Page 1

Intel® Server Board
SE7221BK1-E
Technical Product Specification
Intel order number C91860-001
Revision 1.3
February 2005
Enterprise Platforms and Services Marketing
Page 2
SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Revision History
Date Revision
Number
July 2004 0.5 Preliminary Release; subject to change.
September 2004 0.8 Revised technical details of PCI subsystem, memory support and GMCH.
September 2004 0.9 Revised connectors section
October 2004 1.0 Released revision
November 2004 1.1 Corrected supported CPU matrix
January 2005 1.2 Added Diagnostic LED codes to error handling and reporting section
February 2005 1.3 Modified Diagnostic LED section. Correct supported CPU matrix.
Modifications
This product specification applies to the Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E with BIOS identifier
SE7221BK10.86B.
Changes to this specification will be published in the Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E
Specification Update before being incorporated into a revision of this document.
Revision 1.3
ii
Page 3

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Disclaimers
Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel® products. No license, express or
implied, by estoppels or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document. Except
as provided in Intel's Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products, Intel assumes no liability
whatsoever, and Intel disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating to sale and/or use of Intel
products including liability or warranties relating to fitness for a particular purpose, merchantability, or
infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property right. Intel products are not intended for
use in medical, life saving, or life sustaining applications. Intel may make changes to specifications and
product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked
"reserved" or "undefined." Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility
whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
This document contains information on products in the design phase of development. Do not finalize a
design with this information. Revised information will be published when the product is available. Verify
with your local sales office that you have the latest datasheet before finalizing a design.
Intel Corporation server baseboards contain a number of high-density VLSI and power delivery
components which need adequate airflow to cool. Intel’s own chassis are designed and tested to meet
the intended thermal requirements of these components when the fully integrated system is used
together. It is the responsibility of the system integrator that chooses not to use Intel developed server
building blocks to consult vendor datasheets and operating parameters to determine the amount of
airflow required for their specific application and environmental conditions. Intel Corporation cannot be
held responsible if components fail or the server board does not operate correctly when used outside any
of its published operating or non-operating limits.
The Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may
cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on
request.
This document and the software described in it is furnished under license and may only be used or
copied in accordance with the terms of the license. The information in this manual is furnished for
informational use only, is subject to change without notice, and should not be construed as a commitment
by Intel Corporation. Intel Corporation assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies
that may appear in this document or any software that may be provided in association with this document.
Except as permitted by such license, no part of this document may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval
system, or transmitted in any form or by any means without the express written consent of Intel
Corporation.
Intel® , Pentium® , Itanium, and Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
*Other brands and names may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © Intel Corporation 2005.
iii
Page 4

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Table of contents
1. Introduction ..........................................................................................................................1
2. Server Board Overview........................................................................................................2
2.1 SE7221BK1-E Feature Set......................................................................................2
3. Functional Architecture.......................................................................................................5
3.1 Processor Subsystem..............................................................................................5
3.1.1 Processor VRD........................................................................................................5
3.1.2 Reset Configuration Logic .......................................................................................5
3.1.3 Processor Module Presence Detection ...................................................................5
3.1.4 Processor Support...................................................................................................5
3.1.5 Interrupts and APIC .................................................................................................6
3.2 Memory Subsystem.................................................................................................6
4. The Intel® E7221 Chipset .....................................................................................................9
4.1.1 GMCH Memory Architecture Overview..................................................................10
4.1.2 Graphics Memory Controller Hub (GMCH)............................................................10
4.1.3 ICH6R....................................................................................................................11
4.2 Super I/O ...............................................................................................................13
4.2.1 Serial Ports ............................................................................................................13
4.2.2 BIOS Flash ............................................................................................................14
4.2.3 System Health Support..........................................................................................14
5. I/O Subsystem ....................................................................................................................14
5.1 PCI Subsystem......................................................................................................14
5.1.1 P32-A: 32-bit/33-MHz PCI Subsystem...................................................................14
5.1.2 P32-B 66-MHz PCI-X Subsystem (SE7221BK1LX sku only) .............................15
5.1.3 P64-C 66/100-MHz PCI-X Subsystem...................................................................16
5.1.4 PCI-E x8 ................................................................................................................17
5.2 Video Controller.....................................................................................................17
5.3 Network Interface Controller (NIC) ........................................................................17
5.3.1 NIC Connector and Status LEDs...........................................................................17
5.4 Interrupt Routing....................................................................................................18
5.4.1 Legacy Interrupt Routing .......................................................................................18
5.4.2 APIC Interrupt Routing...........................................................................................18
5.4.3 Serialized IRQ Support..........................................................................................19
Revision 1.3
iv
Page 5

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
5.5
PCI Error Handling.................................................................................................19
6. ACPI Implementation .........................................................................................................23
6.1 ACPI ......................................................................................................................23
6.1.1 Front Panel Switches.............................................................................................23
6.1.2 Wake up Sources (ACPI and Legacy)...................................................................24
7. Connectors .........................................................................................................................25
7.1 Main Power Connector..........................................................................................25
7.2 I2C Header.............................................................................................................26
7.3 Front Panel Connector...........................................................................................26
7.4 VGA Connector......................................................................................................27
7.5 NIC Connector.......................................................................................................27
7.6 IDE Connector.......................................................................................................28
7.7 SATA Connector....................................................................................................29
7.8 USB Connector......................................................................................................29
7.9 Floppy Connector ..................................................................................................30
7.10 Serial Port Connector ............................................................................................30
7.11 Keyboard and Mouse Connector...........................................................................31
7.12 Miscellaneous Headers .........................................................................................31
7.12.1 Fan Header............................................................................................................31
7.12.2 Intrusion Cable Connector.....................................................................................32
7.12.3 HDD LED Header ..................................................................................................32
7.12.4 Rolling BIOS selection header...............................................................................33
8. Configuration Jumpers......................................................................................................33
8.1 System Recovery and Update Jumpers ................................................................33
9. BIOS Setup Utility...............................................................................................................34
9.1 Localization............................................................................................................34
9.2 Console Redirection ..............................................................................................34
9.3 Configuration Reset...............................................................................................34
9.4 Keyboard Commands............................................................................................34
9.5 Entering BIOS Setup .............................................................................................36
9.5.1 Main Menu.............................................................................................................36
9.5.2 Advanced menu.....................................................................................................37
9.5.3 Boot menu .............................................................................................................43
9.5.4 Chipset Menu.........................................................................................................45
9.5.5 Security menu........................................................................................................47
v
Page 6

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
9.5.6 Server menu ..........................................................................................................48
9.5.7 Exit menu...............................................................................................................51
9.6 Upgrading the BIOS...............................................................................................51
9.6.1 Preparing for the Upgrade .....................................................................................51
9.6.2 Flash Architecture and Flash Update Utility...........................................................53
9.6.3 Rolling BIOS and On-line updates.........................................................................53
9.7 Error Handling and Reporting................................................................................56
9.7.1 POST Error Beep Codes .......................................................................................56
9.7.2 BIOS Event Log.....................................................................................................57
9.7.3 POST Progress Codes and Messages..................................................................58
Table 70. POST Code Checkpoints .........................................................................................58
Table 71. Bootblock Initialization Code Checkpoints............................................................61
Table 72. Bootblock Recovery Code Checkpoints ................................................................62
Table 73. DIM Code Checkpoints ............................................................................................63
Table 74. ACPI Runtime Checkpoints.....................................................................................63
9.8 Diagnostic LEDs....................................................................................................64
9.8.1 Diagnostic LED POST Progress Codes ................................................................64
Table 76. Boot Block POST Progress Codes .........................................................................64
Table 77. POST Progress Codes .............................................................................................65
10. Power Information..............................................................................................................68
10.1 Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E Power Budget ...............................................68
10.2 Power Supply Specifications .................................................................................69
10.2.1 Power Timing Requirements .................................................................................69
10.2.2 Dynamic Loading...................................................................................................71
10.2.3 AC Line Transient Specification.............................................................................72
10.2.4 AC Line Fast Transient (EFT) Specification ..........................................................72
11. Absolute Maximum Ratings ..............................................................................................72
11.1 Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) Test Results..............................................73
12. Hardware Monitoring .........................................................................................................73
12.1 Monitored Components .........................................................................................73
12.2 Fan Speed Control.................................................................................................75
12.3 Chassis Intrusion...................................................................................................76
13. Product Regulatory Compliance.......................................................................................76
13.1.1 Product Safety Compliance...................................................................................76
Revision 1.3
vi
Page 7

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
13.1.2
Product EMC Compliance .....................................................................................76
13.1.3 Product Regulatory Compliance Markings ............................................................76
13.2 Electromagnetic Compatibility Notices ..................................................................77
13.2.1 FCC (USA).............................................................................................................77
13.2.2 INDUSTRY CANADA (ICES-003)..........................................................................78
13.2.3 Europe (CE Declaration of Conformity) .................................................................78
13.2.4 Taiwan Declaration of Conformity..........................................................................78
13.2.5 Korean RRL Compliance.......................................................................................78
13.2.6 Australia / New Zealand.........................................................................................79
13.3 Replacing the Back-Up Battery..............................................................................79
13.4 Calculated Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF).................................................80
13.5 Mechanical Specifications .....................................................................................80
Glossary........................................................................................................................................I
vii
Page 8

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
List of Tables
Table 1. Processor Support Matrix ..............................................................................................6
Table 2. Memory Bank Labels and DIMM Population Order........................................................8
Table 3. Characteristics of Dual/Single Channel Configuration with/without Dynamic Mode ......9
Table 4. Supported DDR2 modules...........................................................................................10
Table 5. PCI Bus Segment Characteristics................................................................................14
Table 6. P32-A Configuration IDs..............................................................................................15
Table 7. P32-A Arbitration Connections.....................................................................................15
Table 8. P32-B Configuration IDs..............................................................................................15
Table 9. P32-B Arbitration Connections.....................................................................................16
Table 10. P64-C Configuration IDs............................................................................................16
Table 11. P64-C Arbitration Connections ..................................................................................16
Table 12. PCI-E x 8 Connections..............................................................................................17
Table 13. PCI AND PCI-X Interrupt Routing/Sharing.................................................................18
Table 14. Interrupt Definitions....................................................................................................19
Table 15. Supported Wake Events............................................................................................24
Table 16. Power Connector Pin-out (CN4H1)............................................................................25
Table 17. Auxiliary CPU Power Connector Pin-out (CN4B1).....................................................25
Table 18. HSBP Header Pin-out (J1D1)....................................................................................26
Table 19. LCD Header Pin-out (J1C1).......................................................................................26
Table 20. LEGEND SE_LINK Header Pin-out (J2B1)................................................................26
Table 21. Front Panel 34-Pin Header Pin-out (J1J1).................................................................26
Table 22. VGA Connector Pin-out (J8A1)..................................................................................27
Table 23. NIC1-82541PI(10/100/1000) Connector Pin-out (J5A1)............................................27
Table 24. NIC2-82541PI (10/100/1000) Connector Pin-out (J6A1)...........................................28
Table 25. ATA 40-pin Connector Pin-out (J3J1)........................................................................28
Table 26. SATA Connector Pin-out (J1G1, J1G2, J1J2, J2J1)..................................................29
Table 27. USB Connectors Pin-out (J5A1)................................................................................29
Table 28. Optional USB Connection Header Pin-out (J4F1) .....................................................29
Table 29. Legacy 34-pin Floppy Connector Pin-out (JP3J1).....................................................30
Table 30. External DB9 Serial A Port Pin-out (J8A1).................................................................30
Table 31. 9-pin Header Serial B Port Pin-out (J1B1).................................................................31
Table 32. Keyboard and Mouse PS/2 Connectors Pin-out (KM9A1).........................................31
Revision 1.3
viii
Page 9

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Table 33. Three-pin Fan Headers Pin-out (JP5J1, JP5J2, JP7A1, JP6A1)...............................31
Table 34. Eight-pin Fan Header Pin-out (J6J1, J6J2, J6J3, and J6J4)......................................32
Table 35. Intrusion Cable Connector (J1A1)Pin-Out .................................................................32
Table 36. HDD LED Header (J1E1) Pin-Out..............................................................................32
Table 37. HDD LED Header (J1E1) Pin-Out..............................................................................33
Table 38. System Recovery and Update Jumper Options.........................................................33
Table 39. BIOS Setup Keyboard Command Bar Options..........................................................34
Table 40. BIOS Setup, Main Menu Options...............................................................................36
Table 41. BIOS Setup, Advanced Menu Options.......................................................................37
Table 42. BIOS Setup, Processor configuration sub-menu options...........................................37
Table 43. BIOS Setup IDE Configuration Menu Options ............................................................38
Table 44. BIOS Setup, IDE Device Configuration Sub-menu Selections ..................................39
Table 45. BIOS Setup, Floppy Configuration Sub-menu Selections..........................................40
Table 46. BIOS Setup, Super I/O Configuration Sub-menu.......................................................40
Table 47. BIOS Setup, USB Configuration Sub-menu Selections..............................................41
Table 48. BIOS Setup, USB Mass Storage Device Configuration Sub-menu Selections..........41
Table 49. BIOS Setup, PCI Configuration Sub-menu Selections ..............................................42
Table 50. BIOS Setup, Memory Configuration Sub-menu Selections........................................43
Table 51. BIOS Setup, Boot Menu Selections...........................................................................43
Table 52. BIOS Setup, Boot Settings Configuration Sub-menu Selections...............................44
Table 53. BIOS Setup, Boot Device Priority Sub-menu Selections ...........................................44
Table 54. BIOS Setup, Hard Disk Drive Sub-Menu Selections..................................................44
Table 55. BIOS Setup, Removable Drives Sub-menu Selections..............................................45
Table 56. BIOS Setup, ATAPI CDROM Drives Sub-menu Selections.......................................45
Table 57. BIOS Setup, ATAPI CDROM Drives Sub-menu Selections.......................................45
Table 58. BIOS Setup, ATAPI CDROM Drives Sub-menu Selections.......................................45
Table 59. BIOS Setup, ATAPI CDROM Drives Sub-menu Selections.......................................46
Table 60. BIOS Setup, ATAPI CDROM Drives Sub-menu Selections.......................................47
Table 61. BIOS Setup, Security Menu Options..........................................................................47
Table 62. BIOS Setup, Server Menu Selections........................................................................48
Table 63. BIOS Setup, System Management Sub-menu Selections..........................................49
Table 64. BIOS Setup Serial Console Features Sub-menu Selections.....................................50
Table 65. BIOS Setup, Event Log Configuration Sub-menu Selections ....................................50
Table 66. BIOS Setup, Exit Menu Selections ............................................................................51
Table 67. POST Error Beep Codes ...........................................................................................56
ix
Page 10

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Table 68. BIOS Recovery Beep Codes .....................................................................................57
Table 69. POST Error Messages and Handling.........................................................................57
Table 70. POST Code Checkpoints............................................................................................58
Table 71. Bootblock Initialization Code Checkpoints..................................................................61
Table 72. Bootblock Recovery Code Checkpoints......................................................................62
Table 73. DIM Code Checkpoints...............................................................................................63
Table 74. ACPI Runtime Checkpoints ........................................................................................63
Table 75. POST Progress Code LED Example ..........................................................................64
Table 76. Boot Block POST Progress Codes.............................................................................64
Table 77. POST Progress Codes ...............................................................................................65
Table 78. The Board Power Budget...........................................................................................68
Table 79. The Board Power Supply Voltage Specification ........................................................69
Table 80. Output Voltage Timing...............................................................................................69
Table 81. Turn On/Off Timing....................................................................................................70
Table 82. Transient Load Requirements....................................................................................71
Table 83. AC Line Sag Transient Performance.........................................................................72
Table 84. AC Line Surge Transient Performance......................................................................72
Table 85. Absolute Maximum Ratings.......................................................................................73
Table 86. Monitored Components..............................................................................................73
Table 87. Product Certification Markings....................................................................................77
Table 88. MTBF Data.................................................................................................................80
Revision 1.3
x
Page 11

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
List of Figures
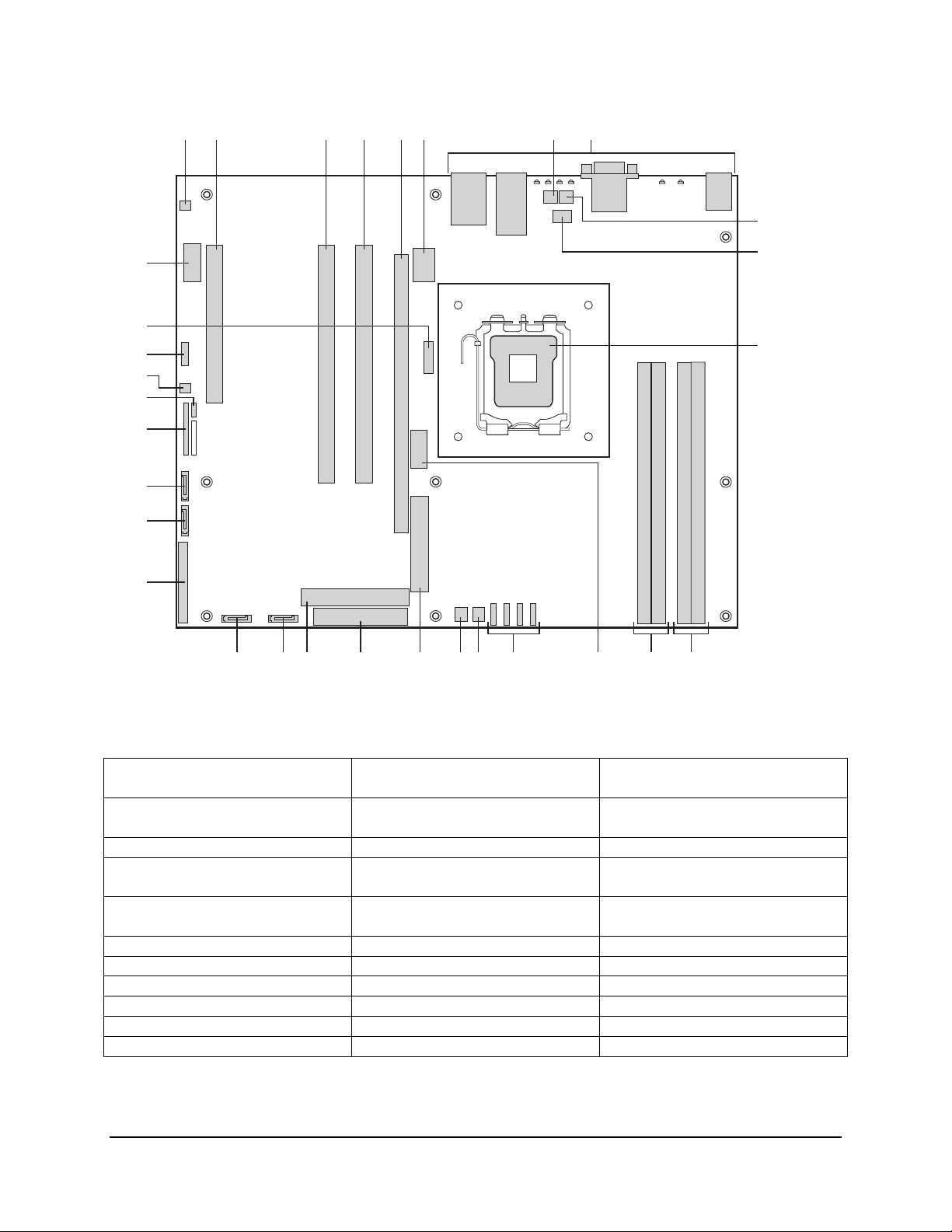
Figure 1. Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E Diagram ..............................................................4
Figure 2. Memory Bank Label Definition......................................................................................8
Figure 3. Interrupt Routing Diagram ..........................................................................................20
Figure 4. ICH6R Interrupt Routing Diagram...............................................................................21
Figure 5. PXH Interrupt Routing Diagram..................................................................................22
Figure 6. System Recovery and Update Jumpers (J1F2)..........................................................33
Figure 7. BIOS Recovery Jumper..............................................................................................56
Figure 8. Output Voltage Timing................................................................................................70
Figure 9. Turn On/Off Timing (Power Supply Signals)...............................................................71
Figure 10. Fan Speed Control Block Diagram...........................................................................75
Figure 11. SE7221BK1-E Server Board Mechanical Drawing....................................................81
Figure 12. sku 1 Pedestal mount I/O shield mechanical drawing.............................................82
Figure 13. sku 2 Pedestal mount I/O shield mechanical drawing.............................................83
xi
Page 12

Page 13

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
1. Introduction
This Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification (TPS) provides a highlevel technical description for the Intel
®
Server Board SE7221BK1-E. It details the architecture
and feature set for all functional sub-systems that make up the server board.
This document is divided into the following main categories:
Chapter 2. Server Board Overview
Chapter 3. Functional Architecture
Chapter 4. The Intel® E7221 Chipset
Chapter 5. I/O Subsystem
Chapter 6. ACPI Implementation
Chapter 7. Connectors
Chapter 8. Configuration Jumpers
Chapter 9. BIOS Setup Utility
Chapter 10. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Chapter 11. Power Information
Chapter 12. Hardware Monitoring
Chapter 13. Product Regulatory Compliance
Chapter 14. Glossary
1
Page 14

