Page 1

Vig390s
Motherboard
Manual
C O M P U T E R S N E T W O R K S S O L U T I O N S
..
®
G r e a t
Minds
T h i n k
®
0
Page 2

Viglen, EMC and the ‘CE’ mark
CE Marking
European standards are being harmonised across borders. If products comply with the same standards in all
European countries, product exporting and importing is made simple - paving our way to a common market. If
you buy a product with a 'CE' mark on it (shown below), on the box, in the manual, or on the guarantee - it
complies with the currently enforced directive(s).
Introduction to EMC
EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) is the term used to describe certain issues with RF (Radio Frequency)
energy. Electrical items should be designed so they do not interfere with each other through RF emissions. E.g.
If you turn on your microwave, your television shouldn't display interference if both items are CE marked to the
EMC directive.
If emitted RF energy is not kept low, it can interfere with other electrical circuitry - E.g. Cars Automatic Braking
Systems have been known to activate by themselves while in a strong RF field. As this has obvious
repercussions ALL electrical products likely to cause RF related problems have to be 'CE' marked from 1st
January 1996 onwards.
If a product conforms to the EMC directive, not only should its RF emissions be very low, but its immunity to RF
energy (and other types) should be high. The apparatus has to resist many 'real world' phenomena such as
static shocks and mains voltage transients.
Viglen’s Environment laboratory
To gain a 'CE' mark, the Viglen computer range has had to undergo many difficult tests to ensure it is
Electromagnetically Compatible. These are carried out in the in-house 'Environment lab' at Viglen Headquarters.
We have made every effort to guarantee that each computer leaving our factory complies fully with the correct
standards. To ensure the computer system maintains compliance throughout its functional life, it is essential you
follow these guidelines.
> Install the system according to Viglen’s instructions
> If you open up your Viglen:
> Keep internal cabling in place as supplied.
> Ensure the lid is tightly secured afterwards
> Do not remove drive bay shields unless installing a 'CE' marked peripheral in its place
> The clips or ‘bumps' around the lips of the case increase conductivity - do not remove or damage.
> Do not remove the ferrite ring from the L.E.D cables.
> Only use your Viglen computer with 'CE' marked peripherals
This system has been tested in accordance with European standards for use in residential and light industrial
areas-this specifies a 10 meter testing radius for emissions and immunity. If you do experience any adverse
affects which you think might be related to your computer, try moving it at least 10 meters away from the affected
item. If you still experience problems, contact Viglen’s Technical Support department who will put you straight
through to an EMC engineer - s/he will do everything possible to help. If modifications are made to your Viglen
computer system, it might breach EMC regulations. Viglen take no responsibility (with regards to EMC
characteristics) of equipment which has been tampered with or modified.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
1
Page 3

Copyrights and Trademarks
Please note
The material in this manual is subject to change without notice.
Trademarks
Microsoft, Windows, Windows NT, Windows 95,Windows 98, Windows ME,
Windows 2000 Pro, Windows XP Pro and MS-DOS are registered trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation. IBM PC, XT, AT and PS/2 are trademarks of International
Business Machines Corporation. Pentium and Pentium Pro are registered
trademarks of Intel Corporation. AMI BIOS is a registered trademark of American
Megatrends. All other trademarks are acknowledged. JAC-UP, Genie, Contender,
Dossier, Vig, Viglen, and Envy are trademarks of Viglen Limited.
Copyright and Patents
This manual and all accompanying software and documentation are copyrighted and
all rights reserved. This product, including software and documentation, may not, in
whole or in part, be copied, photocopied, translated or reduced to any electronic or
machine-readable form, without prior written consent except for copies retained by
the purchaser for backup.
© Copyright 2005 Viglen Limited
All Rights Reserved
Vig390s Manual Version 1.0
Printed in the United Kingdom
Liability
No warranty or representation, either expressed or implied, is made with respect to
this documentation, its quality, performance, merchantability or fitness for a particular
purpose. As a result the documentation is licensed as is, and you, the licensee, are
assuming the entire risk as to its quality and performance. The vendor reserves the
right to revise this operation manual and all accompanying software and
documentation and to make changes in the content without obligation to notify any
person or organisation of the revision or change.
In no event will the vendor be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental or
consequential damages arising out of the use or inability to use this product or
documentation, even if advised of the possibility of such damages. In particular, the
vendor shall not have liability for any hardware, software or data stored or used with
the product, including the costs of repairing, replacing or recovering such hardware,
software or data.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
2
Page 4

Contents
Chapter 1 Overview 5
System Board Components 6
Back Panel Connectors 7
Feature Summary 9
System Processor 10
System Memory 11
Memory Configurations 12
Intel® E7525 chipset (Northbridge) 15
Intel® 6300ESB I/O Controller (Southbridge) 16
Vig390s motherboard block diagram 17
USB Support 18
IDE Support 18
Parallel ATA IDE Interfaces 19
Serial ATA Support 19
Real-Time Clock, CMOS SRAM and Battery 20
I/O Controller 20
Audio Subsystem 22
Audio Connectors 23
LAN Subsystem 24
Hardware Management Subsystem 25
Power Management 26
ACPI 26
Hardware Support 28
Chapter 2 System Board Options 31
Overview of Jumper Settings 33
System Board Jumper Settings 34
Motherboard Connectors 38
Front Panel Connectors 39
Upgrading the CPU 40
Installing & Removing Dual In-Line memory Modules 46
Replacing the Clock/CMOS RAM Battery 48
Chapter 3 Solving Problems 49
Resetting the System 49
Troubleshooting Procedures 50
Problems Operating Add-in Boards 51
Problems and Suggestions 52
Error and Information Messages 54
BIOS Beep Codes 55
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
3
Page 5

Chapter 4 System BIOS 56
What is the BIOS? 56
The Power-on Sequence 56
AMI BIOS 57
Plug and Play: PCI Auto-configuration 58
PCI IDE Support 58
Desktop Management Interface (DMI) 59
Advanced Power Management (APM) 59
Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) 61
Configuring the Motherboard using BIOS Setup 63
Setting the Processor Speed 63
Clearing the Passwords 63
BIOS Setup Program 64
Main Menu 67
Advanced Menu 75
Power Menu 88
Boot Menu 94
Exit Menu 101
Upgrading the BIOS 102
Chapter 5 Technical Information 105
Enhanced IDE 105
Operating Systems and Hard Drives 106
Connector Signal Details 107
Power Supply Connector 110
Motherboard Resources 113
Other Information 115
Chapter 6 Glossary 116
Notes 120
Chapter 7 Suggestions 121
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
4
Page 6

Chapter 1: Overview
Introduction
This manual describes the Viglen Vig390s motherboard inside your computer. The
motherboard is the most important part of your computer. It contains all of the CPU,
memory and graphics circuitry that make the computer work.
The motherboard contains the very latest CPU design, the Intel Xeon™ processor,
which includes Intel NetBurst® Microarchitecture with 800 MHz system bus, Internet
Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, Intel Hyper-Threading Technology hardware support
for multi-threaded applications and Intel’s Extended Memory 64-bit technology
(EM64T). All of which are designed to vastly improve both multimedia and
communications on your PC. The combination of this technology and Viglen
expertise make this a formidable computer.
This manual contains technical information about the Viglen VIG390S motherboard
and other hardware components inside your computer. If you are new to computers
we recommend that you read the user guide first. If you are an experienced
computer user this manual should provide all the information you will need to
perform simple upgrades and maintenance.
We hope that this manual is both readable and informative. If you have any
comments for suggestions about how we could improve the format then please fill
out the form at the back of the manual and send it to us.
Above all we hope that you enjoy using your Viglen computer.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
5
Page 7
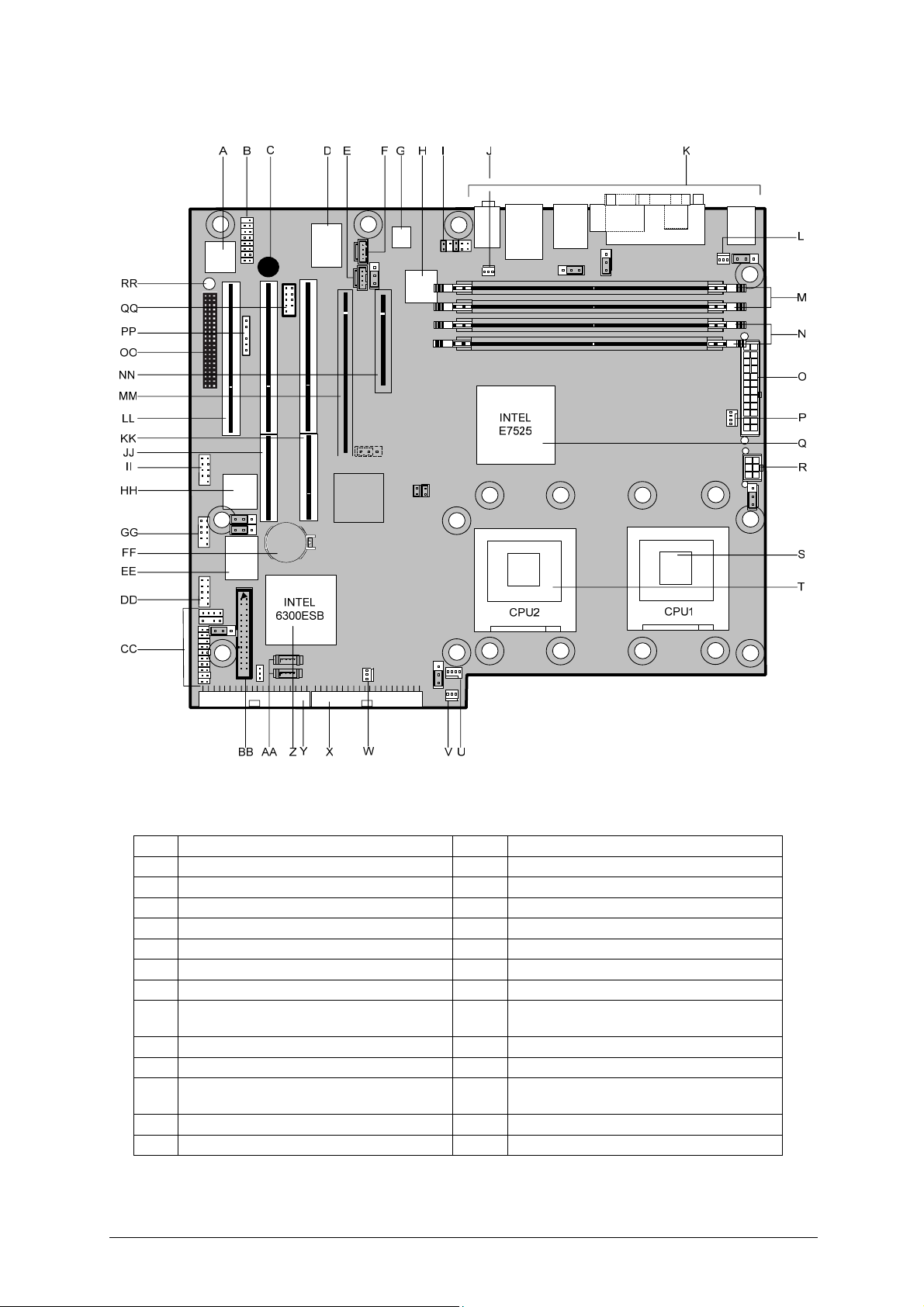
System Board Components
Figure 1: Motherboard Layout & Components
Table 1: Motherboard Layout Descriptions
A 8 Mbit Firmware Hub (FWH) BIOS W Front Chassis Fan 2
B Game port header (optional) X Secondary IDE connector
C Motherboard speaker Y Primary IDE connector
D I/O controller Z Southbridge Intel® 6300ESB
E Aux audio connector AA Serial ATA (S-ATA) connectors
F CD audio connector BB Floppy drive connector
G Audio codec AD1980 CC Front panel audio connector
H LAN controller Broadcom BCM5751 DD Front panel USB connectors 5/6
USB controller (VIA VT6212L)
I Front panel audio connector EE
J Rear Chassis Fan 2 connector FF Battery
K Rear I/O back panel connections GG Front panel USB connectors 7/8
L Rear Chassis Fan 1 connector HH
M Memory DIMM slots B2 A2 II Front IEE1394a header connector
N Memory DIMM slots B1 A1 JJ PCI4 PCI-X connector (64bit)
5/6/7/8
IEE1394a controller TiTBS43AB22A
PCI
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
6
Page 8
O SSI ATX Power connector 24 way KK PCI3 PCI-X connector (64bit)
P CPU1 FAN connector LL PCI5 PCI connector (32bit 5V)
Q Northbridge Intel © E7525 MM PCI2 PCI-Express x 16 connector
R ATX 12V1 connector 6 way NN PCI1 PCI-Express x 4 connector
CPU 1 socket (mPGA604 pin socket
S
for Intel ® Xeon ™) OO
CPU 2 socket (mPGA604 pin socket
T
for Intel ® Xeon ™) PP SMBus connector
U CPU 2 FAN connector QQ Second serial port header
V Front Chassis Fan 1 RR Power to motherboard LED
WIFI proprietary connector (not
supported)
Note:
1. SATA 1 is to be used for Boot disk SATA 2 for data disk.
2. SATA RAID 0/1 is supported by Windows XP + SP1 and Windows 2000Pro + SP4.
3. Windows XP supports 2 CPU’s with hyperthread enabled, if 2 CPU’s are to be used with
Windows 2000Pro hyperthread must be disabled.
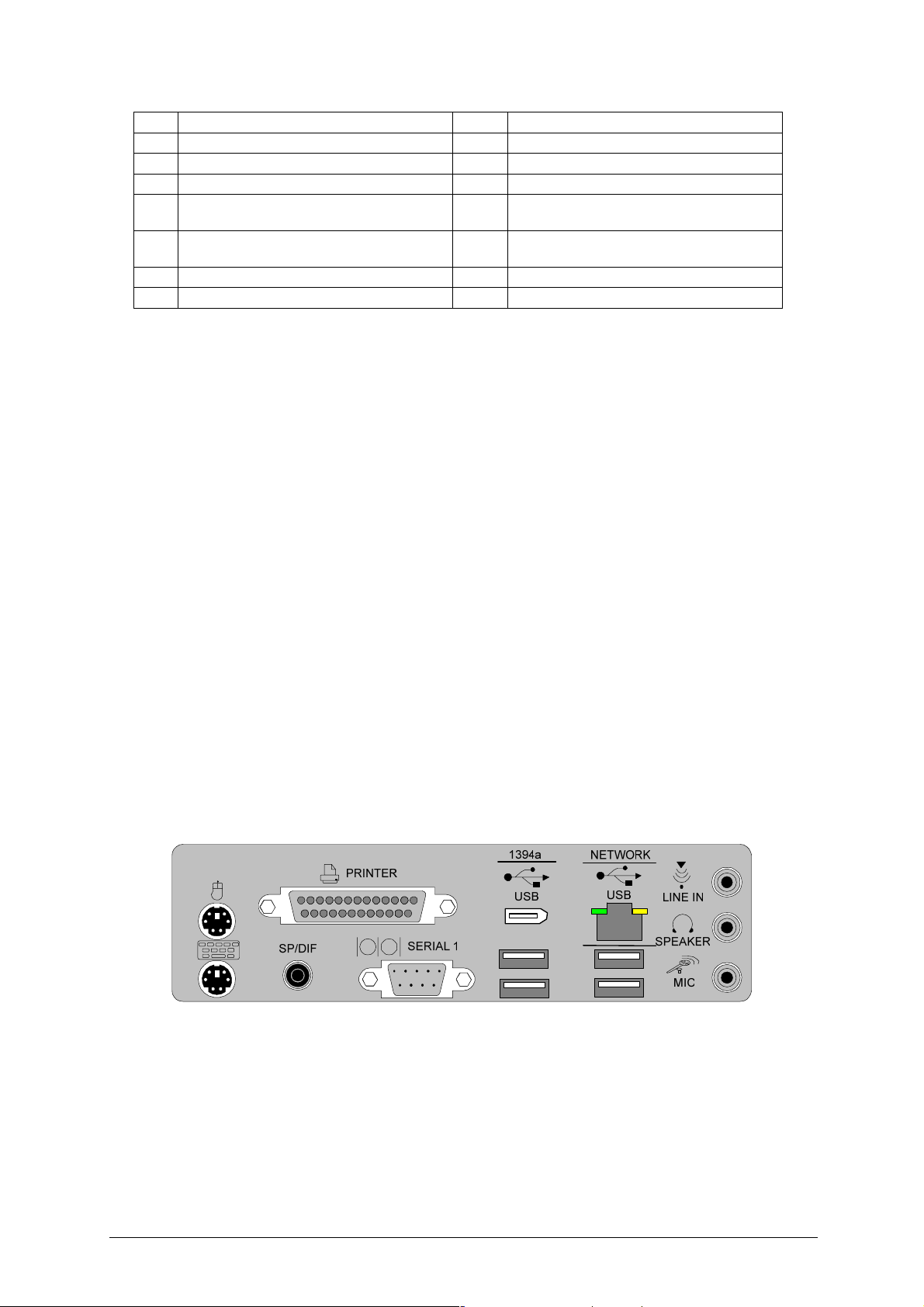
Back Panel Connectors
The motherboard external IO connectors are attached to a metallic I/O shield.
This shield serves several purposes:
• It protects the sensitive motherboard from any external EMC interference.
• It stops the computer from interfering with other electrical devices.
• It allows the motherboard to be easily upgraded in the future without having to
resort to buying a whole new case. Simply change the I/O shield to match the
motherboard.
The I/O shield provides external access to PS/2 keyboard and mouse connectors as
well as one serial port, one parallel port, two USB ports, one LAN Port and the audio
connectors.
Figure 2: I/O shield
Note: Power to the computer should be turned off before a keyboard or mouse is
connected or disconnected.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
7
Page 9
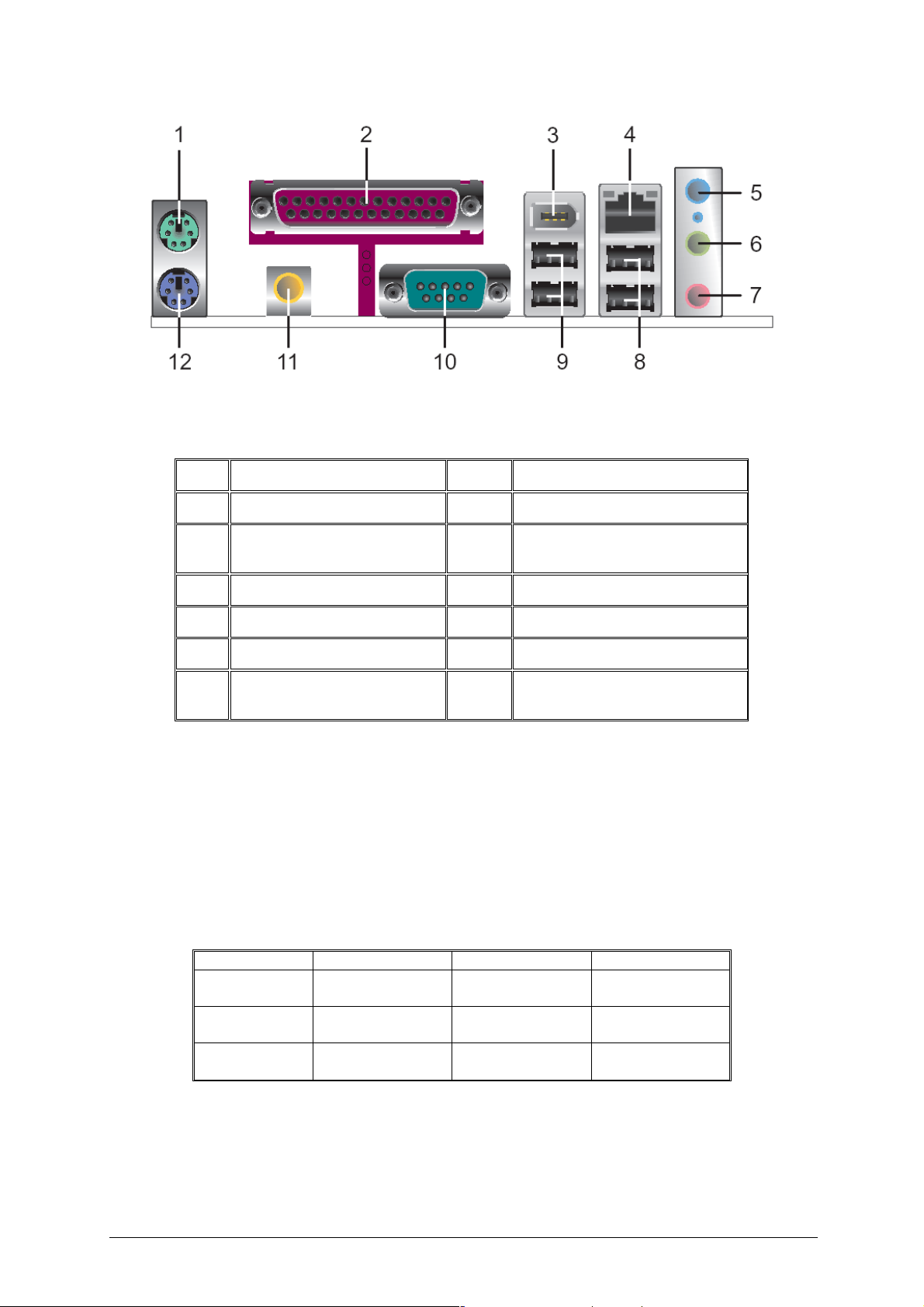
Table 2: Back Panel Connectors.
Figure 3: Back Panel Connectors
Item Description Item Description
1 PS/2* mouse port (Green) 7 Mic in (Pink)
2 Parallel port (Burgundy) 8
3 IEE1394a 9 USB ports (two) 1 and 2
4 LAN RJ45 10 Serial port A (Teal)
5 Audio line In (Blue) 11 SP/DIF 5.1 audio out
6
Line Out (Lime green) L and
R audio
12
USB ports (two) 3 and 4
PS/2 keyboard port (Purple)
Note: The back panel audio out connectors are designed to power headphones or
amplified speakers only. Poor audio quality occurs if passive (non-amplified)
speakers are connected to these outputs.
Audio 2/4/6 Channel configurations
The audio ports may be re configured via the audio control panel, default operation is
2 channel audio.
Table 3: Audio 2/4/6 Channel configurations
Port 2 channel 4 channel 6 channel
Audio line In
(Blue)
Line Out (Lime
green)
Mic in (Pink) Mic In Rear Speaker
Line In Line In Bass/Centre
Line out Front Speaker
Out L & R
Out L & R
Front Speaker
Out L & R
Rear Speaker
Out L & R
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
8
Page 10
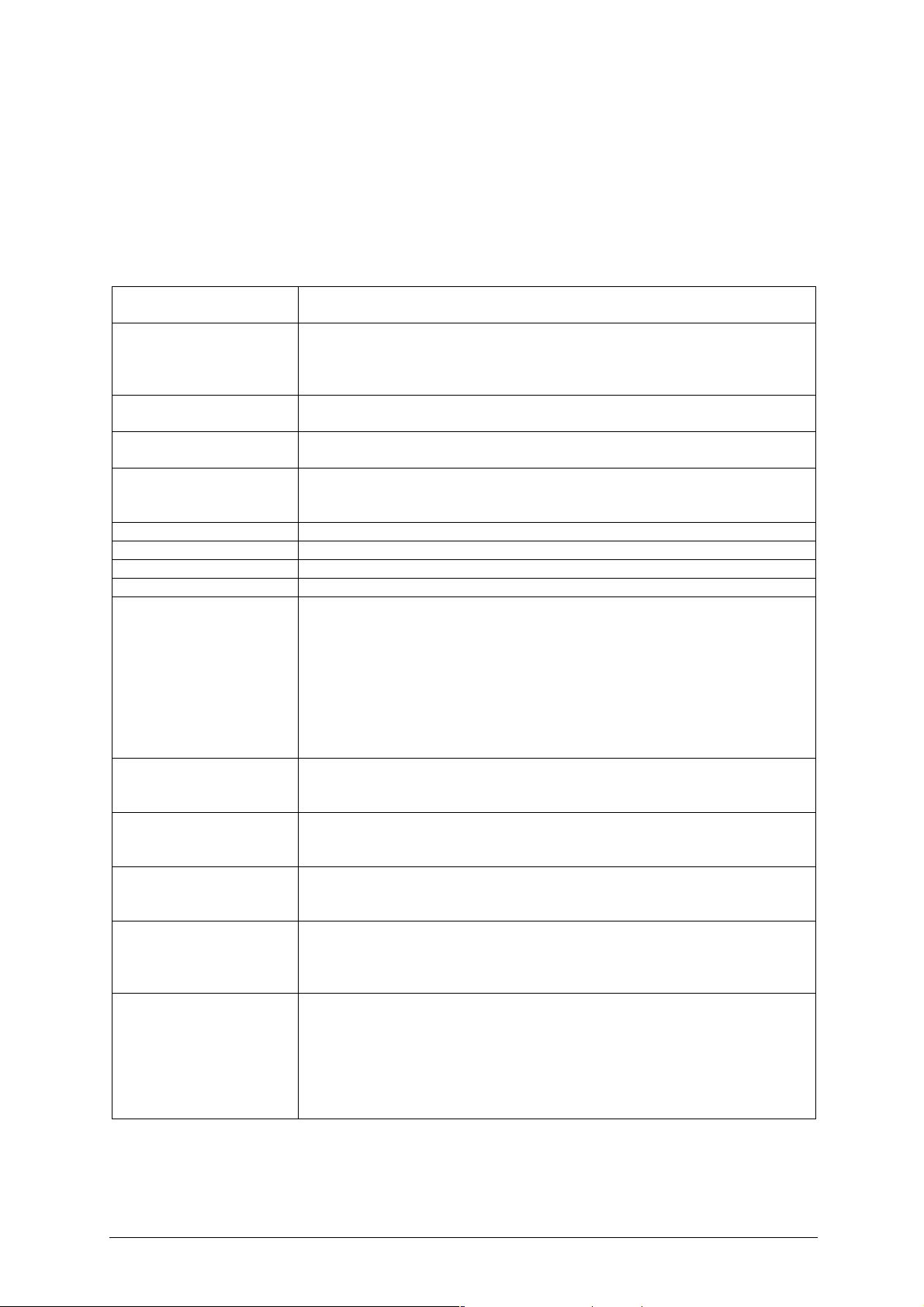
Feature Summary
The VIG390S motherboard supports Intel Pentium Xeon™ processors with 1MB of
third-level cache integrated in a micro PGA 604 Socket package operating at speeds
up to 3.6GHz. Single or dual processors are supported but should be identical in
speed and CPU stepping revision.
Table 4: Feature Summary
Form Factor
Processor
Supported CPU
speeds
Memory
Chipset
Video
Audio
I/O Controller
USB
Peripheral Interfaces
LAN Support
BIOS
Instantly Available PC
Technology
Expansion Capabilities
Hardware Monitor
Subsystem
VIG390S: extended ATX (9.8 inches by 12.0 inches [250.00 millimetres
by 305.00 millimetres])
- Single or dual Pentium Xeon CPU
- 800MHz FSB
- Integrated 512MB second and 1MB third level cache
- Socket micro PGA 604 connector
CPU Speed FSB L2 Cache L3 Cache
3.2. to 3.6GHz 800MHz 512K 1M
- Four 204-pin DDR2 SDRAM Dual Inline DIMM sockets.
- Support for up to 8GB of DDR2 400 ECC 72bit
- Northbridge Intel® 7525 Memory Controller Hub (GMCH)
- Southbridge Intel® 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub (ICH5)
- 8 Mbit Firmware Hub (FWH)
- PCI-Express connector supporting x1 ,x4, x8 and x16 lane VGA cards
- Audio subsystem using the ADI AD1980
- Southbridge Intel® 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub (ICH5)
- Support for USB 2.0 devices
- Eight USB Ports
- One Serial Port
- One Parallel Port
- Two Serial ATA IDE interfaces
- Two Parallel ATA IDE interfaces with UDMA 33, ATA-66/100 support
- One diskette drive interface
- PS/2 keyboard port
- PS/2 mouse port
- One IEEE1394a Port
Gigabit (10/100/1000 Mbits/sec) LAN subsystem using the
Broadcom BMC5751 PCI Express Gigiabit LAN Controller PCI-E 1.0a
interface
- AMI BIOS (resident in the 8 Mbit FWH)
- Support for Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI), Plug
and Play SMBIOS 2.3, WfM2.0,DMA2.0a.
- Support for PCI Local Bus Specification Revision 2.2
- Suspended to RAM support
- Wake on PCI, RS-232, front panel, PS/2 devices and USB ports
- One PCI (32bit 5v) bus add-in card connectors
- Two PCI-X (64bit) bus add-in card connector
- One PCI-Express (x16 lane) add-in card connector
- One PCI-Express (x4 lane) add-in card connector
- Hardware monitoring and fan control ASIC
- Voltage sense to detect out of range power supply voltages
- Thermal sense to detect out of range thermal values
- Four chassis fan connectors with activity monitor(two rear and two
front)
- 2 x CPU Heatsink FAN speed activity monitor
- Thermal Fan speed control
604-pin FC-µPGA4
6 channel audio codec.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
9
Page 11

