Page 1

Page 2

Body Builders Guide
I
Page 3

Body Builders Guide
General Motors Isuzu Commercial Truck, LLC
(GMICT) and American Isuzu Motors Inc.
Is striving to provide you with the most upto-date and accurate information possible.
If you have any suggestion to improve the
Body Builder's Guide, please call GMICT
Application Engineering. In the West Coast
call 1-562-229-5314 and in the East Coast
call 1-404-257-3013
Notice of Rights
All rights reserved. No part of this book may be
reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any
means, electronic, mechanical, recording or
otherwise, without the prior written permission.
Notice of Liability
All specifications contained in this Body Builders Guide
are based on the latest product information available
at the time of publication. The manufacturer reserves
the right to discontinue or change at anytime without
prior notice, any parts, material, colors, special
equipment, specifications, designs and models.
Made and printed in the USA.
II
Page 4

Contents
Introduction
FMVSS
EPA Requirements
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
Clearances
Body Installations
Prohibited Attachment Areas
Subframe Mounting
Crew Cab Body/Frame Requirements
Modification of the Frame
Fluid Lines
Electrical Wiring & Harnessing
Maximum Allowable Current
Exhaust System
Fuel System
Rear Lighting
Servicability
Wheelbase Alteration
Hydraulic Brake System
Body Application Summary Chart
NPR, NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
NPR, NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Diesel
NQR/W5500 Diesel
NPR HD, NQR/W4500 W500 Crew Cab Diesel
FRR/WT
Mechanical & Cab Specifications
Engine Horsepower & Torque Chart
GVW/GCW Ratings
Rear Frame Height Chart
Clutch Engagement Torque
Paint Code Chart
N/W Series Towing Procedure
*
FRR/WT Series Towing Procedure
FSR, FTR & FVR Series Towing Procedure
Weight Distribution
Glossary of Dimensions
Weight Distribution Formulas
Recommended Weight Distribution
Trailer Weight
Performance Calculations
Highway Limits
Federal Bridge Formula Table
Commodity & Material Weights
Approximate Weight of Commodites & Materials
Vehicle Specifications Index
NPR, NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
NPR, NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Diesel
NQR/W5500 Diesel
NPR, NPR HD NQR/W4500 W500 Crew Cab Diesel
FRR/WT
FSR, FTR & FVR
*
NPR, NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas Cab Chssis Electrical
NPR, NPR HD NQR/W3500 W4500 Diesel Cab Chssis Electrical
NPR HD NQR/W4500 W500 Crew Cab Electrical
FRR, FSR, FTR & FVR Cab Chassis Electrical
*
*Note: 2002 FSR, FTR and FVR
Weight Distribution Concepts
Weight Restriction
Gross Axle Weight Rating
Weighing the Vehicle
Tire Inflation
Center of Gravity
III
Page 5

IV
Page 6

Introduction
This guide has been provided as an aid to final stage manufacturers in determining conformity to the applicable
Emission Control and Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards. Final stage manufacturers should maintain current
knowledge of all Emission Regulations and Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards and be aware of their specific
responsibility in regards to each standard.
Any manufacturer making material alterations to this incomplete vehicle during the process of manufacturing the
completed vehicle should be constantly alert to all effects, direct or indirect, on other components, assemblies or
systems caused by such alterations. No alterations should be made to the incomplete vehicle that directly or
indirectly results in any either component, assembly or system being in nonconformance with applicable Emission
Regulations or Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.
General Motors Isuzu Commercial Truck, LLC (GMICT) and American Isuzu Motors Inc. will honor its warranty
commitment (for the cab-chassis only), to the ultimate consumer, provided: (1) the final stage manufacturer has
not made any alterations or modifications which do not conform to any applicable laws, regulations or standards, or
adversely affect the operation of the cab-chassis; and (2) the final stage manufacturer complied with the instructions contained in this guide with respect to the completion of the vehicle. Otherwise, the warranty becomes the
responsibility of the final stage manufacturer.
The final stage manufacturer is solely responsible for the final certification of the vehicle and for compliance with
Emission Control and Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards. The information contained in this guide has been
provided for the final stage manufacturer’s information and guidance.
This guide contains information pertaining to the NPR/W Gas, NPR/W Diesel, NQR/W Diesel, NPR HD/NQR/W
Diesel Crew Cab and FRR/WT Series Chassis Cab and Janesville assembled FSR, FTR and FVR Chassis Cab.
Following is a list of Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards applicable to those vehicles with a GVWR greater than
10,000 lbs. Please refer to the following chart.
V
Page 7
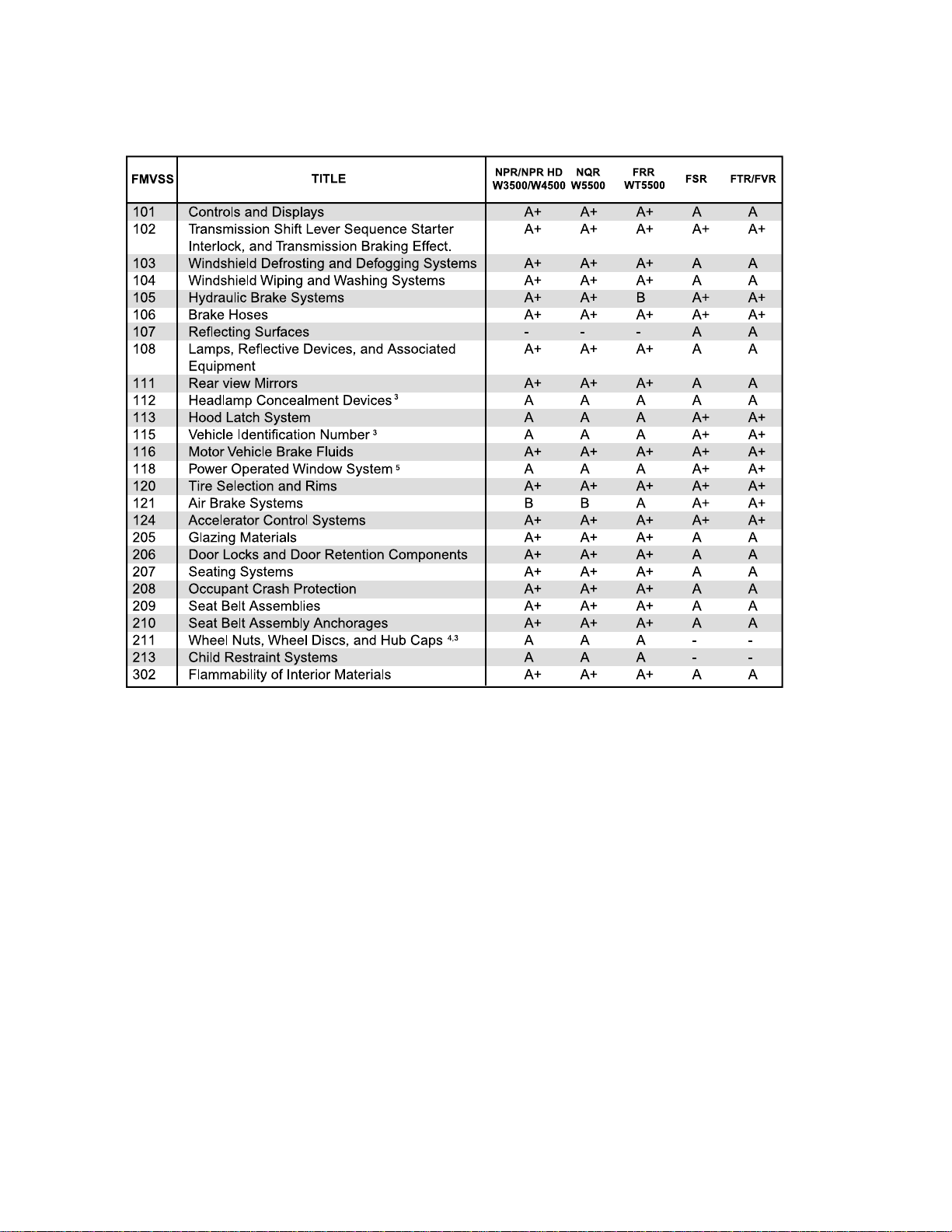
FMVSS Chart
NOTE: This chart is only a guide, for complete information please refer to "Document for Incomplete Vehicle”
provided with each chassis.
Chart Legend:
A Incomplete vehicle; when completed will conform providing no alterations have been made affecting items
covered by FMVSS regulations and "Document for Incomplete Vehicle.
B Incomplete vehicle; when completed by the final manufacturer will conform providing it is completed in
compliance with FMVSS regulations and "Document for Incomplete Vehicle."
+ Meets Canadian Motor Vehicle Safety Standards bearing same FMVSS number.
3 Canadian MVSS only.
4 Not applicable to truck or bus.
5 Not applicable to trucks with a GVWR greater than 10,000 LBS.
VI
Page 8

EPA Requirements
NPR/W Gas, NPR/W Diesel, NQR/W Diesel, NPR HD/NQR/W Diesel Crew Cab and FRR/WT Series Chassis Cab
To assure that U.S.A. and Canada Emission Requirements are met, this Incomplete Vehicle must be completed in
strict accordance with all instructions contained in this document, especially the following instructions which relate
to:
A. Exhaust emission related components
B. Noise emission related components
C. Labels
[A] EXHAUST EMISSION RELA TED COMPONENTS
Compliance of this vehicle with EP A, California and Canada Requirements will be maintained providing
no alterations are made to the components or systems identified below:
1) DIESEL VEHICLES 2) GASOLINE VEHICLES
Injection Pump Vehicle Control Module (VCM)
Injector and High Pressure Lines Fuel Management System
Turbocharger Air Induction System
Charge Air Cooler and Charge Ignition System
Air Cooler Hoses Catalytic Converter System
Engine Control Module (ECM) Positive Crankcase V entilation System
Engine Speed Sensor Exhaust Gas Recirculation System
Engine Coolant T emperature Sensor Evaporative Emission Control System
Intake Manifold Miscellaneous Items Used in Above Systems
Catalytic converter and its location
V ariable swirl system
Exhaust Gas Recirculation System
ADDITIONAL CANADA MOTOR VEHICLE SAFETY ST ANDARD
CMVSS NO. 1 101-EMISSION DEVICE
CMVSS NO. 1 102-CRANKCASE EMISSION (GASOLINE ENGINE ONLY)
CMVSS NO. 1 103-EXHAUST EMISSIONS
CMVSS NO. 1 104-OPACITY (DIESEL ENGINE ONL Y)
CMVSS NO. 1 105- EVAPORATIVE EMISSION (GASOLINE ENGINE ONLY)
[B] NOISE
Compliance of this vehicle with EP A and Canada requirements will be maintained providing no
alterations are made to the components or systems.
CMVSS NO. 1 106-NOISE
This incomplete vehicle, when completed, will conform to the above standards except CMVSS-1106 providing no
alterations are made which effect the function, physical or mechanical properties, environment, locations or vital
spatial clearances of the components identified below:
* Engine assembly
Exhaust emission control system
P.C.V. system (if equipped)
* Intake system
* Exhaust system
Fuel system (if equipped)
* Transmission assembly
* Axle
* Tires
* Fan and drive
Diesel fuel injection controls (if equipped)
Turbocharger and associated controls (if equipped)
* Catalytic converter and its location
V ariable swirl system (if equipped)
VII
Page 9

Conformity with CMVSS 1 106 is not determined solely by the design of the incomplete vehicle. When completed, it
should conform to CMVSS 1 106 providing no alterations are made to the noise attenuation components identified
thus * in the above list.
[C] LABELS
The Emission control related information labels which are permanently affixed are required by government
regulation and must not be obstructed from view or defaced so as to impair its visibility or legibility .
P A R T 3 : Radio Noise
CANADIAN RADIO INTERFERENCE REGULA TIONS
[A] The following statement is applicable to NPR/W Series Chassis-Cab (Gasoline Engine Only).
This incomplete Vehicle, when completed, will conform to the above regulations providing no alterations or substitutions are made which affect any parts or components identified below:
A. Distributor
B. Ignition Wires
C. Spark Plug Wires
FSR, FTR & FVR
U.S. ENVIRONMENT AL PROTECTION AGENCY AND STA TE OF CALIFORNIA EMISSION REQUIREMENTS
To assure that EPA and California Emission Certificate Requirements are met, this incomplete vehicle must be
completed in strict accordance with all instructions contained in this document, especially the following instructions
which relate to:
A. Exhaust emission related components
B. Labels
[D] EXHAUST EMISSION RELATED COMPONENTS
Compliance of this vehicle with EP A and California Certification Requirements will be maintained providing
no alterations are made to the components or systems identified below:
1. DIESEL VEHICLES
Injection Pump
Injector and High Pressure Lines
Turbocharger
Charge Air Cooler and Charge Air Cooler Hoses
Engine Control Module (ECM)
Engine Speed Sensor
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (6HE1-TC only)
Intake Manifold
Catalytic converter and its location (6HE1-TC only)
Air cylinder for variable swirl system (6HE1-TCS only)
[E] LABELS
The Emission control related information labels which are permanently affixed are required by government regula-
tion and must not be obstructed from view or defaced so as to impair its visibility or legibility .
VIII
Page 10

CANADIAN MOTOR VEHICLE SAFETY STANDARDS
CMVSS NO. 1 101-EMISSION DEVICE
CMVSS NO. 1 103-EXHAUST EMISSIONS
CMVSS NO. 1 104-OPACITY
CMVSS NO. 1 106-NOISE
This incomplete vehicle, when completed, will conform to the above standards except CMVSS 1106 providing no
alterations are made which affect the function, physical or mechanical properties, environment, locations or vital
spatial clearances of the components identified below:
Engine assembly*
Exhaust emission control system
P.C.V . system
Intake system*
Exhaust system*
Fuel system
Transmission assembly*
Axle*
Tires*
Fan and drive*
Diesel fuel injection controls
Turbocharger and associated controls
Catalytic converter and its location (6HE1-TC only) *
Air cylinder for variable swirl system (6HE1- TCS only)
Conformity with CMVSS 1 106 is not determined solely by the design of the incomplete vehicle. When completed, it
should conform to CMVSS 1 106 providing no alterations are made to the noise attenuation components identified
thus * in the above list.
Compliance of this vehicle with EP A and California Certification Requirements will be maintained providing no
alterations are made to the components or systems identified below:
Air Inlet System
Diesel Fuel Injection Controls
Engine Assembly with all Components of Exhaust Emission Control System
Exhaust System
Fuel System
Turbocharger and Associated Controls
IX
Page 11

