Page 1
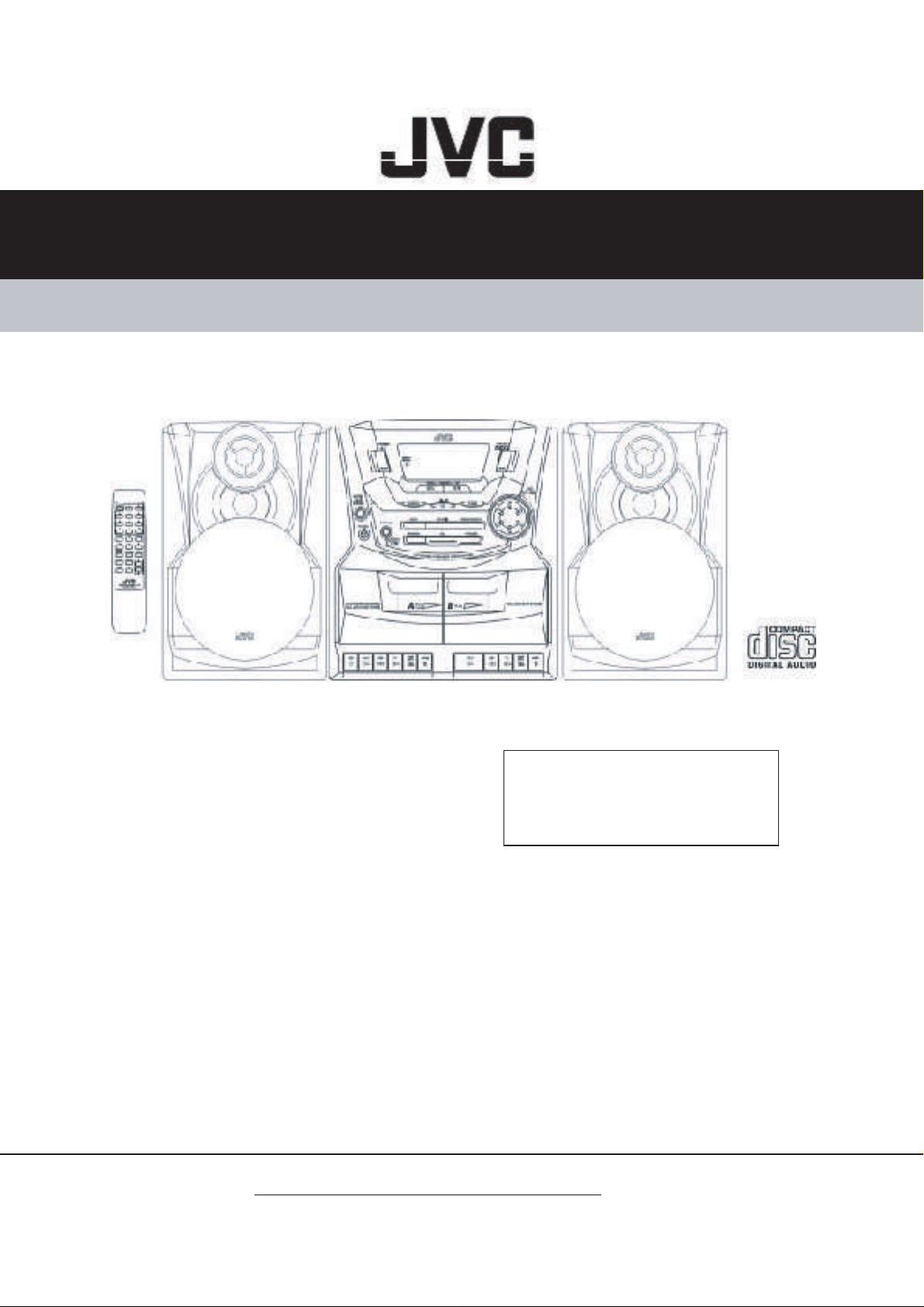
SERVICE MANUAL
CD PORTABLE COMPONENT SYSTEM
PC-X250
PC-X250
Unit No
SP-PCX250
Contents
Safety precaution ------------------ 2 Block/Wiring Diagram ------------------ 25
Disassembly method -------------- 4 Circuit Diagram -------------------------- 27
Adjustment method ---------------- 6 PCB drawing ----------------------------- 29
TOC read ---------------------------- 10 Assembly ---------------------------------- 32
Major IC Description -------------- 11 Packing ------------------------------------ 42
Unit No
CA-PCX250
Area Suffix
J ---- USA
C ---- Canada
Unit No
SP-PCX250
No. 28001
COPYRIGHT © 2001 VICTOR COMPANY OF JAPAN,LTD (By JCA)
Oct. 2001
Page 2
PC-X250
CAUTION
Safety Precautions
1. This design of this product contains special hardware and many circuits and components specially for
safety purposes. For continued protection, no changes should be made ti the original design unless
authorised in writing by the manufacturer. Replacement parts must be identical to those used in the
original circuits. Services should be performed by qualified personel only.
2. Alterations of the design or circuitry of the product should not be made. Any design alterations of the
product should not be made. Any design alterations or additions will void the manufacturer's warranty
and will further relieve the manufacturer of responsibility for personal injury or property damage
resulting therefrom.
3. Many eletrical and mechanical parts in the products have special safety-related characteristics.
These characteristics are often not evident from visual inspection nor can the protection afforded by
them necessarily be obtain by using replaement components rated for higher voltage, the Parts
List of Service manual. Electrical components having such features ate identified by the shading on the
schematics and by (
repalcement which does not have the same safety characteristics as the recommended replacement
parts shown in the Parts List of Service manual may create shock, fire, or other hazards.
4. The leads in the products are routed and dressed with ties, clamps, tubing's, barriers and the like to
be separated from live parts, high temperatures parts, moving parts and/or sharp edges for the
prevention of electric shcok and fire hazard. When service is required, the original leat routing and
dress should be observed, and it should be confirmed that they have been returned to normal, after
re-assembling.
! ) on the parts List in the Service Manual. The use of a substitute
5. Leakage current check (Electrical Shock hazard testing)
After re-assembling the product, always perform an isolation check on the exposed metap Parts of the
product (antenna terminals, knobs, metal cabinet, screw heads, headphone jack, control shafts, etc.)
to be sure the product is safe to operate without danger of electrical shock.
Do not use a line isloation transformer during this check.
Plug the AC line cord directly into the AC outlet. Using a "Leakage Current Tester", measure the
leakage current from each ecposed metal parts of the cabinet, particularly and exposed metal
part having a return path to the chassis, to a known good earth ground. Any leakage current must
not exceed 0.5mA AC (r.m.s.)
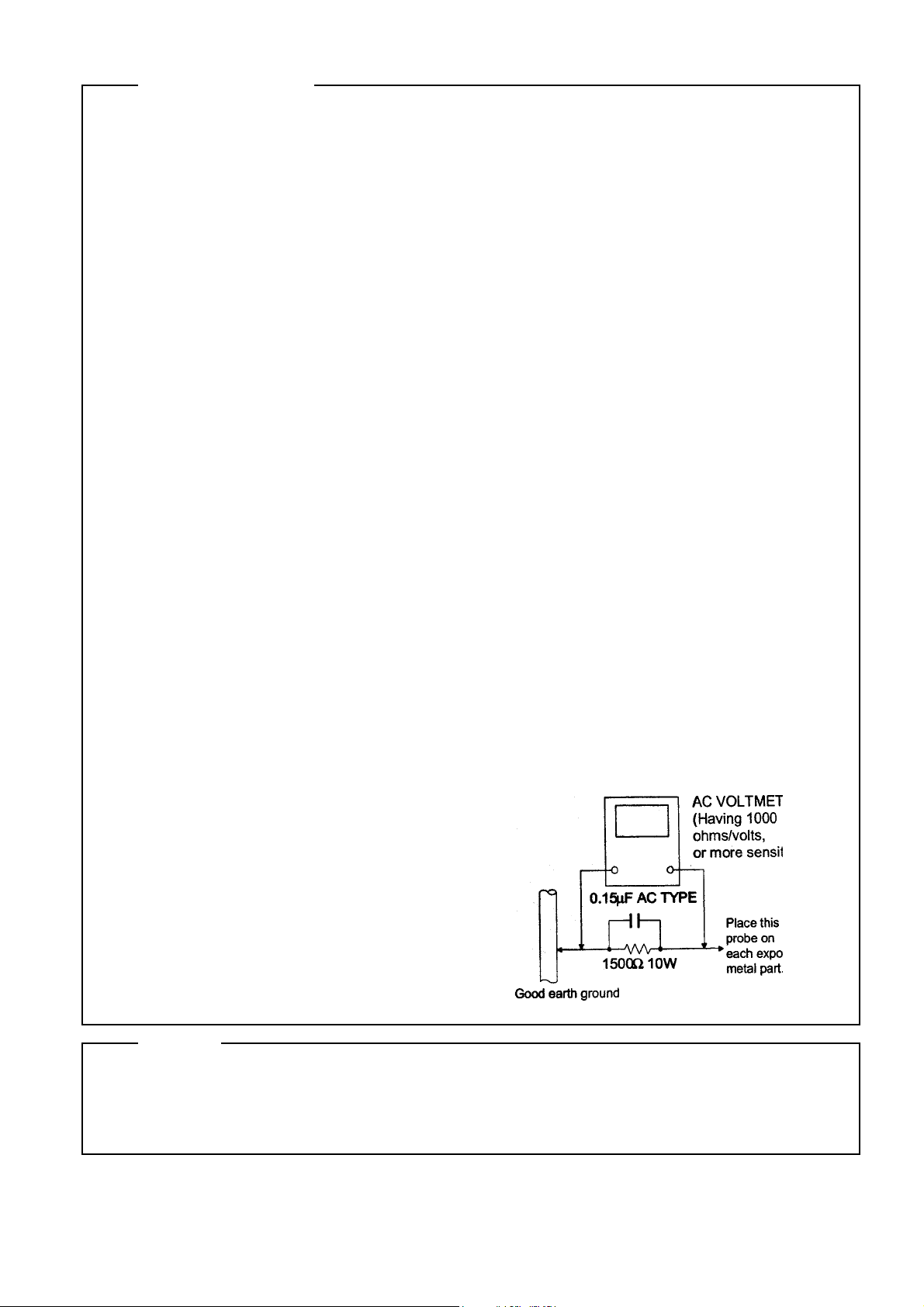
Alternate check method
Plug the AC line cord directly into the AC outlet. Use an AC voltmeter having, 1,000 ohms per
volt or more sensitvity in the following manner. Connect a 1,500 ohm 10W resistor paralleled by a
0.15uF AC-type capacitor between an exposed
metal part and a known good earth ground.
Measure the AC voltage across the resistor with
the AC voltmeter.
Move the resistor connection to each exposed
metal part, particularly and exposed metal part
having a return path to te chassis and
measure the AC voltage across the resistor. Now,
reverse the plug in the AC outlet and repeat
