Page 1

SERVICE MANUAL
DIGITAL VIDEO CAMERA
GR-DVP8EK,GR-DVP8EX,GR-DVP8EY,
GR-DVP9EK,GR-DVP9E
X,GR-DVP9EY,GR-DVP9EZ
For disassembling and assembling of MECHANISM ASSEMBLY, refer to the SERVICE MANUAL No.86700(MECHANISM ASSEMBLY).
SPECIFICATIONS
For General
Power supply : DC 6.3 V(Using AC Power Adapter/Charger)
Power consumption
LCD monitor off, viewfinder on : Approx. 3.9 W
LCD monitor on, viewfinder off : Approx. 4.7 W
Dimensions (W x H x D) : 43mm x 115mm x 80mm
Weight : Approx.350g
Operating temperature :0°C to 40°C
Operating humidity : 35% to 80%
Storage temperature : –20°C to 50°C
Pickup : 1/4" CCD
Lens : F 1.8, f = 3.8 mm to 38 mm, 10:1 power zoom lens
LCD monitor : 2" diagonally measured, LCD panel/TFT active matrix system
Viewfinder : Electronic viewfinder with 0.44" colour LCD
Speaker : Monaural
For Digital Video Camera
Format : DV format (SD mode)
Signal format : PAL standard
Recording/Playback format : Video:Digital component recording
Cassette : Mini DV cassette
Tape speed : SP:18.8mm/s
Maximum recording time
(using 80 min. cassette)
For Digital Still Camera
Storage media : SD Memory Card/MultiMediaCard
Compression system : Still image:JPEG (compatible)
File size
Still image : 4 modes (1600x1200 pixels/1280x960 pixels/1024x768 pixels/
Moving image : 2 modes (240x176 pixels/160x120 pixels)
Picture quality : 2 modes (FINE/STANDARD)
Approximate number of storable images
(The specifications shown pertain specifically to the model GR-DVP8EK and GR-DVP9EK.)
Camcorder
DC 7.2 V(Using battery pack)
(with the LCD monitor closed and the viewfinder pushed back in)
(without grip belt, battery and cassette)
Approx.420g
(incl. grip belt, battery and cassette)
(It is not possible to attach any lens filter or conversion lens.)
For Connectors
S/AV
S-Video input
(GR-DVP9 only)
S-Video output : Y:1.0 V (p-p), 75 Ω, analogue
Video input
(GR-DVP9 only)
Video output : Y:1.0 V (p-p), 75Ω, analogue
Audio input
(GR-DVP9 only)
Audio output : 300 mV (rms), 1kΩ, analogue, stereo
Edit : ø3.5mm, 2-pole
Headphone output :
DV
Input/output
(GR-DVP9 only)
Output
(GR-DVP8 only)
USB :
: Y:0.8 Vto1.2V (p-p), 75 Ω, analogue
C:0.2 Vto0.4 V (p-p), 75 Ω, analogue
C:0.29 V (p-p), 75 Ω, analogue
: Y:0.8 Vto1.2V (p-p), 75Ω, analogue
: 300 mV (rms), 50kΩ, analogue, stereo
Stereo
: 4-pin, IEEE 1394 compliant
: 4-pin, IEEE 1394 compliant
5-pin
AC Power Adapter/Charger
For General
Audio:PCM digital recording, 32kHz 4-channel (12-bit), 48kHz
2-channel (16-bit)
LP:12.5mm/s
: SP:80min.
LP:120min.
Moving image:MPEG4 (compatible)
640x480 pixels)
: pg.39
Power requirement : AC 110V to 240Vd, 50Hz/60Hz
Power consumption :
Output
Charge :
VTR :
Specifications shown are for SP mode unless otherwise indicated. E & O.E. Design and specifications subject
to change without notice.
23W
DC 7.2 V , 1.2 A
DC 6.3 V , 1.8 A
GR-DVP8EK,GR-DVP8EX,GR-DVP8EY,GR-DVP9EK,GR-DVP9EX,GR-DVP9EY,GR-DVP9EZ M3D7S3
COPYRIGHT © 2003 VICTOR COMPANY OF JAPAN, LTD
No.86729
2003/04
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Section Title Page Section Title Page
Important Safety Precautions
INSTRUCTIONS
1. DISASSEMBLY
1.1 BEFORE ASSEMBLY AND DISASSEMBLY............................ 1-1
1.1.1 Precautions ........................................................................... 1-1
1.1.2 Assembly and disassembly................................................... 1-1
1.1.3 Destination of connectors ..................................................... 1-1
1.1.4 Disconnection of Connectors (Wires) ................................... 1-1
1.2 JIGS AND TOOLS REQUIRED FOR DISASSEMBLY,
ASSEMBLY AND ADJUSTMENT............................................. 1-2
1.2.1 Tools required for adjustments .............................................. 1-2
1.3 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY OF CABINET PARTS
AND BOARD ASSEMBLY........................................................ 1-2
1.3.1 Disassembly flow chart ......................................................... 1-2
1.3.2 Disassembly method............................................................. 1-3
1.4 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY OF 5 MONITOR ASSY............. 1-8
1.4.1 5 MONITOR ASSY/HINGE ASSY ....................................... 1-8
1.4.2 HINGE ASSY ........................................................................ 1-8
1.5 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY OF 8 LOWER CASE ASSY...... 1-9
1.6
DISASSEMBLY OF = OP BLOCK ASSY(CCD BOARD ASSY) ..
1.6.1 Precautions ......................................................................... 1-10
1.6.2 Disassembly method........................................................... 1-10
1.6.3 Assembly method................................................................ 1-10
1.6.4 Replacement of service parts ............................................. 1-10
1.7 DISASSEMBLY OF ~ E. VF UNIT .........................................1-11
1.7.1 ~ E. VF UNIT ......................................................................1-11
1.8 EMERGENCY DISPLAY ........................................................ 1-12
1.9 SERVICE NOTE .................................................................... 1-13