System Processor
The VIG390S motherboard supports a single or dual Pentium Xeon™ processor.
The processor’s VID pins automatically program the voltage regulator on the
motherboard to the required processor voltage. In addition, the front side bus speed
is automatically selected. The motherboard currently supports processors that run
internally up to 3.6GHz and have a 512 KB second-level cache and 1MB third-level
cache.
The Intel Xeon™ processor incorporates Intel NetBurst® Microarchitecture with 800
MHz system bus, Internet Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, Intel Hyper-Threading
Technology hardware support for multi-threaded applications and Intel’s Extended
Memory 64-bit technology (EM64T).
The processor also implements MMX™ technology and maintains full backward
compatibility with the 8086, 80286, Intel386 ™, Intel486 ™, Pentium, Pentium Pro,
Pentium II & Pentium III processors. The processor’s numeric coprocessor
significantly increases the speed of floating-point operations and complies with
ANSI/IEEE standard 754-1985.
Microprocessor Packaging
The Xeon™ processor comes in a micro PGA 604 package that connects to the
motherboard through a socket 604 connector. The package consists of:
• Processor card including the processor core and the second-level and third level
cache, burst pipelined synchronous static RAM (BSRAM) and tag RAM.
• Thermal plate.
Second Level Cache
The second-level cache is located on the die of the CPU itself. The cache includes
burst pipelined synchronous static RAM (BSRAM) and tag RAM. All supported
onboard memory can be cached.
Processor Upgrades
The motherboard can be upgraded with an Intel Xeon™ processor that runs at
higher speeds with a maximum of 3.6GHz.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
10
Page 12
System Memory
Main Memory
The motherboard has four DDR2 SDRAM Dual Inline Memory Module (DIMM)
sockets. Support for up to a maximum memory size of 8GB. The BIOS automatically
detects memory type, size, and speed.
The motherboard supports the following memory features:
• 240 pin DDR2 400 MHz SDRAM DIMMs with gold-plated contacts
• Unbuffered, single-sided or double-sided DIMMs with the following restriction:
Double-sided DIMMS with x16 organisation are not supported.
• 8 GB maximum total system memory total amount of addressable memory.
• Minimum total system memory: 256 MB
• 72bit registered ECC DIMMs
• Serial Presence Detect
Notes:
To be fully compliant with all applicable DDR2 SDRAM memory specifications, the
board should be populated with DIMMs that support the Serial Presence Detect
(SPD) data structure. This allows the BIOS to read the SPD data and program the
chipset to accurately configure memory settings for optimum performance. If nonSPD memory is installed, the BIOS will attempt to correctly configure the memory
settings, but performance and reliability may be impacted or the DIMMs may not
function under the determined frequency.
Table 5: Supported Memory Configurations
DIMM
Capacity
256 MB SS 256 Mbit 32 M x 8/empty 8
256 MB SS 512 Mbit 32 M x 16/empty 4
512 MB DS 256 Mbit 32 M x 8/32 M x 8 16
512 MB SS 512 Mbit 64 M x 8/empty 8
512 MB SS 1 Gbit 64 M x 16/empty 4
1024 MB DS 512 Mbit 64 M x 8/64 M x 8 16
1024 MB SS 1 Gbit 128 M x 8/empty 8
2048 MB DS 1 Gbit 128 M x 8/128 M x 8 16
Note: In the second column, “DS” refers to double-sided memory modules (containing two rows of
DDR SDRAM) and “SS” refers to single-sided memory modules (containing one row of DDR
SDRAM).
Configuration
SDRAM
Density
SDRAM Organisation
Front-side/Back-side
Number of
SDRAM Devices
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
11
Page 13
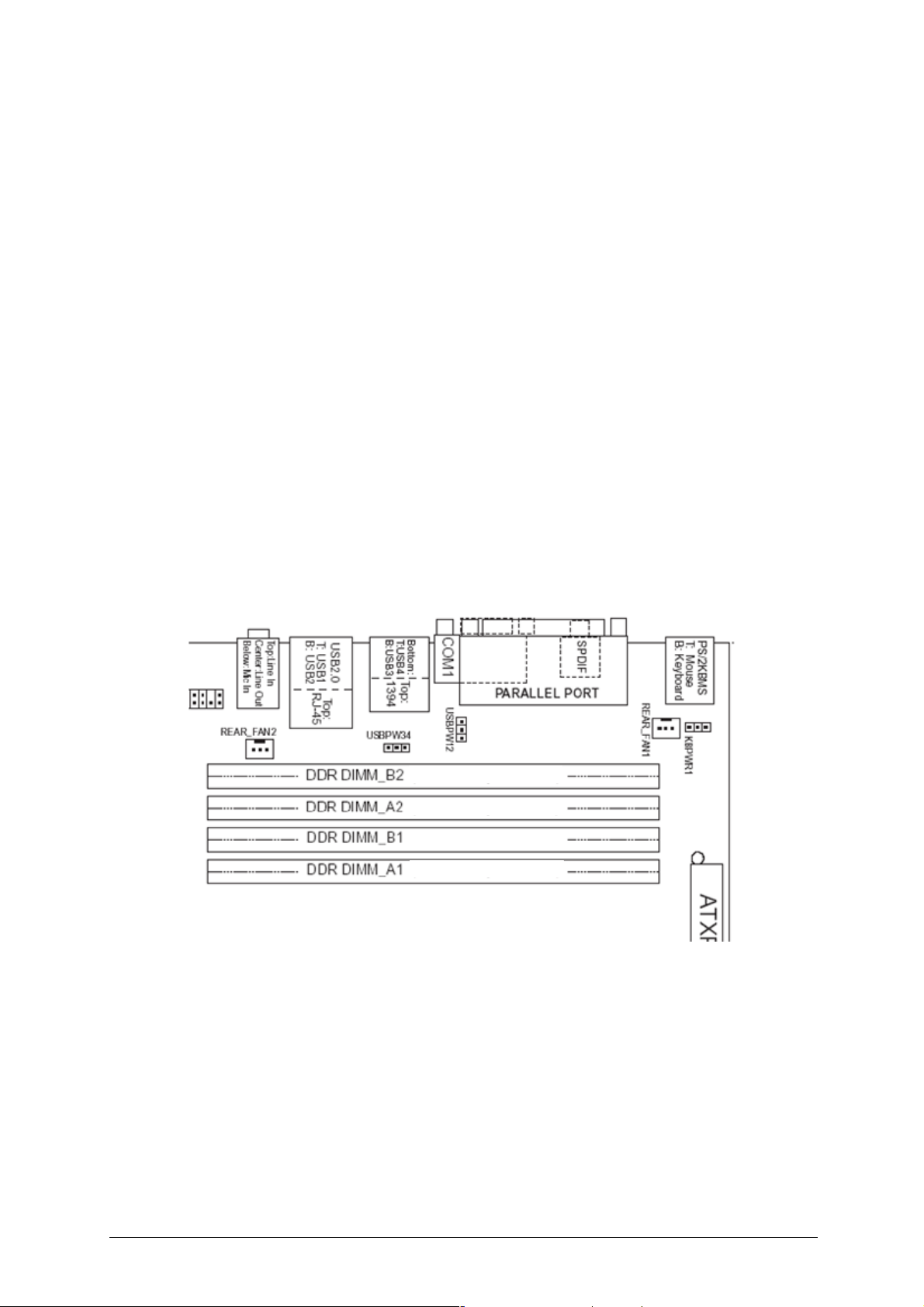
Memory Configurations
The Vig390s with Intel E7525 MCH supports Dual channel (Interleaved) mode
memory organisation:
Dual channel (Interleaved) mode: This mode offers the highest throughput for real
world applications. Dual channel mode is enabled when the installed memory
capacities of both DIMM channels are equal. Technology and device width can vary
from one channel to the other but the installed memory capacity for each channel
must be equal. If different speed DIMMs are used between channels, the slowest
memory timing will be used.
Single channel (Asymmetric) mode: This mode is equivalent to single channel
bandwidth operation for real world applications. This mode is used when only a
single DIMM is installed or the memory capacities are unequal. Technology and
device width can vary from one channel to the other. If different speed DIMMs are
used between channels, the slowest memory timing will be used.
NOTE:
The DIMM A2 and B2 sockets of both channels are blue. The DIMM A1and B1
sockets of both channels are black.
Figure 4: Memory Channel and DIMM Configuration
Dual channel mode: Installed modules must be the same therefore for 1GB total
system memory two 512MB modules would be installed in sockets A1 and B1.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
12
Page 14
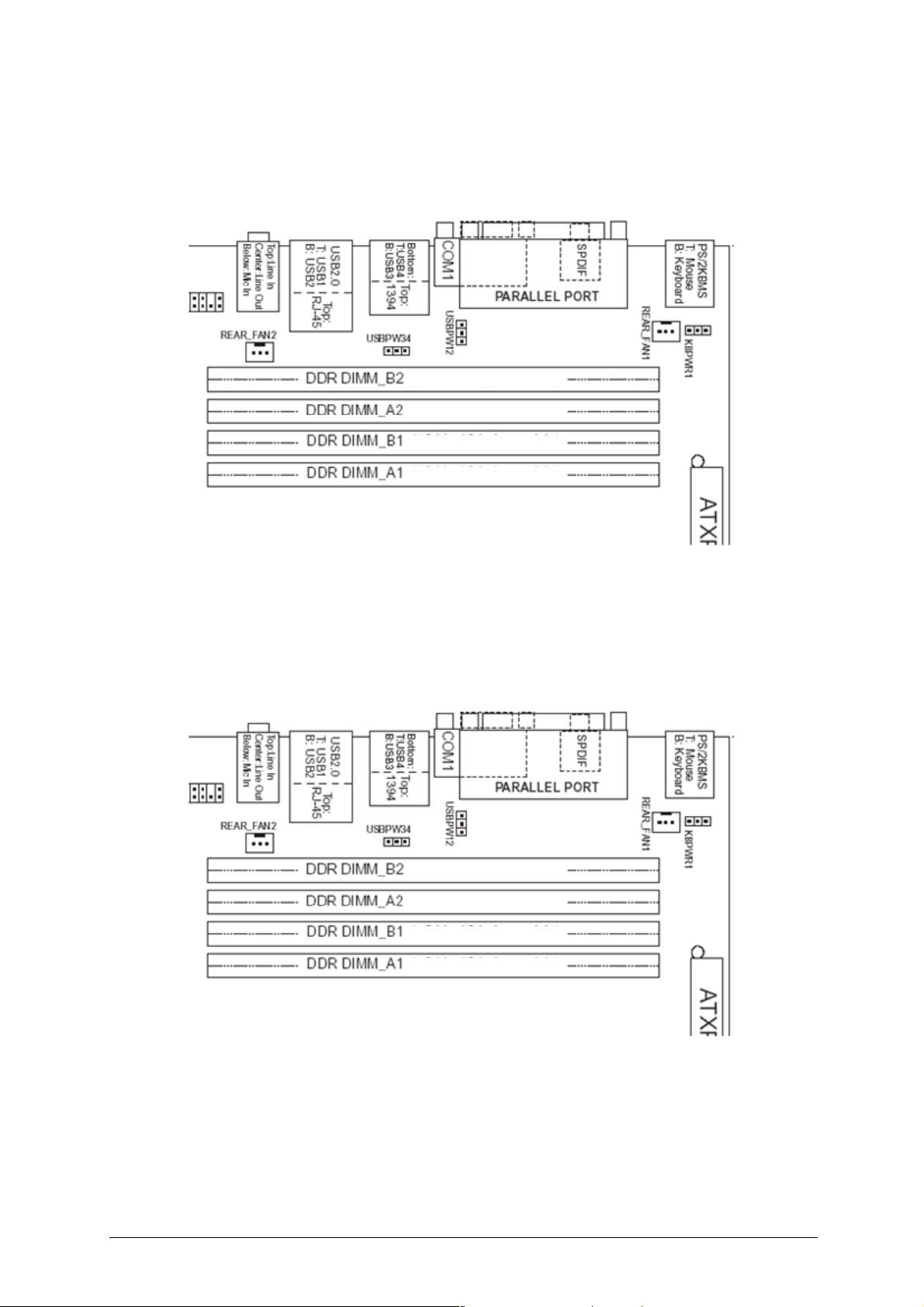
Dual Channel (Interleaved) Mode Configurations
Figure 5 shows a dual channel configuration using two DIMMs. In this example, the
DIMM A1, B1 (black) sockets of both channels are populated with identical DIMMs.
512MB
512MB
Figure 5: Dual Channel (Interleaved) Mode Configuration with Two DIMMs
Figure 6 shows a dual channel configuration using four DIMMs. In this example, the
combined capacity of the two DIMMs in Channel A equal the combined capacity of
the two DIMMs in Channel B. Also, the DIMMs are matched between DIMM1 and
DIMM2 of both channels.
256MB
256MB
512MB
512MB
Figure 6: Dual Channel (Interleaved) Mode Configuration with Four DIMMs
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
13
Page 15
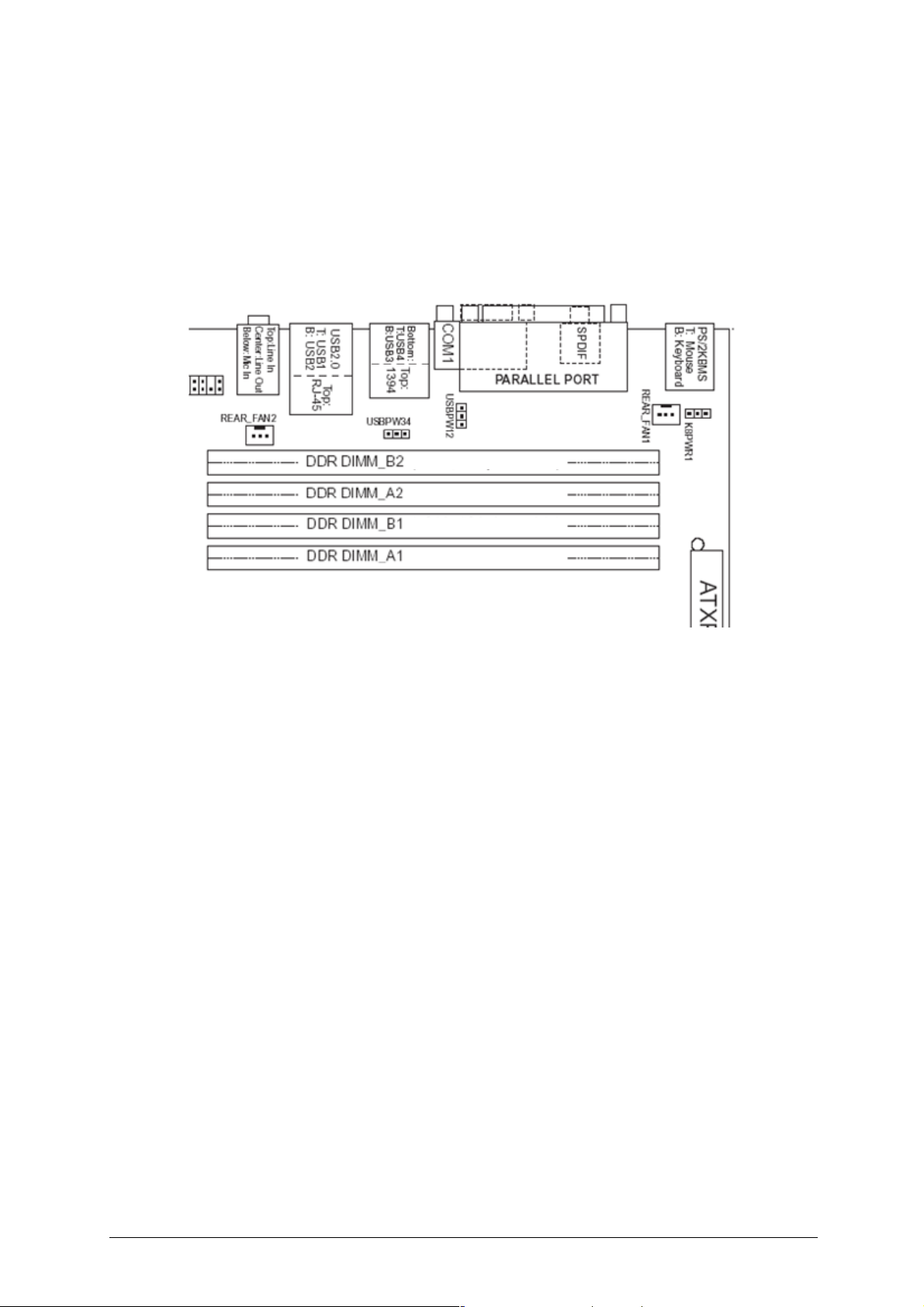
Single Channel (Asymmetric) Mode Configurations (Illustration only)
Note:
Dual channel (Interleaved) mode configurations provide the highest memory
throughput. Figure 7 shows a single channel configuration using one DIMM. In this
example, only the DIMM1 (black) socket of Channel A is populated. Channel B is not
populated.
256MB
Figure 7: Single Channel (Asymmetric) Mode Configuration with One DIMM
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
14
Page 16
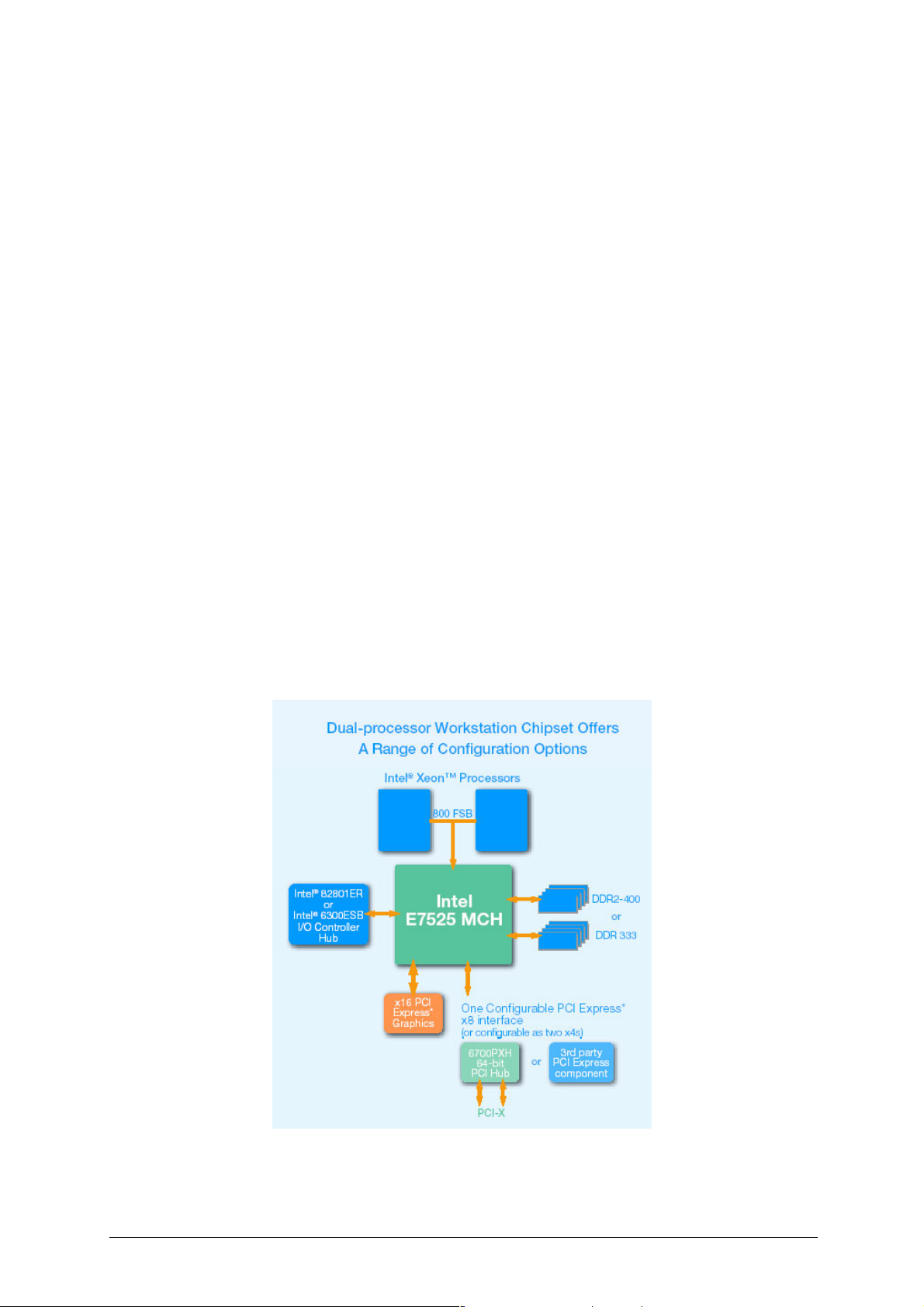
Intel® E7525 chipset (Northbridge)
Intel® E7525 Memory Controller Hub (MCH) chipset, the next generation Intel® dualprocessor (DP) workstation and server chipset technology, offers increased graphics
performance, reduced power consumption, and improved platform reliability and
system manageability.
The Intel® E7525 Chipset MCH is the central hub for all data passing between the
core system elements: processors, memory, PCI Express x16 graphics, PCI Express
I/O and legacy I/O subsystems. It supports dual Intel Xeon processors with 1MB L2
cache over the 800 MHz system bus interface, delivering bandwidth up to 6.4
GB/second. The MCH also supports all of the Intel Xeon processor features, such as
Hyper Threading technology, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology, Intel EM64T
and Streaming SIMD Extensions 3 (SSE3) Instructions.
The PCI Express x16 interface supports a total bandwidth of 8 GB/second (4
GB/second per direction) and directly attaches the MCH to a variety of third-party
graphics adapters. A variety of Intel and third-party I/O solutions communicate
directly with the MCH through the PCI Express x8 interface. The Intel E7525 MCH
has one PCI Express x8 interface that can be bifurcated into two x4 interfaces for
additional configuration flexibility. The bandwidth of the PCI Express x8 is up to 4
GB/second.
The legacy I/O connects to the MCH through the Intel Hub Interface architecture at
256 MB/second. There are two I/O controller hub options: the Intel 82801ER I/O
Controller Hub (ICH5R) and the Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub.
Figure 8: E7525 Block Diagram
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
15
Page 17
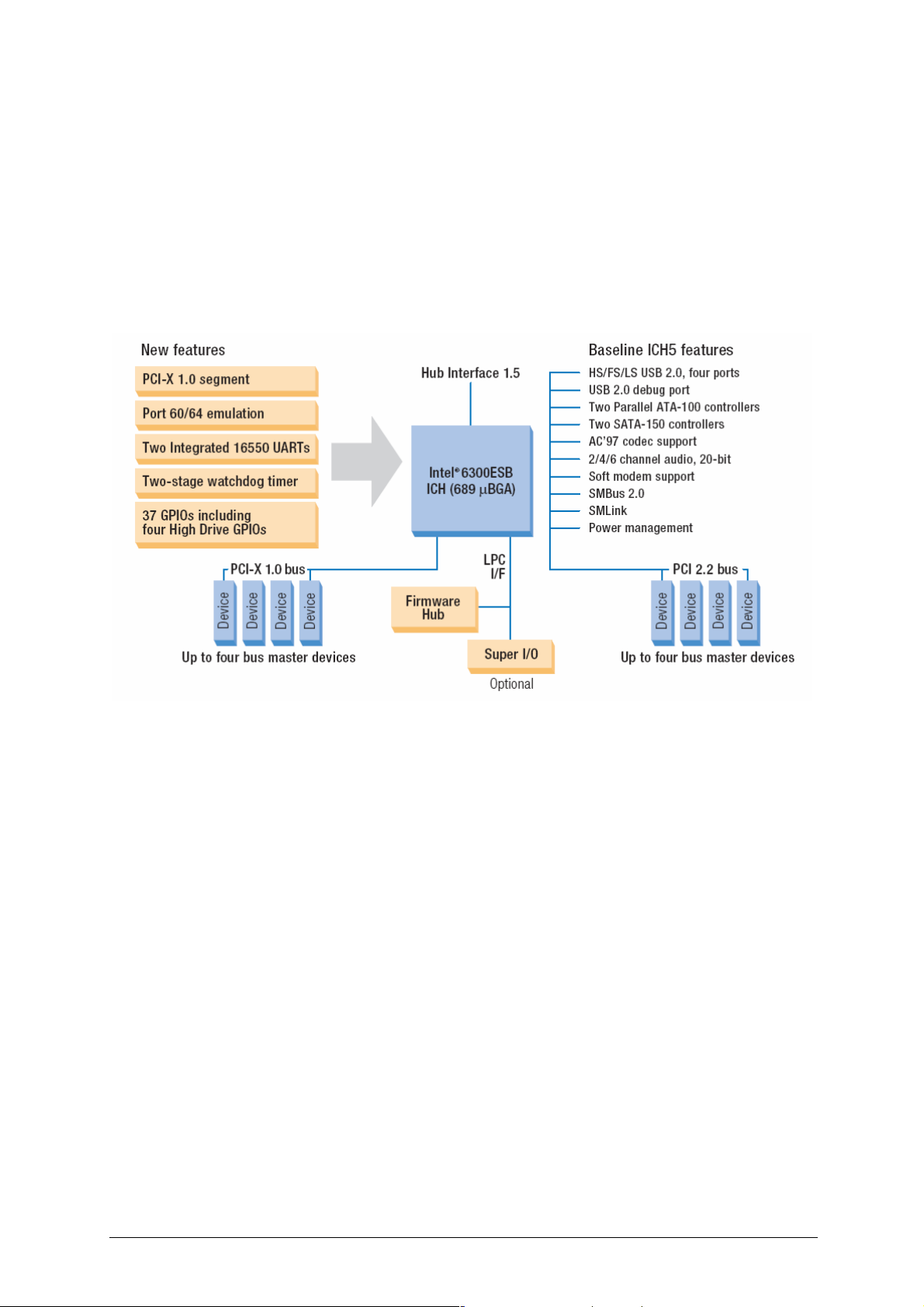
The Intel® 6300ESB I/O Controller (Southbridge)
The Intel® 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub integrates dual independent Serial ATA
controllers, each capable of up to 150 MB/second transfer rate, for the most
demanding storage data transfers and support for optional third party software RAID
0, 1 technology. Four Hi-Speed USB 2.0 ports allow easy I/O connection, while
offering improved bandwidth compared to USB 1.1 devices. The Intel 6300ESB I/O
Controller Hub also includes one PCI-X 64/66 bus supporting up to 4 PCI-X 64/66
MHz interfaces.
Figure 9: 6300 Block Diagram
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
16
Page 18
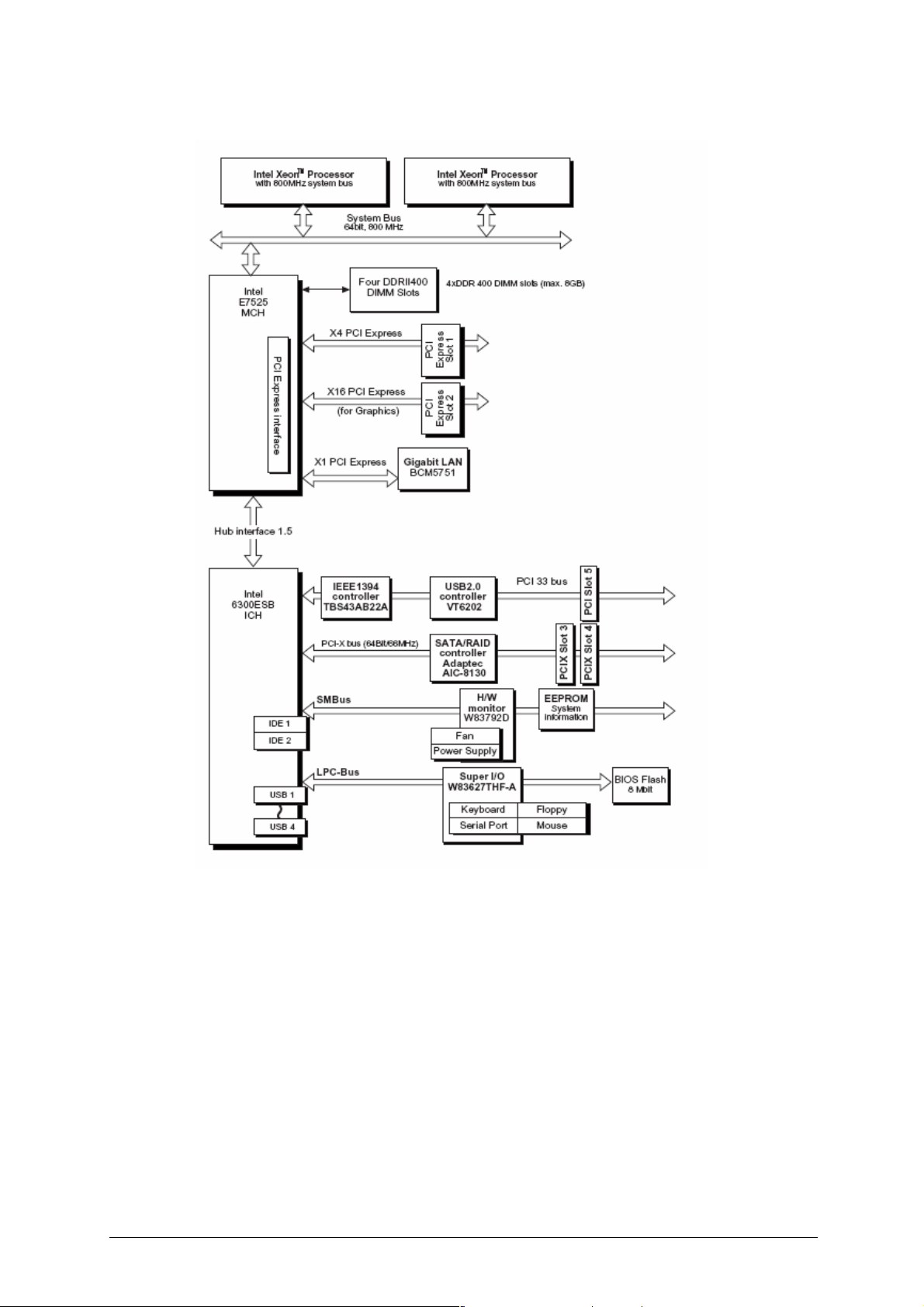
Vig390s motherboard block diagram
Figure 10: Vig390s Block Diagram
The Vig390s motherboard integrates both the Intel E7525 MHC and Intel 6300ESB
I/O controller with the following additional components:
- Gigabit LAN BCM5751
- IEEE1394a controller TBS43AB22A
- USB 2.0 controller VT6202
- H/W monitor W83792B
- Supper I/O controller W83627THF-A
Note: The Adaptec S-ATA RAID controller AIC-8130 is an option not incorporated
into the Vig390s.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
17
Page 19

