Page 1

A Detailed Look Inside the
Intel® NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of
the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
November, 2000
Page 2

A Detailed Look Inside the Intel
®
NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products. No license, express or implied, by estoppel or
otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document. Except as provided in Intel’s Terms and Conditions
of Sale for such products, Intel assumes no liability whatsoever, and Intel disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating
to sale and/or use of Intel products including liability or warranties relating to fitness for a particular purpose, merchantability,
or infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property right. Intel products are not intended for use in medical,
life saving, or life sustaining applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or “undefined.”
Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising
from future changes to them.
The Intel® Pentium® 4 processor may contain design defects or errors known as errata. Current characterized errata are
available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an ordering number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be
obtained by calling 1-800-548-4725 or by visiting Intel’s Website at http://www.intel.com.
Copyright © 2000 Intel Corporation.
* Third-party brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Page 2
Page 3
A Detailed Look Inside the Intel
Revision History
Revision Date Revision Major Changes
11/2000 1.0 Release
®
NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
Page 3
Page 4

A Detailed Look Inside the Intel
®
NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
Table of Contents
ABOUT THIS DOCUMENT................................................................................................................. 5
INTRODUCTION................................................................................................................................ 6
SIMD TECHNOLOGY AND STREAMING SIMD EXTENSIONS 2......................................................... 6
Summary of SIMD Technologies..............................................................................................................................................7
INTEL® NETBURST™ MICRO-ARCHITECTURE................................................................................. 9
The Design Considerations of the Intel NetBurst Micro-architecture............................................................................9
Overview of the Intel NetBurst Micro-architecture Pipeline..........................................................................................10
The Front End.............................................................................................................................................................................10
The Out-of-order Core...............................................................................................................................................................11
Retirement...................................................................................................................................................................................11
Front End Pipeline Detail..........................................................................................................................................................11
Prefetching...................................................................................................................................................................................12
Decoder........................................................................................................................................................................................12
Execution Trace Cache..............................................................................................................................................................12
Branch Prediction.......................................................................................................................................................................12
Branch Hints ...............................................................................................................................................................................13
Execution Core Detail................................................................................................................................................................13
Instruction Latency and Throughput......................................................................................................................................13
Execution Units and Issue Ports ..............................................................................................................................................14
Caches..........................................................................................................................................................................................15
Data Prefetch...............................................................................................................................................................................15
Loads and Stores........................................................................................................................................................................16
Store Forwarding........................................................................................................................................................................17
Page 4
Page 5

A Detailed Look Inside the Intel
®
NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
About this Document
The Intel® NetBurst™ micro-architecture is the foundation for the Intel® Pentium® 4 processor. It includes several
important new features and innovations that will allow the Intel Pentium 4 processor and future IA-32 processors to
deliver industry leading performance for the next several years. This paper provides an in-depth examination of the
features and functions the Intel NetBurst micro-architecture.
Page 5
Page 6
A Detailed Look Inside the Intel
®
NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
Introduction
The Intel® Pentium® 4 processor, utilizing the Intel® NetBurstTM micro-architecture, is a complete processor redesign that delivers new technologies and capabilities while advancing many of the innovative features, such as
“out-of-order speculative execution” and “super-scalar execution”, introduced on prior Intel® micro-architectural
generations. Many of these new innovations and advances were made possible with the improvements in processor
technology, process technology and circuit design and could not previously be implemented in high-volume,
manufacturable solutions. The features and resulting benefits of the new micro-architecture are defined in the
following sections.
This paper begins with a brief introduction of three generations of single-instruction, multiple-data (SIMD)
technology. The rest of this paper describes the principle of operation of the innovations of Intel Pentium 4
processor with respect to the Intel NetBurst micro-architecture and the implementation characteristics of the
Pentium 4 processor.
SIMD Technology and Streaming SIMD Extensions 2
One way to increase processor performance is to execute several computations in parallel, so that multiple
computations are done with a single instruction. The way to achieve this type of parallel execution is to use the
single-instruction, multiple-data (SIMD) computation technique.
