Page 1
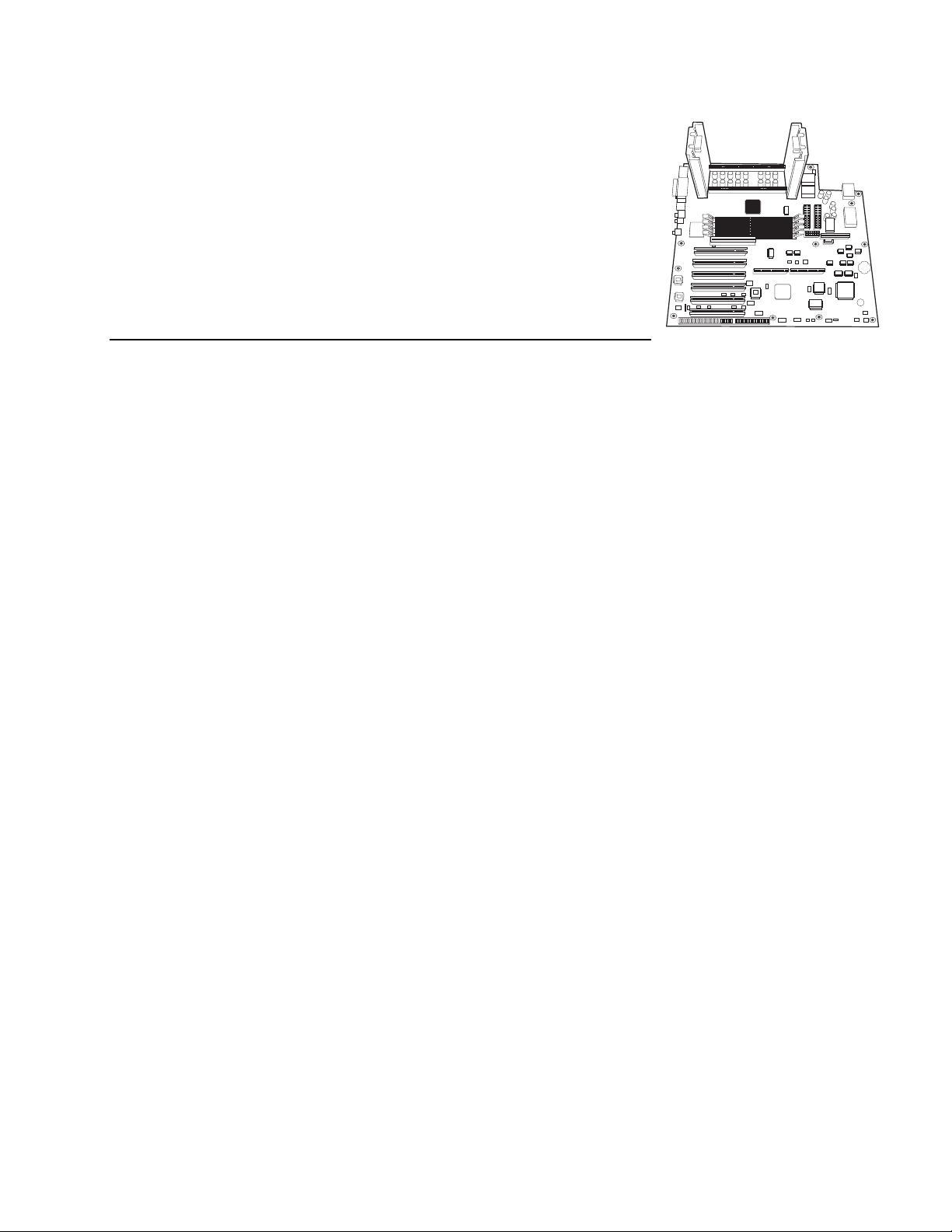
MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Order Number: 713653-001
Page 2

Revision History
Revision Revision History Date
-001 Initial release of the MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide. May 1998
Disclaimer
Intel Corporation (Intel) makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including, but not limited to, the implied
warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Intel assumes no responsibility for any errors that may
appear in this document. Intel makes no commitment to update nor to keep current the information contained in this
document. No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means without prior written
consent of Intel.
An Intel product, when used in accordance with its associated documentation, is "Year 2000 Capable" when, upon
installation, it accurately stores, displays, processes, provides, and/or receives date data from, into, and between the
twentieth and twenty-first centuries, including leap year calculations, provided that all other technology used in combination
with said product properly exchanges date data with it.
Copies of documents which have an ordering number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be
obtained from:
Intel Corporation
P.O. Box 5937
Denver, CO 80217-9808
or call in North America 1-800-548-4725, Europe 44-0-1793-431-155, France 44-0-1793-421-777,
Germany 44-0-1793-421-333, other Countries 708-296-9333.
†
Brands, names, or trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Copyright 1998, Intel Corporation.
Page 3

Contents
Acronyms
......................................................................................................................... 9
1 Motherboard Features
Summary of Features..........................................................................................................12
Board Layout.......................................................................................................................13
Motherboard Part-Function Table........................................................................................14
Microprocessor....................................................................................................................15
Processor Packaging ..........................................................................................................15
Second Level Cache...........................................................................................................15
Processor Options...............................................................................................................15
Form Factor.........................................................................................................................16
Chipset................................................................................................................................16
82443GX PCI/A.G.P. Controller (PAC) (H)..........................................................................17
®
82371EB Xcelerator (PIIX4E) (Q)..............................................................................18
Intel
®
Intel
82093AA I/O Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (IOAPIC).......................19
IDE Support.........................................................................................................................19
Real-Time Clock, CMOS RAM, and Battery........................................................................20
Diskette Drive Controller......................................................................................................20
Accelerated Graphics Port (A.G.P.) Support .......................................................................21
Memory...............................................................................................................................21
Input/Output (I/O) Controller (O)..........................................................................................22
82558 PCI LAN Controller (D).............................................................................................23
EtherExpress
Alert On LAN Component....................................................................................................24
Audio Subsystem ................................................................................................................24
Audio Drivers and Utilities ...................................................................................................25
Hardware Monitor Subsystem.............................................................................................25
Power Supply......................................................................................................................26
Power Supply Considerations..............................................................................................26
Expansion ...........................................................................................................................27
Basic Input/Output System (BIOS)......................................................................................27
BIOS Upgrades...................................................................................................................27
BIOS Flash Memory Organization..............................................................................28
Piezoelectric Speaker (N)....................................................................................................28
PRO/100 WfM PCI LAN Subsystem...........................................................23
™
2 Installation and Removal Procedures
Safety Considerations.........................................................................................................30
How to Install the DRM Fans and Processor Retention Mechanism....................................30
Materials Required......................................................................................................31
How to Install a Single Processor........................................................................................37
How to Install a Second Processor......................................................................................38
How to Remove and Install the Motherboard.......................................................................40
How to Set Processor Speed ..............................................................................................41
Jumper Settings..................................................................................................................42
iii
Page 4

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
How to Remove a Processor...............................................................................................43
How to Upgrade a Processor ..............................................................................................44
How to Install the Termination Card ....................................................................................45
How to Remove the Termination Card ................................................................................46
How to Install Memory.........................................................................................................47
How to Remove Memory.....................................................................................................48
How to Replace the CR2032 Lithium Battery (M)................................................................49
How to Clear Passwords.....................................................................................................51
3 Using the BIOS Setup Program
Setup Program Modes ........................................................................................................54
Modes.................................................................................................................................54
Mode Control.......................................................................................................................54
Setup Program Menus ........................................................................................................55
Menu Functionality..............................................................................................................56
Menu Function Keys............................................................................................................56
Maintenance Menu..............................................................................................................57
Main Menu ..........................................................................................................................57
Advanced Menu ..................................................................................................................58
Peripheral Configuration Submenu......................................................................................59
IDE Configuration Submenus..............................................................................................60
Floppy Options Submenu....................................................................................................61
DMI Event Logging Submenu..............................................................................................62
Video Configuration Submenu.............................................................................................62
Security Menu.....................................................................................................................63
Power Menu........................................................................................................................63
Boot Menu...........................................................................................................................64
Boot Options .......................................................................................................................65
Hard Drive Submenu...........................................................................................................65
Removable Devices Submenu ............................................................................................66
Exit Menu............................................................................................................................66
4 Using the BIOS Features
How to Prepare for the Upgrade..........................................................................................68
Obtaining the BIOS Upgrade File........................................................................................68
Recording the Current BIOS Settings..................................................................................68
Creating a Bootable Floppy Disk.........................................................................................69
Creating the BIOS Upgrade Floppy Disk.............................................................................69
Upgrading the BIOS............................................................................................................70
Recovering the BIOS...........................................................................................................71
Changing the BIOS Language.............................................................................................72
Plug and Play: PCI Autoconfiguration.................................................................................72
ISA Plug and Play ...............................................................................................................73
ISA Legacy Devices............................................................................................................73
PCI IDE Support..................................................................................................................73
Desktop Management Interface (DMI).................................................................................74
Advanced Power Management (APM) ................................................................................74
iv
Page 5

Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)..........................................................75
System States and Power States ...............................................................................75
Wake Up Devices and Events ....................................................................................76
Plug and Play .............................................................................................................76
BIOS Support .............................................................................................................76
Language Support...............................................................................................................76
OEM Logo or Scan Area.....................................................................................................76
USB Legacy Support...........................................................................................................77
BIOS Security Features.......................................................................................................77
Recovering BIOS Data........................................................................................................78
5 Technical Reference
Front Panel Connectors (L).................................................................................................80
Speaker...............................................................................................................................81
Reset Switch.......................................................................................................................81
Power/Sleep LED................................................................................................................82
Hard Drive Activity LED.......................................................................................................82
Infrared Port........................................................................................................................82
Power Switch ......................................................................................................................82
Front Panel Pin Connector Mapping....................................................................................83
Back Panel Connectors (E).................................................................................................84
Keyboard and Mouse Interface ...........................................................................................85
Universal Serial Bus (USB) .................................................................................................85
Parallel Port.........................................................................................................................86
Serial Ports..........................................................................................................................86
I/O Shield....................................................................................................................88
Midboard Connectors..........................................................................................................89
Add-in Card Connectors......................................................................................................90
Audio Connectors................................................................................................................91
CD-ROM Audio ...................................................................................................................92
Telephony ...........................................................................................................................92
Fan Connectors...................................................................................................................93
Thermal Considerations ......................................................................................................94
Power Connectors...............................................................................................................96
Peripheral Interface Connectors..........................................................................................99
Security and Hardware Management Connectors.............................................................100
Chassis Intrusion Connectors............................................................................................102
Wake on LAN Technology Connector ...............................................................................102
Wake on Modem...............................................................................................................102
Memory Map.....................................................................................................................103
DMA Channels..................................................................................................................103
I/O Map.............................................................................................................................104
PCI Configuration Space Map...........................................................................................106
LAN Subsystem Software..................................................................................................107
Interrupts...........................................................................................................................107
PCI Interrupt Routing Map.................................................................................................108
Interrupt Routing Example.................................................................................................109
Contents
v
Page 6

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
A Error Messages
BIOS Beep Codes.............................................................................................................112
BIOS Error Messages .......................................................................................................113
Port 80h POST Codes.......................................................................................................115
B Regulatory and Integration Information
Regulatory Compliance.....................................................................................................122
Product Certification Markings...........................................................................................122
Installation Precautions .....................................................................................................122
Installation Instructions......................................................................................................123
C Environmental Specifications and Reliability Information
Environmental Specifications ............................................................................................126
Reliability Information........................................................................................................126
D Specifications and Customer Support
Online Support..................................................................................................................128
Specifications....................................................................................................................128
Figures
1. MS440GX Main Board Components...........................................................................13
2. MS440GX Custom ATX Form Factor .........................................................................16
3. Procedure Step 2: DRM Stand...................................................................................31
3a. Procedure Step 3: DRM Stand With Fans ..................................................................31
3b. Procedure Step 5: Fan Positioning/Air Flow ...............................................................32
3c. Procedure Step 6: DRM Base With Retention Clip .....................................................32
3d. Procedure Step 7: Fans and Fan Header in Chassis..................................................33
3e. Procedure Step 11a: Installing the DRM.....................................................................33
3f. Procedure Step 13: CPU/Heat Sinks-DRM Tops........................................................34
3g. Procedure Step 14: DRM Tops, Clips, Holes..............................................................34
3h. Procedure Step 16: Processors Installed in the DRM.................................................35
3i. Procedure Step 17: Final DRM-Fan Assembly ...........................................................36
4. Installing a Single Processor ......................................................................................37
5. Installing a Second Processor ....................................................................................39
6. Motherboard Mounting Screw Holes...........................................................................40
7. Configuration Jumper Block........................................................................................42
8. Removing a Processor ...............................................................................................43
9. Installing the Termination Card...................................................................................45
10. Removing the Termination Card.................................................................................46
11. Installing a DIMM........................................................................................................48
12. Replacing the Battery.................................................................................................50
13. Setup Program Menu Structure..................................................................................55
14. Front Panel Connectors..............................................................................................80
15. Back Panel Connectors..............................................................................................84
16. Back Panel I/O Shield Dimensions (ATX Chassis-Independent).................................88
17. Add-in Card Connectors.............................................................................................90
18. Audio Connectors.......................................................................................................91
19. Fan Connectors..........................................................................................................93
vi
Page 7

20. Thermally Sensitive Components...............................................................................94
21. Power Connectors......................................................................................................96
22. Peripheral Interface Connectors.................................................................................99
23. Security and Hardware Management Connectors ....................................................100
Tables
1. Motherboard Part-Function Table...............................................................................14
2. PCI/A.G.P. Controller Features ..................................................................................17
3. 82371EB Xcelerator Features ....................................................................................18
4. DIMM Sizes Supported...............................................................................................21
5. I/O Controller Components.........................................................................................22
6. LAN Controller Functions............................................................................................23
7. Audio Subsystem Resources......................................................................................25
8. Power Usage..............................................................................................................26
9. DC Voltage Tolerances and Estimated Current Requirements
(no PCI or A.G.P. shown)...........................................................................................26
10. Flash Memory Organization........................................................................................28
11. BIOS Setup Configuration Jumper Settings................................................................43
12. Setup Program Modes................................................................................................54
13. Jumper Settings .........................................................................................................54
14. Setup Menu Bar .........................................................................................................56
15. Setup Function Keys ..................................................................................................56
16. Maintenance Menu.....................................................................................................57
17. Main Menu..................................................................................................................57
18. Advanced Menu..........................................................................................................58
19. Peripheral Configuration Submenu.............................................................................59
20. IDE Configuration Submenus .....................................................................................60
21. Floppy Options Submenu...........................................................................................61
22. DMI Event Logging Submenu.....................................................................................62
23. Video Configuration Submenu....................................................................................62
24. Security Menu ............................................................................................................63
25. Power Menu...............................................................................................................63
26. Boot Menu..................................................................................................................64
27. Hard Drive Submenu..................................................................................................65
28. Removable Devices Submenu....................................................................................66
29. Exit Menu ...................................................................................................................66
30. Recommendations for Configuring an ATAPI Device..................................................73
31. Effects of Pressing the Power Switch.........................................................................75
32. Wake Up Devices and Events ....................................................................................76
33. Administrator and User Password Functions..............................................................78
34. Front Panel I/O Connectors........................................................................................81
35. Pin Connector Functionality........................................................................................83
36. PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse Connectors.............................................................................85
37. LAN Connector...........................................................................................................86
38. Audio Line In Connector.............................................................................................86
39. Audio Line Out Connector ..........................................................................................87
40. Audio Mic In Connector ..............................................................................................87
Contents
vii
Page 8