USB Support
The motherboard has four rear USB 2.0 ports; note optional front panel USB adaptor
connector is required to use the internal USB headers to provide up to 4 more
additional ports. One USB peripheral can be connected to each port. For more than
four USB devices, an external hub can be connected to either port. The
motherboard fully supports the universal host controller interface (UHCI) and (EHCI)
and uses UHCI-and EHCI- compatible drivers. The ICH5 provides the USB controller
for all ports.
The port arrangement is as follows:
• Two ports are implemented with stacked back panel connectors, adjacent to
the PS/2 connectors
• Two ports are implemented with stacked back panel connectors, adjacent to
the audio connectors
• Four ports are routed to two separate front panel USB connectors
Note: USB 2.0 drivers are available for Windows 2000 Pro and Windows XP, and
currently not supported by any other operating system.
USB features include:
• Self-identifying peripherals that can be plugged in while the computer is
running.
• Automatic mapping of function to driver and configuration.
• Supports isochronous and asynchronous transfer types over the same set of
wires.
• Supports up to 127 physical devices.
• Guaranteed bandwidth and low latencies appropriate for telephony, audio,
and other applications.
• Error-handling and fault-recovery mechanisms built into the protocol.
Note: Computer systems that have an unshielded cable attached to a USB port may
not meet FCC Class B requirements, even if no device or a low-speed (sub-channel)
USB device is attached to the cable. Use shielded cable that meets the
requirements for high-speed (fully rated) devices.
IDE Support
The VIG390S motherboard provides four IDE interface connectors:
• Two Parallel ATA (P-ATA) IDE connectors, which support a total of four
devices (two per connector)
• Two Serial ATA (S-ATA) IDE connectors, which support one device per
connector
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
18
Page 20

