Page 1

SERVICE MANUAL
Mini DV/S-VHS VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER
VICTOR COMPANY OF JAPAN, LIMITED
VIDEO DIVISION
S40894
SR-VS20E/EK
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL
Power requirement : AC 220 V – 240 V`, 50 Hz/60 Hz
Power consumption
Temperature
Operating : 5°C to 40°C
Storage : –20°C to 60°C
Operating position : Horizontal only
Dimensions (WxHxD) : 435 mm x 124 mm x 391 mm
Weight : 6.7 kg
Input/Output : 21-pin SCART connectors :
VHS DECK VIDEO/AUDIO
Signal system : PAL-type colour signal and CCIR monochrome
Recording system : DA4 (Double Azimuth) head helical scan system
Format : S-VHS/VHS PAL standard
Signal-to-noise ratio : 45 dB
Horizontal resolution
No. 82842
Frequency range : 70 Hz to 10,000 Hz (Normal audio)
Maximum recording time
SR-VS20E/EK
TV
VHS
DV
CABLE/SAT
– –:– –
LCD PROG
1
AUDIO
TV/VCR
2
123
3
456
DAILY/QTDN.
VPS/PDC
WEEKLY/HEBDO
4
789
4
0000
AUX
MENU
0
ENTER/ENTREE
OK
1
PROG
30
SEC
3
2
START
STOP
DATE
PR
DEBUT
FIN
EXPRESS
P
V
R
T
+
T
+
V
V
–
T
–
T
R
V
P
(The specifications shown pertain specifically to the model SR-VS20E)
Power on : 33 W
Power off : 7.9 W
IN/OUT x 1, IN/DECODER x 1
RCA connectors:
VIDEO IN x 1, AUDIO IN x 1, AUDIO OUT x 1
S-Video connectors: IN x 1, OUT x 1
DV connector: IN/OUT x 1
(4-pin, IEEE1394 conformity, digital input/output)
signal, 625 lines 50 fields
(SP/LP) : 250 lines (VHS)
400 lines (S-VHS)
(EP) : 220 lines (VHS)
350 lines (S-VHS)
20 Hz to 20,000 Hz (Hi-Fi audio)
(SP) : 240 min. with E-240 video cassette
(LP) : 480 min. with E-240 video cassette
(EP) : 720 min. with E-240 video cassette
DV IN/OUT
ENTREE/SORTIE DV
VHSDV
A.DUBINSERT
DUB
COPIE
PR
DV VHS
DV DECK VIDEO/AUDIO
Signal system : PAL-type colour signal, 625 lines 50 fields
Recording system : Digital Component Recording
Format : DV format (SD mode)
Cassette : Mini DV Cassette
Maximum recording time
(LP) : 90 min. with M-DV60ME cassette
Audio recording system
TUNER/TIMER
TV channel storage
capacity : 99 positions
Tuning system : Frequency synthesized tuner
Channel coverage : VHF 47 MHz – 89 MHz/
Memory backup time : Approx. 60 min.
ACCESSORIES
Provided accessories : RF cable,
Specifications shown are for SP mode unless otherwise specified.
E.& O.E. Design and specifications subject to change without notice.
S-VHS ET
STARTR.A.EDIT
IN/OUT
PULL-OPEN
(SP) : 60 min. with M-DV60ME cassette
: PCM 48 kHz, 16 bit (2 ch)/
32 kHz, 12 bit (4 ch)
(+AUX position)
104 MHz – 300 MHz/
302 MHz – 470 MHz
UHF 470 MHz – 862 MHz
21-pin SCART/RCA cable,
BNC/RCA adapter x 2,
Satellite Controller RM-SD1,
Infrared remote control unit,
"R6" battery x 2
625
Printed in Japan
This service manual is printed on 100% recycled paper.
COPYRIGHT © 2001 VICTOR COMPANY OF JAPAN, LTD.
No. 82842
January 2001
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Section Title Page Section Title Page
Important Safety Precautions
INSTRUCTIONS
1. DISASSEMBLY
1.1 HOW TO REMOVE THE MAJOR PARTS .................................................... 1-1
1.1.1 Introduction ............................................................................................ 1-1
1.2 HOW TO READ THE DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY .............................. 1-1
1.3 DISCONNECTION OF CONNECTORS (WIRES) ........................................ 1-1
1.4
SCREWS USED CABINET COMPONENTS AND BOARD ASSEMBLIES ..........
1.5 HOW TO REMOVE THE MAJOR PARTS <COM section> .......................... 1-2
1.5.1 Disassembly flow chart .......................................................................... 1-2
1.5.2 Disassembly/assembly method <COM section> ................................... 1-2
1.6 HOW TO REMOVE THE MAJOR PARTS <VHS section> ........................... 1-4
1.6.1 Disassembly flow chart .......................................................................... 1-4
1.6.2 DIsassembly/assembly method <VHS section> .................................... 1-4
1.7 HOW TO REMOVE THE MAJOR PARTS <DV section> .............................. 1-6
1.7.1 Disassembly flow chart .......................................................................... 1-6
1.7.2 Disassembly/assembly method <DV section> ....................................... 1-6
1.8 SERVICE POSITIONS .................................................................................. 1-8
1.8.1 Service position <VHS SIDE> ................................................................. 1-8
1.8.2 Service position <DV SIDE> .................................................................... 1-9
1.9 MECHANISM SERVICE MODE .................................................................. 1-10
1.9.1 How to set the "MECHANISM SERVICE MODE" ................................ 1-10
1.10 CONNECTION .......................................................................................... 1-11
1.11 EMERGENCY DISPLAY FUNCTION ........................................................ 1-13
1.11.1 Displaying the emergency information ................................................ 1-13
1.11.2 Clearing the emergency history ........................................................... 1-13
1.11.3 Emergency content description ........................................................... 1-14
1.11.4 Emergency detail information 1 .......................................................... 1-15
1.11.5 Emergency detail information 2 .......................................................... 1-16
2. MECHANISM ADJUSTMENT (VHS)
2.1 BEFORE STARTING REPAIR AND ADJUSTMENT ..................................... 2-1
2.1.1 Precautions ............................................................................................ 2-1
2.1.2 Checking for Proper Mechanical Operations ......................................... 2-1
2.1.3 Manually Removing the Cassette Tape ................................................. 2-1
2.1.4 Jigs and Tools Required for Adjustment................................................. 2-2
2.1.5 Maintenance and Inspection .................................................................. 2-3
2.2 REPLACEMENT OF MAJOR PARTS ........................................................... 2-6
2.2.1 Before Starting Disassembling (Phase matching between
mechanical parts) ................................................................................... 2-6
2.2.2 How to Set the Mechanism Assembling Mode ....................................... 2-6
2.2.3 Cassette Holder Assembly ..................................................................... 2-6
2.2.4 Pinch Roller Arm Assembly .................................................................... 2-8
2.2.5 Guide Arm Assembly and Press Lever Assembly .................................. 2-8
2.2.6 Audio Control Head................................................................................ 2-8
2.2.7 Loading Motor ........................................................................................ 2-8
2.2.8 Capstan Motor ....................................................................................... 2-9
2.2.9 Pole Base Assembly (supply or take-up side) ........................................ 2-9
2.2.10 Rotary Encoder .................................................................................. 2-10
2.2.11 Clutch Unit ......................................................................................... 2-10
Change Lever Assembly, Direct Gear, Clutch Gear and Coupling Gear .........
2.2.12
2.2.13 Link Lever .......................................................................................... 2-11
2.2.14 Cassette Gear, Control Cam and Worm Gear ................................... 2-11
2.2.15 Control Plate ...................................................................................... 2-11
2.2.16
Loading Arm Gear (supply or take-up side) and Loading Arm Gear Shaft ..........
2.2.17 Take-up Lever, Take-up Head and Control Plate Guide .................... 2-13
2.2.18 Capstan Brake Assembly .................................................................. 2-13
2.2.19 Sub Brake Assembly (take-up side) .................................................. 2-13
2.2.20 Main Brake Assembly (take-up side), Reel Disk (take-up side)
and Main Brake Assembly (supply side) ............................................ 2-13
2.2.21 Tension Brake Assembly, Reel Disk (supply side) and
Tension Arm Assembly ...................................................................... 2-14
2.2.22 Idler Lever, Idler Arm Assembly ......................................................... 2-14
2.2.23 Stator Assembly ................................................................................. 2-14
2.2.24 Rotor Assembly ................................................................................. 2-14
2.2.25 Upper Drum Assembly ....................................................................... 2-15
2.3 COMPATIBILITY ADJUSTMENT ................................................................ 2-16
2.3.1 Checking/Adjustment of FM Waveform Linearity ................................. 2-16
Checking/Adjustment of the Height and Tilt of the Audio Control Head ........
2.3.2
2.3.3
Checking/Adjustment of the Audio Control Head Phase (X-Value) .........
2.3.4 Checking/Adjustment of the Standard Tracking Preset ....................... 2-18
2.3.5 Checking/Adjustment of the Tension Pole Position .............................. 2-18
MECHANISM ADJUSTMENT (DV)
2.9 PREPARATION ........................................................................................... 2-21
2.9.1 Precautions .......................................................................................... 2-21
2.9.2 Tools Required for Adjustments ........................................................... 2-21
2.9.3 Disassembly and Assembly Procedures .............................................. 2-21
2.9.4 Screws and Washers Used in Disassembly/Assembly of the
Mechanism Assembly .......................................................................... 2-21
2.10 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY OF THE MECHANISM ASSEMBLY ............. 2-22
2.10.1 Introduction ........................................................................................ 2-22
2.10.2 Mechanism Modes ............................................................................ 2-22
2.11 MECHANISM TIMING CHART .................................................................. 2-24
2.12 MECHANISM ASSEMBLY/DISASSEMBLY PROCEDURE TABLE ........... 2-25
2.13 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY ...................................................................... 2-27
2.14 LIST OF PROCEDURES FOR DISASSEMBLY ........................................ 2-35
2.15 MECHANISM DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY SHEET .................................. 2-36
2.16 MECHANISM PHASE CHECK/ADJUSTMENT ......................................... 2-38
2.17 POSITIONING THE TENSION POLE ........................................................ 2-39
2.18 COMPATIBILITY AND ERROR RATE ADJUSTMENTS ............................ 2-40
2.18.1 Preparation ........................................................................................ 2-40
2.18.2 Adjustment ......................................................................................... 2-40
2.18.3 Linearity adjustment .......................................................................... 2-41
2.18.4 PB switching point adjustment ........................................................... 2-41
2.18.5 Error rate adjustment ......................................................................... 2-41
2.18.6 Error rate measuring method ............................................................. 2-41
2.19 TAPE EJECTION ....................................................................................... 2-42
1-1
2-10
2-12
2-17
2-17
3. ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENT (VHS)
3.1 PRECAUTION .............................................................................................. 3-1
3.1.1 Required test equipments ...................................................................... 3-1
3.1.2 Required adjustment tools ..................................................................... 3-1
3.1.3 Color (colour) bar signal,Color (colour) bar pattern ............................... 3-1
3.1.4 Switch settings and standard precautions ............................................. 3-1
3.1.5 EVR Adjustment ..................................................................................... 3-1
3.2 SERVO CIRCUIT .......................................................................................... 3-2
3.2.1 Switching point ....................................................................................... 3-2
3.2.2 Slow tracking preset ............................................................................... 3-2
3.3 VIDEO CIRCUIT ........................................................................................... 3-2
3.3.1 D/A level ................................................................................................. 3-2
3.3.2 EE Y level ............................................................................................... 3-3
3.3.3 PB Y level (S-VHS / VHS) ...................................................................... 3-3
3.3.4 REC color (colour) level ......................................................................... 3-3
3.3.5 Video EQ (Frequency response) ........................................................... 3-4
3.3.6 AUTO PICTURE initial setting ............................................................... 3-4
3.3.7 DV EE Y level ......................................................................................... 3-4
3.4 AUDIO CIRCUIT ........................................................................................... 3-5
3.4.1 Audio REC FM ....................................................................................... 3-5
3.5 SYSCON CIRCUIT [SR-VS20E] ................................................................... 3-5
3.5.1 Timer clock ............................................................................................. 3-5
ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENT (DV)
3.6 PREPARATION ............................................................................................. 3-6
3.6.1 Precautions ............................................................................................ 3-6
3.6.2 Equipment required for adjustment ........................................................ 3-6
3.6.3 Tools required for adjustments ............................................................... 3-6
3.6.4 Setup ...................................................................................................... 3-6
4. CHARTS AND DIAGRAMS
NOTES OF SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ................................................................... 4-1
CIRCUIT BOARD NOTES .................................................................................... 4-2
4.1 BOARD INTERCONNECTIONS ................................................................... 4-3
SWITCHING REGULATOR AND REGULATOR SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS ..........
4.2
4.3 VIDEO/AUDIO SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ....................................................... 4-7
4.4 SYSTEM CONTROL SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ............................................. 4-9
4.5 SUB CPU SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ............................................................ 4-13
4.6 TUNER SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ................................................................ 4-15
4.7 VIDEO I/O SWITCH SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ............................................ 4-17
4.8 AUDIO I/O SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ........................................................... 4-19
4.9 CONNECTION SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM .................................................... 4-21
4.10 3D DIGITAL/2M SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ................................................. 4-23
4.11 TERMINAL SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ........................................................ 4-25
4.12 DEMODULATOR SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM .............................................. 4-27
4.13 S-SUB SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ............................................................... 4-29
4.14 MDA SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM .................................................................. 4-31
4.15 PRE/REC SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM .......................................................... 4-33
4.16 ON SCREEN SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ..................................................... 4-35
DISPLAY, EJECT SW, LED/SW, JACK AND JOG SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS .........
4.17
4.18 DV SYSTEM CONTROL SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ................................... 4-39
4.19 DV MSD SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ............................................................ 4-41
4.20 DV MAIN SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ........................................................... 4-43
4.21 DV I/O SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ............................................................... 4-45
4.22 DV V OUT SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ......................................................... 4-47
4.23 AUDIO AD/DA SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ................................................... 4-49
4.24 DV DSP SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ............................................................. 4-51
4.25
SWITCHING REGULATOR AND REGULATOR CIRCUIT BOARDS ..........
4.26 3D DIGITAL/2M AND S-SUB CIRCUIT BOARDS .................................... 4-55
4.27 TERMINAL CIRCUIT BOARD .................................................................. 4-56
4.28 MAIN CIRCUIT BOARD ........................................................................... 4-57
4.29 DEMODULATOR AND ON SCREEN CIRCUIT BOARDS........................ 4-60
4.30
DISPLAY, EJECT SW, JACK, LED/SW AND JOG CIRCUIT BOARDS ..........
4.31 PRE/REC MDA CIRCUIT BOARD............................................................ 4-63
4.32 DV MAIN CIRCUIT BOARD ..................................................................... 4-65
4.33 FDP GRID ASSIGNMENT AND ANODE CONNECTION ......................... 4-71
4.34 REMOTE CONTROL SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ........................................ 4-72
4.35 WAVEFORMS ........................................................................................... 4-73
4.36 VOLTAGE CHARTS.................................................................................. 4-75
4.37 CPU PIN FUNCTION................................................................................ 4-78
4.38 SYSTEM CONTROL BLOCK DIAGRAM (VHS) ....................................... 4-79
4.39 VIDEO BLOCK DIAGRAM(VHS) .............................................................. 4-81
4.40 AUDIO BLOCK DIAGRAM (VHS)............................................................. 4-85
4.41 SYSTEM CONTROL BLOCK DIAGRAM (DV) ......................................... 4-87
4.42 VIDEO BLOCK DIAGRAM (DV) ............................................................... 4-89
5. PARTS LIST
5.1 PACKING AND ACCESSORY ASSEMBLY <M1> ....................................... 5-1
5.2 FINAL ASSEMBLY <M2> ............................................................................. 5-2
5.3 MECHANISM ASSEMBLY (VHS) <M3> ...................................................... 5-4
5.4 MECHANISM ASSEMBLY (DV) <M4>......................................................... 5-6
5.5 ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST ........................................................................... 5-8
SW REGULATOR BOARD ASSEMBLY <01> ................................................... 5-8
REGULATOR BOARD ASSEMBLY <02> .......................................................... 5-9
MAIN BOARD ASSEMBLY <03> ..................................................................... 5-10
3D DIGITAL/2M BOARD ASSEMBLY <05> ..................................................... 5-18
TERMINAL BOARD ASSEMBLY <06> ............................................................ 5-19
AUDIO CONTROL HEAD BOARD ASSEMBLY <12> ..................................... 5-21
DEMOD BOARD ASSEMBLY <14> ................................................................. 5-21
S-SUB BOARD ASSEMBLY <15> ................................................................... 5-22
DV PRE/REC MDA BOARD ASSEMBLY <16> ............................................... 5-23
ON SCREEN BOARD ASSEMBLY <17> ......................................................... 5-24
EJECT SW BOARD ASSEMBLY <27> ............................................................ 5-25
SW/DISPLAY BOARD ASSEMBLY <28> ........................................................ 5-25
JACK BOARD ASSEMBLY <36> ..................................................................... 5-26
LED/SW BOARD ASSEMBLY <47> ................................................................ 5-26
DV MAIN BOARD ASSEMBLY <50> ............................................................... 5-26
LOADING MOTOR BOARD ASSEMBLY <55> ............................................... 5-32
JOG BOARD ASSEMBLY <85> ....................................................................... 5-32
4-5
4-37
4-53
4-61
The following table lists the differing points between Models (SR-VS20EK and SR-VS20E) in this series.
SR-VS20EK SR-VS20E
VIDEO SYSTEM PAL/NTSC PB ON PAL TV PAL/MESECAM(MANUAL)/NTSC PB ON PAL TV
TUNER (BROADCASTING STANDARD) I B/G, D/K
TUNER (STEREO DECODER) NICAM NICAM/A2
DISPLAY (LANG.) ENGLISH 3 LANGUAGE
TIMER (VCR PLUS+) VIDEO PLUS+ DELUXE SHOW VIEW DELUXE
TIMER (VPS) NOT USED USED
Page 3

Important Safety Precautions
Prior to shipment from the factory, JVC products are strictly inspected to conform with the recognized product safety and electrical codes of the
countries in which they are to be sold. However, in order to maintain such compliance, it is equally important to implement the following precautions
when a set is being serviced.
Precautions during Servicing
•
1. Locations requiring special caution are denoted by labels and inscriptions on the cabinet, chassis and certain parts of the product.
When performing service, be sure to read and comply with these
and other cautionary notices appearing in the operation and service manuals.
2. Parts identified by the ! symbol and shaded ( ) parts are
critical for safety.
Replace only with specified part numbers.
Note: Parts in this category also include those specified to com-
ply with X-ray emission standards for products using
cathode ray tubes and those specified for compliance
with various regulations regarding spurious radiation
emission.
3. Fuse replacement caution notice.
Caution for continued protection against fire hazard.
Replace only with same type and rated fuse(s) as specified.
4. Use specified internal wiring. Note especially:
1) Wires covered with PVC tubing
2) Double insulated wires
3) High voltage leads
5. Use specified insulating materials for hazardous live parts. Note
especially:
1) Insulation Tape 3) Spacers 5) Barrier
2) PVC tubing 4) Insulation sheets for transistors
6. When replacing AC primary side components (transformers, power
cords, noise blocking capacitors, etc.) wrap ends of wires securely
about the terminals before soldering.
12. Crimp type wire connector
In such cases as when replacing the power transformer in sets
where the connections between the power cord and power transformer primary lead wires are performed using crimp type connectors, if replacing the connectors is unavoidable, in order to prevent
safety hazards, perform carefully and precisely according to the
following steps.
1) Connector part number : E03830-001
2) Required tool : Connector crimping tool of the proper type which
will not damage insulated parts.
3) Replacement procedure
(1) Remove the old connector by cutting the wires at a point
close to the connector.
Important : Do not reuse a connector (discard it).
cut close to connector
Fig.3
(2) Strip about 15 mm of the insulation from the ends of the
wires. If the wires are stranded, twist the strands to avoid
frayed conductors.
15 mm
Fig.1
7. Observe that wires do not contact heat producing parts (heatsinks,
oxide metal film resistors, fusible resistors, etc.)
8. Check that replaced wires do not contact sharp edged or pointed
parts.
9. When a power cord has been replaced, check that 10-15 kg of
force in any direction will not loosen it.
Power cord
Fig.2
10. Also check areas surrounding repaired locations.
11. Products using cathode ray tubes (CRTs)
In regard to such products, the cathode ray tubes themselves, the
high voltage circuits, and related circuits are specified for compliance with recognized codes pertaining to X-ray emission.
Consequently, when servicing these products, replace the cathode ray tubes and other parts with only the specified parts. Under
no circumstances attempt to modify these circuits.
Unauthorized modification can increase the high voltage value and
cause X-ray emission from the cathode ray tube.
Fig.4
(3) Align the lengths of the wires to be connected. Insert the
wires fully into the connector.
Metal sleeve
Connector
Fig.5
(4) As shown in Fig.6, use the crimping tool to crimp the metal
sleeve at the center position. Be sure to crimp fully to the
complete closure of the tool.
1.25
2.0
5.5
Fig.6
(5) Check the four points noted in Fig.7.
Not easily pulled free
Wire insulation recessed
more than 4 mm
Fig.7
Crimping tool
Crimped at approx. center
of metal sleeve
Conductors extended
I
S40888-01
Page 4

Safety Check after Servicing
•
Examine the area surrounding the repaired location for damage or deterioration. Observe that screws, parts and wires have been returned
to original positions, Afterwards, perform the following tests and confirm the specified values in order to verify compliance with safety
standards.
1. Insulation resistance test
Confirm the specified insulation resistance or greater between power cord plug prongs and externally exposed parts of the set (RF terminals, antenna terminals, video and audio input and output
terminals, microphone jacks, earphone jacks, etc.). See table 1 below.
2. Dielectric strength test
Confirm specified dielectric strength or greater between power cord plug prongs and exposed accessible parts of the set (RF terminals, antenna terminals, video and audio input and output terminals,
microphone jacks, earphone jacks, etc.). See table 1 below.
3. Clearance distance
When replacing primary circuit components, confirm specified clearance distance (d), (d’) between soldered terminals, and between terminals and surrounding metallic parts. See table 1
below.
Fig. 8
4. Leakage current test
Confirm specified or lower leakage current between earth ground/power cord plug prongs and
externally exposed accessible parts (RF terminals, antenna terminals, video and audio input and
output terminals, microphone jacks, earphone jacks, etc.).
Measuring Method : (Power ON)
Insert load Z between earth ground/power cord plug prongs and externally exposed accessible
parts. Use an AC voltmeter to measure across both terminals of load Z. See figure 9 and following
table 2.
Externally
exposed
accessible part
Fig. 9
Z
V
ab
A
c
5. Grounding (Class 1 model only)
Confirm specified or lower grounding impedance between earth pin in AC inlet and externally exposed accessible parts (Video in, Video out,
Audio in, Audio out or Fixing screw etc.).
Measuring Method:
Connect milli ohm meter between earth pin in AC inlet and exposed accessible parts. See figure 10 and grounding specifications.
Fig. 10
Table 1 Specifications for each region
Table 2 Leakage current specifications for each region
Note: These tables are unofficial and for reference only. Be sure to confirm the precise values for your particular country and locality.
II
S40888-01
Page 5

Page 6

SECTION 1
DISASSEMBLY
1.1 HOW TO REMOVE THE MAJOR PARTS
1.1.1 Introduction
This set is a double-deck video recorder integrating a Mini DV
deck and a VHS deck. Its internal structure is divided into three
sections that include the power supply, VHS and DV sections.
Therefore, the removal of major parts will also be described
under three separate sections as listed below.
1. COMMON section
2. VHS section
3. DV section
< TOP VIEW >
1. COMMON section
3. DV section
2. VHS section
Fig. 1-1-1
1.2 HOW TO READ THE DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
Step/
Loc No.
1
Top cover, Bracket COM1
Front panel
2
assembly
Fig. No.
4(S1), 3(S2), 2(L1), (L2)
2(S3)
COM2 8(L3),
CN7507(WR1),
CN3011(WR2)
Point NotePart name
—
<Note
1,2,3,4>
§§ §§ §
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5)
(1) Order of steps in Procedure
When reassembling, perform the step(s) in the reverse order.
These numbers are also used as the identification (location) No.
of parts Figures.
(2) Part name to be removed or installed.
(3) Fig. No. showing procedure or part location.
(4) Identification of part to be removed, unhooked, unlocked,
released, unplugged, unclamped or unsoldered.
P= Spring, W= Washer, S= Screw, L= Locking tab, SD= Solder,
CN**(WR**)= Remove the wire (WR**) from the connector
(CN**).
Note:
• The bracketed ( ) WR of the connector symbol are as-
signed nos. in priority order and do not correspond to
those on the spare parts list.
(5) Adjustment information for installation
1.3 DISCONNECTION OF CONNECTORS (WIRES)
FPC
CONNECTOR
FPC
CONNECTOR
Fig. 1-3-1 Fig. 1-3-2
FPC
CONNECTOR
FPC
CONNECTOR
Fig. 1-3-3 Fig. 1-3-4
FPC
CONNECTOR
Fig. 1-3-5
1.4 SCREWS USED CABINET COMPONENTS AND BOARD ASSEMBLIES
Table 1-4-1 below shows the symbols, shapes, colors and
part numbers of screw that are used in the cabinet components and board assemblies and are appearing in the disassembling/reassembling diagrams in this manual.
When screwing them again in reassembling, be sure to use
them correctly referring to the following table.
Notes:
• Screw that are asterisked (marked with*) in the shape col-
umn are fixed with screw lock agent. If such the screw is
once removed, never use it again.
• The Screw symbols are assigned nos. in priority order and
do not correspond to those on the spare parts list.
SYMBOL PARTS NO. COLOR
S1 QYTDST3006R SILVER BLACK
S2 QYTDST3006M BLACK
S3 QYTDSF3010Z GOLD
S4 QYTDSF2606Z GOLD
S5 QYTDST3006Z GOLD
S6 QYTDSF3008M BLACK
S7 QYTDST2610Z GOLD
S8 PQ21623-2-5 GOLD
S9 PQ40413 BLACK
S10 LP40700-001A BLACK
S11 QYTDSP2004Z GOLD
S12 QYTDST2004Z GOLD
S13 YQ43893 SILVER
Table 1-4-1
1-1
Page 7

