroke.
If the tie-rod [A] do not smoothly stroke or noise is found,
inspect the fasteners and tie-rod bushings (see Rocker
Arm/Tie-Rod Bushing, Sleeve Inspection in the Suspen-
sion chapter).
Page 58

2-36 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Swingarm Pivot Lubrication
Remove the swingarm bearing (see Swingarm Bearing
•
Removal in the Suspension chapter).
Supply grease to the needle bearings and grease seals
•
in accordance with the Periodic Maintenance chart.
Steering System
Steering Play Inspection
Raise the front wheel off the ground with jack (see Front
•
Wheel Removal in the Wheels/Tires chapter).
With the front wheel pointing straight ahead, alternately
•
tap each end of the handlebar. The front wheel should
swing fully left and right from the force of gravity until the
fork hits the stop.
If the wheel binds or catches before the stop, the steering
is too tight.
Feel for steering looseness by pushing and pulling the
•
forks.
If you feel looseness, the steering is too loose.
NOTE
The cables and wiring will have some effect on the mo-
○
tion of the fork which must be taken into account.
Be sure the wires and cables are properly routed.
○
The bearings must be in good condition and properly
○
lubricated in order for any test to be valid.
Steering Play Adjustment
Loosen:
•
Front Fork Clamp Bolts (lower) (both sides)
Stem Head Bolt [A]
Adjust the steering.
•
If the steering is too loose, tighten the steering stem nut
a fraction of a turn using the special tool [B].
If the steering is too tight, loosen the stem nut a fraction
of a turn.
Special Tool - Steering Stem Nut Wrench: 57001-1100
NOTE
Turn the stem nut 1/8 turn at a time maximum.
○
Tighten:
•
Torque - Steering Stem Head Bolt: 44 N·m (4.5 kgf·m, 32
ft·lb)
Front F ork Clamp Bolts (lower): 30 N·m (3.1 kgf·m,
22 ft·lb)
Check the steering again.
•
If the steering is still too tight or too loose, repeat the adjustment.
Page 59

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Steering Stem Bearing Lubrication
Remove the steering stem (see Stem, Stem Bearing Re-
•
moval in the Steering chapter).
Using a high-flash point solvent, wash the upper and
•
lower ball bearings, and wipe the upper and lower outer
races, which are press-fitted into the frame head pipe,
clean off grease and dirt.
Visually check the outer races and the ball bearings.
•
Replace them if they show wear or damage.
Apply a light coat of grease to the upper and lower [A] ball
•
bearings and outer races.
Install the steering stem (see Stem, Stem Bearing Instal-
•
lation in the Steering chapter).
Adjust the steering (see Steering Play Adjustment).
•
Electrical System
Lights and Switches Operation Inspection
First Step
Turn on the ignition switch.
•
The following lights should go on according to below table.
•
Taillight [A]
License Plate Light [B]
Meter Panel Lights [C]
Neutral Indicator Light [D]
Oil Pressure Warning Indicator Light [E]
Water Temperature Warning Indicator Light
[F]
goes on
goes on
goes on
goes on
goes on
goes on
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-37
If the light does not go on, inspect or replace t
item.
Battery (see Charging Condition Inspection in the Electrical System chapter)
Applicable Bulb (see Wiring Diagram in the Electrical
System chapter)
Meter Unit for Meter Lights (see Meter Unit Inspection in
the Electrical System chapter)
Meter Unit for Neutral Indicator Light (see Meter Unit
Inspection in the Electrical System chapter)
Meter Unit for Oil Pressure Warning Indicator Light (see
Meter Unit Inspection in the Electrical System chapter)
Meter Unit for Water Temperature Warning Indicator
Light (see Meter Unit Inspection in the Electrical System
chapter)
Main Fuse 30 A and Taillight Fuse 10 A (see Fuse Inspection in the Electrical System chapter)
Ignition Switch (see Switch Inspection in the Electrical
System chapter)
Neutral Switch (see Switch Inspection in the Electrical
System chapter)
Harness (see Wiring Inspection in the Electrical System
chapter)
he following
Turn off the ignition switch.
•
The all lights should go off.
•
If the light does not go off, replace the ignition switch.
Page 60
2-38 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Second Step
Turn on the turn signal switch [A] (left or right position).
•
The left or right turn signal lights [B] (front and rear) ac-
•
cording to the switch position should flash.
The turn signal indicator light [C] in the meter unit should
•
flash.
If the each light does not flash, inspect or replace the
following item.
Turn Signal Light Bulb (see Turn Signal Light Bulb Replacement in the Electrical System chapter)
Meter Unit for Turn Signal Light Indicator Light (see Meter Unit Inspection in the Electrical System chapter)
Turn Signal Relay Fuse 10 A (see Fuse Inspection in the
Electrical System chapter)
Turn Signal Switch (see Switch Inspection in the Electrical System chapter)
Turn Signal Relay (see Turn Signal Relay Inspection in
the Electrical System chapter)
Harness (see Wiring Inspection in the Electrical System
chapter)
Push the turn signal switch.
•
The turn signal lights and indicator light should go off.
•
If the light does not go off, inspect or replace the following
item.
Turn Signal Switch (see Switch Inspection in the Electrical System chapter)
Turn Signal Relay (see Turn Signal Relay Inspection in
the Electrical System chapter)
Third Step
Set the dimmer switch [A] to low beam position.
•
Start the engine.
•
The low beam headlight should go on.
•
If the low beam headlight does not go on, inspect or replace the following item.
Headlight Low Beam Bulb (see Headlight Bulb Replacement in the Electrical System chapter)
Headlight Fuse 10 A (see Fuse Inspection in the Electrical System chapter)
Dimmer Switch (see Switch Inspection in the Electrical
System chapter)
Headlight Relay (see Relay Circuit Inspection in the
Electrical System chapter)
Harness (see Wiring Inspection in the Electrical System
chapter)
Page 61

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Set the dimmer switch to high beam position.
•
The low beam [A] and high beam [B] headlights should
•
go on.
The high beam indicator light [C] should go on.
•
If the high beam headlight and/or high beam indicator light
does not go on, inspect or replace the following item.
Headlight High Beam Bulb (see Headlight Bulb Replacement in the Electrical System chapter)
Dimmer Switch (see Switch Inspection in the Electrical
System chapter)
Turn off the engine stop switch.
•
The low beam and high beam headlights should stay go-
•
ing on.
If the headlights and high beam indicator light does go off,
inspect or replace the following item.
Headlight Relay (see Relay Circuit Inspection in the
Electrical System chapter)
Turn off the ignition switch.
•
The headlights and high beam indicator light should go
•
off.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-39
Headlight Aiming Inspection
Inspect the headlight beam for aiming.
•
If the headlight beam points to one side rather than
straight ahead, adjust the horizontal beam.
Headlight Beam Horizontal Adjustment
Turn the horizontal adjuster [A] on the headlight with the
•
screwdriver in or out until the beam points straight ahead.
If the headlight beam points too low or high, adjust the
vertical beam.
Headlight Beam Vertical Adjustment
Turn the vertical adjuster [A] on the headlight with the
•
screwdriver in or out to adjust the headlight vertically.
Page 62