Installation of Body & Special Equipment
Installation of Body
&
Special Equipment
April 2002 1
Page 12
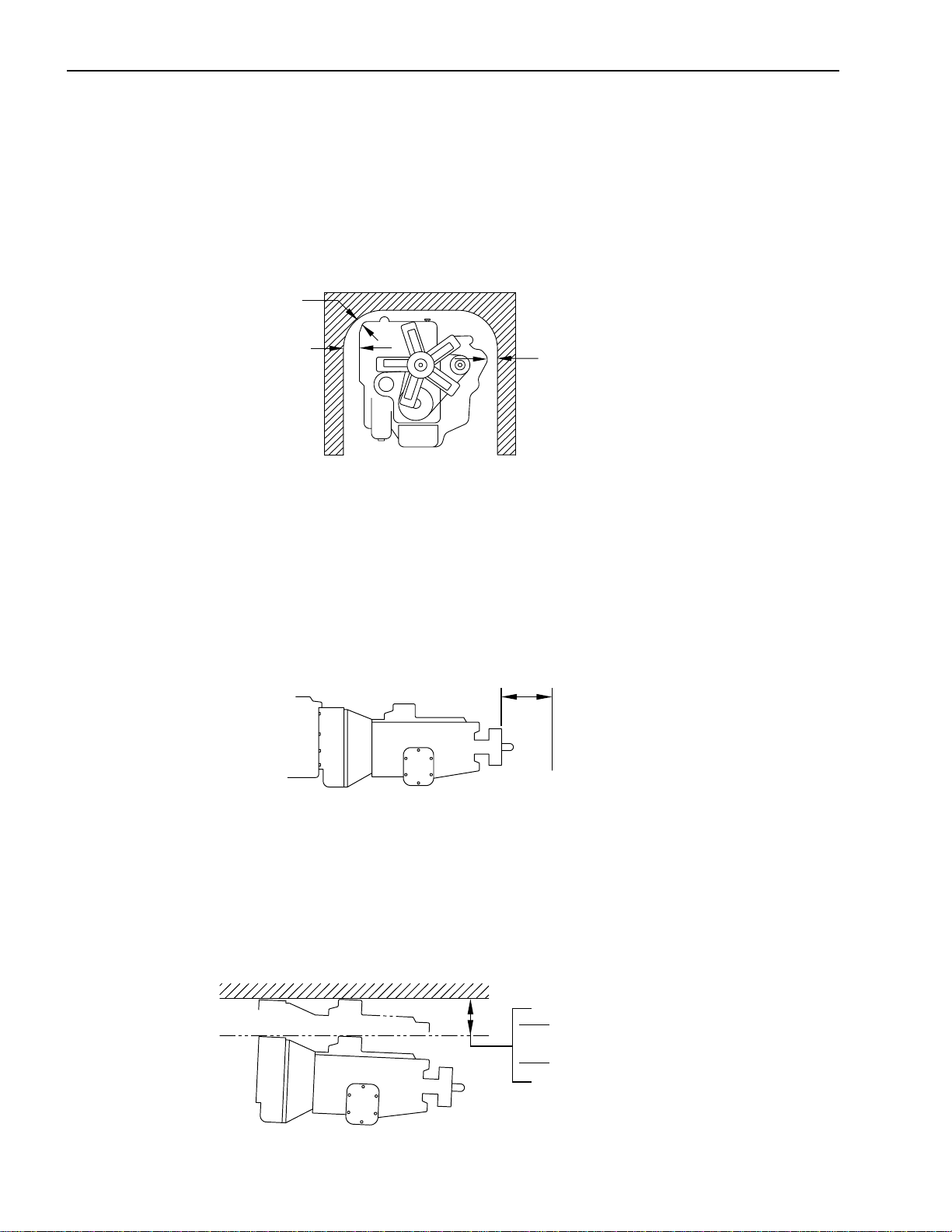
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
Clearances
Engine
At least 1.6 inch clearance should be maintained around the engine. No obstacles should be added in front of the
radiator or intercooler.
1.6 Inch
Clearance
1.6 Inch
Clearance
Engine
1.6 Inch
Clearance
Transmission
The transmission is removed from the rear. Enough clearance must be provided to allow rearward movement of the
transmission assembly. Clearance should be sufficient to allow 5 to 6 inches unrestricted movement of the
transmission assembly. In addition, provide at least 2 inches clearance around the control lever on the side of the
transmission to allow free movement without any binding.
5-6 Inch
Engine
Clearance
Transmission
At least 6 inches clearance should be maintained above the transmission to allow easy removal of the upper cover
for manual transmissions. At least 2 inches clearance should be maintained above the automatic transmission to
allow for transmission removal.
5.9
Inches or More M/T
(150)
2.0
Inches or More A/T
(58)
Transmission
2 April 2002
Page 13
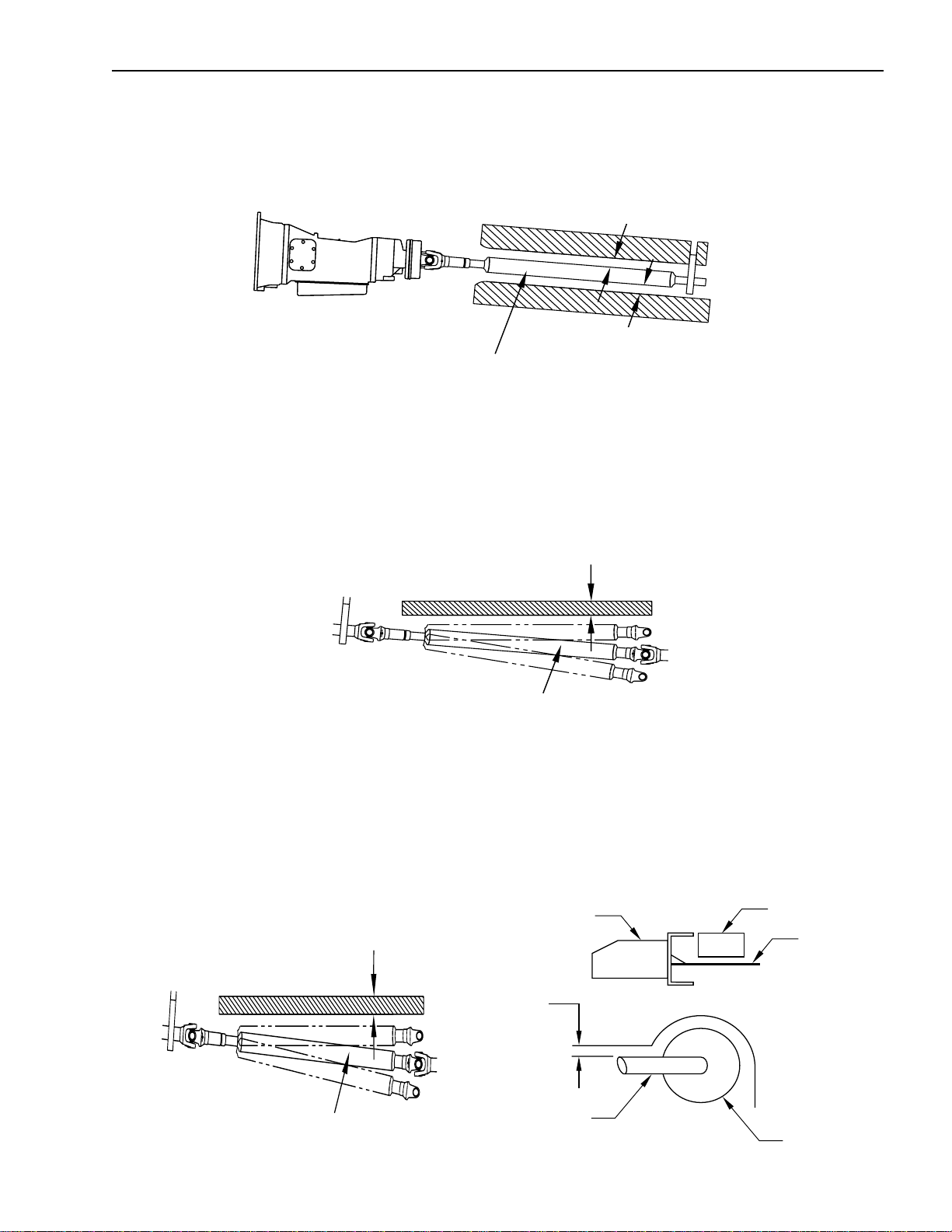
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
Front and Center Propeller Shafts
At least 1.25 inch clearance should be maintained around front and center propeller shafts.
1.25 Inches or more
1.25 Inches or more
Front Propellar Shaft
Rear Propeller Shaft
With the rear springs at maximum deflection, at least 1.25 inch clearance should be provided over the rear propeller
shaft.
1.25 Inches or more
Front Propellar Shaft
Exhaust System
If flammable materials such as wood are used in the body, provide at least 3.9 inches clearance between the body
and any parts of the exhaust pipe, muffler and catalytic converter. If it is impossible to maintain this minimum
clearance, use a heat shield. Also use a heat shield if an oil pump or line is located above the exhaust pipe, muffler
or catalytic converter.
Tool Box
1.25 Inches or more
3.9 Inch
Clerance
Oil Pump
Heat Shield
Front Propellar Shaft
April 2002 3
Exhaust Pipe
Muffler
Page 14
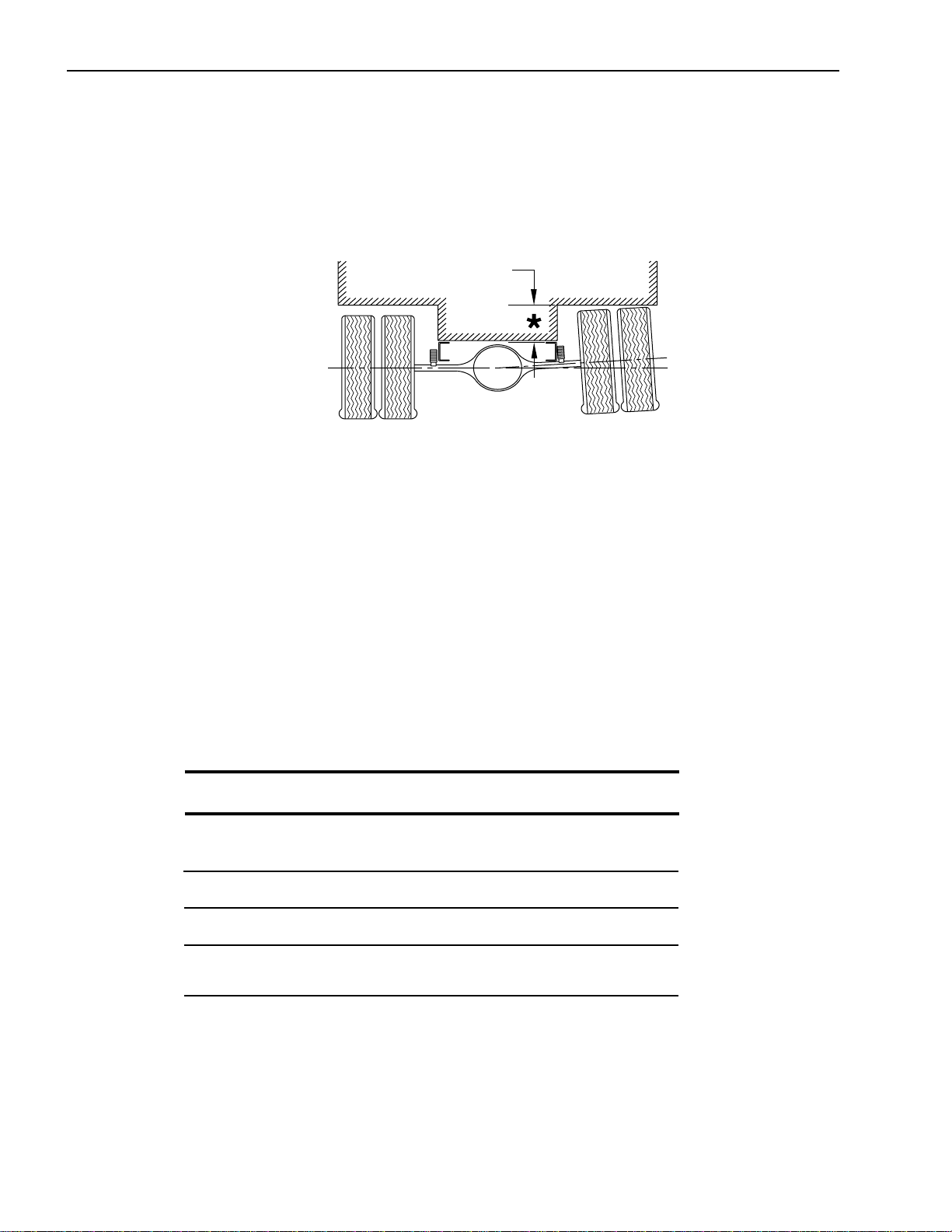
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
Rear Wheel and Axle
The design and installation of the body should allow sufficient clearance for full vertical movement of the rear wheels
and axle when the vehicle travels over rough or unlevel surfaces.
Rear of Body
*NOTE: For recomended clearances
please refer to the Rear Axle Chart in
each models respective section.
Normal Rear
Axle Center Line
Rear Wheels
Over High Spot
Rear Wheels
Over Obstacle
Other Clearances
Transmission control cable may be broken if it is bent by or interferes with the body and its fixtures. To prevent this,
1 inch minimum clearance should be provided. When cable is detached for body mounting, be sure not to bend the
cable.
Accessibility to the grease nipple on the rear spring bracket/shackle should be provided so that serviceability with a
grease gun is not hampered.
MINIMUM
PARTS CLEARANCE LOCATION
Brake Hose 6.7 in. Axle side
1.6 in. Frame side
Parking Brake Cable 1.2 in. -------Fuel Hose 1.6 in. -------Shock Absorber 2.4 in. Axle Side
1.2 in. Frame Side
4 April 2002
Page 15
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
Body Installation
Chassis
To maintain the performance of the truck chassis, either a side member or subframe should always be used for body
mounting. Body mounting with low rigidity will often adversely affect riding comfort.
Special Equipment on the Chassis
When installing special equipment on the chassis, extra consideration must be given to the weight and construction
of the equipment to assure proper distribution of the load. Localization of the load should be prevented. All special
equipment should be properly secured into position. We recommend the use of subframe members when installing
special equipment.
Subframe Design and Mounting
The subframe assembly should be mounted as close to the cab as possible. It should be contoured to match the shape
and dimensions of the chassis frame as closely as possible.
Rear End of the Cab
April 2002 5
Page 16
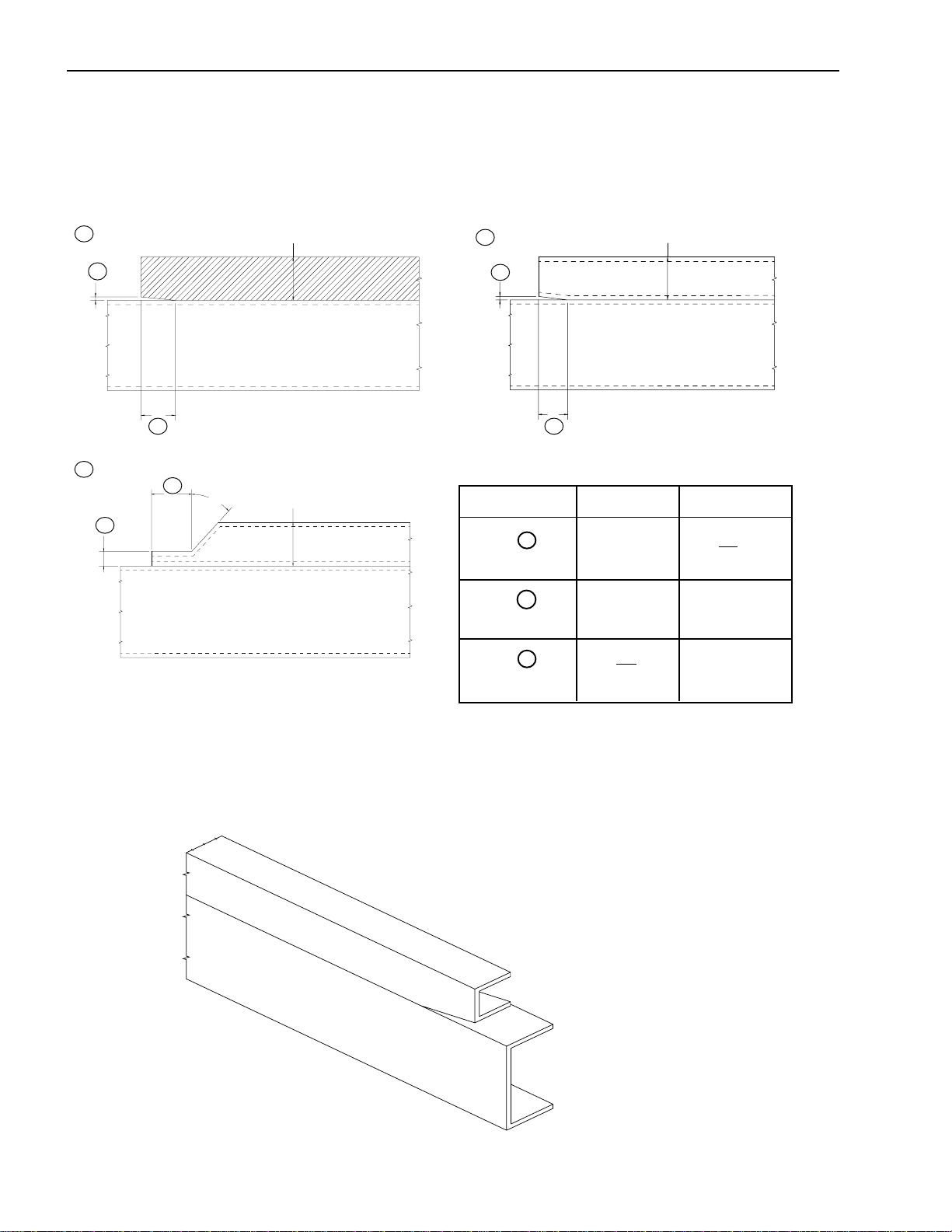
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
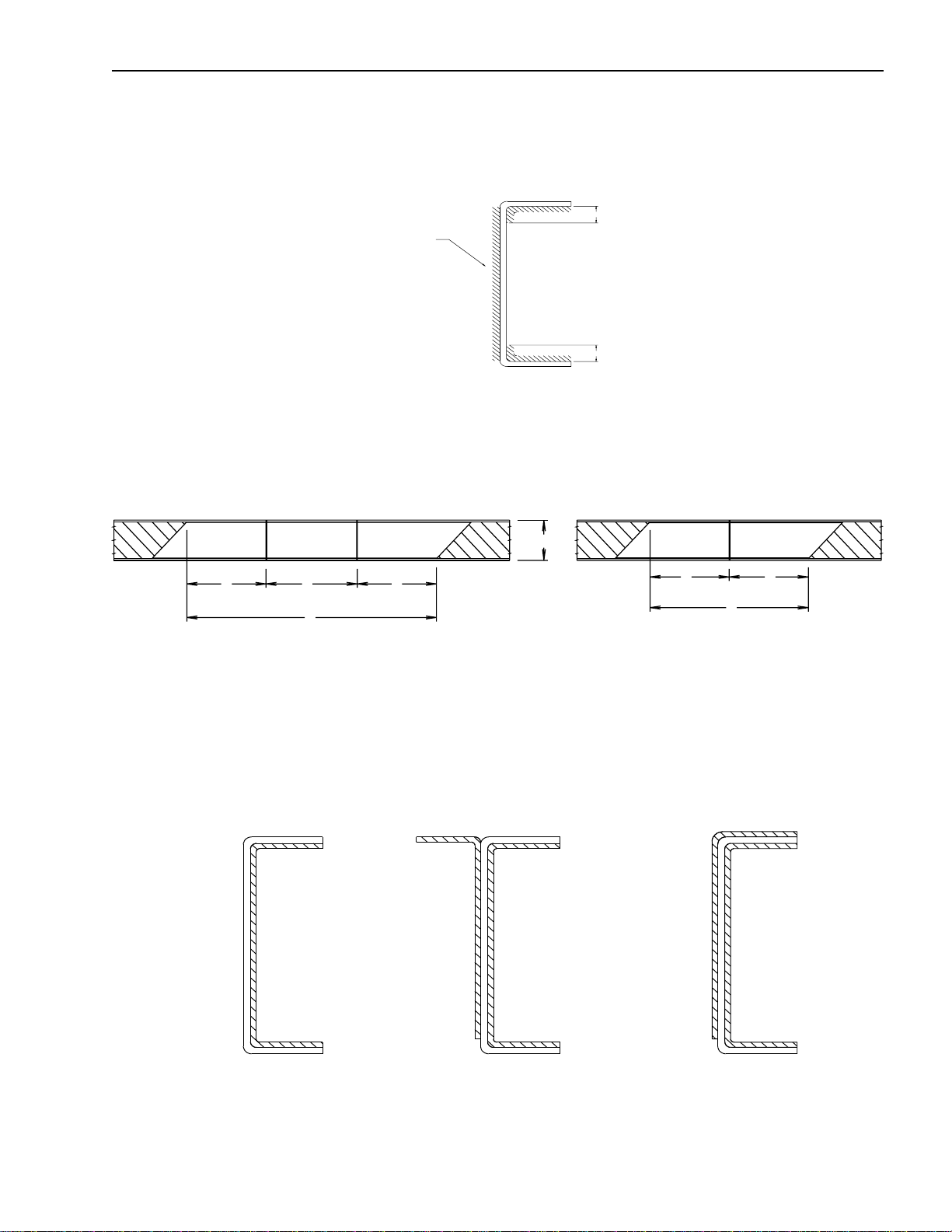
Subframe Contour
Contouring of the front end of the subframe members as shown in the three illustrations below will prevent stresses
from being concentrated on certain areas of the chassis frame.
1
A
3
A
Wooden subframe
B
B
45
o
H
H
Steel subframe
2
Steel subframe
A
B
Drawing A B
1 0.2 in. H
2 0.2 in. H or more
3 H H or more
H
2 ~ H
3
When using a steel subframe, do not close the end of the subframe.
Steel subframe
Chassis frame
6 April 2002
Page 17
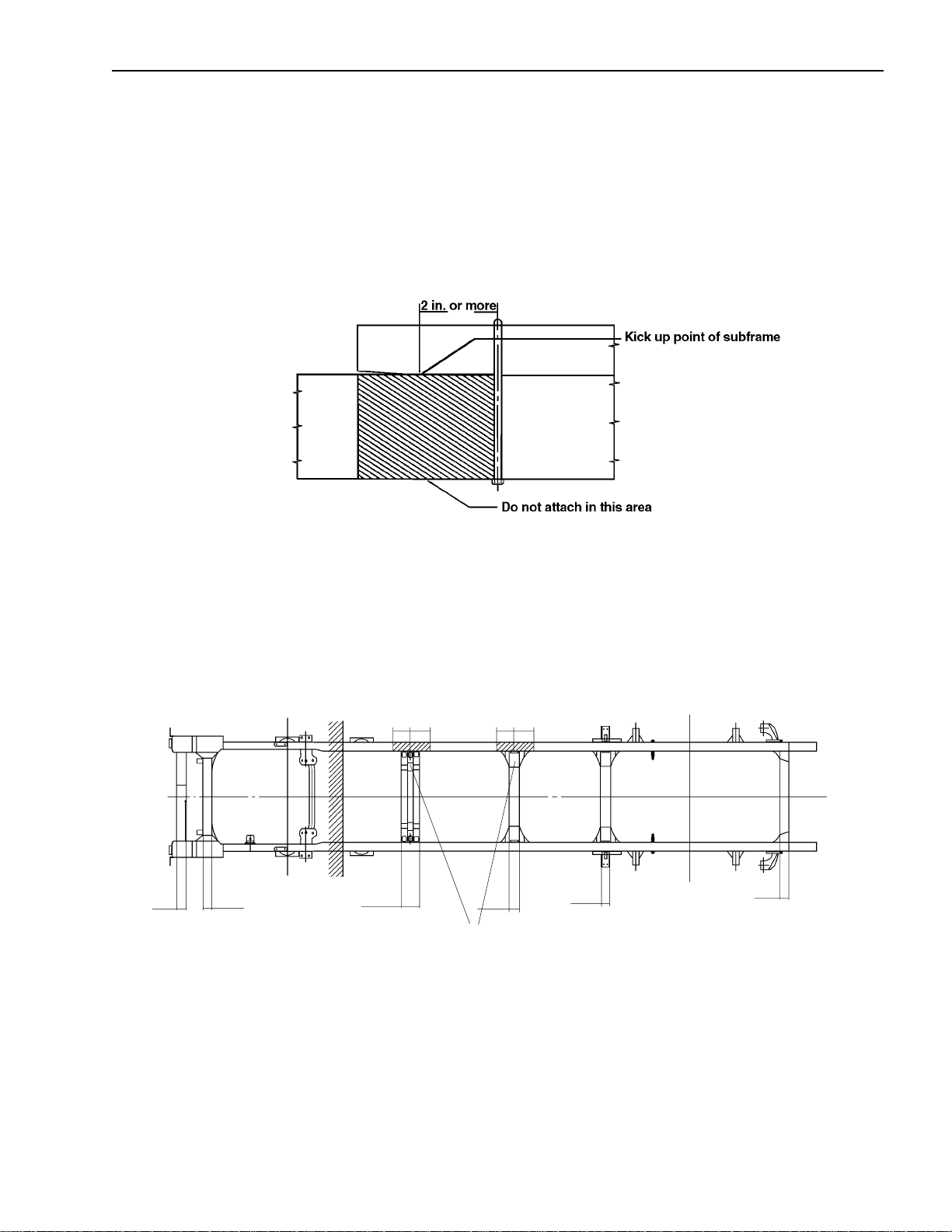
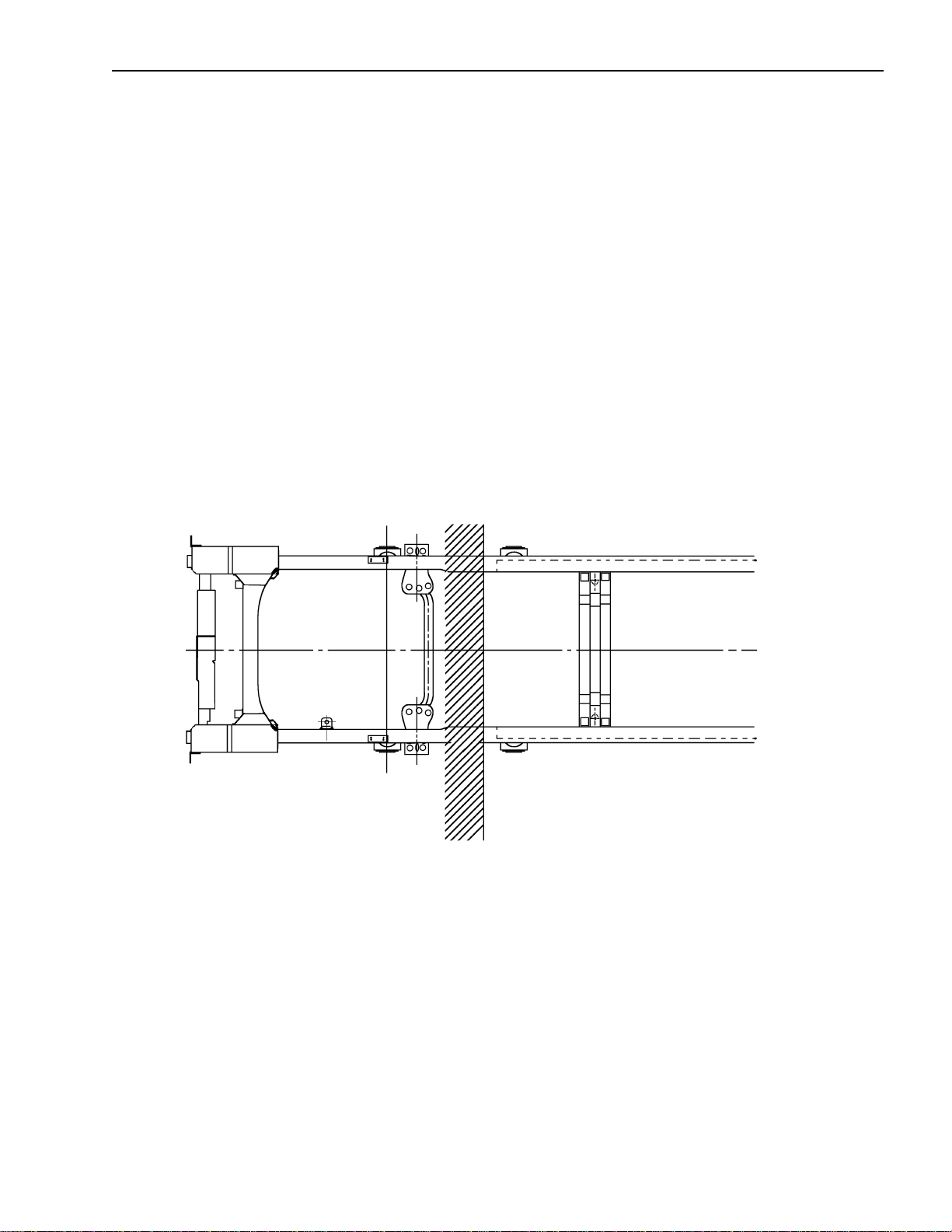
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
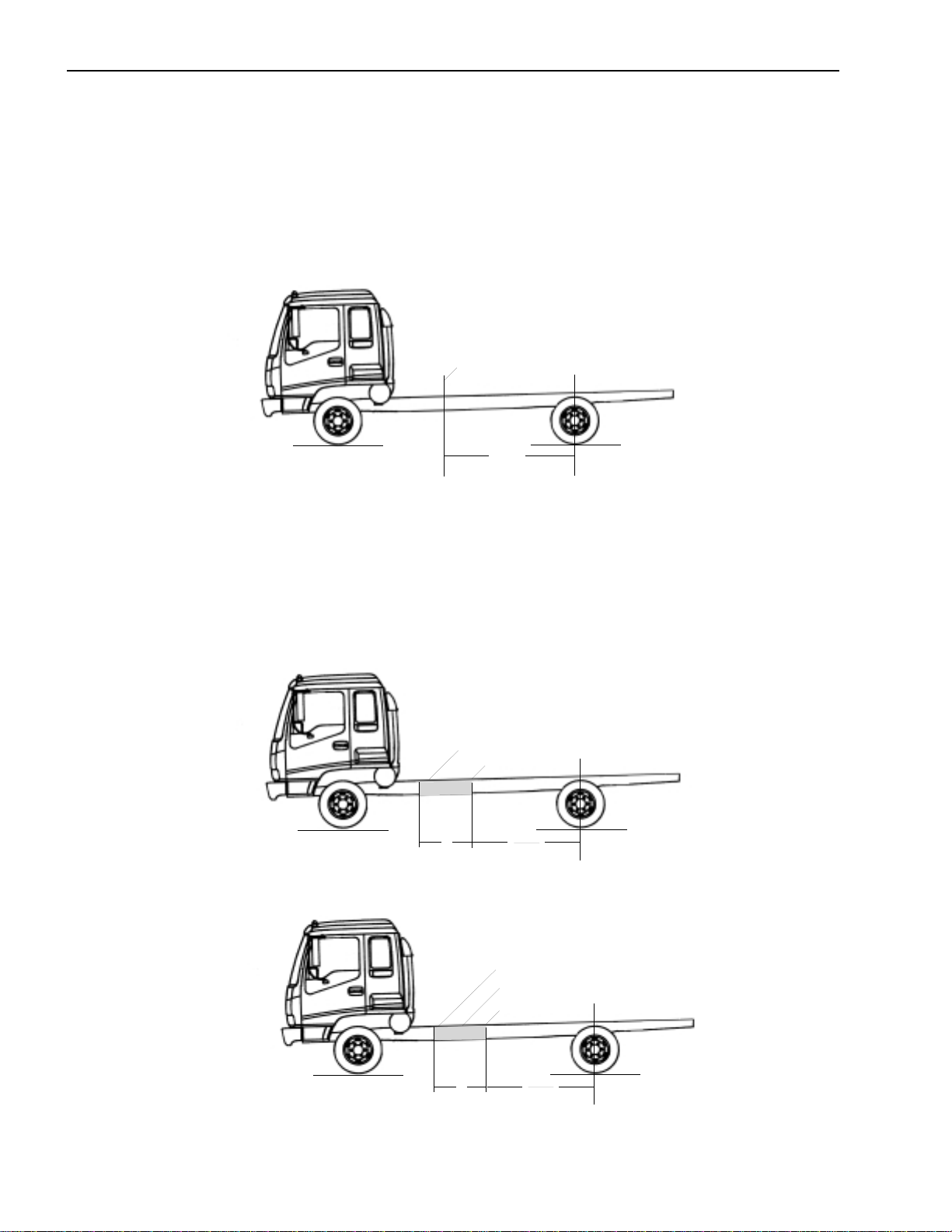
Prohibited Attachment Areas
Do not attach the subframe with a bolt on bracket to the chassis frame at the points indicated by shading in the following
illustrations.
1. At the front end of the subframe. The attaching bolt or bracket must be at least 2 inches behind the kick
up point of the subframe.
2. Within 8 inches of bends in the chassis frame or the attachment points of any cross members.
3.3
8 in. 8 in
6.1
8 in. 8 in
3.1
Do not attach in these areas.
3.12.9
2.8
April 2002 7
Page 18
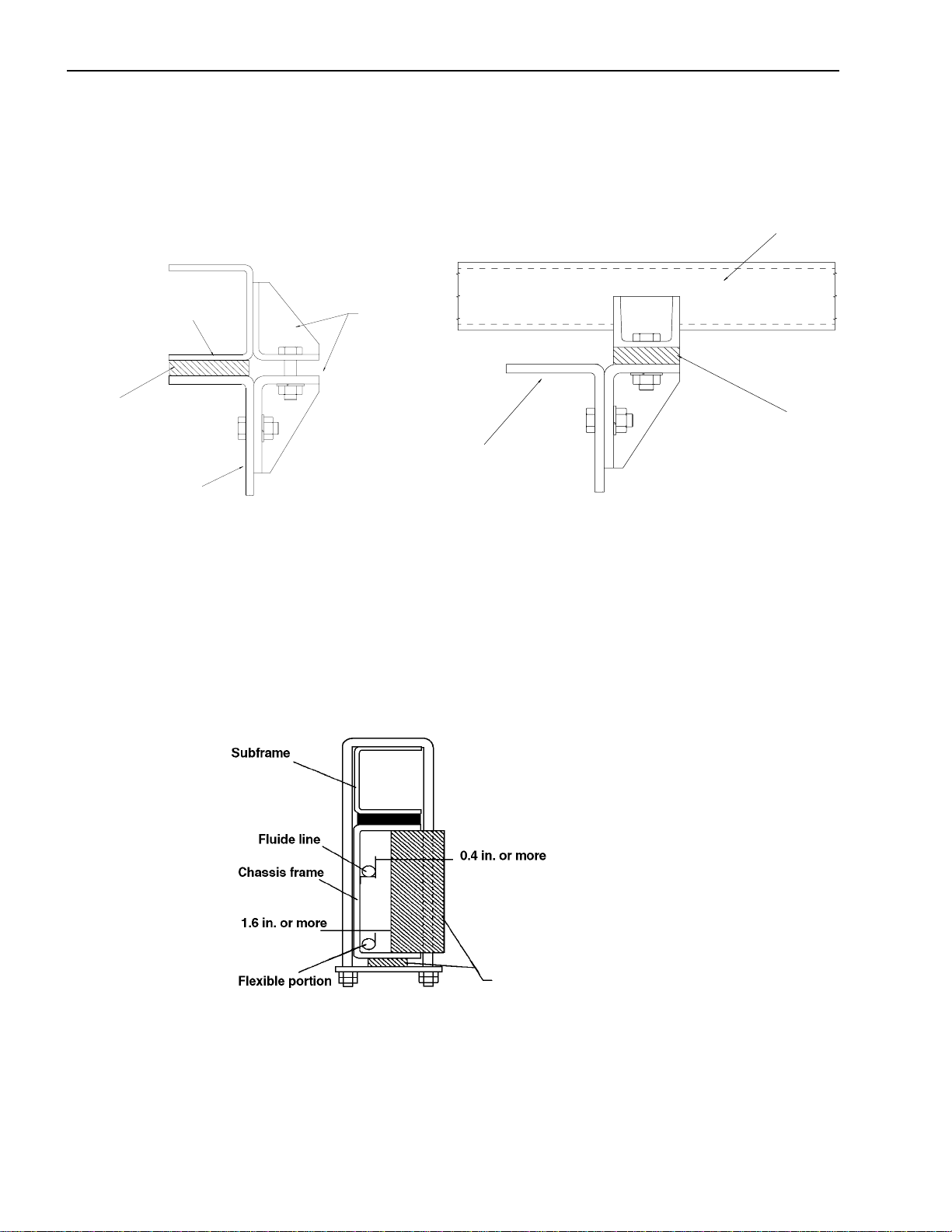
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
Subframe Mounting
Bracket Installation
Mounting brackets should be clamped to the chassis frame using bolts. For proper positions in which to install the
bolts, refer to the preceding section and the section “Modifications to the Chassis Frame.”
Bolster
Subframe member
Cushioning material
Chassis frame
Bracket
Cushioning material
Chassis frame
U-bolt Installation
When U-bolts are used to retain the subframe, reinforcement blocks must be installed in the frame members. This
will prevent distortion of the frame flange as they are tightened. The drawing indicates the correct placement of
reinforcement blocks. If you use wood blocks, be sure that there is sufficient clearance between them and any parts
of the exhaust system.
If any fluid lines or electric cables are located near the reinforcement blocks, you must provide at least 0.4 inch
clearance between rigid or stationary portions, and at least 1.6 inch between moveable or flexible portions of the lines.
Reinforcement block
(Reinforcement blocks should be mounted
securely in installed position)
For the installation positions of the U-bolts, refer to “Prohibited Attachment Areas.”
8 April 2002
Page 19
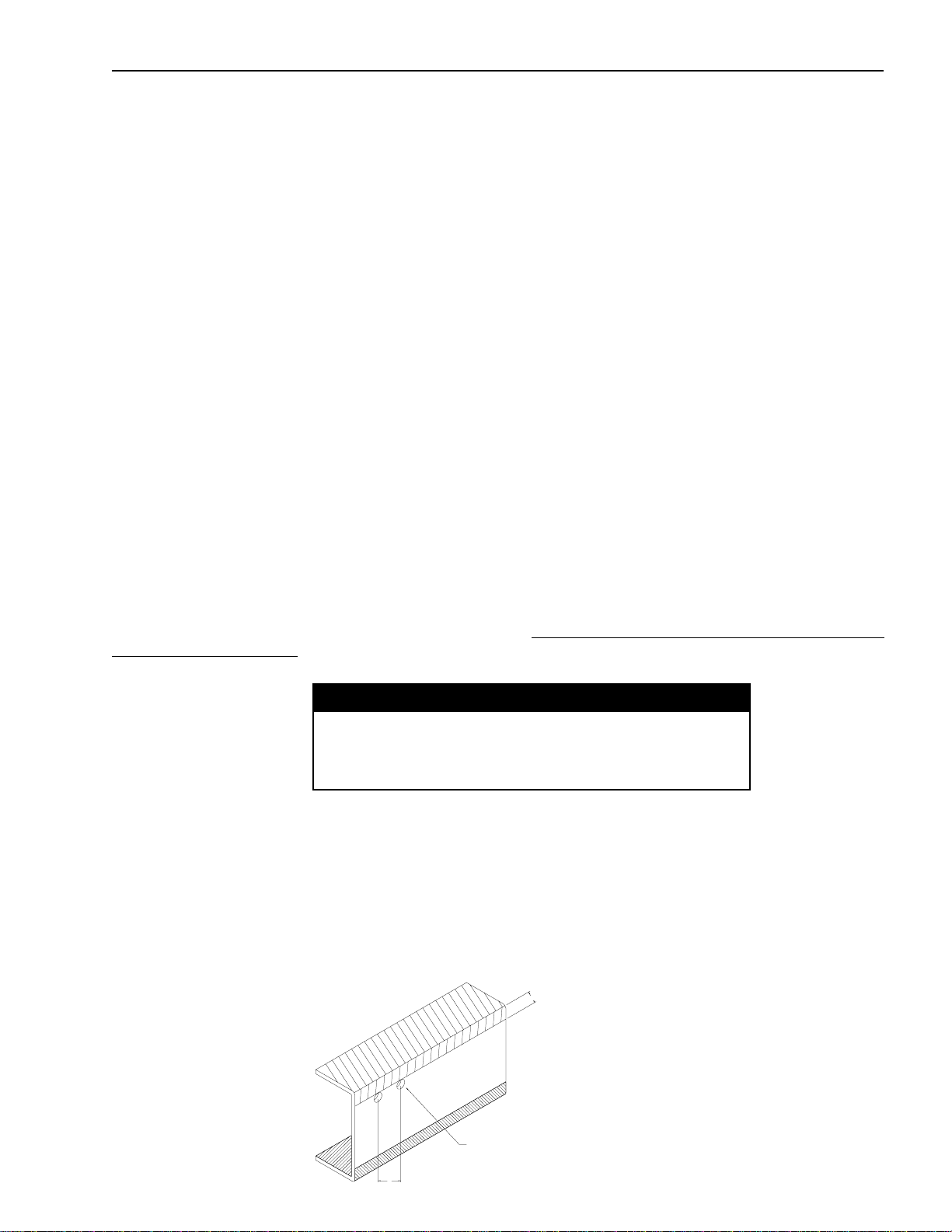
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
Crew Cab Body/Frame Requirement
The Crew Cab NPR HD/W4500 and NQR/W5500 will be available in two wheelbases, 150 and 176 inches. Effective
CA will be 84.7 and 110.7 inches. On this model chassis General Motors Isuzu Commercial Truck, LLC (GMICT)
and American Isuzu Motors Inc. will require that the body installed on the chassis have an understructure
manufactured with any of the following structural steel "C" channels:
4"x1-5/8", 7.25 lbs/ft = ok
5"x1-3/4", 6.7 or 9.0 lbs/ft = ok
6"x2", 8.2, 10.5 or 13.0 lbs/ft = ok
Modification of the Frame
Modification of chassis frame should be kept to an absolute minimum. Modification work should be performed
according the instructions in the following paragraphs.
When modification is complete, chassis frame members should be carefully inspected to eliminate the possibility of
any safety-related defects.
NOTE: PLEASE REFER TO NOTES ON CHASSIS FRAME MODIFICATION WITH ANTILOCK BRAKES ON PAGES 27 AND 28
Working on Chassis Frame
The chassis frame is designed and built with consideration for proper load distribution. Sufficient physical strength
is provided when the load is evenly distributed. Installation of special equipment on the chassis frame can cause
variations in load distribution. If even distribution of load is not kept in mind when the equipment is installed, localization
of stresses on specific areas of the frame could cause cracking of the chassis frame members or other problems,
even if the total weight of the equipment is within the design limit.
The chassis frame is designed as an integral unit. Therefore, we do not recommend cutting the chassis frame
under any circumstances.
Drilling and Welding
IMPORTANT NOTE
For vehicles equipped with electronic or hydra-matic
transmissions electric arc welding must be done with the
negative battery cable disconnected.
1. Do not drill or weld in the shaded portions of the chassis frame members. Do not weld with 0.8 inch from th edges
of any existing holes.
2. Hold the length of any welding beads within 1.2-2.0 inch. Allow at least 1.6 inch between adjacent welding beads.
3. All holes must be drilled. Do not use a torch to make any holes.
4. All riveting must be done with cold rivets. Do not use hot rivets.
5. The flange of the chassis frame must not be cut under any circumstances.
6. The subframe must be attached to the chassis frame with bolts. Do not weld.
B
A
Dimensions: A - not more than 0.51 in. in diameter
C
April 2002 9
B - must be more than 0.8 in.
C - must be more than 1.0 in.
Page 20
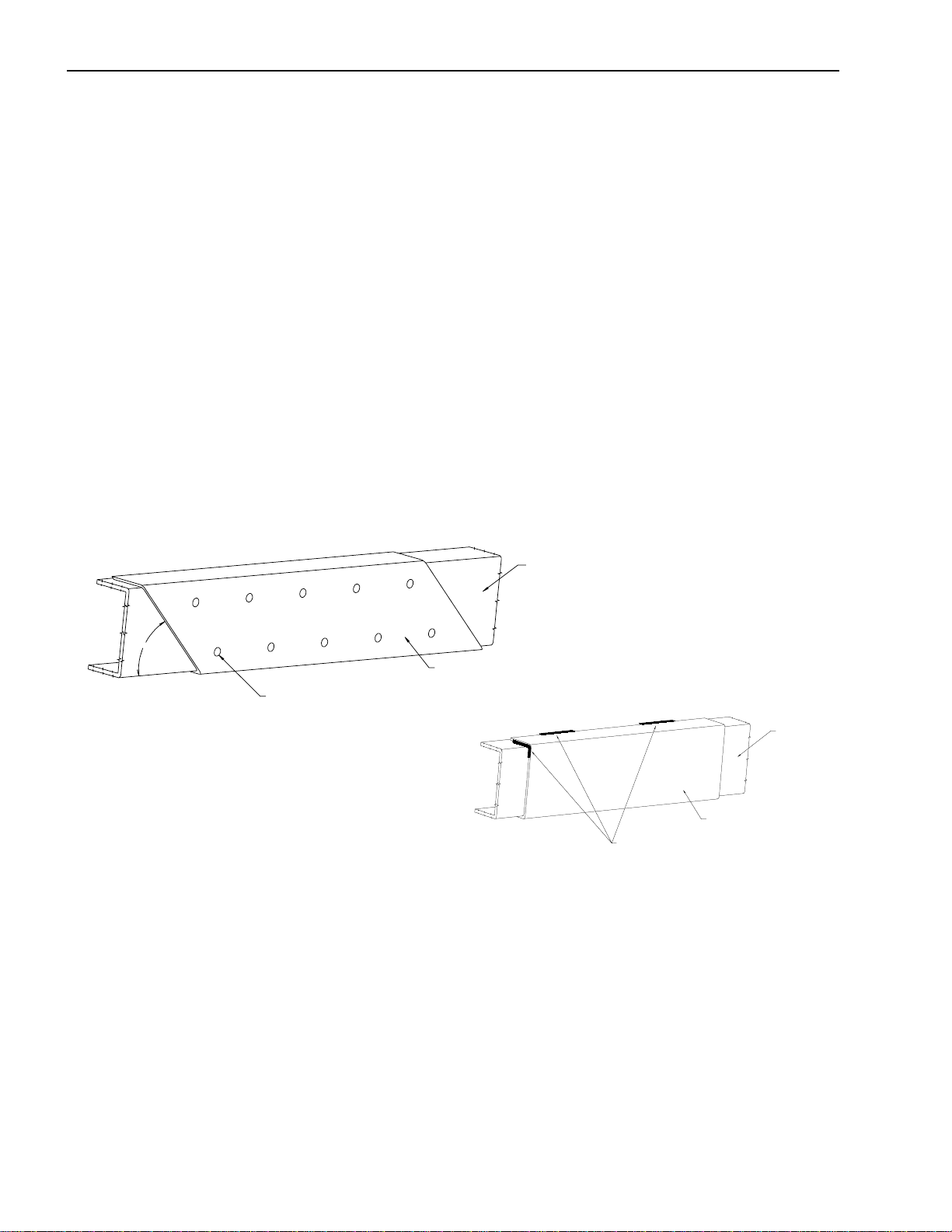
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
Reinforcement of Chassis Frame
Reinforcements must be installed to prevent the considerable variation in the section modulus. They must be welded
so as to avoid localized stresses.
The frame of the NPR/W3500, NPR GAS/W4500 and NQR/W5500 is made of SAPH440 mild steel. The frame of
the FRR is made of HT540A. See the FSR, FTR and FVR section for frame material specifications.
The drawings below illustrates correct and incorrect methods of frame reinforcement.
Welding
1. Keep reinforcement plates and chassis frame free from moisture and water.
2. Avoid cooling with water after welding.
3. Use a suitable means to protect pipes, wires, rubber parts, leaf springs, etc. against heat and
affect of sputtering.
4. Remove fuel tank assembly when welding portions near the fuel tank.
5. Remove coat of paint completely when welding painted areas.
SATISFACTORY
o
45
Fluid Lines
Reinforcement
Plug weld or rivet
UNSATISFACTORY
Frame rail
Frame rail
Reinforcement
Welding is prohibited
Do not disturb the layout of any brake lines or fuel lines unless absolutely necessary. When modification is needed,
follow the instructions below carefully to ensure safety. Brake fluid lines must not be cut and spliced under any
circumstances. We do not recommend the cutting or splicing of any fuel lines, but if it is absolutely necessary, be
sure that the correct fitting and tools are used to form the joint, and then pressure test the joint. Steel lines are metric
sizes.
Preparation of Additional Lines
1. Where possible, use only genuine Isuzu lines as supplied by authorized Isuzu dealers.
2. Use the correct metric flaring and bending tools to form the lines.
3. Avoid repeated bending. Do not use heat for flaring and bending the lines. Before and after
forming the new lines, examine them carefully for scratches, distortion, dents and the presence
of any foreign matter.
10 April 2002
Page 21
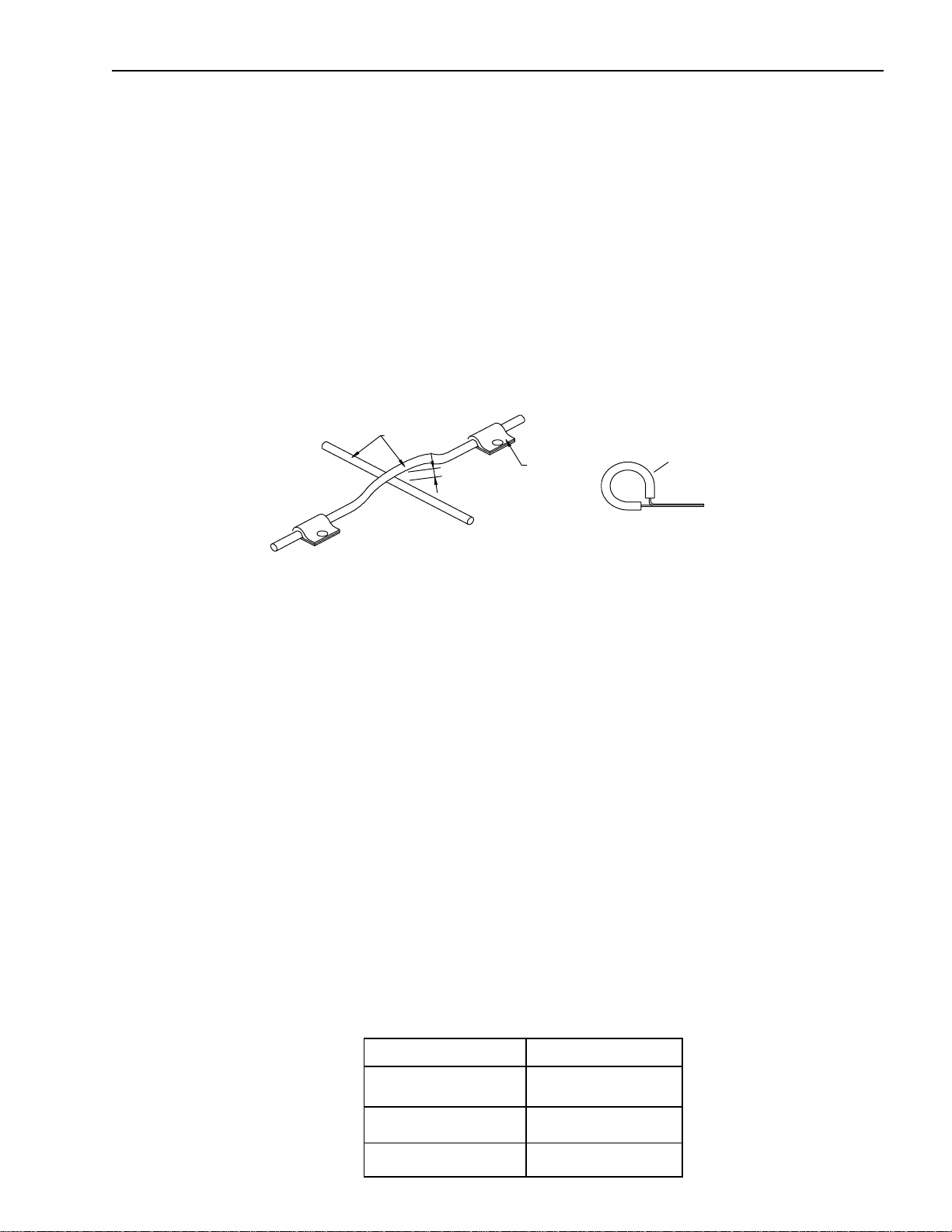
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
Installation of Additional Lines
Install new lines away from adjacent parts and away from any sources of heat.
1. A minimum clearance of 0.4 inch must be maintained between lines. Where necessary, clip the
lines into position in order to maintain this minimum clearance.
2. Minimize any crossing between lines. If a crossing is unavoidable, use the following procedure:
a. At least 0.4 inch clearance should be maintained between lines at the crossing point.
b. If the 0.4 inch clearance cannot be maintained, or if the lines are subject to vibration, clip
them securely.
3. Plan the bends and clipping points of the lines to minimize vibration and the resulting fatigue.
4. Use rust-proofed clips and apply vinyl coating to the portions of the lines to be clipped.
5. Install new lines in positions where they are protected against water, dirt, grit, sand, rocks and
other foreign matter that can come from above or below, or can be flung up by the wheels.
Lines
Clip
0.4 in. or more
Vinyl
Clip
Electrical Wiring and Harnessing
To increase the reliability of the wiring, all frame harnesses are covered with corrugated vinyl tubing. The following instructions apply to extending or modifying these harnesses. See the Electrical Section for information on
commonly used circuits in the NPR, NQR, FRR and W-Series. The FSR, FTR and FVR wiring information can
be found in the service manuals.
Wiring
1. Most wiring connections on Isuzu vehicles are made with terminals. We recommend the use of
terminals when splicing cables and wires.
2. When splicing, use new wire of the same gauge, and do not make splices inside the corrugated
tubing.
3. When making connections to the end of the harness, make sure the connections are electrically
perfect. Use insulating tape as needed to prevent the entry of water, which results in short
circuits and/or corrosion.
4. When making new circuits, or modifying circuits already installed, make the cables only just taut
enough to remove any slack. Use clips or grommets where required to protect cables from heat
or sharp edges. When cables must run near the exhaust system, see the instructions in the
“Exhaust System” section.
5. Always use rustproof clips, and apply vinyl coating to that portion of the clips in direct contact
with the harnesses. No scotch clips or connectors.
6. To minimize the vibration of the harness, clipping points should be set up according to the table.
Harness Diameter Clip Distance
less than 0.2 in. less than 11.8 in.
0.2 in. ~ 0.4 in. approx. 15.7 in.
0.4 in. ~ 0.8 in. approx. 19.7 in.
April 2002 11
Page 22
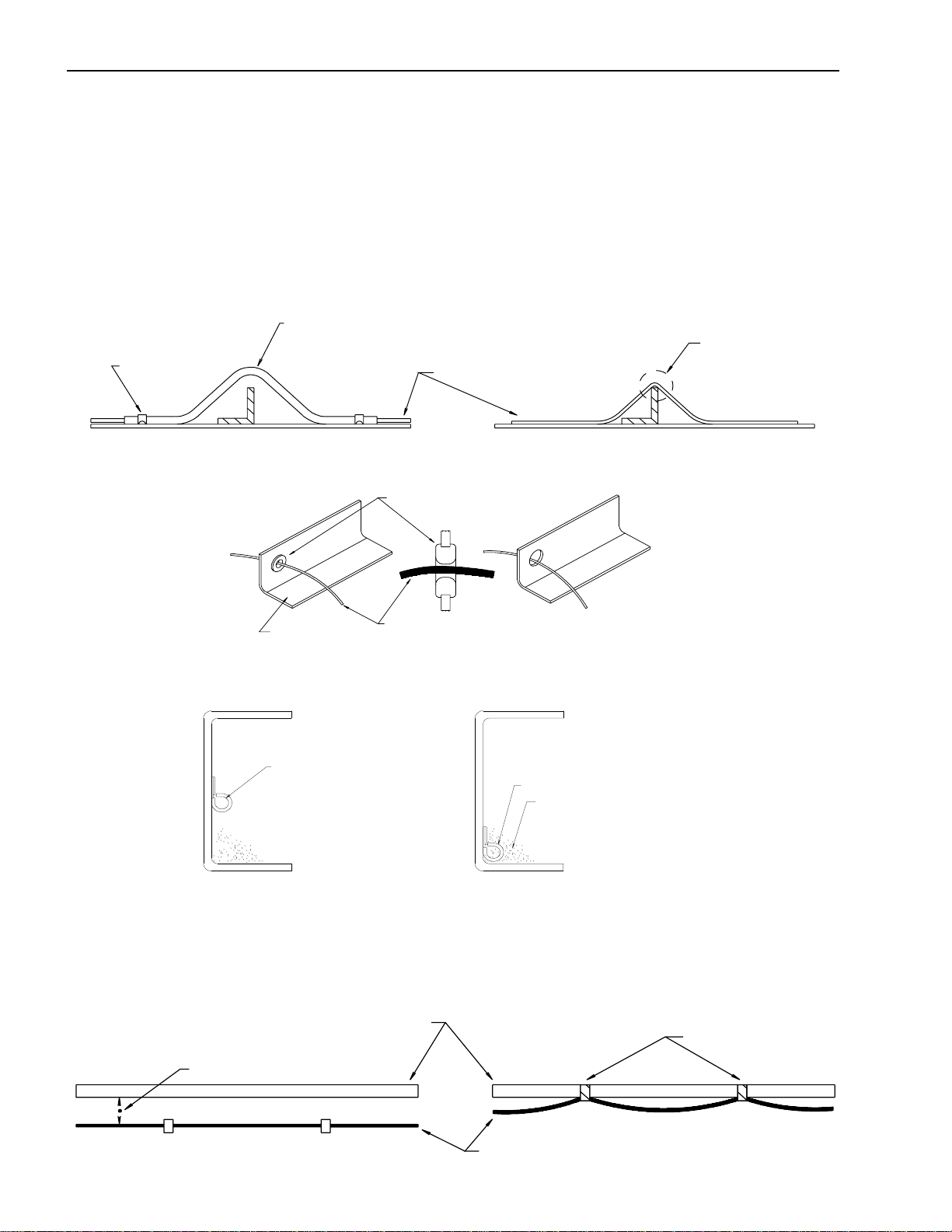
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
7. When changing the length of the battery cable, do not cut or splice the existing cable. Make up a
new cable of the correct length and wire gauge for the load and distance, without splices.
8. When using connectors, use a socket (female) connector on the electrical source side and a
plug (male) connector on the electrical load side to lower the possibility of a short circuit when
disconnected.
9. When connecting cables to moving or vibrating parts such as the engine or transmission, be
sure to maintain sufficient slack in the wiring to absorb the vibration. Follow the example of
existing cables connected by Isuzu. Keep flexible cables clear of other parts.
10. Do not use vinyl tape in the engine compartment. The heat will tend to make it peel off. Use
plated steel clips coated with rubber or vinyl.
Vinyl tube
Clip
Harness
Direct contact*
SATISFACTORY
Rubber grommet
Steel plate
SATISFACTORY
Electric wire
* Cables should not be in contact with sharp edges or pierced holes.
Harness
SATISFACTORY UNSATISFACTORY
UNSATISFACTORY
UNSATISFACTORY
Harness*
The harness receives
the adverse affect of
dirt, grit, or water
* Harnesses should not be installed on inside lower face of the chassis frame.
* Harnesses should not be taped to fuel lines or other lines. A sufficient clearance should be maintained between
harness and pipe lines.
Line
When parallel: 0.4 in. or more
When across: 0.8 in. or more
Harness
12 April 2002
UNSATISFACTORYSATISFACTORY
Taping*
Page 23
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
Wire Color Code
The electrical circuits of the N/W and FRR/WT Series Chassis Cab are connected with low-voltage stranded wire for
automotive applications. The color coding standards are as follows for the N/W and FRR/WT Series Chassis Cab.
Refer to FSR, FTR and FVR service manual for those vehicle wiring color codes.
(1) Black B Starter circuits and grounds
(2) White W Generator (alternator) circuit
(3) Red R Lighting circuit
(4) Green G Signal circuit
(5) Yellow Y Instrument circuit
(6) Brown Br Accessory circuit
(7) Light Green Lg Other circuit
(8) Blue L Windshield wiper motor circuit
Maximum Allowable Current
Harness Design AWG No. of wires/ Cross sectional Maximum allowable
Diameter (mm) equivalent wire diameter (mm) area (mm2) current (Amps)
100 00 217/0.80 109.1 363
85 0 169/0.80 84.96 305
60 1 127/0.80 63.84 248
50 1 108/0.80 54.29 223
40 1 85/0.80 42.73 191
30 2 70/0.80 35.19 171
20 4 41/0.80 20.61 123
15 6 84/0.45 13.36 93
8 8 50/0.45 7.952 68
5 8 65/0.32 5.228 51
3 12 41/0.32 3.297 39
2 14 26/0.32 2.091 29
1.25 16 16/0.32 1.287 21
0.85 18 11/0.32 0.8846 17
0.5 20 7/0.32 0.5629 13
Reference: The values given in the “maximum allowable current” column are based on the ambient temperature
condition of 104o F with temperature increase of 104o F.
Electrical System Modifications
Modifications/add-on wiring must be carefully reviewed to ensure compatibility with the base vehicle wiring by
reviewing system schematics, wire routing paths, harness connections, etc. Due to the wide range of
modifications that may be required for vocational needs, it is not feasible for the O.E.M. to take into account all
potential revisions. For this reason, any person modifying existing vehicle wiring must assume responsibility that
the revisions have not degraded the electrical system performance. Any add-on wiring needs to be properly
fused and routed to prevent cut, pinch, and chafe problems, as well as avoid exposure to excessive heat. Care
must be exercised that existing vehicle interfaces do not have their current load capabilities exceeded, and that
the respective control devices are not overloaded. Added wire size should be at least as large as the wire to
which it is attaching in order for fuse protection to be maintained.
A Packard electric wiring repair kit is available through Kent-Moore (P/N J38125-B) (Phone # 1-800-345-2233)
This kit contains instructions, tools and components for making repairs to wiring harness components. This kit
would also greatly assist in accomplishing necessary add-on wiring such as body marker lamps, so that system
April 2002 13
Page 24
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
reliability/durability is maintained.
Electrical wiring components can be obtained through your authorized Isuzu/GM dealers. Packard Electric
components are also available through Pioneer Standard Company (1-00-PACKARD). Pioneer may also be able
to assist in making necessary wiring additions by providing custom wiring stubs or jumpers to your specifications.
Exhaust System
Modification of the exhaust system should be avoided. If modifications are absolutely necessary, the following points
should be maintained.
1. Maintain the clearance specified in the table on the next page between all parts of the exhaust system and
any fuel lines, brake lines, brake hoses, electrical cables, etc. The exhaust outlet should not point toward
any of these parts.
CLEARANCE
Brake Lines 2.4 in. or more. (If the combined section of a group of parallel brake lines is
more than 7.8 in., a clearance of 7 in. or more should be provided.)
Flexible brake hoses 3.9 in. or more. (The temperature of flexible brake hoses should not exceed
158o F. If the highest temperature is not measurable, a clearance of more
than 15.7 in. should be maintained between the hoses and the exhaust
system.
Wiring harnesses and cables 3.9 in. or more.
Steel fuel lines 3.1 in. or more.
Rubber or vinyl fuel hoses 5.9 in. or more.
2. If a tool box is installed, it should preferably be made from steel. If a wooden tool box is
installed, at least 7.8 inches clearance should maintained between the tool box and any parts of
the exhaust system.
3. If the exhaust system is modified, it is the responsibility of those making the modification to
ensure that the noise level meets appropriate standards.
Fuel System
Relocation of the fuel tank, or installation of additional fuel tanks is not recommended. If modifications to the fuel
system are unavoidable, follow these recommendations:
1. Maintain adequate clearance between the fuel tank and any other device or structure.
2. Do no connect an additional fuel hose.
Rear Lighting
Brackets installed are temporary. Please do not use these brackets for body installation.
Serviceability
No matter what other modifications or changes are made, access to components requiring daily preventive
maintenance or other routine service must not be obstructed. This includes:
1. Inspection, filling and draining of engine oil and cooling water.
2. Inspection, filling and draining of transmission fluid.
14 April 2002
Page 25