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
2. Server Board Overview
2.1 SE7221BK1-E Feature Set
The Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E supports the following feature set:
Processor and Front Side Bus (FSB) support
- Supports single Intel® Pentium® 4 and Celeron® processors in an LGA775 package
- Capable of 800 MT/s on system bus
- Supports Hyper-Threading Technology
- Supports Intel® Extended Memory System 64 Technology (EM64T)
Intel® E7221 chipset components
- GMCH integrated graphics controller in GMCH component (Intel® GMA 900)
- ICH6R I/O controller
- PXH PCI-X Hub
- 12-deep In-Order Queue
Memory System
- 4 DIMM sockets supporting 400/533MHz DDR2 DIMMs
- Data bandwidth per channel of 4.2GB/s or 8.5GB/s in dual channel when using DDR2
533MHz
-Support for up to two DDR2 channels for a total of 4 DIMMs (2 DIMMs /Channel) providing
up to 4GB max memory capacity.
-Support for 256MB, 512MB, 1GB and 2GB DRAM sizes
-Supports Performance Acceleration Technology (PAT)
I/O Subsystem
Four independent PCI Buses:
Segment A: One PCI 32-bit/33-MHz, 5 V connector supporting full length PCI add-in
cards and one embedded device(Supports PCI Specification, Rev 2.3)
One Intel® 10/100/1000 82541PI gigabit Ethernet Controller
Segment B: One PCI 32-bit/66-MHz embedded device (SE7221BK1LX sku only)
One Intel® 10/100/1000 82541PI gigabit Ethernet Controller
Segment C: Two PCI-X 64-bit/66-MHz, 3.3 V slots supporting full length / full height PCI
/ PCI-X add-in cards or one 3.3V PCI-X 64-bit/100-MHz slot with riser card (SE7221BK1LX
sku only)
Segment D: One x8 PCI Express* slot supporting x1/x2/x4/x8 PCI Express* add-in card
or one x8 PCI Express* slot with riser card (SE7221BK1LX sku only)
Serial ATA host controller
- Four independent SATA ports supports data transfer rates up to 1.5 Gb/s (150MB/s) per
port
IDE controller
- One IDE connector, supporting up to two ATA-100 compatible devices
Revision 1.3
2
Page 15

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
USB 2.0
Two external Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports with an additional internal header providing
two optional USB ports for front panel support.
-Supports wake-up from sleeping states S1-S4
-Supports legacy Keyboard/Mouse connections when using PS2-USB dongle
LPC (Low Pin Count) bus segment with one embedded devices:
Super I/O (Super IO) controller chip, NS PC87427, providing all PC-compatible I/O (floppy,
serial, keyboard, mouse, two serial com port ) and integrated hardware monitoring
SSI-compliant connectors for SSI interface support: front panel and power
connectors.
Support for up to four system fans and one processor fan
3
Page 16
SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
HA B C D E F G
I
EE
DD
CC
BB
AA
Z
Y
X
W
V U T S NR Q P
CPU
Socket
O
DIMM 1A Socket
DIMM 2A Socket
M L
DIMM 1B Socket
DIMM 2B Socket
J
K
TP01326
Figure 1. Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E Diagram
A Chassis Intrusion Header
B PCI Slot M DIMM Sockets (two – from left to
C PCI-X 100 SLOT N Front USB Header (optional) Y SATA 1 Connector
D PCI-X 100 SLOT O System Fan Headers (for Intel®
E PCI-Express* or Riser Connector
Slot
F +12v CPU Power Q System Fan #3 (optional) BB HDD LED Header
G System Fan #1 (optional) R Main Power Connector CC HSBP Header
H Back Panel I/O Connectors S Floppy Connector DD Battery
I System Fan #2 (optional) T IDE Connector EE Serial B Header
J CPU Fan (optional) U SATA 4 Connector
K CPU Socket V SATA 3 Connector
Revision 1.3
4
L DIMM Sockets (two – from left to
right: DIMM 1B, DIMM 2B)
right: DIMM 1A, DIMM 2A)
Server Board SR1425BK1-E)
P System Fan #4 AA BIOS Select Jumper
W 34-pin Front Panel Connector
X Serial ATA (SATA) 2 Connector
Z BIOS Control Jumper
Page 17

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
3. Functional Architecture
This chapter provides a high-level description of the functionality distributed between the
architectural blocks of the Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E.
3.1 Processor Subsystem
The Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E supports Intel® Pentium® 4 and Celeron® D
processors in the 775-land package, which is a follow on to Pentium® 4 and Celeron® D
processors in the 478-pin package, with enhancements to the Intel® NetBurst® microarchitecture. Intel® Pentium® 4 and Celeron® D processors built on 90nm process technology
in the 775-land package utilize Flip-Chip Land Grid Array (FC-LGA4) package technology, and
plug into a 775-land LGA socket, referred to as the LGA775 socket. Pentium® 4 and Celeron®
D processors in the 775-land package, like their predecessors in the 478-pin package, are
based on the same Intel® 32-bit micro-architecture and maintain the tradition of compatibility
with IA-32 software. Specific models of the Pentium® 4 Processor in the LGA775 package
support Intel® EM64T (Extended Memory 64 Technology) for 64bit native mode operation with
64bit operating systems. The Intel® Celeron® Processor currently does not support EM64T.
3.1.1 Processor VRD
The Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E has a VRD (Voltage Regulator Down) to support one
processor. It is compliant with the VRM 10.1 DC-DC Converter Design Guide Line and provides
a maximum of 120A, which is capable of supporting the requirements for Intel® Pentium® 4 and
Intel® Celeron® D processors.
The board hardware must monitor the processor VTTEN (Output enable for VTT) pin before
turning on the VRD. If the VTTEN pin of the processors is not identical the Power ON Logic will
not turn on the VRD.
3.1.2 Reset Configuration Logic
The BIOS determines the processor stepping, cache size, etc through the CPUID instruction.
The requirements are as follows:
Processors run at a fixed speed, but can be programmed by BIOS to operate at a lower
or higher speed.
The processor information is read at every system power-on.
Note: The processor speed is the processor power on reset default value. No manual processor
speed setting options exist either in the form of a BIOS setup option or jumpers.
3.1.3 Processor Module Presence Detection
SE7221BK1-E does not support this function.
3.1.4 Processor Support
The Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E supports one processor in the LGA775 package. The
support circuitry on the server board consists of the following:
5
Page 18
SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
LGA775 processor socket supporting 800MHz FSB Intel® Pentium® 4 processor.
Processor host bus AGTL+ support circuitry.
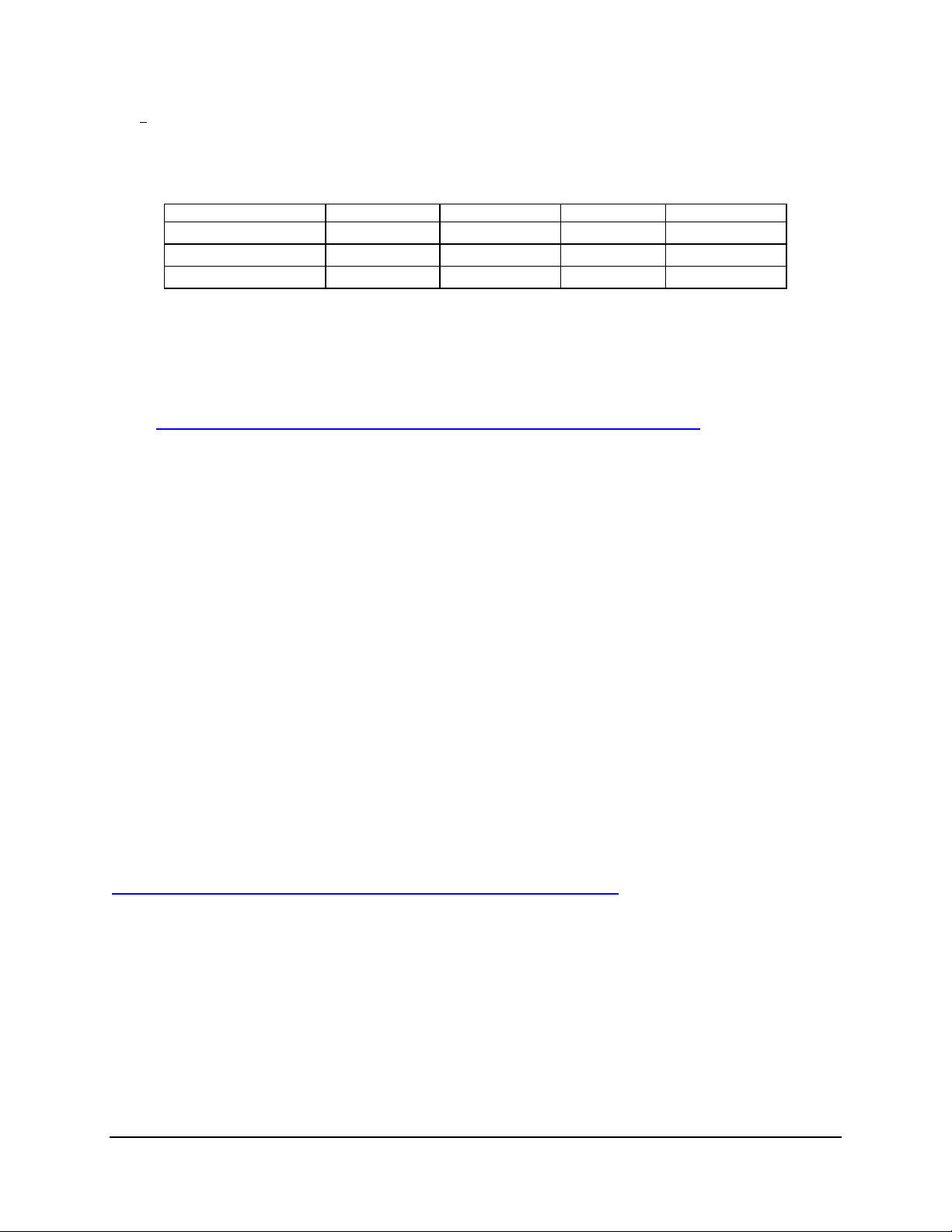
Table 1. Processor Support Matrix
Processor Family Package Type Frequency Cache Size Front Side Bus
Pentium® 4 LGA775 3.0 - 3.8 GHz 2MB L2 800MHz
Pentium® 4 LGA775 2.8 - 3.8 GHz 1MB L2 800MHz
Celeron® D LGA775 2.26 - 2.93 GHz 256K L2 533MHz
Note: The Pentium® 4 Processor Extreme Edition IS NOT supported for use with the
Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E.The board is designed to provide up to 120A of
processor current. Processors with higher current requirements are not supported. For a
complete list of all supported processors, please visit the Intel® Server Board
SE7221BK1-E support site located at the following URL:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/sb/CS-012690.htm
In addition to the circuitry described above, the processor subsystem contains the following:
Reset configuration logic
Server management registers and sensors
3.1.5 Interrupts and APIC
Interrupt generation and notification to the processor is done by the APICs in the ICH6R using
messages on the front side bus.
3.2 Memory Subsystem
The baseboard supports up to four DIMM slots for a maximum memory capacity of 4 GB. The
DIMM organization is x72, which includes eight ECC check bits. The memory interface runs at
400/533MT/s. The memory controller supports memory scrubbing, single-bit error correction and
multiple-bit error detection and Intel® x4 SDDC support with x4 DIMMs. Memory can be
implemented with either single sided (one row) or double-sided (two row) DIMMs.
3.2.1.1 Memory DIMM Support
The board supports un-buffered (not registered) DDR2 400/533-compliant ECC or Non-ECC
DIMMs operating at 400/533MT/s. Only DIMMs tested and qualified by Intel or a designated
memory test vendor are supported on this board. A list of qualified DIMMs is available at
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SE7221BK1E
supported by design, but only fully qualified DIMMs will be supported on the board.
. Note that all DIMMs are
The minimum supported DIMM size is 256 MB. Therefore, the minimum main memory
configuration is 1 x 256 MB or 256 MB. The largest size DIMM supported is 2 GB however, the
maximum main memory configuration is 4 GB implemented by 4 x 1 GB or 2 x 2 GB DIMMs.
Only un-buffered DDR2 400/533 compliant, ECC x8 and Non-ECC x8 or x16 memory
DIMMs are supported
ECC single-bit errors (SBE) will be corrected and multiple-bit error (MBE) will be
detected.
Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E also supports Intel® x4 SDDC with x4 DIMMs.
Revision 1.3
6
Page 19

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
The maximum memory capacity is 4 GB
Note* Although the Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E supports a maximum memory
capacity of 4 GB, system resources consume roughly 750 MB of physical memory in the
maximum memory configuration. As a result, when 4 GB of memory is used, the amount of
memory made available to the operating system is significantly lower than 4 GB; roughly
3200 MB. THIS IS ONLY AN ISSUE WHEN 4 GB OF MEMORY IS USED. A memory
configuration of less than 4 GB will not be susceptible to this issue. Please refer to Intel®
Technical Advisory TA 719-01 on the support web site located at
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SE7221BK1E
.
The minimum memory capacity is 256 MB via 1 x 256 MB DIMM module
3.2.1.2 Memory Configuration
The memory interface between the GMCH and the DIMMs is 64-bit (non-ECC) or 72-bit (ECC)
wide interface.
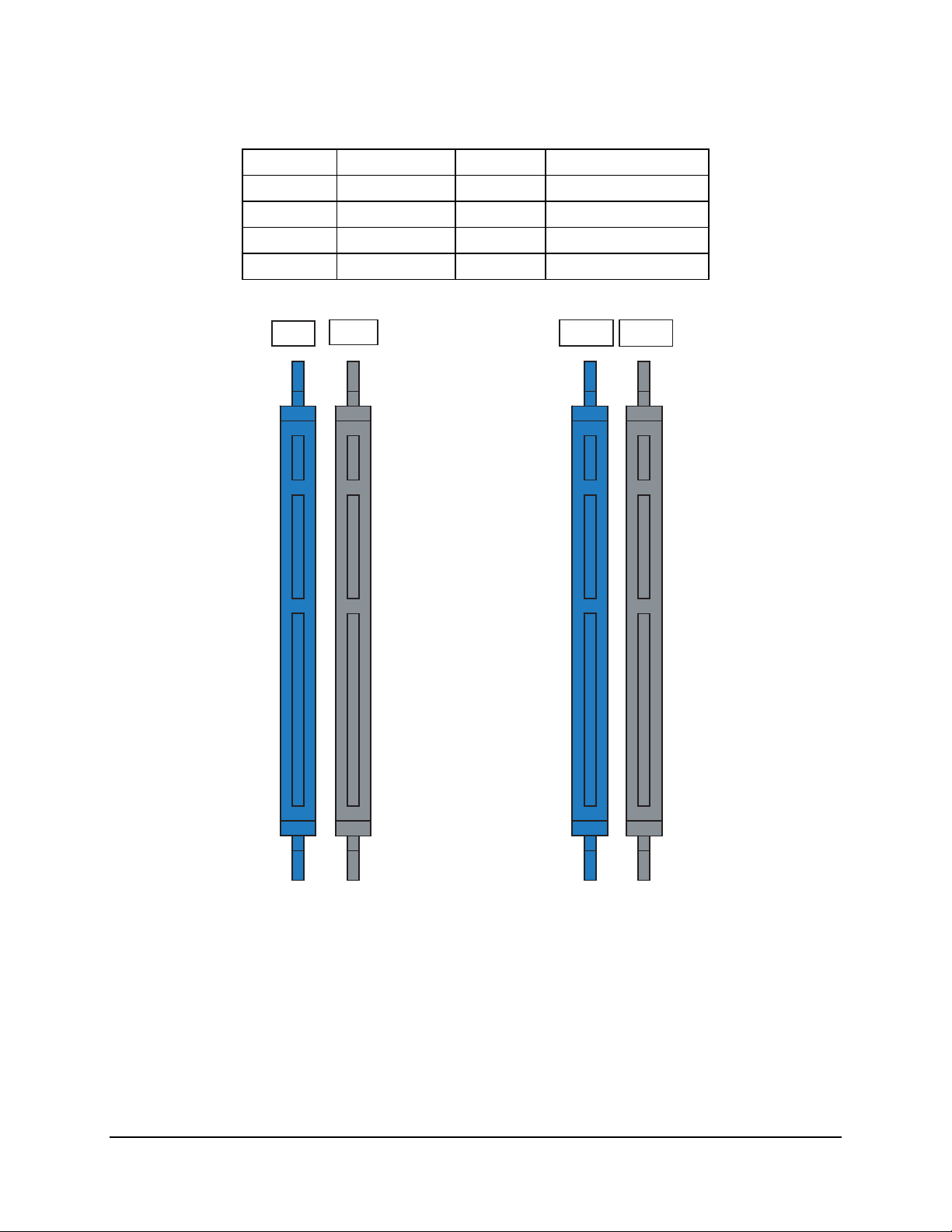
There are two banks of DIMMs, labeled 1 and 2. Bank 1 contains DIMM socket locations
DIMM_1A and DIMM_2A. Bank 2 contains DIMM socket locations DIMM_1B and DIMM_2B.
The sockets associated with each bank or “channel”, are located next to each other and the
DIMM socket identifiers are marked on the baseboard silkscreen, near the DIMM socket. Bank 1
is associated with Memory Channel A while Bank 2 is associated with Memory Channel B.
When only two DIMM modules are being used, the population order must be DIMM_1A,
DIMM_1B to ensure dual channel operating mode.
To reiterate: In order to operate in Dual Channel Dynamic Paging Mode, the following conditions
must be met:
• 2 identical DIMMs are installed, one each in DIMM_1A and DIMM_1B
• 4 identical DIMMs are installed (one in each socket location)
Installing only 3 DIMMs is not supported. Do not use DIMMs that are not “matched”
(same type and speed). Use of identical memory parts is always the preferred method.
See Table 2 and Figure 2 on the following page for reference.
The system design is free to populate or not to populate any rank on either channel, including
either degenerate single channel case.
DIMM and memory configurations must adhere to the following:
DDR2 400/533 , un-buffered, DDR2 DIMM modules
DIMM organization: x72 ECC or x 64 Non-ECC
Pin count: 240
DIMM capacity: 256 MB, 512 MB, 1 GB DIMMs
Serial PD: JEDEC Rev 2.0
Voltage options: 1.8 V
Interface: SSTL2
7
Page 20
SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Table 2. Memory Bank Labels and DIMM Population Order
Location DIMM Label Channel Population Order
J8J1 (DIMM_1A) A
J8J2 (DIMM_2A) A
J9J2 (DIMM_1B) B
J9J1 (DIMM_2B) B
1
3
2
4
J8J1
J8J2
J9J2
J9J1
DIMM_1A
Channel A
DIMM_2A
(Bank 1)
Figure 2. Memory Bank Label Definition
Table 3 summarizes the characteristics of dual and single channel configurations with and
without the use of Dynamic Mode.
Revision 1.3
8
DIMM_1B
Channel B
(Bank 2)
DIMM_2B
Page 21
SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Table 3. Characteristics of Dual/Single Channel Configuration with/without Dynamic Mode
Throughput Level Configuration Characteristics
Highest Dual Channel with Dynamic Paging Mode All DIMMs matched
Dual Channel without Dynamic Paging Mode DIMMs matched from Channel A to Channel B
DIMMs not matched within channels
Single Channel with Dynamic Paging Mode Single DIMM or DIMMs matched with a
channel
Lowest Single Channel without Dynamic Paging
Mode
DIMMs not matched
4. The Intel® E7221 Chipset
The Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E is designed around the Intel® E7221 chipset. The
chipset provides an integrated I/O bridge and memory controller, and a flexible I/O subsystem
core (PCI Express*). The chipset consists of three primary components:
GMCH: Graphics Memory Control Hub. The GMCH accepts access requests from the
host (processor) bus and directs those accesses to memory or to one of the PCI buses.
The GMCH monitors the host bus, examining addresses for each request. Accesses
may be directed to a memory request queue for subsequent forwarding to the memory
subsystem, or to an outbound request queue for subsequent forwarding to one of the
PCI buses. The GMCH also accepts inbound requests from the ICH6R. The GMCH is
responsible for generating the appropriate controls to control data transfer to and from
memory.
The Intel® E7221 GMCH comes with an integrated high performance graphics media
accelerator (Intel® GMA 900) and supports one x8 port configuration PCI-E interface.
Maximum theoretical peak bandwidth on each x8 PCI Express* interface of 2.5 GB/s in
each direction simultaneously, for 5 GB/s per port.
ICH6R: I/O Controller Hub 6R. The ICH6R controller has several components. It
provides the interface for a 32-bit/33-MHz PCI bus. The ICH6R can be both a master
and a target on that PCI bus. The ICH6R also includes a USB 2.0 controller and an IDE
controller. The ICH6R is also responsible for much of the power management functions,
with ACPI control registers built in. The ICH6R also provides a number of GPIO pins and
has the LPC bus to support low speed legacy I/O.
The GMCH and ICH6R chips provide the pathway between processor and I/O systems.
The GMCH is responsible for accepting access requests from the host (processor) bus,
and directing all I/O accesses to one of the PCI buses or legacy I/O locations. If the
cycle is directed to one of the PCI-E segments, the GMCH communicates with the PCI-E
Devices (add-in card, on board devices) through the PCI-E interface. If the cycle is
directed to the ICH6R, the cycle is output on the GMCH’s DMI bus. All I/O for the board,
including PCI and PC-compatible I/O, is directed through the GMCH and then through
the ICH6R provided PCI buses.
PXH: PCI-X Hub The PXH hub is peripheral chips that perform PCI bridging functions
between the PCI Express* interface and the PCI bus. The PXH contains two PCI bus
9
Page 22
SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
interfaces that can be independently configured to operate in PCI (33 or 66 MHz), PCI-X
Mode1 (66,100,133), for either 32 or 64 bits.
4.1.1 GMCH Memory Architecture Overview
The GMCH supports a 72-bit wide memory sub-system that can support a maximum of 4 GB of
DDR2 memory using 1 GB DIMMs. This configuration needs external registers for buffering the
memory address and control signals. The four chip selects are registered inside the GMCH and
need no external registers for chip selects.
The memory interface runs at 400/533MT/s. The memory interface supports a 72-bit wide
memory array. It uses seventeen address lines (BA [2:0] and MA [13:0]) and supports 256 Mb,
512 Mb, 1 Gb DRAM densities. The DDR DIMM interface supports memory scrubbing, single-bit
error correction, and multiple bit error detection and Intel® x4 SDDC with x4 DIMMs.
4.1.1.1 DDR2 Configurations
The DDR2 interface supports up to 4 GB of main memory and supports single- and doubledensity DIMMs. The DDR2 can be any industry-standard DDR2. The following table shows the
DDR2 DIMM technology supported.
Table 4. Supported DDR2 modules
DDR2-400 and DDR2-533 Un-buffered
SDRAM Module Matrix
DIMM
Capacity
256MB 32M x 72 256Mbit 32M x 8 9 /1 / 4 13 / 2 / 10
512MB 64M x 72 256Mbit 32M x 8 18 / 2 / 4 13 / 2 / 10
512MB 64M x 72 512Mbit 64M x 8 9 / 1 / 4 14 / 2 / 10
1GB 128M x 72 512Mbit 64M x 8 18 / 2 / 4 14 / 2 / 10
1GB 128M x 72 1Gbit 128M x 8 9 / 1 / 8 14 / 3 / 10
DIMM
Organization
SDRAM
Density
SDRAM
Organization
# SDRAM
Devices/rows/Banks
# Address bits
rows/Banks/column
4.1.2 Graphics Memory Controller Hub (GMCH)
The GMCH is a 1210-ball FC-BGA device and uses the proven components of previous
generations like the Intel® Pentium® 4 processor bus interface unit, the hub interface unit, and
the DDR2 memory interface unit. In addition, the GMCH incorporates an integrated high
performance graphics media accelerator and a PCI Express* interface. The PCI Express*
interface allows the GMCH to directly interface with the PCI Express* devices (like PXH/PXHD).
The GMCH also increases the main memory interface bandwidth and maximum memory
configuration with a 72-bit wide memory interface.
The GMCH integrates the following main functions:
An integrated high performance main memory subsystem.
Revision 1.3
10
Page 23