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
41. Connector Groups......................................................................................................89
42. ATAPI-Style Telephony Connector(J1E1)...................................................................92
43. ATAPI CD Audio Connector (J2E1)............................................................................92
44. External Speaker Connector (J12A1).........................................................................92
45. MIDI/Joystick Connector (J2E2).................................................................................92
46. Fan Connectors..........................................................................................................94
47. Thermal Considerations for Components ...................................................................95
48. 1x6 Power Connector.................................................................................................97
49. Primary and Secondary Power Supply Connectors (J10H1).......................................97
50. VRM Connector (J13J1).............................................................................................98
51. SCSI LED Connector (J10A1) ....................................................................................99
52. Front and Rear Chassis Intrusion Connectors..........................................................101
53. Wake on LAN Technology Connector (J11A2) .........................................................101
54. Wake-on-Modem Connector (J9A1).........................................................................101
55. Memory Map ............................................................................................................103
56. DMA Channels .........................................................................................................103
57. I/O Map ....................................................................................................................104
58. PCI Configuration Space Map ..................................................................................106
59. Interrupts..................................................................................................................107
60. PCI Device Classes..................................................................................................108
61. PCI Interrupt Routing Map........................................................................................108
62. Beep Codes..............................................................................................................112
63. BIOS Error Messages...............................................................................................113
64. Port 80h Codes ........................................................................................................115
65. Safety Regulations ...................................................................................................122
66. EMC Regulations......................................................................................................122
67. Environmental Specifications....................................................................................126
68. Compliance with Specifications ................................................................................128
viii
Page 9
Acronyms
Acro. Meaning Acro. Meaning Acro. Meaning Acro. Meaning
ACPI
ADPCM
A.G.P.
APM
BIOS
CMOS
CPU
CSMA/CD
DIMM
DMA
DMI
DRAM
DRM
Advanced
configuration
and power
interface
Adaptive
differential
pulse code
modulation
Accelerated
graphics port
Advanced
power
management
Basic input /
output system
Complementary metal
oxide
semiconductor
Central
processing
unit
Carrier sense
multiple
access with
collision
detection
Dual inline
memory
module
Direct memory
access
Desktop
Management
Interface
Dynamic
random
access
memory
Dual retention
mechanism
ECC
ECHS
ECP
EMC
EPP
ESCD
ESD
FIFO
IDE
I/O
IOAPIC
IPL
ISA
Error checking
and correcting
Extended
cylinder head
sector
Extended
capabilities
port
Electromagnetic
compatibility
Enhanced
parallel port
Extended
system
configuration
data
Electrostatic
DISCHARGE
First in, first
out
Integrated
dual channel
enhanced
Input / output
Input Output
Advanced
Programmable
Input
Controller
Initial program
load
Industry
standard
architecture
IRQ
LAN
LBA
LED
MHz
MIF
MIDI
MTBF
NIC
OEM
OS
PAC
PCI
Interrupt
request
Local area
network
Logical block
addressing
Light emitting
diode
Megahertz
Management
information
format
Musical
interface
digital
interface
Mean time
between
failures
Network
interface card
Original
equipment
manufacturer
Operating
System
PCI A.G.P.
c
ontroller
Peripheral
component
interconnect
POST
SCI
S.E.C.C.
SIR
SMI
SMM
SMP
SRAM
UHCI
USB
VID
VPD
WfM
Power-on self
test
Special
circumstance
instructions
Single edge
contact
cartridge
Surface
insulation
resistance
System
management
interrupt
System
management
mode
Symmetric
multiprocessing
Static random
access
memory
Universal host
controller
interface
Universal
serial bus
Voltage ID
Vital product
data
Wired for
management
9
Page 10

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
10
Page 11

1 Motherboard Features
The MS440GX is designed specifically for the DCC, MCAD, and EDA markets with a high
performance workstation.
This chapter describes the features of the MS440GX motherboard. The chapter covers the
following topics:
Topic Page
Summary of Features 12
Board Layout 13
Motherboard Part-Function Table 14
Microprocessor 15
Processor Packaging 15
Second Level Cache 15
Processor Options 15
Form Factor 16
Chipset 16
PCI/A.G.P. Controller 17
82371EB Xcelerator 18
I/O Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller 19
IDE Support 19
Real-Time Clock, CMOS SRAM, and Battery 20
Diskette Drive Controller 20
A.G.P. Support 21
Memory 21
I/O Controller 22
PCI LAN Controller 23
EtherExpress™ PRO/100 WfM PCI LAN Subsystem 23
Alert on LAN Component 24
Audio Subsystem 24
Audio Drivers and Utilities 25
Hardware Monitor Subsystem 25
Power Supply 26
Power Supply Considerations 26
Expansion 27
Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) 27
BIOS Upgrades 27
BIOS Flash Memory Organization 28
Piezoelectric Speaker 28
11
Page 12

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Summary of Features
The MS440GX motherboard features are summarized below.
Form factor Custom ATX (12 inches by 13 inches)
Processor(s) • Two Slot 2 connectors
®
• Support for one or two Pentium
• 100 MHz host bus speed
• Up to 1 MB of L2 cache support on each processor
Chipset
Memory • Four DIMM sockets
I/O Control • National Semiconductor PC97307 I/O controller
Peripheral Interfaces • Two serial ports
Video • One A.G.P. slot
Audio • Crystal Semiconductor CS4235 audio codec
LAN
Hardware Monitor • Microprocessor system hardware monitor (Analog Devices ADM9240 or
Expansion Capabilities • Five PCI slots
BIOS
Intel® 82440GX, consisting of:
• 82443GX PCI/A.G.P. controller (PAC)
• 82371EB PCI ISA IDE Xcelerator (PIIX4E)
• Support for up to 2 GB of 100 MHz SDRAM
• Support for ECC DIMMs only (see Table 4 and associated text)
• Two USB ports
• One parallel port
• Two IDE interfaces with Ultra DMA support
• One diskette drive interface
• Crystal Semiconductor CS9236 wavetable synthesizer
®
• Intel
• Wired for Management (WfM) compliant
• One shared slot for either a PCI or an ISA add-in card
• Intel
• Support for SMBIOS, ACPI, APM, and Plug and Play
82558 10/100 Mbps PCI LAN controller
equivalent)
®
E28F004BXT80 4 Mbit flash memory
II Xeon™ processors
12
Page 13
Motherboard Features
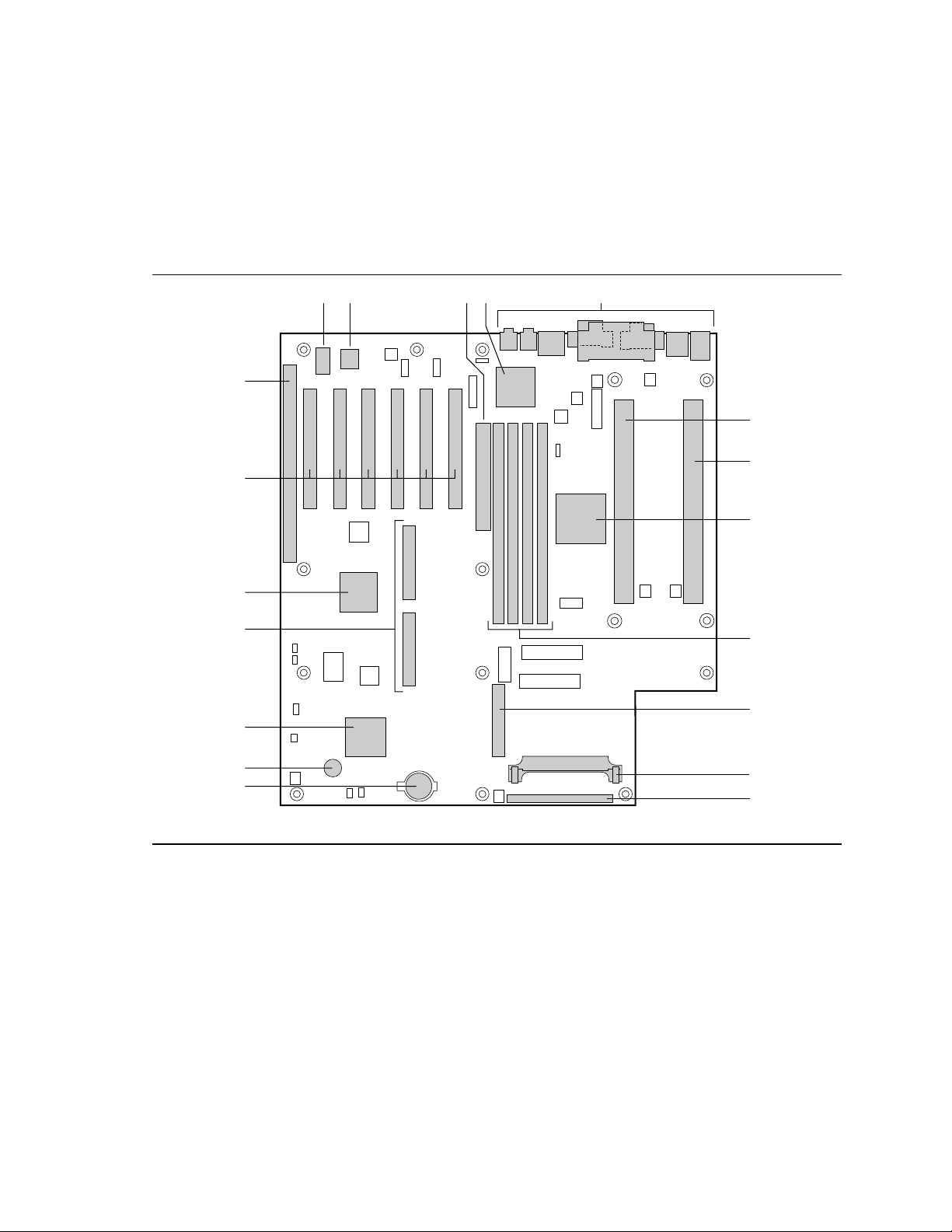
Board Layout
The illustration below is a picture of the MS440GX integrated motherboard. The main board
components are identified by alphabetical callouts.
This board supports the Slot 2 processor (DS2P) family. It is a custom ATX form factor (12”x13”)
board with an ATX I/O panel.
A B C D
S
R
Q
P
O
E
F
G
H
I
J
N
M
K
L
OM08377
Figure 1. MS440GX Main Board Components
13
Page 14
MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Motherboard Part-Function Table
This table identifies the motherboard components called out in Figure 1 and defines the functional
purpose of each.
Table 1. Motherboard Part-Function Table
Callout ID Part (Component) Function
A Intel E28F004BXT80 4 Mbit Flash
Memory
B Crystal Semiconductor CS4235 Audio
Codec
C A.G.P. Connector High performance graphics connector with
D Intel 82558 PCI LAN Controller On board LAN controller with support for
E Back Panel Connectors Keyboard, mouse, USB, parallel, serial, LAN and
F Slot 2 Connector for Boot Processor Connector for Pentium II Xeon processor
G Slot 2 Connector for Application
Processor
H
I DIMM Sockets Support for up to 2GB PC100 compliant SDRAM
J Diskette Drive Connector Supports one or two diskette drives
K VRM Connector Plug-in Voltage Regulator Module for application
L Front Panel Connectors Connectors for PC speaker, reset switch, power
M Battery Provides power to real-time clock and CMOS
N Piezoelectric Speaker Provides BIOS beep codes
O National Semiconductor PC97307 I/O
P IDE Connectors Each connector supports two IDE devices
Q 82371EB (PIIX4E) Provides USB and power management support
R PCI Bus Add-in Board Connectors Support for 33 MHz PCI devices
S ISA Bus Add-in Board Connector Support for ISA compatible add-in cards
Intel® 82443GX (PAC)
Controller
Flash upgradable. Stores BIOS, Setup program,
POST, APM, PCI auto configuration utility and
Plug and Play code
On board audio subsystem with integrated FM
synthesizer
support for 133 MHz data transfer rates (AGP2x)
10Base-T and 100Base-TX interfaces
audio connectors
Connector for Pentium II Xeon processor
AGPset provides bus-control signals, address
paths and data paths for transfers between the
processor’s host bus, PCI bus, the A.G.P. and
main memory
DIMMS
processor
LED, HDD LED, infrared port and power switch
memory
Provides serial and parallel ports, diskette drive,
mouse, keyboard and IR interfaces
in addition to EIDE and UDMA/33 data transfer
rates
14
Page 15

Motherboard Features
Microprocessor
The Intel® MS440GX motherboard supports one or two Pentium II Xeon 400 or 450 MHz
processors, 100 MHz host bus speeds, and L2 caches up to 1MB in size. The processor’s VID pins
automatically program the voltage regulator on the motherboard to the required processor voltage
for the Boot (P0) Processor only.
A plug-in VRM must be used when adding an Application (P1) Processor. If a plug-in VRM is not
used, then the L2 cache will be disabled.
Processor Packaging
Each processor is packaged in a single edge contact cartridge (S.E.C.C.). The cartridge includes
the processor core, second-level cache, thermal plate, and back cover.
The processor connects to the motherboard through the Slot 2 connector, a 330-pin edge connector.
When mounted in a Slot 2 connector, the processor is secured by a retention mechanism attached
to the motherboard.
Second Level Cache
The second-level cache is located on the substrate of the S.E.C.C.. The ECC cache includes
components totaling up to 1 MB in size. All onboard system memory is cacheable.
Processor Options
The following processor configuration options can be used:
• A single 400 MHz processor installed in the boot processor slot (P0) and a terminator card
installed in the application processor slot (P1). P0 is the Slot 2 connector closest to the middle
of the board. See Figure 1 callouts F and G.
• Dual 400 MHz processors. When using two processors, a voltage regulator module (VRM)
must be installed.
• A single 450 MHz processor installed in the boot processor slot (P0) and a terminator card
installed in the application processor slot (P1).
• Dual 450 MHz processors. When using two processors, a voltage regulator module (VRM)
must be installed. See Figure 21, callout D for the location of the VRM connector.
If you are installing two processors, then the following values must be identical for both:
• L2 cache size
• Operating voltages
• Processor speed
CAUTION
If the processor operating voltages for either VCC core or VCC L2 do not match, then the computer
will not boot.
Use configure mode to set the processor speed if necessary.
15
Page 16
MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Form Factor
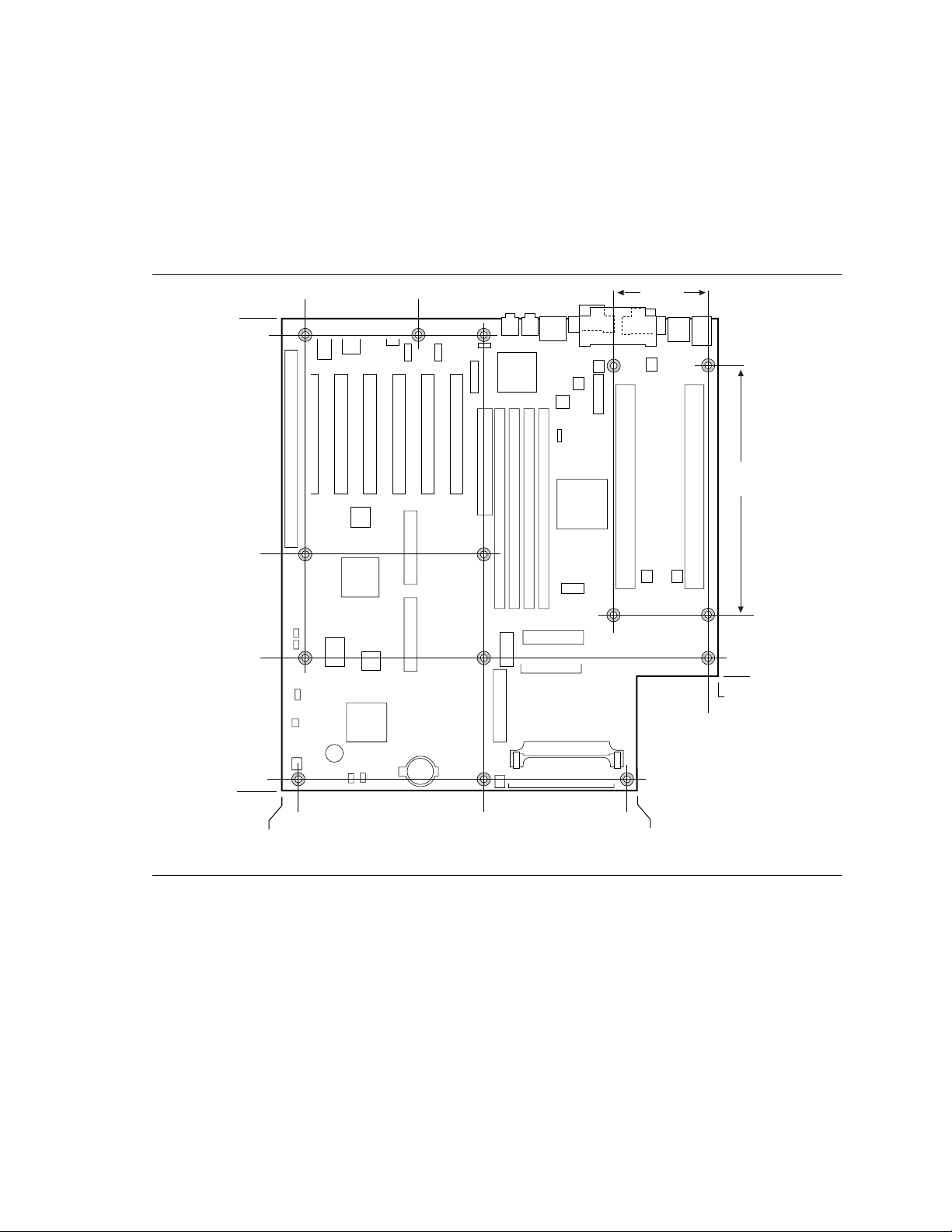
The motherboard is designed to fit into a custom ATX form factor chassis.
The illustration below shows the board mounting hole locations. The mounting holes closest to the
Slot 2 connectors are used for mounting the processor retention mechanism to the board and
chassis.
12.70
12.30
6.20
3.35
3.300.20
2.59
11.40
6.74
2.80
11.55
11.30
0.00
0.30
0.00
0.45
5.10
9.06
9.31
OM07109
Figure 2. MS440GX Custom ATX Form Factor
Chipset
The Intel® 440GX AGPset includes a Host-PCI bridge integrated with both an optimized DRAM
controller and an Accelerated Graphics Port (A.G.P.) interface.
The I/O subsystem of the 440GX is based on the PIIX4E which is a highly integrated PCI-ISA/IDE
Accelerator Bridge. This chipset consists of the Intel 82443GX PCI/A.G.P. controller (PAC) and
®
the Intel
16
82371EB PCI/ISA IDE Xcelerator (PIIX4E) bridge chip.
Page 17
Motherboard Features
82443GX PCI/A.G.P. Controller (PAC) (H)
The Intel 82443GX PCI/A.G.P. Controller (PAC) provides the following functions:
• Bus-control signals
• Address paths
• Data paths for transfers between the processor’s host bus, PCI bus, the A.G.P., and main
memory.
Table 2 lists the PAC features and the functionality each feature supports.
Table 2. PCI/A.G.P. Controller Features
Feature Functionality
Processor Interface Control Support for processor host bus frequencies of 100 MHz only
32-bit addressing
Desktop optimized GTL + compliant host bus interface
Integrated DRAM Controller +3.3V only DIMM DRAM configurations
Up to four double sided DIMMs
100 MHz PC100-compatible Synchronous DRAM
DIMM serial presence detect via SMBus interface
2-, 4-, 8-, 16-, 32-, 64-, and 128-Mbit DRAM devices
SDRAM 64-bit data interface with ECC support
Symmetrical and asymmetrical DRAM addressing
A.G.P. Interface Complies with the A.G.P. specification Rev. 1.0
Support for +3.3V A.G.P. 66/133 MHz devices
Synchronous coupling to the host-bus frequency
PCI Bus Interface Complies with the PCI specification Rev. 2.1
Asynchronous coupling to the host-bus frequency
PCI parity generation support
Data streaming support from PCI-to-DRAM
Support for six PCI bus masters in addition to the host PCI-to-ISA
I/O bridge
Support for concurrent host, A.G.P., and PCI transactions to main
memory
Data Buffering DRAM write buffer with read-around-write capability
Dedicated host-to-DRAM, PCI0-to-DRAM, and PCI1/A.G.P.-to-DRAM
read buffers
A.G.P. dedicated inbound/outbound FIFOs (AGP2X), used for
temporary data storage
Power Management Functions Support for system suspend/resume and power-on suspend
Compliant with ACPI power management
SMBus Support for Desktop
Management Functions
Support for System Management
Mode (SMM)
17
Page 18
MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Intel® 82371EB Xcelerator (PIIX4E) (Q)
The Intel® PIIX4E is a multifunction PCI device implementing the PCI-to-ISA bridge, PCI IDE
functionality, Universal Serial Bus (USB) host/hub function, and enhanced power management.
Table 3 lists the PIIX4E features and the functionality each feature supports.
Table 3. 82371EB Xcelerator Features
Feature Functionality
Multifunction PCI-to-ISA Bridge Support for the PCI bus at 33 MHz
Complies with the PCI specification
Full ISA bus support
USB Controller Two USB ports
Support for legacy keyboard and mouse
Support for UHCI Design Guide, revision 1.1, interface
Integrated Dual Channel Enhanced IDE
Interface
Enhanced DMA Controller Two 8237-based DMA controllers
Interrupt Controller Based on 82C59 Support for 15 interrupts
Power Management Logic Sleep/resume logic
Real-Time Clock 256-byte battery backed CMOS RAM
16-bit Counters/Timers Based on 82C54
Support for up to four IDE devices
PIO Mode 4 transfers at up to 16 MB/sec
Support for Ultra DMA/33 synchronous DMA mode
transfers up to 33 MB/sec
Bus master mode with an 8x32-bit buffer for bus master
PCI IDE burst transfers
Support for PCI DMA with three PC/PCI channels and
distributed DMA protocols
Fast type-F DMA for reduced PCI bus usage
Programmable for edge/level sensitivity
Support for Wake on Modem, Wake on LAN
technology, and Wake on PME
Support for ACPI
System wakes from ACPI sleep state with keyboard
activity
Includes date alarm
†
18
Page 19