2-40 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
NOTE
ON high beam, the brightest points should be slightly
○
below horizontal with the motorcycle on its wheels and
the rider seated. Adjust the headlight to the proper angle according to local regulations.
For US model, the proper angle is 0.4 degrees below
○
horizontal. This is 50 mm (2 in.) drop at 7.6 m (25
ft) measured from the center of the headlight with the
motorcycle on its wheels and the rider seated.
50 mm (2 in.) [A]
Center of Brightest Spot [B]
7.6 m (25 ft) [C]
Low Beam [D]
Height of Headlight Center [E]
High Beam [F]
Sidestand Switch Operation Inspection
Inspect t he sidestand switch [A] operation accordance to
•
below table.
Sidestand Switch Operation
Sidestand
Up Neutral Released
Up Neutral Pulled in
Up In Gear Released
Up
Down Neutral Released
Down Neutral Pulled in
Down
Down
Gear
Position
In Gear
In Gear
In Gear
Clutch
Lever
Pulled in
Released
Pulled in
Engine
Start
Starts
Starts
Doesn’t
start
Starts
Starts
Starts
Doesn’t
start
Doesn’t
start
Engine
Run
Continue
running
Continue
running
Stops
Continue
running
Continue
running
Continue
running
Stops
Stops
Page 63

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
If the sidestand switch operation does not work, inspect
or replace the following item.
Battery (see Charging Condition Inspection in the Electrical System chapter)
Main Fuse 30 A (see Fuse Inspection in the Electrical
System chapter)
Ignition Fuse 10 A (see Fuse Inspection in the Electrical
System chapter)
Ignition Switch (see Switch Inspection in the Electrical
System chapter)
Sidestand Switch (see Switch Inspection in the E lectrical
System chapter)
Engine Stop Switch (see Switch Inspection in the Electrical System chapter)
Starter Button (see Switch Inspection in the Electrical
System chapter)
Neutral Switch (see Switch Inspection in the Electrical
System chapter)
Starter Relay (see Starter Relay Inspection in the Electrical System chapter)
Starter Circuit Relay (see Relay Circuit Inspection in the
Electrical System chapter)
Harness (see Wiring Inspection in the Electrical System
chapter)
If the all parts are good condition, replace the IC Igniter.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-41
Engine Stop Switch Operation Inspection
First Step
Turn on the ignition switch.
•
Set the neutral position.
•
Turn the engine stop switch to stop position [A].
•
Push the starter button.
•
The engine does not start.
•
If the engine starts, inspect or replace the following item.
Engine Stop Switch (see Switch Inspection in the Electrical System chapter)
Second Step
Turn on the ignition switch.
•
Set the neutral position.
•
Turn the engine stop switch to run position [A].
•
Push the starter button and run the engine.
•
Turn the engine stop switch to stop position.
•
Immediately the engine should be stop.
•
If the engine does not stop, inspect or replace the follow-
ing item.
Engine Stop Switch (see Switch Inspection in the Elec-
trical System chapter)
If the engine stop switch is good condition, replace the IC
Igniter.
Page 64

2-42 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Others
Chassis Parts Lubrication
Before lubricating each part, clean off any rusty spots with
•
rust remover and wipe off any grease, oil, dirt, or grime.
Lubricate the points listed below with indicated lubricant.
•
NOTE
Whenever the vehicle has been operated under
○
wet or rainy conditions, or especially after using a
high-pressure water spray, perform the general lubrication.
Pivots: Lubricate with Grease.
Brake Lever
Brake Pedal
Clutch Lever
Rear Brake Joint Pin
Sidestand
Points: Lubricate with Grease.
Clutch Inner Cable Upper and Lower Ends [A]
Throttle Inner Cable Upper and Lower Ends
Cables: Lubricate with Rust Inhibitor.
Clutch Cable
Throttle Cables
Lubricate the cables by seeping the oil between the cable
•
and housing.
The cable may be lubricated by using a commercially
○
available pressure cable lubricator with an aerosol cable
lubricant.
With the cable disconnected at both ends, the inner cable
•
should move freely [A] within the cable housing.
If cable movement is not free after lubricating, if the cable
is frayed [B], or if the cable housing is kinked [C], replace
the cable.
Page 65

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Bolts, Nuts and Fasteners Tightness Inspection
Check the tightness of the bolts and nuts listed here. Also,
•
check to see that each cotter pin is in place and in good
condition.
NOTE
For the engine fasteners, check the tightness of them
○
when the engine is cold (at room temperature).
If there are loose fasteners, retighten them to the specified torque following the specified tightening sequence.
Refer to the appropriate chapter for torque specifications.
If torque specifications are not in the appropriate chapter,
see the Standard Torque Table. For each fastener, first
loosen it by 1/2 turn, then tighten it.
If cotter pins are damaged, replace them with new ones.
Bolt, Nut and Fastener to be checked
Engine:
Clutch Lever Pivot Nut
Engine Mounting Bolts and Nuts
Exhaust Pipe Manifold Holder Nuts
Muffler Body Mounting Bolts
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-43
Wheels:
Front Axle
Rear Axle Nut
Rear Axle Nut Cotter Pin
Brakes:
Brake Lever Pivot Nut
Brake Pedal Bolt
Brake Rod Joint Cotter Pin
Caliper Mounting Bolts
Front Master Cylinder Clamp Bolts
Rear Master Cylinder Mounting Bolts
Suspension:
Front Fork Clamp Bolts
Rear Shock Absorber Bolt and Nut
Swingarm Pivot Shaft Nut
Steering:
Steering Stem Head Bolt
Handlebar Holder Bolts
Others:
Footpeg Stay Bolts
Front Fender Bolts
Sidestand Bolt
Page 66

2-44 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Replacement Parts
Air Cleaner Element Rep lacement
Refer to the Air Cleaner Element Cleaning (see Air
•
Cleaner Element Cleaning).
Fuel Hose Replacement
Refer to Fuel Hose Inspection (see Fuel Hose Inspection).
•
Coolant Change
WARNING
To avoid burns, do not remove the radiator cap or
try to change the coolant when the engine is still
hot. Wait until it cools down. Coolant on tires will
make them slippery and can cause an accident
and injury. Immediately wipe up or wash away any
coolant that spills on the frame, engine, or other
painted parts.
Since coolant is harmful to the human body, do not
use for drinking.
Remove:
•
Lower Fairings (see Lower Fairing Removal in the Frame
chapter)
Radiator Cap [A]
Place a container under the drain bolts [A] at the bottom
•
of the water pump cover and cylinder.
Drain the coolant from the radiator and engine by remov-
•
ing the drain bolts.
Torque - Drain Bolt: 9.8 N·m (1.0 kgf·m, 87 in·lb)
Page 67