HOW TO REMOVE THE MAJOR PARTS <COM section>
1.5
1.5.1 Disassembly flow chart
This flowchart shows the disassembly procedure for the exterior parts and electrical parts.
Basically, reverse this procedure when assembling them.
1 Top cover, Bracket
<Note 5>
When removing the SW REG board assembly or Regulator board assembly, unhook the several spacers connecting it with pliers from the top side.
<Note 6>
Perform the work by leaving fan motor attached to the rear
cover except when replacing the fan motor.
When attaching the rear cover, please be careful with the
wiring.
2 Front panel assembly
Display board assembly, Display/SW board assembly,
3
SW board assembly, LED1, 2 board assembly
4 SW REG board assembly
5 Regulator board assembly
6 Rear cover
Disassembly/assembly method <COM section>
1.5.2
Step/
Loc No.
Top cover, Bracket COM1
1
Front panel
2
assembly
Fig. No.
4(S1), 3(S2), 2(L1), (L2)
2(S3)
COM2 8(L3),
CN7507(WR1),
Point NotePart name
<Note
1,2,3,4>
CN3011(WR2)
Display board assembly,
3
LED/SW board assembly,
Eject SW board assembly,
Jack board assembly,
Jog board assembly
SW REG board
4
assembly
Regulator board
5
assembly
COM3 10(S4)
6(S4), Knob(Jog),
Knob(Shuttle),
COM4 2(S5), 2(L4), (L5)
CN5301(WR3),
COM5 3(L6),
CN5322(WR4),
CN5321(WR5),
<Note 1,
5>
<Note 1,
5>
CN5325(WR6),
CN5324(WR7),
CN5323(WR8)
6
COM6 4(S2), 6(S6),
Fan motor
<NOTE 6>Rear cover
<Note 1>
When attaching the FPC, be sure to connect it in the correct orientation.
<Note 2>
When attaching the front panel assy, make sure that the
door openers of both decks (DV, VHS) are in the down
position.
<Note 3>
When attaching the front panel assy, be careful not to damage the DV terminals.
<Note 4>
When attaching the FPC take care that it is not caught.
Pass the DV-side FPC between the base (2) and DV Main
board assy.
Pass the two VHS-side FPCs below the base (1).
(S3)
6
(S2)
9
Bracket
1
5
(S2)
(S1)
7
(S2)
4
(S1)
3
Top cover
(L2)
8
(S3)
1
1
(S1)
(L1)
2
(S1)
—
—
Fig. COM1
<Note 4>
FPC
<Note 2>
DV SIDE
Base (2)
<Note 3>
DV Main board
assembly
(L3)
(L3)
Base (1)
(L3)
CN3011
<Note 4>
WR2
WR1
(L3)
CN7507
<Note 1>
Supporting
tape side
<Note 2>
VHS SIDE
2
Fig. COM2
1-2
Page 8
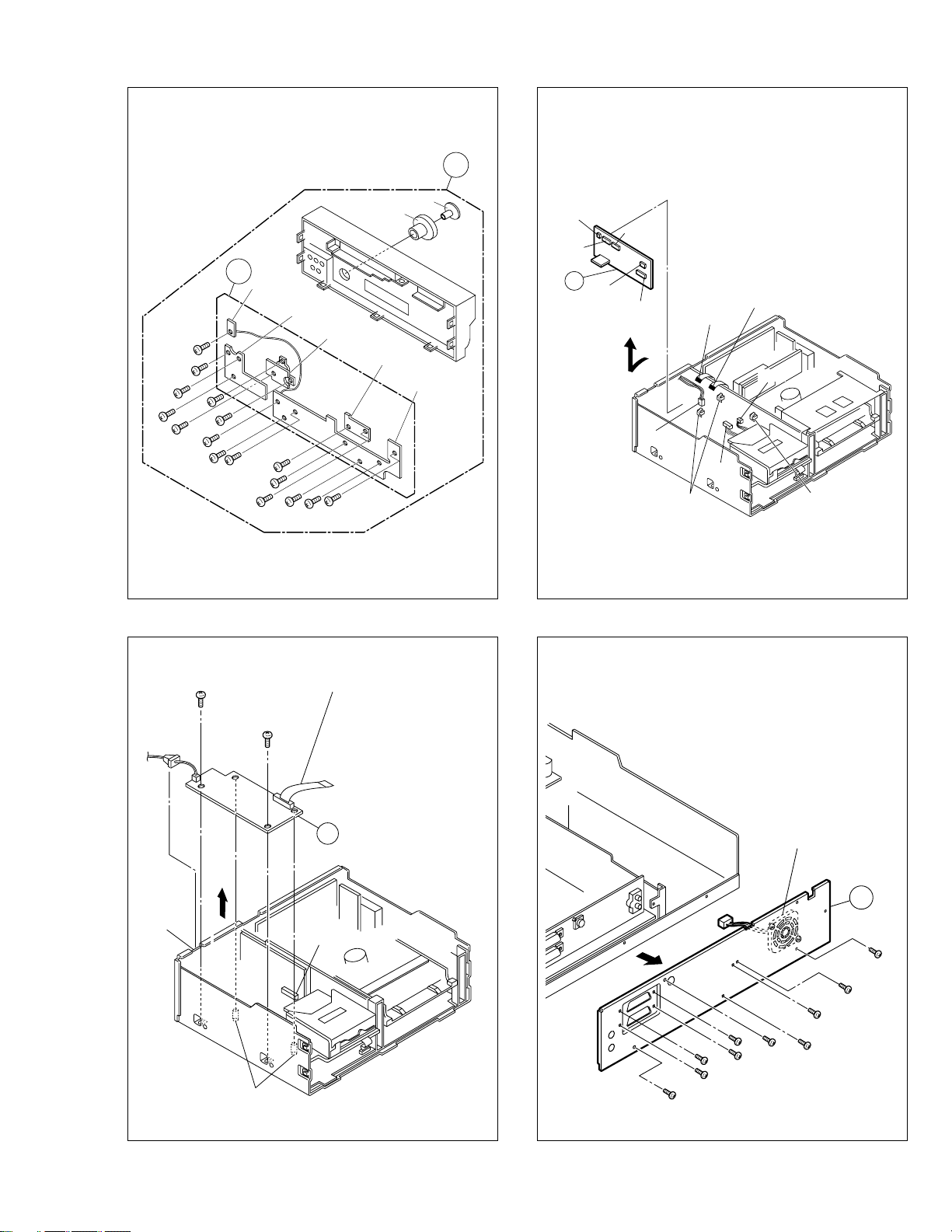
<Note 6>
Fan Motor
6
28
(S2)
29
(S2)
33
(S6)
32
(S6)
35
(S6)
34
(S6)
36
(S6)
37
(S6)
30
(S2)
31
(S2)
22
5
CN5325
CN5324
WR8
WR5
Foil side
<Note 1>
WR4
Foil side
<Note 1>
WR6
WR7
CN5321
CN5322
(L6)
Spacer
<Note 5>
(L6)
Spacer
<Note 5>
CN5323
(S4)
21
(S4)
(S4)
2
Knob (Jog)
Knob (Shuttle)
3
Eject SW
board assembly
Jack board
assembly
11
(S4)
10
(S4)
Jog board assembly
LED/SW board
assembly
Display board
assembly
9
(S4)
20
(S4)
23
(S4)23(S4)
25
(S4)
24
16
(S4)
15
(S4)
14
(S4)
17
(S4)
(S4)
18
(S4)
13
(S4)
12
(L5)
26
(S5)
Fig. COM3
27
(S5)
Fig. COM5
WR3
Supporting
tape side
<Note 1>
4
CN5301
Spacer
<Note 5>
(L4)
Fig. COM4
Fig. COM6
1-3
Page 9
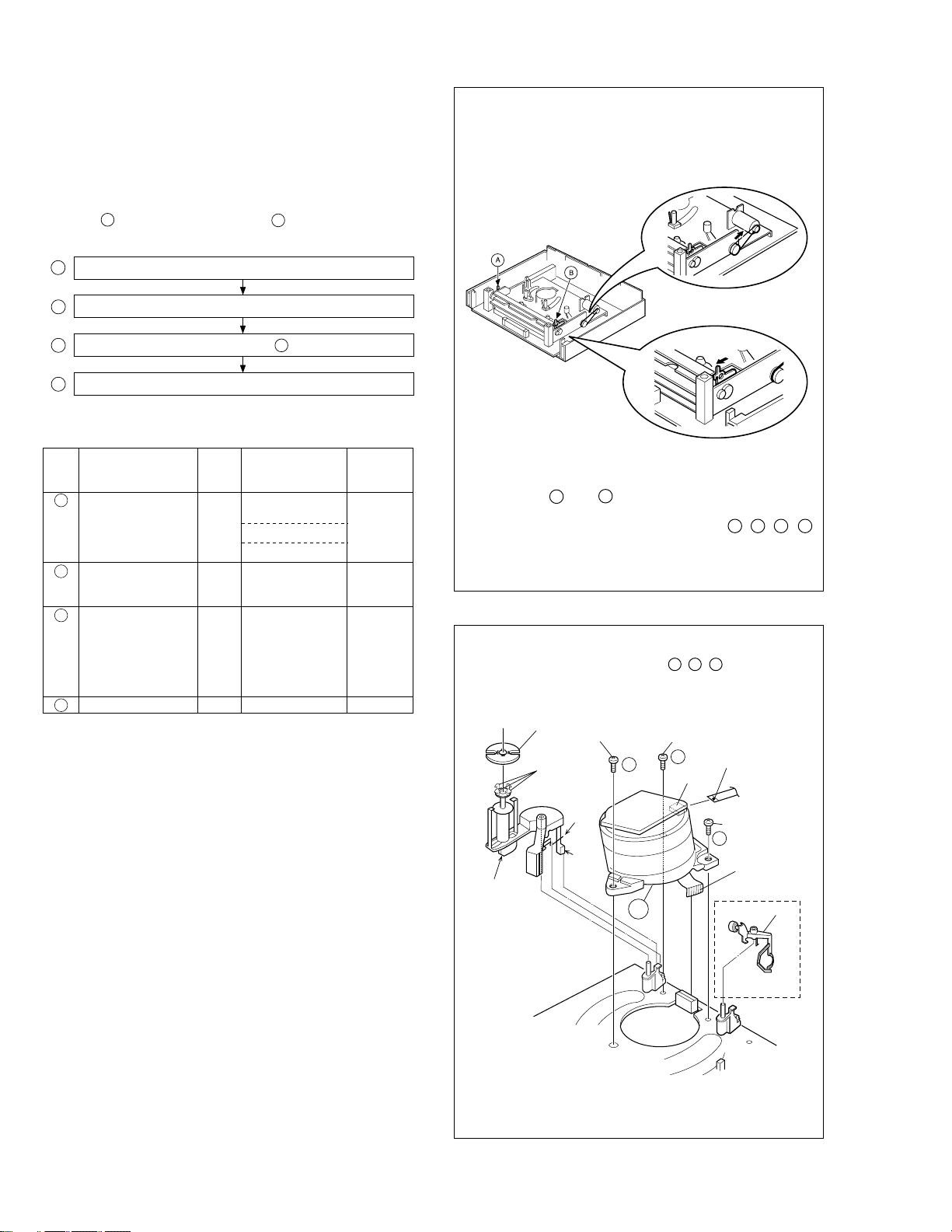
HOW TO REMOVE THE MAJOR PARTS <VHS section>
1.6
1.6.1 Disassembly flow chart
This flowchart shows the disassembly procedure for the exterior parts and electrical parts.
Basically, reverse this procedure when assembling them.
However, it is required to remove the common section parts
as far as 1 “Top cover Bracket” and 2 “Front panel assembly” in advance. (See section 1.5.)
1 Drum assembly
2 Mechanism assembly
3 Main board assembly / 4 Base (1)
4 Base (1)
Procedures for Lowering the Cassette holder assembly
As the mechanism of this unit is integrated with the Housing
assembly, the holder must be lowered and the two screws unscrewed when removing the Mechanism assembly.
Fig. 2
Fig. 1
1.6.2 DIsassembly/assembly method <VHS section>
Step/
Loc No.
1
Drum assembly
(Inertia plate)
(Roller arm assy)
2
Mechanism
assembly
Main board
3 <Note 2>
assembly
Base (1) V4 (S3), 3(S5)4 —
Fig. No.
V1
Point NotePart name
3(S7), CON1(WR9),
CN1(WR10)
4(L1)
(P1), (L2)
V2
2(S8), (S9), (S10),
(L3), (L4),
CN1(WR11),
V3 6(S6), 2(S3), (S5),
CN5321(WR12),
CN5322(WR13),
CN3014(WR14),
CN703(WR15),
CN2601(WR16)
<Note 1,2>
<Note 2,4>
<Note 1>
When attaching or removing the FPC, take care not to disconnect any of the wires.
<Note 2>
When attaching the FPC, be sure to connect it in the correct orientation.
<Note 3>
When attaching wires, connect them in the correct orientation.
Fig. 3
Turn the loading motor pulley in the direction as indicated by
Fig.2. As both A and B levers are lodged twice, push the
levers in the direction as indicated by Fig.3 to release them.
When pushing the levers, do it in the order of A , B , B , A .
When the holder has been lowered, turn the pulley until the
cassette holder is securely in place without allowing any up/
down movement.
Procedures for Lowering the Cassette holder assembly
Note: When installing the Drum assembly, secure the
screws (S7) in the order of a , b , c .
Roller arm
assy
Inertia plate
(L1)
(P1)
(L2)
(S7)
1
a
2
(S7)
WR9
Foil side
c
<Note 2>
CON1
3
(S7)
b
WR10
Foil side
<Note 1,2>
1
Cleaner assy
<Note 4>
• When it is required to remove the screws (S8) retaining the
Mechanism assembly, please refer to the “Procedures for
Lowering the Cassette holder assembly”(See on page 1-5).
• When removing the Mechanism assembly only, unhook the
two spacers connecting it with the Main board assembly with
pliers from the back side of the Main board assembly first,
and then remove the Mechanism assembly.
• When reattaching the Mechanism assembly to the Main
board assembly, take care not to damage the sensors on
the Main board assembly (D3001: LED, Q3002: Start sensor, Q3003: End sensor, S3002: S cassette switch).
1-4
Not use
CN1
Fig. V1
Page 10
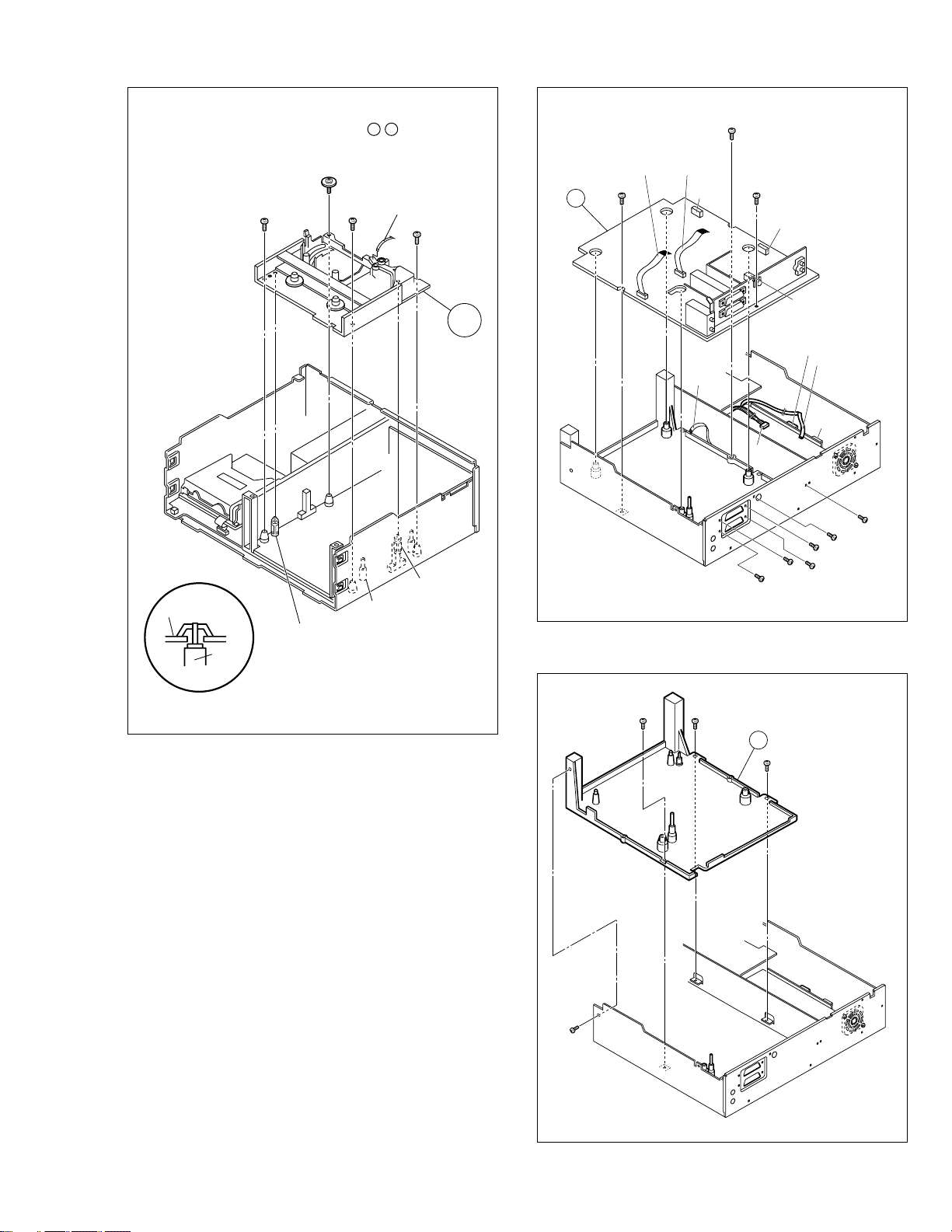
Note: When installing the Mechanism assembly, secure
the screws (S8) in the order of a , b .
6
5
(S8)
<Note 4>
Mechanism assy
Spacer
(S9)
(L3)
Spacer
<Note 4>
4
(S8)
<Note 4>
S3002
S cassette switch
<Note 4>
WR11
Foil side
<Note 2>
(S10)
(L4)
Spacer
<Note 4>
7
2
15
(S3)
WR5
Foil side
<Note 2>
14
(S3)
3
WR4
Foil side
<Note 2>
CN3014
WR12
Foil side
<Note 2>
16
(S5)
WR13
9
(S6)
CN2601
CN703
8
(S6)
(S6)
CN5321
WR14
Foil side
<Note 2>
CN5322
10
(S6)
11
12
(S6)
13
(S6)
Fig. V3
<Note 4>
Fig. V2
17
(S3)
18
(S5)
19
(S5)
4
20
(S5)
Fig. V4
1-5
Page 11
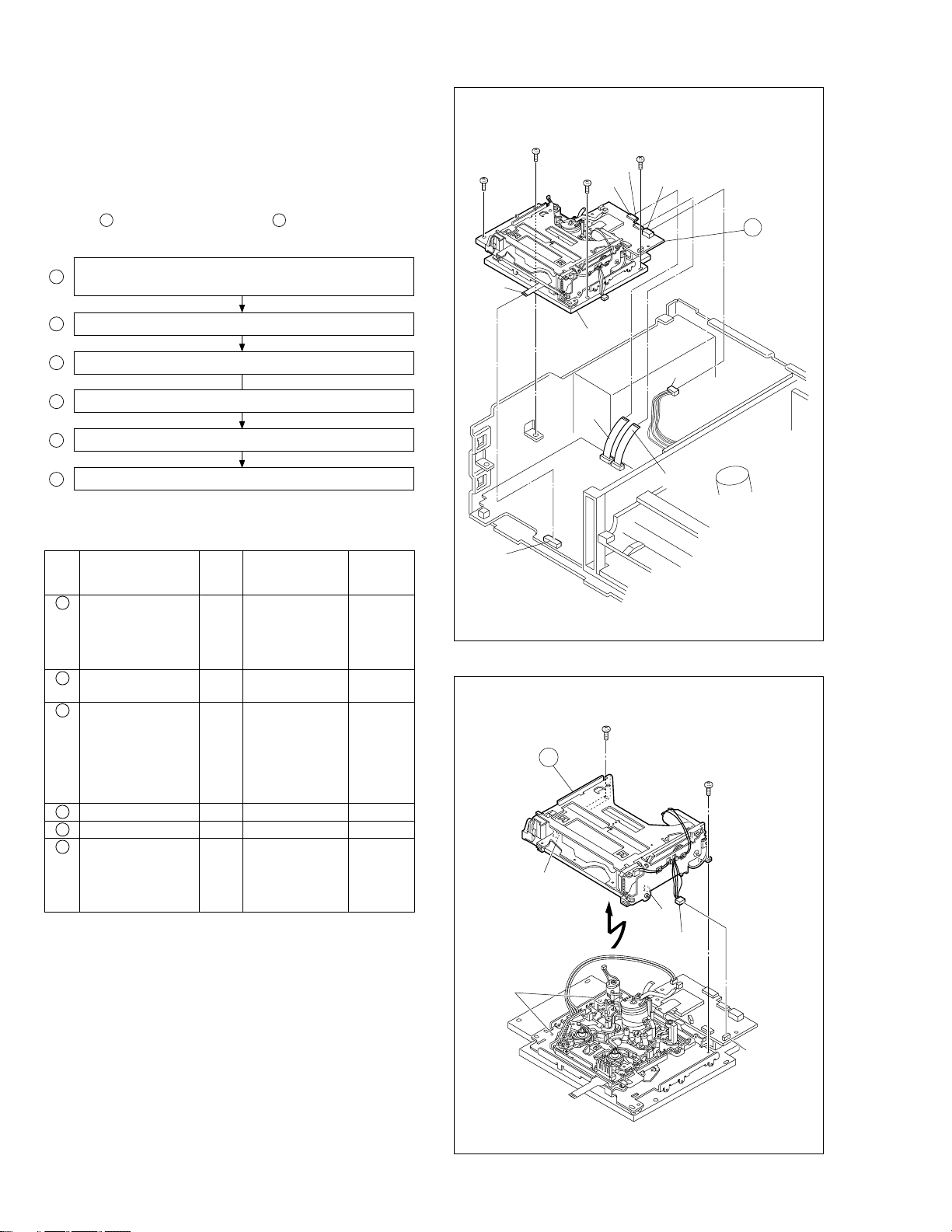
HOW TO REMOVE THE MAJOR PARTS <DV section>
1.7
1.7.1 Disassembly flow chart
This flowchart shows the disassembly procedure for the exterior parts and electrical parts.
Basically, reverse this procedure when assembling them.
However, it is required to remove the common section parts
as far as 1 “Top cover, Bracket” and 2 “Front panel assembly” in advance. (See section 1.5.)
1
Mechanism assembly,
P/R MDA board assembly
2 Cassette housing assembly
3 P/R MDA board assembly
4 Mechanism assembly
5 Drum assembly
6 DV Main board assembly
1.7.2 Disassembly/assembly method <DV section>
Step/
Loc No.
1
Mechanism assembly,
P/R MDA
board assembly
2
Cassette housing
assembly
3
P/R MDA
board assembly
4
Mechanism assembly
5
Drum assembly D5 3(S13)
6
DV Main board
assembly
Fig. No.
D1 4(S5),
D2
D3 (S12),(S11),2(S5),
D4 3(S4), 2(L3)
D6 4(S5),
Point NotePart name
CN1502(WR17),
CN5002(WR18),
CN5506(WR19),
CN5501(WR7)
2(S11),2(L1),2(L2),
CN5507(WR20)
CN5502(WR21),
CN5505(WR22),
CN5503(WR23),
CN5504(WR24),
CN5001(WR25),
Earth plate
CN1002(WR14),
CN3701(WR16),
CN1001(WR8),
CN3501(WR15)
<Note 1>
—
—
—
<Note 2>
<Note 3,4>
<Note 1>
With due regard to operational considerations, remove the
parts located on the base (2) (i.e. Mechanism assembly,
P/R MDA board assembly etc.) together before removing
the major parts.
<Note 2>
Take care not to scratch or damage the drum assembly
by the cleaner assembly when performing work.
<Note 3>
Take care not to damage the board assembly when detaching parts.
<Note 4>
When attaching the FPC, be sure to connect it in the correct orientation.
1
(S5)
WR17
CN1501
(L1)
2
(S5)
(L2)
2
3
(S5)
Base(2)
WR16
(S11)
CN5506
CN5502
Fig. D1
5
Fig. D2
4
(S5)
CN5501
1
<Note 1>
WR7
WR17
6
(S11)
(L2)
WR18
CN5507
1-6
Page 12
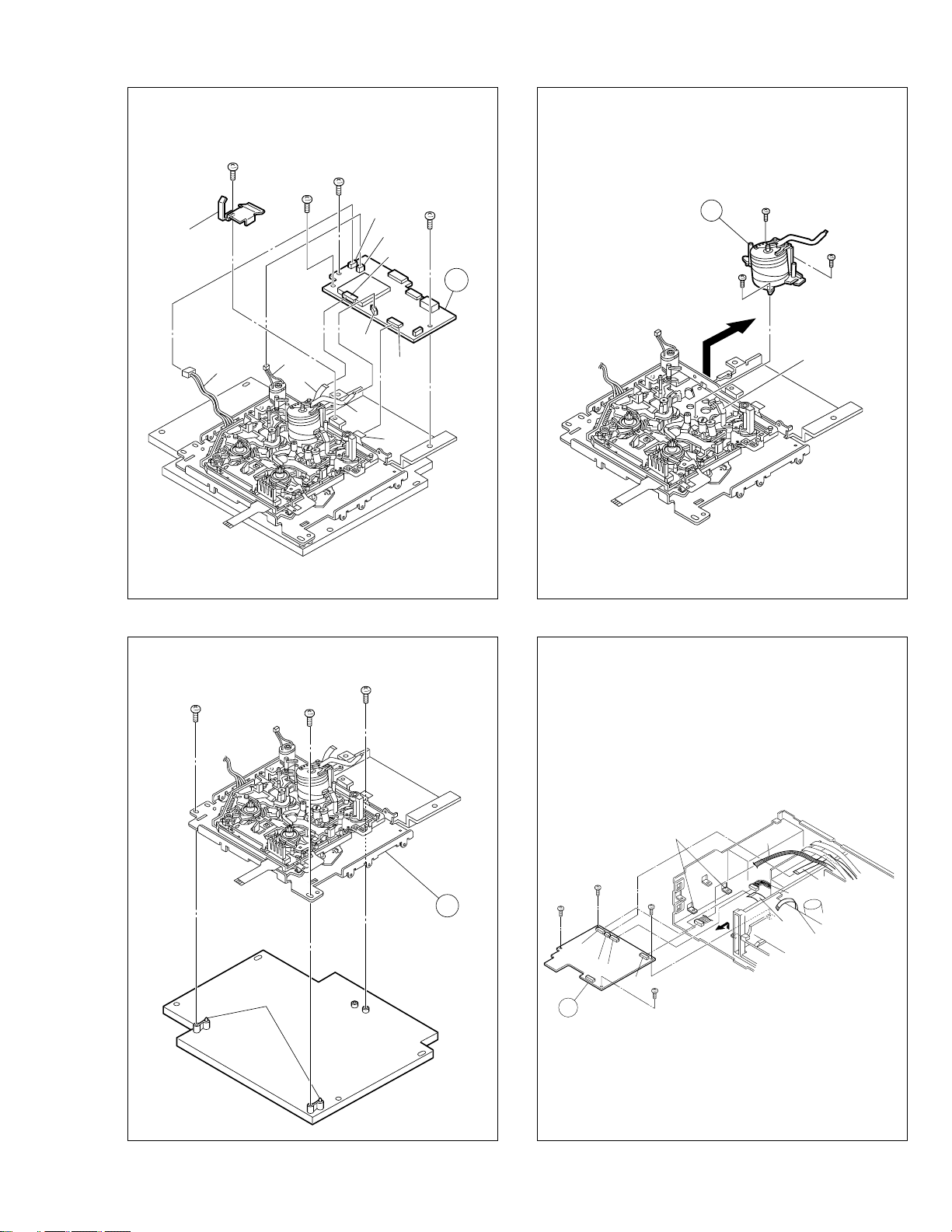
Earth
6
20
(S5)
WR13
CN3501
CN3701
CN1001
CN1002
WR12
<Note 3>
Foil side
<Note 4>
Supporting
tape side
<Note 3>
WR14
WR8
17
(S5)
19
(S5)
18
(S5)
plate
(
7
S12
)
(
S11
9
(S5)
8
)
10
(S5)
CN5505
CN5502
CN5001
5
15
(
S13
3
14
(
)
S13
16
)
(
S13
)
11
(S4)
WR20
WR19
WR23
Fig. D3
12
(S4)
CN5503
WR21
13
(S4)
CN5504
WR22
<Note 2>
Fig. D5
(L3)
Fig. D4
4
Fig. D6
1-7
Page 13
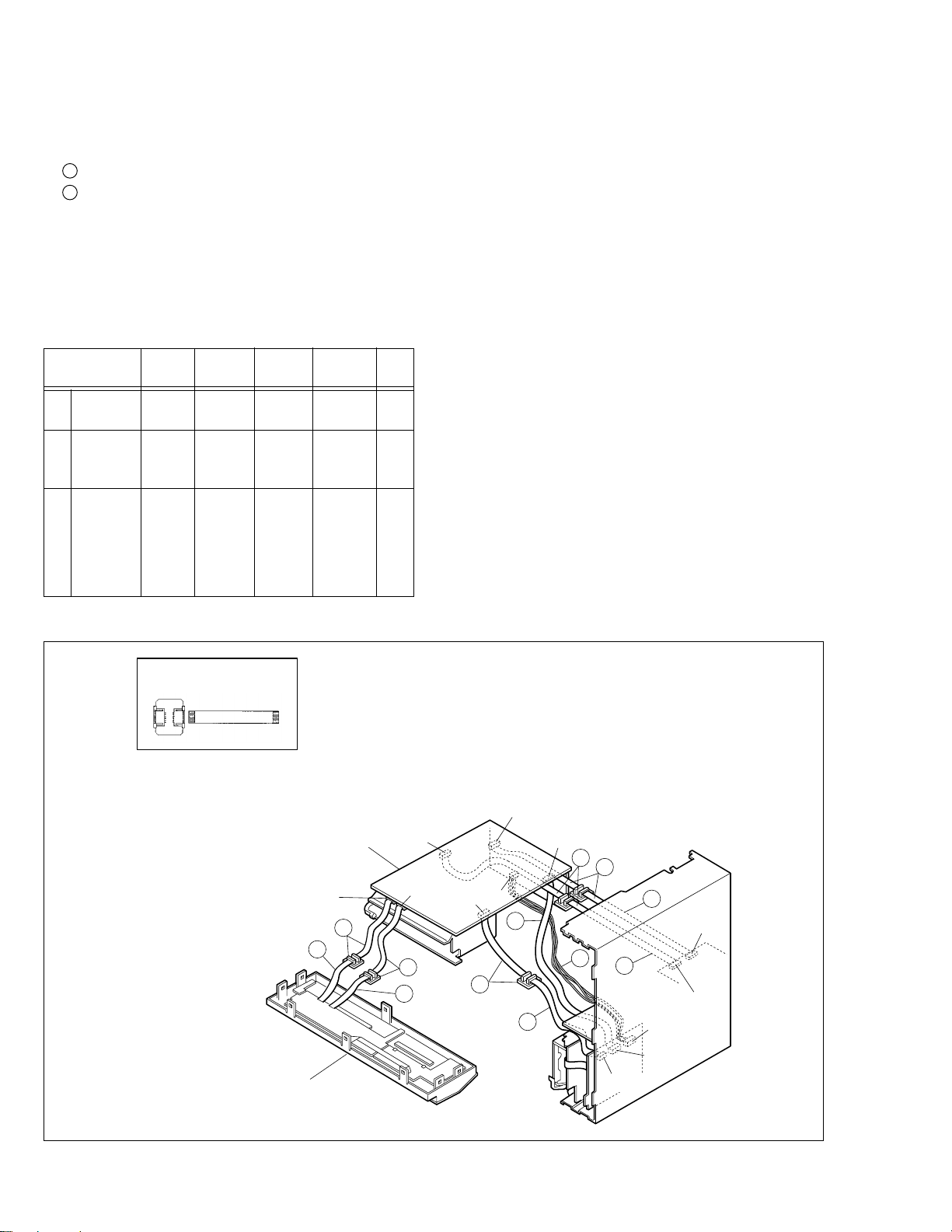
1.8 SERVICE POSITIONS
The servicing locations for use in troubleshooting or servicing of the set are provided separately for the VHS and DV.
I SERVICE POSITIONS <VHS SIDE>
II SERVICE POSITIONS <DV SIDE>
1.8.1 Service position <VHS SIDE>
<Removal>
(1) Remove the top cover and bracket.
(2) Remove the front panel assembly.
(3) Remove the MAIN board assembly together with the
mechanism assembly.
Fig. No.
(Page)
(1)
Top cover,
COM1 9 2 + 1
Bracket (1-3) (No.1-9) (L1,2)
(2) Front
panel
COM2 0 8 2
(1-3) (L3) (CN7507/ —
assembly
(3) Main
board
V2, V3 13 0 5
(1-6) (No.4-16) (CN5321/
assembly
(etc.)
Screw Hook, etc. Connector Note
0 —
CN3011)
CN5322/
CN3014/ —
CN703/
CN2601)
< Installation >
(1) Stand up the bottom chassis assembly so that the DV/
Regulator side is in the lower position.
(2) Connect the PATCH CORD to the three FPCs then con-
nect CN3014, CN7508 and CN7509.
(3) By connecting a total of two FPCs and wires (CN703/
CN2601), carry out the installation so that the Main board
assembly comes in the upper position.
Point: • Take care that the FPCs and wires are not
subjected to stress in this positioning.
(4) Connect the PATCH CORDS to the two FPCs of the front
panel assembly, then connect the CORDS to the
CN7507/CN3011.
For the PATCH CORD is required, see Table 1-8-3.
Table 1-8-1
PATCH CORD
PTU94017B
Main board assembly
CN7507
1
CN7508
6
7
CN2601
D
3
C
4
CN5322
5
CN5321
CN3501
CN7509
CN3011
CN703
CN3014
A
B
2
E
CN3701
1-8
Front panel assembly
Fig. 1-8-1 Service position <VHS side>
CN1002
Page 14
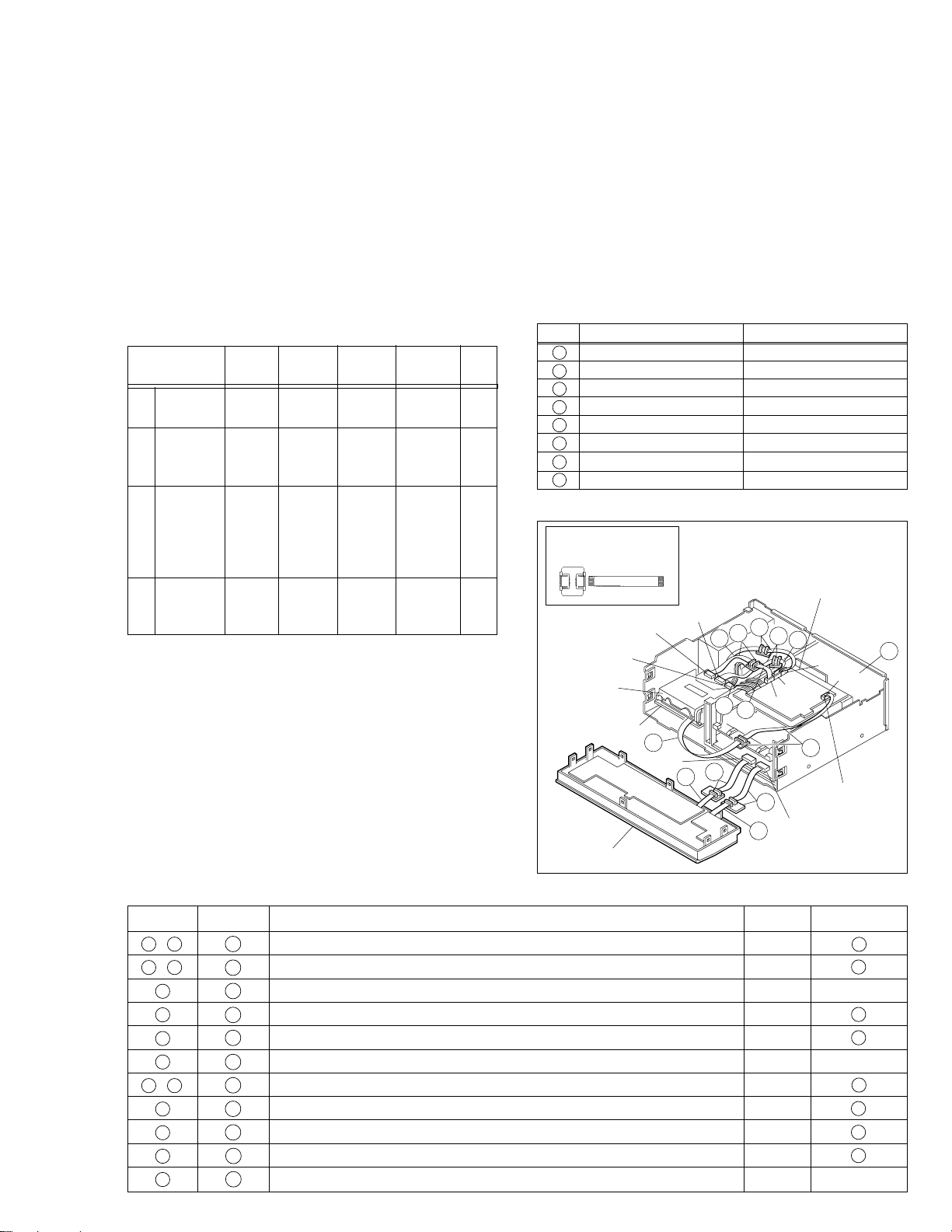
1.8.2 Service position <DV SIDE>
<Removal>
(1) Remove the top cover and bracket.
(2) Remove the front panel assembly.
(3) Remove the mechanism assembly (DV side) together
with the base (2).
(4) Remove the DV Main board assembly.
Note:
Place an insulation sheet on the mechanism assembly
•
(VHS side), then remove the DV Main board assembly
and place it on the insulation sheet.
When removing the DV Main board assembly, only remove a connector CN1002 out of four.
Take care not to damage the parts during operating.
(1)
Top cover,
Fig. No.
(Page)
COM1 9 2 + 1 0 —
Screw Hook, etc. Connector Note
Bracket (1-3) (No.1-9) (L1,2)
(2) Front
panel
assembly
(3)
Mechanism D1 4 0 4
COM2 0 8 2
(1-3) (L3) (CN7507/ —
CN3011)
(DV SIDE)/ (1-7) (No.1-4) (CN1502/
BASE (2) CN5002/ —
CN5506/
CN5501)
(4) DV Main
board
D6 4 0 1
(1-8) (No.17-20) (CN1002)
Note
assembly
Table 1-8-2
< Installation >
For the PATCH CORDS, see Table 1-8-3.
The patch cords that are indicated in Table 1-8-3 are in one
package.
(1) Connect a PATCH CORD to the FPC, and connect the
end to the connector CN1002.
(2) Connect PATCH CORDS to the three connectors/FPCs
(CN5506/CN5002/CN1502).
(3) Place the mechanism assembly (DV side) on the origi-
nal position and connect the four wires/FPCs/connectors
(CN5501/CN5506/CN5002/CN1502).
(4) Connect PATCH CORDS to the two FPCs of the FRONT
PANEL ASSEMBLY, and connect the ends to the
CN7507 and CN3011.
Board to Board Wire
A PTU94022-16 QUQ112-1840CG
B PTU94022-18 QUQ112-1640CG
C PTU94022-13 QUQ212-1340CG
D PTU94022-15 QUQ212-1540CG
E YTU94072-06 QUQ210-0640CG
F YTU94074-15 QUQ105-1540AA
G YTU94074-26 QUQ105-2640AA
H YTU94074-20 QUQ105-2040AA
Table 1-8-3
PATCH CORD
PTU94017B
Insulation sheet
CN5002
CN5501
DV mechanism
assembly
BASE (2)
CN3011
Front panel assembly
CN5506
8
2
E
G
7
11
B
H
10
CN1002
CN1501
CN2001
9
F
A
1
DV Main board
assembly
CN7507
7
CN1502
Fig. 1-8-2 Service position <DV side>
SYMBOL CONNECTOR (WIRE) CONNECTIONS
PIN No
PATCH CORD
I / II 1 MAIN CN7507 — JACK CN7002 16 A
I / II 2 MAIN CN3011 — DISPLAY CN7001 18 B
I 3 MAIN CN703 — DV MAIN CN3501 6 —
I 4 MAIN CN7508 — REGULATOR CN5322 13 C
I 5 MAIN CN7509 — REGULATOR CN5321 15 D
I 6 MAIN CN2601 — DV MAIN CN3701 8 —
I / II 7 MAIN CN3014 — DV MAIN CN1002 6 E
II 8 DV MAIN CN1502 — SENSOR 15 F
II 9 P/R MDA CN5002 — DV MAIN CN2001 26 G
II 10 P/R MDA CN5506 — DV MAIN CN1501 20 H
II 11 REGULATOR CN5324 — P/R MDA CN5501 5 —
Table 1-8-4 Connection of Connectors
1-9
Page 15
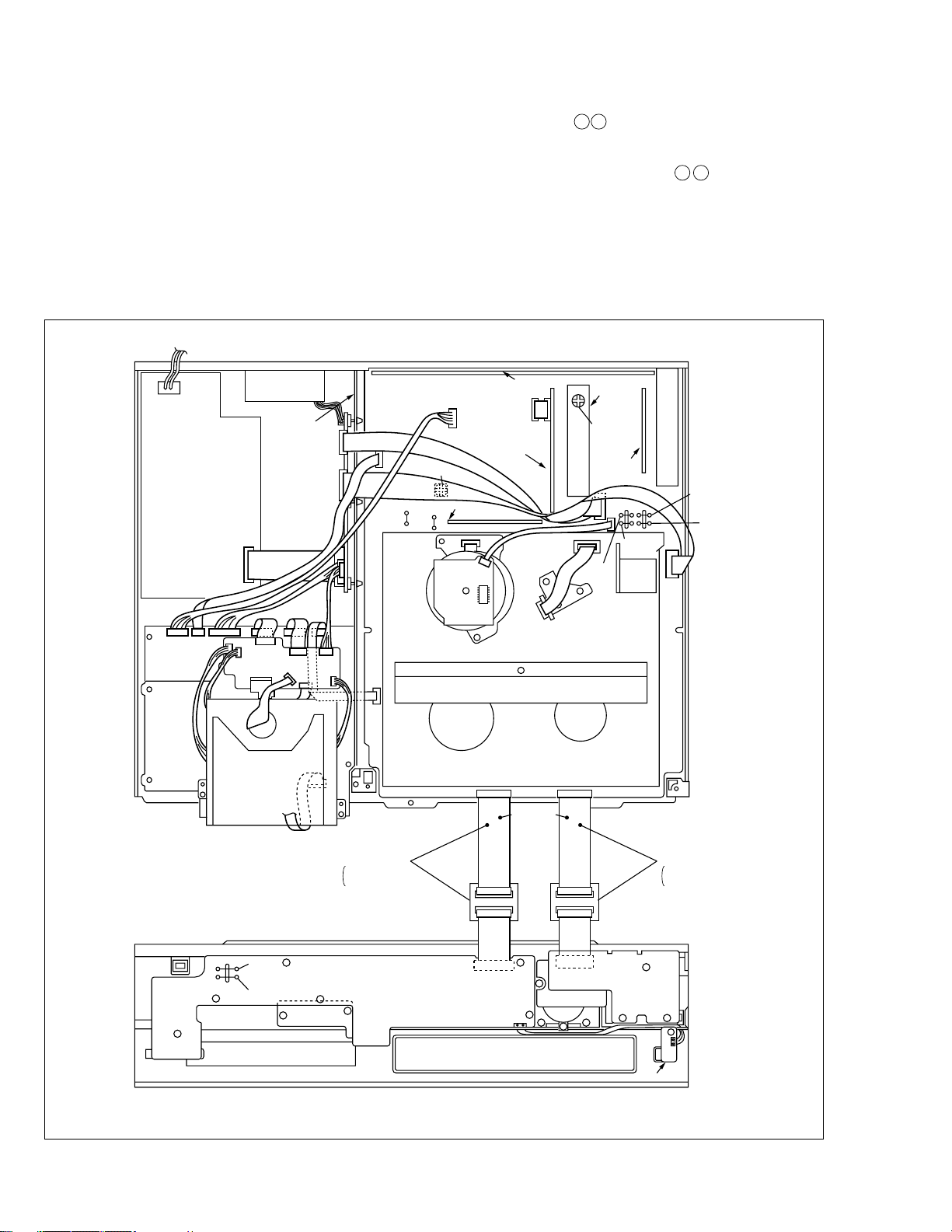
1.9 MECHANISM SERVICE MODE
This model has a unique function to enter the mechanism
into every operation mode without loading of any cassette
tape. This function is called the “MECHANISM SERVICE
MODE”.
1.9.1 How to set the "MECHANISM SERVICE MODE"
(1) Disconnect VCR from AC.
(2) Connect TPGND and TP7001 (TEST) on the Display
board assembly with a jump wire.
(3) Connect VCR to AC.
(4) Press the POWER button.
(5) With lock levers A B on the left and right of the Cassette
holder assembly pulled toward the front, slide the holder
in the same direction as the cassette insertion direction.
(For the positions of lock levers A B , refer to the “Procedures for Lowering the Cassette holder assembly” on
page 1-5 of 1.6 HOW TO REMOVE THE MAJOR PARTS
<VHS section>
(6) The cassette holder lowers and, when the loading has
completed, the mechanism enters the desired mode.
Swithing regulator
board assembly
DV Main
board assembly
Fan
board assembly
P/R MDA
board assembly
DV mechanism
Regulator
Main board assembly
TP GND
Terminal board assembly
S-Sub
board assembly
VR701
DV AG C
TP701
On screen
D AGC
board assembly
TP106
PB FM
VHS mechanism
CN3011 CN7507
Supporting
tape side
3D Digital
/2M board
assembly
VR401
D/A
LEVEL ADJ
Demodulator
board
assembly
TP2253
A.PB FM
TP4001
CTL.P
TP111
D.FF
1-10
TP7001
TEST
TPGND
LED SW
board assembly
PATCH COAD
PTU94022-18
QUQ112-1840CG
Display board assembly
<Front panel assembly>
Fig. 1-9-1
Jack board assembly
Jog board
assembly
Eject SW board assembly
PATCH COAD
PTU94022-16
QUQ112-1640CG
Page 16
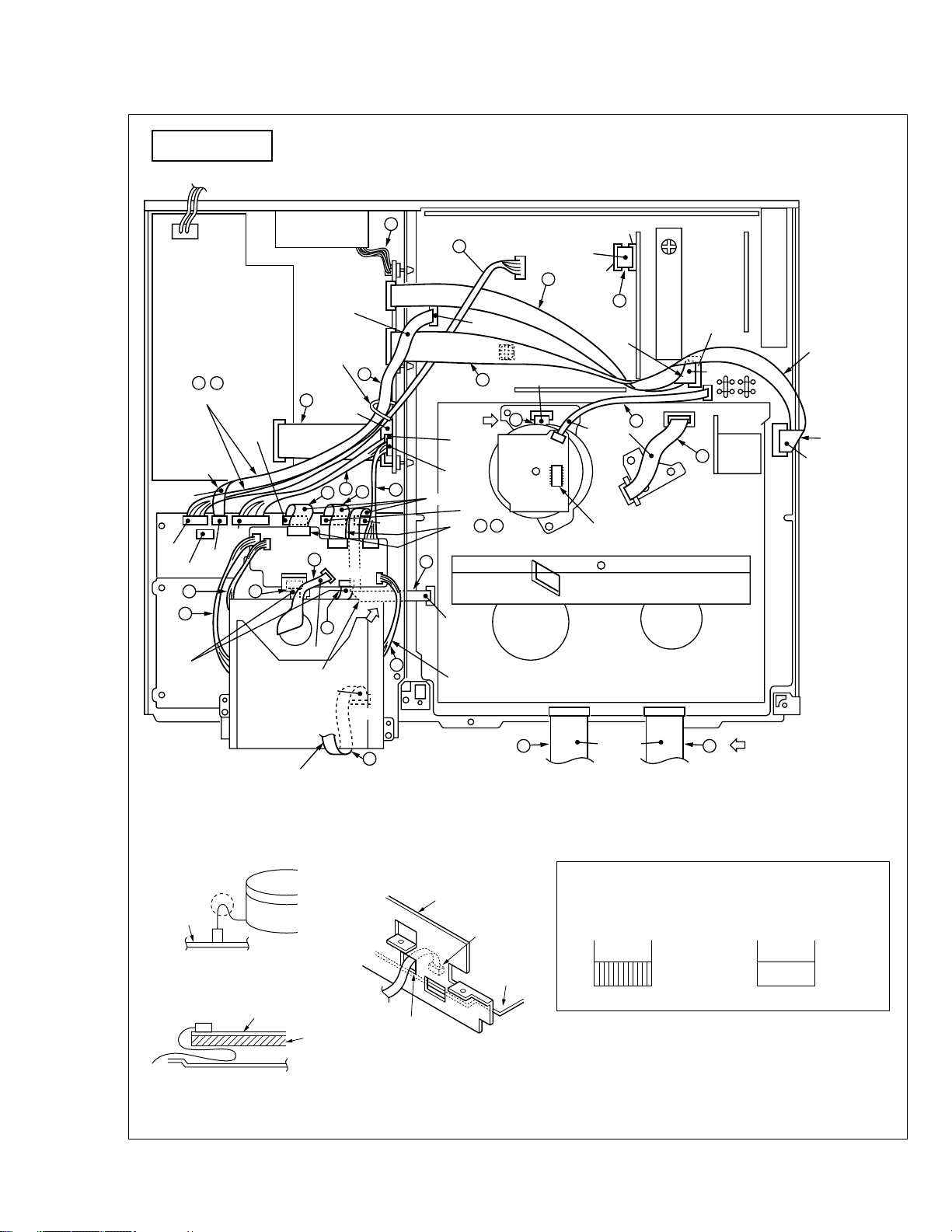
1.10 CONNECTION
Treat the wire so as not to come to
DV cassette housing when attaching
the Front panel assembly.
Absorb the looseness
of the 13 ,
14
wires in
the Main part.
Fix the wire by
Style pin surely.
Foil side
Supporting
tape side
Supporting
tape side
Supporting
tape side
Supporting
tape side
Supporting
tape side
Make a
crease.
Make a
crease.
Make a crease.
A
C
CN5325
CN5321 CN5322
CN5301
(Lower)CN5201
CN703
CN7506
CN512
CN7508
CN2601
CN3001
CN2001
CN1
CN1
CON1
CN7509
CN3014
6
3
14
16
17
4
9
5
8
7
12
13
24
11
18
22
20
19
23
15
12
21
10
Foil side
Foil side
Foil side
Foil side
Foil side
Foil side
Foil side
Foil side
Foil side
Foil side
A/C HEAD
DRUM
Treat the wire
according to the
figure not to
overlap in TP.
Make a crease.
Supporting
tape side
B
Should be confirmed that wire
not touch to IC of the Stator
board assembly.
After attach the Mechanism assembly,
treat the wire according to the figure.
The
21 , 22
wires
should be treat under the
P/R MDA board assembly.
CN1502
CN3501
CN1101
CN3701
CN1001
CN5505
CN5503
CN5504
CN5507
CN5506
CN5501
CN5502
CN5001
CN5002
CN2001
CN5323
(Middle)
CN5324
(Upper)
CN3011 CN7507
CN1501
CN1002
CN1
CN3014
CN3011
CN7507
B
DRUM
Main board
assembly
Main board
assembly
Main board
assembly
Chassis
Absorb the looseness of
the wire in the B part.
Treat the front wires
according to the figure.
Treat the wire
through the hole.
DETALE "B"
DETALE "A" DETALE "C"
Base(1)
[CAUTION]
Insert the FPC wires as shown below.
Foil side Supperting tape side side
TOP VIEW
Fig. 1-10-1 Top view
1-11
Page 17

Fig.
No.
Symbol
Connection
Pin No.
Connected point ←→ Connected point
Type
(FPC/
WIRE)
1 WR1 MAIN CN7507 ←→ JACK CN7002 16 FPC
2 WR2 MAIN CN3011 ←→ DISPLAY CN7001 18 FPC
3 WR3 REGULATOR CN5301 ←→ SW REG CN5201 19 FPC
4 WR4 REGULATOR CN5322 ←→ MAIN CN7508 13 FPC
5 WR5 REGULATOR CN5321 ←→ MAIN CN7509 15 FPC
6 WR6 REGULATOR CN5325 ←→ FAN MOTOR – 2 WIRE
7 WR7 REGULATOR CN5324 ←→ PRE/REC MDA CN5501 5 WIRE
8 WR8 REGULATOR CN5323 ←→ DV MAIN CN1001 10 WIRE
9 WR9 DRUM MOTOR CON1 ←→ MAIN CN3001 5 FPC
10 WR10 MAIN CN1 ←→ UPPER DRUM – 13 FPC
11 WR11 A/C HEAD CN1 ←→ MAIN CN2001 7 FPC
12 WR12 MAIN CN3014 ←→ DV MAIN CN1002 6 FPC
13 WR13 MAIN CN703 ←→ DV MAIN CN3501 6 WIRE
14 WR14 MAIN CN2601 ←→ DV MAIN CN3701 8 FPC
15 WR15 DV MAIN CN1502 ←→ SENSOR – 15 FPC
16 WR16 PRE/REC MDA CN5002 ←→ DV MAIN CN2001 26 FPC
17 WR17 PRE/REC MDA CN5506 ←→ DV MAIN CN1501 20 FPC
18 WR18 PRE/REC MDA CN5507 ←→ DV HOUSING MOTOR – 4 WIRE
19 WR19 PRE/REC MDA CN5502 ←→ DV LOADING MOTOR – 2 WIRE
20 WR20 PRE/REC MDA CN5505 ←→ DV ENCODER – 4 WIRE
21 WR21 PRE/REC MDA CN5503 ←→ DV DRUM MOTOR – 11 FPC
22 WR22 PRE/REC MDA CN5504 ←→ DV CAPSTAN MOTOR – 18 FPC
23 WR23 PRE/REC MDA CN5001 ←→ DV VIDEO HEAD – 10 FPC
24 – MAIN CN7506 ←→ S-SUB CN512 14 FPC
–– DV MAIN CN1101 ←→ Jig CONN. CABLE – 26 –
Table 1-10-1 Connection
1-12
Page 18

1.11 EMERGENCY DISPLAY FUNCTION
Example 1 E : 01 :
03
Previous emergency
Latest emergency
No emergency record
Example 2 E : –– :
––
This unit has a function for storing the history of the past two
emergencies (EMG) and displaying them on each FDP. With
the status of the VCR and mechanism at the moment an emergency occurred can also be confirmed.
FDP display switching
[DV]
FDP display – : –– : –– Normal display
: **Emergency content display
E :
**
E :
**
[VHS]
FDP display
Notes:
•
The emergency detail display
on the latest emergency.
It becomes “ – – : – – : – –” when there is no latest emergency record.
•
When using the Jig RCU, set its custom code to match
the custom code of the VCR.
Jig RCU
[Data transmitting method]
Depress the “ ” ( 3 ) button
after the data code is set.
0 : 00 : 00
E: **:
1: *2 : 34
*
5: *6 :
*
CUSTOM CODE
43: A CODE
53: B CODE
DATA CODE
Fig. 1-11-1 Jig RCU [PTU94023B]
(E:Latest:Previous)
: **Emergency content display
(E:Latest:Previous)
Normal display
Emergency content display
**
(E:Latest:Previous)
Emergency detail display
Emergency detail display
7
*
1 2
show the information
INITIAL MODE
1
2
1.11.1 Displaying the emergency information
(1) Transmit the code “59” from the Jig RCU.
The FDP shows the emergency content in the form of
:**”.
“E:
**
Note:
[DV]
For the emergency content, see “1.11.3 Emergency content description”.
[VHS]
For the emergency content, see “1.11.3 Emergency content description”.
(2) Transmit the code “59” from the Jig RCU again.
The FDP shows the emergency detail information 1 in the
form of “
*
*
3 – : Mechanism sensor information at the moment of
– 4 : Mechanism mode position at the moment of emer-
Note:
•
For the emergency detail information
Emergency detail information
(3) Transmit the code “59” from the Jig RCU once again.
The FDP shows the emergency detail information 2 in the
form of “
*
*
*
Note:
•
For the emergency detail information 2 , see “1.11.5 Emergency detail information
1 : *2 : 34”.
*
1 : Deck operation mode at the moment of emergency
2 : Mechanism operation mode at the moment of emer-
gency
emergency
gency
1
, see “1.11.4
1
”.
5 : *6 :
*
5 : Type of the cassette tape in use 1 .
7 ”.
*
6 : Winding position of the cassette tape in use
7 : Type of the cassette tape in use 2 (Winding area)
2
”.
(4) Transmit the code “59” from the Jig RCU once again to re-
set the display.
1.11.2 Clearing the emergency history
(1) Display the emergency history.
(2) Transmit the code “36” from the Jig RCU.
(3) Reset the emergency display.
(Y292-03e)
1-13
Page 19
1.11.3 Emergency content description
Emergency contents “E08/E09” are for the model with Dynamic Drum (DD).
Note:
FDP CONTENT CAUSE
E01: Loading EMG
E02:
Unloading EMG
E03: Take Up Reel
Pulse EMG
E04: Drum FG
EMG
E05: Cassette Eject
EMG
E06: Capstan FG
EMG
E07: SW Power
Short-Circuit
EMG
E08:
DD Initialized
(Absolute
Position
Sensor)
EMG
E09: DD FG EMG
E0A:Supply Reel
Pulse EMG
EC1 or EU1:
Head clog warning
When the mechanism mode cannot be changed to another mode even when the loading motor has rotated
for more than 4 seconds in the loading direction, [E:01]
is identified and the power is turned off.
When the mechanism mode cannot be changed to another mode even when the loading motor has rotated
for more than 4 seconds in the unloading direction, [E:02]
is identified and the power is turned off.
When the take-up reel pulse has not been generated for
more than 4 seconds in the capstan rotating mode, [E:03]
is identified, the pinch rollers are turned off and stopped,
and the power is turned off. However, the reel EMG is
not detected in STILL/SLOW modes.
When the drum FG pulse has not been input for more
than 3 seconds in the drum rotating mode, [E:04] is identified, the pinch rollers are turned off and stopped, and
the power is turned off.
When the eject operation does not complete in 3 seconds after the start, [E:05] is identified, the pinch rollers
are turned off and stopped, and the power is turned off.
When the cassette insertion operation does not complete
in 3 seconds after the start, the cassette is ejected. In
addition, when the operation does not complete within
3 seconds after the start, [E:05] is also identified and the
power is turned off immediately.
When the capstan FG pulse has not been generated for
more than 1 second in the capstan rotating mode, [E:06]
is identified, the pinch rollers are turned off and stopped,
and the power is turned off.However, the capstan EMG
is not detected in STILL/SLOW/FF/REW modes.
When short-circuiting of the SW power supply with GND
has lasted for 0.5 second or more, [E:07] is identified,
all the motors are stopped and the power is turned off.
When DD tilting does not complete in 4 seconds, [E:08]
is identified, the tilt motor is stopped and the power is
turned off.
When the DD FG pulse is not generated within 2.5 seconds, [E:09] is identified, the tilt motor is stopped and
the power is turned off.
When the supply reel pulse has not been generated for
more than 10 seconds in the capstan rotating mode,
[E:0A] is identified and the cassette is ejected (but the
power is not turned off). However, note that the reel EMG
is not detected in the SLOW/STILL mode.
Presupposing the presence of the control pulse output in the PLAY mode, when the value obtained by mixing the two V.FM output
channels (without regard to the A.FM output) has remained below a certain threshold level for more than 10 seconds, [E:C1] or [E:U1]
is identified and recorded in the emergency history. During the period in which a head clog is detected, the FDP and OSD repeat the
“3-second warning display” and “7-second noise picture display” alternately.
EMG code : “E:C1” or “E:U1” / FDP : “U:01” / OSD : “Try cleaning tape.” or “Use cleaning cassette.”
The head clog warning is reset when the above-mentioned threshold has been exceeded for more than 2 seconds or the mode is
changed to another mode than PLAY.
The mechanism is locked in the middle of mode transition.
1
2
The mechanism is locked at the loading end due to the encoder position
reading error during mode transition.
3
Power is not supplied to the loading MDA.
1
The mechanism is locked in the middle of mode transition.
2
The mechanism is locked at the unloading end due to the encoder position reading error during mode transition.
3
Power is not supplied to the loading MDA.
1
The take-up reel pulse is not generated in the FWD transport modes (PLAY/
FWD SEARCH/FF, etc.) because;
1) The idler gear is not meshed with the take-up reel gear;
The idler gear is meshed with the take-up reel gear, but incapable of wind-
2)
ing due to too large mechanical load (abnormal tension);
3) The take-up reel sensor does not output the FG pulse.
2
The supply reel pulse is not generated in the REV transport modes (REV
SEARCH/REW, etc.) because;
1) The idler gear is not meshed with the supply reel gear.
2) The idler gear is meshed with the supply reel gear, but incapable of winding due to too large a mechanical load (abnormal tension);
3) The supply reel sensor does not output the FG pulse.
3
Power is not supplied to the reel sensors.
1
The drum could not start or the drum rotation has stopped due to too large
a load on the tape, because;
1) The tape tension is abnormally high;
The tape is damaged or a foreign object (grease, etc.) adheres to the tape.
2)
2
The drum FG pulse did not reach the System controller CPU because;
1) The signal circuit is disconnected in the middle;
2) The FG pulse generator (hall device) of the drum is faulty.
3
The drum control voltage (DRUM CTL V) is not supplied to the MDA.
4
Power is not supplied to the drum MDA.
1
The cassette cannot be ejected due to a failure in the drive mechanism of
the housing.
2
When the housing load increases during ejection, the loading motor is
stopped because of lack of headroom in its drive torque.
Housing load increasing factors: Temperature environment (low temperature, etc.), mechanism wear or failure.
3
The sensor/switch for detecting the end of ejection are not functioning normally.
4
The loading motor drive voltage is lower than specified or power is not supplied to the motor (MDA).
5
When the user attempted to eject a cassette, a foreign object (or perhaps
the user's hand) was caught in the opening of the housing.
1
The capstan could not start or the capstan rotation has stopped due to too
large a load on the tape, because;
1) The tape tension is abnormally high (mechanical lock);
2) The tape is damaged or a foreign object (grease, etc.) is adhered to the
tape (occurrence of tape entangling, etc.).
2
The capstan FG pulse did not reach the System controller CPU because;
1) The signal circuit is disconnected in the middle;
2) The FG pulse generator (MR device) of the capstans is faulty.
3
The capstan control voltage (CAPSTAN CTL V) is not supplied to the MDA.
4
Power is not supplied to the capstan MDA.
1
The SW 5 V power supply circuit is shorted with GND.
2
The SW 12 V power supply circuit is shorted with GND.
1 The absolute value sensor is defective. (The soldered parts have separated.)
2 The pull-up resistor at the absolute sensor output is defective. (The soldered parts
have separated.)
3 Contact failure or soldering failure of the pins of the connector (board-to-board) to the
absolute value sensor.
The absolute value sensor data is not sent to the System Controller CPU.
4
1 The FG sensor is defective. (The soldered parts have separated.)
2 The pull-up resistor at the FG sensor output is defective. (The soldered parts have
separated.)
3 Contact failure or soldering failure of the pins of the connector (board-to-board) to the FG sensor.
4 The power to the sensor is not supplied. (Connection failure/soldering failure)
5 The FG pulse is not sent to the System Controller CPU.
The tilt motor is defective. (The soldered parts have separated.)
6
7 The drive power to the tilt motor is not supplied. (Connection failure/soldering failure)
8 The tilt motor drive MDA - IC is defective.
9 Auto-recovery of the DD tilting cannot take place due to overrun.
The supply reel pulse is not generated in the FWD transport mode (PLAY/
1
FWD SEARCH/FF, etc.) because;
1) PLAY/FWD or SEARCH/FF is started while the tape in the inserted cassette is cut in the middle;
2) A mechanical factor caused tape slack inside and outside the supply
reel side of the cassette shell. In this case, the supply reel will not rotate
until the tape slack is removed by the FWD transport, so the pulse is not
generated until then;
3) The FG pulse output from the supply reel sensor is absent.
2
The take-up reel pulse is not generated in the REV transport mode (REV
SEARCH/REW, etc.).
1) REV SEARCH/REW is started when the tape in the inserted cassette
has been cut in the middle;
2) A mechanical factor caused tape slack inside and outside the take-up
reel side of the cassette shell. In this case, the supply reel will not rotate
until the tape slack is removed by the REV transport, so the pulse will
not be generated until that time;
3) The FG pulse output from the take-up reel sensor is absent.
3
The power to a reel sensor is not supplied.
1-14
Table 1-11-1
Page 20

1.11.4 Emergency detail information 1
The status (electrical operation mode) of the VCR and the status (mechanism operation mode/sensor information) of the
mechanism in the latest emergency can be confirmed based on
the figure in EMG detail information 1 .
[FDP display]
1 : *2 : 34
*
1 : Deck operation mode at the moment of emergency
*
2 :
Mechanism operation mode at the moment of emergency
*
3 –
: Mechanism sensor information at the moment of emergency
– 4 :
Mechanism mode position at the moment of emergency
Note:
•
In the Deck operation mode/Mechanism operation mode/
Mechanism mode position, the contents of the code that
is shown on the FDP differs depending on the parts
number of the System Control microprocessor (IC3001)
of the VCR.
For the microprocessor parts number that starts with the
two letters “MN”, refer to the Table of MN and for parts
number with “HD”, refer to the Table of HD.
2 : Mechanism Operation Mode
*
[Table of MN]
Display
00 Command standby (Status without executing command)
02 POWER OFF by EMG occurrence
04 Moving to the adjacent position in the LOAD direction
06 Moving to the adjacent position in the UNLOAD direction
08 Cassette ejection being executed
0A Cassette insertion being executed
0C Tape being loaded
0E Tape being unloaded
10 Mode transition to STOP with pinch roller compression ON
12 Mode transition to STOP with pinch roller compression OFF
14 Mode transition to STOP with pinch roller compression OFF as a result
of POWER OFF
16 Mode transition to STOP with pinch roller compression ON as a result of
POWER ON
18 Mode transition to PLAY
1A Mode transition to FWD SEARCH
1C Mode transition to REC
1E Mode transition to FWD STILL/SLOW
20 Mode transition to REV STILL/SLOW
22 Mode transition to REV SEARCH
24 Mode transition from FF/REW to STOP
26 Mode transition to FF
28 Mode transition to REW
2A 4 sec. of REV as a result of END sensor going ON during loading
2C Short FF/REV as a result of tape sensor going ON during unloading
2E Mechanism position being corrected due to overrun
80 Mechanism in initial position (Dummy command)
Mechanism Operation Mode
1 : Deck Operation Mode
*
[Table of MN]
Display
00 Mechanism being initialized
01 STOP with pinch roller pressure off (or tape present with P.OFF)
02 STOP with pinch roller pressure on
03 POWER OFF as a result of EMG
04 PLAY
0C REC
10 Cassette ejected
20 FF
21 Tape fully loaded, START sensor ON, short FF
22
Cassette identification FWD SEARCH before transition to FF (SP x7-speed)
24 FWD SEARCH (variable speed) including x2-speed
2C INSERT REC
40 REW
42
Cassette identification REV SEARCH before transition to REW (SP x7-speed)
44 REV SEARCH (variable speed)
4C AUDIO DUB
6C INSERT REC (VIDEO + AUDIO)
84 FWD STILL/SLOW
85 REV STILL/SLOW
8C REC PAUSE
8D Back spacing
8E Forward spacing (FWD transport mode with BEST function)
AC INSERT REC PAUSE
AD INSERT REC Back spacing
CC AUDIO DUB PAUSE
CD AUDIO DUB Back spacing
EC INSERT REC (VIDEO + AUDIO) PAUSE
ED INSERT REC (VIDEO + AUDIO) Back spacing
Deck Operation Mode
[Table of HD]
Display
00 STOP with pinch roller pressure off (or tape present with P.OFF)
01 STOP with pinch roller pressure on
04 PLAY
0E REC
11 Cassette ejected
22 FF
26 FWD SEARCH (variable speed) including x2-speed
2E INSERT REC
43 REW
47 REV SEARCH (variable speed)
4C AUDIO DUB
6E INSERT REC (VIDEO+AUDIO)
84 FWD STILL/SLOW
85 REV STILL/SLOW
8F REC PAUSE
AF INSERT REC PAUSE
CD AUDIO DUB PAUSE
EF INSERT REC (VIDEO+AUDIO) PAUSE
Deck Operation Mode
[Table of HD]
Display
00 STOP with pinch roller pressure off
01 STOP with pinch roller pressure on
02 U/L STOP (or tape being loaded)
04 PLAY
05 PLAY (x1-speed playback using JOG)
0E REC
11 Cassette ejected
22 FF
26 FWD SEARCH (variable speed) including x2-speed
2E INSERT REC
43 REW
47 REV SEARCH
4C AUDIO DUB
6E INSERT REC (VIDEO + AUDIO)
84 FWD STILL/SLOW
85 REV STILL/SLOW
8F REC PAUSE
AF INSERT REC PAUSE
C7 REV SEARCH (x1-speed reverse playback using JOG)
CD AUDIO DUB PAUSE
EF INSERT REC (VIDEO + AUDIO) PAUSE
F0 Mechanism being initialized
F1 POWER OFF as a result of EMG
F2 Cassette being inserted
F3 Cassette being ejected
F4 Transition from STOP with pinch roller pressure on to STOP with pinch
roller pressure off
F5 Transition from STOP with pinch roller pressure on to PLAY
F6 Transition from STOP with pinch roller pressure on to REC
F7 Cassette type detection SEARCH before FF/REW is being executed
F8 Tape being unloaded
F9 Transition from STOP with pinch roller pressure off to STOP with pinch
roller pressure on
FA Transition from STOP with pinch roller pressure off to FF/REW
FB Transition from STOP with pinch roller pressure off to REC.P (T.REC,etc.)
FC Transition from STOP with pinch roller pressure off to cassette type de-
tection SEARCH
FD Short REV being executed after END sensor on during unloading
FE Tension loosening being executed after tape loading (STOP with pinch
roller pressure on)
Mechanism Operation Mode
1-15
Page 21
3 – : Mechanism Sensor Information
[Common table of MN and HD]
Display
0– VHS Tab broken ON ON
1– VHS Tab broken ON OFF
2– VHS Tab broken OFF ON
3– VHS Tab broken OFF OFF
4– VHS Tab present ON ON
5– VHS Tab present ON OFF
6– VHS Tab present OFF ON
7– VHS Tab present OFF OFF
8– S-VHS Tab broken ON ON
9– S-VHS Tab broken ON OFF
A– S-VHS Tab broken OFF ON
B– S-VHS Tab broken OFF OFF
C– S-VHS Tab present ON ON
D– S-VHS Tab present ON OFF
E– S-VHS Tab present OFF ON
F– S-VHS Tab present OFF OFF
– 4 : Mechanism Mode Position
Mechanism Sensor Information
S-VHS SW
REC SAFETY SW
START SENSOR
END SENSOR
[Table of MN]
Display
-0 Initial value
-1 EJECT position
-2 Housing operating
-3 U/L STOP position
-4
Tape being loaded/unloaded (When the pole base is located on the front
side of the position just beside the drum)
-5 Tape being loaded/unloaded (When the pole base is located on the rear
side of the position just beside the drum)
-6 Pole base compressed position
-7 FF/REW position
-8 Between FF/REW and STOP with pinch roller compression ON
-9 STOP with pinch roller compression OFF
-A Between STOP with pinch roller compression OFF and REV
-B REV (REV STILL/SLOW) position
-C Between REV and FWD
-D FWD (FWD STILL/SLOW) position
-E Between FWD and PLAY
-F PLAY position
Mechanism Mode Position
[Table of HD]
Display
–0 EJECT position
–1 U/L STOP position
–2 Tape being loaded/unloaded (When the pole base is located on the rear
side of the position just beside the drum)
–3 FF/REW position
–4 STOP with pinch roller pressure off
–5 REV (REV STILL/SLOW) position
–6 FWD (FWD STILL/SLOW) position, PLAY position
–7 Intermediate position during transition between other mechanism modes
Mechanism Mode Position
Note:
•
As the display is always “–7” at any intermediate position
between mechanism modes, the position of transitory
EMG may sometimes not be locatable.
1-16
1.11.5 Emergency detail information 2
The type of the cassette tape and the cassette tape winding position can be confirmed based on the figure in EMG detail information 2 .
[FDP display]
5 : *6 :
*
*
*
*
Note:
•
EMG detail information 2 is the reference information
7
*
5 : Type of the cassette tape in use 1
6 : Winding position of the cassette tape in use
7 :
Type of the cassette tape in use
2
(Winding area)
stored using the remaining tape detection function of the
cassette tape. As a result, it may not identify cassette correctly when a special cassette tape is used or when the
tape has variable thickness.
5 : Cassette tape type 1
*
Display Cassette Tape Type 1
00 Cassette type not identified
16
Large reel/small reel (T-0 to T-15/T-130 to T-210) not classified
82 Small reel, thick tape (T-120) identified/thin tape (T-140) identified
84 Large reel (T-0 to T-60) identified
92
Small reel, thick tape (T-130) identified/thin tape (T-160 to T-210) identified
93
Small reel, thick tape/C cassette (T-0 to T-100/C cassette) not classified
C3
Small reel, thick tape/C cassette (T-0 to T-100/C cassette) being classified
D3
Small reel, thick tape/C cassette (T-0 to T-100/C cassette) being classified
E1 C cassette, thick tape (TC-10 to TC-20) identified
E2 Small reel, thick tape (T-0 to T-100) identified
E9 C cassette, thin tape (TC-30 to TC-40) identified
F1
C cassette, thick tape/thin tape (TC-10 to TC-40) not classified
Notes:
•
Cassette tape type 1 is identified a few times during mode
transition and the identification count is variable depending on
the cassette tape type. If an EMG occurs in the middle of identification, the cassette tape type may not be able to be identified.
•
If other value than those listed in the above table is displayed,
the cassette tape type is not identified.
6 : Cassette tape winding position
*
The cassette tape winding position at the moment of EMG is
displayed by dividing the entire tape (from the beginning to the
end) in 22 sections using a hex number from “00” to “15”.
“00” : End of winding
“15” : Beginning of winding
“FF” : Tape position not identified
7 : Cassette tape type 2 (Winding area)
*
Display Cassette Tape Type 2
00
Cassette type not identified
07
Small reel, thick tape T-5
08 - 0E
C cassette, thick tape TC-10
09 - 15
0A - 16
0A - 16
11 - 14
15 - 18
17 - 1A
1F - 23
21 - 23
21 - 23
22 - 24
22 - 24
22 - 24
22 - 23
23 - 24
25 - 26
27 - 29
29 - 2B
C cassette, thick tape TC-20P
Small reel, thick tape T-20
C cassette, thin tape TC-30
C cassette, thin tape TC-40
Small reel, thick tape T-40
Small reel, thick tape T-60
Small reel, thick tape T-80/DF-160
Small reel, thick tape T-80/DF-180
Small reel, thick tape T-100
Small reel, thick tape T-120/DF-240
Small reel, thin tape T-140
Small reel, thick tape T-130
Small reel, thin tape T-160
Small reel, thin tape T-168
Small reel, thick tape DF-300
Small reel, thin tape T-180/DF-380
Small reel, thin tape T-210/DF-420
Large reel T-5
Large reel T-10
Large reel T-20
Large reel T-30
Large reel T-40
Large reel T-60
0A - 0B
0D - 0F
19 - 1D
1D - 21
1E - 1F
2D - 2F
Note:
•
The values of cassette tape type 2 in the above table are
typical values with representative cassette tapes.
Page 22

SECTION 2
MECHANISM ADJUSTMENT (VHS)
2.1 BEFORE STARTING REPAIR AND ADJUSTMENT
2.1.1 Precautions
(1) Unplug the power cable of the main unit before using your
soldering iron.
(2) Take care not to cause any damage to the conductor
wires when plugging and unplugging the connectors.
(3) Do not randomly handle the parts without identifying
where the trouble is.
(4) Exercise enough care not to damage the lugs, etc. dur-
ing the repair work.
(5) When installing the front panel assembly, be sure to hook
the lug on the back side of the cassette door to the door
opener of the cassette holder. If this operation is neglected it will not be possible to remove the cassette when
ejecting because the housing door cannot be opened.
2.1.2 Checking for Proper Mechanical Operations
Enter the mechanism service mode when you want to operate the mechanism when no cassette is loaded. (See 1.5
MECHANISM SERVICE MODE.)
Loading motor
Pole base assembly
2.1.3 Manually Removing the Cassette Tape
1. In case of electrical failures
If you cannot remove the cassette tape which is loaded because of any electrical failure, manually remove it by taking
the following steps.
(1) Unplug the power cable and remove the top cover,
bracket and front panel assembly. (See 1.3 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY METHOD.)
(2) Unload the cassette by manually turning the loading mo-
tor of the mechanism assembly toward the front. In doing so, hold the tape by the hand to keep the slack away
from any grease. (See Fig.2-1-3a.)
(3) Bring the pole base assembly (supply or take-up side) to
a pause when it reaches the position where it is hidden
behind the cassette tape.
(4) Move the top guide toward the drum while holding down
the lug A of the bracket retaining the top guide. Likewise hold part B down and remove the top guide.
Section C of the top guide is then brought under the
cassette lid. Then remove the top guide by pressing the
whole cassette tape down. (See Fig.2-1-3b.)
(5) Remove the cassette tape by holding both the slackened
tape and the cassette lid.
(6) Take up the slack of the tape into the cassette. This com-
pletes removal of the cassette tape.
Fig. 2-1-3a
C
A
B
Press
Fig. 2-1-3b
2-1
Page 23