Motherboard Features
Intel® 82093AA I/O Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (IOAPIC)
The Intel® 82093AA I/O Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (IOAPIC) provides
interrupt management and incorporates both static and dynamic symmetric interrupt distribution
across all processors in a multiprocessor system. The 82093AA IOAPIC features 24 interrupts as
follows:
• 13 ISA interrupts
• Four PCI interrupts
• One Interrupt/SMI# rerouting
• Two motherboard interrupts
• One interrupt used for INTR input
• Three general purpose interrupts
• SCI BIOS supported steering
IDE Support
The motherboard has two independent bus-mastering IDE interfaces. These interfaces support PIO
Mode 3, PIO Mode 4, ATAPI devices (e.g., CD-ROM), and Ultra DMA synchronous-DMA mode
transfers. The BIOS supports logical block addressing (LBA) and extended cylinder head sector
(ECHS) translation modes. The BIOS automatically detects the IDE device transfer rate and
translation mode.
The motherboard supports LS-120 diskette technology through its IDE interfaces. LS-120 diskette
technology enables users to store 120 MB of data on a single, 3.5-inch removable diskette. LS-120
technology is backward compatible (both read and write) with 1.44 MB and 720 KB DOS-
†
formatted diskettes and is supported by Windows
The motherboard allows connection of an LS-120 compatible drive and a standard 3.5-inch
diskette drive. If an LS-120 drive is connected to an IDE connector and configured as the A drive,
and a standard 3.5-inch diskette drive is configured as a B drive, the standard diskette drive must
be connected to the diskette drive cable's "A" connector (the connector at the end of the cable).
The LS-120 drive can be configured as a boot device, if selected in the BIOS setup utility.
95 and Windows NT† operating systems.
19
Page 20

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Real-Time Clock, CMOS RAM, and Battery
The real-time clock provides a time-of-day clock and a multicentury calendar with alarm features
and century rollover.
The clock is compatible with DS1287 and MC146818 components and it supports 256 bytes of
battery-backed CMOS RAM in two banks that are reserved for BIOS use.
The time, date, and CMOS values can be specified in the Setup program. The CMOS values can
be returned to their defaults by using the Setup program.
An external coin-cell battery powers the real-time clock and CMOS memory. When the computer
is not plugged into a wall socket, then the battery has an estimated life of three years. When the
computer is plugged in, then the 3 V standby current from the power supply extends the life of the
battery.
NOTE
✏
Power is supplied to the chassis intrusion circuit by the battery when no AC power is provided.
Chassis intrusion will be detected when no AC power is available to the system. If the switch is
activated when no AC power is provided, then the drain on the battery is approximately 200 mA.
The clock is accurate to ± 13 minutes/year at 25 ºC with 5 V applied.
Diskette Drive Controller
The diskette drive controller is software compatible with the DP8473 and N82077 diskette drive
controllers and supports both PC-AT
interface can be configured for the following diskette drive capacities and sizes:
• 360 KB, 5.25-inch
• 1.2 MB, 5.25-inch
• 720 KB, 3.5-inch
• 1.2 MB, 3.5-inch (driver required)
• 1.25/1.44 MB, 3.5-inch
†
and PS/2† modes. In the Setup program, the diskette drive
20
Page 21

Motherboard Features
Accelerated Graphics Port (A.G.P.) Support
The Accelerated Graphics Port (A.G.P.) is a high-performance interconnect for graphic-intensive
applications, such as 3D applications.
A.G.P. is independent of the PCI bus. It is intended for exclusive use with graphical display
devices. A.G.P. provides these performance features:
• Pipelined-memory read and write operations that hide memory access latency
• Demultiplexing of address and data on the bus for near 100 percent bus efficiency
• AC timing for 133 MHz data transfer rates, allowing data throughput of 528 MB/sec
An A.G.P. connector is provided on the motherboard to install A.G.P. add-in cards.
Memory
The motherboard has four dual inline memory module (DIMM) sockets.
Minimum memory size is 32 MB; maximum memory size is 2 GB. The BIOS automatically
detects memory type and size.
The motherboard supports the following memory features:
• PC100 compliant 168-pin DIMMs with gold-plated contacts
• 3.3 V unbuffered or registered (not mixed) 100 MHz ECC SDRAM DIMMs only
• Single or double sided DIMMs in the sizes listed in the Table 4.
Table 4. DIMM Sizes Supported
DIMM Size Configuration
16 MB 2 Mbit x 72
32 MB 4 Mbit x 72
64 MB 8 Mbit x 72
128 MB 16 Mbit x 72
256 MB 32 Mbit x 72
512 MB 128 Mbit x 72
Memory can be installed in any order in one, two, three or four sockets.
Memory size can vary between sockets.
Memory speed is 100 MHz only.
21
Page 22
MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Input/Output (I/O) Controller (O)
The I/O controller handles the exchange of information between the processor and external devices
like the mouse and keyboard or a printer that are connected to the computer.
The National Semiconductor PC97307 I/O Controller is an ISA Plug and Play compatible
multifunction I/O device with components and features listed in the table below.
Table 5. I/O Controller Components
Component Feature(s)
Serial Ports Two 16450/16550A software compatible UARTs
Internal send/receive 16-byte FIFO buffer
Four internal 8-bit DMA options for the UART with
SIR support (USI)
Multimode Bidirectional Parallel Port Standard mode: IBM and Centronics compatible
Enhanced parallel port (EPP) mode with BIOS and
driver support
High speed extended capabilities port (ECP) mode
Diskette Drive Controller DP8473 and N82077 compatible
16-byte FIFO buffer
PS/2 diagnostic-register support
High performance digital data separator (DDS)
PC-AT, PS/2, and 3 mode diskette drive mode
support
8042A Compatible Keyboard and Mouse Controller
Support for IrDA† and Consumer Infrared Compliant
Infrared Interface
By default, the I/O controller interfaces are automatically configured during boot up. The I/O
controller can also be manually configured in the Setup program.
22
Page 23
82558 PCI LAN Controller (D)
The Intel 82558 LAN Controller provides the functions listed in Table 6 below.
Table 6. LAN Controller Functions
Motherboard Features
Function
CSMA/CD Protocol Engine
PCI bus interface (Rev 2.1 compliant)
DMA engine for movement of commands, status,
and network data across the PCI bus
Integrated physical layer interface Complete functionality necessary for the 10Base-T
Integrated power management features Support for ACPI
Digitally controlled adaptive equalizations and
transmission
EtherExpress
Includes:
and 100Base-TX interfaces
When in 10 Mbit/sec mode, the interface drives the
cable directly
A complete set of MII management registers for
control and status reporting
802.3µ Auto-Negotiation for automatically
establishing the best operating mode when
connected to other 10 Base-T or 100Base-TX
devices
Support for Wake on LAN technology
PRO/100 WfM PCI LAN Subsystem
™
The Intel EtherExpress PRO/100 Wired for Management (WfM) PCI LAN subsystem is an
Ethernet LAN interface that provides both 10Base-T and 100Base-TX connectivity. Features
include:
• 32-bit direct bus mastering on the PCI bus
• Shared memory structure in the host memory that copies data directly to/from host
memory
• 10Base-T and 100Base-TX capability using a single RJ-45 connector
• IEEE 802.3µ Auto-Negotiation for the fastest available connection
23
Page 24

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Alert On LAN Component
The Alert on LAN component is a companion device to the Intel 82558 LAN controller. Together,
these devices provide a management interface between a remote management console (or
management server) and a client system monitoring instrumentation.
†
When an alert input is asserted, the Alert on LAN component transmits Ethernet
82558 through an 8-bit dedicated data path. Examples of events that can trigger alert messages to
a management server include:
• Chassis intrusion
• System BIOS hang (transmits POST code error)
• LAN leash (transmits an alert that the LAN cable was disconnected)
• Temperature out of specification
• Fan failure
For more information on the Alert on LAN component and its network management capabilities,
contact your local Intel sales office.
packets to the
Audio Subsystem
The optional onboard audio subsystem features the Crystal CS4235, an audio codec with an
integrated FM synthesizer.
The audio subsystem provides all the digital audio and analog mixing functions needed for
recording and playing sound on personal computers. The audio subsystem contains the following
features:
• Stereo analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog converters
• Analog mixing, anti-aliasing, and reconstruction filters
• Line and microphone level inputs
• ADPCM, A-law, or µlaw digital audio compression/decompression
• Full digital control of all mixer and volume control functions
• High-quality, 16-bit, MPC-II compliant onboard audio
• Full duplex operation
†
• AdLib
• Full DOS games compatibility
• MIDI/Game port support
• OPL3 compatible FM synthesizer
• BIOS Setup-based enable/disable
The audio subsystem requires up to two DMA channels and one IRQ. Table 7 shows the IRQ,
DMA channel, and base I/O address options. These options are automatically chosen by the Plug
and Play interface, so there are no default settings.
, Sound Blaster Pro† 2.0, Windows Sound System, and MPU-401 support
24
Page 25
Motherboard Features
Table 7. Audio Subsystem Resources
Resource IRQ (Options) DMA Channel (Options) I/O Address (Options)
Sound Blaster
(DMA playback, DMA / IRQ shared
with Windows Sound System
capture)
Windows Sound System
(DMA playback)
MPU-401
(IRQ shared with Sound Blaster)
MIDI 200-207h
FM Synthesis 388-38Dh
CS4235 Control FF0-FFFh
†
5 best choice
7
9 best choice
11
7
9 best choice
11
5 best choice
7
9 best choice
11
0 best choice
3
0
1 best choice
3
210-21Fh
220-22Fh best choice
230-234h
240-24Fh
250-25Fh
260-26Fh
534-537h best choice
608-60Bh
300-301h
330-331h best choice
332-333h
334-335h
Audio Drivers and Utilities
Audio software and utilities are available from Intel’s World Wide Web site. Audio driver
support is provided for the Microsoft Windows NT
4.0 and Microsoft Windows 98 operating
systems.
Hardware Monitor Subsystem
The hardware monitor subsystem provides low-cost instrumentation capabilities. The features of
the hardware monitor subsystem include:
• Management Level 4 functionality
• Analog Devices ADM 9240 or equivalent.
Integrated temperature and voltage monitoring to detect levels above or below acceptable
values (+12 V, -12 V, +5 V, +3.3 V, and +2.5 V). When suggested ratings for
temperature, fan speed or voltage are exceeded, an interrupt is activated.
Two fan speed sensors
Access through the SMBus
®
• Remote reset capabilities from a remote peer or server through LANDesk
Manager and service layers
• Headers for front and rear chassis intrusion connectors.
3.3 (or later) Client
25
Page 26

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Power Supply
Table 9 lists the power specifications for a computer that contains a motherboard with two
400 MHz Pentium II Xeon processors, 128 MB SDRAM, a 3.5-inch diskette drive, an WD Caviar
3320 3.3 GB Ultra ATA hard drive, a Hitachi CPR 8330 IDE CD-ROM, and a Diamond Viper
330 A.G.P. graphics card. This information is provided only as a guide for calculating
approximate power usage with additional resources added.
Values for the Windows 98 desktop mode are measured at 1280x1024x256 colors and 70 Hz
refresh rate. AC watts are measured with a typical 300 W supply, nominal input voltage and
frequency, with true RMS wattmeter at the line input.
Table 8. Power Usage
Mode Watts (AC) Out of AC Wall Outlet
Windows 98 desktop 60 watts
Windows NT 4.0 desktop 92 watts
Power Supply Considerations
For typical configurations, the motherboard is designed to operate with at least a 300 W power
supply. A higher-wattage power supply should be used for heavily-loaded configurations. The
power supply must comply with the following recommendations:
• The potential relation between 3.3 V DC and +5 V DC power rails
• The current capability of the +5 VSB line
• All timing parameters
• Must meet UL SELV requirements and meet the 240VA energy limit
Table 9. DC Voltage Tolerances and Estimated Current Requirements
shown)
Estimated current with a 400
Acceptable
DC Voltage
+3.3 V ± 5% 20A 20A
+5 V ± 5% 14A 16A
+5 VSB (standby) ± 5% 0.72A 0.72A
-5 V ± 10% 0.0A 0.0A
+12 V ± 5% 2.8A 3.1A
-12 V ± 10% 0.0A 0.0A
Tolerance
MHz processor, 512 KB
cache, and 2 GB RAM
Estimated current with a 450
MHz processor, 512 KB
cache, and 2 GB RAM
(no PCI or A.G.P.
NOTE
✏
Some heavily loaded configurations could require additional +3.3 V and +5 V power for
peripherals. Use the auxiliary power supply connector for this purpose.
26
Page 27