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
A PCI Express* bus which provides an interface to the PCI-Express* devices( Fully
compliant to the PCI Express* Base Specification, Rev 1.0a)
A DMI which provides an interface to the ICH6R
Other features provided by the GMCH include the following:
Full support of ECC on the processor bus
Full support of Intel® x4 SDDC on the memory interface with x4 DIMMs
Twelve deep in-order queue, two deep defer queue
Full support of un-buffered DDR2 ECC DIMMs.
Support for 1 GB DDR2 memory modules
Memory scrubbing
4.1.3 ICH6R
The ICH6R is a multi-function device, housed in a 609-pin mBGA device, providing a DMI bus, a
PCI 32-bit/33 MHz interface, a IDE interface, an integrated Serial ATA Host controller, a USB
controller, a PCI-E x4 interface, and a power management controller. Each function within the
ICH6R has its own set of configuration registers. Once configured, each appears to the system
as a distinct hardware controller sharing the same PCI bus interface.
The primary role of the ICH6R is to provide the gateway to all PC-compatible I/O devices and
features. The board uses the following the ICH6R features:
PCI 32-bit/33MHz interface
LPC bus interface
PCI Express* x4
DMI (Direct Media Interface)
IDE interface, with Ultra ATA 100/66/33 capability
Integrated Serial ATA Host controller
Universal Serial Bus (USB) 2.0 interface
PC-compatible timer/counter and DMA controllers
APIC and 82C59 interrupt controller
Power management
System RTC
Supports Smbus 2.0 Specification
General purpose I/O (GPIO)
The following are the descriptions of how each supported feature is used for ICH6R on the
board.
4.1.3.1 PCI Bus P32-A I/O Subsystem
The ICH6R provides a legacy 32-bit PCI subsystem and acts as the central resource on this PCI
interface. P32-A supports the following embedded devices and connectors:
One Intel®
11
®
82541PI network controller
Page 24

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
One slots capable of supporting full length legacy PCI add-in cards operating at 33 MHz
4.1.3.2 PCI Express* X4 Subsystem
The ICH6R supports one x4-lane PCI Express* interface that can also be configured as a single
x1 or x4-lane port. The PCI Express* interface allows direct connection with the PXH/PXHD or
PCI-E devices. (Fully compliant to the PCI Express* Base Specification, Rev 1.0a)
4.1.3.3 PCI Bus Master IDE Interface
The ICH6R acts as a PCI-based Ultra ATA 100/66/33 IDE controller that supports programmed
I/O transfers and bus master IDE transfers. The ICH6R supports one IDE channel, supporting
two drives each (drives 0 and 1). The baseboard provides a 40-pin (2x20) IDE connector to
access the IDE functionality.
The IDE interface supports Ultra ATA 100/66/33 Synchronous DMA Mode transfers on the 40pin connector.
4.1.3.4 USB Interface
The ICH6R contains one EHCI USB 2.0 controller and four USB ports. The USB controller
moves data between main memory and up to four USB connectors. All ports function identically
and with the same bandwidth. The Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E implements four ports on
the board.
The baseboard provides two external USB ports on the back of the server board. The dual-stack
USB connector is located within the standard ATX I/O panel area. The Universal Serial Bus
Specification, Revision 1.1, defines the external connectors.
The third/fourth USB port is optional and can be accessed by cabling from an internal 9-pin
connector located on the baseboard to an external USB port located either in front or the rear of
a given chassis.
4.1.3.5 SATA interface
The ICH6R contains four SATA ports. The data transfer rates up to 150Mbyte/s.
4.1.3.6 Compatibility Interrupt Controller
The ICH6R provides the functionality of two cascaded 82C59 with 15 interrupts handling.
Support processor system bus interrupt.
4.1.3.7 APIC
The ICH6R integrates an I/O APIC capability with 24 interrupts.
4.1.3.8 Power Management
One of the embedded functions of the ICH6R is a power management controller. This is used to
implement ACPI-compliant power management features. The baseboard does support sleep
states S0, S1, S4, and S5.
Revision 1.3
12
Page 25

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
4.2 Super I/O
National Semiconductor* PC87427Super IO device contains all of the necessary circuitry to
control two serial ports, one parallel port, floppy disk, PS/2-compatible keyboard and mouse and
hardware monitor controller. The baseboard implements the following features:
GPIOs
Two serial ports
Floppy
Keyboard and mouse
Local hardware monitoring
Wake up control
System Health Support
4.2.1 Serial Ports
The board provides two serial ports, an external serial port, and an internal serial header. The
following sections provide details on the use of the serial ports.
4.2.1.1 Serial A
Serial A is a standard DB9 interface located at the rear I/O panel of the server board, below the
video connector. Serial A is designated by as “Serial A” on the silkscreen. The reference
designator is J8A1.
4.2.1.2 Serial B
Serial B is an optional port, accessed through a 9-pin internal header (J1B1). A standard DH-10
to DB9 cable can be used to direct serial B to an external connector on any given chassis. The
serial B interface follows the standard RS232 pin-out. The baseboard has a “Serial_B”
silkscreen label next to the connector and is located beside the PCI32 5V connector.
4.2.1.3 Floppy Disk Controller
The floppy disk controller (FDC) in the Super IO is functionally compatible with floppy disk
controllers in the DP8473 and N844077. All FDC functions are integrated into the Super IO
including analog data separator and 16-byte FIFO. The baseboard provides a standard 34-pin
interface for the floppy disk controller.
4.2.1.4 Keyboard and Mouse
Two external PS/2 ports, located on the back of the baseboard, are provided to access the
keyboard or mouse functions.
4.2.1.5 Fast X-Bus extension for boot flash, memory and I/O.
The fast X-bus Supports I/O and memory read/write operations and 8 bit data bus, 28-bit
addressing.
13
Page 26

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
4.2.1.6 Wake-up Control
The Super IO contains functionality that allows various events to control the power-on and
power-off the system.
4.2.2 BIOS Flash
The board incorporates an Intel® ® 28F320C3 flash memory component. The 28F320C3 is a
high-performance 32-megabit memory component that provides 2096K x 16 of BIOS and nonvolatile storage space. The flash device is connected through the X Bus from Super IO.
4.2.3 System Health Support
I2C interface to LM96000 sensors
Fan Monitor and Control (FMC)
— One PWM-based fan controls
— Software or local temperature feedback control
Chassis intrusion detection
5. I/O Subsystem
5.1 PCI Subsystem
The primary I/O buses for the SE7221BK1-E are 3 independent PCI bus segments (4
independent segments with SE7221BK1LX sku) with PCI, PCI-E and two PCI-X buses. The PCI
buses comply with the PCI Local Bus Specification, Rev 2.3. The P32-A bus segment is
directed through the ICH6R. The P32-B and P64-C bus segment are independently configured
to PXH that is through ICH6R by PCI Express* x 4 interface. The PCI-E x8 bus is directed
through the GMCH. The table below lists the characteristics of the three PCI bus segments.
Table 5. PCI Bus Segment Characteristics
PCI Bus Segment Voltage Width Speed Type PCI I/O Card Slots
PCI 5V 32 bits 33MHz P32-A Slot 1
PCI-X 3.3V 64 bits 66/100MHz P64-C Slot 4; Slot 5, (Slot 6 through riser card)
PCI-E (x8) 3.3V 8 lanes 100MHz Slot 6
5.1.1 P32-A: 32-bit/33-MHz PCI Subsystem
All 32-bit/33-MHz PCI I/O for the board is directed through the ICH6R. The 32-bit/33-MHz PCI
segment created by the ICH6R is known as the P32-A segment. The P32-A segment supports
the following embedded devices and connectors:
One 10/100/1000-T Network Interface Controller: Intel® 82541PI Fast Ethernet
Controller.
5.1.1.1 Device IDs (IDSEL)
Each device under the PCI hub bridge has its IDSEL signal connected to one bit of AD [31:16],
which acts as a chip select on the PCI bus segment in configuration cycles. This determines a
Revision 1.3
14
Page 27
SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
unique PCI device ID value for use in configuration cycles. The following table shows the bit to
which each IDSEL signal is attached for P32-A devices and the corresponding device
description.
Table 6. P32-A Configuration IDs
IDSEL Value Device
19
18 PCI Slot 1 (32b/33MHz)
Intel® 82541PI LAN (NIC1)
5.1.1.2 P32-A Arbitration
P32-A supports two PCI devices: the ICH6R and one PCI bus masters (NIC). All PCI masters
must arbitrate for PCI access, using resources supplied by the ICH6R. The host bridge PCI
interface (ICH6R) arbitration lines REQx* and GNTx* are a special case in that they are internal
to the host bridge. The following table defines the arbitration connections.
Table 7. P32-A Arbitration Connections
Baseboard Signals Device
PCI REQ1_N/GNT_N1 Intel® 82541PI LAN (NIC1)
PCI REQ0_N/GNT_N0 PCI Slot 1 (32bit/33MHz)
5.1.2 P32-B 66-MHz PCI-X Subsystem (SE7221BK1LX sku only)
One 32-bit PCI bus segment is directed through the PXH interface A. This PCI segment, P32-B,
just has an embedded device, Intel® 82541PI LAN (NIC2) clocked at 66MHz. (SE7221BK1LX
sku only)
5.1.2.1 Device IDs (IDSEL)
Each device under the PCI hub bridge has its IDSEL signal connected to one bit of AD [31:16],
which acts as a chip select on the PCI bus segment in configuration cycles. This determines a
unique PCI device ID value for use in configuration cycles. The following table shows the bit to
which each IDSEL signal is attached for P32-B devices and corresponding device description.
Table 8. P32-B Configuration IDs
IDSEL Value Device
19
5.1.2.2 P32-B Arbitration
Intel® 82541PI LAN (NIC2)
P32-B supports one PCI masters. All PCI masters must arbitrate for PCI access using
resources supplied by the PXH. The host bridge PCI interface (PXH) arbitration lines REQx*
15
Page 28
SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
and GNTx* are a special case in that they are internal to the host bridge. The following table
defines the arbitration connections.
Table 9. P32-B Arbitration Connections
Baseboard Signals Device
PCIX REQ_N0/GNT_N0
Intel® 82541PI LAN (NIC2)
5.1.3 P64-C 66/100-MHz PCI-X Subsystem
One 64-bit PCI-X bus segment is directed through the PXH. This PCI-X segment, P64-C,
provides two 3.3V 64-bit PCI-X slots or one 3.3V 64-bit PCI-X riser slot, (SE7221BK1LX sku
only) capable of up to 100 MHz operation (with 1 adapter, either slot is capable of 100MHz,
only speeds of 66MHz are supported with two adapters populated) and supports full-length
PCI and PCI-X adapters.
5.1.3.1 Device IDs (IDSEL)
Each device under the PCI hub bridge has its IDSEL signal connected to one bit of AD [31:16],
which acts as a chip select on the PCI bus segment in configuration cycles. This determines a
unique PCI device ID value for use in configuration cycles. The following table shows the bit to
which each IDSEL signal is attached for P64-C devices and corresponding device description.
Table 10. P64-C Configuration IDs
IDSEL Value Device
17
18 PCI Slot 5 (64bit/66-100MHz)
PCI Slot 4 (64bit/66-100MHz)/ PCI Slot 6 (64bit/100MHz) (Riser, SE7221BK1LX sku
only)
5.1.3.2 P64-C Arbitration
P64-C supports two PCI masters: two PCI-X slots or one riser slot. All PCI masters must
arbitrate for PCI access using resources supplied by the ICH6. The host bridge PCI interface
(ICH6) arbitration lines REQx* and GNTx* are a special case in that they are internal to the host
bridge. The following table defines the arbitration connections.
Table 11. P64-C Arbitration Connections
Baseboard Signals Device
PCI Slot 4 (64bit/66M) / PCI Slot 6 (64bit/100
PCIX REQ_N0/GNT_N0
PCIX REQ_N1/GNT_N1 PCI Slot 5(64bit/66M)
only)
M) (Riser, SE7221BK1LX sku
Revision 1.3
16
Page 29

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
5.1.4 PCI-E x8
In this board, Lanes 0~7 are connected to a x8 PCI-E connector directly. It can support x1, x4, x
8 PCI-E add-in cards.
Table 12. PCI-E x 8 Connections
Lane Device
Lane 0~7 Slot 6 (PCI Express* x 8)
5.2 Video Controller
The Intel® E7221 GMCH includes an integrated graphics engine that supports standard SVGA
drivers with analog display capabilities. 8 MB of memory is pre-allocated in the main memory to
support the internal graphical device when less than 4 GB of physical memory is installed.
However, when the maximum of 4 GB of memory is installed, onboard system resources such
as video consume a considerable amount of memory, leaving just above 3 GB of available
memory for the operating system. Details of this issue have been communicated via the
Technical Advisory TA_719-01 which can be found at:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SE7221BK1-E
.
The baseboard provides a standard 15-pin VGA connector at the rear of the system, in the
standard ATX I/O opening area. The video controller is disabled by default in BIOS Setup when
an off-board video adapter is detected in either the PCI-E or PCI slots.
5.3 Network Interface Controller (NIC)
The Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E supports two 10Base-T/100Base/1000Base-T
(82541PI controller) network interfaces. One is through ICH6R directly, and another one is
through PXH (SE7221BK1LX sku only).
The Intel® 82541PI Gigabit Ethernet is a single, compact component with an integrated Gigabit
Ethernet Media Access Control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) functions. For desktop,
workstation and mobile PC Network designs with critical space constraints, the Intel® 82541PI
allows for a Gigabit Ethernet implementation in a very small area that is footprint compatible
with current generation 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet designs. The Intel® 82541PI integrates
fourth generation gigabit MAC design with fully integrated, physical layer circuitry to provide a
standard IEEE 802.3 Ethernet interface for 1000BASE-T, 100BASE_TX, and 10BASE-T
applications (802.3, 802.3u, and 802.3ab). The controller is capable of transmitting and
receiving data at rates of 1000 Mbps, 100 Mbps, or 10 Mbps. In addition to managing MAC and
PHY layer functions, the controller provides a 32-bit wide direct Peripheral Component
Interconnect (PCI) 2.3 compliant interface capable of operating at 33 or 66MHz.
5.3.1 NIC Connector and Status LEDs
The NICs drive two LEDs located on each network interface connector.
For the NIC 1 connector, the green LED indicates network connection when on, and
Transmit/Receive activity when blinking. The yellow LED indicates 1000-Mbps operation when
lit, the green LED indicates 100-Mbps operation when lit and 10-Mbps when off.
17
Page 30

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
For the NIC 2 connector (SE7221BK1LX sku only), the yellow LED indicates network
connection when on, and Transmit/Receive activity when blinking. The orange LED indicates
1000-Mbps operation when lit, the green LED indicates 100-Mbps operation when lit and 10Mbps when off.
5.4 Interrupt Routing
The board interrupt architecture accommodates both PC-compatible PIC mode and APIC mode
interrupts through use of the integrated I/O APICs in the ICH6.
5.4.1 Legacy Interrupt Routing
For PC-compatible mode, the ICH6 provides two 82C59-compatible interrupt controllers. The
two controllers are cascaded with interrupt levels 8-15 entering on level 2 of the primary
interrupt controller (standard PC configuration). A single interrupt signal is presented to the
processors, to which only one processor will respond for servicing. The ICH6R contains
configuration registers that define which interrupt source logically maps to I/O APIC INTx pins.
The ICH6 handles both PCI and IRQ interrupts. The ICH6R translates these to the APIC bus.
The numbers in the table below indicate the ICH6R PCI interrupt input pin to which the
associated device interrupt (INTA, INTB, INTC, INTD, INTE, INTF, INTG, INTH for PCI bus and
PXIRQ0, PXIRQ1, PXIRQ2, PXIRQ3 for PCI-X bus) is connected. The ICH6R I/O APIC exists
on the I/O APIC bus with the processors.
Table 13. PCI AND PCI-X Interrupt Routing/Sharing
Interrupt INT A INT B INT C INT D
Intel® 82541PI PIRQC
PCI Slot 1 (PCI 32b/33M)
PCI Slot 4 (64b/66M)/ PCI Slot 6
(64bit/100MHz) (Riser,
SE7221BK1LX sku only)
PCI Slot 5 (64b/66M
PIRQF PIRQG PIRQE PIRQH
PXIRQ0 PXIRQ1 PXIRQ2 PXIRQ3
PXIRQ5 PXIRQ6 PXIRQ7 PXIRQ4
5.4.2 APIC Interrupt Routing
For APIC mode, the baseboard interrupt architecture incorporates three Intel® I/O APIC devices
to manage and broadcast interrupts to local APICs in each processor. The Intel® I/O APICs
monitor each interrupt on each PCI device; including PCI slots in addition to the ISA
compatibility interrupts IRQ (0-15).
When an interrupt occurs, a message corresponding to the interrupt is sent across a three-wire
serial interface to the local APICs. The APIC bus minimizes interrupt latency time for
compatibility interrupt sources. The I/O APICs can also supply greater than 16 interrupt levels to
the processor(s). This APIC bus consists of an APIC clock and two bidirectional data lines.
5.4.2.1 Legacy Interrupt Sources
The table below recommends the logical interrupt mapping of interrupt sources on the board.
The actual interrupt map is defined using configuration registers in the ICH6.
Revision 1.3
18
Page 31

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Table 14. Interrupt Definitions
ISA Interrupt Description
INTR Processor interrupt.
NMI NMI to processor.
IRQ0 System timer
IRQ1 Keyboard interrupt.
IRQ2 Slave PIC
IRQ3 Serial port 1 or 2 interrupt from SUPER IO device, user-configurable.
IRQ4 Serial port 1 or 2 interrupt from SUPER IO device, user-configurable.
IRQ5
IRQ6 Floppy disk.
IRQ7 Parallel Port / Generic
IRQ8_L Active low RTC interrupt.
IRQ9 SCI*
IRQ10 Generic
IRQ11 Generic
IRQ12 Mouse interrupt.
IRQ13 Floaty processor.
IRQ14 Compatibility IDE interrupt from primary channel IDE devices 0 and 1.
IRQ15 Secondary IDE Cable
SMI* System Management Interrupt. General purpose indicator sourced by the ICH6R to the processors.
5.4.3 Serialized IRQ Support
The SE7221BK1-E server board supports a serialized interrupt delivery mechanism. Serialized
Interrupt Requests (SERIRQ) consists of a start frame, a minimum of 17 IRQ / data channels,
and a stop frame. Any slave device in the quiet mode may initiate the start frame. While in the
continuous mode, the start frame is initiated by the host controller.
5.5 PCI Error Handling
The PCI bus defines two error pins, PERR# and SERR#, for reporting PCI parity errors and
system errors, respectively. In the case of PERR#, the PCI bus master has the option to retry
the offending transaction, or to report it using SERR#. All other PCI-related errors are reported
by SERR#. SERR# is routed to NMI if enabled by BIOS.
19
Page 32

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
IRQ0
IRQ1
IRQ2
IRQ3
IRQ4
IRQ5
IRQ6
IRQ7
IRQ8
IRQ9
IRQ10
IRQ11
IRQ12
IRQ13
IRQ14
IRQ15
IRQ16
IRQ17
IRQ18
IRQ19
IRQ20
IRQ21
IRQ22
IRQ23
ICH6
ICH6 IOAPIC 0
DMI INTERFACE
ICH6
8259PIC
X8
connector
X8 PCI-E interface
GMCH
INTR
CPU
Figure 3. Interrupt Routing Diagram
Revision 1.3
20
Page 33