Parallel ATA IDE Interfaces
The ICH5’s Parallel ATA IDE controller has two independent bus-mastering Parallel
ATA IDE interfaces that can be independently enabled. The Parallel ATA IDE
interfaces support the following modes:
• Programmed I/O (PIO): processor controls data transfer.
• 8237-style DMA: DMA offloads the processor, supporting transfer rates of up
to 16 MB/sec.
• Ultra DMA: DMA protocol on IDE bus supporting host and target throttling and
transfer rates of up to 33 MB/sec.
• ATA-66: DMA protocol on IDE bus supporting host and target throttling and
transfer rates of up to 66 MB/sec. ATA-66 protocol is similar to Ultra DMA and
is device driver compatible.
• ATA-100: DMA protocol on IDE bus allows host and target throttling. The
ICH5’s ATA-100 logic can achieve read transfer rates up to 100 MB/sec and
write transfer rates up to 88 MB/sec.
Serial ATA Support
The ICH5’s Serial ATA controller offers two independent Serial ATA ports with a
theoretical maximum transfer rate of 150 MB/s per port. One device can be installed
on each port for a maximum of two Serial ATA devices. A point-to-point interface is
used for host to device connections, unlike Parallel ATA IDE which supports a
master/slave configuration and two devices per channel.
For compatibility, the underlying Serial ATA functionality is transparent to the
operating system. The Serial ATA controller can operate in both legacy and native
modes. In legacy mode, standard IDE I/O and IRQ resources are assigned (IRQ 14
and 15). In Native mode, standard PCI resource steering is used. Native mode is the
preferred mode for configurations using the Windows XP and Windows 2000
operating systems.
LS-120 Support
LS-120 MB Diskette technology enables you to store 120MB of data on a single, 3.5”
removable diskette. LS-120 technology is backward (both read and write)
compatible with 1.44MB and 720KB DOS-formatted diskette and is supported by
Windows 95 and Windows NT operating system.
The VIG390S board allows connection of an LS-120 compatible drive and a standard
3½” floppy drive. The LS-120 drive can be configured as a boot device before a
floppy drive, if selected in the BIOS setup utility.
Note: If you connect an LS-120 drive to an IDE connector and configure it as the “A”
drive and configure a standard 3.5” floppy as “B” drive, the standard floppy must be
connected to the floppy drive cable’s “A” connector (the connector at the end of the
cable).
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
19
Page 21

The BIOS setup utility can be configured to boot firstly from either the LS120 or
standard 3½” floppy drive.
Real-Time Clock, CMOS SRAM and Battery
A coin-cell battery (CR2032) powers the real-time clock and CMOS memory. When
the computer is not plugged into a wall socket, the battery has an estimated life of
three years. When the computer is plugged in, the standby current from the power
supply extends the life of the battery. The clock is accurate to ± 13 minutes/year at
25 ºC with 3.3 VSB applied.
Note: If the battery and AC power fail, custom defaults, if previously saved, will be
loaded into CMOS RAM at power-on.
I/O Controller
The I/O controller (Intel® 6300ESB I-O Controller Hub) provides the following
features:
• One serial port (optional second serial port).
• One parallel port with Extended Capabilities Port (ECP) and Enhanced
Parallel Port (EPP) support
• Serial IRQ interface compatible with serialised IRQ support for PCI systems
PS/2-style mouse and keyboard interfaces
• Interface for one 1.44 MB diskette drive
• PCI-X 64/66 ports
• PCI 32/33 ports
• Two P-ATA ports
• Two S-ATA ports with configurable Intel RAID 0 and 1 support
• Intelligent power management, including a programmable wake-up event
interface
• SMBus hardware management support
• Integrated USB hub
By default, the I/O controller interfaces are automatically configured during boot up.
The I/O controller can also be manually configured in the Setup program.
Serial Ports
One 9-pin D-Sub serial port connector is located on the back panel and is compatible
with NS16C550 UARTs.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
20
Page 22

Parallel Port
The connector for the multimode bi-directional parallel port is a 25-pin D-Sub
connector located on the back panel. In the Setup program, the parallel port can be
configured for the following:
• Compatible (standard mode).
• Bi-directional (PS/2 compatible).
• Extended Parallel Port (EPP).
• Enhanced Capabilities Port (ECP).
Floppy Controller
The I/O controller is software compatible with the N82077 floppy drive controllers
and supports both PC-AT and PS/2 modes. In the Setup program, the floppy
interface can be configured for the following floppy drive capacities and sizes:
• 360 KB, 5.25-inch
• 1.2 MB, 5.25-inch
• 720 KB, 3.5-inch
• 1.2 MB, 3.5-inch (driver required)
• 1.25/1.44 MB, 3.5-inch (default configuration)
• 2.88 MB, 3.5-inch
PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Interface
PS/2 keyboard and mouse connectors are located on the back panel. The +5 V lines
to these connectors are protected with a PolySwitch circuit that, like a self-healing
fuse, re-establishes the connection after an over-current condition is removed.
The keyboard controller contains the AMI Megakey keyboard and mouse controller
code, provides the keyboard and mouse control functions, and supports password
protection for power on/reset. A power on/reset password can be specified in Setup.
The keyboard controller also supports the hot-key sequence <Ctrl><Alt><Del> for a
software reset. This key sequence resets the computer’s software by jumping to the
beginning of the BIOS code and running the Power-On Self Test (POST).
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
21
Page 23

Audio Subsystem
The VIG390S motherboard provides a Flex 6 audio subsystem based on the High
Definition Audio subsystem using the ADI AD1980 6 channel audio codec.
The audio subsystem supports the following features:
• Advanced jack sense with Auto Topology Switching that enables the audio codec
to recognise what device is connected to an audio port and alerts the user if the
wrong type of device has been connected.
• Split digital/analog architecture for improved S/N (signal-to-noise) ratio: > 94 dB
The Flex 6 audio subsystem includes the following features:
• Intel 82801EB I/O Controller Hub (ICH5)
• Analog Devices AD1980 audio codec
• Microphone input that supports a single dynamic, condenser, or electrets
microphone
The subsystem has the following connectors:
• ATAPI-style CDROM connector
• Front panel audio connector, including pins for:
o Line In
o Mic in
Audio 2/4/6 Channel configurations
The audio ports may be re configured via the audio control panel, default operation is
2 channel audio.
Table 6: Audio 2/4/6 Channel configurations
Port 2 channel 4 channel 6 channel
Audio line In
(Light Blue)
Line Out
(Lime green)
Mic in
(Pink)
• Back panel audio connectors that are configurable through the audio devices
derivers. The available configurations are shown below:
Line In Line In Bass/Centre
Line out Front Speaker
Out L & R
Mic In Rear Speaker
Out L & R
Front Speaker
Out L & R
Rear Speaker
Out L & R
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
22
Page 24
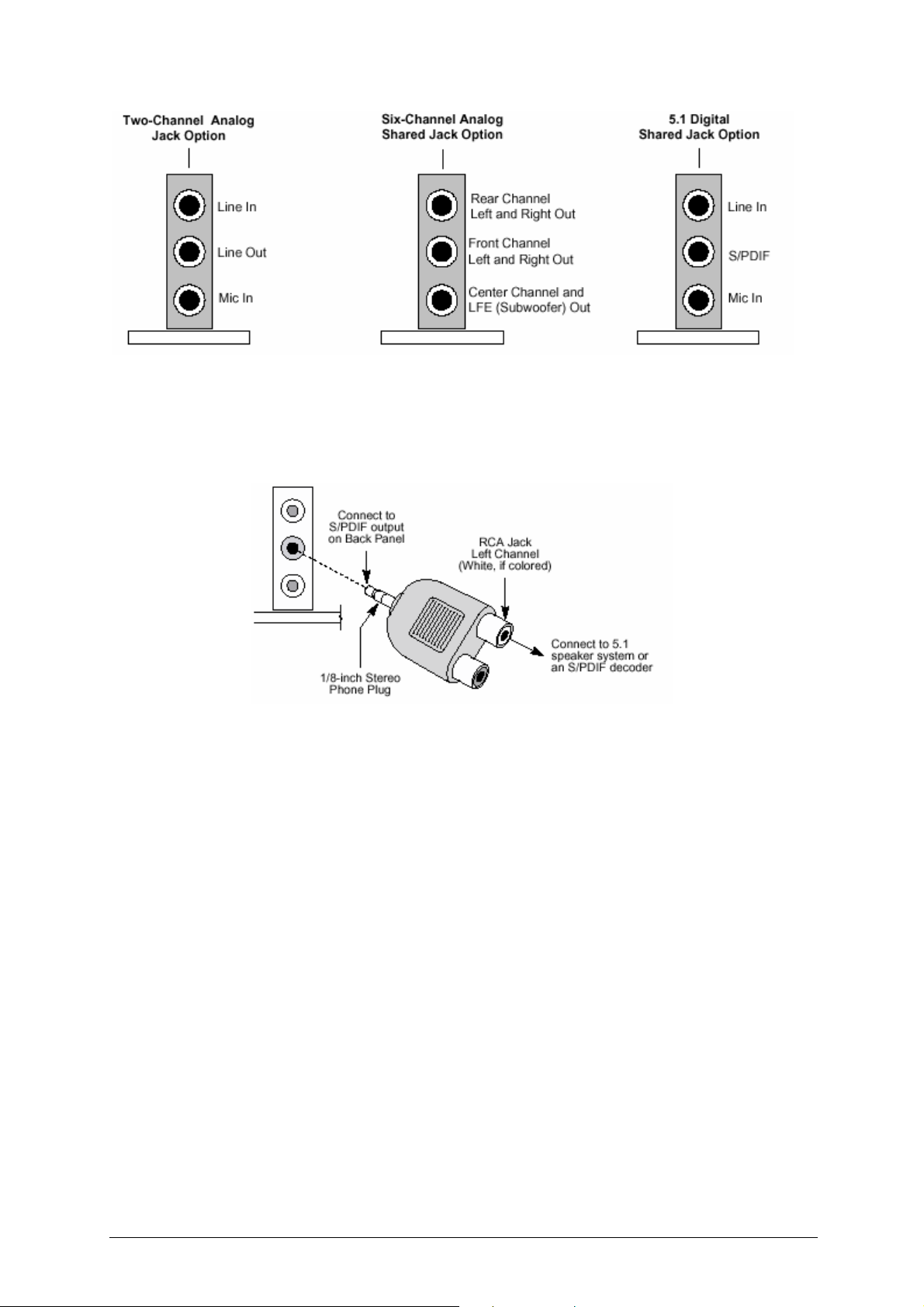
Figure 11: Back Panel Audio Connector Options
Note: To access the S/PDIF signal with the 5.1 Digital Shared Jack option, connect
a 1/8-inch stereo phone plug to RCA jack adapter/splitter as shown in Figure 12.
Figure 12: Adapter for S/PDIF Back Panel Connector
Audio Connectors
Front Panel Audio connector
A 2 x 5-pin connector provides mic in and line out signals for front panel audio
connectors.
Auxiliary Line In Connector
A 1 x 4-pin ATAPI-style connector connects the left and right channel signals of an
internal audio device to the audio subsystem.
ATAPI CDROM Audio Connector
A 1 x 4-pin ATAPI-style connector connects an internal ATAPI CD-ROM drive to the
audio mixer.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
23
Page 25
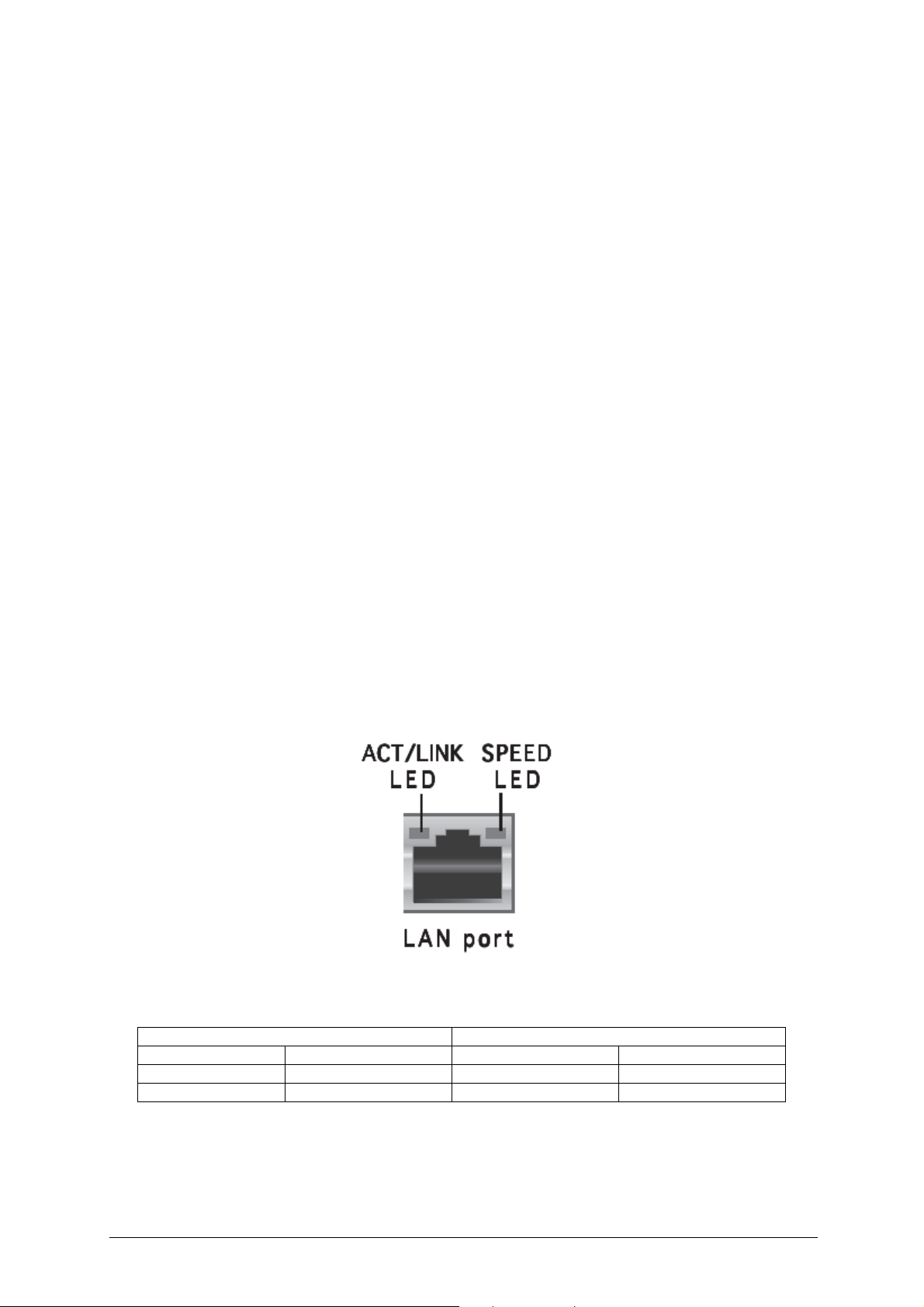
LAN Subsystem
The Network Interface Controller subsystem consists of the Broadcom NetXtreme™
BMC5751 PCI Express Gigabit LAN controller Supporting PCI Express 1.0a
interface.
Features
• 10/100/100BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet
• PCI-Express bus interface
• IEEE802.3 compliant media access controller (MAC)
• TCP,IP, and UDP checksum
• Microsoft® large Send Offload
• Large burst read
• Interrupt coalescing
• Standard-compliant WOL
• SMBUS 2.0 controller
• Alert Standard Format (ASF) 2.0 support
• Supports RJ-45 connector with status indicator LEDs
• Full driver compatibility
• Advanced Power Management support
• Configuration EEPROM that contains the MAC address
RJ-45 LAN Connector LEDs
Two LEDs are built into the RJ-45 LAN connector. The following table describes the
LED states when the board is powered up and the LAN subsystem is operating.
Figure 13: LAN Connector
Table 7: LAN Connector LEDs
ACT/LINK LED SPEED LED
OFF No link Off 10Mbps
Green Linked Orange 100Mbps
Blinking Data activity Green 1 Gbps
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
24
Page 26

Hardware Management Subsystem
The hardware management features enable the Desktop Boards to be compatible
with the Wired for Management (WfM) specification. The Desktop Board has several
hardware management features, including the following:
• Fan monitoring and control (through the hardware monitoring and fan control
ASIC)
• Thermal and voltage monitoring
• Chassis intrusion detection
Hardware Monitoring and Fan Control ASIC
The features of the hardware monitoring and fan control ASIC include:
• Internal ambient temperature sensor
• Two remote thermal diode sensors for direct monitoring of processor
temperature and ambient temperature sensing
• Power supply monitoring of voltages (+5 V, +12 V, +3.3 V, Vbat 3.3, Vcore1
and Vcore2) to detect levels above or below acceptable values
• Thermally monitored closed-loop fan control, for all fans, that can adjust the
fan speed as needed.
• SMBus interface
Thermal Monitoring
Table 8: Hardware Monitor Options
Item Description
A Thermal diode, located on processor die
B Remote ambient temperature sensor
C MB ambient temperature sensor
D Processor fan speed
E Rear chassis fan speed
F Front chassis fan speed
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
25
Page 27

Power Management
Power management is implemented at several levels, including:
• Software support through Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)
• Hardware support:
o Power connector
o Fan connectors
o LAN wake capabilities
o Instantly Available PC technology
o Resume on Ring
o Wake from USB
o Wake from PS/2 devices
o Power Management Event signal (PME#) wake-up support
ACPI
ACPI gives the operating system direct control over the power management and
Plug and Play functions of a computer. The use of ACPI with the VIG390S
motherboard requires an operating system that provides full ACPI support. ACPI
features include:
• Plug and Play (including bus and device enumeration)
• Power management control of individual devices, add-in boards (some add-in
boards may require an ACPI-aware driver), video displays, and hard disk drives
• Methods for achieving less than 15-watt system operation in the poweron/standby sleeping state
• A Soft-off feature that enables the operating system to power-off the computer
• Support for multiple wake-up events
• Support for a front panel power and sleep mode switch
Table 9 lists the system states based on how long the power switch is pressed,
depending on how ACPI is configured with an ACPI-aware operating system.
Table 9: Effects of Pressing the Power Switch
If the system is in this
state…
Off
(ACPI G2/G5 – soft off)
On
(ACPI G0 – working state)
On
(ACPI G0 – working state)
Sleep
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
Sleep
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
…and the power switch is
pressed for
Less that four seconds Power-on
Less than four seconds Soft off/Standby
More than four seconds Fail safe power-off
Less that four seconds Wake-up
More than fore seconds Power-off
…the system enters this state
(ACPI G0 – working)
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
(ACPI G2/G5 – soft-off)
(ACPI G0 – working state)
(ACPI G2/G5 – Soft off)
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
26
Page 28
System States and Power States
Under ACPI, the operating system directs all system and device power state
transitions. The operating system puts devices in and out of low-power states based
on user preferences and knowledge of how devices are being used by applications.
Devices that are not being used can be turned off. The operating system uses
information from applications and user settings to put the system as a whole into a
low-power state.
Table 10 lists the power states supported by the VIG390S motherboard along with
the associated system power targets. See the ACPI specification for a complete
description of the various system and power states.
Table 10: Power States and Targeted System Power
Global States Sleeping States Processor
States
G0 – working
state
G1 – sleeping
state
G1 – sleeping
state
G1 – Sleeping
state
G2/S5 S5 – Soft off.
G3 –
Mechanical off
AC power is
disconnected
for the
computer
S0 – working C0 – working D0 – working state Full Power > 30W
S1 – Processor
stopped
S3 – Suspend to
RAM.
S4 – Suspended
to disk.
saved
No power to the
system
C1 – stop grant D1, D2, D3 – device
No power D3 – no power except
No power D3 – no power except
No power D3 – no power except
No power D3 – no power for
Device States Targeted System
Power
5W < power <
specification specific
for wake-up logic
for wake-up logic
for wake-up logic
wake-up logic, except
when provided by
battery or external
source
52.5W
Power < 5W
Power < 5W
Power < 5W
No power to the
system. Service
can be performed
safely.
Wake-up Devices and Events
Table 11 lists the devices or specific events that can wake the computer from
specific states.
Table 11: Wake-up Devices and Events
These devices/events can wake up the computer… …from this state
LAN S1, S3, S4, S5
Modem (Back panel Serial Port A) S1, S3
PME# signal S1, S3, S4, S5
Power switch S1, S3, S4, S5
PS/2 devices S1, S3
RTC alarm S1, S3, S4, S5
USB S1, S3
Note: The use of these wake-up events from an ACPI state requires an operating
system that provides full ACPI support. In addition, software, drivers, and peripherals
must fully support ACPI wake events.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
27
Page 29