1-10
2. MECHANISM
Refer to the SERVICE MANUAL No.86700(MECHANISM ASSEMBLY)
4.24 W/B AND CCD SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS ............................. 4-49
4.25 EJECT AND VF BL SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS ...................... 4-50
4.26 MAIN CIRCUIT BOARD ......................................................... 4-51
4.27 OP MDA CIRCUIT BOARD .................................................... 4-57
4.28 BOTTOM CIRCUIT BOARD ................................................... 4-59
4.29 MONITOR, CCD, EJECT AND VF BL CIRCUIT BOARDS.... 4-61
4.30 VOLTAGE CHARTS ............................................................... 4-63
4.31 POWER SYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM ................................... 4-67
4.32 VIDEO SYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM...................................... 4-69
5. PARTS LIST
5.1 EXPLODED VIEW ...................................................................... 5-1
5.1.1 PACKING AND ACCESSORY ASSEMBLY <M1> ................ 5-1
5.1.2 FINAL ASSEMBLY <M2>...................................................... 5-2
5.1.3 MECHANISM ASSEMBLY <M3> .......................................... 5-4
5.1.4 ELECTRONIC VIEWFINDER ASSEMBLY <M4> ................. 5-5
5.1.5 MONITOR ASSEMBLY <M5> ............................................... 5-5
5.2 PARTS LIST ................................................................................ 5-6
PACKING AND ACCESSORY PARTS LIST<M1>.......................... 5-6
FINAL PARTS LIST<M2>................................................................ 5-6
MECHANISM PARTS LIST<M3>.................................................... 5-8
ELECTRIC VIEWFINDER PARTS LIST<M4> ................................ 5-8
MONITOR PARTS LIST<M5>......................................................... 5-9
MAIN BOARD ASSEMBLY <01> .................................................... 5-9
OP MDA BOARD ASSEMBLY <02> ............................................. 5-19
BOTTOM BOARD ASSEMBLY <03>............................................ 5-20
MONITOR BOARD ASSEMBLY <04> .......................................... 5-20
CCD BOARD ASSEMBLY <05> ................................................... 5-20
EJECT BOARD ASSEMBLY <06>................................................ 5-21
VF BL BOARD ASSEMBLY <07> ................................................. 5-21
3. ADJUSTMENT
3.1 PRECAUTION.......................................................................... 3-1
3.1.1 Precaution ............................................................................. 3-1
3.1.2 Required test equipment ....................................................... 3-1
3.1.3 Tools required for adjustments .............................................. 3-1
3.2 MECHANISM COMPATIBILITY ADJUSTMENT ...................... 3-2
3.2.1 Jig connector cable connection............................................. 3-2
3.2.2 Tape pattern check................................................................ 3-3
3.3 ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENT .................................................. 3-3
3.3.1 Electrical adjustment with PERSONAL COMPUTER ........... 3-3
3.3.2 Setup..................................................................................... 3-3
4. CHARTS AND DIAGRAMS
NOTES OF SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ............................................... 4-1
CIRCUIT BOARD NOTES ................................................................ 4-2
4.1 BOARD INTERCONNECTIONS................................................. 4-3
4.2 SYSCON-CPU SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM.................................... 4-5
4.3 SERVO SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ............................................... 4-7
4.4 MDA SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM.................................................... 4-9
4.5 AUDIO AD/DA SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM .................................. 4-11
4.6 MAIN AUDIO SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM .................................... 4-13
4.7 DV MAIN SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM........................................... 4-15
4.8 PRE/REC SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM.......................................... 4-17
4.9 VIDEO I/O SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM......................................... 4-19
4.10 CDS/AD SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM .......................................... 4-21
4.11 CAM.DSP SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ....................................... 4-23
4.12 TG/VDR SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM .......................................... 4-25
4.13 REGCON SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ........................................ 4-27
4.14 REG SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ................................................ 4-29