each measurement. Voltage measured Any must
not exceed 0.75 V AC (r.m.s.). This corresponds
to 0.5 mA AC (r.m.s.).
1. This equipment has been designed and manufactured to meet international safety standards.
2. It is the legal responsibility of the repairer to ensure that these safety standards are maintained.
3. repairs must be made in accordance with the relevant safety standards.
4. It is essential that safety critical components are replaced by approved parts.
5. It mains voltage selector is provided, check setting for local voltage.
1 - 2
Warning
Burrs formed during moulding may be left over on some parts of the chassis. Therefore,
pay attention to such burrs in the case of performing repair of this system.
Page 3
PC-X250
Preventing static electricity
Electrostatic discharge (ESD), which occurs when static electricity stored in the body, fabric, etc. is discharged,
can destroy the laser diode in the traverse unit (optical pcikup). Take care to prevent this when performing repairs.
1.1. Grounding to prevent damage by static electricity
Static electricity in the work area can destroy the optical pickup (laser diode) in devicessuch as DVD players.
Be careful to use proper grounding in the area where repairs are being performed.
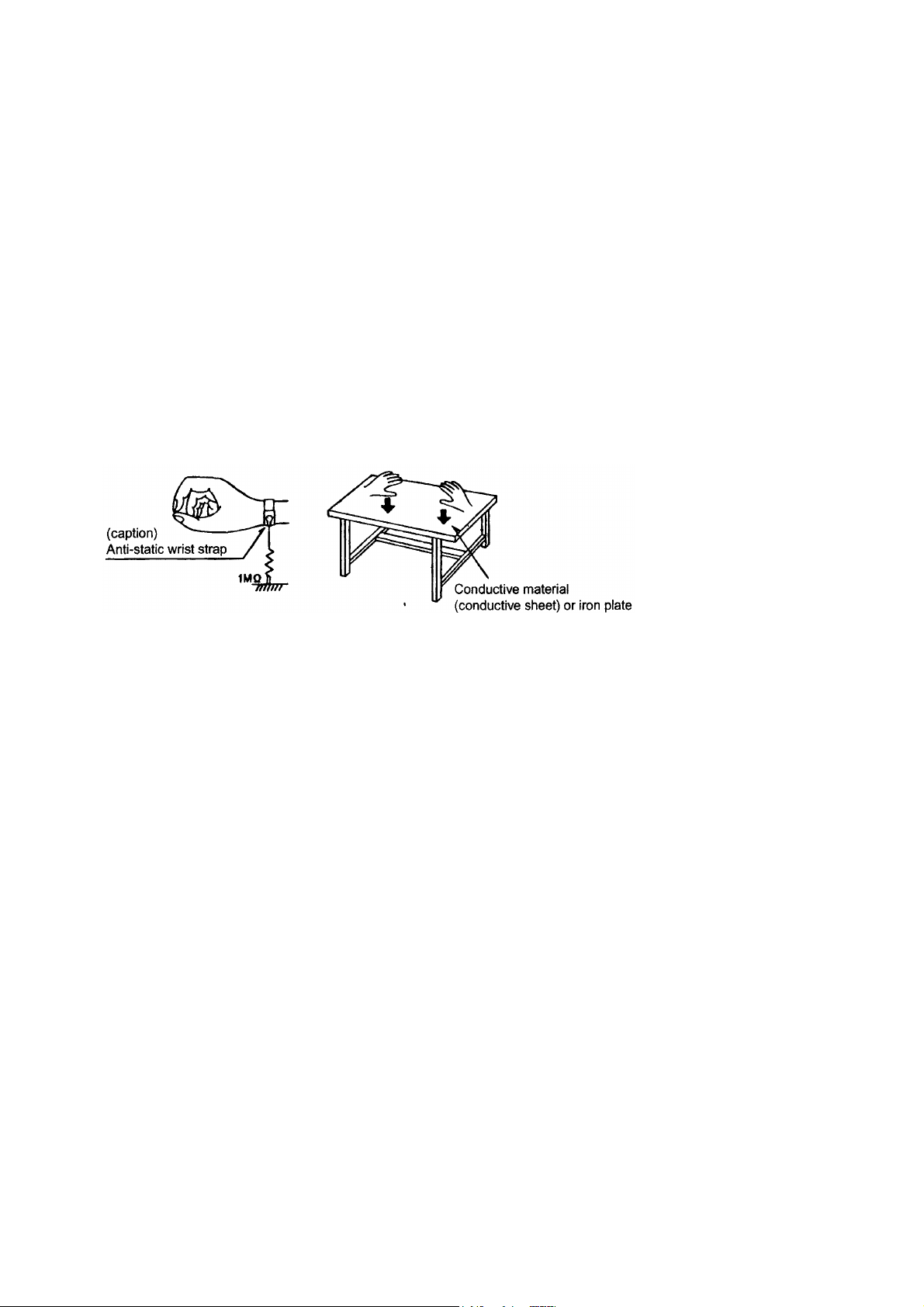
1.1.1. Gound the workbench
1.
Ground the workbench by laying conductive material (such as a conductive sheet) or an iron plate over
it before placing the traverse unit (optical pickup) on it.
1.1.2. Ground yourself
1.
Use an anti-static wrist starp to release and static electricity built up in your body.
1.1.3. Handling the optical pcikup
1.
In order to maintain quality during transport and before installation, both sides of the laser diode on the
replacement optical pickup are storted. After replacement, return the shorted parts to their original condition.
(Refer to the text.)
2.
Do not use a tester to check the condition of the laserdiode in the optical pickup. The tester's internal power
source can easily destory the laser diode.
1.2. Handling the traverse unit (optical pickup)
1.
Do not subject the traverse unit (optical pcikup) to strong shocks, as it is a sensitive, complex unit.
2.
Cut off the shorted part of the flexible cable using nippers, etc. after replacing the optical pickup. For specific
details, refer to the replacement procdeure in the text. Remove the anti-static pin when replacing the traverse
unit. Be careful not to take too long a time when attaching itto the connector.
3.
Handle the flexible cable carefully as it may break when subjected to strong force.
4.
It is not possible to adjust the semi-fixed resistor that adjusts the laser power. Do not return it.
1 - 3
Page 4
PC-X250
Disassembly method
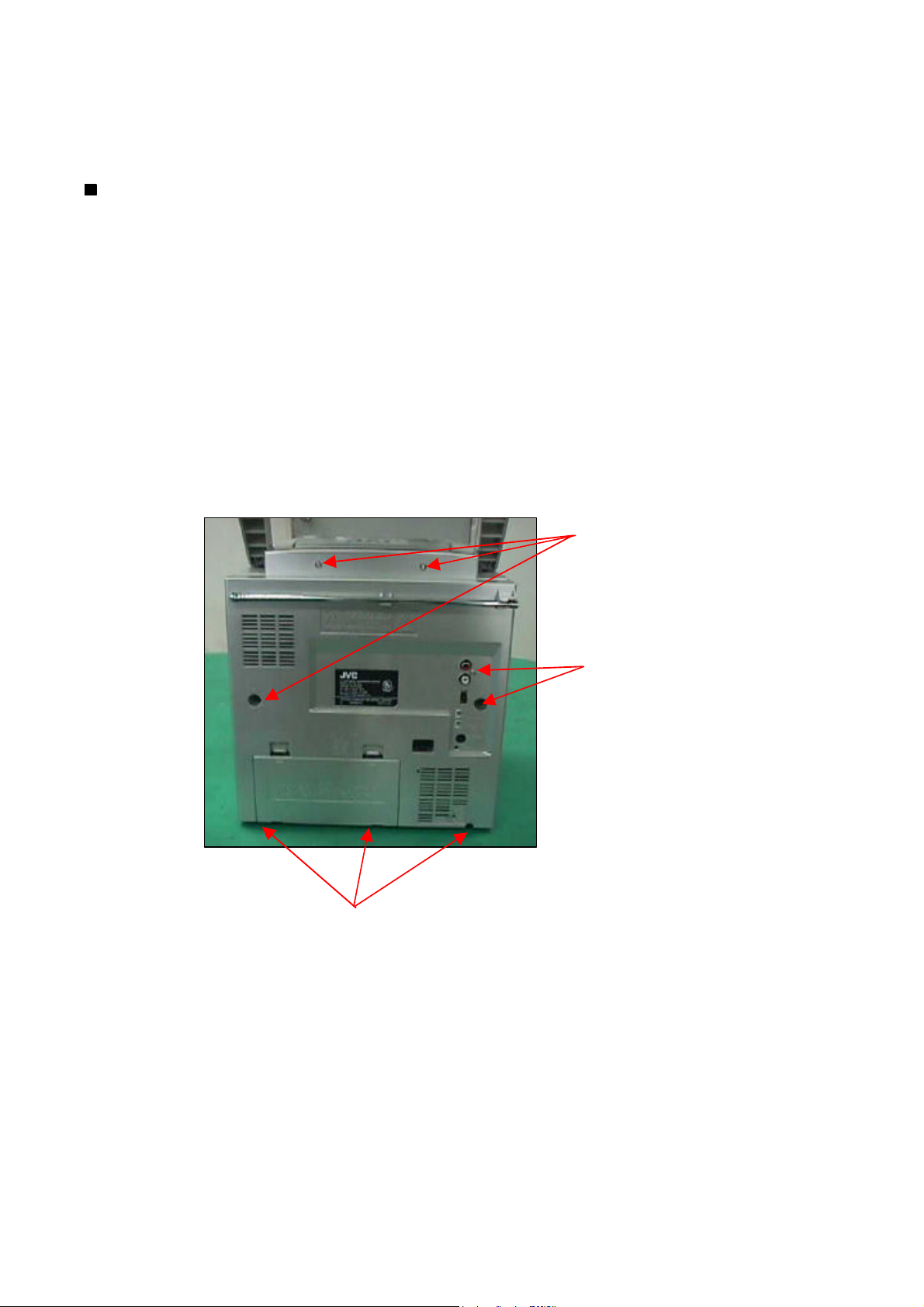
Removing the rear panel
1.
From behind the body, remove the Five screws
A
retaining the rear panel.
2.
Then remove the Two screws
B
retaining the bottom of rear panel.
3.
Take out the rear panel from the body.
Note:
Be careful of the FM antenna white wire, it is connection with the tuner PCB up side.
You can directly take out from the tuner PCB.
When you re-assembly the product, plug the FM antenna white wire into the Tuner PCB's
"FM ANT" position.
Screw A.
Screw A.
Screw B.
1 - 4
Page 5
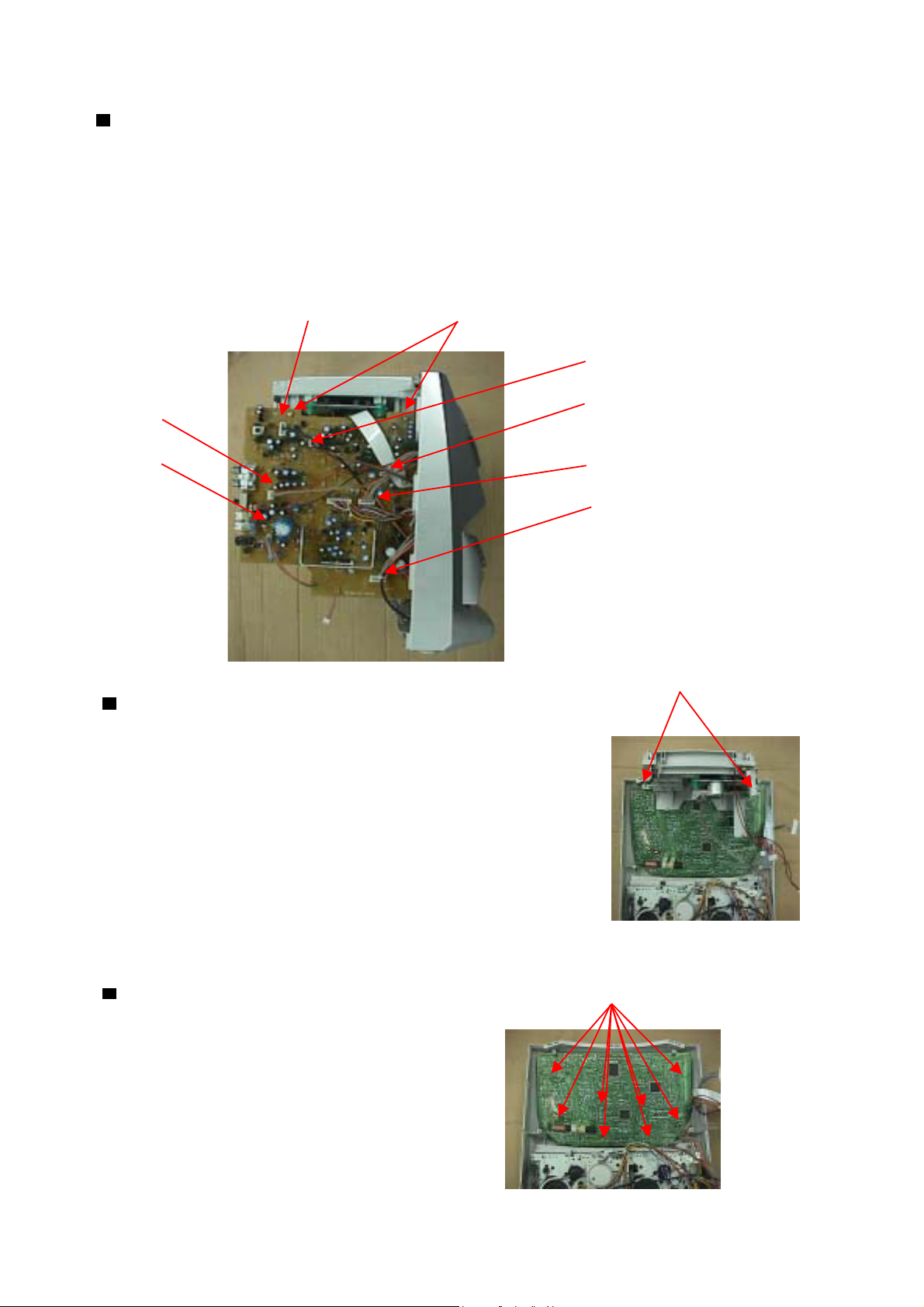
Removing the Audio Board
1.Open & remove the rear panel
2. Remove the Connector CN201, CN202, CN203, CN405, CN502, CN801
& CN301 on the Audio Board.
3. Remove the two Screws C retaining the Audio Board.
CN202 Screw C
CN201
CN502
CN203
CN801 CN405
CN301
PC-X250
Removing the CD Mechanism
1 Open & remove the rear panel
2 Remove the Audio PCB
3 Remove the Two Screws D retaining the CD Tray Backet.
Removing the Tuner PCB Screw E
1 Open & remove the rear panel.
2 Remove the Audio PCB.
3 Remove CD mechanism.
Screw D
4 Remove the Eight Screws E retaining
on the Tuner Board.
1 - 5
Page 6