Motherboard Features
Expansion
The MS440GX motherboard has seven expansion slots for installing add-cards such as video or
network cards that expand the capabilities of your computer.
The expansion slots available are as follows:
• Five PCI slots
• One shared slot (for a PCI or ISA card)
• One AGP 2X slot
Basic Input/Output System (BIOS)
The MS440GX motherboard uses an Intel/Phoenix BIOS which is stored in flash memory. The
BIOS can be upgraded using a disk-based program.
The contents of flash memory includes the following items:
• BIOS
• Setup Program
• Power-on Self Test (POST)
• Advanced Power Management (APM)
• PCI Auto-configuration Utility
• Windows 98-ready Plug and Play Code
The MS440GX motherboard supports system BIOS shadowing, allowing the BIOS to execute
from 64-bit onboard write-protected DRAM.
During POST, the BIOS displays a message identifying the type of BIOS and the revision code.
The initial production BIOS is identified as 4M4SG0X0.86E.
BIOS Upgrades
NOTE
✏
Please review the instructions distributed with the upgrade before attempting a BIOS upgrade.
The BIOS can be upgraded from a diskette using the Intel Flash Memory Update utility that is
available from Intel. This utility does BIOS upgrades as follows:
• Updates the flash BIOS from a file on a disk
• Updates the language section of the BIOS
• Makes sure that the upgrade BIOS matches the target system to prevent accidentally installing
a BIOS for a different type of system.
BIOS upgrades and the update utility are available from Intel through the Intel World Wide Web
site.
Chapter 4 details the procedure for executing a BIOS upgrade.
27
Page 28

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
BIOS Flash Memory Organization
The Intel E28F004BXT80 4-Mbit flash component is organized as 512 KB x 8 bits and is divided
into areas as described in Table 10. The table shows the addresses in the ROM image in normal
mode (the addresses change in BIOS Recovery Mode).
Table 10. Flash Memory Organization
Address (Hex) Size Description
FFFFC000 - FFFFFFFF 16 KB Boot Block
FFFFA000 - FFFFBFFF 8 KB Vital Product Data (VPD) Extended System Configuration Data
(ESCD) (DMI configuration data / Plug and Play data)
FFFF9000 - FFFF9FFF 4 KB Used by BIOS (e.g., for Event Logging)
FFFF8000 - FFFF8FFF 4 KB OEM logo or Scan Flash Area
FFF80000 - FFFF7FFF 480 KB Main BIOS Block
Piezoelectric Speaker (N)
The onboard piezoelectric speaker is enabled by a jumper on pins 1 and 2 of the front panel
connector.
The onboard speaker can be disabled by removing the jumper. An outboard speaker can be
connected in its place by a jumper on pins 1 and 4.
This speaker provides error beep code information during the POST in the event that the computer
cannot use the video interface. The speaker is not connected to the audio subsystem and does not
receive output from the audio subsystem.
28
Page 29

2 Installation and Removal Procedures
This chapter explains how to remove and install the MS440GX motherboard and its various
component parts. The chapter covers the following topics:
Topic or Procedure Page
Safety Considerations 30
How to Install the Processor Retention Mechanism 30
How to Install a Single Processor 37
How to Install a Second Processor 38
How to Remove and Install the Motherboard 40
How to Set Processor Speed 41
Jumper Settings 42
How to Remove a Processor 43
How to Upgrade a Processor 44
How to Install the Termination Card 45
How to Remove the Termination Card 46
How to Install Memory 47
How to Remove Memory 48
How to Replace the Battery 49
How to Clear Passwords 51
29
Page 30

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Safety Considerations
CAUTION
Before removing or installing the motherboard or any other system component, observe the
following safety guidelines:
See Appendix B: Regulatory & Integration Information for safety requirements and precautions.
Always follow the steps in the procedure in the correct order (i.e., as written).
Set up a log to record identification information about your computer.
Wear an antistatic wrist wrap and place the motherboard on a conductive foam pad when working
on it.
WARNINGS
The procedures in this section assume that you are familiar with the general terminology
associated with personal computers and with the safety practices and regulatory compliance
required for using and modifying electronic equipment including but not limited to the
following:
Turn off system AC power by unplugging the AC power cord from the wall outlet. Disconnect
the computer from any telecommunications systems, networks, and modems attached before
performing any of the procedures described in this section else personal injury or equipment
damage can result.
CAUTION
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage components. Therefore, protect against electrostatic
discharge (ESD) by performing the procedures described in this section only at an ESD
workstation or by wearing an antistatic wrist wrap and attaching it to a metal part of your
computer’s chassis.
How to Install the DRM Fans and Processor Retention Mechanism
NOTES
✏
Dual Retention Mechanism (DRM) fans must be installed in the DRM end stands prior to installing
the processor retention mechanism on the motherboard.
The following procedure table combines the fan installation and processor retention mechanism
installation procedures.
30
Page 31

Installation and Removal Procedures
Materials Required:
• 2 40mm fans
• 2 DRM stands (see Figure 3)
• 4 Fan screws (P/N 656880-002)
• 2 DRM tops (see Figure 3f)
• 2 Processors (CPUs) with attached heatsinks (see Figure 3g)
• 2 Retention clips (see Figure 3c)
• 1 Small tie wrap
Procedure To: Install DRM Fans and the Processor Retention Mechanism
Step Action
1 Observe the safety precautions in Safety Considerations at the beginning of this chapter.
2 Obtain one of the DRM stands.
Figure 3.
3 Place the two Delta 40mm fans in the DRM stand pocket.
Position the fans with air flow away from the DRM.
Air
flow
Figure 3a.
OM08275
OM08276
SIDE VIEW
Continued
31
Page 32

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Procedure
(continued)
Step Action
4 Orient power cables to the upper left corner as illustrated in Step 3.
4a Run the power cables down the left side of the DRM base as illustrated in Step 3.
4b Tie wrap the cables leaving approximately 2 inches of cable hanging beyond the base.
5 Attach fans in the DRM stand with 2 fan screws placed in opposite corners.
Position the fans with air flow away from the DRM.
40mm Fans (2) Stacked
P1
Processor
Air Flow
Heat Sink
P0
Processor
Heat Sink
DRM Top
DIMM sockets
OM08277
Figure 3b.
IF more air flow is needed, then position 2 fans in the other DRM stand and secure them with air
flow into (towards) the DRM.
6 Apply a retention clip to the tops of the DRM bases.
Keypost E1
Keypost E2
Figure 3c.
Retention Clip
OM08278
Continued
32
Page 33

Installation and Removal Procedures
Procedure
(continued)
Step Action
7 Take the DRM base with 40mm fans attached and connect the two fans to the processor fan
headers on the motherboard.
40mm Fan
Headers
120mm Fan
Header
OM08279
Figure 3d.
8 Locate the Slot 2 processor connectors (A and B) and the four attachment screw holes (C1-C4)
shown in Figure 3e.
9 Properly position the processor retention mechanisms (D1 and D2) relative to the Slot 2
connectors.
10 Fit the keyposts (Step 6 illustration, callouts E1 and E2) on the processor retention mechanisms
into the holes in the motherboard base.
When properly seated, the bases of the processor retention mechanism should fit flush with the
motherboard.
11 Mount the DRM base to the motherboard with fan air flow pointing toward the back of the chassis.
11a Use four 6-32x1/2 or 5/8 inch screws (chassis dependent) to attach DRM bases to motherboard.
Torque screws to 6 inch pounds.
Retention
Mechanism (D1)
Keyposts (E3&E4)
Screw Holes
(C1/C2)
Processor
Connecter (B)
Processor
Connecter (A)
Figure 3e.
Retention
Mechanism (D2 )
Keyposts (E1&E2)
OM08280
Screw Holes (C3/C4)
Continued
33
Page 34

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Procedure
(continued)
Step Action
12 Assemble the other DRM base, mount it on the other side of the Slot 2 connectors with 1/2 or
5/8 inch screws (chassis dependent).
13 Obtain the CPU/Heat sinks and the DRM tops.
DRM T op
OM08281
Figure 3f.
14 Secure one of the DRM tops to the processor with the holes facing toward the DIMM sockets on
the motherboard.
NOTE
✏
The DRM tops snap into two recesses on the sides of the processor.
Retention
Clips
Holes
CPUs
DIMM Slots
Heatsinks
OM08282
Figure 3g.
Continued
34
Page 35

Installation and Removal Procedures
Procedure
(continued)
Step Action
15 Secure the other DRM top to the processor with the holes facing toward the DIMM slots.
NOTE
✏
If using a Termination Card, then secure the DRM top to the card in the same manner.
The DRM top is necessary to lock the Termination Card down and provide a way to remove it
from the connector by pulling it up and out.
16 Install the two processors (CPUs) in the DRM with the heat sinks facing the DIMM slots.
NOTE
✏
Check hole placement of the DRM top relative to the retainer clip holes before installation
to ensure correct alignment. Use 4 ½ inch screws to secure tops to retainer clip.
DRM T op
Retention Clip
DRM T op
Retention Hole
Heatsink
DIMM Slots
D
Figure 3h.
Dual Retention Mechanism (DRM)
Processor (CPU) Connector
OM08285
Continued
35
Page 36

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Procedure
(continued)
Step Action
17 The final fan/CPU-heat sink/DRM assembly should appear as shown in the illustration below.
CPU Heat sinks
DRM top
CPU
DRM base
DRM 40mm Fans
OM08283
Figure 3i.
36
Page 37

How to Install a Single Processor
Procedure To: Install a Single Processor
Step Action
1 Observe the safety precautions in Safety Considerations at the beginning of this chapter.
2 Turn OFF the computer.
3 Disconnect the computer’s power cord and all external peripheral equipment.
4 Remove any peripherals that block access to the P0 processor’s Slot 2 connector.
5 Remove the antistatic packaging from the new processor.
6 Secure a DRM top (D) to the processor by snapping the clips (H1 and H2) into the holes on each
side of the processor.
7
8
Orient the P0 processor (A) so that the heat sink (B) is closest to the DIMM sockets.
Slide the processor into the retention mechanism
H1
A
Installation and Removal Procedures
(E).
C
D
H2
B
E
F
E
DIMM Slots
G
OM08284
Figure 4.
9 Press down firmly on the processor until it is seated in the P0 processor Slot 2 connector (G) and
fasten with screws.
10 Lock down DRM top into retainer clips (F) on tops of DRM bases with 6-32x1/2 inch screws (C).
11 If there is no Termination Card in the P1 processor Slot 2 connector then install one using the
procedure entitled “How to Install a Termination Card”.
12 Replace any peripheral equipment that was removed in Steps 3 and 4 above.
13 Set the processor speed using the procedure entitled “How to Set the Processor Speed”.
37
Page 38

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
How to Install a Second Processor
NOTE
✏
It may be necessary to reload the operating system to realize optimum performance when
upgrading from a single processor to a dual processor configuration.
If installing two processors, then the following values must be identical for both processors:
L2 cache size and type (ECC); Operating voltages; Bus and Core frequencies.
The core stepping value may differ by one step (eg., C0 to C1). These values may be determined by
checking the parameters of the s-spec number, a five character code (eg., SL28R) printed on the
top edge of the S.E.C.C.. For information about s-spec parameters, refer to the Pentium II
processor quick reference guide at the Intel developer’s web site.
Procedure To: Install a Second Processor
Step Action
1 Observe the safety precautions in Safety Considerations at the beginning of this chapter.
2 Turn OFF the computer.
3 Disconnect the computer’s power cord and all external peripheral equipment and remove any
peripherals that block access to the P1 processor Slot 2 connector.
4 If there is a Termination Card installed in the P1 processor Slot 2 connector then remove it using
the procedure entitled “How to Remove a Termination Card”.
5 Remove the antistatic packaging from the second processor.
6 Secure a DRM top (E) to the processor by snapping the clips (F) into the holes on each side of
the processor.
7
Orient the P1 processor (A) so that the heat sink (B) faces the DIMM slots.
Continued
38
Page 39

Installation and Removal Procedures
Procedure
(continued)
Step Action
8
Slide the processor into the processor retention mechanism
(C).
E
F
A
B
C
D
D
OM08285
Figure 5.
9 Press down firmly on the processor until it is seated in the P1 Slot 2 connector (D) and fasten
with screws.
10 Replace any peripheral equipment that was removed in Step 3 above.
11 Set the processor speed using the procedure entitled “How to Set the Processor Speed”.
39
Page 40

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
How to Remove and Install the Motherboard
Refer to your chassis manual for detailed instructions on removal and installation.
WARNING
Motherboard removal or installation should be done only by qualified technical personnel.
Disconnect the computer from its power source before performing the removal or installation
procedures noted here and before opening the computer. Failure to observe these precautions
may result in personal injury or equipment damage.
Procedure To: Remove the Motherboard
Step Action
1 Remove processor/heatsink/DRM assembly/Termination Card (if applicable) using procedures
“How to Remove a Processor” and “How to Remove a Termination Card”.
2 Remove the four screws attaching the DRM bases to the chassis.
3 Disconnect fan cables from fan headers
4 Locate the motherboard mounting screw holes in Figure 6 below.
5 Remove the 11 motherboard mounting screws.
6 Carefully extract the board by its edges.
7 Place board component-side up on a grounded, static free surface.
3.300.20
12.70
12.30
6.20
3.35
0.00
0.30
0.00
0.45
5.10
Figure 6. Motherboard Mounting Screw Holes
9.06
2.59
11.40
6.74
2.80
11.55
11.30
9.31
OM07109
40
Page 41

Installation and Removal Procedures
How to Set Processor Speed
CAUTION
Selecting a processor speed greater than the rated speed of the installed processor(s) may damage
the processor(s).
Set processor speed after you have installed or upgraded the processor.
The procedure that follows assumes that:
• The computer is turned OFF
• The cover has been removed
• The configuration jumper block (J4J1) has the jumper set on pins 1-2 for normal mode
Procedure To: Set Processor Speed
Step Action
1 Observe the safety precautions in Safety Considerations at the beginning of this chapter.
2 Locate the configuration jumper block (see figure below).
3 Move the jumper to pins 2-3.
4 Replace the computer cover.
5 Turn ON the computer.
6 Allow the computer to boot up.
7 The computer starts the Setup Program.
8 Setup displays the Maintenance Menu.
9 Select the Processor Speed feature using the arrow keys.
10 Press the <ENTER> key.
11 Setup displays a pop-up screen with available processor speeds.
12 Select a speed using the arrow keys. (Choose 400 for a 400 MHz processor).
CAUTION
Do not exceed the rated speed or damage to the processor may result.
13 Press the <ENTER> key to confirm the speed.
14 The Maintenance Menu is re-displayed.
15 Press <F10> to save the current values then Exit Setup.
16 Turn OFF the computer.
17 Remove the computer cover.
18 Move the jumper back to pins 1-2 on the jumper block (J4J1) to restore normal operation.
19 Replace the cover.
20 Turn ON the computer.
21 Verify the processor speed in the startup information displayed by the BIOS.
41
Page 42

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Jumper Settings
CAUTION
Do not move jumpers with the power ON. Always turn OFF the power and unplug the power cord
from the computer before changing jumpers.
NOTE
✏
There is no jumper setting for configuring the processor speed or bus frequency. The feature for
configuring the processor speed is in the Setup program using configure mode.
A
1
1
A LAN enable/disable jumper block
B BIOS Setup configuration jumper block
B
OM07120
42
Figure 7. Configuration Jumper Block
Page 43