4.15 VF MAIN SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ......................................... 4-31
4.16 MONITOR MAIN SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM............................. 4-33
4.17 DSC SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ................................................ 4-35
4.18 USBDRV SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM......................................... 4-37
4.19 SD SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM................................................... 4-39
4.20 WBSEN/SW SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM.................................... 4-41
4.21 OPDRV SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ........................................... 4-43
4.22 BOTTOM SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ........................................ 4-45
4.23 MONITOR SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM....................................... 4-47
Page 3
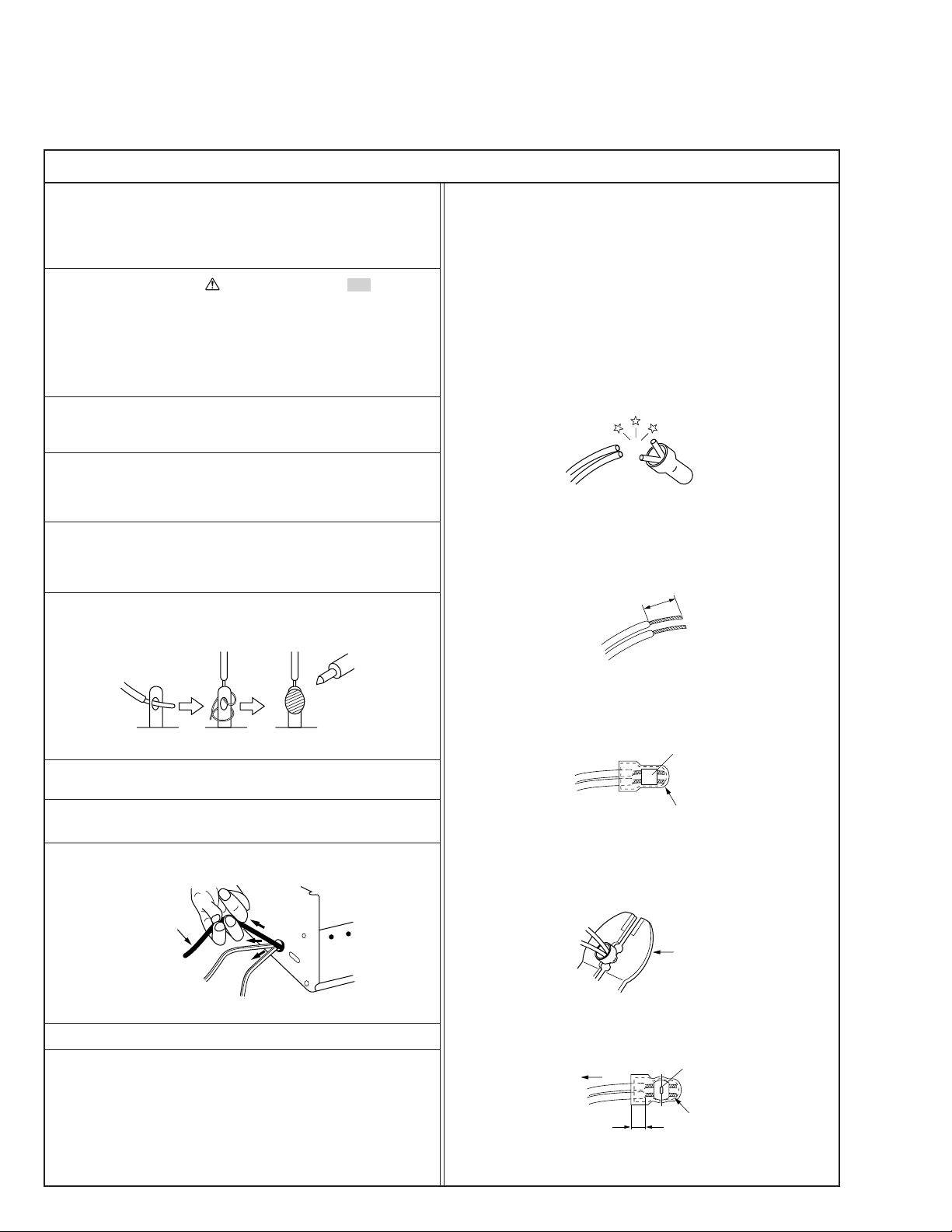
Important Safety Precautions
Connector
Metal sleeve
Prior to shipment from the factory, JVC products are strictly inspected to conform with the recognized product safety and electrical codes
of the countries in which they are to be sold. However, in order to maintain such compliance, it is equally important to implement the
following precautions when a set is being serviced.
v
Precautions during Servicing
1. Locations requiring special caution are denoted by labels and
inscriptions on the cabinet, chassis and certain parts of the
product. When performing service, be sure to read and comply with these and other cautionary notices appearing in the
operation and service manuals.
2. Parts identified by the symbol and shaded ( ) parts are
critical for safety.
Replace only with specified part numbers.
Note: Parts in this category also include those specified to com-
ply with X-ray emission standards for products using
cathode ray tubes and those specified for compliance
with various regulations regarding spurious radiation
emission.
3. Fuse replacement caution notice.
Caution for continued protection against fire hazard.
Replace only with same type and rated fuse(s) as specified.
4. Use specified internal wiring. Note especially:
1) Wires covered with PVC tubing
2) Double insulated wires
3) High voltage leads
5. Use specified insulating materials for hazardous live parts.
Note especially:
1) Insulation Tape 3) Spacers 5) Barrier
2) PVC tubing 4) Insulation sheets for transistors
6. When replacing AC primary side components (transformers,
power cords, noise blocking capacitors, etc.) wrap ends of
wires securely about the terminals before soldering.
12. Crimp type wire connector
In such cases as when replacing the power transformer in sets
where the connections between the power cord and power
transformer primary lead wires are performed using crimp type
connectors, if replacing the connectors is unavoidable, in order to prevent safety hazards, perform carefully and precisely
according to the following steps.
1) Connector part number : E03830-001
2) Required tool : Connector crimping tool of the proper type
which will not damage insulated parts.
3) Replacement procedure
(1) Remove the old connector by cutting the wires at a point
close to the connector.
Important : Do not reuse a connector (discard it).
cut close to connector
Fig.3
(2) Strip about 15 mm of the insulation from the ends of
the wires. If the wires are stranded, twist the strands to
avoid frayed conductors.
15 mm
Fig.1
7. Observe that wires do not contact heat producing parts
(heatsinks, oxide metal film resistors, fusible resistors, etc.)
8. Check that replaced wires do not contact sharp edged or
pointed parts.
9. When a power cord has been replaced, check that 10-15 kg of
force in any direction will not loosen it.
Power cord
Fig.2
10. Also check areas surrounding repaired locations.
11. Products using cathode ray tubes (CRTs)
In regard to such products, the cathode ray tubes themselves,
the high voltage circuits, and related circuits are specified for
compliance with recognized codes pertaining to X-ray emission.
Consequently, when servicing these products, replace the cathode ray tubes and other parts with only the specified parts.
Under no circumstances attempt to modify these circuits.
Unauthorized modification can increase the high voltage value
and cause X-ray emission from the cathode ray tube.
Fig.4
(3) Align the lengths of the wires to be connected. Insert
the wires fully into the connector.
Fig.5
(4) As shown in Fig.6, use the crimping tool to crimp the
metal sleeve at the center position. Be sure to crimp fully
to the complete closure of the tool.
1.25
2.0
5.5
Fig.6
(5) Check the four points noted in Fig.7.
Not easily pulled free
Wire insulation recessed
more than 4 mm
Fig.7
Crimping tool
Crimped at approx. center
of metal sleeve
Conductors extended
1
S40888-01
Page 4
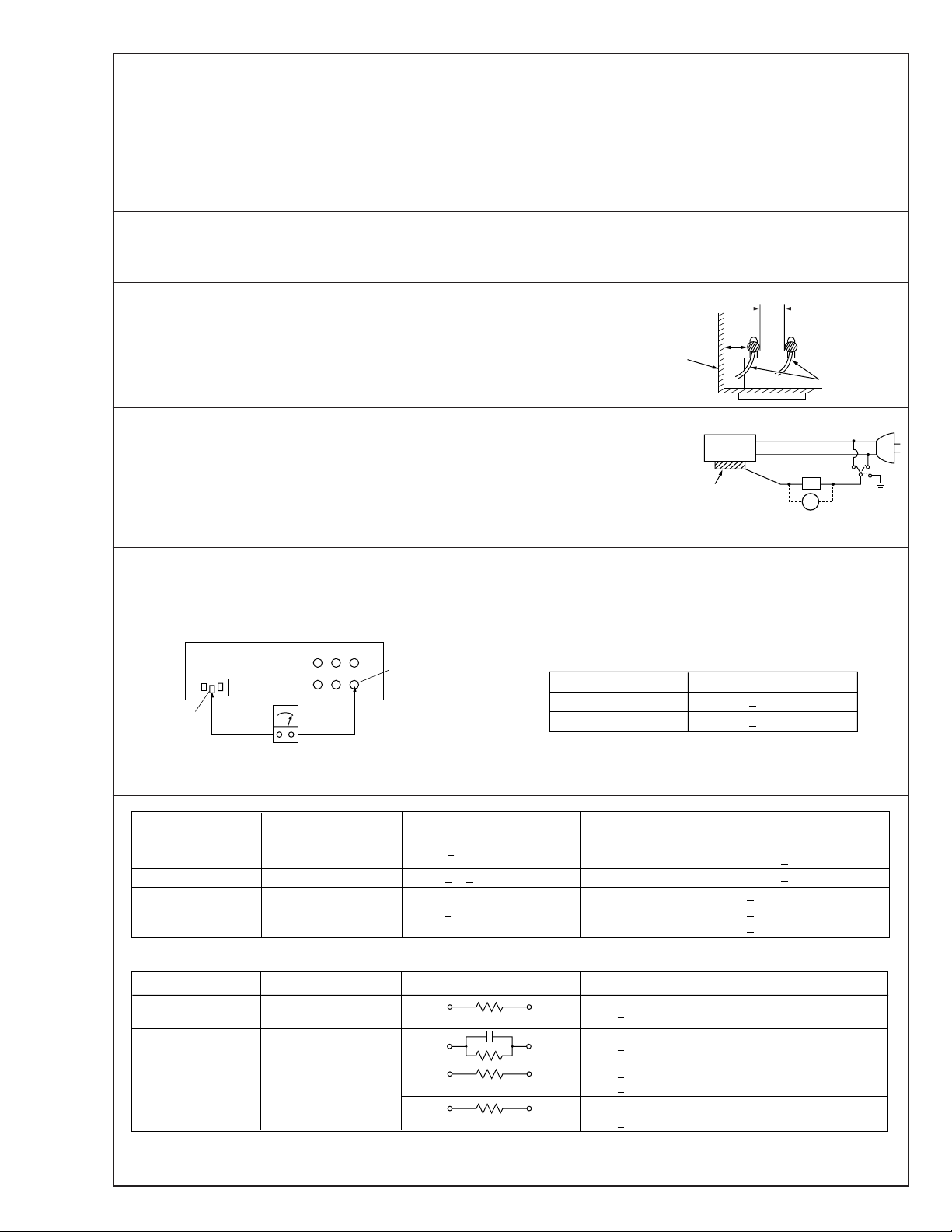
v
d'
d
Chassis
Power cord,
primary wire
Safety Check after Servicing