PC-X250
Adjustment method
Measurement instruments required for Tuner section
adjustment
Low frequency oscillator Voltage applied to tuner ---------- +B:DC 4.9V
1
This oscillator should have a capacity to output VT:DC 12V
0dBs to 600 at an oscillation frequency of Reference measurement ----- 26.1mV(0.28V)/3
50Hz-20KHz output
Input positions ----- AM : Standard loop antenna
Electronic voltmeter FM : TP1 (hot) and TP2 (GND)
2
Distortion meter
3
Frequency counter Standard measurement position of volume
4
Wow & flutter meter
5
Test tape Bass ----------------------------------------------------- Off
6
TCC-112 : Tape speed and running unevenness (3KHz) Active hoper bass pro ------------------------ Off
TCC-140 : Reference level (1KHz) Up and down adjustment of volume ----- Vol : 23
TCC-182A : Head angle (8KHz) , playback frequency
characteristics (1KHz) and dubbing frequency Precautions for measurement
characteristics (125Hz and 8KHz) 1 Apply 30PF and 33 Kohm to the IF sweeper output
Because of frequency - mixed tape with 63 , 1 , 10 and side and 0.082UF and 100 Kohm in series to the
14KHz (250nWb/m -24dB) , use this tape together sweeper input side .
with a filter . 2 The IF sweeper output level should be made as
Black tape low as possible within the adjustable range .
7
TYPE I : AC - 225 3 Since the IF sweeper is a fixed device , there is no
TYPE II : AC - 514 need to adjust this sweeper .
8 Torque gauge : For play and back tension 4 Since a ceramic oscillator is used , there is no need
FWD(TW2111A) , REV(TW2121a) and FF/REW(TW2231A) to perform any MIX adjustment .
5 Since a fixed coil is used , there is no need to
Measurement conditions adjust the FM tracking .
6 The input and output earth systems are separated .
Power supply voltage ---------------- AC 120V (60Hz) In case of simultaneously measuring the voltage in
Reference output -------------- Speaker : 0.866V/3 both of the input and output systems with an
Headphone : 0.245V/32 electronic voltmeter for two channels , therefore , the
Reference frequency and ----- 1KHz , AUX : 450~500mV earth should be connected particularly carefully .
input level 7 In the case of BTL connection amp. , the minus
Input for confirming recording and ------- AUX : -28dBs terminal of speaker is not for earthing . Therefore , be
playback characteristics sure not to connect any other earth terminal to this
Measurement output terminal ---------- Speaker J3002 terminal . This system is of an BTL system .
* Load resistance --------------------------- 3 8 For connecting a dummy resistor when measuring
the output , use the wire with a greater code size .
Radio Input signal 9 Whenever any mixed tape is used , use the band
pass filter (DV-12V)
AM frequency -------------------------------- 400Hz
AM modulation ---------------------------------- 30%
FM frequency --------------------------------- 1 KHz
FM frequency deviation ------------------------ 22.5KHz
1 - 6
Page 7
TAPE DECK ADJUSTMENTS
1 HEAD AZIMUTH ADJUSTMET
( 1 ) Load the test tape TCC-182A 8KHz for azimuth
adjustment.
( 2 ) Press the PLAY button.
( 3 ) Use a cross-tip screwdriver to turn the screw for azimuth
adjustment so that the left and right output are maximized
( 4 ) Press the STOP button
( 5 ) After completion of the adjustment. Use thread lock(TB-1401B)
to secure the azimuth-adjustment screw.
2 AC BIAS FREQUENCY ADJUSTMENTS
( 1 ) Connect frequency counter to CN202(BS);
( 2 ) R/P swith in recording state;
( 3 ) Adjusting T801 use a plastic screwdriver, AC bias frepuency ;61kHz +/- 1kHz..
PC-X250
3 TAPE SPEED ADJUSTMENT
( 1 ) Insert the test tape(MTT-111N,3,000 HZ)
( 2 ) Press the PLAY button.
( 3 ) Use a flat-tip screwdriver to turn the VR 501.
Adjust VR501 so that the frequency counter
become 3,000Hz
TAPE HEAD AND SPEED ADJUSTMENT DIAGRAM
CASS DECK
E HEAD
A
L. SW
P/R HEAD
P HEAD
A DECK B DECK
A
L. SW
1 - 7
Page 8
PC-X250
Tape recorder section
Items Measrrnment methed
Confirmation Test tape 1 Playback the test tape TCC-182A (8KHz) Maximum Adjust the head
of head angle :TA-182A(8KHz) 2 With the recording & playback mechanism, output azimuth screw
Confirmation Test tape Adjust VR501 so that the frequrncy counter Tape speed VR501
of tape speed :TCC-112(3000Hz) reading becomes 3,010Hz +/-15Hz when of deck
Measurement Standard Adjusting]
conditions Values positions
Measurement output adjust the head azimuth screw so that the only when the
terminal left and right output levers become head has been
:Speaker terminal maximum, After adjustment, lock the head changed
Sperker R azimuth at least by half turn.
(Load resistance:3 )
:Headphone terminal
playing back the test tape TCC-112 (3000Hz) with :3,010Hz
Measurement output playback and recording mechanism after +/-15Hz
terninal ending forward winding if the taoe.
:Headphone terminal
Reference Values for Confirmation Items
ITEMS Measrrnment methed
Wow & flutter Test tape When the test tape TCC-112 (3000Hz) has been 0.25% or
Measurement Standard Adjusting]
conditions Values positions
:TCC-112(3000Hz) played back with the recording and playback less
mecganism at the beginning of forward (WRMS)
Measurement outut winding, the frequency counter reading of
terminal wow & flutter should be 0.25% or less
:Headphone terminal (WRMS).
1 - 8
Page 9