Hardware Support
CAUTION!
Ensure that the power supply provides adequate +5 V standby current if LAN wake
capabilities and Instantly Available PC technology features are used. Failure to do so
can damage the power supply. The total amount of standby current required
depends on the wake devices supported and manufacturing options.
The VIG390S motherboard provides several power management hardware features,
including:
• Power connector
• Fan connectors
• LAN wake capabilities
• Instantly Available PC technology
• Resume on Ring
• Wake from USB
• Wake from PS/2 keyboard
• PME# signal wake-up support
LAN wake capabilities and Instantly Available PC technology require power from the
+5 V standby line. The sections discussing these features describe the incremental
standby power requirements for each.
Resume on Ring enables telephony devices to access the computer when it is in a
power-managed state. The method used depends on the type of telephony device
(external or internal).
Note: The use of Resume on Ring and Wake from USB technologies from an ACPI
state requires an operating system that provides full ACPI support.
Power Connector
SSI ATX 12V compliant power supplies can turn off the system power through
system control. When an ACPI-enabled system receives the correct command, the
power supply removes all non-standby voltages.
When resuming from an AC power failure, the computer returns to the power state it
was in before power was interrupted (on or off). The computer’s response can be set
using the Last Power State feature in the BIOS Setup program’s Boot menu.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
28
Page 30

LAN wake Capabilities
CAUTION!
For LAN wake capabilities, the +5 V standby line for the power supply must be
capable of providing adequate +5 V standby current. Failure to provide adequate
standby current when implementing LAN wake capabilities can damage the power
supply.
LAN wake capabilities enable remote wake-up of the computer through a network.
The LAN subsystem PCI bus network adapter monitors network traffic at the Media
Independent Interface. Upon detecting a Magic Packet* frame, the LAN subsystem
asserts a wake-up signal that powers up the computer. Depending on the LAN
implementation, the VIG390S motherboard supports LAN wake capabilities with
ACPI in the following ways:
• The PCI bus PME# signal for PCI 2.2 compliant LAN designs
• The onboard LAN subsystem
Instantly Available PC Technology
CAUTION!
For Instantly Available PC technology, the +5 V standby line for the power supply
must be capable of providing adequate +5 V standby current. Failure to provide
adequate standby current when implementing Instantly Available PC technology can
damage the power supply.
Instantly Available PC technology enables the VIG390S motherboard to enter the
ACPI S3 (Suspend-to-RAM) sleep-state. While in the S3 sleep-state, the computer
will appear to be off (the power supply is off, and the front panel LED is amber if dual
coloured, or off if single coloured.) When signalled by a wake-up device or event, the
system quickly returns to its last known wake state.
The use of Instantly Available PC technology requires operating system support and
PCI 2.2 compliant add-in cards and drivers.
Resume on Ring
The operation of Resume on Ring can be summarised as follows:
• Resumes operation from ACPI S1 or S3 states
• Detects incoming call similarly for external and internal modems
• Requires modem interrupt be unmasked for correct operation
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
29
Page 31

Wake from USB
USB bus activity wakes the computer from ACPI S1 or S3 states.
Note: Wake from USB requires the use of a USB peripheral that supports Wake
from USB.
Wake from PS/2 Devices
PS/2 device activity wakes the computer from an ACPI S1 or S3 state.
PME# Signal Wake-up Support
When the PME# signal on the PCI bus is asserted, the computer wakes from an
ACPI S1, S3, S4, or S5 state (with Wake on PME enabled in BIOS).
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
30
Page 32

Chapter 2: System Board Options
The VIG390S motherboard is capable of accepting up to two Xeon™ CPU’s. RAM
can be upgraded to a maximum of 8GB using DDR2 400 SDRAM DIMMs ECC
Unbuffered memory.
WARNING!
Unplug the system before carrying out the procedures described in this
chapter. Failure to disconnect power before you open the system can result
in personal injury or equipment damage. Hazardous voltage, current, and
energy levels are present in this product. Power switch terminals can have
hazardous Voltages present even when the power switch is off.
The procedures assume familiarity with the general terminology associated
with personal computers and with the safety practices and regulatory
compliance required for using and modifying electronic equipment.
Do not operate the system with the cover removed. Always replace the cover
before turning on the system.
As the colours of the wires in the mains lead of this computer may not correspond with the
coloured markings identifying the terminals in your plug precede as follows:
The wire which is coloured green-and-yellow must be connected to the terminal in the plug
which is marked by the letter E or by the safety Earth symbol Q or coloured green or
green-and-yellow.
The wire which is coloured blue must be connected to the terminal which is marked with
the letter N or coloured black.
The wire which is coloured brown must be connected to the terminal which is marked with
the letter L or coloured red.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
31
Page 33

CAUTION!
The Viglen VIG390S motherboard
and associated components are
sensitive electronic devices. A small
static shock from your body can
cause expensive damage to your
equipment.
Make sure you are earthed and free of static charge before you open the computer
case. If you are unsure about upgrading your computer, return it to Viglen so a
qualified engineer can perform the upgrade.
STEPS TO TAKE TO PREVENT STATIC DISCHARGE:
1. The best way to prevent static discharge is to buy an anti-static strap from your
local electrical shop. While you are wearing the strap and it is earthed, static
charge will be harmlessly bled to ground.
2. Do not remove the component from its anti-static protective packaging until you
are about to install it.
3. Hold boards by the edges - try not to touch components / interface strips etc.
Note: We recommend that you return your computer to the service department for
upgrading. Any work carried out is fully guaranteed. Upgrades should only be carried
out by persons who are familiar with handling IC's, as incorrect installation will
invalidate the guarantee.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
32
Page 34

Overview of Jumper Settings
The VIG390S motherboard contains the latest technology to offer an almost
jumperless configuration. All Xeon™ CPUs are automatically detected and the
Speed is automatically set from the information provided by the CPU.
CAUTION!
Never remove jumpers using large pliers as this can damage the pins. The best way
to remove a jumper is to use a small pair of tweezers or fine needle-nosed pliers.
Never remove a jumper when the computer is switch on. Always switch the
computer off first.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
33
Page 35

System Board Jumper Settings
The following figure shows the jumper locations of the motherboard. Please refer to
the following tables describing each jumper’s configuration.
CAUTION!
Do not move the jumper with the power on. Always turn off the power and unplug
the power cord from the computer before changing a jumper, taking all necessary
anti static precautions.
Note: There is no jumper setting for configuring the processor speed or bus
frequency. The feature for configuring the processor speed is in the Setup program
using configure mode. See BIOS Section for information about configure mode.
LAN_EN1
3
2
1
DEFAULT
ENABLE
DISABLE
FRONT
PANEL
AUDIO
DEFAULT
3
2
1
DEFAULT
+5V
+5VSB
USBPW34
1 2 3
1 2 3
DEFAULT
+5V
USBPW12
1
1
2
2
3
3
+5VSB
KBPWR1
1 2 3
DEFAULT
+5V
1 2 3
+5VSB
1 2 3
DEFAULT
ENABLE
1 2 3
DEFAULT
ENABLE
1 2 3
DEFAULT
NORMAL
1394_EN1
USB_EN1
CLRTC1
1 2 3
DISABLE
1 2 3
DISABLE
1 2 3
CLEAR
CMOS
INTEL
E7525
INTEL
6300ESB
FM_CPU2
DEFAULT
DC MODE
3
2
1
PWM
CPU2
3
2
1
Figure 14: Jumper Configurations
CPU1
FM_CPU1
DEFAULT
DC MODE
3
3
2
2
1
1
PWM
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
34
Page 36

CLEAR CMOS Jumper Settings (CLRTC1)
The table below describes the jumper settings; if the jumper removed and the
computer is powered-up then a system boot failure will occur.
Table 12: CLEAR CMOS Jumper Settings (CLRTC1)
Function/Mode Jumper Setting Configuration
(Default)
Normal
CLEAR CMOS 2-3
1-2
CMOS data is retained when system is off
With power off, mains power disconnected
move jumper to pins 2 and 3 for about 5 ~ 10
seconds. This will also rest the Real Time
Clock and system BIOS set passwords.
USB Jumper (USB_EN1)
The table below describes the jumper settings; if the jumper removed and the
computer is powered-up then a system boot failure will occur.
Table 13: USB Jumper (USB_EN1)
Function/Mode Jumper Setting Configuration
(Default)
Enable
Disable 2-3
1-2
Enables front USB 2.0 controller for USB
6/6/7 and 8.
Disables front USB 2.0 controller.
IEEE1394a Jumper (1394_EN1)
The table below describes the jumper settings; if the jumper removed and the
computer is powered-up then a system boot failure will occur.
Table 14: IEEE1394a Jumper (1394_EN1)
Function/Mode Jumper Setting Configuration
(Default)
Enable
Disable 2-3
1-2
Enables front IEEE-1394a controller for
IEEE1394a 2.
Disables front IEEE-1394a controller.
LAN Jumper (LAN_EN1)
The table below describes the jumper settings; if the jumper removed and the
computer is powered-up then a system boot failure will occur.
Table 15: LAN Jumper (LAN_EN1)
Function/Mode Jumper Setting Configuration
(Default)
Enable
1-2
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
Enables onboard LAN controller., this may
also be controlled via additional BIOS
setting.
35
Page 37

Disables onboard LAN controller. If set to
Disable 2-3
disabled this may not be enabled via
additional BIOS setting.
Front Panel audio Jumpers (Front panel audio)
The table below describes the jumper settings; if the jumper removed and the
computer is powered-up then a system boot failure will occur.
Table 16: Front Panel audio Jumpers (Front panel audio)
Function/Mode Jumper Setting Configuration
(Default)
5-6
and
9-10
Allows audio to pass to rear I/O with no front
audio cable. The audio line signals are routed
back to the line connector.
Jumpers removed for front panel audio
Front panel
audio
Table 17: Front panel Audio Connector
Pin Signal name Pin Signal name
1 MIC_IN 2 Ground
3 MIC_BIAS 4 +5V
5 RIGHT_OUT 6 RIGHT_IN
7 Ground 8 Key
9 LEFT_OUT 10 LEFT_IN
none
cable. Audio line out and mic in signals are
available for front panel audio connectors on this
connector when no jumpers are installed.
USB power Jumper (USBPW34)
The table below describes the jumper settings; if the jumper removed and the computer is
powered-up then a system boot failure will occur.
Table 18: USB power Jumper (USBPW34)
Function/Mode Jumper Setting Configuration
(Default)
+5
2-3
Default mode +5V connection for USB ports
3 and 4.
Changing the jumpers to the +5VSB will
+5VSB 1-2
enable wake up from suspend with a USB
device connected to USB ports 3 or 4.
USB power Jumper (USBPW12)
The table below describes the jumper settings; if the jumper removed and the
computer is powered-up then a system boot failure will occur.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
36
Page 38

Table 19: USB power Jumper (USBPW12)
Function/Mode Jumper Setting Configuration
(Default)
+5
+5VSB 1-2
2-3
Default mode +5V connection for USB ports
1 and 2.
Changing the jumpers to the +5VSB will
enable wake up from suspend with a USB
device connected to USB ports 1 or 2.
Keyboard Power Jumper (KBPWR1)
The table below describes the jumper settings; if the jumper removed and the
computer is powered-up then a system boot failure will occur.
Table 20: Keyboard Power Jumper (KBPWR1)
Function/Mode Jumper Setting Configuration
(Default)
+5V
+5VSB 2-3
1-2
Default mode +5V, keyboard operation will
not wake system from suspend modes.
The Keyboard power jumper is set to
+5VSB, this enables keyboard operation to
wake the system from suspend.
CPU1 FAN power Jumper (FM_CPU1)
The table below describes the jumper settings; if the jumper removed and the
computer is powered-up then a system boot failure will occur.
Table 21: CPU1 FAN power Jumper (FM_CPU1)
Function/Mode Jumper Setting Configuration
(Default)
DC mode
PWM 1-2
Note: this will be set at time of manufacture according to the type of Heatsink fitted.
2-3
Default mode for 3 wire DC Heatsink fan
control.
Alternative mode for 4 wire PWM Heatsink
fan control.
CPU2 FAN power Jumper (FM_CPU2)
The table below describes the jumper settings; if the jumper removed and the
computer is powered-up then a system boot failure will occur.
Table 22: CPU2 FAN power Jumper (FM_CPU2)
Function/Mode Jumper Setting Configuration
(Default)
DC mode
PWM 1-2
Note: This will be set at time of manufacture according to the type of Heatsink fitted.
2-3
Default mode for 3 wire DC Heatsink fan
control.
Alternative mode for 4 wire PWM Heatsink
fan control.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
37
Page 39

Motherboard Connectors
There are connectors on the motherboard for FAN, IDE, Power supply, CD audio,
Floppy, IDE, & Front Panel Connectors. The location and/or details of these
connections are shown below.
CD
10
Front Panel
Audio
19
2
1
Rear Chassis
FAN
INTEL
E7525
Rear Chassis
FAN
1
ATX 2.2
Power Connector
24
12
13
1
CPU1
FAN
1
PSU
ATX
12V
FRONT USB
FRONT USB
Front pannel
connectors
HEADER
1
7
HEADER
1
7
COM2
Header
1
Game Port
Header
FRONT
1394A
HEADER
2
1
7
10
2
10
2
10
INTEL
6300ESB
Aux
CD
Audio
1
Aux
Audio
CPU2
FAN
1
2
5
Floppy Drive
Connector
31
331
1
SATA
1
SATA
2
SATA
connectors
202
PRIMARY
PCI IDE Connector
2
1
40
39
1
FRONT Chassis
FAN
20
SECONDARY
b
PCI IDE Connector
b
1
FRONT Chassis
FAN
40
39
Figure 15: Motherboard Connectors
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
38
Page 40

Front panel connections
The following are all connectors situated along the front edge of the motherboard. They are
often connected to buttons and LED’s situated on the front panel.
H.D.D.
LED
Power
Switch
Reset
Switch
Figure 16: Front panel connectors
+
Front pannel
connectors
+
Power
LED
A - Hard Disk L.E.D. Connector
This goes to the Hard Disk L.E.D. on the front panel, which lights up when the IDE
Hard Disk is in use.
B - Reset switch connector
When these pins are shorted, it will cause the computer to perform a cold reboot.
C - Power L.E.D.
This attaches to the power L.E.D on the front panel, to display if the computer is
active or not.
D- Power Switch On/Off
When these pins are shorted it turns the computer on and off.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
39
Page 41

Upgrading the CPU
CAUTION!
Allow time for the processor and heatsink to cool before touching either of them.
The Intel Xeon™ processor together with Level 2 cache chips are housed in a
protective package.
The design of the VIG390S computer makes it a simple job to replace or upgrade the
processor. To do so please refer to the figures below follow the instructions:
1. Read the warnings at the start of this chapter and ensure a static free environment
2. Remove the lid from the computer by removing the four screws at the rear of the
case
3. Locate the CPU module by referring to figure 17 if necessary
4. Locate the heat sink screws, and remove heat sink (and unplug FAN cable)
5. Lift arm on Socket to release the CPU
6. Lift the CPU Vertically upwards until it is clear of the socket
You can now fit the replacement CPU and heat sink into the socket.
• Installing CPU’s
Figure 17: CPU Heatsink mounting holes
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
40
Page 42

Note: in the figure above the circled holes are not motherboard mounting holes
these hold the Heatsink clips fitted to the motherboard as shown below in figures 18
and 19.
Figure 18: CPU sockets showing Heatsink clips
Figure 19: Back of MB showing Heatsink clips
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
41
Page 43

Figure 20: CPU sockets
If one CPU is to be installed it should be installed in socket for CPU1 as shown
above. Lift the socket arm up as shown for both sockets in figure 21 install CPU
noting correct orientation.
Figure 21: CPU fitted in ZIF socket
Now repeat for second CPU if required; and lock both CPU sockets with each socket
locking arm.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
42
Page 44

Figure 22: Xeon CPU heatsink
Fitting the heatsinks the figure above shows a typical Heatsink from top and bottom;
note the circled pillars that must locate through the motherboard. Note also that if
Heatsink thermal paste is not already applied to heatsinks this must now be done.
Figure 23: Mounting Heatsink to MB
Carefully locate each Heatsink over each CPU and allow the pillars to align with
mounting plates and fixing points through motherboard.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
43
Page 45

Figure 24: Securing Heatsink through MB
Now tighten all four screws diagonally to secure Heatsink in place and repeat for
second Heatsink if necessary.
Figure 25: Heatsink fan cable points
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
44
Page 46

Once both heatsinks are secured locate and connect the fna cables of each Heatsink
to the appropriate CPU fan header, for CPU 1 “CPU FAN” and for CPU2 “CPU FAN
2”.
Figure 26: Two Heatsinks fitted through MB
You should now have two CPU’s and Heatsink/s secured with fan cable/s connected
correctly.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
45
Page 47

Installing & Removing DDR SDRAM In-line Memory Modules
Installing Memory
You can install from 256MB to 8GB of memory in the motherboard DIMM sockets.
The board has four 240-pin DDR2 72bit registered ECC SDRAM DIMM sockets.
The motherboard supports the following memory features:
• 240-pin DIMMs with gold-plated contacts.
• ECC (72-bit).
• 256MB, 512MB, 1GB and 2GB (in the future) modules.
When adding memory, follow these guidelines:
• The BIOS detects the size and type of installed memory.
Note:
DDR SDRAM’s must meet the JEDEC Solid State Technology Association
specifications.
http://www.jedec.org/
To install DIMMs, follow these steps:
1. Observe the precautions in “Upgrading and ESD precautions”. Turn off the
computer and all peripheral devices.
2. Remove the computer cover and locate the DIMM sockets.
3. Holding the DIMM by the edges, remove it from its antistatic package.
4. Make sure the clips at either end of the socket are pushed away from the socket.
5. Position the DIMM above the socket. Align the two small notches in the bottom
edge of the DIMM with the keys in the socket. Insert the bottom edge of the
DIMM into the socket.
6. When the DIMM is seated, push down on the top edge of the DIMM until the
retaining clips at the ends of the socket snap into place. Make sure the clips are
firmly in place.
7. Replace the computer cover.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
46
Page 48

Removing Memory
To remove a DIMM, follow these steps:
1. Observe the precautions in “Upgrading and ESD precautions”.
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the computer. Turn off the computer.
3. Remove the computer cover.
4. Gently spread the retaining clips at each end of the socket. The DIMM pops out
of the socket. Hold the DIMM by the edges, lift it away from the socket, and store
it in an antistatic package.
5. Reinstall and reconnect any parts you removed or disconnected to reach the
DIMM sockets.
Figure 27: Removing DIMMs
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
47
Page 49

Replacing the Clock/CMOS RAM Battery
A lithium battery is installed in a socket on the system board.
The battery has an estimated life expectancy of seven years. When the battery
starts to weaken, it loses voltage; when the voltage drops below a certain level, the
system settings stored in CMOS RAM (for example, the date and time) may be
wrong.
If the battery fails, you will need to replace it with a CR2032 battery or an equivalent.
As long as local ordinance permits, you may dispose of individual batteries as
normal rubbish. Do not expose batteries to excessive heat or any naked flame.
Keep all batteries away from children.
CAUTION!
Danger of explosion if the battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the
same or equivalent type recommended by Viglen. Discard used batteries according
to manufacturer’s instructions.
The battery is listed as board component ‘FF’ on the diagram on Figure 1.
To replace the battery, carry out the following:
1. Observe the precautions in “Before You Begin.”
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the system.
3. Turn off the system.
4. Remove any components that are blocking access to the battery.
5. Figure 1 shows the battery location. Gently pry the battery free from its socket,
taking care to note the "+" and "-" orientation of the battery (Figure 28).
6. Install the new battery in the socket.
+
1
+
2
Figure 28: Removing the Battery
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
48
Page 50