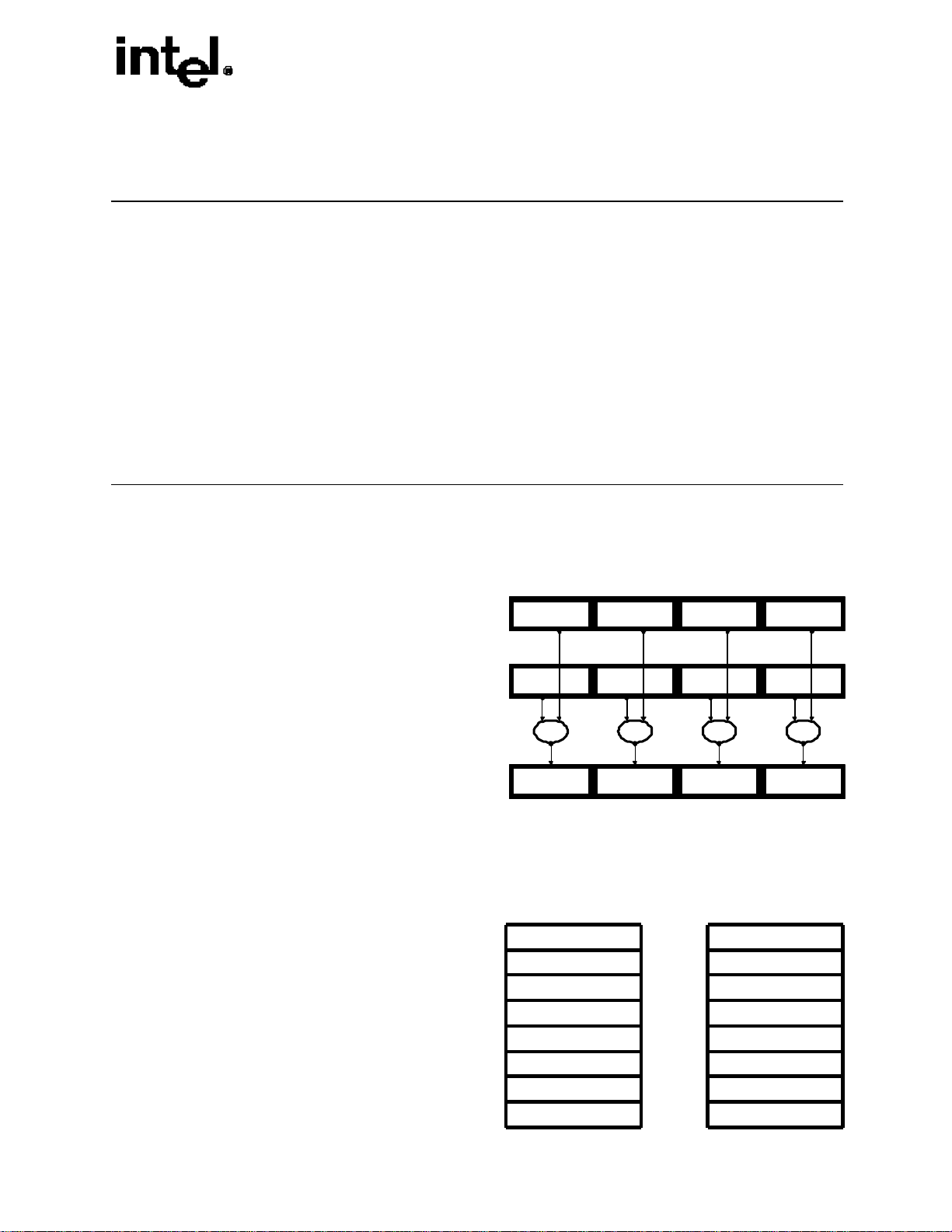
Figure 1 shows a typical SIMD computation. Here two
sets of four packed data elements (X1, X2, X3, and X4,
and Y1, Y2, Y3, and Y4) are operated on in parallel, with
the same operation being performed on each
Figure 1 Typical SIMD Operations
X4 X1X2X3
corresponding pair of data elements (X1 and Y1, X2 and
Y2, X3 and Y3, and X4 and Y4). The results of the four
parallel computations are a set of four packed data
elements.
SIMD computations like those shown in Figure 1 were
introduced into the Intel IA-32 architecture with the Intel
Y4 Y1 Y2 Y3
op opopop
MMX™ technology. The Intel MMX technology allows
SIMD computations to be performed on packed byte,
word, and doubleword integers that are contained in a set
X4 op Y4 X1 op Y1X2 op Y2X3 op Y3
of eight 64-bit registers called the MMX registers (see Figure 2).
The Pentium III processor extended this initial SIMD computation model with the introduction of the Streaming
SIMD Extensions (SSE). The Streaming SIMD
Extensions allow SIMD computations to be
Figure 2 Registers available to SIMD Instructions
performed on operands that contain four packed
single-precision floating-point data elements. The
operands can be either in memory or in a set of eight
128-bit registers called the XMM registers (see
Figure 2). The SSE also extended SIMD
computational capability with additional 64-bit MMX
instructions.
The Pentium 4 processor further extends the SIMD
computation model with the introduction of the
Streaming SIMD Extensions 2 (SSE2). The SSE2
extensions also work with operands in either memory
or in the XMM registers. The SSE2 extends SIMD
MM7
MM6
MM5
MM4
MM3
MM2
MM1
MM0
128 Bit XMM Registers64 Bit MMXTM Registers
XMM7
XMM6
XMM5
XMM4
XMM3
XMM2
XMM1
XMM0
Page 6
Page 7

A Detailed Look Inside the Intel
®
NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
computations to operate on packed double-precision floating-point data elements and 128-bit packed integers. There
are 144 instructions in the SSE2 that can operate on two packed double-precision floating-point data elements, or on
16 packed byte, 8 packed word, 4 doubleword, and 2 quadword integers.
The full set of IA-32 SIMD technologies (the Intel MMX technology, the SSE extensions, and the SSE2 extensions)
gives the programmer the ability to develop algorithms that can combine operations on packed 64- and 128-bit
integer and single and double-precision floating-point operands.
This SIMD capability improves the performance of 3D graphics, speech recognition, image processing, scientific,
and other multimedia applications that have the following characteristics:
§ inherently parallel
§ regular and recurring memory access patterns
§ localized recurring operations performed on the data
§ data-independent control flow.
The IA-32 SIMD floating-point instructions fully support the IEEE* Standard 754 for Binary Floating-Point
Arithmetic. All SIMD instructions are accessible from all IA-32 execution modes: protected mode, real address
mode, and Virtual 8086 mode.