2. In case of mechanical failure
If you cannot remove the cassette tape which is loaded because of any mechanical failure, manually remove it by taking the following steps.
(1) Unplug the power cable and remove the top cover, front
panel assembly and others so that the mechanism assembly is visible. (See 1.3 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY
METHOD.)
(2) While keeping the tension arm assembly of the mecha-
nism assembly free from tension, pull the tape on the pole
base assembly (supply or take-up side) out of the guide
roller. (See Fig.2-1-3c.)
(3) Take the spring of the pinch roller arm assembly off the
hook of the press lever assembly, and detach it from the
tape. (See Fig.2-1-3d.)
(4) In the same way as in the electrical failure instructions in
2.1.3-1(4), remove the top guide.
(5) Raise the cassette tape cover. By keeping it in that posi-
tion, draw out the cassette tape case from the cassette
holder and take out the tape.
(6) By hanging the pinch roller arm assembly spring back
on the hook, take up the slack of the tape into the cassette.
Pole base assembly (take-up side)
2.1.4 Jigs and Tools Required for Adjustment
Roller driver
PTU94002
Back tension cassette gauge
PUJ48076-2
Alignment tape
(SP, stairstep, PAL)
MHPE
A/C head positioning tool
PTU94010
Jig RCU
PTU94023B
Alignment tape
(LP, stairstep, PAL)
MHPE-L
Torque gauge
PUJ48075-2
Pole base assembly
(supply side)
Tension arm assembly
Fig. 2-1-3c
Take the spring
off the hook, and
detach it from the
tape.
Guide pole guard
2-2
Pinch roller arm assembly
Press lever assembly
Fig. 2-1-3d
Page 24

2.1.5 Maintenance and Inspection
1. Location of major mechanical parts
In this chapter, the two mechanism speeds are described by comparing the speeds of the standard type and the high-speed
FF/REW type.
It is possible to distinguish between these two types of mechanism by the diameters of their capstan pulleys.
The capstan pulley diameter for the standard type is approx. 32 mm.
The capstan pulley diameter for the high-speed FF/REW type is approx. 43 mm.
For information on the different parts used in the two mechanism types, please refer to the “Replacement of major parts”.
UV catcher2 (supply and take-up side)
Stator assembly
T2
Full erase head
T26
Pole base assembly
T25
(supply side)
Tension arm
T24
assembly
Adjust pin
T23
Tension brake
T22
assembly
T1
T3
Drum assembly
T5 T7
T6
Head base
Audio control head
Loading motor
Guide pole guard
T8
Pinch roller arm
T9
assembly
Lid guide
T10
Press lever
T11
assembly
Guide arm
T12
assembly
Reel disk
T13
(take-up side)
Sub brake assembly
T14
(take-up side)
Belt
B22
(loading motor)
B21
Control cam
B20
B19
Cassette gear
B18
Worm gear
Brake lever
Rec safety lever
B1
Reel disk
T20
(supply side)
Main brake assembly
(supply side)
Idler lever
T17T19T21
Idler arm assembly
T16T18
Pole base assembly (take-up side)
Fig. 2-1-5a Mechanism assembly top side
Capstan motor
Belt (capstan)
B2
Capstan brake assembly
B3 B5
Loading arm gear (take-up side)
B4
Loading arm gear (supply side)
Main brake assembly
T15
(take-up side)
Plate
B6
(supply side)
Control
B7
bracket1
Control plate
B8
Tension arm
B9
bearing
Link lever
B17
Rotary encoder guide
B16
Rotary encoder
B15
B14
Direct gear
B13
Change lever assembly
B12
B10
Clutch unit
Take-up head
Fig. 2-1-5b Mechanism assembly bottom side
Take-up lever
B11
2-3
Page 25

Guide rail Roller cam assembly
L2L1
Fig. 2-1-5c Mechanism assembly left side
R1
Opener guide
Door
R2
opener
Drive gear
R3
Cassette housing bracket
R4
R5
Limit gear
Loading motor
Worm gear
Belt (loading motor)
Fig. 2-1-5d Mechanism assembly right side
2. Cleaning
Regular cleaning of the transport system parts is desirable
but practically impossible. So make it a rule to carry out cleaning of the tape transport system whenever the machine is
serviced.
When the video head, tape guide and/or brush get soiled,
the playback picture may appear inferior or at worst disappear, resulting in possible tape damage.
(1) When cleaning the upper drum (especially the video
head), soak a piece of closely woven cloth or Kimu-wipe
with alcohol and while holding the cloth onto the upper
drum by the fingers, turn the upper drum
counterclockwise.
Note:
• Absolutely avoid sweeping the upper drum vertically
as this will cause damage to the video head.
(2) To clean the parts of the tape transport system other than
the upper drum, use a piece of closely woven cloth or a
cotton swab soaked with alcohol.
(3) After cleaning, make sure that the cleaned parts are com-
pletely dry before using the video tape.
3. Lubrication
With no need for periodical lubrication, you have only to lubricate new parts after replacement. If any oil or grease on
contact parts is soiled, wipe it off and newly lubricate the
parts.
Note:
• See the “mechanism assembly” diagram of the parts
list for the lubricating or greasing spots, and for the
types of oil or grease to be used.
4. Suggested servicing schedule for main components
The following table indicates the suggested period for such
service measures as cleaning,lubrication and replacement.
In practice, the indicated periods will vary widely according
to environmental and usage conditions.However, the indicated components should be inspected when a set is brought
for service and the maintenance work performed if necessary. Also note that rubber parts may deform in time,even if
the set is not used.
System Parts Name
Upper drum assembly
A/C head
Lower drum assembly
Pinch roller arm assembly
Full erase head
Tension arm assembly
Capstan motor (Shaft)
Guide arm assembly
Capstan motor
Capstan brake assembly
Main brake assembly
Belt (Capstan)
Belt (Loading motor)
Loading motor
Clutch unit
Worm gear
Control plate
Brush
Tension brake assembly
Other Drive Tape transport
Rotary encoder
: Cleaning
¤
: Inspection or Replacement if necessary
R
Operation Hours
~1000H ~2000H
¤R R
¤R ¤R
¤¤R
¤¤
¤¤
¤¤
¤¤
¤¤
R
R
R
RR
R
R
R
R
R
¤R ¤R
RR
R
Table 2-1-5a
5. Disassembling procedure table
The following table indicates the order in which parts are removed for replacement. To replace parts, remove them in
the order of 1 to 18 as shown in the table. To install them,
reverse the removal sequence.
The symbols and numbers preceding the individual part
names represent the numbers in the “Location of major mechanical parts” table. Also, the “T”, “B”, and “T/B” on the right
of each part name shows that the particular part is removed
from the front, from the back, and from both sides of the
mechanism, respectively.
2-4
Page 26

R4 R1 R3 T9 T12 T11 B15 B12 B14 B13 B17 B21 B7 B8 B5 B4 B11 T14 T15 T13 T22 T24 T18 B19
Symbols and numbers
Removal parts
(Reference items)
Replacement parts
Symbols and numbers
2.2.3 Guide rail T 1
L2
2.2.3 Roller cam assembly T 1
R4
2.2.3 Cassette housing bracket T 1
R1
2.2.3 Opener guide T 2
R2
2.2.3 Door opener T 3
2.2.3 Relay gear T 3
R5
2.2.3 Limit gear T 3
2.2.3 Cassette holder assembly T 6
R3
2.2.3 Drive gear T 4
2.2.3 Drive arm T 8
T9
2.2.4 Pinch roller arm assembly T 1
T12
2.2.5 Guide arm assembly T 1
T11
2.2.5 Press lever assembly T 3
T6
2.2.6 Audio control head T 1
T7
2.2.7 Loading motor T 1
B1
2.2.8 Capstan motor T/B 1
T1
2.2.9 UV catcher2 T 1
T17
2.2.9
Pole base assembly (take-up side)
T25
2.2.9
Pole base assembly (supply side)
B15
2.2.10 Rotary encoder B 1
B12
2.2.11 Clutch unit B 1
B14
2.2.12 Change lever assembly B 3
B13
2.2.12 Direct gear B 4
2.2.12 Clutch gear B 5
2.2.12 Coupling gear (
B17
2.2.13 Link lever B 1
B18
2.2.14 Cassette gear B 2
B20
2.2.14 Control cam B 2
B21
2.2.14 Worm gear B 1
T10
- Lid guide T/B 5
B7
2.2.15 Control bracket1 B 1
B8
2.2.15 Control plate B 6
B5
2.2.16 Loading arm gear (supply side) B 7
B4
2.2.16
Loading arm gear (take-up side)
2.2.16 Loading arm gear shaft B 9
2.2.17 Take-up lever T/B 7
B11
B10
2.2.17 Take-up head T/B 8
2.2.17 Control plate guide T/B 8
B3
2.2.18 Capstan brake assembly T/B 7
T14
2.2.19
Sub brake assembly(take-up side)
T15
2.2.20
Main brake assembly(take-up side)
T19
2.2.20
Main brake assembly(supply side)
T13
2.2.20 Reel disk (take-up side) T/B 16
T22
2.2.21 Tension brake assembly T/B 9
T20
2.2.21 Reel disk (supply side) T/B 10
T24
2.2.21 Tension arm assembly T/B 10
B9
2.2.21 Tension arm bearing T/B 10
T18
2.2.22 Idler lever T/B 17
T16
2.2.22 Idler arm assembly T/B 18
B19
- Brake lever (
B16
- Rotary encoder guide T/B 19
2) B 6
*
1
) T/B 18
*
L1L1L2
Number of removal steps
Guide rail
Roller cam assembly
Cassette housing bracket
Opener guide
112
12
12
12 3
3
4 5
5 6
Relay gear
6 7
Front (T)/Back (B) of mechanism
1 2 3 4 5
12
T/B 2
T/B 2
B8
T/B 15
1 2 3 4
T/B 16
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
T/B 9
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Cassette holder assembly
Drive gear
8
7
Table 2-1-5b
Note:
• The parts with marked (
nisms (standard type or high-speed FF/REW type).
1 : Uses the standard type mechanism only.
*
2 : Uses the high-speed FF/REW type mechanism only.
*
) have different types of mecha-
*
T1
Drive arm
Pinch roller arm assembly
Guide arm assembly
Press lever assembly
UV catcher2
Rotary encoder
1
2
1
1
1
12
12
1 2 3 4 5
12
3 4
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 2 3 4 5 6
9 10 11 12 13 14
9 10 11 12 13 14 15
9 10 11 12 13 14 15
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
Clutch unit
Change lever assembly
Direct gear
Clutch gear
Link lever
2
3
3
4
1
1
Worm gear
Control bracket1
Control plate
5
6
7
Loading arm gear (supply side)
Loading arm gear (take-up side)
Take-up lever
Sub brake assembly (take-up side)
Main brake assembly (take-up side)
Reel disk (take-up side)
Tension brake assembly
Tension arm assembly
8
7
7
9
9
9
)
1
*
(
Idler lever
Brake lever
2-5
Page 27
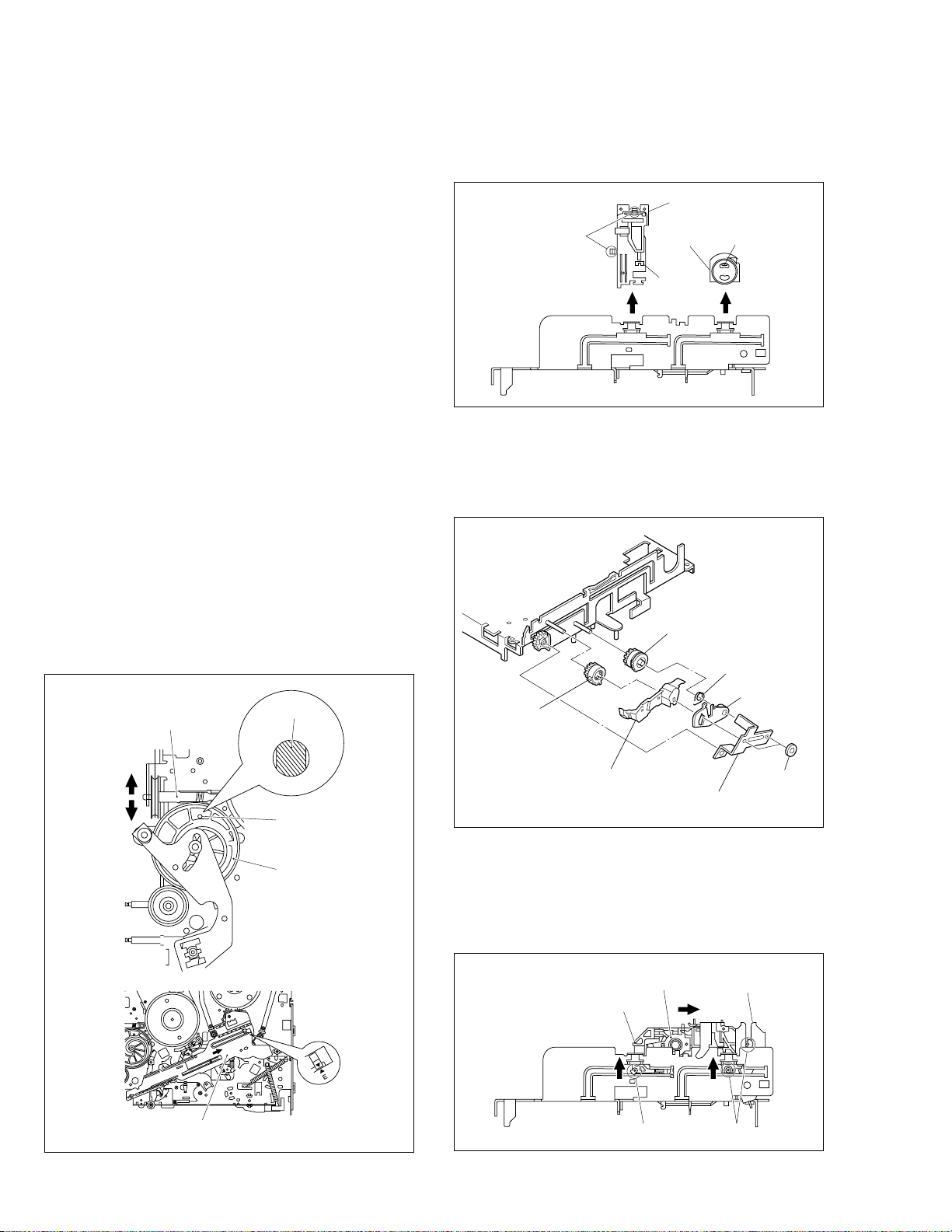
g
2.2 REPLACEMENT OF MAJOR PARTS
2.2.1 Before Starting Disassembling (Phase matching
between mechanical parts)
The mechanism of this unit is closely linked with the rotary
encoder and system controller circuits.
Since the system controller detects the status of mechanical operation in response to phases of the rotary encoder
(internal switch positions), the mechanism may not operate
properly unless such parts as the rotary encoder, control
plate, loading arm gear, control cam, cassette gear, limit gear,
relay gear and drive gear are installed in their correct positions.
Especially, this model is not provided with any cassette housing assembly, so that cassette loading and unloading must
be accomplished by operation of the cassette holder assembly. The latter is in turn driven by such parts as the drive
gear, relay gear and limit gear. Exercise enough care, therefore, to have the phases of all this gear matching one another. (For information on phase matching of the mechanism,
see the instructions on how to install individual parts.)
This unit is provided with a mechanism assembly mode. It is
therefore necessary to enter this mode for assembling and
disassembling procedures.
This mode is usually not in use, manually set it when it is
required.
2.2.3 Cassette Holder Assembly
1. How to remove
(1) Remove the guide rail and roller cam assembly. (See
Fig.2-2-3a.)
(3 lugs on the guide rail and one lug on the roller cam
assembly)
Guide rail
Lugs
Roller cam
assembly
Lug
Lug
Fig. 2-2-3a
(2) Remove the two slit washers and remove the cassette
housing bracket. (See Fig.2-2-3b.)
(3) Remove the opener guide, spring(A), door opener, relay
gear and limit gear. (See Fig.2-2-3b.)
2.2.2 How to Set the Mechanism Assembling Mode
Remove the mechanism assembly and place it bottom side
up. (See SECTION 1 DISASSEMBLY.) Turn the worm gear
toward the front so that the guide hole of the control cam is
brought into alignment with the hole at the mechanism assembly chassis. This position renders the mechanism assembling mode operational. Make sure that the control plate is
located in alignment with the mark E. (See Fig.2-2-2a.)
Worm gear
Chassis hole
Guide hole
Control cam
Limit gear
Spring(A)
Opener guide
Relay gear
Door opener
Cassette housing bracket
Slit washers
Fig. 2-2-3b
(4) While swinging the lock levers (R) and (L) of the cassette
holder assembly toward the front, slide the cassette
holder assembly until its legs come to where the guide
rail and the roller cam assembly have been removed (so
that the drive arm is upright). (See Fig.2-2-3c.)
Lock lever (L)
Cassette holder assembly
Drive arm
(Upright)
2-6
Control plate
Fig. 2-2-2a
Mark E
Le
Fig. 2-2-3c
Legs
Page 28

While holding the left side of the cassette holder, lift the
A
B
C
Cassette holder assembly
Drive arm
Lock lever (R)
Cassette holder assembly
(5)
cassette holder assembly so that the three legs on the
left side are all released. Then pull the legs A and B
on the right side out of the rail and also pull up the leg C .
(See Fig.2-2-3d and Fig.2-2-3e.)
(6) Draw out the drive gear, and remove the drive arm.
Cassette holder assembly
Fig. 2-2-3d
Cassette holder assembly
A
2. How to install (Phase matching)
A
(1) Insert the section
of the drive arm into the section B
of the main deck.
(2) Insert the section 1 of the drive gear into the round hole,
and the section 2 into the square hole on the drive arm.
(See Fig.2-2-3f.)
(3) Hold the drive arm upright and fit the leg C on the right
side of the cassette holder assembly into the groove. (See
Fig.2-2-3g.)
(4) While swinging the lock lever (R) of the cassette holder
assembly toward the front, put the legs A and B into
the rail. (See Fig.2-2-3g.)
(5) Drop the three legs on the left side of the cassette holder
assembly into the groove at one time. (See Fig.2-2-3h.)
(6) Slide the whole cassette holder assembly toward the front
to bring it to the eject end position.
(7) Install the limit gear so that the notch on the outer cir-
cumference of the limit gear is brought into alignment with
the guide hole on the main deck. (See Fig.2-2-3i.)
(8) Install so that the notch on the periphery of the relay gear
is aligned with the notch of the main deck and that hole
A of the relay gear is aligned with the hole A of the limit
gear and that hole B of the relay gear is aligned with the
hole B of the drive gear. (See Fig.2-2-3i.)
(9) Install the door opener, opener guide, spring(A) and cas-
sette housing bracket and fasten the two slit washers.
Fig. 2-2-3e
Main deck right side
Drive arm
Hole
B
C
Drive arm
Fig. 2-2-3g
Hole
Drive gear
1
2
A
B
Fig. 2-2-3h
Fig. 2-2-3f
2-7
Page 29

Relay gear
B
Guide holeNotches Notch
2.2.6 Audio Control Head
1. How to remove
(1) Remove the two screws (A) and remove the audio con-
trol head together with the head base.
(2) When replacing only the audio control head, remove the
three screws (B) while controlling the compression spring.
Head base
B
AA
Drive gear Limit gear
Fig. 2-2-3i
2.2.4 Pinch Roller Arm Assembly
1. How to remove
(1) Remove the spring from the hook of the press lever as-
sembly.
(2) Remove the slit washer and remove the pinch roller seat
2. (See Fig.2-2-4a.)
(3) Remove the pinch roller arm assembly by pulling it up.
Slit washer
Pinch roller seat2
Spring
Pinch roller arm
Press lever assembly
Pinch roller arm assembly
assembly
Fig. 2-2-4a
2.2.5 Guide Arm Assembly and Press Lever Assembly
1. How to remove
(1) Remove the spring and expand the lug of the lid guide in
the arrow-indicated direction. Then remove the guide arm
assembly by pulling it up.
(2) Remove the press lever assembly by pulling it up. (See
Fig.2-2-5a.)
Screws(A)
Audio control head
Fig. 2-2-6a
Screws(B)
Audio control head
Compression
Audio control head
board assembly
Head base
springs
Fig. 2-2-6b
2. How to install
(1) To make the post-installation adjustment easier, set the
temporary level as indicated in Fig.2-2-6c. Also make sure
that the screw center (centre) is brought into alignment
with the center (centre) position of the slot.
A/C head
12.4 mm
Head base
Screw
2-8
Tension
spring
LugLid guide
Fig. 2-2-5a
Press lever
assembly
Guide arm
assembly
Head base
Audio control head
Fig. 2-2-6c
2.2.7 Loading Motor
1. How to remove
(1) Remove the belt wound around the worm gear.
(2) Open the two lugs of the motor guide and remove the
loading motor, loading motor board assembly and motor
guide altogether by pulling them up.
(3) When replacing the loading motor board assembly, take
care with the orientation of the loading motor. (Install so
that the loading motor label faces upward.)
(4) When the motor pulley has been replaced, choose the
fitting dimension as indicated in Fig.2-2-7a.
Page 30

Loading motor board assembly
Loading motor
Lugs
Motor guide
6.5 ± 0.2 mm
LABEL
Motor pulley
Worm gear
Belt
Fig. 2-2-7a
2.2.8 Capstan Motor
1. How to remove
(1) Remove the belt (capstan) on the mechanism assembly
back side.
(2) Remove the three screws (A) and remove the capstan
motor.
Screws(A)
Screw(A)
Capstan motor
Belt
Fig. 2-2-8a
Spacer
Spacer
2. How to install (Centering the mounting position)
When the capstan motor has once been removed and then
reinstalled out of the initial correct position in the rotational
direction, the capstan motor current may be unstable during
operation in high or low temperatures. This may result in
greater Wow & Flutter and occasionally in power breakdown
because of current over - load. Install the capstan motor while
following the procedure given below.
(The capstan motor is centrally located when the unit is
shipped from the factory.)
(1) Provisionally tighten the three screws (A) securing the
capstan motor.
(2) Install the mechanism assembly to which the capstan
motor is provisionally fastened on the bottom chassis
which incorporates the Main board assembly. (No need
to tighten the screws for mounting the mechanism.)
Make sure that all the connectors for the mechanism assembly and the Main board assembly are correctly installed as indicated in Fig. 2-2-8b.
(3) Making sure that the connector for the capstan motor is
correctly mounted, and securely tighten the three screws
(A).
Note:
• When the capstan motor has been replaced with a new
one, perform recording in the EP(or LP) mode for at
least 2 minutes at normal temperatures immediately before starting the FF/REW or SEARCH operations (Aging).
2.2.9 Pole Base Assembly (supply or take-up side)
1. How to remove
(1) Remove the UV catcher 2 on the removal side by loos-
ening the screw (A).
(2) Remove the pole base assembly on the supply side from
the mechanism assembly by loosening the screw (B) on
the mechanism assembly back side and sliding the pole
base assembly toward the UV catcher 2.
(3) As for the pole base assembly on the take-up side, turn
the pulley of the loading motor to lower the cassette
holder because the screw (B) is hidden under the control plate. (See the “Procedures for Lowering the Cassette
holder assembly” of 1.3 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY
METHOD.) Further turn the motor pulley to move the cassette holder until the screw (B) is no longer under the control plate (in the half-loading position). Then remove it as
done for the supply side by removing the screw (B).
Note:
• After reinstalling the Pole base assembly and the UV
catcher2, be sure to perform compatibility adjustment.
Fig. 2-2-8b
Connector for
the capstan motor
Screw(A)
UV catcher2
Screw(A)
UV catcher2
Screw(B)
Fig. 2-2-9a
2-9
Page 31

2.2.10 Rotary Encoder
1. How to remove
(1) Remove the screw (A) and remove the rotary encoder
by pulling it up. (See Fig. 2-2-10a.)
Rotary encoder (Front side)
Screw(A)
Guide marks
2.2.12 Change Lever Assembly, Direct Gear, Clutch
Gear and Coupling Gear
1. How to remove
(1) Release the two lugs of the rotary encoder guide in the
arrow-indicated direction and remove the change lever
assembly.
(2) Remove the slit washer retaining the direct gear and re-
move the latter.
Take care so as not to lose the washer and spring. (See
Fig.2-2-12a.)
Rotary encoder (Back side)
Positioning pin of the rotary encoder
Fig. 2-2-10a
Mark E
Shaft of the rotary encoder guide
Control plate
Fig. 2-2-10b
2. How to install (Phase matching)
(1) Make sure that the mark E of the control plate is in align-
ment with the mark
of the loading arm gear shaft and
bring the guide marks on the rotary encoder into alignment as indicated in Fig.2-2-10a. (See Fig. 2-2-10a and
Fig. 2-2-10b.)
(2) Turn over the rotary encoder with its guide marks kept in
alignment and install it by fitting on the shaft of the rotary
encoder guide and the positioning pin.
(3) Tighten the screw (A) to complete the installation.
2.2.11 Clutch Unit
(1) Remove the belt wound around the capstan motor and
the clutch unit.
(2) Remove the slit washer and remove the clutch unit.
Change lever
assembly
Spring(B)
Lugs
Note:
• The parts with marked (
speed FF/REW type).
1 : Uses the standard type mechanism only.
*
2:
Uses the high-speed FF/REW type mechanism only.
*
Slit washer
Washer (*1)
Spacer
Direct gear
Spring(A)
Position the projecting
side down.
1)
Spacer (
*
) have different types of mechanisms (standard type or high-
*
Clutch gear
Spring (C)
Coupling gear (
2)
*
Fig. 2-2-12a
2. How to install
(1) Install the clutch gear, spring (A), spring (C), direct gear,
spacer and others to the individual shafts of the main
deck, and finally the slit washer. (See Fig.2-2-12a.)
(2) Let the spring (B) drops into the rotary encoder guide hole
and install the change lever assembly.(Take care not to
mistake a direction of the spring.) The point is to slightly
lift the clutch gear and catch it from the both sides with
the assembly. (See Fig.2-2-12b.)
Rotary encoder guide
Spring(B)
Change lever assembly
Clutch gear
2-10
Belt
Clutch unit
Fig. 2-2-11a
Slit washer
Main deck Main deck
Fig. 2-2-12b
Page 32

2.2.13 Link Lever
1. How to remove
(1) Remove the two slit washers.
(2) Remove the link lever by lifting it from the shaft retained
by the slit washers. Then swing the link lever
counterclockwise and remove it from the locking section
of the control plate.
Slit washers
2.2.14 Cassette Gear, Control Cam and Worm Gear
1. How to remove
(1) Remove the control cam by lifting it.
(2) Open the two lugs of the cassette gear outward and pull
the latter off.
(3) Remove the belt wound around the worm gear and the
loading motor.
(4) Open the lug of the lid guide outward and remove the
worm gear.
Link lever
Locking section of the
control plate
Fig. 2-2-13a
2. How to install (Phase matching)
(1) Slide the control plate so that its mark E is aligned with
the mark
on the loading arm gear shaft. (See Fig.2-2-
13b.)
(2) Rotate the worm gear until the guide hole of the control
cam is aligned exactly with the guide hole of the main
deck. (See Fig.2-2-13c.)
(3) Insert the link lever into the locking section of the control
plate. (See Fig.2-2-13a.)
(4) Rotate the link lever clockwise so that it is installed on
the shafts in the center (centre) and on the left of the control cam.
(5) Fasten the slit washers at these two points.
Loading motor
Belt
Lug
Worm gear
Lugs
Cassette gear
Lid guide
Control cam
Fig. 2-2-14a
2.2.15 Control Plate
1. How to remove
(1) Remove the screw (A) retaining the control bracket 1 and
remove the latter.
(2) Slide the control plate as indicated by the arrow and re-
move the control plate. (See Fig.2-2-15a.)
Shaft of the rotary encoder guide
Fig. 2-2-13b
Worm gear
Main deck
guide hole
Control cam
guide hole
Cassette gear
Fig. 2-2-13c
Control plate
Control cam
Mark E
Screw(A)
Control
bracket1
Control
plate
Fig. 2-2-15a
2. How to install (Phase matching)
(1) Adjust the position of the idler arm assembly pin as indi-
cated in Fig.2-2-15b (to the left of center (centre) of the
R section).
(2) Bring the guide hole of the take-up lever into alignment
with the hole at the control plate guide and fix the position by inserting a 1.5 mm hexagonal wrench.
2-11
Page 33

(3) Install the control plate so that the section A of the load-
ing arm gear shaft fits into the hole (A) of the control plate,
the section B of the control plate guide into the hole (B),
and the control plate comes under the section C of the
rotary encoder guide and the section D of the loading arm
gear shaft while press-fit the pole base assmebly (supply side) as indicated by the arrow. It is important that
the tension arm assembly shaft is positioned closer toward you than the control plate. (See Fig.2-2-15c.)
(4) Make sure that the mark E of the control plate is in align-
ment with the mark
of the loading arm gear shaft. (See
Fig.2-2-15c.)
(5) Pull off the hexagonal wrench for positioning.
(3) Turn the loading arm gear (take-up side) clockwise so
that the notch of the loading arm gear (take-up side) is
in alignment with the projection of the loading arm gear
shaft and lift it.
Likewise, turn the loading arm counterclockwise so that
the notch is in alignment with the projection and remove
the loading arm gear (take-up side). (See Fig.2-2-16a and
Fig. 2-2-16b.)
(4) When removing the loading arm gear shaft, be sure of
first removing the screw retaining the drum assembly (on
the back side of the loading arm gear shaft). Then remove the screw (C) and remove the loading arm gear
shaft by sliding it.
Idler arm assembly
pin
R section
Guide hole of the
control plate guide
Section D
1.5mm hexagonal wrench
Fig. 2-2-15b
Section A
Section D
Hole A
Pressfit
Insert
Take-up lever
Pole base assembly
(supply side)
Section A
Hole A
Pole base assembly
(take-up side)
Screw(B)
Torsion arm
Loading arm gear
(take-up side)
Projection B
Guide marks
Projection A
Pole base assembly
(supply side)
Screw(A)
Loading arm gear
(supply side)
Fig. 2-2-16a
Loading arm gear shaft
Loading arm gear (take-up side)
Notch
Screw(C)
Loading arm gear shaft
Section C
Section C
Section B
Hole B
Hole B
Section B
Control plate
Tension arm assembly
shaft
Fig. 2-2-15c
2.2.16 Loading Arm Gear (supply or take-up side) and
Loading Arm Gear Shaft
1. How to remove
(1) Remove the loading arm gear (supply side) by loosen-
ing the screw (A). (See Fig. 2-2-16a.)
(2) Remove the screw (B) and remove the torsion arm from
the pole base assembly (take-up side). (See Fig.2-2-16a.)
2-12
Fig. 2-2-16b
2. How to install
(1) Align the notch of the loading arm gear (take-up side) to
the projection B of the loading arm gear shaft and slip it
over. Then rotate it clockwise for alignment with the projection A and slip it down to the bottom. (See Fig.2-216b.)
(2) Then turn the loading arm gear (take-up side)
counterclockwise. Hang the torsion arm on the pole base
assembly (take-up side) and tighten the screw (B).
(3) Install the loading arm gear (supply side) so that the guide
mark of the loading arm gear (take-up side) is in alignment with the guide mark of the loading arm gear (supply side). Then hang the torsion arm on the pole base
assembly (supply side) and tighten the screw (A). (See
Fig.2-2-16a.)
Page 34

2.2.17 Take-up Lever, Take-up Head and Control Plate
Lug(D)
Lug(C)
SpringLug(E)
Lug(A)
Lug(B)
Main brake assembly
(take-up side)
Reel disk
(take-up side)
Main brake assembly
(supply side)
Notch
Guide
(1) Remove the spring of the take-up lever from the main
deck.
(2) Remove the lug (A) of the take-up lever from the main
deck and pull out the take-up lever and the take-up head
together.
(3) Remove the screw (A).
(4) Align the idler arm assembly pin in the center (centre) of
the R section of the control plate guide, remove the con-
trol plate guide lugs (B) and (C) from the main deck, and
remove the control plate guide.
Idler arm assembly pin
Lug(C)
Screw(A)
Take-up lever
Take-up head
Lug(A)
Lug(B)
Control plate guide
Fig. 2-2-17a
2.2.18 Capstan Brake Assembly
1. How to remove
(1) Move the lug (A) of the capstan brake assembly in the
arrow-indicated direction so that it comes into alignment
with the notch of the main deck. (See Fig. 2-2-18a.)
(2) Remove the lug (B) of the capstan brake assembly from
the main deck and remove the capstan brake assembly.
Spring
Sub brake
Lug(A)
Lug(B)
assembly
(take-up side)
Lug(C)
Fig. 2-2-19a
2.2.20 Main Brake Assembly (take-up side), Reel Disk
(take-up side) and Main Brake Assembly (supply side)
1. How to remove
(1) Move the main brake assembly (take-up side) in the ar-
row-indicated direction and remove the reel disk (takeup side).
Remove the spring attached to the main brake assembly.
(2)
(3) Remove the lug (A) of the main brake assembly (take-
up side) and pull out the lug (B) after bringing it into alignment with the main deck notch.
(4) Remove the lugs (C), (D) and (E) of the main brake as-
sembly (supply side) from the main deck and pull them
off. (See Fig.2-2-20a.)
(5) When installing the main brake assembly (take-up side),
slide the brake lever in the direction as indicated by the
arrow to prevent it from hitting the projection of the main
brake assembly (take-up side). (See Fig.2-2-20b.)
Lug(B)
Lug(A)
Capstan brake assembly
Fig. 2-2-18a
2.2.19 Sub Brake Assembly (take-up side)
1. How to remove
(1) Remove the spring attached to the lid guide and sub
brake assembly (take-up side).
(2) Bring the lug (A) of the sub brake assembly (take-up side)
into alignment with the notch of the main deck.
(3) Remove the lugs (B) and (C) of the sub brake assembly
(take-up side) from the main deck and remove the sub
brake assembly (take-up side).
Fig. 2-2-20a
(
1)
*
Brake
lever
Note:
• The parts with marked ( *) have different types of mechanisms (standard type
or high-speed FF/REW type).
1 : Uses the standard type mechanism only.
*
Rotary encoder guide
Projection of the main
brake assembly
(take-up side)
Fig. 2-2-20b
2-13
Page 35

2.2.21 Tension Brake Assembly, Reel Disk (supply side)
(
)
and Tension Arm Assembly
1. How to remove
(1) Remove the three lugs of the tension brake assembly
from the main deck and pull them off.
(2) Remove the reel disk (supply side) by loosening in the
arrow-indicated direction the main brake assembly (supply side).
(3) Remove the tension spring on the back of the main deck.
Then release the lug of the tension arm bearing in the
arrow-indicated direction and draw out the tension arm
assembly. (See Fig. 2-2-21a.)
Lug of the tension
arm bearing
Tension arm
assembly
Reel disk
(supply side)
2.2.23 Stator Assembly
(1) Remove the flat cable.
(2) Remove the two screws (A).
(3) Remove the stator assembly by lifting in the arrow-indi-
cated direction. (Take care that the brush spring does not
jump out.)
(4) After installation, be sure to perform the PB switching
point adjustment according to the electrical adjustment
procedure.
Screws(A)
Tension brake
assembly
Lugs
Tension spring Main brake assembly
supply side
Fig. 2-2-21a
2.2.22 Idler Lever, Idler Arm Assembly
1. How to remove
(1) Remove the lug of the idler lever from the main deck and
remove the hook fitted in the idler arm assembly hole by
lifting it.
(2) Remove the slit washer and pull out the idler arm assem-
bly.
Lug Idler lever
Stator assembly
Flat cable
(Take care not to mix up the
polar faces when installing.)
Fig. 2-2-23a
2.2.24 Rotor Assembly
(1) Remove the stator assembly.
(2) Remove the two screws (B) and remove the rotor assem-
bly.
Note:
• When installing the rotor assembly, note that a normal
picture cannot be obtained without ensuring the phase
matching as mentioned below.
(3) Match the phases of the upper drum assembly and the
rotor assembly as indicated in Fig.2-2-24a.
(4) Place the upper drum assembly hole (a) over the rotor
assembly holes (b) (with three holes to be aligned) and
tighten the two screws (B). (See Fig.2-2-24a.)
2-14
Fig. 2-2-22a
Hook
Idler arm
assembly
Slit washer
Screws (B)
Screw holes
Upper drum
assembly
Rotor assembly
Fig. 2-2-24a
Hole(a)
The hole is not in
line but is offset
toward the right.
Hole(b)
Page 36

2.2.25 Upper Drum Assembly
1. How to remove
(1) Remove the stator assembly and rotor assembly.
(2) Loosen the screw of the collar assembly using a 1.5 mm
hexagonal wrench and remove the collar assembly. Also
remove the brush, spring and cap at one time.
(3) Remove the upper drum assembly and remove the
washer using tweezers.
Note:
• When replacement is required, control the up- down
movement of the brush. Never apply grease.
Lower drum assembly
Coil parts
Upper drum assembly
Spring
Brush
Upper drum
assembly
Washer
Collar
assembly
Loosen
Cap
Shaft
1.5 mm
hexagonal wrench
Lower drum assembly
Fig. 2-2-25a
2. How to install
(1) Clean the coil parts of the lower drum assembly and the
newly installed upper drum assembly with an air brush
in advance. (See Fig.2-2-25b.)
(2) Install a new washer and upper drum assembly on the
drum shaft. (See Fig.2-2-25a.)
Note:
• When replacing the upper drum assembly, replace it
the together with the washer.
(3) Install the cap to the upper drum assembly.
(4) Position the collar assembly as indicated in Fig.2-2-25c
while controlling its up- down movement.
(5) Secure the collar assembly in position with a hexagonal
wrench while pressing its top with the fingers.
(6) After installation, gently turn the upper drum assembly
with your hand to make sure that it turns normally. Then
install the brush and the spring.
(7) Install the rotor assembly and stator assembly according
to Fig 2-2-23a and 2-2-24a.
(8) When installation is complete, clean the upper drum as-
sembly and lower drum assembly and carry out the following adjustments.
• PB switching point adjustment
• Slow tracking adjustment
• Compatibility adjustment (Be sure to check for compat-
ibility for the EP (or LP) mode.)
Upper drum
assembly
Collar
assembly
Fig. 2-2-25b
Fig. 2-2-25c
Press
Fig. 2-2-25d
Collar
assembly
Tighten
2-15
Page 37

2.3 COMPATIBILITY ADJUSTMENT
Notes:
• Although compatibility adjustment is very important,
it is not necessary to perform this as part of the normal servicing work. It will be required when you have
replaced the audio control head, drum assembly or any
part of the tape transport system.
• To avoid any damage to the alignment tape while performing the compatibility adjustment, get a separate
cassette tape (for recording and play back) ready to
be used for checking the initial tape running behavior.
• Unless otherwise specified, all measuring points and
adjustment parts are located on the Main board.
• When using the Jig RCU, set its custom code to match
the custom code of the VCR.
Jig RCU
[Data transmitting method]
Depress the “ ” ( 3 ) button
after the data code is set.
(6) Make sure that the V.PB FM waveform varies in parallel
and linearly with the tracking operation again. When required, perform fine-adjustment of the guide roller of the
pole base assembly (supply or take-up side).
(7) Unload the cassette tape once, play back the alignment
tape (A1) again and confirm the V.PB FM waveform.
(8) After adjustment, confirm that the tape wrinkling does not
occur at the roller upper or lower limits. (See Fig. 2-31d.)
[Perform adjustment step (9) only for the models
equipped with SP mode and EP (or LP) mode.]
(9) Repeat steps (1) to (8) by using the alignment tape (A2).
CUSTOM CODE
43: A CODE
53: B CODE
DATA CODE
INITIAL MODE
Fig. 2-3a Jig RCU [PTU94023B]
2.3.1 Checking/Adjustment of FM Waveform Linearity
Signal (A1) •
(A2) •
Mode (B) • PB
Equipment (C) • Oscilloscope
Measuring point (D) • TP106 (PB. FM)
External trigger (E) • TP111 (D.FF)
Adjustment part (F) • Guide roller [Mechanism assembly]
Specified value (G) • Flat V.PB FM waveform
Adjustment tool (H) • Roller driver [PTU94002]
Alignment tape(SP, stairstep, PAL) [MHPE]
Alignment tape(LP, stairstep, PAL) [MHPE-L]
(1) Play back the alignment tape (A1).
(2) Apply the external trigger signal to D.FF (E), to observe
the V.PB FM waveform at the measuring point (D).
(3) Press the channel buttons (+, –) simultaneously to enter
the manual tracking mode. This also brings tracking to
the center (centre).
(4) Make sure that there is no significant level drop of the
V.PB FM waveform caused by the tracking operation, with
its generally parallel and linear variation ensured. Perform the following adjustments when required. (See Fig.
2-3-1a.)
(5) Reduce the V.PB FM waveform while pressing the chan-
nel buttons (+, –) during playback. If a drop in level is
found on the left side, turn the guide roller of the pole
base assembly (supply side) with the roller driver to make
the V.PB FM waveform linear.
If a drop in level is on the right side, likewise turn the guide
roller of the pole base assembly (take-up side) with the
roller driver to make it linear. (See Fig. 2-3-1c.)
Max level
Proper waveform variation
Improper waveform variation
Fig. 2-3-1a
Roller driver
Fig. 2-3-1b
Min level
Guide roller (supply side)
2-16
Page 38

A
(2)
(3)
(1)
AUDIO OUT
Head base
Audio control head
CTL. P
Level drop at the guide roller (supply side)
C
Level drop at the guide roller (take-up side)
• Proper waveform variation: Always flat
B
the manual tracking mode. This also brings tracking to
the center (centre).
(4) Adjust the AUDIO OUT waveform and Control pulse
waveform by turning the screws (1), (2) and (3) little by
little until both waveforms reach maximum. The screw (1)
and (3) are for adjustment of tilt and the screw (2) for azimuth.
D
(3) Press the channel buttons (+, –) simultaneously to enter
• Improper waveform variation:
Higher Lower
Fig. 2-3-1c
Fig. 2-3-2a
2.3.3 Checking/Adjustment of the Audio Control Head
Improper
(a) Guide roller
(b) Guide pole
Fig. 2-3-1d
Proper
Phase (X-Value)
Signal (A1) •
Mode (B) • PB
Equipment (C) • Oscilloscope
Measuring point (D) • TP106 (PB. FM)
External trigger (E) • TP111 (D.FF)
Adjustment part (F) •
Specified value (G) • Maximum V.PB FM waveform
Adjustment tool (H) • A/C head positioning tool [PTU94010]
Alignment tape(SP, stairstep, PAL) [MHPE]
A/C head base [Mechanism assembly]
(1) Play back the alignment tape (A1).
2.3.2 Checking/Adjustment of the Height and Tilt of the
Audio Control Head
Note:
• Set a temporary level of the height of the A/C head in
advance to make the adjustment easier after the A/C
head has been replaced. (See Fig.2-2-6c.)
Signal (A) •
Mode (B) • PB
Equipment (C) • Oscilloscope
Measuring point (D1) • AUDIO OUT terminal
(D2) • TP4001 (CTL. P)
External trigger (E) • TP111 (D.FF)
Adjustment part (F) • A/C head [Mechanism assembly]
Specified value (G) • Maximum waveform
(1) Play back the alignment tape (A).
Alignment tape(SP, stairstep, PAL) [MHPE]
(2) Apply the external trigger signal to D.FF (E), to observe
the AUDIO OUT waveform and Control pulse waveform
at the measuring points (D1) and (D2) in the ALT mode.
(2) Apply the external trigger signal to D.FF (E), to observe
the V.PB FM waveform at the measuring point (D).
(3) Press the channel buttons (+, –) simultaneously to enter
the manual tracking mode. This also brings tracking to
the center (centre).
(4) Loosen the screws (4) and (5), then set the A/C head
positioning tool to the innermost projected part of the A/
C head. (See Fig. 2-3-3a.)
(5) Turn the A/C head positioning tool fully toward the cap-
stan. Then turn it back gradually toward the drum and
stop on the second peak point position of the V.PB FM
waveform output level. Then tighten the screws (4) and
(5).
(6) Perform the tracking operation and make sure that the
V.PB FM waveform is at its maximum.
If it is not at maximum, loosen the screws (4) and (5),
and turn the A/C head positioning tool to bring the A/C
head to a position, around where the waveform reaches
its maximum for the first time. Then tighten the screws
(4) and (5).
2-17
Page 39

[Perform adjustment steps (7) to (10) only for 2 Head
models equipped with LP mode.]
(7) Then play back the alignment tape (A2).
(8) Press the channel buttons (+, –) simultaneously to enter
the manual tracking mode. This also brings tracking to
the center (centre).
(9) Perform the tracking operation and make sure that the
V.PB FM waveform is at its maximum.
(10)
If it is not at maximum, loosen the screws (4) and (5),
and turn the A/C head positioning tool to bring the A/C
head to a position, around where the waveform reaches
its maximum for the first time. Then tighten the screws
(4) and (5).
Note:
• After adjusting, always perform the confirmation and
re-adjustment of the item 2.3.4.
Toward the drum
A/C head positioning tool
To the drum
Audio control head
Toward the capstan
Head base
Screw
Screw
To the capstan
(4)
(5)
Fig. 2-3-3a
Alignment tape
[SP, stairstep]
played with the
SP head
Alignment tape
[EP(LP), stairstep]
played with the
EP(LP) head
(1) Play back the alignment tape (A).
(2) Apply the external trigger signal to D.FF (E), to observe
the V.PB FM waveform at the measuring point (D).
(3) Confirm that the automatic tracking operation is com-
pleted.
(4) Set the VCR to the Auto adjust mode by transmitting the
code (F) twice from the Jig RCU. When the VCR enters
the stop mode, the adjustment is completed.
(5) If the VCR enters the eject mode, perform adjustment for
the audio control head phase (X-value) again.
2.3.5 Checking/Adjustment of the Tension Pole Position
Signal (A) • Back tension cassette gauge
Mode (B) • PB
Adjustment part (F) • Adjust pin [Mechansim assembly]
Specified value (G) • 25 - 51 gf•cm (2.45 – 5 × 10-3 Nm]
[PUJ48076-2]
(1) Play back the back tension cassette gauge (A).
(2) Check that the indicated value on the left side gauge is
within the specified value (G).
(3) If the indicated value is not within the specified value (G),
perform the adjustment in a following procedure.
1) Set the VCR to the mechanism service mode. (See
1.5 MECHANISM SERVICE MODE.)
2) Set the VCR to the play back mode and adjust by turning adjustment pin to align the tension arm assembly
edge with the main deck hole (A) on the right edge
marker. (See Fig. 2-3-5a)
Tension arm
assembly
Hole (A)
Edge
Waveform output
X-value adjustment point
Drum side Control head position Capstan side
Maximum
Fig. 2-3-3b
2.3.4 Checking/Adjustment of the Standard Tracking
Preset
Signal (A) •
Mode (B) • PB ¥ Auto adjust
Equipment (C) • Oscilloscope
Measuring point (D) • TP106 (PB. FM)
External trigger (E) • TP111 (D.FF)
Adjustment part (F) • Jig RCU: Code “50”
Specified value (G) • STOP mode
Adjustment tool (H) • Jig RCU [PTU94023B]
Alignment tape(LP, stairstep, PAL) [MHPE-L]
(Maximum V.PB FM waveform)
Marker
0.5 mm
Tension arm assembly
Tension brake assembly
Adjust pin
Fig. 2-3-5a
2-18
Page 40

Mechanism Timing Chart
Mechanism mode
Control plate mark
Rotary encoder
Control cam angle
EJECT
END
E U CI
HIGH
C CH
LOW
HIGH
B CH
LOW
HIGH
A CH
LOW
0
CASS-
UP
69 136 370 412.
CASS-INS
FF/REW
FR
230
STOP
ST
264.
REV
R
7
318.
7
SLOW/STILLPPLAY
SL
42
Rotary encoder
angle
Pole base
Pinch roller
Guide arm
Tension arm
Main brake S
Main brake T
Sub brake S
Sub brake T
Capstan brake
Direct gear
Change lever 2
Idler position
Take-up lever
Rec safety switch
Operation mode
HALF PRESS
CONTACT
ON PLAY
ON REV
CONTACT
(C-INS)
HALF REV
HALF FF/REW
CONTACT
CONTACT
IN FF/REW
OUT PLAY
SUPPLY
CENTER
TAKE-UP
READY
RESET
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
0
20 42.652.
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
6
6
114.
150.4167.8178.
8
Timer REC
(drum at stop)
POWER OFF
(cassette loaded)
207.2218.2240.2251.
standby
STOP
Backspace Slow FOR
Search REW
Slow REW
2
293.2304.2320.4335
REC pause
REC
Search FF
STOP
(
drum
in motion)
2-19
Page 41

2-20
Page 42

MECHANISM ADJUSTMENT (DV)
2.9 PREPARATION
2.9.1 Precautions
(1) Observe the specified screw tightening torque when at-
taching parts. The torque should be 0.04 Nm (0.4 kgfcm)
unless otherwise specified.
(2) Always disconnect the power supply unit before proceed-
ing to solder or attach parts.
(3) When plugging or unplugging a wire, be careful not to
damage the connector.
(4) When replacing a part, be careful not to damage other
parts or to mistakenly attach parts.
2.9.2 Tools Required for Adjustments
TORQUE DRIVER
12
YTU94088
Tool for replacing tip IC
4
PTS40844-2
BIT
YTU94088-003
Table 2-9-1 Tools Required for Adjustments
2.9.3 Disassembly and Assembly Procedures
The following table shows the steps for assembling or disassembling the mechanism parts. Read the following descriptions carefully before actual assembly/disassembly operations.
: Order of disassembly steps. Reverse this order when
(1)
assembling.
: Name of the disassembled/assembled part.
(2)
: Surface where the disassembled/assembled part is
(3)
mounted. T = Top. B: Bottom.
: Number of disassembly drawing.
(4)
Tool for installing slit washer
3
YTU94121A
: Parts to be removed in disassembly/assembly, such as
(5)
screws, washers and springs, and the points.
Symbol Name & Point
S Screw
W Washer
P Spring
*
Connector, lock(L), soldering(SD),
shield, etc.
[Example] • (W1) = Remove the washer W1.
• (P1) = Remove the spring P1.
: Notes for disassembly/assembly.
(6)
: For the phase alignment in disassembly/assembly and
(7)
the parts which require phase adjustments after assembly, see “2.16 MECHANISM PHASE CHECK/ADJUSTMENT”.
2.9.4 Screws and Washers Used in Disassembly/Assembly of the Mechanism Assembly
Table 2-9-1 shows the symbols, designs, part numbers and
colors of the screws and washers used in the mechanism
assembly.
When disassembling or assembling the mechanism assembly, be sure to attach screws and washers correctly by referring to the following table.
(S1)
(S2)
(S3)
Symbol
(W1)
(W2)
(W3)
Part numberSymbol
QYTDSP2004Z
YQ43893
YQ43893-7
Part number
YQ44246
YQ44246-3
YQ43933-2
Color
GOLD
SILVER
BLACK
Color
RED
BLACK
BLACK
Table 2-9-2
Step
/Loc Part Name
No.
1
A Cassette housing assembly/ B Mechanism assembly T 1
Fig.
No.
2(S1),(L1) – (L5)
Point Note Discription
1
2 1 Drum assembly T 2 3(S2) 2,3
3 2 Motor bracket assembly T 2 4(S2) 2,4
4 3 Middle catcher assembly T 3 3(S2) —
§§ §§§§§
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7)
2-21
Page 43