Installation and Removal Procedures
Table 11 describes the settings of the BIOS Setup configuration jumper block.
Table 11. BIOS Setup Configuration Jumper Settings
Mode Jumper Setting Description
Normal 1-2 The BIOS uses current configuration information and passwords for
booting. (Default)
Configure 2-3 After the POST runs, Setup runs automatically.
The maintenance menu is displayed.
Recovery Off (jumper
removed)
The BIOS attempts to recover the BIOS from a diskette.
A recovery diskette is required.
How to Remove a Processor
Procedure To: Remove a Processor
Step Action
1 Observe the safety precautions in Safety Considerations at the beginning of this chapter.
2 Turn OFF the computer.
3 Disconnect the computer’s power cord and all external peripheral equipment.
4 Remove any peripherals that block access to the processor.
5 Remove the screws from the DRM top (B)
6 Remove the processor (C) from the Slot 2 connector (D) by pulling the processor vertically
upward as shown by the arrows in the illustration below.
NOTE
✏
Do not rock the processor (CPU) out of the DRM (E).
C
D
7 Store the processor in an antistatic package.
B
E
OM08286
Figure 8.
43
Page 44

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
How to Upgrade a Processor
NOTES
✏
If your motherboard has one microprocessor, then you can upgrade the computer by replacing this
processor with a faster one or by installing an application processor.
If your motherboard has two microprocessors, then you can upgrade by replacing these processors
with two faster processors.
If your operating system supports single processors only (such as Windows 95), then use the
sequence of procedures listed under “Upgrading a Single Processor”.
If your operating system supports dual-processing capability (such as Windows NT or UNIX
you will be running software programs that require additional processing power, then use the
sequence of procedures listed under “Upgrading from Single to Dual Processors”.
If your computer has two microprocessors and you want more processing power, then use the
sequence of procedures listed under “Upgrading Dual Processors”.
†
) and
If you install only one processor on a motherboard, then it must go in the boot (P0) processor
connector. In a single processor configuration, you must install a Termination Card in the empty
application (P1) processor connector to ensure proper operation of the computer.
Procedure Reference Table
To Upgrade Use Procedures
a Single Processor How to Remove a Processor
How to Install a Single Processor
How to Set Processor Speed
from Single to Dual Processors How to Remove the Termination Card
How to Install a Second Processor
How to Set Processor Speed
Dual Processors How to Remove a Processor
How to Install a Single Processor
How to Install a Second Processor
How to Set Processor Speed
44
Page 45

How to Install the Termination Card
Procedure To: Install the Termination Card
Step Action
1 Observe the safety precautions in Safety Considerations at the beginning of this chapter.
2 Turn OFF the computer.
3 Disconnect the computer’s power cord and all external peripheral equipment.
4 Remove any peripherals that block access to the processor Slot 2 connector.
5 Remove the screws from the DRM top as shown in Figure 9 below.
6 Secure a DRM top (A) to the Termination Card (B) by snapping the clips (C) into the holes (or
slots) in each side of the Card.
7
8
Slide the Termination Card
Ensure that the alignment notches
into the Retention Mechanism
(B)
(E1 and E2)
in the Termination Card fits over the key in the
P1 Processor Slot 2 connector (F) shown in the illustration below.
Installation and Removal Procedures
.
(D)
A
C
B
E1
F
D
E2
E
OM08287
Figure 9.
9 Press down firmly on the Termination Card until it is seated in the P1 slot connector.
NOTE
✏
A Termination Card will never be used in the P0 slot connector.
Fasten the DRM cap into place with screws as shown in Figure 9 above.
45
Page 46

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
How to Remove the Termination Card
Procedure To: Remove the Termination Card
Step Action
1 Observe the safety precautions in Safety Considerations at the beginning of this chapter.
2 Turn OFF the computer.
3 Disconnect the computer’s power cord and all external peripheral equipment.
4 Remove any peripherals that block access to the processor Slot 2 connector.
5 Remove the two screws holding the DRM Top over the P1 slot Termination Card.
6 Using the DRM top (A) as a handle, lift the Termination Card (B) up and out of the processor Slot
2 connector (C) and the processor retention mechanism (D) as shown by the arrows in the
illustration below.
NOTE
✏
Do not rock the Termination Card out of the connector - pull vertically upward.
A
B
C
D
OM08288
Figure 10.
46
Page 47

Installation and Removal Procedures
How to Install Memory
NOTE
✏
You can install from 32 MB to 2 GB of 100 MHz SDRAM in the motherboard DIMM sockets.
Memory can be installed in one, two, three or four sockets.
DIMM size can vary between sockets.
The MS440GX motherboard supports the following types of memory:
• 168-pin 3.3V DIMMs with gold-plated contacts
• Single or double-sided DIMMs (See Table 4)
• 100 MHz SDRAM
DIMM socket locations are shown in Figure 1/Callout I.
Procedure To: Install DIMMs
Step Action
1 Observe the safety precautions in Safety Considerations at the beginning of this chapter.
2 Disconnect the computer’s power cord and all external peripheral equipment.
3 Remove the computer cover and locate the DIMM sockets.
4 Holding the DIMM by its edges, remove it from its antistatic package.
5 Ensure that the clips at either end of the socket are pushed away from the socket.
Continued
47
Page 48

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Procedure
Step Action
6 Position the DIMM above the socket and align the two small notches in the bottom edge of the
(continued)
DIMM with the keys in the socket.
1,2,3,4
7 Insert the bottom edge of the DIMM into the socket.
8 When the DIMM is seated, then press down on the top edge of the DIMM until the retaining clips
at the ends of the socket snap into place.
9 Make sure that the clips are firmly in place.
10 Replace the computer cover.
How to Remove Memory
Procedure To: Remove DIMMs
Step Action
1 Observe the safety precautions in Safety Considerations at the beginning of this chapter.
2 Turn OFF the computer.
3 Disconnect the computer’s power cord and all external peripheral equipment.
4 Remove the computer cover and locate the DIMM sockets (See Figure 1/ Callout I).
5 Gently spread the retaining clips at each end of the socket.
6 The DIMM pops out of the socket.
7 Holding the DIMM by its edges, lift it away from the socket and store it in an antistatic package.
OM08289
Figure 11.
48
Page 49

Installation and Removal Procedures
How to Replace the CR2032 Lithium Battery (M)
When your computer is turned off, a lithium battery maintains the current time-of-day clock and
the current values in CMOS RAM.
The battery should last about seven years. When the battery begins to fail, it loses voltage; when
the voltage drops below a certain level, the Setup program settings stored in CMOS RAM (for
example, the date and time) might not be accurate. Replace the battery with an equivalent one.
WARNING
Danger of explosion if the battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the same or
equivalent type recommended by the equipment manufacturer. Discard used batteries according
to manufacturer’s instructions.
ATTENTION
Il y a danger d’explosion s’il y a remplacement incorrect de la batterie. Remplacer uniquement
avec une batterie du méme type ou d’un type recommandé par le constructeur. Mettre au rébut
les batteries usagées conformément aux instructions du fabricant.
ADVARSEL!
Lithiumbatteri - Eksplosionsfare ved fejlagtig håndtering. Udskiftning må kun ske med batteri
af samme fabrikat og type. Levér det brugte batteri tilbage til leverandøren.
ADVARSEL
Lithiumbatteri - Eksplosjonsfare. Ved utskifting benyttes kun batteri som anbefalt av
apparatfabrikanten. Brukt batteri returneres apparatleverandøren.
VARNING
Explosionsfara vid felaktigt batteribyte. Använd samma batterityp eller en ekvivalent typ som
rekommenderas av apparattillverkaren. Kassera använt batteri enligt fabrikantens instruktion.
VAROITUS
Paristo voi räjähtää, jos se on virheellisesti asennettu. Vaihda paristo ainoastaan
laitevalmistajan suosittelemaan tyyppiin. Hävitä käjtetty paristo valmistajan ohjeiden
mukaisesti.
49
Page 50

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Procedure To: Replace the Battery
Step Action
1 Observe the safety precautions in Safety Considerations at the beginning of this chapter.
2 Record CMOS settings.
3 Turn OFF the computer.
4 Disconnect the computer’s power cord and all external peripheral equipment.
5 Remove the computer cover. .
6 Locate the battery on the motherboard (See Figure 1/ Callout M)
7 Gently pry the battery free from its socket using a small flat bladed screwdriver. Note the
orientation of the “+” on the battery
B
A
C
OM08290
Figure 12.
8 Install the new battery in the socket, orienting the “+” as shown in the illustration.
9 Replace the computer cover.
10 Update CMOS records with any changes.
50
Page 51

Installation and Removal Procedures
How to Clear Passwords
NOTE
✏
This procedure assumes that the motherboard is installed in the computer and the configuration
jumper block (J4J1) has the jumper set on pins 1-2 for normal mode.
Procedure To: Clear Passwords
Step Action
1 Observe the safety precautions in Safety Considerations at the beginning of this chapter.
2 Turn OFF the computer.
3 Disconnect the computer’s power cord and all external peripheral equipment.
4 Remove the computer cover. .
5 Locate the configuration jumper block (See Figure 11, Configuration Jumper Block).
6 Move the jumper to pins 2-3.
7 Replace the cover and turn ON the computer.
8 Allow the computer to boot up.
9 The computer starts the Setup Program and the Maintenance Menu is displayed.
10 Use the arrow keys to select CLEAR PASSWORDS from the Maintenance Menu.
11 Press <ENTER> key.
12 Setup displays a pop-up screen requesting confirmation of clearing the password.
13 Select YES then Press <ENTER> key.
14 Setup displays the Maintenance Menu once again.
15 Press <F10> to save current values and EXIT Setup.
16 Turn OFF the computer.
17 Remove the computer cover.
18 On the Jumper Block (J4J1) move the jumper back to pins 1-2 to restore normal operation.
19 Replace the computer cover.
51
Page 52

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
52
Page 53

3 Using the BIOS Setup Program
This chapter provides an overview of the BIOS Setup Program. This program enables you to
change the BIOS settings of your computer.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Topic Page
Setup Program Modes 54
Setup Program Menus 55
Menu Functionality 56
Menu Function Keys 56
Maintenance Menu 57
Main Menu 57
Advanced Menu 58
Peripheral Configuration Submenu 59
IDE Configuration Submenu 60
Floppy Options Submenu 61
DMI Event Logging Submenu 62
Video Configuration Submenu 62
Security Menu 63
Power Menu 63
Boot Menu 64
Boot Options 65
Hard Drive Submenu 65
Removable Devices Submenu 66
Exit Menu 66
53
Page 54

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Setup Program Modes
NOTE
✏
The Setup Program is used for viewing and changing the BIOS settings for your computer.
It is recommended that you write down the current Setup settings for reference puproses. Then
when you make changes to these settings, update your record accordingly.
To access Setup, press the <F2> key after the Power-On Self Test (POST) memory test begins but
before the operating system boot begins.
Modes
The Setup Program has three modes of operation as shown in Table 12.
Table 12. Setup Program Modes
Operational mode Is used for ...
Normal Normal system operations.
Configure Configuring the processor speed.
Clearing passwords.
Recovery Recovering the BIOS data.
Mode Control
The Setup Program’s operational mode is controlled by the setting of the configuration jumper
block J4J1. The jumper is usually set to Normal mode at the factory.
Table 13 shows the jumper settings for the different Setup modes.
Table 13. Jumper Settings
Mode Jumper Description
Normal 1-2 BIOS uses current configuration and passwords for booting.
Configure 2-3 After the POST runs, Setup starts and displays the Maintenance Menu.
This menu displays options for setting the processor speed and clearing
passwords.
Recovery None BIOS recovers data from a recovery diskette.
Refer to Section 4 for information on BIOS data recovery during an
upgrade.
54
Page 55

Setup Program Menus
This diagram illustrates the Setup Program’s menu structure.
SETUP Menu
Menu Bar
Maint.
Features
Processor
Speed
Clear all
Passwords
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Processor 0 Type
Processor 1 Type
Processor Speed
Cache RAM
System Memory
Memory Bank 0
Memory Bank 1
Memory Bank 2
Memory Bank 3
Language
ECC Configuration
System Time
Plug and Play O/S
Reset Configuration
Data
Numlock
Fan Monitoring
Power LED Type
User
Password
Is
Admin.
Password
Is
Set User
Password
Set Admin.
Password
Clear
User
Password
User
Setup
Access
Unattended
Start
Using the BIOS Setup Program
Power
Mgmt.
Inactivity
Timer
Hard
Drive
VESA
Video
Power
Down
Fan
Always
On
QuickBoot
Mode
Scan User
Flash Area
After
Power
Failure
On LAN
On Modem
Ring
On PME
First Boot
Device
Second
Boot
Device
Third Boot
Device
Fourth
Boot
Device
Fifth Boot
Device
Exit
Saving
Changes
Exit
Discarding
Changes
Load
Setup
Defaults
Load
Custom
Defaults
Save
Custom
Defaults
Discard
Changes
Submenus
System Date
Peripheral
Configuration
IDE Configuration
Floppy Options
DMI Event Logging
Video Configuration
OM08291
Figure 13. Setup Program Menu Structure
Hard Drive
Remov.
Devices
55
Page 56

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Menu Functionality
Table 14 explains the functionality associated with each Setup Program menu screen.
Table 14. Setup Menu Bar
Setup Menu Screen Functionality
Maintenance Specifies the processor speed and clears the Setup passwords.
This menu is only available in configure mode.
Main Allocates resources for hardware components.
Advanced Specifies advanced features available through the chipset.
Security Specifies passwords and security features.
Power Specifies power management features.
Boot Specifies boot options and power supply controls.
Exit Saves or discards changes to the Setup program options.
Menu Function Keys
Table 15 shows the function keys available for use with the Setup Program menu screens.
Table 15. Setup Function Keys
Setup Key Description
<F1> or <Alt-H> Brings up a help screen for the current item.
<Esc> Exits the menu.
<←> or <→> Selects a different menu screen.
<↑> or <↓> Moves cursor up or down.
<Home> or <End> Moves cursor to top or bottom of the window.
<PgUp> or <PgDn> Moves cursor to top or bottom of the window.
<F5> or <-> Selects the previous value for a field.
<F6> or <+> or <Space> Selects the next value for a field.
<F9> Load the default configuration values for the current menu.
<F10> Save the current values and exit Setup.
<Enter> Executes command or selects the submenu.
<+> or <-> Toggles to next or previous submenu selection.
56
Page 57

Using the BIOS Setup Program
Maintenance Menu
Use this menu to set the processor speed and clear Setup passwords. Setup only displays this menu
in configure mode.
Table 16. Maintenance Menu
Feature Options Description
Processor Speed 300 MHz
350 MHz
400 MHz
450 MHz
500 MHz
Clear All Passwords No options Clears the user and administrator passwords.
Specifies the processor speed in megahertz.
Main Menu
This menu reports processor and memory information. Use the Main Menu to configure the
system date, system time, floppy options, and IDE devices.
Table 17. Main Menu
Feature Options Description
Processor 0 Type No options Displays processor type.
Processor 1 Type No options Displays processor type.
Processor Speed No options Displays processor speed.
Cache RAM No options Displays size of second-level cache.
System Memory No options Displays the total amount of RAM on the motherboard.
Memory Bank 0,1,2,3 No options Specifies the size and type of DIMMs installed in each
respective memory bank.
Language English (US) Selects the language used by the BIOS.
ECC Configuration None Specifies the ECC memory configuration.
System Time Hour, minute, and
second
System Date Month, day, and
year
Specifies the current time.
Specifies the current date.
57
Page 58

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Advanced Menu
Use this menu to set advanced features that are available through the chipset.
Table 18. Advanced Menu
Feature Options Description
Plug & Play O/S No (default)
Yes
Reset Configuration Data No (default)
Yes
Numlock Auto (default)
On
Off
Fan Monitoring Fan 4 J8L1
Fan 3 J8M1and J13A1
Fan 2 J2L1 and J14G1
Fan 1 J2K1 and J3J1
Power LED Type Single Color (default)
Dual Color
Peripheral Configuration
submenu
IDE Configuration submenu No options Reports type of connected IDE device.
Floppy Options submenu No options When selected, displays the Floppy Options
DMI Event Logging
submenu
Video Configuration
submenu
No options Configures peripheral ports and devices.
No options Configures DMI Events Logging.
No options Configures video features.
Specifies if a Plug and Play operating system is
being used.
No lets the BIOS configure all devices and steers
SCI to INT20 of the IOAPIC.
Yes lets the operating system configure Plug and
Play devices and steers SCI to INT9 of the
IOAPIC.
Not required with a Plug and Play operating
system.
Clears the BIOS configuration data on the next
boot.
Specifies the power on state of the Numlock
feature on the numeric keypad of the keyboard.
Sets which fan headers are monitored.
Set this option based on what type of LED is used
for power LED on your chassis.
A single color LED is typically Green or OFF.
A dual color LED can be Green, Yellow or OFF.
A single color LED will blink during SUSPEND,
whereas a two-color LED will turn Yellow.
When selected, displays the Peripheral
Configuration submenu.
When selected, displays the Primary IDE Master
submenu.
submenu.
When selected, displays the DMI Events Logging
submenu.
When selected, displays the Video Configuration
submenu.
58
Page 59