The SSE2 and SSE extensions, and the Intel MMX technology are architectural extensions in the IA-32 Intel
architecture. All existing software continues to run correctly, without modification, on IA-32 microprocessors that
incorporate these technologies. Existing software also runs correctly in the presence of new applications that
incorporate these SIMD technologies.
®
The SSE and SSE2 instruction sets also introduced a set of cacheability and memory ordering instructions that can
improve cache usage and application performance.
For more information on SSE2 instructions, including the cacheability and memory operation instructions, refer to
the IA-32 Intel® Architecture Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 1, Chapter 11 and Volume 2, Chapter 3, which
are available at: http://developer.intel.com/design/pentium4/manuals/.
Summary of SIMD Technologies
The paragraphs below summarize the new features of the three SIMD technologies (MMX technology, SSE, and
SSE2) that have been added to the IA-32 architecture in chronological order.
MMX Technology
§ Introduces 64-bit MMX registers.
§ Introduces support for SIMD operations on packed byte, word, and doubleword integers.
The MMX instructions are useful for multimedia and communications software.
For more information on the MMX technology, refer to the IA-32 Intel® Architecture Software Developer’s Manual,
Volume 1, available at http://developer.intel.com/design/pentium4/manuals/.
Streaming SIMD Extensions
§ Introduces 128-bit XMM registers.
§ Introduces 128-bit data type with four packed single-precision floating-point operands.
§ Introduces data prefetch instructions.
§ Introduces non-temporal store instructions and other cacheability and memory ordering instructions.
§ Adds extra 64-bit SIMD integer support.
Page 7
Page 8
A Detailed Look Inside the Intel
®
NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
The SSE instructions are useful for 3D geometry, 3D rendering, speech recognition, video encoding and decoding.
For more information on the Streaming SIMD Extensions, refer to the IA-32 Intel® Architecture Software
Developer’s Manual, Volume 1, available at http://developer.intel.com/design/pentium4/manuals/.
Streaming SIMD Extensions 2
§ Adds 128-bit data type with two packed double-precision floating-point operands.
§ Adds 128-bit data types for SIMD integer operation on 16-byte, 8-word, 4-doubleword, or 2-quadword
integers.
§ Adds support for SIMD arithmetic on 64-bit integer operands.
§ Adds instructions for converting between new and existing data types.
§ Extends support for data shuffling.
§ Extends support for cacheability and memory ordering operations.
The SSE2 instructions are useful for 3D graphics, scientific computation, video decoding/encoding, and encryption.
For more information, refer to the IA-32 Intel® Architecture Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 1, available at
http://developer.intel.com.com/design/pentium4/manuals/.
Page 8
Page 9

A Detailed Look Inside the Intel
®
NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
Intel® NetBurst™ Micro-architecture
The Pentium® 4 processor is the first hardware implementation of a new micro-architecture, the Intel NetBurst
micro-architecture. To help reader understand this new micro-architecture, this section examines in detail the
following:
§ the design considerations the Intel NetBurst micro-architecture
§ the building blocks that make up this new micro-architecture
§ the operation of key functional units of this micro-architecture based on the implementation in the Pentium 4
processor.
The Intel NetBurst micro-architecture is designed to achieve high performance for both integer and floating-point
computations at very high clock rates. It has the following features:
§ hyper pipelined technology to enable high clock rates and frequency headroom to well above 1GHz
§ rapid execution engine to reduce the latency of basic integer instructions
§ high-performance, quad-pumped bus interface to the 400 MHz Intel NetBurst micro-architecture system bus.
§ execution trace cache to shorten branch delays
§ cache line sizes of 64 and 128 bytes
§ hardware prefetch
§ aggressive branch prediction to minimize pipeline delays
§ out-of-order speculative execution to enable parallelism
§ superscalar issue to enable parallelism
§ hardware register renaming to avoid register name space limitations
The Design Considerations of the Intel® NetBurstTM Micro-architecture
The design goals of Intel NetBurst micro-architecture are: (a) to execute both the legacy IA-32 code and applications
based on single-instruction, multiple-data (SIMD) technology at high processing rates; (b) to operate at high clock
rates, and to scale to higher performance and clock rates in the future. To accomplish these design goals, the Intel
NetBurst micro-architecture has many advanced features and improvements over the Pentium Pro processor microarchitecture.
The major design considerations of the Intel NetBurst micro-architecture to enable high performance and highly
scalable clock rates are as follows:
§ It uses a deeply pipelined design to enable high clock rates with different parts of the chip running at different
clock rates, some faster and some slower than the nominally-quoted clock frequency of the processor. The
Intel NetBurst micro-architecture allows the Pentium 4 processor to achieve significantly higher clock rates as
compared with the Pentium III processor. These clock rates will achieve well above 1 GHz.
§ Its pipeline provides high performance by optimizing for the common case of frequently executed
instructions. This means that the most frequently executed instructions in common circumstances (such as a
cache hit) are decoded efficiently and executed with short latencies, such that frequently encountered code
sequences are processed with high throughput.
§ It employs many techniques to hide stall penalties. Among these are parallel execution, buffering, and
speculation. Furthermore, the Intel NetBurst micro-architecture executes instructions dynamically and out-ororder, so the time it takes to execute each individual instruction is not always deterministic. Performance of a
particular code sequence may vary depending on the state the machine was in when that code sequence was
entered.
