Page 1
Intel® Entry Server Board
SE7221BA1-E
Technical Product Specification
Revision 1.5
Apr 10, 2005
Enterprise Platforms and Services Division
Page 2
Revision History Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
ii Revision 1.5
Revision History
Date Revision
Number
Modifications
September
30, 2004
0.8 Initial Draft
Oct 20, 2004 0.9 Second Draft
Nov 11, 2004 0.99 Final Draft
Dec 31, 2004 1.00 Release
Jan 4, 2004 1.1 Web links updated
Jan 25, 2005 1.2 Updated
Sep 16, 2005 1.3 Updated with supported video resolutions
Oct 5, 2005 1.4 Update the memory information
Apr 10, 2006 1.5 Updated release
Page 3

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Disclaimers
Revision 1.5 iii
Disclaimers
Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel® products. No license, express or implied,
by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document. Except as
provided in Intel's Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products, Intel assumes no liability whatsoever,
and Intel disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating to sale and/or use of Intel products including
liability or warranties relating to fitness for a particular purpose, merchantability, or infringement of any
patent, copyright or other intellectual property right. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life
saving, or life sustaining applications. Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions
at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked
"reserved" or "undefined." Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility
whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
This document contains information on products in the design phase of development. Do not finalize a
design with this information. Revised information will be published when the product is available. Verify
with your local sales office that you have the latest datasheet before finalizing a design.
Intel Corporation server baseboards contain a number of high-density VLSI and power delivery
components which need adequate airflow to cool. Intel’s own chassis are designed and tested to meet
the intended thermal requirements of these components when the fully integrated system is used
together. It is the responsibility of the system integrator that chooses not to use Intel developed server
building blocks to consult vendor datasheets and operating parameters to determine the amount of
airflow required for their specific application and environmental conditions. Intel Corporation cannot be
held responsible if components fail or the server board does not operate correct ly when used ou tside any
of its published operating or non-operating limits.
The Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E
may contain design defects or errors known as errata
which may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are
available on request.
This document and the software described in it is furnished under license and may only be used or
copied in accordance with the terms of the license. The information in this manual is furnished for
informational use only, is subject to change without notice, and should not be construed as a commitment
by Intel Corporation. Intel Corporation assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies
that may appear in this document or any software that may be provided in association with this document.
Except as permitted by such license, no part of this document may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval
system, or transmitted in any form or by any means without the express written consent of Intel
Corporation.
Intel, Pentium, Itanium, and Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
*Other brands and names may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © Intel Corporation 2004-2005
.
Page 4

Table of Contents Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
iv Revision 1.5
Table of Contents
1. Introduction ..........................................................................................................................1
2. Server Board Overview........................................................................................................3
2.1 Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E SKU Availability.....................................3
2.2 Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E Feature Set............................................3
2.3 Block Diagram .........................................................................................................4
2.4 Board Layout ....................................................................... ....................................5
3. Functional Architecture.......................................................................................................6
3.1 Processor Subsystem....................................................................... .......................6
3.1.1 Processor VRD................................................. .......................................................6
3.1.2 Reset Configuration Logic....................................................................................... 6
3.1.3 Processor Module Presence Detection ........................... ....................................... .6
3.1.4 Processor Support...................................................................................................6
3.1.5 Interrupts and APIC.................................................................................................7
3.2 Memory Subsystem.................................................................................................7
3.2.1 DIMM Socket Features:...........................................................................................7
3.2.2 Supported DIMM Configurations .............................................................................8
3.2.3 Memory Configurations............................................................................................8
3.3 Intel 7221 Chipset..................................................................................................12
3.3.1 USB Interface........................................................................................................12
3.3.2 IDE Support...........................................................................................................12
3.3.3 Real-Time Clock, CMOS SRAM, and Battery........................................................13
3.4 I/O Controller ..................................... ..................................... ...............................14
3.4.1 Serial Port..............................................................................................................14
3.4.2 Parallel Port......................................................................... ..................................14
3.4.3 Diskette Drive Controller........................................................................................ 14
3.4.4 Keyboard and Mouse Interface..............................................................................14
3.5 Hardware Management Subsystem......................... ........................................ ......14
3.5.1 Hardware Monitoring and Fan Control ASIC................................................... ......14
3.5.2 Thermal Monitoring.......................................................................................... ......15
3.5.3 Fan Monitoring......................................................................................... ..............16
3.5.4 Chassis Intrusion and Detection.................................................. ..........................16
3.6 Power Management...............................................................................................16
Page 5

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Table of Contents
Revision 1.5 v
3.6.1 Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) ...........................................16
3.6.2 System States and Power States........................................ ..................................17
3.6.3 Hardware Support..................................................................................................18
4. Maps and Interrupts........................................................................................................... 21
4.1 Memory Resources................................................................................................21
4.1.1 Memory Map..........................................................................................................21
4.1.2 Addressable Memory.............................................................................................21
4.2 Fixed I/O Map........................................................................................................23
4.3 DMA Channels.......................................................................................................23
4.4 PCI Configuration Space Map....................................................... ........................24
4.5 Interrupts................................................................................................................24
4.6 PCI Conventional Interrupt Routing Map...............................................................25
5. Input Output Subsystem....................................................................................................27
5.1 PCI Subsystem......................................................................................................27
5.1.1 PCI Express* Connectors......................................................................................27
5.1.2 PCI 32....................................................................................................................27
5.2 LAN Subsystem.....................................................................................................27
5.2.1 Marvell Yukon* 88E8050 Gigabit Ethernet Controller............................................27
5.2.2 Intel® 82551QM Integrated 10/100 LAN controller................................................28
5.2.3 RJ-45 LAN Connector with Integrated LEDs .........................................................28
5.2.4 Alert Standard Format (ASF) Support ...................................................................29
5.3 Hardware Management Subsystem......................... ........................................ ......30
5.3.1 Hardware Management.........................................................................................30
5.3.2 Hardware Monitoring and Fan Control ASIC................................................... ......30
6. Connections and Jumper Blocks .....................................................................................31
6.1 Connectors ............................................................................................................31
6.1.1 Back Panel Connectors.........................................................................................31
6.1.2 Component-side Connectors.................................................................................32
6.1.3 Front Panel USB Connectors ................................................................................35
6.1.4 Power Supply Connectors.....................................................................................36
6.1.5 Add-in Card Connectors........................................................................................37
6.2 Jumper Blocks.................................................... ..................................... ..............37
7. System BIOS.......................................................................................................................39
7.1 BIOS Identification String.......................................................................................39
7.2 Introduction............................................................................................................39
Page 6

Table of Contents Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
vi Revision 1.5
7.3 BIOS Flash Memory Organization.........................................................................40
7.4 Resource Configuration................................................................. ........................40
7.4.1 PCI Autoconfiguration............................................................................................40
7.4.2 PCI IDE Support....................................................................................................40
7.5 System Management BIOS (SMBIOS).................................................. ................41
7.6 Legacy USB Support. ............................................................................................41
7.7 BIOS Updates ........................................................................................................42
7.7.1 Language Support.................................................................................................42
7.7.2 Custom Splash Screen..........................................................................................42
7.8 Boot Options..........................................................................................................42
7.8.1 CD-ROM Boot........................................................................................................42
7.8.2 Network Boot.........................................................................................................42
7.8.3 Booting Without Attached Devices ........................................................................42
7.9 BIOS Security Features.........................................................................................43
7.10 Error Messages and Beep Codes..........................................................................44
7.10.1 BIOS Error Messages............................................................................................44
7.10.2 Port 80h POST Codes...........................................................................................45
7.11 Bus Initialization Checkpoints................................................................................49
7.12 Speaker .................................................................................................................50
7.13 BIOS Beep Codes .................................................................................................50
8. General Specification.........................................................................................................51
8.1 Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E Power Budget......................................51
8.1.1 DC Loading............................................................................................................51
9. Platform Management........................................................................................................53
9.1 Platform Management Overview............................ ................................................53
10. Error Reporting...................................................................................................................53
10.1 Fault Resilient Booting...........................................................................................53
11. Design and Environmental Specifications.......................................................................53
11.1 Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E Design Specification............................53
12. Regulatory Compliance ...................................... ..................................... ..........................55
12.1 Safety Regulations.................................................................................................55
12.2 EMC Regulations...................................................................................................55
12.2.1 FCC Compliance Statement (USA).......................................................................56
12.2.2 Canadian Compliance Statement..........................................................................56
12.3 European Union Declaration of Conformity Statement..........................................56
Page 7

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Table of Contents
Revision 1.5 vii
12.4 Product Ecology Statements .................................................................................57
12.4.1 Disposal Considerations........................................................................................57
12.4.2 Recycling Considerations......................................................................................57
12.5 Product Certification Markings (Board Level) ........................................................58
13. Miscellaneous Board Information.....................................................................................59
13.1 ATX Baseboard Mechanical Specifications...........................................................59
13.2 I/O Shield Mechanical Specification ......................................................................59
13.3 Thermal Considerations................................................ .........................................60
13.4 Calculated Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF).................................................. .63
13.5 Environmental........................................................................................................63
13.6 Clearing CMOS......................................................................................................63
13.7 Supported video resolution....................................................................................64
Glossary........................................................................................................................................I
Reference Documents................................................................ ..................................... ..........III
Page 8

List of Figures Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
viii Revision 1.5
List of Figures
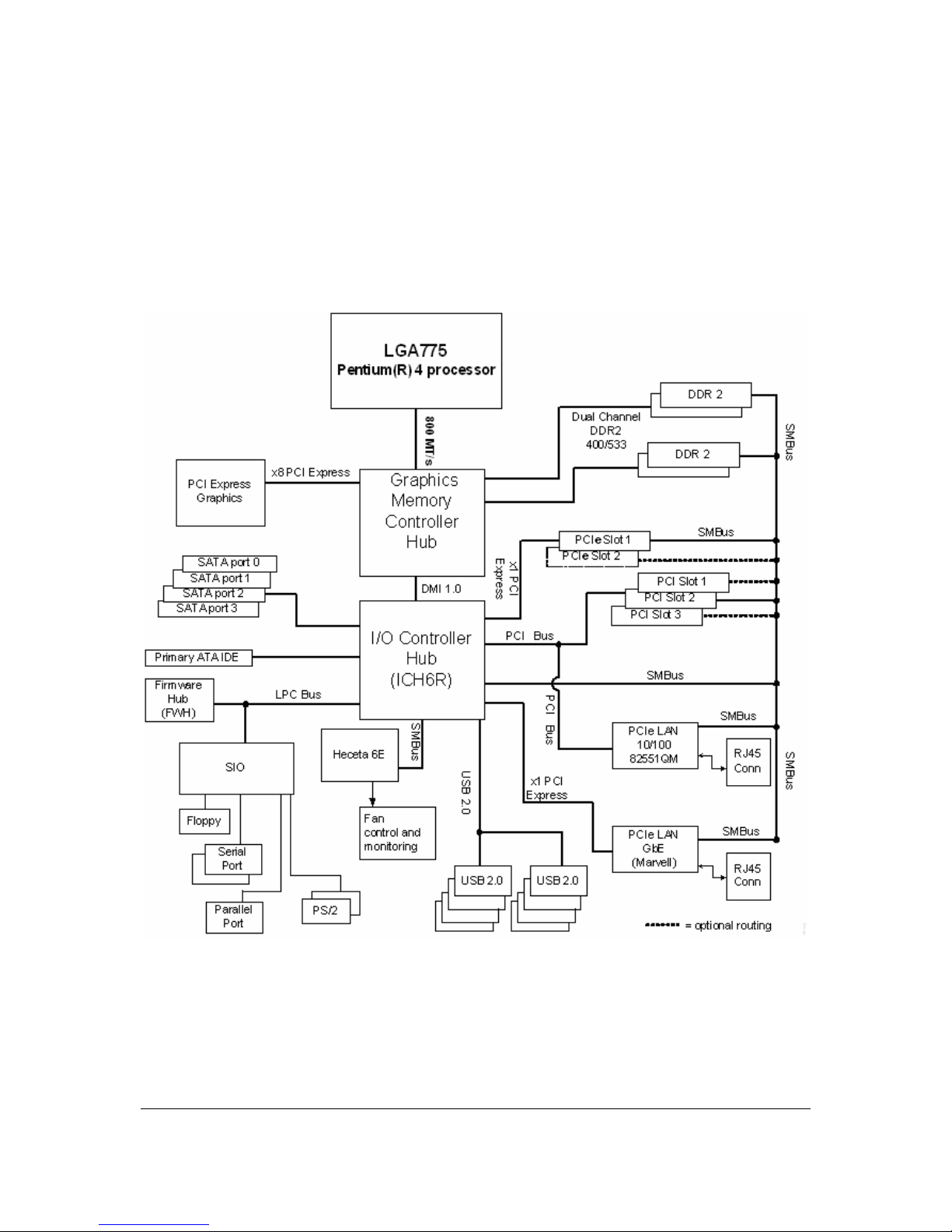
Figure 1. Block Diagram ...................................................................... ........................................4
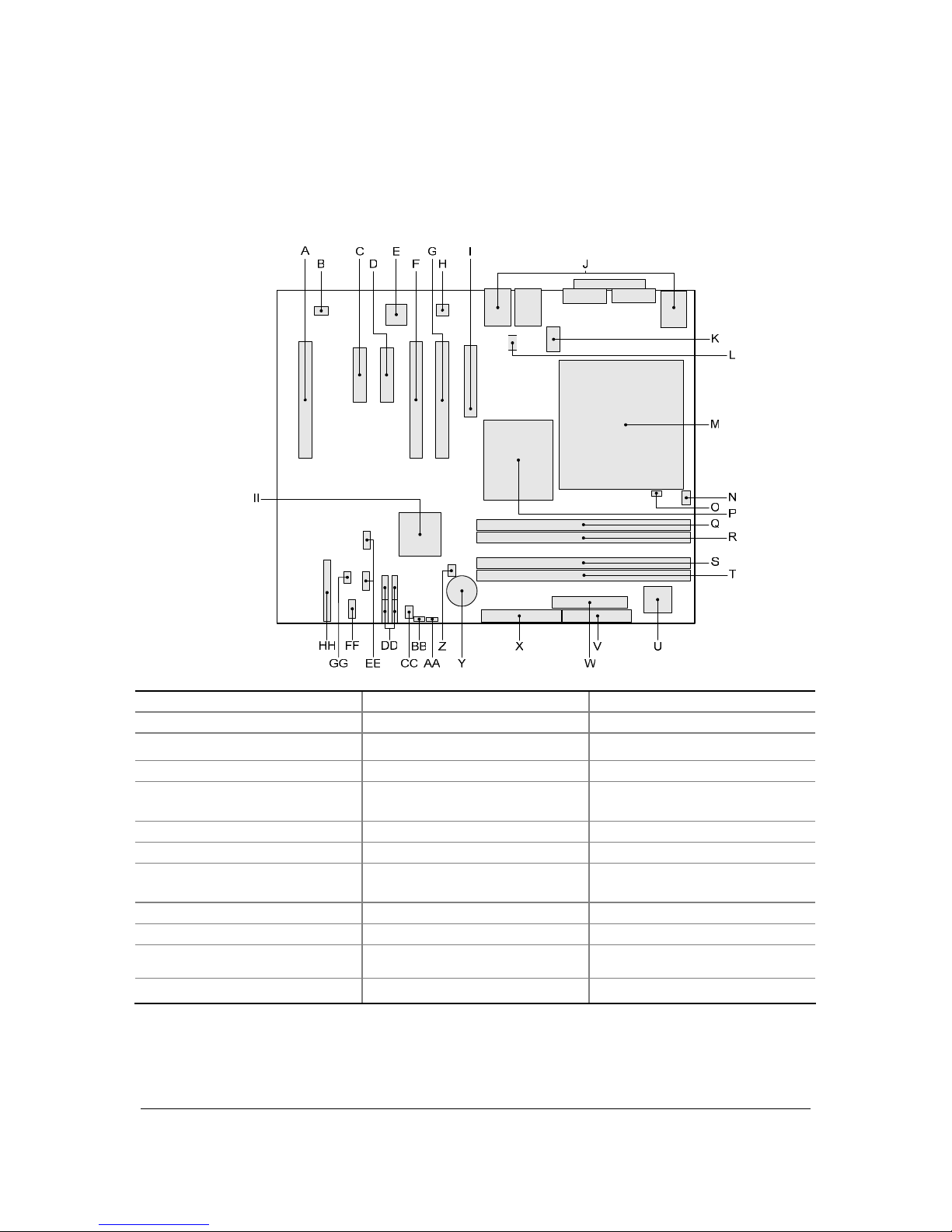
Figure 2. Intel ® Server Board SE7221BA1-E Components........................................................5
Figure 3. Dual Channel (Interleaved) Mode Configurations.........................................................9
Figure 4. Dual Channel (Interleaved) Mode Configuration with Two DIMMs...............................9
Figure 5. Dual Channel (Interleaved) Mode Configuration with Three DIMMs..........................10
Figure 6. Dual Channel (Interleaved) Mode Configuration with Four DIMMs............................10
Figure 7. Single Channel (Asymmetric) Mode Configuration with One DIMM...........................11
Figure 8. Single Channel (Asymmetric) Mode Configuration with Three DIMMs.......................11
Figure 9. Thermal Monitoring................................... ..................................... .............................15
Figure 10. Detailed System Memory Address Map....................................................................22
Figure 11. LAN Connector LED Locations.................................................................................28
Figure 12. Back Panel Connectors............................................................................................31
Figure 13. Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E Component-side Connectors..................32
Figure 14. SSI Connector ..........................................................................................................35
Figure 15. Connection Diagram for Front Panel USB Connectors ............................................36
Figure 16. Location of the Jumper Block ...................................................................................38
Figure 17. Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E Dimensions.............................................59
Figure 18. I/O Shield..................................................................................................................60
Figure 19. Processor Heatsink for Omni-directional Airflow ......................................................61
Figure 20. Localized High Temperature Zones..........................................................................62
Page 9