Electrical Performance
PC-X250
ITEMS Measrrnment methed
Adjustment of Mode:Forward or 1 With the recording and playback
recording bias reverse mode mechanism, load thd test tapes
current Recording mode TDK-60 , and set the mechanism to the recording 4.5 A
(Reference Test tape and pausing condition in advance . +/-0.5 A
Value) TDK-60
Adjustment of Reference frequency 1 with the recording and playback Output
recording and :1KHz and 8KHz mechanism, load the test tapes (TDK-60) deviation
playback (REF.:-20dB) and set the mechanism to the between
frequency Test tape recording and pausing condition in 1KHz and
characteristics TDK-60 advance 8KHz
Measurement Standard Adjusting
conditions Values positions
Measurement output 2 After connecting 100 in series to the
termial recorder head, measure the bias current
:Both recording and with a valve voltmeter at both of the
headphone terminals terminals
Measurement input 2 While repetitively inputting the reference :-1dB +/-2dB
terminal frequency signal of 1KHz and 10KHz from
:OSC IN OSC IN, record and playback the tape.
Reference Values for Electrical Function Confirmation Items
Items Measrrnment methed
Recording Forward or reverse 1 While changing over to and form BIAS 1 61KHz
bias Test tape and 2, confirm that the frequency is +/-1KHz
frequency TDK-60 changed
Measurement Standard Adjusting
conditions Values positions
Measurement 2 With the recording and playback
terminal : BIAS TP on mechanism, load the test tape.
P.C. board (TDK-60 ) , and set the
mechanism to the recording and pausing
condition in advance.
3 Confirm that the BIAS TP frequency on the
P.C. board is 61KHz +/-1KHz
1 - 9
Page 10