2.10 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY OF THE MECHANISM
ASSEMBLY
2.10.1 Introduction
The disassembly and assembly of the mechanism assembly should usually be performed in the ASSEMBLY mode.
(Table 2-10-1)
Note that the mechanism is in the cassette in (C-IN) mode
when the mechanism assembly is taken out of the set and
that the C-IN mode should be switched to the ASSEMBLY
mode in this case.
To set the ASSEMBLY mode, apply 3 V DC to the electrodes
on the upper part of the loading motor as shown in Fig. 210-7.
MODE
PARTS
1
ROTARY
ENCORDER
R. ENC -20
MAIN CAM GEAR 0
2
3
36°
C-IN
ASSEMBLY
17°
S. FF
30.33°
36.33°
0
15
33.33
40
Table 2-10-1
2.10.2 Mechanism Modes
The mechanism has 6 modes as shown in Table 2-11-1. The
current mode can be confirmed by the positioning of the “
”
marking on the sub-cam gear and the “ ” marking on the
mechanism.
See the following figures (Figs. 2-10-1 to -6) for details.
Note:
•
This mechanism assembly has another ASSEMBLY
mode. However, this mode cannot be identified from the
markings because it corresponds to an intermediate position between the C-IN ( C ) mode and S-FF ( H ) mode.
This mode can be confirmed by the rotary encoder
phase. See Fig. 2-10-7.
LOADING END
87°
166.66
PLAY REV STOP FF/REW
223.66°
229.66°
226.66
185
140
190.33°
196.33°
169.66°
193.33
160
270.33°
273.33
220
276.33°
303.66°
306.66
245
1. Checking the mechanism mode
C H P
H
Fig. 2-10-1 Fig. 2-10-2 Fig. 2-10-3
R S F
Fig. 2-10-4 Fig. 2-10-5 Fig. 2-10-6
2-22
Page 44
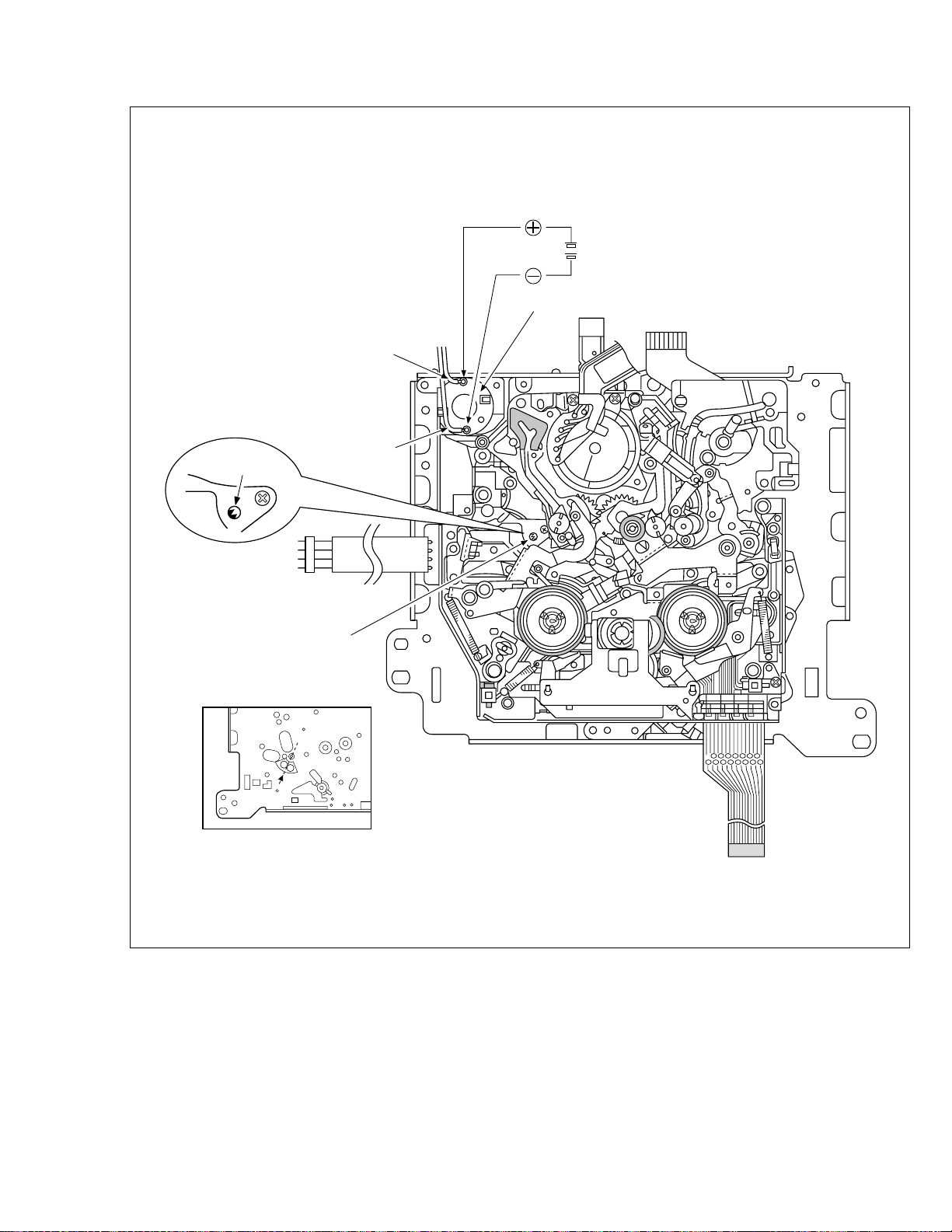
2. Setting/checking the ASSEMBLY mode
Wire (Brown)
Note:
• In this ASSEMBLY mode, only the 2
gear teeth of the rotary encoder are
marked (red coloring).
Marking
Wire (Red)
(Colored red)
DC 3 V
Motor Bracket Assembly (Loading Motor)
Rotary Encoder
< ASSEMBLY >
C
H
Fig. 2-10-7
2-23
Page 45

2.11 MECHANISM TIMING CHART
See following table (Table 2-11-1).
MODE
PARTS
36°
1
ROTARY
ENCODER
2
3
ROTARY ENCODER
MAIN CAM 0
SUB CAM
POLE BASE
CTL PLATE
FF/REW
MAIN BRAKE(SUP)
MAIN BRAKE(TU)
SUB BRAKE
ON(REV MODE PRESS UP)
ON(PLAY MODE)
PINCH ROLLER
EXIT GUIDE ARM
HALF LOADING
TENSION ARM
BAND ARM PLATE
CLUTCH LOCK
SUP CENTRRING
OFF
S/REV
PLAY
ON 1
ON 2
OFF
ON 1
ON 2
OFF
OFF
OFF
ASSY
OFF
OFF 1
OFF 2
OFF
OFF 1
OFF 2
ASSEMBLY
C-IN
17°
-20
0
15
0
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
S. FF
30.33°
33.33
40
4015
36.33°
87°
LOADING END
169.66°
166.66
140
140
PLAY REV STOP FF/REW
270.33°
276.33°
223.66°
226.66
185
185
229.66°
303.66°
273.33
220
220
306.66
245
245
190.33°
193.33
160
160
196.33°
CENTERRING ARM
2-24
S/REV
Table 2-11-1
Page 46

2.12 MECHANISM ASSEMBLY/DISASSEMBLY PROCEDURE TABLE
Step
/Loc Part Name
No.
1 A Cassette housing assembly/ B Mechanism assembly
2 1
Drum assembly T 2-13-2 3(S2) 2,3
3
2 Motor bracket assembly T 2-13-2 4(S2) 2,4
4 3 Middle catcher assembly T 2-13-3 3(S2) —
5 4 Reel cover assembly T 2-13-3 (S2), 2(L6) 5
6 5 Pinch roller arm assembly T 2-13-4 (W1), (L7) 6
7 6 Sub brake assembly T 2-13-4 (P1), (W1), (L8) —
8 7 Band arm plate sub assembly T 2-13-4 (S3), (L9), (P2), (W2) 7,8
9 8 Tension arm sub assembly T 2-13-4 (P3) 8
10 9 EXIT guide arm assembly T 2-13-5 (W1) —
11 10 Swing arm assembly T 2-13-5 ——Position alignment
12 11 Sub deck assembly T 2-13-6 4(S2) 9 Position alignment
13 12 Main brake (Sup) assembly T 2-13-6 (P4), (L10) —
14 13 Main brake (Take up) assembly T 2-13-6 (P5), (L11) —
15 14 Reel disk assembly (Sup) T 2-13-7 ——
16 15 Reel disk assembly (Take up) T 2-13-7 ——
17 16 Prism T 2-13-7 (S2) —
18 17 Control plate T 2-13-7 2(L12) —
19 18 Guide rail (Take up) assembly T 2-13-8 4(S2) 10 Position alignment
20 19 Guide rail (Sup) assembly T 2-13-8 (S2), 2(L13) 10 Position alignment
21 20 Base plate assembly T 2-13-8 (S2), 2(L14) —
22 21 Ent. guide base assembly T 2-13-9 (S2) —
23 22 Worm wheel 2 T 2-13-9 — 11 Phase alignment
24 23 Timing belt T 2-13-9 ——
25 24 Center gear assembly T 2-13-9 ——
26 25 Reel drive pulley assembly T
27 26 Push plate T
28 27 Clutch lock gear(2) T
29 28 Clutch lock gear (1) T
30 29 Tension control arm assembly T
31 30 Brake control arm assembly T
32 31 Charge arm assembly T
33 32 Connect gear 2 T
34 33 Connect gear 2 T
35 34 Rotary encoder assembly T
36 35 Main cam T
37 36 Arm gear 1 assembly T
38 37 Centering arm assembly T
39 38 Sub cam T
40 39 Arm gear 2 assembly T
41 40 Clutch lock lever assembly T
42 41 Capstan motor T
43 42 Drum base deck T
Fig.
No.
T 2-13-1 2(S1),(L1) – (L5) 1
2-13-10
2-13-10
2-13-10
2-13-10
2-13-11
2-13-11
2-13-11
2-13-12
2-13-12
2-13-13
2-13-13
2-13-13
2-13-13
2-13-14
2-13-14
2-13-14
2-13-15
2-13-15
(W1) —
(W1) —
(W3) —
(P6) —
(L15) 12 Position alignment
(W1), (L16) 12 Position alignment
(L17) 13 Position alignment
(S2) — (Phase alignment)
(S2) — (Phase alignment)
2(S2) 14 Phase alignment
(W1) 15 Phase alignment
Collar 15,16 Position alignment
(L18) 15 Position alignment
(S2) 17 Phase alignment
— 17 Position alignment
(L19) 17,18 Position alignment
(P7), Adjust nut — Vertical adjustment
3(S2) —
Point Note Discription
Table 2-12-1
2-25
Page 47

TOP VIEW
21
11
22
8
34
35
14
37
7
29
2 19 42 1 18 41 3
9
23
25
5
15
10
38
39
31
30
17 12 16 36 20 4 32 26
Fig. 2-12-1
6
40
–
33 24 1328
2-26
Page 48

2.13 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY
1.
A Cassette Housing Assembly/ B Mechanism Assembly
1
(S1)
<Note 1> : If the wires for the cassette housing motor are
connected to the circuit board, remove them before disassembly.
(L3)
A
(L4)
(L1)
Fig. 2-13-1
(L5)
<Note1>
2
(S1)
(L2)
B
2. 1 Drum assembly / 2 Motor bracket assembly
3
4
(S2)
(S2)
8
(S2)
<Note2>
9
(S2)
6
(S2)
7
(S2)
<Note4>
2
<Note3>
<Note2>
1
5
(S2)
<Note 2> : If wires are connected to the circuit board, re-
move them before disassembly.
<Note 3> : Be careful not to damage the drum assembly
when removing it.
<Note 4> : The bracket (DV) may come in the way of re-
moval of screw (7). Be sure to remove the
bracket before proceeding to the screw removal.
Fig. 2-13-2
2-27
Page 49

3. 3
Middle Catcher Assembly/
4
<Note5>
(L6)
(L6)
4 Reel Cover Assembly
13
(S2)
Fig. 2-13-3
12
(S2)
10
(S2)
<Note 5> : Once the reel cover assembly has been re-
moved, the parts located below it tend to slip out
easily: Be careful.
11
(S2)
3
4.
5 Pinch Roller Arm Assembly/ 6 Sub Brake Assembly/
7 Band Arm Plate Sub Assembly/ 8 Tension Arm Sub
Assembly
<Note 8>:
How to install the spring
Step 1
Hook a
8
Step 2
Hook b
(W1)
(P2)
14
(S3)
(P3)
(W2)
7
<Note7>
NOTE8
5
Step 3
<Note6>
(L9)
<Note 6> : When attaching this part, fit it in the boss (L7)
on the charge arm assembly.
<Note 7> : When attaching or removing this part, take care
of the handling of the band section.
<Note 8> : After fitting the spring on the shaft, engage it with
hook a first then with hook b .
After attaching it, set it to the positioning shown
in “Step 3” and confirm that band arm plate sub
assembly 7 can be rotated in the direction of
the arrow as shown below.
(W1)
2-28
6
(P1)
(L8)
Fig. 2-13-4
(L7)
Fig. 2-13-4A
Page 50

5.
9 EXIT Guide Arm Assembly/ 10 Swing Arm Assembly
10
9
(W1)
Fig. 2-13-5
6.
11 Sub Deck Assembly/ 12 Main Brake (Sup) Assembly/
13 Main Brake (Take up) Assembly
15
(S2)
(P4)
(P5)
13
12
(
L10
16
(S2)
)
(
L11
<Note9>
18
(S2)
)
17
(S2)
11
<Note 9> : When attaching the sub deck assembly, make
sure to adjust the phase of the control plate.
Fig. 2-13-6
2-29
Page 51

7.
14 Reel disk assembly (Sup) / 15 Reel disk assembly
(Take up) / 16 Prism / 17 Control plate
14
15
19
(S2)
17
(
)
L12
(
)
L12
Fig. 2-13-7
8.
18 Guide rail (Take up) assembly / 19 Guide rail (Sup)
assembly / 20 Base plate assembly
11
16
20
(
L14
<Note 10> : When attaching, set the alignment markings of
the two gears so that the markings face oppo-
(
)
L13
24
<Note10>
(S2)
19
25
(S2)
)
21
(S2)
20
(S2)
22
(S2)
18
23
(S2)
site to each other.
19
18
Fig. 2-13-8A
2-30
Fig. 2-13-8
Page 52

9.21 Ent. guide base assembly /
23
Timing belt / 24 Center gear assembly
26
(S2)
22
21
<Note11>
22
Worm wheel 2 /
23
24
<Note 11> : How to attach the worm wheel 2 22 .
22
34
Align the phase of the rotary encoder assembly 34 ,
then attach it by aligning the phase hole of the mechanism assembly.
Fig. 2-13-9A
Phase alignment
Mark (Red)
Fig. 2-13-9
10.
25
Reel drive pulley assembly / 26
27
Clutch lock gear(2) / 28 Clutch lock gear (1)
(W1)
26
27
(W3)
(P6)
28
Push plate
(W1)
25
Fig. 2-13-10
2-31
Page 53

29 Tension control arm assembly/ 30 Brake control
11.
arm assembly /
31
Charge arm assembly
(
)
L16
(W1)
30
(
<Note12>
(
)
L15
L17
)
<Note13>
29
31
<Note 12> : How to attach the tension control arm assem-
bly 29 / Brake control arm assembly 30 .
34
30
Boss
29
(Phase alignment)
35
Align the phase of the main cam 35 , then attach it by
fitting the bosses into the cam slot.
Fig. 2-13-11A
<Note 13> : How to attach the charge arm assembly 31 .
Fig. 2-13-11
12. 32 Connect gear 2 / 33 Connect gear 2
27
(S2)
32
28
(S2)
33
31
39
38
Phase alignment
Boss
(Phase alignment)
Align the phase of the sub cam 38 , then attach it by
fitting the boss into the cam slot.
Fig. 2-13-11B
2-32
Fig. 2-13-12
Page 54

13.
34 Rotary encoder assembly / 35 Main cam /
36
Arm gear 1 assembly / 37 Centering arm assembly
<Note 14> :
How to attach the rotary encoder assembly 34 .
COLLAR
<Note15>
36
<Note14>
34
(
)
L18
<Note16>
29
(S2)
37
<Note15>
Fig. 2-13-13
30
(S2)
(W1)
35
<Note15>
34
Mark (colored : red)
35
Phase alignment
Align the phase of the main cam 35 , then attach it by
placing the (red) coloured markings (on 2 gear teeth)
within the encircled area.
Fig. 2-13-13A
<Note 15> : How to attach the main cam 35 .
Boss
Phase alignment
35
Boss
36
Phase alignment
37
Phase alignment
Align the phases of the arm gear 1 assembly 36 and
centering arm assembly 37 , then attach the arm gear 1
assembly 36 /centering arm assembly 37 by fitting the
bosses into the lower cam slot, and fit the slit washer.
Fig. 2-13-13B
<Note 16> :
How to remove the centering arm assembly 37
The center arm assembly is located behind the
mechanism assembly when the phase is
aligned correctly. The center arm assembly can
be removed by displacing it in the direction of
the arrow.
L18
37
Phase alignment
Fig. 2-13-13C
2-33
Page 55

14.38
Sub cam / 39
Arm gear 2 assembly /
40 Clutch lock lever assembly
<Note 17> : How to attach the sub cam 38 .
15.41
<Note17>
40
<Note18>
(
)
L19
Fig. 2-13-14
Capstan motor / 42
31
(S2)
<Note17>
38
Drum base deck
<Note17>
39
Boss
39
38
Phase alignment
Phase alignment
40
Phase alignment
Align the phases of the arm gear 2 assembly 39 and
clutch lock lever assembly 40 , then attach them by
fitting the boss into the lower cam slot and tighten the
screws.
Fig. 2-13-14A
<Note 18> :
How to remove the clutch lock lever assembly 40
L19 is located behind the mechanism assembly when the phase is aligned correctly. The
clutch lock lever assembly can be removed by
displacing it in the direction of the arrow.
Phase alignment
40
42
32
(S2)
33
(S2)
ADJUST NUT
Fig. 2-13-15
34
(S2)
L19
Fig. 2-13-14B
41
(P7)
2-34
Page 56

2.14 LIST OF PROCEDURES FOR DISASSEMBLY
24
23
17
29
(S2)
34
(W2)
7
(P3)
12
29
30
(S2)
25
(S2)
20
COLOR
14(S3)
26
(S2)
21
8
(W1)
27
28
13
16
(S2)
35
37
26
(W3)
(P6)
(W1)
32
14
(S2)
30
22
15
11
33
(S2)
(W1)
15
27
(S2)
32
(S2)
ADJ.
NUT
(P7)
28
(S2)
33
19
(S2)
16
34
(S2)
(W1)
6
17
(S2)
(S2)
42
18
18
(W1)
25
21
(S2)
31(S2)
19
41
38
10
20
(S2)
(S2)
(S2)
12
(S2)
(S2)
31
22
23
4
24
9(S2)
8(S2)
5
10
(S2)
4
(S2)
6(S2)
11
(S2)
3
(W1)
13
(S2)
7(S2)
2
3
(S2)
5
(S2)
1
(W1)
9
36
40
Note :
• For the greasing and oiling locations,
see “SECTION 5 PARTS LIST” (Page 5-6).
B
Fig. 2-14-1
39
2-35
Page 57

2.15 MECHANISM DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY SHEET
Fig. No.
No.
Type
A 1 2 3 4 7 11
1 18234567891011121314151617
S1
Attachin
Ref. Fig.
Screw Management Table
2-13-1 2-13-2 2-13-3
A Cassette housing assembly
1
(S1)
(L4)
(L1)
(L3)
(L5)
2
(S1)
(L2)
1 Drum assembly
3
(S2)
4
(S2)
5
(S2)
S2×3
2 Motor bracket assembly
9
(S2)
8
(S2)
6
(S2)
7
(S2)
S2×4
3 Middle catcher assembly
10
(S2)
12
(S2)
11
(S2)
S2 S2 S2
2-13-4
2-13-6
4 Reel cover assembly
13
(S2)
S2, L6×2
5
Pinch roller arm assembly
(W1)
W1, L7
6 Sub brake assembly
(W1)
S2S1 S2 S2 S2 S2 S2 S2 S2 S2 S2 S2 S2 S3
S1×2, L1-L5
S2×3
P1, W1, L8
17 Control plate 18 Guide rail (Take up) assembly 19 Guide rail (Sup)
assembly
(
)
L13
21
(S2)
20
(S2)
22
(S2)
23
(S2)
L12×2 S2×4 S2, L13×2
24 Center
gear
assembly
25 Reel drive
pulley
assembly
(W1)
26 Push
plate
(W1)
27 Clutch
lock gear
(2)
(W3)
28 Clutch
lock
gear (1)
(P6)
29 Tension control arm
assembly
(
)
L15
30
(
L16
W1 W1 W3 P6 L15 W1, L16
35 Main cam 36 Arm gear 1 assembly
(W1)
Collar
37
Centering arm assembly
(
)
L18
38 Sub cam
31
(S2)
(P1)
24
(S2)
Brake
control arm
assembly
) (W1)
2-36
W1 COLLAR L18 S2
Fig. 2-15-1A
Page 58

16 18 19 20 21 32 33 34 38 42
19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
S2 S2 S2 S2 S2 S2 S2 S2 S2
S2 S2 S2 S2 S2 S2 S2
2-13-7 2-13-9
7 Band arm plate sub
assembly
(P2)
14
(S3)
(W2)
11 Sub deck assembly
S3, P2, L9, W2
8 Tension arm sub
assembly
(P3)
P3
9
EXIT guide arm assembly
(W1)
S2×4
10 Swing arm assembly
16
(S2)
18
(S2)
2-13-14
17
(S2)
12
Main
Brake(Sup)
assembly
(P4)
13
Main
Brake(Take up)
assembly
(P5)
2-13-12 2-13-13 2-13-152-13-8
15
(S2)
P4, L10 P5, L11
14
Reel disk
assembly
(Sup)
15
Reel disk
assembly
(Take up)
16 Prism
19
(S2)
W1
20 Base plate assembly
21 Ent. guide base
22 Worm wheel 2 23 Timing belt
S2
assembly
25
(S2)
26
(S2)
S2, L14×2 S2
31 Charge arm assembly 32 Connect gear 2 33 Connect gear 2 34 Rotaly encoder
assembly
33
(S2)
29
(S2)
32
(S2)
(
L17
)
27
(S2)
L17 S2 S2
39 Arm gear 2 assembly 40 Clutch lock lever
41 Capstan motor 42 Drum base deck
assembly
(
)
L19
28
(S2)
S2×2
ADJUST NUT
(P7)
L19 S2×3ADJUST NUT, P7
30
(S2)
34
(S2)
Fig. 2-15-1B
2-37
Page 59
2.16 MECHANISM PHASE CHECK/ADJUSTMENT
See Fig. 2-16-1.
Worm Wheel 2
22
See Fig. 2-13-9A.
Rotary Encoder Assembly
34
See Figs. 2-13-9A and
2-13-13A.
35
Main Cam
See Figs. 2-13-13A and 2-13-13B.
Arm Gear 1 Assembly
36
See Fig. 2-13-13B.
Centering Arm Assembly
37
See Fig. 2-13-13B.
Arm Gear 2 Assembly
39
See Fig. 2-13-14A.
Sub Cam
38
See Fig. 2-13-14A.
Clutch Lock Lever Assembly
40
See Fig. 2-13-14A.
2-38
Fig. 2-16-1
Page 60

2.17 POSITIONING THE TENSION POLE
See Fig. 2-17-1.
Tension Arm Sub
Assembly
B section
C
D section
Fig. 2-17-1
Adjustment Method
Note:
•
Remove the cassette housing assembly in advance.
1. Set the mechanism mode to the PLAY mode. (See pages
2-20 and 21.)
2. Loosen a screw A .
3. Check the location of the tip (section B ) of the tension
arm assembly to make sure that it is within area C .
If it is located outside, turn part D to bring it within the
specified area.
4. Tighten the screw A .
Note :
Tightening torque for the screw A : 0.06 Nm (0.6
kgfcm)
Screw A
2-39
Page 61
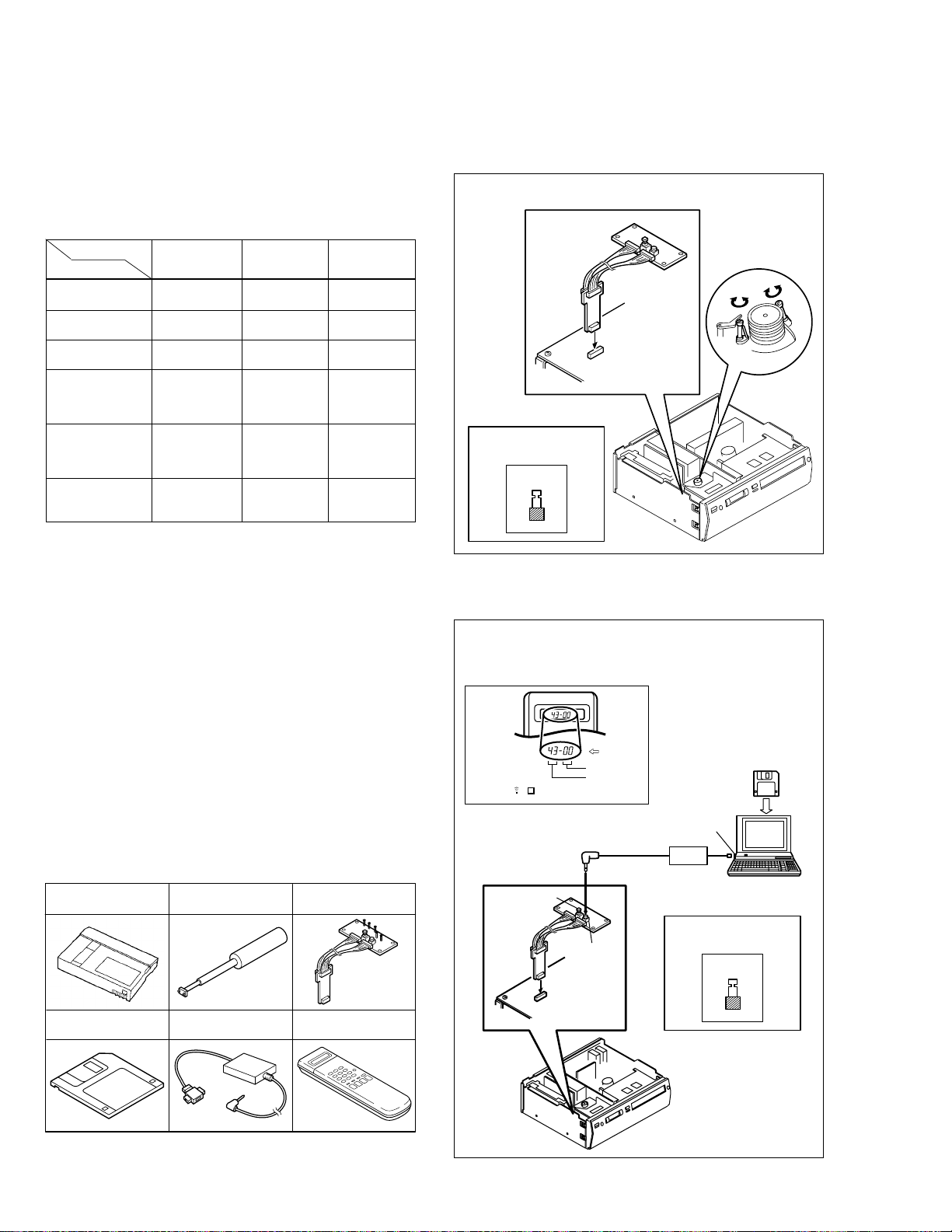
2.18
COMPATIBILITY AND ERROR RATE ADJUSTMENTS
2.18.1 Preparation
Before disassembly and adjustment, back up the data stored
in the EEPROM (IC1007 on the DV MAIN board) using the
Service Support System Software (SSS software).
Table 2-18-1 shows the important service points for the compatibility and error rate adjustments.
Adjustment Item
Service Point
Drum replacement Required Required Required
Transport part Required Not Check
replacement Note 1
Transport part Required Not Check
(drum) repair Note 1
IC5001
(PRE/REC amp on Not Not Check
PRE/REC MDA
board) replacement
IC2001
(PB. EQ on DV Not Not Required
MAIN board)
replacement
DV MAIN board
replacement Not Required Required
Note 2
Linearity
Adjustment
Note 1
PB Switching
Point Adjustment
Adjustmenmt
Error Rate
Table 2-18-1
Note 1 :
• The linearity adjustment is required only after servicing or
replacing the drum or the take up/supply guide rail.
Note 2 :
•
After replacing the DV MAIN board, write the original data in
the EEPROM of the new board. If write communication is not
possible, mount the original EEPROM on the new board.
When adjustments of more than one item are required, use
the following order for the adjustments.
2.18.3 Linearity Adjustment
∫
2.18.4 PB Switching Point Adjustment
∫
2.18.5 Error Rate Adjustment
2.18.2 Adjustment
The actual adjustment requires the following preparation.
1. Tools required for adjustment
Alignment tape
US : MC-1
PAL : MC-2
Guide driver
YTU94085
Jig connector cable
PTU94018B
2. Procedure
1. Take out the 7 screws (1 to 7), then remove the top cover.
(See Fig. COM1 on page 1-3 of section 1.5.)
2. Connect the jig connector cable to CN1101 on the DV
MAIN board.
Jig Connector Cable
PTU94018B
CN1101
DV MAIN PWB
<Note> : Switch setting of the
Jig connector cable
Switch OFF
(UP)
Fig. 2-18-2
3. Setup for computer adjustment
– Setup by extending the jig connector –
When performing the adjustment by the SSS software, set the VCR
to external communication mode by transmitting the code “6C” from
the Jig RCU.
Jig RCU
[PTU94023B]
[Data transmitting method]
Depress the “ ” ( 3 ) button
after the data code is set.
Switch
INITIAL MODE
DATA CODE
CUSTOM CODE
43: A CODE
53: B CODE
<JLIP>
PC Cable
QAM0099-002
<Note> : Switch setting of the
Service Support Software
RS-232C Port
Jig connector cable
Switch OFF
JVC
MENU
Personal Computer
(UP)
2-40
SSS software
PTU94016-3
PC cable
US : QAM0099-002
PAL : QAM0099-005
Fig. 2-18-1
Jig RCU
PTU94023B
CN1101
DV MAIN PWB
Fig. 2-18-3
Page 62

2.18.3 Linearity adjustment
The “PB Switching Point” in the Adjustment Utility of
the SSS software is adjusted automatically.
Load the alignment tape.
The following flowchart shows the linearity check/adjustment
procedure.
Connect an oscilloscope (CH: + Slope) and, while triggering
it with the HID signal, observe the ENV OUT waveform.
Play the alignment tape, then set “ATF” (Auto Tracking
Find) in “Deck Controller” of the SSS Software to ON.
(Note 3)
2.18.4 PB switching point adjustment
The following flowchart shows the PB switching point adjustment procedure.
Ensure that the ENV OUT waveform is linear and parallel,
without a noticeable drop or variation in the overall level. If
the waveform linearity is poor or there is a noticeable drop
in level, adjust the guide roller by turning it with the roller
driver.
Set “ATF” (Auto Tracking Find) to OFF using “Deck
Controller” of the SSS Software (Note 4). Observe the ENV
OUT waveform to confirm that the overall waveform
balance and linearity levels vary in accordance with the
tracking variation as shown in Fig. 2-18-3.
Repeat above steps
as required.
No
The linearity adjustment is complete if the PB ENV
waveform is ideally stable and varies ideally according to
the tracking variation. To close, play a prerecorded tape and
check the audio and video.
Is the PB ENV waveform ideally
stable and does it vary ideally
according to the tracking variation?
Yes
2.18.5 Error rate adjustment
The following flowchart shows the error rate adjustment procedure.
Record a color bar signal for about 5 minute s. (Note 6)
While playing the recorded signal, adjust “
Frequency (ME SP)
“Deck Section” of the Adjustment Utility.
To adjust VCO Center Frequency (ME SP) : Set Viterbi OFF.
To adjust VCO Center Frequency (ME LP) : Set Viterbi ON.
No
” or “
VCO Center Frequency (ME LP)
Is the obtained error rate minimum
(almost the typical value)?
VCO Center
” in
Yes
The error rate adjustment is complete when the minimum
error rate which is no higher than the typical value is
obtained. (Note 5)
HID waveform
PB ENV
waveform
Fig. 2-18-4 PB ENV Waveform
Note 3 :
• The VHS section has an A/C head, and the first tracking
position can be locked using the CTL pulse and drum FF
when AT is off. Therefore, the linearity of the VHS section
can usually be adjusted with AT off. However, this adjustment method is not available with the DV section, which
does not have the A/C head. If ATF is turned off, the DV
section performs tracking only of the speed system. Therefore, as time passes, the servo will be lost and the linearity
adjustment will become difficult.
Note 4 :
• Since the speed servo function is active when ATF is off,
there will be no problem even if the DVC ATF function is
off, provided that it is for a few minutes.
CH1
CH2
Adjust variation
in the parallelism
Note 5 :
• The “typical value” refers to the following:
CH1 or CH2: < 498.; with Viterbi OFF. Inter-channel difference: < 10 times between CH1 and CH2.
Note 6 :
• It is desirable to use a brand-new tape or an unused section of tape. This is to assure the adjustment reliability because using a damaged tape increases the error rate.
2.18.6 Error rate measuring method
It is not necessary to use the error rate jig (YTU93083) or a
frequency counter. The Service Support System Software
displays the error rates of video CH1, CH2 and totals. When
measuring the error rate of a channel, be sure to total the
values of the video and the audio errors.
2-41
Page 63

2.19 TAPE EJECTION
If a loaded cassette tape cannot be ejected due to a failure
in the electrical circuitry, take the cassette tape out using the
following procedure.
However, this method consists of a forced driving of the loading motor. Therefore, the following description assumes that
there is no trouble in the mechanism operations.
1. Unplug the power plug from the power outlet, then remove the top cover.
2. Apply 3 V DC to the electrodes (Red wire: + pole. Brown
wire: - pole) on the upper part of the loading motor to perform the unloading operation so that the pole base assemblies are returned on the inner side of the tape. At
this time, the exit guide arm assembly should return toward the drum assembly and the mechanism should enter the C-IN mode.
As the tape is left without winding, be careful not to damage the tape or leave grease on it.
–
DC 3 V
+
Motor Bracket Assembly (Loading Motor)
Wire (Brown)
3. If the tape is slack, wind it up by turning the shaft on the
topside of the capstan motor in the direction of the arrow
using a pointed tool (chip IC replacement jig).
This operation may be difficult because the shaft is located below the housing motor of the cassette housing
assembly. Be careful not to damage parts during it.
4. After confirming that the tape is fully wound up, take out
the cassette tape by turning the gear of the cassette housing assembly in the direction of the arrow.
Note :
• After ejecting the tape, check that grease or similar for-
eign material is not attached to the wound tape. Also
perform similar checking for the mechanism assembly,
particularly the tape transport system.
Exit Guide Arm Assembly
Cassette Housing Motor
Wire (Red)
Pole Base Assembly (Supply)
Rotary Encoder Assembly
[3] Tape winding [4] Tape ejection
Capstan motor Cassette housing assembly, side view
A B
Chip IC replacement jig
Shaft
A
Pole Base Assembly (Take-Up)
B
Cassette Housing Assembly
Gear
2-42
Capstan motor
Ejection direction
Fig. 2-19-1
Page 64

SECTION 3
ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENT (VHS)
3.1 PRECAUTION
The following adjustment procedures are not only necessary
after replacement of consumable mechanical parts or board
assemblies, but are also provided as references to be referred to when servicing the electrical circuitry.
In case of trouble with the electrical circuitry, always begin a
service by identifying the defective points by using the measuring instruments as described in the following electrical adjustment procedures. After this, proceed to the repair, replacement and/or adjustment. If the required measuring instruments
are not available in the field, do not change the adjustment
parts (variable resistor, etc.) carelessly.
3.1.1 Required test equipments
• Color (colour) television or monitor
• Oscilloscope: wide-band, dual-trace, triggered delayed
sweep
• Frequency counter
• Signal generator: RF / IF sweep / marker
• Signal generator: stairstep, color (colour) bar [PAL]
• Recording tape
• Digit-key remote controller(provided)
3.1.2 Required adjustment tools
Jig RCU
PTU94023B
Alignment tape
(SP, stairstep, PAL)
MHPE
Alignment tape
(LP, stairstep, PAL)
MHPE-L
Jig RCU
[Data transmitting method]
Depress the “ ” ( 3 ) button
after the data code is set.
CUSTOM CODE
43: A CODE
53: B CODE
DATA CODE
INITIAL MODE
Fig. 3-1-4a Jig RCU [PTU94023B]
• Set the switches as shown below unless otherwise
specified on the relevant adjustment chart. The
switches that are not listed below can be set as desired.
If the VCR is not equipped with the functions detailed
below, setup is not required.
AUTO PICTURE/VIDEO CALIBRATION/
B.E.S.T./D.S.P.C.
PICTURE CONTROL/SMART PICTURE
VIDEO STABILIZER OFF
TBC ON
Digital 3R ON
VIDEO NAVIGATION/TAPE MANAGER
OFF
NORMAL/NATURAL
OFF
• Unless otherwise specified, all measuring points and
adjustment parts are located on the Main board.
• In the Signal column of the adjustment chart, “Ext. Sinput” means the Y/C separated video signal and “Ext.
input” means the composite video signal input.
Burst
LPF
PTU93006
0.3 V
Alignment tape
(S-VHS, SP/LP, color (colour) bar)
s
Colour bar pattern [PAL]
(75%)
White
U Black
V
Yellow
Cyan
White
100%
MH-2H
Green
Magenta
Red
Blue
Alignment tape
(SP stairstep, NTSC)
MHP
3.1.3
Color (colour) bar signal,Color (colour) bar pattern
s
Colour bar signal [PAL]
White(100%)
White(75%)
0.7 V
1V
0.3 V
Horizontal sync
Yellow
Cyan
Green
Magenta
Red
VU
V(R-Y)
U(B-Y)
Blue
3.1.4 Switch settings and standard precautions
The SW settings of the VCR and the standard precautions
for the electrical adjustments are as follows.
• When using the Jig RCU, set its custom code to match
the custom code of the VCR.
3.1.5 EVR Adjustment
Some of the electrical adjustments require the adjustment
performed by the EVR system. The Main board assembly
have EEPROMs for storing the EVR adjustment data and
user setups.
Notes:
• In the EVR adjustment mode, the value is varied with
the channel buttons (+, –). The adjusted data is stored
when the setting mode changes (from PB to STOP,
when the tape speed is changed, etc.). Take care to
identify the current mode of each adjustment item
when making an adjustment.
• When changing the address setting in the EVR adjustment mode, use the Jig RCU or the remote controller
having numeric keypad with which a numeric code can
be directly input.
The remote control code of the Jig RCU corresponds
to each of the digit keys on the remote controller as
follows.
Digit-key 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Code 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
• As the counter indication and remaining tape indication are not displayed FDP during the EVR adjustment
mode, check them on the TV monitor screen.
• When performing the EVR adjustment, confirm that the
FDP indication is changed to the EVR mode, as shown
below.
3-1
Page 65

FDP
Fig. 3-1-5a EVR mode
3.2 SERVO CIRCUIT
3.2.1 Switching point
Signal (A1) • Stairstep signal
Mode (B) • PB
(A2)
(A3) •
•
Alignment tape(SP, stairstep, PAL) [MHPE]
Alignment tape(SP, stairstep, NTSC) [MHP]
• TBC: OFF
Equipment (C) • Oscilloscope
Measuring point (D1) •
(D2) • TP106 (PB FM)
External trigger (E) • TP111 (D.FF)/slope : –
Adjustment part (F) • Jig RCU: Code “51” or “52”
Specified value (G) • 8.0 ± 0.5H [MHPE]
VIDEO OUT terminal (75Ø terminated)
• 7.5 ± 0.5H [MHP]
Adjustment tool (H) • Jig RCU [PTU94023B]
(1) Play back the signal (A1) of the alignment tape (A2).
(2) Apply the external trigger signal to D.FF (E) to observe
the VIDEO OUT waveform and V.PB FM waveform at the
measuring points (D1) and (D2).
(3) Press the channel buttons (+, –) simultaneously to enter
the manual tracking mode. This also brings tracking to
the center (centre).
(4) Adjust tracking by pressing the channel buttons (+, –) so
that the V.PB FM waveform becomes maximum.
(5) Transmit the code (F) from the Jig RCU to adjust so that
the trigger point of the VIDEO OUT waveform is changed
from the trailing edge of the V.sync signal becomes the
specified value (G).
(6) Set the VCR to the stop mode or eject mode.
(7) Play back the signal (A1) of the alignment tape (A3).
(8) Repeat steps (2) to (6).
Trigger point
Switching point
V.sync
(1) Record the signal (A2) in the mode (B1), and play back
the recorded signal.
(2) Press the channel buttons (+, –) simultaneously to enter
the manual tracking mode. This also brings tracking to
the center (centre).
(3) Set the VCR to the FWD slow (+1/6×) mode.
(4) Transmit the code (F) from the Jig RCU to adjust so that
the noise bar becomes the specified value (G) on the TV
monitor in the slow mode.
(5) Set the VCR to the Stop mode.
(6) Confirm that the noise bar is (G) on the TV monitor in
the slow mode.
(7) Repeat steps (3) to (6) in the REV slow (–1/6×) mode.
(8) Repeat steps (1) to (7) in the mode (B2).
Note:
• For FWD slow (+1/6×) playback, transmit the code “08”
from the Jig RCU to enter the slow playback mode, and
transmit the code “D0” for REV slow (–1/6×) mode.
3.3 VIDEO CIRCUIT
3.3.1 D/A level
Signal (A1) • Ext. S-input / Ext. input
Mode (B) • S-VHS
(A2) • Color (colour) bar signal [PAL]
(A3) • S-VHS tape
• EE
Equipment (C) • Oscilloscope
Measuring point (D) •
Adjustment part (F) • VR1401 (D/A LEVEL ADJ)
Specified value (G) • 1.00 ± 0.015 Vp-p (reference value)
(Note)
(1) Insert the cassette tape (A3) to enter the mode (B).
(2) Observe the Y OUT waveform at the measuring point (D).
(3) Check the Y level value when the External S-input (Y/C
separated video signal).
(4) Switch the input signal to the External input (composite
video signal), and adjust the adjustment part (F) so that
the Y level becomes the same value observed in step
(3).
Note:
• The specified value (G) is just a reference value to be
obtained when the External S-Video (Y/C separated
video) signal is input. In actual adjustment, set it to
the value observed in step (3).
Y OUT terminal (75Ø terminated)
[3D DIGITAL/2M board]
Fig. 3-2-1a Switching point
3.2.2 Slow tracking preset
Signal (A1) • Ext. input
(A2) • Color (colour) bar signal [PAL]
Mode (B1) • S-VHS SP
(B2) • S-VHS LP
Measuring point (D) • TV-Monitor
Adjustment part (F) • Jig RCU: Code “71“ or “72”
Specified value (G) • Minimum noise
Adjustment tool (H) • Jig RCU [PTU94023B]
3-2
V. rate
Specified
value (G)
H. rate
Fig. 3-3-1a D/A level
Page 66

1 kØ 39 µH 180 µH
120 pF 180 pF
PB. FM
629 [kHz]
PB COLOR
(PB COLOUR)
3.3.2 EE Y level
Signal (A1) • Ext. input
Mode (B) • EE
Equipment (C) • Oscilloscope
Measuring point (D) • Y OUT terminal (75Ø terminated)
EVR mode (F1)
EVR address (F2) •
Specified value (G) • 1.00 ± 0.03 Vp-p
Adjustment tool (H) • Jig RCU [PTU94023B]
(1) Observe the Y OUT waveform at the measuring point (D).
(2) Set the VCR to the EVR mode by transmitting the code
(F1) from the Jig RCU.
(3) Set the EVR address to (F2) by pressing the button of
the digit-key remote controller.
(4) Adjust with the channel buttons (+, –) on the VCR (or on
the remote controller) so that the Y level of the Y OUT
waveform becomes the specified value (G).
(5) Release the EVR mode of the VCR by transmitting the
code (F1) from the Jig RCU again. (When the EVR mode
is released, the adjusted data is memorized.)
3.3.3 PB Y level (S-VHS / VHS)
Signal (A1) • Ext. input
Mode (B1) • S-VHS SP
Equipment (C) • Oscilloscope
Measuring point (D) • Y OUT terminal (75Ø terminated)
EVR mode (F1) • Jig RCU: Code “57”
EVR address (F2) • A:11 (Press remote controller
Specified value (G) • 1.00 ± 0.03 Vp-p
Adjustment tool (H) • Jig RCU [PTU94023B]
(1) Observe the Y OUT waveform at the measuring point (D).
(2) Record the signal (A2) in the mode (B1), and play back
the recorded signal.
(3) Press the channel buttons (+, –) simultaneously to enter
the manual tracking mode. This also brings tracking to
the center (centre).
(4) Set the VCR to the EVR mode by transmitting the code
(F1) from the Jig RCU.
(5) Set the EVR address to (F2) by pressing the button of
the digit-key remote controller.
(6) Adjust with the channel buttons (+, –) on the VCR (or on
the remote controller) so that the Y level of the Y OUT
waveform becomes the specified value (G).
(A2) • Color (colour) bar signal [PAL]
• Jig RCU: Code “57”
A:11 (Press remote controller “1” key twice)
• Digit-key remote controller
Specified
value (G)
H. rate
Fig. 3-3-2a EE Y level
(A2) • Color (colour) bar signal [PAL]
(B2) • VHS SP
“1” key twice)
• Digit-key remote controller
(7) Release the EVR mode of the VCR by transmitting the
code (F1) from the Jig RCU again. (When the EVR mode
is released, the adjusted data is memorized.)
(8) Repeat steps (2) to (7) in the mode (B2).
Specified
value (G)
H. rate
Fig. 3-3-3a PB Y level
3.3.4 REC color (colour) level
Signal (A1) •
(A2) • Ext. input
(A3) • Color (colour) bar signal [PAL]
Mode (B1) • S-VHS SP
(B2) • S-VHS LP
Equipment (C) • Oscilloscope
Measuring point (D1) • TP106 (PB FM)
(D2) • PB color (colour) output of the LPF
External trigger (E) • TP111 (D.FF)
EVR mode (F1) • Jig RCU: Code “57”
EVR address (F2) • A:02 (Press remote controller
Specified value (G) • SP: “B” x 125 ± 5%
Alignment tape(S-VHS, SP/LP, Color(colour)
bar) [MH-2H]
“0” and “2” keys)
• LP: “B” x 125 ± 5%
Adjustment tool (H1) • Jig RCU [PTU94023B]
(1)
Connect the adjustment tool (H3) to the measuring point (D1).
(2)
Apply the external trigger signal to D.FF (E) to observe the
PB color (colour) waveform at the measuring point (D2).
(3) Play back the signal (A3) in the mode (B1) of the align-
ment tape (A1).
(4) Press the channel buttons (+, –) simultaneously to enter
the manual tracking mode. This also brings tracking to
the center (centre).
(5) Adjust tracking by pressing the channel buttons (+, –) so
that the PB color (colour) waveform becomes maximum.
Make a note of the higher PB color (colour) level as “B”
at this time.
(6) Record the signal (A3) in the mode (B1), and play back
the recorded signal.
(7) Set the VCR to the EVR mode by transmitting the code
(F1) from the Jig RCU.
(8) Set the EVR address to (F2) by pressing the button of
the digit-key remote controller.
(H2) • Digit-key remote controller
(H3) • LPF [PTU93006] (See Fig. 3-3-4a.)
Fig. 3-3-4a LPF
3-3
Page 67

(9) Adjust with the channel buttons (+, –) on the VCR (or on
the remote controller) so that the higher level channel becomes the specified value (G) of the note "B" level as
shown in Fig. 3-3-4b. (Adjust before recording, then confirm it by playing back.)
(10)
After adjustment, record the signal (A3) then playing it
back again. At this time, confirm that there is no inverting phenomenon or noise appearing on the playback
screen.
(11)
Release the EVR mode of the VCR by transmitting the
code (F1) from the Jig RCU again. (When the EVR mode
is released, the adjusted data is memorized.)
(12)
Repeat steps (3) to (11) in the mode (B2).
Note:
• After adjusting, always perform the confirmation and
re-adjustment of the item 3.4.1.
Specified
value (G)
V. rate
Fig. 3-3-4b REC color (colour) level
3.3.5 Video EQ (Frequency response)
Signal (A1) • Ext. S-input
Mode (B1) • S-VHS SP
Equipment (C) • Oscilloscope
Measuring point (D1) • Y OUT terminal (75Ø terminated)
Frequency marker(D2) • 3 [MHz]
External trigger (E) • TP111 (D.FF)
EVR mode (F1) • Jig RCU: Code “57”
EVR address (F2) • A:03 (Press remote controller
Specified value (G) • SP: 3.6 ± 0.4 div. (–1 ± 1 dB)
(A2) • Video sweep signal
(B2) • S-VHS LP
(B3) • Picture Control / Smart Picture
REC : Normal / Natural
PB : Edit / Distinct
“0” and “3” keys)
• LP: 3.2 ± 0.4 div. (–2 ± 1 dB)
Adjustment tool (H) • Jig RCU [PTU94023B]
• Digit-key remote controller
(1) Apply the external trigger signal to D.FF (E) to observe
the Y OUT waveform at the measuring point (D1).
(2) Record the signal (A2) in the mode (B1), and play back
the recorded signal.
(3) Press the channel buttons (+, –) simultaneously to enter
the manual tracking mode. This also brings tracking to
the center (centre).
(4) Set the VCR to the EVR mode by transmitting the code
(F1) from the Jig RCU.
(5) Set the EVR address to (F2) by pressing the button of
the digit-key remote controller.
(6) Set the slope of the oscilloscope to the channel having
higher (D2) marker level of the Y OUT waveform [signal
(A2)]. Then set the 100 kHz marker level to the “4” scale
on the oscilloscope. In this condition, adjust with the channel buttons (+, –) on the VCR (or on the remote controller) so that the (D2) marker level reaches the specified
value (G).
3-4
(7) Release the EVR mode of the VCR by transmitting the
code (F1) from the Jig RCU again. (When the EVR mode
is released, the adjusted data is memorized.)
(8) Repeat steps (2) to (7) in the mode (B2).
Scale 4
(4 div.)
Specified
value (G)
Four scale
100 kHz
1 MHz
2 MHz
Frequency
marker (D2)
5 MHz
V. rate
Fig. 3-3-5a Video EQ (Frequency Response)
3.3.6 AUTO PICTURE initial setting
Signal (A1) • Ext. input
Mode (B) •
Adjustment part (F) • Jig RCU : Code “58”
Specified value (G) • STOP mode
Adjustment tool (H) • Jig RCU [PTU94023B]
(A2)
• Video: Optional
(A3) • VHS tape
EE ¥ Auto adjust (SP/LP REC ¥ PB)
(1) Insert the cassette tape (A3).
(2) Set the VCR to the Auto adjust mode by transmitting the
code (F) from the Jig RCU. When the VCR enters the
stop mode, the adjustment is completed. When the VCR
enters the eject mode, repeat steps (1) to (2) again.
3.3.7 DV EE Y level
Signal (A1) • Ext. input
Mode (B) • VHS
Equipment (C) • Oscilloscope
Measuring point (D) •
Adjustment part (F) • VR701 (DV AGC)
Specified value (G) • 1.02 ± 0.02 Vp-p
(A2) • Color (colour) bar signal [PAL]
• EE
TP701 (DV AGC)
(1) Observe the VIDEO OUT waveform at the measuring
point (D).
(2) Adjust the adjustment part (F) so that the Y level of the
VIDEO OUT waveform becomes the specified value (G).
Note:
•
After adjusting, always perform the confirmation and
re-adjustment of the Electrical adjustment (DV).
Specified
value (G)
H. rate
Fig. 3-3-7a DV EE Y level
Page 68