Installation of Body & Special Equipment
3. Adjustment, removal and installation of the fan belts.
4. Inspection, filling and removal of the battery and battery cover.
5. Inspection and filling of brake fluid.
6. Inspection and bleeding of the brake system and servo unit.
7. Maintenance of clearance for tightening of check bolt on brake safety cylinder.
8. Operation of the spare tire carrier, including mounting and dismounting of the spare tire.
9. Adjustment, removal and installation of distributor and/or cover.
WHEELBASE ALTERATION
With certain applications, it may become necessary to alter the wheelbase of the chassis. The next two sections
provide the suggested guidelines for accomplishing either shortening or lengthening of the wheelbase.
SHORTENING/LENGTHENING THE WHEELBASE WITHOUT ALTERING THE FRAME
Since the frame is an integral part of the chassis, it is recommended that the frame not be cut if it is possible to avoid
it. When shortening/lengthening the wheelbase on some models, it is possible to do so without cutting the frame. This
is possible on models which have a straight frame rail. If the chassis does not have a straight frame rail, it may still
be necessary to cut the frame. For instructions on shortening/lengthening these chassis, refer to the ALTERING THE
WHEELBASE BY ALTERING THE FRAME section of this book. Otherwise, the wheelbase may be shortened/
lengthened by removing the rear suspension, drilling new suspension mounting holes at the appropriate spot in the
frame, and sliding the rear suspension, suspension liner, and suspension crossmembers forward or aft. The
suspension and suspension crossmembers' rivet holes left in the frame rail flange must be filled with GRADE 8 bolts
and hardened steel washers at both the bolt head and nut, HUC bolts or GRADE 8 flanged bolts and hardened steel
washers at the nut. When shortening/lengthening the wheelbase in this manner, the following guidelines must be
adhered to:
1. All frame drilling must comply with the DRILLING AND WELDING section of this book.
2. All rivet holes left in the frame rail flange from the suspension and suspension crossmembers
must be either filled with GRADE 8 bolts and hardened steel washers at both the bolt head and
nut, HUC bolts or GRADE 8 flanged bolts and hardened steel washers at the nut.
3. The components required to be slid forward or aft are the suspension and suspension hangers,
suspension crossmembers and suspension frame liner.
ALTERING THE WHEELBASE BY ALTERING THE FRAME
Even on a straight frame rail, it may be desirable to cut the frame and lengthen or shorten the wheelbase rather than
simply sliding the rear suspension back or forward. The following section offers some guidelines and suggestions
for cutting and lengthening or shortening the frame.
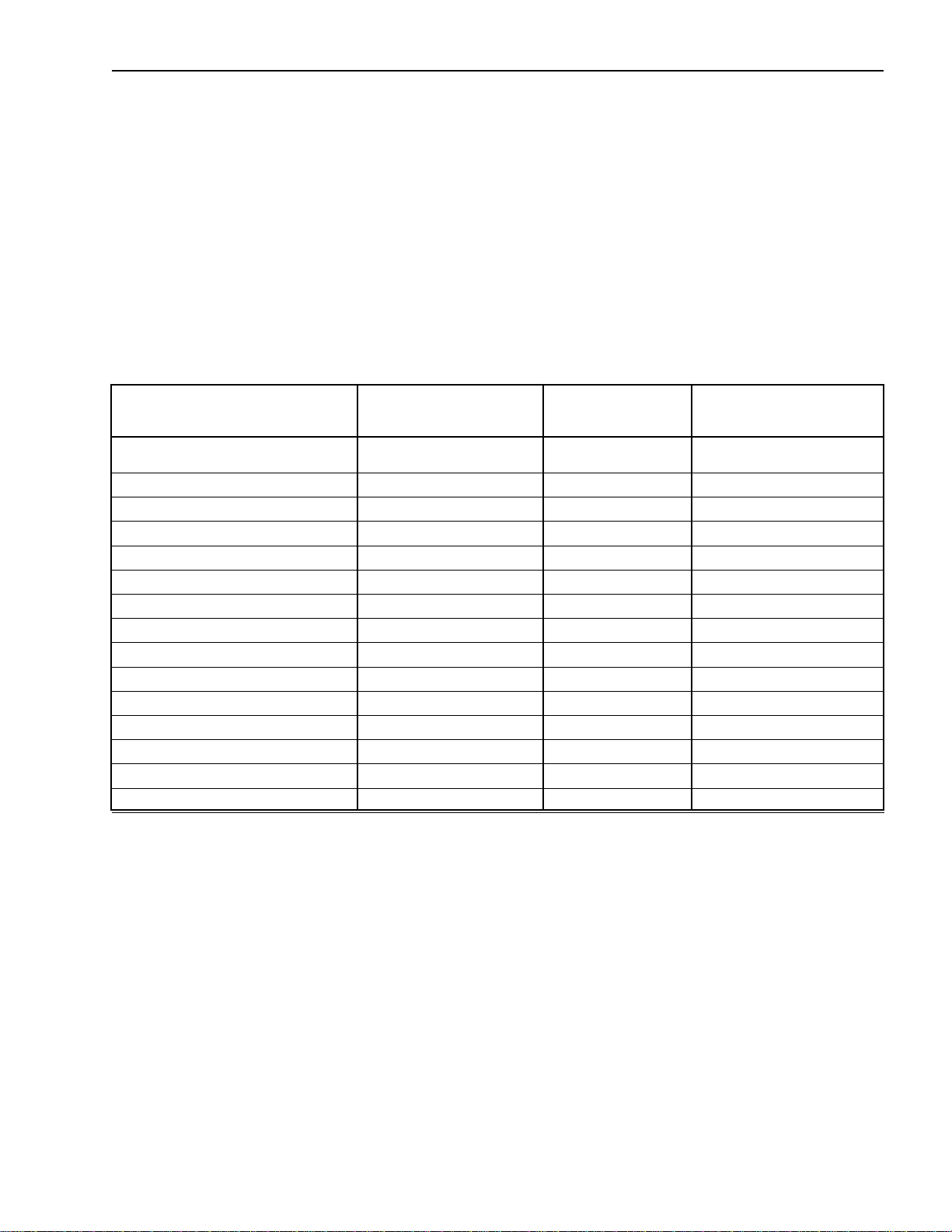
GLOSSARY OF TERMS-CHASSIS WHEELBASE ALTERATION
CA - Length from back-of-cab to rear axle center line in inches.
AL - Added length (in case of a lengthened wheelbase). Difference between WB (new) and WB (old).
SL - Shortened length (in case of shortened wheelbase). Difference between WB (old) and WB (new).
April 2002 15
Page 26
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
1. Determine the added length (AL) or shortened length (SL) required to lengthen or shorten chassis.
(For added wheelbase: New CA = CA + AL; For shortened wheelbase: New CA = CA - SL)
2. Obtain the material to be used as the insert for the lengthened wheelbase in the correct length (AL). The
insert must have the same cross sectional dimensions and yield strength as the original frame rail.
3. Divide the new CA by two (2). Measure (new CA)/2 from the center of the rear axle forward and mark this
point on the chassis frame (see figure below).
Cut Point
1/2 New CA
4. Cut the chassis frame at this point. If the wheelbase is to be lengthened, addition of the previously
obtained insert (of length AL determined in step 1) will be made at this time. If the wheelbase is to be
shortened, measure the distance (SL) forward of this cut and remove a length (SL) section from the
chassis frame (see figure below). Insure that an adequate area on the frame remains for the required
addition of the necessary reinforcements. These are the only suggested places for cutting the frame and
reinforcements but may be changed upon the advice of General Motors Isuzu Commercial Truck, LLC
(GMICT) and American Isuzu Motors Inc. Application Engineering.
Section to be Added
Cut Point
AL
Lengthening the Wheelbase
New CA
2
Second Cut Point
Section to be Removed
First Cut Point
SL
New CA
2
Shortening the Wheelbase
16 April 2002
Page 27
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
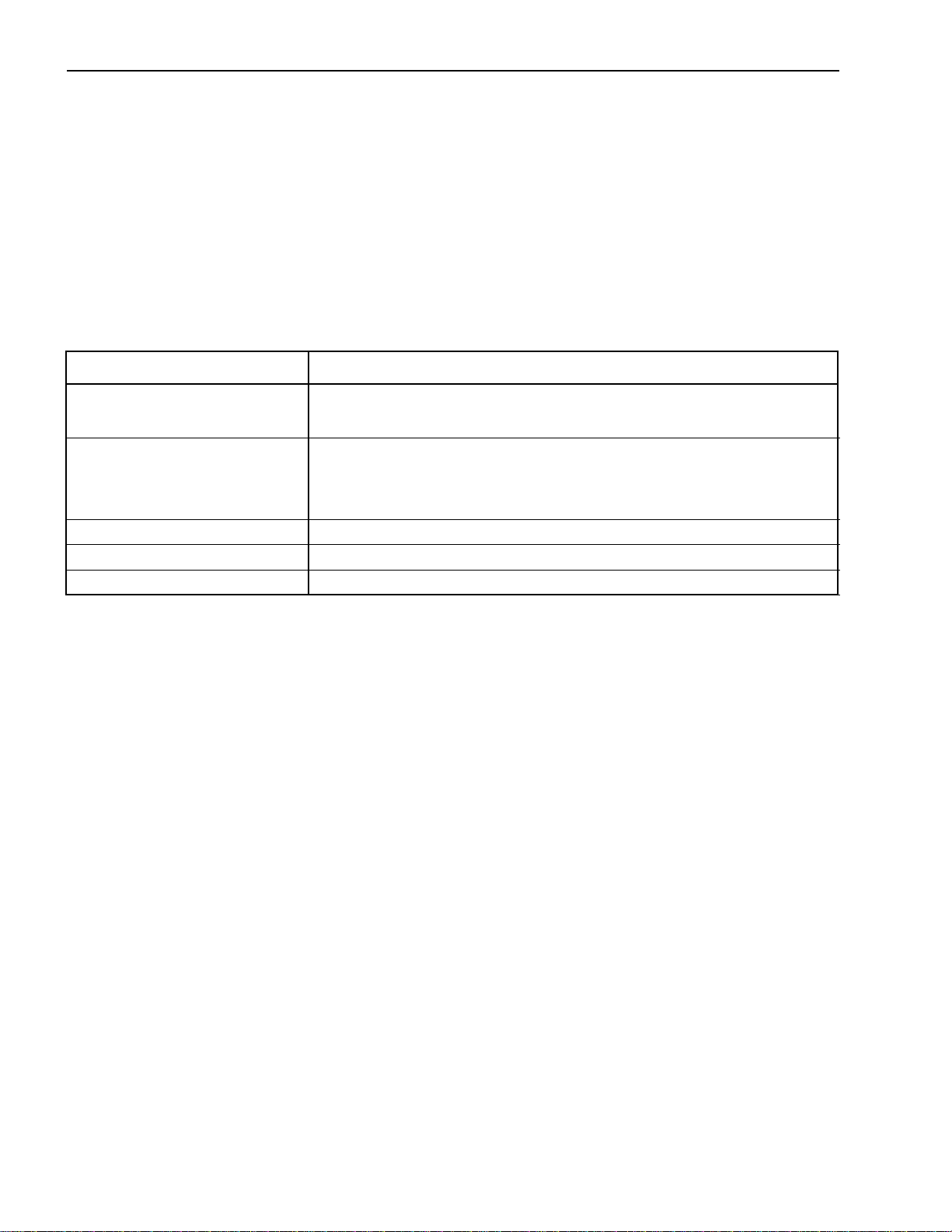
5. When welding the insert (length AL for wheelbase lengthening) to the original frame rail, a continuous butt weld
must be used at the splices. When shortening the wheelbase, weld the ends of the chassis frame together with
a continuous butt weld over the junction of the frame ends. Weld both the inside and outside of the frame rails
using welding techniques prescribed by established welding standards (ref. SAE J1147) and in accordance with
this guide. An example of this weld is shown below.
BUTT WELD 100 % - Weld can be inside or outside
of member or, as shown, a combination of both
1.0 in. or more
1.0 in. or more
6. Determine the appropriate additional internal reinforcements which are required using this equation:
Reinforcement Length = AL + 6 x (original frame rail web depth).
The figure below shows how this reinforcement is to be placed over the extended or shortened section of the
frame rail.
D
AL3 x D 3 x D
6 x D + AL
Lengthened Wheelbase
3 x D
Shortened Wheelbase
3 x D
6 x D
D = Original frame rail web depth
The suggested cross section of this reinforcement is a snug fit inner channel. If the new wheelbase exceeds
the upper limit of the optional wheelbases of this model, i.e.; a “long bridge”, it may be necessary to use an “inverted
L” reinforcement in addition to the snug fit channel reinforcement (see figures below). Application Engineering should
be consulted for approval of such cases. It should be noted that these methods of reinforcements, and any other
methods which may be used, require a 45 degree angled cut at both ends to avoid stress concentrations in the frame
(note the figures under item 7).
OR
Snug fit inner channel with "Inverted L" for "Long Bridge" wheelbasesSnug fit inner channel
April 2002 17
Page 28
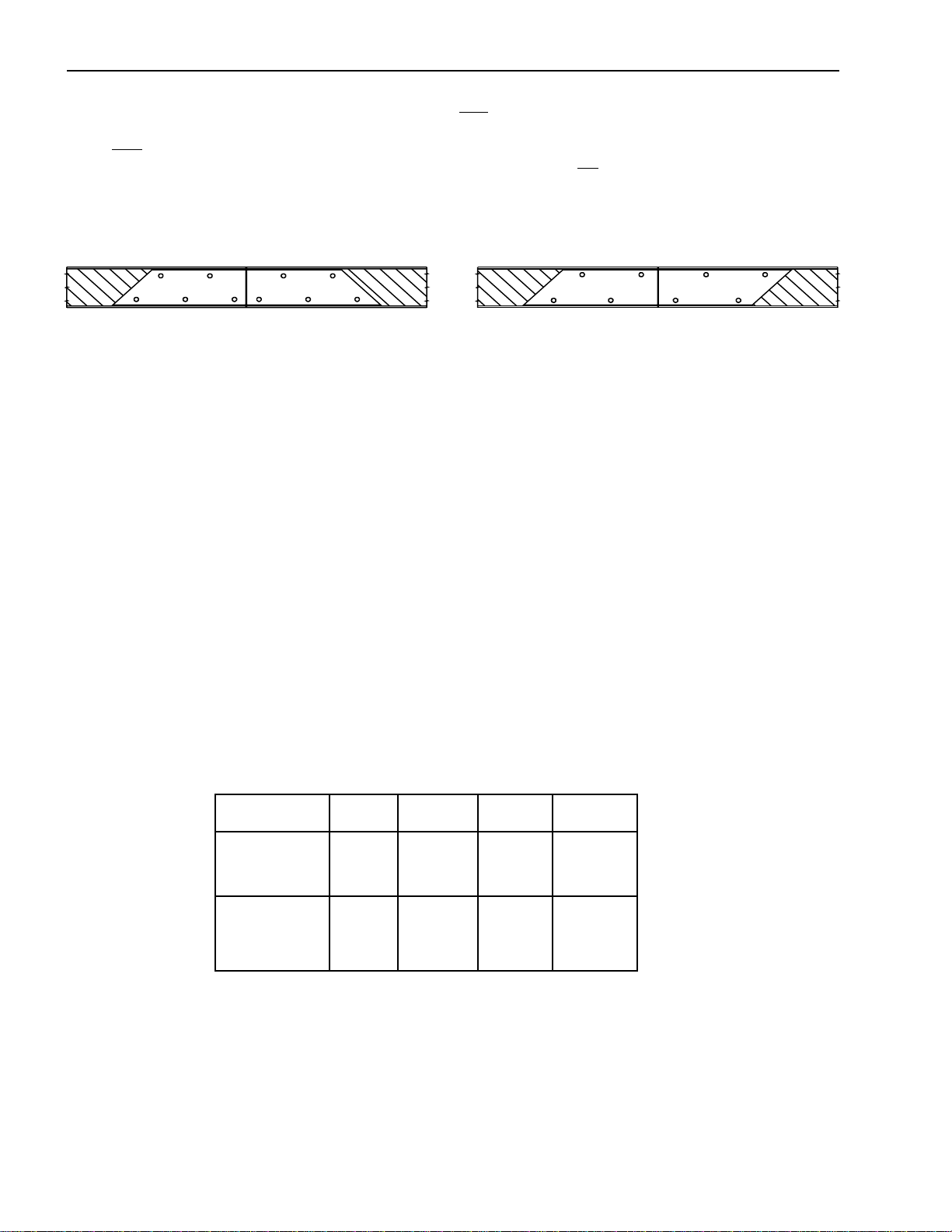
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
7. The reinforcements must be fastened securely to only the web of the original chassis frame rail. The
reinforcement must be held rigidly in place using either HUC bolts, GRADE 8 bolts and hardened steel washers
at both the bolt head and nut, or GRADE 8 flanged bolts and hardened steel washers at the nut. Below are some
suggested bolt patterns. It should be noted that these bolt patterns must not align the bolts vertically, i.e.: the bolt
pattern must be staggered.
8. Lengthening the frame will also require extending the brake lines, basic chassis electrical harnesses, excluding
ABS wiring harness. It is recommended that the original brake lines be removed and replaced with brake lines
of the same diameter as the original lines and of the appropriate length. The electrical harness must be extended
in accordance with the ELECTRICAL WIRING AND HARNESSING section of this book.
9. The propeller shafts’ overall length will also need to be lengthened or shortened. If the extension is within the limits
of the optional wheelbases of the respective model, the exact propeller shaft lengths and angles are given on or
about Page 12 of the respective sections of this book. If the modified wheelbase exceeds the optional wheelbases
of the respective model, the following guidelines must be adhered to:
A. Propeller Shaft Length
The maximum propeller shaft lengths (pin to pin) for the respective models are shown in the table below.
NPR NPR GAS NQR FRR
Propeller
Shaft 3.25 3.0 3.0 4.0
Diameter (in)
Maximum
Propeller Shaft 50.8 50.8 50.8 62.0
Length (in)
18 April 2002
Page 29
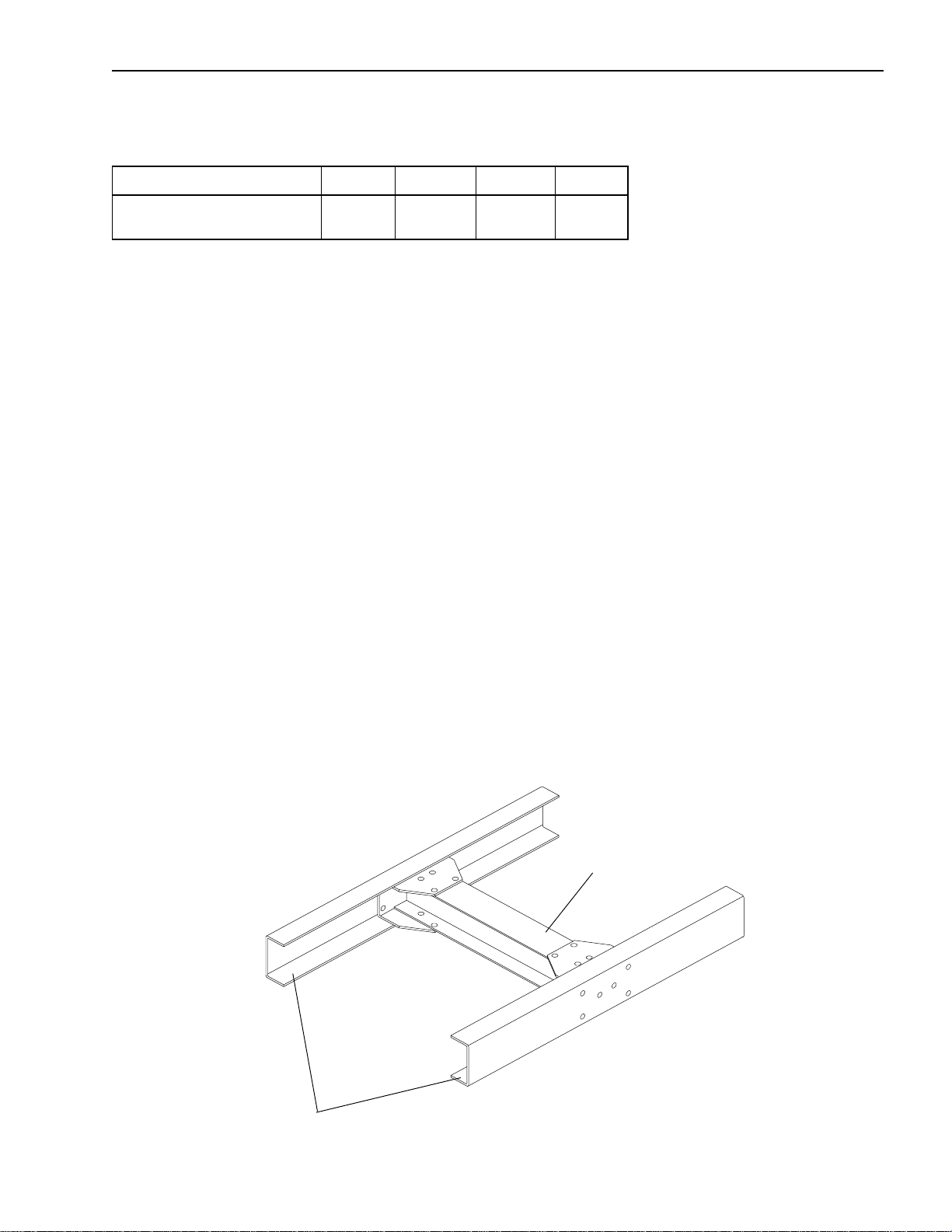
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
B. Propeller Shaft Angles
The maximum propeller shaft angles, with respect to the previous shaft, are shown in the table below.
NPR/W NPR/W GAS NQR/W FRR/WT
Maximum Propeller
Shaft Angle 5.7
o
5.1
o
5.7
o
5.5
o
C. The propeller shaft angles must be designed such that the angles will cancel to avoid propeller shaft whip.
D. The propeller shaft yokes must be assembled such that the propeller shaft yokes are “in phase.” “In
phase” means that the yokes at either end of a given propeller shaft assembly are in the same plane.
10. Extending the frame will also require relocation and/or addition of crossmembers. If the extension is within the
limits of the optional wheelbases of the respective model, the exact cross member locations and dimensions
are given in the respective model sections of this book. If the modified wheelbase exceeds the optional
wheelbases of the respective model, the following guidelines must be adhered to:
A. The cross member location will largely be determined by the propeller shaft lengths and where the center
carrier bearing locations are for the propeller shaft assembly.
B. A cross member must be located at the front and rear spring hangers of the rear suspension (refer to the
appropriate section of this book to see where these suspension cross members are to be located).
C. The cross member must be constructed such that it supports both the upper and lower flange on each
frame rail (see drawing below). A cross member such as the one below may be constructed, or Isuzu
cross members may be obtained from your Isuzu parts dealer.
Additional crossmember
Frame rails
April 2002 19
Page 30
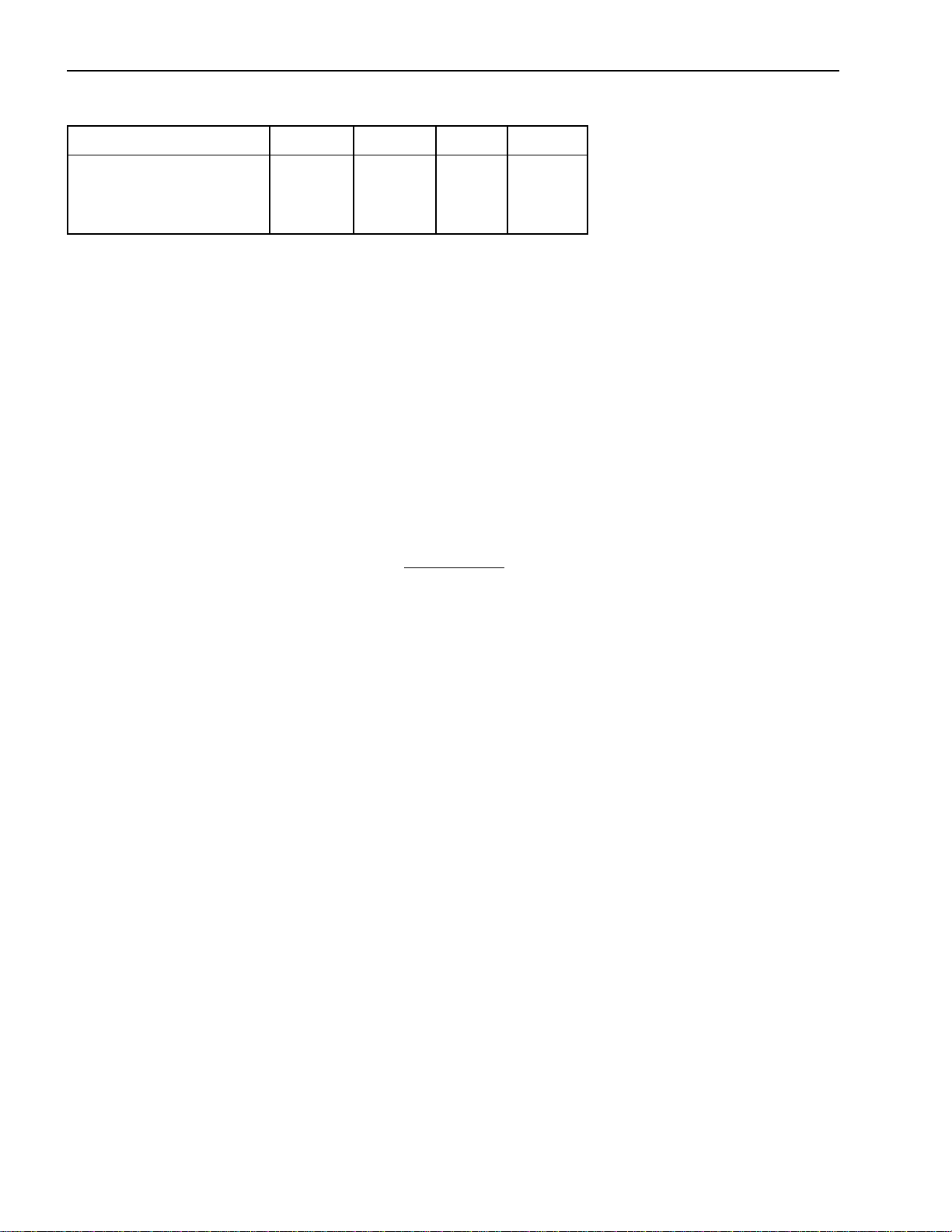
Installation of Body & Special Equipment
D. The maximum distance between crossmembers for the respective models is given in the table below.
NPR/W NPR/W GAS NQR/W FRR/WT
Maximum Distance 35.7 35.7 35.7 49.8
Between Cross
Members (in)
E. The drilling for any additional holes in the frame rails must comply to the DRILLING AND WELDING
section of this book.
11. All other aspects of lengthening or shortening the wheelbase must comply with the applicable section of
this Body Builder's Guide. For special applications and longer than recommended body lengths, GMICT
Application Engineering must be consulted for approval. In the West Coast call 1-562-229-5314 and in
the East Coast call 1-404-257-3013
12. Please contact applications engineering for guidelines on N/W SERIES CHASSIS frame modifications when
the vehicle is equipped with an Antilock Brake System.
FRR SERIES CHASSIS
Please contact applications engineering for guidelines on FRR SERIES CHASSIS frame modifications when the
vehicle is equipped with an Antilock Brake System
FSR FTR FVR
WHEN MAKING WHEELBASE MODIFICATIONS TO THE 1997, MODEL YEAR AND ABOVE FSR, FTR, AND
FVR HYDRAULIC BRAKE CHASSIS AND AIR BRAKE CHASSIS THE FOLLOWING SHOULD BE STRICTLY
OBSERVED.
13. The Crew Cab NPR HD/W4500 and NQR/W5500 will be available in two wheelbases, 150 and 176 inches.
Effective CA will be 84.7 and 110.7 inches. On this model chassis General Motors Isuzu Commercial Trucks
will require that the body installed on the chassis have an understructure manufactured with any of the following
structural steel "C" channels:
4"x1-5/8", 7.25 lbs/ft = ok
5"x1-3/4", 6.7 or 9.0 lbs/ft = ok
6"x2", 8.2, 10.5 or 13.0 lbs/ft = ok
HYDRAULIC BRAKE SYSTEM
1. BEFORE WORK BEGINS
As with any electrical work on the chassis the battery should be disconnected before electrical work is started.
2. ABS PROGRAM
The antilock brake system (ABS) computer will hold its codes when disconnected and reprogramming as a result
of battery disconnection will not be necessary. If the wheelbase is changed the trim level of the ABS system
must be readjusted per the instructions in the service manual. An Authorized Isuzu dealer should do this
reprogramming using appropriate tools.
For your reference and to help you determine if the system needs to be reprogrammed the following provisions
apply to all ABS systems with hydraulic brakes. The ABS module has four (4) programs: A, B, C, and D. These
programs are tied to the wheelbase and axle combination of the chassis. (The axle and wheel base codes can be
found on the passenger’s visor.)
A is for the FL1 axle and covers wheelbase from 140 (FQT), 158 (EG5), 170 (EH8) inches.
B is for the FL2 axle and covers wheelbase from 140 (FQT), 158 (EG5), 170 (EH8), 188 (EK8), 200 (EM2)
inches.
20 April 2002
Page 31