Chapter 3: Solving Problems
The first part of this chapter helps you identify and solve problems that might occur
when the system is in use. The second part lists error code messages that might be
displayed.
Please remember that if you cannot solve the problem by yourself then you should
contact your suppliers Technical Support for further assistance.
Viglen Technical Support can be reached in the following ways:
Telephone: 020 8758 7000
Fax: 020 8758 7080
Email: techsupport@viglen.co.uk
You can also look for support information on our web site:
http://www.viglen.co.uk
Device drivers and various useful utilities can be downloaded from our ftp site:
ftp://ftp.viglen.co.uk
Resetting the System
Before checking your system for hardware problems, it is always a good idea to try
resetting your computer and see if a re-boot can solve the problem. Most software
related problems can be solved simply by re-booting your PC.
Table 23: Resetting the System
To do the following Press
Soft boot: Clear the system memory and
reload the operating system (also called
warm reset).
Cold boot: Clear the system memory, halt
power to all peripherals, restart POST, and
reload the operating system.
<Ctrl + Alt + Del>
Power off/on or reset button (at front
of the system)
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
49
Page 51

Troubleshooting Procedure
This section provides a step-by-step troubleshooting procedure to identify a problem
and locate its source.
CAUTION!
1. Turn off the system and any peripheral devices before you disconnect any
peripheral cables from the system. Otherwise, you can permanently damage the
system or the peripheral devices.
2. Make sure the system is plugged into a properly grounded power outlet.
3. Make sure your keyboard and video display are correctly connected to the
system. Turn on the video display, and turn up its brightness and contrast
controls to at least two-thirds of the maximum (refer to the documentation supplied
with the video display).
4. If the operating system normally loads from the hard disk drive, make sure there is
no diskette in the diskette drive. If the operating system normally loads from a
diskette, insert the operating system diskette into the drive.
5. Turn on the system. If the power indicator does not light, but the system seems
to be operating normally, the indicator is probably defective. Monitor the power-on
self test (POST) execution. Each time you turn on the system, the POST checks
the system board, memory, keyboard, and certain peripheral devices.
Note: If the POST does not detect any errors, the system beeps once and boots up.
Errors that do not prevent the boot process (non-fatal errors) display a message that
looks similar to the following:
Error Message Line 1
Error Message Line 2
Press <F1> for Set-up, <F2> to Boot
You can note the error and press <F2> to resume the boot- up process, or
<F1> to enter Set-up.
Errors that prevent the boot process from continuing (fatal errors), are communicated
by a series of audible beeps. If this type of error occurs, refer to the error codes and
messages listed at the end of this chapter.
6. Confirm that the operating system has loaded.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
50
Page 52

Problems Operating Add-in Boards
Problems related to add-in boards are usually related to improper board installation
or interrupt and address conflicts. Go through the checklist below to see if you can
correct the problem. If the problem persists after you have checked and corrected all
of these items, contact the board vendor's customer service representative.
Did you install the add-in board according to the manufacturer’s instructions?
Check the documentation that came with the board. Are all cables installed properly?
The following items are suggestions for troubleshooting problems related to PCI/ISA
legacy (non-Plug and Play) add-in boards.
• If the PCI/ISA board uses an interrupt, run Set-up and set the interrupt that is
being used by the PCI/ISA board to Used by PCI/ISA Card. Please refer to
the BIOS manual for details of how to do this.
• If the PCI/ISA legacy board uses memory space between 80000H - 9FFFFH,
run Set-up and set conventional memory to 256 K.
• If the PCI/ISA legacy board uses shared memory between C8000H - DFFFH,
run Set-up and enable shared memory for the appropriate memory space.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
51
Page 53

Problems and Suggestions
Table 24: Problems and Suggestions
What happens What to do
Application software
problems
Characters onscreen are distorted
or incorrect
Try resetting the system.
Make sure all cables are installed correctly.
Verify that the system board jumpers are set properly.
Verify that your system hardware configuration is set correctly. In
Setup, check the values against the system settings you recorded
previously. If an error is evident (wrong type of drive specified, for
example), make the change in Setup and reboot the system. Record
your change.
Make sure the software is properly configured for the system. Refer to
the software documentation for information.
Try a different copy of the software to see if the problem is with the
copy you are using.
If other software runs correctly on the system, contact the vendor of
the software that fails.
If you check all of the above with no success, try clearing CMOS
RAM and reconfiguring the system. Make sure you have your list of
system settings available to re-enter, because clearing CMOS RAM
sets the options to their default values.
Make sure the brightness and contrast controls are properly adjusted
on the monitor.
Make sure the video signal cable and power cables are properly
installed.
Characters do not
appear on screen
CMOS RAM settings
are wrong
Diskette drive light
does not go on when
drive is in use or is
tested by POST
Make sure your monitor is compatible with the video mode you have
selected.
Make sure the video display is plugged in and turned on.
Check that the brightness and contrast controls are properly adjusted.
Check that the video signal cable is properly installed.
Make sure a video board is installed, enabled, and the jumpers are
positioned correctly.
Reboot the system.
If system settings stored in CMOS RAM change for no apparent
reason (for example, the time of day develops an error), the backup
battery may no longer have enough power to maintain the settings.
Replace the battery (Chapter 2).
Make sure the power and signal cables for the drive are properly
installed.
Check that the drive is properly configured and enabled in Setup.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
52
Page 54

Table 24: Problems and Suggestions (Continued)
What happens What to do
Hard drive light does
not go on when drive
is in use or is tested
by POST
Power-on light does
not go on
Prompt doesn't
appear after system
boots
Setup, can't enter
System halts before
completing POST
Make sure the power and signal cables for the drive are properly
installed.
Make sure the front panel connector is securely attached to the
system board headers.
Check that the drive is properly configured and enabled in Setup.
Check the drive manufacturer's manual for proper configuration for
remote hard disk drive activity.
If the system is operating normally, check the connector between the
system board and the front panel. If OK, the light may be defective.
It’s probably switched off.
A serious fault may have occurred consult your dealer service
department / Technical Support.
If you can't enter Setup to make changes, check the switch that
disables entry into Setup (Chapter 2). If the switch is set to allow
entry into Setup, you might need to clear CMOS RAM to the default
values and reconfigure the system in Setup.
This indicates a fatal system error that requires immediate service
attention. Note the screen display and write down any beep code
emitted. Provide this information to your dealer service department /
Technical Support.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
53
Page 55

Error and Information Messages
The rest of this chapter describes beep codes, and error messages that you might
see or hear when you start up the system:
BIOS Error Messages
Table 25: BIOS Error Messages
Error Message Explanation
GA20 Error An error occurred with Gate A20 when switching to protected mode
during the memory test.
Pri Master HDD Error
Pri Slave HDD Error
Sec Master HDD Error
Sec Slave HDD Error
Pri Master Drive - ATAPI
Incompatible
Pri Slave Drive - ATAPI
Incompatible
Sec Master Drive - ATAPI
Incompatible
Sec Slave Drive - ATAPI
Incompatible
A: Drive Error No response from diskette drive.
Cache Memory Bad An error occurred when testing L2 cache. Cache memory may be bad.
CMOS Battery Low The battery may be losing power. Replace the battery soon.
CMOS Display Type Wrong The display type is different than what has been stored in CMOS.
CMOS Checksum Bad The CMOS checksum is incorrect. CMOS memory may have been
CMOS Settings Wrong CMOS values are not the same as the last boot. These values have
CMOS Date/Time Not Set The time and/or date values stored in CMOS are invalid. Run
DMA Error Error during read/write test of DMA controller.
FDC Failure Error occurred trying to access diskette drive controller.
HDC Failure Error occurred trying to access hard disk controller.
Checking NVRAM..... NVRAM is being checked to see if it is valid.
Update OK! NVRAM was invalid and has been updated.
Updated Failed NVRAM was invalid but was unable to be updated.
Keyboard Error Error in the keyboard connection. Make sure keyboard is connected
KB/Interface Error Keyboard interface test failed.
Memory Size Decreased Memory size has decreased since the last boot. If no memory was
Memory Size Increased Memory size has increased since the last boot. If no memory was
Could not read sector from corresponding drive.
Corresponding drive in not an ATAPI device. Run Setup to make sure
device is selected correctly.
Check Setup to make sure type is correct.
corrupted. Run Setup to reset values.
either been corrupted or the battery has failed.
Setup to set correct values.
properly.
removed then memory may be bad.
added there may be a problem with the system.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
54
Page 56

Table 25: BIOS Error Messages (Continued)
Error Message Explanation
Memory Size Changed Memory size has changed since the last boot. If no memory was
added or removed then memory may be bad.
No Boot Device Available System did not find a device to boot.
Off Board Parity Error A parity error occurred on an off-board card. This error is followed by
an address.
On Board Parity Error A parity error occurred in onboard memory. This error is followed by
an address.
Parity Error A parity error occurred in onboard memory at an unknown address.
NVRAM/CMOS/PASSWOR
D cleared by Jumper
<CTRL_N> Pressed CMOS is ignored and NVRAM is cleared. User must enter Setup.
NVRAM, CMOS, and passwords have been cleared. The system
should be powered down and the jumper removed.
BIOS Beep Codes
If an unrecoverable hardware problem occurs the computer may emit a number of
beeps from the speaker. These are known as beep codes. The pitch and duration
of the beep codes may vary but there will always be a set number of beeps. These
beeps stem from the BIOS’s initial check on the system and will normally occur in the
first few seconds of power on.
Beeps codes represent a terminal error. If the BIOS detects a terminal error
condition, it outputs an error beep code, halts the POST, and attempts to display a
port 80h code on a POST card’s LED display.
Table 26: Beep Codes
Beeps Description
2 long +
Floppy controller
2 short
2 long +
4 short
Hardware component failure
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
55
Page 57

Chapter 4: System BIOS
What is the BIOS?
The BIOS (Basic Input Output System) is an important piece of software which is
stored in a ROM (Read Only Memory) chip inside the computer. It consists of the
basic instructions for controlling the disk drives, hard disk, keyboard and
serial/parallel ports. The BIOS also keeps a list of the specifications of the computer
in battery-backed RAM (also known as the CMOS RAM) and provides a special
Setup program to change this information.
The BIOS in your Viglen computer is guaranteed to be fully compatible with the IBM
BIOS. It has been written by American MegaTrends Inc. (AMI), an industrial leader in
the field of BIOS software.
The Power-on sequence
When the computer is first switched on, certain instructions in the BIOS are executed
to test various parts of the machine. This is known as the POST (Power-On Self
Test) routine. When you switch the computer on (or when you press the Reset
button or press <Ctrl> + <Alt>+ <Delete> keys, which has the same effect), you can
see on the monitor that it counts through the memory, testing it. The floppy disk
drives are then accessed and tested, and the various interfaces are checked. If there
are any errors, a message is displayed on the screen.
Having passed all the tests, and if you have activated the password facility, the BIOS
then asks you to enter the boot password to continue. The following section
describes how to do this. The BIOS then loads the operating system, either - MS
DOS, Windows 2000 Professional or Windows XP Pro /Home, etc. - from the hard
disk (or floppy disk if one is inserted in Drive A:). The computer is then ready for use.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
56
Page 58

AMI BIOS
Introduction
The motherboard uses an AMI BIOS, which is stored in flash memory and can be
upgraded using a disk-based program. In addition to the BIOS, the flash memory
contains the Setup program, Power-On Self Test (POST), Advanced Power
Management (APM), the PCI auto-configuration utility, and is Windows Plug and
Play. This motherboard supports system BIOS shadowing, allowing the BIOS to
execute from 64-bit onboard write-protected DRAM.
The BIOS displays a message during POST identifying the type of BIOS and the
revision code.
BIOS Upgrades
A new version of the BIOS can be upgraded from a diskette using the iFLASH.EXE
utility that is available from Intel. This utility does BIOS upgrades as follows:
• Updates the flash BIOS from a file on a disk.
• Updates the language section of the BIOS.
• Makes sure that the upgrade BIOS matches the target system to prevent
accidentally installing a BIOS for a different type of system.
BIOS upgrades and the AFUDOS.exe utility may be available online at
www.viglen.co.uk or by request.
Note: Please review the instructions distributed with the upgrade utility before
attempting a BIOS upgrade.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
57
Page 59

BIOS Flash Memory Organisation
The Intel Firmware Hub (FWH) includes a 8 Mbit flash memory device. Internally, the
device is grouped into eight 64-KB blocks that are individually erasable, lockable,
and unlockable.
The 8-Mbit flash component is organised as 256 KB x 8 bits and is divided into areas
as described in Table 27. The table shows the addresses in the ROM image in
normal mode (the addresses change in BIOS Recovery Mode).
Table 27: Typical Flash Memory Organisation
Address (Hex) Size Description
FFFFC000 – FFFFFFFF 16 KB Boot Block
FFFFA000 – FFFFBFFF 8 KB Vital Product Data (VPD) Extended System
Configuration Data (ESCD) (DMI configuration data
/ Plug and Play data)
FFFF9000 - FFFF9FFF 4 KB Used by BIOS (e.g., for Event Logging)
FFFF8000 - FFFF8FFF 4 KB OEM logo or Scan Flash Area
FFFC0000 - FFFF7FFF 228 KB Main BIOS Block
Plug and Play: PCI Auto-configuration
The BIOS automatically configures PCI devices and Plug and Play devices. PCI
devices may be onboard or add-in cards. Plug and Play devices are ISA add-in
cards built to meet the Plug and Play specification. Auto-configuration lets a user
insert or remove PCI or Plug and Play cards without having to configure the system.
When a user turns on the system after adding a PCI or Plug and Play card, the BIOS
automatically configures interrupts, the I/O space, and other system resources. Any
interrupts set to Available in Setup are considered to be available for use by the addin card.
PCI interrupts are distributed to available ISA interrupts that have not been assigned
to an ISA card or to system resources. The assignment of PCI interrupts to ISA
IRQs is non-deterministic. PCI devices can share an interrupt, but an ISA device
cannot share an interrupt allocated to PCI or to another ISA device. Autoconfiguration information is stored in the extended system configuration data (ESCD)
format.
PCI IDE Support
If Auto is selected as a primary or secondary IDE in Setup, the BIOS automatically
sets up the two local-bus IDE connectors with independent I/O channel support. The
IDE interface supports hard drives up to PIO Mode 4 and recognises any ATAPI
devices, including CD-ROM drives, tape drives and Ultra DMA drives. Add-in ISA
IDE controllers are not supported. The BIOS determines the capabilities of each
drive and configures them so as to optimise capacity and performance. To take
advantage of the high-capacity storage devices, hard drives are automatically
configured for logical block addressing (LBA) and to PIO Mode 3 or 4, depending on
the capability of the drive. To override the auto-configuration options, use the specific
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
58
Page 60

IDE device options in Setup. The ATAPI specification recommends that ATAPI
devices be configured as shown in Table 28.
Table 28: Recommendations for Configuring an ATAPI Device
Configuration
Normal, no ATAPI ATA
Disk and CD-ROM for enhanced IDE
systems
Legacy IDE system with only one cable ATA ATAPI
Enhanced IDE with CD-ROM and a tape or
two CD-ROMs
Primary Cable Secondary Cable
Drive 0 Drive 1 Drive 0 Drive 1
ATA ATAPI
ATA ATAPI ATAPI
Plug and Play
If Plug and Play operating system is selected in Setup, the BIOS auto-configures
only ISA Plug and Play cards that are required for booting (IPL devices). If Plug and
Play operating system is not selected in Setup, the BIOS auto-configures all Plug
and Play ISA cards.
Desktop Management Interface (DMI)
Desktop Management Interface (DMI) is an interface for managing computers in an
enterprise environment. The main component of DMI is the management
information format (MIF) database, which contains information about the computing
system and its components. Using DMI, a system administrator can obtain the
system types, capabilities, operational status, and installation dates for system
components. The MIF database defines the data and provides the method for
accessing this information. The BIOS enables applications such as Intel LANDesk®
Client Manager to use DMI. The BIOS stores and reports the following DMI
information:
• BIOS data, such as the BIOS revision level.
• Fixed-system data, such as peripherals, serial numbers, and asset tags.
• Resource data, such as memory size, cache size, and processor speed.
• Dynamic data, such as event detection and error logging.
DMI does not work directly under non-Plug and Play operating systems (e.g.,
Windows NT). However, the BIOS supports a DMI table interface for such operating
systems. Using this support, a DMI service-level application running on a non-Plug
and Play OS can access the DMI BIOS information.
Advanced Power Management (APM)
The BIOS supports APM and standby mode. The energy saving standby mode can
be initiated in the following ways:
• Time-out period specified in Setup.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
59
Page 61

• Suspend/resume switch connected to the front panel sleep connector.
• From the operating system, such as the Suspend menu item in Windows 95.
In standby mode, the motherboard reduces power consumption by using SMM
capabilities, spinning down hard drives, and reducing power to or turning off VESA
DPMS-compliant monitors. Power-management mode can be enabled or disabled in
Setup.
While in standby mode, the system retains the ability to respond to external
interrupts and service requests, such as incoming faxes or network messages. Any
keyboard or mouse activity brings the system out of standby mode and immediately
restores power to the monitor.
The BIOS enables APM by default, but the operating system must support an APM
driver for the power-management features to work. For example, Windows 95
supports the power-management features upon detecting that APM is enabled in the
BIOS.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
60
Page 62

Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)
ACPI gives the operating system direct control over the power management and
Plug and Play functions of a computer. ACPI requires an ACPI-aware operating
system. ACPI features include:
• Plug and Play (including bus and device enumeration) and APM functionality
normally contained in the BIOS.
• Power management control of individual devices, add-in boards, video displays,
and hard disk drives.
• Methods for achieving less than 30-watt system operation in the Power On
Suspended sleeping state, and less than 5-watt system operation in the
Suspended to Disk sleeping state.
• A soft-off feature that enables the operating system to power off the computer.
• Support for multiple wake up events.
• Support for a front panel power and sleep mode switch. Table 29 describes the
system states based on how long the power switch is pressed, depending on how
ACPI is configured with an ACPI-aware operating system.
Table 29: Effects of Pressing the Power Switch
If the system is in this
state…
Off Less than 4 seconds Power On
On Less than 4 seconds Soft Off/ Suspended
On More than 4 seconds Fail safe power off
Sleep Less than 4 seconds Wake up
… and the power switch is
pressed for
…the system enters
this state
Under ACPI, the operating system directs all system and device power state
transitions. The operating system puts devices in and out of low-power state based
on user preferences and knowledge of how devices are being used by applications.
Devices that are not being used can be turned off. See Power Management section
in Chapter 1, Page 28 for more information on ACPI.
Language Support
The Setup program and help messages can be supported in 32 languages. The
default language is American English, which is present unless another language is
programmed into the BIOS using the flash memory update utility.
Boot Options
In the Setup program, the user can choose to boot from a floppy drive, hard drive,
CD-ROM, or the network. The default setting is for the floppy drive to be the primary
boot device and the hard drive to be the secondary boot device. By default the third
and fourth devices are disabled.
Booting from CD-ROM is supported in compliance to the El Torito bootable CD-ROM
format specification. Under the Boot menu in the Setup program, CD-ROM is listed
as a boot device. Boot devices are defined in priority order. If the CD-ROM is
selected as the boot device, it must be the first device.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
61
Page 63

The network can be selected as a boot device. This selection allows booting from a
network add-in card with a remote boot ROM installed
.
OEM Logo or Scan Area
A 4 KB flash-memory user area at memory is for displaying a custom OEM logo
during POST.
USB Support
The USB connectors allow any of several USB devices to be attached to the
computer. Typically, the device driver for USB devices is managed by the operating
system. However, because keyboard and mouse support may be needed in the
Setup program before the operating system boots, the BIOS supports USB
keyboards and mice.
BIOS Setup Access
Access to the Setup program can be restricted using passwords. User and
supervisor passwords can be set using the Security menu in Setup. The default is
no passwords enabled.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
62
Page 64