3.4 AUDIO CIRCUIT
Notes:
• This adjustment should be done after the “REC color
(colour) level adjustment” for the video circuit has
been completed.
• GND (Ground) should be taken from the Tuner shield
case.
3.4.1 Audio REC FM
Signal (A1) • Ext. input
Mode (B) • S-VHS LP
Equipment (C) • Oscilloscope
Measuring point (D) • TP2253 (A. PB FM)
External trigger (E) • TP111 (D.FF)
EVR mode (F1) • Jig RCU: Code “57”
EVR address (F2) • A: 30 (Press remote controller “3”
Specified value (G1) • 450 ± 100 mVp-p
Adjustment tool (H) • Jig RCU [PTU94023B]
• Audio: No signal
(A2)
(A3) •
(G2) • More than 300 mVp-p
Video: Color (colour) bar signal [PAL]
and “0” keys.)
• Digit-key remote controller
(1) Apply the external trigger signal to D.FF (E) to observe
the Audio PB FM waveform at the measuring point (D).
(2) Record the signal (A3) with no audio signal input in the
mode (B), and play back the recorded signal.
(3) Press the channel buttons (+, –) simultaneously to enter
the manual tracking mode. This also brings tracking to
the center (centre).
(4) If the A.PB FM level is not within the specified value (G1),
perform the adjustment in a following procedure.
(5) Set the VCR to the EVR mode by transmitting the code
(F1) from the Jig RCU.
(6) Set the EVR address to (F2) by pressing the button of
the digit-key remote controller.
(7) Adjust with the channel buttons (+, –) on the VCR (or on
the remote controller) so that the A.PB FM level of the
higher channel level becomes the specified value (G1).
(Adjust before recording, then confirm it by playing back.)
(8) If the specified value (G1) is not obtained, adjust with the
channel buttons (+, –) so that the waveform level of the
lower channel level becomes the specified value (G2).
(Adjust before recording, then confirm it by playing back.)
(9) Release the EVR mode of the VCR by transmitting the
code (F1) from the Jig RCU again. (When the EVR mode
is released, the adjusted data is memorized.)
3.5 SYSCON CIRCUIT [SR-VS20E]
Note:
•
When perform this adjustment, remove the Mechanism
assembly.
3.5.1 Timer clock
Signal (A) • No signal
Mode (B) • EE
Equipment (C) • Frequency counter
Measuring point (D1) • IC3001 pin 61
Short point (D2) • IC3001 pin 24
Adjustment part (F) • C3025 (TIMER CLOCK)
Specified value (G) • 1024.008 ± 0.001 Hz
(D3) • C3026 + and –
(976.5549 ± 0.0010 µsec)
(1) Connect the frequency counter to the measuring point
(D1).
(2) Connect the short wire between the short point (D2) and
Vcc (5V).
(3) Short the leads of capacitor (D3) once in order to reset
the microprocessor of the SYSCON.
(4) Disconnect the short wire between the short point (D2)
and Vcc then connect it again.
(5) Adjust the Adjustment part (F) so that the output fre-
quency becomes the specified value (G).
Specified
value (G2)
V. rate
Fig. 3-4-1a Audio REC FM
Specified
value (G1)
3-5
Page 69

ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENT (DV)
3.6 PREPARATION
3.6.1 Precautions
(1) The DV section of this model is based on a special ad-
justment method using a PC. However, ordinary adjustment is required only when the part listed below has been
replaced. In this case, the adjustment should be performed by a service center equipped with the required
facilities.
2
PROM (IC1007 on DV main board)
• E
In case of trouble with the electrical circuitry, First identify the faulty position with a measuring tool as described
below. Proceed to repair, replacement and/or adjustment
only after the troubleshooting.
(2) When observing a chip TP, use an IC clip or similar tool
to protect the chip against stress. When replacing a chip
part (IC, particularly), remove solder completely before
replacing. (This is to prevent separation of the pattern.)
(3) The connectors are fragile. Be careful when plugging or
unplugging a wire.
3.6.2 Equipment required for adjustment
1 Personal computer (Windows compatible)
2 Color monitor
3 Oscilloscope (2-CH, 100 MHz or more)
4 Frequency counter
3.6.4 Setup
1. Setup for computer adjustment
— Setup by extending the jig connector —
When performing the adjustment by the Service Support Software,
set the VCR to external communication mode by transmitting the code
“6C” from the Jig RCU.
Jig RCU
[PTU94023B]
INITIAL MODE
DATA CODE
[Data transmitting method]
Depress the “ ” ( 3 ) button
after the data code is set.
Switch
DV MAIN PWB
CN1101
<JLIP>
CUSTOM CODE
43: A CODE
53: B CODE
PC Cable
QAM0099-002
<Note> : Switch setting of the
Service Support Software
RS-232C Port
Personal Computer
Jig connector cable
Switch OFF
(UP)
JVC
MENU
3.6.3 Tools required for adjustments
Alignment tape
US : MC-1
PAL : MC-2
PC cable
US : QAM0099-002
PAL : QAM0099-005
Jig connector cable
PTU94018B
Jig RCU
PTU94023B
Fig. 3-6-3a
SSS software
PTU94016-3
Fig. 3-6-4a Setup for Computer Adjustment
3-6
Page 70

SECTION 4
24
C331
11/10
22201816
WF25
C329
0.1/50
C330
0.1/50
R344
47K
R343
18K
R345
10K
R346
15K
Measurement point
Waveform number
CHARTS AND DIAGRAMS
NOTES OF SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
Safety precautions
The Components identified by the symbol are
critical for safety. For continued safety, replace safety
critical components only with manufacturer's recommended parts.
1. Units of components on the schematic diagram
Unless otherwise specified.
1) All resistance values are in ohm, 1/6 W, 1/8 W (refer to
parts list).
Chip resistors are 1/16 W.
K or k: k (1000 ), M: M (1000k )
2) All capacitance values are in µF, (P: PF).
3) All inductance values are in µH, (m: mH).
4) All diodes are 1SS133, MA165 or 1N4148M (refer to parts
list).
2. Indications of control voltage
AUX : Active at high
AUX or AUX(L) : Active at low
3. Interpreting Connector indications
1
2
Removable connector
3
1
2
Wire soldered directly on board
3
4) Indication on schematic diagram
Voltage Indications for REC and PB mode on the schematic diagram are as shown below.
REC mode
12 3
2.5
(5.0)
PB mode
1.8
PB and REC modes
(Voltage of PB and REC modes
are the same)
Note: If the voltages are not indicated on the schematic
diagram, refer to the voltage charts.
5. Waveform measurement
1) Video circuits
REC : Colour bar signal in SP mode, normal VHS mode
PB : Alignment tape, colour bar SP mode, normal VHS
mode
2) Audio circuits
REC : 1KHz, –8 dBs sine wave signal in SP mode, normal
VHS mode
PB : REC then playback it
3) Movie Camera circuits
Measured using a correctly illuminated gray scale or colour
bar test chatrs in the E-E mode
4) Indication on schematic diagram
Waveform indications on the schematic diagram are as
shown below.
1
Non-removable Board connector
2
3
1
2
4
Board to Board
3
Connected pattern on board
The arrows indicate signal path
4. Voltage measurement
1) Video circuits
REC : Colour bar signal in SP mode, normal VHS mode
PB : Alignment tape, colour bar SP mode, normal VHS
mode
— : Unmeasurable or unnecessary to measure
2) Audio circuits
REC : 1KHz, –8 dBs sine wave signal in SP mode, Nor-
mal VHS mode
PB : REC then playback it
3) Movie Camera circuits
Measured using a correctly illuminated gray scale or colour
bar test charts in the E-E mode
5) Waveform indications
Waveform number
WF25
REC/PB 1.2 Vp-p
50 mV/2 msec/DIV
Oscilloscope Volts and Time/Division, Probe 10 : 1
Mode : REC or PB modes
Waveform name or
measurement point
ALC OUT
Level : 1.2 Vp-p
4-1
Page 71

6. Signal path Symbols
The arrows indicate the signal path as follows.
Playback signal path
Playback and recording signal path
Recording signal path
(including E-E signal path)
Capstan servo path
CIRCUIT BOARD NOTES
1. Foil and Component sides
1) Foil side (B side) :
Parts on the foil side seen from foil face (pattern face)
are indicated.
2) Component side (A side) :
Parts on the component side seen from component face
(parts face) indicated.
Drum servo path
(Example)
R-Y
Playback R-Y signal path
Y
Recording Y signal path
7. Indication of the parts for adjustments
The parts for the adjustments are surrounded with the circle as
shown below.
8. Indication of the parts not mounted on the circuit board
“OPEN” is indicated by the parts not mounted on the circuit
board.
R216
OPEN
2. Parts location guides
Parts location are indicated by guide scale on the circuit board.
REF No. LOCATION
Category: IC
Horizontal “A” zone
Vertical “6” zone
(A : Component side)
(D : Discrete component)
B : Foil side
C : Chip component
IC
IC101 B C 6 A
Note:
For general information in service manual, please refer
to the Service Manual of GENERAL INFORMATION Edition 4 No. 82054D (January 1994).
4-2
Page 72

4.1 BOARD INTERCONNECTIONS
5
4
3
2
1
87
S/P CONVERTER
85 JOG
DRUM MOTOR
5758CAP MDA
55
LOADING MOTOR
50 DV MAIN
LED/SW
47
U.DRUM
41
JACK
36
28
DISPLAY
27
EJECT SW
ON SCREEN
17
P/R MDA16
S-SUB
15
DEMOD.
14
12
A/C HEAD
06
TERMINAL
05
3D D/2M
MAIN
REGULATOR
02
SW REGULATOR01
NO NAME
LIVE
NEUTRAL
AC220V-240V
50/60Hz
CN5001
0 1 SW REGULATOR
J2001
DV IN/OUT
SENSOR
CN1502
CASSETTE SW
MIC 1
GND
TU REEL LED
TU REEL SENSOR
MIC 2
SUP REEL LED
SUP REEL SENSOR
END SENSOR
MIC 3
LED
GND
START SENSOR
GND
REC SAFETY SW
M
DV
HOUSING MOTOR
CN5501
4.5V(M)
FF/REW 6V
AL5V(DV)
GND(M)
CN5507
GND
HOUSING SW
HOUSING MOTOR+
HOUSING MOTOR-
CN5505
R.ENC3
R.ENC2
R.ENC1
GND
DV
ENCORDER
# MARK ELEMENTS ARE NOT MOUNTED
MDA 6V
DV VIDEO HEAD
CN1501
CN5506
CN5001
CN1101
(For ADJ.)
GND
GND
13
25
26
GND
UNREG
SHG_STOP
LD ON
CAP FG
DRUM FG
DRUM PG
(GND)
(GND)1SGND
GND1F2F
CN5201
DC3.5V[-]
GND
DC3.5V[+]
GND
GND
S.PROTECT
GND
48V
12V
4V
4V
BT2
4V
-29V
6V[DV]
AUDIO[-]
6V
6V
17V
10
12
11
23
24
HID
SPA
ATFI
FS_PLL
REC_MON
0
5
DV MAIN
(DV SYSCON Page 4-39)
(DV MSD Page 4-41)
(DV MAIN Page 4-43)
(DV I/O Page 4-45)
(DV V OUT Page 4-47)
(AUDIO AD/DA Page 4-49)
(DV DSP Page 4-51)
MDA IN
MDA CLK
MDA OUT
MDA CS
CAP BAK
1 6 P/R MDA
GND
2S
M
FAN MOTOR
CN5301
7
8
9
19
21
22
20
JLIP_TX
JLIP_RX
ENV_OUT
MAIN-VCO
AL_3VSYS
PB_VCO GND
MOTOR GND
HOUSING IN
CAP REF
DRUM REF
HOUSING OUT
HOUSING SW
GND
(MDA Page 4-31)
(PRE/REC Page 4-33)
FG OUT
PG OUT
COIL U
CN5503
DV DRUM MOTOR
GND
CN5325
FAN12V
0032 REGULATOR
4.5V(M)
6V/3.2V(M)6VGND(M)
CN5324
3
4
5
6
17
18
16
SBT
RST
SBE
SBD
GND
VPPC_5V
D_REG_3V
CAM SW2
CAM SW3
CAM SW1
PB_ENV
CN2001
CN5002
COIL U
COIL V
COIL V
COIL W
COIL W
COIL COMMON
M
AL5V(DV)
1
2
15
14
JIG_SPT
JIG_SCK
JIG_MOD
VPPD_5V
REC_CTL
REC_H
PBH
HID1
GND(M)
PG/FG COMMON
MS MODEL ONLY
87
CN5321
AUDIO(-)7V
CN5323
CN1001
AGC_GAIN
HID3
GND
DUMP_CTL
VREF_1.1
LOAD.MOTOR+
LOAD>MOTOR-
CN5502
M
LOADING
MOTOR
S/P CONVERTER
GND
GND
DRUM12V
GND
VRB_AGC
CN5504
M12/17V
AL3.3V
ATF_GAIN
AL3.3V
COIL V
VRB_ATF
COIL V
GND
AL2.5V
ATF_IN
COIL W
-29V
DC3.5V[-]
AL2.5V
REF_CLK
GND
COIL W
COIL U
GND
M12V
AL5V
AGC_OUT
DV CAPSTAN MOTOR
GND
DC3.5V[+]
FF/REW(H)
REC_CLK
REC_DATA
COIL U
MR VCC
V.UP[H]
P.CTL[H]
RECCADJ
MONI_CHG
HG IN+
HG V+
M
P.SAVE[L]
GND
HG V-
NC
AL6V
CN5322
CN3501
CN3701
CN1002
D_REG2.9
REG_5V
HG U+
HG IN-
NC
A_REG2.9
A_REG2.5
HG W-
HG W+
HG U-
OPEN
0
6 TERMINAL
(Page 4-25)
S-OUT
CN7103
CN7503
C_OUT
C_TO_DIGI
DC3.5V[+]
CH+12V
TUNER
GND
V_FROM_OSD
Y/V_TO_DIGI
Y_FROM_DIGI
LED1
-29V
J7102
AV1
J7103
AV2/DECODER
SYS_GND
I2C_CLK2
I2C_DATA2
SCR[H]
P50_I/O
SECAM/MESECAM[H]
OSD_P.CTL[L]
VIDEO OUT
4948474645444342414039383736353433323130292827
CN513
BAIS_FOR_C_OUT
PB_COLOR
V.PULSE
MAIN_ALC_DET
C_FROM_DIGI
SECAM_PB_COLOR
Y_TO_SUB
LED2
LED3
LED4
LED5
LED6
SW12V
B.BACK[H]
OUT1_L2[H]
OUT1_D[H]
C.BOX/SAT_CTL
SW5V
CN7104
CN7504
TU(30V)
MB(SW5V)
LOCK(L)
SW1
SW2
AFT
FROM PS Y
P.MUTE[L]
TP
IF OUT
AUDIO OUT
SIF OUT
GND
GND
TO PS Y
FROM PS C
FRONT_V_IN
WIDE_DET
FRONT_Y_IN
FRONT_C_IN
FRONT_Y_IN
GND
CN7507
36
J7001 J7002 J7003J7004 J7005
GND
SW5V
TO PS C
V_TO_OSD
GND
REAR2_V_IN
FRONT_C_INNCGND
FRONT_V_IN
JACK
(Page 4-38)
SW5V
CHARA_DATA
PAUSE
Y_TO_V
NC
GND
FRONT_A[L]
GND
RCA_A.OUT[R]
PLL CLK
PLL DATA
REC_COLOR
V_FROM_A/V
GND
FRONT_A[R]
LINE_OUT[R]
A.IN1[R]
A.IN1[L]
RCA_A.OUT[L]
NC
RF AGC
TU CE
JSA/SHUTTLE_A
JSB/SHUTTLE_B
GND
SHUTTLE[L]/NC
L IN R IN R.PAUSES IN V IN
LINE_OUT[L]
TU(30V)
VIDEO IN
J2/JOG_A
A.IN2[R]
A.IN2[L]
MOD B(SW5V)
MOD SCL
V_FROM_OSD
REAR2_C_IN
REAR2_Y_IN
REAR1_C_IN
REAR1_Y_IN
CAP_CTL_V
CAP_REV[L]
FULL ERASE
CTL HEAD(-)
J1/JOG_B
CTL HEAD(+)
CN7002
DEC_OUT[R]
DEC_OUT[L]
AUDIO IN
MOD SDA
C_OUT
Y_OUT
TO PS C
FROM PS C
TO PS Y
FROM PS Y
CN3003
GND[C]
CAP_FG
SW5V
GND[M]
MOTOR12V
CN2002
GND(C)
A.ERASE
GND(C)
CN7003
#
FW7007
BB(AL5V)
26
NC
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
CN702
SW5V
SW5V
GND
GND
GND
NC
GND
CN2001
REC
PB
RF IN
RF OUT
CN7506
MS MODEL ONLY
57
CAP MDA
FULL ERASE HEAD
CN1
12
A/C HEAD
OPEN
85
FW7008
OPEN
M
JOG
(Page 4-38)
F.E
R/P
A.E
CTL
J7101
SW5VNCGND
GND
GND
FROM PS
TO PS C Y
CN7509
NC
NC
AL6V
P.SAVE[L]
V.UP[H]
P.CTL[H]
GND
DC3.5V[+]
-29V
DC3.5V[-]
GND
GND
M12/17V
DRUM12V
M12V
CN7508
CH+12V
RF5V
BT2
GND
GND
GND
SW12V
AL12V
AUDIO(-)
SW5V
SW5V(2)
48V
AL5.8V
CN2601
GND
DV A PB(R)
GND
DV A PB(L)
GND
DV A REC (R)
DV A REC (R)
GND
DV A REC(L)
CN3014
RXD
TXD
DAIL_PLAY
DIAL_OFF
DIAL_AUTO
HOUSING_SW
EP CH1
TO PS C
EP CH1
EP CH2
41
EP CH2
EP CH1
EP CH2
CN703
SP CH1
GND
D_C_IN
D_Y/V_IN
SP CH1
SP CH2
SP CH2
U.DRUM
SP CH2
SP CH1
GND
D_C_OUT
FMA CH1
COMMON
FMA CH1
D_Y_OUT
CN851CN704
FMA CH2
FLY. E
FMA CH2
2fsc
CN1401CN501
FLY. E
1
OSD_CS
0
fsc
CN1
FLY. E
CN701
S.CLK
GND
SW5V
7
S.DATA_ERSYS
5
C_TO_DIGI
EDS[H]/I2C_CLK2
SW5V[2]
NC
ON SCREEN
(Page 4-35)
GND
GND
GND
TO PS Y
TO PS C
FROM PS C
EDS_CS/I2C_DATA2
SWD_S.DATA
CHARA_DATA
P.MUTE[L]
V_FROM_OSD
SYNC_DET[H]
3D DIGITAL/2M
(Page 4-23)
Y_FROM_DIGI
GND
KILLER_DET
Y/V_TO_DIGI
EE[L]
C_FROM_DIGI
DRUM_12V
GND(M)
DRUM_CTL_V
D.PG
CN3001
58
DRUM MOTOR
M
OSD-IN
GND
V_TO_OSD
I2C_CLK_A/V
I2C_DATA_A/V
V.P.C T L
D.FG
TUNER_VIDEO
GND
CN7101
CN7501
1 4 DEMOD.
SW5V
OSD_C
OSD_Y
SW12V
D.FF
V.REF
TRICK[H]
SLOW_PULSE
CN3002
55
LOADING
MOTOR
27
SWD_Y
D_P.MUTE[H]
LDM1
LDM2
M
GND
D_Y/V_IN
SWD_C
GND
TERM_D_C
GND
(Page 4-27)
CN3004
ROTARY
ENCODER
FW7006
(Page 4-38)
EJECT SW
TERM_D_Y
GND
CN6701 CN6701
LSB
LSC
SIF
CN1
FG1
FG2
MR GND
TERM_C_OUT
GND
TERM_Y_OUT
GND
COMP
LSA
GND
GND
SW5V
FW7005
CHARA_DATA
DEMOD(R)
DEMOD(L)
CN512
1
CN3011
CN7001
J7103
SAT CTL
CN7102
CN7502
I2C CLK
TU A MUTE
GND
REAR1_Y_IN
5
CN511
CN502
AL5V
RCU5V
FW7003
FW7004
4
J7105
AUDIO OUT(L/R)
REAR1_C_IN
GND
REAR1_V_IN
GND
REAR2_V_IN
I2C DATA
NC
03
MAIN
(VIDEO/AUDIO Page 4-7)
(SYSCON Page 4-9)
(SUB CPU Page 4-13)
(TUNER Page 4-15)
(VIDEO I/O SW Page 4-17)
(AUDIO I/O Page 4-19)
(CONNECTION Page 4-21)
GND
GND
GND
REAR2_Y_IN
REAR1_C_IN
REAR2_C_IN
S-SUB
(Page 4-29)
Fsc
SW5V
SW5V
EE[L]
I2C_DATA_A/V
I2C_CLK_A/V
RC_IN
S.CLK
S.DATA_TOSYS
S>DATA_FRSYS
GND
STB
2 8 DISPLAY
(Page 4-37)
(Page 4-38)
LED/SW
7
Y_OUT
GND
B.UP_GND
GND
GND
DC3.5V[-]
p10291001a_rev1
DCBA
4-3 4-4
HGFE
Page 73

4.2 SWITCHING REGULATOR AND REGULETOR SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
##
ICP-N20
CP5324
REGULATOR02
5
220-240V
50Hz
CN5001
4
3
2
1
F5001
T2AL
/250
0
##
VA5001
##
R5001
4.7M
1/2W
SW.REG
C5001 C5002
0.068 0.033
/250
##
SG5001
QAF0046-242
##
VA5002
IC5101
STR-F6552
OCP/FB S D VCC GND
C5104
470p
MY
/50
C5004
0.0022
/250
GROUND POINT
FOR PRIMARY
VOLTAGE
LF5001
PELN1204-01-01
QQR0977-001
##
B5002
MY
##
B5001
C5103
33p
/1kV
K5101
QQR0678-001
QQR0621-001
R5104
680
D5103
R5103
1SS133
3.3k
1SS270A
R5105
0.47
1W
DANGEROUS VOLTAGE
LF5002
/250
R5101
2SD1819A/RS/
2SC4081/RS/
2PC4081/R/
68k
2W
Q5301
MY
R5302
4.7k
R5313
560
R5314
10k
C5007
/400
82
C5105
0.022
/50
PC5101
PC123F2
ON3171/R/
PS2561L-1(WL)
R5307
220
MY
IC5301
L5431
MM1431AT
C5304
47
/25
C5106
0.0047
/1k
R5108
47
1/2W
D5101
SARS01
D5102
AU01Z
1SR153-400
10ELS2
ERA18-02
PG104RS
R5305
22k
C5303
0.033
##
RD2.7ES/B2/
MTZJ2.7B
D5001
RBV-406
C5006
R5107
680k
1/4W
##
R5106
C5101
C5102
27
/35
C5302
0.047
/50
R5318
D5306
##
R5102
10
/50
MY
R5303
12k
##
R5312
R5304
3k
QQS0092-001
##
R5315
T5001
R5317
33k
Q5302
DTA114EUA
UN5111
RN2302
PDTA114EU
C5305
0.01
/50
D5201
AK04
11EQS04
1S4
D5202
FML-12S
FCF06A20
YG901C2
SF5LC20U
ER602FCT
MY
D5206
FMB-24
FSQ05A04B
YG801C04
SF5SC4
SB640FCT
##
D5203
FMB-24
FSQ05A04B
YG801C04
SF5SC4
SB640FCT
##
D5205
FML-12S
FCF06A20
YG901C2
SF5LC20U
ER602FCT
D5204
1SR153-400
10ELS2
ERA18-02
PG104RS
D5308
1SS133
1SS270A
D5210
AU01Z
1SR153-400
ERA18-02
10ELS2
PG104RS
D5211
AU01Z
1SR153-400
ERA18-02
10ELS2
PG104RS
CP5301
ICP-N25
CP
D5207
FMB-24
FSQ05A04B
YG801C04
SF5SC4
SB640FCT
C5202
820
/16
D5208 SHORT
AK04
11EQS04
1S4
C5204
D5301
RD15ES/B1/
MTZJ15A
C5212
2200
/10
##
L5204
33µ
B5003
D5311
1SS133
1SS270A
C5206
D5310
1SS133
1SS270A
C5207
4.7
/100
C5208
/50
18
C5201
220
/6.3
2200
/10
180
/25
D5309
1SS133
1SS270A
R5306
47
1/4W
C5210
R5308
1k
R5311
680
/10
47k
FR
L5203
33µ
L5202
33µ
D5312
1SS133
1SS270A
L5201
33µ
C5203
R5309
1.2k
R5316
1k
C5211
220
/10
C5205
220
/10
220
/16
C5213
220
/10
L5205
33µ
D5307
1SS133
1SS270A
D5303
MTZA7.5A
RD7.5ES/B1/
D5304
1SS133
1SS270A
D5305
RD27ES/B3/
MTZJ27C
C5301
0.01
/50
R5310
820
2W
CN5201
DC3.5V[-]
GND
DC3.5[+]
GND
GND
S.PROTECT
GND
48V
12V
4V
4V
BT2
4V
-29V
6V[DV]
AUDIO[-]
6V
6V
17V
CN5301
Q5326
2SD2375/QP/
Q5327
2SD1819A/RS/
2PC4081/R/
2SC4081/RS/
##
B5303
R5351
2.2k
Q5340
UN5111
DTA114EUA
RN2302
PDTA114EU
CP5322
CP
ICP-N25
Q5339
2SD2144S/UV/
D5333
1SS133
1SS270A
RD5.1JS/B2/
MA4051N/M/
R5327
470
R5347
4.7k
R5352
1k
Q5321
2SD2528/QP/
R5328
R5326
470
C5325
0.001
/50
D5327
##
B5301
Q5337
2SB1239
D5322
1SS133
1SS270A
R5323
470
Q5322
2SD1819A/RS/
2SC4081/RS/
2PC4081/R/
1k
R5329
10k
R5348
2.2k
Q5341
UN5211
DTC114EUA
RN1302
PDTC114EU
R5322
470
VR5321
C5324
0.001
/50
D5325
RD5.1JS/B2/
MA4051N/M/
SHORT
B5309
D5328
1SS133
1SS270A
C5326
100
/10
D5326
1SS133
R5324
1SS270A
1k
##
B5302
0Ø
C5321
R5325
100
/10
10k
##
IC5322
IN OUT GND REF ON/OFF
##
C5327
0.01
/50
R5345
4.7k
R5346
2.2k
##
D5321
R5340
100
Q5335
PQ5EV3
1W
R5341
510
R5342
470
##
R5335
4.7k
2SB1256
D5334
11ES2
ERA15-02
1A3G
Q5336
UN5215
DTC114TUA
2SD2144S/UV/
##
1SS133
1SS270A
##
R5334
Q5330
D5335
7.5k
R5338
10k
C5332
22
/16
Q5329
DTA114EUA
UN5111
RN2302
PDTA114EU
0Ø
B5310
##
C5328
100
/10
CP
Q5331
2SB1068/KU/
R5339
1k
2SD1450/ST/
Q5328
2SD1302/ST/
R5330
470
C5322 C5323
R5331
10 100
/50 /16
47k
##
B5305
Q5334
UN5111
DTA114EUA
C5333
100
/10
RN2302
PDTA114EU
IC5321
SHORT
B5307
R5343
47k
PQ15RW11
R5344
C5334
IN OUT GND REF
C5329 C5330
0.01 100
/50 /10
R5336
4.7k
B5306
SHORT
2SD1450/ST/
2SD1302/ST/
220
220
/16
1SS133
1SS270A
B5308
R5337
1k
Q5333
D5331
##
Q5332
DTC114EUA
UN5211
RN1302
PDTC114EU
ICP-N25
C5335
100
/16
D5336
MTZJ12A
RD12ES/B1/
D5330
1SS133
1SS270A
D5323
11ES2
ERA15-02
CP
CP5321
D5332
##
L5321
100µ
##
Q5338
DTC114EUA
UN5211
RN1302
PDTC114EU
11ES2
ERA15-02
1A3G
D5324
11ES2
ERA15-02
1A3G
Q5323
2SA1267/YG/
2SA933AS/RS/
R5332
10k
R5333
1k
##
B5304
D5329
1SS133
1SS270A
CP5323
ICP-N251A3G
CP
Q5324
DTC114EUA
UN5211
RN1302
PDTC114EU
C5331
100
/10
TO MAIN (CONNECTION)
CN7509
CN5321
NC
NC
AL6V
P.SAVE[L]
V.UP[H]
P.CTL[H]
GND
DC3.5V[+]
-29V
DC3.5V[-]
GND
GND
M12/17V
DRUM12V
M12V
TO FAN MOTOR
CN5325
FAN12V
GND
TO MAIN
(CONNECTION)
CN5322
CN7508
CH+12V
RF5V
BT2
GND
GND
GND
SW12V
AL12V
AUDIO[-]
SW5V
SW5V[2]
48V
AL5.8V
##
CN5326
12V
GND
GND
5V
OPEN
TO DV MAIN
CN5323
(DV SYSCON)
CN1001
AUDIO[-]7V
AL5V
GND
AL3.3V
AL3.3V
GND
AL3.3V
AL3.3V
GND
FF/REW[H]
TO P/R MDA
CN5501
CN5324
4.5V[M]
FF/REW_6V
6V[DV]
AL5V[DV]
GND[M]
GROUND POINT
FOR SECONDARY
VOLTAGE
## MARK ELEMENTS ARE NOT MOUNTED
p20189001a_rev1.1
1
DCBA
4-5 4-6
HGFE
Page 74

The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
4.3 VIDEO/AUDIO SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
MAIN (VIDEO/AUDIO)0 3
TO
CONNECTION, AUDIO I/O
FMA_OUT[L]
FMA_OUT[R]
DEC_OUT[L]
DEC_OUT[R]
A.IN1[L]
FMA_CH2
FMA_CH1
LP/EP_CH2
LP/EP_CH1
NC
SP_CH2
SP_CH1
TO
TUNER, AUDIO I/O
FLY.E
A.IN1[R]
A.IN2[L]
A.IN2[R]
A.SEL_IN[L]
A.SEL_IN[R]
TU_AUDIO
DEMOD[L]
DEMOD[R]
TO SYSCON
A.FF
A.ENV/ND[L]
A.MUTE[H]
H.REC_ST[H]
EDS_CS/PAL_PB[H]
TO CONNECTION
SW5V
SW12V
TO U. DRUM
TO A/C HEAD
CN1
CN2001
P/R
A.E
CTL
TO SYSCON
CTL[+]
CTL[-]
TO FOLL ERASE HEAD
CN2002
FE
TO SYSCON
FULL_E_ON[L]
N.REC[L]
N.REC_ST[H]
TO
SECAM
SECAM_DET
PB_FM
REC_COLOR
SECAM[H]
C.SYNC
SW5V
TO_PS_C
PB_COLOR
TO
VIDEO I/O SW
TO_PS_C
GND
GND
C402
0.022
C401
0.01
R401 R402
220 680
C403
130p 47p
GND
CN1
B42
SP_SHORT[H]
LP_SHORT[H]
R21 R22
2.2k 2.2k
Q1
2SC4081/S/
C69
0.1
C2051
330p
OPEN
R2052
GND
10µ
L15
#
B56
EE[L]
fsc
GND
#
#
B57
L26
SHORT
L25
#
SHORT
R61
OPEN
B22
#
Q31
OPEN
#
IC2
MM1113XF
#
C76
0.01
2Fsc
B44
OPEN
0Ø
Q2
2SC4081/S/
Q4
2SC4081/S/
Q3
2SC4081/S/
C70
0.1
OPEN
R2051
MY
R2053
C2052
4.7k
0.033
C2061
0.033
C59
C60
B4
OPEN
#
C77
#
0.01
C78
0.01
C129
OPEN
H
H
VHS[H]
B46
#
C75
OPEN
B2
OPEN
5
4
3
2
C405
OPEN
Q401
C406
R403 R405
0.001
560 68k
Q402
C404
D1
OPEN
0.01
C1
0.01
C2
0.01
C3
0.01
C4
T2051
PELN0860
MY
T2052
PELN0861
0.1
220
/6.3
Q14
#
EE[H]/5_PB[H]
FLY_ON[H]
R404
47k
L401
15µ
C2053
R2054
C2055
10
C2062
R2061
C2064
/16
10
EE[L]/5_PB[L]
C407
15p
/16
330
/6.3
0.0047
15k
R406
39k
Q403
L1
10µ
C5
Q2051
C2054
0.01
0.0033
27k
TP106
B49 B48
0Ø
#
R24
330
FLY_REC[H]
R409
10k
Q405
L402
SHORT
R408
47k
R407
4.7k
C409
OPEN
Q404
Q2251
R2252
4.7k
C2003
C2256
/6.3 /16
47 47 0.010.01
TO SHEELD
TP111
0.001
0.1
D.FF
C7
C8
R2057
Q2052
R2056
100
R2055
3.3
R2064
Q2061
47k
R2063
Q2062
150
R2062
C2063
3.3
0.01
R65
OPEN
R23
1.8k
B5
PB FM
B50
L17
5.6µ
C93
22p
OPEN
Q5
OPEN
B1
R68
2.2k
OPEN
OPEN
L2251
10µ
L2001
10µ
R77
10k
47k
R2058
18k
Q2053
R2059
47k
R2060
18k
Q2054
R2065
18k
R113
100
C130
OPEN
C71
OPEN
C103
0.01
R2011
10k
R2020
1k
D2001
1SS355
Q2004
R25
R27
10k
220
R29
680
Q7
C72 L18
47p 22µ
R26 R28
6.8k 220
L19
12µ
C74
OPEN
L2252
150µ
C2255
180p
Q2252
DTC114EUA
Q2003
Q8
TP2253
R2251
1k
C2251 C2252C2004
Q2001
R2018
4.7k
R2019
4.7k
Q2002
B3
0Ø
R32
470
C73
12p
Q9
R30
0Ø
R31
1.5k
OPEN
C51
R2012
15k
C2227
0.1
C2253
K2251
0.1
K2252
0.1
C2254
K2253
C87
OPEN
C88
OPEN
C89
OPEN
C90
OPEN
4.7
C2005
/25
R2014
220k
R2015C2007
18022
/16
C2006
0.012
4.7
/25
C2008
C2009
0.001
R2016
39k
C2010
R2017
OPEN
0Ø
B2012
B2011
0.0015
18k
C2011
4.7
/50
C65
1
#
C2021
0.01
Q2011
#
5_PB[H]
VHS[H]
SHORT
SHORT
SHORT
C6
0.1
/25
IC1
JCP8020-MSD-2
R2207
R2217
R2218
R2219
R2220
/16
C2226
10
R2013
6.8k
C2013
OPEN
C61
Q16
OPEN
SP[H]
Q17
R34
39p
R92
1.5k
C109
0.22
R2003
0Ω
R2206
0Ω
R2208
100
100
R2209
R2004
R2005
0Ω
R2006
39k
R2007
39k
R2213
0Ω
39k
39k
39k
/25
C2225
4.7
R2226
R2222
R2223
R2224
R2225
12k
12k
12k
15k
C2224
0.01
R
R2227
12k
/50
/50
/25
/16
C2223
C2222
C2220
C2219
0.47
0.47
4.7
10
C2221
0.01
L
R
L
R
Y
39k
12k
15k
12k
12k
/50
12k
C2228
0.1
R2009
C2218
R2008
0.47
R2010
R2215
100p
C2230
/16
/16
C2217
C2002
10
10
L
L
R
L
R
C
C
C
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
C15
0.1
0.01
C84
R1
6.8k
L20
68µ
R35
OPEN
R33
8p
R93
2.2k
OPEN
6.8k
0.5
L2
C10
150p
C12
OPEN
2
OPEN
/25
C11
0.1
C13
4.7
OPEN
R2
1.5k
0.5
C2012
R3
R104
B54
6.8k
OPEN
Q38
C110
82p
L24
27µ
C106
L28
820p
68µ
C62
OPEN
C91
OPEN
0.1
R75
C14
0.1
R90
390
C17 C52 C19C18
C63
R70
C16
3.3 2.21
0.1
0Ω
/50
B8
R62
100
ET_PB[H]
/50
C2216
0.47
C
OPEN
OPEN
C82
OPEN
Q28
OPEN
R2210
R2211
C2213
C2214
C
C9
OPEN
2.2
/50/50
/50
R54
1.5k
Q18
10k
10k
10
/16
10
/16
OPEN
100p
R2230
C2229
/25
C2215
4.7
L
R
HIFI MODEL HIFI MODEL
C
C
C
C
Ω
0
C23
0.1
R4
#
C92
OPEN
L22
OPEN
220
/6.3
C21C20
R69
0.11
OPEN
C22
/50
C.SYNC
#
D8
SHORT
C2208 C2001
4.7 4.7
/50 /50
R
C
Ω
R5
0
C24
0.1
R2121
B2101
150
0Ω
C2121
D2121
/16
MTZJ8.2C
47
R2231
OPEN
C2207
D2201
/16
47
11ES2
C2205
/50
L
L3
10µ
SB_GAIN
C81
OPEN
0.01
C80
820
#
L14
100µ
R47
#
R91
OPEN
1
C2204
C2203
/16
10
0.001
R2228 R2229
C2201
10k 56k
0.1
/16
10
C40
C2231
0.001
C2202
0.033
0Ω
R9
I2C _D ATA
0Ω
R8
I2C_CLK
R36
0Ø
C104
OPEN
B38
B18
0Ø
R80
R48
OPEN
1k
#
B26
Q34
Q21
OPEN
B35B55
OPEN
#
R73
C79
39p
OPEN
C95
V.PULSE
Q37
OPEN
SECAM[H]
C36
4.7
/25
C32
OPEN
6p
C25
D3
SHORT
R72
OPEN
OPEN
C114
180p
B45
OPEN
1.8K
L11
L12
QQR0967-001
C96
R76
R114
L27
33µ
C108
68p
C113
OPEN
Q40
OPEN
R79
C37
OPEN
1
X2
OPEN
C35
0.01
OPEN
0.1
C26
OPEN
OPEN
100k
L4
10µ
C105
OPEN
R46
270
C94
0Ω
L13
33µ
C64
22p
Q39
OPEN
Q41
MESECAM[H]
X1
QAX0576
B37
0Ø
M_TRICK[L]
R-Y_REV
EE[L]
R82
R84
R85
R40
2.2k
R41
3.9k
Q10
OPEN
ET_PB[H]/AGC_CTL
OPEN
OPEN
R42
680
R81
OPEN
EE[L]/5_PB[L]
SP[H]
D6
MTZJ5.1C
3.58NTSC[H]
C41
C42
OPEN
OPEN
R88
0Ω
Q24
B19
OPEN
2Fsc
R51
1.2k
Fsc
R44
OPEN
Q12
OPEN
R45
R43
OPEN
OPEN
Q11
OPEN
3.58NTSC[H]
TO SYSCON, SUB CPU
LP_SHORT[H]
SP_SHORT[H]
D.FF
VIDEO_ENV
FLY.ON[H]/VHS[H]
FLY.REC[H]
I2C_DATA_A/V
I2C_CLK_A/V
3.58NTSC[H]
SEC.DET/KIL/BIT_IN
V.PULSE
NORM/MESEC/S
C.SYNC/V.REF
SB_GAIN
SP[H]
EE[L]/5_PB[L]
JUST/EDS[H]/SECAM
ET_PB[H]/AGC_CTL
BS_P.CTL/MESECAM[H]
5_PB[H]
TRICK[H]/M_TRICK[L]
B58
OPEN
L5
QQR0657-019
C45
C38
C39
0.1
OPEN
330
/6.3
OPEN
OPEN
C54
R39
C131
0.01
C53
R38
1k
100p
0.1
C34
/50
680
2.2
C33
R7
/6.3
100
C31
27k
C30
0.033
3.3
0.022
R66
OPEN
C.SYNC/V.REF
0.47
/50
Q25
Q32
OPEN
AGC_CTL
R6
C29
C28
C27
OPEN
B59
V.REF C.SYNC
C112
OPEN
3.58NTSC[H]
DIFFERENCE TABLE
1
#
MODEL
HR-DVS2EU
HR-DVS2EK
SYMBOL
: Used
: Not used
IC2 Q14 D8
R4 R47
C76-C79
L14 L25
B22 B26 B46 B50 B55-B57
VHS[H]
TO SYSCON
FRONT_V_IN
TO CONNECTION
BS_VIDEO
REAR1_V_IN
TUNER_VIDEO
MAIN_ALC_DET
TO CONNECTION
fsc
REC_COLOR
Y_TO_AV
V_FROM_AV
C.SYNC/V.REF
SECAM_PB_COLOR
Y_TO_SUB
PB_COLOR
KILLER_DET
GND
2SC4081/QRS/.
2SA1576A/QR/.
DTC144WUA.
DTA144WUA.
p10304001a_rev0
HR-DVS2MS
DCBA
4-7 4-8
HGFE
Page 75

4.4 SYSTEM CONTROL SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
TO CONNECTION
I2C_CLK_A/V
I2C_DATA_A/V
V.P_CTL
SLOW_P/CNR_CTL
TRICK[H]/M_TRICK[L]
D.FF
V.PULSE
TO VIDEO/AUDIO
N.REC_ST[H]
A.MUTE[H]
EDS_CS/PAL_PB[H]
JUST/EDS[H]/SECAM
SP[H]
3.58NTSC[H]
5
4
3
2
I2C_DATA_A/V
I2C_CLK_A/V
FULL_E_ON[L]
EE[L]/5_PB[L]
SP_SHORT[H]
LP_SHORT[H]
FLY.ON[H]/VHS[H]
H.REC_ST[H]
TRICK[H]/M_TRICK[L]
BS_P.CTL/MESECAM[H]
C.SYNC/V.REF
NORM/MESEC/S
SEC.DET/KIL/BIT_IN
ET_PB[H]/AGC_CTL
TO DRUM MOTOR
DRUM_12V
DRUM_CTL_V
TO LOADING MOTOR
CAP_CTL_V
CAP_REV[L]
TO
ROTARY ENCODER
TO CONNECTION
TO
CONNECTION
JSA/SHUTTLE_A
JSB/SHUTTLE_B
SHUTTLE[L]/NC
TO DISPLAY
CN7001
S.DATA_TOSYS
S.DATA-FRSYS
B.UP_GND
TO DV MAIN (DV SYSCON)
CN1002
RXD/KBUS_D
DIAL_PLAY[L]/KBUS_CLK
DIAL_OFF[L]/KBUS_REQ
DIAL_AUTO[L]/NC
HOUSING_SW/NC
FLY.REC[H]
VIDEO_ENV
A.ENV/ND[L]
GND[M]
CN3002
TO
CAP MDA
CN3003
GND[C]
CAP_FG
GND[M]
M12/17V
CN3004
GND[C]
DRUM12V
DC3.5V[+]
J2/JOG_A
J1/JOG_B
DC3.5V[-]
DC3.5V[+]
TXD/NC
CN3001
SW5V
DC3.5V[-]
P.SAVE[L]
RCU5V
N.REC[L]
V.PULSE
SB_GAIN
D.PG
LDM1
LDM2
LSB
LSC
LSA
GND[M]
M12/17V
P.CTL[H]
V_UP[H]
CN3011
S.CLK
RC_IN
CN3014
VHS[H]
A.FF
D.FF
GND
CTL[+]
CTL[-]
D.FG
NC
AL5.8V
M12V
SW12V
SW5V
GND
48V
-29V
AL 5V
GND
#
AL5V
STB
GND
-29V
LED1
LED2
LED3
LED4
LED5
LED6
#
L3011
SHORT
L3012
C3001
SHORT
0.1
C3004
0.1
CP
CP3003
ICP-N25
GND[M]
COMMON_USE_M12/DRUM12V
D4001
1SS355
Q3011
Q3010
2SC4081/QRS/
DTC144WU
2SD1819A/QRS/
R4019
10K
R4021
10k
drum_ctl_v
dpg
dfg
B3004
OPEN
CP3002
ICP-N15
ICP-N25
CP
CP4001
C3010
QEZ0244-229
EDL
C3011
OPEN
CP
R3205
180
D3001
LNB2301L01VI
R3614
OPEN
R3201
R3206 R3207
18k 18k
Q3002 Q3003
PTZ-NV16 PTZ-NV16
START
SENSOR SENSOR
[for_EDL]
#
D3011
1SS133
R3251
10k
ICP-N15
IC3004
10k
CP3004
CP
C3042
470
/6.3
#
BA6956AN
Vref
LDM1
LDM2
C3002
L3001
SHORT
C3003
10
END
C3007
OPEN
R3215 R3216
R3214
10k 10k
10k
D3004 D3005
11ES2 11ES2
R3237 R3238 R3239
10k 10k 10k
D3012
1SS133
#
B3003
B3002
B3001
VCC
GND
LMC1
LMC2
Q3001
2SD1819A/QRS/
2SC4081/QRS/
2PC4081/R/
0.01
R3202
4.7k 10k
/16
LMC1
LMC2
R3208 R3210
PC3001 PC3002
GP3S123 GP3S123
SUPPLY TAKE UP
REEL SENSOR REEL SENSOR
C3008
OPEN
Q3005
2SD1819A/QRS/
2SC4081/QRS/
2PC4081/R/
R3222
4.7k
C3012
100
/6.3
Q3004
2SD1819A/QRS/
2SC4081/QRS/
2PC4081/R/
D3003
##
RD33ES/B2
R3219R3218
4.7k4.7k
R3244
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
Q4003
#
DTC114EU
TP4001
C4017
CTL.P
#
R3204
2.2k
LMC3
R3203
R3217
5.6k
R3212
R3211R3209
470k180 180
27k27k
D3002
1SS133
1N4148M
R3213
330k
B4001
OPEN
R3220
100k
JSA
JSB
STL[L]
#
R3247
4.7k
R3241
0.0022
Q4001
#
DTC114EU
#
C4010
0.022
C4005
#
0.0022
R4007
C3014
C3015
R3258
#
R3252
#
4.7K
OPEN
#
##
S3001
QSW0602-004
REC_SAFETY
100k
10K
R4020
OPEN
C4001
#
DTC114EU
0.1
C4002
C4003
0.001
C4004
22
/16
C4006
T
C4007
R4005
C4008
5.6k
C4009
1k
OPEN
0.1
R3011
R3012
R3013
R3014
R3015
R3016
R3245
#
R3017
OPEN
#
R3018
R3019
#
R3246
R3020
R3021
OPEN
R3022 C3024
R3025
R3026
R3027
R4008
R3233
10K
D3007
1SS355
# R3107
6.8k
100p
0.056
0.1
C4014
C4013
C3033
R4018
1k
R4017
1k
R4001
4.7k
#
C4016
560p
TP3910
#
C4015
0.001
Q4002
560
560
R4003
R4004
CTL[+]
SVss
CTL[-]
47
/6.3
CTLBIAS
T
0.01
CTLFB
CTLAMPOUT
1
CTLSMTIN
0.056
CFG
SVcc
AVcc
0
NORM/MESEC/S
0
SEC.DET/KIL/BIT_IN
0
PAUSE
OPEN
START_SENSOR
OPEN
END_SENSOR
0
TU_SYNC
4.7k
SUB_BUSY/WIDE_DET2
4.7k
RF_AGC/LED
SCR_ID[H]/WIDE_DET
OPEN
BS_ANT/AFC
0
VIDEO_ENV
0
A.ENV/ND[L]
AVss
CTL_GAIN
0
LSA
0
LSB
0
LSC
1k
CAP_REV[L]
TP3911
C3049
OPEN
R3234
#
10k
0
1k
1k
R4013
R3105
R3106
R3104
#
Vcc
Vss
DFG
DPG
SP[H]
CTLREF
V.PULSE
P.MUTE[L]
/M_PULSE
P50_IN
P50_OUT
LMC1
LMC2
LOCK[L]
ET_PB[H]/AGC_CTL
FRONT[H]/EXP1_DATA
RC
0
0
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
4.7k
4.7k
R3030
R3031
R3029
R3035
R3036
R3033
R3034
R3032
#
#
#
10K
R3257
Q3007
#
DTC144WU
#
D3008
1SS355
R4016
10k
0.22
0.0047
B3025
#
C4011
C4012
0
R4014
#
22k
R4015
2.2k
4.7k1k1k00001k00000
1k
1SS355
R4012
R4011
R4010
R4009
R3097
R3096
R3095
#
CAPPWM
R3094
V.FF
A.FF
SHTL[L]
C.SYNC
JSA/STLA
S_CASS[H]
D4002
R3103
DRUMPWM
SUB_CS/EXP2_DATA
SUB_OSD_ON/V_UP[H]
IC3001
HD6432194BA21F
SP_CONV/BS/KBUS_REQ
JUST/EDS[H]/SECAM
KBUS_DATA_IN
Vss
SB_G[PWM]
1.5k00
OPEN
R3038
R3039
0.01
C3040
POWER_DET
STB/TEST
R3040
REC_SAFTY
0
R3042
R3041
COMPU_OUT
PROTECT
Vcc
RMO/ANT_CTL[H]
SUB_DATA_IN/
TP3901
1k1k220
R3044
#
R3046
0.1
C3016
SUB_DATA_OUT/
TP3902
R3047
LMC3
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
R3090
R3092
R3091
R3093
OSD_CS
SYNC_DET[H]
JSB/STLB/S1_DC
BS_P.CTL[H]/MESECAM[H]
FLY.ON[H]/VHS[H]
KBUS_DATA_OUT
KBUS_CLK
I2C_DATA_A/V
I2C_CLK_A/V
SUB_CLK/
00470
R3049
R3050
R3051
R3048
#
R3089
R3088
R3087
R3086
#
#
B.BACK[H]/P.SAVE[L]
TRICK[H]/M_TRICK[L]
SUB_RESET/
DV_P.MUTE[H]
DV_A.MUTE/FF/REW[L]
TU_V_MUTE[H]
TU_A_MUTE[H]
SP_SHORT[H]
LP_SHORT[H]
N.REC_ST[H]
SP_FG
S.DATA_TOSYS
S.DATA_FRSYS
S.CLK H.REC_ST[H]
0
0
470
470
R3052
R3053
R3054
R3055
R3085
#
#
SLOW_P/
PAL_PB[H]
I2C_DATA2
I2C_CLK2
A.MUTE[H]
TU_FG
1k
R3056
#
OPEN
C3039
CNR_CTL
EDS_CS/
V.P.CTL
EXP_CLK
MODE
OSC2
OSC1
TU_DATA
TU_CLK
TU_CE
C3017
C3018
C3019
C3020
C3021
R3235
R3236
B3024
#
S3002
QSW0695-001
OPEN
10k
R3225
S.CASS
C3038
#
CNR_CTLSLOW_P/
#
BU2090FS
R3613
R3605
R3604
R3603
R3602
R3601
#
B3016
#
#
B3015
R3606
R3607
R3608
R3609
R3610
R3611
R3612
IC3601
#
C3602
0.1
0
OPEN
OPEN
10k
OPEN
R3076
470
R3075
470
R3074
OPEN
R3073
0
R3072
0
R3069
X3002
100
QAX05271/4W
C3037
R3229
C3036
1M
#
C3041
X3001
C3025
#
#
10k 470
R3060
#
R3059
#
R3058
#
R3057
SDA
SCLWPVCCA0
A1A2VSS
IC3003
#
AT24C16-10PC
24LC16B/P
OPEN
R3255
#
R3254
#
C3054
0.1
12p
18p
R3066
4.7k
C3026
OPEN
IC3002
30p
S-80727AN-DQ-X
##
470
1k
1k
R3259
OPEN
OPEN
C3050
OPEN
R3260
C3032
OPEN
OPEN
R3231R3230
C3031
1k4.7k
0.1
C3030
22
T
C3027
10
/6.3
C3028 C3029
100p 100p
VCCWPSCL
SDA
A0A1A2
VSS
IC3005
OPEN
0.1
T
/16
R3261
OPEN
R3262
OPEN
IC3006
#
TC7S04F
B3019
#
B3026
#
B3017
B3014
B3011
B3012
B3013
B3018
#
#
#
#
#
#
Vss
R3083
Vcc
R3081
R3080
R3079
#
R3078
#
R3077
TP3904
R3071
10k
Vcc
[OUT]
Vss
TP3905
[IN]
RES
#
X1
R3063
##
X2
4.7k
NMI
FWE
R3062 R3061
## #
TP3903
TP3908
TP3907
R3223
4.7k
TP3906
R3224
4.7k
OPEN
0.1
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
C3022
OPEN
1k
1k
C3035
C3034
OPEN
Q3009
DTC144WU
R3256
10K
C3603
10k
2.2k
2.2k
2.2k
2.2k
2.2k
2.2k
2.2k
2.2k
2.2k
2.2k
2.2k
10k
OPEN#OPEN
MAIN (SYSCON)0 3
B3022
#
B3021
#
B3023
#
B3020
#
IC3651
#
BU2090FS
VCC
D_YV
D_VHS
DEC[H]
OUT1D
OUT2D
OUT1L2
AUDIO/VIDEO
BIL_SEL/
CONTROL
VSS
CLK
DATA1
FRONT
SPCONV/BS
D_VHS/SEP
D_R2/R1Y/FV
SPCONV/DBS/DF D_TU
C3604
#
0.1
VCC
LED1
LED2
LED3
LED4
LED6
TUNER/REG
C3652
#
CONTROL
FULL_E_ON
VSS
CLK
DATA2
N.REC[L]
EE[L]/5PB[L]
SW1
SW2
P.CTL[H] LED5
OPEN#OPEN
C3653
C3654
#
TO SUB CPU, CONNTRTION
B.BACK[H]/P.SAVE
P.MUTE[L]
PAUSE
SCR_ID[H]/WIDE_DET
SUB_BUSY/WIDE_DET2
OUT1_D[H]
OUT1_L2[H]
I2C_CLK2
I2C_DATA2
EDS_CS/PAL_PB[H]
JUST/EDS[H]/SECAM
FF/REW[L]
S1_DC
S2_DC
SECAM/MESECAM[H]
P50_I/O
ANT_CTL[H]/RMO
SUB_CPU
TO
OSD_CS2 (NC)
SECAM/MESECAM[H]
S2_DC
S1_DC
3.58NTSC[L]
FLY.REC[H]
VHS[H]
BIL_SEL/DEC[H]
OUT2_D[H]
OUT1_D[H]
OUT1_L2[H]
D_VHS[H]
D_TU[H]
SP_CONV/D_BS/D_F
D_R2/D_R1Y/D_FV
D_VHS[H]/D_SEPA[H]
SP_CONV[H]/BS[H]
TO VIDEO_I/O,
CONNECTION
D_P.MUTE[H]
SYNC_DET[H]
OSD_CS
S.CLK2
S.DATA_FRSYS
SWD_S.DATA
OUT2_D[H]
D_YV[H]
D_VHS[H]
D_TU[H]
SP_CONV/D_BS/D_F
D_R2/D_R1Y/D_FV
D_VHS[H]/D_SEPA[H]
SP_CONV[H]/BS[H]
FROM/TO BS_TUNER
BS_P.CTL/MESECAM[H]
ANT_CTL[H]/RMO
SEC.DET/KIL/BIT_IN
BS_ANT/AFC
I2C_DATA2
I2C_CLK2
FROM/TO TUNER
JUST_CLK
LOCK[L]
SW1
SW2
RF_AGC/LED
BS_ANT/AFC
TU_SYNC[H]
I2C_DATA2
I2C_CLK2
BIL_SEL/DEC[H]
TU_V_MUTE[H]
TU_A_MUTE[H]
TU_DATA
TU_CLK
TU_CE
AL5V
TO AUDIO_I/O
BIL_SEL/DEC[H]
OUT2_D[H]
OUT1_D[H]
D_A.MUTE[H]
D_YV[H]
D_VHS[H]
D_TU[H]
SP_CONV/D_BS/D_F
D_R2/D_R1Y/D_FV
SP_CONV[H]/BS[H]
FRONT[H]
TO_SUB_CPU
SW2
SW1
EE[L]/5_PB[L]
N.REC[L] (NC)
SUB_RESET/EXP_CLK
SUB_CS/EXP2_DATA
SUB_CLK/KBUS_CLK
SUB_OUT/KBUS_OUT
SUB_IN/KBUS_IN
SUB_OSD_ON
SUB_BUSY/WIDE_DET2
AL5V
S.CLK
D.A MUTE(H)
S.DATA2_FRSYS(NC)
GND
B_UP5V
P.DOWN
LED1
LED2
LED3
LED4
LED5
FULL_E_ON[H]
P.CTL[H]
P.SAVE[L]
V_UP[H]
RXD
TXD
DIAL_PLAY[L]
DIAL_OFF[L]
DIAL_AUTO[L]
HOUSING_SW
NC
1
## Marked elements may differ depending on the model.
Be sure to check the Parts List.
p10290001a_rev3
DCBA
4-9 4-10
HGFE
Page 76