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS List of Tables
Revision 1.5 ix
List of Tables
Table 1. Supported Memory Configurations................................................................................8
Table 2. Power Switch Options..................................................................................................17
Table 3. Power States and Targeted System Power.................................................................17
Table 4. Wake-up Devices and Events.......................................................................................19
Table 5. System Memory Map...................................................................................................21
Table 6. I/O Map........................................................................................................................23
Table 7. DMA Channels.............................................................................................................23
Table 8. PCI Configuration Space Map .....................................................................................24
Table 9. Interrupts......................................................................................................................25
Table 10. PCI Interrupt Routing Map.........................................................................................26
Table 11. LAN Connector LED States.......................................................................................29
Table 12. Back Panel Connectors .............................................................................................32
Table 13. Front Chassis Fan and Rear Chassis Fan Connectors ............................................33
Table 14. Processor Fan Connector and Auxiliary Rear Fan Connector..................................33
Table 15. Chassis Intrusion Connector......................................................................................33
Table 16. SCSI Hard Drive Activity LED Connector (Optional)..................................................33
Table 17. Serial ATA Connectors ..............................................................................................33
Table 18. Auxiliary Power Output Connector.............................................................................34
Table 19. Front Panel SSI Connector........................................................................................34
Table 20. Main Power Connector ..............................................................................................36
Table 21. ATX12V Power Connector.........................................................................................37
Table 22. BIOS Setup Configuration Jumper Settings...............................................................38
Table 23. CMOS Clear Jumper Configuration...........................................................................38
Table 24. BIOS Setup Program Menu Bar.................................................................................39
Table 25. BIOS Setup Program Function Keys .........................................................................40
Table 26. Supervisor and User Password Functions.................................................................43
Table 27. BIOS Error Messages................................................................................................44
Table 28. Uncompressed INIT Code Checkpoints.....................................................................45
Table 29. Boot Block Recovery Code Checkpoints...................................................................45
Table 30. Runtime Code Uncompressed in F000 Shadow RAM...............................................46
Table 31. Bus Initialization Checkpoints....................................................................................49
Table 32. Upper Nibble High Byte Functions.............................................................................49
Page 10

List of Tables Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
x Revision 1.5
Table 33. Lower Nibble High Byte Functions.............................................................................49
Table 34. Beep Codes...............................................................................................................50
Table 35. DC Power Budget......................................................................................................51
Table 36. Safety Regulations.....................................................................................................55
Table 37. EMC Regulations.......................................................................................................55
Table 38. Product Certification Markings..................................................................... ..............58
Table 39. Thermal Considerations for Components ..................................................................62
Table 40. Calculated Mean Time Between Failure....... .............................................................63
Table 41. Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E Environmental Specifications...................63
Page 11

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Introduction
Revision 1.5 1
1. Introduction
This Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E Technical Product Specification (TPS) provides a
high-level technical description for the Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E. It details the
architecture and feature set for all functional sub-systems that make up the server board.
This document is divided into the following main categories:
Chapter 2: Server Board Overview
Chapter 3: Functional Architecture
Chapter 4: Technical Reference
Chapter 5: Connectors and Jumper Blocks
Chapter 6: Overview of BIOS Features
Chapter 7: BIOS Setup Program
Chapter 8: Error Reporting and Handling
Chapter 9: General Specifications
Page 12

Introduction Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
2 Revision 1.5
<This page intentionally left blank.>
Page 13

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Server Board Overview
Revision 1.5 3
2. Server Board Overview
2.1 Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E SKU Availability
2.2 Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E Feature Set
The Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E provides the following feature set:
• Support for an Intel® Pentium® 4 processor in an LGA775 socket
• Intel® Pentium® 4 Processors Extreme Edition
• Intel® Pentium® 4 Processors
• Intel® Celeron® D Processors
• 800 and 533 MHz system bus
• Intel®
7221 Chipset
• Intel® E7221MC Memory Controller Hub (GMCH)
• Intel®
82801FR I/O Controller Hub (ICH6-R)
• 8 Mbit Firmware Hub (FWH)
• Support for 4 GB of Un-buffered ECC memory
• Four 240-pin DDR2 SDRAM Dual Inline Memory Module (DIMM) sockets
• Support for DDR2 400 MHz and DDR2 533 MHz DIMMs
• Intel® E7221MC GMCH integrated PCI Express* x8 Graphics Controller
• Marvell Yukon* 88E8050 PCI Express* Gigabit Ethernet Controller
• Intel® 82551QM Integrated 10/100 LAN Controller
• Expansion Capabilities
• Three PCI Conventional bus add-in card connectors (SMBus routed to PCI Conventional
bus connector 2)
• Two PCI Express* x4 bus add-in card connectors with x1 throughput.
• One PCI Express* x8 bus add-in card connector with x8 throughput
• Four external USB 2.0 ports on the back panel and two 2x5 USB connectors on the
mother board. Each connector supports two additional USB ports for a total of eight USB
2.0 ports on the platform.
• One external Serial Port
• One external Parallel Port
• Four Serial ATA interfaces
• One Parallel ATA IDE interface with UDMA 33, ATA-66/100 support
• One diskette drive interface
• Hardware Monitor Subsystem
• Hardware monitoring and fan control ASIC
• Voltage sense to detect out of range power supply voltages
• Thermal sense to detect out of range thermal values
Page 14
Server Board Overview Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
4 Revision 1.5
• Four fan connectors
• Four fan sense inputs used to monitor fan activity
2.3 Block Diagram
The figure below shows a block diagram of the Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E.
Figure 1. Block Diagram
Page 15
Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Server Board Overview
Revision 1.5 5
2.4 Board Layout
The figure below shows the location of the major components on the Intel® Entry Server Board
SE7221BA1-E.
A Conventional PCI slot 3 M LGA775 processor socket Y Battery
B Rear fan connector
N CPU fan connector Z Intruder connector
C PCIE slot 2 (x4 Connector) O Hardware Management controller AA BIOS configuration jumper
D PCIE slot 1 (x4 Connector)
P Intel
®
E7221MC GMCH
BB Clear CMOS jumper
E Intel® 82551QM LAN controller
Q Channel A DIMM 0 (Blue) Socket CC Front fan connector
F Conventional PCI slot 2
R Channel A DIMM 1 (Black) Socket DD Serial ATA connectors
G Conventional PCI slot 1
S Channel B DIMM 0 (Blue) Socket
EE Front panel USB connectors
H Marvell Yukon* 88E8050 PCI
Express* Gigabit Ethernet Controller
T Channel B DIMM 1 (Black) Socket FF Serial B connector
I PCI Express* 1 x8 slot U I/O controller
GG SCSI LED connector
J Back Panel I/O V Diskette drive connector
HH Front panel connector
K 2 x4 power connector W 2x12 Power connector
II Intel
®
82801FR ICH6R I/O
Controller Hub
L Vreg fan connector X Parallel ATA IDE connector
Figure 2. Intel ® Server Board SE7221BA1-E Components
Page 16