PC-X250
Flow of functional operation until TOC read
Check Point
Power ON Power Key
Tracking error waveform at TOC reading
pin 15 of
IC901(TO)
VREF
Approx
1.8V
Approx 3sec
Slider turns REST
SW ON.
Automatic tuning
of TE offset
Laser ON
Detection of disc
Automatic tuning of
Focus offset
Automatic measurement of
Focus A-curve amplitude
Disc is rotated
Focus servo ON
(Tracking servo ON)
Check that the voltage at the pin
16 of IC903 is OV (a moument)?
Check that the voltage at the
pin64 of IC901 + side is + 5V?
Confirm that the Focus error
s-cuve signal at the pin16 of
IC901 is approx.2V p-p
Confirm that the signal from
pin27 IC901 is 0V as a
accelerated pulse during
approx.400ms
Tracking
servo
off status
Disc status
to rotate
Automatic measurement
of TO amplitude and
automatic tuning of
TO balance
500mV/div, 2mS/div Fig.1
Tracking
servo
on status
TOC reading
finishes
Disc to be
braked to
stop
Automatic measurement of
Tracking error amplitude
Automatic tuning of
Tracking error balance
Automatic tuning of
Focus error balance
Automatic tuning of
Focus error gain
Automatic tuning of
Tracking error gain
TOC reading
Play a disc
Confirm the waveform of
the Tracking error signal
at the pin15 of IC901 (R975)
(See fig-1)
Confirm the eys-pattern
at the lead of TP1
1 - 10
Page 11

