Page 1

R
Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the
FC-PGA2 Package
Thermal Design Guidelines
June 2001
Order Number: 249660-001
Page 2

Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
R
Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products. No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual
property rights is granted by this document.
Except as provided in Intel’s Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products, Intel assumes no liability whatsoever, and Intel disclaims any express or
implied warranty, relating to sale and/or use of Intel products including liability or wa rranties relating to fitness for a par ticular purpose, merchantability, or
infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property right.
Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life saving, or life sustaining applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked "reserved" or "undefined." Intel reserves these for future
definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Intel and Pentium are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
Copies of documents which have an ordering number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be obtained from:
Intel Corporation
www.intel.com
or call 1-800-548-4725
* Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2001, Intel Corporation
2 249660-001
Page 3

Intel
R
®
Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
Contents
Introduction ..................................................................................................................................7
1.
1.1. Document Scope............................................................................................................. 7
1.2. References......................................................................................................................7
1.3. Definition of Terms..........................................................................................................8
2. Importance of Thermal Management........................................................................................... 9
3. FC-PGA2 Processor Packaging Technology............................................................................. 11
4. Thermal Specifications............................................................................................................... 13
4.1. Processor Case Temperature....................................................................................... 13
5. Designing for Thermal Performance.......................................................................................... 15
5.1. Airflow Management...................................................................................................... 15
5.2. Recommended Fan Performance and Limitations........................................................ 16
5.3. Bypass........................................................................................................................... 16
5.4. Heatsink Solutions and Keep-in Areas.......................................................................... 16
5.5. Thermal Interface Management.................................................................................... 16
5.5.1. Bond Line Thickness...................................................................................17
5.5.2. Interface Material Area................................................................................17
5.5.3. Interface Material Performance................................................................... 17
5.6. Fans...............................................................................................................................17
5.6.1. Placement ................................................................................................... 18
5.6.2. Fan Direction...............................................................................................18
5.6.3. Size and Quantity........................................................................................18
5.6.4. Venting ........................................................................................................ 18
5.6.4.1. Placement....................................................................................... 18
5.6.4.2. Area and Size................................................................................. 18
5.6.4.3. Vent Shape..................................................................................... 19
6. Alternative Cooling Solutions ..................................................................................................... 21
6.1. Ducting.......................................................................................................................... 21
6.1.1. Ducting Placement...................................................................................... 21
6.2. System Components.....................................................................................................21
6.2.1. Placement ................................................................................................... 21
6.2.2. Power ........................................................................................................ 21
7. Thermal Metrology for FC-PGA2 Packaged Processors........................................................... 23
7.1. Thermal Resistance ...................................................................................................... 23
7.2. Thermal Solution Performance ..................................................................................... 24
7.3. Local-ambient Temperature Measurement Guidelines................................................. 25
7.3.1. Local-ambient Temperature Measurement for a Passive Heatsink............ 25
7.3.2. Local-ambient Temperature Measurement for an Active Heatsink............. 26
7.4. Processor Measurements for Thermal Specifications .................................................. 26
7.4.1. Processor Case Temperature Measurements............................................27
7.4.2. About the High Power Application............................................................... 31
7.4.3. Executing the High Power Application Software ......................................... 31
249660-001 3
7.4.1.1. Heatsink Preparation...................................................................... 30
Page 4

Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
8.
Conclusion..................................................................................................................................33
Figures
Figure 3-1. FC-PGA2 Mechanical Specifications .....................................................................11
Figure 5-1. Example of Air Exchange Through a µATX PC Chassis.......................................15
Figure 7-1. Processor-Heatsink Thermal Resistance Relationships........................................23
Figure 7-2. Local-ambient Thermocouple Measurement Locations (Passive Heatsink)..........25
Figure 7-3. Local-ambient Thermocouple Measurement Locations (Active Heatsink).............26
Figure 7-4. Locating Geometric Center of Processor...............................................................28
Figure 7-5. Thermocouple Preparation.....................................................................................28
Figure 7-6. Thermocouple Adhesive Placement ......................................................................29
Figure 7-7. Example of Machined Heatsink with Thermocouple Groove.................................30
Figure 7-8. Example of Dimensioning for Thermocouple Groove............................................31
Tables
R
Table 3-1. FC-PGA2 Processor Package Dimensions.............................................................12
Table 7-1. List of Items for Thermocouple Attach....................................................................27
Equations
Equation 1. Case to Ambient Thermal Resistance...................................................................23
Equation 2. Case to Ambient Thermal Resistance...................................................................24
4 249660-001
Page 5
Intel
R
Revision History
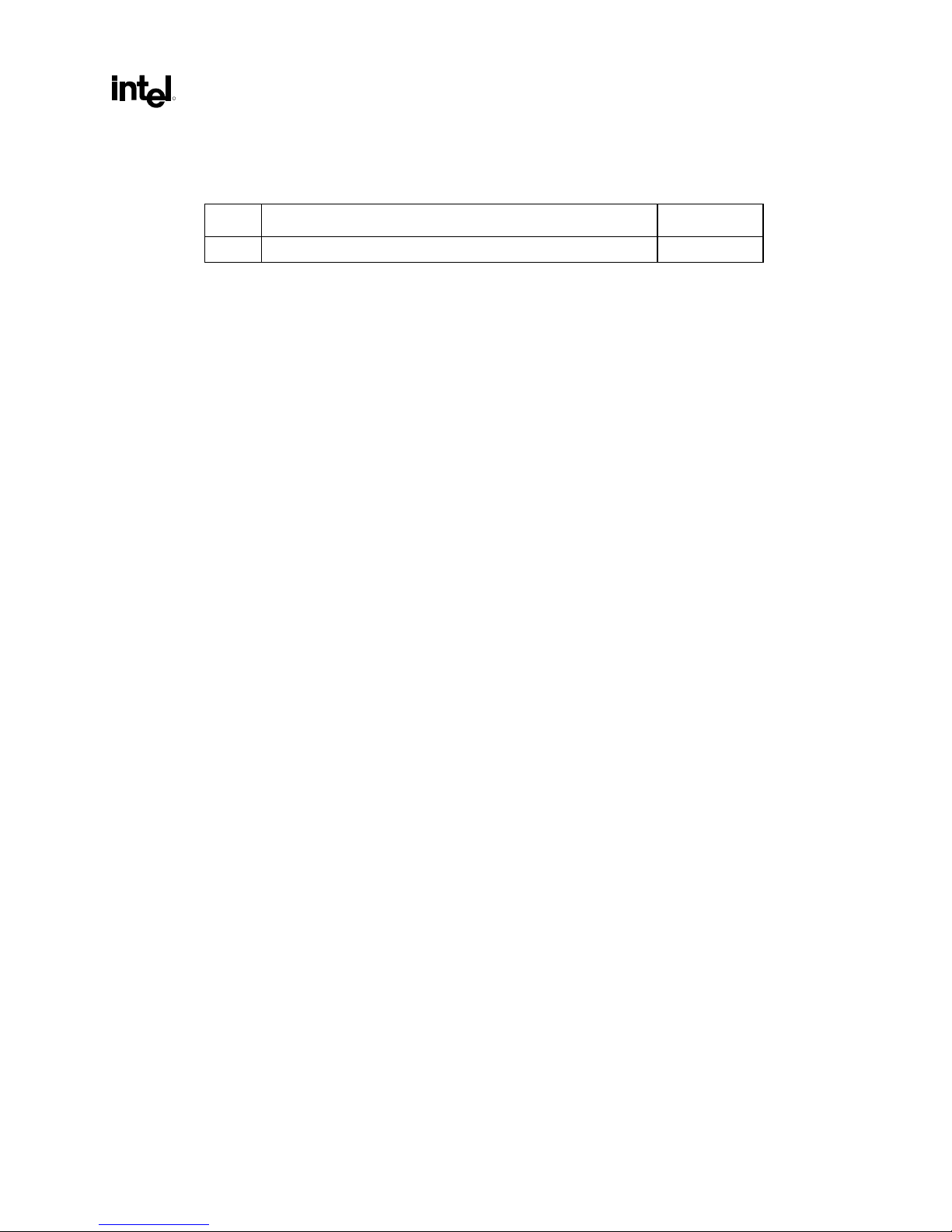
Rev. Description Date
-001 • Initial Release June 2001
®
Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
249660-001 5
Page 6

Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
R
This page is intentionally left blank.
6 249660-001
Page 7

Intel
R
®
Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
1. Introduction
In a system environment, the processor's temperature is a function of both the system and component
thermal characteristics. The system level thermal constraints consist of the local-ambient temperature at
the processor and the airflow over the processor, as well as the physical constraints at and above the
processor. The processor’s temperature depends on the component power dissipation, size and material
(effective thermal conductivity) of the integrated heat spreader, and the presence of a thermal cooling
solution.
All of these parameters are aggravated by the continued push of technology to increase performance
levels (higher operating speeds, GHz) and packaging size and density (more transistors). As operating
frequencies increase and packaging size decreases, the power density increases and the thermal cooling
solution space and airflow become more constrained. The result is an increased importance on system
design to ensure that thermal design requirements are met for each component in the system.
1.1. Document Scope
This document discusses thermal management techniques for Intel® Pentium® III processors in the FCPGA2 package with an integrated heat spreader, which is primarily intended for the desktop and server
segments. The physical dimensions and power numbers used in this document are for reference only.
Please refer to the respective datasheets for the product dimensions, thermal power dissipation, and
maximum case temperature. In case of conflict, the specifications in the processor datasheets supercede
any data in this document.
1.2. References
Document Title Order Number
Pentium® III Processor for the PGA370 Socket Datasheet 245264
Intel® Pentium® III Processor with 512Kb L2 Cache Datasheet 249657
370-Pin Socket (PGA370) Desi gn Gui del i nes 244410
AP-905 Pentium® III Processor Thermal Design Guidelines 245087
FC-PGA2 Package Thermal / Mechanic al S ol ution Functional Specific ations Contact your Intel Field
Performance ATX Desktop S ystem Thermal Design Suggestions v 1.0 http://www.formfactors.org
ATX Thermal Design Suggestions v1.0 http://www.formfactors.org
Performance MicroATX Desktop System Thermal Design Suggesti ons v1.0 http://www.formfactors.org
MicroATX Thermal Design Suggestions v1.0 http://www.formfactors.org
FlexATX Thermal Design Suggestions v1.0 http://www.formfactors.org
Evaluation Board for Microprocessor System Temperature Monitor or EVAL-
ADM1021
Analog Devices EVAL-ADM1021 kit datasheet http://www.analog.com
Maxim Integrated Products M AX1617EV Kit datasheet http://www.maxim-ic.com
Sales Representative
http://www.analog.com
249660-001 7
Page 8

Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
1.3. Definition of Terms
• TLA - the measured ambient temperature locally surrounding the processor. The ambient
temperature should be measured just “upstream” of a passive heatsink, or at the fan inlet for an
active heatsink. (See Section 7.3: Local-ambient Temperature Measurement Guidelines)
• T
AMBIENT-OEM
defined by the system designer (OEM).
• T
AMBIENT-EXTERNAL
• T
AMBIENT-MAX
system in maximum external temperature conditions and measuring the ambient temperature locally
surrounding the processor. Under these conditions, T
• T
CASE-MAX
datasheet.
• T
CASE
• TIM - Thermal Interface Material. The thermally conductive compound between the heatsink and
the processor case. This material fills the air gaps and voids, and enhances the spreading of the heat
from the case to the heatsink.
- the thermal resistance of the thermal interface material. Also referred to as θCS (case to sink
• θ
TIM
thermal resistance).
- the target worst-case ambient temperature at a given external system location as
- the measured ambient temperature at the OEM defined external system location.
- the target worst-case local-ambient temperature. It is determined by placing the
- the maximum allowed case temperature of the processor, as specified in the processor
- the measured case temperature of the processor.
LA
= T
AMBIENT-MAX
R
.
- the thermal resistance between the processor’s case and the ambient air. This is defined and
• θ
CA
controlled by the system thermal solution.
• P
• PGA370 Socket - a through-hole mount Zero Insertion Force (ZIF) socket designed to accept the
- the maximum processor power, as specified in the processor’s datasheet.
MAX
®
Intel
Pentium® III processor in the FC-PGA2 package.
• FC-PGA2 package - the Flip Chip Pin Grid Array processor package with an integrated heat
spreader (IHS).
• ACPI - Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (See http://www.teleport.com/~acpi/
)
• Bypass - the area between a passive heatsink or air pass-through and any object that can ac t to form
a duct. For this example it can be expressed as a dimension away from the outside dimension of the
fins to the nearest surface.
• TDP - Thermal Design Power. The processor thermal power specification in the processor
datasheet. OEMs must design their processor thermal solutions to meet the TDP as listed in the
respective datasheets. (Also known as Thermal Design Point.)
®
• Intel
Pentium® III processor in the FC-PGA2 package - any Pentium® III processor with CPUID
06Bxh, as well as t he higher frequencies of Intel
the Pentium
®
III Processor for the PGA370 Socket Datasheet for further details).
®
Pentium® III processors with CPUID 068xh (see
8 249660-001
Page 9

Intel
R
®
Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
2. Importance of Thermal Management
The objective of thermal management is to ensure that the temperature of all components in a system is
maintained within functional limits. The functional temperature limit is the range within which the
electrical circuits can be expected to meet their specified performance requirements. Operation outside
the functional limit can degrade system performance, cause logic errors or cause component and/or
system damage. Temperatures exceeding the maximum operating limits may result in irreversible
changes in the operating characteristics of the component.
249660-001 9
Page 10

Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
R
This page is intentionally left blank.
10 249660-001
Page 11

Intel
R
®
Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
3. FC-PGA2 Processor Packaging
Technology
The Intel® Pentium® III processor is available in Flip Chip Pin Grid Array 2 (FC-PGA2) packaging. The
FC-PGA2 package consists of the microprocessor silicon core with integrated L2 cache mounted on a
pinned substrate. The silicon core is encased by a heat spreader, which is integrally mounted to the FCPGA2 substrate. The Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS) is designed to improve thermal performance and is
the interface for attaching a heatsink. The processor core is mounted with the back of the die facing up,
hence the term “flip chip.” The pin grid array on the backside of the interposer is not fully populated and
there may be small, low power, surface mounted components in the center of the pin field. The processor
package connects to the motherb oard by plugging into a 370-pin ZIF socket (PGA370). See Figure
3-1and Table 3-1 (below) for a complete mechanical dimensioning. A description of the socket can be
found in the 370-Pin Socket (PGA370) Design Guidelines. Refer to the processor datasheets for package
mechanical loading specifications.
Figure 3-1. FC-PGA2 Mechanical Specifications
249660-001 11
Page 12

Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
Table 3-1. FC-PGA2 Processor Package Dimensions
Symbol Millimeters Inches
Minimum Maximum Notes Minimum Maximum Notes
A1 2.266 2.690 0.089 0.106
A2 0.980 1.180 0.038 0.047
B1 30.800 31.200 1.212 1.229
B2 30.800 31.200 1.212 1.229
C1 33.000 max 1.299 max
C2 33.000 max 1.299 max
D 49.428 49.632 1.946 1.954
D1 45.466 45.974 1.790 1.810
G1 0.000 17.780 0.000 0.700
G2 0.000 17.780 0.000 0.700
G3 0.000 0.889 0.000 0. 035
H 2.540 Nominal 0.100 Nominal
L 3.048 3.302 0.120 0.130
ΦP 0.431 0.483 0.017 0.019
R
Pin TP 0.508 Diametric True Position (Pin-to-Pin) 0.020 Diametric True Position (Pin-t o-P i n)
NOTES:
1. Capacitors will be placed on the pin-side of the FC-PGA 2 package in the area defined by G1, G2, and G3. This
area is a keep-out zone for motherboard designers.
2. In case of confli ct, the processor datasheets supercede this doc ument.
12 249660-001
Page 13

Intel
R
®
Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
4. Thermal Specifications
For the purposes of this design guideline, the following assumptions have been made about the
requirements for proper operation and reliability of the processor:
• Considering the power dissipation levels and typical system ambient environments (T
processor's temperature cannot be maintained at or below the specified guidelines without additional
thermal enhancement to dissipate the heat generated by the processor.
• The thermal characterization data described in later sections illustrates that both a thermal-cooling
device and reasonable system airflow are needed. The size and type (passive or active) of thermal
cooling device and the amount of system airflow are related and can be traded against each other to
meet specific system design constraints. In typical systems, board layout, spacing, and component
placement limit the thermal solution size. Airflow is determined by the size and number of fans,
along with their placement in relation to the components and the airflow channels within the system.
In addition, acoustic noise constraints may limit the size, number, and types of fans that can be used
in a particular design.
To develop a reliable, cost-effective thermal solution, all of the above variables must be considered.
Thermal characterization and simulation should be carried out at the entire system level accounting for
the thermal requirements of each component.
4.1. Processor Case Temperature
The Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS) is intended to provide the common interface and attach location for
all thermal solutions for FC-PGA2 packaged processors. The IHS acts to spread the heat from the small
area of the processor die to the larger surface area of the IHS, allowing more efficient heat transfer using
heatsink thermal solutions. These solutions can be active or passive. Active solutions are those where a
fan is directly attached to the heatsink. A passive heatsink uses system airflow forced in some manner to
pass-through the hea tsink fins. Considera t ions in heatsink design i nclude:
LA
), the
• Local-ambient temperature at the heatsink (T
• Surface area of the heatsink
• Property of materials (including thermal resistance or conductivity)
• Volume and velocity of airflow over the heatsink surface area
• Power being dissipated by the processor and its associated power density
• Physical volumetric constraints placed by the system
Techniques for measuring case temperatures are provided in Section 7: Thermal Metrology.
249660-001 13
LA
)
Page 14

Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
R
This page is intentionally left blank.
14 249660-001
Page 15

Intel
R
®
Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
5. Designing for Thermal Performance
5.1. Airflow Management
It is important to manage the volume and velocity of air that flows within the system, as well as how it
flows, to maximize the amount of cool air that flows over the processor. Total system airflow can be
increased by adding one or more fans to the system, or by increasing the output (increasing the speed or
size) of an existing system fan(s). Managing the airflow direction using baffles or ducts can also increase
local airflow. An important consideration in airflow management is the temperature of the air flowing
over the processor. Heating effects from chipset, voltage regulators, add-in boards, memory, and disk
drives greatly reduce the cooling efficiency of this air, as d oes re-circulation of warm interi or air thro ugh
the system fan. Care must be taken to minimize the heating effects of other system components, and to
eliminate warm air re-circulation.
If no air path exists across the processor heatsink, the warm air from the processor will not be removed
from the system, resulting in localized heating ("hot spots") around the processor(s). Passive heatsink fin
designs should be aligned with the direction of the airflow.
Figure 5-1 shows two examples of air exchange through a µATX style PC chassis. The system on the left
is an example of a center mounted power supply, and the one on the right is an example of a top mounted
power supply. Both are examples of good air exchange incorporating the power supply fan as well as an
additional system fan (additional system fan shown as the three large arrows entering the front bezel).
For further info rmation, reference the system thermal design sugge st ions for the appropriate form factor
available at http://www.formfactors.org/
Figure 5-1. Example of Air Exchange Through a µATX PC Chassis
.
System Fan Intake
System Fan Intake
249660-001 15
Page 16

Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
5.2. Recommended Fan Performance and Limitations
For active thermal solutions, the fan must often demonstrate a functional lifetime of 40,000 hours or
greater. In addition, the fan should demonstrate performance to the reliability criteria outlined in the FC-
PGA2 Package Thermal/Mechanical Solution Functional Specifications.
5.3. Bypass
Bypass is the distance around a passive heatsink where air may travel without passing through the fins of
the heatsink. A heatsink will have infinite bypass if it is sitting in free space, while a heatsink that has a
duct, or other devices surrounding it which are 0.2 in (5.1mm) away from the outer edges of the heatsink,
has a bypass of 0.2 i n (5.1mm). A smaller bypass forces more air to pass through the fins of the heatsink,
instead of around the heatsink. This is especially important as the heatsink fin density increases. The
higher the fin density, the more resistance the heatsink poses to the air and the more likely the air will
travel around the heatsink instead of through it unless the bypass is small. Air traveling around the
heatsink will have no affect on cooling the processor.
5.4. Heatsink Solutions and Keep-in Areas
R
One method used to improve thermal performance is to increase the surface area of the device by
attaching a metallic heatsink. To maximize the heat transfer, the thermal resistance from the heatsink to
the air can be reduced b y maximizing the airflow through the heatsink fins as well as by maximizing the
surface area of the heatsink itself. Although there have been many advancements in fin density and
geometries that allow for a better performing heatsink, an active or more advanced thermal solution may
be needed. Intel is enabling reference active and passive heatsinks for FC-PGA2 packaged processors.
Please see the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal/Mechanical Solution Functional Specifications for further
details.
5.5. Thermal Interface Management
To optimize the heatsink design for FC-PGA2 packaged processors, it is important to understand the
impact of factors related to the interface between the processor and the heatsink base. Specifically, the
interface material bond line thickness, area, and bulk thermal conductivity should be managed to realize
the most effective thermal solution.
Thermal interface material must be applied between the processor IHS and the heatsink to improve
thermal conduction from the IHS to the heatsink. Thermal interface material also serves as a mechanical
load element during mechanical stress testing (i.e. mechanical shock). Many thermal interface materials
can be pre-applied to the heatsink base prior to shipment from the heatsink supplier and allow direct
heatsink attach, without the need for a separate thermal interface material dispense or attach process in
the final assembly factory.
All thermal interface materials must be sized and positioned on the heatsink base in a way that ensures
the entire processor IHS area is covered. It will be important to compensate for heatsink-to-processor
attach positional alignment when selecting the proper thermal interface material size.
If a pre-applied thermal interface material is specified, it may have a protective application tape. This
tape must be removed prior to heatsink attach.
16 249660-001
Page 17