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Remove:
•
Hoses [A]
Mounting Bolts [B] and Reserve Tank [C]
Remove the cap [D] and pour the coolant of the reserve
•
tank into the container.
Install:
•
Hoses
Reserve Tank
Tighten the drain bolt with the specified torque.
•
Torque - Drain Bolt: 9.8 N·m (1 .0 kgf·m, 87 in·lb)
Fill the radiator up to the radiator filler neck [A] with
•
coolant, and install the radiator cap.
NOTE
Pour in the coolant slowly so that it can expel the air
○
from the engine and radiator.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-45
Fill the reserve tank up to the full level line with coolant,
•
and install the cap.
CAUTION
Soft or distilled water must be used with the antifreeze (see below for antifreeze) in the cooling system.
If hard water is used in the system, it causes scales
accumulation in the water passages, and considerably reduces the efficiency of the cooling system.
Water and Coolant Mixture Ratio (Recommended)
Soft Water: 50%
Coolant: 50%
Freezing Point: −35°C (−31°F)
Capacity: 1.5 L (1.59 US qt)
NOTE
Choose a suitable mixture ratio by referring to the
○
coolant manufacturer’s directions.
Page 68

2-46 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Bleed the air from the cooling system as follows.
•
Start the engine with the radiator cap removed and run it
○
until no more air bubbles [A] can be seen in the coolant.
Tap the radiator hoses to force any air bubbles caught
○
inside.
Stop the engine and add coolant up to the radiator filler
○
neck.
Install the radiator cap.
•
Start the engine, warm it up thoroughly until the radiator
•
fan turns on and then stop the engine.
Check the coolant level in the reserve tank after the en-
•
gine cools down.
If the coolant level is lower than the low level line, add
coolant to the full level line.
CAUTION
Do not add more coolant above the full level line.
Radiator Hose and O-ring Replacement
Drain the coolant (see Coolant Change).
•
Remove:
•
Thermostat Housing [A] (see Water Pump Removal in
the Cooling System chapter)
Water Pump Cover [B] (see Water Pump Removal in the
Cooling System chapter)
Hoses [C]
Pipe [D]
O-rings [E]
Apply grease to the new O-rings and install them.
•
Install the new hoses and tighten the clamps securely.
•
Fill the coolant (see Coolant Change).
•
Check the cooling system for leaks.
•
Page 69

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Engine Oil Change
WARNING
To avoid a serious burn, never touch the exhaust
pipe during oil change.
Warm up the engine sufficiently with the motorcycle
•
standing on its side stand, and stop the engine.
Place an oil pan under the engine and remove the drain
•
bolt [A] to drain the oil.
Replace the drain bolt gaskets with new ones if they are
•
damaged.
The oil in the oil filter can be drained by removing the filter.
○
After draining the oil, tighten the drain bolts.
•
Torque - Oil Drain Bolts: 19.6 N·m (2.0 kgf·m, 14.5 ft·lb)
Oil Filter Mounting Bolt: 19.6 N·m (2.0 kgf·m, 14.5
ft·lb)
Pour in the specified type and amount of oil.
•
Recommended Engine Oil
Type :
Viscosity:
Capacity: 1.3 L (1.4 US qt) (When filter is not remov e d)
API SE, SF or SG
API SH, SJ or SL with JASO MA
SAE 10W - 40
1.6 L (1.7 US qt) (When filter is removed)
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-47
NOTE
Although 10W-40 engine oil is the recommended oil
○
for most conditions, the oil viscosity may need to be
changed to accommodate atmospheric conditions in
your riding area.
Oil Filter Replacement
Drain the engine oil (see Engine Oil change).
•
Remove the oil filter mounting bolt [A].
•
Page 70

2-48 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Replace the oil filter with a new one.
•
Apply engine oil to the O-rings [A] before installation after
•
inspecting its damage.
Install the oil filter mounting bolt [B] with a specified
•
torque.
Torque - Oil Filter Mounting Bolt: 19.6 N·m (2.0 kgf·m, 14.5
ft·lb)
Pour in the specified type and amount of oil (see Engine
•
Oil Change).
Brake Hose and Pipe Replacement
CAUTION
Brake fluid quickly ruins painted plastic surfaces;
any spilled fluid should be completely washed away
immediately.
Remove the banjo bolts.
•
When removing the brake hose, take care not to spill the
•
brake fluid on the painted or plastic parts.
When removing the brake hoses [A], temporarily secure
•
the end of the brake hose to some high place to keep fluid
loss to a minimum.
Immediately wash away any brake fluid that spills.
•
There are washers on each side of the brake hose fitting.
•
Replace them with new ones when installing.
Tighten:
•
Torque - Brake Hose Banjo B olts: 25 N·m (2.5 kgf·m, 18
ft·lb)
When installing the hoses [A], avoid sharp bending, kink-
•
ing, flatting or twisting, and route the hoses according to
Cable, Wire, and Hose Routing section in the Appendix
chapter.
Fill the brake line after installing the brake hose (see
•
Brake Fluid Change).
Brake Fluid Change
NOTE
The procedure to change the front brake fluid is as fol-
○
lows. Changing the rear brake fluid is the same as for
the front brake.
Page 71

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Level the brake fluid reservoir.
•
Remove the reservoir cap and diaphragm.
•
Remove the rubber cap from the bleed valve [A] on the
•
caliper.
Attach a clear plastic hose [B] to the bleed valve, and run
•
the other end of the hose into a container.
Fill the reservoir with fresh specified brake fluid.
•
Change the brake fluid.
•
Repeat this operation until fresh brake fluid comes out
○
from the plastic hose or the color of the fluid changes.
1. Open the bleed valve [A].
2. Apply the brake and hold it [B].
3. Close the bleed valve [C].
4. Release the brake [D].
NOTE
The fluid level must be checked often during the chang-
○
ing operation and replenished with fresh brake fluid. If
the fluid in the reservoir runs out any time during the
changing operation, the brakes will need to be bled
since air will have entered the brake line.
Front Brake: Repeat the above steps for the other
○
caliper.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-49
Remove the clear plastic hose.
•
Install the diaphragm and reservoir cap.
•
Tighten:
•
Torque - Front Brake Reservoir Cap Screws: 1.5 N·m (0.15
kgf·m, 13 in·lb)
Follow the procedure below to install the rear brake fluid
•
reservoir cap correctly.
First, tighten the rear brake fluid reservoir cap [B] clock-
○
wise [C] by hand until slight resistance is felt indicating
that the cap is seated on the reservoir body, then tighten
the cap an additional 1/6 turn [D] while holding the brake
fluid reservoir body [A].
Tighten the bleed valve, and install the rubber cap.
•
Torque - Bleed Valve: 5.5 N·m (0.55 kgf·m, 49 in·lb)
After changing the fluid, check the brake for good braking
•
power, no brake drag, and no fluid leakage.
If necessary, bleed the air from the lines.
Page 72