Description of major ICs
LC587008
PC-X250
System Block Diagram for the LC587008, LC587006 and LC587004
RAM: Data memory
ROM: Program memory
DP: Data pointer register
BNK: Bank register
APG: RAM page flags
AC: Accumulator
ALU: Arithmetic and logic unit
B: B register
OPG: ROM page flag
PC: Program counter
IR: Instruction register
STS1: Status register 1
STS2: Status register 2
STS3: Status register 3
STS4: Status register 4
STS5: Status register 5
PLA: Segment data and strobe programmable logic
array
WAIT.C:Waiting time counter
1 - 11
Page 12

PC-X250
LC72131 Block Diagram
1 - 12
Page 13

LC72131 Pin Functions
Pin No.
Symbol (MFP pin Nos. are Type Functions Circuit configuration
in parentheses.)
XIN
XOUT
FMIN
AMIN
CE
CL
DI
DO
V
DD
1 (1)
22 (20)
16 (14)
15 (13)
3 (2)
5 (4)
4 (3)
6 (5)
17 (15)
Xtal OSC
Local oscillator
signal input
Local oscillator
signal input
Chip enable
Clock
Data input
Data output
Power supply
¥ Crystal resonator connection
(4.5/7.2 MHz)
¥ FMIN is selected when the serial data input DVS bit is
set to 1.
¥ The input frequency range is from 10 to 160 MHz.
¥ The input signal passes through the internal divide-by-
two prescaler and is input to the swallow counter.
¥ The divisor can be in the range 272 to 65535. However,
since the signal has passed through the divide-by-two
prescaler, the actual divisor is twice the set value.
¥ AMIN is selected when the serial data input DVS bit is
set to 0.
¥ When the serial data input SNS bit is set to 1:
Ñ The input frequency range is 2 to 40 MHz.
Ñ The signal is directly input to the swallow counter.
Ñ The divisor can be in the range 272 to 65535, and
the divisor used will be the value set.
¥ When the serial data input SNS bit is set to 0:
Ñ The input frequency range is 0.5 to 10 MHz.
Ñ The signal is directly input to a 12-bit programmable
divider.
Ñ The divisor can be in the range 4 to 4095, and the
divisor used will be the value set.
Set this pin high when inputting (DI) or outputting (DO)
serial data.
¥ Used as the synchronization clock when inputting (DI) or
outputting (DO) serial data.
¥ Inputs serial data transferred from the controller to the
LC72131.
¥ Outputs serial data transferred from the LC72131 to the
controller.
The content of the output data is determined by the
serial data DOC0 to DOC2.
¥ The LC72131 power supply pin (V
DD
= 4.5 to 5.5 V)
¥ The power on reset circuit operates when power is first
applied.
PC-X250
1 - 13
Page 14

PC-X250
LC72131 Pin Functions
Symbol (MFP pin Nos. are Type Functions Circuit configuration
V
SS
BO1
BO2
BO3
BO4
IO1
IO2
Pin No.
in parentheses.)
21 (19)
7 (6)
8 (7)
9 (8)
10 (9)
11 (10)
13 (12)
Ground
Output port
I/O port
¥ The LC72131 ground Ñ
¥ Dedicated output pins
¥ The output states are determined by BO1 to BO4 bits in
the serial data.
Data: 0 = open, 1 = low
¥ A time base signal (8 Hz) can be output from the BO1
pin. (When the serial data TBC bit is set to 1.)
¥ Care is required when using the BO1 pin, since it has a
higher on impedance that the other output ports (pins
BO2 to BO4).
¥ All output ports are set to the open state following a
power on reset.
¥ I/O dual-use pins
¥ The direction (input or output) is determined by bits IOC1
and IOC2 in the serial data.
Data: 0 = input port, 1 = output port
¥ When specified for use as input ports:
The state of the input pin is transmitted to the controller
over the DO pin.
Input state: low = 0 data value
high = 1 data value
¥ When specified for use as output ports:
The output states are determined by the IO1 and IO2
bits in the serial data.
Data: 0 = open, 1 = low
¥ These pins function as input pins following a power on
reset.
PD
AIN
AOUT
IFIN
18 (16)
19 (17)
20 (18)
12 (11)
Charge pump
output
LPF amplifier
transistor
IF counter
¥ PLL charge pump output
When the frequency generated by dividing the local
oscillator frequency by N is higher than the reference
frequency, a high level is output from the PD pin.
Similarly, when that frequency is lower, a low level is
output. The PD pin goes to the high impedance state
when the frequencies match.
¥ The n-channel MOS transistor used for the PLL active
low-pass filter.
¥ Accepts an input in the frequency range 0.4 to 12 MHz.
¥ The input signal is directly transmitted to the IF counter.
¥ The result is output starting the MSB of the IF counter
using the DO pin.
¥ Four measurement periods are supported: 4, 8, 32, and
64 ms.
1 - 14
Page 15
LC75342 Pin Assignment
DI 1 30 CL
CE 2 29 VDD
VSS 3 28 VREF
TEST 4 27 NC
LOUT 5 26 ROUT
LBASS2 6 25 RBASS2
LBASS1 7 24 RBASS1
LTRE 8 23 RTRE
LC75342
LIN 9 22 RIN
LSELO 10 21 RSELO
L4 11 20 R4
L3 12 19 R3
L2 13 18 R2
L1 14 17 R1
NC 15 16 NC
TOP VIEW
PC-X250
LC75342 Pin Functions.
Pin No. Pin Description Notes
¥ Connection to the 0.5 ´ VDDvoltage generator circuit used as the
28 Vref
V
SS
V
DD
2CE
1
30
4
DI
CL
V
SS
analog signal ground.
Applications must connect a capacitor of about 10 µF between this pin
and VSSto exclude power supply ripple.
¥ Ground3
¥ Power supply29
¥ Chip enable
Data is written to the internal latch when this pin goes from high to low.
The internal analog switches operate at this point. Data transfer is
enabled when this pin is high.
¥ Serial data and clock inputs used for IC control.
¥ Electronic volume and tone control testing
This pin must be tied to VSSduring normal operation.
15
16
27
NC
¥ Unused.
These pins must be left open or connected to VSSduring normal
operation.
1 - 15
Page 16

PC-X250
LC75342 Pin Functions
Pin No. Pin Description Notes
14
13
12
11
17
18
19
20
10
21
7
6
24
25
L1
L2
L3
L4
R1
R2
R3
R4
LSEL0
RSEL0
LBASS1
LBASS2
RBASS1
RBASS2
¥ Input signal connections
¥ Input selector outputs
¥ Connections for the resistors and capacitors that form the bass band
filters.
1 - 16
9
22
5
26
8
23
LIN
RIN
LOUT
ROUT
LTRE
RTRE
¥ Volume control and equalizer input
¥ Volume and equalizer outputs
¥ Connections for the capacitors that form the treble band filters.
Page 17

LC78622 Pin Assignment
PC-X250
LC78622 Pin Function
Pin No. Symbol I/O Function
51 SBCK I Subcode readout clock input. This is a Schmitt input. (Must be connected to 0 V when unused.)
52 FSX O Output for the 7.35 kHz synchronization signal divided from the crystal oscillator
53 WRQ O Subcode Q output standby output
54 RWC I Read/write control input. This is a Schmitt input.
55 SQOUT O Subcode Q output
56 COIN I Command input from the control microprocessor
57 CQCK I Input for both the command input clock and the subcode readout clock. This is a Schmitt input.
58 RES I Chip reset input. This pin must be set low briefly after power is first applied.
59 TST11 O Test output. Leave open. (Normally outputs a low level.)
60 16M O 16.9344 MHz output.
61 4.2M O 4.2336 MHz output
62 TEST5 I Test input. A pull-down resistor is built in. Must be connected to 0 V.
63 CS I Chip select input. A pull-down resistor is built in. Must be connected to 0 V if not controlled.
64 TEST1 I Test input. No pull-down resistor. Must be connected to 0 V.
Note: The same potential must be supplied to all power supply pins, i.e., VDD, VVDD, LVDD, RVDD, and XVDD.
1 - 17
Page 18