Functional Architecture Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
6 Revision 1.5
3. Functional Architecture
3.1 Processor Subsystem
The Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E supports Intel® Pentium® 4 and Celeron® D
processors in the 775-land package, with enhancements to the Intel
®
NetBurst® micro-
architecture. The Intel
®
Pentium® 4 and Celeron® processors built on 90 nm process in the
775-land package utilize Flip-Chip Land Grid Array (FC-LGA4) package technology, and plug
into a 775-land LGA socket, referred to as the LGA775 socket. Pentium® 4 and Celeron
®
D
processors in the 775-land package are based on the same Intel® 32-bit micro-architecture and
maintain the tradition of compatibility with IA-32 software. This generation of the Pentium
®
4
Processor also supports Intel
®
EM64T (Extended Memory 64 Technology) for 64bit native mode
operation with 64bit operating systems. The Intel
®
Celeron® D Processor does not support
Intel
®
EM64T.
3.1.1 Processor VRD
The Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E has a VRD (Voltage Regulator Down) to support
one processor. The VRD is compliant with the VRM 10.1 specification and provides a maximum
of 120A, which is capable of supporting the requirements for Intel
®
Pentium® 4 and Intel®
Celeron
®
D processors.
The board hardware monitors the processor VTTEN (Output enable for VTT) pin before turning
on the VRD. If the VTTEN pin of the processors is not identical, then the Power ON Logic will
not turn on the VRD.
3.1.2 Reset Configuration Logic
The BIOS determines the processor stepping, cache size, etc through the CPUID instruction.
The requirements are as follows:
• The Processor will run at a fixed speed, but can be programmed by BIOS to operate at a
lower or higher speed.
• The processor information is read at every system power-on.
• No manual processor speed setting options exist either in the form of a BIOS setup
option or jumpers.
3.1.3 Processor Module Presence Detection
Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E does not support this function.
3.1.4 Processor Support
The Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E supports one Intel® Pentium® 4 or Celeron® D
processor in an LGA775 processor socket with an 800 or 533 MHz system bus.
Check the Intel® web site http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/se7221ba1-e/
for the most up-to-date list of supported processors.
Page 17
Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Functional Architecture
Revision 1.5 7
CAUTION
1. Use only the processors listed on web site above. Use of unsupported
processors can damage the board, the processor, and the power supply.
2. Use only ATX12V or EPS 12V-compliant power supplies.
3.1.5 Interrupts and APIC
Interrupt generation and notification to the processor is accomplished by the APICs in the
ICH6R using messages on the front side bus.
3.2 Memory Subsystem
The baseboard supports up to four DIMM slots for a maximum memory capacity of 4 GB. The
DIMM organization is x72, which includes eight ECC che ck bits. The memory interface runs at
400/533MT/s. The memory controller supports memory scrubbing, single-bit error correction and
multiple-bit error detection. Memory can be implemented with either single sided (one row) or
double-sided (two row) DIMMs.
3.2.1 DIMM Socket Features:
The Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E has four DIMM sockets and supports the following
memory features:
• 1.8 V (only) DDR2 SDRAM DIMMs
• Un-buffered, single-sided or double-sided DIMMs with the following restriction:
Double-sided DIMMS with x16 organization are not supported.
• 4 GB maximum total system memory. Minimum total system memory: 128 MB
• Un-buffered, ECC DIMMS
• Serial Presence Detect
• DDR2 533 MHz 128MB, 256MB, 512MB and 1GB SDRAM DIMM
• DDR2 400 MHz 128MB, 256MB, 512MB and 1GB SDRAM DIMM
Check the Intel® web site http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/se7221ba1-e/
for the most up-to-date list of supported memory.
NOTES
• Remove any card inserted into the PCI Express* x8 slot before installing or upgrading
memory to avoid interference with the memory retention mechanism.
• To be fully compliant with all applicable DDR SDRAM memory specifications, the
board should be populated with DIMMs that support the Serial Presence Detect (SPD)
data structure. This allows the BIOS to read the SPD data and program the chipset to
accurately configure memory settings for optimum performance. If non-SPD memory
is installed, the BIOS will attempt to correctly configure the memory settings, but
performance and reliability may be impacted or the DIMMs may not function under the
determined frequency.
• Please ensure that the memory module is fully seated and both latches are secure. If
the module is not fully installed the memory may not be recognized by the BIOS.
• The memory controller hub (MCH) cannot support identifying which slot the memory
error has occured. The MCH can only determine the channel for the memory error
Page 18
Functional Architecture Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
8 Revision 1.5
• Regardless of the physical memory installed, there will always 64KB base memory and
8MB system memory occupied by system memory allocation, the left part will be
accounted as extended memory. The memory amount showed on post is extended
memory.
Supported DIMM Configurations
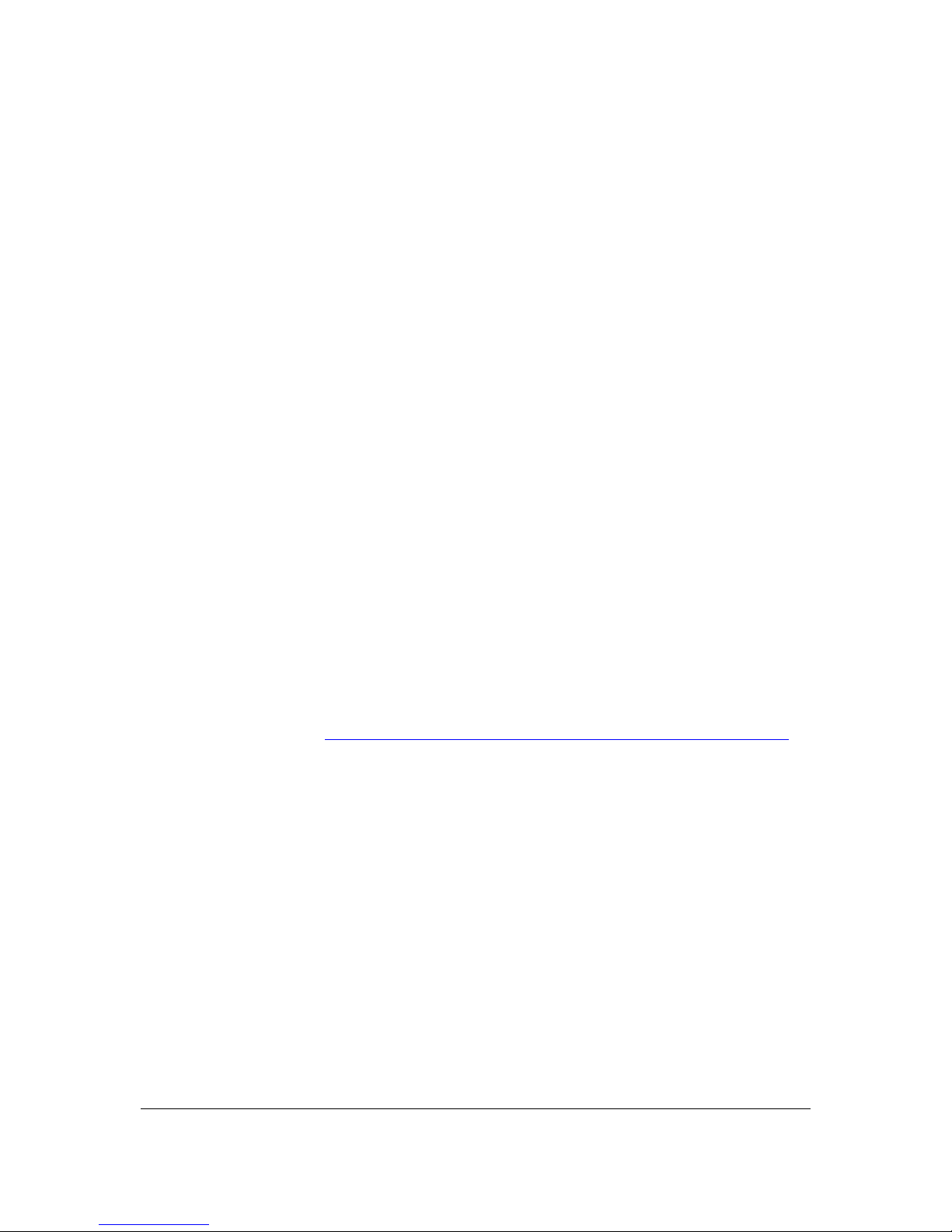
Table 1. Supported Memory Configurations
DIMM
Capacity
Configuration
SDRAM Density SDRAM Organization
Front-side/Back-side
Number of SDRAM
Devices
128 MB SS 256 MB 16 M x 16/empty 4
256 MB SS 256 MB 32 M x 8/empty 8
256 MB SS 512 MB 32 M x 16/empty 4
512 MB DS 256 MB 32 M x 8/32 M x 8 16
512 MB SS 512 MB 64 M x 8/empty 8
512 MB SS 1 GB 64 M x 16/empty 4
1024 MB DS 512 MB 64 M x 8/64 M x 8 16
1024 MB SS 1 GB 128 M x 8/empty 8
2048 MB DS 1 GB 128 M x 8/128 M x 8 16
Note: In the second column, “DS” refers to double-sided memory modules (containing two rows of SDRAM) and “SS”
refers to single-sided memory modules (containing one row of SDRAM).
3.2.2 Memory Configurations
The Intel® E7221MC GMCH supports two types of memory organization:
• Dual channel (Interleaved) mode. This mode offers the highest throughput for real
world applications. Dual channel mode is enabled when the installed memory capacities
of both DIMM channels are equal. Technology and device width can vary from one
channel to the other but the installed memory capacity for each channel must be equal.
If different speed DIMMs are used between channels, the slowest memory timing will be
used.
• Single channel (Asymmetric) mode. This mode is equivalent to single channel
bandwidth operation for real world applications. This mode is used when only a single
DIMM is installed or the memory capacities are unequal. Technology and device width
can vary from one channel to the other. If different speed DIMMs are used between
channels, the slowest memory timing will be used.
NOTE
The DIMM0 sockets of both channels are blue. The DIMM1 sockets of both channels are black.
Page 19
Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Functional Architecture
Revision 1.5 9
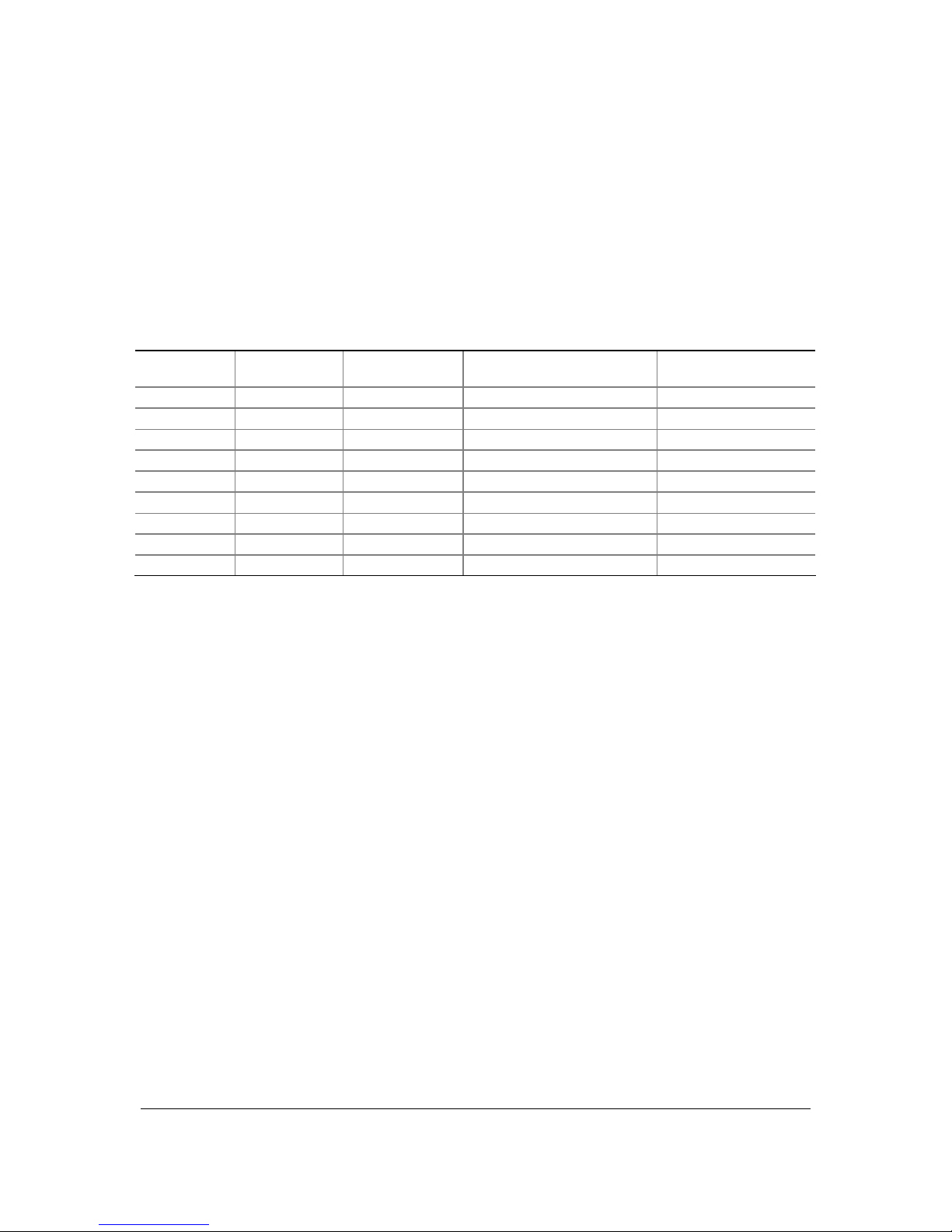
3.2.2.1 Memory channel and DIMM configuration.
OM16677
Channel A, DIMM
0
Channel A, DIMM 1
Channel B, DIMM
0
Channel B, DIMM 1
`
Figure 3. Dual Channel (Interleaved) Mode Configurations
3.2.2.2 Dual Channel (Interleaved) Mode Configurations
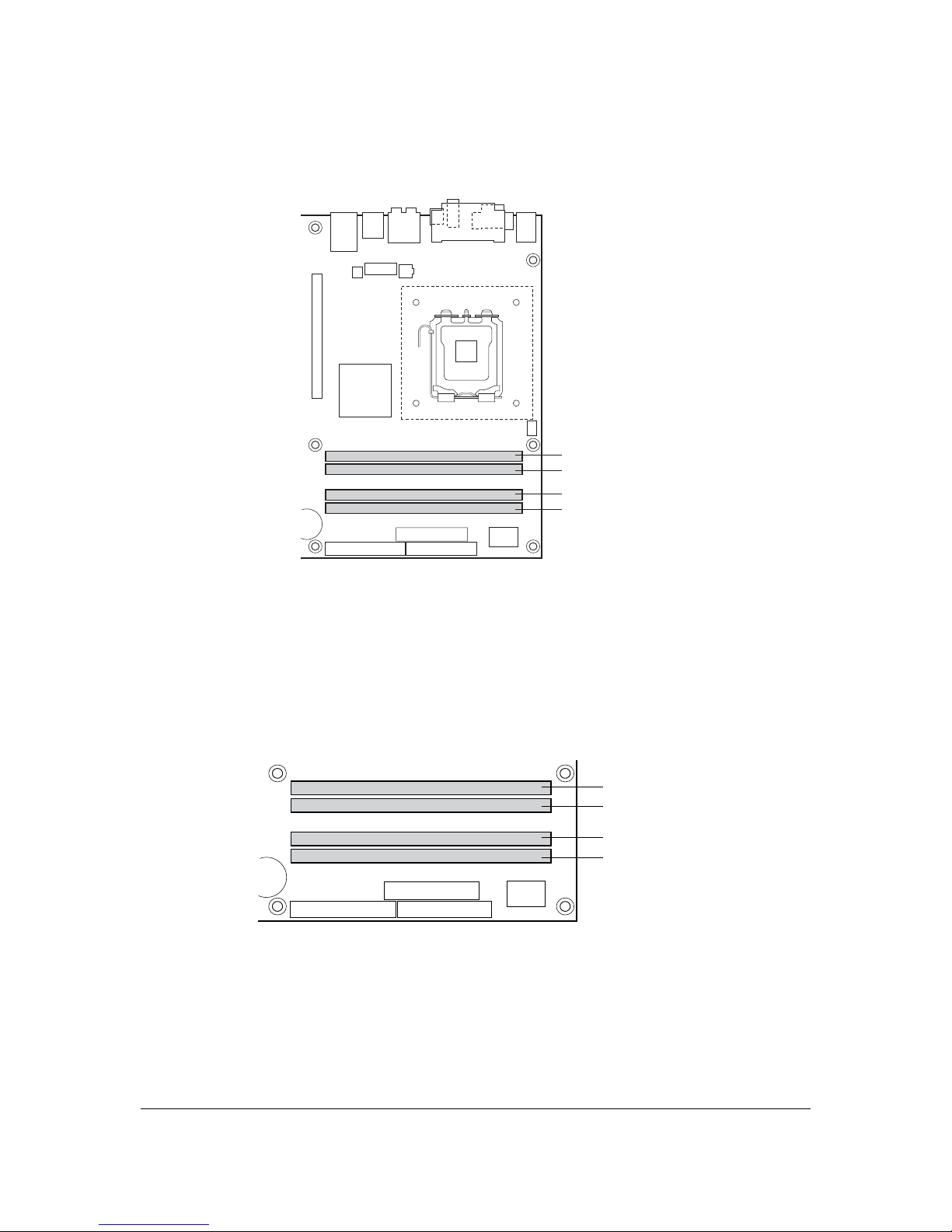
The following figure shows a dual channel configuration using two DIMMs. In this example, the
DIMM0 (blue) sockets of both channels are populated with identical DIMMs.
OM17123
Channel A, DIMM 0
Channel A, DIMM 1
Channel B, DIMM 0
Channel B, DIMM 1
1 GB
1 GB
Figure 4. Dual Channel (Interleaved) Mode Configuration with Two DIMMs
Page 20
Functional Architecture Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
10 Revision 1.5
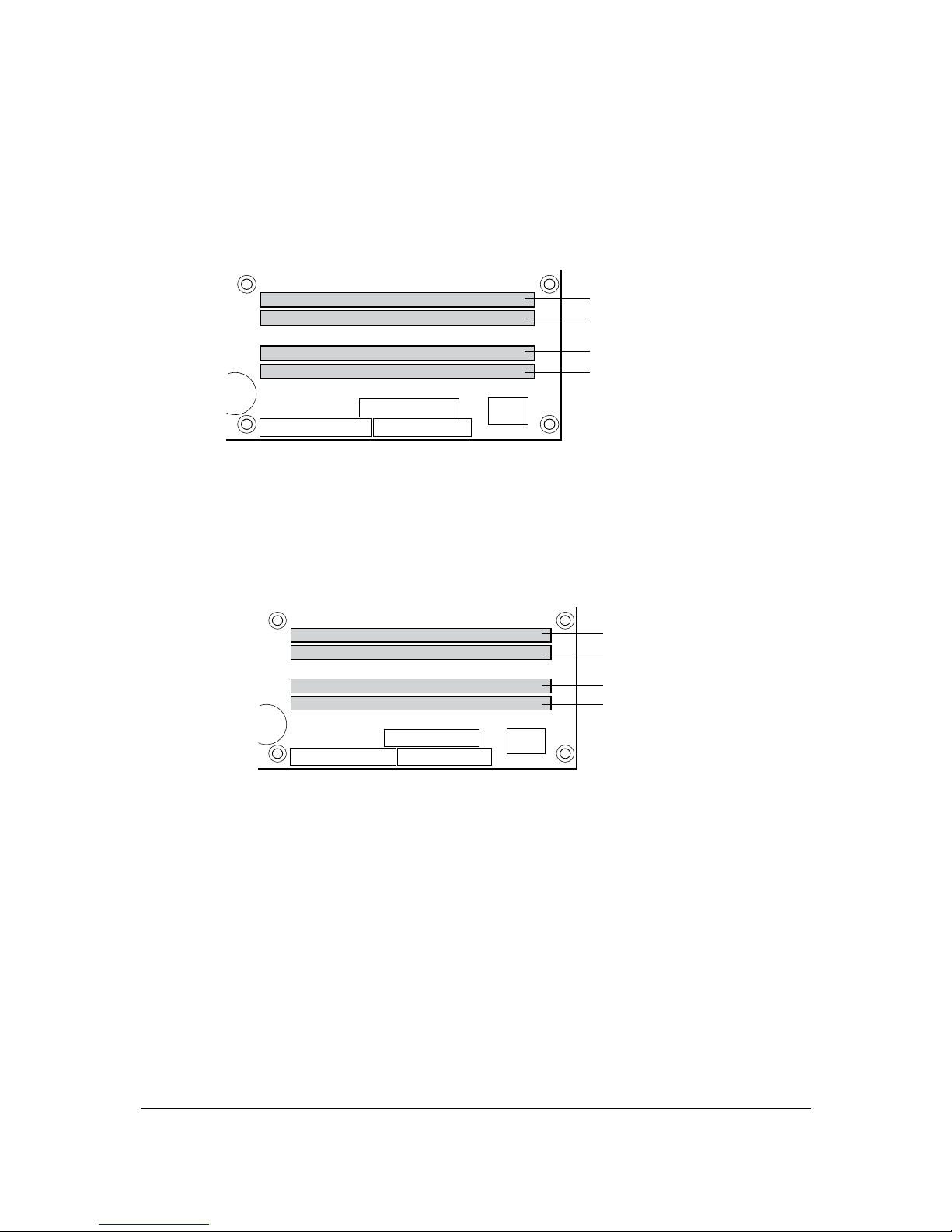
The following figure shows a dual channel configuration using three DIMMs. In this example,
the combined capacity of the two DIMMs in Channel A equal the capacity of the single DIMM in
the DIMM0 (blue) socket of Channel B.
OM17122
Channel A, DIMM 0
Channel A, DIMM 1
Channel B, DIMM 0
Channel B, DIMM 1
256 MB
512 MB
256 MB
Figure 5. Dual Channel (Interleaved) Mode Configuration with Three DIMMs
Figure 6 shows a dual channel configuration using four DIMMs. In this example, the combined
capacity of the two DIMMs in Channel A equal the combined capacity of the two DIMMs in
Channel B. Also, the DIMMs are matched between DIMM0 and DIMM1 of both channels.
OM17124
Channel A, DIMM 0
Channel A, DIMM 1
Channel B, DIMM 0
Channel B, DIMM 1
256 MB
256 MB
512 MB
512 MB
Figure 6. Dual Channel (Interleaved) Mode Configuration with Four DIMMs
Page 21
Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Functional Architecture
Revision 1.5 11
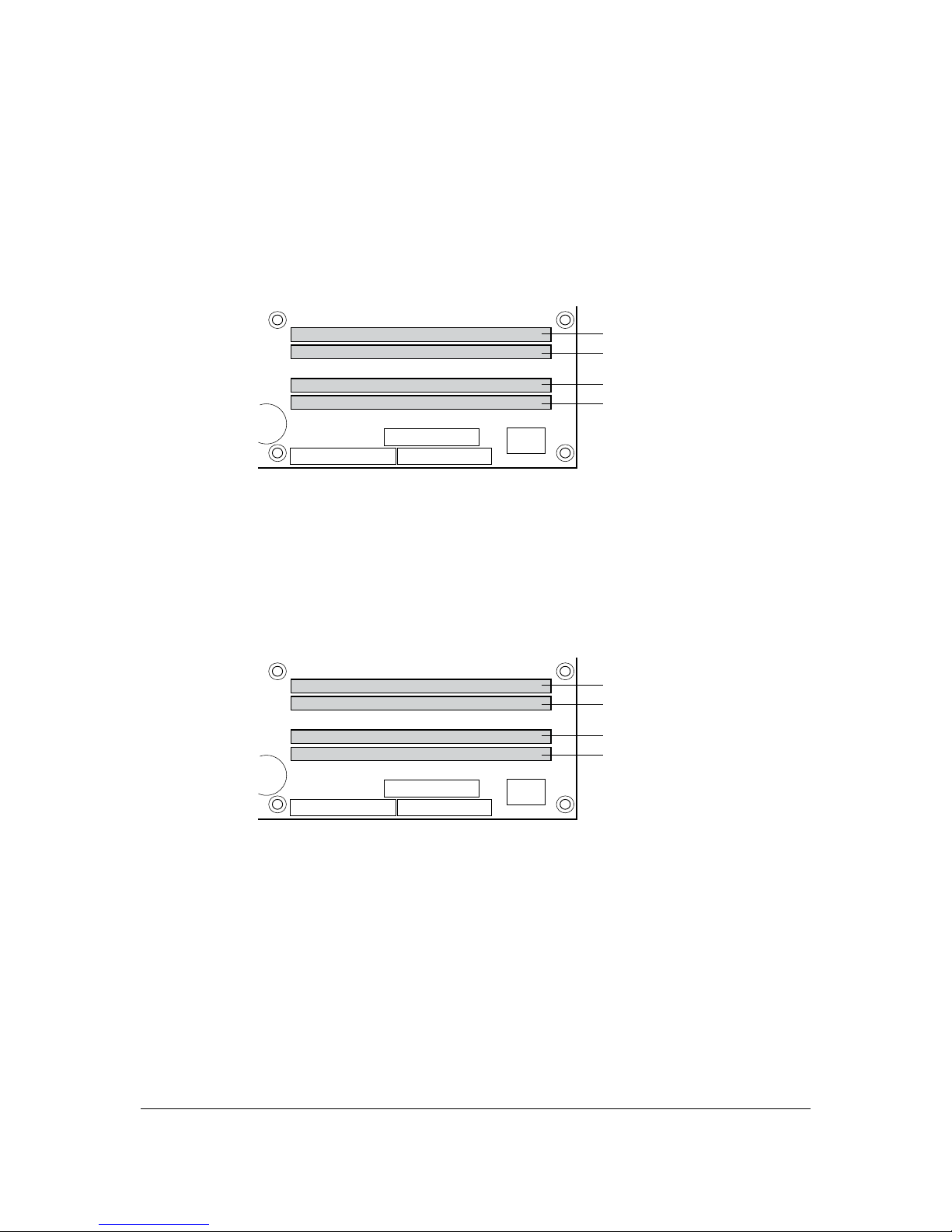
3.2.2.3 Single Channel (Asymmetric) Mode Configurations
NOTE
Dual channel (Interleaved) mode configurations provide the highest memory throughput.
Figure 7 shows a single channel configuration using one DIMM. In this example, only the
DIMM0 (blue) socket of Channel A is populated. Channel B is not populated.
OM17125
Channel A, DIMM 0
Channel A, DIMM 1
Channel B, DIMM 0
Channel B, DIMM 1
256 MB
Figure 7. Single Channel (Asymmetric) Mode Configuration with One DIMM
Figure 8 shows a single channel configuration using three DIMMs. In this example, the
combined capacity of the two DIMMs in Channel A does not equal the capacity of the single
DIMM in the DIMM0 (blue) socket of Channel B.
OM17126
Channel A, DIMM 0
Channel A, DIMM 1
Channel B, DIMM 0
Channel B, DIMM 1
256 MB
512 MB
512 MB
Figure 8. Single Channel (Asymmetric) Mode Configuration with Three DIMMs
Page 22