Installation of Body & Special Equipment
C is for the FL1 axle and covers wheelbase from 188 (EK8), 200 (EM2), 218 (FPL), 233 (EQ8), 248 (ES5)
inches.
D is for the FL2 axle and covers wheelbase from 218 (FPL), 233 (EQ8), 248 (ES5) inches.
Moving between program/ wheelbase groups A, B, C or D will require that the system be reprogrammed
Moving wheelbase within a program group will not require reprogramming.
3. ABS COMPUTER LOCATION
a. The ABS computer is located under the cab on the front crossmember and is an integral part of the brake
fluid modulation system. These components can not be relocated.
4. ABS ELECTRICAL HARNESSES
a. The harness can not be cut and spliced
b. The only approved way to make the harness longer is to purchase the appropriate wheelbase harness
from the Isuzu parts department
c. Extra wire resulting from a frame shortening can be coiled and secured to the frame.
5. HYDRAULIC BRAKE LINES
a. Hydraulic brake lines should be shortened or lengthened using appropriate fittings and steel lines.
AIR BRAKE SYSTEM
1. BEFORE WORK BEGINS
a. As with any electrical work on the chassis the battery should be disconnected before electrical work is
started.
2. ABS PROGRAM
The antilock brake system (ABS) computer will hold its codes when disconnected and reprogramming as a result
of battery disconnection will not be necessary. If the front axle is changed the trim level of the ABS system must
be readjusted per the instructions in the service manual. An Authorized Isuzu dealer using the appropriate tools
should do this reprogramming.
3. ABS COMPUTER LOCATION
a. The ABS computer is located back of cab on the power steering bracket. This component can not be
relocated.
15. ABS ELECTRICAL HARNESSES
a. The harness can not be cut and spliced
b. The only approved way to make the harness longer is to purchase the appropriate wheelbase harness
from the Isuzu parts department.
c. Extra wire resulting from a frame shortening can be coiled and secured to the frame.
8 AIR BRAKE LINES
a. Air brake lines should be shortened or lengthened using appropriate fittings and hose material.
April 2002 21
Page 32

Installation of Body & Special Equipment
22 April 2002
Page 33

Body Applicaton Summary Chart
Body Application
Summary Chart
April 2002 23
Page 34

Body Application Summary Chart
2002 GAS & 2003 DIESEL MODEL YEAR BODY APPLICA TION SUMMARY CHART
MODEL/GVWR WB BOC 10 ft. 12 ft. 14 ft. 16 ft. 18 ft. 20 ft. 22 ft. 24 ft.
NPR/W3500 GAS 109 9.25 X X
12,000 lbs 132.5 9.25 X
150 9.25 X X
176 9.25 X
NPR HD/W4500 GAS 109 9.25 X X
14,050 lbs 132.5 9.25 X
150 9.25 X X
176 9.25 X
NPR/W3500 DSL 109 9.25 X
12,000 lbs 132.5 9.25 X
150 9.25 X X
176 9.25 X
NPR HD/W4500 DSL 109 9.25 X
14,500 lbs 132.5 9.25 X
150 9.25 X X
176 9.25 X
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
NPR HD/W4500 CREW
CAB DSL 150 4.2 X
14,500 lbs 176 4.2 X
(3)
(4)
NQR/W5500 DSL 109 9.25 X
17,950 lbs 132.5 9.25 X
150 9.25 X X
176 9.25 X
NQR/W5500 CREW
CAB DSL 150 4.2 X
17,950 lbs 176 4.2 X
(3)
(4)
MT/AT
FRR/WT5500 DSL 14 8 7.5/10 X
(2)
X
18000/19,500 167 7.5/10 X
179 7.5/10 X
191 7.5/10 X
218
10.0/10
Notes:
1. NPR, NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Diesel 20’ ft. body requires Isuzu/GM Application Engineering Department approval.
2. BOC 10.0 inches. For MT
X
UNIT: INCH
3. 16’ Dovetail landscape (12’ deck plus 4’ dovetail).
4. 18’ Dovetail landscape (14’ deck plus 4’ dovetail).
Important
Body selection recommendations are based on water level weight distribution and no accessories, liftgate or refrigeration units. This
table is intended for reference and does not preclude the necessity for an accurate weight distribution calculation.
24 April 2002
Page 35

Body Applicaton Summary Chart
2002 GAS & 2003 DIESEL MODEL YEAR*
BODY & PAYLOAD WEIGHT DISTRIBUTION
(% FRONT/% REAR)
MODEL GVWR WB CA CE OAL BOC 10 12 14 16 18 20
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
NPR/W3500 GAS 12,000 109 88.4 131.5 199.5 9.25 18/82 7/93
NPR HD/W4500 GAS 14,050 109 88.4 131.5 199.5 9.25 18/82 7/93
NPR/W3500 GAS 12,000 132.5 111.9 155 223 9.25 14/86
NPR HD/W4500 GAS 14,050 132.5 111.9 155 223 9.25 14/86
NPR/W3500 GAS 12,000 150 129.4 172.5 240.5 9.25 16/84 8/92
NPR HD/W4500 GAS 14,050 150 129.4 172.5 240.5 9.25 16/84 8/92
NPR/W3500 GAS 12,000 176 155.4 198.5 266.3 9.25 15/85
NPR HD/W4500 GAS 14,050 176 155.4 198.5 266.3 9.25 15/85
MODEL GVWR WB CA CE OAL BOC 10 12 14 16 18 20
MANUAL/AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
NPR/W3500 DSL 12,000 109 88.4 131.5 199.5 9.25 7/93
NPR HD/W4500 DSL 14,500 109 88.4 131.5 199.5 9.25 7/93
NPR/W3500 DSL 12,000 132.5 111.9 155 223 9.25 14/86
NPR HD/W4500 DSL 14,500 132.5 111.9 155 223 9.25 14/86
NPR/W3500 DSL 12,000 150 129.4 172.5 240.5 9.25 16/84 8/92
NPR HD/W4500 DSL 14,500 150 129.4 172.5 240.5 9.25 16/84 8/92
NPR/W3500 DSL 12,000 176 155.4 198.5 266.3 9.25 15/85
NPR HD/W4500 DSL 14,500 176 155.4 198.5 266.3 9.25 15/85
MODEL GVWR WB CA CE OAL BOC 10 12 14 16 18 20
MANUAL/AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
NQR/W5500 DSL 17,950 109 88.4 131.5 199.5 9.25 7/93
NQR/W5500 DSL 17,950 132.5 111.9 155 223 9.25 14/86
NQR/W5500 DSL 17,950 150 129.4 172.5 240.5 9.25 16.84 8/92
NQR/W5500 DSL 17,950 176 155.4 198.5 266.3 9.25 15/85 8/92
*NPR, NPR HD/W3500, W4500 GAS and DIESEL 20 foot body requires Isuzu/GM Application Engineeering Department approval.
IMPORTANT:
Weight distribution percentages listed do not include added accessories, liftgate or refrigeration units.
Percentages based on water-level distribution of body and payload weight which is determined by subtracting
chassis wet weight (including 200 lb. driver) from GVWR. These tables are intended for reference and do not
preclude the necessity for an accurate weight distribution calculation.
April 2002 25
Page 36

Body Application Summary Chart
2003 MODEL YEAR DIESEL CREW CAB BODY & PAYLOAD WEIGHT DISTRIBUTION
(% FRONT/% REAR)
MODEL GVWR WB CA CE OAL BOC 10 12 14 16
NPR HD/W4500 CREW CAB DSL 14,500 150 88.9 132 240.5 4.2 8/92
NPR HD/W4500 CREW CAB DSL 14,500 176 114.9 158 266.5 4.2 15/85
MODEL GVWR WB CA CE OAL BOC 10 12 14 16
NQR HD/W5500 CREW CAB DSL 17,850 150 88.9 132 240.5 4.2 16/84 8/92
NQR HD/W5500 CREW CAB DSL 17,850 176 114.9 158 266.5 4.2 15/85 8/92
IMPORTANT:
Weight distribution percentages listed do not include added accessories, liftgate or refrigeration units.
Percentages based on water-level distribution of body and payload weight which is determined by subtracting
chassis wet weight (including 200 lb. driver and a crew of 6 @200 lbs each) from GVWR. These tables are
intended for reference and do not preclude the necessity for an accurate weight distribution calculation.
26 April 2002
Page 37

Manual Transmission
Body Applicaton Summary Chart
2003 MODEL YEAR
BODY & PAYLOAD WEIGHT DISTRIBUTION
(% FRONT/% REAR)
MODEL GVWR WB CA CE OAL BOC 14 16 18 20 22 24
FRR/WT5500 18000/19500 148 117.1 180.6 259.3 7.5 16/841 10/90
FRR/WT5500 18000/19500 167 136.2 206.5 285.2 7.5 12/88
FRR/WT5500 18000/19500 179 148.0 226.2 304.9 7.5 11/89
FRR/WT5500 18000/19500 191 159.8 243.9 322.2 7.5 11/89
FRR/WT5500 18000/19500 218 187.4 283.3 362.0 10.0 15/85
Automatic Transmission
MODEL GVWR WB CA CE OAL BOC 14 16 18 20 22 24
FRR/WT5500 18000/19500 148 117.1 180.6 259.3 10 15/85 7/93
FRR/WT5500 18000/19500 167 136.2 206.5 285.2 10 10/90
FRR/WT5500 18000/19500 179 148.0 226.2 304.9 10 9/91
FRR/WT5500 18000/19500 191 159.8 243.9 322.2 10 9/91
FRR/WT5500 18000/19500 218 187.4 283.3 362.0 10 15/85
NOTES:
1. BOC 10.0 Inches. For MT
IMPORTANT:
Weight distribution percentages listed do not include added accessories, liftgate or refrigeration units.
Percentages based on water-level distribution of body and payload weight which is determined by subtracting
chassis wet weight (including 200 lb. driver) from GVWR. These tables are intended for reference and do not
preclude the necessity for an accurate weight distribution calculation.
April 2002 27
Page 38

Mechanical & Cab Specifications
Mechanical
Cab Specifications
&
26 April 2002
Page 39

Mechanical & Cab Specifications
The following table presents Net versus Gross Horsepower and Torque ratings for 2003 Isuzu/W-Series Truck
Product Engines:
ENGINE NET HP
1
NET TORQUE
MODEL APPLICATION HP/RPM LBS-FT/RPM HP/RPM LBS-FT/RPM
GMPT- NPR/W3500,
5.7L-V8 NPR HD/W4500
N/A N /A 250/4400 330/2800
GAS
ISUZU NPR/W3500,
4HE1-TC NPR HD/W4500 137/2800 268/1300 142/2800 275/1300
M/T DIESEL
ISUZU NPR/W3500,
4HE1-TC NPR HD/W4500, 169/2700 339/2000 175/2700 347/2000
A/T NQR/W5500
DIESEL
ISUZU NQR/
4HE1-TC W5500 169/2700 339/2000 175/2700 347/2000
M/T DIESEL
1
GROSS HP
1
GROSS TORQUE
1
ISUZU FRR/
6HK1-TC WT5500 193/2400 426/1500 200/2400 441/1500
M/T DIESEL
ISUZU FRR/
6HK1-TC WT5500 193/2400 426/1500 200/2400 441/1500
A/T DIESEL
NOTE: 1. Horsepower and Torque Ratings measured under SAE J1349 standards.
GVW/GCW Ratings
The following table presents GVW ratings and corresponding GCW ratings for each model truck:
TRUCK MODEL TRANSMISSION GVWR (lbs) GCWR (lbs)
NPR/W3500 GAS AUTOMATIC 12,000 15,000
NPR HD/W4500 GAS AUTOMATIC 14,050 17,050
NPR/W3500 DIESEL AUTOMATIC 12,000 18,00 0
NPR/W3500 DIESEL MANUAL 12,000 18,000
NPR HD/W4500 DIESEL AUTOMATIC 14,500 19,500
NPR HD/W4500 DIESEL MANUAL 14,500 20,500
NQR/W5500 DIESEL AUTOMATIC 17,950 19,500
NQR/W5500 DIESEL MANUAL 17,950 22,500
FRR/WT5500 DIESEL AUTOMATIC 18,000/19,500 26,000
FRR/WT5500 DIESEL MANUAL 18,000/19,500 30,000
1
2
1 The NPR/W3500, NPR HD/W4500 and NQR/W500 are note approved for Hot Shot applications.
2 GCWR 20,950 with addition of optional Isuzu Transmission Oil Cooler.
April 2002 27
Page 40

Mechanical & Cab Specifications
The following chart provides the rear frame height for each model/GVWR with standard tires:
GVWR STANDARD FRAME HT (in)
MODEL (lbs) TIRE FH STD. TIRES
NPR/W3500 GAS
NPR HD/W4500 GAS
NPR/W3500 DIESEL
NPR HD/W4500 DIESEL
NQR/W5500 DIESEL 17,950
FRR/WT5500 DIESEL 18,000/19,500
FSR/FTR/FVR (2) (2) (2)
(1) 191 and 218 WB have frame height of 37.3 inches
(2) Refer to FSR, FTR, and FVR section
11,050 215/85R-16E 32
14,050 225/70R-19.5F 32.75
12,000 215/85R-16E 32
14,050 215/85R-16E 32
225/70R-19.5F 32.8
225/70R-19.5F 35.3 (1)
CLUTCH ENGAGEMENT TORQUE CHART
The following table provides the engagement torque of the engines currently in use in Isuzu medium duty trucks:
Torque at
Engine (lbs-ft) (RPM)
ISUZU 4HE1-TC (142 HP) 260 1,000
ISUZU 4HE1-TC (175 HP) 265 1,000
ISUZU 6HK1-TC (200 HP) 331 1,000
ISUZU 6HK1-TC (230 HP) 368 1,000
28 April 2002
Page 41