Page 9
Page 10

A Detailed Look Inside the Intel
®
NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
Overview of the Intel® NetBurstTM Micro-architecture Pipeline
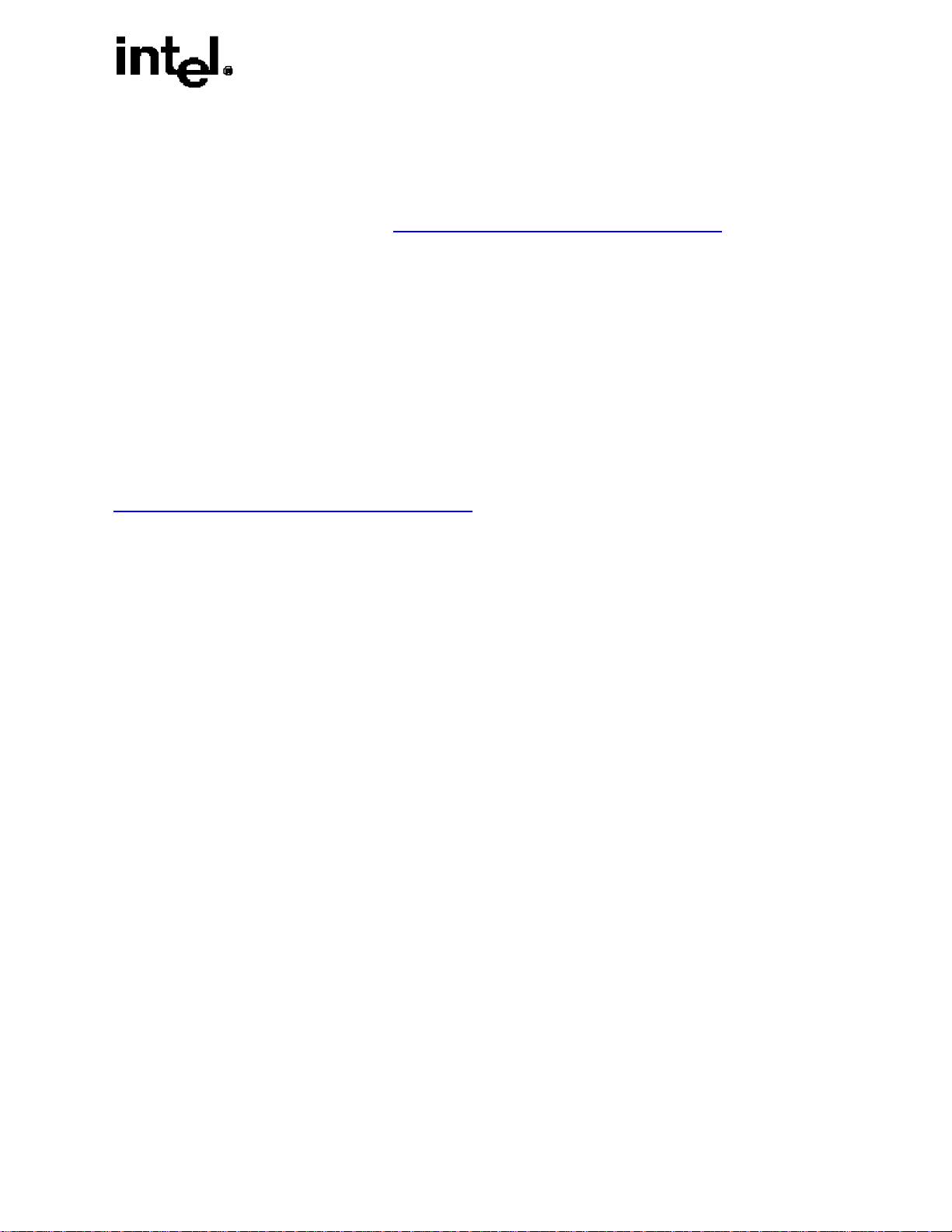
The pipeline of the Intel NetBurst micro-architecture contain three sections:
§ the in-order issue front end
§ the out-of-order superscalar execution core
§ the in-order retirement unit.
Figure 3 The Intel® NetBurstTM Micro-architecture
The front end supplies instructions in program order to
System Bus
the out-of-order core. It fetches and decodes IA-32
instructions. The decoded IA-32 instructions are
translated into micro-operations (µops). The front end’s
primary job is to feed a continuous stream of µops to
the execution core in original program order.
The core can then issue multiple µops per cycle, and
3rd Level Cache
Optional, Server Product Only
aggressively reorder µops so that those µops, whose
inputs are ready and have execution resources available,
can execute as soon as possible. The retirement section
2nd Level Cache
ensures that the results of execution of the µops are
processed according to original program order and that
the proper architectural states are updated.
Fetch/Decode
Front End
Figure 3 illustrates a block diagram view of the major
functional blocks associated with the Intel NetBurst
micro-architecture pipeline. The paragraphs that follow
Figure 3 provide an overview of each of the three
BTBs/Branch Prediction
sections in the pipeline.
The Front End
The front end of the Intel NetBurst micro-architecture consists of two parts:
§ fetch/decode unit
§ execution trace cache.