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
y
ppy
p
Q
A
A
A
Timer
board
Ke
Cascade
Serial Port2/ISA
Serial Port1/ISA
ISA
Flo
/ISA
ISA
RTC
SCI/ISA
ISA
ISA
Mouse/ISA
Co
rocessor Error
P IDE/ISA
Not Used
Super I/O
Serialized IRQ Interface
SERIR
SERIRQ
PCI Interface
ICH6 Interrupt
Routing
N/
N/A
INTEL 82541PI(NIC1)
N/
Slot 1 INTC
Slot 1 INT
Slot 1 INTD
Figure 4. ICH6R Interrupt Routing Diagram
PIRQA#
PIRQB#
PIRQC#
PIRQD#
PIRQE#
PIRQF#
PIRQG#
PIRQH#
21
Page 34

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
A
A
(
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
,
,
,
,
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
INTEL 82541PI
Slot 4 INTA
Slot 4 INTB
Slot 4 INTC
Slot 4 INTD
Slot 5 INTD
Slot 5 INT
Slot 5 INTB
Slot 5 INTC
N/A
N/
N/
NIC2)
N/
N/
N/
N/
N/
N/
N/
N/
N/
N/
N/
N/
Slot 6 INTA
Slot 6 INTB
Slot 6 INTC
Slot 6 INTD
N/
N/
N/
N/
N/
N/
N/
N/
PCI-X
Interface
PXH
PCI-X
Interface
Figure 5. PXH Interrupt Routing Diagram
Revision 1.3
22
Page 35

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
6. ACPI Implementation
6.1 ACPI
An ACPI-aware operating system generates an SMI to request that the system be switched into
ACPI mode. The BIOS responds to enable ACPI mode. The system automatically returns to
legacy mode upon hard reset or power-on reset.
The SE7221BK1-E platform supports S0, S1, S4, and S5 states. When the system is operating
in ACPI mode, the OS retains control of the system and OS policy determines the entry
methods and wake up sources for each sleep state
Note: Sleep entry and wake up event capabilities are provided by the hardware but are enabled
by the operating system.
S0 Sleep State
S1 Sleep State
S4 Sleep State
S5 Sleep State
The S0 sleep state is when everything is on. This is the state that no sleep is
enabled.
The S1 sleep state is a low wake-up latency sleep state. In this state, no
system context is lost (Processor or chipset). The system context is
maintained by the hardware.
The S4 Non-Volatile Sleep state (NVS) is a special global system state that
allows system context to be saved and restored (relatively slowly) when
power is lost to the baseboard. If the system has been commanded to enter
the S4 sleep state, the operating system will write the system context to a
non-volatile storage file and leave appropriate context markers.
The S5 sleep state is similar to the S4 sleep state except the operating
system does not save any context nor enable any devices to wake the
system. The system is in the “soft” off state and requires a complete boot
when awakened.
6.1.1 Front Panel Switches
The baseboard supports two front panel buttons:
Power button
Reset button
Power Button Off to On:
23
The power button input (J1J1 pin 11and 13) provides
FP_PWR_BTN_N signal to the mBMC (PC87431M). mBMC will
output a MBMC_PWR_BTN_N signal to ICH6. If the PWRBTN#
signal of ICH6R is asserted, the assertion causes a wake event.
And then, the SLP_S3 signal of ICH6R will be not asserted. The
SLP_S3 signal will be passed to the PS_ON# signal of ATX power
Page 36

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
supply through an inverter, and then transition to an ON state.
Power Button On to Off
(Legacy):
The ICH6 is configured to generate an SMI due to a power button
event. The BIOS services this SMI and sets the state of the
machine in the ICH6 and Super IO to the OFF state.
Power Button On to Off
(ACPI):
If an ACPI operating system is loaded, the power button switch
generates a request (via SCI) to the OS to shutdown the system.
The OS retains control of the system and determines what sleep
state (if any) the system transitions to.
Reset Button:
NMI Button:
The reset button will generate a hard reset to the system.
The NMI button will force an NMI to the processors.
6.1.2 Wake up Sources (ACPI and Legacy)
The baseboard is capable of wake up from several sources under a non-ACPI configuration,
such as when the operating system does not support ACPI. The wake up sources are defined in
the following table.
Table 15. Supported Wake Events
Wake Event Supported via ACPI
(by sleep state)
Power Button Always wakes system Always wakes system
PME from PCI 32/33 S1, S4 S5
PME from primary PCI 64/66 S1, S4 S5
RTC Alarm S1, S4 No
Mouse S1 No
Keyboard S1 No
USB S1 No
Under ACPI, the operating system programs the ICH6R and Super IO to wake up on the
desired event, but in legacy mode, the BIOS enables/disables wake up sources based on an
option in BIOS Setup. The operating system or a driver must clear any pending wake up status
bits in the associated hardware (such as the Wake on LAN status bit in the LAN application
specific integrated circuit (ASIC), or PCI Power Management Event (PME) status bit in a PCI
device. The legacy wake up feature is disabled by default.
Supported Via Legacy Wake
Revision 1.3
24
Page 37

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
7. Connectors
7.1 Main Power Connector
The main power supply connection is obtained using the 24-pin connector. The following table
defines the pin-outs of the connector.
Table 16. Power Connector Pin-out (CN4H1)
Pin Signal 18 AWG Color Pin Signal 18 AWG Color
1* +3.3VDC
2 +3.3VDC Orange 15 COM Black
3* COM Black 16 PSON# Green
4* +5VDC Red 18 COM
5 COM Black 20 Reserved N.C.
6 +5VDC Red 21 +5VDC Red
7 COM Black 22 +5VDC Red
8 PWR OK Gray 23 +5VDC Red
9 5 VSB Purple 24 COM Black
10 +12V3 Yellow
11 +12V3 Yellow
12 +3.3VDC Orange
3.3V RS Orange (24AWG)
COM RS Black (24AWG)
5V RS Red (24AWG)
Orange 13 +3.3VDC Orange
14 -12VDC Blue
17 COM Black
19 COM Black
Black
Table 17. Auxiliary CPU Power Connector Pin-out (CN4B1)
Pin Signal 18 AWG color Pin Signal 18 AWG Color
1 COM Black 5* +12V1 White
2 COM Black
3 COM Black 6 +12V1 White
4 COM Black 7 +12V2 Brown
8* +12V2 Brown
12V1 RS Yellow (24AWG)
12V2 RS Yellow (24AWG)
25
Page 38

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
7.2 I2C Header
Table 18. HSBP Header Pin-out (J1D1)
Pin Signal Name Description
1 HR_SMB_5V_DAT Data Line
2 GND GROUND
3 HR_SMB_5V_CLK Clock Line
4 GND GROUND
Table 19. LCD Header Pin-out (J1C1)
Pin Signal Name Description
1 HR_SMB_5V_DAT Data Line
2 GND GROUND
3 HR_SMB_5V_CLK Clock Line
4 P5V_STBY POWER
Table 20. LEGEND SE_LINK Header Pin-out (J2B1)
Pin Signal Name Description
1 MBMC_SMC_PHL_DAT Data Line
2 GND GROUND
3 MBMC_SMC_PHL_CLK Clock Line
4 P5V_STBY POWER
5 POST_STATUS_N
6 FP_RST_BTN_N
7 P5V
8 FP_PWR_BTN_N
7.3 Front Panel Connector
A standard SSI 34-pin header is provided to support a system front panel. The header contains
reset, NMI, power control buttons, and LED indicators. The following table details the pin-out of
this header.
Table 21. Front Panel 34-Pin Header Pin-out (J1J1)
Signal Name Pin Pin Signal Name
P5V_STB 1 2 P5V_STB
KEY 3 4 P5V_STB
FP_PWR_LED_N 5 6 NC
P5V 7 8 P5V_STB
HDD_LED# 9 10 FP_STATUS_LED2_N
Revision 1.3
26
Page 39

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Signal Name Pin Pin Signal Name
FP_PWR_BTN_N 11 12 LAN1_ACT_N
GND 13 14 LAN1_LINK_UP_N
FP_RST_BTN_N 15 16 MBMC_SMC_PHL5V_DAT
RESET switch (GND) 17 18 MBMC_SMC_PHL5V_CLK
NC 19 20 NC
GND 21 22 LAN2_ACT_N
NMI switch# 23 24 LAN2_LINK_UP_N
Key 25 26 Key
P5V_STB 27 28 P5V_STB
FP_ID_LED_N 29 30 FP_STATUS_LED1_N
FP_ID_BTN_N 31 32 P5V
GND 33 34 NC
Note: NC (No Connect) in this project
7.4 VGA Connector
The following table details the pin-out of the VGA connector. This connector is combined with
COM1 connector.
Table 22. VGA Connector Pin-out (J8A1)
Signal Name Pin Pin Signal Name
RED B1 B9 Fused VCC (+5V)
GREEN B2 B10 GND
BLUE B3 B11 NC
NC B4 B12 DDCDAT
GND B5 B13 HSY
GND B6 B14 VSY
GND B7 B15 DDCCLK
GND B8
Note: NC (No Connect) in this project
7.5 NIC Connector
The Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E supports two NIC RJ45 connectors. The following
tables detail the pin-out of the connector.
Table 23. NIC1-82541PI(10/100/1000) Connector Pin-out (J5A1)
Signal Name Pin Pin Signal Name
LGND_LAN1 1 10 LAN1_TRDN3
LAN1_TRDP0 2 11 LAN1_LINK_UP_N
LAN1_TRDN0 3 12 LAN1_ACT_N
LAN1_TRDP1 4 LAN1_TRDP3 9
LAN1_TRDN1 5 13 LAN1_LINK100_N
27
Page 40

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Signal Name Pin Pin Signal Name
P1V8_STB_LAN1 6 14 P3V3_STB
LAN1_TRDP2 7 15 LAN1_LINK1000_N
LAN1_TRDN2 8 16 LINK100_L
Table 24. NIC2-82541PI (10/100/1000) Connector Pin-out (J6A1)
Signal Name Pin Pin Signal Name
P1V8_STB_LAN2 1 10 LAN2_TRDN0
LAN2_TRDN2 2 11 LAN2_TRDP0
LAN2_TRDP2 3 12 P1V8_STB_LAN2
LAN2_TRDP1 4 13 LAN2_LINK100_N
LAN2_TRDN1 5 14 LAN2_LINK1000_N
P1V8_STB_LAN2 6 15 LAN2_LINK_UP_N
P1V8_STB_LAN2 7 16 LAN2_ACT_N
LAN2_TRDP3 8 17 GND_CHASSIS
LAN2_TRDN3 9 18 GND_CHASSIS
7.6 IDE Connector
The board provides one 40-pin ATA-100 IDE connector.
Table 25. ATA 40-pin Connector Pin-out (J3J1)
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 RESET# 2 GND
3 IDE_DD7 4 IDE_DD8
5 IDE_DD6 6 IDE_DD9
7 IDE_DD5 8 IDE_DD10
9 IDE_DD4 10 IDE_DD11
11 IDE_DD3 12 IDE_DD12
13 IDE_DD2 14 IDE_DD13
15 IDE_DD1 16 IDE_DD14
17 IDE_DD0 18 IDE_DD15
19 GND 20 KEY
21 IDE_DMAREQ 22 GND
23 IDE_IOW# 24 GND
25 IDE_IOR# 26 GND
27 IDE_IORDY 28 GND
29 IDE_DMAACK# 30 GND
31 IRQ_IDE 32 Test Point
33 IDE_A1 34 DIAG
35 IDE_A0 36 IDE_A2
37 IDE_DCS0# 38 IDE_DCS1#
39 IDE_HD_ACT# 40 GND
Revision 1.3
28
Page 41

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
7.7 SATA Connector
ICH6R integrated a SATA controller with four SATA ports output. The pin-out for these four
connectors is listed below.
Table 26. SATA Connector Pin-out (J1G1, J1G2, J1J2, J2J1)
Pin Signal Name
1 GND
2 SATA0_TX_P
3 SATA0_TX_N
4 GND
5 SATA0_RX_N
6 SATA0_RX_P
7 GND
7.8 USB Connector
The following table provides the pin-out for the dual external USB connectors. This connector is
combined with a RJ45 (connected to COM2 signals).
Table 27. USB Connectors Pin-out (J5A1)
Pin Signal Name
U1 GND
U2 USB_B5_P
U3 USB_B5_N
U4 VCC_USB5
U5 GND
U6 USB_B4_P
U7 USB_B4_N
U8 VCC_USB4
A header on the server board provides an option to support one additional USB connector. The
pin-out of the header is detailed in the following table.
Table 28. Optional USB Connection Header Pin-out (J4F1)
Signal Name Pin Pin Signal Name
Fused VCC (+5V /w over
current monitor of both port 1)
USB_B2_N 3 4 USB_B1_N
USB_B2_P 5 6 USB_B1_P
GND 7 8 GND
Key 9 10 NC
1 2 Fused VCC (+5V /w over current monitor of both port 0)
29
Page 42

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
7.9 Floppy Connector
The board provides a standard 34-pin interface to the floppy drive controller. The following
tables detail the pin-out of the 34-pin floppy connector.
Table 29. Legacy 34-pin Floppy Connector Pin-out (JP3J1)
Signal Name Pin Pin Signal Name
GND 1 2 FDDENSEL
GND 3 4 Unused
KEY 5 6 FDDRATE0
GND 7 8 FDINDEX#
GND 9 10 FDMTR0#
GND 11 12 FDR1#
GND 13 14 FDR0#
GND 15 16 FDMTR1#
Unused 17 18 FDDIR
GND 19 20 FDSTEP#
GND 21 22 FDWDATA#
GND 23 24 FDWGATE#
GND 25 26 FDTRK0#
Unused 27 28 FLWP#
GND 29 30 FRDATA#
GND 31 32 FHDSEL#
GND 33 34 FDSKCHG#
7.10 Serial Port Connector
Two serial ports are provided on the Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E.
A standard, external DB9 serial connector is located on the back edge of the baseboard
to supply a Serial A interface. This connector is combined with VGA connector (J8A1)
A Serial B port is provided through a 9-pin header (J1B1) on the server board.
The following tables detail the pin-outs of these two ports.
Table 30. External DB9 Serial A Port Pin-out (J8A1)
Signal Name Pin Pin Signal Name
DCD-P T1 T6 DSR-P
RXD-P T2 T7 RTS-P
TXD-P T3 T8 CTS-P
DTR-P T4 T9 RI-P
GND T5
Revision 1.3
30
Page 43

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Table 31. 9-pin Header Serial B Port Pin-out (J1B1)
Signal Name Pin Pin Signal Name
DCDB 1 2 DSRB
RXDB 3 4 RTSB
TXDB 5 6 CTSB
DTRB 7 8 RIB
GND 9 10 Key
7.11 Keyboard and Mouse Connector
Two PS/2 ports are provided for use by a keyboard and a mouse. The following table details the
pin-out of the PS/2 connectors.
Table 32. Keyboard and Mouse PS/2 Connectors Pin-out (KM9A1)
PS/2 Connectors Pin Signal Name
Keyboard
Mouse
K1 RKBDATA
K2 NC
K3 GND
K4 P5V_KB_MS
K5 RKBCLK
K6 NC
M1 MSEDATA
M2 NC
M3 GND
M4 P5V_KB_MS
M5 RMSCLK
M6 NC
7.12 Miscellaneous Headers
7.12.1 Fan Header
There are four 3-pin fan headers. (JP5J1, JP5J2, JP7A1, and JP6A1) These fan headers have
the same pin-out and are detailed below.
Table 33. Three-pin Fan Headers Pin-out (JP5J1, JP5J2, JP7A1, JP6A1)
Pin Signal Name Type Description
1 Ground Power GROUND is the power supply ground
2 Fan Power Power Fan Power with FAN_SPEED_CNTL1 (Fan speed control)
3 Fan Tach Out FAN_TACH signal is connected to the LM96000 to monitor the FAN
speed.
31
Page 44

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
There are also four 8-pin fan headers. (J6J1, J6J2, J6J3, J6J4) These fan headers have the
same pin-out and are detailed below.
Table 34. Eight-pin Fan Header Pin-out (J6J1, J6J2, J6J3, and J6J4)
Pin Signal Name Type Description
1 Fan Power Power Fan Power with FAN_SPEED_CNTL1 (Fan speed control)
2 Fan Tach Out FAN_T ACH signal is connected to the Super IO/LM96000 to monitor the
FAN speed.
3 Ground Power GROUND is the power supply ground
4 NC
5 Ground Power GROUND is the power supply ground
6 Ground Power GROUND is the power supply ground
7 Fan Tach Out FAN_T ACH signal is connected to the Super IO/LM96000 to monitor the
FAN speed.
8 Fan Power Power Fan Power with FAN_SPEED_CNTL1 (Fan speed control)
7.12.2 Intrusion Cable Connector
Table 35. Intrusion Cable Connector (J1A1)Pin-Out
Pin Signal Name
1 INTRUDER_N
2 GND
7.12.3 HDD LED Header
There is a 1x2 pin Header for HDD LED Connection. This jumper reserves for PCI add-in card
which supports the SCSI or SATA interface with external HDD LED activity cable.
Table 36. HDD LED Header (J1E1) Pin-Out
Pin Signal Name
1 HDD_LED_ACT_N
2 NC
Revision 1.3
32
Page 45
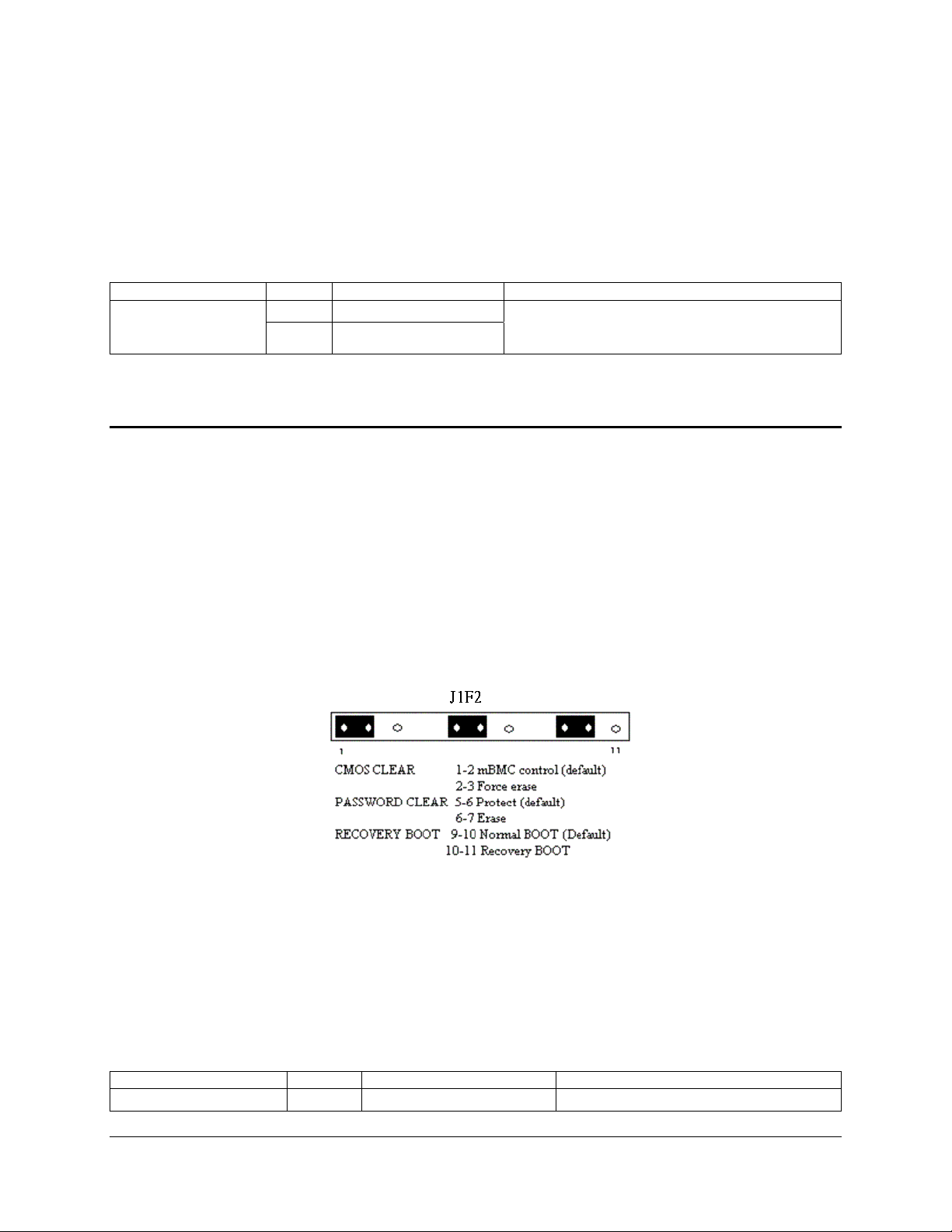
SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
7.12.4 Rolling BIOS selection header
There is a 1x3 pin Header that is used to configure the function of rolling BIOS. The figure
below shows the jumper pins and their functions. The factory defaults are set to a primary BIOS
mode for each function.
Table 37. HDD LED Header (J1E1) Pin-Out
Function Pin – Pin Function Description
Rolling BIOS selection
1-2
Primary BIOS (Default)
2-3 Secondary BIOS
Although some details of this feature are described
within this manual, please refer to section 9.6.3 for
complete details.
8. Configuration Jumpers
This section describes configuration jumper options on the Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E.
8.1 System Recovery and Update Jumpers
An 11-pin (Key in pin 4, 8) Header (J1F2), located just beside the PCI Slot 1 connectors,
provides a total of three 3-pin jumper blocks that are used to configure several system recovery
and update options. The figure below shows the jumper pins and their functions. The factory
defaults are set to a protected mode for each function.
Three jumpers are stored on six pins during normal operation. Please refer to below figure for
the detail function.
Figure 6. System Recovery and Update Jumpers (J1F2)
The following table describes each jumper option.
Table 38. System Recovery and Update Jumper Options
Function Pin – Pin Function Description
CMOS CLEAR 1-2
33
MBMC control
These three pins are connected to GPIs of
Page 46