PC-X250
LC78622 Pin Functions
Pin No. Symbol I/O Function
1 DEFI I Defect detection signal (DEF) input. (Must be connected to 0 V when unused.)
2 TAI I Test input. A pull-down resistor is built in. Must be connected to 0 V.
3 PDO O External VCO control phase comparator output
4 VV
SS
5 ISET AI PDO output current adjustment resistor connection
6 VV
DD
7 FR AI VCO frequency range adjustment
8 V
SS
9 EFMO O
10 EFMIN I EFM signal input
11 TEST2 I Test input. A pull-down resistor is built in. Must be connected to 0 V.
12 CLV
13 CLV
14 V/P O
15 HFL I Track detection signal input. This is a Schmitt input.
16 TES I Tracking error signal input. This is a Schmitt input.
17 TOFF O Tracking off output
18 TGL O Tracking gain switching output. Increase the gain when low.
19 JP
20 JP
+
Ð
21 PCK O EFM data playback clock monitor. Outputs 4.3218 MHz when the phase is locked.
22 FSEQ O
23 V
DD
24 CONT1 I/O General-purpose I/O pin 1
25 CONT2 I/O General-purpose I/O pin 2
26 CONT3 I/O General-purpose I/O pin 3 must be either set up as input ports and connected to 0 V, or set up as output ports and
27 CONT4 I/O General-purpose I/O pin 4
28 CONT5 I/O General-purpose I/O pin 5
29 EMPH O De-emphasis monitor pin. A high level indicates playback of a de-emphasis disk.
30 C2F O C2 flag output
31 DOUT O Digital output. (EIAJ format)
32 TEST3 I Test input. A pull-down resistor is built in. Must be connected to 0 V.
33 TEST4 I Test input. A pull-down resistor is built in. Must be connected to 0 V.
34 N.C. Ð Unused. Must be left open.
35 MUTEL O Left channel mute output
36 LV
DD
37 LCHO O one-bit D/A converter Left channel output
38 LV
39 RV
SS
SS
40 RCHO O
41 RV
DD
42 MUTER O Right channel mute output
43 XV
44 X
45 X
46 XV
DD
OUT
IN
SS
47 SBSY O Subcode block synchronization signal output
48 EFLG O C1, C2, single and double error correction monitor pin
49 PW O Subcode P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W output
50 SFSY O Subcode frame synchronization signal output. This signal falls when the subcodes are in the standby state.
Ð
PLL pins
Internal VCO ground. Must be connected to 0 V.
Ð Internal VCO power supply
Ð Digital system ground. Must be connected to 0 V.
Slice level control
+
O
Ð
Disc motor control output.
O Three-value output is also possible when specified by microprocessor command.
EFM signal output
Rough servo/phase control automatic switching monitor output. Outputs a high level during rough servo and a low level
during phase control.
O
Track jump output.
O Three-value output is also possible when specified by microprocessor command.
Synchronization signal detection output. Outputs a high level when the synchronization signal detected from the EFM
signal and the internally generated synchronization signal agree.
Ð Digital system power supply.
Controlled by serial data commands from the microprocessor. Any of these that are unused
left open.
Ð
Left channel
Left channel power supply
Ð Left channel ground. Must be connected to 0 V.
Ð Right channel ground. Must be connected to 0 V.
Right channel
Right channel output
Ð one-bit D/A converter Right channel power supply
Ð Crystal oscillator power supply.
O
Connections for a 16.9344 crystal oscillator element
I
Ð Crystal oscillator ground. Must be connected to 0 V.
1 - 18
Page 19

LA6541D Pin Assignment
PC-X250
1
Level Shift
4
Level Shift
2
Level Shift
Regulator
3
Level Shift
1 - 19
Page 20

PC-X250
LA6541D Pin Functions
Pin No. Pin Name Description (Function)
1V
CC
2 Mute ON/OFF control for all BTLAMP outputs
3V
1 BTL AMP 1 input
IN
4 VG1 BTL AMP 1 input (for gain control)
5V
6V
1 BTL AMP 1 output (non-inverting side)
O
2 BTL AMP 1 output (inverting side)
O
7 GND GND (minimum electric potential)
8 GND GND (minimum electric potential)
9 GND GND (minimum electric potential)
10 V
11 V
3 BTL AMP 2 output (inverting side)
O
4 BTL AMP 2 output (non-inverting side)
O
12 VG2 BTL AMP 2 input (for gain control)
13 V
2 BTL AMP 2 input
IN
14 REG OUT Connection for collector of external transistor (PNP); 5 V supply output
15 REG IN Connection for base of external transistor (PNP)
16 RES
17 C
18 V
D
3 BTL AMP 3 input
IN
19 VG3 BTL AMP 3 input (for gain control)
20 V
21 V
5 BTL AMP 3 output (non-inverting side)
O
6 BTL AMP 3 output (inverting side)
O
22 GND GND (minimum electric potential)
23 GND GND (minimum electric potential)
24 GND GND (minimum electric potential)
25 V
26 V
7 BTL AMP 4 output (inverting side)
O
8 BTL AMP 4 output (non-inverting side)
O
27 VG4 BTL AMP 4 input (for gain control)
28 V
29 V
30 V
4 BTL AMP 4 input
IN
REF
CC
Power supply (shorted with pin 30)
Reset output
Reset output delay time setting (with capacitor)
Reference voltage input for level shift circuit
Power supply (shorted with pin 1)
1 - 20
Page 21

LA9241M Equivalent Circuit Block Diagram
Microcontroller
INTERFACE
PC-X250
1 - 21
Page 22