Mechanical & Cab Specifications
April 2002 29
Page 42

30 April 2002
CV CHART 2
ISUZU
PAINT
CODE
301-W-30102 N/A Accuride White
B302-P801-0 730 Adriatic B lue ( Soli d)
W301-P801-0 729 Arc White
WE8774 N/A *Bright Red
0133-P1 N/A Calm White
WE5398 N/A *Dark Green Gray
U715-P801-0 809 Doeskin Tan
0172-P1 844 Glacier White
WE9907 N/A *Medium Adriatic Blue
B721-P801-0 801 Medium Blue
N507-P901-0 845 Polar Silver
R725-P801-0 810 Red Orange
WE9885 N/A *Rose Black
G021-P801-0 989 Sunbelt Green
U716-P801-0 815 Tangier Orange
Y719-P801-0 812 Wheatland Yellow
G705-P801-0 807 Woodland Green
ISUZU
OPTION
CODE
ISUZU
COLOR
NAME
AKZO
NOBEL
CODE
FLNA40154
FLNA50274
FLNA40156
FLNA30252
FLNA40252
FLNA90856
FLNA80050
FLNA40155
FLNA90857
FLNA50172
FLNA91205
FLNA20079
FLNA90858
FLNA60290
FLNA20080
FLNA10182
FLNA60181
BASF
R-M
CODE
RM25319 IS-25319
730 730
RM25318 IS-25318
27427 IS-27427
HS14391 IS-820
27425 IS-27425
27406 IS-U715
RM15602 IS-844
27426 IS-27426
27403 IS-B721
23664 845
27407 IS-R725
27428 IS-27428
605301 989
27409 IS-U716
27408 IS-Y719
27404 IS-G705
BASF
GLAS
CODE
DUPONT
CODE
F2499 8AR8 91513
W9775 2NV9B 19320
W9774 2NV8 91512
C8508 TC78B 75057
G8477 KK27 91522
B9329 2NP9B 36575
B8462 KPL5B 28613
H8620 ND92 90330
B9321 2NY4B 190401
B8041 KPL2B 190217
F2193 EPW3B 36658
B8250 KPL4B 61784
B9218 1AB2B 95057
M6682 WMK4 401420
B9043 KPL6B 61785
B9042 KPL7B 83931
B8046 KPL3B 48339
ICI
AUTO
COLOR
PPG
CODE
SHERWIN
WILLIAMS/
MARTIN
SENOUR
51548 15593
57541 50287
51400 10280
34983 34169
34657 16222
47155 65071
56203 21882
35478 10281
46829 56120
56143 55934
56991 73192
56202 21881
45738 74223
61559 67847
56204 21883
56144 21884
56201 64962
SPIES
HECKER
CODE
STANDOX
301-W-30102
730
729
N/A
0133-P1
N/A
809
844
N/A
801
845
810
N/A
989
815
812
807
Mechanical & Cab Specifications
NOTES:
1. ST ANDBOX uses paint code found in vehicle for paint identification.
2. GM-Based colors. No Isuzu Option Code.
Page 43

Mechanical & Cab Specifications
N/W Series Towing Procedures
NOTE: When towing, disconnect the propeller shaft at the rear
axle to ensure the automatic transmission is not damaged.
Proper equipment must be used to prevent damage to vehicles during any towing. State and local laws which apply to
vehicles in tow must be followed. Vehicles should not be towed at speeds in excess of 55 mph (90 km/h). Connect to the
main structural parts of the vehicle. DO NOT attach to bumpers, tow hooks or brackets. Use only equipment designed for
this purpose. Follow the instructions of the wrecker manufacturer. A safety chain system must be used. The procedures
below must be followed when towing to prevent possible damage.
FRONT END TOWING (FRONT WHEELS OFF GROUND)
To prepare a disabled vehicle for front end towing with front wheels
raised off the ground, the following steps are necessary:
• Block the rear wheels of the disabled vehicle.
• Disconnect the propeller shafts at the rear axle. Secure the propeller shafts to the frame or crossmember.
• If there is damage or suspected damage to the rear axle, remove the axle shafts.
• Cover the hub openings to prevent the loss of lubricant or entry of dirt or foreign objects.
• Place 4” x 4” wood beam against the towing guide behind the bumper. (If no 4” x 4” is available, then remove the bumper.)
Ensure towing chains do not contact the horns or the bumper.
1. Horns
2. Bumper (removed for towing)
3. Filler
AFTER TOWING
After towing the vehicle, block the rear wheels and install axle shafts or propeller shaft. Apply the parking brake before
disconnecting from the towing vehicle.
FRONT END TOWING (ALL WHEELS ON THE GROUND)
Your vehicle may be towed on all wheels provided the steering is operable. Remember that power steering and brakes will
not have power assist. There must be a tow bar installed between the towing vehicle and the disabled vehicle.
1. Bumper
2. Towing Chain
3. Towing GUide
4. Front Axle
5. Tow Hook
To prepare a disabled vehicle for front end towing with all wheels on the ground, the following steps are necessary:
• Block the wheels of the disabled vehicle.
• Disconnect the propeller shafts at the rear axle. Secure the propeller shafts to the frame or crossmember.
• Provide wood blocking to prevent towing chains and bar from contacting the bumper.
• If there is damage or suspected damage to the rear axle, remove the axle shafts.
• Cover the hub openings to prevent the loss of lubricant or entry of dirt or foreign objects.
April 2002 31
Page 44

Mechanical & Cab Specifications
After Towing
After towing the vehicle, block the rear wheels and install axle shafts or propeller shaft. Apply the parking brake before
disconnecting from the towing vehicle. Check and fill rear axle with oil if required.
REAR END TOWING
When towing a vehicle with rear wheels raised, secure the steering wheel to maintain straight-ahead position. Make certain
that the front axle is not loaded above the front axle Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) as indicated on the vehicle’s VIN
and Weight Rating plate.
SPECIAL TOWING INSTRUCTIONS
1. All state and local laws regarding such items as warning signals, night illumination, speed, etc., must be followed.
2. Safety chains must be used.
3. No vehicle should ever be towed over 55 mph (90 km/h).
4. Loose or protruding parts of damaged vehicles should be secured prior to moving.
5. A safety chain system completely independent of the primary lifting and towing attacment must be used.
6. Operators should refrain from going under a vehicle which is being lifted by the towing equipment unless the vehicle is
adequately supported by safety stands.
7. No towing operation which for any reason jeopardizes the safety of the wrecker operator or any bystanders or other
motorists should be attempted.
FRR/WT TOWING PROCEDURE
Y our vehicle should be towed by an authorized dealership or professional towing service to prevent damage.
Proper equipment must be used and state (Provincial in Canada) and local laws, which apply to vehicles in tow,
must be followed. Vehicles should not be towed in excess of 55 mph (90 km/h).
Connect to the main structural parts of the vehicle. Do not attach to bumpers, tow hooks or brackets. Use only
equipment designed for this purpose. Follow the instructions of the wrecker manufacturer.
A safety chain system must be used.
FRONT END TOWING (FRONT WHEELS OFF THE GROUND)
BEFORE TOWING
Block the rear wheels of the disabled vehicle.
Release the parking brake as described under “Air Operated Parking Brake” in this section.
Drain rear axle oil and remove the axle shafts. Cover the hub openings to prevent the loss of lubricant or entry of
dirt or foreign objects.
AFTER TOWING
After towing the vehicle, block the rear wheels, remove the covers from the hub openings and install the axle
shafts. Apply the parking brake before disconnecting from the towing vehicle. Check and fill rear axle with oil if
required.
FRONT END TOWING (ALL WHEELS ON THE GROUND)
Y our vehicle may be towed on all wheels provided the steering is operable. Remember that power steering will
not have power assist. If air pressure is exhausted, the vehicle will not have brakes. There must be a tow bar
installed between the towing and the disabled vehicle.
BEFORE TOWING
Block the wheels of the disabled vehicle.
Disconnect the propshaft at the rear axle. Secure the propshaft to the frame or crossmember.
If there is, damage or suspected damage to the rear axle, drain oil and remove the axle shafts. Cover the hub
openings to prevent the loss of lubricant or entry of dirt or foreign objects.
AFTER TOWING
After towing the vehicle, block the rear wheels and install axle and propeller shafts. Check for proper phasing of
universal joints. Apply the parking brake before disconnecting from the towing vehicle. Check and fill rear axle
with oil if required.
32 April 2002
Page 45

Mechanical & Cab Specifications
REAR END TOWING (REAR WHEELS OFF THE GROUND)
BEFORE TOWING
Secure the steering wheel to maintain straight-ahead position. Make certain that the front axle is not loaded
above the front axle Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) as indicated on the vehicle’s VIN and Weight Rating
plate.
AFTER TOWING
Block the rear wheels and release the steering. Apply the parking brake before disconnecting from the towing
vehicle. Check and fill the rear axle with oil as required.
SPECIAL TOWING INSTRUCTIONS
1 . Call your local authorized dealership or professional towing service.
2. All state and local laws regarding such items as warning signals, night illumination, speed, etc. must be
followed.
3. Safety chains must be used.
4. No vehicle should ever be towed over 55 mph (90 km/h).
5. Loose or protruding parts of damaged vehicles should be secured before moving.
6. A safety chain system completely independent of the primary lifting and towing attachment must be used.
7. Operators should refrain from going under a vehicle, which is being lifted by the towing equipment unless the
vehicle is adequately supported by safety stands.
8. No towing operation, which for any reason jeopardizes the safety of the wrecker operator or any bystanders or
other motorists, should be attempted.
FSR, FTR & FVR SERIES TOWING PROCEDURE
CAUTION
• Never let passengers ride in a vehicle that is being towed.
• Never tow faster than safe or posted speeds.
• Never tow with damaged parts not fully secured.
• Never get under your vehicle after it has been lifted.
• Always use separate safety chains on each side when towing a vehicle.
Try to have a GM/Isuzu dealer or a professional towing service any tow your vehicle. They can provide the right
equipment and knowledge to tow it without damage.
Before you do anything, turn on the hazard warning flashers (if they have not been damaged).
When you call, tell the towing service:
• That your vehicle has rear-wheel drive.
• The make, model and year of your vehicle.
• Whether you can still move the shift lever.
• An estimation of the total weight plus cargo so that the towing company can use the proper equipment.
• If there was an accident, what was damaged.
When the towing service arrives, let the tow operator know that the owner’s manual contains detailed towing
instructions. The operator may want to see them.
April 2002 33
Page 46

Mechanical & Cab Specifications
T owing Your Vehicle From the Front (Front Wheels Off the Ground)
BEFORE TOWING
Block the rear- wheels of the disabled vehicle. On vehicles with air brakes, release the emergency brake system
by compressing brake chamber springs as outlined in this section. (Note: This is to prevent the possibility of the
emergency brake being applied during towing.)
On vehicles with hydraulic brakes, release the parking brake fully by moving the lever handle to the fully released
position.
T owing the Vehicle with the Front Bumper Removed
1. Remove the front bumper.
2. Connect and lock the lift chains to the front axle, outside of the spring
anchor plates as shown.
3. Connect lift chains to the tow bar and raise the tow bar until lift chain slack
has been taken up.
4. Raise the vehicle to the required height.
Rear Axle
Disconnect the propshaft at the rear axle. Secure the propshaft to the frame or crossmember.
After T owing
Block the rear wheels and install axle and propeller shafts.
Check for proper phasing of universal joints. Apply the emergency brake system before disconnecting from the
towing vehicle. Check and fill the rear axle with oil as required.
T owing Your Vehicle From the Front (All Wheels On the Ground)
Your vehicle may be towed on all wheels provided the steering is working. Remember that the power brakes and
power steering will not have power assist. Vehicles with air brakes will not have brakes. There must be a tow bar
installed between the towing vehicle and the disabled vehicle.
Before T owing
Block the wheels of the disabled vehicle. On vehicles with air brakes, release the emergency brake system by
compressing brake chamber springs as outlined in this section. (Note: This is to prevent the possibility of the
emergency brake being applied during towing.)
On vehicles with hydraulic brakes, release the parking brake fully by moving the lever handle to the fully released
position.
If there is, damage or suspected damage to the axle(s), remove the axle shafts. Cover the hub openings to
prevent the loss of lubricant or entry of dirt or foreign objects.
After T owing
Block the rear wheels and install axle and propshafts. Check for proper phasing of universal joints. Apply the
parking brake system before disconnecting from the towing vehicle. Check and fill rear axle with oil as required.
T owing Your Vehicle From the Rear (Rear Wheels Off the Ground)
CAUTION
• Never let passengers ride in a vehicle that is being towed.
• Never tow faster than safe or posted speeds.
• Never tow with damaged parts not fully secured.
• Never get under your vehicle after it has been lifted.
• Always use separate safety chains on each side when towing a vehicle.
34 April 2002
Page 47

Mechanical & Cab Specifications
Before T owing
Secure the steering wheel to maintain straight-ahead position. Make certain that the front axle is not loaded
above the front axle Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) as indicated on the vehicle’ s Certification/T ire label.
After T owing
Block the rear wheels and release the steering wheel. Apply the parking brake system before disconnecting from
the towing vehicle. Check and fill the rear axle with oil as required.
Releasing Air-Operated Parking Brakes
If your vehicle has air brakes, you could have a special towing problem. If your vehicle has to be towed because
you had a complete loss of air pressure from both systems, the parking brakes may have applied. The tow
operator can release the brakes manually by using the following steps. Then your vehicle can be with all wheels
or just the rear wheels on the ground.
1. Block the wheels of the vehicle.
2. Remove the release stud and nut from the side pocket of the brake chamber. Some chambers have studs that
are visible at all times.
3. Remove the rubber cap from the rear of the chamber.
4. Put the release stud, nut and flat washer into the chamber.
5. Turn the stud clockwise one quarter of a turn.
6. Using a 3/4" wrench, turn the stud nut clockwise several turns to release the brakes. Follow the same procedure to release the other brake.
7. At the repair facility , apply air pressure of at least 70 psi (480 kPa) to the brake chambers, either from an
external air supply or the vehicle’s air system.
8. Turn the stud nut counterclockwise several turns. Remove the stud from the chamber.
9. Put the stud into the side pocket of the chamber, and replace the rubber cap.
April 2002 35
Page 48

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
Weight Distribution
Concepts
April 2002 31
Page 49

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
Weight Restrictions
The Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) and the Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) of each Incomplete Vehicle
are specified on the cover of its Incomplete Vehicle Document in conformance to the requirements of Part 568.4 of
the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Regulations. The final stage manufacturer is responsible under Part 567.5, to place
the GVWR and the GAWR of each axle on the Final Vehicle Certification Label. The regulation states that the
appropriate rating “shall not be less than the sum of the unloaded vehicle weight, rated cargo load, and 150 pounds
times the vehicle’s designated seating capacity.”
Unloaded vehicle weight means the weight of a vehicle with maximum capacity of all fluids necessary for operation
of the vehicle, but without cargo or occupants.
During completion of this vehicle, GVWR and GAWR may be affected in various ways, including but not limited to
the following:
1) The installation of a body or equipment that exceeds the rated capacities of the Incomplete Vehicle.
2) The addition of designated seating positions which exceeds the rated capacities of this Incomplete
Vehicle.
3) Alterations or substitution of any components such as axles, springs, tires, wheels, frame, steering and
brake systems that may affect the rated capacities of this Incomplete Vehicle.
Use the following chart to assure compliance with the regulations. Chassis curb weight and GVW rating is located
on Page 2 in each vehicle section. Always verify the results by weighing the completed vehicle on a certified scale.
Curb Weight of Chassis lbs.
From required vehicle section
PLUS weight of added body
components, accessories or other
permanently attached
components.
+
Body, liftgate, reefer, etc.
PLUS total weight of passengers, air
conditioning and all load or
cargo.
EQUALS Gross Vehicle Weight lbs
(GVW) of completed vehicle.
+
=
Driver, passengers,
accessories and load.
Should equal GVWR from
required vehicle section
32 April 2002
Page 50

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
Gross Axle Weight Rating
The Gross Vehicle Weight is further restricted by the Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR). The maximum GAWR
for both front and rear axles is listed in each Vehicle Section. Weight distribution calculations must be performed to
ensure GAWR is not exceeded. Always verify the results by weighing the completed vehicle on a certified scale.
Note: Although the Front Gross Axle Weight Rating (FGAWR) plus the Rear Gross Axle Weight Rating
(RGAWR) may exceed the Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR), the total GVW may not exceed
the respective maximum GVWR.
The variation in the GAWR's allow the second stage manufacturer some flexibility in the design of the weight
distribution of the attached unit.
Weighing the Vehicle
Front and rear GAWR's and total GVWR should be verified by weighing a completed loaded vehicle. Weigh the
front and rear of the vehicle separately and combine the weights for the total GVWR. All three weights must be less
than the respective maximum shown in the vehicle sections.
Tire Inflation
Tire inflation must be compatible with GAWR and GVWR as specified on the cover of the Incomplete Vehicle
Document for each vehicle.
Center of Gravity
The design of the truck body should be such that the center of gravity of the added load does not exceed the
guidelines as listed in each Vehicle Section. If the body is mounted in such a way that the center of gravity height
exceeds the maximum height of the center of gravity designated for each model, the directional stability at braking
and roll stability at cornering will be adversely affected. A vertical and/or horizontal center of gravity calculation must
be performed if a question in stability arises to ensure the designed maximum height of the center of gravity is not
violated.
April 2002 33
Page 51

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
Weight Destribution
A truck as a commercial vehicle has but one purpose.
That purpose is to haul some commodity from one place
to another. A short distance or a long distance, the weight
to be hauled, more than any other factor, determines the
size of the truck. A small weight requires only a small
truck; a large weight requires a large truck. A simple
principle, but it can easily be misapplied. In any case,
selecting the right size truck for the load to be hauled will
ensure that the job will be done and that is will be able to
be done with some degree of reliability and within the
legal limitations of total gross weight and axle gross
weights.
Not only must a truck be selected that will handle the
total load, but the weight must also be properly distributed
between the axles. This is of extreme importance from
both a functional and economic aspect. If a truck
consistently hauls less than its capacity, the owner is not
realizing full return on his investment and his operating
costs will be higher than they should be. If the truck is
improperly loaded or overloaded, profits will be reduced
due to increased maintenance costs and potential fines
resulting from overloading beyond legal limitations. Careful
consideration must be given to distribution of the load
weight in order to determine how much of the total,
including chassis, cab, body and payload, will be carried
on the front axle and how much will be carried on the rear
axle, on the trailer axles and the total. Moving a load a few
inches forward or backward on the chassis can mean the
difference between acceptable weight distribution for the
truck or an application that will not do the job satisfactorily.
Every truck has a specific capacity and should be
loaded so that the load distribution is kept within Gross
Axle Weight Ratings (GAWR) and the truck’s Gross
Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) or Gross Combination
Weight Rating (GCWR) for a tractor/trailer and the weight
laws and regulations under which the truck will operate.
Improper weight distribution will cause problems in many
areas:
1. Excessive front end wear and failure
a. Tie-rod and king pin wear
b. Front axle failure
c. Overloading of front suspension
d. Wheel bearing failure
2. Rapid tire wear
a. When the weight on a tire exceeds its rating
capacity, accelerated wear will result and could
result in tire failure.
3. Rough, erratic ride
a. If the center of the payload is directly over or slightly
behind the rear axle, the lack of sufficient weight on
the front axle will create a bobbing effect, very
rough ride, and erratic steering. This condition will
be magnified when the truck is going up hill.
4. Hard steering
a. When loads beyond the capacity of the front axle
are imposed upon it, the steering mechanism is
also overloaded and hard steering will result.
b. Excessive overloading could result in steering
component damage or failure.
5. Unsafe operating and conditions.
a. Poor traction on the steering axle effects the safety
of the driver and equipment, particularly on wet, icy
and slippery surfaces. Experience indicates that
approximately 30 % of the total weight at the
ground on a truck or tractor should be on the front
axle with a low cab forward vehicle.
b. When a truck is overloaded, a dangerous situation
may exist because minimum speeds cannot always
be maintained, directional control may not be
precise and insufficient braking capacity can cause
longer than normal braking distances.
6. High maintenance costs
a. Improper weight distribution and overloading cause
excessive wear and premature failure of parts.
Additional stresses impose on the frame by the
misapplication of wheel bases, may be instrumental
in causing the frame to crack or break.
34 April 2002
Page 52

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
7. Noncompliance with weight laws and regulations
a. When there is the possibility that axle loads will
exceed existing weight laws and regulations, careful
weight distribution is necessary to provide a correct
balance between front and rear axle loads, and
total load within legal limitations.
In this way, maximum payloads may be carried without
exceeding legal limits. If the body is too long for a
wheelbase, the center of the body and payload is placed
directly over the rear axle. This places all the payload on
the rear axles, resulting in overloading the rear tires, rear
axle springs and wheel bearings and potentially exceeding
the rear axle legal weight limit. The front axle is then
carrying no part of the payload and is easily lifted off the
ground when going over rough terrain, creating a very
rough ride and temporary loss of steering control. If the
body is too short for the wheelbase used, frame stress
may be increased and may result in excessive loads on
the front axle. Excessive front axle loads increase wear
on the king pins and bushings, wheel bearings and
steering gear. Excessive front axle loads also over stress
the front axle, springs, tires and wheels. All of these
contribute directly to higher maintenance costs and hard
steering, both of which are undesirable.
April 2002 35
Page 53

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
Weight distribution analysis involves the application of
basic mathematical principles to determine the proper
positioning of the payload and body weight in relation to
the wheelbase of the truck chassis.
It is much less expensive to work all of this out on
paper, make mistakes on paper and correct them there
CA
BBC
BOC
than to set up the truck incorrectly and either have it fail
to do the job or much worse, fail completely.
It is important to become familiar with the dimensions
of the truck as these will be needed to perform the
necessary calculations.
CE
CG
FH
AB
BA
Glossary of Dimensions
WB
OAL
BBC - Bumper to back of cab
BA - Bumper to axle
CA - Cab to axle
AB - Axle to back of cab
BOC - Back of cab clearance
CE - Cab to end of frame
CG - Center of gravity of body and payload from axle
WB - Wheelbase
AF
OAL - Overall length
AF - Axle to end of frame
FH - Frame height
36 April 2002
Page 54

WEIGHT DISTRIBUTION FORMULAS
Weight Restrictions & Specifications
W
F
C
D
B
A
W
WB
F
W
R
W
F
F
B
WB
C
L/2
D
CoG
W
A
A = Front axle to back - of - cab
B = Distance between cab and body or trailer
C = Front of body to C.G. or front of trailer to kingpin
D = Distance C.G. of body or fifth wheel is ahead of rear axle
F = (A + B + C) or distance C.G. of weight of fifth wheel is behind front axle
WB = Wheelbase
W = Weight of body plus payload, or kingpin load
Wf= Portion of W transferred to front axle
Wr= Portion of W transferred to rear axle
Basic Formulas: (a) W x D = Wf x WB (c) WB = (A + B + C + D) = (F + D)
or
(b) W x F = Wr x WB (d) W=Wf x W
r
L/2
W
R
1. Wf= W x D 5. Wr=W x F
WB WB
2. D=Wf x WB 6. F=Wr x WB
W W
3. WB = W x D 7. WB = W x F
W
f
W
r
4. W=Wf x WB 8. W=Wr x WB
D F
April 2002 37
Page 55

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
WEIGHT DISTRIBUTION FORMULAS IN WORDS
To find:
1. Weight transferred to front axle = (Total weight) x (Distance C.G. is ahead of the rear axle)
(Wheelbase)
2. Distance C.G. must be placed = (Weight transferred to the front axle) x (Wheelbase)
ahead of rear axle (T otal weight)
3. Wheelbase = (Total weight) x (Distance C.G. is ahead of the rear axle)
(Weight to be transferred to the front axle)
4. Total Weight = (Weight to be transferred to the front axle) x (Wheelbase)
(Distance C.G. is ahead of the rear axle)
5. Weight transferred to the rear axle = (Total weight) x (Distance C.G. is behind the front axle)
(Wheelbase)
6. Distance C.G. must be placed = (Weight transferred to the rear axle) x (Wheelbase)
behind the front axle (T otal weight)
7. Wheelbase = (Total weight) x (Distance C.G. is behind the front axle)
(Weight to be transferred to the rear axle)
8. Total weight = (Weight to be transferred to the rear axle) x (Wheelbase)
(Distance C.G. is behind the front axle)
9. Remember - Total weight must always equal weight transferred to the rear axle plus
the weight transferred to the front axle.
38 April 2002
Page 56

100 lb.
Weight Restrictions & Specifications
P lb.
To find the value of "P", the leverages must be
equal for balance.
i.e.
100 lb x 8 in = "P" x 20 in
or
"P" = 100 lb x 8 in
20 in
Therefore:
"P" = 40 lb
20"
8"
Pivot
This same approach is used to determine axle
loadings on a tractor or truck chassis. Assuming the
rear axle serves as a pivot point, the front axle load can
be determined by applying the lever principle.
Kingpin
Load
(W)
5th wheel location (ahead
of rear axle CL) (D)
Wheelbase (WB)
Front axle
load
(WF)
Front Axle Load:
= Kingpin Load x 5th Wheel Location
Wheelbase
Rear Axle Load:
= Kingpin Load - Front Axle Load
Example: (4) A tractor has a wheelbase of 150 inches.
If the kingpin load is 20,000 lb and the fifth
wheel location is 15 inches, find the total
weight on the front and rear axles. The tare
weight of the tractor is 7,000 lb on the front
axle and 4,400 lb on the rear axle.
Front Axle = Load
20,000 x 15 = 2,000 lb
150
WB
Rear axle
load
(WR)
Rear Axle Load = 20,000 - 2,000
= 18,000 lb
Therefore:
Total Front Axle Weight = 2,000 + 9,000 lb
Total Rear Axle Weight = 4,400 + 18,000 lb
= 22,400 lb
In calculating the weight distribution for a truck, the
same lever principle is applied; however, there is one
change in the initial consideration of the method of loading
the truck body. Instead of the trailer kingpin location
ahead of the rear axle center line, we must determine
the position of the center of gravity of the payload and
body weight in relation to the rear axle center line.
April 2002 39
Page 57

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
For our calculations we assume that the payload is
distributed in the truck body so that the load is supported
evenly over the truck body floor (water level distribution).
The weight of the body itself is also considered to be
evenly distributed along the truck frame. In this manner
we can add the payload and body weights together and
calculate the distribution on the vehicle chassis as an
evenly distributed load on the truck frame rails.
So that we can make the necessary calculation in a
simple manner, the total body and payload weight is
considered to act at the center of gravity which will be at
the center of the body length.
18'
Body + Payload = 15,000 lb.
9'
150"
7'24"
In the case of a tractor/trailer or a tractor with a set of
doubles or triple trailers, each units is handled as a
separated unit and then combined to determine the total.
This simple example illustrates how the principles are
applied. Using the formulas, find the weight distributed to
each axle.
W
300 lb.
24"
96"
Front
Front Weight Rear Weight
A. WF = W x D A. Total weight -
WB
B. 300 x 24 B. 300 - 75
96
C. = 75 lb. C . = 225 lb.
Rear
Example:
Front Axle Load =
(Body Weight + Payload) x C of G location
Wheelbase
Rear Axle Load =
(Body Weight + Payload) - Front Axle Load
Therefore, Front Axle Load =
15,000 x 24 = 2400 lb
150
Rear Axle Load = 15,000-2,400 = 12,600 lb
If the truck tare weight without the body is 5,000 lb on
the front axle and 2,400 lb on the rear axle, then
Total Front Axle Weight =
5,000 + 2,400 = 7,400 lb
and Total Rear Axle Weight =
2,400 + 12,600 = 15,000 lb
This same lever principle is applied in all calculations
of weight distribution, whether we are dealing with
concentrated loads as with a kingpin load acting on a fifth
wheel or if it be with an evenly distributed load as with a
truck body. The same approach is made in calculating an
evenly distributed load on a trailer.
The body manufacturer can provide the body length
and weight, or actual measurements of the body may be
taken with a tape. Generally, (D) is unknown. This you
must find logically, or with a tape measure.
Find (D) and then solve for Wf and Wr.
B
3"
48" D
60"
132"
L
96"
3000 lb
D = 60-3-48 = 9 inches
Wf = 205
Wr = 2,795
40 April 2002
Page 58

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
RECOMMENDED WEIGHT DISTRIBUTION % OF GROSS VEHICLE WEIGHT BY AXLE
CONVENTIONAL (2 Axle)
Front Axle Rear Axle
25% Desired 75%
20-30% Permissible 70-80%
COE (2 Axle)
Front Axle Rear Axle
33 1/3% Desired 66 2/3%
30-35% Permissible 65-70%
Front Axle Rear Axle
20% Desired 80%
18-25% Permissible 75-82%
CONVENTIONAL (3 Axle)
COE (3 Axle)
Front Axle Rear Axle
25% Desired 75%
20-30% Permissible 70-80%
April 2002 41
Page 59

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
Calculating tractor/trailer weight distribution can be
thought of in the same terms as calculating full trucks.
W
W
In the following example, a 50,000 pound payload at
water level loading. Calculate the payload (PL) weight
transfer to kingpin and the rear axle.
C/L Payload
W
F
W
R
W
W
F
R
The weight at the center of the body and the load when
applied is the same as the single point load of the kingpin
on the fifth wheel.
W
W
KP
W
F
W
R
W
RT
TRAILER WEIGHT
L
D
D
45'
D
48"36"
WB
NOTE: Apply the same principles
used with truck chassis
A. Payload at Kingpin
PLkp = W x D
WB
Calculate the “D” dimension
OAL/2 - AF = D
45 feet/2 - 48 inches = 222 inches
KP
RAS
PLkp = 50,000 lb x 222 in = 24,342 lb
456 in
PLkp = 24,342 lb
B. Payload at Rear Tandem
PLrt = W - PL
kp
Kingpin
3,500 lb.
WB
Rear
Tandem
6,500 lb.
PLrt = 50,000 lb - 24,342 lb = 25,658 lb
PLrt = 25,658 lb
Fill in:
L = 40 feet
RAS = 48 inches
KP = 36 inches
WB = ? 396
D = ? 204
42 April 2002
Once the weight on the kingpin is determined, it can
then be treated on the tractor the same as a weight on a
straight truck.
Page 60

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
Due to the variations in hauling and wheelbase
requirements from one truck application to another, there
is no one specific 5th wheel setting that will apply in all
cases.
A “rule of thumb” which has proven satisfactory in
many cases sets the 5th wheel one inch ahead of the rear
axle for each 10 inches of wheelbase. In the case of
tandem axles, the wheelbase is measured from the
center line of the front axle to the midpoint between the
tandem rear axles. The location of the 5th wheel fixes the
load distribution between the front and rear axles. Too far
forward and the front axle is overloaded. If too far back,
the front axle may be too lightly loaded and cause an
unsafe steering and braking control situation at the front
axle.
A tractor on a hill with the 5th wheel set at the axle
center line or too close to it will result in an unsafe handling
situation by transferring too much weight to the rear axle
and actually unloading the front axle.
April 2002 43
Page 61