Examine the area surrounding the repaired location for damage or deterioration. Observe that screws, parts and wires have been
returned to original positions, Afterwards, perform the following tests and confirm the specified values in order to verify compliance with safety standards.
1. Insulation resistance test
Confirm the specified insulation resistance or greater between power cord plug prongs and
externally exposed parts of the set (RF terminals, antenna terminals, video and audio input
and output terminals, microphone jacks, earphone jacks, etc.). See table 1 below.
2. Dielectric strength test
Confirm specified dielectric strength or greater between power cord plug prongs and exposed
accessible parts of the set (RF terminals, antenna terminals, video and audio input and output
terminals, microphone jacks, earphone jacks, etc.). See table 1 below.
3. Clearance distance
When replacing primary circuit components, confirm specified clearance distance (d), (d’) between soldered terminals, and between terminals and surrounding metallic parts. See table 1
below.
Fig. 8
4. Leakage current test
Confirm specified or lower leakage current between earth ground/power cord plug prongs
and externally exposed accessible parts (RF terminals, antenna terminals, video and audio
input and output terminals, microphone jacks, earphone jacks, etc.).
Measuring Method : (Power ON)
Insert load Z between earth ground/power cord plug prongs and externally exposed accessible parts. Use an AC voltmeter to measure across both terminals of load Z. See figure 9 and
following table 2.
Externally
exposed
accessible part
Z
V
Fig. 9
ab
c
5. Grounding (Class 1 model only)
Confirm specified or lower grounding impedance between earth pin in AC inlet and externally exposed accessible parts (Video in,
Video out, Audio in, Audio out or Fixing screw etc.).
Measuring Method:
Connect milli ohm meter between earth pin in AC inlet and exposed accessible parts. See figure 10 and grounding specifications.
AC inlet
Earth pin
AC Line Voltage
100 V
100 to 240 V
110 to 130 V
110 to 130 V
200 to 240 V
Exposed accessible part
Milli ohm meter
Fig. 10
Region
Japan
USA & Canada
Europe & Australia R 10 MΩ/500 V DC
Region Load Z
Insulation Resistance (R)
≤
R 1 MΩ/500 V DC
≥≥
1 MΩ R 12 MΩ/500 V DC
≤
Table 1 Specifications for each region
Grounding Specifications
Region
USA & Canada
Europe & Australia
Dielectric Strength
AC 1 kV 1 minute
AC 1.5 kV 1 miute
AC 1 kV 1 minute
AC 3 kV 1 minute
AC 1.5 kV 1 minute
(Class 2)
(Class 1)
Grounding Impedance (Z)
≤
Z 0.1 ohm
≤
Z 0.5 ohm
Clearance Distance (d), (d')
≤
d, d' 3 mm
≤
d, d' 4 mm
≤
d, d' 3.2 mm
≤
d 4 mm
≤
d' 8 mm (Power cord)
≤
d' 6 mm (Primary wire)
a, b, cLeakage Current (i)AC Line Voltage
100 V
110 to 130 V
110 to 130 V
220 to 240 V
Note: These tables are unofficial and for reference only. Be sure to confirm the precise values for your particular country and locality.
Japan
USA & Canada
Europe & Australia
Table 2 Leakage current specifications for each region
1 kΩ
0.15 µF
1.5 kΩ
2 kΩ
50 kΩ
2
≤
i 1 mA rms Exposed accessible parts
≤
i 0.5 mA rms
≤
i 0.7 mA peak
≤
i 2 mA dc
≤
i 0.7 mA peak
≤
i 2 mA dc
Exposed accessible parts
Antenna earth terminals
Other terminals
S40888-01
Page 5
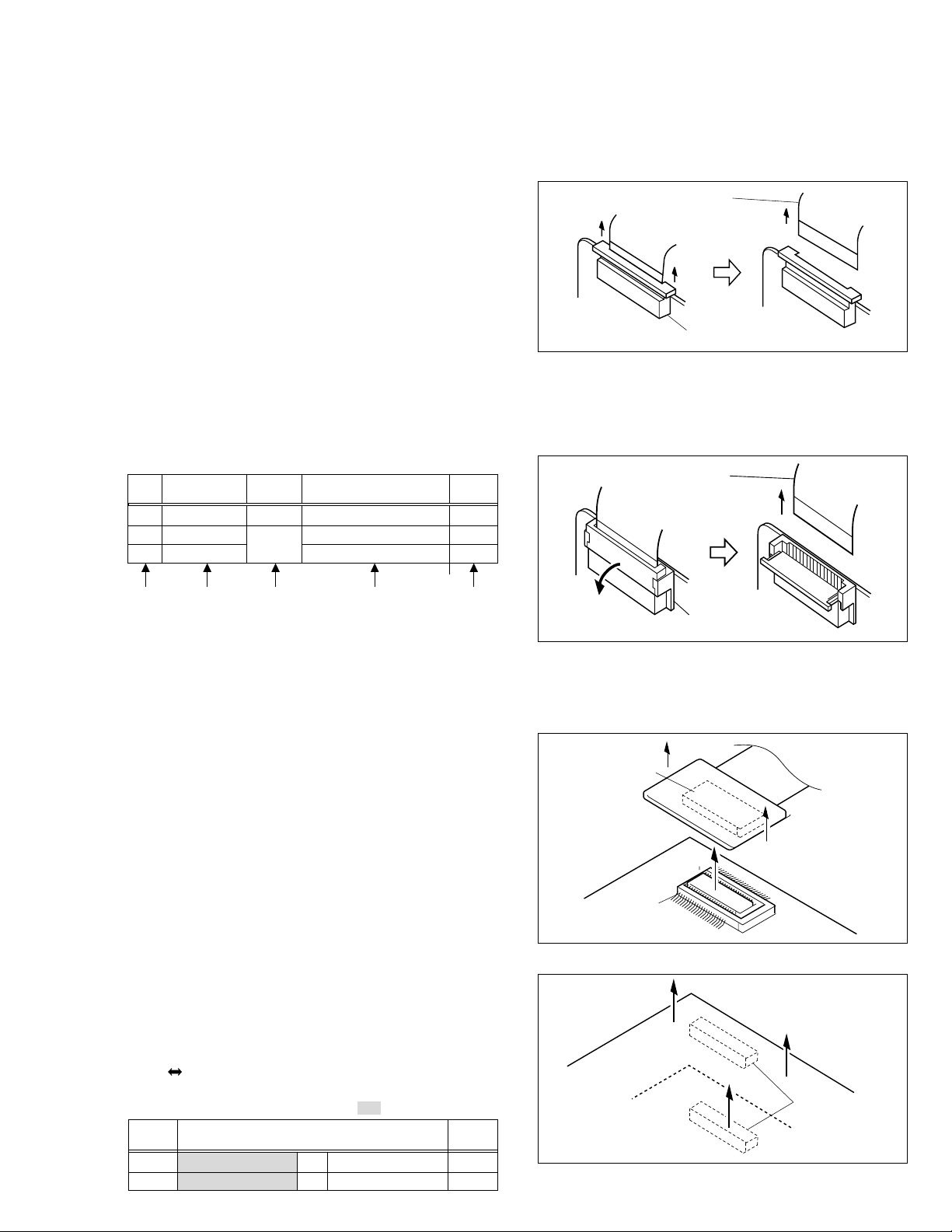
SECTION 1
DISASSEMBLY
1.1 BEFORE ASSEMBLY AND DISASSEMBLY
1.1.1 Precautions
1. Be sure to remove the power supply unit prior to mounting and soldering of parts.
2. When removing a component part that needs to disconnect the connector and to remove the screw for removing itself, first disconnect the connecting wire from the
connector and then remove the screw beforehand.
3. When connecting and disconnecting the connectors, be
careful not to damage the wire.
4. Carefully remove and handle the part to which some
spacer or shield is attached for reinforcement or insulation.
5. When replacing chip parts (especially IC parts), desolder
completely first (to prevent peeling of the pattern).
6. Tighten screws properly during the procedures.
Unless specified otherwise, tighten screws at a torque
of 0.078N
•
m(0.8kgf•cm).
1.1.2 Assembly and disassembly
STEP
No.
1
2
3
PART
COVER(UNDER) Fig.1-3-1 (S1)—
COVER(SHOE) Fig.1-3-2 2(S2),2(L2)—
MIC COVER ASSY
Fig.No.
POINT NOTE
(S3a),2(S3b) —
1.1.4 Disconnection of Connectors (Wires)
Connector
Pull both ends of the connector in the arrow direction, remove the lock and disconnect the flat wire.
Flat wire
Connector
Fig. 1-1-1 Connector 1
Extend the locks in the direction of the arrow for unlocking
and then pull out the wire. After removing the wire, immediately restore the locks to their original positions because
the locks are apt to come off the connector.
Flat wire
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5)
(1) Indicate the disassembly steps. When assembling, per-
form in the reverse order of these steps. This number
corresponds to the number in the disassembly diagram.
(2) Indicates the name of disassembly/assembly parts.
(3) Indicates the number in the disassembly diagram.
(4) Indicates parts and points such as screws, washers,
springs which must be removed during disassembly/
assembly.
Symbol Name, Point
S Screw
L Lock, Pawl, Hook