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
PASSWORD CLEAR
RECOVERY BOOT
2-3 Force erase
5-6
6-7 Erase
9-10
10-11 Recovery BOOT
Protect
Normal BOOT
SUPER IO. The system BIOS reads these
GPIs status and decides whether or not to
execute related task. The clear CMOS status
is reflected to ICH6. Defaults are in bold.
9. BIOS Setup Utility
The BIOS Setup utility is provided to perform system configuration changes and to display
current settings and environment information.
The BIOS Setup utility stores configuration settings in system non-volatile storage. Changes
affected by BIOS Setup will not take effect until the system is rebooted. The BIOS Setup Utility
can be accessed when prompted during POST by using the F2 key.
9.1 Localization
The BIOS Setup utility uses the Unicode standard and is capable of displaying setup forms in
English, French, Italian, German, and Spanish. BIOS supports these languages for console
strings as well.
9.2 Console Redirection
BIOS Setup is functional via console redirection over various terminal standards emulation.
This may limit some functionality for compatibility, e.g., usage of colors or some keys or key
sequences or support of pointing devices.
9.3 Configuration Reset
There are different mechanisms for resetting the system configuration to default values. When
a reset system configuration request is detected, the BIOS will load the default system
configuration values during the next POST.
A reset system configuration request can be generated by moving the Clear CMOS jumper.
9.4 Keyboard Commands
The Keyboard Command Bar supports the following keys:
Table 39. BIOS Setup Keyboard Command Bar Options
Key Option Description
Enter Execute Command The Enter key is used to activate sub-menus when the selected feature is a sub-menu,
or to display a pick list if a selected option has a value field, or to select a sub-field for
multi-valued features like time and date. If a pick list is displayed, the Enter key will
undo the pick list, and allow another selection in the parent menu.
Revision 1.3
34
Page 47
SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Key Option Description
ESC Exit The ESC key provides a mechanism for backing out of any field. This key will undo the
pressing of the Enter key. When the ESC key is pressed while editing any field or
selecting features of a menu, the parent menu is re-entered.
When the ESC key is pressed in any sub-menu, the parent menu is re-entered. When
the ESC key is pressed in any major menu, the exit confirmation window is displayed
and the user is asked whether changes can be discarded. If “No” is selected and the
Enter key is pressed, or if the ESC key is pressed, the user is returned to where they
were before ESC was pressed without affecting any existing any settings. If “Yes” is
selected and the Enter key is pressed, setup is exited and the BIOS continues with
POST.
↑
↓
↔
Tab Select Field The Tab key is used to move between fields. For example, Tab can be used to move
- Change Value The minus key on the keypad is used to change the value of the current item to the
+ Change Value The plus key on the keypad is used to change the value of the current menu item to the
F9 Setup Defaults Pressing F9 causes the following to appear:
F7 Discard Changes Pressing F7 causes the following message to appear:
Select Item The up arrow is used to select the previous value in a pick list, or the previous options
in a menu item's option list. The selected item must then be activated by pressing the
Enter key.
Select Item The down arrow is used to select the next value in a menu item’s option list, or a value
field’s pick list. The selected item must then be activated by pressing the Enter key.
Select Menu The left and right arrow keys are used to move between the major menu pages. The
keys have no affect if a sub-menu or pick list is displayed.
from hours to minutes in the time item in the main menu.
previous value. This key scrolls through the values in the associated pick list without
displaying the full list.
next value. This key scrolls through the values in the associated pick list without
displaying the full list. On 106-key Japanese keyboards, the plus key has a different
scan code than the plus key on the other keyboard, but will have the same effect.
Load Setup Defaults?
[OK] [Cancel]
If “OK” is selected and the Enter key is pressed, all setup fields are set to their default
values. If “Cancel” is selected and the Enter key is pressed, or if the ESC key is
pressed, the user is returned to where they were before F9 was pressed without
affecting any existing field values.
Discard Changes?
[OK
] [Cancel]
If “OK” is selected and the Enter key is pressed, all changes are not saved and setup is
exited. If “Cancel” is selected and the Enter key is pressed, or the ESC key is pressed,
the user is returned to where they were before F7 was pressed without affecting any
existing values.
35
Page 48

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Key Option Description
F10 Save Changes and
Exit
Pressing F10 causes the following message to appear:
Save configuration changes and exit setup?
[OK] [Cancel]
If “OK” is selected and the Enter key is pressed, all changes are saved and setup is
exited. If “Cancel” is selected and the Enter key is pressed, or the ESC key is pressed,
the user is returned to where they were before F10 was pressed without affecting any
existing values.
9.5 Entering BIOS Setup
The BIOS Setup utility is accessed by pressing the <F2> hotkey during POST.
9.5.1 Main Menu
The first screen displayed when entering the BIOS Setup Utility is the Main Menu selection
screen. This screen displays the major menu selections available: The following tables describe
the available options on the top level and lower level menus. Default values are shown in bold
text.
Table 40. BIOS Setup, Main Menu Options
Feature Options Help Text Description
System Overview N/A N/A
AMIBIOS N/A N/A
Version N/A N/A BIOS ID string (excluding the build
time and date)
Build Date MM/DD/YY N/A BIOS build date
Processor N/A N/A
Type N/A N/A Processor brand ID string
Speed N/A N/A Calculated processor speed
Count N/A N/A Detected number of physical
processors
System Memory N/A N/A
Size N/A N/A Amount of physical memory
detected
System Time HH:MM:SS Use [ENTER], [TAB] or [SHIFT-
TAB] to select a field.
Use [+] or [-] to configure system
time.
System Date DAY MM/DD/YYYY Use [ENTER], [TAB] or [SHIFT-
TAB] to select a field.
Use [+] or [-] to configure System
date.
Configures the system time on a 24
hour clock. Default is 00:00:00
Configures the system date.
Default is [Tue 01/01/2002]. Day of
the week is automatically
calculated.
Revision 1.3
36
Page 49

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Feature Options Help Text Description
Language
English
French
German
Italian
Spanish
Use [ENTER], [Up Arrow], [Down
Arrow] to select language.
Select the current default language
used by BIOS.
9.5.2 Advanced menu
Table 41. BIOS Setup, Advanced Menu Options
Feature Options Help Text Description
Processor Configuration N/A Configure processors. Selects submenu.
IDE Configuration N/A Configure the IDE device(s). Selects submenu.
Floppy Configuration N/A Configure the Floppy drive(s). Selects submenu.
Super IO Configuration N/A Configure the Super I/O Chipset. Selects submenu.
USB Configuration N/A Configure the USB support. Selects submenu.
PCI Configuration N/A Configure PCI devices. Selects submenu.
Memory Configuration N/A Configure memory devices. Selects submenu.
9.5.2.1 Processor configuration sub-menu
Table 42. BIOS Setup, Processor configuration sub-menu options
Feature Options Help Text Description
Manufacturer Intel N/A Displays processor manufacturer
string
Brand String N/A N/A Displays processor brand ID string
Frequency N/A N/A Displays the calculated processor
speed
FSB Speed N/A N/A Displays the processor front-side bus
speed.
Cache L1 N/A N/A Displays cache L1 size.
Cache L2 N/A N/A Displays cache L2 size.
Cache L3 N/A N/A Displays cache L3 size. Visible only
if the processor contains an L3
cache.
Processor Retest Enabled
Disabled
Max CPUID Value
Limit
Enabled
Disabled
If enabled, all processors will be
activated and retested on the next
boot. This option will be
automatically reset to disabled on the
next boot.
This should be enabled in order to
boot legacy OSes that cannot
support processors with extended
CPUID functions.
Rearms the processor sensors.
Only displayed if the Intel®
Management Module is present.
37
Page 50

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Feature Options Help Text Description
Hyper-Threading
Technology
Enabled
Disabled
"ENABLE: Enable CPU
Hyperthreading for HT enabled
processor(s).
DISABLE: Disable CPU
Hyperthreading for HT enabled
processor(s)." Controls
Hyperthreading state. Primarily used
to support older Operating Systems
that do not support Hyperthreading.
Controls Hyper-Threading state.
Primarily used to support older
Operating Systems that do not
support Hyper Threading.
9.5.2.2 IDE configuration sub-menu
Table 43. BIOS Setup IDE Configuration Menu Options
Feature Options Help Text Description
ATA/IDE
configuration
Legancy IDE Channel SATA Only
Configure S-ATA as
Stagger Spinup
support
Primary IDE Master N/A While entering setup, BIOS auto
Primary IDE Slave N/A While entering setup, BIOS auto
Secondary IDE
Master
Disabled
Compatible
Enhanced
PATA Pri,SATA,Sec
SATA Pri,PATA,Sec
PATA Only
IDE
RAID
AHCI
Disabled
Enabled
N/A While entering setup, BIOS auto
Disable:SATA and PATA
controller will be disabled
SATA Only:SATA controller
enabled only.
PATA Pri,SATA Sec:PATA
controller is primary ,SATA is
secondary
SATA Pri,PATA Sec: SATA
controller is primary ,PATA is
secondary
PATA Only:PATA controller
enabled only.
In Enhance mode this item will be
This item showed when Configure
detects the presence of IDE
devices. This displays the
status of auto detection of IDE
devices.
detects the presence of IDE
devices. This displays the
status of auto detection of IDE
devices.
detects the presence of IDE
devices. This displays the
status of auto detection of IDE
devices.
Controls state of integrated SATA and P-ATAcontroller.
This option will be hided when
ATA/IDE configuration Disabled
In compatible mode this item will
be used.
showed
S-ATA as RAID/AHCI
Selects submenu with additional
device details.
Selects submenu with additional
device details.
Selects submenu with additional
device details.
Revision 1.3
38
Page 51
SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Feature Options Help Text Description
Secondary IDE Slave N/A While entering setup, BIOS auto
detects the presence of IDE
devices. This displays the
status of auto detection of IDE
devices.
Third IDE Master N/A While entering setup, BIOS auto
detects the presence of IDE
devices. This displays the
status of auto detection of IDE
devices.
Third IDE Slave N/A While entering setup, BIOS auto
detects the presence of IDE
devices. This displays the
status of auto detection of IDE
devices.
Hard Disk Write
Protect
IDE Detect Time Out
(Sec)
ATA(PI) 80Pin Cable
Detection
Disabled
Enabled
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
Host & Device
Host
Device
Disable/Enable device write
protection. This will be effective
only if device is accessed
through BIOS.
Select the time out value for
detecting ATA/ATAPI device(s).
Select the mechanism for
detecting 80Pin ATA(PI) Cable.
Selects submenu with additional
device details.
Selects submenu with additional
device details.
Selects submenu with additional
device details.
Primarily used to prevent
unauthorized writes to hard
drives.
Primarily used with older IDE
devices with longer spin up times.
Table 44. BIOS Setup, IDE Device Configuration Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
Device N/A N/A Display detected device info
Vendor N/A N/A. Display IDE device vendor.
Size N/A N/A Display IDE DISK size.
LBA Mode N/A N/A Display LBA Mode
Block Mode N/A N/A Display Block Mode
PIO Mode N/A N/A Display PIO Mode
Async DMA N/A N/A Display Async DMA mode
Ultra DMA N/A N/A Display Ultra DMA mode.
S.M.A.R.T. N/A N/A Display S.M.A.R.T. support.
Type Not Installed
Auto
CDROM
ARMD
LBA/Large Mode Disabled
Auto
Select the type of device connected
to the system.
Disabled: Disables LBA Mode.
Auto: Enabled LBA Mode if the
device supports it and the device is
not already formatted with LBA
Mode disabled.
The Auto setting should work in
most cases.
The Auto setting should work in
most cases.
39
Page 52

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Feature Options Help Text Description
Block (Multi-Sector
Transfer)
PIO Mode
DMA Mode
S.M.A.R.T.
32Bit Data Transfer
Disabled
Auto
Auto
0
1
2
3
4
Auto
SWDMA0-2
MWDMA0-2
UWDMA0-5
Auto
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled: The Data transfer from
and to the device occurs one sector
at a time.
Auto: The data transfer from and to
the device occurs multiple sectors at
a time if the device supports it.
Select PIO Mode. The Auto setting should work in
Selcet DMA Mode.
Auto :Auto detected
SWDMA :SinglewordDMAn
MWDMA :MultiwordDMAn
UWDMA :UltraDMAn
S.M.A.R.T. stands for SelfMonitoring, Analysis and Reporting
Technology.
Enable/Disable 32-bit Data Transfer
The Auto setting should work in
most cases.
most cases.
The Auto setting should work in
most cases.
The Auto setting should work in
most cases.
9.5.2.3 Floppy configuration sub-menu
Table 45. BIOS Setup, Floppy Configuration Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
Floppy A Disabled
1.44 MB 3 1/2"
Onboard Floppy Controller Disabled
Enabled
Select the type of floppy drive
connected to the system.
Allows BIOS to Enable or
Disable Floppy Controller.
Note: Intel no longer
validates 720 Kb &
2.88 Mb drives.
9.5.2.4 Super I/O configuration sub-menu
Table 46. BIOS Setup, Super I/O Configuration Sub-menu
Feature Options Help Text Description
Serial Port1 Address Disabled
3F8/IRQ4
2F8/IRQ3
3E8/IRQ4
2E8/IRQ3
Allows BIOS to Select Serial Port1
Base Addresses.
Option that is used by other serial port
is hidden to prevent conflicting
settings.
Revision 1.3
40
Page 53
SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Serial Port 2 Address Disabled
3F8/IRQ4
2F8/IRQ3
3E8/IRQ4
2E8/IRQ3
Allows BIOS to Select Serial Port2
Base Addresses.
Option that is used by other serial port
is hidden to prevent conflicting
settings.
9.5.2.5 USB configuration sub-menu
Table 47. BIOS Setup, USB Configuration Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
USB Devices
Enabled
USB Function Disabled
Legacy USB Support Disabled
Port 64/60 Emulation
USB 2.0 Controller
USB 2.0 Controller
mode
USB Mass Storage
Device Configuration
N/A N/A List of USB
devices detected
by BIOS.
Enables USB HOST controllers. When the item is
2 USB ports
All Ports
Enables support for legacy USB. AUTO option disables
Enabled
Auto
Disabled
Enabled
Enabled
Disabled
FullSpeed
HiSpeed
N/A Configures the USB Mass Storage Device Class. Selects submenu
legacy support if no USB devices are connected.
Enables I/O port 60/64h emulation support. This should
be enabled for the complete USB keyboard legacy
support for non-USB aware OS.
N/A
Configures the USB 2.0 controller in HiSpeed (480 Mbps)
or FullSpeed (12 Mbps).
disabled, Legacy
USB Support,
USB 2.0
Controller, and
USB 2.0 Controller
mode will all
disappear.
When USB 2.0
Controller is
disabled, it will
disappear.
with USB Device
enable.
9.5.2.5.1 USB mass storage device configuration sub-menu
Table 48. BIOS Setup, USB Mass Storage Device Configuration Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
USB Mass Storage
Reset Delay
Device #1 N/A N/A Only displayed, if
41
10 Sec
20 Sec
30 Sec
40 Sec
Number of seconds POST waits for the USB mass
storage device after start unit command.
a device is
detected, includes
a DeviceID string
returned by the
USB device.
Page 54

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Emulation Type
Device #n N/A N/A Only displayed, if
Emulation Type
Auto
Floppy
Forced
FDD
Hard Disk
CDROM
Auto
Floppy
Forced
FDD
Hard Disk
CDROM
If Auto, USB devices less than 530 MB will be emulated
as Floppy and remaining as hard drive. Forced FDD
option can be user to force a HDD formatted drive to boot
as FDD (Ex. ZIP drive).
If Auto, USB devices less than 530 MB will be emulated
as Floppy and remaining as hard drive. Forced FDD
option can be user to force a HDD formatted drive to boot
as FDD (Ex. ZIP drive).
a device is
detected.
Includes a
DeviceID string
returned by the
USB device.
9.5.2.6 PCI configuration sub-menu
This sub-menu provides control over PCI devices and their option ROM’s. If the BIOS is
reporting POST error 146, use this menu to disable option ROM’s that are not required to boot
the system.
Table 49. BIOS Setup, PCI Configuration Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
Onboard Video Disabled
Enabled
Onboard NIC 1 Disabled
Enabled
Onboard NIC 1 ROM Disabled
Enabled
Onboard NIC 2 Disabled
Enabled
Onboard NIC 2 ROM Disabled
Enabled
Slot 1 Option ROM
Slot 4 Option ROM
Slot 5 Option ROM
Slot 6 Option ROM
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enable/Disable on board VGA Controller
PCI 32/33
PCI-X 100Mhz
PCI-X 100Mhz
Super Slot
Revision 1.3
42
Page 55
SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
9.5.2.7 Memory configuration sub-menu
This sub-menu provides information about the DIMM’s detected by BIOS. The DIMM number is
printed on the baseboard next to each device.
Table 50. BIOS Setup, Memory Configuration Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
DIMM_1A Installed
Not Installed
DIMM_1B Installed
Not Installed
DIMM_2A Installed
Not Installed
DIMM_2B Installed
Not Installed
Extended Memory Test 1 MB
1 KB
Every Location
Disabled
Memory Retest Enabled
Disabled
Informational display.
Informational display.
Informational display.
Informational display.
Settings for extended memory test
If "Enabled", BIOS will activate and
retest all DIMM’s on the next
system boot.
This option will automactically
reset to "Disabled" on the next
system boot.
9.5.3 Boot menu
Table 51. BIOS Setup, Boot Menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
Boot Settings Configuration N/A Configure settings during system boot. Selects submenu.
Boot Device Priority N/A Specifies the boot device priority sequence. Selects submenu.
Hard Disk Drives N/A Specifies the boot device priority sequence from
available hard drives.
Removable Drives N/A Specifies the boot device priority sequence from
available removable drives.
ATAPI CDROM Drives N/A Specifies the boot device priority sequence from
available ATAPI CD-ROM drives.
43
Selects submenu.
Selects submenu.
Selects submenu.
Page 56

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
9.5.3.1 Boot settings configuration sub-menu selections
Table 52. BIOS Setup, Boot Settings Configuration Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
Quick Boot Disabled
Enabled
Quiet Boot
Bootup Num-Lock
PS/2 Mouse Support Disabled
POST Error Pause Disabled
Hit <F2> Message Display Disabled
Scan User Flash Area
Disabled
Enabled
Off
On
Enabled
Auto
Enabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Allows BIOS to skip certain tests while booting. This
will decrease the time needed to boot the system.
Disabled: Displays normal POST messages.
Enabled: Displays OEM Logo instead of POST
messages.
Select power-on state for numlock.
Select support for PS/2 mouse.
If enabled, the system will wait for user intervention
on critical POST errors. If disabled, the system will
boot with no intervention, if possible.
Displays "Press <F2> to run Setup" in POST.
Allows BIOS to scan the Flash ROM for user
binaries.
9.5.3.2 Boot device priority sub-menu selections
Table 53. BIOS Setup, Boot Device Priority Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
1st Boot Device Varies Specifies the boot sequence from the
available devices.
A device enclosed in parenthesis has
been disabled in the corresponding type
menu.
nth Boot Device Varies Specifies the boot sequence from the
available devices.
A device enclosed in parenthesis has
been disabled in the corresponding type
menu.
Number of entries will vary based on
system configuration.
9.5.3.2.1 Hard disk drive sub-menu selections
Table 54. BIOS Setup, Hard Disk Drive Sub-Menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
1st Drive Varies Specifies the boot sequence from the available
devices.
nth Drive Varies Specifies the boot sequence from the available
devices.
Varies based on system configuration.
Varies based on system configuration.
Revision 1.3
44
Page 57