Peripheral Configuration Submenu
Use this submenu to configure the computer peripherals.
Table 19. Peripheral Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
Serial port A Disabled
Enabled
Auto (default)
Serial port B Disabled
Enabled
Auto (default)
Mode Normal (default)
IrDA
ASK-IR
Parallel port Disabled
Enabled
Auto (default)
Mode Output Only
Bi-directional
EPP
ECP (default)
Audio Disabled
Enabled (default)
LAN Disabled
Enabled (default)
Embedded PXE
Support
Legacy USB
Support
Disabled
Enabled (default)
Disabled (default)
Enabled
Configures serial port A.
Auto assigns the first free COM port, normally COM1,
the address 3F8h, and the interrupt IRQ4.
An * (asterisk) displayed next to an address indicates
a conflict with another device.
Configures serial port B.
Auto assigns the first free COM port, normally COM2,
the address 2F8h, and the interrupt IRQ3.
An * (asterisk) displayed next to an address indicates
a conflict with another device.
If either serial port address is set, that address will not
appear in the list of options for the other serial port.
Selects the mode for serial port B.
Configures the parallel port.
Auto assigns LPT1 the address 378h and the interrupt
IRQ7.
An * (asterisk) displayed next to an address indicates
a conflict with another device.
Selects the mode for the parallel port.
Output Only operates in AT
Bi-directional operates in bidirectional PS/2-
compatible mode.
EPP is Extended Parallel Port mode, a high-speed
bidirectional mode.
ECP is Enhanced Capabilities Port mode, a high-
speed bidirectional mode.
Enables or disables the onboard audio subsystem.
Enables or disables the LAN.
Enables or disables the embedded PXE support.
Enables support for legacy universal serial bus.
Using the BIOS Setup Program
†
-compatible mode.
59
Page 60

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
IDE Configuration Submenus
This submenu is for configuring IDE devices, including:
• Primary IDE master
• Primary IDE slave
• Secondary IDE master
• Secondary IDE slave
Table 20. IDE Configuration Submenus
Feature Options Description
IDE Controller Disabled
Primary
Secondary
Both (default)
Hard Disk Pre-Delay Disabled (default)
3 Seconds
6 Seconds
9 Seconds
12 Seconds
15 Seconds
21 Seconds
30 Seconds
Type None
ATAPI Removable
CD-ROM
IDE Removable
Other ATAPI
User
Auto (default)
Cylinders 1 to XXXX Specifies number of disk cylinders.
Heads 1 to 16 Specifies number of disk heads.
Sectors 1 to 64 Specifies number of disk sectors.
Maximum Capacity No options Reports the maximum capacity for the hard
Multi-Sector Transfers Disabled
2 Sectors
4 Sectors
8 Sectors
16 Sectors (default)
Configures the IDE Controller.
Both specifies that both the Primary and
Secondary channels are used.
Specifies hard disk pre-delay time.
Specifies the IDE configuration mode for IDE
devices.
IDE Removable allows the cylinders, heads,
and sectors fields to be changed.
Auto automatically fills in the values for the
cylinders, heads, and sectors fields.
disk.
Value calculated from number of cylinders,
heads, and sectors.
Specifies number of sectors per block for
transfers from the hard drive to memory.
Check the hard drive’s specifications for
optimum setting.
Continued
60
Page 61

Using the BIOS Setup Program
Table 20. IDE Configuration Submenus
Feature Options Description
LBA Mode Control Disabled
Enabled (default)
(continued)
Enables or disables logical block addressing
(LBA) in place of the Cylinders, Heads, and
Sectors fields.
CAUTION
Changing the LBA Mode Control after a
hard drive has been formatted can
corrupt data on the drive
Transfer Mode Standard
Fast PIO 1
Fast PIO 2
Fast PIO 3
Fast PIO 4
FPIO 3 / DMA 1 (default)
Mastering
FPIO 4 / DMA 2
Ultra DMA Disabled (default)
Mode 0
Mode 1
Mode 2
Specifies method for transferring data between
the hard drive and system memory.
Specifies the ultra DMA mode for the hard
drive.
.
Floppy Options Submenu
This submenu is used to configure diskette drives.
Table 21. Floppy Options Submenu
Feature Options Description
Floppy Disk Controller Disabled
Enabled (default)
Diskette A: Disabled
360 KB, 5¼″
1.2 MB, 5¼″
720 KB, 3½″
1.44/1.25 MB, 3½″ (default)
2.88 MB, 3½″
Diskette B: Disabled (default)
360 KB, 5¼″
1.2 MB, 5¼″
720 KB, 3½″
1.44/1.25 MB, 3½″
2.88 MB, 3½″
Floppy Write Protect Disabled (default)
Enabled
Configures the diskette drive
controller.
Specifies the capacity and physical
size of diskette drive A.
Specifies the capacity and physical
size of diskette drive B.
Disables or enables write protect for
the diskette drive(s).
61
Page 62

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
DMI Event Logging Submenu
Use this submenu to configure the DMI event logging features.
Table 22. DMI Event Logging Submenu
Feature Options Description
Event log capacity No options Indicates if there is space available in the event log.
Event log validity No options Indicates if the contents of the event log are valid.
View DMI event log No options Enables viewing of DMI event log.
Clear all DMI event logs No (default)
Yes
Event Logging Disabled
Enabled (default)
ECC Event Logging Disabled
Enabled (default)
Mark DMI events as read No options Marks all DMI events as read.
Clears the DMI Event Log after rebooting.
Enables logging of DMI events.
Enables logging of ECC events.
Video Configuration Submenu
Use this submenu to configure video features.
Table 23. Video Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
Palette Snooping Disabled (default)
Enabled
Controls the ability of a primary PCI graphics controller to
share a common palette with an ISA add-in video card.
62
Page 63

Security Menu
Use this menu to set passwords and security features.
Table 24. Security Menu
Feature Options Description
User Password Is No options Reports if there is a user password set.
Administrator Password Is No options Reports if there is an administrator
Set User Password Password can be up to seven
alphanumeric characters.
Set Administrative Password Password can be up to seven
alphanumeric characters.
Clear User Password No options Pressing <Enter> clears the user
User Setup Access None
View Only (default)
Limited Access
Full
Unattended Start Disabled (default)
Enabled
Using the BIOS Setup Program
password set.
Specifies the user password.
Specifies the administrator password.
password.
Enables or disables user access to the
Setup program.
Enables the unattended start feature.
When enabled, the computer boots, but
the keyboard is locked.
The user must enter a password to
unlock the computer or boot from a
diskette.
Power Menu
Use this menu to set power management features.
Table 25. Power Menu
Feature Options Description
Power Management Disabled
Enabled (default)
Inactivity Timer Off (default)
1 Minute
5 Minutes
10 Minutes
20 Minutes
30 Minutes
60 Minutes
120 Minutes
Hard Drive Disabled
Enabled (default)
VESA† Video Power Down
Fan Always On No (default)
Disabled
Enabled (default)
Yes
Enables or disables the BIOS power
management feature.
Specifies the amount of time before the
computer enters standby mode.
Enables power management for hard
disks during standby and suspend modes.
Enables power management for video
during standby and suspend modes.
Select YES to force a fan to remain on
when the system is in a power-managed
state.
63
Page 64

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Boot Menu
Use this menu to specify the boot features and the boot sequence.
Table 26. Boot Menu
Feature Options Description
QuickBoot Mode Disabled
Enabled (default)
Scan User Flash Area Disabled (default)
Enabled
After Power Failure Stay Off
Last State (default)
Power On
On LAN Stay Off
Power On (default)
On Modem Ring Stay Off (default)
Power On
On PME Stay Off (default)
Power On
First Boot Device
Second Boot Device
Third Boot Device
Fourth Boot Device
Fifth Boot Device
Hard Drive submenu No options Lists available hard drives.
Removable Devices
submenu
Removable devices
Hard Drive
ATAPI CD-ROM Drive
Network boot
LANDesk Service Agent
No options Lists available removable devices.
Enables the computer to boot without running certain
POST tests.
Enables the BIOS to scan the flash memory for user
binary files that are executed at boot time.
Specifies how the computer responds following a
power failure.
Stay Off keeps power OFF until the power button is
pressed.
Last State restores previous power state before a
power failure.
Power On restores power without restoring previous
power state.
Specifies how the computer responds to a LAN wakeup
event when the power is OFF.
Specifies how the computer responds to an incoming
call on an installed modem when the power is off.
Specifies how the computer responds to a PCI power
management enable event when the power is OFF.
Specifies the boot sequence from the available
devices. To Specify Boot Sequence:
1. Select the boot device with <↑> or <↓>.
2. Press <+> to move the device up the list or <-> to
3. The operating system assigns a drive letter to each
4. Changing the order of the devices changes the
When selected, displays the Hard Drive submenu.
When selected, displays the Removable Devices
submenu.
move the device down the list.
boot device in the order listed.
drive lettering.
64
Page 65

Using the BIOS Setup Program
Boot Options
In the Setup program, the user can choose to boot from a diskette drive, hard drive, CD-ROM, or
the network. The default setting is for the diskette drive to be the primary boot device and the hard
drive to be the secondary boot device.
Booting from CD-ROM is supported in compliance to the El Torito bootable CD-ROM format
specification. Under the Boot menu in the Setup program, CD-ROM is listed as a boot device.
Boot devices are defined in priority order.
The network can be selected as a boot device. This selection allows booting from a network add-in
card or on-board LAN with a remote boot ROM installed. The LANDesk Service Agent can be
used to perform service boots if the network is equipped with a suitable LANDesk Configuration
Manager server.
Hard Drive Submenu
Use this submenu to configure the boot sequence for hard drives.
Table 27. Hard Drive Submenu
Options Description
Installed hard drive
Bootable ISA Cards
Specifies the boot sequence for the hard drives attached to the computer.
To Specify Boot Sequence:
1. Select the boot device with <↑> or <↓>.
2. Press <+> to move the device up the list or <-> to move the device down
the list.
3. The operating system assigns a drive letter to each device in the order
listed.
4. Changing the order of the devices changes the drive lettering.
65
Page 66

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Removable Devices Submenu
Use this submenu to configure the boot sequence for removable devices.
Table 28. Removable Devices Submenu
Options Description
Legacy Floppy Drives Specifies the boot sequence for the removable devices attached to the
computer.
To Specify Boot Sequence:
1. Select the boot device with <↑> or <↓>.
2. Press <+> to move the device up the list or <-> to move the device down
the list.
3. The operating system assigns a drive letter to each device in the order
listed.
4. Changing the order of the devices changes the drive lettering.
Exit Menu
Use this menu to exit the Setup Program, save changes, load defaults, and save defaults.
Table 29. Exit Menu
Feature Description
Exit Saving Changes Exits and saves the changes in CMOS RAM.
Exit Discarding Changes Exits without saving any changes made in Setup.
Load Setup Defaults Loads the default values for all the Setup options.
Load Custom Defaults Loads the custom defaults for Setup options.
Save Custom Defaults Saves the current values as custom defaults.
Normally, the BIOS reads the Setup values from flash memory.
If this memory is corrupted, then the BIOS reads the custom defaults.
If no custom defaults are set, then the BIOS reads the factory defaults.
Discard Changes Discards changes without exiting Setup.
The option values present when the computer was turned on are used.
66
Page 67

4 Using the BIOS Features
The MS440GX motherboard uses an Intel/Phoenix BIOS, which is stored in flash memory and can
be upgraded using a disk-based program.
The flash memory also contains the BIOS Setup Program (described in Chapter 3), Power-On Self
Test (POST), Advanced Power Management (APM), the PCI auto-configuration utility, and
Windows 98-ready Plug and Play code.
This motherboard supports system BIOS shadowing, allowing the BIOS to execute from 64-bit
onboard write-protected DRAM.
The BIOS displays a message during POST identifying the type of BIOS and the revision code.
The initial production BIOS is identified as 4M4SG0X0.86E.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Topic/Procedure Page
How to Prepare for the Upgrade 68
Obtaining the BIOS Upgrade File 68
Recording the Current BIOS Settings 68
Creating a Bootable Floppy Disk 69
Creating the BIOS Upgrade Floppy Disk 69
Upgrading the BIOS 70
Recovering the BIOS 71
Changing the BIOS Language 72
Plug and Play: PCI Autoconfiguration 72
ISA Plug and Play 73
ISA Legacy Devices 73
PCI IDE Support 73
Desktop Management Interface (DMI) 74
Advanced Power Management (APM) 74
Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) 75
Language Support 76
OEM Logo or Scan Area 76
USB Legacy Support 77
BIOS Security Features 77
Recovering the BIOS Data 78
67
Page 68

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
How to Prepare for the Upgrade
Before attempting to upgrade the BIOS, prepare for the upgrade process as follows:
• Obtain the BIOS upgrade file
• Record the current BIOS settings
• Create a bootable floppy disk
• Create the BIOS upgrade floppy disk
Obtaining the BIOS Upgrade File
Use the BIOS upgrade file to upgrade to a new version of the BIOS.
The BIOS upgrade file is a compressed self-extracting archive that contains all the files you need
to upgrade the BIOS. The file contains the following elements:
• New BIOS files
• BIOS recovery files
• Intel Flash Memory Update Utility
You can obtain the BIOS upgrade file from the Intel World Wide Web site:
http://www.intel.com.
NOTE
✏
Please review the instructions distributed with the update utility before attempting a BIOS
upgrade.
The Intel Flash Memory Update Utility allows you to:
Upgrade the BIOS in flash memory.
•
Update the language section of the BIOS.
•
Recording the Current BIOS Settings
1. Boot the computer and press
Press <F2> Key if you want to run SETUP
NOTE
✏
Do not skip step 2. You will need these settings to configure your computer at the end of the
upgrade procedure.
when you see the message:
<F2>
2. Write down the current settings in the BIOS Setup program.
68
Page 69

Using the BIOS Features
Creating a Bootable Floppy Disk
NOTE
✏
If your drive A is an LS-120 diskette drive, then you must use a 1.44-MB floppy diskette as the
bootable BIOS upgrade floppy disk. The computer is unable to recover a BIOS from an LS-120
diskette.
Procedure To: Create a Bootable Floppy Disk
Step Action
1 Use a DOS or Windows 95 system to create the floppy disk.
2 Insert a floppy disk in floppy drive A.
3or
for a formatted floppy disk, type: sys a:
4 Press <Enter>.
Creating the BIOS Upgrade Floppy Disk
Obtain the BIOS upgrade and then use the procedure in the following table.
Procedure To: Create the BIOS Upgrade Floppy Disk
Step Action
1 Copy the BIOS upgrade file to a temporary directory on your hard disk.
2 From the C:\ prompt, change to the temporary directory.
3 To extract the file, type the name of the BIOS upgrade file, for example: 10006BI1.EXE
4 Press <Enter>. The extracted file contains the following files:
LICENSE.TXT, BIOINSTR.TXT, BIOS.EXE
5 Read the LICENSE.TXT file, which contains the software license agreement and the
BIOINSTR.TXT file, which contains the instructions for the BIOS upgrade.
6 Insert a bootable floppy disk into drive A.
7 To extract the BIOS.EXE file to the floppy disk, change to the temporary directory that holds the
BIOS.EXE file and type: BIOS A:
8 Press <Enter>.
9 The floppy disk now holds the new BIOS files, the Intel Flash Update Utility, and the recovery
files.
69
Page 70

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Upgrading the BIOS
Procedure To: Upgrade the BIOS
Step Action
1 Boot the computer with the BIOS upgrade floppy disk in drive A.
2 The flash memory update utility screen appears.
3 Select Update Flash Memory From a File.
4 Select Update System BIOS.
5 Press <Enter>.
6 Use the arrow keys to select the correct .bio file.
7 Press <Enter>.
8 When the utility asks for confirmation to flash the new BIOS into memory.
Then select Continue with Programming.
9 Press <Enter>.
10 When the utility displays the message upgrade is complete.
Then remove the floppy disk.
11 Press <Enter>.
12 As the computer boots, check the BIOS identifier (version number) to ensure that the upgrade
was successful.
13 When you see the message Press <F2> Key if you want to run SETUP
Then Press <F2> to enter the BIOS Setup Program.
14 For proper operation, load the BIOS Setup Program defaults by pressing <F9>.
15 Press <Enter> to accept the defaults.
16 Set the options in the BIOS Setup Program to the settings you wrote down before the BIOS
upgrade.
17 Press <F10> to save the settings.
18 Press <Enter> to accept the settings.
19 Turn OFF the computer and reboot.
70
Page 71