SD Soldering
CN Connector
(Example)
• 2 (S1) : Remove the two screws (S1) for removing the
part 1.
• CN 1a: Disconnect the connector 1a.
• SD 1 : Unsolder at the point SD 1.
(5) Precautions on disassembly/assembly.
1.1.3 Destination of connectors
Note:
Three kinds of double-arrows in connection tables respectively show kinds of connector/wires.
↔ : Wire
⇔ : Flat wire (FPC, FFC)
: Board to Board connector
[Example]
NOTE:
Remove the parts marked in
CONN.
No.
CN
a MAIN CN112 ⇔ SUB OPE UNIT – 8
4
CN
b MAIN CN113 ⇔ MONITOR CN401 39/33
4
CONNECTOR
.
Pin No.
Connector
Fig. 1-1-2 Connector 2
B-B connector
Pull the board by both the sides in the direction of the arrow for disconnecting the B-B connector.
Connector
Connector
Fig. 1-1-3 Connector 3
Connector
Fig. 1-1-4 Connector 4
1-1
Page 6
1.2 JIGS AND TOOLS REQUIRED FOR DISASSEMBLY, ASSEMBLY AND ADJUSTMENT
1.2.1 Tools required for adjustments
1
Torque driver
YTU94088
2
Bit
YTU94088-003
1.3 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY OF CABINET PARTS AND BOARD ASSEMBLY
1.3.1 Disassembly flow chart
This flowchart indicates the disassembly step for the cabinet parts and board assembly in order to gain access to
item(s) to be serviced. When reassembling, perform the
step(s) in reverse order.
3
5
Tweezers
P-895
Cleaning cloth
KSMM-01
Chip IC replacement jig
4
PTS40844-2
Table 1-2-1
1. Torque driver
Be sure to use to fastening the mechanism and exterior
parts because those parts must strictly be controlled for
tightening torque.
2. Bit
This bit is slightly longer than those set in conventional
torque drivers.
3. Tweezers
To be used for removing and installing parts and wires.
4. Chip IC replacement jig
To be used for replacement of IC.
5. Cleaning cloth
Recommended cleaning cloth to wipe down the video
heads, mechanism (tape transport system), optical lens
surface.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
!
@
COVER (UNDER)
COVER (SHOE)
MIC COVER ASSY
UPPER CASE ASSY
(Inc.MONITOR ASSY)
MONITOR ASSY
SHUTTER ASSY
BOTTOM ASSY
LOWER CASE ASSY
(Inc.MICROPHONE
/E.VF UNIT
/OP MDA BOARD ASSY/SHOE ASSY
/OP BLOCK ASSY)
MAIN BOARD ASSY
MECHANISM ASSY
MICROPHONE
OP BLOCK ASSY
1-2
#
$
%
E. VF UNIT
OP MDA BOARD ASSY
SHOE ASSY
Table 1-3-1
Page 7
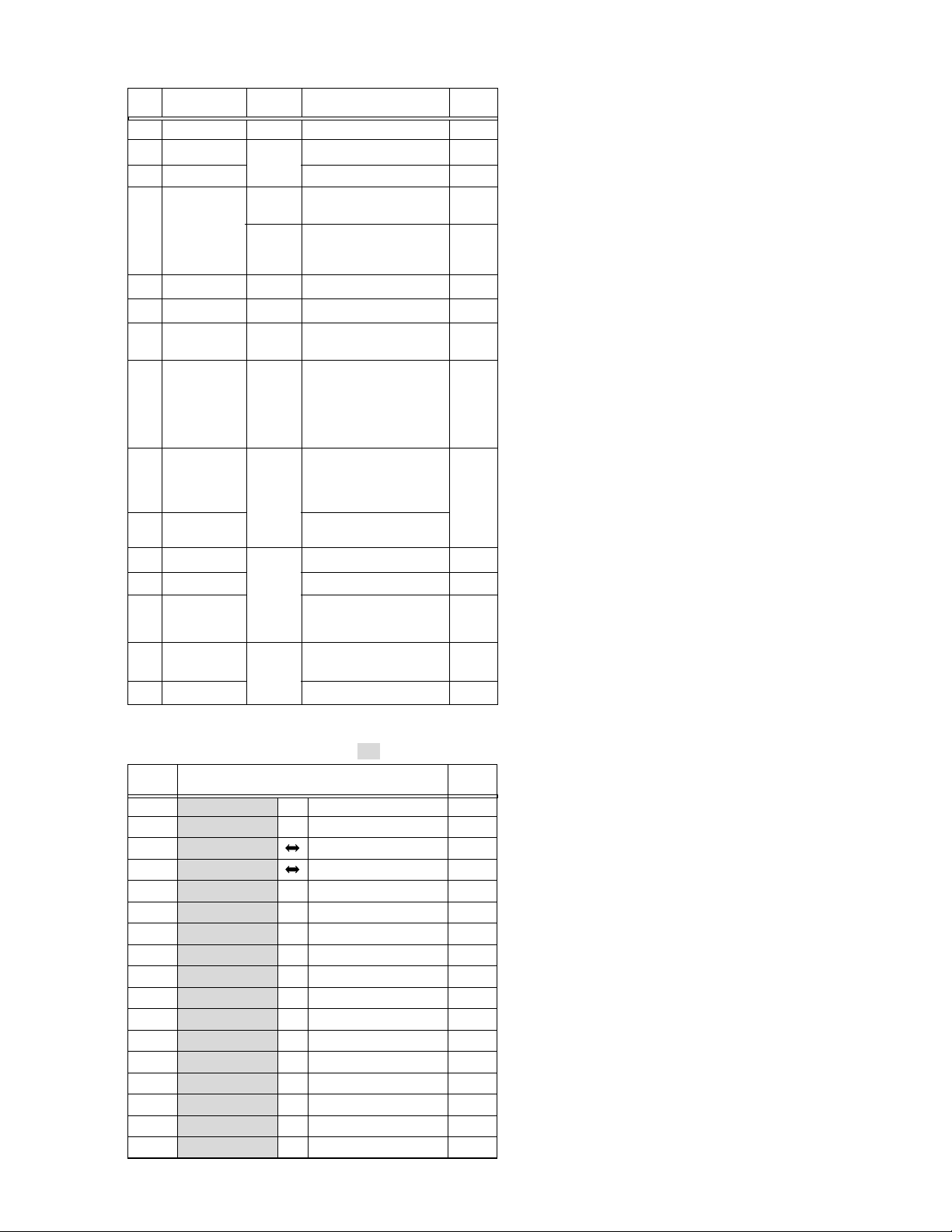
1.3.2 Disassembly method
STEP
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
!
PART
COVER (UNDER) Fig.1-3-1 (S1)—
COVER (SHOE) Fig.1-3-2 2(S2), 2(L2)—
MIC COVER ASSY
UPPER CASE ASSY
(Inc.MONITOR ASSY)
MONITOR ASSY Fig.1-3-4 2(S5a), GUIDE(MONI), 2(S5b) NOTE5
SHUTTER ASSY Fig.1-3-5(S6
BOTTOM ASSY Fig.1-3-6
LOWER CASE ASSY
(Inc. MICROPHONE,
E.VF UNIT, CN8c, CN8d, CN8e, 3(S8)
OP MDA BOARD
ASSY,SHOE ASSY,
OP BLOCK ASSY)
MAIN BOARD ASSY
MECHANISM ASSY
MICROPHONE Fig.1-3-9a — NOTE!
Fig.No.
(S3a), 2(S3b) —
Fig.1-3-3a (SD CARD) NOTE4a
Fig.1-3-3b
Fig.1-3-7 CN8a, CN8b, NOTE8
Fig.1-3-8 SHEET(SHUTTER), 2(S9)—
(S4a), (S4b), 3(S4c), 2(S4d),
2(S4e), (S4f),
CN 4a, CN4b
CN 7, 2(S 7a), 2(S7b), 3(S7c),
(S7d)
SHEET(SHUTTER),
(L9a), SHIELD ASSY, CN 9a,
CN 9b, CN 9c, CN 9d,
(L9b), CN 9e, CN 9f
(S0a),BRACKET(PRE/REC),
3(S0b),BRACKET(MECHA) ASSY
POINT NOTE
)
NOTE4b
NOTE4c
NOTE4d
NOTE
6
NOTE7
@ OP BLOCK ASSY (S@), 2(S$a) NOET@
E.VF UNIT
#
OP MDA BOARD Fig.1-3-9b 2(S$b), CN@ NOTE$
$
ASSY NOTE$
SHOE ASSY
%
(S#a), (S#b), CN# NOTE#a
CN%
, 2(S%)
NOTE#b
NOTE#c
NOTE
%
a
b
NOTE 4a:
NOTE 4b:
NOTE 4c:
NOTE 4d:
NOTE 5:
NOTE 6:
NOTE 7:
NOTE 8:
NOTE !:
NOTE @:
NOTE #a:
NOTE #b:
NOTE $a:
NOTE @, #c, $b, % :
If a card is installed, remove it in advance.
Be careful not to damage the battery removal switch.
When disassembling, ensure that the lock lever is in the
low position and set the battery removal switch only to
the up position.
A screw (14) is located inside the Cover (MULTI/USB).
Slide down the shutter and remove the screw (15).
Refer to Sec. 1.4 for the disassembly method.
Be careful not to damage or lose the parts.
Take care of the removed screws.
For the disassembly/assembly of the E. VF UNIT, SHOE
ASSY, OP MDA BOARD ASSY, and OP BLOCK ASSY,
see Sec. 1.5 for the disassembly method.
Leave the MICROPHONE connected to the OP BLOCK
ASSY.
Refer to Sec. 1.6 for the disassembly method.
Be careful not to cut the FPC wire or damage any of
the switches during work.
Refer to Sec. 1.7 for the disassembly method.
Be careful not to lose the parts.
When assembling, attach the OP BLOCK ASSY, E.VF
UNIT and the SHOE ASSY on the OP MDA BOARD
ASSY and install them together in the LOWER CASE
ASSY.
Table 1-3-2
NOTE:
Remove the parts marked in .
CONN.
No.
CN
a MAIN CN112 ⇔ SUB OPE UNIT - 8
4
CN
b MAIN CN113 ⇔ MONITOR CN401 39/33
4
CN7MAIN CN107 BOTTOM CN301 50
CN8a MAIN CN110 OP MDA CN201 80
CN
b MAIN CN111 ⇔ CCD - 20
8
CN
c MAIN CN109 ⇔ ZOOM OPE UNIT - 13
8
CN
d MAIN CN108 ↔ EJECT SW - 2
8
CN
e MAIN CN115 ↔ MICROPHONE - 4
8
CN
a MAIN CN102 ⇔ LOADING MOTOR - 6
9
CN
b MAIN CN103 ⇔ ROTARY ENCODER - 6
9
CN
c MAIN CN101 ⇔ HEAD - 8
9
CN
d MAIN CN106 ⇔ SENSOR - 16
9
CN
e MAIN CN105 ⇔ CAPSTAN MOTOR - 18
9
CN
f MAIN CN104 ⇔ DRUM MOTOR - 11
9
CN@ OP MDA CN204 ⇔ OP BLOCK ASSY - 24
CN# OP MDA CN203 ⇔ VF BL CN7001 20
CN% OP MDA CN202 ⇔ SHOE ASSY - 16/13
CONNECTOR
Pin No.
Table 1-3-3
1-3
Page 8