Functional Architecture Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
12 Revision 1.5
3.3 Intel 7221 Chipset
The Intel® 7221 chipset consists of the following devices:
• Intel® E7221MC Graphics Memory Controller Hub (GMCH) with Direct Media Interface
(DMI) interconnect
• Intel® 82801FR I/O Controller Hub (ICH6-R) with DMI interconnect
• Firmware Hub (FWH)
The GMCH is a centralized controller for the system bus, the memory bus, the PCI Express*
Graphics bus, and the DMI interconnect. The ICH6-R is a centraliz ed contro ller for the board’s
I/O paths. The FWH provides the nonvolatile storage of the BIOS.
3.3.1 USB Interface
The Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E supports up to eight USB 2.0 ports, supports
UHCI and EHCI, and uses UHCI- and EHCI-compatible drivers.
The ICH6-R provides the USB controller for all ports. The port arrangement is as follows:
• Four ports are implemented with dual stacked back panel, RJ45 combination
connectors.
• Four ports are routed to two separate front panel USB connectors.
3.3.2 IDE Support
The Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E provides five IDE interface connectors:
• One parallel ATA IDE connector, which supports two devices.
• Four serial ATA IDE connectors.
3.3.2.1 Parallel ATA IDE Interface
The ICH6-R’s Parallel ATA IDE controller has one bus-mastering Parallel ATA IDE interface.
The Parallel ATA IDE interface supports the following modes:
• Programmed I/O (PIO): processor controls data transfer.
• 8237-style DMA: DMA offloads the processor, supporting transfer rates of up to 16
MB/sec.
• Ultra DMA: DMA protocol on IDE bus supporting host and target throttling and transfer
rates of up to 33 MB/sec.
• ATA-66: DMA protocol on IDE bus supporting host and target throttling and transfer
rates of up to 66 MB/sec. ATA-66 protocol is similar to Ultra DMA and is device driver
compatible.
• ATA-100: DMA protocol on IDE bus allows host and target throttling. The ICH6-R’s
ATA-100 logic can achieve read transfer rates up to 100 MB/sec and write transfer
rates up to 88 MB/sec.
• The Parallel ATA IDE interface also supports ATAPI devices (such as CD-ROM drives)
and ATA devices using the transfer modes. The BIOS supports Logical Block
Addressing (LBA) and Extended Cylinder Head Sector (ECHS) translation modes.
The drive reports the transfer rate and translation mode to the BIOS.
Page 23

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Functional Architecture
Revision 1.5 13
3.3.2.2 Serial ATA Interfaces
The ICH6-R’s Serial ATA controller offers four independent Serial ATA ports with a theoretical
maximum transfer rate of 150 MB/s per port. One device can be installed on each port for a
maximum of four Serial ATA devices. A point-to-point interface is used for host to device
connections, unlike Parallel ATA IDE which supports a master/slave configuration and two
devices per channel.
For compatibility, the underlying Serial ATA functionality is transparent to the operating system.
The Serial ATA controller can operate in both legacy and native modes. In legacy mode,
standard IDE I/O and IRQ resources are assigned (IRQ 14 and 15). In Native mode, standard
PCI Conventional bus resource steering is used. Native mode is the preferred mode for
configurations using the Windows* XP and Windows* 2000 operating systems.
3.3.2.3 Serial ATA RAID
The ICH6-R supports RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Drives) level 0 and Raid level 1
on the Serial ATA ports as follows:
• RAID 0 supports data striping. Two physical drives, of identical size, can be teamed
together to create one logical drive. As data is written or retrieved from the logical
drive, both drives operate in parallel, thus increasing the throughput.
• RAID 1 supports data mirroring. Two physical drives, of identical size, maintain
duplicate sets of all data on separate disk drives. Level 1 provides the highest data
reliability because two complete copies of all information are maintained.
• RAID 10 combines both striping and mirroring to provide a high data transfer rates and
data redundancy. Four physical drives, of identical size are required for the RAID
group.
3.3.2.4 RAID Boot Configuration Overview
A RAID array can be created by using the existing Serial ATA ports, correctly configuring the
BIOS, and installing drivers. The following steps are required to succ essfully establish a RAID
configuration.
1. Enable RAID Support in BIOS.
2. Create a RAID array.
3. Load the RAID driver while installing the Operating System.
4. Format the RAID array.
3.3.2.5 SCSI Hard Drive Activity LED Connector (Optional)
The SCSI hard drive activity LED connector is a 1 x 2-pin connector that allows an add-in
hard drive controller to use the same LED as the onboard IDE controller. For proper operation,
this connector should be wired to the LED output of the add-in hard drive controller. The LED
indicates when data is being read from, or written to, either the add-in hard drive controller or
the onboard IDE controller (Parallel ATA or Serial ATA).
3.3.3 Real-Time Clock, CMOS SRAM, and Battery
A coin-cell battery (CR2032) powers the real-time clock and CMOS memory. When the
computer is not plugged into a wall socket, the battery has an estimated life of three years.
Page 24

Functional Architecture Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
14 Revision 1.5
When the computer is plugged in, the standby current from the power supply extends the life of
the battery. The clock is accurate to ± 13 minutes/year at 25 ºC with 3.3 VSB applied.
3.4 I/O Controller
The I/O controller provides the following features:
• One serial port
• One parallel port with Extended Capabilities Port (ECP) and Enhanced Parallel Port
(EPP) support
• Serial IRQ interface compatible with serialized IRQ support for PCI Conventional bus
systems
• PS/2-style mouse and keyboard interfaces
• Interface for one 1.44 MB or 2.88 MB diskette drive
• Intelligent power management, including a programmable wake-up event interface
• PCI Conventional bus power management support
The BIOS Setup program provides configuration options for the I/O controller.
3.4.1 Serial Port
The Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E has one serial port connector located on the back
panel, and a serial port B header on the board. The serial ports support data transfers at
speeds up to 115.2 Kbs/sec with BIOS support.
3.4.2 Parallel Port
The 25-pin D-Sub parallel port connector is located on the back panel. Use the BIOS Setup
program to set the parallel port mode.
3.4.3 Diskette Drive Controller
The I/O controller supports one diskette drive. Use the BIOS Setup program to configure the
diskette drive interface.
3.4.4 Keyboard and Mouse Interface
PS/2 keyboard and mouse connectors are located on the back panel.
3.5 Hardware Management Subsystem
The hardware management features enable the Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E to be
compatible with the Wired for Management Specification (WfM). The Server Board has several
hardware management features, including the following:
• Fan monitoring and control (through the hardware monitoring and fan control ASIC)
• Thermal and voltage monitoring
• Chassis intrusion detection
3.5.1 Hardware Monitoring and Fan Control ASIC
The features of the hardware monitoring and fan control ASIC include:
• Internal ambient temperature sensor
Page 25

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Functional Architecture
Revision 1.5 15
• Two remote thermal diode sensors for direct monitoring of processor temperature and
ambient temperature sensing
• Power supply monitoring of five voltages (+5 V, +12 V, +3.3 VSB, +1.5 V, and +VCCP)
to detect levels above or below acceptable values
• Thermally monitored closed-loop fan control, for all three chassis fans, that can adjust
the fan speed or switch the fans on or off as needed
• SMBus interface
3.5.2 Thermal Monitoring
Figure 9 shows the location of the sensors and fan connections on the Server Board.
OM16679
B
A
C
E
F
G
D
1
3
1
3
1
4
1
4
Item Description
A Remote ambient temperature sensor
B Thermal diode, located on processor die
C Ambient temperature sensor, internal to hardware monitoring and fan control ASIC
D Processor fan connector
E VReg chassis fan connector
F Front chassis fan connector
G Rear fan connector
Figure 9. Thermal Monitoring
Page 26

Functional Architecture Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
16 Revision 1.5
3.5.3 Fan Monitoring
Fan monitoring can be implemented using Intel Se rver Utilities, Intel Server Management
Software or third-party software. The level of monitoring and control is dependent on the
hardware monitoring ASIC used with the Server Board.
3.5.4 Chassis Intrusion and Detection
The Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E supports a chassis security feature that detect s if
the chassis cover is removed. The security feature uses a mechanical switch on the chassis
that attaches to the chassis intrusion connector. When the chassis cover is removed, the
mechanical switch is in the open position.
3.6 Power Management
Power management is implemented at several levels, including:
• Software support through Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)
• Hardware support:
⎯ Power connector
⎯ Fan connectors
⎯ LAN wake capabilities
⎯ Instantly Available PC technology
⎯ Resume on Ring
⎯ Wake from USB
⎯ Wake from PS/2 devices
⎯ Power Management Event signal (PME#) wake-up support
⎯ PCI Express* WAKE# signal support
3.6.1 Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)
ACPI gives the operating system direct control over the power management and Plug and Play
functions of a computer. The use of ACPI with the SE7221BA1-E server board requires an
operating system that provides full ACPI support. ACPI features include:
• Plug and Play (including bus and device enumeration)
• Power management control of individual devices, add-in boards (some add-in boards
may require an ACPI-aware driver), video displays, and hard disk drives
• Methods for achieving less than 15-watt system operation in the power-on/standby
sleeping state
• A Soft-off feature that enables the operating system to power-off the computer
• Support for multiple wake-up events (see Table 4. Wake-up Devices and Events)
• Support for a front panel power and sleep mode switch
Page 27

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Functional Architecture
Revision 1.5 17
The following table lists the system states based on how long the power switch is pressed,
depending on how ACPI is configured with an ACPI-aware operating system.
Table 2. Power Switch Options
If the system is in this state…
…and the power switch is
pressed for
…the system enters this state
Off
(ACPI G2/G5 – Soft off)
Less than four seconds Power-on
(ACPI G0 – working state)
On
(ACPI G0 – working state)
Less than four seconds Soft-off/Standby
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
On
(ACPI G0 – working state)
More than four seconds Fail safe power-off
(ACPI G2/G5 – Soft off)
Sleep
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
Less than four seconds Wake-up
(ACPI G0 – working state)
Sleep
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
More than four seconds Power-off
(ACPI G2/G5 – Soft off)
Note: These functions are yet to be determined and validated
3.6.2 System States and Power States
Under ACPI, the operating system directs all system and device power state transitions. The
operating system puts devices in and out of low-power states based on user preferences and
knowledge of how devices are being used by applications. Devices that are not being used can
be turned off. The operating system uses information from applications and user settings to put
the system as a whole into a low-power state.
The following table lists the power states supported by Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E
along with the associated system power targets. See the ACPI Specification for a complete
description of the various system and power states.
Table 3. Power States and Targeted System Power
Global States
Sleeping States
Processor
States
Device States
Targeted System
Power
(Note 1)
G0 – working
state
S0 – working C0 – working D0 – working state. Full power > 30 W
G1 – sleeping
state
S1 – Processor
stopped
C1 – stop grant D1, D2, D3 – device
specification
specific.
5 W < power < 52.5 W
G1 – sleeping
state
S4 – Suspend to disk.
Context saved to
disk.
No power D3 – no power
except for wake-up
logic.
Power < 5 W
(Note 2)
G2/S5 S5 – Soft off.
Context not saved.
Cold boot is required.
No power D3 – no power
except for wake-up
logic.
Power < 5 W
(Note 2)
G3 – mechanical
off AC power is
disconnected
from the
computer.
No power to the
system.
No power D3 – no power for
wake-up lo gic,
except when
provided by battery
or external source.
No power to the system.
Service can be performed
safely.
Notes:
Page 28

Functional Architecture Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
18 Revision 1.5
1. Total system power is dependent on the system configuration, including add-in boards and peripherals powered
by the system chassis’ power supply.
2. Dependent on the standby power consumption of wake-up devices used in the system.
3.6.3 Hardware Support
The Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E provides several power management hardware
features, including:
• Power connector
• Fan connectors
• LAN wake capabilities
• Instantly Available PC technology
• Resume on Ring
• Wake from USB
• Wake from PS/2 keyboard
• PME# signal wake-up support
• WAKE# signal wake-up support
LAN wake capabilities and Instantly Available PC technology require power from the +5 V
standby line. Resume on Ring enables telephony devices to access the computer when it is in
a power-managed state. The method used depends on the type of telephony device (external
or internal).
NOTE
The use of Resume on Ring and Wake from USB technologies from an ACPI state
requires an operating system that provides full ACPI support.
3.6.3.1 Power Connector
ATX12V-compliant power supplies can turn off the system power through system control. When
an ACPI-enabled system receives the correct command, the power supply removes all nonstandby voltages.
When resuming from an AC power failure, the server returns to the power state it was in before
power was interrupted (on or off). The server’s response can be set using the Last Power State
feature in the BIOS Setup program’s Boot menu.
3.6.3.2 Fan Connectors
The function/operation of the fan connectors is as follows:
• The fans are on when the board is in the S0 or S1 state.
• The fans are off when the board is off or in the S4 or S5 state.
• Each fan connector is wired to a fan tachometer input of the hardware monitoring and
fan control ASIC
• All fan connectors support closed-loop fan control that can adjust the fan speed or
switch the fan on or off as needed.
• All fan connectors have a +12 V DC connection
Page 29

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Functional Architecture
Revision 1.5 19
3.6.3.3 Wake-up Devices and Events
The following table lists the devices or specific events that can wake the computer from specific
states.
Table 4. Wake-up Devices an d Events
These devices/events can wake up the computer… …from this state
LAN S1, S4, S5
(Note)
Modem (back panel Serial Port A) S1
PME# signal S1, S4, S5
(Note)
Power switch S1, S4, S5
PS/2 devices S1
RTC alarm S1, S4, S5
USB S1
WAKE# S1, S4, S5
Note: For LAN and PME# signal, S5 is disabled by default in the BIOS Setup program. Setting this option to Power
On will enable a wake-up event from LAN in the S5 state.
NOTE
The use of these wake-up events from an ACPI state requires an operating system that
provides full ACPI support. In addition, software, drivers, and peripherals must fully
support ACPI wake events.
Page 30