Bus Unit
8-Way
Trace Cache
Microcode ROM
Frequently used paths
Less frequently used paths
1st Level Cache
4-way
Execution
Out-Of-Order Core
Branch History Update
Retirement
The front end performs several basic functions:
§ prefetches IA-32 instructions that are likely to be executed
§ fetches instructions that have not already been prefetched
§ decodes instructions into µops
§ generates microcode for complex instructions and special-purpose code
§ delivers decoded instructions from the execution trace cache
§ predicts branches using highly advanced algorithm.
The front end of the Intel NetBurst micro-architecture is designed to address some of the common problems in highspeed, pipelined microprocessors. Two of these problems contribute to major sources of delays:
§ the time to decode instructions fetched from the target
§ wasted decode bandwidth due to branches or branch target in the middle of cache lines.
The execution trace cache addresses both of these problems by storing decoded IA-32 instructions. Instructions are
fetched and decoded by a translation engine. The translation engine builds the decoded instruction into sequences of
Page 10
Page 11

A Detailed Look Inside the Intel
®
NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
µops called traces, which are stored in the execution trace cache. The execution trace cache stores these µops in the
path of program execution flow, where the results of branches in the code are integrated into the same cache line.
This increases the instruction flow from the cache and makes better use of the overall cache storage space since the
cache no longer stores instructions that are branched over and never executed. The execution trace cache can deliver
up to 3 µops per clock to the core.
The execution trace cache and the translation engine have cooperating branch prediction hardware. Branch targets
are predicted based on their linear address using branch prediction logic and fetched as soon as possible. Branch
targets are fetched from the execution trace cache if they are cached there, otherwise they are fetched from the
memory hierarchy. The translation engine’s branch prediction information is used to form traces along the most
likely paths.
The Out-of-Order Core
The core’s ability to execute instructions out of order is a key factor in enabling parallelism. This feature enables the
processor to reorder instructions so that if one µop is delayed while waiting for data or a contended resource, other
µops that appear later in the program order may proceed around it. The processor employs several buffers to smooth
the flow of µops. This implies that when one portion of the entire processor pipeline experiences a delay, that delay
may be covered by other operations executing in parallel (for example, in the core) or by the execution of µops
which were previously queued up in a buffer (for example, in the front end).
The delays described in this paper must be understood in this context. The core is designed to facilitate parallel
execution. It can dispatch up to six µops per cycle through the issue ports. (The issue ports are shown in Figure 4.)
Note that six µops per cycle exceeds the trace cache and retirement µop bandwidth. The higher bandwidth in the
core allows for peak bursts of greater than 3 µops and to achieve higher issue rates by allowing greater flexibility in
issuing µops to different execution ports.
Most execution units can start executing a new µop every cycle, so that several instructions can be in flight at a time
for each pipeline. A number of arithmetic logical unit (ALU) instructions can start two per cycle, and many floatingpoint instructions can start one every two cycles. Finally, µops can begin execution, out of order, as soon as their
data inputs are ready and resources are available.
Retirement
The retirement section receives the results of the executed µops from the execution core and processes the results so
that the proper architectural state is updated according to the original program order. For semantically-correct
execution, the results of IA-32 instructions must be committed in original program order before it is retired.
Exceptions may be raised as instructions are retired. Thus, exceptions cannot occur speculatively, they occur in the
correct order, and the machine can be correctly restarted after an exception.
When a µop completes and writes its result to the destination, it is retired. Up to three µops may be retired per cycle.
The Reorder Buffer (ROB) is the unit in the processor which buffers completed µops, updates the architectural state
in order, and manages the ordering of exceptions.
The retirement section also keeps track of branches and sends updated branch target information to the Branch
Target Buffer (BTB) to update branch history. Figure 3 illustrates the paths that are most frequently executing
inside the Intel NetBurst micro-arachitecture: an execution loop that interacts with multi-level cache hierarchy and
the system bus.
The following sections describe in more detail the operation of the front end and the execution core.
Front End Pipeline Detail
The following information about the front end operation may be useful for tuning software with respect to
prefetching, branch prediction, and execution trace cache operations.
Page 11
Page 12

A Detailed Look Inside the Intel
®
NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
Prefetching
The Intel NetBurst micro-architecture supports three prefetching mechanisms:
§ the first is for instructions only
§ the second is for data only
§ the third is for code or data.
The first mechanism is hardware instruction fetcher that automatically prefetches instructions. The second is a
software-controlled mechanism that fetches data into the caches using the prefetch instructions. The third is a
hardware mechanism that automatically fetches data and instruction into the unified second-level cache.
The hardware instruction fetcher reads instructions along the path predicted by the BTB into the instruction
streaming buffers. Data is read in 32-byte chunks starting at the target address. The second and third mechanisms is
described in Data Prefetch.
Decoder
The front end of the Intel NetBurst micro-architecture has a single decoder that can decode instructions at the
maximum rate of one instruction per clock. Complex instruction must enlist the help of the microcode ROM. The
decoder operation is connected to the execution trace cache discussed in the section that follows.
Execution Trace Cache
The execution trace cache (TC) is the primary instruction cache in the Intel NetBurst micro-architecture. The TC
stores decoded IA-32 instructions, or µops. This removes decoding costs on frequently-executed code, such as
template restrictions and the extra latency to decode instructions upon a branch misprediction.
In the Pentium 4 processor implementation, the TC can hold up to 12K µops and can deliver up to three µops per
cycle. The TC does not hold all of the µops that need to be executed in the execution core. In some situations, the
execution core may need to execute a microcode flow, instead of the µop traces that are stored in the trace cache.