1
1
1
(S )
3
5
3
(S b)
6
3
(S b)
4
3
(S a)
2
(L )
2
2
(S )
2
(S )
3
2
Fig. 1-3-1
NOTE a
Fig. 1-3-2
NOTE b
4
COVER
4
BATT. RELEASE
SWITCH
(SD)
LOCK LEVER
4
1-4
Fig. 1-3-3a
Page 9

4
6
(S )
21
6
NOTE
6
CN a
NOTE d
4
15
4
(S f)
: 0.118 N•m (1.2 kgf•cm)
∗
CN
COVER
(M/USB)
Fig. 1-3-3b
4
b
16
4
(S e)
4
∗
12
4
(S d)
(S a)
13
4
(S c)
7
4
8
4
(S b)
10
(S c)
(S d)
(S c)
4
NOTE c
14
4
(S e)
11
∗
4
9
4
4
GUIDE
(MONI)
∗
17
5
(S a)
∗
18
5
(S a)
∗
19
5
(S b)
NOTE
5
5
4
∗
20
5
(S b)
: 0.098 N•m (1.0 kgf•cm)
∗
Fig. 1-3-4
Fig. 1-3-5
1-5
Page 10

CASS.
COVER
26
7
(S c)
CASS.
COVER
NOTE
8
8
NOTE
23
7
(S a)
7
24
7
(S b)
25
7
(S b)
22
7
(S a)
(S a)
Fig. 1-3-6
23
7
29
7
(S d)
24
7
(S b)
(S c)
CN
25
7
(S b)
27
7
7
28
7
(S c)
7
32
8
(S )
SHEET
(SHUTTER)
CN e
8
8
CN a
CN d
31
8
(S )
CN b
8
CN c
30
8
(S )
8
8
Fig. 1-3-7
SHEET
(SHUTTER)
33
9
(S )
34
9
(S )
10
(L a)
SHIELD
ASSY
BRACKET
(PRE/REC)
36
10
(S b)
BRACKET(MECHA) ASSY
9
CN a
9
38
10
(S b)
9
9
CN c
37
10
(S b)
9
35
10
(S a)
9
CN e
CN f
(L b)
CN b
9
CN d
9
9
1-6
Fig. 1-3-8
Page 11

41
14
(S a)
40
14
(S a)
15
NOTE b,c
13
13
13
CN
42
13
(S a)
8
NOTE
14
13
a
43
13
(S b)
NOTE a
13
OP MDA
PWB
SW
46
15
(S )
Fig. 1-3-9a
47
15
(S )
NOTE
15
15
11
NOTE
39
12
(S )
12
12
11
NOTE
12
NOTE a
14
KNOB
(VIDEO
/DSC)
14
NOTE b
14
Fig. 1-3-9b
CN
15
CN
(S b)
(S b)
12
44
14
45
14
1-7
Page 12

1.4 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY OF 5 MONITOR ASSY
1.4.1 5 MONITOR ASSY/HINGE ASSY
1. Remove the three screws (1 to 3) and then remove the
monitor cover by disengaging the two hooks (L5a, L5b)
at the top and bottom.
NOTE
a:
Be careful not to lose part (Rib).
5
2. Pull out the part (sensor) from the MONITOR CASE ASSY.
3. Release the lock of the connector CN5a. Disengage the
two hooks (L5c, L5d) to remove the HINGE ASSY from
MONITOR CASE ASSY, then remove the FPC from the
HINGE ASSY.
NOTE
b:
When removing the parts out of the MONITOR
5
CASE ASSY, be very careful not to damage the
FPC and parts.
4. Take out the LCD MODULE, BACK LIGHT and MONITOR BOARD ASSY from the MONITOR CASE ASSY. Be
careful with the hooks (L5e, L5f) on the two sides.
Disconnect the FPC ASSY from the connector (CN5b)
and remove the LCD MODULE. Be careful with the hooks
(L5g ,L5h) on the two sides.
MONITOR
CASE ASSY
1.4.2 HINGE ASSY
1. Remove the two screws (4,5) to take out the FPC ASSY
while removing the HINGE COVER (L).
NOTE
c:
Be careful not to lose any part during the above-
5
mentioned process.
2. Remove the HINGE COVER (U) from HINGE ASSY.
3. Remove the FPC ASSY from the HINGE ASSY.
d:
NOTE
Be careful not to lose any part during the abobe
5
mentioned process.
NOTE5e:
When reassembling, wind the FPC ASSY around
the HINGE ASSY by three turns and a half.
Be careful not to break the FPC wire during the
work.
: 0.058 N•m (0.6 kgf•cm)
∗
5
NOTE e
FPC ASSY
HINGE
ASSY
5
(L f)
b
a
5
(L e)
LCD
MODULE
HINGE
COVER(L)
5
NOTE d
HINGE
ASSY
FPC ASSY
5
NOTE b,d,e,f
5
(L d)
b
(L h)
5
(L g)
SENSOR
5
(L c)
MAGNET
NOTE c
BACK LIGHT
5
c
(S c)
(S c)
5
∗
4
5
HINGE
COVER(U)
∗
5
5
c
5
CN b
CN c
CN a
NOTE a
RIB
1
5
(S a)
2
5
(S a)
NOTE c
MARKING
MONITOR
BOARD ASSY
5
5
5
5
(L a)
a
5
MONITOR
COVER
5
(L b)
3
5
(S a)
1-8
Fig. 1-4-1
Page 13

1.5 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY OF 8 LOWER CASE
ASSY
When performing disassembly/assembly work to this model,
the parts that are most complicated and require special attention are the E. VF UNIT and the OP MDA BOARD ASSY,
OP BLOCK ASSY and SHOE ASSY, all of which are mounted
inside the LOWER CASE ASSY.
Care should be taken in handling these parts as they are
mounted inside the LOWER CASE ASSY (except the E.VF
UNIT) and there is a lack of adequate space to work conveniently. This section gives further details regarding the disassembly procedures, although they have been described
in previous sections.
1. See Fig. 1-5-1.
(1) While moving the ! MICROPHONE out of way, remove
the screw (39) and take out the @ OP BLOCK ASSY.
(2) Remove two screws (40, 41) and open the $ OP MDA
BOARD ASSY.
40
14
(S a)
13
CN
8
14
41
14
(S a)
(3) Remove two screws (42, 43) to disconnect the connec-
tor (CN203), then take out the FPC to remove the # E.
VF UNIT.
NOTE #a :
Be careful not to damage the FPC or the
switches when carrying out this work.
2. See Fig. 1-5-2.
(1) Remove the two screws (44, 45) in order to free the $
OP MDA board assembly.
(2) Remove the two screws (46, 47) and take out the $ OP
MDA BOARD ASSY together with the @ OP BLOCK
ASSY and the % SHOE ASSY.
NOTE@:
Be careful not to lose the KNOB(VIDEO/DSC),
which may slip out during the disassembly.
(3) Disconnect the FPCs from the connectors on the @ OP
BLOCK ASSY and the % SHOE ASSY.
13
13
a
(S b)
NOTE b
13
42
(S a)
43
13
13
15
NOTE
13
NOTE a
OP MDA
PWB
SW
46
15
(S )
Fig. 1-5-1
47
15
(S )
NOTE
15
KNOB
(VIDEO
/DSC)
NOTE
11
15
12
15
CN
45
(S b)
NOTE
39
12
(S )
12
14
11
12
14
14
NOTE b
Fig. 1-5-2
CN
44
(S b)
12
14
1-9
Page 14

1.6 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY OF @ OP BLOCK ASSY
(CCD BOARD ASSY)
1.6.1 Precautions
1. Carefully handle the CCD IMAGE SENSOR, OP LPF,
LENS, etc. during the disassembly work. Pay the most
careful attention to the surface of those parts not to get
it soiled, scratched or dusty. If some of those surfaces
gets soiled with fingerprints, etc., wipe it out with silicone
paper, clean chamois, cleaning cloth or the like.
2. The new CCD IMAGE SENSOR is occasionally shipped
from the factory as a protection seal is applied onto its
transparent glass. If so, leave the protection seal as it is
and remove it just before installing the CCD IMAGE SENSOR in the OP BLOCK ASSY.
3. The orientation of the OP LPF is an important factor for
installation. If there some marking on the OP LPF, be sure
to note it down before removing and to reassemble it very
carefully as it was referring to the marking.
1.6.2 Disassembly method
1. Unsolder at the 14 points (SD@) and remove the CCD
BOARD ASSY.
2. Remove the two screws (1, 2) and then remove the CCD
BASE ASSY.
NOTE
a:
Carefully remove the CCD BASE ASSY, because
@
the SPACE RUBBER and OP LPF may be removed together with the CCD IMAGE SENSOR.
NOTE@b:
1.6.3 Assembly method
1. Install the OP LPF with the @ OP BLOCK ASSY.
2. With the SPACER RUBBER left attached to the CCD
3. Set the CCD BOARD ASSY in the CCD BASE ASSY, and
1.6.4 Replacement of service parts
Service parts to be supplied for the OP BLOCK ASSY are
as follows.
When replacing a part, be very careful not to get the FPC
wire broken or damaged by soldering (overheating).
1. FOCUS MOTOR
2. ZOOM MOTOR
3. IRIS MOTOR UNIT
NOTE
NOTE@d:
When replacing the CCD IMAGE SENSOR, don’t
replace it individually but replace the CCD BASE
ASSY in whole with a new one.
BASE ASSY, install the assembly in the OP BLOCK ASSY
and clamp it using the two screws (1, 2).
fasten it by soldering at the 14 points (SD@).
c:
When soldering the FPC wire of the FOCUS MO-
@
TOR or ZOOM MOTOR during the replacement
work, be sure to keep the tip of a soldering iron
approximately 1 mm above the terminal.
The IRIS MOTOR UNIT includes one FPC ASSY
and two sensors.
∗
3
12
(S b)
NOTE d
12
IRIS MOTOR
UNIT
FOCUS MOTOR
NOTE c
12
∗
5
12
(S c)
∗
4
12
(S b)
∗
8
12
(S c)
OP BLOCK
OP
SIDE
∗
9
12
(S c)
OP LPF
NOTE a
12
CCD
SIDE
BLUE
(S c)
(S a)
SPACER
RUBBER
∗
(S c)
6
∗
12
ZOOM MOTOR
NOTE c
(SD )
1
∗
12
7
12
12
2
∗
12
(S a)
CCD BASE
ASSY
NOTE a,b
12
CCD BOARD
ASSY
<05>
12
1-10
: 0.118 N•m (1.2 kgf•cm)
∗
Fig. 1-6-1
Page 15