Functional Architecture Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
20 Revision 1.5
<This page intentionally left blank.>
Page 31

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Maps and Interrupts
Revision 1.5 21
4. Maps and Interrupts
In this section, Table 5 describes the system memory map, Table 6 shows the I/O map, Table 7
lists the DMA channels, Table 8 defines the PCI configuration space map, and Table 9
describes the interrupts.
4.1 Memory Resources
4.1.1 Memory Map
The following table lists the system memory map.
Table 5. System Memory Map
Address Range (decimal) Address Range (hex) Size Description
1024 K - 4194304 K 100000 - FFFFFFFF 4095 MB Extended memory
960 K - 1024 K F0000 - FFFFF 64 KB Runtime BIOS
896 K - 960 K E0000 - EFFFF 64 KB Reserved
800 K - 896 K C8000 - DFFFF 96 KB Potential available high DOS memory
(open to the PCI Conventional bus).
Dependent on video adapter used.
640 K - 800 K A0000 - C7FFF 160 KB Video memory and BIOS
639 K - 640 K 9FC00 - 9FFFF 1 KB Extended BIOS data (movable by
memory manager software)
512 K - 639 K 80000 - 9FBFF 127 KB Extended conventional memory
0 K - 512 K 00000 - 7FFFF 512 KB Conventional memory
4.1.2 Addressable Memory
The Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E utilizes 4 GB of addressable system memory.
Typically the address space that is allocated for PCI Conventional bus add-in cards, PCI
Express* configuration space, BIOS (firmware hub), and chipset overhead resides above the
top of DRAM (total system memory). On a system that has 4 GB of system memory installed, it
is not possible to use all of the installed memory due to system address space being allocated
for other system critical functions. These functions include the following:
• BIOS/firmware hub (2 MB)
• Local APIC (19 MB)
• Digital Media Interface (40 MB)
• Front side bus interrupts (17 MB)
• PCI Express* configuration space (256 MB)
• MCH base address registers, internal graphics ranges, PCI Express* ports (up to 512
MB)
• Memory-mapped I/O that is dynamically allocated for PCI Conventional and PCI
Express* add-in cards
The amount of installed memory that can be used will vary based on add-in cards and BIOS
settings. Figure 10 shows a schematic of the system memory map. All installed system
memory can be used when there is no overlap of system addresses.
Page 32

Maps and Interrupts Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
22 Revision 1.5
Upper BIOS
area (64 KB)
Lower BIOS
area
(64 KB;
16 KB x 4)
Add-in Card
BIOS and
Buffer area
(128 KB;
16 KB x 8)
Standard PCI/
ISA Video
Memory (SMM
Memory)
128 KB
DOS area
(640 KB)
1 MB
960 KB
896 KB
768 KB
640 KB
0 KB
0FFFFFH
0F0000H
0EFFFFH
0E0000H
0DFFFFH
0C0000H
0BFFFFH
0A0000H
09FFFFH
00000H
FLASH
APIC
Reserved
0 MB
640 KB
1 MB
Top of usable
DRAM (memory
visible to the
operating
system)
PCI Memory Range -
contains PCI, chipsets,
Direct Media Interface
(DMI), and ICH ranges
(approximately 750 MB)
DOS
Compatibility
Memory
DRAM
Range
OM17140
~20 MB
4 GB
Top of System Address Space
Figure 10. Detailed System Memory Address Map
Page 33

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Maps and Interrupts
Revision 1.5 23
4.2 Fixed I/O Map
Table 6. I/O Map
Address (hex) Size Description
0000 - 00FF 256 bytes Used by the Server Board SE7221BA1-E. Refer to the ICH6-R
data sheet for dynamic addressing information.
0170 - 0177 8 bytes Secondary Parallel ATA IDE channel command block
01F0 - 01F7 8 bytes Primary Parallel ATA IDE channel command block
0228 - 022F
(Note 1)
8 bytes LPT3
0278 - 027F
(Note 1)
8 bytes LPT2
02E8 - 02EF
(Note 1)
8 bytes COM4
02F8 - 02FF
(Note 1)
8 bytes COM2
0374 - 0377 4 bytes Secondary Parallel ATA IDE channel control block
0377, bits 6:0 7 bits Secondary IDE channel status port
0378 - 037F 8 bytes LPT1
03E8 - 03EF 8 bytes COM3
03F0 - 03F5 6 bytes Diskette channel
03F4 – 03F7 1 byte Primary Parallel ATA IDE channel control block
03F8 - 03FF 8 bytes C OM1
04D0 - 04D1 2 bytes Edge/level triggered PIC
LPTn + 400 8 bytes ECP port, LPTn base address + 400h
0CF8 - 0CFB
(Note 2)
4 bytes PCI Conventional bus configuration address register
0CF9
(Note 3)
1 byte Reset control register
0CFC - 0CFF 4 bytes PCI Conventional bus configuration data register
FFA0 - FFA7 8 bytes Primary Parallel ATA IDE bus master registers
FFA8 - FFAF 8 bytes Secondary Parallel ATA IDE bus master registers
Notes:
1. Default, but can be changed to another address range.
2. Dword access only.
3. Byte access only.
NOTE: Some additional I/O addresses are not available due to ICH6-R address aliasing. The ICH6-R
data sheet provides more information on address aliasing:
http://developer.intel.com/design/chipsets/datashts
4.3 DMA Channels
Table 7. DMA Channels
DMA Channel Number Data Width System Resource
0 8 or 16 bits Open
1 8 or 16 bits Parallel port
2 8 or 16 bits Diskette drive
3 8 or 16 bits Parallel port (for ECP or EPP)
4 8 or 16 bits DMA controller
5 16 bits Open
Page 34

Maps and Interrupts Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
24 Revision 1.5
DMA Channel Number Data Width System Resource
6 16 bits Open
7 16 bits Open
4.4 PCI Configuration Space Map
Table 8. PCI Configuration Space Map
Bus
Number (hex)
Device
Number (hex)
Function
Number (hex) Description
00 00 00 Memory controller of Intel® SE7221BA1-E component
00 01 00 PCI Express* x16 graphics port
00 1C 00 PCI Express* port 1 (PCI Express* x1 bus connector 1)
00 1C 01 PCI Express* port 2 (Gigabit Ethernet controller bridge)
00 1C 02 PCI Express* port 3 (PCI Express* x1 bus connector 2)
(Note 1)
00 1C 03 PCI Express* port 4 (not used)
00 1D 00 USB UHCI controller 1
00 1D 01 USB UHCI controller 2
00 1D 02 USB UHCI controller 3
00 1D 03 USB UHCI controller 4
00 1D 07 EHCI controller
00 1E 00 PCI bridge
00 1F 00 PCI controller
00 1F 01 Parallel AT A I DE controller
00 1F 02 Serial AT A controller
00 1F 03 SMBus controller
(Note 2)
00 00 Gigabit Ethernet Controller
(Note 2)
00 00 PCI Conventional bus connector 1
(Note 2)
01 00 PCI Conventional bus connector 2
(Note 2)
02 00 PCI Conventional bus connector 3
(Note 2)
03 00 PCI Conventional bus connector 4
(Note 2)
05 00 IEEE-1394a controller
Notes:
1. Bus number is dynamic and can change based on add-in cards used.
4.5 Interrupts
The interrupts can be routed through either the Programmable Interrupt Controller (PIC) or the
Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC) portion of the ICH6-R component. The
APIC is supported in Windows* 2000 and Windows* XP operating systems and supports a total
of 24 interrupts.
Page 35

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Maps and Interrupts
Revision 1.5 25
Table 9. Interrupts
IRQ System Resource
NMI I/O channel check
0 Reserved, interval timer
1 Reserved, keyboard buffer full
2 Reserved, cascade interrupt from slave PIC
3 User available
4
COM1
(Note 1)
5 LPT2 (Plug and Play option)/User available
6 Diskette drive
7
LPT1
(Note 1)
8 Real-time clock
9 User available
10 User available
11 User available
12 Onboard mouse port (if present, else user available)
13 Reserved, math coprocessor
14 Primary IDE/Serial ATA (if present, else user available)
15 Serial ATA (if present, else user available)
16
(Note 2)
User available (through PIRQA)
17
(Note 2)
User available (through PIRQB)
18
(Note 2)
User available (through PIRQC)
19
(Note 2)
User available (through PIRQD)
20
(Note 2)
User available (through PIRQE)
21
(Note 2)
User available (through PIRQF)
22
(Note 2)
User available (through PIRQG)
23
(Note 2)
User available (through PIRQH)
Notes:
1. Default, but can be changed to another IRQ.
2. Available in APIC mode only.
4.6 PCI Conventional Interrupt Routing Map
This section describes interrupt sharing and how the interrupt signals are connected between
the PCI Conventional bus connectors and onboard PCI Conventional devices. The PCI
Conventional specification describes how interrupts can be shared between devices attached to
the PCI Conventional bus. In most cases, the small amount of latency added by interrupt
sharing does not affect the operation or throughput of the devices. In some special cases
where maximum performance is needed from a device, a PCI Conventional device should not
share an interrupt with other PCI Conventional devices. Use the following information to avoid
sharing an interrupt with a PCI Conventional add-in card.
PCI Conventional devices are categorized as follows to specify their interrupt grouping:
Page 36

Maps and Interrupts Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
26 Revision 1.5
• INTA: By default, all add-in cards that require only one interrupt are in this category.
For almost all cards that require more than one interrupt, the first interrupt on the card
is also classified as INTA.
• INTB: Generally, the second interrupt on add-in cards that require two or more
interrupts is classified as INTB. (This is not an absolute requirement.)
• INTC and INTD: Generally, a third interrupt on add-in cards is classified as INTC and
a fourth interrupt is classified as INTD.
The ICH6-R has eight Programmable Interrupt Request (PIRQ) input signals. All PCI
Conventional interrupt sources either onboard or from a PCI Conventional add-in card connect
to one of these PIRQ signals. Some PCI Conventional interrupt sources are electrically tied
together on the board and therefore share the same interrupt. Table 10 shows an example of
how the PIRQ signals are routed.
For example, using Table 10 as a reference; assume an add-in card using INTA is plugged into
PCI Conventional bus connector 3. In PCI bus connector 3, INTA is connected to PIRQB, which
is already connected to the ICH6-R audio controller. The add-in card in PCI Conventional bus
connector 3 now shares an interrupt with the onboard interrupt source.
Table 10. PCI Interrupt Routing Map
ICH6-R PIRQ Signal Name
PCI Interrupt Source
PIRQA PIRQB PIRQC PIRQD PIRQE PIRQF PIRQG PIRQH
IEEE-1394a controller INTA
PCI bus connector 1 INTD INTA INTB INTC
PCI bus connector 2 INTC INTB INTA INTD
PCI bus connector 3 INTD INTC INTA INTB
PCI bus connector 4 INTB INTA INTC INTD
NOTE: In PIC mode, the ICH6-R can connect each PIRQ line internally to one of the IRQ signals (3, 4, 5,
6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, and 15). Typically, a device that does not share a PIRQ line will have a unique
interrupt. However, in certain interrupt-constrained situations, it is possible for two or more of the PIRQ
lines to be connected to the same IRQ signal. Refer to Table 10 for the allocation of PIRQ lines to IRQ
signals in APIC mode.
PCI interrupt assignments to the USB ports, Serial ATA ports, and PCI Express* ports are dynamic.
Page 37

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Input Output Subsystem
Revision 1.5 27
5. Input Output Subsystem
5.1 PCI Subsystem
5.1.1 PCI Express* Connectors
The Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E provides the following PCI Express* connectors:
• One PCI Express* x8 connector. The x8 interface supports simultaneous (full duplex)
transfer speeds up to 8 GBytes/sec. Single-ended (half duplex) transfers are
supported at up to 4 GBytes/sec.
• Three PCI Express* x4 connectors. The x4 connectors will only function at x1
bandwidth. This connection support was selected to be able to have the additional
PCI Express* connections available and due to the greater availability of x4 adapter
cards.
• The PCI Express* interface supports the PCI Conventional bus configuration
mechanism so that the underlying PCI Express* architecture is compatible with PCI
Conventional compliant operating systems. Additional features of the PCI Express*
interface include the following:
• Support for the PCI Express* enhanced configuration mechanism
• Automatic discovery, link training, and initialization
• Support for Active State Power Management (ASPM)
• SMBus 2.0 support
• Wake# signal supporting wake events from ACPI S1, S4, or S5
• Software compatible with the PCI Power Management Event (PME) mechanism
defined in the PCI Power Management Specification Rev. 1.1
NOTE
The Intel Server Board SE7221BA1-E features PCI Express x4 connectors, routed with a x1 lane and
limited to x1 throughput. Please refer to the PCI Express* Card Electromechanical Specification for
more information.,
5.1.2 PCI 32
Three 32-bit, 33 MHz PCI conventional slots.
5.2 LAN Subsystem
• The LAN subsystem includes one Marvell Yukon* 88E8050 Gigabit (10/100/1000
Mbits/sec) and one Intel® 82551QM Integrated 10/100 LAN controller. Both network
controllers are available through the rear ATX I/O shield RJ-45 LAN connectors and
have integrated status LEDs.
5.2.1 Marvell Yukon* 88E8050 Gigabit Ethernet Controller
The Marvell Yukon* 88E8050 is an integrated PCI Express* Gigabit Ethernet controller with the
following functions:
• x1 PCI Express* link
• Basic 10/100/1000 Ethernet LAN connectivity
• IEEE 802.1p and 802.1q support
• 10/100/1000 IEEE 802.3 compliant
Page 38

Input Output Subsystem Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
28 Revision 1.5
Green LED Green/Yellow LED
OM16513
NIC 1 NIC 2
• Compliant to 802.3x flow control support
• Jumbo frame support
• TCP, IP, UDP checksum offload
• Automatic MDI/MDIX crossover
• Full device driver compatibility
• Configuration EEPROMs that contain the MAC address and ASF 2.0 support
• Wake On LAN technology power management support
• PCI Express* Active State Power Management Support (L0s)
• ASF 2.0 support
5.2.2 Intel® 82551QM Integrated 10/100 LAN controller
The Intel® 8255QM Fast Ethernet controller provides the following functions:
• Basic 10/100 Ethernet LAN connectivity
• IEEE 802.3 10Base-T and 100Base-TX Compatible PHY
• IEEE 802.3x 100Base-TX Flow Control Support
• IEEE 802.3u Auto-Negotiation support
• TCP, IP, UDP checksum offload
• Full device driver compatibility
• Wake On LAN technology power management support.
• Wired for management
5.2.3 RJ-45 LAN Connector with Integrated LEDs
Two LEDs are built into the RJ-45 LAN connectors (as shown in Figure 11).
Table 11 describes the LED states when the board is powered up and the Gigabit LAN
subsystem is operating.
Figure 11. LAN Conn ector LED Locations
Page 39

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Input Output Subsystem
Revision 1.5 29
Table 11. LAN Connector LED States
LED Color LED State Condition
Off LAN link is not established.
On LAN link is established.
Left Green
Blinking LAN activity is occurring.
N/A Off 10 Mbits/sec data rate is selected.
Green On 100 Mbits/sec data rate is selected.
Right
Yellow
On
1000 Mbits/sec data rate is selected.
5.2.4 Alert Standard Format (ASF) Support
The boards provide the following ASF support for the onboard 10/100/1000 LAN subsystem,
PCI Express* x1 bus add-in LAN cards, and PCI Conventional bus add-in LAN cards installed in
PCI Conventional bus slot 2:
• Monitoring of system firmware progress events, including:
• BIOS present
• Primary processor initialization
• Memory initialization
• Video initialization
• PCI resource configuration
• Hard-disk initialization
• User authentication
• Starting operating system boot process
• Monitoring of system firmware error events, including:
• Memory missing
• Memory failure
• No video device
• Keyboard failure
• Hard-disk failure
• No boot media
• Boot options to boot from different types of boot devices
• Reset, shutdown, power cycle, and power up options
Page 40