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
PERFORMANCE CALCULATIONS
The following calculations have been included to help the users of this book determine the performance characteristics required by their customers and to select the appropriate model vehicle:
1. Speed Formula
This formula can be used to determine:
1. Top speed of the vehicle.
2. Speed in a given gear .
3. Final ratio required for a given speed.
(60) X (RPM)
MPH @ Governed Speed =
Definitions in formulas:
RPM = Revolutions per minute of the engine
Rev/Mile = Tire revolutions per mile
Gear Ratio = The product of the axle ratio times the transmission ratio
60 = Time Constant
(Rev/Mile) X (Gear Ratio)
2.
Example:
NPR 12,000 GVWR automatic transmission.
RPM = 3,000
Rev/Mile = 674
Gear Ratio = .703 x 5.375
(60) X (3000)
MPH @ Governed Speed =
(674) X (.703 X 5.375)
MPH @ Governed Speed = 70 MPH
Grade Horsepower Formula
This formula can be used to determine horsepower required for a given grade and speed.
Horsepower Req'd. for a given grade =
GVWR X Grade X Speed
37,500 X Efficiency Factor
+ AHP
Definitions in formula:
GVWR = Gross Vehicle Weight Rating
Grade = Grade anticipated in percent
Speed = Speed in miles per hour
37,500 = Constant
Efficiency Factor = Factor for losses in drivetrain due to friction (use 0.9 for a 90%
efficient driveline)
AHP Resistance = Horsepower required to overcome wind force
44 April 2002
Page 62

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
Example:
NPR 11,050 GVWR automatic transmission with a van body.
GVWR = 12,000 lbs.
Grade = 1 percent
Speed = 55 MPH
37,500 = Constant
Efficiency Factor = 0.9
AHP Resistance = 53.6 HP (See following formula (3) for calculation)
HP Required for Grade =
12,000 X 1 X 55
HP Required for Grade = 73.22
3. Air Resistance Horsepower Formula
This formula is used to determine the horsepower required to overcome air resistance at a
given speed.
Air Resistance Horsepower =
F A X Cd X (MPH)
Definitions in formula:
FA = Frontal area of vehicle in square feet
Cd = Aerodynamic Drag Coefficient
MPH = Speed of vehicle in miles per hour
156,000 = Constant
Frontal area is calculated by multiplying the height of the vehicle by the width of the vehicle
and subtracting the open area under the vehicle from the total.
Aerodynamic Drag Coefficients
(Source Material: Motor Truck Engineering Handbook)
37,500 X 0.9
156,000
+ 53.67
3
:
0.70 for most trucks, semitrailer combinations with tanks or van bodies
0.77 for double and triple trailers and flatbeds with loads
1.00 car and boat haulers
Example:
NPR 12,000 GVWR van body with 96 inches wide, 115 inches high (84" body height + 31"
frame height).
(96) (115)
FA = - 3.2
FA = 73.47 FT
X
(12) (12)
2
Cd = 0.70
Speed = 55 MPH
73.47 X 0.70 X (55)
3
Air Resistance HP =
156,000
Air Resistance HP = 54.85
April 2002 45
Page 63

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
4. Engine Horsepower Formula
This formula can be used to derive the output at a given RPM and torque.
Horsepower =
Torque X RPM
Definitions in formula:
Torque = Twisting output of engine given in lb-ft
RPM = Revolutions per minute of engine
5252 = Constant
Example:
NPR 12,000 GVWR automatic transmission.
Torque = 347 lb-ft
RPM = 2000
132 HP =
( 347) X (2000)
5. Gradeability Formula
This formula can be used to determine how large of a grade a vehicle can climb.
5252
5252
Percent Grade =
1200 X (T) X (E) X (C) X (R)
GVWR X r
- RR
Definitions in formula:
1200 = Constant
T = Maximum Torque of Engine
E = Engine Efficiency (0.9)
C = Driveline Efficiency (0.9)
R = Transmission Ratio X Axle Ratio
RR = Rolling Resistance (see chart on following page)
GVWR= Gross Vehicle Weight Rating
r = Loaded radius of tire.
Example:
NPR 12,000 GVWR automatic transmission on concrete highway.
T = 347 lb-ft
E = 0.9
C = 0.9
R = .703 X 5.375 (in overdrive)
RR = 1.0
GVWR= 12,000
r = 14.1 in
46 April 2002
Page 64

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
Percent Grade =
Percent Grade = 6.53 - 1
Gradeability = 5.53%
6. Startability Formula
This formula is used to determine what type of a grade a vehicle can be started on.
Startability =
Definitions in formula:
1200 X (347) X (0.9) X (0.9) X (.703) X (5.375)
12,000 X 14.1
ROAD ROLLING RESIST ANCE:
Road Rolling Resistance - Expressed in Percent Grade.
Road Surface
Concrete, excellent 1.0 Cobbles, ordinary 5.5
Concrete, good 1.5 Cobbles, poor 8.5
Concrete, poor 2.0 Snow, 2 inch 2.5
Asphalt, good 1.25 Snow, 4 inch 3.75
Asphalt, fair 1.75 Dirt, smooth 2.5
Asphalt, poor 2.25 Dirt, sandy 3.75
Macadam, good 1.5 Mud 3.75 to 15.0
Macadam, fair 2.25 Sand, level soft 6.0 to 15.0
Macadam, poor 3.75 Sand, dune 16.0 to 30.0
(1200) X (CET) X (E) X (C) X (R)
(GVWR X r)
- 10%
- 1.0
1200 = Constant
CET = Clutch Engagement Torque
E=0.9
C=0.9
R = Transmission X Axle Ratio
10% = Average break away resistance and static inertia constant
GVWR = Gross Vehicle Weight Rating
r = Loaded radius of tire
Example:
NPR 12,000 GVWR manual transmission.
CET = 260 lb-ft
R = 6.02 X 4.10
GVWR = 12,000 lb
r = 14.1 in
Startability =
(1200) X (260) X (0.9) X (0.9) X (6.02 X 4.10)
(12,000 X 14.1)
Startability = 26.86%
- 10%
April 2002 47
Page 65

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
7. Vertical Center of Gravity Formula
These formulas are used to estimate the vertical center of gravity of a completed vehicle in order to
determine whether maximum allowable limits have been exceeded. This formula should be used when
encountering high center of gravity loads.
7.1 Wv X (Vv) = Mv
7.2 Wb X (Vb) = Mb
7.3 Wp X (Vp) = Mp
7.4 We X (Ve) = Me
7.5 VCg =
Definitions in formula:
VCg = The total average vertical center of gravity of the completed vehicle ( vehicle,
Wv = Weight of Vehicle
Wb = Weight of Body
Wp = Weight of Payload
We = Weight of Equipment
Vv = Distance from ground to center of gravity of the vehicle
Vb = Distance from ground to center of gravity of the body
Vp = Distance from ground to center of gravity of the payload
V e = Distance from ground to center of gravity of the equipment
Mv = Moment of vehicle
Mb = Moment of Body
Mp = Moment of payload
Me = Moment of equipment
(Mv + Mb + Mp + Me)
(Wv + Wb + Wp + We)
body , payload and equipment)
Example:
NPR 12,000 GVWR automatic transmission, 132" WB, 14' body length, 84" high body , full payload of
boxes stacked to a maximum height of 48" above the flooring.
Wv = 5291 lbs
Wb = 2100 lbs
Wp = 4609 lbs
Vv = 24.9 in
Vb = 80 in
Vp = 62 in
(from vehicle specifications)
(from body manufacturer)
(GVWR - (Wv + Wb + We))
(from Body Builder 's Guide, NPR section, page 6)
(from body manufacturer)
(1/2 of payload height + frame height +
height from frame to flooring)
Mv = 5291 X 24.9 = 131,746 lb-in
Mb = 2100 X 80 = 168,000 lb-in
Mp = 4609 X 62 = 285,758 lb-in
We, Ve, Me = None in this example
VCg =
VCg = = 48.8 inches
48.8 < 54.0 inches (54 inches is maximum allowable VCg per mfg. specifications
(131,746 + 168,000 + 285,758)
(5291 + 2100 + 4609)
(528,504)
(12,000)
- from Body Builder's Guide, NPR section, page 6)
(from 7.1)
(from 7.2)
(from 7.3)
Since maximum VCg for this truck is not exceeded, 48" stack height above flooring is acceptable.
48 April 2002
Page 66

8. Horizontal Center of Gravity Formula
These formulas are used to estimate the horizontal center of gravity of a completed vehicle in order to determine
whether it exists between the centerlines of the front and rear axles. This formula should be used when a load
and/or permanent equipment (liftgate, reefer unit, snow plow, etc.) is installed on either extremes along the
completed vehicle's overall length.
8.1 Wv X (Hv) = Mv
8.2 Wb X (Hb) = Mb
8.3 Wp X (Hp) = Mp
8.4 We X (He) = Me
(Mv + Mb + Mp + Me)
8.5 HCg =
(Wv + Wb + Wp + We)
Definitions in formula:
HCg = The total average horizontal center of gravity of the completed vehicle ( vehicle,
body, payload and equipment)
Wv = Weight of Vehicle
Wb = Weight of Body
Wp = Weight of Payload
We = Weight of Equipment
Hv = Distance from front axle to center of gravity of the vehicle
Hb = Distance from front axle to center of gravity of the body
Hp = Distance from front axle to center of gravity of the payload
He = Distance from front axle to center of gravity of the equipment
Mv = Moment of vehicle
Mb = Moment of Body
Mp = Moment of payload
Me = Moment of equipment
Weight Restrictions & Specifications
Example:
NPR 12,000 GVWR automatic transmission, 132" WB, 14' body length, full payload of boxes stacked and
distributed evenly throughout the flooring, 1,000 lb reefer unit attached in front of body.
Wv = 5291 lbs
Wb = 2100 lbs
Wp = 3609 lbs
We = 1000 lbs
Hv = 42.4 in
Hb = 107.5 in
Hp* = 107.5 in
(from vehicle specifications)
(from body manufacturer)
(GVWR - (Wv + Wb + We))
(from equipment manufacturer)
(from Body Builder 's Guide, NPR section, page 6)
(from body manufacturer)
(1/2 of payload length + distance from front axle
to front of body)
He = 17.5 in
Mv = 5291 X 42.4 = 224,338 lb-in
Mb = 2100 X 107.5 = 225,750 lb-in
Mp = 3609 X 107.5 = 387,967 lb-in
Me = 1000 X 17.5 = 17,500 lb-in
HCg =
(224,338 + 225,750 + 387,967 + 17,500)
(from equipment manufacturer)
(from 8.1)
(from 8.2)
(from 8.3)
(from 8.4)
(5291 + 2100 + 3609 + 1000)
HCg = = 71.3 inches
(855,555)
(12,000)
71.3 < 132 inches(132 inches is the wheelbase dimension)
Since the HCg for this truck is not greater than the WB or negative (-) (denotes HCg forward of front
axle centerline), it exists between the centerlines of the front and rear axles.
*
NOTE: Hp and Hb dimensions are the same in this example because CG of body and payload happen to be at the same point.
April 2002 49
Page 67

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
HIGHWAY SYSTEM LIMITS
The Federal Government established the Federal
Bridge Gross Weight Formula to provide a standard to
control the spacing of truck axles on trucks that use
highway bridges. This is intended to space loads out over
a distance to avoid too high a concentration in one area
that could cause damage. The truck’s gross weights,
axle weight and axle spacings are set in order to keep axle
loads and gross weight loads with the limits set by the
Federal Government. The Bridge Formula Table is used
to check trucks to make sure that Federal weight limit
requirements are met and that the allowable gross and
axle weights are in the correct relationship with the
spacing of axles to prevent high load concentrations on
highway bridges.
The Federal Government has established the following
formula to be used to determine the allowable weight
limits and axle spacings for trucks.
W = 500 ( LN + 12N = 36)
N-1
Where:
W = The total gross weight that may be carried on any
group of two or more consecutive axles to the
nearest 500 lb.
L = The distance (spacing) in feet between the outer
axles of any group of two or more consecutive
axles.
N = The number of axles in the group under
consideration; except that two consecutive sets
of tandem axles may carry a gross load of 34,000
lb each provided the overall distance between
the first and last axles of such consecutive sets
of axles in 36 feet or more.
BRIDGE FORMULA DEFINITIONS
The following definitions are used for bridge formula
calculations.
Gross Weight:
The total weight of a truck (and/or trailer) combined
with the weight of the load being hauled. The Federal
gross weight limits on interstate highways and federal-aid
highways and reasonable access is 80,000 lb.
Single Axle Weight:
The total weight at the ground by all wheels of an axle
whose centers may be included between parallel
transverse planes forty inches apart, extending across
the width of the truck. The Federal single axle weight limit
on the Interstate system and reasonable access is 20,000
lb.
Tandem Axle Weight:
The total weight at the ground of two or more consecutive axles whose centers may be included between parallel vertical planes spaced more than forty inches but not
more than ninety-six inches apart, extending across the
full width of the truck. The Federal tandem axle weight
limit on the interstate system and reasonable access is
34,000 lb.
CONSECUTIVE AXLE WEIGHT:
The Federal law states that any two consecutive or
more axles may not exceed the weight as computed by
the formula even though the single axles, tandem axles,
and gross weights are within the legal requirements.
EXCEPTION TO THE BRIDGE FORMULA:
There is one exception to the use of the Federal Bridge
Formula: Two consecutive sets of tandem axles may
carry a gross load of 34,000 lb each, providing the overall
distance between the first and last axles of such
consecutive sets of tandem axles is 36 feet or more.
OTHER FEDERAL PROVISIONS:
Maximum Width: 102" Overall
Length: States cannot set overall length limits on tractor,
semitrailer or tractor - semitrailer, trailer
combinations. States must allow tractors with
double trailers. States must allow semitrailers of
up to 48 feet in length for doubles combinations.
There is also not limitation on overall length for
semitrailer or doubles combinations.
These width and length dimensions apply to trucks
operating on Interstate highways and federal-aid highways
designed by the Federal Highway Administration. This
also provides for reasonable access to the interstate
highways.
50 April 2002
Page 68

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
FEDERAL BRIDGE FORMULA TABLE
Distance in feet between the 2 OR MORE CONSECUTIVE AXLES
MAXIMUM LOAD IN POUNDS ON ANY GROUP OF
extremes of any group of 2
or more consecutive axles 2 3456789
Axles Axles Axles Axles Axles Axles Axles Axles
4 34,000
5 34,000
6 34,000
7 34,000
*
*
*
*
8 and less 34,000*34,000
8 and more 38,000 42,000
9 39,000 42,500
10 40,000 43,500
11 44,000
12 45,000 50,000
13 45,500 50,500
14 46,500 51,500
15 47,000 52,000
16 48,000 52,500 58,000
17 48,500 53,500 58,500
18 49,500 54,000 59,000
19 50,000 54,500 60,000
20 51,000 55,500 60,500 66,000
21 51,500 56,000 61,000 66,500
22 52,500 56,500 61,500 67,000
23 53,000 57,500 62,500 68,000
24 54,000 58,000 63,000 68,500 74,000
25 54,500 58,500 63,500 69,000 74,500
26 55,500 59,500 64,000 69,500 75,000
27 56,000 60,000 65,000 70,000 75,500
28 57,000 60,500 65,500 71,000 76,500 82,000
29 57,500 61,500 66,000 71,500 77,000 82,500
30 58,500 62,000 66,500 72,000 77,500 83,000
31 59,000 62,500 67,500 72,500 78,000 83,500 90,000
32 60,000 63,500 68,000 73,000 78,500 84,500 90,500
33 64,000 68,500 74,000 79,000 85,000 91,000
34 64,500 69,000 74,500 80,000 85,500 91,500
35 65,500 70,000 75,000 80,500 86,000 92,000
36 66,000+ 70,500 75,500 81,000 86,500 93,000
37 66,500+ 71,000 76,000 81,500 87,000 93,500
38 67,500+ 72,000 77,000 82,000 87,500 94,000
39 68,000 72,500 77,500 82,500 88,500 94,500
40 68,500 73,000 78,000 83,500 89,000 94,500
41 69,500 73,500 78,500 84,000 89,500 95,000
42 70,000 74,000 79,000 84,500 90,000 95,500
43 70,500 75,000 80,000 85,000 90,500 96,000
44 71,500 75,500 80,500 85,500 91,000 96,500
45 72,000 76,000 81,000 86,000 91,500 97,500
46 72,500 76,500 81,500 87,000 92,500 98,000
47 73,500 77,500 82,000 87,500 93,000 98,500
48 74,000 78,000 83,000 88,000 93,500 99,000
49 74,500 78,500 83,500 88,500 94,000 99,500
50 75,500 79,000 84,000 89,000 94,500 100,000
51 76,000 80,000 84,500 89,500 95,000 100,500
52 76,500 80,500 85,000 90,500 95,500 101,000
53 77,500 81,000 86,000 91,000 96,500 102,000
54 78,000 81,500 86,500 91,500 97,000 102,500
55 78,500 82,500 87,000 92,000 97,500 103,000
56 79,500 83,000 87,500 92,500 98,000 103,500
57 80,000 83,500 88,000 93,000 98,500 104,000
58 84,000 89,000 94,000 99,000 104,500
59 85,000 89,500 94,500 99,500 105,000
60 85,500 90,000 95,000 100,500 105,500
* Tandem Axle by Definition
+ Exception to Federal Bridge Formula Table and Law. See Text for Explanation.
Note: All permissible load calculations are to the nearest 500 lb Maximum load on any single axle, 20,000 lb.
Weights over 80,000 lb are in excess of the Federal GVW on the National Highway Network.
April 2002 51
Page 69

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
Commodity
Material Weights
&
52 April 2002
Page 70

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
APPROXIMATE WEIGHTS OF COMMODITIES AND MATERIALS
Lb. Per No. of
Product Size Container Cu. Ft. Lb. Per
Acetone .................................................................................................50 6.6 gallon
Alcohol, Commercial ..............................................................................51 6.8 gallon
Proof spirits............................................................................... 57 7.6 gallon
Alfalfa seed .........................................................bushel ............................. -- 60 bushel
Aluminum, Pure (cast) ..............................................................................165 4450 cu. yard
Apples, Fresh .......................................... basket-bushel ....................... -- 48 bushel
Western, box .............................. 11.5"x12"x20" ....................... -- 50 box
New England, box................... 11.25"x14.5"x17.5" ................... -- 56 box
Standard barrel ....................... 17" hd., 28.5" stave ................... -- 160 barrel
Dried ................................................. bushel ............................. -- 24 bushel
Apricots, Fresh ................................................ bushel ............................. -- 48 bushel
Western, box ............................... 5.5"x12"x20" ........................ -- 23 box
Artichokes, Box ............................................. 10"x11.5"x22" ....................... -- 44 box
Asbestos ............................................................................................... 153 4130 cu. yard
Asparagus, Crate......................................................
Loose.................................... 11.5" high x 9.57" top ................. -- 38 crate
Bunches.............................. 11" bottom x 19.38" long............... -- 31 crate
Avacados, Box ......................................... 5.75"x11.25"x17.5" ................... -- 16 box
Bananas, Single stem....................................... bunch ............................. -- 45-65 bunch
Barley ......................................................... bushel ............................. -- 48 bushel
Barytes, Mineral....................................................................................280 7560 cu. yard
Basalt, Rock ....................................................................................... 185 5000 cu. yard
Beans, dry Lima.................................................. bushel ............................. -- 56 bushel
White ................................................bushel ............................. -- 60 bushel
Castor ............................................... bushel ............................. -- 46 bushel
Fresh Lima.................................................. bushel ............................. -- 39 bushel
String ................................................ bushel ............................. -- 36 bushel
..................................................hamper, 5 peck ...................... -- 45 hamper
Beef, Slack barrel....................... 21"x30" stave (200 lb. net) ............. -- 254 barrel
Beer, Wood barrel.............................0.5 barrel (16 gal.).................... -- 205 barrel
Wood barrel .............................0.25 barrel (8 gal.) .................... -- 105 barrel
Steel barrel ..............................0.5 barrel (16 gal.).................... -- 190 barrel
Steel barrel ..............................0.25 barrel (8 gal.).................... -- 95 barrel
Dutchman ................................0.13 barrel (4 gal.).................... -- 51 barrel
Case carton-24, 12 oz.
Regular bottles........................ 17.25"x11.5"x9.88" ................... -- 45 case
Steinie bottles ........................ 18.38"x12.13"x7.38" .................. -- 40 case
Tin cans ....................................16.13"x11"x5.13"..................... -- 28 case
Wooden case-24, 12 oz.
Regular bottles............................ 21"x13.5"x10" ....................... -- 35 case
Steinie bottles ............................22"x13.75"x7.5"...................... -- 46 case
Beets .........................................................bushel ............................. -- 50-60 bushel
Small crate................................9.75"x13.75"x24"..................... -- 50 crate
Western crate ............................. 14"x19"x24.5" ....................... -- 95 crate
Note: Beer cases vary as to size and shape. Suggest checking with local source.
April 2002 53
Page 71

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
APPROXIMATE WEIGHTS OF COMMODITIES AND MATERIALS
Lb. Per No. of
Product Size Container Cu. Ft. Lb. Per
Berries-crate 24 pint......................................9.75" x 9.97" x 20".................... -- 25 crate
24 quart .................................11.75" x 11.75" x 24".................. -- 48 crate
32 quart ..................................15.5" x 11.75" x 24"................... -- 63 crate
Bluegrass seed ......................................................... bushel ............................. -- 44 bushel
Bluestone ............................................................................................... 120 3240 cu. yard
Bone ............................................................................................... 115 3110 cu. yard
Borax ...............................................................................................110 2970 cu. yard
Bran .........................................................bushel ............................. -- 20 bushel
Brick-
Soft ............................................ 2.25" x 4" 8.25"...................... -- 4320 M
Common ...................................2.25" x 4" x 8.25"..................... -- 5400 M
Hard........................................ 2.25" x 4.25" x 8.5"................... -- 6480 M
Pressed ................................... 2.38" x 4" x 8.38" .................... -- 7500 M
Paving......................................... 2.25" x 4" 8.5" ....................... -- 6750 M
Paving block ...............................3.5" x 4" x 8.5"....................... -- 8750 M
Fire .............................................2.5" x 4.5" x 9"....................... -- 7000 M
Broccoli- Bushel crate...........................12.75" x 12.75" x 17" .................. -- 30 bushel
Brussel sprouts, Crate .................................... 7.75" x 10.5" x 21.38" ................. -- 26 crate
Buckwheat ......................................................... bushel ............................. -- 49 bushel
Butter-tub, Small.......................................... 15" dia. x 5.75" ...................... -- 25 tub
Standard ......................................15" dia. x 15"........................ -- 70 tub
Case, 30 - 1-lb. bricks .................... 10.75" x 8.75" x 10.5" ................. -- 32 case
9-lb. pail .............................................. pail ............................... -- 10 pail
Cabbage ......................................................... bushel ............................. -- 38 bushel
Hamper.......................................... 1.5 bushel .......................... -- 58 hamper
Crate.......................................12.75" x 18.5" x 19"................... -- 60 crate
Western crate ........................... 14" x 19" x 24.5" ..................... -- 85 crate
Barrel crate ........................ 12.75" x 18.75" x 37.38" ............... -- 110 crate
Calf, Live (average).................................per head........................... -- 140-160 head
Cantaloupe, Crate-
Pony ...................................... 11.75"x11.75"x23.5" .................. -- 58 crate
Standard ................................ 12.75"x12.75"x23.5" .................. -- 68 crate
Jumbo.....................................13.75"x13.75"x23.5................... -- 78 crate
Pony flat.................................. 4.75"x12.75"x23.5" ................... -- 26 crate
Standard flat ........................... 5.25"x14.25"x23.5" ................... -- 28 crate
Jumbo flat ............................... 5.75"x15.25"x23.5" ................... -- 32 crate
Honeydew (Casaba) ............... 6.38"x15.13"x23.5" ................... -- 35 crate
Carbolic acid ................................................................................................. 60 8.0 gallon
Carrots, Topped ............................................. bushel ............................. -- 55 bushel
With tops .......................................... bushel ............................. - - 40 bushel
Crate........................................11.75"x14.13"x24".................... -- 60 crate
Castor oil ................................................................................................. 61 8.1 gallon
Cauliflower ......................................................... bushel ............................. -- 30 bushel
Crate........................................... 9.38"x19"x24" ....................... -- 50 crate
Cedar* .................................................................................................30 2500 M. Bd. ft.
54 April 2002
Page 72

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
APPROXIMATE WEIGHTS OF COMMODITIES AND MATERIALS
Lb. Per No. of
Product Size Container Cu. Ft. Lb. Per
Celery Standard crate .........................11.63"x22"x22.63".................... -- 70 crate
Half crate ................................. 10.75"x13"x20.38 .................... -- 35 crate
Northern crate...........................16.5"x21.25"x22"..................... -- 85 crate
Cement Block...............................................8"x8"x16"........................... -- 42 each
Block..............................................8"x12"x16".......................... -- 58 each
Portland ............................................. sack .............................. -- 94 sack
Portland ............................. barrel (4 sacks per barrel) .............. -- 376 barrel
Chalk ............................................................................................... 137 3700 cu. yard
Charcoal, Oak ........................................................................................... 33 890 cu. yard
Pine .......................................................................................... 23 620 cu. yard
Cheese, Small box................................... 15" dia. x 5.25" ...................... -- 25 box
Medium box .................................15" dia x 7.5"........................ -- 35 box
Large box..................................... 15" dia. x 15" ........................ -- 70 box
Cherries, Un-stemmed ..................................... bushel ............................. -- 56 bushel
Stemmed .......................................... bushel ............................. -- 64 bushel
Lug box.................................. 5.63:x11.88"x19.75" .................. -- 17 box
Chestnut (lumber)...............................................................................................37 3080 M. Bd. ft.
Chestnuts ......................................................... bushel ............................. -- 50 bushel
Chickens- Live, broilers (20 avg.) ................standard crate....................... -- 58 crate
Fowl (12 avg.) .............................standard crate....................... -- 78 crate
Standard crate (empty) .................24"x35"x13"......................... -- 18 crate
Cinder blocks, 8"x8"x16" ................................................................................... -- 35 each
8"x12"x16" ................................................................................. -- 45 each
Cinders .................................................................................................50 1350 cu. yard
Clay, Dry lumps .................................................................................85 2300 cu. yard
Wet lumps .............................................................................. 110 2970 cu. yard
Wet packed ............................................................................ 135 3650 cu. yard
Fire ......................................................................................... 125 3375 cu. yard
Cork ................................................................................................. 15 405 cu. yard
Corn, Ear.................................................... bushel ............................. -- 35 bushel
Shelled.............................................. bushel ............................. -- 56 bushel
Sweet corn (green) ........................... bushel ............................. -- 43 bushel
Crate........................................12.88"x12.88"x24".................... -- 60 crate
Corn meal ......................................................... bushel ............................. -- 44 bushel
Corn oil .................................................................................................58 7.8 gallon
Corn syrup .................................................................................................86 11.5 gal.
Cotton, Gin bale ......................................30" x 48" x 54"....................... -- 515 bale
Standard bale .............................24" x 28" x 56"....................... -- 515 bale
Comp. bale .................................20" x 24" x 56"....................... -- 515 bale
Cotton seed ......................................................... bushel ............................. -- 32 bushel
Cottonseed oil .................................................................................................58 7.8 gal.
Cottonwood (lumber)
Cow, Live-feeder (avg.)............................per head........................... -- 600 head
*
............................................................................................................................................................
37 3080 M. Bd. ft.
Butcher (avg.) .................................per head........................... -- 800 head
Butcher steer (avg.) ........................per head........................... -- 1100 head
April 2002 55
Page 73

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
APPROXIMATE WEIGHTS OF COMMODITIES AND MATERIALS
Lb. Per No. of
Product Size Container Cu. Ft. Lb. Per
Cranberries- 0.25 barrel box ........................... 9.5" x 11" x 14" ...................... -- 28 box
0.25 barrel box.......................12.25" x 14.75" x 22" .................. -- 60 box
Cream .................................................................................................64 8.5 gallon
Creosote .................................................................................................68 9.2 gallon
Crude oil .................................................................................................56 7.5 gallon
Cucumbers ......................................................... bushel ............................. -- 55 bushel
Crate.......................................9.75" x 13.75" x 24"................... -- 75 crate
Case ......................................... 5" x 13.25" x 19" ..................... -- 26 case
Earth, Loose, dry loam .......................................................................76 2050 cu. yard
Packed......................................................................................95 2565 cu. yard
Wet .........................................................................................125 3375 cu. yard
Eggplant, Hamper............................................. bushel ............................. -- 40 bushel
Crate........................................ 14" x 11.75" x 24" .................... -- 54 crate
Eggs, 30 doz. crate ..............................12" x 12" x 26"....................... -- 55 crate
Elm, Soft
Fertilizer, Commercial ................................... burlap bag .......................... -- 100-200 bag
Fir,Douglas ............................................................ 32 ........................... 2670 M. Bd. ft.
Fish, fresh- Barrel ......................................19" head, 29" stave................... -- 300 barrel
Flour, Barrel ................................... 19.13" head, 30" stave ................ -- 215 barrel
Fuel oil, Furnace grade ..........................................................................56 7.5 gallon
Furniture, Household ..................................................................................7 1915 cu. yard
Garbage, Dry, paper wrapped .............................................................15-30 405-810 cu. yard
Gasoline .................................................................................................45 6.0 gallon
Glass, Common window ....................................................................... -- 162 cu. foot
Glue ................................................................................................. 80 2160 cu. yard
Glycerine .................................................................................................79 10.5 gallon
Grapefruit, Western box ............................11.5" x 11.5" x 24".................... -- 68 box
Grapes, Basket............................................... bushel ............................. -- 48 box
Gravel, Dry ............................................................................................ 95 2565 cu. yard
Greens .........................................................bushel ............................. -- 25 bushel
Groceries, Misc. asst’d ............................................................................... 30 810 cu. yard
Hay, Bale .............................................26" x 30" 46" ........................ -- 210 bale
*
..............................................................................................................................................................
*
...........................................................................................................................................................
Rock
38 3170 M. Bd. ft.
45 3750 M. Bd. ft.
Eastern ..................................................................................... 25 2080 M. Bd. ft.
0.5 barrel ............................. 18.5" head, 23.5" stave................ -- 160 1/2 barrel
Diesel engine ............................................................................ 52 7.0 gallon
Wet ...........................................................................................50 1240 cu. yard
Plate or crown............................................................................ -- 161 cu. foot
0.25" plate.................................................................................. -- 3.3 sq. foot
Southern box .......................... 12.75" x 12.75" 27" ................... -- 90 box
Lug box................................. 5.63" x 16.38" x 17.5" ................. -- 30 box
Western keg .............................. 15.5" dia. x 14" ...................... -- 45 keg
Basket..............................................12 quart............................ -- 18 basket
Wet .........................................................................................125 3375 cu. yard
Bale ............................................17" x 22" x 43"....................... -- 115 bale
Bale ............................................. 14" x 16" 43" ........................ -- 85 bale
56 April 2002
Page 74