#DIFFERENCE TABLE
ITEM
JOG/S
CTL_GAIN
SEC.DET/KIL/BIT_IN
SUB_BUSY/W.DET2
RF_AGC/LED
SCR_ID/WIDE
P50_IN
RMO/ANT_CTL
JUST/EDS/SECAM
EEPROM
TU_CE/CLK/DATA
SP_CONV/BS/KBUS_REQ
TU_CLK
TU_DATA
CRYSTAL
EXPANDA
FRONT[H]/EXP1_DATA
SP_CONV/BS/KBUS_REQ
JUST_CLK
BS_P.CTL
SUB_D.IN/KBUS
D.IN/RXD
SUB_D.OUT/KBUS
D.OUT/TXD
SUB_CLK/KBUS
CLK/DIAL_PLAY
SP_CONV/BS/KBUS_REQ
/DIAL_OFF
CN3014
KBUS_DATA
SUB_OSD_ON/V.UP
D_P.MUTE
D_A.MUTE/FF/REW
EDS
OSD
JBS/STLB/S1_DC
CN3011
SUB_RESET/EXP.CLK
FF/REW
SUB_CLK/KBUS_CLK
B.BACK/P.SAVE
IN_SELA/EXP1_DATA
SUB_CS/EXP2_DATA
M_PULSE
P50_OUT/M_PULSE
V.FF
B3003
D3011
D3012
C4010
Q4001
R3252
R3245
R3017
R3018
R3247
R3019
R3258
R3234
Q3007
D3008
R3257
R3044
R3056
IC3003
R3057
R3060
R3061
R3059
C3028
C3029
X3001
C3025
C3041
C3024
IC3601
IC3651
C3602
C3603
C3604
C3652
C3653
C3654
B3015
B3016
B3020
R3256
B3011
B3019
B3012
B3013
B3014
CN3014
IC3006
B3026
B3017
R3078
R3255
R3254
B3024
Q3009
B3021
B3022
B3023
B3025
CN3011
R3079
C4015
Q4002
C4016
Q4003
C4017
C4005
R3048
B3018
R3033
R3104
Q3010
Q3011
R3107
R3034
R4011
R4014
: Used
X : Not used
SD1EU/EK SD1MS
OPEN
X
4.7k
4.7k
X
6.8k
4.7k
10k
X
0Ω
1k
16k
1k
OPEN
OPEN
QAX0445
X
22p
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
1-6pin
X
X
1k (10kΩ)
OPEN
OPEN
X
X
X
X
1-18pin
1k
680p (330p)
X
220
X
0Ω
4.7k
X
0Ω 0Ω 4.7k 4.7k
4.7k (2.2k) 4.7k 1k 1k
0Ω (2.2k) 0Ω 1.8k 1.8k
OPEN OPEN OPEN
XXX
4.7k
4.7k 4.7k
X
6.8k X 4.7k
4.7k X X
10k X X
XXX
0Ω X1k
16k 8k 8k
1k 1k 1k
OPEN OPEN OPEN
OPEN OPEN OPEN
QAX0444 QAX0444 QAX0444
XXX
10p 10p 10p
12p 12p 12p
XXX
XX
XXX
XXX
XXX
XXX
XXX
1-6pin 1-6pin 1-6pin
XXX
XXX
1k 1k 1k
OPEN OPEN OPEN
OPEN OPEN OPEN
XXX
XX
XXX
XXX
1-18pin 1-18pin 1-18pin
1k 1k 1k
680p 680p0.001
XXX
220 220 220
XXX
0Ω 0Ω 0Ω
4.7k 4.7k 4.7k
X XX
SD1US SD1DOM
4.7k
4.7k
4.7k
XX
X
X
HV4DOM HV4PAL HV4MS HV4US
XXXX
OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN
XXXX
4.7k
XXX
1k1k1k
XXXX 1k 1k 1k 1k
4.7k 4.7k 4.7k 4.7k
4.7k 4.7k 4.7k
4.7k 6.8k 6.8k X
XX10k 10k
XX
XXXX
1k 0Ω 0Ω X
1k 1k 1k 1k
8k
470 470 470 470
OPEN
OPEN
QAX0444 QAX0445 QAX0444 QAX0444
10p X 10p 10p
12p 22p 12p 12p
X
XXXX
XXXX
XXXX
1-6pin 1-6pin 1-6pin 1-6pin
XXXX
1k 1k 1k 1k
OPEN
OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN
1-18pin 1-18pin 1-18pin 1-18pin
1k 1k 1k 1k
680p 680p 680p 0.001
220
1k
1k
4.7k
2.7k
0Ω
8k 8k 8k
OPEN OPEN OPEN
OPEN OPEN OPEN
XXX
OPEN OPEN OPEN
XXX
XXXX
220 220 220
1k 1k 1k
1k 1k 1k
0Ω 0Ω
2.7k 2.7k
0Ω 0Ω
X
XXX
p10290001a_rev3
4.7k
4.7k
4.7k
2.7k
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
XX 4.7k 4.7k
X
XXX
XXX
X
0Ω
4-11 4-12
Page 77

4.5 SUB CPU SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
0 3 MAIN(SUB CPU)
TO
4.7k47k
R3425R3424
5
R3419
Q3302
DTC144WUA
Q3304
DTC144WUA
R3417
/50
R3360
1k
1k
1k
1k
1k
1k
1k
1k
1k
1k
1k
1k
1k
NC
P.DOWN
NC
SUB_CS
NC
NC
GND
VDD
X2
X1
GND
XT2
XT1
VDD
AVREF
NC
NC
SW1
SW2
V.UP[H]
EE[L]
1K
R3358
SUB_RESET
NC
FF/REW[L]
1k1k1k1K1k
1k
1K
R3357
HOUSING_SW
DIAL_AUTO[H]
DIAL_OFF[H}
DIAL_PLAY[H]
NCNCGND
R3416
#
1k
R3355
NC
OPEN
1k
1k1k1k
R3354
R3353
NC
BUCKUP5V
1k1k1k
1k
R3352
R3351
R3350
NC
NC
IN_SEL_B
SP_CONV[H]/D_BS[H]/DV_F[H]
D_VHS[H]/D_SEPA[H]
SECAM/MESECAM[H]
NC
RXD
TXD
1k
Q3303
TP3303
DTC144WUA
R3402
47k
R3369
CF3301
QAX0227-001
UPD780053GC042
R3361
R3362
R3363
R3364
R3365
R3366
TP3301
R3371
1k
L3301
R3376
R3377
R3378
R3379
R3380
C3312
C3311
IC3301
10µ
0.01
3.3
C3313
0.047
1M
TO_AUDIO_I/0
IN_SEL_A
IN_SEL_B
4
3
TO
SYSCON
BIL_SEL/DEC[H]
EE[L]/5_PB[L]
FF/REW[L]
SYSCON
B_UP5V
NC
SUB_OSD_ON
GND
S.CLK
S. DATA
CSB
SW1
SW2
TP3302
TP3306
VDD Y X X1TOX0
IC3302
TC74HC4053AF
A
B
C
R3412
1k
1k1k1k
1k
1k
1k
R3349
R3348
R3346
R3347
R3343
R3344
NC
NC
NC
NC
IN_SEL_A
NC
BIL_SEL/DEC[H]
5_PB[H]
FLY_REC[H]
FULL_E_ON[H]
OUT1_L2[H]
OUT1_D[H]
OUT2_D[H]
D_R2[H]/D_R1Y[H]/D_FV[H]
VHS[H] S1_DC
3.58NTSC[L]
OSD_CS
SO1
SCK1NCSUB_BUSY
SUB_IN
SUB_OUT
1k
1k
1k1k1k
1k
1k
#
1k
R3342
N.REC[H]
D_VHS[H]
D_TU[H]
SUB_CLK
P.CTL[H]
0
R3418
R3411
LED4
LED3
LED2
LED1
LED5
S2_DC
P.SAVE[L]
0
R3341
1k
GND
100
10k
B3301
OPEN
Q3308
DTC144WUA
Q3307
R3340
R3339
R3338
R3337
R3336
R3335
R3334
R3332
R3331
R3330
R3329
R3328
R3327
R3326
R3325
R3324
R3323
R3322
R3321
1k
0
0
0
0
0
1k
1k
1k
1K
1k
1k
1K
1K
1K
0
0
4.7K
SHORT
D3301
DTC144WUA
SYSCON
RXD
TXD
DIAL_PLAY[L]
DIAL_OFF[L]
DIAL_AUTO[L]
HOUSING_SW
LED4
LED3
LED2
LED1
LED5
D_A MUTE[H]
TO VIDEO/AUDIO
5_PB[H]
TO
SYSCON, VIDEO I/O
FULL_E_ON[H]
FLY_REC[H]
S2_DC
S1_DC
DV_SEPA[L] (NC)
OUT1_L2[H]
GND
OUT1_D[H]
OUT2_D[H]
D_VHS[H]
D_TU[H]
SP_CONV/D_BS/D_F
D_A2/D_R1Y/D_FV
VHS[H]
VHS_DV[H]
3.58NTSC[L]
SECAM/MESECAM[H]
TO
VIDEO_I/O
OSD_CSB
OSD_CLK
OSD_DATA
VSSVEEINHZ0ZZ1Y0Y1
C3310 R3401
0.01 10k
2
TO
SYSCON
SUB_BUSY
SUB_CLK
SUB_RESET
P.DOWN
SUB_CS
SUB_OUT
SUB_IN
1
# MARK ELEMENTS ARE NOT MOUNTED.
DCBA
4-13 4-14
R3301
R3302
TP3305
TP3304
R3303
R3305
R3306
#
C3302
OPEN
R3308
R3309
R3310
R3311
R3312
R3313
#
#
C3301
OPEN
C3303
OPEN
R3314
R3315
R3316
R3317
R3318
R3319
R3320
Q3305
DTC144WUA
R3403
10k
Q3306
DTC144WUA
p20174001a_rev1
TO
SYSCON
AL5V
P.SAVE[L]
P.CTL[H]
V_UP[H]
HGFE
Page 78

The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
4.6 TUNER SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
0
3 MAIN (TUNER)
#
TU6001
ANT IN ANT OUT
MATSUSHITA
5
4
OPEN
3
2
TO
SYSCON
LOCK [L]
TU_CE
TU_DATA
TU_CLK
I2C_CLK2
I2C_DATA2
BS_ANT/AFC
TU_A_MUTE[H]
TU_V_MUTE[H]
BIL_SEL/DEC/[H]
RF_AGC/LED
JUST_CLK
SW1
SW2
TU_SYNC[H]
PAL/MS
BB(AL5V)
AUDIO IN
MOD SDA
MOD B(AL5V)
MOD SCL
VIDEO IN
RF AGC
PLL CLK
PLL DATA
MB(SW5V)
LOCK(L)
TU(30V)
IF OUT
AUDIO OUT
SIF OUT
VIDEO OUT
MB(SW5V)
TU CE
IF IN
NTSC
NC(GND)
AUDIO IN
CH SW
MOD B(SW5V)
CONV.CTL(H)
VIDEO IN
NC
NC(GND)
(RF AGC)
(BT)
(BT)
TU CE
PLL CLK
PLL DATA
NC
NC(5V)
MB(SW5V)
LOCK(L)
TU(30V)
IF OUT
IF IN
SW 1
NC
SW 2
NC
AUDIO OUT
(SIF OUT)
AFT
AFT
VIDEO OUT
NC(OPEN)
ANT IN ANT OUT
#
TU6001
ALPS
PAL/MS NTSC
BB(AL5V)
MOD SDA CH SW
MOD B(AL5V)
MOD SCL CONV.CTL(H)
VIDEO IN VIDEO IN
TU(30V)
RF AGC (RF AGC)
NC
MB(SW5V)
SW 1
SW 2
AUDIO OUT AUDIO OUT
SIF OUT SIF OUT
AFT AFT
AUDIO INAUDIO IN
MOD B(SW5V)
TU CETU CE
PLL CLKPLL CLK
PLL DATAPLL DATA
MB(SW5V)
LOCK(L)LOCK(L)
TU(30V)TU(30V)
IF OUTIF OUT
VIDEO OUTVIDEO OUT
#
B6001
NC
NCNC
TPTP
L6002
#
10
#
L6005
10
#
R6025
10k
#
C6014
#
R6024
#
R6023
R6022
#
0
R6020
#
0
#
R6021
L6001
#
10
#
C6027
220p
CH
#
C6028
220p
CH
#
R6060
10k
#
R6061
10k
0
#
C6023
#
C6006
D6002
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
# DIFFERENCE TABLE
TUNER
OPEN
TUNER
ATS+ K6080
VIDEO BUFFER
TU_V_MUTE
TU_A_MUTE
AUDIO OUT
AFC
MB(SW5V)
PLL CLK
PLL DATA
TU CE
SYSTEM SW R6060,R6061
SYNC DET
DEMOD
DEMOD PWB ASSY
9V REG
DEMOD REG
PASS CON
SW12V B6607
DEMOD OUT
MUTE Q6501,Q6502
TUNER MONO B6510
DEMOD
SELECTION
TO
CONNECTION
GND
RF5V
SW5V
SW12V
#
#
C6555
SIF
COMP
B6035
R6601
BT2
TO
SYSCON
AL5V
TO VIDEO/AUDIO, AUDIO I/O
DEMOD[L]
GND
DEMOD[R]
TO VIDEO/AUDIO
TU_AUDIO
TO DEMOD
CN6701
CN6701
##
PAL/MS
/ARC
US JPN
NC
NC
JUST
_CLK
I2C
I2C
LED
_DATA
_DATA
I2C
I2C
BIL
_CLK
_CLK
_SEL
TU
TU
TU
_MUTE
_MUTE
_MUTE
DEMOD
DEMOD
DEMOD
_[R]
_[R]
_[R]
DEMOD
DEMOD
DEMOD
_[L]
_[L]
_[L]
SW5V
SW9V
SW9V
GND
GND
GND
COMP
COMP
COMP
SIF
TO
CONNECTION
TU_VIDEO
GND
KOREA
NC
LED
MODE
_SEL
NC
DEMOD
_[R]
DEMOD
_[L]
SW12V
GND
SIF
Q6551
#
2SC3243/DE
#
#
C6551
/16
47
R6508
#
#
R6509
L6032
SHORT
C6040
0.1
#
R6511
R6510
#
CF6031
OPEN
5.07MHz
#
C6037
/16
10
#
B6034
R6044
#
8.2k
#
Q6040
2SC4081/RS
#
R6043
22k
0.01
#
C6022
#
C6020
#
C6021
C6007
#
C6008
#
0.01
#
C6005
/50
10
HZ30-2L
#
R6038
5.6k
#
C6024
0.056
R6031
0
#
B6033
#
B6032
R6040 R6041
##
470 180k
#
C6041
#
#
R6551
R6552
270
100
##
D6551C6552
MTZJ10B
0.01
#
Q6501
DTC143T
#
C6519
#
Q6502
DTC143T
#
C6520
#
K6080
600
#
R6034 R6030
1M 1k
#
C6033
#
Q6031
DTC144E
2SB1218A/QR
2SA1576A/QR
2PA1576/R
#
R6032
#
R6033
R6042
#
2.7k
#
R6045
470
Q6041
#
2SA1576/RS
#
C6042
T6040
#
PELN0806
470p
#
B6030
#
Q6030
#
Q6032
DTC144E
C6032
#
0.047
#
C6043
0.022
#
C6554
0.01
#
#
B6607
B6566
#
B6510
#
R6553
I2C _ DATA
470
LED/RF_AGC
#
B6552
#
R6554
I2C_CLK
470
BIL_SEL
#
B6554
#
C6553
#
B6563
#
B6565
#
#
R6046
10k
#
Q6042
#
D6040
DTC114EU
DA204U
#
C6044
/50
2.2
Used
Not Used
SYMBOL EU/EK
TU6001
R6025,B6035
R6030,Q6030
B6030
Q6031
R6034
C6033
B6032
Q6032
B6033
R6032
R6033
R6038
C6032
B6034
C6037
B6001
C6024
C6027,C6028CENELEC
C6005
C6006TU(30V)
L6005 10 10
C6007
C6008
L6001
C6014,L6002BB(AL5V)
R6020
R6023
C6020
R6024
C6021
R6022
C6022
C6023LOCK
R6040~R6046,
C6040~C6044,
Q6040~Q6042,
D6040,T6040
SYMBOL EU/EK
CN6701 LPA10094* LPA10094* PB11087* PB11087* PB11076* PB11076*
R6551,R6552,
Q6551,D6551
C6551,C6552
C6553
C6554
C6555
R6508,R6510
R6509,R6511
C6519,C6520
R6553,R6554
B6552,B6554
B6563
B6565
B6566
R6601
FRANCE
ALPS ALPS MATSUSHITA MATSUSHITA
QAU0151 QAU0152 QAU0198 QAU0198
00
3.9k
3.3k
1.8k
1.8k
0.047
330/10 330/10
470 470
470 470R6021
470 470
FRANCE
33/16 33/16
0.01 0.01
00
00
JAPAN
MS
DVS2 PVS100USDVS2 PVS100
0.0047
00
SHORT SHORT
SHORT SHORT
1k 1k
1k 1k
1k 1k
JAPAN
MS
DVS2 PVS100USDVS2 PVS100
00 0
QAU0216
12k
SHORT
SHORT
1k
1k
1
DCBA
4-15 4-16
p10306001a_rev0
HGFE
Page 79

4.7 VIDEO I/O SWITCH SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
0 3 MAIN (VIDEO I/O SW)
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
B701
0Ø
IC706
PQ05TZ1U
ON/OFF
OUTNCGND
IC711
OPEN
C792
OPEN
C793 C796
OPEN OPEN
B735
OPEN
MM1113XF
C795
OPEN
HH
Vcc GND
5
TO
CONNECTION[MAIN]
REAR2_Y_IN/TERM_D_Y
V_FROM_OSD
TERM_Y_OUT
REAR2_C_IN/TERM_D_C
TERM_C_OUT
Y_OUT
C_OUT
CHARA_DATA
V_TO_OSD
GND
4
3
2
TO
CONNECTION[MAIN]
OUT2_D[H]
B.BACK[H]
I2C_DATA2
I2C_CLK2
P.MUTE[L]
TO ON SCREEN
CN851
CN704
OSD_CS
S.CLK
S.DATA_FRSYS
EDS[H]/
I2C_CLK2
EDS_CS/
I2C_DATA2
SWD_S.DATA
CHARA_DATA
P.MUTE[L]
V_FROM_OSD
SYNC_DET[H]
OSD_IN
V_TO_OSD
SW5V
OSD_C
OSD_Y
SW12V
D_P.MUTE[H]
D_Y/V_IN
TO
SYSCON
D_P.MUTE[H]
SWD_S.DATA
SYNC_DET[H]
OSD_CS
S.CLK2
S.DATA_FRSYS
D_YV[H]
S2_DC/A_SEARCH[H]
TO
SUB_CPU
OSD_CSB
OSD_CLK
OSD_DATA
TO VIDEO/AUDIO
TO_PS_C
TO
S/P_CONV.
CN701
#
TO_PS_C
TO_PS_Y
FROM_PS_C
SW5V
TO
S_SUB
CN702 CN513
FROM_PS_Y
TO_PS_Y
FROM_PS_C
TO_PS_C
SW5V
SW5V
2Fsc
GND
2Fsc
CN1
GND
GND
GND
N.C
GND
GND
GND
L701
4.7µ
IC701
OPEN
Vcc NC
12dB
C701
OPEN
GND
C702 C703
OPEN OPEN
0Ø
B707
B734
OPEN
B710
OPEN
B740
OPEN
1212
B741
0Ø
B731
B732
B733
0Ø
0Ø
0Ø
L712
#
4.7µ
#
Q726
R779
#
1k
#
R778
1k
R701
OPEN
Q702
OPEN
R702
OPEN
Q701
OPEN
R703
OPEN
#
FL701 FL702
PELN1199#PELN1198
R716
1.5k
±0.5%
Q708
±0.5%
±0.5%
N
C759
2.2
H
H
Vcc GND
C760
0.01
B724
OPEN
H
Vcc GND
C787 C788
OPEN OPEN
R720 R721
2.2k 2.2k
R717
0Ω
R718
Q709
270
R719
470
R767
0Ω
/50
Q710
R768
0Ω
C761
/50
2.2
C789
OPEN
C790
OPEN
#
R780
1.2k
Q704
#
Q727
R708 R709 R710
10k 0Ω 560
C705
0.01
#
#
R781
Q728
1k
#
R782
100
#
R783
1k
R712
6.8k
Q706
Q705
C706
47
R713
/6.3
3.9k
R714
R711
82
680
#
C780 C781
0.01 47
#
#
C783
/6.3
10
#
C782
0.01
R715
OPEN
Q707
Vcc
6dB
GND
/16
#
R784
0Ω
C708 C709
0.01 47
/6.3
C707
OPEN
IC705
MM1117XF
B721
0Ø
C756 C762
OPEN
C757
/50
2.2
C758
100p
B723
OPEN
C784
OPEN
IC710
OPEN
#
IC709
MM1031XM
C785
OPEN
C786
OPEN
R704
33k
C704
Q703
0.01
R706
270
±0.5%
R705
22k
R707
560
±0.5%
#
C779
15p
##
L713
100µ
R722
470
±0.5%
Q712
R723
470
±0.5%
Q711
B713
OPEN
IN
D706
1SS355
100p
C763 C764
/50 /6.3
1100
OPEN
B725
B726 0Ø
C791
47
/6.3
L714
4.7µ
R724
1k
C712 C714
IC702
0.01 0.01
H
H
Vcc GND
C710
C713
OPEN
C711
0.01
0.01
LPF
H.Sync
Sep.
0.0033
0.01
TPGND
C765
C766
B727
0Ø
C797
OPEN
H
C794
OPEN
C715L702
224.7µ
IC707
AN3916
B.G.
KEYED/
Ref
PEAK
Def.
Sync
LH
Clamp
C767
0.047
/16
/6.3
C768
C769
C770
22
10
C807
C798
OPEN
/16
GCA Amp
Di
Clamp
C771
4.7
/25
/16OPEN
R769
1.2k
10
IC703
MM1228XF
C716R725
OPEN
1M
H
Vcc GND
R726
390k
C717
/50
1
TP701
R772
1k
R773
R770
22k
470
R775
18k
Q725
R774
C772
0.01
R771
#
IC712
L715
4.7µ
270k
C773
47p
470
C801 C803
0.01 0.01
H
H
Vcc GND
C802
0.01
#
C799
C800
/6.3
47
0.01
OPEN
C720C718
2.22.2
/50/50
Q730
R786
OPEN
DTA144WUA
0Ø
OPEN
B715
#
C778
OPEN
DTA144WUA
R785
Q729
B738
B739
OPEN
OPEN
B718
B717
B716
#
Q731
OPEN
470
TO DV MAIN
(DV V OUT) CN3501
CN703
D_C_IN
GND
D_Y/V_IN
D_C_OUT
GND
D_Y_OUT
B737
OPEN
TO
SYSCON
D_R2/D_R1Y/D_FV
D_TU[H]
SP_CONV[H]/BS[H]
SP_CONV/D_BS/D_F
D_VHS[H]
0Ø
D_VHS[H]/D_SEPA[H]
TO
CONNECTION
SW5V
SW12V
AL5.8V
SWD_C
SWD_Y
BS_VIDEO
REAR1_Y_IN
REAR2_V_IN
REAR1_V_IN
TUNER_VIDEO
FRONT_Y_IN
FRONT_V_IN
REAR1_C_IN
FRONT_C_IN
H
C721
6dB
100p
C719
0.01
C774
/16#
10
#
C775
OPEN
VR701
50k
D AGC
B728
#
Q713
R730
R727
1M
±0.5%
C722
0.01
R776
#
0Ω
#
IC708
MM1115XF
NC
#
B722
NC
C804
OPEN
IC713
OPEN
NC
NC
C805
OPEN
B729
0Ø
B730
OPEN
1k
R728
Q714
270
±0.5%
R729
270
B714
OPEN
C777
#
/16
10
H
R777
0Ω
#
C776
0.01
C806
OPEN
H
1
# DIFFERENCE TABLE
S.NO
MODEL
HR-DVS2EU/EK
HR-DVS2MS
IC708,
IC709 B722
Q726~
Q728
R776,
R778~ R784
C778, C779~ C783, C800
C774~
L712
B728
B716,
FL702
FL701,
CN701
X
DCBA
IC712
MM1111XF
MM1113XFX
4-17 4-18
## Marked elements may differ depending on the model.
Be sure to check the Parts List.
Used
Not used
X
2SC4081/QRS/.
2SA1576A/QR/.
p10305001a_rev1
HGFE
Page 80

4.8 AUDIO I/O SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
03
MAIN (AUDIO I/O)
TO
SYSCON, SUB CPU
DV_A.MUTE[H]
IN_SEL_B
B2607
#
B2608
R2691
R2692
#
B2609
#
#
B2610
D2602
OPEN
/50
C2607
1
C2606
/50
R2626
22k
C2610
100p
R2624
5.6K
C2611
100p
R2625
5.6K
#NAME?
1
#
R2636
10k
BAX2 X1 X X0 X3VDD
/16
#
IC2604
BA15218F
C2604
47
/16
#
R2640
#
R2622
22k
100k
R2621
#
5.6K
#
C2609
100p
R2618
1k
VCC
#
R2619
22k
#NAME?
#
C2608
100p
#
#
R2639
R2620
5.6K
100k
Y0 Y2 Y Y3 Y1 INH VEE VSS
IC2603
BU4052BCF
R2611 R2614
R2610 R2613
1k 10k1k 1k
#
R2612
1k
#
R2615
R2616R2617
1k
1k1k
BAX2 X1 X X0 X3VDD
VCC
IC2602
BA15218F
C2605
/16
10
C2602
100p
C2603
100p
R2637
100k
#NAME?
R2638
100k
C2683
47
IC2601
BU4052BCF
/16
R2609
1k
R2607R2608
1k1k
Y0 Y2 Y Y3 Y1 INH VEE VSS
R2602
R2601 R2604
1k 1k
R2603
1k
1k
C2682
47
R2606
1k
R2605
10k
/16
C2601
10
BAX2 X1 X X0 X3VDD
Y0 Y2 Y Y3 Y1 INH VEE VSS
IC2606
BU4052BCF
R2628
R2627 R2630
1k1k1k 1k
0Ω
R2689
R2690
/16
D2601
OPEN
OPEN
R2629
1k
R2632R2635
R2633R2634
1k1k
1k1k
R2631
C2612
10k
10
5
B2604
OPEN
VDD Y
XX1X0ABC
TO DV MAIN
(AUDIO AD/DA)
CN3701
CN2601
DV_A_REC[L]
GND
DV_A_REC[R]
4
DV_A_PB[L]
DV_A_PB[R]
GND
GND
GND
B2603
R2684
10k
IC2610
BU4053BCF
OPEN
R2685
2.2k
Q2601
2SC4081/QRS/
220
R2681
10k
R2682
Q2602
2SC4081/QRS/
R2683
2.2k
10k
R2686
C2681
10
R2687
220
VSSVEEINHZ0ZZ1Y0Y1
R2688
220
/16
IC2605
BA15218F
VCC
R2623
22k
IN_SEL_A
D_R2/D_R1Y/D_FV
SP_CONV/D_BS/D_F
D_VHS[H]
D_TU[H]
FRONT[H]
SP_CONV[H]/BS[H]
OUT1_D[H]
OUT2_D[H]
BIL_SEL/DEC[H]
D_YV[H]
TO CONNECTION
AL5.8V
0Ω
AL12V
220
AUDIO[-]
GND
11
3
TO
CONNECTION
GND
RCA_A.OUT[R]
RCA_A.OUT[L]
A.IN1[R]
A.IN1[L]
LINE_OUT[R]
LINE_OUT[L]
A.IN2[R]
A.IN2[L]
DEC_OUT[R]
DEC_OUT[L]
2
TO
CONNECTION
F.AUDIO[R]
F.AUDIO[L]
TO
TUNER
DEMOD[R]
DEMOD[L]
FROM
BS_AUDIO[R]
BS_AUDIO[L]
NC
BS
R2661
10k
10k
R2665
10k
R2667
R2660
220
R2662
220
R2663
R2664
10k
220
R2666
220
#
C2614
1
#
C2613
1
#
C2660
#
C2661
##
B2602 B2601
00
#
IC2609
LA7151
/16
/16
10
10
C2656
C2657
/16
10
#
#
/16
10
VccGND NC
/16
10
C2658
#
#
C2659
10
R2659
C2655
10
/16
/16
C2654
100p
VCC
C2652
10
IC2608
BA15218F
/16
C2653
100p
–VCC
Y0 Y2 Y Y3 Y1 INH VEE VSS
IC2607
BU4052BCF
R2652
R2651 R2654
1k1k 1k
R2656
R2657R2658
1k
1k1k
BAX2 X1 X X0 X3VDD
#
C2651
10
R2668
/16
10k
TO
VIDEO/AUDIO
A.SEL_IN[R]
A.SEL_IN[L]
FMA_OUT[R]
FMA_OUT[L]
GND
DEMOD[R]
DEMOD[L]
A.IN1[R]
A.IN1[L]
DEC_OUT[R]
DEC_OUT[L]
A.IN2[R]
A.IN2[L]
R2655R2653
10k1k
p10336001a_rev0
1
B2601,B2602
B2607,B2608
Used
Not used
IC2609
C2656-C2661
MODEL
NTSC
PAL/MS
SYMBOL
B2609 B2610
R2636R2668
MODEL
With BS
W/O BS
IC2604
,R2612,R2615SYMBOL
R2619-R2622,R2639,R2640
C2608,C2609,C2613,C2614
DCBA
4-19 4-20
HGFE
# DIFFERENCE TABLE
SYMBOL
MODEL
With DVC
With HDD
Page 81

4.9 CONNECTION SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
GND
DET_OUT[W]
GND
DET_IN
GND
OPEN
DET_OUT[M-N]
TO
BS
GND
DET_OUT[M-N]
DET_IN
DET_OUT[W]
AFC_IN
BIT_IN
BIT_OUT
BS_VIDEO
BS_SW5V
AL17V
AL6V
AUDIO I/O
TO
GND
RCA_A.OUT[R]
RCA_A.OUT[L]
A.IN1[R]
A.IN1[L]
LINE_OUT[R]
LINE_OUT[L]
A.IN2[R]
A.IN2[L]
DEC_OUT[R]
DEC_OUT[L]
F.AUDIO[L]
F.AUDIO[R]
AUDIO[-]
TO
TUNER
TUNER_VIDEO
RF5V
BT2
SW12V
SW5V
GND
TO VIDEO/AUDIO
TUNER_VIDEO
REAR1_V_IN
BS_VIDEO
fsc
KILLER_DET
C.SYNC/V.REF
PB_COLOR
SECAM_PB_COLOR
MAIN_ALC_DET
Y_TO_SUB
Y_TO_AV
V_FROM_AV
REC_COLOR
SW5V
SW12V
FRONT_V_IN
GND
AL5V(NC)
TO SYSCON
JUST/EDS[H]/SECAM
EDS_CS/PAL_PB[H]
S1_DC
S2_DC
PAUSE
I2C_CLK2
I2C_DATA2
SCR_ID[H]/WIDE_DET
P50_I/O
SECAM/MESECAM[H]
B.BACK[H]/P.SAVE
OUT1_L2[H]
OUT1_D[H]
AL5V
ANT_CTL[H]/RMO
OUT2_D[H]
TO SYSCON, AUDIO I/O
GND
I2C_CLK_A/V
I2C_DATA_A/V
V.P_CTL
D.FF
TRICK[H]/M_TRICK[L]
SLOW_P/CNR_CTL
V.PULSE
P.MUTE[L]
SUB_BUSY/WIDE_DET2
P.SAVE[L]
V_UP[H]
P.CTL[H]
DC3.5V[+]
-29V
DC3.5V[-]
GND[M]
M12/17V
DRUM12V
M12V
SW12V
AL12V
SW5V
48V
AL5.8V
Used
X
# DIFFERENCE TABLE
HR-DVS2
B7501
B7502
B7503
B7504
B7505
B7506
B7507
B7508
B7509
NC
B7510
B7511
B7512
B7513
B7514
B7515
B7516
B7517
B7518
B7519
R7513
R7501
R7502
R7503
R7504
C7501
C7502
D7501
D7502
C7505
~C7514
C7515
Q7501
R7505
R7506
R7507
L7501
C7503
R7508
Q7502
R7512
Q7503
R7509
R7510
R7511
C7504
CN7510
D7503
CN7501
CN7502
CN7503
CN7505
CN7507
CN7508
CN7509
D7505
R7514
## Marked elements may differ depending on the model.
Be sure to check the Parts List.
Not used
EK
EU MS
XXX
XXX
XXXXX
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
XXXX
X
X
X
XXXX
XXXXXXX
XXX
XXXXXX
1 -15 1 -15X1 -15 3 -15
1 -5X1 -5X1 -5X1 -7X1 -7 1 -7
1 -14 1 -14 1 -14 7 -16 7 -16 8 -15
X X X 1 -11 1 -11X
1 -16 1 -16 1 -16 1 -16 1 -16 1 -10
1 -13 1 -13 1 -13 3 -13 3 -13 3 -13
3 -15 3 -15 3 -15 1 -15 3 -15 1 -15
DOM US
XX
XXX
XXX
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
XXXXX
XXXXX
HR-PVS100
XX
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
XX
XXX
3 -15 3 -6
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
OPEN
REC_COLOR
TO S_SUB CN511
CN502
#
R7513
5
B7516
#
TO
VIDEO_I/O SW
TERM_Y_OUT
TERM_C_OUT
REAR2_Y_IN/TERM_D_Y
REAR2_C_IN/TERM_D_C
REAR1_Y_IN
REAR1_C_IN
REAR1_V_IN
REAR2_V_IN
SWD_C
SWD_Y
BS_VIDEO
TUNER_VIDEO
B.BACK[H]
P.MUTE[L]
SW12V
AL5.8V
SW5V
FRONT_V_IN
FRONT_C_IN
4
3
2
1
FRONT_Y_IN
CHARA_DATA
V_TO_OSD
V_FROM_OSD
I2C_CLK2
I2C_DATA2
OUT2_D[H]
S-SUB CN512
TO
CN7506
REAR1_Y_IN
REAR1_C_IN
REAR2_Y_IN
REAR2_C_IN
Y_OUT
C_OUT
V_FROM_OSD
OPEN
TO JACK
CN7002
#
FRONT_Y_IN
FRONT_C_IN
FRONT_V_IN
PAUSE
FRONT_A(L)
FRONT_A(R)
J1/JOG_B
J2/JOG_A
SHUTTLE[L]/NC
GND/NC
JSB/SHUTTLE_B
JSA/SHUTTLE_A
TO SYSCON
JSA/SHUTTLE_A
JSB/SHUTTLE_B
SHUTTLE[L]/NC
J2/JOG_A
J1/JOG_B
TO REGULATOR
CN5321
#
BS_SW5V
AL17V
P.SAVE[L]
V.UP[H]
P.CTL[H]
DC3.5V[+]
DC3.5V[-]
M12/17V
DRUM12V
TO REGULATOR
CN5322
#
CH+12V
AUDIO[-]
SW5V[2]
AL5.8V
C_OUT
Y_OUT
#
CN7510
CN7507
CN7509
AL6V
-29V
M12V
CN7508
RF5V
SW12V
AL12V
SW5V
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
NC
GND
##
D7504
GND
1SS355
#
D7503
1SS355
#
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
BT2
GND
GND
GND
48V
R7510
75
#
#
R7511C7504
75
SHORT
#
R7509
75
#
C7515
0.1
B7501
#
B7519
#
B7512
##
#
B7502
2.2k
B7513
#
B7518
B7517
OPEN
TO 3D DIGITAL/2M CN1401
CN501
TO TERMINAL CN7101
#
#
#
D7501
#
#
1SS355
R7501
B7508
10k
##
C7501 C7502
0.01 0.01
R7503 D7502
10k
##
R7502 R7504
100k 100k
CN7501
GND
CARA_DATA
fsc
GND
C_TO_DIGI
SW5V[2]
Y/V_TO_DIGI
EE[L]
Y_FROM_DIGI
GND
C_FROM_DIGI
KILLER_DET
I2C_CLK_A/V
I2C_DATA_A/V
V.P.CTL
V.REF
D.FF
TRICK[H]
SLOW_PULSE
EE[L]
I2C_DATA_A/V
I2C_CLK_A/V
Fsc
SW5V
SW5V
GND
GND
C_TO_DIGI
Y/V_TO_DIGI
Y_FROM_DIGI
C_FORM_DIGI
PB_COLOR
V.PULSE
SECAM_PB_COLOR
MAIN_ALC_DET
Y_TO_SUB
P.MUTE[L]
WIDE_DET
FRONT_Y_IN
FRONT_C_IN
FRONT_V_IN
REAR2_V_IN
GND
V_TO_OSD
CHARA_DATA
Y_TO_AV
GND
V_FROM_AV
GND
GND
TERM_C_OUT
TERM_Y_OUT
GND
TERM_D_Y
#
1SS355
TERM_D_C
GND
SW'D_C
GND
SW'D_Y
GND
CN7502
TUNER_VIDEO
TO TERMINAL CN7102
#
#
D7505
1SS355
#
B7510
B7509
#
B7504
#
B7505
#
GND
GND
REAR1_C_IN
REAR1_Y_IN
B7503
#
##
B7506 B7507
GND
REAR2_V_IN
REAR1_V_IN
##
B7515B7514
OPEN
CN7503
S1_DC
S2_DC
TO TERMINAL CN7103
#
SW12V
SYS_GND
SW5V
#
R7506
4.7k
OUT1_D[H]
C.BOX/SAT_CTL
#
R7507
10
1/2W
OSD_P.CTL[L]
B.BACK[H]
OUT1_L2[H]
R7514
#
#
Q7501
2SC1317/RS/
#
R7505
220
CH+12V
I2C_CLK2
I2c_DATA2
SCR[H]
P50_I/O
SECAM/MESECAM[H]
6.8k
#
L7501
100µ
#
C7503
470
/6.3
TO TERMINAL
CN7104
CN7504
A.IN2[L]
DEC_OUT[R]
DEC_OUT[L]
#
R7508
5.6k
A.IN2[R]
#
A.IN1[L]
LINE_OUT[R]
LINE_OUT[L]
Q7502
DTC144WU
RCA_A.OUT[L]
A.IN1[R]
GND
RCA_A.OUT[R]
C7505
#
C7506
#
C7507
#
#
C7508
#
C7509
#
C7510
#
C7511
#
C7512
#
C7513
#
C7514
#
R7512
5.6k
CN7505
GND
GND
AFC_IN
BIT_IN
BIT_OUT
TO TERMINAL
#
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
#
B7511
#
Q7503
DTC144WU
0
3 MAIN(CONNECTION)
DCBA
4-21 4-22
p10308001a_rev0
HGFE
Page 82

4.10 3D DIGITAL/2M SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
0 5 3D DIGITAL/2M
1k
R1447
R1448
R1449
5
LC1402
R1450
##
R1451
R1452
R1453
4
TO MAIN(CONNECTION)
CN501
CN1401
SLOW_PULSE
TRICK[H]
D.FF
V.REF
V.P_CTL
I2C_DATA
I2C_CLK
KILLER_DET
C_FROM_DIGI
GND
Y_FROM_DIGI
EE[L]
V/Y_TO_DIGI
SW5V[2]
C_TO_DIGI
GND
Fsc
R1454
3
LC1401
QQR0657-013
2
1k
1k
QQR0657-010
1k
470
470
##
1k
1k
C1459
C1460
C1461
C1462
C1464
C1465
C1467
C1466
C1468
##
C1469
CHCHCHCH
CH
CH
Q1419
DTC124T
C1463
33
/6.3
R1460
27k
47p
47p
47p
47p
47p
47p
47p
47p
100p
47p
R1446
1k
6.8k
R1441
R1442
6.8k
##
B1409
Q1414
Q1401
2SC1317(RS)
R1401
180
R1402
100
C1401 C1402
33
/16
D1401
RD4.3ESB2
MTZJ4.3B-T2
MCO0
VRBY
R1427
R1428
39k
0.1
C1473
33k
MCO1
VRTC
0.1
C1438
MCO2
VRBC
MCO3
CIN
VSS
IC1401
JCP8026
AVSS2
C1439
0.1
C1454
CWE
FSCIN
0.1
C1440
1
0.1
C1455
TS1
MON3
VSS25
VDD25
MON2
DRAMTE
MON1
0.1
C1430
MON0
##
D1404
##
D1403
1SS355
C1403
330
/6.3
L1401
10µ
0.01
1SS355
R1404
1.8k
##
R1405
2.2k
C1406
0.01
Q1422
##
DTC124T
C1410
4.7
/25
C1411
0.1
R1459
680
Q1420 Q1421
R1463
100
Q1418
Q1402
C1404
0.1
R1411
1.5k
##
R1412
2.2k
Q1406
##
##
R1461 R1462
1K 10K
CH
C1407
68p
CH
C1412
68p
C1416
/16
10
R1416
100k
Q1417
R1458
680
C1405
0.1
C1415
0.1
Q1408
R1418
470
C1421
33p
L1404
CH##CH
6.8µ
C1422
R1407
2.7k
Q1403
C1423
0.1
#
R1410
L1405
C1432
C1433
0.1
##
R1415
C1434
R1434
15k
VR1401
D/A LEVEL ADJ.
0.1
220
10µ
C1429
330
/6.3
#
R1408
#
Q1404
R1414
820
Q1407
C1417
0.1
CH
Q1410
##
R1425
R1426
68p
560
C1408
CH
33p
R1406
470
L1402
6.8µ
##
C1409
CH
39p
C1413
33p
CH
L1403
R1413
#
6.8µ
##
CH
C1414
39p
2SC4081(S)
R1417
100
R1421
#
C1420
VDD33
SLOWP
TRICK
DFFI
VR
VPLS
VSS
SDATA
SCLK
KILLER
VDD25
COMP
1
AVDD1
COUT
AVSS1
YOUT
IREF
AVDD2
VREF
CLAMP
YVIN
VRTY
##
B1416
0.1
C1435
0.1
C1436
C1424
0.01
0.1
C1472
0.1
C1437
R1435
R1436
22k
10k
VR1401
6.8k
VDD33
AVDD3
MCO4
PFSC
MCO5
TCPOUT
C1425
0.01
C1471
0.1
C1453
VSS
RSTW
MCO7
MCO6
VDD33
SWRCK
RSTR
MCI7
MCI6
MCI5
MCI4
CRE
MCI3
MCI2
MCI1
MCI0
MINTEST
TCLK
CKMODE
MTO
VDD25
RST
VDD33
VSS
VOUT
VDD33
AVSS3
PVREF
PIREF
PCOMP
RFSC
AVDD4
R1439
1
27k
47k
R1438
C1445
C1442
0.1
C1444
0.1
3.9k
0.1
0.1
R1437
C1443
C1441
##
R1430
2.2k
##
C1427
6p
CH
Q1412
L1406
0.1
R1429
1.5k
R1431
820
33µ
CHCH
C1428C1426
22p39p
Q1413
R1432
1.8k
1SS133
D1402
B1412
C1452
0.1
4.7
C1451
/25
C1450
0.1
C1449
0.1
C1448
/6.3
330
R1440
47k
C1447
0.1
C1446
/6.3
100
L1407
10µ
0Ø
R1433
51
#
CH
C1470
#
L1409
33p
1µ
R1455
680
p10276001a_rev1
1
## MARK ELEMENTS ARE NOT MOUNTED.
ALL SINGLE DIODE:1SS133 OR 1N4148.
ALL PNP TRANSISTOR:2SA1576A(QR) OR 2SB1218A(QR) OR 2PA1576(R)
ALL NPN TRANSISTOR:2SC4081(QRS) OR 2SD1819A(QRS) OR 2PC4081(R)
ALL NPN DIGITAL TRANSISTOR:DTC144WUA OR UN521E OR RN1309
DCBA
4-23 4-24
# DIFFERENCE TABLE
Q1404 R1408 R1410 R1421
PAL/MS
NTSC
Used
Not used
R1413
1.2k 390 390
330 33p 1u
470
330240OPEN
C1470 L1409
OPEN OPEN
HGFE
Page 83