Configuring the Motherboard using BIOS Setup
Before You Begin
CAUTION!
• Always follow the steps in each procedure in the correct order.
• Set up a log to record information about your computer, such as model, serial
numbers, installed options, and configuration information.
• Use an anti-static wrist strap and a conductive foam pad when working on the
motherboard.
WARNINGS
The procedures in this chapter assume familiarity with the general terminology
associated with personal computers and with the safety practices and regulatory
compliance required for using and modifying electronic equipment.
Disconnect the computer from its power source and from any telecommunications
links, networks, or modems before performing any of the procedures described in
this chapter. Failure to disconnect power, telecommunications links, networks, or
modems before you open the computer or perform any procedures can result in
personal injury or equipment damage. Some circuitry on the motherboard may
continue to operate even though the front panel power button is off.
CAUTION!
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage components. Perform the procedures
described in this chapter only at an ESD workstation. If such a station is not
available, you can provide some ESD protection by wearing an anti-static wrist strap
and attaching it to a metal part of the computer chassis.
Setting the Processor Speed
There is no need to set the processor speed as this is automatically set by the BIOS.
Check the BIOS utility Advanced sub menu CPU Configuration for the correct
detection for the CPU or CPU’s installed in the motherboard.
Note: The BIOS does allow changing of the CPU clock ratio, we do not recommend
the use of this option.
Clearing the Passwords
Note: Passwords can be cleared individually from the normal BIOS Utility setup
mode if the password to be changed is known, if no passwords have been set they
can be set as described later in this section.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
63
Page 65

BIOS Setup Program
The Setup program is for viewing and changing the BIOS settings for a computer.
Setup is accessed by pressing the <Delete> key after the Power-On Self Test
(POST) memory test begins and before the operating system boot begins.
Table 30 shows the menus available from the menu bar at the top of the Setup
screen.
Table 30: Setup Menu Bar
Setup Menu Screen Description
Main Allocates resources for hardware components.
Advanced Specifies advanced features available through the chipset.
Power Specifies power management features.
Boot Specifies boot options and power supply controls.
Exit Saves or discards changes to the Setup program options.
Table 31 shows the function keys available for menu screens.
Table 31: Setup Function Keys
Setup Key Description
<←> or <→>
<↑> or <↓>
<Tab> Selects a field
<Enter> Executes command or selects the submenu
<F10> Save the current values and exits the BIOS Setup program
<Esc> Exits the menu
Selects a different menu screen (Moves the cursor left or right)
Selects an item (Moves the cursor up or down)
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
64
Page 66

BIOS Screen layout
Menu Items Menu BAR Configuration fields General Help
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
System Time [12:31:32]
System date [Thu 01/20/2005]
Legacy Diskette A [1.44M, 3.5 in]
8 Primary P-ATA IDE Master : [HDS722512VLAT20]
8 Primary P-ATA IDE Slave : [Not Detected]
8 Secondary P-ATA IDE Master: [Sony CD-RW CRX]
8 Secondary P-ATA IDE Slave : [Not Detected]
8 S-ATA 1 : [HDS724040KLSA80]
8 S-ATA 2 : [HDS724040KLSA80]
8IDE Configuration
8System Information
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Use [ENTER] , [TAB]
or [Shift-TAB] to
select a field.
Use [+] or [-] to
configure system time.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 29: BIOS Screen Layout
Note: Sub-menu items indicated by “
8
” Navigation Keys
Menu Bar
Shows the menu screen options available, the currently selected menu screen is
high lighted. On entering the BIOS setup utility the Main screen menu is the first to
be shown. Use the left and right arrow keys switch select the available screens
shown in the menu bar.
Menu items
These are items relating to each menu bar heading and may have an associated
configuration filed.
Configuration fields
These show the value set or automatically detected for the corresponding menu
item. A configuration filed is either an indication of an automatic detection and may
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
65
Page 67

not be changed or an item that may be configured and permanently changed. To
change each field follow the navigation key guide either Press <ENTER> key or <->
or <+> keys to change selected filed. To save the desired change/s the “Save and
Exit” option is selected by either F10 directly or via the exit menu and then selecting
“Save and Exit”.
Navigation keys
The keys that are indicated are used to select items change configuration fields,
save and exit the BIOS setup utility
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
System Time [12:31:32]
System date [Thu 01/20/2005]
Legacy Diskette A [1.44M , 3.5 in.]
8 Primary P-ATA IDE Master : [HDS722512VLAT20]
8 Primary P-ATA IDE Slave : [Not Detected]
8 Secondary P-ATA IDE Master: [Sony CD-RW CRX]
8 Secondary P-ATA IDE Slave : [Not Detected]
8 S-ATA 1 : [HDS724040KLSA80]
8 S-ATA 2 : [HDS724040KLSA80]
8IDE Configuration
8System Information
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Pop up Window appears for options when <Enter> is pressed using the “↑” and “↓”
arrows keys to select an option and enter to set the option.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Options
Disabled
360K , 5.25 in.
1.2M , 5.25 in.
720K , 3.5 in.
1.44M , 3.5 in.
2.88M , 3.5 in.
Figure 30: Pop up Windows
Use [ENTER] , [TAB]
or [Shift-TAB] to
select a field.
Use [+] or [-] to
configure system time.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
66
Page 68

Main Menu
This menu is for configuring the system date, system time, hard drives, optical
drives, IDE configuration and system configuration.
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
System Time [12:31:32]
System date [Thu 01/20/2005]
Legacy Diskette A [1.44M, 3.5 in]
8 Primary P-ATA IDE Master : [HDS722512VLAT20]
8 Primary P-ATA IDE Slave : [Not Detected]
8 Secondary P-ATA IDE Master: [Sony CD-RW CRX]
8 Secondary P-ATA IDE Slave : [Not Detected]
8 S-ATA 1 : [HDS724040KLSA80]
8 S-ATA 2 : [HDS724040KLSA80]
8IDE Configuration
8System Information
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 32: Main Menu
Feature Options Description
System Time Hour, minute, and
second
System Date Month, day, and year Shows the current system date; and allows setting of
Legacy Diskette A
Primary P-ATA IDE
Master
• Disabled
• 360K , 5.25 in
• 1.2M , 5.25 in
• 720K , 3.5 in
• 1.44 , 3.5 in
(default)
• 2.88 , 3.5 in
None
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Use [ENTER] , [TAB]
or [Shift-TAB] to
select a field.
Use [+] or [-] to
configure system time.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Figure 31: Main Menu
Shows the current system time; and allows setting of
system time.
system date.
Floppy drive controller options, allows selection of
correct configuration the floppy drive connected.
Displays a detected P-ATA drive.
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
A P-ATA IDE device is listed to the right otherwise not
detected will be displayed. An example HDD is
shown.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
67
Page 69

Primary P-ATA IDE
Slave
Secondary P-ATA
IDE Master
Secondary P-ATA
IDE Slave
S-ATA 1
S-ATA 2
IDE Configuration
System Information
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
Displays a detected P-ATA drive.
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
A P-ATA IDE device is listed to the right otherwise not
detected will be displayed.
Displays a detected P-ATA drive.
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
A P-ATA IDE device is listed to the right otherwise not
detected will be displayed. An example CD-ROM is
shown.
Displays a detected P-ATA drive.
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
A P-ATA IDE device is listed to the right if detected,
otherwise not detected will be displayed.
Displays a detected S-ATA drive.
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
A S-ATA IDE device is listed to the right if detected,
otherwise not detected will be displayed.
Displays a detected S-ATA drive.
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
A S-ATA IDE device is listed to the right if detected,
otherwise not detected will be displayed.
IDE controller configuration
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
System information sub menu
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
68
Page 70

Main / Primary P-ATA IDE Master or Slave Sub-menu
This menu shows a detected hard drive or CD-ROM features and allows
configuration settings to be made. The example is of a hard drive.
Main
Primary P-ATA IDE Master
Device : Hard Drive
Vendor : HDS722512VLAT20
Size : 123.5GB
LBA Mode : Supported
Block Mode : 16 Sectors
PIO Mode : 4
Async DMA : Multi DMA Word-2
Ultra DMA : Ultra MDA-5
SMART Monitoring: Supported
Type [Auto]
LBA/Large Mode [Auto]
Block [Multi-sector Transfer] [Auto]
PIO Mode [Auto]
DMA Mode [Auto]
SMART Monitoring [Auto]
32Bit Data Transfer [Disabled]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Select the type
of device connected
to the system.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 32: Main / Primary P-ATA IDE Master or Slave Sub-menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 33: Main/Primary P-ATA IDE Master or Slave Sub-menu
Feature Options Description
Device none Displays detected device connected
Vendor none Displays the detected vendor name and model of
device
LBA Mode none Displays the detected translation mode or set by user
Block Mode none Displays the detected Block mode or set by user
PIO Mode none Displays the detected PIO mode or set by user
Async DMA none Displays the detected asynchronous DMA mode or
set by user
Ultra DMA none Displays the detected Ultra DMA mode or set by user
SMART
none Displays SMART monitoring support
Monitoring
Type
• Not Installed
• Auto [Default]
• CDROM
Specifies the IDE configuration mode for IDE devices
User allows capabilities to be changed
Auto fills-in capabilities from ATA/ATAPI devices
• ARMD
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
69
Page 71

LBA/ Large Mode
Block [Multi-sector
Transfer]
PIO Mode
DMA Mode
SMART
Monitoring
32Bit Data
Transfer
• Disabled
• Auto [Default]
• Disabled
• Auto [Default]
• Auto [Default]
• 0
• 1
• 2
• 3
• 4
• Auto [Default]
• SWDMA0
• SWDMA1
• SWDMA2
• MWDMA0
• MWDMA0
• MWDMA1
• MWDMA2
• UDMA 0
• UDMA 1
• UDMA 2
• UDMA 3
• UDMA 4
• UDMA 5
• Auto [Default]
• Disabled
• Enabled
• Disabled
[Default]
• Enabled
Displays whether automatic translation mode is
enabled from the hard disk
(This item is read only unless Type is set to User)
Displays whether automatic multiple sector data
transfers are enabled
(This item is read-only unless Type is set to User)
Sets the PIO mode
(This item is read-only unless Type is set to User)
Specifies the DMA mode for the drive
Auto = Auto-detected
SWDMAn = Single Word DMAn
SWDMAn = Multi Word DMAn
UDMAn = Ultra DMAn
(This item is read-only unless Type is set to User)
Enables/disables S.M.A.R.T. (Self Monitoring Analysis
and Reporting Technologies)
(This Item is read-only unless Type is set to User)
Enables/disables 32Bit data transfer
(This Item is read-only unless Type is set to User)
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
70
Page 72

Main / Secondary P-ATA IDE Master or Slave Sub-menu
This menu shows a detected hard drive or CD-ROM drive features and allows
configuration settings to be made. The example is of a CD-ROM drive.
Main
Secondary P-ATA IDE Master
Device : ATAPI CD-ROM
Vendor : SONY CD-RW CRX230ED
LBA Mode : Supported
PIO Mode : 4
Async DMA : Multi DMA Word-2
Ultra DMA : Ultra MDA2
Type [Auto]
PIO Mode [Auto]
DMA Mode [Auto]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Select the type
of device connected
to the system.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 33: Main / Secondary P-ATA IDE Master or Slave sub menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 34: Main / Secondary P-ATA IDE Master or Slave Sub-menu
Feature Options Description
Device none Displays detected device connected
Vendor none Displays the detected vendor name and model of
device
LBA Mode none Displays the detected translation mode or set by user
Block Mode none Displays the detected Block mode or set by user
PIO Mode none Displays the detected PIO mode or set by user
Async DMA none Displays the detected asynchronous DMA mode or
set by user
Ultra DMA none Displays the detected asynchronous Ultra DMA mode
or set by user
Type
• Not Installed
• Auto [Default]
• CDROM
• ARMD
Specifies the IDE configuration mode for IDE devices
User allows capabilities to be changed
Auto fills-in capabilities from ATA/ATAPI devices
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
71
Page 73

PIO Mode
DMA Mode
• Auto [Default]
• 0
• 1
• 2
• 3
• 4
• Auto [Default]
• SWDMA0
• SWDMA1
• SWDMA2
• MWDMA0
• MWDMA0
• MWDMA1
• MWDMA2
• UDMA 0
• UDMA 1
• UDMA 2
Sets the PIO mode
(This item is read-only unless Type is set to User)
Specifies the DMA mode for the drive
Auto = Auto-detected
SWDMAn = Single Word DMAn
SWDMAn = Multi Word DMAn
UDMAn = Ultra DMAn
(This item is read-only unless Type is set to User)
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
72
Page 74

Main menu / IDE Configuration Sub-menu
This menu shows the IDE controller configuration.
Main
IDE Configuration
Onboard IDE Operate Mode [Enhanced Mode]
Enhanced Mode Support On [S-ATA]
Configure S-ATA as RAID [No]
IDE Detect Time Out (Sec) [35]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
When in AHCI/RAID
Mode SATA
Connector is
forced to Negative
mode.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 34: IDE Configuration Sub-menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 35: IDE Configuration Sub-menu
Feature Options Description
Device
• Enhance Mode
[Default]
• Compatibly Mode
Enhanced mode allows the translation of all P-ATA
and S-ATA port devices under Windows 2000 Pro and
Windows XP.
Compatibility is required for S-ATA devices under
DOS.
Enhanced mode
support On
• S-ATA [Default]
• P-ATA + S-ATA
Defines the S-ATA and P-ATA ports translated under
enhanced mode as required.
• P-ATA
Configure S-ATA
as RAID
•
Yes
•
No [Default]
RAID enable option for S-ATA devices
Once enabled devices are configured under controller
boot option during BIOS POST boot. Press <ctrl> + A
during BIOS post boot to configure RAID.
IDE Detect Time
Out (Sec)
•
0
•
5
•
10
•
15
•
20
•
25
•
30
•
35 [Default]
Hard drive pre delay time.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
73
Page 75
Main / System Information Sub-menu
This menu displays system information.
Main
AMIBIOS
Version : 08.00.10
Build Date : 02/16/05
Processor
Type : Intel (R) Xeon (TM) CPU 3.6
Speed : 3600 MHz
Count : 2
System Memory
Size : 1024MB
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 35: Main / System Information Sub-menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 36: Main / System Information Sub-menu
Feature Options Description
Version None Note this is the BIOS Utility version not the BIOS
version that is displayed during BIOS POST boot
Build Date None Note this is the BIOS Utility build date not the BIOS
build date that is displayed during BIOS POST boot
Type None Displays CPU type installed
Speed None Displays CPU speed
Count None Displays the number of CPU’s installed
Size None Displays the total system memory
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
74
Page 76

Advanced menu
This menu is for access to configure advanced features.
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
8Instant Music Configuration
8Speech Configuration
8PCI Express Configuration
8USB Configuration
8MPS Configuration
8CPU Configuration
8Chipset
8Onboard Device Configuration
8PCI PnP
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 37: Advanced menu
Feature Options Description
Instant Music Configuration None Not supported.
Speech Configuration None Sub menu for speech configuration
PCI Express Configuration
USB Configuration None Sub menu for USB configuration
MPS Configuration None Sub menu for MPS configuration
CPU Configuration None Sub menu for CPU configuration
Chipset None Sub menu for chipset configuration
Onboard Device Configuration None Sub menu for onboard device configuration
PCI PnP None Sub menu for PCI PnP
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Configure Instant
Music.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Figure 36: Advanced Menu
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
None Sub menu for PCI Express configuration
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
75
Page 77

Advanced / Speech Configuration Sub-menu
This menu allows configuration of speech options.
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
Speech Option
Speech POST Reporter [Enabled]
Report IDE Error [Disabled]
Report System Booting [Disabled]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Disable/Enable Speech
IC for Error Reporting
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 37: Advanced / Speech Configuration Sub-menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 38: Advanced / Speech Configuration sub menu
Feature Options Description
Speech Post
Reporter
Report IDE Error
Report System
Booting
• Disabled
• Enabled [Default]
• Disabled
[Default]
• Enabled
• Disabled
[Default]
• Enabled
.BIOS post error audio speech enabled, via onboard
audio.
Reports IDE error via onboard audio
Reports system booting error via onboard audio
Note: for all the options above Speakers must be connected to onboard sound
during BIOS POST boot.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
76
Page 78

Advanced / PCI Express Configuration Sub-menu
The menu below allows the configuration of the PCI-Express LAN
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
PCI Express
Onboard LAN [Enabled]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Auto: Visible if card
Enabled: Always visible
Disable: Always hide
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 38: Advanced / PCI Express Configuration sub menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 39: Advanced / PCI Express Configuration sub menu
Feature Options Description
Onboard LAN
• Disabled
. Enables or disables onboard LAN
• Enabled [Default]
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
77
Page 79

Advanced / USB Configuration Sub-menu
This menu allows USB controller configuration
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
USB Configuration
Module Version – 2.23.2-7.4
USB Devices Enabled; None
USB Function [All USB Ports]
Legacy USB Support [Auto]
USB 2.0 controller [Enabled]
USB Controller Mode [HiSpeed]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Enables USB Host
Controller.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 39: Advanced / USB Configuration sub menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 40: Advanced / USB Configuration sub menu
Feature Options Description
USB Function
Legacy USB
Support
USB 2.0 controller
USB Controller
Mode
• Disabled
• All USB Ports
[Default]
• 2 USB Ports
• Disabled
• Enabled
• Auto [Default]
• Enabled [Default]
• Auto Disabled
• Hi Speed
[Default]
• Full Speed
Allows enable or disable the USB function.
Allows the system to detect the presence of USB
devices at
start up. If detected, the USB controller
legacy mode is enabled. If no USB device is detected,
the legacy USB support is disabled.
Allows you to enable or disable the USB 2.0
controller.
Allows the USB 2.0 controller mode to HiSpeed (480
Mbps) or
FullSpeed (12 Mbps).
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
78
Page 80

Advanced / MPS Configuration Sub-menu
This menu allows the Multi-Processor Table to be configured.
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
MPS Configuration
MPS Revision [1.4]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Select MPS
Revision
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 40: Advanced / MPS Configuration sub menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 41: Advanced / MPS Configuration sub menu
Feature Options Description
MPS Revision
• 1.4 [Default]
• 1.1
Allows selection of the multi-processor system
revision.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
79
Page 81
Advanced / CPU Configuration Sub-menu
This manus configures the CPU settings
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
Configure Advance CPU settings
Manufacturer: Intel
Brand String: Intel(R )Xeon (TM) CPU 3.6GHz
Frequency : 3600 MHZ
FSB Speed : 800 MHz
Ratio Status: Locked
Ratio Actual Value : 18
CPU Lock Free [Auto]
Hyper Thread Technology [Enabled]
Max CPUID Value Limit [Disabled]
Execute Disable Function [Disabled]
Enhanced C1 Control [Auto]
CPU Internal Thermal Control [Auto]
Intel (R) SpeedStep (tm) tech. [Automatic]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Unlock locked CPU and
let is run at lower
multiplier setting.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 41: Advanced / CPU Configuration Sub-Menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 42: Advanced / CPU Configuration Sub-menu
Feature Options Description
CPU Lock Free
• Auto [Default]
• Disabled
• Enabled
Hyper Thread
Technology
Max CPUID Value
Limit
• Disabled
• Enable [Default]
• Disabled
[Default]
• Enable
Execute Disable
Function
• Disabled
[Default]
• Enable
Enhanced C1
Control
CPU Internal
Thermal Control
• Auto [Default]
• Disabled
• Auto [Default]
• Disabled
Not supported, allows setting CPU clock to lower
than fixed value
Allows enable or disable the processor HyperThreading Technology.
Enabled allows legacy operating systems to boot even
without support for CPUs with extended CPUID
functions.
Allows enable or disable the processor
function.
Allows enable or disable the processor Enhanced C1
control
CPU Internal Thermal Control.
It is not recommended to disable this feature.
function.
not recommended.
execute disable
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
80
Page 82

Intel (R) SpeedStep
(tm) tech.
• Maximum Speed
• Minimum Speed
CPU Intel (R) SpeedStep (tm) tech Control.
It is not recommended to disable this feature.
• Automatic
[Default]
• Disabled
Advanced / Chipset Sub-menu
This menu allows the configuration of chipset features
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
Advanced Chipset Settings
Warning: Setting wrong values in bellow sections
may cause system to malfunction.
8Northbridge Configuration
8Southbridge Configuration
Onboard LAN Option [Enabled]
OnBoard LAN Boot ROM [Enabled]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Options for NB.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 42: Advanced / Chipset Sub-menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 43: Advanced / Chipset Sub-menu
Feature Options Description
Northbridge
None Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
Configuration
Southbridge
Configuration
Onboard LAN
Option
Onboard LAN Boot
ROM
None Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
• Enable [Default]
Onboard LAN enable disable
• Disable
• Enable [Default]
• Disabled
Onboard LAN boot ROM enable disable
Note: if disabled LAN will not function under DOS
or other none PnP OS.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
81
Page 83