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
APPROXIMATE WEIGHTS OF COMMODITIES AND MATERIALS
Lb. Per No. of
Product Size Container Cu. Ft. Lb. Per
Hog, Live (average).................................per head........................... -- 225-250 head
Honey .................................................................................................90 12.0 gallon
Horse, Live (average).................................per head........................... -- 1200-1500 head
Horseradish roots ....................................................... bushel ............................. -- 35 bushel
Ice .................................................................................................57 1540 cu. yard
Ice (mfg.), Block...........................................11" x 22" x 32"....................... -- 250 block
Block...........................................14" x 14" x 40"....................... -- 255 block
Block...........................................11" x 22" x 56"....................... -- 440 block
Ice Cream, 2.5 gal. can,
Full................................................ 9" dia. x 11"......................... -- 18 can
Empty ........................................................................................ -- 6 can
5 gal. can,
Full................................................ 9" dia. x 21"......................... -- 35 can
Empty ........................................................................................ -- 11 can
Kale ......................................................... bushel ............................. -- 25 bushel
Kerosene ................................................................................................. 50 6.6 gallon
Lamb, Live (avg.).......................................per head........................... -- 75-85 head
Lard, Barrel ...................................... 18" head, 30" stave................... -- 425 barrel
Lath-standard length 29 in. Packed in bundles of 50.
...................................... Avg. bundle-diameter 9 inches .......... -- 25 bundle
Leather, Dry ............................................................................................55 1485 cu. yard
Wet ...........................................................................................65 1755 cu. yard
Lemons, Western box ...............................10" x 13" x 25"....................... -- 80 box
Southern box ......................... 12.75" x 12.75" x 27".................. -- 90 box
Lentils .........................................................bushel ............................. -- 60 bushel
Lettuce, Hamper............................................. bushel ............................. -- 25 bushel
Hamper.......................................... 1.5 bushel .......................... -- 38 hamper
Basket................................... 8.5" x 11.75" x 21.38" ................. -- 17 basket
Crate..................................... 18.75" x 17.5" x 24.5" ................. -- 75 crate
1/2 crate.................................. 9.5" x 13.5" x 24.5" ................... -- 40 1/2 crate
Lime, Hydrated ........................................... bushel ............................. -- 30 bushel
Barrel (small) .......................16.5" head, 27.5" stave ............... 62 210 barrel
Barrel (large)............................................................................62 320 barrel
Limes, Western box ...............................10" x 13" x 25"....................... -- 80 box
Southern box ......................... 12.75" x 12.75" x 27".................. -- 90 box
Linseed oil ................................................................................................. 59 7.9 gallon
Lubricating oil ................................................................................................. 52 7.0 gallon
Malt, Barley ............................................... bushel ............................. -- 28 bushel
Rye ................................................... bushel ............................. -- 32 bushel
Brewer’s grain................................... bushel ............................. -- 40 bushel
Maple syrup ......................................................... ga llon ............................82 11 gallon
Maple, Hard (lumber)* ..........................................................................44 3670 M. Bd. ft.
Meal-corn ......................................................... bushel ............................. -- 44 bushel
Milk, Bulk ..........................................................................................64 8.6 gallon
*
Soft
..............................................................................................................................................................
34 2830 M. Bd. ft.
5 gallon can .............................. 10.25" dia. x 19" ..................... -- 62 can
10 gallon can ...............................13" dia. x 23"........................ -- 115 can
Crate-20.5 pt. bottles ............ 8.5" x 12.75" x 16.75" ................. -- 33 crate
20 pt. bottles ......................... 8.5" x 12.75" x 16.75" ................. -- 54 crate
April 2002 57
Page 75

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
APPROXIMATE WEIGHTS OF COMMODITIES AND MATERIALS
Lb. Per No. of
Product Size Container Cu. Ft. Lb. Per
Millet ......................................................... bushel ............................. -- 50 bushel
Molasses ................................................................................................. 90 12 gallon
Barrel ................................... 20.25" head, 34" stave ................ -- 675 barrel
Mortar, Lime........................................................................................110 2970 cu. yard
Mud, Flowing ................................................................................... 106 2860 cu. yard
Packed.................................................................................... 125 3375 cu. yard
Muriatic acid, 40% ..........................................................................................40 10 gallon
Naptha, Petroleum ................................................................................. 42 5.6 gallon
Nitric acid, 91% .......................................................................................... 94 12.5 gallon
Oak-red, Black
Oats ......................................................... bushel ............................. -- 32 bushel
Okra, Hamper.......................................... 1/2 bushel .......................... -- 18 hamper
Oleomargarine (mfg.-tub) ................................ 21" head, 34" stave................... -- 70 tub
Olive oil .................................................................................................58 7.7 gallon
Onions dry, Basket............................................... bushel ............................. -- 55 bushel
Oranges, Western box ............................11.5" x 11.5" x 24".................... -- 80 box
Oysters (shucked or meats)
Paint, Lead and oil ............................................................................ 127 17 gallon
Paper, Average solid............................................................................58 1565 cu. yard
Paraffin .................................................................................................56 1510 cu. yard
Parsley, Bushel crate...........................12.75" x 12.75" x 17".................. -- 30 crate
Parsnips ......................................................... bushel ............................. -- 50 bushel
Peaches, Basket............................................... bushel ............................. -- 48 bushel
Peanuts, Unshelled.......................................... bushel ............................. -- 22 bushel
Peanut oil ................................................................................................. 57 7.6 gallon
Pears, Basket...............................................bushel ............................. -- 50 bushel
*
..........................................................................................................................................................
*
.........................................................................................................................................................
White
42 3500 M. Bd. ft.
48 4080 M. Bd. ft.
Hamper.............................................bushel ............................. -- 34 bushel
Cases ........................................................................................ -- 15-65 case
Bag ................................................. 17" x 32" ........................... -- 50 bag
Crate...................................... 20.5" x 11.5" x 10.5" .................. -- 58 crate
Green (with tops) .............................. bushel ............................. -- 32 bushel
Southern box ......................... 12.75" x 12.75" x 27".................. -- 90 box
Bushel box ........................... 10.75" x 10.75" x 23.5" ................ -- 65 box
Crate-with 5.1 gal. cans
(11.5 lb. per gal.).........................18" x 12" x 24"....................... -- 67 crate
With shells (bags) ............................. bushel ............................. -- 75 bushel
Newspaper rolls ........................ 34.25" x 35" dia. ..................... -- 500 roll
.................................................. 51.5" x 35" dia. ...................... -- 1000 roll
................................................. 64.25" x 35" dia. ..................... -- 1300 roll
1/2 bushel .................................................................................. -- 25 basket
Crate.......................................10.5" x 11.25" x 24"................... -- 50 crate
Western box ......................... 5.5" x 12.25" x 19.75" ................. -- 22 box
Bag ............................................................................................ -- 100 bag
Western box ........................ 9.63" x 12.13" x 19.75" ................ -- 51 box
58 April 2002
Page 76

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
APPROXIMATE WEIGHTS OF COMMODITIES AND MATERIALS
Lb. Per No. of
Product Size Container Cu. Ft. Lb. Per
Peas, Dry ....................................................bushel ............................. -- 60 bushel
Fresh hamper ................................... bushel ............................. -- 35 hamper
Hamper.............................................40 qts.............................. -- 45 hamper
Pecans, Large bag .................................................................................. -- 100 bag
Small bag................................................................................... -- 50 bag
Peppers, Basket............................................... bushel ............................. -- 25 basket
Crate......................................14.13" x 11.75" x 24" .................. -- 45 crate
Petroleum .................................................................................................56 7.5 gallon
Phosphate rock ...............................................................................................200 5400 cu. yard
Pine, Long leaf
North Carolina
Oregon
Red
White
Yellow-long leaf
Short leaf
Pineapples, Crate......................................... 11" x 12.5" x 36" ..................... -- 85 crate
Pitch ................................................................................................. 70 1900 cu. yard
Plums, Basket............................................... bushel ............................. -- 56 bushel
Western box ......................... 5.63" x 16.38" x 17.5" ................. -- 25 box
Pomegranates, Box ..........................................6.5" x 12" x 24.63".................... -- 30 box
Popcorn, Ear ....................................................bushel ............................. -- 70 bushel
Shelled.............................................. bushel ............................. -- 56 bushel
*
Poplar
.................................................................................................27 2250 M. Bd. ft.
Porcelain ...............................................................................................150 4050 cu. yard
Pork (dressed), Barrel (200 lb. net) ..................18" head, 29" stave ................... -- 240 barrel
Potatoes, Sweet................................................ bushel ............................. -- 55 bushel
White or Irish .................................... bushel ............................. -- 60 bushel
Bag ............................................... 1.67 bushel ......................... -- 102 bag
Barrel .................................. 17.13" head, 28.5" stave ............... -- 185 barrel
Prunes, Box ...................................... 5.63" x 16.38" x 19.75" ................ -- 25 box
Box ...................................... 5.63" x 11.88" x 19.75" ................ -- 22 box
Quinces ......................................................... bushel ............................. -- 50 bushel
Radishes, Basket............................................... bushel ............................. -- 34 bushel
Crate.......................................9.75" x 13.75" x 24"................... -- 40 crate
Redwood
*
.................................................................................................30 2500 M. Bd. ft.
Resin ................................................................................................. 68 1835 cu. yard
Rhubarb (pie plant)..................................................... bushel ............................. -- 50 bushel
Box ..........................................5.25" x 11.5" x 22".................... -- 24 box
Rice, Unhulled ...........................................bushel ............................. -- 43 bushel
Rock, Crushed (avg.) ........................................................................100 2700 cu. yard
Romaine, Crate.................................... 13.88" x 18.88" x 24.5" ................ -- 64 crate
Crate......................................12.25" x 13" x 15.25" .................. -- 27 crate
Rubber goods .................................................................................................94 2540 cu. yard
Rutabagas .........................................................bushel ............................. -- 56 bushel
*
................................................................................................................................................
*
*
.....................................................................................................................................................
*
..............................................................................................................................................................
*
.........................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
*
*
..............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................................
44 3670 M. Bd. ft.
36 3000 M. Bd. ft.
32 2670 M. Bd. ft.
30 2500 M. Bd. ft.
26 2170 M. Bd. ft.
44 3670 M. Bd. ft.
38 3170 M. Bd. ft.
April 2002 59
Page 77

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
APPROXIMATE WEIGHTS OF COMMODITIES AND MATERIALS
Lb. Per No. of
Product Size Container Cu. Ft. Lb. Per
Rye .........................................................bushel ............................. -- 56 bushel
Salt-rock, Solid........................................................................................ 136 3670 cu. yard
Coarse ...................................................................................... 45 1215 cu. yard
Fine...........................................................................................50 1350 cu. yard
Barrel (avg.) ............................................................................... -- 280 barrel
Sand-
Fine, Dry .......................................................................................... 110 2970 cu. yard
Wet .........................................................................................125 3375 cu. yard
Coarse, Dry ............................................................................................95 2565 cu. yard
Wet .........................................................................................120 3240 cu. yard
Mixed ............................................................................................... 115 3100 cu. yard
Sandstone, Solid........................................................................................147 3970 cu. yard
Crushed .................................................................................... 86 2325 cu. yard
Shale, Solid........................................................................................172 4645 cu. yard
Crushed .................................................................................... 92 2485 cu. yard
Sheep, Live (avg.) ....................................... per head ........................... -- 125-150 head
Shingles-packed in bundles of 200-250. Size of bundle
..............................................(avg.) 24" x 20" x 10".................. -- 50 bundle
Snow, Moist-packed ............................................................................ 50 1350 cu. yard
Soft drinks, Half depth bottle box 24-6 to 8 oz. bottles
............................................. 12.25" x 18.75" x 8.5" ................. -- 39 box
Full depth bottle box 12-24 to 32 oz. bottles
............................................ 13.38" x 18.5" x 12.25" ................ -- 60 box
Sorghum syrup ................................................................................................. 86 11.5 gallon
Soybeans .........................................................bushel ............................. -- 60 bushel
Soybean oil .................................................................................................58 7.7 gallon
Spinach, Hamper............................................. bushel ............................. -- 20 bushel
Spruce
*
Squash .........................................................bushel ............................. -- 46 bushel
Starch ................................................................................................. 96 2590 cu. yard
Stone, Crushed (avg.) ........................................................................ 100 2700 cu. yard
Straw, Bale ............................................17" x 22" x 42"....................... -- 110 bale
Street sweepings ................................................................................................ 32 865 cu. yard
Sugar ............................................................................................... 100 2700 cu. yard
Sugar, Bag (100 lb. net) ........................................................................ -- 101 bag
Sugar cane syrup ...............................................................................................85 11.3 gallon
Sulphur ............................................................................................... 125 3375 cu. yard
Sulfuric acid, 87%.............................................................................................112 15 gallon
Sweet corn, Basket............................................... bushel ............................. -- 45 bushel
Sycamore
Basket............................................... bushel ............................. -- 27 basket
.................................................................................................28 2330 M. Bd. ft.
Rip-rap......................................................................................65 1755 cu. yard
Bale ............................................26" x 30" x 46"....................... -- 180 bale
Barrel (22 lb. empty) ............ 19.13" head, 30" stave ................ -- 345 barrel
Case .........................................24 - 5-lb. cartons ..................... -- 135 case
Case 60 - 2-lb. cartons............................................................... -- 135 case
Crate...........................................13" x 13" x 24"....................... -- 60 crate
*
.................................................................................................37 3080 M. Bd. ft.
*
Kiln dried lumber averages 10% to 15% lighter and green lumber 40% to 50% heavier than air dried. All weights
in table.
60 April 2002
Page 78

Weight Restrictions & Specifications
APPROXIMATE WEIGHTS OF COMMODITIES AND MATERIALS
Lb. Per No. of
Product Size Container Cu. Ft. Lb. Per
Tallow ................................................................................................. 60 1620 cu. yard
Tanks,
Acetylene 102 cu. ft. .......................................... empty ............................. -- 70 tank
...........................................................filled............................... -- 75 tank
310 cu. ft........................................... empty ............................. -- 200 tank
...........................................................filled............................... -- 220 tank
Oxygen 150 cu. ft. .......................................... empty ............................. -- 80 tank
...........................................................filled............................... -- 92 tank
300 cu. ft........................................... empty ............................. -- 133 tank
...........................................................filled............................... -- 153 tank
Tar .................................................................................................65 1755 cu. yard
Tile, Solid........................................................................................115 3100 cu. yard
Partition (construction) .............................................................. 40 1080 cu. yard
Tomatoes, Basket...............................................bushel ............................. -- 55 bushel
Lug box....................................7.25" x 14" x 17.5".................... -- 35 box
Crate.......................................10.5" x 11.25" x 24"................... -- 48 crate
Basket.......................................8.5" x 8.75" x 20"..................... -- 18 basket
Basket (paper) ....................... 4.25" x 8.5" x 16.25" .................. -- 9 basket
Basket (wood)......................... 5.5" x 7.25" x 16.5" ................... -- 10 basket
Turpentine .................................................................................................54 7.2 gallon
Turnips, Basket............................................... bushel ............................. -- 54 bushel
Vetch seed ......................................................... bushel ............................. -- 60 bushel
Vinegar .................................................................................................64 8.5 gallon
Walnuts, Bulk .................................................. bushel ............................. -- 50 bushel
Bag ................................................. 2 bushel ........................... -- 100 bag
Water, Fresh ........................................................................................63 8.4 gallon
Wheat, Bulk .................................................. bushel ............................. -- 60 bushel
Bag ................................................ 1.5 bushel .......................... -- 90 bag
Wool, Pressed ....................................................................................82 2215 cu. yard
April 2002 61
Page 79

NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
MODEL NPR GAS/W3500 GAS
GVWR 12,000 lb
WB 109 in, 132.5 in, 150 in, 176 in.
ENGINE GMPT 8-cylinder, V Block 4-cycle, OHV, water cooled, Sequential Port Fuel Injection
Model/Displacement GMPT-V8/350 CID (5.7 liters)
HP (Gross) 250 HP @ 4200 rpm
Torque (Gross) 330 lb-ft torque @ 2800 rpm
Equipment Sequential Port Fuel Injection (SFI), mass air flow meter, powertrain control module
(VCM), onboard diagnostics, oxygen sensors, catalytic convertor, map sensor, with
external oil cooler.
TRANSMISSION 4L80-E Hydra-Matic 4-speed automatic with lock-up converter and overdrive.
STEERING Integral power steering 20.9:1 ratio. Tilt and telescoping steering column.
FRONT AXLE Reverse Elliot "I" -beam rated at 6,830 lb.
Suspension Semi-elliptical steel alloy leaf springs with stabilizer bar and shock absorbers.
GAWR 4,700 lb
REAR AXLE Full floating single speed with hypoid gearing rated at 11,020 lb.
Suspension Semi-elliptical steel alloy leaf springs and shock absorbers.
GAWR 7,950 lb
WHEELS 16 x 6. 6 hole disc wheels, painted white.
TIRES 215/85R-16E (10 pr) tubeless steel belted radials, all season tread Front/Rear.
BRAKES Dual circuit vacuum assisted hydraulic service brakes with load sensing proportioning
valve in rear brake circuit and a metering valve between the master cylinder and 6-way
joint on the front brake lines. Disc front and self-adjust outboard mounted drum rear. The
parking brake is a mechanical, cable actuated, internal expanding drum type,
transmission mounted. Anti-lock brake system.
FUEL TANK 30 gal. rectangular steel fuel tank. Mounted between the frame rails with electric type fuel
pump (mounted in tank). Through the rail fuel fill.
FRAME Ladder type channel section straight frame rail 33.5 inches wide through the total length
of the frame. Yield strength 44,000 psi, section modulus 7.20 in3., RBM 316,800.
CAB All steel, low cab forward, BBC 68.0 in, 45
o
mechanical tilt with torsion assist.
Equipment Jersey knit covered high back driver's seat with two occupant passenger seat. Two-
way roof ventilator, dual cab-mounted exterior mirrors. Tilt and telescoping steering
column. Tinted glass.
ELECTRICAL 12 volt, negative ground, Delco maintenance free battery (located under cab), 600 CCA,
80 Amp alternator with integral regulator.
OPTIONS Air conditioning; AM/FM cassette stereo radio; spare wheel; 6" stainless steel mirrors.
Power windows and Door Locks.
NOTE: These selected specifications are subject to change without notice.
April 2002 1
Page 80

NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
MODEL NPR HD GAS/W4500 GAS
GVWR 14,050 lb
WB 109 in, 132.5 in, 150 in, 176 in.
ENGINE GMPT 8-cylinder, V Block 4-cycle, OHV, water cooled, Sequential Port Fuel Injection
Model/Displacement GMPT-V8/350 CID (5.7 liters)
HP (Gross) 250 HP @ 4200 rpm
Torque (Gross) 330 lb-ft torque @ 2800 rpm
Equipment Sequential Port Fuel Injection (SFI), mass air flow meter, powertrain control module
(VCM), onboard diagnostics, oxygen sensors, catalytic convertor, map sensor, with
external oil cooler.
TRANSMISSION 4L80-E Hydra-Matic 4-speed automatic with lock-up converter and overdrive.
STEERING Integral power steering 20.9:1 ratio. Tilt and telescoping steering column.
FRONT AXLE Reverse Elliot "I" -beam rated at 6,830 lb.
Suspension Semi-elliptical steel alloy leaf springs with stabilizer bar and shock absorbers.
GAWR 5,360 lb
REAR AXLE Full floating single speed with hypoid gearing rated at 11,020 lb.
Suspension Semi-elliptical steel alloy leaf springs and shock absorbers.
GAWR 9,880 lb
WHEELS 19.5 x 6.0 6 hole disc wheels, painted white.
TIRES 225/70R-19.5F (12 ply) tubeless steel belted radials, premium highway tread Front/Rear.
BRAKES Dual circuit vacuum assisted hydraulic service brakes with load sensing proportioning
valve in rear brake circuit and a metering valve between the master cylinder and 6-way
joint on the front brake lines. Disc front and self-adjust outboard mounted drum rear. The
parking brake is a mechanical, cable actuated, internal expanding drum type, transmission
mounted. Anti-lock brake system.
FUEL TANK 30 gal. rectangular steel fuel tank. Mounted between the frame rails with electric type fuel
pump (mounted in tank). Through the rail fuel fill.
FRAME Ladder type channel section straight frame rail 33.5 inches wide through the total length of
the frame. Yield strength 44,000 psi, section modulus 7.20 in3., RBM 316,800.
CAB All steel, low cab forward, BBC 68.0 in, 45
o
mechanical tilt with torsion assist.
Equipment Jersey knit covered high back driver's seat with two occupant passenger seat. Two-
way roof ventilator, dual cab-mounted exterior mirrors. Tilt and telescoping steering
column. Tinted glass.
ELECTRICAL 12 volt, negative ground, Delco maintenance free battery (located under cab), 600 CCA,
80 Amp alternator with integral regulator.
OPTIONS Air conditioning; AM/FM cassette stereo radio; spare wheel; 6" stainless steel mirrors.
Power windows and Door Locks.
NOTE: These selected specifications are subject to change without notice.
2 April 2002
Page 81

VEHICLE WEIGHTS, DIMENSIONS AND RATINGS
NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
Variable Chassis Dimensions:
Unit WB CA* CE* OAL AF
Inch 109.0 88.4 131.5 199.5 43.1
Inch 132.5 111.9 155.0 223.0 43.1
Inch 150.0 129.4 172.5 240.5 43.1
Inch 176.0 155.4 198.5 266.3 43.1
* Effective CA & CE are CA or CE less BOC.
Dimension Constants: 12,000 GVW
Code Inches Code Inches
AH 7.9 BW 83.3
AW 65.6 CW 65.0
BA 47.4 FW 33.5
BBC 68.0 OH 87.4
BOC 9.25 OW 78.5
FH 32.0*
12,000 lb GVWR with 4L80-E Hydra-Matic Transmission
Model Federal
Chassis Cab and Maximum Payload Weights
Model WB Unit Front Rear Total Payload
BB1 109.0 in lb 3,160 1,799 4,959 7,041
BB2 132.5 in lb 3,204 1,821 5,025 6,975
BB3 150.0 in lb 3,226 1,843 5,069 6,931
BB4 176.0 in lb 3,270 1,865 5,135 6,865
Dimension Constants: 14,050 GVW
Code Inches Code Inches
AH 8.6 BW 84.0
AW 65.6 CW 65.0
BA 47.4 FW 33.5
BBC 68.0 OH 88.1
BOC 9.25 OW 78.5
FH 32.8
14,050 lb GVWR with 4L80-E Hydra-Matic Transmission
Model California/Federal
Chassis Cab and Maximum Payload Weights
Model WB Unit Front Rear Total Payload
CE1 109.0 in lb 3,230 1,874 5,104 8,946
CE2 132.5 in lb 3,274 1,896 5,170 8,880
CE3 150.0 in lb 3,296 1,918 5,214 8,836
CE4 176.0 in lb 3,340 1,940 5,280 8,770
Vehicle Weight Limits:
GVWR
Designed maximum 12,000 lb 14,050 lb
GAWR, Front 4,700 lb 5,360 lb
GAWR, Rear 7,950 lb 9,880 lb
12,000 lb GVWR with 4L80-E Hydra-Matic Transmission
Model California
Chassis Cab and Maximum Payload Weights
Model WB Unit Front Rear Total Payload
AB1 109.0 in lb 3,160 1,799 4,959 7,041
AB2 132.5 in lb 3,204 1,821 5,025 6,975
AB3 150.0 in lb 3,226 1,843 5,069 6,931
AB4 176.0 in lb 3,270 1,865 5,135 6,865
April 2002 3
Technical Notes:
Chassis Curb Weight reflects standard equipment and
fuel, but no driver or payload.
Maximum Payload Weight is the allowed maximum for
equipment, body, payload and driver and is calculated
by subtracting chassis curb weight from the GVWR.
Page 82

NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
FRAME & CROSSMEMBER SPECIFICATIONS
Unit: Inch
CROSS MEMBER TYPE/LOCATION
Wheel Frame
Base Thick A B C-A/T D-A/T E F G
109 0.24 37.0 28.3 11.1 AA -- CC DD
52.0 26.0 33.0
132.5 0.24 37.0 28.3 11.1 AA BB CC DD
52.0 59.4 26.0 33.0
150.0 0.24 37.0 28.3 11.1 AA BB CC DD
52.0 59.4 26.0 33.0
176.0 0.24 37.0 28.3 11.1 AA BB CC DD
52.0 59.4 26.0 33.0
A/T=A/T=
Automatic TransmissionAutomatic Transmission
A/T=
Automatic Transmission
A/T=A/T=
Automatic TransmissionAutomatic Transmission
4 April 2002
Page 83

FRAME CHART
NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
WB FRAME FRAME
FL THICKNESS
109 186.0 0.24
132.5 209.6 0.24
150.0 227.4 0.24
176.0 253.4 0.24
Unit: Inch
April 2002 5
Page 84

NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
AUXILIARY VIEWS
7.1 9.8
9
8.1
UNIT: INCH
1
Rear View
Catalitic Converters
4
12.4
2
Rear View
Muffler
.39
7.3
3
Side Veiw
In Frame Tank
6
Rear View
ABS Controller
5
11.4
13.75
Rear View
Emission Canister
Rear View
In Frame Tank
6 April 2002
Page 85

BODY BUILDER WEIGHT INFORMATION CHART
NPR/NPR HD Series
Wheel Base
GVWR Axle 109 in 132.5 in 150 in 176 in
A/T A/T A/T A/T
12,000 Front 3153 3197 3219 3263 573
Rear 1742 1764 1786 1808 871
Total 4895 4961 5005 5071 1444
14,050 Front 3230 3274 3296 3340 705
Rear 1874 1896 1918 1940 1134
Total 5104 5170 5214 5280 1839
A/T =A/T =
A/T =
A/T =A/T =
CAB TILTCAB TILT
CAB TILT
CAB TILTCAB TILT
16.94"
(430.3mm)
NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
Unit: lb
Unsprung
Weight
Automatic TransmissionAutomatic Transmission
Automatic Transmission
Automatic TransmissionAutomatic Transmission
GRID SCALE: ONE SQUARE= 2" (50.8mm) X 2" (50.8mm)
28.0"
(711.1mm)
34.25"
(869.95mm)
CENTER OF GRAVITY
The center of gravity of the chassis-cab.
Unit: Inch
GVWR WB V H A/T
12,000 109 21.7 38.8
132.5 20.1 47.1
150 19.7 53.5
176 18.1 62.8
14,050 109 21.7 40.0
132.5 20.0 48.6
150 19.7 55.2
176 18.1 64.7
A/T = Automatic Transmission
60.24"
(1530.1mm)
2.76"
(70.1mm)
The center of gravity of the completed vehicle with a
full load should not exceed 54 inches above ground
level for the 12,000 lb GVWR, 58 inches above ground
level for the 14,050 lb GVWR, and must be located
horizontally between the centerlines of the front and
rear axles.
32.0 in32.0 in
32.0 in
32.0 in32.0 in
V = Vertical Center of Gravity
H = Horizontal Center of Gravity
Note: The maximum dimensions for a body installed on the NPR are 96 inches wide (outside) by 90 inches
high (inside). Any larger body applications must be approved by Isuzu Application Engineering. In the
West Coast call 1-562-699-0500; in the East Coast call 1-770-475-9195 extension 353.
April 2002 7
Page 86

NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
FRONT AXLE CHARTFRONT AXLE CHART
FRONT AXLE CHART
FRONT AXLE CHARTFRONT AXLE CHART
FORMULAS FOR CALCULATING HEIGHT DIMENSIONS
A = TIRE LOADED RADIUS - B
C = CENTERLINE OF AXLE TO TOP OF FRAME RAIL AT CURB POSITION
D = CENTERLINE OF AXLE TO TOP OF FRAME RAIL AT DESIGN LOAD
CH = C + TIRE UNLOADED RADIUS
DH = D + TIRE LOADED RADIUS
Unit: Inch
Tire Radius Tire Radius
Tire Radius
Tire Radius Tire Radius
TIRETIRE
TIRE
TIRETIRE
215/85R 16-E 11,050 lb 4,700 lb 7.7 6.4 13.0 12.5 27.3 26.6 65.6 15.2 14.1
225/70R 19.5 14,050 lb 5,360 lb 8.4 7.0 13.6 13.1 29 28.1 65.6 15.4 15
GVWRGVWR
GVWR
GVWRGVWR
GAWRGAWR
GAWR
GAWRGAWR
AA
A
AA
BB
B
BB
CC
C
CC
DD
D
DD
CHCH
CH
CHCH
DHDH
DH
DHDH
TRACKTRACK
TRACK
TRACKTRACK
UnloadUnload
Unload
UnloadUnload
LoadLoad
Load
LoadLoad
8 April 2002
Page 87