PC-X250
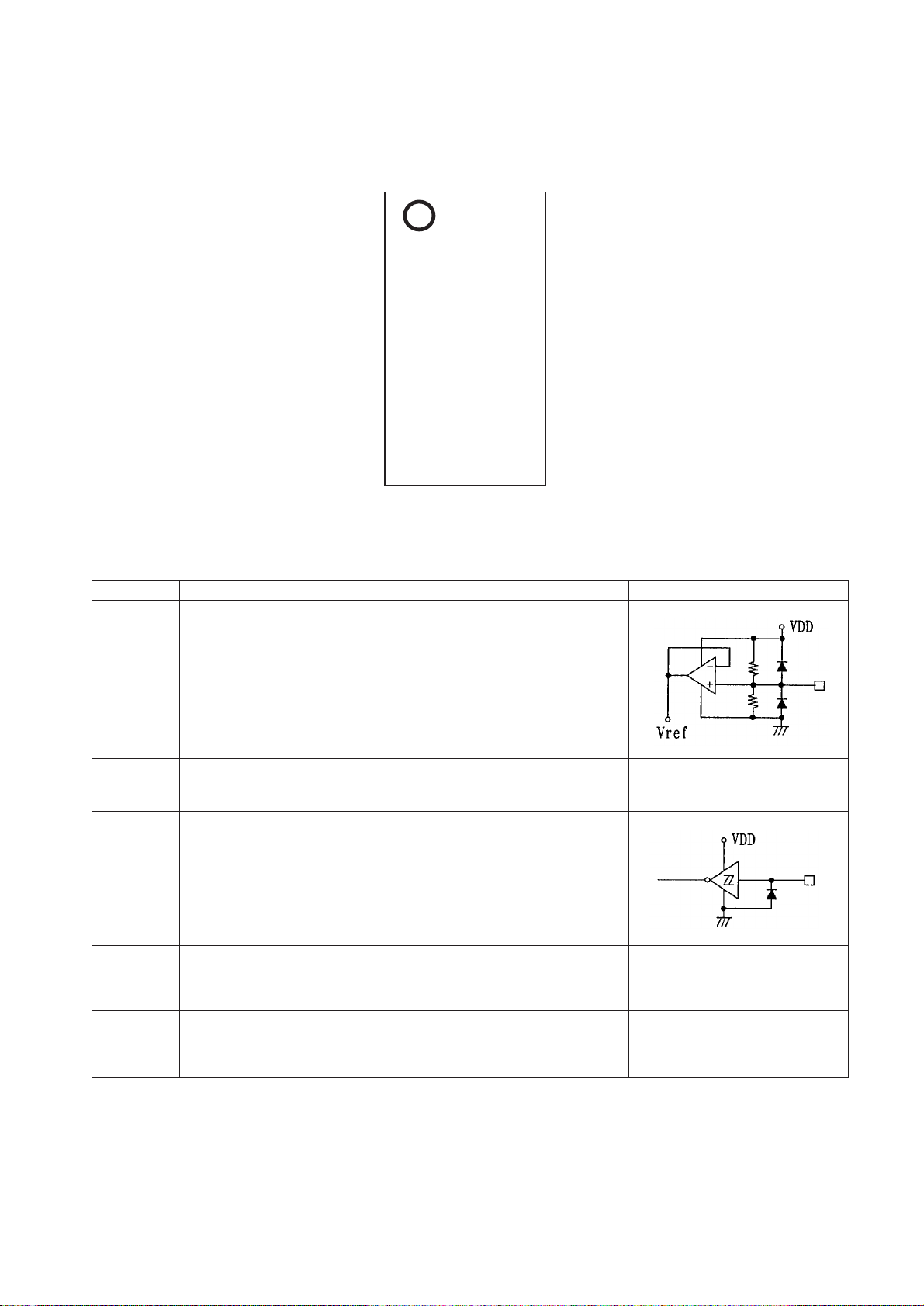
Pin
No.
1 FIN2 Pickup photodiode connection pin.Added to FIN1 pin to generate the RF signal, subtracted from FIN1 pin to generate
2 FIN1 Pickup photodiode connection pin.
3 E Pickup photodiode connection pin. Subtracted from F pin to generate the TE signal.
4 F Pickup photodiode connection pin.
5 TB TE signal DC component input pin.
6TE
7 TE TE signal output pin.
8 TESI TES (Track Error Sense) comparator input pin. The TE signal is input through a bandpass filter.
9 SCI Shock detection input pin.
10 TH Tracking gain time constant setting pin.
11 TA TAamplifier output pin.
12 TD
13 TD Tracking phase compensation setting pin.
14 JP Tracking jump signal (kick pulse) amplitude setting pin.
15 TO Tracking control signal output pin.
16 FD Focusing control signal output pin.
17 FD
18 FA Pin for configuring the focusing phase compensation constant between the FD
19 FA
20 FE FE signal output pin.
21 FE
22 AGND Analog signal GND.
23 NC No connection
24 SP CV
25 SPG 12-cm spindle mode gain setting resistor connection pin.
26 SP
27 SPD Spindle control signal output pin.
28 SLEQ Sled phase compensation constant connection pin.
29 SLD Sled control signal output pin.
30 SL
31 SL
32 JP
33 JP
34 TGL Input pin for tracking gain control signal from DSP. Gain is low when TGL is high.
35 TOFF Input pin for tracking off control signal from DSP. Tracking servo is off when TOFF is high.
36 TES Output pin for TES signal to DSP.
37 HFL The High Frequency Level is used to determine whether the main beam is positioned over a bit or over the mirrored
38 SLOF Sled servo off control input pin
39 CV
40 CV
41 RFSM RF output pin.
42 RFS
43 SLC Slice Level Control is an output pin that controls the data slice level used by the DSP for the RF waveform.
44 SLI Input pin used by DSP for controlling the data slice level.
45 DGND Digital system GND pin.
46 FSC Focus search smoothing capacitor output pin.
47 TBC Tracking Balance Control; EF balance adjustment variable range setting pin
48 NC No connection
49 DEF Disc defect detection output pin.
50 CLK Reference clock input pin. 4.23 MHz signal from the DSP is input.
51 CL Microprocessor command clock input pin.
Pin
No.
52 DAT Microprocessor command data input pin.
53 CE Microprocessor command chip enable input pin.
54 DRF RF level detection output (Detect RF).
55 FSS Focus Search Select; focus search mode (± search/+search vs. the reference voltage) switching pin
56
57 REFI By-pass capacitor connection pin for reference voltage.
58 VR Reference voltage output pin.
59 LF2 Disc defect detection time constant setting pin.
60 PH1 RF signal peak hold capacitor connection pin.
61 BH1 RF signal bottom hold capacitor connection pin.
62 LDD APC circuit output pin.
63 LDS APC circuit input pin.
64
LA9241 Pin Functions
Symbol Contents
the FE signal.
?
Pin which connects the TE signal gain setting resistor between this pin and TE pin.
?
Pin for configuring the tracking phase compensation constant between the TD and VR pins.
?
Pin for configuring the focusing phase compensation constant between the FD and FA pins.
?
Pin for configuring the focusing phase compensation constant between the FA and FE pins.
?
Pin which connects the FE signal gain setting resistor between this pin and FE pin.
+
and CV?pins input signal single-end output.
?
Spindle phase compensation constant connection pin, along with the SPD pin.
?
Input pin for sled movement signal from microprocessor.
+
Input pin for sled movement signal from microprocessor.
?
Input pin for tracking jump signal from DSP.
+
Input pin for tracking jump signal from DSP.
surface.
?
Input pin for CLV error signal from DSP.
+
Input pin for CLV error signal from DSP.
?
RF gain setting and EFM signal 3T compensation constant setting pin, along with the RFSM pin.
Symbol Contents
V
2 Servo system and digital system VCCpin.
CC
V
1 RF system VCCpin.
CC
?
and FA?pins.
1 - 22
Page 23

BA3126 Block Diagram
BA3308 Block Diagram
PC-X250
1 - 23
Page 24

PC-X250
BA3416BL Block Diagram
1 - 24
 Loading...
Loading...