2-50 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Master Cylinder Rubber Parts Replacement
Front Master Cylinder Disassembly
Remove the front master cylinder (see Front Master Cylin-
•
der Removal in the Brakes chapter).
Remove the reservoir cap and diaphragm, and pour the
•
brake fluid into a container.
Unscrew the locknut and pivot bolt, and remove the brake
•
lever.
Pull the dust cover out of place, and remove the circlip.
•
Special Tool - Inside Circlip Pliers: 57001-143
Pull out the piston [A], secondary cup [B], primary cup [C],
•
and return spring [D].
CAUTION
Do not remove the secondary cup from the piston
since removal will damage it.
Rear Master Cylinder Disassembly
NOTE
Do not remove the push rod clevis for master cylinder
○
disassembly since removal requires brake position adjustment.
Remove the rear master cylinder (see Rear Master Cylin-
•
der Removal in the Brakes chapter).
Remove the circlip.
•
Special Tool - Inside Circlip Pliers: 57001-143
Pull out the push rod with the piston stop.
•
Take off the piston [A], secondary cup [B], primary cup [C]
•
and return spring [D].
Remove the circlip [F] and pull out the brake hose con-
•
nector [G] and O-ring [H].
Special Tool - Inside Circlip Pliers: 57001-143
CAUTION
Do not remove the secondary cup from the piston
since removal will damage it.
Master Cylinder Assembly
Before assembly, clean all parts including the master
•
cylinder with brake fluid or alcohol.
CAUTION
Except for the disc pads and disc, use only disc
brake fluid, isopropyl alcohol, or ethyl alcohol for
cleaning brake parts. Do not use any other fluid for
cleaning these parts. Gasoline, engine oil, or any
other petroleum distillate will cause deterioration of
the rubber parts. Oil spilled on any part will be difficult to wash off completely, and will eventually deteriorate the rubber used in the disc brake.
Page 73

Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Apply brake fluid to the removed parts and to the inner
•
wall of the cylinder.
Take care not to scratch the piston or the inner wall of the
•
cylinder.
Apply silicone grease (ex. PBC grease).
•
Brake Lever Pivot Bolt
Brake Lever Pivot Contact
Push Rod Contact (Rear)
Dust Cover
Tighten:
•
Torque - Brake Lever Pivot Bolt: 1.0 N·m (0.10 kgf·m, 9
in·lb)
Brake Lever Pivot Bolt Locknut: 5.9 N·m (0.60
kgf·m, 52 in·lb)
Caliper Rubber Parts Replacement
Caliper Disassembly
Remove a front Caliper (see Front Caliper Removal in the
•
Brakes chapter).
Remove the pads and anti-rattle spring (see Pad Removal
•
in the Brakes chapter).
If compressed air is available, the piston may be removed
using compressed air as follows.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-51
Insert the wooden board of 5 mm (0.2 in.) thick inside the
•
caliper opening or cover the caliper opening with a clean,
heavy cloth [A].
Lightly apply compressed air [B] to the hose joint opening
•
until the pistons hit the wooden board or heavy cloth.
WARNING
To avoid serious injury, never place your fingers or
palm in front of the piston. If you apply compressed
air into the caliper, the piston may crush your hand
or fingers.
Pull out the pistons by hand.
•
Immediately wipe up any brake fluid that spills. It may ruin
•
painted or plated surfaces.
Remove the dust seals and fluid seals.
•
Remove the bleed valve and rubber cap.
•
NOTE
If compressed air is not available, do as follows for both
○
calipers coincidentally, with the brake hose connected
to the caliper.
Prepare a container for brake fluid, and perform the
○
work above it.
Remove the spring and pads (see Brake Pad Removal).
○
Pump the brake lever or pedal until the pistons come
○
out of the cylinders, and then disassemble the caliper.
Page 74
2-52 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Periodic Maintenance Procedures
Caliper Assembly
Clean the caliper parts except for the pads.
•
CAUTION
For cleaning of the parts, use only disc brake fluid,
ispopropyl alcohol, or ethyl alcohol.
Install the bleed valve and rubber cap.
•
Torque - Bleed Valve: 5.5 N·m (0.55 kgf·m, 49 in·lb)
Replace the fluid seals [A] and dust seals [B] with new
•
one.
Apply brake fluid to the fluid seals and dust seals, and
•
install them into the cylinder by hand.
Apply brake fluid [A] to the outside of the pistons and push
•
them into each cylinder by hand without scratching the
cylinder and piston skirt.
Apply silicone grease [B] to the caliper holder shaft and
•
holder holes, and install the caliper holder [C], rubber boot
[D] and dust cover [E].
Install the anti-rattle spring [F] and pads in the caliper (see
•
Pad Installation in the Brakes chapter).
Spark Plug Replacement
Remove:
•
Spark Plugs (see Spark Plug Removal in the Electrical
System chapter)
Remove the spark plugs using the 16 mm plug wrench
•
[A].
Owner’s Tool - Spark Plug Wrench, 16 mm: 92110-0044
Insertthesparkplugverticallyintotheplugholewiththe
•
spark plug installed in the plug wrench [A].
Owner’s Tool - Spark Plug Wrench, 16 mm: 92110-0044
Tighten:
•
Torque - Spark Plugs: 13 N·m (1.3 kgf·m, 115 in·lb)
Install:
•
Spark Plugs (see Spark Plug Installation in the Electrical
System chapter)
Page 75