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
9.5.3.2.2 Removable drive sub-menu selections
Table 55. BIOS Setup, Removable Drives Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
1st Drive Varies Specifies the boot sequence from the available
devices.
nth Drive Varies Specifies the boot sequence from the available
devices.
Varies based on system configuration.
Varies based on system configuration.
9.5.3.2.3 ATAPI CDROM drives sub-menu selections
Table 56. BIOS Setup, ATAPI CDROM Drives Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
1st Drive Varies Specifies the boot sequence from the available
devices.
nth Drive Varies Specifies the boot sequence from the available
devices.
Varies based on system configuration.
Varies based on system configuration.
9.5.4 Chipset Menu
Table 57. BIOS Setup, ATAPI CDROM Drives Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
North Bridge
Configuration
South Bridge
Configuration
Intel PCI Express* –
PCI-X configuration
System management sub-menu selections
9.5.4.1 North Bridge Chipset Configuration
Feature Options Help Text Description
DRAM Frequency
Configure DRAM
Timing by SPD
N/A Configure North Bridge features Opens sub screen to configure NB
N/A Configure South bridge features Opens sub screen to configure SB
N/A Configure PXH device Opens sub screen to configure
PXH
Table 58. BIOS Setup, ATAPI CDROM Drives Sub-menu Selections
AUTO
333Mhz
400Mhz
533Mhz
Disabled
Enabled
DRAM frequency to be
programmed
N/A Whether to read the DRAM Timing
DRAM frequency selection
paramaters from SPD or from User
setup
45
Page 58
SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Feature Options Help Text Description
DRAM CAS#
Latency
DRAM RAS# to
CAS# Delay
DRAM RAS#
Precharge
DRAM RAS#
Activate to
Precharge
Boots Grapchics
Adapter priority
Internal Graphics
Mode Select
3, 2.5, 2
2 DRAM Clocks
3 DRAM Clocks
4 DRAM Clocks
5 DRAM Clocks
2 DRAM Clocks
3 DRAM Clocks
4 DRAM Clocks
5 DRAM Clocks
4 DRAM Clocks
5 DRAM Clocks
6 DRAM Clocks
7 DRAM Clocks
8 DRAM Clocks
9 DRAM Clocks
10 DRAM Clocks
11 DRAM Clocks
12 DRAM Clocks
13 DRAM Clocks
14 DRAM Clocks
15 DRAM Clocks
IGD
PCI/IGD
Disabled
Enabled, 1MB
Enabled, 8MB
Select CAS latency to be used Greyed when DRAM timing
programming are done using SPD.
Selects the CAS latency value to
be programmed when manual
configuration of DRAM parameters
are used.
Select RAS# to CAS# delay Greyed when DRAM timing
programming are done using SPD.
RAS to CAS delay setting will be
programmed into DRAM timing
register when manual setting is
selected
Select RAS# precharge Greyed when DRAM timing
programming are done using SPD.
RAS# precharge setting will be
programmed into DRAM timing
register when manual setting is
selected
Select RAS# Activate to precharge Greyed when DRAM timing
programming are done using SPD.
RAS# activate to precharge setting
will be programmed into DRAM
timing register when manual
setting is selected
Select which graphics controller to
be used as primary boot device
Select the amount of memory used
by Internal Graphics device
IGD – Integrated Video has more
priority
PCI/IGD – Offboard video has
more priority
Enabled / Disable internal graphics
and Select the sieze of memory to
be used
9.5.4.2 South Bridge Chipset Configuration
Table 59. BIOS Setup, ATAPI CDROM Drives Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
SLP_S4# Min
Assertion
Revision 1.3
46
4-5 Seconds
3-4 Seconds
2-3 Seconds
1-2 Seconds
Select Timing for SLP_S4# pin SLP_S4# pin timing selection
Page 59
SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
PCI-EX Port
Configuration
VC1 for Root Port
N/A N/A Title
Disabled
Enabled
Enable / Disable VC1 feature VC1 feature setting on PCI Express*
Root port
9.5.4.3 PXH Bridge Configuration
Table 60. BIOS Setup, ATAPI CDROM Drives Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
PCI Bus frequency
IO Port Decode
RAS Sticky error
handling
VGA 16 Bit decode Disabled
Auto
33Mhz PCI
66Mhz PCI
66Mhz PCI-X M1
100Mhz PCI-X M1
133 Mhx PCI-X M1
66Mhz PCI-X M2
100Mhz PCI-X M2
133 Mhx PCI-X M2
4K Decode
1K Decode
Clear Errors
Leave Errors
Enabled
Allows selection of the maximum
PCI Bus speed to be programmed,
default will always be set to Auto
where Bus speed will be decided
based on the capabilities of the
device on the Bus.
Select the decode range for IO IO decode range
Select the method of handling for
sticky RAS errors
Enabled/Disable decoding of VGA
for devices behind PXH
Select Bus speed and operating
frequency of bus coming out PXH
RAS errors handing method selection
9.5.5 Security menu
Table 61. BIOS Setup, Security Menu Options
Feature Options Help Text Description
Administrator
Password is
User Password is N/A Install / Not installed Informational display.
Set Admin
Password
Set User Password N/A Set or clear User password This node is grayed out until
User Access Level No Access
47
N/A Install / Not installed Informational display.
N/A Set or clear Admin password Set password to null to clear.
Admin password is installed.
Set password to null to clear.
This node is grayed out and
becomes active only when Admin
password is set.
View Only
Limited
Full Access
LIMITED: Allows only limited fields
to be changed such as Date and
Time.
NO ACCESS: Prevents User
access to the Setup Utility.
VIEW ONLY: Allows access to the
Setup Utility but the fields can not
be changed.
Page 60
SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Feature Options Help Text Description
Clear User
Password
Fixed disk boot
sector protection
Password On Boot
Secure Mode Timer
Secure Mode Hot
Key (Ctrl-Alt- )
Secure Mode Boot
Front Panel Switch
Inhibit
NMI Control
N/A Immediately clears the user
password.
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
1 minute
2 minutes
5 minutes
10 minutes
20 minutes
60 minutes
120 minutes
[Z]
[L]
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Enable/Disable Boot Sector Virus
Protection.
If enabled, requires password
entry before boot.
Period of key/PS/2 mouse
inactivity specified for Secure
Mode to activate. A password is
required for Secure Mode to
function. Has no effect unless at
least one password is enabled.
Key assigned to invoke the secure
mode feature. Cannot be enabled
unless at least one password is
enabled. Can be disabled by
entering a new key followed by a
backspace or by entering delete.
When enabled, allows the host
system to complete the boot
process without a password. The
keyboard will remain locked until a
password is entered. A password
is required to boot from diskette.
Disables the Power Switch and the
Reset Switch when Secure mode
is activated. A password is
required to unlock the system. This
cannot be enabled unless at least
one password is enabled. This
option is only present if the system
includes an embedded video
controller.
Enable / disable NMI control
through mBMC for the front panel
NMI button.
Admin uses this option to clear
User password (Admin password
is used to enter setup is required).
This node is hidden if
Administrator password is not
installed.
This node is grayed out if a
password is not installed.
This node is grayed out if a
password is not installed.
This node is grayed out if a
password is not installed.
This node is grayed out if a
password is not installed.
This node is grayed out if a
password is not installed.
Password is not required for this
option.
9.5.6 Server menu
Table 62. BIOS Setup, Server Menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
System management N/A N/A Selects submenu.
Serial Console Features N/A N/A Selects submenu.
Event Log configuration N/A Configures event logging. Selects submenu.
Revision 1.3
48
Page 61

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Feature Options Help Text Description
Assert NMI on PERR Disabled
Enabled
Assert NMI on SERR Disabled
Enabled
Resume on AC Power Loss
Late POST Timeout
Hard Disk OS Boot Timeout
PXE OS Boot Timeout
OS Watchdog Timer Policy
Stays Off
Power On
Disabled
5 minutes
10 minutes
15 minutes
20 minutes
Disabled
5 minutes
10 minutes
15 minutes
20 minutes
Disabled
5 minutes
10 minutes
15 minutes
20 minutes
Stay On
Reset
Power Off
If enabled, NMI is generated. SERR option
needs to be enabled to activate this option.
If enabled, NMI is generated on SERR and
logged.
Determines the mode of operation if a power
loss occurs. Stays off, the system will remain off
once power is restored. Power On, boots the
system after power is restored.
This controls the time limit for add-in card
detection. The system is reset on timeout.
This controls the time limit allowed fo booting an
operating system from a Hard disk drive. The
action taken on timeout is determined by the OS
Watchdog Timer policy setting.
This controls the time limit allowed for booting
an operating system using PXE boot. The action
taken on timeout is determined by OS
Watchdog Timer policy setting.
Controls the policy upon timeout. Stay on action
will take no overt action. Reset will force the
system to reset. Power off will force the system
to power off.
Platform Event Filtering
Enabled
Disabled
Disable trigger for system sensor events inside
BMC.
Applicable for all
BMCs.
9.5.6.1 System management sub-menu selections
Table 63. BIOS Setup, System Management Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
Board Part Number: N/A N/A Field contents varies
Board Serial Number N/A N/A Field contents varies
System Part Number N/A N/A F ield contents varies
System Serial Number N/A N/A Field contents varies
Chassis Part Number N/A N/A Field contents varies
Chassis Serial Number N/A N/A Field contents varies
BIOS Version N/A N/A BIOS ID string (excluding the
build time and date).
BMC Device ID N/A N/A Field contents varies
BMC Firmware Revision N/A N/A Field contents varies
BMC Device Revision N/A N/A Field contents varies
49
Page 62

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
PIA Revision N/A N/A Field contents varies
SDR Revision N/A N/A Field contents varies
9.5.6.2 Serial Console features sub-menu selections
Table 64. BIOS Setup Serial Console Features Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
BIOS Redirection Port
Baud Rate 9600
Flow Control No Flow Control
Terminal Type PC-ANSI
Disabled
Serial 1
Serial 2
19.2K
38.4K
57.6K
115.2K
CTS/RTS
XON/XOFF
CTS/RTS + CD
VT100+
VT-UTF8
If enabled, BIOS uses the specified serial port to
redirect the console to a remote ANSI terminal.
Enabling this option disables Quiet Boot.
N/A
If enabled, it will use the Flow control selected.
CTS/RTS = Hardware
XON/XOFF = Software
CTS/RTS + CD = Hardware + Carrier Detect for
modem use.
VT100+ selection only works for English as the
selected language. VT-UTF8 uses Unicode. PCANSI is the standard PC-type terminal.
9.5.6.3 Event Log configuration sub-menu selections
Table 65. BIOS Setup, Event Log Configuration Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text Description
Clear All Event Logs
Event Logging Disabled
Critical Event Logging Disabled
Disabled
Enabled
Enabled
Enabled
Setting this to Enabled will clear the DMI event log after
system booting.
Select enabled to allow logging of events. Allow records
If enabled, BIOS will detect and log events for system
critical errors. Critical errors are fatal to system operation.
These errors include PERR, SERR, ECC.
to be sent to
SEL.
Enable SMM
handlers to
detect and
log events to
SEL.
Revision 1.3
50
Page 63

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Feature Options Help Text Description
ECC Event Logging
PCI Error Logging
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Enables or Disables ECC Event Logging. Grayed out if
"Critical
Event
Logging"
option is
disabled.
Enables or Disables PCI Error Logging. Grayed out if
"Critical
Event
Logging"
option is
disabled.
9.5.7 Exit menu
Table 66. BIOS Setup, Exit Menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text
Save Changes
and Exit
Discard
Changes and
Exit
Discard
Changes
Load Setup
Defaults
Load Custom
Defaults
Save Custom
Defaults
N/A Exit system setup after saving the changes.
F10 key can be used for this operation.
N/A Exit system setup without saving any changes.
ESC key can be used for this operation.
N/A Discards changes done so far to any of the setup questions.
F7 key can be used for this operation.
N/A Load Setup Default values for all the setup questions.
F9 key can be used for this operation.
N/A Load custom defaults.
N/A Save custom defaults
9.6 Upgrading the BIOS
9.6.1 Preparing for the Upgrade
Before you upgrade the BIOS, prepare for the upgrade by recording the current BIOS settings,
obtaining the upgrade utility, reviewing the release notes, and making a copy of the current
BIOS.
9.6.1.1 Recording the Current BIOS Settings
1. Boot the computer and press <F2> when you see the message:
Press <F2> Key if you want to run SETUP
2. Write down the current settings in the BIOS Setup program or go to the Exit menu and
choose to “Save Custom Defaults”.
Note: Do not skip step 2. You will need these settings to configure your computer at the
end of the procedure.
51
Page 64

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
If you chose to “Save Custom Defaults,” after the new BIOS is flashed, you can restore your
settings from the “Load Custom Default” option.
9.6.1.2 Obtaining the Upgrade Utility
You can upgrade to a new version of the BIOS using the new BIOS files and the BIOS upgrade
utility. You can obtain the BIOS upgrade file and the utility from the Intel Customer Support Web
site: http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SE7221BK1-E
.
9.6.1.3 Creating a Bootable Diskette
1. Use a DOS system to create the diskette.
2. Insert a diskette in diskette drive A.
3. At the C:\ prompt, for an unformatted diskette, type:
format a:/s
or, for a diskette that has already been formatted, type:
sys a:
4. Press <Enter>.
9.6.1.4 Flash Update Utility
The BIOS flash utility suite is compatible with DOS, WIN NT 4.0 / 2000 / XP, and LINUX
operating environments.
The afuXXX AMI Firmware Update Utilities are required for BIOS updates.
[1] In DOS
1.The flash bootable disk must have ROM image and afudos.
2.Enter in DOS.
3. Run AFUDOS /i<ROM filename> [/n] [/p[b][n][c]].
[2] In WIN NT 4.0 / 2000 / XP
1. The flash disk must have ROM image, AMIFLDRV.SYS and AFUWIN.EXE.
2. Enter in WIN NT 4.0 / 2000 / XP.
3. Run command AFUWIN /i<ROM filename> [/n] [/p[b][n][c]].
[3] In LINUX
1.The flash disk must have ROM image and AFULNX.
2.Enter in linux and include floppy device.
3.Run command ./afulnx /i<ROM filename> [/n] [/p[b][n][c]].
[4] In EFI Shell
1. The flash disk must have ROM image and AFUEFI.
2. Boot to EFI Shell with the flash disk.
3. Do a map -r to obtain the file system on the disk.
4. Change drive to the flash disk. E.g., if the flash disk is fs0:, type fs0: at the prompt.
Revision 1.3
52
Page 65

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Run command afuefi [/n] [/p[b][n][c]] <ROM filename> to perform the update.
The afuXXX utilities format and usage:
afuXXX /i<ROM filename> [/n] [/p[b][n][c]] [/r<registry_path>] [/s] [/k] [/q] [/h]
/n - don't check ROM ID
/pbnc b - Program Boot Block
n - Program NVRAM
c - Destroy System CMOS
/r - registry path to store result of operation (only for Windows version)
/k - Program non-critical block only
/s - leave signature in BIOS
/q - silent execution
/h - print help
9.6.2 Flash Architecture and Flash Update Utility
The flash ROM contains system initialization routines, the BIOS Setup Utility, and runtime
support routines. The exact layout is subject to change, as determined by Intel. A 64 KB user
block is available for user ROM code or custom logos. The flash ROM also contains initialization
code in compressed form for on-board peripherals, like SCSI, NIC and video controllers. The
flash ROM also contains support for the Rolling single boot BIOS update feature.
The complete ROM is visible, starting at physical address 4 GB minus the size of the flash ROM
device. The Flash Memory Update utility loads the BIOS image minus the recovery block to the
secondary flash partition, and notifies the BIOS that this image should be used on the next
system re-boot. Because of shadowing, none of the flash blocks are visible at the aliased
addresses below 1 MB.
9.6.3 Rolling BIOS and On-line updates
The Online Update nomenclature refers to the ability to update the BIOS while the server is
online, in operation, as opposed to having to put the server out of operation while doing a BIOS
update. The Rolling BIOS nomenclature refers to the capability for having two copies of BIOS,
viz. the one in use, and the other to which an updated BIOS version can be written. When
ready, the system can roll forward to the new BIOS. In case of a failure with the new version,
the system can roll back to the previous version.
While the exact nature of hardware changes for the support of on-line update / rolling BIOS are
out of scope of this document, BIOS relies on specialized hardware and additional flash space
for this. Flash is divided into two partitions, viz. primary and secondary. The active partition
from which the system boots shall be referred to as the primary partition. The AMI FLASH
update suite and Intel On-line updates preserve the existing BIOS image on the primary
partition. BIOS updates are diverted to the secondary partition. After the update, a notification
flag will be set. During the subsequent boot following BIOS update, system will continue to
attempt to boot from primary BIOS partition. On determining that a BIOS update occurred in the
previous boot, system will attempt to boot the new BIOS. If a failure happens, specialized
hardware will switch back to the BIOS on the other partition, thus affecting a “Roll Back”.
53
Page 66

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
9.6.3.1 Recovery Mode
Three conditions can cause the system to enter recovery mode. Pressing a hot-key, setting the
recovery jumper, and damage to both partitions of the ROM image will cause the system to
enter recovery and update System ROM without the boot-block.
• BIOS Recovery
The recovery disk must include the BIOS image file AMIBOOT.ROM. The 2 MB
AMIBOOT.ROM file may be used on a 2.88MB floppy media (to go with a 2.88 MB legacy or
USB floppy device), a USB mass storage device (i.e. a USB disk on key, must be USB 1.1
or 2.0 compliant), a USB CDROM (USB 1.1 or 2.0 compliant), an ATAPI mass storage
device, or an ATAPI CDROM or DVD.
The recovery mode procedure is as follows:
1) Insert the Recovery media with AMIBOOT.ROM into the system as appropriate
based on whatever device is used.
2) Power on system, and when progress code E9 is displayed on port 80h,the system
will detect the disk.(if there is no image file present, the system will cycle through
progress code F1 to EF.)
3) When F3 is displayed on port 80h, the system will read the BIOS image file.
4) The screen will display flash progress and show if NVRAM and CMOS have been
destroyed.
5) When recovery mode is complete, the system will halt and the system can be
powered off.
NOTE: There are three different hot-keys that can be invoked:
<Ctrl+Home> - Recovery with CMOS destroyed and NVRAM preserved.
<Ctrl+PageDown> - Recovery with both CMOS and NVRAM preserved.
<Ctrl+PageUp> - Recovery with both CMOS and NVRAM destroyed.
• Multi-Disk Recovery
With this new feature the System Recovery can be made from Multiple Floppy Disks to
support ROM image greater than 1MB.
Usage:
1) Use the SPLIT.EXE utility to split the ROM image.
Execute the following command at the command prompt:
split <File Name To Be Split> <New File Name> <File Size in KB>
For Example:
C:\split AMIBOOT.ROM AMIBOOT 1024
2) The above command will create the files of sizes 1MB each (1024 KB) with names
AMIBOOT.000, AMIBOOT.001... and so on, depending upon the AMIBOOT.ROM file
size.
3) Load the first disk AMIBOOT.000
Revision 1.3
54
Page 67

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
4) After reading the file it increments the file extension and then searches for
AMIBOOT.001 in the same floppy.
5) If doesn't find the file in the floppy it will beep for once (1sec) and search again.
6) If it finds the first file and if it needs more files it will increment the file extension and
searches again for AMIBOOT.002 this time it beeps 2 times (each beep 1sec long and
with 0.5sec gap)
7) This continues until the total file size read is equal to the ROM image size.
Summary of Beep codes
Beep Code List:
This uses the standard beep codes used by AMI Core8 for Recovery with some additional
codes. They are… (each beep is 1sec long with 0.5sec gap)
1) 1 long beep Insert for AMIBOOT.001 File
2) 2 long beeps Insert for AMIBOOT.002 File
3) 3 long beeps Insert for AMIBOOT.003 File
Limitations:
1) Maximum Files supported 1000 files (AMIBOOT.000 to AMIBOOT.999)
• Manually Recovering the BIOS
A BIOS recovery can also be manually initiated. This option would be used only when the
BIOS is corrupt, but the ROM checksum error does not occur during POST. To manually
initiate a BIOS recovery, use the following steps:
1) Power down and unplug the system from the AC power source.
2) Move the recovery jumper at J1F2 from the storage position at pins 9 and 10 to
cover pins 10 and 11. See the figure below.
3) Insert the Crisis Recovery Diskette into the A: diskette drive.
4) Plug the system into the AC power source and power it on.
5) A blue screen will be displayed and the recovery process will automatically run. The
system will continue to beep throughout the recovery process. The recovery process
is complete when the beeping stops.
6) Remove the diskette.
7) Power down and unplug the system from the AC power source.
8) Move the BIOS recovery jumper at J1F2 back to the original position, covering
storage pins 9 and 10.
55
Page 68

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
9) Plug the system into the AC power source and power it up to confirm that the
recovery was successful.
Figure 7. BIOS Recovery Jumper
9.7 Error Handling and Reporting
9.7.1 POST Error Beep Codes
Table 67. POST Error Beep Codes
Beeps Error Message POST Progress Code Description
1 Fatal error System halted because of
an unspecified fatal error
that was detected.
2 Processor error System halted because a
fatal error related to a
processor was detected.
3 Memory error System halted because a
fatal error related to the
memory was detected.
4 Motherboard error System halted because a
fatal error related to the
system motherboard
hardware was detected.
Revision 1.3
56
Page 69

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Table 68. BIOS Recovery Beep Codes
Beeps Error Message POST Progress Code Description
1 Recovery Started E9h Start of recovery process
2 Recovery Boot Error Flashing series of POST
codes: EFh, FAh, FBh,
F4h, FCh, FDh, FFh
Series of long
low-pitched
single beeps
2 long highpitched beeps
Recovery Failed FDh Unable to process valid BIOS recovery
Recovery Complete FFh BIOS recovery succeeded, ready for power-
Unable to boot to floppy, ATAPI, or ATAPI
CD-ROM. Recovery process will retry.
images. BIOS already passed control to
operating system and flash utility.
down, reboot.
9.7.2 BIOS Event Log
The BIOS will output the current boot progress codes on the video screen. Progress codes are
32 bit quantities plus optional data. The 32 bit numbers include Class, subclass and Operation
information. Class and subclass point to the type of the hardware that is being initialized, where
as the Operation field represents the specific initialization activity. Based upon the data bit
availability to display Progress Code, a progress code can be customized to fit the data width.
The higher the data bit, higher the granularity of information, which could send on the progress
port. The progress codes may be reported by system BIOS or option ROMs.
The Response section in following table is divided in 3 different types:
• Warning – The message is displayed on screen and error is logged in SEL. System will
continue booting with degraded state. User may want to replace erroneous unit
• Pause – The message is displayed on screen and user input is required to continue.
User can take immediate corrective action or can choose to continue booting.
• Halt – System cannot boot unless error is resolved. User needs to replace faulty part
and restart the system.
Table 69. POST Error Messages and Handling
Error Code Error Message Response
100 Timer Error Warning
103 CMOS Battery Low Warning
104 CMOS Settings Wrong Warning
105 CMOS Checksum Bad Warning
10B CMOS memory size different Warning
112 CMOS time not set Warning
140 Refresh timer test failed Halt
141 Display memory test failed Warning
142 CMOS Display Type Wrong Pause
147 Unknown BIOS error. Error code = 147 (this is really a
PMM_MEM_ALLOC_ERR)
148 Password check failed Halt
149 Unknown BIOS error. Error code = 149 (this is really SEGMENT_REG_ERR) Halt
14A Unknown BIOS error. Error code = 14A (this is really ADM_MODULE_ERR) Warning
14B Unknown BIOS error. Error code = 14B (this is really Warning
Halt
57
Page 70