Input Output Subsystem Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
30 Revision 1.5
5.3 Hardware Management Subsystem
5.3.1 Hardware Management
The hardware management features enable Intel® Server Boards to be compatible with the
Wired for Management (WfM) specification. The Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E has
several hardware management features, including the following:
• Fan monitoring and control (through the hardware monitoring and fan control ASIC)
• Thermal and voltage monitoring
• Chassis intrusion detection
5.3.2 Hardware Monitoring and Fan Control ASIC
The features of the hardware monitoring and fan control ASIC include:
• Internal ambient temperature sensor
• Two remote thermal diode sensors for direct monitoring of processor temperature and
ambient temperature sensing
• Power supply monitoring of five voltages (+5 V, +12 V, +3.3 VSB, +1.5 V, and +VCCP)
to detect levels above or below acceptable values
• Thermally monitored closed-loop fan control, for all three chassis fans, that can adjust
the fan speed or switch the fans on or off as needed
• SMBus interface
Page 41

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Connections and Jumper Blocks
Revision 1.5 31
6. Connections and Jumper Blocks
6.1 Connectors
CAUTION
Only the following connectors have over-current protection: back panel USB, front panel USB,
and PS/2.
The other internal connectors are not over-current protected and should connect only to devices
inside the computer’s chassis, such as fans and internal peripherals. Do not use these connectors
to power devices external to the computer’s chassis. A fault in the load presented by the external
devices could cause damage to the computer, the power cable, and the external devices themselves.
This section describes the board’s connectors. The connectors are divided into two
groups:
• Back panel I/O connectors
• Component-side I/O connectors
6.1.1 Back Panel Connectors
Figure 12 shows the location of the back panel connectors. Additionally, the back panel
connectors are color-coded. Table 12 lists the colors used (when applicable).
TP01371
C
DB FA E
Figure 12. Back Panel Connectors
Page 42

Connections and Jumper Blocks Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
32 Revision 1.5
The table below lists the back panel connectors identified in the preceding figure.
Table 12. Back Panel Connectors
Back Panel
Connectors
Description
A
PS/2 mouse port [Green]
B
PS/2 keyboard port [Purple]
C
Serial port A [Teal]
D
Parallel port [Burgundy]
E
PCI Express* Graphics
F
Magic Jack RJ45/USB Marvell Yukon* PCI Express* Gigabit Ethernet port
G
Magic Jack RJ45/USB Intel® 82551QM Integrated 10/100 LAN port
H
6.1.2 Component-side Connectors
The following figure shows the locations of the component-side connectors of the Intel® Entry
Server Board SE7221BA1-E.
Figure 13. Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E Component-side Connectors
Page 43

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Connections and Jumper Blocks
Revision 1.5 33
Table 13. Front Chassis Fan and Rear Chassis
Fan Connectors
Pin Signal Name
1 Control
2 +12 V
3 Tach
Table 14. Processor Fan Connector and Auxiliary
Rear Fan Connector
Pin Signal Name
1 Ground
2 +12 V
3 FAN_TACH
4 FAN_CONTROL
Table 15. Chassis Intrusion Connector
Pin Signal Name
1 Intruder
2 Ground
Table 16. SCSI Hard Drive Activity LED Connector (Optional)
Pin Signal Name
1 SCSI_ACT#
2 No connect
Table 17. Serial ATA Connectors
Pin Signal Name
1 Ground
2 TXP
3 TXN
4 Ground
5 RXN
6 RXP
7 Ground
Page 44

Connections and Jumper Blocks Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
34 Revision 1.5
Table 18. Auxiliary Power Output Connector
Pin Signal Name
1 +12 V
2 Ground
3 Ground
4 +5 V
Table 19. Front Panel SSI Connector
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 Power LED Anode 2 5Vsb
3 Key 4 Unused
5 Power LED Cathode 6 Unused
7 HDD Act. LED Anode 8 Unused
9 HDD Act. LED Cathode 10 Unused
11 Power Switch 12 Nic #1 Act. LED Anode
13 Power Switch (Gnd) 14 Nic #1 Act. LED Cathode
15 Reset Switch 16 SMBus SDA
17 Reset (Gnd) 18 SMBus SCL
19 ACPI Sleep Switch 20 Chassis Intrusion
21 ACPI Sleep Switch (Gnd) 22 Nic #2 Act. LED Anode
23 Unused 24 Nic #2 Act. LED Cathode
25 Key 26 Key
27 Unused 28 Unused
29 Unused 30 Unused
31 Unused 32 Unused
33 Unused 34 Unused
Page 45

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Connections and Jumper Blocks
Revision 1.5 35
Figure 14. SSI Connector
6.1.3 Front Panel USB Connectors
Figure 15 is a connection diagram for the front panel USB connectors.
• The +5 V DC power on the USB connector is fused.
• Pins 1, 3, 5, and 7 comprise one USB port.
• Pins 2, 4, 6, and 8 comprise one USB port.
• Use only a front panel USB connector that conforms to the USB 2.0 specification for
high-speed USB devices.
Page 46

Connections and Jumper Blocks Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
36 Revision 1.5
OM15963
8
6
4
2
7
5
3
1
Key (no pin)
No Connect
10
Power
(+5 V DC)
D−
D+
Ground
D+
Ground
D−
Power
(+5 V DC)
One
USB
Port
One
USB
Port
Figure 15. Connection Diagram for Front Panel USB Connectors
6.1.4 Power Supply Connectors
The board has three power supply connectors:
• Main power – a 2 x 12 connector. This connector is compatible with 2 x 10 connectors
previously used on Intel® Server boards. The board supports the use of ATX12V or
EPS 12V power supplies with either 2 x 10 or 2 x 12 main power cables. When using
a power supply with a 2 x 10 main power cable, attach that cable on the right most
pins of the main power connector, leaving pins 11, 12, 23, and 24 unconnected.
• ATX12V power – a 2 x 2 connector. This connector provides power directly to the
processor voltage regulator and must always be used. Failure to do so will prevent the
board from booting.
Table 20. Main Power Connector
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 +3.3 V 13 +3.3 V
2 +3.3 V 14 -12 V
3 Ground 15 Ground
4 +5 V 16 PS-ON# (power supply remote on/off)
5 Ground 17 Ground
6 +5 V 18 Ground
7 Ground 19 Ground
8 PW RGD (Power Good) 20 No connect
9 + 5 V (Standby) 21 +5 V
10 +12 V 22 +5 V
11 +12 V 23 +5 V
12 2x12 connector detect 24 Ground
Page 47

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Connections and Jumper Blocks
Revision 1.5 37
Table 21. ATX12V Power Connector
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 Ground 2 Ground
3 Ground 4 Ground
5 +12 V 6 +12 V
7 +12 V 8 +12 V
6.1.5 Add-in Card Connectors
The Intel® Server Board SE7221BA1-E has the following add-in card connectors:
• PCI Express* x8: one connector supporting simultaneous transfer speeds up to 8
GBytes/sec
• PCI Express* x4: The board has two PCI Express* x4 connectors.
• PCI Conventional (rev 2.2 compliant) bus: The SE7221BA1-E board has three PCI
Conventional bus add-in card connectors.
Note the following considerations for the PCI Conventional bus connectors:
• All of the PCI Conventional bus connectors are bus master capable.
• SMBus signals are routed to PCI Conventional bus connector 2. This enables PCI
Conventional bus add-in boards with SMBus support to access sensor data on the
Server Board. The specific SMBus signals are as follows:
⎯ The SMBus clock line is connected to pin A40.
⎯ The SMBus data line is connected to pin A41.
6.2 Jumper Blocks
CAUTION
Do not move the jumper with the power on. Always turn off the power and unplug the power cord
from the computer before changing a jumper setting. Otherwise, the board could be damaged.
Figure 16 shows the location of the jumper blocks. The 3-pi n jumper block s determine the BIOS
Setup program’s mode. Table 22 describes the jumper settings for the three modes: normal,
configure, and recovery. When the jumper is set to configure mode and the computer is
powered-up, the BIOS compares the processor version and the microcode version in the BIOS
and reports if the two match. Table 23 describes the jumper settings for clearing CMOS.
Page 48

Connections and Jumper Blocks Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
38 Revision 1.5
OM16682
31
J6J3
Figure 16. Location of the Jumper Block
Table 22. BIOS Setup Configuration Jumper Settings
Function/Mode Jumper Setting Configuration
Normal
1-2
1
3
The BIOS uses current configuration information and
passwords for booting.
Configure
2-3
13
After the POST runs, Setup runs automatically. The
maintenance menu is displayed.
Recovery
None
13
The BIOS attempts to recover the BIOS configuration. A
recovery diskette is required.
Table 23. CMOS Clear Jumper Configuration
Function/Mode Jumper Setting Configuration
Normal
1-2
1
3
The BIOS uses current configuration information.
Clear CMOS
2-3
13
During POST, the CMOS configuration is reset to default
values.
No Jumper
None
13
Normal operation, BIOS uses current configuration information.
Page 49

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS System BIOS
Revision 1.5 39
7. System BIOS
7.1 BIOS Identification String
7.2 Introduction
The Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E uses an Intel / AMI BIOS that is stored in the
Firmware Hub (FWH) and can be updated using a disk-based program. The FWH contains the
BIOS Setup program, POST, the PCI auto-configuration utility, and Plug and Play support.
The BIOS displays a message during POST identifying the type of BIOS and a revision code.
The initial production BIOS’s are identified as BA72210A.86B.0155.2005.0110.1040.
When the BIOS Setup configuration jumper is set to configure mode and the computer is
powered-up, the BIOS compares the CPU version and the microcode version in the BIOS and
reports if the two match.
The BIOS Setup program can be used to view and change the BIOS settings for the computer.
The BIOS Setup program is accessed by pressing the <F2> key after the Power-On Self-Test
(POST) memory test begins and before the operating system boot begins. The menu bar is
shown below.
Maintenance Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
NOTE
The maintenance menu is displayed only when the server board is in configuration mode. Refer to
Table 22 for jumper settings..
Table 24 lists the BIOS Setup program menu features.
Table 24. BIOS Setup Program Menu Bar
Maintenance Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Clears passwords
and displays
processor
information
Displays
processor and
memory
configuration
Configures
advanced
features
available
through the
chipset
Sets
passwords
and security
features
Configures
power
management
features and
power supply
controls
Selects boot
options
Saves or
discards
changes to
Setup
program
options
Page 50

System BIOS Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
40 Revision 1.5
Table 25 lists the function keys available for menu screens.
Table 25. BIOS Setup Program Function Keys
BIOS Setup Program Function Key Description
<←> or <→>
Selects a different menu screen (Moves the cursor left or right)
<↑> or <↓>
Selects an item (Moves the cursor up or down)
<Tab> Selects a field (Not implemented)
<Enter> Executes command or selects the submenu
<F9> Load the default configuration values for the current menu
<F10> Save the current values and exits the BIOS Setup program
<Esc> Exits the menu
7.3 BIOS Flash Memory Organization
The Firmware Hub (FWH) includes an 8 Mbit (1024 KB) symmetrical flash memory device.
7.4 Resource Configuration
7.4.1 PCI Autoconfiguration
The BIOS can automatically configure PCI devices. PCI devices may be onboard or add-in
cards. Auto configuration lets a user insert or remove PCI cards without having to configure the
system. When a user turns on the system after adding a PCI card, the BIOS automatically
configures interrupts, the I/O space, and other system resources. Any interrupts set to Available
in Setup are considered to be available for use by the add-in card.
7.4.2 PCI IDE Support
If you select Auto in the BIOS Setup program, the BIOS automatically sets up the
PCI IDE connector with independent I/O channel support. The IDE interface supports hard
drives up to ATA-66/100 and recognizes any ATAPI compliant devices, including CD-ROM
drives, tape drives, and Ultra DMA drives. The BIOS determines the capabilities of each drive
and configures them to optimize capacity and performance. To take advantage of the high
capacities typically available today, hard drives are automatically configured for Logical Block
Addressing (LBA) and to PIO Mode 3 or 4, depending on the capability of the drive. You can
override the auto-configuration options by specifying manual configuration in the BIOS Setup
program.
To use ATA-66/100 features the following items are required:
• An ATA-66/100 peripheral device
• An ATA-66/100 compatible cable
• ATA-66/100 operating system device drivers
Page 51

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS System BIOS
Revision 1.5 41
7.5 System Management BIOS (SMBIOS)
The main component of SMBIOS is the Management Information Format (MIF) database, which
contains information about the computing system and its components. Using SMBIOS, a
system administrator can obtain the system types, capabilities, operational status, and
installation dates for system components. The MIF database defines the data and provides the
method for accessing this information. The BIOS enables applications such as third-party
management software to use SMBIOS. The BIOS stores and reports the following SMBIOS
information:
• BIOS data, such as the BIOS revision level
• Fixed-system data, such as peripherals, serial numbers, and asset tags
• Resource data, such as memory size, cache size, and processor speed
• Dynamic data, such as event detection and error logging
Non-Plug and Play operating systems, require an additional interface for obtaining the SMBIOS
information. The BIOS supports an SMBIOS table interface for such operating systems. Using
this support, an SMBIOS service-level application running on a non-Plug and Play operating
system can obtain the SMBIOS information.
7.6 Legacy USB Support
Legacy USB support enables USB devices to be used even when the operating system’s USB
drivers are not yet available. Legacy USB support is used to access the BIOS Setup program,
and to install an operating system that supports USB. By default, Legacy USB support is set to
Enabled.
Legacy USB support operates as follows:
1. When you apply power to the computer, legacy support is disabled.
2. POST begins.
3. Legacy USB support is enabled by the BIOS allowing you to use a USB keyboard to
enter and configure the BIOS Setup program and the maintenance menu.
4. POST completes.
5. The operating system loads. While the operating system is loading, USB keyboards
and mice are recognized and may be used to configure the operating system.
(Keyboards and mice are not recognized during this period if Leg acy USB support was
set to Disabled in the BIOS Setup program.)
6. After the operating system loads the USB drivers, all legacy and non-legacy USB
devices are recognized by the operating system, and Legacy USB support from the
BIOS is no longer used.
To install an operating system that supports USB, verify that Legacy USB support in the BIOS
Setup program is set to Enabled and follow the operating system’s installation instructions.
Page 52

System BIOS Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
42 Revision 1.5
7.7 BIOS Updates
The BIOS can be updated using either of the following utilities:
• Intel
®
Express BIOS Update utility, which enables automated updating while in the
Windows environment. Using this utility, the BIOS can be updated from a file on a hard
disk, a 1.44 MB diskette, or a CD-ROM.
• Intel® Flash Memory Update Utility, which requires creation of a boot diskette and
manual rebooting of the system. Using this utility, the BIOS can be updated from a file
on a 1.44 MB diskette or a CD-ROM.
Both utilities verify that the updated BIOS match the target system to prevent accidentally
installing incompatible BIOS.
BIOS Updates are available at:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/se7221ba1-e/
7.7.1 Language Support
The BIOS Setup program and help messages are supported in US English. Additional
languages are available in the Integrator’s Toolkit utility. Check the Intel website for details.
7.7.2 Custom Splash Screen
During POST, an Intel® splash screen is displayed by default. This splash screen can be
augmented with a custom splash screen. The Integrator’s Toolkit that is available from Intel®
can be used to create a custom splash screen.
7.8 Boot Options
In the BIOS Setup program, the user can choose to boot from a diskette drive, hard drives,
CD-ROM, or the network. The default setting is for the diskette drive to be the first boot device,
the hard drive second, and the ATAPI CD-ROM third. The fourth device is disabled.
7.8.1 CD-ROM Boot
Booting from CD-ROM is supported in compliance to the El Torito CD-ROM Boot Specification.
Under the Boot menu in the BIOS Setup program, ATAPI CD-ROM is listed as a boot device.
Boot devices are defined in priority order. Accordingly, if there is not a bootable CD in the CDROM drive, the system will attempt to boot from the next defined drive.
7.8.2 Network Boot
The network can be selected as a boot device. This selection allows booting from the onboard
LAN or a network add-in card with a remote boot ROM installed.
Pressing the <F12> key during POST automatically forces booting from the LAN. To use this
key during POST, the User Access Level in the BIOS Setup program's Security menu must be
set to Full.
7.8.3 Booting Without Attached Devices
For use in embedded applications, the BIOS has been designed so that after passing POST,
the operating system loader is invoked even if the following devices are not present:
• Video adapter
• Keyboard
• Mouse
Page 53