1.7 DISASSEMBLY OF # E. VF UNIT
1.7.1
NOTE#a:
NOTE#b:
1. Draw the FRAME (VF) out of the CASE ASSY.
2. Remove the EYECUP and pull out the GUIDE (VF).
<CASE ASSY>
3. While holding the GUIDE (VF), pull out the CASE ASSY,
4. Remove the three screws (3-5) and draw out the EYE
NOTE
5. Draw out the GUIDE(VF).
E. VF UNIT
#
When disassembling the E. VF UNIT, remove the
FRAME (VF) from the CASE ASSY depending on
the situation.
Be very careful not to get the inside of the VF
soiled or dusty during and after disassembling the
E. VF UNIT.
remove the two screws (1, 2) and remove the CAP (VF).
PIECE SUB ASSY.
c:
A LENS ASSY and a LEVER are mounted on the
#
EYE PIECE SUB ASSY. When removing this assembly, be careful not to damage them.
<FRAME (VF)>
6. Remove the screw (6) first and then LCD MODULE/
HOLDER (LCD).
7. Get the two hooks (L#a, L#b) disengaged and then remove the HOLDER (LCD).
NOTE
8. Disconnect the connector (CN#b) and remove the LCD
NOTE#e:
d:
Carefully proceed with the above-mentioned work
#
not to damage any part.
MODULE.
Pay heed the parts not to damage any thing.
: 0.069 N•m (0.7 kgf•cm)
∗
FPC ASSY
NOTE d
B/L PWB
13
(L
a)
13
CN a
13
CN b
13
(L b)
LCD MODULE
NOTE b,e
(S a)
∗
2
13
(S a)
3
∗
13
(S b)
13
HOLDER
(LCD)
13
∗
1
13
∗
13
(S c)
FRAME(VF)
NOTE a,b
CAP(VF)
6
13
∗
4
13
(S b)
CASE ASSY
NOTE a,c
13
LENS
∗
5
13
(S b)
GUIDE(VF)
LEVER
CASE ASSY
EYE PIECE
SUB ASSY
NOTE c
NOTE c
LENS
13
EYE CUP
13
Fig. 1-7-1
1-11
Page 16

1.8 EMERGENCY DISPLAY
Whenever some abnormal signal is input to the syscon CPU,
an error number (E01, as an example) is displayed on the
LCD monitor or (in the electronic view finder).
In every error status, such the message as shown below
alternately appear over and over.
• In an emergency mode, all operations except turning on/
off the POWER switch are ineffectual.
LCD
display
E01 LOADING
E02 UNLOADING
E03 TU & SUP REEL
Emergency
mode
FG
Details
In the case the encoder position is not shifted
to the next point though the loading motor has
rotated in the loading direction for 4 seconds
or more. This error is defined as [E01].
In the case the encoder position is not shifted
to the next point though the loading motor has
rotated in the unloading direction for 4 seconds
or more. This error is defined as [E02].
In the case no REEL FG is produced for 4 seconds or more in the capstan rotation mode after loading was complete, the mechanism mode
is shifted to STOP with the pinch roller set off.
This error is defined as [E03].
However, no REEL EMG is detected in the
SLOW/STILL mode.
Example (in case of the error number E01):
E01
UNIT IN
SAFEGUARD MODE
E01
REMOVE AND
REATTACH BATTERY
Possible cause
1. The mechanism is locked during mode shift.
2. The mechanism is locked at the mechanism loading
end, because the encoder position is skipped during
mechanism mode shift.
3. No power is supplied to the loading MDA.
1. The mechanism is locked during mode shift.
2. The mechanism is locked at the mechanism loading
end, because the encoder position is skipped during
mechanism mode shift.
1. The idler gear does not engage with the reel disk well.
2. Though the idler gear and reel disk are engaged with
each other, the tape is not wound because of overload to the mechanism.
3. No FG pulse is output from the reel sensor.
4. No power is supplied to the reel sensor.
5. Tape transport operation takes place with a cassette
having no tape inside.
6. The tape slackens and no pulse is produced until the
slack is taken up and the tape comes into the normal
status.
E04 DRUM FG
E05 –
E06 CAPSTAN FG
In the case there is no DRUM FG input in the
drum rotation mode for 4 seconds or more. This
error is defined as [E04], and the mechanism
mode is shifted to STOP with the pinch roller
set off.
–
In the case no CAPSTAN FG is produced in
the capstan rotation mode for 2 seconds or
more. This error is defined as [E06], and the
mechanism mode is shifted to STOP with the
pinch roller set off.
However, no CAPSTAN EMG is detected in the
STILL/FF/REW mode.
Table 1-8-1
1. The drum cannot be started or drum rotation is stopped
because tape transport load is too high.
1) Tape tension is extremely high.
2) The tape is damaged or soiled with grease, etc.
2. The DRUM FG signal is not received by the syscon
CPU.
1) Disconnection in the middle of the signal line.
2) Failure of the DRUM FG pulse generator (hall ele-
ment).
3. No drum control voltage is supplied to the MDA.
4. No power is supplied to the DRUM MDA.
–
1. The CAPSTAN FG signal is not received by the syscon
CPU.
1) Disconnection in the middle of the signal line.
2) Failure of the CAPSTAN FG pulse generator (MR
element).
2. No capstan control voltage is supplied to the MDA.
3. No power is supplied to the CAPSTAN MDA.
4. The capstan cannot be started or capstan rotation is
stopped because tape transport load is too high.
1) Tape tension is extremely high. (Mechanical lock-
ing)
2) The tape is damaged or soiled with grease, etc.
(Tape tangling occurs, etc.)
(DVC_03)
1-12
Page 17

1.9 SERVICE NOTE
Symbol No.
Removing order of screw
Place to stick screw
Reference drawing
Screw tightening torque
Symbol No.
Removing order of screw
Place to stick screw
Reference drawing
Screw tightening torque
Symbol No.
Removing order of screw
Place to stick screw
Reference drawing
Screw tightening torque
Symbol No.
Removing order of screw
Place to stick screw
Reference drawing
Screw tightening torque
Symbol No.
Removing order of screw
Place to stick screw
Reference drawing
Screw tightening torque
< NOTE >
1) : : Don’t reuse the screw, because screw lock bond was applied to them.
2) Pay careful attention to tightening torque for each screw.
I : 0.078N·m (0.8kgf·cm) II : 0.118N·m (1.2kgf·cm) III : 0.098N·m (1.0kgf·cm)
IV : 0.069N·m (0.7kgf·cm) V : 0.058N·m (0.6kgf·cm)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
12 3
7890!
#5
@
@# %$
456
I II
I
IIIII
22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47
/
IV
1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 6
II
IV
123456789
Fig.1-3-1
Fig.1-3-4 Fig.1-3-5
Fig.1-4-1
Fig.1-6-1
Fig.1-7-1
Fig.1-3-2
Fig.1-3-6 Fig.1-3-7
Fig.1-3-3b
Fig.1-3-8 Fig.1-3-9a Fig.1-3-9b
1.3 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY OF CABINET PARTS AND BOARD ASSEMBLY
1.4 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY OF 5 MONITOR ASSY
1.6 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY OF = OP BLOCK ASSY (CCD BOARD ASSY)
1.7 DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY OF ~ E. VF UNIT
Use the following chart to manage CABINET PARTS AND BOARD ASSY that are removed for screws.
Table 1-9-1
1-13
Page 18

SECTION 2
MECHANISM
For disassembling and assembling of MECHANISM ASSEMBLY, refer to the SERVICE MANUAL No.86700(MECHANISM ASSEMBLY).
MECHANISM ASSEMBLY
2-1
Page 19