FUEL SYSTEM 3-1
Fuel System
Table of Contents
Exploded View........................................................................................................................ 3-2
Specifications ......................................................................................................................... 3-8
Special Tools .......................................................................................................................... 3-9
Throttle Grip and Cables ........................................................................................................ 3-10
Free Play Inspection ......................................................................................................... 3-10
Free Play Adjustment........................................................................................................ 3-10
Throttle Cable Removal .................................................................................................... 3-10
Throttle Cable Installation ................................................................................................. 3-10
Throttle Cable Lubrication................................................................................................. 3-10
Choke Cable........................................................................................................................... 3-11
Free Play Inspection ......................................................................................................... 3-11
Free Play Adjustment........................................................................................................ 3-11
Choke Cable Removal ...................................................................................................... 3-11
Choke Cable Installation ................................................................................................... 3-11
Choke Cable Lubrication and Inspection .......................................................................... 3-11
Carburetors............................................................................................................................. 3-12
Idle Speed Inspection ....................................................................................................... 3-12
Idle Speed Adjustment...................................................................................................... 3-12
Engine Vacuum Synchronization Inspection..................................................................... 3-12
Engine Vacuum Synchronization Adjustment ................................................................... 3-12
Pilot Screw Adjustment ..................................................................................................... 3-12
Service Fuel Level Inspection ........................................................................................... 3-13
Service Fuel Level Adjustment ......................................................................................... 3-14
Fuel System Cleanliness Inspection ................................................................................. 3-15
Carburetor Removal.......................................................................................................... 3-16
Carburetor Installation....................................................................................................... 3-17
Carburetor Separation ...................................................................................................... 3-17
Carburetor Joining ............................................................................................................ 3-17
Carburetor Disassembly ................................................................................................... 3-19
Carburetor Assembly ....................................................................................................... 3-19
Carburetor Cleaning.......................................................................................................... 3-20
Carburetor Inspection ....................................................................................................... 3-21
Air Cleaner.............................................................................................................................. 3-23
Air Cleaner Element Removal........................................................................................... 3-23
Air Cleaner Element Installation........................................................................................ 3-23
Air Cleaner Housing Removal........................................................................................... 3-23
Air Cleaner Housing Installation........................................................................................ 3-24
Air Cleaner Housing Disassembly .................................................................................... 3-24
Air Cleaner Housing Assembly ......................................................................................... 3-24
Oil Draining ...................................................................................................................... 3-25
Fuel Tank ................................................................................................................................ 3-26
Fuel Tank Removal ........................................................................................................... 3-26
Fuel Tank Installation ........................................................................................................ 3-26
Fuel Tap Removal ............................................................................................................. 3-27
Fuel Tap Installation .......................................................................................................... 3-27
Fuel Tank and Tap Cleaning ............................................................................................. 3-27
Fuel Tap Inspection........................................................................................................... 3-28
Fuel Tank and Cap Inspection .......................................................................................... 3-28
3
Page 76

3-2 FUEL SYSTEM
Exploded View
Page 77

Exploded View
1. Throttle Cable (accelerator)
2. Throttle Cable (decelerator)
3. Choke Cable
4. Idle Adjusting Screw
5. Air Cut Valve
6. Jet Needle
7. Vacuum Valve
8. Float Valve
9. Needle Jet
10. Needle Jet Holder
11. Main Jet
12. Pilot Jet
13. Pilot Air Screw
14. Float
15. Plug
CL: Apply cable lubricant.
G: Apply grease.
FUEL SYSTEM 3-3
Page 78

3-4 FUEL SYSTEM
Exploded View
Page 79
Exploded View
FUEL SYSTEM 3-5
No. Fastener
1 Fuel Tap Mounting Bolts 2.5 0.25 22 in·lb
2 Fuel Gauge Mounting Bolts 6.9 0.7 61 in·lb
3 Air Cleaner Housing Cap Bolts 2.5 0.25 22 in·lb
4 Air Cleaner Housing Screws 1.15 0.12 10 in·lb
5 Air Cleaner Housing Mounting Bolts 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
6
Air Cleaner Housing Clamp Screws
7. Vacuum Switch Valve
AO: Apply motor oil (SE, SF or SG class SAE 10W-30).
N·m kgf·m ft·lb
2.0 0.2 18 in·lb
Torque
Remarks
Page 80

3-6 FUEL SYSTEM
Exploded View
Page 81

Exploded View
FUEL SYSTEM 3-7
No. Fastener
Torque
N·m kgf·m ft·lb
1 Separate Bracket Bolt 9.8 1.0 87 in·lb
2. Canister
3. Separator
4. Green Hose
5. Blue Hose
6. White Hose
7. Red Hose
Remarks
Page 82

3-8 FUEL SYSTEM
Specifications
Item Standard
Throttle Grip and Cable
ThrottleGripFreePlay 2 ∼ 3mm(0.08∼ 0.12 in.)
Choke Cable Free Play 2 ∼ 3mm(0.08∼ 0.12 in.)
Carburetor
Make, Type Keihin, CVK30
Main Jet #98
Optional Main Jet #92, 95, 100, 102
Main Air Jet #100
Jet Needle #L: N9VU, #R: N9VW
Needle Jet #6
Pilot Jet #38
Pilot Air Jet #100
Starter Jet #48
Pilot Screw (turns out) #L:21/2,#R:13/4
Throttle Valve 11° 00’
Idle Speed 1 300 ±50 r/min (rpm)
Carburetor Synchronization Vacuum Less than 2.7 kPa (2 cmHg) difference between two
carburetors.
Service Fuel Level 0.5 ±1 mm (0.02 ±0.04 in.) above the mating surface of
carburetor float bowl.
Float Height 17 ±2 mm (0.67 ±0.08 in.)
Air Cleaner Element
Type Polyurethane foam
Page 83

Special Tools
FUEL SYSTEM 3-9
Fuel Level Gauge:
57001-1017
Pilot Screw Adjuster, A:
57001-1239
Page 84

3-10 FUEL SYSTEM
Throttle Grip and Cables
Free Play Inspection
Refer to Throttle Control System Inspection in the Peri-
•
odic M aintenance chapter (see Throttle Control System
Inspection in the Periodic Maintenance chapter).
Free Play Adjustment
Refer to Throttle Control System Inspection in the Peri-
•
odic M aintenance chapter (see Throttle Control System
Inspection in the Periodic Maintenance chapter).
Throttle Cable Removal
Split the right handlebar switch housing [A] removing the
•
screws [B], and remove the throttle cable upper ends from
the throttle grip.
Remove:
•
Front Seat (see Front Seat Removal in the Frame chapter)
Side Cover (see Side Cover Removal in the Frame chapter)
Right Lower Fairing (see Lower Fairing Removal in the
Frame chapter)
Loosen the locknuts [A] and remove the lower end of the
•
accelerator cable [B] from the pulley.
Loosen the locknuts [C] and remove the lower end of the
•
decelerator cable [D] from the pulley.
Pull out the throttle cables upward
•
Throttle Cable Installation
Install the throttle cables in accordance with the Cable,
•
Wire and Hose Routing in the Appendix chapter.
Install the accelerator cable first and then decelerator ca-
•
ble.
After installation, adjust each cable properly (see Throttle
•
Cable Inspection in the Periodic Maintenance chapter).
WARNING
Operation with incorrectly routed or improperly adjusted cables could result in an unsafe riding condition.
Throttle Cable Lubrication
Refer to Chassis Parts Lubrication Perform in the Peri-
•
odic Maintenance chapter (see Chassis Parts Lubrication
Perform in the Periodic Maintenance chapter).
Page 85