4.11 TERMINAL SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
TERMINAL
06
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
C7104 C7108
0.01 0.01
L7101
5
TO CONNECTION
CN7501
CN7101
CHARA_DATA
GND
TERM_Y_OUT
GND
TERM_C_OUT
GND
TERM_D_Y
GND
TERM_D_C
GND
SWD_C
GND
SWD_Y
GND
TUNER_VIDEO
4.7µ
Q7102
R7102
1k
R7105
±0.5%
R7104
560
±0.5%
470
Q7103
R7107
10k
Q7104
R7108
820
R7109
1k
Q7105 Q7106
DTC144WU DTC144WU
D7101
DA204U
R7110
3.9k
R7111
4.7k
R7112
1.5k
R7113
270
2SC4226/4/
Q7107
2SC4226/4/
R7114
Q7108
1.5k
R7115
3.9k
R7116
5.6k
R7117
1.5k
R7118
270
2SC4226/4/
Q7109
2SC4226/4/
Q7110
R7119
1.5k
R7120
R7121
560
±0.5%
3.3k
Q7111
DTC144WU
R7169
6.8k
R7122
±0.5%
Q7113
470
Q7112
R7123
1k
C7101 C7102
0.01 47
L7102
4.7µ
/6.3
C7103
47
/16
R7136
75
4
IC7103
C7120
2.2
/50
CLAMP
C7140
0.1
REG_2.5V
R7126
270
C7121
27p
C7123
0.01
C7122
0.01
C7142 C7150
0.1 0.01
DRIVER
CLAMP
6dB 6dB
CLAMP CLAMP CLAMP
IC7104
BH7636S
C7143
0.1
C7141
C7144
OPEN
OPEN
L7112
L7111
OPEN
OPEN
R7143
100
V
Y
6dB
12dB6dB
Y/C_MIC-6dB
4dB
C
R7145
100
BUFFER
DRIVER
BUFFER
C7147
C7145 C7148
0.1 0.1
0.1
C7146
33p
L7113
1µ
R7144 R7146
100 100
C7149
L7114
OPEN
OPEN
R7127
560
±0.5%
R7167
4.7k
C7124 C7168
0.01 47
Q7115
R7128
470
±0.5%
C7151
10
/16
R7168
270
BUFFER
Q7114
BUFFER
BUFFER
CURRENT
LIMITER
EXP1
C7152 C7153
/16 /16
10 10
R7147
100
CLK
I2C-BUS
CONTROL
R7148
R7129
1k
DATA
EXP2
100
G
R7130 Q7116
/6.3
C7125 C7126
47 0.01
/16
Q7122
C7154
L7115
0.01
4.7µ
0Ω
C7127
33p
L7104
SHORT
Q7118
R7149 R7151
6.8k 560
R7131
15k
R7132
10k
Q7123 Q7124
R7150 R7153
1k 4.7k
Q7119
Q7120
R7152
2.7k
R7154
0Ω
R7133
330
1/2W
C7129
100
/16
R7134
68
Q7117
DTC114EU ±0.5%
R7170
4.7k
R7171
33k
R7172
10k
C7155
R7155
47
3.3k
V.GNDY/V.IN
Y/V.OUT
GND
R7135
75
±0.5%
D7103
OPEN
R7158
C7169
0.01
/6.3
1k
R7157
75
Y.IN V.GND
GND GND GND
V.OUT V.GND
R7156
75
D7104
OPEN
L7103
4.7µ
C7119C7118
0.01100
/6.3
MM1024AF
TO MAIN (CONNECTION)
CN7502
CN7102
REAR1_C_IN
GND
REAR1_V_IN
GND
REAR2_V_IN
3
TO MAIN (CONNECTION)
CN7503
CN7103
SYS_GND
SW12V
SW5V
C.BOX/SAT_CTL
OUT1_D[H]
OUT1_L2[H]
B.BACK[H]
OSD_P.CTL[L]
SECAM/MESECAM[H]
P50_I/O
SCR[H]
I2C_DATA2
I2C_CLK2
CH+12V
2
L7110
SHORT
C7139C7138
100100
/16/16
H
6dB
H
Vcc GND
IC7101
MM1224XF
C7105
C7106
0.01
0.1
C7107
0.01
L7105
0.22µ
J7102
AV1
GND
V.GND
Q7121
L7116
1µ
J7104
AV2/DECODER
GND
RAPIO SW
C/R G B GND
R7159
75
±0.5%
R7124
75
R7137
0Ω
FUNC.SWRAPIO SW
SCRAMBLE
(H)
C7109 C7115
10 1
/16 /50
H
IC7102
MM1228XF
C7112C7111C7110
10100p
C7130
680p
C7156
(L)
GNDBGNDGGNDC/R
680p
(L)
C7132
680p
A.INA.IN A.GND
(R)
A.OUT A.OUT
(L) (R)
C7133C7131
0.0010.001
C7158
680p
A.INA.IN A.GND
(R)
A.OUT A.OUT
(L) (R)
C7134
C7136
OPEN OPEN
L7106
4.7µ
L7107
4.7µ
L7108
4.7µ
L7109
4.7µ
C7137C7135
OPENOPEN
C7160
C7162
OPEN OPEN
L7117
4.7µ
L7118
4.7µ
L7119
4.7µ
L7120
4.7µ
C7163C7161C7159C7157
0.0010.001
OPENOPEN
H
6dB
Vcc GND
C7113
0.01
/16OPEN
R7138
100
R7139
100
R7140
100
R7141
100
R7160
100
R7161
100
R7162
100
R7163
100
C7114
100p
R7125
±0.5%
C7116
330
/6.3
75
C7117
330
/6.3
R7142
100
L7121
R7164
4.7µ
100
R7165
100
L7123
SHORT
C7164
OPEN
C7165
OPEN
L7122
C7166
0.001
4.7µ
C7167
0.001
J7101
S-OUT
34
12
J7103
SAT_CTL
RCA_A.OUT[R]
J7105J7105
RCA_A.OUT[L]
TO MAIN (CONNECTION)
CN7504
CN7104
GND
RCA_A.OUT[R]
RCA_A.OUT[L]
A.IN1[R]
A.IN1[L]
LINE_OUT[R]
LINE_OUT[L]
A.IN2[R]
A.IN2[L]
DEC_OUT[R]
DEC_OUT[L]
YC
p10293001a_rev0
1
2SC4081/QRS/.
2SA1576A/QR/.
DCBA
4-264-25
LAST NO VACANT NO
7101~
R
7172
7101,
C
L
D
Q
IC
J
7103, 7106, 7166
7169
7128
7123
7104
7102
7124
7101
7104
7105
HGFE
Page 84

4.12 DEMODULATOR SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
5
4
TO MAIN (TUNER)
CN6701
CN6701
NC
I2C_DATA
I2C_CLK
3
TU_A_MUTE
DEMOD_[R]
DEMOD_[L]
SW5V
GND
COMP
SIF
2
1 4 DEMOD
L6701
C6701
0.01
R6702
6.8k
R6701
3.9k
1µ
Q6701
2SC3936/BC
R6703
47
C6702
0.0022
L6702
3.3µ
#
C6705
0.001
R6705
270
R6704
# DIFFERENCE TABLE
SYMBOL
R6713R6715
22k22k
C6714C6716 C6715C6717
DACM_L
R6719
R6712R6714
DACM_R
10k
0.00680.0068 2.22.2
1k1k
VREF2
D_CTR_OUT0
#
C6719
R6720
10
5.6k
/16
R6721
5.6k
#
C6706
0.01
CAPL_M
AHVSS
AGNDC
NC
NC
NC
SC1_IN_L
SC1_IN_R
VREFTOP
MONO_IN
AVSS
C6720
/16
10
0.01
#
C6722
/16
10
#
C6703
C6704
0.01
#
#
2.2600
R6718
C6724
A GND
D GND
C6723
0.01
/50
#
K6707
1k
#
R6706
150
K6701
600
R6716C6718
470.01
K6706
600
AHVSUP
AVSUP
K6702
#
R6707
NC
ANA_IN1+
600
SC1_OUT_L
ANA_IN-
CH CHCH
C6707
47p
VREF1
SC1_OUT_R
MSP34VCDT
TESTEN
XTAL_IN
C6708
8p
IC6701
TP
XTAL_OUTTPD_CTR_OUT1
X6701
18.432MHz
C6709
1p
TP
ADR_SEL
/50/50
TP
RESETQ
DVSUP
I2C_DA
I2C_CL
STANDBYQ
DVSS
R6711
680k
C6713
0.22
TP
TP
TP
TP
TP
TP
K6705
K6704
600
K6703
600
D6701
1SS133
1N4148M
#
R6710C6721
600
#
C6712
0.01
#
C6711
100p
CH
R6709
100
R6708
100
CH
#
C6710
100p
PRE AMP
MONO IN
ANALOG
Vcc
I2C_bus
DIGITAL
Vcc
DAC Vcc C6718
R6706
C6705
C6703
C6724
K6707
R6718
R6707
C6706
C6710
C6711
R6710
C6712
C6722
STEP UP EU/EK
Used
Not used
FRANCE MS
22 47 47 47
10 12 12 12
BASIC
EU/EK
3SYSTEM 4SYSTEM
180p 220p
ARC
p20162001a_rev2
1
DCBA
4-27 4-28
HGFE
Page 85

The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
4.13 S-SUB SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
TO MAIN (CONNECTION)
CN502
5
4
3
CN511
EE[L]
I2C_DATA
I2C_CLK
SW5V
SW5V
C_TO_DIGI
Y/V_TO_DIGI
Y_FROM_DIGI
C_FROM_DIGI
PB_COLOR
V.PULSE
SECAM_PB_COLOR
MAIM_ALC_DET
Y_TO_SUB
P.MUTE[L]
WIDE_DET
FRONT_Y_IN
FRONT_C_IN
FRONT_V_IN
REAR2_V_IN
V_TO_OSD
CHARA_DATA
Y_TO_AV
V_FROM_AV
REC_COLOR
Fsc
GND
GND
GND
GND
B503
0Ø
R516
0Ø
R517
L501
10µ
#
R527 C535
C512
0.01
/25
0Ø
R501
OPEN
Pre LPF2
C514
0.01
CL2
Pre LPF1
Pre LPF1
A7
OPEN
OPEN
C536
C537
CR
CLK DATA
ADJ
IIC LOGIC
ATT9
DIGI/PB
EXT PB Y
EXT PB Y
220
C509
/6.3
10
/16
0.01
C511
C510
GND1
BAND GAP
CONV
DIGI/PB
PB
A9
REC
A8
DIGI
BF2
CONV
DIGI
REC REC
PB*CONV
VCC1
C3
C2
S1/S2 DET
CONV
VCA
REC
REC
PB*D15
C.K.
V4
V3
C572 C573C570 C571
100p 100p100p 100p
Pre LPF2
C515
0.01
C566
#
0.01
R526
Q501
OPEN
R525
1.2M
C538
OPENOPEN
C516
C517
C518
C519
C520
0.01
0.1
0.1
2.2
/50
4.7
0Ø
R518B501
OPEN
IC501
JCP8018
A6
CL1 ATT7
REC
PB
AGC
GCL
EXT PB C
EXT PB C
COMP IN
Y/C IN
PB
V5
V3/V4
AGC DET
S.SEP
ATT6
/25
ATT1 ATT2 ATT3 ATT4 ATT5
R531 R534 R535
100 100 100
C569
C568
100p
100p
Y1
R533R532
100100
REC
C1
Y3
Y2
3.3K 0.01
BF1
CONV
PB*CONV
N.C.
PB
+-
BB
C508C513
0.474.7
/50
EE/PB SP/EP
PB
N/S-LPF
REC
PB
TRAP
A4
A5
BB
BB
BB
R536
100
CL3
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
1 5 S-SUB
C564
#
0.01
N
L505
OPEN
OPEN
REC
GND2
C575
VHS
S-VHS
PB
EQ
V MUTEV FBC
C MUTE
Y FBC
Y MUTE
REC
A12
A13
A10
A11
VCC2
A14
ATT8 CL6
D16
L503
10µ
C521
4.7
PB
CL4
#
1
CL5
L502
R503
C503
C502
A1
D7&D8
BIAS
A2
C501
2.2
A3
C507
220
/6.3
C506
0.1
/25
C505
4.7
/25
/50
C563
#
0.01
C504
OPEN
0.01
220
2.2
/50
4.7
/25
C522C562
C523
/50
L504
10µ
C524
R507
R509
300p
CH
C525
300p
CH
1.2k
1.6k
270p
±2
CH
3.3k
R504
3.9k
IC502
VC2076DP
SP
SP
R
2.2
/50
/50
2.2
PP
NON LINEAR
PROCESS
R505
R510
1k
R506
390
R508
150
±0.5
C526
C527
100p
180p
CH CH
C528
R
C534
C533
C529
R
SP SP
470
R511
±0.5
3.3k
0.01
470
/6.3
R515
3.3k
±0.5
R514
C530
R513
±2
82p
CH
R512
1k
±0.5
220p
±2
CH
1.5k
±0.5
±0.5
C531
300p
±2
CH
C532
300p
±2
CH
±2
±2
TO MAIN (P/S CONV)
#
CN513
SW5V
SW5V
TO_PS_C
GND
FROM_PS_C
GND
TO_PS_Y
GND
FROM_PS_Y
OPEM
C553
C551 C554 C557 C560 C561
11111
/50 /50 /50 /50 /50
0.01
10K
## ## ##
R522
TO MAIN (CONNECTION)
CN7506
2
BIAS_FOR_C_OUT
CN512
REAR1_Y_IN
GND
REAR1_C_IN
GND
REAR2_Y_IN
GND
REAR2_C_IN
GND
Y_OUT
GND
C_OUT
GND
V_FROM_OSD
C552
0.01
C556
0.01
C555
0.01
10K
R523
C559
0.01
C558
0.01
10K
R524
C576
OPEN
p20168001a_rev0
Used
DIFFERENCE TABLE
1
#
CN513
C562 C563
C564
C566
Not used
R527
MS
OTHERS
## Marked elements may differ depending on the model.
Be sure to check the Parts List.
DCBA
4-29 4-30
HGFE
Page 86

The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
0.022
0.022
0.022
C5531
C5532
22
470K
2K
0Ω
150K
0.1
0.1
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
TO DV CAPSTAN MOTOR
CN5504
QGF0501F1-18X
COIL_V
COIL_V
COIL_W
COIL_W
COIL_U
COIL_U
MR_VCC
HG_IN+
R5510
1K
R5511
0.1
/6.3
33k
R5548
270K
OPEN
C5537
/6.3
LC5503
PELN1148-223X
OPEN
C5546C5545
R5513
C5540
0.01
0.1
R5535
OPEN
R5536
82k
R5546
R5537
39k
Q5501
DTA114EUA-X
10K
R5544R5543
33k33K
R5545
33K
C5541
0.1
R5512
C5534
L5501
0Ω
1K
D5504
DAP222-X
2.7K
C5521
1
C5552
10
LC5501
PELN1148-223X
C5539
0.01
C5535
1022
PELN1148-223X
FIN
VCC
RIN
VREF
/16
LC5502
VM
OUT 2
OUT 1
GND
BA6417F-X
C5551
0.01
IC5502
C5536
/16/16
10
LC5505
PELN1148-223X
C5547
0.1
D5503
DAP222-X
HG_V+
HG_V-
HG_U+
HG_IN-
HG_W-
HG_W+
HG_U-
FG1
MR_GND
FG2
TO REGULATOR
CN5324
CN5501
QGA2001F2-05V
MDA_4.5V
FF/REW_6V
MDA_6V
AL_5V[DV]
MOTOR_GND
TO
DV ENCODER
CN5505
QGA1201C2-04X
R.ENC3
R.ENC2
R.ENC1
GND
TO DV MAIN (DV MSD)
CN1501
CN5506
QGF0503F2-20X
CAM_SW3
CAM_SW2
CAM_SW1
GND
HOUSING_SW
HOUSING_OUT
HOUSING_IN
CAP_REF
DRUM_REF
MOTOR_GND
NC
MDA_IN
MDA_CLK
MDA_CS
CAP_BRK
LD_ON
CAP_FG
DRUM_FG
DRUM_PG
GND
TO HOUSING MOTOR
CN5507
QGA1201C2-04X
GND
HOUSING_SW
HOUSING_M
HOUSING_M
TO PRE/REC
REG_5V
4.14 MDA SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
1 6 P/R MDA (MDA)
10K
10K
10K
D1
D2
L.REV
C.UNCC.RNF
R5547
1.8
R5509
0.68
1/2W
C5517 C5516
OPEN
R5520
R5521
D0
DOUT
0.1 0.1
DIN
C.V
R5522
CS
C.FGSOUT
C.VM
R5523
NC
CLK
C.BRK
C.RCC
C.EC
C.ECR
C.PCI
C.PCV
C.VS
Vcc
C.FG+
C.FG-
C.FGOUT
C.HU+
C.HU-
C.HV+
C.HV-
C.HW+
C.HW-
C.WH
C.VH
C.W
C.UH
Q5502
2SB1302/T/-X
C5515
0.1
Q5503
2SB1302/T/-X
R5515
R5516
R5530
R5514
C5523
C5522
C5520
C5519
C5518
Q5504
2SB1302/T/-X
20K
39K
0.022
47K
5
C5530
OPEN
T
R5529
1M
C5529
OPEN
C5502
/16
10
C5503
10
/10
T
C5505
0.1
C5512
4
TO
LOADING MOTOR
CN5502
QGA1201C2-02X
LOAD_M
LOAD_M
C5501
0.01
C5513
C5511
C5510
D5502
DAP222-X
R5534
0Ω
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
510
510
R5526
R5527
R5501
R5503
4.7K
510
R5528
680
510
R5525
R5504
0Ω
R5533
C5504
OPEN
R5502
120K
C5506
0.0015
100k
C5507
C5508
C5509
R5505
TEST2
D.PGSOUT
D.PGOUT
D.PG -
D.FGPG+
D.FG -
D.FGOUT
D.FGSOUT
GND1
D.UI N
D.VIN
D.WI N
0.01
0.01
0.01
D.COM
DCC3
DCC2
DCC1
22k
DCC
D.UH
D.VH
D.WH
R5506
0.22
1/4W
3
TO DV DRUM MOTOR
CN5503
QGF0504C1-11X
FG_OUT
PG_OUT
COIL_U
COIL_U
COIL_V
COIL_V
COIL_W
COIL_W
COIL_COMMON
PG/FG_COMMON
MOTOR_GND
R5551
R5552
R5553
R5554
R5555
R5556
R5557
R5558
R5559
R5560
R5561
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
C5544
0.1
QA5501
BA6254FS-X
2
C5548
0.22
C5549
0.22
C5550
0.22
0.1
C5528
TEST1
GND1
0.047
C5527
START
DETECT
D.U
D.VM
R5519
D.OSC
D.V
C5526
0.1
C5525
D.PCV
D.RNF
C5524
D.PCI
L.REF
R5518
OPEN
D.ECR
D.W
R5517
0Ω
R5531
NC
GND2
D.EC
IC5501
BA6865KV
L.FWD
GND2
L.GNDNCUNREG
C5514
/16
10
2SC4097/QR/-X
D4
R5549
1k
R5550
10k
D3
Q5505
1
DCBA
4-31 4-32
p20172001a_rev0
HGFE
Page 87

4.15 PRE/REC SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
1
6
P/R MDA (PRE/REC)
L5005
NQL144K-100X
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
10µ
HID3
VCC3
22
C5037
/6.3
C5035
C5036
0.1
VDD2.8
MONI_CHG
0.1
DUMP
HEAD_VCC
PBIN_R
REC_R
22k
R5035
HEAD_GND
HEAD_GND
HEAD_GND
HEAD_GND
DX3
DY3
HEAD_GND
DX2
DY2
HEAD_GND
DX1
DY1
HEAD_GND
HEAD_GND
X3
Y3
R5026
240
0Ω
0Ω
TO DV VIDEO HEAD
CN5001
QGF0501F1-10X
GND
2S
2F
GND
1S
1F
GND
(GND)
(GND)
GND
X2
Y2
R5023
240
R5021
240
X1
Y1
R5018
240
R5020
R5019
C5047
C5048
TP5009
REC_CLK
C5049
C5054
OPEN
TP5007
REC_DATA
0.1
C5050
0.1
C5055
0.1
C5062
0.1
/6.3
22
PB_OUT
AGC_IN
AGC_CTL
AGC_DET
PB_GND
AGC_OUT
AGC_BUFF_IN
REG_1.1V
AGC_BUFF_OUT
VRB_AGC
MAIN_GND
ATF_GAIN
VCA_OUT
ATF_IN
VRB_ATF
ATF_OUT
C5003
0.1
R5058
10K
C5051
C5052
C5053
0.1
1000p
C5056
C5058
C5060
C5063
0.1
0.1
4.7
0.1
4.7
5
R5056
OPEN
R5057
22K
TP5001
R5101
R5102
R5111
R5112
R5114
R5115
R5117
R5118
R5119
R5121
PB_ENV
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
L5004
10µ
NQL144K-100X
C5034
0.1
R5006
OPEN
IC5002
TC7SH00FU-X
TP5011
AGC_OUT
R5059 R5060
OPEN OPEN
TP5010
ATF_OUT
4
3
TO DV MAIN
CN2001
CN5002
QGF0503F2-26X
PB_ENV
REC_CTL
REC_H
PBH
HID1
HID3
GND
DUMP_CTL
AGC_GAIN
VREF_1.1
AGC_OUT
VRB_AGC
ATF_GAIN
VRB_ATF
ATF_IN
GND
REF_CLK
REC_CLK
REC_DATA
RECCADJ
MONI_CHG
GND
D_REG_3V
REG_5V
A_REG_3V
A_REG_2.5V
0.047
PB_MONI
ATF_GNDTCPB_GND
C5046
0.047
DCS_C3
DCS_C2
MUSIN_EVR
C5045
0.047
DCS_C1
C5042
C5044
OPEN
R_CTL
VCC5
OPEN
REC_H
C5041
OPEN
IC5001
JCY0132
REF_CLK
ADREF
REC_DATA
C5040
C5039
OPEN OPEN
HID1
PB_H
REC_GND
REC_CLK
0.1
HID2
REC_GAIN
C5038
2
TO MDA
REG_5V
L5001
NQL144K-100X
C5064
0.1
R5003
0Ω
C5005
R5002
R5001
OPEN
OPEN
10µ
/6.3
220.1
C5002
0.1
C5004
0.022
0.047
R5007
R5004
470
100k
L5002
NQL144K-100X
C5007
0.1
0.1
10µ
C5008C5066C5065 C5006
C5010
0.1
L5003
NQL144K-100X
0.1
10µ
C5009
/6.3 /6.3
22
C5011
1k
R5014
C5012
22
0.1
p20171001a_rev0
1
DCBA
4-33 4-34
HGFE
Page 88

4.16 ON SCREEN SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
1 7 ON SCREEN
5
B856
OPEN
C855
OPEN
0Ø
B851
CDLR
SEO_OUT
(BEP_C)
OSC_IN
L858
22µ
C867 C868
33p 33p
R857
0Ø
C856
L852
1
C857
0Ø
OPEN
B852
SYN_IN
(SYN_IN)
OSC_OUT
22µ
56p
B853
VDD1
(VDD1)
SYNC_DET
CS1
R875
OPEN
B861
0Ø
C869 C870 C871
OPEN
B854
(CVCR)
OPEN
C858
0.47
CV_IN
SCLK
100p 100p
C859
OPEN
(13)(14)(15(16)(17)(18)(19)(20)(21)(22)(23)(24)
VSS2
CVOUT
SD ATA
VDD2NCNC
R876
5.1k
C872 R877
0.1 1.8k
NC
L853
10µ330
IC851
LC74775-9750
NC
NC
NC
C873
4.7
/25
C874
0.22
5.6k
R878
0.22
C875
B862
0Ø
/6.3
220
C876
R889
4.7k
C877 C878
47 0.01
/16
B863
OPEN
R856
OPEN
C851
C852 C853 R853
0.22 1 10k
R852
OPEN
R890
330
C864
/6.3
RST
VDD1
CPDT
VSS1
XTAL_IN
R891
1k
L857R873
C865
33µ0Ø
10p
C866
OPENOPEN
L851
D852
D853
D854
1µ
R851
OPEN
D851
SHORT
10k
10k
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
R870
R869
R868
1.5k
100
100
Q856
OPEN
B860
0Ø
R871
DTA144WU
R872
Q861
4
TO MAIN (VIDEO I/O SW)
CN704
EDS_CS/
3
OSD_CS
S.DATA_FRSYS
EDS[H]/
I2C_CLK2
I2C_DATA2
SWD_S.DATA
CHARA_DATA
P.MUTE[L]
V_FROM_OSD
SYNC_DET[H]
V_TO_OSD
D_P.MUTE[H]
D_Y/V_IN
CN851
2Fsc
S.CLK
OSD_IN
GND
SW5V
OSD_C
OSD_Y
SW12V
(CDLR)
MUTE
R854 R855
OPEN OPEN
CS2
SEP_IN
(BEP_IN)
CHABLK
C854
OPEN
(SEP_OUT)
LN21
R874
0Ø
C860
0.01
R858
OPEN
Q851
OPEN
R888
4.7k
R880
0Ø
B855
0Ø
Q852
OPEN
L854 R860
SHORT
0Ø 1k
R859
OPEN
C884
0.1
R879
3.3k
R881
470
Q857
B857
OPEN
B858
OPEN
Q853
C885
0.1
R883 R884
8.2k 2.7k
Q858
R882
180k
C879
0.1
C880
OPEN
R885
15k
C886
0.1
B859
OPEN
R863
1k
R861
R862
NC
NC
1k
IC852
MM1115XF
Q859
C881
470p
L855
C862
C861 L856
15p 82µ
27µ
C863
47p
100p
R886
680
C882
0.022
T851
PELN0806
Q854
L859
4.7µ
D855
DA204U
R864
1.8k
R865
680
Q855
R866
680 1.8k
Q860
DTC114EU
C883
2.2
/50
R867
R887
10k
2
p20192001a_rev0
1
DCBA
4-35 4-36
2SC4081/QRS/.
2SA1576A/QR/.
HGFE
Page 89

4.17 DISPLAY, EJECT SW, LED/SW, KACK AND JOG SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS
D7017
OPEN
CN7002
CN7003
(CONNECTION)
MAIN
TO
##
C7022
#
0.01
OPEN
GND
GND
TO MAIN (CONNECTION)
D7061
##
D7062
##
#
CN7507
Y1_IN
GND
C1_IN
GND
C7061 R7063
0.01 75
V1_IN
GND
R7061
75
R7062
R.PAUSE
0Ω
FRONT_A[L]
FRONT_A[R]
GND
L7064
SHORT
J2/JOG_A
J1/JOG_B
D7066
JSB/SHUTTLE_B
GND/NC
SHUTTLE[L]/NC
D7065
D7064
JSA/SHUTTLE_A
#
FW7007
C7063
OPEN
C7065
OPEN
D7063
L7061
L7062
#
FW7008
10
10
#
8 5 JOG
PEMC0786-02
B7094
#
C7062
680p
C7064
680p
#
L7063
SHORT
UN7091
####
B7092B7093
JOG/SHUTTLE
UNIT
J7001
S_IN
J7005
R.PAUSE
J7004
L_IN
J7003
R_IN
J7002
V_IN
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
DISPLAY28
DI7001
DI7001
QLF0031
QLF0033
F+
5
4
F+
NP
NC
P1
P2
P3
P4
P5
P6
P7
P8
P9
P10
P11
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
P12
P13
P14
P15
P16
1G
2G
3G
4G
5G
6G
NC
NP
F-
F-
D7002
RD9.1ES/B2/
MTZJ9.1B
G5
G4
G3
G2
G1
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
S6
R7013
10k
G6
G7
S7S8S9
LED3
LED2
C7020
##
S11
S10
AN0
AN1
AN2
AN3
AN4
AN5
RESET
Xin
VSS
C7021
##
Xout
VDD
S16
VDD
S15
S14
S13
S12
CS
Sin
VEE
VEE
Sout
SCLK
LED1
33p
C7006
##
IC7001
M35500BGP
D7006
D7005
D7004
R7001
R7002
R7003
R7004
33p
33p
C7004
C7005
##
##
C7010
0.1
C7013
C7009
15p
######
##
C7008
0.022
C7014
D7011
D7010
D7009
470
470
470
470
33p
C7003
/50
C7002
C7001
10
0.001
##
10k
10k
10k
R7040
R7020
R7030
C7016
C7017
C7018
C7015
##
##
##
10k
R7006
15k
R7010
###
VHS-REC
VHS-PLAY
VHS
10k
10k
R7007
R7008
15k
15k
R7011
R7012
R7059
R7058
R7057
330
330
330
TO MAIN (SYSCON)
CN3011
CN7001
RCU_5V
AL5V
S_CLK
S_DATA_TOSYS
S_DATA_FRSYS
STB
RC_IN
GND[C]
BU_GND
#
Q7001
DTC114E
OPEN
DC[-]
DC[+]
-28V
LED1
LED2
LED3
LED4
LED5
LED6
#
R7060
10K
9 0 LED#
#
#
FW7001
FW7002
#
HDR-LED
SELU5E20C
#
R7056
100
#
D7019
10kΩ
4 7 LED/SW
D7018
#
RECLINK
D7012
#
FW7003
#
FW7004
DV/HDR
D7001
##
11ES2
R7051
L7001
SHORT
D7013
D7014
D7015
#
C7007C7019
/6.3
470.022
#
D7016
330
D/H
PLAY
R7052
330
D/H
REC
R7053
330
DV
VHS
R7054
330
VHS
DV
#
R7055
330
0Ω
R7014
0Ω
D7003
R7015
C7012
C7011
10
##
##
/6.3
VCC
GND
V.OUT
IC7002
PNA4652M00XB
R7064
75
S7017
TP7001
TEST
39k
TPGND
#
S7010
DV/HDR RECLINK
S7028
36JACK
2 7 EJECT SW
FW7005
FW7006
VHS
EJECT
S7011
3
S7001
POWER
R7023
R7024 R7025 R7026
2.2k
2.7k 4.7k 6.8k 39k1.8k1.2k
#
S7002 S7007
CH+
PAUSE STOP CH- REC PLAY
S7012S7005 S7014
DV
S-VHS
EJECT
ET
R7027 R7038
R7028R7022R7021
15k
S7013
VHS
S7004 S7015
S7003
R7041
1.2k
S7022
S7021
DV VHS DUB/OK
VHS DV
/LEFT
/RIGHT
R7033
R7034
2.2k 2.7k
S7006
RAE IN.OUT START INSERT A.DUB
/REW
#####
R7042
R7043 R7044 R7045 R7046 R7047
1.8k
2.2k 2.7k 4.7k 6.8k 15k
S7023
R7035
4.7k
S7018
/A.DUB /FF /MENU /NAVI
R7037R7032R7031
R7036
15k1.8k1.2k
6.8k
S7016
S7019
##
S7026 S7027
UP DOWN
2
p10309001a_rev1
Used
Not used
# DIFFERENCE TABLE
HR-DVS2
EU/EK/MS
1
/DOM/U
HR-PVS100
8
UN7091
B7094
FW7007
FW7008
5
JOG
X
X
CN70029D7017
FW7001
FW7002
R7060 S7028 R7046
Q7001
1-16
1-10
0
LED
D7018 R7043
S7026 R7044
S7027 R7045
R7047
X
S7014
D7015
D7016
R7055
FW7003
FW7004
1-4
1-6
X
##:NOT USED
1N4148M OR 1SS133
DCBA
4-37 4-38
HGFE
Page 90

4.18 DV SYSTEM CONTROL SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
TO
DV MSD, DV MAIN,
AUDIO AD/DA,
DV V OUT
AL_5V
REG_5V
A_REG_5V
AL_5V[–]
TO REGULATOR
CN5323
CN1001
QGA2001F2-10V
AL_5V[-]
AL_5V
GND
AL_3V
AL_3V
GND
AL_3V
MDA_CTL
TO DV MAIN
FF REW_H
TO
DV MAIN, AUDIO AD/DA
A_REG_3V
TO DV MAIN
TO
DV MAIN
REG_1.8V
TO
DV DSP
REG_1.80V
AL_3V
AL_3V
GND
GND
5
4
TO MAIN (SYSCON)
CN3014
CN1002
QGF1016F2-06W
HOUSING_SW
DIAL_AUTO
DIAL_OFF
DIAL_PLAY
TXD
RXD
3
2
TO DV DSP
DSP_RST
TO
DV DSP
BUS15
BUS14
BUS13
BUS12
BUS11
BUS10
TO
DV DSP
RWSEL
TO
DV I/O
CRE
CHWE
CLWE
CALE
BUS9
BUS8
BUS7
BUS6
BUS5
BUS4
BUS3
BUS2
BUS1
BUS0
MFLD
OSD_VD
CLR
MVD
OMT
L1011
L1012
L1013
L1015
K1012
NQR0129-002X
C1068
0.1
C1070
22
/6.3
R1100
0Ω
TXD RXD
TP1001 TP1002
2SC4617/RS/-X
R1036
OPEN
10µ
39µ
39µ
39µ
C1055
100
Q1002
0
/6.3
NQL144K-100X
NQL17CM-390X
NQL17CM-390X
NQL17CM-390X
C1056
0.1
NCOUT
GND
Q1001
2SC4617/RS/-X
R1064
R1065
10K
IN CONT
22
4.7K
C1069
/6.3
DV MAIN (DV SYSCON)5
LC1003
LC1005
IC1009
MM1426CN-W
R1062
4.7K
R1063
10K
LC1002
PELN1148-223X
PELN1148-223X
C1057
100
/6.3
C1067
0.1
4.7K
R1061
D1002
SB007W03Q-X
PELN1148-223X
C1058
0.1
NCOUT
GND
RA1006
100K
IN CONT
IC1010
MM1426CN-W
RA1005
100K
NRZ0040-104XNRZ0040-104X
IC1002
TC7W04FU-X
C1063
100 0.1
/6.3
C1064
Q1011
2SB1302/ST/-X
R1092
DTC144EE-X
C1053
/6.3
22
R1091
10K
1k
Q1012
C1021
0.1
R1051
R1052
C1054
0.1
2SB1302/ST/-X
Q1013
R1093
10K
R1094
270
0.1
C1062
Q1014
DTC144EE-X
NRZ0040-102X
NRZ0040-102X
22k
33k
0.1
C1061
C1010
RA1003
1K
RA1004
1K
R1045
R1046
R1047
R1048
C1011
0.1
D1001
SB007W03Q-X
R1049
R1050
2SB1302/ST/-X
Q1015
0.1
R1095
10K
R1096
270
Q1016
DTC144EE-X
1K
1K
1K
1K
10K
0Ω
1K
R1053
C1051
/6.3
22
CALE
VDD
VSS
DIAL_DSCPB
DIAL_ST
DIAL_MANU
DIAL_AUTO
DIAL_OFF
DIAL_PLAY
CAS_SW
HOUSING_SW
MONITOR_SW
VF_SW
DSP_RST_1
CLR
RWSEL
F/Z_RST
CDS_RST
CDS_STBY
V_MUTE
JLIP_ENABLE
VDD
IRIS_O/C
M32_WKUP
F_LED
SMUTE
A_P_CTL
L_MUTE
MMC_L
DSC_RFLS
A_MUTE
R1002
R1097
OPEN
C1052
0.1
1K
R1043
CRE
CLWE
CHWE
RTC_CS
DAC_CS
STO_OPEN
BATT_SW
BUS0
BUS1
BUS2
BUS3
M32_STS
1K
0Ω0Ω0Ω0Ω0Ω0Ω0Ω
#########
R1003
R1004
R1005
R1006
Q1017
0.1
C1008
SRV_RST
WB_IR_DET
2SB1302/ST/-X
R1098
10K
R1099
1k
DTC144EE-X
Q1018
1K
R1041
AVDD
VRefH
MONI_RVS
L_OPEN
L_CLOSE
NRZ0040-102X
TG_CS
AVH_DET
CDS/AGC_CS
K1011
IC1005
NQR0129-002X
S-80823ANNP-W
RA1002
1K
NRZ0040-102X
OP_SERMO
IC1001
MN1021617FN
PWR_CTL
0Ω
R1012
BUS7
0Ω0Ω0Ω
R1013
BUS8
#
R1014
BUS9
BUS10
###
R1015
SRV_RDY
BUS11
BUS12
BUS13
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
###
R1018
R1019
R1020
VDD
C1001
VSS
BUS4
BUS5
BUS6
R1009
R1010
R1011
0.1
VDD
NC VSS
RA1001
STRB_AD
BUS14
0Ω
R1021
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
R1083
10k
2.2K
IC1007
25LC160-I/SN-X
L1018
39µ
10K
R1038
CS
SO
WP
VSS
NQL17CM-390X
10K
R1037
HOLD
22
C1059
C1071
R1085
100K
IC1008
VCC
SCK
SI
C1045
0.1
C1060
0.1
/6.3
#
R1073
47K
#
NQL024J-390X
R1074
1K
#
OPEN
TC7W08F-X
PWR_CTL
#
R1075
0Ω
SBT2
#
R1076
0Ω
#
L1001
39µ
#
C1073C1072
C1075
OPEN
33P0.1
#
C1074
18P
R1079
OPEN
HD
CS
VD
DATA
PCL
VDD
CKO
OSCO
VC2
OSCI
BLK2
TEST
VC1
VSS BLK1
#
IC1003
UPD6461GS-921-X(DOM)
UPD6461GS-946-X(EU/EK/US)
R1077
1K
F_PTR_AD
BUS15
0Ω
R1022
OUT
HALL_AD
Z_PTR_AD
MODE0
MODE1
NQR0129-002X
C1041
BATT_CHK
MODE2
0.1
VRefL
SRV_CS
K1001
C1002
R1081
C1007
0.1
0Ω
0.1
AVSS
CLK_4MHz
R1082
D1003
VDD
VSS
M32_CLK
M32_DT_OUT
F/Z_CS
VDD
OPEN
OPEN
RESERVE4
AFZ_DATA
M32_DT_IN
S_DT_OUT
SDRAM_PWR
STOROBE_CHG
TIMER_OUTNR_DET
EEPROM_CS
ODD_EVEN
MENU_P_A
JLIP_INT
GATE_PULSE
OSCI
OSCO
0Ω
R1026
R1025
C1003
NAX0294-001X
AFZ_CLK
S_CLK
S_DT_IN
MVD0
DSC_PS
SCR_LR
SCR_UD
M32_CS
RTC_INT
VDIN
STO_OFF
FLD_FMC
VSS
X1001
24MHz
RS5C314-X
CLKCSXin
SIO
VSS
Xout
INTR
R1035
R1033
R1084
100K
C1042
X1002
32KHz
C1043
C1044
0.1
12P
12P
VDD
NAX0005-001X
1K
SBT
SBD
0Ω
C1006
0.1
IC1006
TXD
RXD
VDD
FRP
R1032
OPEN
C1004
TL1038
R1031
R1030
1K
1K
1K
R1029
0Ω
R1027
100K
R1028
0Ω
OMT
MVD
RST
OPEN
TO
DV I/O
DAC_CS
AFZ_DATA
AFZ_CLK
TO DV MSD
AL_3VSYS
TO
DV MAIN
PWR_CTL
MAIN_VCO
PB_VCO
ENV_OUT
MONI_CHG
ATFI
FS_PLL
SBE
SPA
JIG_CONN
CN1101
QGB0801L1-26X
UNREG
1K
R1126
R1125
#
0Ω
#
IC1004
TC7ST32F-X
R1078
GND
CHG_STOP
1K
SPA
HID
FS_PLL
ATFI
REC_MON
ENV_OUT
PB_VCO
GND
MAIN_VCO
JLIP_RX
AL_3VSYS
JLIP_TX
SBT
SBD
RST
VPPC_5V
SBE
GND
D_REG_3V
JIG_MOD
VPPD_5V
JIG_SPT
JIG_SCK
TO
DV MSD
JIG_SCK
JIG_SPT
VPPD
JIG_MOD
HTD1
SRV_RST
S_CLK
S_DT_OUT
S_DT_IN
MVD0
EEPROM_CS
SRV_CS
SRV_RDY
CAS_SW
HOUSING_SW
TO DV MAIN, DV DSP
D_REG_3V
TO
DV MSD
ODD_EVEN
SCR_LR
SCR_UD
V_MUTE
OSD_DATA
OSD_CS
OSD_CLK
TO
DV I/O, DV V OUT
OSD_HD
OSD_VD
IND
FRG
#
0Ω
TO
DV I/O
CLKOSD
p10285001a_rev0
1
DCBA
4-39 4-40
HGFE
Page 91

4.19 DV MSD SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
R1501
L1501
NQL144K-100X
TAPE_LED
VDD
VSS
TBC_VD
VDDH
TBC_CLK
TBC_IN
TBC_OUT
TBC_CS
VPP
ANA_CS
VSS
EEP_CLK
EEP_IN
EEP_OUT
MDA_CLK
MDA_IN
VDD
MDA_CS
SYS_CLK
SYS_IN
SYS_OUT
READY
VSS
TXD
RXD
OSD_CLK
OSD_DATA
OSD_CS
MIC_SCL
VDDH
0Ω
10µ
C1522 C1523
0.1 0.1
0Ω
R1563
TSR
T_REEL
VDD
S_REEL
D.FG
DRUM_FG
HID_IN
C.FG
SRV_FRP
FRP
VSS
SPA
TSR
REMOTE
VSS
MIC_SDA
MIC_CTL
C.BRK
LD_ON
TBC_RST
PHY_PD
PHY_CNA
PHY_RST
EXT_IN_L
HOUSING_OUT
HOUSING_IN
HOUSING_SW
0Ω
0Ω
R1503
R1502
CASETTE_SW
C.SD
VSS
NOINT
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
R1562
R1560
R1558
VD
SRV_TRK
CAP_REF
DRUM_REF
PWM27O
HID
VDDH
0Ω
R1553
S_IN_L
0Ω
R1552
ASPECT1
ASPECT2
ADC_DEM0
ADC_DEM1
VSS
ADC_PWD0
ADC_PWD1
IC1501
MN103004KFB(PAL)
ADM12
ADM13
ADM14
0Ω
R1514
SCR_UD
0Ω
R1515
SCR_LR
0Ω
R1516
ODD_EVEN
VDDB
RA1501
NRZ0040-0R0X
ADM15
0Ω
NRZ0040-0R0X
VDDH
V_MUTE
EEPROM_CS
1k
R1504
R1505
RWSEL
VSS
AS
R1506
1k
0Ω
R1546
R1547
AGC_RST
VDD
MSELECT
DRUM_FG
DRUM_PG
CMODE
VSS
VREFH
WE1
ADM3
ADM4
ADM5
ADM6
ADM7
ADM8
ADM9
ADM10
ADM11
VSS
RA1502 RA1503 RA1504
0Ω 0Ω 0Ω
NRZ0040-0R0X
NRZ0040-0R0X
C1501
0.1
NMI
AVDD
MMOD0
MMOD1
PVSS
PVDD
WE0
ADM2
ADTRG
ADM1
VDDB
REC_SAFE
REEL_LED
MONI_CHG
REDKADM0
0Ω
R1517
S_SENS
E_SENS
BCID1
BCID2
BCID3
S_DC_IN
AVSS
CAM0
CAM1
CAM2
VDDH
REC_H
HID3
CLK27SEL
DV_RST
D_GAIN
FFREW_H
DV_CS
EQ_CS
SYSCLK
VDDH
OSCO
OSCI
EXMOD0
EXMOD1
FRQS
RESET
0Ω
R1518
R1519
T_REEL
S_REEL
IC1502
TC7W14FK-X
TAPE_LED
Q1603
UMC3N-W
REEL_LED
0.1
0.01
0.01
0.01
C1508
C1506
C1507
C1505
3.3k
2k
R1535
R1536
RA1505
NRZ0040-102X
1k
NRZ0040-102X
RA1506
1K
NRZ0040-102X
RA1507
1K
RA1508
1K
NRZ0040-102X
PBH
R1528
R1527
R1540
R1526
R1525
R1524
R1520
R1522
R1521
C1502
0.1
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
C1504
0.1
R1523
C1503
OPEN
EXT_IN_L
EXT_IN_H
0Ω
2.2k
2.2k
1k
VSS
VDD
CS0
CS1
VSS
4.7k
RA1510
47K
NRZ0040-473X
3.3k
3.3k
R1537
R1538
Q1501
DTA114EE-X
RA1509
1k
NRZ0040-102X
3.3k
R1539
L1502
10µ
NQL144K-100X
C1510
47
/6.3
/6.3
47
SCK
SPT
R1531
OPEN
OPEN
R1631
Q1602
UMC3N-W
330
R1632
IC1601
TC4W53FU-X
100
R1661
68k
R1665
47K
R1634
68k
R1666
330
R1635
OPEN
R1662
R1667
33
R1663
R1668
1k
1k
330
R1636
R1655C1509
R1653
R1651
R1650
R1649
R1648
R1647
R1646
R1645
R1644
R1642
R1641
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
TO
AUDIO AD/DA
CMODE
TO
SENSOR
CN1502
QGF0503C1-15V
REC_SAFTY_SW
GND
START_SENSOR
GND
LED
MIC_3
E_SENSOR
SUP_REEL_SENSOR
SUP_REEL_LED
MIC_2
TU_REEL_SENSOR
TU_REEL_LED
GND
MIC_1
CASETTE_SW
TO
DV SYSCON
CAS_SW
TO
DV MAIN, DV SYSCON
PBH
REC_H
HID3
MONI_CHG
CLK27SEL
TO
DV MAIN
FFREW_H
TO
DV MAIN
DV_CS
DV_RST
DV_WAIT
DWE
DALE
DRWSEL
DRE
ADDT00
ADDT01
ADDT02
ADDT03
ADDT04
ADDT05
ADDT06
ADDT07
ADDT08
ADDT09
ADDT10
ADDT11
ADDT12
ADDT13
ADDT14
ADDT15
TO
DV SYSCON
JIG_SCK
JIG_MOD
JIG_SPT
VPPD
TO
DV SYSCON
AL_3VSYS
GND
TO AUDIO AD/DA
ADC_PWD1
ADC_PWD0
ADC_DEM1
ADC_DEM0
TO DV V OUT
AGC_RST
ASPECT1
5
4
3
ASPECT2
TO
DV SYSCON
TO
DV DSP
TO
DV MAIN
SRV_TRK
SRV_FRP
TO
DV SYSCON
HOUSING_SW
TO P/R MDA (MDA)
CN5506
QGF0508F1-20X
CAM_SW3
CAM_SW2
CAM_SW1
HOUSING_SW
HOUSING_OUT
HOUSING_IN
CAP_REF
DRUM_REF
MOTOR_GND
MDA_CLK
CAP_BRK
DRUM_FG
DRUM_PG
TO DV DSP
NTSC_L
TO DV I/O
TBC_VD
TBC_CLK
TBC_SDI
TBC_SDO
TBC_CS
TBC_RST
EXT_IN_L
CLK27A
TO
DV SYSCON
EEPROM_CS
S_DT_OUT
SRV_RDY
SRV_RST
OSD_CLK
OSD_DATA
OSD_CS
V_MUTE
SCR_UD
ODD_EVEN
PWM27O
AL_5V
MDA_IN
MDA_CS
LD_ON
CAP_FG
SRV_CS
S_CLK
S_DT_IN
SCR_LR
MVD0
MVD
HID1
CN1501
R1564
0Ω
R1594
OPEN
FRP
SPA
TSR
R1566 R1565
TP1507
TP1509
TP1501
TP1504
R1582
R1583
R1584
R1585
R1586
R1578
R1579
R1580
R1581
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
R1588
R1589
R1590
3.3k 3.3k
C1516 C1515
0.022 0.022
C1521
0.1
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
1k
1k
1k
0Ω
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
R1568 R1567
3.3k 3.3k
C1517C1518
0.0220.022
R1601
0Ω
0Ω
R1602
0Ω
R1603
GND
R1605
0Ω
R1606
0Ω
0Ω
R1607
0Ω
R1608
0Ω
R1609
0Ω
R1611
NC
GND
R1612
R1613
R1614
R1615
R1616
R1617
R1618
R1619
TL1801
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
TBC_VD
R1591
R1592
R1593
R1569
TP1508
10K
TP1510
10K
10K
TP1503
TP1505
R1587
R1575
R1576
R1577
D1501
0Ω
OPEN
SB007W03Q-X
R1570
2
5
0
DV MAIN (DV MSD)
1
p10286001a_rev0
DCBA
4-424-41
HGFE
Page 92

The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
EXTDATA0
HSP
0Ω
R2015
330P
EXTFRP
RECDATA
VCC
AMP+
TL2021
EXTREQ
EXTACCESS
RECCLK
RECCTL
X2001
NAX0141-001X
NORI1
NORI2
AMP-
GND
VSS
SPA
42M
TRICSW
AMPO
C2103
R2145
2.2k
Note :
VSS
VDDL
VSS
VDDH1
0.1
C2007
R2016
R2017
C2008
12P
0.01
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
0.1
C2031
AD4
AD5
AD6
AD7
AD8
AD9
VSS
ADRS10
VSS
0Ω
12P
ADRS8
ADRS9
OSC4185I
OSC4185O
C2104
1000p
C2009
R2146
ADRS7
DISCRI
10k
ADRS6
REFCLK
5.6k
R2018
VSS
ADRS5
BUSCLK
ADVIN1
ADAVD1
ADAVS1
0.1
C2010
2.2k
R2019
R2148
K2002
NQR0129-002X
C2116
0.1
R2149
0Ω
VDDL
ADVRH1
VSS
VDDL
VDDH6
ADRS0
ADRS1
ADRS2
ADRS3
ADRS4
VDDH6
ADVRL1
VSS
PWM27O
VDDH1
OSC27I
OSC27O
CLK27I
CLK27O
CLK27SEL
0.1
L2009
2.2µ
C2014
C2011
NQL024J-2R2X
C2015
33P
1000P
R2027
220K
10k
R2022
D2002
UV007ECB-X
C2020
0.1
22k
R2023
OPEN
C2118
IC2006
OPEN
VSS
VSSVDD2
CLK41MVSS2
VSS
VSS VSS
C2117
AD10
AD11
AD12
AD13
AD14
AD15
VSS
CLK135O
VDDL
FRRES
FRREF
TRKREF
SERVOFRREF
SERVOTRKREF
PHYTPA
PHYTPB
PHYTPBIAS
PHYXTPA
PHYXTPB
10k
0.1
R2020
C2016
1K
R2021
0.1
VSS
DVSS
DVDD
AVSS
AVDD
XI
0.1
512FS
XO
C2017
1
2.4k
R2033
AD1
AD2
AD3
CPUBUSTYPE
CPUDSLOGIC
CPUWAITLOGIC
VCO
PHYFIL
PHYRO
PHYRF
PHYFIL
3.9k
R2035
R2034
C2018
AD0
CPUWAIT
XINT
XCPUCS
XCPURW
XCPUDSTB1
XCPUDSTB0
CPUALE
OUTV
OUTH
BRSI3
BRSI2
BRSI1
BRSI0
YSI3
YSI2
YSI1
YSI0
BRSO3
BRSO2
BRSO1
BRSO0
YSO3
YSO2
YSO1
YSO0
AODAT0
AODAT1
VSS
AOBCK
AOLRCK
DODAT
VDDL
DOBCK
DOLRCK
AIDAT0
AIDAT1
AIMCK
AIBCK
AILRCK
DIDAT
DIMCK
DIBCK
DILRCLK
OSC11O
OSC11I
OSC24O
OSC24I
VCXO12O
VCXO12I
VCXO11O
VCXO11I
VAUDAVD
VCIAUD
VAUDAVS
VDDH2
PWMAUDIO
VDDH1
VDDH7
PHYAVS3
PHYVSR
PHYVSA
PHYVDR
PHYVDA
XRESET
3.9k4700p
ADDT15
ADDT14
ADDT13
ADDT12
ADDT11
ADDT10
ADDT09
ADDT08
ADDT07
ADDT06
ADDT05
ADDT04
TO
ADDT03
DV MSD
ADDT02
ADDT01
ADDT00
TL2018
INV
INH
VSS
565656
56
R2038
R2039
R2036
R2037
TL2017
TL2016
TL2015
TL2014
TL2013
TL2012
5.1k
R2040
TL2009
TL2008
TL2007
C2019
270p
R2049
R2042
R2032
0Ω
5TO0
R2062
0Ω
R2061
0Ω
R2060
0Ω
R2059
0Ω
R2058
0Ω
R2057
0Ω
R2056
0Ω
R2055
0Ω
R2054
0Ω
R2053
0Ω
R2052
0Ω
R2051
OPEN
0Ω
C2025
R2041
0Ω
R2044
X2003
24.576M
C2023
C2022
10K
R2046
C2024
6p
6p
0.1
0.1
OPEN
C2026
1000P
D2003
NQL024J-100X
UV007ECB-X
NQR0276-001X
L2011
R2043
1M
NAX0206-001X
10K
DV MAIN (DV MAIN)
4.7K
R2050
10µ
NQL024J-100X
C2028
C2027
15P
R2047
1000P 15P
220K 220K
D2004
UV007ECB-X
L2015
L2010
10µ
C2029
R2048
R2098
DV_WAIT
DV_CS
DRWSEL
DRE
DWE
DALE
INV
INH
OUTV
OUTH
DCO3
DCO2
DCO1
TO
DCO0
DV DSP
DYO3
DV I/O
DYO2
DYO1
DYO0
DCI3
DCI2
DCI1
DCI0
DYI3
DYI2
DYI1
DYI0
TO
AUDIO AD/DA
AODAT
AIDAT
AIMCK
AIBCK
AILRCK
TO
DV SYSCON
FS_PLL
TO
DV MSD
DV_RST
CLK27SEL
TO
DV DSP DV I/O
CLK135O
CLK27A
0Ω
J2001
QNZ0097-001
TPA+
TPA-
TPB+
TPB-
DV MSD, DV SYSCON
SRV_FRP
SRV_TRK
TSR
M_VCO CTL
FRP
FSPLLCTL
SPA
PWM27O
FFREW_H
TO
DV IO
M_VCOCTL
FSPLLCTL
4.20 DV MAIN SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
TO
DV SYSCON
DSP_RST
TL2028
TL2029
5
L2007
IN
CONT
NQL144K-100X
C2108
22
OUT
GND
L2008
/6.3
NOISE
10µ
C2109
/6.3
22
MM1385JN-X
NQL144K-100X
10µ
IC2004
C2111
1
REF_CLK
REC_CLK
C2110
22
C2112
/6.3
22
/6.3
A_REG_2.5V
D_REG_2.5V
NQL144K-100X
A_REG_2.5V
D_REG_2.5V
NQL144K-100X
L2001
L2002
10µ
C2051
TL2041
TL2042
TL2043
TL2044
C2036
0.1
C2037
0.1
TL2045
TL2046
TL2047
TL2048
TL2049
TL2050
TL2051
TL2052
TL2053
TL2054
TL2055
C2038
0.1
TL2056
TL2057
TL2058
TL2059
TL2060
TL2061
TL2062
TL2063
TL2064
TL2065
TL2066
TL2067
TL2068
TL2069
TL2070
TL2071
0.1
C2039
TL2072
TL2073
C2040
0.1
C2041
0.1
TL2074
TL2075
TL2076
TL2077
TL2078
C2042
0.1
0.1
C2043
C2044
0.1
10µ
C2052
C2054
C2053
L2003
/6.3
22
L2004
10µ
NQL144K-100X
C2055
22
10µ
NQL144K-100X
/6.3
C2056
L2005
10µ
NQL144K-100X
L2006
10µ
NQL144K-100X
C2059
22
/6.3
C2058
C2057
0.1
1
22
/6.3
1
0.1
22
/6.3
C2060
MON0
MON1
VDDH4
VDDL
MON2
MON3
MON4
MON5
VSS
MON6
MON7
MON8
MON9
MON10
MON11
MON12
VDDH4
VDDL
MON13
MON14
MON15
MON16
MON17
MON18
MON19
VSS
MON20
MON21
MON22
MON23
VDDH4
MON24
MON25
MON26
MON27
VDDH1
PLLAVD
PLLAVS
VDDA
VSS
VDDH3
VSS
VSS
VDDH3
VDDL
VSS
VDDH2
VDDH2
VDDL
VSS
VSS
MTEST
PHYAVD2
BUSRST
PHYAVS2
PMODE
PWR3
PWR1
PWR2
VDDL
PHYAVS1
PHYAVD3
PHYAVD1
VSS
VDDH0
VDDL
VSS
K2001
NQR0129-002X
C2061
C2062
22
/6.3
0.1
1
TO DV SYSCON TO DV MAIN, DV DSP
TO
DV SYSCON
AL_3V
PWR_CTL
GND
MM1385NN-X
C2106
10.1
IC2003
C2107
4
TO
DV SYSCON
SBE
PB_VCO
MAIN_VCO
ATFI
frTOom
DV I/O
TO
DV MSD
TO P/R MDA (PRE/REC)
CN5002
QGF0508F1-26X
TO
DV SYSCON
TO DV MAIN
TO
DV SYSCON
ENV_OUT
RECCADJ
ATF_GAIN
AGC_GAIN
DUMP_CTL
MONI_CHG
REC_H
CN2001
PB_ENV
REC_CTL
REC_H
DUMP_CTL
AGC_GAIN
VREF_1.1
AGC_OUT
VRB_AGC
ATF_GAIN
VRB_ATF
ATF_IN
REF_CLK
REC_CLK
REC_DATA
RECCADJ
MONI_CHG
D_REG2.9
REG_5V
A_REG2.9
A_REG2.5
REG_5V
A_REG_3V
D_REG_3V
A_REG_2.5V
D_REG_2.5V
REG_1.8V
HID1
HID3
PBH
0Ω
R2126
R2125
0Ω
0Ω
R2124
R2123
R2122
R2121
R2119
R2118
R2117
R2116
R2115
R2114
R2113
R2112
R2110
R2109
R2108
R2107
R2106
R2104
R2103
R2102
R2101
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
PBH
HID1
HID3
GND
GND
GND
GND
3
2
1
C2113
R2087
0.1
1M
TL2025TL2026
R2088
0Ω
TL2027
R2089
0Ω1M0Ω
0Ω
R2086
R2085
R2084
TL2024
VSS
TDI
TCK
TMS
TDO
TRST
DCTEST0
DCTEST1
VPD
TBST
TL2023
TTST
TL2022
PBI
0.1
C2033
DRAMVCC12
DRAMVCC21
DRAMVCC22
0.1
C2032
DRAMVCC02
DRAMVCC01
DRAMVCC11
VSS
VSS
VDDH5
EXTDATA1
EXTDATA2
EXTDATA3
EXTDATA4
EXTDATA5
EXTDATA6
EXTDATA7
IC2001
JCY0133
VCO D/AA/D A/DD/A
ADVIN0
ADAVD0
ADAVS0
ADVRH0
ADVRL0
EXDATAI7
EXDATAI6
EXDATAI5
EXDATAI4
EXDATAI3
EXDATAI2
EXDATAI1
EXDATAI0
PBCLKO
V4185AVS
VCI4185
V4185AVD
DAAOUT0
DAVRO0
DAVREF0
DAAVS0
DAAVD0
DAAOUT1
DAVR01
DAVREF1
DAAVS1
DAAVD1
SBE
R2141
R2142
560
R2013
10K
R2014
C2101
HID
0.1
0.1
C2005
C2006
IC2002
JCY0136-X
0.1
0Ω
0Ω
C2102
0.1
C2001
0.1
C2002
IC2007
TLC2940IPW-X
PBCLKI
TL2002
0Ω
0Ω
560
0.1
10K
R2140
C2003
R2011
R2012
R2010
R2150
2.2K
VCO
C2114
C2115
0.011M0.1
p10287001a_rev0
DCBA
4-43 4-44
HGFE
Page 93