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Error Code Error Message Response
LANGUAGE_MODULE_ERR)
14D Primary Master Hard Disk Error Pause
14E Primary Slave Hard Disk Error Pause
14F Secondary Master Hard Disk Error Pause
150 Secondary Slave Hard Disk Error Pause
151 Primary Master Drive - ATAPI Incompatible Pause
152 Primary Slave Drive - ATAPI Incompatible Pause
153 Secondary Master Drive - ATAPI Incompatible Pause
154 Secondary Slave Drive - ATAPI Incompatible Pause
8100 Processor failed BIST Warning
8110 Processor Internal error (IERR) Warning
8120 Processor Thermal Trip error Warning
8160 Processor unable to apply BIOS update Pause
8170 Processor L2 cache Failed Pause
8180 BIOS does not support current stepping for Processor Pause
8190 Watchdog Timer failed on last boot Warning
8191 12:1 Core to bus ratio: Processor Cache disabled Pause
8192 L2 Cache size mismatch Pause
8193 CPUID, Processor Stepping are different Pause
8194 CPUID, Processor Family are different Pause
8195 Front Side Bus Speed mismatch. System Halted Pause
8197 CPU Speed mismatch Pause
8300 Baseboard Management Controller failed to function Pause
8301 Front Panel Controller failed to Function Pause
84F2 Server Management Interface Failed Pause
84F3 BMC in Update Mode Pause
84F4 Sensor Data Record Empty Pause
84FF System Event Log Full Warning
9.7.3 POST Progress Codes and Messages
9.7.3.1 POST Code Checkpoints
Table 70. POST Code Checkpoints
Checkpoint Description
03 Disable NMI, Parity, video for EGA, and DMA controllers. Initialize BIOS, POST, Runtime data
area. Also initialize BIOS modules on POST entry and GPNV area. Initialized CMOS as mentioned
in the Kernel Variable "wCMOSFlags."
04 Check CMOS diagnostic byte to determine if battery power is OK and CMOS checksum is OK.
Verify CMOS checksum manually by reading storage area. If the CMOS checksum is bad, update
CMOS with power-on default values and clear passwords. Initialize status register A.
Initializes data variables that are based on CMOS setup questions. Initializes both the 8259
compatible PICs in the system
Revision 1.3
58
Page 71

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Checkpoint Description
05 Initializes the interrupt controlling hardware (generally PIC) and interrupt vector table.
06 Do R/W test to CH-2 count reg. Initialize CH-0 as system timer. Install the POSTINT1Ch handler.
Enable IRQ-0 in PIC for system timer interrupt.
Traps INT1Ch vector to "POSTINT1ChHandlerBlock."
08 Initializes the CPU. The BAT test is being done on KBC. Program the keyboard controller
command byte is being done after Auto detection of KB/MS using AMI KB-5.
C0 Early CPU Init Start -- Disable Cache - Init Local APIC
C1 Set up boot strap processor Information
C2 Set up boot strap processor for POST
C5 Enumerate and set up application processors
C6 Re-enable cache for boot strap processor
C7 Early CPU Init Exit
0A Initializes the 8042 compatible Key Board Controller.
0B Detects the presence of PS/2 mouse.
0C Detects the presence of Keyboard in KBC port.
0E Testing and initialization of different Input Devices. Also, update the Kernel Variables.
Traps the INT09h vector, so that the POST INT09h handler gets control for IRQ1. Uncompress all
available language, BIOS logo, and Silent logo modules.
13 Early POST initialization of chipset registers.
24 Uncompress and initialize any platform specific BIOS modules.
30 Initialize System Management Interrupt.
2A Initializes different devices through DIM.
See DIM Code Checkpoints section of document for more information.
2C Initializes different devices. Detects and initializes the video adapter installed in the system that
have optional ROMs.
2E Initializes all the output devices.
31 Allocate memory for ADM module and uncompress it. Give control to ADM module for initialization.
Initialize language and font modules for ADM. Activate ADM module.
33 Initializes the silent boot module. Set the window for displaying text information.
37 Displaying sign-on message, CPU information, setup key message, and any OEM specific
information.
38 Initializes different devices through DIM. See DIM Code Checkpoints section of document for more
information.
39 Initializes DMAC-1 & DMAC-2.
3A Initialize RTC date/time.
3B Test for total memory installed in the system. Also, Check for DEL or ESC keys to limit memory
test. Display total memory in the system.
3C Mid POST initialization of chipset registers.
40 Detect different devices (Parallel ports, serial ports, and coprocessor in CPU, … etc.) successfully
installed in the system and update the BDA, EBDA…etc.
50 Programming the memory hole or any kind of implementation that needs an adjustment in system
RAM size if needed.
52 Updates CMOS memory size from memory found in memory test. Allocates memory for Extended
BIOS Data Area from base memory.
60 Initializes NUM-LOCK status and programs the KBD typematic rate.
75 Initialize Int-13 and prepare for IPL detection.
78 Initializes IPL devices controlled by BIOS and option ROMs.
59
Page 72

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Checkpoint Description
7A Initializes remaining option ROMs.
7C Generate and write contents of ESCD in NVRam.
84 Log errors encountered during POST.
85 Display errors to the user and gets the user response for error.
87 Execute BIOS setup if needed / requested.
8C Late POST initialization of chipset registers.
8D Build ACPI tables (if ACPI is supported)
8E Program the peripheral parameters. Enable/Disable NMI as selected
90 Late POST initialization of system management interrupt.
A0 Check boot password if installed.
A1 Clean-up work needed before booting to OS.
A2 Takes care of runtime image preparation for different BIOS modules. Fill the free area in F000h
segment with 0FFh. Initializes the Microsoft IRQ Routing Table. Prepares the runtime language
module. Disables the system configuration display if needed.
A4 Initialize runtime language module.
A7 Displays the system configuration screen if enabled. Initialize the CPU’s before boot, which
includes the programming of the MTRR’s.
A8 Prepare CPU for OS boot including final MTRR values.
A9 Wait for user input at config display if needed.
AA Uninstall POST INT1Ch vector and INT09h vector. De-initializes the ADM module.
AB Prepare BBS for Int 19 boot.
AC End of POST initialization of chipset registers.
B1 Save system context for ACPI.
00 Passes control to OS Loader (typically INT19h).
Revision 1.3
60
Page 73

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
9.7.3.2 Boot Block Initialization Code Checkpoints
The Boot Block initialization code sets up the chipset, memory and other components before
system memory is available. The following table describes the type of checkpoints that may
occur during the boot block initialization.
Table 71. Bootblock Initialization Code Checkpoints
Checkpoint Description
Before D1 Early chipset initialization is done. Early super I/O initialization is done including RTC
and keyboard controller. NMI is disabled.
D1 Perform keyboard controller BAT test. Check if waking up from power management
suspend state. Save power-on CPUID value in scratch CMOS.
D0 Go to flat mode with 4GB limit and GA20 enabled. Verify the bootblock checksum.
D2 Disable CACHE before memory detection. Execute full memory sizing module. Verify
that flat mode is enabled.
D3 If memory sizing module not executed, start memory refresh and do memory sizing in
Bootblock code. Do additional chipset initialization. Re-enable CACHE. Verify that flat
mode is enabled.
D4 Test base 512KB memory. Adjust policies and cache first 8MB. Set stack.
D5 Bootblock code is copied from ROM to lower system memory and control is given to it.
BIOS now executes out of RAM.
D6 Both key sequence and OEM specific method is checked to determine if BIOS recovery
is forced. Main BIOS checksum is tested. If BIOS recovery is necessary, control flows
to checkpoint E0. See Bootblock Recovery Code Checkpoints section of document for
more information.
D7 Restore CPUID value back into register. The Bootblock-Runtime interface module is
moved to system memory and control is given to it. Determine whether to execute
serial flash.
D8 The Runtime module is uncompressed into memory. CPUID information is stored in
memory.
D9 Store the Uncompressed pointer for future use in PMM. Copying Main BIOS into
memory. Leaves all RAM below 1MB Read-Write including E000 and F000 shadow
areas but closing SMRAM.
DA Restore CPUID value back into register. Give control to BIOS POST
(ExecutePOSTKernel). See POST Code Checkpoints section of document for more
information.
61
Page 74

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
9.7.3.3 Boot Block Recovery Code Checkpoints
The Boot block recovery code gets control when the BIOS determines that a BIOS recovery
needs to occur because the user has forced the update or the BIOS checksum is corrupt. The
following table describes the type of checkpoints that may occur during the Bootblock recovery
portion of the BIOS:
Table 72. Bootblock Recovery Code Checkpoints
Checkpoint Description
E0 Initialize the floppy controller in the super I/O. Some interrupt vectors are initialized.
DMA controller is initialized. 8259 interrupt controller is initialized. L1 cache is enabled.
E9 Set up floppy controller and data. Attempt to read from floppy.
EA Enable ATAPI hardware. Attempt to read from ARMD and ATAPI CDROM.
EB Disable ATAPI hardware. Jump back to checkpoint E9.
EF Read error occurred on media. Jump back to checkpoint EB.
E9 or EA Determine information about root directory of recovery media.
F0 Search for pre-defined recovery file name in root directory.
F1 Recovery file not found.
F2 Start reading FAT table and analyze FAT to find the clusters occupied by the recovery
file.
F3 Start reading the recovery file cluster by cluster.
F5 Disable L1 cache.
FA Check the validity of the recovery file configuration to the current configuration of the
flash part.
FB Make flash write enabled through chipset and OEM specific method. Detect proper
flash part. Verify that the found flash part size equals the recovery file size.
F4 The recovery file size does not equal the found flash part size.
FC Erase the flash part.
FD Program the flash part.
FF The flash has been updated successfully. Make flash write disabled. Disable ATAPI
hardware. Restore CPUID value back into register. Give control to F000 ROM at
F000:FFF0h.
Revision 1.3
62
Page 75

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
9.7.3.4 DIM Code Checkpoints
The Device Initialization Manager Module gets control at various times during BIOS POST to
initialize different BUSes. The following table describes the main checkpoints where the DIM
module is accessed.
Table 73. DIM Code Checkpoints
Checkpoint Description
2A Initialize different buses and perform the following functions: Reset, Detect, and Disable (function 0);
Static Device Initialization (function 1); Boot Output Device Initialization (function 2). Function 0
disables all device nodes, PCI devices, and PnP ISA cards. It also assigns PCI bus numbers.
Function 1 initializes all static devices that include manual configured onboard peripherals, memory
and I/O decode windows in PCI-PCI bridges, and noncompliant PCI devices. Static resources are
also reserved. Function 2 searches for and initializes any PnP, PCI, or AGP video devices.
38 Initialize different buses and perform the following functions: Boot Input Device Initialization (function
3); IPL Device Initialization (function 4); General Device Initialization (function 5). Function 3 searches
for and configures PCI input devices and detects if system has standard keyboard controller. Function
4 searches for and configures all PnP and PCI boot devices. Function 5 configures all onboard
peripherals that are set to an automatic configuration and configures all remaining PnP and PCI
devices.
9.7.3.5 ACPI Runtime Checkpoints
ACPI checkpoints are displayed when an ACPI capable operating system either enters or
leaves a sleep state. The following table describes the type of checkpoints that may occur
during ACPI sleep or wake events.
Table 74. ACPI Runtime Checkpoints
Checkpoint Description
AC First ASL check point. Indicates the system is running in ACPI mode.
AA System is running in APIC mode.
01, 02, 03, 04, 05 Entering sleep state S1, S2, S3, S4, or S5.
10, 20, 30, 40, 50 Waking from sleep state S1, S2, S3, S4, or S5.
63
Page 76

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
9.8 Diagnostic LEDs
All port 80 codes are displayed using the Diagnostic LEDs found on the back edge of the
baseboard. The diagnostic LED feature consists of a hardware decoder and four dual color
LEDs. During POST, the LEDs will display all normal POST codes representing the progress of
the BIOS POST. Each code will be represented by a combination of colors from the four LEDs.
The LEDs are capable of displaying three colors: Green, Red, and Amber. The POST codes are
divided into two nibbles, an upper nibble and a lower nibble. Each bit in the upper nibble is
represented by a Red LED and each bit in the lower nibble is represented by a green LED. If
both bits are set in the upper and lower nibbles then both Red and Green LEDs are lit, resulting
in an Amber color. If both bits are clear, then the LED is off.
In the below example, BIOS sends a value of ACh to the Diagnostic LED decoder. The LEDs
are decoded as follows:
Red bits = 1010b = Ah
Green bits = 1100b = Ch
Since the red bits correspond to the upper nibble and the green bits correspond to the lower
nibble, the two are concatenated to be ACh.
Table 75. POST Progress Code LED Example
LEDs Red Green Red Green Red Green Red Green
Ach 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0
Result Amber Green Red Off
MSB LSB
9.8.1 Diagnostic LED POST Progress Codes
Table 76. Boot Block POST Progress Codes
Diagnostic LED
Decoder
10h Off Off Off R
11h Off Off Off A
12h Off Off G R Get start of initialization code and check BIOS header.
13h Off Off G A Memory sizing.
14h Off G Off R
G=Green, R=Red,
A=Amber
Hi Low
The NMI is disabled. Start Power-on delay. Initialization code checksum
verified.
Initialize the DMA controller, perform the keyboard controller BAT test, start
memory refresh, and enter 4 GB flat mode.
Test base 512K of memory. Return to real mode. Execute any OEM patches
and set up the stack.
Description
Revision 1.3
64
Page 77

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Diagnostic LED
Description
Decoder
G=Green, R=Red,
A=Amber
Hi Low
15h Off G Off A
Pass control to the uncompressed code in shadow RAM. The initialization code
is copied to segment 0 and control will be transferred to segment 0.
Control is in segment 0. Verify the system BIOS checksum.
16h Off G G R
If the system BIOS checksum is bad, go to checkpoint code E0h.
Otherwise, going to checkpoint code D7h.
17h Off G G A Pass control to the interface module.
18h G Off Off R Decompress of the main system BIOS failed.
19h G Off Off A Build the BIOS stack. Disable USB controller. Disable cache.
1Ah G Off G R Uncompress the POST code module. Pass control to the POST code module.
1Bh A R Off R Decompress the main system BIOS runtime code.
1Ch A R Off A Pass control to the main system BIOS in shadow RAM.
E0h R R R Off
Start of recovery BIOS. Initialize interrupt vectors, system timer, DMA controller,
and interrupt controller.
E8h A R R Off Initialize extra module if present.
E9h A R R G Initialize floppy controller.
Eah A R A Off Try to boot floppy diskette.
Ebh A R A G If floppy boot fails, intialize ATAPI hardware.
Ech A A R Off Try booting from ATAPI CD-ROM drive.
Eeh A A A Off Jump to boot sector.
Efh A A A G Disable ATAPI hardware.
Table 77. POST Progress Codes
Diagnostic LED
Decoder
G=Green, R=Red,
A=Amber
Hi Low
20h Off Off R Off Uncompress various BIOS Modules
22h Off Off A Off Verify password Checksum
24h Off G R Off Verify CMOS Checksum.
26h Off G A Off Read Microcode updates from BIOS ROM.
28h G Off R Off
2Ah G Off A Off Go to Big Real Mode
2Ch G G R Off Decompress INT13 module
2Eh G G A Off
30h Off Off R R Keyboard/Mouse port swap, if needed
32h Off Off A R
Description
Initializing the processors. Set up processor registers. Select least featured
processor as the BSP.
Keyboard Controller Test: The keyboard controller input buffer is free. Next,
issuing the BAT command to the keyboard controller
Write Command Byte 8042: The initialization after the keyboard controller BAT
command test is done. The keyboard command byte will be written next.
65
Page 78

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Diagnostic LED
Decoder
34h Off G R R
36h Off G A R Disable and initialize 8259
38h G Off R R Detect Configuration Mode, such as CMOS clear.
3Ah G Off A R Chipset Initialization before CMOS initialization
3Ch G G R R
3Eh G G A R
40h Off R Off Off Calculate CPU speed
42h Off R G Off Init interrupt Vectors: Interrupt vector initialization is done.
44h Off A Off Off Enable USB controller in chipset
46h Off A G Off Initialize SMM handler. Initialize USB emulation.
48h G R Off Off Validate NVRAM areas. Restore from backup if corrupted.
4Ah G R G Off
4Ch G A Off Off Validate date and time in RTC.
4Eh G A G Off Determine number of micro code patches present
50h Off R Off R Load Micro Code To All CPUs
52h Off R G R Scan SMBIOS GPNV areas
54h Off A Off R Early extended memory tests
56h Off A G R Disable DMA
58h G R Off R Disable video controller
5Ah G R G R 8254 Timer Test on Channel 2
5Ch G A Off R
5Eh G A G R
60h Off R R Off Initialize memory test parameters
62h Off R A Off
64h Off A R Off Start USB controllers in chipset
66h Off A A Off Set up video parameters in BIOS data area.
68h G R R Off Activate ADM: The display mode is set. Displaying the power-on message next.
6Ah G R A Off Initialize language module. Display splash logo.
6Ch G A R Off
G=Green, R=Red,
A=Amber
Hi Low
Description
Keyboard Init: The keyboard controller command byte is written. Next, issuing
the pin 23 and 24 blocking and unblocking commands
Init System Timer: The 8254 timer test is over. Starting the legacy memory
refresh test next.
Check Refresh Toggle: The memory refresh line is toggling. Checking the 15
second on/off time next
Load defaults in CMOS RAM if bad checksum or CMOS clear jumper is
detected.
Enable 8042. Enable timer and keyboard IRQs. Set Video Mode: Initialization
before setting the video mode is complete. Configuring the monochrome mode
and color mode settings next.
Init PCI devices and motherboard devices. Pass control to video BIOS. Start
serial console redirection.
Initialize AMI display manager Module. Initialize support code for headless
system if no video controller is detected.
Display Sign on message, BIOS ID and processor information.
6Eh G A A Off Detect USB devices
70h Off R R R Reset IDE Controllers
72h Off R A R Displaying bus initialization error messages.
74h Off A R R
76h Off A A R Ensure Timer Keyboard Interrupts are on.
Revision 1.3
66
Display Setup Message: The new cursor position has been read and saved.
Displaying the Hit Setup message next.
Page 79

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Diagnostic LED
Decoder
78h G R R R Extended background memory test start
7Ah G R A R Disable parity and NMI reporting.
7Ch G A R R
7Eh G A A R
80h R Off Off Off
82h R Off G Off
84h R G Off Off
86h R G G Off
88h A Off Off Off Display USB devices
8Ah A Off G Off
8Ch A G Off Off Lock out PS/2 keyboard/mouse if unattended start is enabled.
8Eh A G G Off
90h R Off Off R Display IDE mass storage devices.
92h R Off G R Display USB mass storage devices.
94h R G Off R Report the first set of POST Errors To Error Manager.
96h R G G R
98h A Off Off R
9Ah A Off G R
9Ch A G Off R Init FDD Devices. Report second set of POST errors To Error messager
9Eh A G G R Extended background memory test end
A0h R Off R Off
A2h R Off A Off Set Base Expansion Memory Size
A4h R G R Off Program chipset setup options, build ACPI Tables, build INT15h E820h table
A6h R G A Off Set Display Mode
A8h A Off R Off Build SMBIOS table and MP tables.
Aah A Off A Off Clear video screen.
Ach A G R Off Prepare USB controllers for operating system
Aeh A G A Off One Beep to indicate end of POST. No beep if silent boot is enabled.
000h Off Off Off Off POST completed. Passing control to INT 19h boot loader next.
G=Green, R=Red,
A=Amber
Hi Low
Description
Test 8237 DMA Controller: The DMA page register test passed. Performing the
DMA Controller 1 base register test next
Init 8237 DMA Controller: The DMA controller 2 base register test passed.
Programming DMA controllers 1 and 2 next.
Enable Mouse and Keyboard: The keyboard test has started. Clearing the
output buffer and checking for stuck keys. Issuing the keyboard reset command
next
Keyboard Interface Test: A keyboard reset error or stuck key was found. Issuing
the keyboard controller interface test command next.
Check Stuck Key Enable Keyboard: The keyboard controller interface test
completed. Writing the command byte and initializing the circular buffer next.
Disable parity NMI: The command byte was written and global data initialization
has completed. Checking for a locked key next
Verify RAM Size: Checking for a memory size mismatch with CMOS RAM data
next
Init Boot Devices: The adapter ROM had control and has now returned control
to BIOS POST. Performing any required processing after the option ROM
returned control.
Boot Password Check: The password was checked. Performing any required
programming before Setup next.
Float Processor Initialize: Performing any required initialization before the
coprocessor test next.
Enable Interrupts 0,1,2: Checking the extended keyboard, keyboard ID, and
NUM Lock key next. Issuing the keyboard ID command next
Prepare And Run Setup: Error manager displays and logs POST errors. Waits
for user input for certain errors. Execute setup.
67
Page 80