The Pentium 4 processor is optimized so that most frequently-executed IA-32 instructions come from the trace
cache, efficiently and continuously, while only a few instructions involve the microcode ROM.
Branch Prediction
Branch prediction is very important to the performance of a deeply pipelined processor. Branch prediction enables
the processor to begin executing instructions long before the branch outcome is certain. Branch delay is the penalty
that is incurred in the absence of a correct prediction. For Pentium 4 processor, the branch delay for a correctly
predicted instruction can be as few as zero clock cycles. The branch delay for a mispredicted branch can be many
cycles; typically this is equivalent to the depth of the pipeline.
The branch prediction in the Intel NetBurst micro-architecture predicts all near branches, including conditional,
unconditional calls and returns, and indirect branches. It does not predict far transfers, for example, far calls, irets,
and software interrupts.
In addition, several mechanisms are implemented to aid in predicting branches more accurately and in reducing the
cost of taken branches:
§ dynamically predict the direction and target of branches based on the instructions’ linear address using the
branch target buffer (BTB)
§ if no dynamic prediction is available or if it is invalid, statically predict the outcome based on the offset of the
target: a backward branch is predicted to be taken, a forward branch is predicted to be not taken
§ return addresses are predicted using the 16-entry return address stack
§ traces of instructions are built across predicted taken branches to avoid branch penalties.
Page 12
Page 13

A Detailed Look Inside the Intel
®
NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
The Static Predictor. Once the branch instruction is decoded, the direction of the branch (forward or backward) is
known. If there was no valid entry in the BTB for the branch, the static predictor makes a prediction based on the
direction of the branch. The static prediction mechanism predicts backward conditional branches (those with
negative displacement), such as loop-closing branches, as taken. Forward branches are predicted not taken.
Branch Target Buffer. Once branch history is available, the Pentium 4 processor can predict the branch outcome
before the branch instruction is even decoded, based on a history of previously-encountered branches. It uses a
branch history table and a branch target buffer (collectively called the BTB) to predict the direction and target of
branches based on an instruction’s linear address. Once the branch is retired, the BTB is updated with the target
address.
Return Stack. Returns are always taken, but since a procedure may be invoked from several call sites, a single
predicted target will not suffice. The Pentium 4 processor has a Return Stack that can predict return addresses for a
series of procedure calls. This increases the benefit of unrolling loops containing function calls. It also mitigates the
need to put certain procedures inline since the return penalty portion of the procedure call overhead is reduced.
Even if the direction and target address of the branch are correctly predicted well in advance, a taken branch may
reduce available parallelism in a typical processor, since the decode bandwidth is wasted for instructions which
immediately follow the branch and precede the target, if the branch does not end the line and target does not begin
the line. The branch predictor allows a branch and its target to coexist in a single trace cache line, maximizing
instruction delivery from the front end.
Branch Hints
The Pentium 4 processor provides a feature that permits software to provide hints to the branch prediction and trace
formation hardware to enhance their performance. These hints take the form of prefixes to conditional branch
instructions. These prefixes have no effect for pre-Pentium 4 processor implementations. Branch hints are not
guaranteed to have any effect, and their function may vary across implementations. However, since branch hints are
architecturally visible, and the same code could be run on multiple implementations, they should be inserted only in
cases which are likely to be helpful across all implementations.
Branch hints are interpreted by the translation engine, and are used to assist branch prediction and trace construction
hardware. They are only used at trace build time, and have no effect within already-built traces. Directional hints
override the static (forward-taken, backward-not taken) prediction in the event that a BTB prediction is not
available. Because branch hints increase code size slightly, the preferred approach to providing directional hints is
by the arrangement of code so that
(i) forward branches that are more probable should be in the not-taken path, and
(ii) backward branches that are more probable should be in the taken path. Since the branch prediction information
that is available when the trace is built is used to predict which path or trace through the code will be taken,
directional branch hints can help traces be built along the most likely path.
Execution Core Detail
The execution core is designed to optimize overall performance by handling the most common cases most
efficiently. The hardware is designed to execute the most frequent operations in the most common context as fast as
possible, at the expense of less-frequent operations in rare context. Some parts of the core may speculate that a
common condition holds to allow faster execution. If it does not, the machine may stall. An example of this pertains
to store forwarding. If a load is predicted to be dependent on a store, it gets its data from that store and tentatively
proceeds. If the load turned out not to depend on the store, the load is delayed until the real data has been loaded
from memory, then it proceeds.
Instruction Latency and Throughput
The superscalar, out-of-order core contains multiple execution hardware resources that can execute multiple µops in
parallel. The core’s ability to make use of available parallelism can be enhanced by:
Page 13
Page 14

A Detailed Look Inside the Intel
®
NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
§ selecting IA-32 instructions that can be decoded into less than 4 µops and/or have short latencies
§ ordering IA-32 instructions to preserve available parallelism by minimizing long dependence chains and
covering long instruction latencies
§ ordering instructions so that their operands are ready and their corresponding issue ports and execution units
are free when they reach the scheduler.
This subsection describes port restrictions, result latencies, and issue latencies (also referred to as throughput) that
form the basis for that ordering. Scheduling affects the way that instructions are presented to the core of the
processor, but it is the execution core that reacts to an ever-changing machine state, reordering instructions for faster
execution or delaying them because of dependence and resource constraints. Thus the ordering of instructions is
more of a suggestion to the hardware.