4.21 DV I/O SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
TO DV V OUT
C_GCTL
5 0 DV MAIN (DV I/O)
5
AO4
AO5
AO6
AO7
AO8
AO9
AO10AO11
VrefUVcc
AO12DOLD
L3151
10µ
C3011
NQL144K-100X
C3132
C3131
22
/6.3
2.7k
Q
GND
1.5k
R3078
AVSS(D/A)
AVDD(D/A)
IREF1
YCOUT
ABAR1
COMP1
YSOUT
VREF1
AVSS(D/A)
AVDD(D/A)
CLPY
VYIN
AVSS(A/D)
AVDD(A/D)
VRM
VRL
VRH
CIN
AVSS(A/D)
SCANMODE
COUT
SCANEN
OPEN
R3168
VREF2
VSS
0.1
100
0.1
0.1
C3016
C3017
R3076
OPEN
R3081
R3075
CROUT
ABAR2
COMP2
CBOUT
VDD(CORE)
OUTH
OUTV
CSO0
0Ω0Ω0Ω0Ω0Ω0Ω0Ω0Ω0Ω
R3024
R3025
R3026
0.1
C3009
C3012
0.1
/6.3
22
R3079
R3080
0Ω
R3008
0Ω
2.7k
1.5k
R3073
0.1
820
270
100
0.1
R3007
0Ω
0.1
0.1
0.1
0.1
0.1
0.1
VCC
IC3103
OPEN
CK
D
TO DV V OUT
DAC 3V
DV_Y
DV_C
680
OPEN
4.7
R3104
R3122
R3121
820
10µ
Q3102
CH
R3140
R3138
C3126
R3139
*
47k
OPEN
39k
0Ω
820
680
R3105
1k
2SC4081/RS/-X
HN1B04FU/YG/-X
Q3112
R3123
270
*
CH
R3142
1.5k
R3141
820
C3108
/6.3
22
R3106
270
Q3113
C3118
4.7
R3124
470k
Q3132C3125
HN1B04FU/YG/-X
R3143
270
C3109
0.1
Q3114
R3125
270
2SC4081/RS/-X
Q3133
C3127
0.1
C3101
0.1
0.1
C3119
2SC4081/S/-X
C3128
C3001
R3003
R3004
R3005
C3002
C3003
C3004
C3005
C3006
C3007
C3008
0.1
R3163
R3102
1k
R3101
0Ω
4
R3114
680
R3111
C3111
56k
0.1
Q3111
C3112
C3121
R3113
22
/6.3
47
R3112
47k
2SA1576A/RS/-X
R3131
R3134
56k
680
Q3131
R3133
0.1
22
R3132
47k
2SA1576A/RS/-X
PELN0969-04Y
TO DV V OUT
Y_OUT
C_OUT
TO DV MSD
EXT_IN_L
3
C3103
0.1
/6.3
TO DV SYSCON
A_REG_5V
D_REG_3V
REG_1.80V
C3102
22
GND
L3103
NQL144K-100X
22
C3106
2SA1576A/RS/-X
R3115
820
R3116
18k
C3114 C3115
Q3115
DTC144EE-X
R3135
10µ
K3101LC3101
NQR0129-002X
Q3101
NQL024J-150X
C3113
8p
CH
L3111
15µ
CH CH
8p 12p
NQL024J-150X
C3124
12p
820
R3136
L3131
18k
15µ
CH CH
C3122 C3123
8p
C3107
CH
OPEN
0.1
C3116
R3118
R3103
330
R3117
2.2k
47k
4.7
2SA1576A/RS/-X
R3120
C3117
R3119
56k
R3137
2.2k
L3104
NQL144K-100X/6.3
2
C3140
C3141
0.1
0.1
IC3101 IC3102
TC7SH04F-X
R3161
R3162
C3142
8P
1M
270
NAX0218-001X
X3101
27MHz
TC7SH04F-X
C3143
8P
C3144
OPEN
VrefL
IC3151
M62366GP-X
GND
AO1
AO2 AO 3
CLK
DI
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
820
0.1
R3069
R3071
R3070
C3015
R3074
OPEN
VRVGVB
BLK1
BLK2
VBLK
AVSS
AVDD
IREF2
IC3001
JCP8029
CSO1
CSO2
CSO3
VSS
VDD(I/O)
YSO0
YSO1
YSO2
YSO3
0Ω
R3027
R3028
R3029
R3032
R3033
R3034
R3035
0.1
C3010
0Ω
R3065
0Ω
C3014
0.1
R3062
R3063
R3072
R3077
VSS
CLKOSD
VDOUT
HDOUT
CSYNC
AMUTE
VDD(CORE)
SDOUT
ADDATEST
RAMTEST
CSI1
CSI2
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
R3061
OPEN
R3056
0Ω
OPEN
R3060
OPEN
R3059
R3058
0Ω
R3057
C3013
R3048
R3054
0Ω
0Ω
0.1
0Ω
R3164
0Ω
ZCNT
RST
CLK
VSS
CS
SCLK
SDIN
YSI3
YSI2
YSI1
YSI0
CSI3
R3064
VC1
VC2
VDD(I/O)
INH
INV
CSI0
Y_GCTL
TO
DV MAIN
FSPLLCTL
M_VCOCTL
TO
DV MAIN
AGC_GAIN
DUMP_CTL
ATF_GAIN
RECCADJ
TO
DV SYSCON
AFZ_DATA
AFZ_CLK
DAC_CS
FRG
IND
CLKOSD
OSD_VD
OSD_HD
TO
DV MSD
TBC_VD
TBC_RST
TBC_CS
TBC_CLK
TBC_SDI
TBC_SDO
TO
DV MAIN/DV DSP/DV MSD
CLK27A
ANACTL
AYO3
AYO2
AYO1
AYO0
ACO3
ACO2
ACO1
ACO0
INVA
INHA
TO
DV DSP/DV MAIN
DYO3
DYO2
DYO1
DYO0
DCO3
DCO2
DCO1
DCO0
INV
INH
DV DSP
TO
CLK27B
CLK135
p10288001a_rev0
1
DCBA
4-45 4-46
HGFE
Page 94

4.22 DV V OUT SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
TO
DV SYSCON
A_REG_5V
C3521
22
/6.3
5
GND
IC3502
MM1385HN-X
5
0 DV MAIN (DV V OUT)
TO DV I/O
DAC_3V
IN
CONT
C3522
0.1
4
C3537
15p
CH
R3527
4.7k
TO
DV I/O
R3526
680
DV_C
3
TO
DV I/O
DV_Y
R3521
680
L3533
12µ
NQL024J-120X
C3532
15p
CH
R3522
4.7k
L3531
12µ
NQL024J-120X
TO
DV I/O
C_GCTL
Y_GCTL
TO
2
DV SYSCON
IND
FRG
TO
DV MSD
ASPECT1
C3538C3536
47p12p
C3533C3531
47p12p
[POST FILTER]
[POST FILTER]
NQL024J-270X
L3534
27µ
CHCH
C3539
[POST FILTER]
[POST FILTER]
NQL024J-270X
L3532
27µ
CHCH
C3534
GND
2SA1576A/RS/-X
CH
39p
2SA1576A/RS/-X
CH
39p
OUT
NB
C3524
0.1
R3531
R3533
R3529
Q3503
R3528
3.3k
R3524
Q3502
R3523
3.3k
2.2k
2.2k
OPEN
OPEN
C3523
22
/6.3
R3532
R3534
C3540
C3535
0.1
C3515
22
/6.3
C3513
0.1
0Ω
C3512
0.1
C3510
220k
R3509
10k
R3510
0.1
C3511
C3509
0.1
IC3501
NJM2538V-X
[VIDEO_AMP]
Ref.
0.1
LPF
-12dB
C3501
0.1
0Ω
0Ω
C3502
0.1
0.1
C3514
GCA
6±3dB
CLAMP
2.2M
LOGIC
VCC1VCC2CLAMP
CHA BLK
R3511
C3504
22
75
Buf.
Comp.
20k
R3502
/6.3
Ω
10k
+12dB
6dB
10k
R3512
GND
220k Ω
C3505
75
Ω
Buf.
+18dB
-6dB
+12dB
75
Ω
Buf.
/6.3
100
R3503
10k
Q3501
DTC144EE-X
R3504
120
C3506
22
R3505
/6.3
68
R3506
TL3502
C_OUT
R3507
68
TL3501
Y_OUT
TO
MAIN (VIDEO I/O SW)
CN703
CN3501
QGA2001F2-06V
Y_PB[DV]
GND
R3508
75
75
22p
C3507
22p
C3508
C_PB[DV]
Y/V_REC[DV]
GND
C_REC[DV]
TO
DV I/O
C_OUT
Y_OUT
-12dB
ATT
BPF
PWR
SAVE
ATTATT
GCA
6±3dB
-12dB
0.1
C3503
ATT
CLAMP
-12dB
R3501
ASPECT2
AGC_RST
p30073001a_rev0
1
DCBA
4-47 4-48
HGFE
Page 95

4.23 AUDIO AD/DA SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
50
5
4
TO MAIN (AUDIO I/O)
CN2601
CN3701 10
QGF1016F4-08W
DV_A_REC[L]
GND
DV_A_REC[R]
GND
DV_A_PB[L]
GND
3
DV_A_PB[R]
GND
2
R3731
R3732
R3733
R3734
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
DV MAIN (AUDIO AD/DA)
R3735
0Ω
0Ω
R3736
C3721
C3738
R3728
R3722
OPEN
OPEN
220
R3721
220
2.2k
R3726
1k
R3727
2.2k
C3737
OPEN
C3736
OPEN
VCC
IC3703 IC3702
BA15218F-XE BA15218F-XE
C3722
C3723
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
R3723
1k
R3724
VEE
R3725
OPEN
R3711
3k
R3712
3k
VCC
C3724
C3725
0.0033
OPEN
C3733
0.0033
C3735
C3731
0.1
C3734
0.0068
OPEN
VEE
R3713 R3715
1k 0Ω
C3726
0.0068
C3728
0.1
R3719
1k
R3714
1k
C3729
47
/16
L3702
NQL144K-100X
C3730
/16
47
R3717
10k
C3732
OPEN
R3718R3720
0Ω1k
C3727
OPEN
10µ
R3701
R3702
R3716
10k
220
R3740
18K
18K
C3717
C3718
10
C3703
0.1
C3701
C3702
R3703 R3704
8.2K 8.2K
/16
/16
1.0
1.0
C3715
C3704
10
L3701
10µ
NQL144K-100X
C3714
/16
10
0.1
C3716
0.1
VA
VB
AGND
VRDA
VRAD
AINR
/16
C3706 C3707
C3705 C3708
150P 150P
C3712
/16
10
VCOM
IC3701
AK4518-VF-X
VCMR
0.1 0.1
C3713
AOUTR
VCML
0.1
R3707
OPEN
AOUTL
AINL
R3706
OPEN
DEM0
PWAD
C3709
/16
10
DEM1
PWDA
R3709
R3708
R3710
OPEN
CMODE
MCLK
10
OPEN
SDTI
LRCK
VD
SCLK
C3711
/16
10
C3710
0.1
DGND
SDTO
R3705
0Ω
TO
DV SYSCON
AL_5V
A_REG_8V
GND
AL_5V [–]
TO
DV_MSD
ADC_DEM0
ADC_DEM1
CMODE
ADC_PWD0
ADC_PWD1
TO
DV_MAIN
AODAT
AIBCK
AILRCK
AIMCK
AIDAT
p30074001a_rev0
1
DCBA
4-49 4-50
HGFE
Page 96

4.24 DV DSP SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
The Parts Number, value and rated voltage etc. in the Schematic Diagram are for references only.
Note :
When replacing the parts, refer to the Parts List.
TL4035
RAE1
DSCO7
FMRE1
CLKDSC
RAD
HDDSC
WAD
#
VDDSC
FMWE1
FLDDSC
#
22
TL4034
R4035
TL4033
#
0.1
C4023
IE1
VDDE
MCLK
OUTV
OUTH
VSS
DYI3
DYI2
DYI1
VDDI
DCI0
DCI1
DCI2
DCI3
DVC_I/O_IF
&EVR
DSYI0
DSYI1
DSYI2
DSYI3
DSYI4
DSYI5
DSYI6
DSYI7
DSCI0
DSCI1
DSCI2
VDDE
ADDVSS
DSCI3
TO
DV I/O
CLK27B
5
4
CLK135
TO
DV MAIN
CLK135O
TO
DV SYSCON, DV MSD
CHWE
CLWE
CALE
BUS15
BUS14
BUS13
BUS12
BUS11
BUS10
BUS9
BUS8
BUS7
BUS6
BUS5
BUS4
BUS3
BUS2
BUS1
BUS0
MFLD
RWSEL
CRE
CLR
MVD
OMT
3
TO
DV I/O
ANACNT
INHA
INVA
ACO3
ACO2
ACO1
ACO0
AYO3
AYO2
AYO1
AYO0
0Ω
0Ω
R4001
R4002
2
TO
DV MSD
NTSC_L
R4037
R4039
R4038
NRZ0040-0R0X
0Ω0Ω0Ω
RA4002
NRZ0040-0R0X#NRZ0040-0R0X
RA4001
#
#
#
RA4004
RA4003
R4003
R4004
R4005
5
0Ω
0Ω
OPEN
#
#
#
#
0Ω
#
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω
NRZ0040-0R0X
0
TL4036
C4027
#
0.1
TL4041
R4006
R4007
R4008
C4030
C4031
R4036
C4032
C4033
C4034
#
#
#
C4001
#
0.1
#
0.1
#
0Ω
#
0.1
#
0.1
#
0.1
TL4042
TL4043
0Ω
TL4044
0Ω
TL4045
TL4046
0Ω
TL4047
TL4048
#
0.1
R4009
1k
VDDI
VSS
ADDVDDE
CLK27
CLK18
CLK13
ID
VDTG
HDTG
LHFO
ADDVDDE
VSS
ADIN9
ADIN8
ADIN7
ADIN6
ADIN5
ADIN4
ADIN3
ADIN2
ADIN1
ADIN0
VDDI
ADDVSS
ADDVDDE
RE
HWE
LWE
ALE
BUS15
BUS14
BUS13
BUS12
BUS11
BUS10
BUS9
BUS8
BUS7
BUS6
BUS5
BUS4
BUS3
BUS2
BUS1
BUS0
VSS
CLR
VDCPU
HDCPU
FRP
OMT
AFBEND
FLDCPU
BEND
VSS
DSTB
VPD
CS
RWSEL
VDDI
CLKOSD
HDOSD
VDOSD
BLK1
BLK2
VC1
VC2
VR
VG
VB
VBLK
ADDVSS
#
VDDI
VDDE
FMC3
FMC2
FMC1
FMC0
FMY7
TG_IF
AD_CONV_IN
OSD_IF CPU_IF
VDMDA
PWM
CLK45
VSS
CSYNCI
HDANA
VDDE
DV MAIN (DV DSP)
FMY6
VDANA
FMY5
ANACNT
FMY4
AYO0
FMY3
AYO1
FMY2
AYO2
FMY1
FMY0
#
0.1
C4026
TMY2
TMY3
TMY4
TMY5
TMY6
TMY7
TMC0
TMC1
TMC2
TMC3
ADDVSS
ADDVDDE
TMY1
TMY0
0.1
#
#
0.1
C4025
C4024
VSS
IE2
FMWR
WAE1
VDDI
RAE2
WAE2
FMWE2
FMRE2
ADDVDDE
MEMORY_I/O
IC4001
OPEN
[CAMERA_DSP]
YCA&IWD&DVIF&FMC&SSG&DAC&ENC
DSC_OUT DSC_INANALOG_IN
DSCO6
DSCO5
DSCO4
DSCO3
DSCO2
DSCO1
DSCO0
DSYO7
DSYO6
DSYO5
DSYO4
DSYO3
DSYO2
DSYO1
DSYO0
ADDVDDE
AYO3
ACO0
ACO1
ACO2
VSS
ACO3
INHA
INVA
VDDE
ADDVSS
C4002
#
0.1
DYI0
DSCI4
0Ω
#
R4034
INV
DSCI5
0Ω
R4033
INH
DSCI6
0Ω
###
R4032
TL4032
#
R4031
DCO3
DSCI7
R4011
R4030
DCO2
DCO1
[L:N_H:M]
[L:NT_H:PS]
CPUSEL0
TVSEL
#
R4010
1M 0Ω
0Ω0Ω0Ω
###
R4029
1M
#
R4012
#
0.1
C4022
VSS
DCO0
VDDI
[L:MN2_H:MN3]
CPUSEL1
VDDI
ADDVDDE
#
C4003
0.1
0Ω
0Ω
#
#
R4027
R4028
DYO3
TCK
0Ω
#
1K
#####
R4013
R4041
DYO2
TMS
C4004
0Ω
#
R4025
R4026
TL4031
DYO1
DYO0
CSYNC
ADDVSS
VDDI
VSS
ADDVDDE
NAND1_A
NAND1_B
R4020
NAND1_O
0Ω
NAND2_A
R4021
NAND2_B
0Ω
NAND2_O
ADDVDDE
ADDVSS
ADDVDDE
VSS
VDDE
VSS
VDDE
VSS
ADDVDDE
ADDVSS
ADDVDDE
EOUT12
EOUT11
EOUT10
TL4025
EOUT9
TL4024
EOUT8
EOUT7
EOUT6
EOUT5
EOUT4
EOUT3
TL4023
EOUT2
TL4022
EOUT1
TL4021
AVDDE1
VREFH1
VREFL1
AVSSE1
EVR
NC
AVDDE2
VREFH2
VREFL2
AVSSE2
DVDDM
AVDDE3
VREFH3
VREFL3
AVSSE3
NC
AVDDV1
AVSSV1
Y2_OUT
Y_OUT
VREFY
IREFY
C_OUT
VREFC
IREFC
R-Y_OUT
B-Y_OUT
VREFVF
IREFVF
K_OUT
VREFLK
VREFHK
AVSSV2
DAC_ENC_OUT
AVSSA
AVDDV2
DVDDM
AVDDA
DACTEST
VSS
ADDVSS
VDDI
TDOUT
TDIN
TRST
ADDVSS
1M
1K
1K
R4042
0.1
R4043
R4044
C4007
22
R4046
1K
#
R4045
#
/6.3
#
C4020
0.1
#
#
R4022
0Ω
C4005
0.1
1M
#
#
L4001
NQL144K-100X
C4008
0.1
C4021
10µ
#
#
C4009
0.1
#
100
RA4006
#
NRZ0040-101X
#
C4013
0.1
#
C4012
0.1
##
R4015
1M 0Ω
#
C4011
0.1
R4016
0Ω
#
#
L4002
#
#
C4010
0.1
/6.3
22
IC4002
[FILED_MEMORY]
[FILED_MEMORY]
C4040
R4017
R4018
C4015
0.1
10µ
NQL144K-100X
0.1
##
1M
#
#
OPEN
VSS
DIN5
DIN4
DIN3
DIN2
DIN1
DIN0
RCLK
RXAD
WADE/RX
RADE/RX
RR
RXINC
RE
OE
DO0
DO1
VCC
DO2
DO3
VSS
DO4
DO5 VCC
#
C4017
22
/6.3
##
C4016
0.1
DIN6
DIN7
DIN8
DIN9
DIN10
DIN11
WCLK
WXAD
WR/TR
WXINC
DO11
DO10
VCC
DO9
DO8
VSS
DO7
DO6
L4003
WE
IE
C4018
10µ
0.1
#
NQL144K-100X
C4042
C4041
0.1
TO
DV MAIN
OUTH
OUTV
DYI3
DYI2
DYI1
DYI0
DCI3
DCI2
DCI1
DCI0
#
RA4008
100
NRZ0040-101X
#
0.1
#
RA4007
100
NRZ0040-101X
#
#
10µ
L4004
NQL144K-100X
#
C4046
0.1
C4045
#
22
/6.3
INH
INV
DYO3
DYO2
DYO1
DYO0
DCO3
DCO2
DCO1
DCO0
TO
DV MAIN
A_REG_2.5V
TO
DV SYSCON
TO
DV SYSCON
REG_1.80V
D_REG_3V
GND
DSP_RST
1
DCBA
4-51 4-52
p10289001a_rev0
HGFE
Page 97

4.25 SWITCHING REGULATOR AND REGULATOR CIRCUIT BOARDS
<01> SW REG, <02> REGULATOR
LPB10119-001D
02
LPA10119
REGURATOR PWB ASS'Y
CP5323
SW.REG PWB
LPB10119 -001D
D5333
19
D5310
ST2
C5205
D5309
L5202
V1
C5331
10
2
1
L5205
C5211
Q5324
18
L5203
4
Q5323
B
D5324
D5331
D5335
D5307
C5213
1
L5201
CN5326
CN5324
R5333
CN5323
CN5301
C5202
C5204
1
R5332
R5309
CN5201
L5204
B5003
C5212
C5210
E
B5303
B5307
R5351
B
Q5339
5
D5301
CP5321
1
C5203
D5204
D5312
D5206
D5205
18
2
C5206
C5326
D5323
D5321
19
R5308
1
CP5301
B5309
D5201
D5208
D5311
C5305
D5203
E
B5310
R5316
D5303
R5345
Q5340
R5329
C5328
D5202
R5311
E
D5328
D5327
R5328
R5317
R5327
C5304
C5301
C5201
D5207
C5207
B
9
R5352
Q5327
C5327
D5330
D5210
Q5335
R5315
18
R5347
C5325
R5335
1
D5329
D5306
D5308
R5310
E
R5326
R5349
5
3
C5302
D5334
B
IC5322
R5303
R5307
C5208
1
E
Q5326
B
R5334
R5312
R5318
R5302
4
2
L5321
Q5302
R5304
R5306
D5304
Q5337
CP5322
B5304
R5353
R5314
3
R5305
R5348
D5211
D5322
R5336
R5350
C5329
2
1
IC5301
C5303
Q5330
Q5301
D5305
E
C5330
R5313
PC5101
1
R5346
B5301
R5341
B
R5337
4
IC5321
1
T5001
C5101
7
D5101
SOLDERED
SIDE
2
3
4
R5102
1
B5308
D5332
D5102
W5383
C5332
R5342
C5333
C5105
D5103
C5103
D5104
01
LPA10119
Q5336
CN5321
Q5341
SW REG PWB
R5104
R5103
1
3
5
C5106
R5106
SW REG PWB ASS'Y
B
C5104
R5107
14
K5101
15
C5321
Q5321
4
CP5324
R5323
E
LPB10119 -001D
C5102
R5105
2
IC5101
R5101
LF5002
2
R5340
1
D5336
C5334
C5324
W5384
R5322
CN5322
D5001
C5002
R5343
C5322
Q5322
D5325
W5382
Q5334
C5323
Q5332
B5306
D5326
R5324
R5325
LPA10119
13 1
12
C5335
B
R5344
E
R5331
R5330
D5337
Q5328
B
E
VR5321
SW5V
ADJ
C5004
C5007
SW.REG PWB ASS'Y
W5381
CN5325
2
B5305
Q5333
Q5329
E
Q5331
B
R5338
R5339
Q5338
B5302
C5006
B5002
R5001
VA5001
LF5001
SG5001
B5001
VA5002
CN5001
LIVE
BRN
C5001
NEUTRAL
BLU
F5001
FC5001FC5002
DANGEROUS VOLTAGE
COMPONENT PARTS LOCATION GUIDE
REF.NO. LOCATION REF.NO. LOCATION REF.NO. LOCATION REF.NO. LOCATION RE
CAPACITOR
C5001 A D 11D
C5002 A D 8C
C5004 A D 9E
C5006 A D 8D
C5007 A D 9D
C5101 A D 6C
C5102 A D 7E
C5103 A D 6C
C5104 A D 7E
C5105 B C 6E
C5106 A D 6B
C5201 A D 4E
C5202 A D 2B
C5203 A D 3E
C5204 A D 2B
C5205 A D 1D
C5206 A D 3A
C5207 A D 4A
C5208 A D 4B
C5210 A D 3A
C5211 A D 2D
C5212 A D 2D
C5213 A D 2E
C5301 A D 4F
C5302 A D 5E
C5303 A D 5E
C5304 A D 4F
C5305 A D 3F
CONNECTOR
CN5001 A D 11B
CN5201 A D 3F
DIODE
D5001 A D 7C
D5101 A D 6B
D5102 A D 6E
D5103 A D 6E
D5104 A D 6C
D5201 A D 4E
D5202 A D 4C
D5203 A D 3D
D5204 A D 4B
D5205 A D 3A
D5206 A D 3B
D5207 A D 4B
D5208 A D 4E
D5210 A D 4B
D5211 A D 5B
D5301 A D 3C
D5303 A D 4A
D5304 A D 5A
D5305 A D 5A
D5306 A D 4F
D5307 A D 2F
D5308 A D 4F
D5309 A D 1C
D5310 A D 1E
COMPONENT PARTS LOCATION GUIDE
REF.NO. LOCATION REF.NO. LOCATION REF.NO. LOCATION REF.NO. LOCATION REF.NO.
CAPACITOR
C5321 A D 7B
C5322 A D 9C
C5323 A D 9C
C5324 A D 8A
C5325 A D 4D
C5326 A D 3D
C5327 B C 4B
C5328 A D 3C
C5329 B C 5B
C5330 A D 5C
C5331 A D 2D
C5332 A D 6D
C5333 A D 6C
C5334 A D 8C
C5335 A D 9D
CONNECTOR
CN5301 A D 1B
CN5321 A D 6E
CN5322 A D 8E
CN5323 A D 3C
CN5324 A D 2D
CN5325 A D 9E
CN5326 A D 2D
DIODE
D5321 A D 4B
D5322 A D 5D
D5323 A D 3C
D5324 A D 2C
D5325 A D 9B
D5326 A D 9B
D5327 A D 4D
D5328 A D 4D
D5329 A D 4A
D5330 A D 4A
D5331 A D 1C
D5332 A D 6A
D5333 A D 1A
D5334 A D 4E
D5335 A D 1C
D5336 A D 8C
D5337 A D 9C
IC
IC5321 A D 5B
IC5322 A D 4B
COIL
L5321 A D 4A
TRANSISTOR
Q5321 A D 7A
Q5322 B C 8B
Q5323 A D 2D
Q5324 B C 2C
Q5326 A D 4D
Q5327 B C 4C
<SW REG>
D5311 A D 3C
D5312 A D 3C
IC
IC5101 A D 7E
IC5301 A D 5F
COIL
L5201 A D 2C
L5202 A D 2B
L5203 A D 2A
L5204 A D 3E
L5205 A D 2E
TRANSISTOR
Q5301 B C 5F
Q5302 B C 5F
RESISTOR
R5001 A D 9B
R5101 A D 8C
R5102 A D 6E
R5103 B C 7E
R5104 A D 7E
R5105 A D 7E
R5106 A D 5B
R5107 A D 7B
R5302 B C 4D
R5303 B C 4E
R5304 B C 5F
R5305 B C 5E
<REGULATOR>
Q5328 A D 9C
Q5329 B C 9C
Q5330 A D 5C
Q5331 A D 9B
Q5332 B C 9C
Q5333 A D 9C
Q5334 B C 9D
Q5335 A D 4E
Q5336 B C 7E
Q5337 A D 5E
Q5338 B C 9B
Q5339 A D 3D
Q5340 B C 4D
Q5341 B C 7D
RESISTOR
R5322 B C 8B
R5323 B C 8A
R5324 B C 9B
R5325 B C 9A
R5326 B C 4C
R5327 B C 4C
R5328 B C 4C
R5329 B C 3C
R5330 B C 9C
R5331 B C 9C
R5332 B C 2C
R5333 B C 2C
R5334 B C 4C
R5306 A D 5A
R5307 B C 4D
R5308 B C 3F
R5309 B C 3F
R5310 A D 4A
R5311 B C 4A
R5312 B C 5F
R5313 B C 5F
R5314 B C 5F
R5315 B C 4F
R5316 B C 4E
R5317 B C 4F
R5318 B C 5E
OTHER
CP5301 A D 3E
F5001 A D 11C
FC5001 A D 11C
FC5002 A D 11D
K5101 A D 7E
LF5001 A D 10C
LF5002 A D 8B
PC5101 A D 5F
SG5001 A D 9B
T5001 A D 5D
VA5001 A D 10C
VA5002 A D 10A
R5335 B C 4C
R5336 B C 5B
R5337 B C 5C
R5338 B C 9B
R5339 B C 9B
R5340 A D 8B
R5341 B C 6D
R5342 B C 6C
R5343 B C 8C
R5344 B C 9C
R5345 B C 4E
R5346 B C 6E
R5347 B C 4E
R5348 B C 5D
R5349 B C 4C
R5350 B C 5B
R5351 B C 3D
R5352 B C 4D
R5353 B C 5C
VR5321 A D 9B
OTHER
CP5321 A D 3D
CP5322 A D 5D
CP5323 A D 1C
CP5324 A D 8E
4-53 4-54
Page 98

4.26 3D DIGITAL/2M AND S-SUB CIRCUIT BOARDS
<05> 3D DIGITAL/2M
LPB10105-001B
COPMONENT PARTS LOCATION GUIDE <3D DIGITAL/2M>
REF.NO.
CAPACITOR
C1401
C1402
C1403
C1404
C1406
C1407
C1408
C1409
C1410
C1412
C1413
C1414
C1415
C1416
C1420
C1421
C1422
C1423
C1424
C1426
C1427
C1428
C1429
C1430
C1432
C1433
C1434
C1435
C1436
C1437
C1438
C1439
C1440
C1441
C1442
C1443
C1444
C1445 CB
LOCATION
DA
CB
A
CDB
B
CCB
CB
B
DCA
CBC1411
B
CCB
CB
B
DCA
CBC1417
B
CCB
CB
B
CCB
CBC1425
B
CCB
CB
D
A
C
B
C
B
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
6A
5A
5B
1C
1DCBC1405
3B
1C
1C
2C
3B
3B
2B
2B
2B
1B
4A
4B
5B
5C
5B
6B
2D
2D
2C
2C
2C
3C
4E
3D
3D
3D
3D
3C
3C
3C
3C
3C
3B
3B
4B
3B
4C
REF.NO.
C1446
C1447
C1448
C1449
C1450
C1452
C1453
C1454
C1455
C1459
C1460
C1461
C1462
C1463
C1464
C1465
C1466
C1467
C1468
C1469
C1470
C1471
C1472
C1473
CONNECTOR
CN1401
D1401
D1402
D1403
D1404
IC1401
L1401
L1402
L1403
L1404
L1405
DIODE
COIL
D
BAC
DA
C
BBC
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
D
A
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
C
B
BC
DA
AD
D
A
C
B
C
B
BICC
D
AAD
DA
D
AAD
REF.NO. LOCATION
L1407
L1409
TRANSISTOR
Q1401
Q1402
Q1404
Q1406
Q1407
Q1408
Q1410
Q1413
Q1414
Q1417
Q1418
Q1419
Q1421
Q1422
RESISTOR
R1401
R1402
R1404
R1405
R1406
R1407
R1408
R1410
R1411
R1412
R1413
R1414
R1415
R1416
R1418
R1421
R1425
R1426
R1427
LOCATIONLOCATION
A
A
A
B
B
B
B
B
B
BQ1412
B
B
B
B
B
BQ1420
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
BR1417
B
B
B
B
B
BR14282CDAL1406
5C
5C
5C
4C
4C
5DDAC1451
5C
5D
5D
4E
1B
2B
2B
2A
2B
3B
3B
3A
3B
4A
4A
5A
2D
3C
3C
5A
5A
6C
3B
2E
4D
5B
2C
2B
5C
4B
REF.NO.
B
R1429
5B
D
R1430
5A
D
R1431
R1432
5B
D
R1433
1C
C
2DCBQ1403
R1435
1D
C
R1436
2B
C
R1437
1C
C
R1438
4B
C
R1439
5C
C
R1440
2C
C
R1441
2C
C
R1442
3B
C
R1446
5B
C
R1447
4B
C
R1448
2A
C
R1449
4B
C
R1450
5B
C
R1451
4E
C
R1452
R1453
5A
R1454
C
5A
R1455
C
2C
R1458
C
2C
R1459
C
2D
R1460
C
1D
R1461
C
2D
R1462
C
2D
R1463
C
2B
VR1401
C
2B
C
1B
C
LC1401
1B
C
LC1402
3D
C
3B
C
4B
C
3B
C
5B
C
5C
C
5C
C
2D
C
2D
C
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
OTHER
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
A
A
A
CC2C
CC2C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
D1E
D2A
2C
2CC
2C
3DCBR1434
2E
1E
4B
4C
4B
5C
4A
4A
4B
1A
2A
2A
2A
3A
3A
3A
4A
5A
5B
4B
2A
5B
5B
4B
4AD
<15> S-SUB
LPB10103-001A
COPMONENT PARTS LOCATION GUIDE <S-SUB>
REF.NO.
C501
C502
C504
C505
C506
C507
C508
C510
C511
C512
C513
C514
C516
C517
C518
C519
C520
C522
C523
C524
C525
C526
C528
C529
C530
C531
C532
C534
C535
C536
C537
C538
C552
C553
C554
LOCATION
CAPACITOR
A
A
AC503
B
A
B
A
A
A
B
B
A
B
BC515
B
B
B
A
A
A
A
B
B
B
BC527
B
B
B
B
B
A
B
B
B
B
AC551
B
B
A
D
5D
D
5D
D
4D
C
4E
D
1D
C
4E
D
4E
D
2E
2DDAC509
D
2C
C
3C
C
2D
D
2D
C
3C
C
3B
C
4B
C
4B
C
3C
D
4B
D
3C
1DDAC521
D
2B
D
2B
C
1C
C
1C
C
1C
C
1B
C
1B
C
1B
C
1A
C
1A
C
1B
2ACBC533
D
2A
C
2D
C
2D
C
2D
C
3B
D
4B
C
4B
C
4B
D
5B
REF.NO.
C555
C556
C557
C559
C560
C561
C562
C563
C566
C568
C569
C570
C571
C573
C575
C576
CONNECTOR
CN511
CN512
CN513
IC501
IC502
L501
L502
L503
L504
L505
TRANSISTOR
Q501
RESISTOR
R501
R503
R504
R505
R506
R507
LOCATION
B
B
A
BC558
B
A
A
A
B
BC564
B
B
B
B
B
BC572
B
B
B
A
A
A
IC
B
A
COIL
A
A
A
A
A
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
5CC
5B
DC6C
5C
DC6D
6DD
4E
CD4D
3B
CC4B
4BC
5B
CC5C
5C
CC3D
5DC
D3A
5E
DD1E
4D
DC1C
2B
DD5E
D
3E
D
2A
D
3E
C3B
3C
CC4E
C
1C
C
1C
C
1C
C1C
REF.NO.
R508
R509
R510
R5115CC
R512
R513
R514
R515
R516
R518
R522
R523
R524
R525
R5266CC
R527
R531
R532
R533
R534
R536 5CCB
LOCATION
CB
B
CCB
B
CCB
CB
B
CCB
B
CCB
CB
B
CCB
B
CCB
CB
B
CCB
1C
1C
1B
1BCB
1B
1A
1A
1B
2D
2DCBR5172DC
3B
4B
5C
5C
3B
3BCB
3D
4B
4B
5B
6C
5CCBR535
4-55
Page 99

4.27 TERMINAL CIRCUIT BOARD
F
<06> TERMIANL
LPB10114-001C
R7140
R7141
C7127
Q7116
C7125
C7106
C7113
R7105
C7120
C7169
R7171
R7170
W7218
R7132
R7131
C7168
4
3
5
8
8
W7219
R7130
W7221
J7101
C7111
R7104
W7220
16
R7134
S-OUT
9
C7133
C7131
L7105
J7102
D7103
R7135
W7223
L7104
Q7122
L7111
2
1
4
IC7101
14
C7112
1
C7114
W7206
L7102
C7119
C7118
LPB10114 -001C
R7102
R7129
C7124
W7208
R7127
C7135
L7108
L7109
C7137
TERMINAL PWB ASS'YLPA10114
R7172
Q7124
Q7123
Q7117
C7129
C7126
06
R7124
W7209
W7207
W7210
R7125
C7103
Q7103
Q7114
Q7115
R7128
R7133
C7107
Q7102
W7213
1
L7106
2
C7134
C7132
C7136
C7130
R7137
AV1
20
21
R7173
L7113
L7112
24
C7142
C7140
IC7104
W7204
C7147
C7150
R7145
C7141
13
W7222
R7168
C7117
C7116
C7104
C7108
C7101
C7110
C7109
R7123
IC7102
C7105
C7115
8
C7123
IC7103
C7121
R7126
1
W7203
C7122
L7101
L7103
RCA A.OUT RCA A.OUT
L7122
C7165
R7165
TERMINAL PWB
R7139
R7136
W7205
C7102
R7138
L7107
C7144
C7143
Q7112
W7217
Q7104
R7109
Q7106
C7161
C7163
R7163
1
C7138
12
R7167
R7122
Q7105
R7112
D7101
R7162
C7145
C7139
C7153
R7121
Q7113
2
L7120
R7143
C7146
R7108
L7119
L7116
R7159
D7104
R7156
W7202
R7107
R7110
R7144
C7148
1
1
C7157
J7104
L7114
R7146
Q7108
R7113
C7167
C7149
W7216
R7148
R7114
Q7107
J7105
21
R7115
C7159
2
C7170
AV2/DECODER
20
C7151
W7215
L7110
C7152
R7147
J7103
SAT-CTL
R7116
Q7109
R7117
R7119
R7111
C7166
L7117
Q7121
Q7118
W7214
2
C7158
L7118
1
R7120
R! L!
C7156
R7157
R7169
W7212
R7118
1
R7158
R7151
R7142
2
Q7111
C7164
R7160
R7154
Q7120
W7201
Q7110
L7121
C7160
R7161
C7162
R7149
3
R7164
R7155
Q7119
R7150
W7211
L7123
R7152
C7154
R7153
C7155
5
CN7102
14
CN7103
11
15
CN7101
11
CN7104
L7115
1
1
COPMONENT PARTS LOCATION GUIDE
<TERMINAL>
REF.NO.
LOCATION
CAPACITOR
C7101 B C 5C
C7102 A D 5C
C7103 A D 5D
C7104 B C 6D
C7105 B C 5C
C7106 B C 6E
C7107 B C 7E
C7108 B C 6D
C7109 A D 6D
C7110 B C 5D
C7111 B C 6E
C7112 A D 6D
C7113 B C 6E
C7114 B C 5D
C7115 A D 5D
C7116 A D 7D
C7117 A D 7D
C7118 A D 3D
C7119 B C 3D
C7120 A D 4E
C7121 B C 4D
C7122 B C 3D
C7123 B C 4D
C7124 B C 4E
C7125 A D 9E
C7126 B C 9E
C7127 B C 10E
C7129 A D 10E
C7130 B C 13C
C7131 B C 13D
C7132 B C 13C
C7133 B C 14D
C7134 B C 13C
C7135 B C 14E
C7136 B C 13C
C7137 B C 13E
C7138 A D 10C
C7139 A D 9C
C7140 B C 10C
C7141 B C 9D
C7142 B C 10D
C7143 B C 10C
C7144 B C 10C
C7145 B C 10C
C7146 B C 10C
C7147 B C 9C
C7148 B C 10C
C7149 B C 10B
C7150 B C 9D
C7151 A D 10B
C7152 A D 9B
C7153 A D 9C
C7154 B C 11A
C7155 A D 12A
C7156 B C 13B
C7157 B C 13C
C7158 B C 13B
C7159 B C 14B
C7160 B C 13A
C7161 B C 14C
C7162 B C 13A
C7163 B C 13C
C7164 B C 1B
C7165 B C 1C
C7166 B C 1B
C7167 B C 1C
C7168 A D 9E
C7169 B C 11E
C7170 B C 13B
CONNECTOR
CN7101 A D 3A
CN7102 A D 9A
CN7103 A D 6A
CN7104 A D 1A
DIODE
D7101 B C 3C
D7103 A D 12D
D7104 A D 12C
IC
IC7101 B C 6D
IC7102 B C 5D
IC7103 B C 4D
IC7104 A D 10C
JACK
J7101 A D 7E
J7102 A D 12D
J7103 A D 7B
J7104 A D 12B
J7105 A D 2B
COIL
L7101 A D 3C
L7102 A D 4D
L7103 A D 3D
L7104 A D 10D
L7105 A D 13D
L7106 A D 14C
L7107 A D 13C
L7108 A D 14D
L7109 A D 13D
L7110 A D 9B
L7111 A D 9D
L7112 A D 10C
L7113 A D 11C
L7114 A D 10C
L7115 A D 11A
L7116 A D 13C
L7117 A D 14B
L7118 A D 13B
L7119 A D 14C
L7120 A D 13C
REF.NO.
LOCATION
L7121 A D 1A
L7122 A D 1C
L7123 A D 1A
TRANSISTOR
Q7102 B C 5E
Q7103 B C 5E
Q7104 B C 4C
Q7105 B C 3C
Q7106 B C 3C
Q7107 B C 3C
Q7108 B C 4C
Q7109 B C 3B
Q7110 B C 3B
Q7111 B C 3B
Q7112 B C 6C
Q7113 B C 5C
Q7114 B C 4E
Q7115 B C 4E
Q7116 B C 10E
Q7117 B C 10E
Q7118 B C 11A
Q7119 B C 11A
Q7120 B C 11A
Q7121 B C 12B
Q7122 B C 9D
Q7123 B C 11E
Q7124 B C 11E
RESISTOR
R7102 B C 5E
R7104 B C 5E
R7105 B C 5E
R7107 B C 4C
R7108 B C 3C
R7109 B C 4C
R7110 B C 3C
R7111 B C 3B
R7112 B C 3C
R7113 B C 3C
R7114 B C 3B
R7115 B C 3B
R7116 B C 3B
R7117 B C 3B
R7118 B C 3B
R7119 B C 3B
R7120 B C 3B
R7121 B C 5C
R7122 B C 6C
R7123 B C 5D
R7124 B C 7E
R7125 B C 5E
R7126 B C 3D
R7127 B C 4E
R7128 B C 4E
R7129 B C 5E
R7130 B C 10E
R7131 B C 10E
R7132 B C 10E
R7133 A D 9E
R7134 A D 12D
R7135 B C 11D
R7136 B C 11C
R7137 B C 13C
R7138 B C 14C
R7139 B C 13C
R7140 B C 14E
R7141 B C 13E
R7142 B C 7A
R7143 B C 11C
R7144 B C 10C
R7145 B C 9D
R7146 B C 10B
R7147 B C 8B
R7148 B C 8B
R7149 B C 11A
R7150 B C 11A
R7151 B C 11A
R7152 B C 11A
R7153 B C 11A
R7154 B C 12A
R7155 B C 12A
R7156 B C 11C
R7157 B C 11B
R7158 B C 12B
R7159 B C 12C
R7160 B C 14A
R7161 B C 13A
R7162 B C 14C
R7163 B C 13C
R7164 B C 1A
R7165 B C 1C
R7167 B C 8C
R7168 B C 8D
R7169 A D 6B
R7170 B C 11E
R7171 B C 11E
R7172 B C 11E
R7173 B C 11D
REF.NO.
LOCATION
RE
4-56
Page 100

4.28 DISPLAY,EJECT SW, JACK, LED/SW AND JOG CIRCUIT BOARDS
27 EJECT SW, 28 DISPLAY, 36 JACK, 47 LED/SW, 85 JOG
LPB10126-001C
CN7003
2
2
R7033
2
J7005
R.PAUSE
R7037
R7038
R7058
R7059
C7002
1
L7061
5
R7063
R7064
R7057
D7010
VHS-
CN7001
3
R7062
D7009
PLAY
J7004
1
C7061
VHS
D7006
D7011
VHSREC
L IN
3
2
4
21
D7004
S7013
VHS
B
2
6
D7005
Q7001
R7060
1
C7065
D7066
D7065
D7061
L7062
R7061
E
2
1
J7002
V IN
D7062
D7064
D7063
R7003
R7004
3435
S7004
REC
R7001
2
1
C5
FRONT PWB
LPA10126 -
16
15
S7005
PAUSE
22
C7001
2530
-
LPA10126
EJECT SW AS.
63
JACK PWB ASS'Y
CN7002
C7020
12
23
IC7001
33
21
DI7001
FW7006
72
EJECT
VHS
S7011
LPB10126 001C
1
FW7007
6
R7032
R7031
R7002
C7005
C7006
C7003
C7004
32
C7064
FW7005
21
S7012
S-VHS
ET
R7036
R7035
S7019
START
/FF
S7018
IN.OUT
/A.DUB
J7003
R IN
3
L7063
1
C7062 C7063
3
1
L7064
R7028
R7027
S7015
RAE/REW
R7034
18
17
LPB10126 -001C
B7094
16 FW7008
B7092
C2
B7093
2
1
R7022
S7006
PLAY
C7021
11
C7010
1
44
34
15
R7010
R7023
C7009
C7008
10
R7011
R7012
R7051
R7026
R7025
R7024
C7018
R7008
R7007
R7054
R7006
FRONT PWB
85
LPA10126 -
JOG PWB ASS'Y
UN7091
8
FW7003
61
R7021
S7007
STOP
C7014
C7015
C7016
C7017
R7041
C7013
R7040
2
1
4
5
D7002
R7020
R7030
1
FW7004
6
D7012
S7010
DV/
C7019
C6
1
LPA10126 LED/SW PWB ASS'Y
DV/
HDR
HDR
D7013
D/H PLAY
D7014
D/H REC
C7007
D7001
R7013
L7001
LPA10126 C4
LED PWB ASS'Y
90
LPB10126 -001C
C3
47
S7028
RECLINK
R7052
R7053
C7022
FRONT PWB
S7017
D7019
FW7002
LPB10126 -001C
FRONT PWB
2
A.DUB
FW7001
/NAVI
S7002
CH+
D7017
HDR-LED
12
D7018
RECLINK
1
R7056
VHS DV
S7016
INSERT
/MENU
S7003
CH-
D7016
VHS
R7042
S7022
DV
/RIGHT
R7043
S7023
DUB/OK
S7027
DOWN
S7026
D7015
UP
VHS
S7021
VHS DV
/LEFT
3
R7015
IC7002
D7003
C7012
S7001
POWER
C1
C7011
1
S7014
DV EJECT
R7014
82
DV
R7046
R7045
R7055
R7047
R7044
TPGND
TP7001
TEST
LPA10126 -
DISPLAY PWB ASS'Y
4-57 4-58
 Loading...
Loading...