Using the BIOS Features
Recovering the BIOS
Although unlikely, if an interruption should occur during a BIOS upgrade, the BIOS could be
damaged. If a BIOS upgrade interruption does occur, then follow the procedure in the following
table to recover the BIOS. This procedure uses recovery mode for the BIOS Setup Program.
NOTE
✏
Because of the small amount of code available in the non-erasable boot block area, there is no
video support. You will not see anything on the screen during this procedure. Monitor the
procedure by listening to the speaker and looking at the floppy drive LED.
Procedure To: Recover the BIOS
Step Action
1 Turn OFF the computer.
2 Disconnect the computer’s power cord and disconnect all external peripherals.
3 Remove the computer cover and locate the configuration jumper block.
4 Remove the jumper from the BIOS Setup configuration jumper block (J4J1) to set recovery mode
for Setup. See page 42 for the location of the BIOS Setup configuration jumper block.
5 Insert the bootable BIOS upgrade floppy disk into floppy drive A.
6 Replace the computer cover, connect the power cord, turn ON the computer, and allow it to boot.
The recovery process will take a few minutes.
7 Listen to the speaker.
Two beeps and the end of activity in drive A indicate successful BIOS recovery.
A series of continuous beeps indicates failed BIOS recovery.
8 If recovery fails, return to Step 1 and repeat process.
9 If recovery is successful, turn off the computer and disconnect its power cord.
10 Remove the computer cover and continue with the following steps.
11 Replace the jumper back on to pins 1-2 on the BIOS Setup configuration jumper block (J4J1) to
set normal mode for Setup.
12 Leave the upgrade disk in drive A, replace the computer cover, and connect the computer’s
power cord.
13 Turn on the computer and continue with the BIOS upgrade procedure.
71
Page 72

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Changing the BIOS Language
You can use the BIOS upgrade utility to change the language the BIOS uses for messages and the
Setup program. Use a bootable floppy disk containing the Intel Flash Memory Update Utility and
language files (see “Upgrading the BIOS” on Page 70).
Procedure To: Change the BIOS Language
Step Action
1 Boot the computer with the bootable floppy disk in drive A.
2 The BIOS upgrade utility screen appears.
3 Select Update Flash Memory From a File.
4 Select Update Language Set.
5 Press <Enter>.
6 Select drive A and use the arrow keys to select the correct .lng file.
7 Press <Enter>.
8 When the utility asks for confirmation that you want to flash the new language into memory,
select Continue with Programming.
9 Press <Enter>.
10 When the utility displays the message upgrade is complete, remove the floppy disk.
11 Press <Enter>.
12 The computer will reboot and the changes will take effect.
Plug and Play: PCI Autoconfiguration
The BIOS can be set to automatically configure PCI devices and Plug and Play devices. PCI
devices may be onboard or add-in cards. Plug and Play devices are add-in cards built to meet the
Plug and Play specification.
Autoconfiguration lets a user insert or remove PCI or Plug and Play cards without having to
configure the system. When a user turns on the system after adding a PCI or Plug and Play card,
the BIOS can automatically configure interrupts, the I/O space, and other system resources. Any
interrupts set to Available in Setup are considered to be available for use by the add-in card.
PCI interrupts are distributed to available ISA interrupts that have not been assigned to an ISA
card or to system resources. The assignment of PCI interrupts to ISA IRQs is dependent upon a
number of factors including type and number of add-in cards, slot selection, and operating system.
Any change to the hardware or system software configuration can cause a change to the interrupt
configuration of existing devices. PCI devices can share an interrupt, but an ISA device cannot
share an interrupt allocated to PCI or to another ISA device. Autoconfiguration information is
stored in the extended system configuration data (ESCD) format.
For information about the versions of PCI and Plug and Play supported by this BIOS, see Plug and
Play Specification Version 1.0a, May 5, 1994, Compaq Computer Corp., Phoenix Technologies
Ltd., Intel Corporation.
72
Page 73

Using the BIOS Features
ISA Plug and Play
If Plug and Play operating system is selected in Setup, then the BIOS autoconfigures only ISA
Plug and Play and PCI cards that are required for booting (IPL devices). If Plug & Play OS is not
selected in Setup, then the BIOS autoconfigures all Plug and Play ISA and PCI cards.
NOTE
✏
If Plug & Play OS is selected in Setup, then PCI or PnP add-in cards that are not required for
booting will not be available unless they are initialized and assigned resources by the operating
system or other program.
ISA Legacy Devices
ISA legacy devices are not autoconfigurable, therefore the resources for them must be reserved in
the Setup program or with an ISA configuration utility.
PCI IDE Support
If Auto is selected as a primary or secondary IDE device in Setup, then the BIOS automatically
sets up the two local-bus IDE connectors with independent I/O channel support. The IDE interface
supports PIO Mode 3, PIO Mode 4, and Ultra DMA hard drives and recognizes any ATAPI
devices, including CD-ROM drives, tape drives, and LS-120 diskette drives.
The BIOS determines the capabilities of each drive and configures them so as to optimize capacity
and performance. To take advantage of the high-capacity storage devices, hard drives are
automatically configured for logical block addressing (LBA) and to PIO Mode 3, PIO Mode 4, or
Ultra DMA depending on the capability of the drive.
To override the autoconfiguration options, use the specific IDE device options in Setup. The
ATAPI specification recommends that ATAPI devices be configured as shown in Table 32.
Table 30. Recommendations for Configuring an ATAPI Device
Primary Cable Secondary Cable
Configuration
Normal, no ATAPI ATA
Disk and CD-ROM for enhanced IDE systems ATA ATAPI
Legacy IDE system with only one cable ATA ATAPI
Enhanced IDE with CD-ROM and a tape or
two CD-ROMs
Drive 0 Drive 1 Drive 0 Drive 1
ATA ATAPI ATAPI
73
Page 74

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Desktop Management Interface (DMI)
Desktop Management Interface (DMI) is an interface for managing computers in an enterprise
environment. The main component of DMI is the management information format (MIF)
database, which contains information about the computing system and its components such as
system types, capabilities, operational status, and installation dates for system components.
The MIF database defines the data and provides the method for accessing this information.
The BIOS stores and reports the following DMI information:
• BIOS data, such as the BIOS revision level
• Fixed-system data, such as peripherals, serial numbers, and asset tags
• Resource data, such as memory size, cache size, and processor speed
• Dynamic data, such as event detection and error logging
OEMs can use a utility that programs flash memory so the BIOS can report on system and chassis
information. This utility is available through Intel sales offices.
DMI does not work directly under non-Plug and Play operating systems (e.g., Windows NT 4.0).
However, the BIOS supports a DMI table interface for such operating systems. Using this support,
a DMI service-level application running on a non-Plug and Play OS can access the DMI BIOS
information.
Advanced Power Management (APM)
The BIOS supports APM and standby mode. The energy saving standby mode can be initiated in
the following ways:
• Time-out period specified in Setup
• From the operating system, such as the Suspend menu item in Windows 98
In standby mode, the motherboard reduces power consumption by using SMM capabilities,
spinning down hard drives, and reducing power to or turning off VESA DPMS-compliant
monitors. Power-management mode can be enabled or disabled in Setup.
While in standby mode, the system retains the ability to respond to external interrupts and service
requests, such as incoming faxes or network messages. Any keyboard or mouse activity brings the
system out of standby mode and immediately restores power to the monitor.
The BIOS enables APM by default; but the operating system must support an APM driver for the
power-management features to work. Windows 98 supports the power management features upon
detecting that APM is enabled in the BIOS.
74
Page 75

Using the BIOS Features
Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)
ACPI gives the operating system direct control over the power management and Plug and Play
functions of a computer. ACPI requires an ACPI-aware operating system. ACPI features include:
• Plug and Play (including bus and device enumeration) and APM functionality normally
contained in the BIOS
• Power management control of individual devices, add-in boards (some add-in boards may
require an ACPI-aware driver), video displays, and hard disk drives
• A Soft-off feature that enables the operating system to power off the computer
• Support for multiple wake up events (see Table 32)
• Support for a front panel power and sleep mode switch. Table 31 describes the system states
based on how long the power switch is pressed, depending on how ACPI is configured with an
ACPI-aware operating system
Table 31. Effects of Pressing the Power Switch
…and the power switch is
If the system is in this state…
Off Less than four seconds Power on
On Less than four seconds Soft off/Suspend
On More than four seconds Fail safe power off
Sleep Less than four seconds Wake up
pressed for …the system enters this state
System States and Power States
Under ACPI, the operating system directs all system and device power state transitions. The
operating system puts devices in and out of low-power states based on user preferences and
knowledge of how devices are being used by applications. Devices that are not being used can be
turned off. The operating system uses information from applications and user settings to put the
system as a whole into a low-power state.
75
Page 76

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Wake Up Devices and Events
The table below describes which devices or specific events can wake the computer from specific
states. Sleeping states S4BIOS and S5 are the same for the wake up events.
Table 32. Wake Up Devices and Events
These devices/events can wake
up the computer… …from this state
Power switch S1, S4BIOS, S5
RTC alarm S1, S4BIOS, S5
LAN S1, S4BIOS, S5
Modem S1, S4BIOS, S5
IR command S1
USB S1
PS/2 keyboard S1
PS/2 mouse S1
Sleep button S1
Plug and Play
In addition to power management, ACPI provides controls and information so that the operating
system can facilitate Plug and Play device enumeration and configuration. ACPI is used only to
enumerate and configure motherboard devices that do not have other hardware standards for
enumeration and configuration. PCI devices on the motherboard, for example, are not enumerated
by ACPI.
BIOS Support
The BIOS supports both APM and ACPI. If the board is used with an ACPI-aware operating, the
BIOS provides ACPI support. Otherwise, it defaults to APM support.
Language Support
Five languages are available: American English, German, Italian, French, and Spanish. The
default language is American English unless another language is programmed into the BIOS using
the flash memory update utility.
The BIOS includes extensions to support the Kanji character set and other non-ASCII character
sets. Translations of other languages may become available at a later date.
OEM Logo or Scan Area
A 4 KB flash-memory user area at memory location FFFF8000h-FFFF8FFFh is for displaying a
custom OEM logo during POST. A utility is available from Intel to assist with installing a logo
into the flash memory. Contact Intel customer support for further information.
76
Page 77

Using the BIOS Features
USB Legacy Support
USB legacy support enables USB keyboards and mice to be used even when no operating system
USB drivers are in place. By default, USB legacy support is disabled and is only intended to be
used in accessing BIOS Setup and installing an operating system that supports USB.
This sequence describes how USB legacy support operates in the default (disabled) mode.
1. When you power up the computer, USB legacy support is disabled.
2. POST begins.
3. USB legacy support is temporarily enabled by the BIOS. This allows you to use a USB
keyboard to enter the Setup program or the maintenance mode.
4. POST completes and disables USB legacy support (unless it was set to Enabled while in
Setup).
5. The operating system loads. While the operating system is loading, USB keyboards and mice
are not recognized. After the operating system loads the USB drivers, the USB devices are
recognized.
To install an operating system that supports USB, enable USB Legacy support in BIOS Setup and
follow the operating system’s installation instructions. Once the operating system is installed and
the USB drivers configured, USB legacy support is no longer used. USB Legacy Support can be
left enabled in BIOS Setup if needed.
NOTES
✏
If USB legacy support is enabled, then do not mix USB and PS/2 keyboards and mice. For
example, do not use a PS/2 keyboard with a USB mouse, or a USB keyboard and a PS/2 mouse.
Do not use USB devices with an operating system that does not support USB. USB legacy is not
intended to support the use of USB devices in a non USB operating system.
USB legacy support is for keyboards and mice only. Hubs and other USB devices are not
supported.
BIOS Security Features
The BIOS includes security features that restrict access to the BIOS Setup program and who can
boot the computer. An administrator password and a user password can be set for the Setup
program and for booting the computer using options on the Security Menu (see Figure 13) with the
following restrictions:
Password Modes
• If in Administrator Mode, then the administrator password gives unrestricted access to view
and change all Setup options in the Setup Program.
• If in User Mode, then the user password gives restricted access to view and change Setup
options in the Setup Program.
77
Page 78

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Password Sets
• If only the administrator password is set, then press the <ENTER> key at the password prompt
of the Setup Program to allow the user restricted access to Setup.
• If both administrator and user passwords are set then users can enter either password to access
Setup and privileges afforded are dependent upon which password is entered.
• When the user password is set, then who can boot the computer is restricted and the password
prompt will be displayed before the computer is booted.
• If only the administrator password is set then the computer boots without asking for a
password.
• If both passwords are set then enter either password to boot the computer.
Table 33 shows the effects of setting the administrator and user passwords. This table is for
reference only and is not displayed on the screen.
Table 33. Administrator and User Password Functions
Administrator
Password Set
Neither Can change all
Administrator
only
User only N/A Can change
Administrator
and user set
* If no password is set, then any user can change all Setup options.
Mode User Mode Setup Options
options *
Can change all
options
Can change all
options
Can change
all options *
Can change a
limited number
of options
all options
Can change a
limited number
of options
None None None
Administrator
Password
Enter Password
Clear User Password
Administrator
Password
Enter Password
Password to
Enter Setup
Administrator None
User User
Administrator
or user
Recovering BIOS Data
Some types of failure can destroy the BIOS. For example, the data can be lost if a power outage
occurs while the BIOS is being updated in flash memory. The BIOS can be recovered from a
diskette using the BIOS recovery mode
To create a BIOS recovery diskette, a bootable diskette must be created and the recovery files
copied to it. The recovery files are available from Intel. Contact Intel customer support for further
information.
Password
During Boot
Administrator
or user
NOTE
✏
If the computer is configured to boot from an LS-120 diskette), then the BIOS recovery diskette
must be a standard 1.44 MB diskette, not a 120 MB diskette
78
Page 79

5 Technical Reference
This chapter describes the location, pinouts, and signals associated with the various types of
connectors used in the MS440GX motherboard.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Topic/Procedure Page
Front Panel Connectors 80
Front Panel I/O Connectors 81
Speaker 81
Reset Switch 81
Power/Sleep LED 82
Hard Drive Activity LED 82
Infrared Port 82
Power Switch 82
Front Panel Pin Connector Mapping 83
Back Panel Connectors 84
Keyboard and Mouse Interface 85
Universal Serial Bus (USB) 85
Parallel Port 86
Serial Ports 86
I/O Shield 88
Midboard Connectors 89
Add-in Card Connectors 90
Audio Connectors 91
CD-ROM Audio 92
Telephony 92
Fan Connectors 93
Thermal Considerations 94
Power Connectors 96
Peripheral Interface Connectors 99
Security and Hardware Management Connectors 100
Chassis Intrusion connectors 102
Wake on LAN Technology Connector 102
Wake on Modem 102
Memory Map 103
DMA Channels 103
I/O Map 104
PCI Configuration Space Map 106
LAN Subsystem Software 107
Interrupts 107
PCI Interrupt Routing Map 108
Interrupt Routing Example 109
79
Page 80

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Front Panel Connectors (L)
The illustration below shows the location of the front panel connectors. Table 34 indicates the
functional purpose of each connector identified in the illustration.
21654810 1312 15 17 201918 2422 25 2726
A
A Speaker D Hard disk drive activity LED
B Reset switch E Infrared port
C Power/sleep LED F Power switch
BC DE
Figure 14. Front Panel Connectors
F
OM07112
80
Page 81

Table 34. Front Panel I/O Connectors
Call-out Connector/Function Pin Signal Name
A SPEAKER/
Provides error beep code information during the
POST and is not connected to audio
subsystem.
B RESET SWITCH/
Resets the motherboard and initiates running
the POST.
NONE 7 Key
C POWER/SLEEP LED/
Displays indicating if computer is ON or in sleep
mode.
NONE 11 Key
D HARD DISK DRIVE ACTIVITY LED/
Visually indicate if data is being read from or
written to an IDE or SCSI hard drive.
NONE 16 Key
E INFRARED PORT/
Can be configured to support an IrDA module
enabling data files to be transferred to/from
various portable devices.
NONE 23
F POWER ON SWITCH/
Enables system to be powered ON or OFF.
1
2
3
4
5
6
8
9
10
12
13
14
15
17
18
19
20
21
22
24
25
26
27
BUZZER_B1
BUZZER_A2
Key
+5V
FP_RESET#
Ground
GREEN/YELLOW_INV
Key
YEL_BLNK#
+5V
DASDACTIVE#
Key
+5V
IRLS1
IRTX
Ground
IRRX
Key
+5V
Key
+5V
No Connect (N.C.)
Ground
SWITCH
Technical Reference
Speaker
Connect pins 1 and 2 to use the built-in speaker. Leave the jumper off pins 1 and 2 and connect
the external speaker to J12A1 to use the external speaker. See page 91 for the location of the
external speaker connector.
Reset Switch
Pins 5 and 6 can be connected to a momentary SPST type switch that is normally open.
When the switch is closed, then the motherboard resets and runs the POST.
81
Page 82