SECTION 3
INF adjustment lens
YTU92001B
10
INF adjustment lens holder
YTU94087
11
Camera stand
YTU93079
12
Light box assembly
YTU93096A
13
Gray scale chart
YTU94133A
14
Color bar chart
YTU94133C
15
Cleaning cloth
KSMM-01
16
PC cable
QAM0099-005
7
Alignment tape
MC-1
8
Service support system
YTU94057-66
9
Jig connector cable
YTU93106C
5
6
Communication cable
YTU93107A
Torque driver
YTU94088
1
Bit
YTU94088-003
2
34
Guide driver (Hexagonal)
D-770-1.27
Adjustment driver
YTU94028
ADJUSTMENT
3.1 PRECAUTION
3.1.1 Precaution
Both the camera and deck sections of this model needs a
personal computer for adjustment except simple adjustment
with potentiometers. If some of the following parts is replaced
for repair or other reason, the repaired set must be adjusted
with a personal computer.
• OP block
2
• E
PROM (IC1003 of MAIN board)
In the event of malfunction with electrical circuits, troubleshooting with the aid of proper test instruments most be done
first, and then commence necessary repair, replacement and
adjustment, etc.
1. In case of wiring to chip test points for measurement,
use IC clips, etc. to avoid any stress.
2. Since connectors are fragile, carefully handle them in disconnecting and connecting.
3. Shortcircuit between operation unit and DECK chassis.
3.1.2 Required test equipment
1. Color TV monitor
2. AC power adapter/charger
3. Oscilloscope (dual-trace type, observable 100 MHz or
higher frequency)
Note :
It is recommended to use one observable 300 MHz
or higher frequency.
3.1.3 Tools required for adjustments
4. Digital voltmeter
5. Frequency counter (with threshold level adjuster)
6. Personal computer
Table 3-1-1
3-1
Page 20

1. Torque driver
Be sure to use to fastening the mechanism and exterior parts because those parts must strictly be controlled for tightening torque.
2. Bit
This bit is slightly longer than those set in conventional
torque drivers.
3. Guide driver
To be used to turn the guide roller to adjustment of the
linearity of playback envelope.
4. Adjustment driver
To be used for adjustment.
5. Jig connector cable
To be connected to the Jig connector jack of the main
board and used for measurement and adjustment.
MAIN
CN114
VF_RPD 40
CVF_G 20
CVF_R 39
CVF_B 19
VF_COM 38
MT_RPD 18
MT_G 37
MT_R 17
MT_B 36
MT_COMCS 16
MT_PSIG 35
GND 15
GND 34
MONI_CHG 14
SBE 33
SPA 13
FRP 32
FS_PLL 12
DISCRI 31
HID1 11
ATFI 30
MAIN_VCO 10
ENV_OUT 29
PB_CLK 9
TRST 28
TCMK 8
TMS 27
TDO 7
TDI 26
JLIP_RX 6
JLIP_TX 25
IF_TX 5
AL_3VSYS 24
CJIG_RST 4
VPPC 23
SRV_RX 3
SRV_TX 22
REG_3V 2
DRST 21
VPPD 1
JIG CONN. BOARD
(PIN NO.)
40 VF_RPD
39 CVF_R
38 VF_COM
37 MT_G
36 MT_B
35 MT_PSIG
33 SBE
32 FRP
31 DISCRI
30 ATFI
29 ENV_OUT
28 TRST
27 TMS
26 TDI
25 JLIP_TX
20 CVF_G
19 CVF_B
18 MT_RPD
17 MT_R
16 MT_COMCS
15 GND
14 MONI_CHG
13 SPA
12 FS_PLL
11 HID1
10 MAIN_VCO
9 PB_CLK
8 TCMK
7 TDO
6 JLIP_RX
10. INF adjustment lens
To be used for adjustment of the camera system. For
the usage of INF adjustment lens, refer to the Service
Bulletin No. YA-SB-10035.
11. INF lens holder
To be used together with the camera stand (12) for operating the Videocamera in the stripped-down condition such as the status without the exterior parts or for
using commodities that are not yet conformable to the
interchangeable ring. For the usage of the INF lens
holder, refer to the Service Bulletin No. YA-SB-10035.
12. Camera stand
To be used together with the INF adjustment lens
holder. For the usage of the Camera stand, refer to the
Service Bulletin No. YA-SB-10035.
13. Light box assembly
To be used for adjustment of the camera system. For
the usage of the Light box assembly, refer to the Service Bulletin No. YA-SB-10035.
14. Gray scale chart (for Light box assembly)
To be used for adjustment of the camera system. For
the usage of the Gray scale chart, refer to the Service
Bulletin No. YA-SB-10035.
15. Color bar chart (for Light box assembly)
To be used for adjustment of the camera system. For
the usage of the Color bar chart, refer to the Service
Bulletin No. YA-SB-10035.
16. Cleaning cloth
Recommended cleaning cloth to wipe down the video
heads, mechanism (tape transport system), optical lens
surface.
3.2 MECHANISM COMPATIBILITY ADJUSTMENT Note:
When an adjustment is performed with the lower case cover
attached, first slide the Cover (M.ADJ) open and then perform the compatibility adjustment.
Be sure not to damage the cover plate when sliding it open
to make an adjustment because it must be re-positioned after completing the adjustment.
3.2.1 Jig connector cable connection
Remove one screw (1) first and the cover (JIG) next.
NOTE)
The JIG connector board uses 30 of the 40 pins of
CN114 on the Main board.
Pins 1 to 5, 21 to 24 and 34 of CN114 on the Main board
are not used.
Fig. 3-1-3-1
6. Communication cable
Connect the Communication cable between the PC
cable and Jig connector cable when performing a PC
adjustment.
7. PC cable
To be used to connect the Videocamera and a personal
computer with each other when a personal computer
issued for adjustment.
8. Alignment tape
To be used for check and adjustment of interchangeability of the mechanism.
9. Service support system
To be used for adjustment with a personal computer.
Software can be downloaded also from JS-net.
3-2
GUIDE ROLLER
(SUPPLY) ASSY
COVER
(M.ADJ)
GUIDE ROLLER
(TAKE-UP) ASSY
Jig connector
JLIP_RX
JLIP_TX
GND
Communication cable
RED
WHITE
BLACK
Jig Connector
TO ENV_OUT
Fig. 3-2-1-1
TO HID1
waveform
trigger
1
COVER
(JIG)
OscilloscopeJig connector
Page 21

3.2.2 Tape pattern check
ENV_OUT
HID1
Flatten the waveform.
Misalignment of guide roller
height on the take-up side
Misalignment of guide
roller height on the
supply side
COVER
(JIG)
Jig connector
cable
Service Support System
RS232C
COM Port
PC cable
Personal Computer
RED
JLIP_RX
WHITE
BLACK
JLIP_TX
GND
JIG CONNECTOR COMMUNICATION CABLE
Communication cable
CN114
(JIG CONN.)
MENU
20 1
40 21
1
(1) Play back the compatibility adjustment tape.
(2) While triggering the HID1, observe the waveform of
ENV_OUT.
(3) Confirm that the waveform is free from remarkable
level-down, and entirely parallel and straight.
Moreover, perform the following adjustment as required.
(4) In case any level-down is observed on the left hand
side, straighten the level by turning the GUIDE
ROLLER(SUPPLY).
In case any level-down is observed on the right hand
side, however, straighten the level by turning the
GUIDE ROLLER(TAKE-UP).
(5) After adjustment, try the unloading motion once, and
confirm that the waveform is flat (straight) when the
tape has been played back again.
Moreover, perform readjustment as required.
(6) When the recording has been played back again, play
back the self-recording to confirm that the waveform
is flat.
Fig. 3-2-2-1
Fig. 3-2-2-2
3.3 ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENT
3.3.1
Electrical adjustment with PERSONAL COMPUTER
Electrical adjsutment except for B/W VF ASSEMBLY is
performed by using PERSONAL COMPUTER. As for the
cable connection, see Fig. 3-3-1-1. Read README.TXT
file to use the software for SERVICE SUPPORT SYSTEM
properly.
3.3.2 Setup
1. Setup for electrical adjustment with personal computer.
NOTE:
Remove one screw (1) first and the cover (JIG)
next.
Fig. 3-3-1-1 Connection for Service support system
3-3
Page 22

VICTOR COMPANY OF JAPAN, LIMITED
12,3-chome,Moriya-cho,Kanagawa-ku,Yokohama,Kanagawa-prefecture,221-8528,JapanAV & MULTIMEDIA COMPANY.
Printed in Japan
0304 VP
 Loading...
Loading...