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS System BIOS
Revision 1.5 43
7.9 BIOS Security Features
The BIOS includes security features that restrict access to the BIOS Setup program and who
can boot the computer. A supervisor password and a user password can be set for the BIOS
Setup program and for booting the computer, with the following restrictions:
• The supervisor password gives unrestricted access to view and change all the Setup
options in the BIOS Setup program. This is the supervisor mode.
• The user password gives restricted access to view and change Setup options in the
BIOS Setup program. This is the user mode.
• If only the supervisor password is set, pressing the <Enter> key at the password
prompt of the BIOS Setup program allows the user restricted access to Setup.
• If both the supervisor and user passwords are set, users can enter either the
supervisor password or the user password to access Setup. Users have access to
Setup respective to which password is entered.
• Setting the user password restricts who can boot the computer. The password prompt
will be displayed before the computer is booted. If only the supervisor password is set,
the computer boots without asking for a password. If both passwords are set, the user
can enter either password to boot the computer.
• For enhanced security, use different passwords for the supervisor and user passwords.
• Valid password characters are A-Z, a-z, and 0-9. Passwords may be up to 16
characters in length.
Table 26 shows the effects of setting the supervisor password and user password. This table is
for reference only and is not displayed on the screen.
Table 26. Supervisor and User Password Functions
Password Set
Supervisor
Mode
User Mode
Setup Options
Password to
Enter Setup
Password
During Boot
Neither Can change all
options
(Note)
Can change all
options
(Note)
None None None
Supervisor only Can change all
options
Can change a
limited number
of options
Supervisor Password Supervisor None
User only N/A Can change all
options
Enter Password
Clear User Password
User User
Supervisor and
user set
Can change all
options
Can change a
limited number
of options
Supervisor Password
Enter Password
Supervisor or
user
Supervisor or
user
Note: If no password is set, any user can change all Setup options.
Page 54

System BIOS Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
44 Revision 1.5
7.10 Error Messages and Beep Codes
7.10.1 BIOS Error Messages
Table 27 lists the error messages and provides a brief description of each.
Table 27. BIOS Error Messages
Error Message Explanation
GA20 Error An error occurred with Gate A20 when switching to protected mode
during the memory test.
Pri Master HDD Error
Pri Slave HDD Error
Could not read sector from corresponding drive.
Pri Master Drive - ATAPI Incompatible Pri
Slave Drive - ATAPI Incompatible
Corresponding drive in not an ATAPI device. Run Setup to make sure
device is selected correctly.
A: Drive Error No response from diskette drive.
Cache Memory Bad An error occurred when testing L2 cache. Cache memory may be bad.
CMOS Battery Low The battery may be losing power. Replace the battery soon.
CMOS Display Type Wrong The display type is different than what has been stored in CMOS.
Check Setup to make sure type is correct.
CMOS Checksum Bad The CMOS checksum is incorrect. CMOS memory may have been
corrupted. Run Setup to reset values.
CMOS Settings Wrong CMOS values are not the same as the last boot. These values have
either been corrupted or the battery has failed.
CMOS Date/Time Not Set The time and/or date values stored in CMOS are invalid. Run Setup to
set correct values.
DMA Error Error during read/write test of DMA controller.
FDC Failure Error occurred trying to access diskette drive controller.
HDC Failure Error occurred trying to access hard disk controller.
Checking NVRAM..... NVRAM is being checked to see if it is valid.
Update OK! NVRAM was invalid and has been updated.
Updated Failed NVRAM was invalid but was unable to be updated.
Keyboard Error Error in the keyboard connection. Make sure keyboard is connected
properly.
KB/Interface Error Keyboard interface test failed.
Memory Size Decreased Memory size has decreased since the last boot. If no memory was
removed then memory may be bad.
Memory Size Increased Memory size has increased since the last boot. If no memory was
added there may be a problem with the system.
Memory Size Changed Memory size has changed since the last boot. If no memory was added
or removed then memory may be bad.
No Boot Device Available System did not find a device to boot.
Off Board Parity Error A parity error occurred on an off-board card. This error is followed by
an address.
On Board Parity Error A parity error occurred in onboard memory. This error is followed by an
address.
Parity Error A parity error occurred in onboard memory at an unknown address.
Page 55

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS System BIOS
Revision 1.5 45
Error Message Explanation
NVRAM/CMOS/PASSWORD cleared by
Jumper
NVRAM, CMOS, and passwords have been cleared. The system
should be powered down and the jumper removed.
<CTRL_N> Pressed CMOS is ignored and NVRAM is cleared. User must enter Setup.
7.10.2 Port 80h POST Codes
During the POST, the BIOS generates diagnostic progress codes (POST-codes) to I/O port 80h.
If the POST fails, execution stops and the last POST code generated is left at port 80h.
This code is useful for determining the point where an error occurred.
Displaying the POST-codes requires a PCI bus add-in card, often called a POST card. The
POST card can decode the port and display the contents on a medium such as a sevensegment display.
NOTE:
The POST card must be installed in PCI bus connector 1.
The tables below offer descriptions of the POST codes generated by the BIOS. Table 28
defines the uncompressed INIT code checkpoints, Table 29 describes the boot block recovery
code checkpoints, and Table 30 lists the runtime code uncompressed in F000 shadow RAM.
Some codes are repeated in the tables because that code applies to more than one operation.
Table 28. Uncompressed INIT Code Checkpoints
Code Description of POST Operation
D0 NMI is Disabled. Onboard KBC, RTC enabled (if present). Init code Checksum verification starting.
D1 Keyboard controller BAT test, CPU ID saved, and going to 4 GB flat mode.
D3 Do necessary chipset initialization, start memory refresh, and do memory sizing.
D4 Verify base memory.
D5 Init code to be copied to segment 0 and control to be transferred to segment 0.
D6 Control is in segment 0. To check recovery mode and verify main BIOS checksum. If either it is recovery
mode or main BIOS checksum is bad, go to check point E0 for recovery else go to check point D7 for
giving control to main BIOS.
D7 Find Main BIOS module in ROM image.
D8 Uncompress the main BIOS module.
D9 Copy main BIOS image to F000 shadow RAM and give control to main BIOS in F000 shadow RAM.
Table 29. Boot Block Recovery Code Checkpoints
Code Description of POST Operation
E0 Onboard Floppy Controller (if any) is initializ ed. Compressed recovery code is uncompressed in
F000:0000 in Shadow RAM and give control to recovery code in F000 Shadow RAM. Initialize interrupt
vector tables, initialize system timer, initialize DMA controller and interrupt controller.
E8 Initialize extra (Intel Recovery) Module.
E9 Initialize floppy drive.
EA Try to boot from floppy. If reading of boot sector is successful, give control to boot sector code.
Page 56

System BIOS Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
46 Revision 1.5
Code Description of POST Operation
EB NA
EC Try to boot from ATAPI. If reading of boot sector is successful, give control to boot sector code.
EF Booting from floppy and ATAPI device failed. Give two beeps. Retry the booting procedure again (go to
check point E9).
Table 30. Runtime Code Uncompressed in F000 Shadow RAM
Code Description of POST Operation
03 NMI is Disabled. To check soft reset/power-on.
05 BIOS stack set. Going to disable cache if any.
06 POST code to be uncompressed.
07 CPU init and CPU data area init to be done.
08 CMOS checksum calculation to be done next.
0B Any initialization before keyboard BAT to be done next.
0C KB controller I/B free. To issue the BAT command to keyboard controller.
0E Any initialization after KB controller BAT to be done next.
0F Keyboard command byte to be written.
10 Going to issue Pin-23,24 blocking/unblocking command.
11 Going to check pressing of <INS>, <END> key during power-on.
12 To init CMOS if "Init CMOS in every boot" is set or <END> key is pressed. Going to disable DMA and
Interrupt controllers.
13 Video display is disabled and port-B is initialized. Chipset init about to begin.
14 8254 timer test about to start.
19 About to start memory refresh test.
1A Memory Refresh line is toggling. Going to check 15 µs ON/OFF time.
23 To read 8042 input port and disable Megakey GreenPC feature. Make BIOS code segment writeable.
24 To do any setup before Int vector init.
25 Interrupt vector initialization to begin. To clear password if necessary.
27 Any initialization before setting video mode to be done.
28 Going for monochrome mode and color mode setting.
2A Different buses init (system, static, output devices) to start if present. (See Section 7.11 for details of
different buses. )
2B To give control for any setup required before optional video ROM check.
2C To look for optional video ROM and give control.
2D To give control to do any processing after video ROM returns control.
2E If EGA/VGA not found then do display memory R/W test.
2F EGA/VGA not found. Display memory R/W test about to begin.
30 Display memory R/W test passed. About to look for the retrace checking.
31 Display memory R/W test or retrace checking failed. To do alternate Display memory R/W test.
32 Alternate Display memory R/W test passed. To look for the alternate display retrace checking.
34 Video display checking over. Display mode to be set next.
37 Display mode set. Going to display the power-on message.
38 Different buses init (input, IPL, general devices) to start if present. (See Section 7.11 for details of
different buses. )
Page 57

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS System BIOS
Revision 1.5 47
Code Description of POST Operation
39 Display different buses initialization error messages. (See Section 7.11 for details of different buses.)
3A New cursor position read and saved. To display the Hit <DEL> message.
40 To prepare the descriptor tables.
42 To enter in virtual mode for memory test.
43 To enable interrupts for diagnostics mode.
44 To initialize data to check memory wrap around at 0:0.
45 Data initialized. Going to check for memory wrap around at 0:0 and finding the total system memory size.
46 Memory wrap around test done. Memory size calculation over. About to go for writing patterns to test
memory.
47 Pattern to be tested written in extended memory. Going to write patterns in base 640k memory.
48 Patterns written in base memory. Going to find out amount of memory below 1M memory.
49 Amount of memory below 1M found and verified. Going to find out amount of memory above 1M memory.
4B Amount of memory above 1M found and verified. Check for soft reset and going to clear memory below
1M for soft reset. (If power on, go to check point # 4Eh).
4C Memory below 1M cleared. (SOFT RESET) Going to clear memory above 1M.
4D Memory above 1M cleared. (SOFT RESET) Going to save the memory size. (Go to check
point # 52h).
4E Memory test started. (NOT SOFT RESET) About to display the first 64k memory size.
4F Memory size display started. This will be updated during memory test. Going for sequential and random
memory test.
50 Memory testing/initialization below 1M complete. Going to adjust displayed memory size for
relocation/shadow.
51 Memory size display adjusted due to relocation/ shadow. Memory test above 1M to follow.
52 Memory testing/initialization above 1M complete. Going to save memory size information.
53 Memory size information is saved. CPU registers are saved. Going to enter in real mode.
54 Shutdown successful, CPU in real mode. Going to disable gate A20 line and disable parity/NMI.
57 A20 address line, parity/NMI disable successful. Going to adjust memory size depending on
relocation/shadow.
58 Memory size adjusted for relocation/shadow. Going to clear Hit <DEL> message.
59 Hit <DEL> message cleared. <WAIT...> message displayed. About to start DMA and interrupt controller
test.
60 DMA page register test passed. To do DMA#1 base register test.
62 DMA#1 base register test passed. To do DMA#2 base register test.
65 DMA#2 base register test passed. To program DMA unit 1 and 2.
66 DMA unit 1 and 2 programming over. To initialize 8259 interrupt controller.
7F Extended NMI sources enabling is in progress.
80 Keyboard test started. Clearing output buffer, checking for stuck key, to issue keyboard reset command.
81 Keyboard reset error/stuck key found. To issue keyboard controller interface test command.
82 Keyboard controller interface test over. To write command byte and init circular buffer.
83 Command byte written, global data init done. To check for lock-key.
84 Lock-key checking over. To check for memory size mismatch with CMOS.
85 Memory size check done. To display soft error and check for password or bypass setup.
86 Password checked. About to do programming before setup.
87 Programming before setup complete. To uncompress SETUP code and execute CMOS setup.
Page 58

System BIOS Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
48 Revision 1.5
Code Description of POST Operation
88 Returned from CMOS setup program and screen is cleared. About to do programming after setup.
89 Programming after setup complete. Going to display power-on screen message.
8B First screen message displayed. <WAIT...> message displayed. PS/2 Mouse check and extended BIOS
data area allocation to be done.
8C Setup options programming after CMOS setup about to start.
8D Going for hard disk controller reset.
8F Hard disk controller reset done. Floppy setup to be done next.
91 Floppy setup complete. Hard disk setup to be done next.
95 Init of different buses optional ROMs from C800 to start. (See Section 7.11 for details of different buses.)
96 Going to do any init before C800 optional ROM control.
97 Any init before C800 optional ROM control is over. Optional ROM check and control will be done next.
98 Optional ROM control is done. About to give control to do any required processing after optional ROM
returns control and enable external cache.
99 Any initialization required after optional ROM test over. Going to setup timer data area and printer base
address.
9A Return after setting timer and printer base address. Going to set the RS-232 base address.
9B Returned after RS-232 base address. Going to do any initialization before Coprocessor test.
9C Required initialization before Coprocessor is over. Going to initialize the Coprocessor next.
9D Coprocessor initialized. Going to do any initialization after Coprocessor test.
9E Initialization after Coprocessor test is complete. Going to check extended keyboard, keyboard ID and
num-lock.
A2 Going to display any soft errors.
A3 Soft error display complete. Going to set keyboard typematic rate.
A4 Keyboard typematic rate set. To program memory wait states.
A5 Going to enable parity/NMI.
A7 NMI and parity enabled. Going to do any initialization required before giving control to optional ROM at
E000.
A8 Initialization before E000 ROM control over. E000 ROM to get control next.
A9 Returned from E000 ROM control. Going to do any initialization required after E000 optional ROM
control.
AA Initialization after E000 optional ROM control is over. Going to display the system configuration.
AB Put INT13 module runtime image to shadow.
AC Generate MP for multiprocessor support (if present).
AD Put CGA INT10 module (if present) in Shadow.
AE Uncompress SMBIOS module and init SMBIOS code and form the runtime SMBIOS image in shadow.
B1 Going to copy any code to specific area.
00 Copying of code to specific area done. Going to give control to INT-19 boot loader.
Page 59

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS System BIOS
Revision 1.5 49
7.11 Bus Initialization Checkpoints
The system BIOS gives control to different buses at several checkpoints for various tasks. Table
31 describes the bus initialization checkpoints.
Table 31. Bus Initialization Checkpoints
Checkpoint Description
2A Different buses init (system, static, and output devices) to start if present.
38 Different buses init (input, IPL, and general devices) to start if present.
39 Display different buses initialization error messages.
95 Init of different buses optional ROMs from C800 to start.
While control is inside the different bus routines, additional checkpoints are output to port 80h
as WORD to identify the routines under execution. In these WORD checkpoints, the low byte of
the checkpoint is the system BIOS checkpoint from which the control is passed to the different
bus routines. The high byte of the checkpoint is the indication of which routine is being
executed in the different buses. Table 32 describes the upper nibble of the high byte and
indicates the function that is being executed.
Table 32. Upper Nibble High Byte Functions
Value Description
0 func#0, disable all devices on the bus concerned.
1 func#1, static devices init on the bus concerned.
2 func#2, output device init on the bus concerned.
3 func#3, input device init on the bus concerned.
4 func#4, IPL device init on the bus concerned.
5 func#5, general device init on the bus concerned.
6 func#6, error reporting for the bus concerned.
7 func#7, add-on ROM init for all buses.
Table 33 describes the lower nibble of the high byte and indicates the bus on which the routines
are being executed.
Table 33. Lower Nibble High Byte Functions
Value Description
0 Generic DIM (Device Initialization Manager)
1 On-board System devices
2 ISA devices
3 EISA devices
4 ISA PnP devices
5 PCI devices
Page 60

System BIOS Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
50 Revision 1.5
7.12 Speaker
A 47 Ω inductive speaker is mounted on the Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E. The
speaker provides audible error code (beep code) information during POST.
7.13 BIOS Beep Codes
Whenever a recoverable error occurs during POST, the BIOS displays an error message
describing the problem (see Table 34). The BIOS also issues a beep code (one long tone
followed by two short tones) during POST if the video configuration fails (a faulty video card or
no card installed) or if an external ROM module does not properly checksum to zero.
An external ROM module (for example, a video BIOS) can also issue audible errors, usually
consisting of one long tone followed by a series of short tones. For more information on the
beep codes issued, check the documentation for that external device.
There are several POST routines that issue a POST terminal error and shut down the system if
they fail. Before shutting down the system, the terminal-error handler issues a beep code
signifying the test point error, writes the error to I/O port 80h, attempts to initialize the video and
writes the error in the upper left corner of the screen (using both monochrome and color
adapters).
If POST completes normally, the BIOS issues one short beep before passing control to the
operating system.
Table 34. Beep Codes
Beep Description
1 CPU error
3 Memory error
4 Thermal Trip
One 2000Hz signal (about 1 sec long)
One 1500Hz signal (about 1 sec long)
One 2000Hz signal (about 1 sec long)
One 1500Hz signal (about 1 sec long)
8 Video Error
Page 61