Advanced / Northbridge Configuration Sub-menu
This menu configures Northbridge options
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
Northbridge Chipset Configuration
DIMM SPEED:DDR2 400
Memory Remap Feature [Enabled]
Memory Mirror/Sparing [Enabled]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Options for NB.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 43: Advanced / Northbridge Configuration Sub-menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 44: Advanced / Northbridge Configuration Sub-menu
Feature Options Description
DIMM Speed None Displays DDR2 DIMM speed detected
Memory Remap
Feature
Memory
Mirror/Sparing
• Enabled [Default]
• Disable
• Disabled Default]
• Mirroring
• Sparing
Allows remapping the overlap PCI memory over the
total physical memory.
Allows memory RAS mirroring or sparing.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
82
Page 84

Advanced / Southbridge configuration Sub-menu
This menu allows the configuration of Southbridge options
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
Onboard AC’97 Audio [Auto]
South Bridge Chipset Configuration
Options for NB.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 44: Advanced / Southbridge configuration Sub-menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 45: Advanced / Southbridge configuration Sub-menu
Feature Options Description
Onboard AC’97
Audio
• Auto Default]
• Disabled
Onboard audio configuration
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
83
Page 85

Advanced / Onboard Device Configuration Sub-menu
This menu configures the serial, parallel and game port.
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
Configuration Win627EHF Super IO Chipset
Serial Port1 Address [3F8/IRQ4]
Serial Port2 Address [2F8/IRQ3]
Parallel port Address [378]
Parallel Port Mode [Normal]
Parallel Port IRQ [IRQ7]
Onboard Game/Midi Port [Disabled]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Allows BIOS to select
serial port base
address.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 45: Advanced / Onboard Device Configuration Sub-menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 46: Advanced / Onboard Device Configuration Sub-menu
Feature Options Description
Serial Port1
Address
Serial Port2
Address
Parallel Port
Address
• Disabled
• 3F8/IRQ4
[Default]
• 3F8/IRQ4
• 2F8/IRQ3
• Disabled
• 2F8/IRQ3
[Default]
• 3E8/IRQ4
• 2E8/IRQ3
• Disabled
• 378 [Default]
• 278
• 3BC
Serial port system resource setting or disable
Serial port system resource setting or disable
Parallel port system resource setting or disable
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
84
Page 86

Parallel Port Mode
Parallel Port IRQ
Onboard
Game/Midi Port
• Normal [Default]
• Bi-Directional
• EPP
• ECP
• IRQ5
• IRQ7 [Default]
• Disabled
[Default]
• 200/300
• 200/330
• 208/300
• 208/330
Additional Parallel port system resource setting
IF Parallel Port Address is set to “Disabled” this option
will not be shown
Additional Parallel port system resource setting
IF Parallel Port Address is set to “Disabled” this option
will not be shown
Onboard Game/Midi Port system resource setting or
disable
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
85
Page 87

Advanced / PCI PnP Sub-menu
This menu allows advanced configuration of PCI BUS
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
Advanced PCI/PnP Settings
Warning: Setting wrong values in bellow sections
May cause system to malfunction.
Plug And Play O/S [No]
PCI Latency Timer [64]
Allocate IRQ To PCI VGA [Yes]
Pallet Snooping [Disabled]
PCI IDE BusMaster [Enabled]
Offboard PCI/ISA IDE Card [Auto]
IRQ-3 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-4 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-5 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-7 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-9 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-10 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-11assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-14 assigned to [PCI Device]
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
NO: lets the BIOS
configure all the
devices in the system.
Yes: lets the
Operating system
Configure Plug and
Play (PnP) devices not
required for boot if
your system has a Plug
and Play operating
system.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Figure 46a: Advanced / PCI PnP Sub-Menu
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
Offboard PCI/ISA IDE Card [Auto]
IRQ-3 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-4 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-5 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-7 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-9 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-10 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-11assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-14 assigned to [PCI Device]
IRQ-15 assigned to [PCI Device]
DMA Channel 0 [PCI Device]
DMA Channel 1 [PCI Device]
DMA Channel 3 [PCI Device]
DMA Channel 5 [PCI Device]
DMA Channel 6 [PCI Device]
DMA Channel 7 [PCI Device]
Reserved Memory Size [Disabled]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Size of memory block
to reserve for legacy
ISA devices.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Figure 46b: Advanced / PCI PnP Sub-menu (use arrow keys to view all of menu items as above)
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
86
Page 88

A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 47: Advanced / PCI PnP Sub-menu
Feature Options Description
Plug And Play O/S
PCI Latency Timer
Allocate IRQ To PCI
VGA
Pallet Snooping
PCI IDE BusMaster
Offboard PCI/ISA
IDE Card
IRQ-3 assigned to
To
IRQ-15 assigned to
DMA Channel 0
to
DMA Channel 7
Reserved Memory
Size
• NO [Default]
• Yes
• 32
• 64 [Default]
• 96
• 128
• 160
• 192
• 224
• 248
• Yes [Default]
• No
• Disabled
[Default]
• Enabled
• Disabled
• Enabled [Default]
• Auto [Default]
• PCI Slot1
• PCI Slot2
• PCI Slot3
• PCI Slot4
• PCI Slot5
• PCI Slot6
• PCI Device
[Default]
• Reserved
• PCI Device
[Default]
• Reserved
• Disabled
[Default]
• 16k
• 32k
• 64k
PnP play OS setting if set to “NO” the BIOS
configures system resources, otherwise resources are
set by PnP OS.
Allows the value in units of PCI clocks for the PCI
device latency timer register.
When set to [Yes], BIOS assigns an IRQ to PCI VGA
card if the card
requests for an IRQ. When set to [No].
It is not recommended this is set to “NO”
Support for legacy Video capture cards.
It is not recommended this is set to “Enabled”
PCI bus master control.
It is not recommended this is set to “Disabled”
Allows assignment of a PCI slot to a PCI IDE card,
when required.
When set to [PCI Device], the specific IRQ is free for use of
PCI/PnP devices. When set to [Reserved], the IRQ is
reserved for legacy ISA
devices.
When set to [PCI Device], the specific DMA channel is
free for use of PCI/PnP devices. When set to
[Reserved], the DMA channel is reserved for
Legacy ISA devices.
Allows you to set the reserved memory size.
Some adaptors with ROM options may require memory to
be reserved.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
87
Page 89

Power Menu
A
This menu configures power management
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
System Mode [S3 only]
Repost Video on S3 Resume [NO]
ACPI 2.0 Support [No]
ACPI APIC Support [Enabled]
8 APM Configuration
8 Hardware Monitor
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Select the ACPI state
used for System
Suspend.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Figure 47: Power Menu
Table 48: Power Menu
Feature Options Description
System Mode
Repost Video on
S3 Resume
CPI 2.0 Support
ACPI APIC
Support
APM
Configuration
Hardware Monitor
• S1 (POS) only
• S3 only [Default]
• No [Default]
• Yes
• No [Default]
• Yes
• Enabled [Default]
• Disabled
None
None
Configures standby power mode, S1 suspend or S3
suspend to RAM. Note: Windows 2000 Pro does not
support S1
Some VGA cards may require “Repost Video on S3
Resume” signal after suspend.
Enables Advanced Configuration and Power
Interface (ACPI) 2.0 specifications.
Enable or disable the Advanced Configuration and
Power
Interface (ACPI) support
Power management device configuration
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
Hardware monitor device configuration
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
88
Page 90

Power / APM Configuration Sub-menu
This menu allows the configuration of APM features
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
APM Configuration
Power Management/APM [Enabled]
Video Power Down Mode [Suspended]
Hard Drive Power Down Mode [Suspended]
Suspend Time Out [Disabled]
Throttle Slow Clock Ratio [50%]
Power Button Mode [On/Off]
Restore on AC Power Loss [Power Off]
Power On By PS/2 Keyboard [Disabled]
Power On By PS/2 Mouse [Disabled]
Power On Ring [Disabled]
Power On LAN [Disabled]
Power On By PME# [Disabled]
Power On By RTC Alarm [Disabled]
RTC Alarm Date
RTC Alarm Hour
RTC Alarm Minute
RTC Alarm Second
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Enable or Disable
APM.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 48: Power / APM Configuration Sub-menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 49: Power / APM Configuration Sub-menu
Feature Options Description
Power
Management/AP
M
Video Power
Down Mode
Hard Drive Power
Down Mode
• Disabled
• Enabled [Default]
• Disabled
• Standby
• Suspended
[Default
• Disabled
• Standby
• Suspended
[Default
Enables or disables advanced power management
Defines video power down state
Defines hard drive power down state in standby or
suspend.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
89
Page 91

Suspend Time
Out
Throttle Slow
Clock Ratio
Power Button
Mode
Restore on AC
Power Loss
Power On By
PS/2 Keyboard
Power On By
PS/2 Mouse
Power On Ring
Power On LAN
Power On By
PME#
Power On By RTC
Alarm
RTC Alarm Date
• Disabled
[Default]
• 1 min
• 2 min
• 4 min
• 8 min
• 10 min
• 20 min
• 30 min
• 40 min
• 50 min
• 60 min
• 87.5%
• 75%
• 62.5%
• 50% [Default]
• 37.5%
• 25%
• 12.5%
• On/Off [Default]
• Suspend
• Power Off
[Default]
• Power On
• Last Sate
• Disabled
[Default]
• Enabled
• Disabled
[Default]
• Enabled
• Disabled
[Default]
• Enabled
• Disabled
[Default]
• Enabled
• Disabled
[Default]
• Enabled
• Disabled
[Default]
• Enabled
1 to 31 and Every
day
Defines suspend time controlled by motherboard
Defines CPU throttle speed under power control state
Defines power button function
Defines how motherboard will respond after power
failure has been restored
Power on by key board option
Power on by PS/2 Mouse option
Power on by Modem Ring option
Power on by LAN option
Power on by LAN PME# event option in soft off mode.
Power on by real time clock option
Set on date option
Note this will only be displayed if “Power On By RTC
Alarm” is set to “Enabled”
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
90
Page 92

RTC Alarm Hour
RTC Alarm Minute
RTC Alarm
Second
00 to 23
00 to 59
00 to 60
Set on hour option
Note this will only be displayed if “Power On By RTC
Alarm” is set to “Enabled”
Set on minute option
Note this will only be displayed if “Power On By RTC
Alarm” is set to “Enabled”
Set on second option
Note this will only be displayed if “Power On By RTC
Alarm” is set to “Enabled”
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
91
Page 93

Power / Hardware Monitor Sub-menu
This menu configures and shows hardware monitor features
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
Hardware Monitor
CPU1 Temperature [49
CPU2 Temperature [49
MB Temperature [47
CPU1 Fan Speed [2096RPM]
CPU1 Fan Speed [2098RPM]
Front1 Fan Speed [1562RPM]
Front2 Fan Speed [N/A]
Rear1 Fan Speed [2743RPM]
Rear2 Fan Speed [N/A]
Smart Fan Control [Enabled]
VCORE1 Voltage [1.320V]
VCORE2 Voltage [1.180V]
3.3 Voltage [3.345V]
5V Voltage [5.094V]
5VSB Voltage [5.046V]
VBAT Voltage [3.12V]
12V Voltage [12.053V]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
o
C/120oF]
o
C/120oF]
o
C/16.6oF]
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 49: Power / Hardware Monitor Sub-menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 50: Power / Hardware Monitor Sub-menu
Feature Options Description
CPU1
Temperature
• ??
o
C/???oF
[Default]
Displays monitored CPU temperature or can be set to
ignore
• Ignored
CPU2
Temperature
• ??
[Default]
o
C/???oF
Displays monitored CPU temperature or can be set to
ignore
• Ignored
MB Temperature
• ??
[Default]
o
C/???oF
Displays monitored MB temperature or can be set to
ignore
• Ignored
CPU1 Fan Speed
• ????RPM
[Default]
• Ignored
Displays monitored CPU fan speed or can be set to
ignore
Note if a FAN is not detected “N/A” will be displayed
instead of the “fan speed” RPM
CPU2 Fan Speed
• ????RPM
[Default]
• Ignored
Displays monitored CPU fan speed or can be set to
ignore
Note if a FAN is not detected “N/A” will be displayed
instead of the “fan speed” RPM
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
92
Page 94

Front1 Fan Speed
Front2 Fan Speed
Rear1 Fan Speed
Rear2 Fan Speed
Smart Fan Control
VCORE1 Voltage
VCORE2 Voltage
Loss
3.3 Voltage
5V Voltage
5VSB Voltage
VBAT Voltage
12V Voltage
• ????RPM
[Default]
• Ignored
• ????RPM
[Default]
• Ignored
• ????RPM
[Default]
• Ignored
• ????RPM
[Default]
• Ignored
• Enabled [Default]
• Disabled
• Ignored
• ?.???V [Default]
• Ignored
• ?.???V [Default]
• Ignored
• ?.???V [Default]
• Ignored
• ?.???V [Default]
• Ignored
• ?.???V [Default]
• Ignored
• ?.???V [Default]
• Ignored
• ?.???V [Default]
Displays monitored front1 fan speed or can be set to
ignore
Note if a FAN is not detected “N/A” will be displayed
instead of the “fan speed” RPM
Displays monitored front2 fan speed or can be set to
ignore
Note if a FAN is not detected “N/A” will be displayed
instead of the “fan speed” RPM
Displays monitored rear1 fan speed or can be set to
ignore
Note if a FAN is not detected “N/A” will be displayed
instead of the “fan speed” RPM
Displays monitored rear2 fan speed or can be set to
ignore
Note if a FAN is not detected “N/A” will be displayed
instead of the “fan speed” RPM
Motherboard thermal control enable, this controls fan
speeds according to CPU/s and MB temperature.
This means the system runs at low noise level
automatically
Displays monitored voltage or can be set to ignore
Displays monitored voltage or can be set to ignore
Displays monitored voltage or can be set to ignore
Displays monitored voltage or can be set to ignore
Displays monitored voltage or can be set to ignore
Displays monitored voltage or can be set to ignore
Displays monitored voltage or can be set to ignore
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
93
Page 95

Boot Menu
This menu configures boot options
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
Boot Settings
8Boot Device Priority
8Boot Settings Configuration
8Security
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Specifies the Boot
Device Priority
sequence.
A virtual floppy disk
drive (floppy Drive B:
) may appear when you
set the CD-ROM drive
As the first boot
device.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Figure 50: Boot Menu
Table 51: Boot Menu
Feature Options Description
Boot Device
Priority
Boot Settings
Configuration
Security None Security sub menu
None Boot device priority select sub menu
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
None Boot Settings Configuration sub menu
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
Press <Enter> to view this Sub menu
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
94
Page 96

Boot / Boot device Priority Sub-menu
This menu configures boot device priority
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
Boot Device Priority
1st Boot Device [1st Floppy Drive]
2nd Boot Device [PM- HDS722512VLAT20]
3rd Boot Device [PS-Sony CD-RW CRX2]
4th Boot Device [MBA V7.6.6 Slot 02]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Specifies the Boot
Device Priority
sequence from the
available devices.
A device enclosed in
parenthesis has been
disabled in the
corresponding type
menu.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 51: Boot / Boot device Priority Sub-menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 52: Boot / Boot device Priority Sub-menu
Feature Options Description
1st Boot Device
st
Floppy
• 1
drive[Default]
st
HDD detected
• 1
st
CD-ROM
• 1
st
boot device selection
1
Allows the 1
st
boot device to be changed to another
as desired
optical drive
detected
• MBA V7.6.6 Slot
0200
• Disabled
2nd Boot Device
st
Floppy drive
• 1
st
HDD
• 1
detected[Default]
st
CD-ROM
• 1
nd
boot device selection
2
Allows the 2
nd
boot device to be changed to another
as desired
optical drive
detected
• MBA V7.6.6 Slot
0200
• Disabled
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
95
Page 97

3rd Boot Device
4th Boot Device
st
Floppy drive
• 1
st
HDD detected
• 1
st
CD-ROM
• 1
optical drive
detected[Default]
• MBA V7.6.6 Slot
0200
• Disabled
st
Floppy
• 1
drive[Default]
st
HDD detected
• 1
st
CD-ROM
• 1
optical drive
detected
• MBA V7.6.6 Slot
0200[Default]
• Disabled
rd
3
boot device selection
Allows the 3
rd
boot device to be changed to another
as desired
th
boot device selection
4
Allows the 4
th
boot device to be changed to another
as desired
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
96
Page 98

Boot / Hard Drives Sub-menu
This menu allows the HDD boot order to be configured
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
Hard Drives
1st Boot Device [PM-HDS722512VLAT20]
2nd Boot Device [3M-HDS724040KLSA80]
3rd Boot Device [4M-HDS724040KLSA80]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Specifies the
Boot Device
Priority sequence
from the available
Hard Drives.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 52: Boot / Hard Drives sub menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 53: Boot / Hard Drives Sub-menu
Feature Options Description
1st Boot Device
• 1st HDD
detected[Default]
nd
• 2
• 3
HDD detected
rd
HDD detected
The first boot HDD.
st
Allows the 1
boot device to be changed to another
detected HDD as desired
• Disabled
2nd Boot Device
• 1st HDD detected
nd
• 2
HDD
detected[Default]
rd
HDD detected
• 3
The second boot HDD.
nd
Allows the 2
boot device to be changed to another
detected HDD as desired
• Disabled
3rd Boot Device
• 1st HDD detected
nd
• 2
• 3
HDD detected
rd
HDD
The third boot HDD.
Allows the third boot device to be changed to another
detected HDD as desired
detected[default]
• Disabled
Note: if les HDD’s are installed then a 3rd or 2nd boot device will not be shown; if
more HDD’s are installed then a 4th etc. boot devices will be shown.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
97
Page 99

Boot / Boot Setting Configuration Sub-menu
This menu sets BIOS boot options
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
Boot Setting Configuration
Quick Boot [Enabled]
Full Screen Logo [Enabled]
Bootup Num-Lock [On]
PS/2 Mouse Support [Auto]
Wait For “F1” If Error [Enabled]
Hit “DEL” Message Display [Enabled]
Interrupt 19 capture [Enabled]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Allows BIOS to Skip
certain tests while
booting. This will
decrease the time
needed to boot the
system.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 53: Boot / Boot Setting Configuration Sub-menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 54: Boot / Boot Setting Configuration Sub-menu
Feature Options Description
Quick Boot
Full Screen Logo
Bootup Num-Lock
• Enabled [default]
• Disabled
• Enabled [default]
• Disabled
• On [Default]
Quick boot performs a limited BIOS POST boot check
for a faster boot time
Enables or disables the BIOS boot logo screen from
being displayed
Num lock on boot enable or disable
• Off
PS/2 Mouse
Support
• Auto [Default]
• Enabled
PS/2 mouse detection on boot option
• Disabled
Wait For “F1” If
Error
Hit “DEL” Message
Display
Interrupt 19 capture
• Enabled [default]
• Disabled
• Enabled [default]
• Disabled
• Enabled [default]
• Disabled
On error pause after BIOS POST with error message
and F1 to resume
Display Hit “Del” to enter BIOS Util on power up
When set to [Enabled], this function allows the option
ROMs to trap
Interrupt 19. This is required by some
PCI cards that provide a ROM based setup utility.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
98
Page 100

Boot / Security Settings Sub-menu
This menu configures the system supervisor and user passwords
Main Advanced Power Boot Exit
Security Settings
Supervisor Password : Not Installed
User Password : Not Installed
Change Supervisor Password
User Access Level [Full Access]
Change User Password
Clear User Password
Password Check [Setup]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
<Enter> to change
Password.
<Enter again to
disable password.
← Select Screen
↑↓ Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
v02.53 (C) Copyright 1985-2002, American Magatrends, Inc.
Figure 54: Boot / Security Settings Sub-menu
A detailed description of each of the features is given in the following table.
Table 55: Boot / Security Settings Sub-menu
Feature Options Description
Supervisor
Password
User Password
Change
Supervisor
Password
User Access
Level
Not Installed
[Default]
Not installed
[Default]
None Press <Enter> to set Supervisor password.
• Full Access
[Default]
Not installed is displayed when a “Supervisor
Password” has not been set.
Not installed is displayed when a “User Password”
has not been set.
The password will need to be set twice with a
conformation windows and <Enter> to confirm.
Will not be displayed unless a “Supervisor Password”
has been set.
• No Access
• View only
• Limited
Change User
Password
None Will not be displayed unless a “Supervisor Password”
has been set.
Press <Enter> to set user password.
The password will need to be set twice with a
conformation windows and <Enter> to confirm.
Vig390s Motherboard Manual V1.0
99
 Loading...
Loading...