Choke Cable
Free Play Inspection
Refer to Choke Operation Inspection in the Periodic Main-
•
tenance chapter (see Choke Operation in the Periodic
Maintenance chapter).
Free Play Adjustment
Refer to Choke Operation Inspection in the Periodic Main-
•
tenance chapter (see Choke Operation in the Periodic
Maintenance chapter).
Choke Cable Removal
Split the left handlebar switch housing [A], and remove
•
the choke cable [B] upper end from the choke lever [C].
Remove:
•
Front Seat (see Front Seat Removal in the Frame chap-
ter)
Fuel Tank (see Fuel Tank Removal)
Remove the choke cable end from the cable bracket of
•
carburetor.
Pull out the choke cable upward.
•
FUEL SYSTEM 3-11
Choke Cable Installation
Install the choke cable in accordance with the Cable,
•
Wire, and Hose Routing section in Appendix chapter.
After installation, adjust the cable properly.
•
WARNING
Operation with an incorrectly routed or improperly
adjusted cable could result in an unsafe riding condition.
Choke Cable Lubrication and Inspection
Whenever the cable is removed, or in accordance with
•
the Periodic Maintenance Chart, lubricate the choke cable
(see General Lubrication in the Appendix chapter).
Apply a thin coating of grease to the cable lower end.
○
Use a commercially available pressure cable lubricator to
○
lubricate the cable.
With the cable disconnected at both ends, the cable
○
should move freely in the cable housing.
Page 86

3-12 FUEL SYSTEM
Carburetors
Idle Speed Inspection
Refer to Idle Speed Inspection in the Periodic Mainte-
•
nance chapter (see Idle Speed Inspection in the Periodic
Maintenance chapter).
Idle Speed Adjustment
Refer to Idle Speed Adjustment in the Periodic Mainte-
•
nance chapter (see Idle Speed Adjustment in the Periodic
Maintenance chapter).
Engine Vacuum Synchronization Inspection
Refer to Engine Vacuum Synchronization Inspection in
•
the Periodic Maintenance chapter (see Engine Vacuum
Synchronization Inspection in the Periodic Maintenance
chapter).
Engine Vacuum Synchronization Adjustment
Refer to Engine Vacuum Synchronization Inspection in
•
the Periodic Maintenance chapter (see Engine Vacuum
Synchronization Inspection in the Periodic Maintenance
chapter).
Pilot Screw Adjustment
If the engine idle is still not stable, adjust the pilot screw to
obtain the proper idle speed using the pilot screw adjuster
[A].
Special Tool - Pilot Screw Adjuster: 57001-1239
Turn in the pilot screw fully but not tightly, and then back
○
it out the specified turns. To set the screw to its original
position.
Pilot Screw Setting:
#L: 2 1/2
#R: 1 3/4
NOTE
The standard number of turns the pilot screw must be
○
backed out varies by carburetor. The values given in the
specifications should be used only when the number of
the original back out turns is unavailable.
Page 87

Carburetors
Service Fuel Level Inspection
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain conditions. Turn the ignition
switch OFF. Do not smoke. Make sure the area is
well-ventilated and free from any source of flame
or sparks; this includes any appliance with a pilot
light.
Situate the motorcycle so that it is perpendicular to the
•
ground.
Remove:
•
Front Seat (see Front Seat Removal in the Frame chap-
ter)
Fuel Tank (see Fuel Tank Removal)
Prepare an auxiliary fuel tank and connect the fuel hose
•
to the carburetor.
Prepare a fuel hose.
•
FUEL SYSTEM 3-13
Connect the fuel level gauge [A] to the carburetor float
•
bowl with the fuel hose.
Special Tool - Fuel Level Gauge: 57001-1017
Hold the gauge vertically against the side of the carburetor
•
body so that the “middle” line [B] is several millimeters
higher than the mating surface [C] of the carburetor float
bowl.
Feed fuel to the carburetor, then turn the carburetor drain
•
plug out a few turns.
Wait until the fuel level in the gauge settles.
•
Page 88

3-14 FUEL SYSTEM
Carburetors
Keeping the gauge vertical, align the “middle” line with the
•
mating surface.
NOTE
Do not lower the “middle” line below the mating surface
○
of the carburetor float bowl. If the gauge is lowered
and then raised again, the fuel level measured shows
somewhat higher than the actual fuel level. If the gauge
is lowered too far, dump the fuel out of it into a suitable
container and start the procedure over again.
Read the fuel level [E] in the gauge and compare to the
•
specification.
Screw in the carburetor drain plug [D].
•
Stop feeding and remove the fuel level gauge.
•
If the fuel level is incorrect, adjust it (see Service Fuel
Level Adjustment).
Service Fuel Level (above the mating surface of carburetor
float bowl)
Standard: 0.5 mm ±1 mm (0.02 ±0.04 in .)
Service Fuel Level Adjustment
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain conditions. Turn the ignition
switch OFF. Do not smoke. Make sure the area is
well-ventilated and free from any source of flame
or sparks; this includes any appliance with a pilot
light.
Remove the carburetor, and drain the fuel into a s uitable
•
container.
Remove the fittings with water hose.
•
Remove the float bowl.
•
Slide out the pivot pin [A] with a suitable tool [B], and
•
remove the float [C] and float valve needle [D].
Page 89

Carburetors
Bend the tang [A] on the float arm very slightly to change
•
the float height. Increasing the float height lowers the fuel
level and decreasing the float height raises the fuel level.
Float height
Standard: 17 ±2 mm (0.67 ±0.08 in.)
NOTE
Do not push the needle rod [A] in during the float height
○
measurement [B].
Assemble the carburetor, and recheck the fuel level.
•
If the fuel level cannot be adjusted by this method, the
float or the float valve [C] is damaged.
FUEL SYSTEM 3-15
Fuel System Cleanline ss Inspection
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain conditions. Turn the ignition
switch OFF. Do not smoke. Make sure the area is
well-ventilated and free from any source of flame
or sparks; this includes any appliance with a pilot
light.
Remove:
•
Right Lower Fairing (see Lower Fairing Removal in the
Frame chapter)
Connect a suitable hose [A] to the fitting at the bottom of
•
each carburetor float bowl.
Run the lower end of the carburetor drain hose into a suit-
•
able container.
Turn out each drain plug [B] a few turns and drain the float
•
bowls with a hexagon wrench [C].
Check to see if water or dirt comes out.
•
Tighten the drain plug.
•
If any water or dirt appears during the above inspection,
clean the fuel system (see Carburetor Cleaning and Fuel
Tank Cleaning).
Page 90