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS General Specification
Revision 1.5 51
8. General Specification
8.1 Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E Power Budget
8.1.1 DC Loading
Table 35 lists the DC loading characteristics of the board. This data is based on a DC analysis
of all active components within the board that impact its power delivery subsystems. Minimum
values assume a light load placed on the board that is similar to an environment with no
applications running and no USB current draw. Maximum values assume a load placed on the
board that is similar to a heavy gaming environment with a 500 mA current draw per USB port.
These calculations are not based on specific processor values or memory configurations but are
based on the minimum and maximum current draw possible from the board’s power delivery
subsystems to the processor, memory, and USB ports.
Use the datasheets for add-in cards, such as PCI, to determine the overall system power
requirements. The selection of a power supply at the system level is dependent on the system’s
usage model and not necessarily tied to a particular processor speed.
Table 35. DC Power Budget
Device +3.3 V +5 V +12 V -12 V +5 VSB
Server Board 1.2A 2.6A 0.00 0.05A 1.0A
Processor 15A
Memory DIMMs 6A
Fans
Processor Fan * 1A
Front Panel Fan 0.8A
Rear Panel Fan 0.8A
Aux Fan 0.8A
Keyboard/Mouse 345mA
PCI Slots (3) 7.6A 5A 3.75mA
PCIe Slots
x4 Slots (2) ** 3A 0.5A
x8 Slot (1) *** 3A 5.5A
USB Ports (8) 500mA
Total Current 33 12 25 Total
Total Power 109 60 293 467Watts
Processor Fan must be connected to the Processor Fan Header (4 wire)
** Each PCI card may not exceed 25 Watts of power
*** Power budget for x1 slots based on x1 power consumption
**** Power budget for x8 slot based on x16 power consumption. Graphic adapters that require additional power, will
need a chassis power supply with the power source for the card.
NOTE: The Server Boards is designed to provide 2A (average) of +5V current for each add-in board. The total
+5 V current draw for add-in boards for the boards is as follows: A fully loaded Intel® Entry Server Board
SE7221BA1-E (all PCI and PCI Express slots populated) must not exceed 14A.
Page 62

General Specification Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
52 Revision 1.5
<This page intentionally left blank.>
Page 63

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Platform Management
Revision 1.5 53
9. Platform Management
9.1 Platform Management Overview
TBD
10. Error Reporting
10.1 Fault Resilient Booting
TBD
11. Design and Environmental Specifications
11.1 Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E Design Specification
TBD
Page 64

Design and Environmental Specifications Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
54 Revision 1.5
<This page intentionally left blank.>
Page 65

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Regulatory Compliance
Revision 1.5 55
12. Regulatory Compliance
This section describes the Server Boards’ compliance with U.S. and international safety and
electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations.
12.1 Safety Regulations
Table 36 lists the safety regulations the Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E complies with
when correctly installed in a compatible host system.
Table 36. Safety Regulations
Regulation Title
UL 60950-1:2003/
CSA C22.2 No. 60950-1-03
Information Technology Equipment – Safety - Part 1: General Requirements
(USA and Canada)
EN 60950-1:2002 Information Technology Equipment – Safety - Part 1: General Requirements
(European Union)
IEC 60950-1:2001, First Edition Information Technology Equipment – Safety - Part 1: General Requirements
(International)
12.2 EMC Regulations
Table 37 lists the EMC regulations the Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E complies with
when correctly installed in a compatible host system.
Table 37. EMC Regulations
Regulation Title
FCC (Class B) Title 47 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Parts 2 and 15, Subpart B, Radio
Frequency Devices. (USA)
ICES-003 (Class B) Interference-Causing Equipment Standard, Digital Apparatus. (Canada)
EN55022: 1998 (Class B) Limits and methods of measurement of Radio Interference Characteristics of
Information Technology Equipment.
(European Union)
EN55024: 1998 Information Technology Equipment – Immunity Characteristics Limits and
methods of measurement. (European Union)
AS/NZS 3548 (Class B) Australian Communications Authority, Standard for Electromagnetic
Compatibility. (Australia and New Zealand)
CISPR 22, 3rd Edition (Class B) Limits and methods of measurement of Radio Disturbance Characteristics of
Information Technology Equipment. (International)
CISPR 24: 1997 Information Technology Equipment – Immunity Characteristics – Limits and
Methods of Measurements. (International)
VCCI (Class B) Voluntary Control for Interference by Information Technology Equipment.
(Japan)
Page 66

Regulatory Compliance Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
56 Revision 1.5
12.2.1 FCC Compliance Statement (USA)
Product Type: Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential environment. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning
the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or
more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment to a different electrical branch circuit from that to which the
receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Any changes or modifications to the equipment not expressly approved by Intel® Corporation
could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
12.2.2 Canadian Compliance Statement
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appereil numérique de la classe B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
12.3 European Union Declaration of Conformity Statement
We, Intel® Corporation, declare under our sole responsibility that the product: Intel® Entry
Server Board SE7221BA1-E is in conformity with all applicable essential requirements
necessary for CE marking, following the provisions of the European Council Directive
89/336/EEC (EMC Directive) and Council Directive 73/23/EEC (Safety/Low Voltage Directive).
The product is properly CE marked demonstrating this conformity and is for distribution within all
member states of the EU with no restrictions.
This product follows the provisions of the European Directives 89/336/EEC and 73/23/EEC.
Dansk Dette produkt er i overensstemmelse med det europæiske direktiv 89/336/EEC &
73/23/EEC.
Dutch Dit product is in navolging van de bepalingen van Europees Directief 89/336/EEC &
73/23/EEC.
Suomi Tämä tuote noudattaa EU-direktiivin 89/336/EEC & 73/23/EEC määräyksiä.
Français Ce produit est conforme aux exigences de la Directive Européenne 89/33 6/EEC &
73/23/EEC.
Page 67

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Regulatory Compliance
Revision 1.5 57
Deutsch Dieses Produkt entspricht den Bestimmungen der Europäischen Richtlinie 89/336/EEC
& 73/23/EEC.
Icelandic Þessi vara stenst reglugerð Evrópska Efnahags Bandalagsins númer 89/336/ EEC &
73/23/EEC.
Italiano Questo prodotto è conforme alla Direttiva Europea 89/336/EEC & 73/23/EEC.
Norsk Dette produktet er i henhold til bestemmelsene i det europeiske direktivet 89/336/ EEC &
73/23/EEC.
Portuguese Este produto cumpre com as normas da Diretiva Européia 89/336/EEC &
73/23/EEC.
Español Este producto cumple con las normas del Directivo Europeo 89/336/EEC & 73/23/EEC.
Svenska Denna produkt har tillverkats i enlighet med EG-direktiv 89/336/EEC & 73/23/EEC.
12.4 Product Ecology Statements
The following information is provided to address worldwide product ecology concerns and
regulations.
12.4.1 Disposal Considerations
This product contains the following materials that may be regulated upon disposal: lead solder
on the printed wiring board assembly.
12.4.2 Recycling Considerations
Intel® encourages its customers to recycle its products and their components (e.g., batteries,
circuit boards, plastic enclosures, etc.) whenever possible. In the U.S., a list of recyclers in your
area can be found at:
http://www.eiae.org/
In the absence of a viable recycling option, products and their components must be
disposed of in accordance with all applicable local environmental regula tions.
Page 68

Regulatory Compliance Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
58 Revision 1.5
12.5 Product Certification Markings (Board Level)
Table 38 lists the board’s product certification markings.
Table 38. Product Certification Markings
Description Marking
UL joint US/Canada Recognized Component mark. Includes adjacent UL file
number for Intel® Server Boards: E210882 (component side).
FCC Declaration of Conformity logo mark for Class B equipment; includes
Intel® name and SE7221BA1-E model designation (component side).
CE mark. Declares compliance to European Union (EU) EMC directive
(89/336/EEC) and Low Voltage directive (73/23/EEC) (component side). The
CE mark should also be on the shipping container.
Australian Communications Authority (ACA) C-Tick mark. Includes adjacent
Intel® supplier code number, N-232. The C-tick mark should also be on the
shipping container.
Printed wiring board manufacturer’s recognition mark: consists of a unique UL
recognized manufacturer’s logo, along with a flammability rating (solder side).
V-0 or 94V-0
Page 69

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Miscellaneous Board Information
Revision 1.5 59
13. Miscellaneous Board Information
13.1 ATX Baseboard Mechanical Specifications
The Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E is designed to fit into an ATX-form-factor chassis .
Figure 17 illustrates the mechanical form factor for the Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E.
Dimensions are given in inches [millimeters]. The outer dimensions are 10.20 inches by 9.60
inches [259.08 millimeters by 243.84 millimeters]. Location of the I/O connectors and mounting
holes are in compliance with the ATX specification.
OM16684
6.100
[154.94]
3.100
[78.74]
3.750
[95.25]
6.450
[163.83]
6.500
[165.10]
6.200
[157.48]
5.200
[132.08]
2.850
[72.39]
1.800
[45.72]
0.00
2.600
[66.04]
4.900
[124.46]
0.00
Figure 17. Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E Dimensions
13.2 I/O Shield Mechanical Specification
Figure 18. I/O Shield is the Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E general purpose I/O
shield mechanical drawing.
Page 70

Miscellaneous Board Information Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
60 Revision 1.5
Figure 18. I/O Shield
13.3 Thermal Considerations
CAUTION
A chassis with a maximum internal ambient temperature of 35 oC at the processor fan inlet
is a requirement. Use a processor heatsink that provides omni-directional airflow (as
shown in Figure 19) to maintain required airflow across the processor voltage regulator
area.
Page 71

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Miscellaneous Board Information
Revision 1.5 61
OM16996
Figure 19. Processor Heatsink for Omni-directional Airflow
CAUTION
Failure to ensure appropriate airflow may result in reduced performance of both the
processor and/or voltage regulator or, in some instances, damage to the server board.
For a list of chassis that have been tested with Intel server boards please refer to the
following website:
http://support.intel.com/support/processors/pentium4/
All responsibility for determining the adequacy of any thermal or system design remains
solely with the integrator. Intel makes no warranties or representations that merely
following the instructions presented in this document will result in a system with adequate
thermal performance.
CAUTION
Ensure that the ambient temperature does not exceed the Server Board’s maximum
operating temperature. Failure to do so could cause components to exceed their
maximum case temperature and malfunction.
CAUTION
Ensure that proper airflow is maintained in the processor voltage regulator circuit. Failure
to do so may result in damage to the voltage regulator circuit. The processor voltage
regulator area (Figure 20, item A) can reach a temperature of up to 85
o
C in an open
chassis.
Page 72

Miscellaneous Board Information Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
62 Revision 1.5
Figure 20 shows the locations of the localized high temperature zones.
OM16683
B
A
CD
Item Description
A Processor voltage regulator area
B Processor
C Intel® E7221MC MCH
D Intel® 82801FR ICH6-R
Figure 20. Localized High Temperature Zones
Table 39. Thermal Considerations for Components provides maximum case temperatures for
the Intel
® Server Board SE7221BA1-E components that are sensitive to thermal changes. The
operating temperature, current load, or operating frequency could affect case temperatures.
Maximum case temperatures are important when considering proper airflow to cool the
SE7221BA1-E Server Board.
Table 39. Thermal Considerations for Components
Component Maximum Case Temperature
Intel® Pentium® 4 processor For processor case temperature, see processor datasheets and
processor specification updates
Intel® 7221 MCH TBD oC (under bias)
Intel® 82801FR ICH6-R 110 oC (under bias)
Page 73

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Miscellaneous Board Information
Revision 1.5 63
13.4 Calculated Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF)
The MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) for the Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E as
configured from the factory is shown in Table 40.
Table 40. Calculated Mean Time Between Failure
Product Code Calculated MTBF Operating Temperature
SE7221BA1 105,577 Hrs 55 Degrees C
13.5 Environmental
Table 41 lists the environmental specifications for the Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E,
TBD.
Table 41. Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E Environmental Specifications
Parameter Specification
Temperature
Non-Operating
-40
°C to +70 °C
Operating
0
°C to +55 °C
Shock
Unpackaged 50 g trapezoidal waveform
Velocity change of 170 inches/second
Packaged Half sine 2 millisecond
Product Weight (pounds) Free Fall (inches) Velocity Change (inches/sec)
<20 36 167
21-40 30 152
41-80 24 136
81-100 18 118
Vibration
Unpackaged 5 Hz to 20 Hz: 0.01 g² Hz sloping up to 0.02 g² Hz
20 Hz to 500 Hz: 0.02 g² Hz (flat)
Packaged 5 Hz to 40 Hz: 0.015 g² Hz (flat)
40 Hz to 500 Hz: 0.015 g² Hz sloping down to 0.00015 g² Hz
13.6 Clearing CMOS
Clear the CMOS with the following procedure:
• Remove power from the system
• Move CMOS clear jumper from Pin 1 – 2 to 2 – 3.
• Replace power to the server and power on.
Page 74

Miscellaneous Board Information Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
64 Revision 1.5
• Shutdown the server after 5 to 10 seconds and remove power from the system.
• Move the CMOS jumper back to Pin 1 – 2
• Restore power and power on the server
CMOS settings will be restored to default settings.
Supported video resolution SE7221BA1-E Supported Video Modes
Pixel
Resolution Refresh Rates 8 bpp 16 bpp 32bpp
640x480 60,75,85 Supported Supported Supported
800x600 60,75,85 Supported Supported Supported
1024x768 60,75,85 Supported Supported Supported
1280x1024 60,75,85 Supported Supported Supported
1600x1200 60,75,85 Supported Supported Supported
1920x1440 60,75,85 Supported Supported
Page 75

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Glossary
Revision 1.5 I
Glossary
This appendix contains important terms used in the preceding chapters. For ease of use,
numeric entries are listed first (e.g., “82460GX”) with alpha entries following (e.g., “AGP 4x”).
Acronyms are then entered in their respective place, with non-acronyms following.
Term Definition
ACPI Advanced Configuration and Power Interface
ANSI American National Standards Institute
AP Application Processor
ASIC Application Specific Integrated Circuit
BIOS Basic input/output system
Byte 8-bit quantity.
CMOS In terms of this specification, this describes the PC-AT compatible region of battery-backed
128 bytes of memory, which normally resides on the server board.
DMA Direct Memory Access
ECC Error Correcting Code
EMC Electromagnetic Compatibility
EPS External Product Specification
FDC Floppy Disk Controller
FRU Field replaceable unit
GB 1024 MB.
GUID Globally Unique ID
HDG Hardware Design Guide
IA Intel® architecture
IP Internet Protocol
IRQ Interrupt Request
KB 1024 bytes
LAN Local area network
LBA Logical Block Address
MB 1024 KB
MBE Multi-Bit Error
Ms milliseconds
MTBF Mean Time Between Failures
NIC Network Interface Card
NMI Non-maskable Interrupt
OEM Original equipment manufacturer
Ohm Unit of electrical resistance
PIO Programmable I/O
PME Power Management Event
PnP Plug and Play
POST Power-on Self Test
RAM Random Access Memory
ROM Read Only Memory
RTC Real Time Clock
Page 76

Glossary Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS
II Revision 1.5
Term Definition
SBE Single-Bit Error
SDRAM Synchronous Dynamic RAM
SEL System event log
SM Server Management
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol
SPD Serial Presence Detect
SSI Server Standards Infrastructure
TBD To be Determined Later
TPS Technical Product Specification
USB Universal Serial Bus
VGA Video Graphic Adapter
VRM Voltage Regulator Module
Word 16-bit quantity
Page 77

Intel® Entry Server Board SE7221BA1-E TPS Reference Documents
Revision 1.5 III
Reference Documents
Refer to the following documents for additional information:
14 Board Set Specification, Intel® Corporation, document number xx-xxxx.
15 System Specification, Intel® Corporation, document number xx-xxxx.
16 Wired for Management Baseline Specification, v 2.0, Intel® Corporation
http://www.intel.com/labs/manage/wfm/wfmspecs.htm
 Loading...
Loading...