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Power/Sleep LED
These pins can be connected to a multicolor LED that lights when the computer is powered on or
in sleep mode. The possible states for this LED are:
If state = OFF, then Power is OFF.
If state = GREEN, then Power is ON.
If state = YELLOW, then in Sleep Mode.
Hard Drive Activity LED
These pins can be connected to an LED to provide a visual indicator that data is being read from or
written to an IDE or SCSI hard drive, as well as add-in cards that provide an activity signal. For
the LED to function properly, the IDE drive must be connected to the onboard IDE controller.
This LED will also show activity for devices connected the the hard drive LED header.
Infrared Port
Serial Port 2 can be configured to support an IrDA module connected to the front panel infrared
connector. After the IrDA interface is configured, files can be transferred to or from portable
devices such as laptop computers, PDAs, and printers using application software.
Power Switch
Pins 26 and 27 can be connected to a front panel power switch. Because of debounce circuitry on
the motherboard, the switch must pull the SW_ON# pin to ground for at least 50 ms to signal the
power supply to switch on or off. At least two seconds must pass before the power supply will
recognize another on/off signal.
NOTE
✏
When BIOS is active, the power switch is recognized immediately. When BIOS is not active
(POST, system lock-up) then the power switch is only recognized if held in for four seconds.
CAUTION
If you need to turn off the computer during POST, then hold the power switch in for four seconds;
otherwise the computer will not switch off.
82
Page 83

Technical Reference
Front Panel Pin Connector Mapping
This table describes the operational effect(s) of connecting various devices such as switches and
LED lights to the Front Panel pin connectors.
Table 35. Pin Connector Functionality
If pin numbers .... are connected to a .... Then the operational effect is ....
5,6 Momentary SPST type switch that is
normally OPEN.
8,9,10,11 Multicolor LED that lights when the
computer is ON.
OR in Sleep Mode.
If using a single color LED, it will blink
during suspend state.
12,13,14,15 LED
There are two SCSI LED headers
(J10E1 and J10A1) on the board.
If you connect a SCSI card’s LED cable
to either of them and connect the Hard
Drive Activity LED on the front panel,
then the LED will work either when the
IDE hard drive or the SCSI drive is
operating.
When using a SCSI controller card with
an activity signal, connect a cable from
the card’s drive activity header to
header J10E1 or J10A1.
17,18,19,20,21,22 IrDA module TO enable transfer of files to or from
26,27 Front Panel power switch that pulls the
SW_ON# pin to ground for at least
50 ms
To reset the motherboard and run the
POST when the switch is closed.
To visually display one of three states:
OFF = Power OFF
Green = Power ON
Yellow = Sleep
To provide a visual indication of data
being read from or written to an IDE or
SCSI hard drive.
AND show activity for devices
connected to the hard drive LED
header.
NOTE
✏
IDE drive must be connected to
the onboard IDE controller.
portable devices such as laptop
computers, PDAs, and printers using
applications software.
TO turn the computer’s power supply
ON or OFF.
NOTE
✏
At least 2 seconds must pass
before the power supply will
recognize another ON/OFF
signal.
CAUTION
IF you need to turn OFF the
computer during POST
THEN hold the power switch IN
for 4 seconds
ELSE the computer will not
switch OFF.
83
Page 84

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Back Panel Connectors (E)
The figure below shows location of the back panel connectors.
A
C
D
BF
E
G
I
J
HK
A PS/2 Keyboard or Mouse G Serial Port B
B PS/2 Keyboard or Mouse H LAN
C USB Port 1 I Audio Line Input
D USB Port 0 J Audio Line Output
E Parallel Port K Microphone Input
F Serial Port A
Figure 15. Back Panel Connectors
OM07122
84
Page 85

Technical Reference
Keyboard and Mouse Interface
PS/2 keyboard and mouse connectors are located on the back panel (see Figure 15/Callouts A
and B). The 5V lines to these connectors are protected with a PolySwitch
healing fuse, reestablishes the connection after an over-current condition is removed.
NOTE
✏
The mouse and keyboard can be plugged into either of the PS/2 connectors. Power to the
computer should be turned off before a keyboard or mouse is connected or disconnected.
The keyboard controller contains the AMI Megakey keyboard and mouse controller code, provides
the keyboard and mouse control functions, and supports password protection for power on/reset. A
power on/reset password can be specified in Setup.
The keyboard controller also supports the hot-key sequence <Ctrl><Alt><Del> for a software
reset. This key sequence resets the computer’s software by jumping to the beginning of the BIOS
code and running the Power-On Self Test (POST).
†
circuit that, like a self-
Table 36. PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse Connectors
Pin Signal Name
1 Data
2 No connect
3 Ground
4 +5 V (fused)
5 Clock
6 No connect
Universal Serial Bus (USB)
The motherboard has two USB ports. One USB peripheral can be connected to each port. For
more than two USB devices, an external hub can be connected to either port. The motherboard
fully supports the universal host controller interface (UHCI) and uses UHCI-compatible software
drivers.
NOTE
✏
Computer systems that have an unshielded cable attached to a USB port may not meet FCC
Class B requirements, even if no device or a low-speed USB device is attached to the cable. Use
shielded cable that meets the requirements for high-speed devices.
85
Page 86

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Parallel Port
The connector for the multimode bidirectional parallel port is a 25-pin D-Sub connector located on
the back panel (see Figure 15/Callout E). In the Setup program, the parallel port can be configured
for the following:
• Compatible (standard mode)
• Bidirectional (PS/2 compatible)
• Extended Parallel Port (EPP)
• Enhanced Capabilities Port (ECP)
Refer to the MS440GX Motherboard Technical Product Specification for connector pinout
information.
Serial Ports
The two 9-pin D-Sub serial port connectors on the back panel are compatible with 16450 and
16550A UARTs.
Refer to the MS440GX Motherboard Technical Product Specification for connector pinout
information.
Table 37 shows the pinouts for the LAN Connector.
Table 37. LAN Connector
Pin Signal Name
1 TX+
2 TX3 RX+
4 No connect
5 No connect
6 RX7 No connect
8 No connect
Table 38. Audio Line In Connector
Pin Signal Name
Sleeve Ground
Tip Audio Left In
Ring Audio Right In
86
Page 87

Table 39. Audio Line Out Connector
Pin Signal Name
Sleeve Ground
Tip Audio Left Out
Ring Audio Right Out
Table 40. Audio Mic In Connector
Pin Signal Name
Sleeve Ground
Tip Mono In
Ring Electret Bias Voltage
Technical Reference
87
Page 88

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
I/O Shield
Systems based on the MS440GX motherboard need the back panel I/O shield to pass EMI
compliance verification. The back panel I/O shield must meet specific dimension and material
requirements.
Figure 16 shows the critical dimensions of a chassis-independent I/O shield.
Additional design considerations for I/O shields relative to chassis requirements are described in
the ATX form factor specification.
0.201
0.00
0.461
1.209
1.216
1.433
1.689
0.207
0.00
0.409
0.773
1.534
1.803
Note: Material = 0.010 ±.0.001 Stainless Steel, Alloy 301 Half Hard
Outside(Rear)
View of Shield
2.959
4.180
5.184
5.785
5.975
0.617
1.207
1.450
1.489
6.183
88
OM07110
Figure 16. Back Panel I/O Shield Dimensions (ATX Chassis-Independent)
Page 89

Technical Reference
Midboard Connectors
This section addresses the location and functionality associated with the Midboard family of
motherboard connectors. The Midboard connectors are organized into the following functional
groups.
Table 41. Connector Groups
Connector Family Functional Group(s) See Figure/Table No.
Add-in Card Connectors ISA
PCI
A.G.P.
Audio ATAPI-style Telephony
ATAPI CD Audio
External Speaker
MIDI/Joystick
Fans Processor heatsink fans (4)
Front chassis fans (2)
Rear chassis fans (1)
Power 1 x 6
Primary and Secondary
VRM
Peripheral Interfaces Diskette
SCSI LED
IDE
Security and Hardware
Management
Front and Rear Intrude
Wake on LAN
Wake on Modem
See MS440GX
Technical Product
Specification (Order No.
710790-001)
18/42
18/43
18/44
18/45
See MS440GX
Technical Product
Specification (Order No.
710790-001)
21/48
21/49
21/50
See MS440GX
Technical Product
Specification (Order No.
710790-001)
23/52
23/53
23/54
89
Page 90

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Add-in Card Connectors
When the motherboard is installed in a chassis, there are a maximum of seven slots available for
installing add-in cards. The table immediately below Figure 17 identifies the seven slots by their
callout locations. All of the PCI bus connectors are bus master capable.
Figure 17 shows the location of the add-in card connectors.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
A ISA slot (shared with PCI bus connector 6) E PCI bus connector 3
B PCI bus connector 6 (shared with ISA bus
connector
C PCI bus connector 5 G PCI bus connector 1
D PCI bus connector 4 H A.G.P. connector
Figure 17. Add-in Card Connectors
90
F PCI bus connector 2
OM07115
Page 91

Technical Reference
Audio Connectors
Figure 18 shows the locations of the audio connectors. Tables 42 through 45 list the pinouts of the
audio connectors.
A
1
4
C
B
1
4
12
16
15
D
1
A ATAPI CD-ROM
B ATAPI-style telephony
C MIDI/Joystick
D External speaker
Figure 18. Audio Connectors
The audio connectors include the following:
• Back panel connectors: Line In, Line Out, Mic In
• CD-ROM audio (ATAPI)
• Telephony (ATAPI-style)
OM07118
91
Page 92

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
CD-ROM Audio
A 1 x 4-pin ATAPI-style connector is available for connecting an internal CD-ROM drive to the
audio mixer.
Telephony
A 1 x 4-pin ATAPI-style connector is available for connecting the monaural audio signals of an
internal telephony device, such as a modem, to the audio subsystem. A monaural audio-in and
audio-out signal interface is necessary for telephony applications such as speakerphones, modems,
and answering machines.
Table 42. ATAPI-Style Telephony
Connector(J1E1)
Pin Signal Name
1 MONO_IN (from external device)
2 Ground
3 Ground
4 TEL_MICIN
Table 43. ATAPI CD Audio Connector (J2E1)
Pin Signal Name
1 Left CD In
2 Ground
3 Ground
4 Right CD In
Table 44. External Speaker Connector
(J12A1)
Pin Signal Name
1 +5V
2 BUZZER_A
Table 45. MIDI/Joystick Connector (J2E2)
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 +5 V (fused) 9 Ground
2 +5 V (fused) 10 JBCY
3 JAB1 11 JACY
4 JBB1 12 JBB2
5 JACX 13 JAB2
6 JBCX 14 MIDI-IN
7 No connect 15 +5 V (fused)
8 MIDI-OUT 16 MIDI-PRESENT GP#
92
Page 93

Technical Reference
Fan Connectors
There are seven fan connectors on the motherboard. Four connectors are used for processor
heatsink fans and three are for chassis fans.
Figure 19 shows the location of the fan connectors. Table 46 lists the pinouts of the fan
connectors. The table immediately below Figure 19 indicates the maximum current ratings for the
fan connectors.
A B
1
1
1
C
1 1
D
E
G
1
1
F
OM07113
Component Max. Current Rating Component Max. Current Rating
A Rear chassis fan 600 mA E Processor heatsink fan 150 mA
B Processor heatsink fan 150 mA F Front chassis fan 1 500 mA
C Processor heatsink fan 150 mA G Front chassis fan 2 300 mA
D Processor heatsink fan 150 mA
Figure 19. Fan Connectors
93
Page 94

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Table 46. Fan Connectors
Pin Signal Name
1 TACH_OUT
2 +12 V
3 FAN_ENABLE
Thermal Considerations
Figure 20 shows the locations of the thermally-sensitive components. Table 47 lists the maximum
component case temperatures for motherboard components that could be sensitive to thermal
changes. Case temperatures could be affected by the operating temperature, current load, or
operating frequency. Maximum case temperatures are important when considering proper airflow
to cool the motherboard.
A
E
D
C
A Slot 2 (Application Processor) D 82371EB PIIX4E
B Slot 2 (Boot Processor) E 82443GX PAC
C Battery Case
Figure 20. Thermally Sensitive Components
B
OM07121
CAUTION
An ambient temperature that exceeds the board’s maximum operating temperature by 5 oC to 10 oC
might cause components to exceed their maximum case temperature. For information about the
maximum operating temperature, see the environmental specifications in Appendix C. When
determining system compliance, consideration should be given for maximum rated ambient
temperatures.
94
Page 95

Technical Reference
CAUTION
The motherboard printed wiring substrate is rated for 105 oC. Care should be taken to ensure the
maximum temperature of any component does not exceed the aboard substrate rating. This limit
should include a correction value for the maximum ambient operation temperature.
Table 47. Thermal Considerations for Components
Component Maximum Case Temperature Motherboard Location(s) (Fig. 1)
Pentium II Xeon processor 75 oC (thermal plate) F and G
Intel 82443GX (PAC) 105 oC (thermal plate) H
Intel 82371EB (PIIX4E) 85 oC (thermal plate) Q
Lithium Battery 70 oC (case) M
PWB Substrate 105 oC
95
Page 96

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Power Connectors
There are three power supply connectors and one connector for a VRM. Figure 21 shows the
power connectors. Tables 48 through 50 list the pinouts of the power connectors.
The primary and secondary power supply connectors are identical; either may be used with the
6-pin power connector for system configurations requiring less than 300 W. If the system power
requirements exceed 300 W, a power supply with two 20-pin connectors and a 6-pin connector
can be used, or dual power supplies can be used. VRMs used with this board must be compatible
with the VRM 8.3 DC-DC Converter Design Guidelines document.
1
1
11
1
6
11
2
1
10
20
10
20
40
39
A
B
C
D
OM07114
A 1x6 Power connector C Primary power supply connector
B Secondary power supply connector D VRM connector
Figure 21. Power Connectors
When the motherboard is used with an ATX-compliant power supply that supports remote power
ON/OFF, then the board can turn OFF system power through software control.
96
Page 97

Technical Reference
Table 48. 1x6 Power Connector
Pin Signal Name
1 Ground
2 Ground
3 Ground
4 +3.3 V
5 +3.3 V
6 +5 V (Keyed)
Table 49. Primary and Secondary Power Supply Connectors (J10H1)
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 +3.3 V 11 +3.3 V
2 +3.3 V 12 -12 V
3 Ground 13 Ground
4 +5 V 14 PWS_ON# (power supply remote on/off
control)
5 Ground 15 Ground
6 +5 V 16 Ground
7 Ground 17 Ground
8 PWRGD (Power Good) 18 -5 V
9 +5 VSB 19 +5 V
10 +12 V 20 +5 V
97
Page 98

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Table 50. VRM Connector (J13J1)
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 5VIN 21 VSS
2 5VIN 22 VCC
3 5VIN 23 VCC
4 5VIN 24 VSS
5 5VIN 25 VSS
6 5VIN 26 VCC
7 12VIN 27 VCC
8 12VIN 28 VSS
9 12VIN 29 VSS
10 SENSE 30 VCC
11 No connect 31 VCC
12 OUTEN 32 VSS
13 VID0 33 VSS
14 VID1 34 VCC
15 VID2 35 VCC
16 VID3 36 VSS
17 VID4 37 VSS
18 PWRGOOD 38 VCC
19 VCC 39 VCC
20 VSS 40 VSS
98
Page 99

Peripheral Interface Connectors
Figure 22 shows the location of the peripheral interface connectors.
12
D
Technical Reference
39 40
12
C
B
1
39 40
A Diskette Drive
B SCSI LED
C Secondary IDE
D Primary IDE
Figure 22. Peripheral Interface Connectors
Table 51. SCSI LED Connector (J10A1)
Pin Signal Name
1 SCSI_LED#
2 Ground
12
A
33 34
OM07116
99
Page 100

MS440GX Motherboard Product Guide
Security and Hardware Management Connectors
Figure 23 shows the security and hardware management connectors. Tables 52 through 54 list the
pinouts of the security and hardware management connectors.
D
C
1
1
1
1
BA
A Rear Chassis Intrusion
B Front Chassis Intrusion
C Wake On LAN technology connector
D Wake On Modem
Figure 23. Security and Hardware Management Connectors
OM07117
100
 Loading...
Loading...