3-16 FUEL SYSTEM
Carburetors
Carburetor Removal
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain conditions. Turn the ignition
switch OFF. Do not smoke. Make sure the area is
well-ventilated and free from any source of flame
or sparks; this includes any appliance with a pilot
light.
Remove:
•
Front Seat (see Front Seat Removal in the Frame chapter)
Fuel Tank (see Fuel Tank Removal)
Lower Fairings (see Lower Fairing Removal in the Frame
chapter)
Battery (see Battery Removal in the Electrical System
chapter)
Battery Damper
Battery Case Screws [A]
Battery Case [B]
Remove the air cleaner housing mounting bolts [A].
•
Loosen the carburetor holder clamps [B] off the air cleaner
•
ducts.
Pull the air cleaner housing rearward.
•
Remove the throttle cable and choke cable (see Throttle
•
Cable and Choke Cable Removal)
Remove:
•
Bolts [C]
Bracket [D]
Carburetor [E]
Stuff the pieces of lint-free, clean cloths into the carbure-
•
tor holder and the air cleaner duct to keep dirt out of the
engine and air cleaner.
WARNING
If dirt or dust is allowed to pass through into the
carburetor, the throttle may become stuck, possibly
causing an accident.
CAUTION
If dirt gets through into the engine, excessive engine wear and possibly engine damage will occur.
Page 91

Carburetors
Carburetor Installation
Route the cables, harness, and hoses correctly (see Ca-
•
ble, Wire and Hose Routing section in the Appendix chapter).
Tighten the clamps for the carburetor holders and slide
•
back the spring bands for the air cleaner housing securely.
Check fuel leakage from the carburetor.
•
WARNING
Fuel spilled from the carburetor is hazardous.
Adjust the following items if necessary.
•
Idle Speed (see Idle Speed Adjustment in the Periodic
Maintenance chapter)
Carburetor Synchronization (see Carburetor Synchro-
nization Adjustment in the Periodic Maintenance c hap-
ter)
Throttle Cable (see Throttle Control System Inspection
in the Periodic Maintenance c hapter)
Choke Cable
FUEL SYSTEM 3-17
Carburetor Separation
Remove the carburetor (see Carburetor Removal).
•
Pull out the air cut valve hoses [A], [B], [C] of the air cut
•
valve.
Remove the choke plunger lever [D], spring [E] and car-
•
buretor mounting plates [F], [G].
Gently, separately the carburetors each other.
•
Carburetor Joining
When installing the carburetor, check to see that the O
•
-rings [A] are in place.
Page 92

3-18 FUEL SYSTEM
Carburetors
Install the fitting [A] and spring [B] as shown.
•
Install the connecting plates [A] [B] and spring [C] as
•
shown.
The center lines of the carburetor bores must be parallel
•
both horizontally and vertically. If they are not, loosen
the mounting screws and align the carburetors on a flat
surface. Retighten the mounting screws.
After installing the choke mechanism, check to see that
•
the choke plunger lever slides right to left smoothly without abnormal friction.
CAUTION
Fuel mixture trouble could result if the choke
plunger does not seat properly in its rest position
after the choke lever is returned.
Visually synchronize the throttle (butterfly) valves.
•
Check to see that all throttle valves open and close
○
smoothly without binding when turning the pulley.
Visually check the clearance [A] between the throttle
○
valve and the carburetor bore in each carburetor.
If there is a difference between two carburetors, turn the
balance adjusting screw [B] to obtain the same clearance.
Install the carburetors (see Carburetor Installation).
•
Adjust the synchronization (see Carburetor Synchroniza-
•
tion Adjustment in the Periodic Maintenance Chapter).
Page 93

Carburetors
Carburetor Disassembly
Remove the carburetors (see Carburetor Removal).
•
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain conditions. Turn the ignition
switch OFF. Do not smoke. Make sure the area is
well-ventilated and free from any source of flame
or sparks; this includes any appliance with a pilot
light.
For the Canada model, remove the pilot screw plug as
•
follows: punch a hole in the plug and pry there with an
awl or other suitable tool.
Turn in the pilot screw and count the number of turns until
•
it seats fully but not tightly, and then remove the screw.
This is to set the screw to its original position when assembling.
CAUTION
FUEL SYSTEM 3-19
During carburetor disassembly, be careful not to
damage the diaphragm. Never use a sharp edge to
remove the diaphragm.
Remove:
•
Spring [A]
Spring Seat [B]
Jet Needle [C]
Vacuum Piston [D]
Needle Jet [E]
Needle Jet Holder [F] and Main Jet [G]
Pilot Screw [H]
Carburetor Assembly
Turn in the pilot screw [A] fully but not tightly, and then
•
back it out the same number of turns counted during disassembly.
Install the pilot screw plug as follows: install a new plug [B]
•
in the pilot screw hole of the carburetor body, and apply a
small amount of a bonding agent [C] to the circumference
oftheplugtofixtheplug.
CAUTION
Do not apply too much bonding agent to the plug or
the pilot screw itself may be fixed.
Page 94

3-20 FUEL SYSTEM
Carburetors
To install the needle jet [A], turn the carburetor body up
•
-side down, and drop the needle jet into place so that the
smaller diameter end [B] of the jet goes in first.
Carefully screw in the needle jet holder [A]. It will seat
•
against the needle jet, pushing the end of the jet into the
carburetor bore.
Main Jet [B]
CAUTION
Do not apply force to the jet or overtighten it, as
this could damage the jet or the carburetor body,
requiring replacement.
Install the float bowl.
•
Slip the jet needle [B] through the hole in the center of
•
the vacuum piston, and put the spring seat [C] on the top
of the needle. Turn the seat so that it does not block the
hole at the bottom of the vacuum piston [A].
Spring [D]
Install the carburetor top cover.
•
Turn in the pilot screw fully but not tightly, and then back it
•
out the same number of turns counted during disassembly.
When removing the air cut valve assembly, unscrew the
•
mounting screws [B] and remove the cover [C], spring [D],
O-ring [E] and diaphragm [F].
Install:
•
Left Carburetor [A]
Air Cut Valve Body [G]
Air Cut Valve Mounting Plate [H]
Carburetor Cleaning
WARNING
Clean the carburetor in a well-ventilated area, and
take care that there is no spark or flame anywhere
near the working area; this includes any appliance
with a pilot light. Because of the danger of highly
flammable liquids, do not use gasoline or low-flash
point solvents to clean the carburetor.
Page 95