The Intel® Pentium® 4 Processor Optimization Reference Manual lists the IA-32 instructions with their latency,
their issue throughput, and in relevant cases, the associated execution units. Some execution units are not pipelined,
such that µops cannot be dispatched in consecutive cycles and the throughput is less than one per cycle.
The number of µops associated with each instruction provides a basis for selecting which instructions to generate. In
particular, µops which are executed out of the microcode ROM involve extra overhead. For the Pentium II and
Pentium III processors, optimizing the performance of the decoder, which includes paying attention to the 4-1-1
sequence (instruction with four µops followed by two instructions each with one µop) and taking into account the
number of µops for each IA-32 instruction, was very important. On the Pentium 4 processor, the decoder template is
not an issue. Therefore it is no longer necessary to use a detailed list of exact µop count for IA-32 instructions.
Commonly used IA-32 instructions, which consist of four or less µops, are provided in the Intel® Pentium® 4
Processor Optimization Reference Manual to aid instruction selection.
Execution Units and Issue Ports
Each cycle, the core may dispatch µops to one or more of the four issue ports. At the micro-architectural level, store
operations are further divided into two parts: store data and store address operations. The four ports through which
µops are dispatched to various execution units and to perform load and store operations are shown in Figure 4. Some
ports can dispatch two µops per clock because the execution unit for that µop executes at twice the speed, and those
execution units are marked “Double speed.”
Port 0. In the first half of the cycle,
Figure 4 Execution Units and Ports of the Out-of-order Core
port 0 can dispatch either one
floating-point move µop (including
floating-point stack move, floating-
Port 0
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
point exchange or floating-point
store data), or one arithmetic
logical unit (ALU) µop (including
arithmetic, logic or store data). In
the second half of the cycle, it can
dispatch one similar ALU µop.
Port 1. In the first half of the cycle,
port 1 can dispatch either one
floating-point execution (all
floating-point operations except
moves, all SIMD operations) µop
or normal-speed integer (multiply,
shift and rotate) µop, or one ALU
(arithmetic, logic or branch) µop.
ALU 0
Double
speed
ADD/SUB
Logic
Store Data
Branches
Note:
FP_ADD refers to x87 FP, and SIMD FP add and subtract operations
FP_MUL refers to x87 FP, and SIMD FP multiply operations
FP_DIV refers to x87 FP, and SIMD FP divide and square-root operations
MMX_ALU refers to SIMD integer arithmetic and logic operations
MMX_SHFT handles Shift, Rotate, Shuffle, Pack and Unpack operations
MMX_MISC handles SIMD reciprocal and some integer operations
FP Move
FP Move
FP Store Data
FXCH
ALU 1
Double
speed
ADD/SUB
Integer
Operation
Normal
speed
Shift/Rotate
FP
Execute
FP_ADD
FP_MUL
FP_DIV
FP_MISC
MMX_SHFT
MMX_ALU
MMX_MISC
Memory
Load
All Loads
LEA
Prefetch
Memory
Store
Store
Address
In the second half of the cycle, it can dispatch one similar ALU µop.
Port 2. Port 2 supports the dispatch of one load operation per cycle.
Page 14
Page 15

A Detailed Look Inside the Intel
®
NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
Port 3. Port 3 supports the dispatch of one store address operation per cycle.
Thus the total issue bandwidth can range from zero to six µops per cycle. Each pipeline contains several execution
units. The µops are dispatched to the pipeline that corresponds to its type of operation. For example, an integer
arithmetic logic unit and the floating-point execution units (adder, multiplier, and divider) share a pipeline.
Caches
The Intel NetBurst micro-architecture can support up to three levels of on-chip cache. Only two levels of on-chip
caches are implemented in the Pentium 4 processor, which is a product for the desktop environment. The level
nearest to the execution core of the processor, the first level, contains separate caches for instructions and data: a
first-level data cache and the trace cache, which is an advanced first-level instruction cache. All other levels of
caches are shared. The levels in the cache hierarchy are not inclusive, that is, the fact that a line is in level i does not
imply that it is also in level i+1. All caches use a pseudo-LRU (least recently used) replacement algorithm. Table 1
provides the parameters for all cache levels.
Table 1 Pentium 4 Processor Cache Parameters
Level Capacity Associativity
(ways)
Line Size
(bytes)
Access Latency (clocks),
Integer/floating-point
Write Update Policy
First 8KB 4 64 2/6 write through
TC 12K µops N/A N/A N/A N/A
Second 256KB 8 128 7/7 write back
A second-level cache miss initiates a transaction across the system bus interface to the memory sub-system. The
system bus interface supports using a scalable bus clock and achieves an effective speed that quadruples the speed of
the scalable bus clock. It takes on the order of 12 processor cycles to get to the bus and back within the processor,
and 6-12 bus cycles to access memory if there is no bus congestion. Each bus cycle equals several processor cycles.
The ratio of processor clock speed to the scalable bus clock speed is referred to as bus ratio. For example, one bus
cycle for a 100 MHz bus is equal to 15 processor cycles on a 1.50 GHz processor. Since the speed of the bus is
implementation- dependent, consult the specifications of a given system for further details.
Data Prefetch
The Pentium 4 processor has two mechanisms for prefetching data: a software-controlled prefetch and an automatic
hardware prefetch.