REAR AXLE CHARTREAR AXLE CHART
REAR AXLE CHART
REAR AXLE CHARTREAR AXLE CHART
2.50 MINIMUM2.50 MINIMUM
2.50 MINIMUM
2.50 MINIMUM2.50 MINIMUM
CLEARANCECLEARANCE
CLEARANCE
TIRE TIRE
TIRE
TIRE TIRE
SECTIONSECTION
SECTION
SECTIONSECTION
HWHW
HW
HWHW
KHKH
KH
KHKH
CLEARANCECLEARANCE
BETWEENBETWEEN
BETWEEN
BETWEENBETWEEN
BODY AND TIRESBODY AND TIRES
BODY AND TIRES
BODY AND TIRESBODY AND TIRES
KWKW
KW
KWKW
AA
A
AA
DWDW
DW
DWDW
CWCW
CW
CWCW
EWEW
EW
EWEW
HHHH
HH
HHHH
LWLW
LW
LWLW
WHEEL OFFSETWHEEL OFFSET
WHEEL OFFSET
WHEEL OFFSETWHEEL OFFSET
TIRE CLEARANCETIRE CLEARANCE
TIRE CLEARANCE
TIRE CLEARANCETIRE CLEARANCE
TIRE TIRE
TIRE
TIRE TIRE
RADIUSRADIUS
RADIUS
RADIUSRADIUS
TIRE TIRE
TIRE
TIRE TIRE
LOADEDLOADED
LOADED
LOADEDLOADED
RADIUS RADIUS
RADIUS
RADIUS RADIUS
B, C B, C
B, C
B, C B, C
AND DAND D
AND D
AND DAND D
CHCH
CH
CHCH
DHDH
DH
DHDH
Normal rear
axle center
line
NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
REAR BODYREAR BODY
REAR BODY
REAR BODYREAR BODY
EE
E
EE
DEFINITIONSDEFINITIONS
DEFINITIONS
DEFINITIONSDEFINITIONS
A CENTER LINE OF AXLE TO BOTTOM OF AXLE BOWL.
B CENTER LINE OF AXLE TO TOP OF FRAME RAIL AT
METAL TO METAL POSITION.
C CENTER LINE OF AXLE TO TOP OF FRAME RAIL AT CURB
POSITION.
D CENTER LINE OF AXLE TO TOP OF FRAME RAIL AT
DESIGN LOAD.
E REAR TIRE CLEARANCE:
MINIMUM CLEARANCE REQUIRED FOR TIRES AND
CHAIN MEASURED FROM THE TOP OF THE FRAME AT
THE VERTICAL CENTER LINE OF THE REAR AXLE,
WHEN REAR WHEELS ON ONE SIDE RIDE OVER A
HIGH SPOT.
CH REAR FRAME HEIGHT:
VERTICAL DISTANCE BETWEEN THE NORMAL TOP OF
FRAME RAIL AND THE GROUND-LINE THROUGH THE
CENTER LINE OF THE REAR AXLE AT CURB POSITION.
DH REAR FRAME HEIGHT:
VERTICAL DISTANCE BETWEEN THE NORMAL TOP OF
FRAME RAIL AND THE GROUND-LINE THROUGH THE
CENTER LINE OF THE REAR AXLE AT DESIGN LOAD.
DW MINIMUM DISTANCE BETWEEN THE INNER SURFACES
OF THE REAR TIRES.
EW MAXIMUM REAR WIDTH:
OVERALL WIDTH OF THE VEHICLE MEASURED AT THE
OUTER MOST SURFACE OF THE REAR TIRES.
HH REAR TIRE CLEARANCE:
MINIMUM CLEARANCE BETWEEN THE REAR AXLE AND
THE GROND-LINE.
HW DUAL TIRE SPACING:
DISTANCE BETWEEN THE CENTER LINES OF THE
TIRES IN A SET OF DUAL TIRES.
When all of rear wheels
ride over a high spot.
KH TIRE BOUNCE CLEARANCE:
MINIMUM DISTANCE REQUIRED FOR TIRE BOUNCE AS
MEASURED FROM THE CENTER LINE OF THE REAR
AXLE AND THE TOP OF THE REAR TIRE WHEN ONE
WHEEL RIDES OVER A HIGH SPOT.
CW TRACK DUAL REAR WHEEL VEHICLES:
DISTANCE BETWEEN THE CENTER LINES OF THE
DUAL WHEELS MEASURED AT THE GROUND-LINE.
TIRE SECTION
TIRE RADIUS
TIRE LOADED RADIUS
TIRE CLEARANCE
FORMULAS FOR CALCULATING REAR WIDTHFORMULAS FOR CALCULATING REAR WIDTH
FORMULAS FOR CALCULATING REAR WIDTH
FORMULAS FOR CALCULATING REAR WIDTHFORMULAS FOR CALCULATING REAR WIDTH AND HEIGHT DIMENSIONSAND HEIGHT DIMENSIONS
AND HEIGHT DIMENSIONS
AND HEIGHT DIMENSIONSAND HEIGHT DIMENSIONS
CW = TRACK
CH = TIRE LOADED RADIUS + C
DH = TIRE LOADED RADIUS + D
DW = TRACK + 2 TIRE SECTIONS - TIRE CLRARANCE
EW = TRACK + 2 TIRE SECTIONS + TIRE CLEARANCE
HH = TIRE LOADED RADIUS - A
JH = KH - B
KH = TIRE RADIUS + 3.00 INCHES
KW = DW - 5.00 INCHES
LW = 1.00 INCH MINIMUM CLEARANCE BETWEEN TIRES AND
NOTE:NOTE:
NOTE: TRACK AND OVERALL WIDTH MAY VARY
NOTE:NOTE:
SPRINGS
SEE TIRE CHART FOR VALUES
}
When rear wheels on one
side ride over a high spot.
WITH OPTIONAL EQUIPMENT.
TireTire
Tire
TireTire
GAWRGAWR
GAWR
GAWRGAWR
TrackTrack
Track
TrackTrack
CWCW
CW
CWCW
AA
A
AA
BB
B
BB
CC
C
CC
DD
D
DD
EE
E
EE
Unit: Inch
215/85R16-E 7950/8760 65.0 6.5 10.6 14.9 13.3 7.8
225/70R 19.5 9880 65 11.6 10.6 14.9 13.0 8.4
April 2002 9
Page 88

NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
SUSPENSION DEFLECTION CHARTS FOR NPR GASSUSPENSION DEFLECTION CHARTS FOR NPR GAS
SUSPENSION DEFLECTION CHARTS FOR NPR GAS
SUSPENSION DEFLECTION CHARTS FOR NPR GASSUSPENSION DEFLECTION CHARTS FOR NPR GAS
FRONT LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTIONFRONT LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTION
FRONT LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTION
FRONT LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTIONFRONT LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTION
(PER AXLE)(PER AXLE)
(PER AXLE)
(PER AXLE)(PER AXLE)
S
U
S
P
E (lbs)
N
10,000
S
I
O
N
5,000
L
O
A
D
K = 1,508 lb/in
12,000 GVW
S
U
S
P
E (lbs)
N
S
I
O
N
L
O
A
D
10,000
5,000
0
REAR LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTIONREAR LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTION
REAR LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTION
REAR LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTIONREAR LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTION
(PER AXLE)(PER AXLE)
(PER AXLE)
(PER AXLE)(PER AXLE)
1
VERTICAL SPRING DEFLECTION
K = 5,204 lb/in
12,000 GVW
K = 1,664 lb/in
12,000 GVW
2
34
(INCHES)
5
0
10 April 2002
1
VERTICAL SPRING DEFLECTION
2
34
(INCHES)
5
Page 89

NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
SUSPENSION DEFLECTION CHARTS FOR NPR HD GASSUSPENSION DEFLECTION CHARTS FOR NPR HD GAS
SUSPENSION DEFLECTION CHARTS FOR NPR HD GAS
SUSPENSION DEFLECTION CHARTS FOR NPR HD GASSUSPENSION DEFLECTION CHARTS FOR NPR HD GAS
FRONT LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTIONFRONT LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTION
FRONT LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTION
FRONT LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTIONFRONT LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTION
(PER AXLE)(PER AXLE)
(PER AXLE)
(PER AXLE)(PER AXLE)
S
U
S
P
E (lbs)
10,000
N
S
I
O
N
5,000
L
O
A
D
K = 1,843 lb/in
14,050 GVW
S
U
S
P
E (lbs)
N
S
I
O
N
L
O
A
D
10,000
5,000
0
REAR LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTIONREAR LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTION
REAR LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTION
REAR LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTIONREAR LEAF SPRING LOAD VS. DEFLECTION
(PER AXLE)(PER AXLE)
(PER AXLE)
(PER AXLE)(PER AXLE)
1
VERTICAL SPRING DEFLECTION
K = 6,935 lb/in
14,050 GVW
K = 1,921 lb/in
14,050 GVW
2
34
(INCHES)
5
0
April 2002 11
1
VERTICAL SPRING DEFLECTION
2
(INCHES)
3
45
Page 90

NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
TIRE AND DISC WHEEL CHARTTIRE AND DISC WHEEL CHART
TIRE AND DISC WHEEL CHART
TIRE AND DISC WHEEL CHARTTIRE AND DISC WHEEL CHART
TIRETIRE
TIRE
TIRETIRE
SINGLE SINGLE
SINGLE
SINGLE SINGLE
TIRE SIZETIRE SIZE
TIRE SIZE
TIRE SIZETIRE SIZE
TIRE LOAD LIMIT AND TIRE LOAD LIMIT AND
TIRE LOAD LIMIT AND
TIRE LOAD LIMIT AND TIRE LOAD LIMIT AND
COLD INFLATION PRESSURESCOLD INFLATION PRESSURES
COLD INFLATION PRESSURES
COLD INFLATION PRESSURESCOLD INFLATION PRESSURES
DUAL DUAL
DUAL
DUAL DUAL
LBLB
LB
LBLB
PSIPSI
PSI
PSIPSI
LBLB
LB
LBLB
MAXIMUM MAXIMUM
MAXIMUM
MAXIMUM MAXIMUM
TIRE LOAD LIMITS TIRE LOAD LIMITS
TIRE LOAD LIMITS
TIRE LOAD LIMITS TIRE LOAD LIMITS
FRONTFRONT
FRONT
FRONTFRONT
PSIPSI
PSI
PSIPSI
2 SINGLE2 SINGLE
2 SINGLE
2 SINGLE2 SINGLE
REARREAR
REAR
REARREAR
4 DUAL4 DUAL
4 DUAL
4 DUAL4 DUAL
215/85R 16-E 2430 70 2210 70 4860 8840 12,000
225/70R 19.5 3315 85 3115 85 6630 12460 14,050
TIRE SIZETIRE SIZE
TIRE SIZE
TIRE SIZETIRE SIZE
GVWRGVWR
GVWR
GVWRGVWR
(lb)(lb)
(lb)
(lb)(lb)
TIRE RADIUS TIRE RADIUS
TIRE RADIUS
TIRE RADIUS TIRE RADIUS
LOADED LOADED
LOADED
LOADED LOADED
FRONTFRONT
FRONT
FRONTFRONT
REARREAR
REAR
REARREAR
UNLOADED UNLOADED
UNLOADED
UNLOADED UNLOADED
FRONTFRONT
FRONT
FRONTFRONT
REARREAR
REAR
REARREAR
TIRETIRE
TIRE
TIRETIRE
SECTIONSECTION
SECTION
SECTIONSECTION
WIDTHWIDTH
WIDTH
WIDTHWIDTH
TIRETIRE
TIRE
TIRETIRE
CLEAR-CLEAR-
CLEAR-
CLEAR-CLEAR-
ANCEANCE
ANCE
ANCEANCE
215/85R 16-E 12 ,000 14.05 14.05 15.21 15.21 8.54 1.46 6.0
225/70R 19.5 14,0 50 15.00 15. 20 15.4 0 15.80 8.8 1 .2 6.0
DISC WHEELDISC WHEEL
DISC WHEEL
DISC WHEELDISC WHEEL
WHEELWHEEL
WHEEL
WHEELWHEEL
SIZESIZE
SIZE
SIZESIZE
BOLTBOLT
BOLT
BOLTBOLT
HOLESHOLES
HOLES
HOLESHOLES
BOLTBOLT
BOLT
BOLTBOLT
CIRCLECIRCLE
CIRCLE
CIRCLECIRCLE
DIADIA
DIA
DIADIA
FT/RRFT/RR
FT/RR
FT/RRFT/RR
NUT SIZENUT SIZE
NUT SIZE
NUT SIZENUT SIZE
REARREAR
REAR
REARREAR
++
+
++
STUD SIZESTUD SIZE
STUD SIZE
STUD SIZESTUD SIZE
NUT/STUDNUT/STUD
NUT/STUD
NUT/STUDNUT/STUD
TORQUETORQUE
TORQUE
TORQUETORQUE
++
+
++
SPECSSPECS
SPECS
SPECSSPECS
INNERINNER
INNER
INNERINNER
CIRCLECIRCLE
CIRCLE
CIRCLECIRCLE
OUTSIDEOUTSIDE
OUTSIDE
OUTSIDEOUTSIDE
OFFSETOFFSET
OFFSET
OFFSETOFFSET
DISC DISC
DISC
DISC DISC
THK THK
THK
THK THK
GVWRGVWR
GVWR
GVWRGVWR
RIMRIM
RIM
RIMRIM
TYPETYPE
TYPE
TYPETYPE
(lb)(lb)
(lb)
(lb)(lb)
Unit: Inch
DESIGNDESIGN
DESIGN
DESIGNDESIGN
WIDTHWIDTH
WIDTH
WIDTHWIDTH
Unit: Inch
MATERIALMATERIAL
MATERIAL
MATERIALMATERIAL
RIMRIM
RIM
RIMRIM
MFG.MFG.
MFG.
MFG.MFG.
16x6.00K 6JIS 8.75 1.6142 0.8268 289 ft-lb 6.46 5.0 0.35 5o DC Steel
(41mm) (21mm) (392 N-M) TOPY
BUD HEX SQUARE
19.5x6.00 6JIS 8.75 1.6142 0.8268 325 ft-lb 6.46 5.0 0.39 5
o
DC Steel
(41mm) (21mm) (440 N-M) TOPY
BUD HEX SQUARE
+ O.D. Wrench Sizes
TIRE TIRE
TIRE
TIRE TIRE
SECTIONSECTION
SECTION
SECTIONSECTION
WIDTH WIDTH
WIDTH
WIDTH WIDTH
CC
C
CC
of DISC WHEELof DISC WHEEL
of DISC WHEEL
of DISC WHEELof DISC WHEEL
LL
L
LL
TIRE CLEARANCETIRE CLEARANCE
TIRE CLEARANCE
TIRE CLEARANCETIRE CLEARANCE
RIM OFFSET - REFER TO DISCRIM OFFSET - REFER TO DISC
RIM OFFSET - REFER TO DISC
RIM OFFSET - REFER TO DISCRIM OFFSET - REFER TO DISC
WHEEL SHOWN AT RIGHTWHEEL SHOWN AT RIGHT
WHEEL SHOWN AT RIGHT
WHEEL SHOWN AT RIGHTWHEEL SHOWN AT RIGHT
OFFSETOFFSET
OFFSET
OFFSETOFFSET
CC
C
CC
LL
L
LL
of DISC WHEELof DISC WHEEL
of DISC WHEEL
of DISC WHEELof DISC WHEEL
12 April 2002
Page 91

PROPELLER SHAFTPROPELLER SHAFT
PROPELLER SHAFT
PROPELLER SHAFTPROPELLER SHAFT
NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
WBWB
WB
WBWB
109 in
132.5 in
PLANE VIEW PLANE VIEW
PLANE VIEW
PLANE VIEW PLANE VIEW
BB
B
BB
AA
A
AA
AA
A
AA
SIDE VIEW SIDE VIEW
SIDE VIEW
SIDE VIEW SIDE VIEW
DD
D
DD
CC
C
BB
B
BB
BB
B
BB
CC
DD
D
DD
CC
C
CC
DD
D
DD
150 in
176 in
BB
B
BB
AA
A
AA
CC
DD
D
DD
CC
C
TYPICAL INSTALLATIONS SHOWING YOKES "IN PHASE". "IN PHASE" MEANS THAT THE YOKES AT
EITHER END OF A GIVEN PROPELLER SHAFT ASSEMBLY ARE IN THE SAME PLANE.
NPR EFINPR EFI
NPR EFI
NPR EFINPR EFI
(109 in WB) (132.5 in, 150 in and 176 in WB)
11
1
11
22
2
11
1
11
22
2
22
11
1
11
22
11
1
11
22
2
22
11
1
11
33
3
TRANSMISSIONTRANSMISSION
TRANSMISSION
TRANSMISSIONTRANSMISSION
AXLEAXLE
AXLE
AXLEAXLE
TRANSMISSIONTRANSMISSION
TRANSMISSION
TRANSMISSIONTRANSMISSION
33
AXLEAXLE
AXLE
AXLEAXLE
1. UNIVERSAL JOINT
2. PROPELLER SHAFT
3. CENTER CARRIER BEARING
PLANE VIEW PLANE VIEW
PLANE VIEW
PLANE VIEW PLANE VIEW
WHEEL BASEWHEEL BASE
WHEEL BASE
WHEEL BASEWHEEL BASE
109 in -- 3.5
132.5 in 2.1
150 in 0
176 in 0
AA
A
AA
A/TA/T
A/T
A/TA/T
BB
B
BB
A/TA/T
A/T
A/TA/T
o
o
o
o
0
2.7
1.8
o
o
o
NOTE: ALL DRIVELINE ANGLES ARE AT UNLOADED CONDITION (AT CURB POSITION WITH TYPICAL
CARGO BODY).
April 2002 13
SIDE VIEW SIDE VIEW
SIDE VIEW
SIDE VIEW SIDE VIEW
CC
C
CC
A/TA/T
A/T
A/TA/T
-- 6.4
o
1.5
o
0.7
o
4.0
A/T =A/T =
A/T =
Automatic TransmissionAutomatic Transmission
Automatic Transmission
A/T =A/T =
Automatic TransmissionAutomatic Transmission
DD
D
DD
A/TA/T
A/T
A/TA/T
2.4
5.3
6.0
o
o
o
o
Page 92

NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
PROPELLER SHAFT (CONTINUED)PROPELLER SHAFT (CONTINUED)
PROPELLER SHAFT (CONTINUED)
PROPELLER SHAFT (CONTINUED)PROPELLER SHAFT (CONTINUED)
WBWB
WB
WBWB
No. of ShaftsNo. of Shafts
No. of Shafts 1222
No. of ShaftsNo. of Shafts
Trans. TypeTrans. Type
Trans. Type
Trans. TypeTrans. Type
Shaft #1 O.D.Shaft #1 O.D.
Shaft #1 O.D. 3.0 3.0
Shaft #1 O.D.Shaft #1 O.D.
ThicknessThickness
Thickness 0.083
ThicknessThickness
LengthLength
Length 34.05 24.10 41.85 52.1
LengthLength
TypeType
Type ABBB
TypeType
Shaft #2 O.D.Shaft #2 O.D.
Shaft #2 O.D. 3.0 3.5
Shaft #2 O.D.Shaft #2 O.D.
ThicknessThickness
Thickness 0.083
ThicknessThickness
LengthLength
Length N/A 33.46 33.46 49.2
LengthLength
TypeType
Type N/A C C C
TypeType
109109
109
109109
A/TA/T
A/T
A/TA/T
132.5132.5
132.5
132.5132.5
A/TA/T
A/T
A/TA/T
150150
150
150150
A/TA/T
A/T
A/TA/T
UNIT: INCH
176176
176
176176
A/TA/T
A/T
A/TA/T
Figure 1.2 NPR/W-SERIES GAS Propshaft Dimensions
TypeType
Type
TypeType
AA
Type
A 1st shaft in 1 piece driveline.
AA
BB
Type
B 1st shaft in 2 piece driveline.
BB
CC
Type
C 2nd shaft in 2 piece driveline.
CC
DescriptionDescription
Description
DescriptionDescription
IllustrationIllustration
Illustration
IllustrationIllustration
Length
Length
Length
14 April 2002
Page 93

BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGRAMBRAKE SYSTEM DIAGRAM
BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGRAM
BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGRAMBRAKE SYSTEM DIAGRAM
Vacuum Over HydraulicVacuum Over Hydraulic
Vacuum Over Hydraulic
Vacuum Over HydraulicVacuum Over Hydraulic
NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
PLEASE REFER TO INTRODUCTION SECTION OF BOOK FOR ANTI-LOCK
SYSTEM CAUTIONS AND WHEEL BASE MODIFICATION REQUIREMENTS
NPR/W3500 GAS 12,000 GVW
NPR HD/W4500 GAS 14,500 GVW
April 2002 15
Page 94

NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
THROUGH THE RAIL FUEL FILL
Installation instructions:
Disconnect battery .
Loosen hose from the tie downs.
Remove shipping plate from chassis.
Extend hose out from the driver side of the rail to body rail.
The filler neck must be mounted to allow the fill plate
bracket to be parallel to the frame horizontal (see figure 1).
Filler hose is set for 96 inches outside width body .
Filler neck (Dimension A) must be between 6.85 inches
and 8.5 inches above frame.
Secure the filler plate to the bottom of the body and check
for leaks.
Ensure that fill hose does not sag, creating an area where
the fuel could pool in the fill hose.
Reconnect battery .
16 April 2002
Page 95

NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
Rear View Fuel Fill
Dimension A = 6.85 - 8.5 inches (174-216mm)
Top View Fuel Fill
Dimensions:
B = 28.85 inches (733mm)
C = 34.00 inches (863mm)
D = 39.29 inches (998mm)
E = 46.61 inches (1 184mm)
F = 96.00 inches (2438mm)
April 2002 17
Page 96

NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
Top View
Body Width Adjustment:
90 inch Body Dim E = 682.8mm
86 inch Body Dim E = 632.0mm
80 inch Body Dim E = 555.8mm
Through the Rail
Fuel Fill
Frame Hole
18 April 2002
Page 97

NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Gas
No.
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
Description
FEDERAL P ARTS
HOSE, FUEL FILLER
HOSE , BREATHER
CLIP, RUBBER HOSE
CLIP, FILLER HOSE
CALIFORNIA P ARTS
HOSE, FUEL FILLER
HOSE , BREATHER
CLIP, RUBBER HOSE
CLIP, FILLER HOSE
Part Number
ISUZU
897213-6540
897214-2710
897177-5810
802465-8140
897213-6540
897229-9180
815699-8250
802465-8140
Part Number
GM
897213-6540
897214-2710
897177-5810
802465-8140
897213-6540
897229-9180
815699-8250
802465-8140
Qty.
1
1
2
2
1
1
2
2
April 2002 19
Page 98

NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Diesel
MODEL NPR Diesel/W3500 NPR HD Diesel/W4500
GVWR 12,000 lb 14,500 lb
WB 109 in, 132.5 in, 150 in, 176 in
ENGINE Isuzu 4-cylinder, in-line 4-cycle, turbocharged, intercooled, direct injection diesel.
Model/Displacement 4HE1-TC/290 CID (4.75 liters)
HP (Gross) 142 HP/2800 RPM (Manual Transmission) 175 HP/2700 RPM (Automatic Transmission)
Torque (Gross) 275 lb ft torque/1300 RPM 347 lb ft torque/2000 RPM
Equipment Dry element air cleaner with vertical intake; 2 rows 506 in
diameter fan with viscous drive. Cold weather starting device and an oil cooler.
CLUTCH Single, dry plate, 11.8 in dia, actuated by self adjusting hydraulic master/slave cylinder.
* TRANSMISSION MXA5C 5-speed manual, all forward gears synchronized. Fifth gear is direct. Available
Optional Transmission: Aisin 450-43 LE 4-speed overdrive automatic transmission with
lock-up capability in 2nd, 3rd and 4th and PTO capability.
STEERING Integral power steering 20.9:1 ratio. Tilt and telescoping steering column.
FRONT AXLE Reverse Elliot "I" -Beam rated at 6,830 lb.
Suspension Semi-elliptical steel alloy leaf springs with stabilizer bar and shock absorbers.
GAWR 4,700 lb 5,360 lb
2
radiator; 6 blade 18.7 in
REAR AXLE Full floating single speed with hypoid gearing rated at 11,020 lb.
Suspension Semi-elliptical steel alloy leaf springs and shock absorbers.
GAWR 7,950 lb 9,880 lb
WHEELS 16x6.0 6 hole disc wheels, painted white.
TIRES 215/85R-16E (10 pr) tubeless steel belted radials, all season front and rear.
BRAKES Dual circui t vac u um ass ist ed hyd rau li c servic e brake s with lo ad sensing proportioning
valve in rear brake circuit and a metering valve between the master cyl ind er and 6- way
join t on the fron t b r a ke lines. D i s c f ro n t a nd sel f -adju s t outbo a r d m ounted drum re a r.
The parking brake is a mechanical, cable actuated, internal expanding drum type,
transmission mounted. The exhaust brake is standard and is vacuum operated. Antilock brake system.
FUEL TANK 30 gal. rectangular steel fuel tank mounted in frame rail behind rear axle. Fuel water
seperator mounted on rail.
FRAME Ladder type channel section straight frame rail 33.5 in wide through the total length of the
frame. Yield strength 44,000 psi section modulus 7.20 in3. RBM 316,800.
CAB All steel low cab forward, BBC 68.0 in, 45o mechanical tilt with torsion assist.
Equipment Jersey knit covered high back driver's seat with two occupant passenger seat. Two way
roof ventilator, dual cab mounted exterior mirrors. Tilt and telescoping steering column.
Tinted glass.
ELECTRICAL 12 Volt, negative ground, dual Delco maintenance free batteries, 750 CCA each, 110 Amp
alternator with integral regulator.
OPTIONS Air Conditioning; AM/FM cassette stereo radio; PTO; engine block heater; engine oil
pan heater; Fuel Tank mounted on right hand rail (33 gal); spare wheel; 6" stainless steel
convex mirrors. Power windows and door locks.
NOTE: These selected specifications are subject to change without notice.
*All Transmissions have a PTO gear in all wheelbases.
April 2002 1
Page 99

NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Diesel
VEHICLE WEIGHTS, DIMENSIONS AND RATINGS
Variable Chassis Dimensions:
Unit WB CA* CE* OAL AF
Inch 109.0 88.4 131.5 199.5 43.1
Inch 132.5 111.9 155.0 223.0 43.1
Inch 150.0 129.4 172.5 240.5 43.1
Inch 176.0 155.4 198.5 266.3 43.1
* Effective CA & CE are CA or CE less BOC.
Dimension Constants:
Code Inches Code Inches
AH 7.9 BW 83.3
AW 65.6 CW 65.0
BA 47.4 FW 33.5
BBC 68.0 OH 87.4
BOC 9.25 OW 78.5
FH 32.0
In-Frame Tank
12,000 lb GVWR Manual Transmission Model
Chassis Curb and Maximum Payload Weights
Model WB Unit Front Rear Total Payload
NA1 109.0 in lb 3472 1885 5357 6643
NA2 132.5 in lb 3516 1907 5423 6577
NA3 150.0 in lb 3560 1929 5489 6511
NA4 176.0 in lb 3605 1951 5556 6444
In-Frame Tank
14,500 lb GVWR Manual Transmission Model
Chassis Curb and Maximum Payload Weights
Model WB Unit Front Rear Total Payload
NE1 109.0 in lb 3483 1885 5368 9132
NE2 132.5 in lb 3527 1907 5434 9066
NE3 150.0 in lb 3571 1929 5500 9000
NE4 176.0 in lb 3616 1951 5567 8933
In-Frame Tank
12,000 lb GVWR Automatic Transmission Model
Chassis Curb and Maximum Payload Weights
Model WB Unit Front Rear Total Payload
NB1 109.0 in lb 3538 1929 5467 6533
NB2 132.5 in lb 3582 1951 5533 6467
NB3 150.0 in lb 3627 1973 5600 6400
NB4 176.0 in lb 3671 1995 5666 6334
In-Frame Tank
14,500 lb GVWR Automatic Transmission Model
Chassis Curb and Maximum Payload Weights
Model WB Unit Front Rear Total Payload
NF1 109.0 in lb 3549 1929 5478 9022
NF2 132.5 in lb 3593 1951 5544 8956
NF3 150.0 in lb 3638 1973 5611 8889
NF4 176.0 in lb 3682 1995 5677 8823
Side Mounted Tank
12,000 lb GVWR Manual Transmission Model
Chassis Curb and Maximum Payload Weights
Model WB Unit Front Rear Total Payload
NA1 109.0 in lb 3660 1620 5280 6720
NA2 132.5 in lb 3704 1642 5346 6654
NA3 150.0 in lb 3748 1664 5412 6588
NA4 176.0 in lb 3792 1687 5479 6521
Side Mounted Tank
14,500 lb GVWR Manual Transmission Model
Chassis Curb and Maximum Payload Weights
Model WB Unit Front Rear Total Payload
NE1 109.0 in lb 3671 1620 5291 9209
NE2 132.5 in lb 3715 1642 5357 9143
NE3 150.0 in lb 3759 1664 5423 9077
NE4 176.0 in lb 3803 1687 5490 9010
Side Mounted Tank
12,000 lb GVWR Automatic Transmission Model
Chassis Curb and Maximum Payload Weights
Model WB Unit Front Rear Total Payload
NB1 109.0 in lb 3726 1664 5390 6610
NB2 132.5 in lb 3770 1687 5457 6543
NB3 150.0 in lb 3814 1709 5523 6477
NB4 176.0 in lb 3858 1731 5589 6411
Side Mounted Tank
14,500 lb GVWR Automatic Transmission Model
Chassis Curb and Maximum Payload Weights
Model WB Unit Front Rear Total Payload
NF1 109.0 in lb 3737 1664 5401 9099
NF2 132.5 in lb 3781 1687 5468 9032
NF3 150.0 in lb 3825 1709 5534 8966
NF4 176.0 in lb 3869 1731 5600 8900
Vehicle Weight Limits:
GVWR
Designed maximum 12,000 lb 14,500 lb
GAWR, Front 4,700 lb 5,360 lb
GAWR, Rear 7,950 lb 9,880 lb
Technical Notes:
Chassis Curb Weight reflects standard equipment and
fuel, but no driver or payload.
Maximum Payload Weight is the allowed maximum for
equipment, body, payload and driver and is calculated by
subtracting chassis curb weight from the GVWR.
2 April 2002
Page 100

FRAME & CROSSMEMBER SPECIFICATIONSFRAME & CROSSMEMBER SPECIFICATIONS
FRAME & CROSSMEMBER SPECIFICATIONS
FRAME & CROSSMEMBER SPECIFICATIONSFRAME & CROSSMEMBER SPECIFICATIONS
NPR NPR HD/W3500 W4500 Diesel
Unit: Inch
Unit: Inch
CROSS MEMBER TYPE/LOCATION CROSS MEMBER TYPE/LOCATION
CROSS MEMBER TYPE/LOCATION
CROSS MEMBER TYPE/LOCATION CROSS MEMBER TYPE/LOCATION
WheelWheel
Wheel
WheelWheel
BaseBase
Base
BaseBase
109 0.24 37.0 28.3 8.4 8.4 AA AA -- CC DD
132.5 0.24 37.0 28.3 8.4 8.4 AA AA BB CC DD
150.0 0.24 37.0 28.3 8.4 8.4 AA AA BB CC DD
176.0 .024 37.0 28.3 8.4 8.4 AA AA BB CC DD
April 2002 3
FrameFrame
Frame
FrameFrame
ThickThick
Thick
ThickThick
AA
A
AA
BB
C-M/TC-M/T
B
C-M/T
BB
C-M/TC-M/T
C-A/TC-A/T
C-A/T
C-A/TC-A/T
D-M/TD-M/T
D-M/T
D-M/TD-M/T
40.5 44.7 26.0 33.0
40.5 44.7 59.4 26.0 33.0
40.5 44.7 59.4 26.0 33.0
40.5 44.7 59.4 26.0 33.0
D-A/TD-A/T
D-A/T
D-A/TD-A/T
EE
E
EE
FF
F
FF
M/T=M/T=
Manual TransmissionManual Transmission
M/T=
Manual Transmission
M/T=M/T=
Manual TransmissionManual Transmission
A/T=A/T=
Automatic TransmissionAutomatic Transmission
A/T=
Automatic Transmission
A/T=A/T=
Automatic TransmissionAutomatic Transmission
GG
G
GG
 Loading...
Loading...