Carburetors
CAUTION
Do not use compressed air on an assembled carburetor, or the floats may be crushed by the pressure,
and the vacuum piston diaphragm may be damaged. Remove as many rubber or plastic parts
from the carburetor as possible before cleaning the
carburetor with a cleaning solution. This will prevent damage to or deterioration of the parts. The
carburetor body has plastic parts that cannot be
removed. Do not use a strong carburetor cleaning
solution which could attack these parts; instead,
use a mild high-flash point cleaning solution safe
for plastic parts. Do not use wire or any other hard
instrument to clean carburetor parts, especially
jets, as they may be damaged.
Disassemble the carburetor (see Carburetor Disassem-
•
bly).
Immerse all the metal parts in a carburetor cleaning solu-
•
tion.
Rinse the parts in water.
•
When the parts are clean, dry them with compressed air.
•
Blow through the air and fuel passages with compressed
•
air.
Assemble the carburetor (see Carburetor Assembly).
•
FUEL SYSTEM 3-21
Carburetor Inspection
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain conditions. Turn the ignition
switch OFF. Do not smoke. Make sure the area is
well-ventilated and free from any source of flame
or sparks; this includes any appliance with a pilot
light.
Remove the carburetors (see Carburetor Removal).
•
Before disassembling the carburetors, check the fuel level
•
(see Fuel Level Inspection).
If the fuel level is incorrect, inspect the rest of the carburetor before correcting it.
Slide the choke plunger lever [A] right to the left to check
•
that the choke plungers move smoothly.
If the choke plungers do not work properly, replace the
carburetors.
Turn the throttle cable pulley to check that the throttle but-
•
terfly valves [B] move smoothly and return by spring tension.
If the throttle valves do not move smoothly, replace the
carburetors.
Page 96

3-22 FUEL SYSTEM
Carburetors
Disassemble the carburetors (see Carburetor Disassem-
•
bly).
Clean the carburetors (see Carburetor Cleaning).
•
Check that the O-rings on the float bowl and pilot s crew
•
and the diaphragm on the vacuum piston are in good condition.
If any of the O-rings or diaphragms are not in good condition, replace them.
Check the O-ring and diaphragm of coasting enricher sys-
•
tem.
If any of the O-ring or diaphragm are not in good condition,
replace them.
Check the plastic tip [A] of the float valve needle [B]. It
•
should be smooth, without any grooves, scratches, or
tears.
If the plastic tip is damaged [C], replace the needle.
Push the rod [D] in the other end of the float valve needle,
•
and then release it [E].
If the rod does not spring out, replace the needle.
Check the tapered portion [A] of the pilot screw [B] for
•
wear or damage.
If the pilot screw is worn or damaged on the tapered portion, it will prevent the engine from idling smoothly. Replace it.
Check that the vacuum piston [A] moves smoothly in the
•
carburetor body. The surface of the piston must not be
excessively worn.
If the vacuum piston does not move smoothly, or if it is
very loose in carburetor body, replace the carburetor.
Page 97

Air Cleaner
Air Cleaner Element Removal
Refer to Air Cleaner Cleaning in the Periodic Maintenance
•
chapter (see Air Cleaner Cleaning in the Periodic Maintenance chapter).
Air Cleaner Element Installation
Refer to Air Cleaner Cleaning in the Periodic Maintenance
•
chapter (see Air Cleaner Cleaning in the Periodic Maintenance chapter).
Air Cleaner Housing Removal
Remove:
•
Front Seat (see Front Seat Removal in the Frame chap-
ter)
Rear Seat (see Rear Seat Removal in the Frame chap-
ter)
Fuel Tank (see Fuel Tank Removal)
Rear Fender (see Rear Fender Removal in the Frame
chapter)
Pull out the rear axle and place the rear wheel [A] on the
•
ground.
FUEL SYSTEM 3-23
Take out the bolts [A] and remove the fuel tank bracket
•
[B].
Pull out the starter relay [C].
•
Remove the rear brake reservoir bolt [A] and disconnect
•
the clamp [B], and free the rear brake reservoir and main
harness from the frame.
Remove the air cleaner cap [C].
•
Remove:
•
Carburetor Holder Clamps [A] (Loosen)
Air Cleaner Housing Mounting Bolts [B]
Air Suction Valve Hose [C]
Remove the air cleaner housing [D], pulling out the duct
•
portion [E] from the grommet.
Page 98

3-24 FUEL SYSTEM
Air Cleaner
Cover the carburetors intakes with a clean, lint-free towel
•
to keep dirt or other foreign material from entering.
WARNING
If dirt or dust is allowed to pass through into the carburetors, the butterfly valves may become stuck,
possibly causing an accident.
CAUTION
If dirt gets through into the engine, excessive engine wear and possibly engine damage will occur.
Air Cleaner Housing Installation
Install the air cleaner housing clamps [A] as shown.
•
Approx. 18° [B]
Air Cleaner Housing Disassembly
Remove:
•
Air Cleaner Housing (see Air Cleaner Housing Removal)
Air Cleaner Element (see Air Element Removal in the
Periodic Maintenance chapter)
Screw [A]
Right Cover [B]
Flame Arrester
Air Cleaner Housing Assembly
Install the flame arrester [A].
•
Be sure the O-ring [B] is i n position.
•
Page 99

Air Cleaner
Apply a bonding agent to the slash portion [A] of the air
•
cleaner housing.
Oil Draining
Remove the drain cap [A] at the lower end of the air
•
cleaner housing and drain water or oil accumulates in the
air cleaner housing.
Be sure to install the cap firmly, or the air is drawn in
•
through it.
WARNING
Be sure to install the cap in the air cleaner housing
after draining. Oil on tires make them slippery and
can cause an accident and injury.
FUEL SYSTEM 3-25
Page 100

3-26 FUEL SYSTEM
Fuel Tank
Fuel Tank Removal
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain conditions. Make sure the area
is well-ventilated and free from any source of flame
or sparks; this includes any appliance with a pilot
light. Do not smoke. Turn the ignition switch OFF.
Be prepared for fuel spillage; any spilled fuel must
be completely wiped up immediately.
Remove the side covers (see Side Covers Removal in the
•
Frame chapter).
Turn the fuel tap position to the ON [A] position.
•
Remove:
•
Front Seat (see Front Seat Removal in the Frame chapter)
Lower Fairings (see Lower Fairing Removal in the Frame
chapter)
Fuel Tank Mounting Bolts [A]
Fuel Hose [B]
Vacuum Hose [C]
Fuel Level Sensor Connector [D]
Fuel Tank
Drain the fuel tank if necessary.
•
Arrange a suitable container under the fuel tap.
○
Turn the fuel tap position to the PRI position to drain the
○
fuel into the container.
Fuel Tank Installation
Read the above WARNING mentioned in Fuel Tank Re-
•
moval.
Route the hose correctly.
•
Be sure the hoses are clamped securely to prevent fuel
•
leaks.
Be sure the rubber dampers [A] are in position.
•
If any dampers is damaged or deteriorated, replace it.
 Loading...
Loading...