Software-controlled prefetch is enabled using the four prefetch instructions introduced with Streaming SIMD
Extensions (SSE) instructions. These instructions are hints to bring a cache line of data into the desired levels of the
cache hierarchy. The software-controlled prefetch is not intended for prefetching code. Using it can incur significant
penalties on a multiprocessor system where code is shared.
Software-controlled data prefetch can provide optimal benefits in some situations, and may not be beneficial in other
situations. The situations that can benefit from software-controlled data prefetch are the following:
§ when the pattern of memory access operations in software allows the programmer to hide memory latency
§ when a reasonable choice can be made of how many cache lines to fetch ahead of the current line being
executed
§ when an appropriate choice is made for the type of prefetch used. The four types of prefetches have different
behaviors, both in terms of which cache levels are updated and the performance characteristics for a given
processor implementation. For instance, a processor may implement the non-temporal prefetch by only
returning data to the cache level closest to the processor core. This approach can have the following effects:
a) minimizing disturbance of temporal data in other cache levels
Page 15
Page 16

A Detailed Look Inside the Intel
®
NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
b) avoiding the need to access off-chip caches, which can increase the realized bandwidth compared to a
normal load-miss, which returns data to all cache levels.
The situations that are less likely to benefit from software-controlled data prefetch are the following:
§ In cases that are already bandwidth bound, prefetching tends to increase bandwidth demands, and thus not be
effective.
§ Prefetching too far ahead may cause eviction of cached data from the caches prior to actually being used in
execution; not prefetching far enough ahead can reduce the ability to overlap memory and execution latencies.
§ When the prefetch can only be usefully placed in locations where the likelihood of that prefetch’s getting used
is low. Prefetches consume resources in the processor and the use of too many prefetches can limit their
effectiveness. Examples of this include prefetching data in a loop for a reference outside the loop, and
prefetching in a basic block that is frequently executed, but which seldom precedes the reference for which the
prefetch is targeted.
Automatic hardware prefetch is a new feature in the Pentium 4 processor. It can bring cache lines into the unified
second-level cache based on prior reference patterns.
Pros and Cons of Software and Hardware Prefetching. Software prefetching has the following characteristics:
§ Handles irregular access patterns, which would not trigger the hardware prefetcher
§ Handles prefetching of short arrays and avoids hardware prefetching’s start-up delay before initiating the
fetches
§ Must be added to new code; does not benefit existing applications.
In comparison, hardware prefetching for Pentium 4 processor has the following characteristics:
§ Works with existing applications
§ Requires regular access patterns
§ Has a start-up penalty before the hardware prefetcher triggers and begins initiating fetches. This has a larger
effect for short arrays when hardware prefetching generates a request for data beyond the end of an array,
which is not actually utilized. However, software prefetching can recognize and handle these cases by using
fetch bandwidth to hide the latency for the initial data in the next array. The penalty diminishes if it is
amortized over longer arrays.
§ Avoids instruction and issue port bandwidth overhead.
Loads and Stores
The Pentium 4 processor employs the following techniques to speed up the execution of memory operations:
§ speculative execution of loads
§ reordering of loads with respect to loads and stores
§ multiple outstanding misses
§ buffering of writes
§ forwarding of data from stores to dependent loads.
Performance may be enhanced by not exceeding the memory issue bandwidth and buffer resources provided by the
machine. Up to one load and one store may be issued each cycle from the memory port’s reservation stations. In
order to be dispatched to the reservation stations, there must be a buffer entry available for that memory operation.
There are 48 load buffers and 24 store buffers. These buffers hold the µop and address information until the
operation is completed, retired, and deallocated.
The Pentium 4 processor is designed to enable the execution of memory operations out of order with respect to other
instructions and with respect to each other. Loads can be carried out speculatively, that is, before all preceding
Page 16
Page 17

A Detailed Look Inside the Intel
®
NetBurst™ Micro-Architecture of the Intel Pentium® 4 Processor
branches are resolved. However, speculative loads cannot cause page faults. Reordering loads with respect to each
other can prevent a load miss from stalling later loads. Reordering loads with respect to other loads and stores to
different addresses can enable more parallelism, allowing the machine to execute more operations as soon as their
inputs are ready. Writes to memory are always carried out in program order to maintain program correctness.
A cache miss for a load does not prevent other loads from issuing and completing. The Pentium 4 processor supports
up to four outstanding load misses that can be serviced either by on-chip caches or by memory.
Store buffers improve performance by allowing the processor to continue executing instructions without having to
wait until a write to memory and/or cache is complete. Writes are generally not on the critical path for dependence
chains, so it is often beneficial to delay writes for more efficient use of memory-access bus cycles.
Store Forwarding
Loads can be moved before stores that occurred earlier in the program if they are not predicted to load from the
same linear address. If they do read from the same linear address, they have to wait for the store’s data to become
available. However, with store forwarding, they do not have to wait for the store to write to the memory hierarchy
and retire. The data from the store can be forwarded directly to the load, as long as the following conditions are met:
§ Sequence: The data to be forwarded to the load has been generated by a programmatically earlier store, which
has already executed.
§ Size: the bytes loaded must be a subset of (including a proper subset, that is, the same) bytes stored.
§ Alignment: the store cannot wrap around a cache line boundary, and the linear address of the load must be the
same as that of the store.
Page 17
 Loading...
Loading...