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
10. Power Information
10.1 Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E Power Budget
The following table shows the power consumed on each supply line for the SE7221BK1-E
baseboard that is configured with one
GB DDR2 DIMMs stacked burst at 70% max. The numbers provided in the table should be used
for reference purposes only. Different hardware configurations will produce different numbers.
The numbers in the table reflect a common usage model operating at a higher than average
stress levels.
Table 78. The Board Power Budget
processor (128W max). This configuration includes four 1
Watts AMPS
FUNCTIONAL
UNIT
BASEBOARD INPUT
TOTALS
BASEBOARD
DISCRETE TOTALS
BASEBOARD
CONVERTERS
BASEBOARD
CONFIG TOTATLS
SYSTEM
COMPONENTS
SYSTEM TOTALS 335.85W 6.26 10.87 9.14 9.28 0.05 1.67 Amps
3.3v/5v combined
power
Utilization Power 3.3V 5.V 12.V 12V
50% 32.02W 1.51 1.17 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
Efficiency 41.90W 3.24 7.29 0.00 9.28 0.00 1.67
246.80W 1.52 0.00 6.38 0.00 0.05 0.00
45.12W 0.00 2.40 2.76 0.00 0.00 0.00
290.73W 6.26W 8.47W 6.38W 9.28W 0.05W 1.67
Power Supply Rail Voltages Units
-12v 5VSB
VRM
Power Supply
Requirements –
1U
350W peak
3.3V/5V
combined power
12V + 12WRM max of 20A
Revision 1.3
68
300W 14A 18A Max 12V+ 12V
VRM
100W 1Amin 1Amin 2Amin 2Amin 0Amin 1Amin
0.5A 2A
Page 81

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
10.2 Power Supply Specifications
This section provides power supply design guidelines for the baseboard, including voltage and
current specifications, and power supply on/off sequencing characteristics.
Table 79. The Board Power Supply Voltage Specification
PARAMETER TOLERANCE MIN NOM MAX UNITS
+ 3.3V - 5% / +5% +3.14 +3.30 +3.46 Vrms
+ 5V - 5% / +5% +4.75 +5.00 +5.25 Vrms
+ 12V - 5% / +5% +11.40 +12.00 +12.60 Vrms
- 12V - 10% / +10% -11.40 -12.00 -13.08 Vrms
+ 5VSB - 5% / +5% +4.75 +5.00 +5.25 Vrms
10.2.1 Power Timing Requirements
These are the timing requirements for the power supply operation. The output voltages must
rise from 10% to within regulation limits (Tvout_rise) within 5 to 70ms, except for 5VSB - it is
allowed to rise from 1.0 to 70ms. The +3.3V, +5V and +12V output voltages should start to rise
approximately at the same time. All outputs must rise monotonically. The +5V output needs
to be greater than the +3.3V output during any point of the voltage rise. The +5V output must
never be greater than the +3.3V output by more than 2.25V. Each output voltage shall reach
regulation within 50ms (Tvout_on) of each other during turn on of the power supply. Each
output voltage shall fall out of regulation within 400msec (Tvout_off) of each other during turn
off. Refer to the table below for the timing requirements for the power supply being turned on
and off via the AC input, with PSON held low and the PSON signal, with the AC input applied.
Table 80. Output Voltage Timing
Item Description MIN MAX UNITS
Tvout_rise Output voltage rise time from each main output. 5.0 * 70 * msec
Tvout_on All main outputs must be within regulation of each
other within this time.
T vout_off All main outputs must leave regulation within this
time.
50 msec
400 msec
• The 5VSB output voltage rise time shall be from 1.0ms to 25.0ms
69
Page 82

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
_
Vout
V1
10%
Vout
V2
V3
rise
Tvout
Tvout_on
Tvout_off
Figure 8. Output Voltage Timing
Table 81. Turn On/Off Timing
Item Description MIN MAX UNITS
Tsb_on_delay
T ac_on_delay
Tvout_holdup
Tpwok_holdup
Tpson_on_delay
T pson_pwok
Tpwok_on
T pwok_off
Tpwok_low
Tsb_vout
T5VSB_holdup
Delay from AC being applied to 5VSB being within
regulation.
Delay from AC being applied to all output voltages
being within regulation.
Time all output voltages stay within regulation after
loss of AC.
Delay from loss of AC to de-assertion of PWOK
Delay from PSON# active to output voltages within
regulation limits.
Delay from PSON# deactive to PWOK being de-
asserted.
Delay from output voltages within regulation limits to
PWOK asserted at turn on.
Delay from PWOK de-asserted to output voltages
(3.3V, 5V, 12V, -12V) dropping out of regulation
limits.
Duration of PWOK being in the de-asserted state
during an off/on cycle using AC or the PSON signal.
Delay from 5VSB being in regulation to O/Ps being in
regulation at AC turn on.
Time the 5VSB output voltage stays within regulation
after loss of AC.
1500
2500
21
20 msec
5 400
50
100 1000
1 200
100
50 1000
70
msec
msec
msec
msec
msec
msec
msec
msec
msec
msec
Revision 1.3
70
Page 83

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
pwoTp
w
AC Input
T
vout_holdup
Vout
T
PWOK
sb_on_delay
T
AC_on_delay
T
T
pwok_on
T
pwok_holdup
pwok_off
T
pwok_low
T
sb_on_delay
T
pwok_on
T
son_p
5VSB
T
sb_vout
T
5VSB_holdup
PSON
T
pson_on_delay
AC turn on/off cycle
PSON turn on/off cycle
Figure 9. Turn On/Off Timing (Power Supply Signals)
10.2.2 Dynamic Loading
The output voltages shall remain within limits specified for the step loading and capacitive
loading specified in the table below. The load transient repetition rate shall be tested between
50Hz and 5kHz at duty cycles ranging from 10%-90%. The load transient repetition rate is only
a test specification. The ∆ step load may occur anywhere within the MIN load to the MAX load
conditions.
Table 82. Transient Load Requirements
Notes
Output
+3.3V 5.0A
+5V 6.0A
12V 9.0A
+5VSB 0.5A
1) Step loads on each 12V output may happen simultaneously.
2) For Load Range 2 (light system loading), the tested step load size should be 60% of those listed.
∆ Step Load Size
(See note 2)
Load Slew Rate Test capacitive Load
0.25 A/µsec 250 µF
0.25 A/µsec 400 µF
0.25 A/µsec 500 µF
0.25 A/µsec 20 µF
71
Page 84

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
10.2.3 AC Line Transient Specification
AC line transient conditions shall be defined as “sag” and “surge” conditions. “Sag” conditions
are also commonly referred to as “brownout”, these conditions will be defined as the AC line
voltage dropping below nominal voltage conditions. “Surge” will be defined to refer to conditions
when the AC line voltage rises above nominal voltage.
The power supply shall meet the requirements under the following AC line sag and surge
conditions.
Table 83. AC Line Sag Transient Performance
AC Line Sag
Duration Sag Operating AC Voltage Line Frequency Performance Criteria
Continuous 10% Nominal AC Voltage ranges 50/60Hz No loss of function or performance
0 to 1 AC
cycle
> 1 AC cycle >10% Nominal AC Voltage ranges 50/60Hz Loss of function acceptable, self
100% Nominal AC Voltage ranges 50/60Hz No loss of function or performance
recoverable
Table 84. AC Line Surge Transient Performance
AC Line Surge
Duration Surge Operating AC Voltage Line Frequency Performance Criteria
Continuous 10% Nominal AC Voltages 50/60Hz No loss of function or performance
0 to ½ AC
cycle
30% Mid-point of nominal AC
Voltages
50/60Hz No loss of function or performance
10.2.4 AC Line Fast Transi ent (EFT) Specification
The power supply shall meet the EN61000-4-5 directive and any additional requirements in
IEC1000-4-5:1995 and the Level 3 requirements for surge-withstand capability, with the
following conditions and exceptions:
• These input transients must not cause any out-of-regulation conditions, such as overshoot
and undershoot, nor must it cause any nuisance trips of any of the power supply protection
circuits.
• The surge-withstand test must not produce damage to the power supply.
• The supply must meet surge-withstand test conditions under maximum and minimum DC-
output load conditions.
11. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Operating the board at conditions beyond those shown in the following table may cause
permanent damage to the system. The table is provided for stress testing purposes only.
Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect system
reliability.
Revision 1.3
72
Page 85

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Table 85. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature
Voltage on any signal with respect to ground -0.3 V to Vdd + 0.3V 2
3.3 V Supply Voltage with Respect to ground -0.3 V to 3.63 V
5 V Supply Voltage with Respect to ground -0.3 V to 5.5 V
Notes:
1. Chassis design must provide proper airflow to avoid exceeding the processor maximum case
temperature.
2. VDD means supply voltage for the device
5 °C to 50 °C 1
-55 °C to +150 °C
11.1 Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) Test Results
This section provides results of MTBF testing done by a 3rd party testing facility. MTBF is a
standard measure for the reliability and performance of the board under extreme working
conditions. For the SE7221BK1-E server board, MTBF was measured at 190,727 hours at 40
degrees Centigrade.
12. Hardware Monitoring
12.1 Monitored Components
The Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E has an integrated LM96000 chip that is responsible for
hardware monitoring. The LM96000 chip provides basic server hardware monitoring which
alerts a system administrator if a hardware problem occurs on the board. The NS super IO
PC87427 has implemented some FAN speed control/monitor pins. Below is a table of monitored
headers and sensors on the board.
Table 86. Monitored Components
Item Description
Voltage
Fan Speed
P_VCC (PIN #24) Monitors processor voltage LM96000
P12V (PIN #21) Monitors +12Vin for system +12V supply LM96000
P1V8 (PIN #22) Monitors 1.8V DDRII power LM96000
P5V (PIN #20) Monitors +5V LM96000
PWM1 (PIN #24) Controls system front fans
(JP5J1,JP5J2,JP7A1,JP6A1,J6J3,J6J1,J6J4,J6J2)
PWM2 (PIN #10) Controls CPU fans (J7A1) LM96000
PWM3 (PIN #13) N/A LM96000
TACH1 (PIN #11) Monitors CPU fan (J7A1) LM96000
TACH2 (PIN #12) Monitors SYS FAN_3 (JP5J1) LM96000
TACH3 (PIN #9) Monitors SYS FAN_4 (JP5J2) LM96000
LM96000
73
Page 86

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Temperature
FANIN0 (PIN #66) Monitors SYS FAN_2 (JP7A1) / SYS FAN_5A (J6J1) Super IO
FANIN1 (PIN #81) Monitors SYS FAN_1 (JP6A1) / SYS FAN_5B (J6J1) Super IO
FANIN2 (PIN #77) Monitors SYS FAN_6A (J6J2) Super IO
FANIN3 (PIN #76) Monitors SYS FAN_6B (J6J2) Super IO
FANIN4 (PIN #75) Monitors SYS FAN_8A (J6J4) Super IO
FANIN5 (PIN #83) Monitors SYS FAN_8B (J6J4) Super IO
FANIN6 (PIN #36) Monitors SYS FAN_7A (J6J3) Super IO
FANIN7 (PIN #9) Monitors SYS FAN_7B (J6J3) Super IO
H_THEMP_DA/C Monitors processor temperature LM96000
Revision 1.3
74
Page 87

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
12.2 Fan Speed Control
LM96000
PWM1
PWM2
TACH1
TACH2
TACH3
Super IO
PC87427
FANIN0
FANIN1
FANIN2
PWM
CKT
FAN SPEED CNTL1
CPU
FAN
SYS
FAN3
SYS
FAN4
SYS
FAN2
SYS
FAN1
SYS FAN5
A
J7A11
JP5J1
JP5J2
JP7A1
JP6A1
J6J1
FANIN3
SYS FAN6
A
J6J2
FANIN4
75
FANIN5
FANIN6
FANIN7
Figure 10. Fan Speed Control Block Diagram
SYS FAN8
A
....................
SYS FAN7
A
J6J4
J6J3
Page 88

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
12.3 Chassis Intrusion
The Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E supports a chassis security feature that detects if the
chassis cover is removed. For the chassis intrusion circuit to function, the chassis’ power supply
must be connected to AC power. The security feature uses a mechanical switch on the chassis
that attaches to the chassis intrusion connector. When the chassis cover is removed the
mechanical switch is in the closed position.
13. Product Regulatory Compliance
13.1.1 Product Safety Compliance
The SE7221BK1-E complies with the following safety requirements:
UL 1950 - CSA 950 (US/Canada)
EN 60 950 (European Union)
IEC60 950 (International)
CE – Low Voltage Directive (73/23/EEC) (European Union)
EMKO-TSE (74-SEC) 207/94 (Nordics)
GOST R 50377-92 (Russia)
13.1.2 Product EMC Compliance
The SE7221BK1-E has been has been tested and verified to comply with the following
electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations when installed in a compatible Intel host
system. For information on compatible host system(s), contact your local Intel representative.
FCC (Class A Verification) – Radiated & Conducted Emissions (USA)
ICES-003 (Class A) – Radiated & Conducted Emissions (Canada)
CISPR 22, 3
EN55022 (Class A) – Radiated & Conducted Emissions (European Union)
EN55024 (Immunity) (European Union)
CE – EMC Directive (89/336/EEC) (European Union)
VCCI (Class A) – Radiated & Conducted Emissions (Japan)
AS/NZS 3548 (Class A) – Radiated & Conducted Emissions (Australia / New Zealand)
RRL (Class A) Radiated & Conducted Emissions (Korea)
BSMI CNS13438 (Class A) Radiated & Conducted Emissions (Taiwan)
GOST R 29216-91 (Class A) Radiated & Conducted Emissions (Russia)
GOST R 50628-95 (Immunity) (Russia)
rd
Edition (Class A) – Radiated & Conducted Emissions (International)
13.1.3 Product Regulatory Compliance Markings
This product is provided with the following product certification markings:
Revision 1.3
76
Page 89

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Table 87. Product Certification Markings
UL Recognition Mark
CE Mark
Russian GOST Mark
Australian C-Tick Mark
BSMI DOC Marking
BSMI EMC Warning
RRL MIC Mark
13.2 Electromagnetic Compatibility Notices
13.2.1 FCC (USA)
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
For questions related to the EMC performance of this product, contact:
Intel Corporation
5200 N.E. Elam Young Parkway
Hillsboro, OR 97124
1-800-628-8686
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
77
Page 90

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning
the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or
more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit other than the one to which the receiver
is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the grantee of this device could void
the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
The customer is responsible for ensuring
compliance of the modified product.
Only peripherals (computer input/output devices, terminals, printers, etc.) that comply with FCC
Class A or B limits may be attached to this server product. Operation with noncompliant
peripherals is likely to result in interference to radio and TV reception.
All cables used to connect to peripherals must be shielded and grounded. Operation with
cables, connected to peripherals, that are not shielded and grounded may result in interference
to radio and TV reception.
13.2.2 INDUSTRY CANADA (ICES-003)
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits for radio noise emissions from digital
apparatus set out in the interference-causing equipment standard entitled: “Digital Apparatus,”
ICES-003 of the Canadian Department of Communications.
Cet appareil numérique respecte les limites bruits radioélectriques applicables aux appareils
numériques de Classe A prescrites dans la norme sur le matériel brouilleur: “Apparelis
Numériques”, NMB-003 édictee par le Ministre Canadian des Communications.
13.2.3 Europe (CE Declaration of Conformity)
This product has been tested in accordance to, and complies with the Low Voltage Directive
(73/23/EEC) and EMC Directive (89/336/EEC). The product has been marked with the CE Mark
to illustrate its compliance.
13.2.4 Taiwan Declaration of Conformity
This product has been tested and complies with CNS13438. The product has been marked with
the BSMI DOC mark to illustrate compliance.
13.2.5 Korean RRL Compliance
This product has been tested and complies with MIC Notices No. 1997-41 and 1997-42. The
product has been marked with the MIC logo to illustrate compliance.
Revision 1.3
78
Page 91

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
The English translation for the above is as follows:
1. Type of Equipment (Model Name): SE7221BK1-E
2. Certification No.: Contact Intel Representative
3. Name of Certification Recipient: Intel
4. Date of Manufacturer: Marked on Product
5. Manufacturer / Nation : Intel
13.2.6 Australia / New Zealand
This product has been tested and complies with AS/NZS 3548. The product has been marked
with the C-Tick mark to illustrate compliance.
13.3 Replacing the Back-Up Battery
The lithium battery on the server board powers the RTC for up to 10 years in the absence of
power. When the battery starts to weaken, it loses voltage, and the server settings stored in
CMOS RAM in the RTC (for example, the date and time) may be wrong. Contact your customer
service representative or dealer for a list of approved devices.
WARNING
Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the same or equivalent
type recommended by the equipment manufacturer. Discard used batteries according to
manufacturer’s instructions.
ADVARSEL!
Lithiumbatteri - Eksplosionsfare ved fejlagtig håndtering. Udskiftning må kun ske med batteri af
samme fabrikat og type. Levér det brugte batteri tilbage til leverandøren.
ADVARSEL
Lithiumbatteri - Eksplosjonsfare. Ved utskifting benyttes kun batteri som anbefalt av
apparatfabrikanten. Brukt batteri returneres apparatleverandøren.
VARNING
Explosionsfara vid felaktigt batteribyte. Använd samma batterityp eller en ekvivalent typ som
rekommenderas av apparattillverkaren. Kassera använt batteri enligt fabrikantens instruktion.
VAROITUS
Paristo voi räjähtää, jos se on virheellisesti asennettu. Vaihda paristo ainoastaan
laitevalmistajan suosittelemaan tyyppiin. Hävitä käytetty paristo valmistajan ohjeiden mukaisesti.
79
Page 92

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
13.4 Calculated Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
The MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) for the Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E as
configured from the factory is shown in the table below.
Table 88. MTBF Data
Product Code Calculated MTBF Operating Temperature
SE7221BK1 TBD hours 35 degrees C
SE7221BK1LX TBD hours 35 degrees C
13.5 Mechanical Specifications
The following figure shows the Intel® Server Board SE7221BK1-E mechanical drawing. This
drawing will be updated in a future revision of this document.
Revision 1.3
80
Page 93

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Figure 11. SE7221BK1-E Server Board Mechanical Drawing
81
Page 94

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
The following figures show the I/O shield mechanical drawings for use in pedestal mount
applications such as the Intel® Server Chassis SC5200 for both sku ’s (SE7221BK1-E and
SE7221BK1-E (LX).
Figure 12. sku 1 Pedestal mount I/O shield mechanical drawing
Revision 1.3
82
Page 95

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Figure 13. sku 2 Pedestal mount I/O shield mechanical drawing
83
Page 96

Page 97

Glossary SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Glossary
This appendix contains important terms used in the preceding chapters. For ease of use,
numeric entries are listed first (e.g., “82460GX”) with alpha entries following (e.g., “AGP 4x”).
Acronyms are then entered in their respective place, with non-acronyms following.
Term Definition
ACPI Advanced Configuration and Power Interface
ANSI American National Standards Institute
AP Application Processor
ASIC Application Specific Integrated Circuit
ASR Asynchronous Reset
BGA Ball-grid Array
BIOS Basic input/output system
Byte 8-bit quantity.
CMOS In terms of this specification, this describes the PC-AT compatible region of battery-backed 128
bytes of memory, which normally resides on the server board.
DCD Data Carrier Detect
DMA Direct Memory Access
DMTF Distributed Management Task Force
ECC Error Correcting Code
EMC Electromagnetic Compatibility
EPS External Product Specification
ESCD Extended System Configuration Data
FDC Floppy Disk Controller
FIFO First-In, First-Out
FRU Field replaceable unit
GB 1024 MB.
GPIO General purpose I/O
GUID Globally Unique ID
Hz Hertz (1 cycle/second)
HDG Hardware Design Guide
I2C
IA Intel® architecture
ICMB Intelligent Chassis Management Bus
IERR Internal error
IMB Inter Module Bus
IP Internet Protocol
IRQ Interrupt Request
ITP In-target probe
KB 1024 bytes
KCS Keyboard Controller Style
LAN Local area network
LBA Logical Block Address
LCD Liquid crystal display
Inter-integrated circuit bus
I
Page 98

Glossary SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification
Term Definition
LPC Low pin count
LSB Least Significant Bit
MB 1024 KB
MBE Multi-Bit Error
Ms milliseconds
MSB Most Significant Bit
MTBF Mean Time Between Failures
Mux multiplexor
NIC Network Interface Card
NMI Non-maskable Interrupt
OEM Original equipment manufacturer
Ohm Unit of electrical resistance
PBGA Pin Ball Grid Array
PERR Parity Error
PIO Programmable I/O
PMB Private Management Bus
PMC Platform Management Controller
PME Power Management Event
PnP Plug and Play
POST Power-on Self Test
PWM Pulse-Width Modulator
RAIDIOS RAID I/O Steering
RAM Random Access Memory
RI Ring Indicate
RISC Reduced instruction set computing
RMCP Remote Management Control Protocol
ROM Read Only Memory
RTC Real Time Clock
SBE Single-Bit Error
SCI System Configuration Interrupt
SDR Sensor Data Record
SDRAM Synchronous Dynamic RAM
SEL System event log
SERIRQ Serialized Interrupt Requests
SERR System Error
SM Server Management
SMI Server management interrupt. SMI is the highest priority nonmaskable interrupt
SMM System Management Mode
SMS System Management Software
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol
SPD Serial Presence Detect
SSI Server Standards Infrastructure
TPS Technical Product Specification
UART Universal asynchronous receiver and transmitter
Revision 1.3
II
Page 99

SE7221BK1-E Technical Product Specification Glossary
Term Definition
USB Universal Serial Bus
VGA Video Graphic Adapter
VID Voltage Identification
VRM Voltage Regulator Module
Word 16-bit quantity
ZCR Zero Channel RAID
III
 Loading...
Loading...