Intel
R
®
Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
5.5.1. Bond Line Thickness
Any gap between the processor’s heat spreader and the heatsink base will impact thermal solution
performance. The larger the gap between the two surfaces, the greater the thermal resistance. The
thickness of the gap is determined by the flatness of both the heatsink base and the integrated heat
spreader, the thickness of the thermal interface material (i.e. thermal grease) used between these two
surfaces, and the clamping force applied by the heatsink retention clip(s). In comparison with FC-PGA
packaged processors, the addition of the IHS will distribute the vertical force created by the attach
clip(s). For the same applied force (e.g. the same heatsink attach clip configuration), this will result in
lower pressure applied to the thermal interface material. This will lead to an increase in thermal interface
bond line thickness and thermal resistance.
5.5.2. Interface Material Area
The size of the contact area between the integrated heat spreader and the heatsink base will impact the
thermal resistance; increasing contact area typically decreases thermal resistance. It is recommended that
the thermal interface material should cover the entire surface of the integrated heat spreader area (31mm
x 31mm) to optimize the thermal interface performance on FC-PGA2 packaged processors.
5.5.3. Interface Material Performance
Two factors impact the performance of the interface material between the processor and the heatsink
base:
1. Thermal resistance of the material
2. Wetting/filling characteristics of the material
Thermal resistance is a description of the ability of the thermal interface material to transfer heat from
one surface to another. The higher the thermal resistance, the less efficient the interface is at transferring
heat. The thermal resistance of the interface material has a significant impact on the thermal performance
of the overall thermal solution. The higher the thermal resistance, the larger the temperature drop is
across the interface and the more efficient the thermal solution must be to achieve the desired cooling.
The wetting or filling characteristic of the thermal interface material is its ability, under the load applied
by the heatsink retention mechanism, to spread and fill the gap between the processor and the heatsink.
Since air is an extremely poor thermal conductor, the more completely the interface material fills the
gaps, the lower the temperature drop across the interface. Thermal interface material area-size also
becomes significant, as the larger the desired area-size, the higher the force required to spread the
thermal interface material.
5.6. Fans
Fans are needed to move the air through the chassis and/or directly through the processor heatsink. The
airflow rate of a fan is usually directly related to the acoustic noise level of the fan and system.
Maximum acceptable noise levels may limit the fan output or the number of fans selected for a system.
The maximum noise levels may differ from country to country. Fan/heatsink assemblies are one type of
advanced solution that can be used to cool the processor. Intel has worked with fan/heatsink vendors and
computer manufacturers to make fan/heatsink cooling solutions available in the industry. Please consult
such a vendor to acquire the proper solution for your needs.
249660-001 17
Page 18

Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
5.6.1. Placement
Proper placement of the fans can ensure that the processor is being properly cooled. Because of the
difficulty in building, measuring, and modifying a mechanical assembly for thermal evaluation, models
are typically developed and used to simulate a proposed design for thermal effectiveness, and to
determine the optimum location for fans and vents within a chassis. Investments for prototype
assemblies can then be made to verify that the system components and processor thermal specifications
are met.
5.6.2. Fan Direction
If the fan(s) are not moving air across the processor heatsink, cooling will not occur. This may cause the
processor to operate well above the recommended specification values. Two possibilities exist for
blowing air across a passive heatsink. Air can be blown down vertically or horizontally across the
heatsink. This may depend on the layout of other components on the board and/or within the chassis.
The intake fan sho uld blow through a passive heatsink parallel to the fins if p ossible. Bo th of these
factors are considerations when laying out components on the board and in the chassis.
The direction of the airflow can be modified with baffles or ducts to direct the airflow over the processor.
This will increase the local flow over the processor and may eliminate the need for a second fan, a larger
fan, or a higher speed fan. For an actively cooled heatsink, the system airflow direction may not be as
critical for proper thermal performance, but it will be important to manage warm air re-circulation.
R
5.6.3. Size and Quantity
It does not necessarily hold true that the larger the fan the more air it blows. A small blower using
ducting might direct more air over the heatsink than a large fan blowing non-directed air over the
heatsink.
5.6.4. Venting
Intake venting should be placed at the front (user side) of the system. They should be located to optimize
cooling of processor and peripherals (drives and add-in cards). A good starting point would be the lower
50% of the front panel (bezel). Intake vents directly in front of the intake fan, is the optimal location.
The ideal design will provide airflow directly over the processor heatsink.
5.6.4.1. Placement
In most cases, an exhaust fan and vent located at the power supply is sufficient. However, depending on
the number, location, and types of add-in cards, exhaust venting may be necessary near the cards. This
should be modeled or prototyped for the optimum thermal potential. A system should be modeled for the
worst case, i.e., all expansion slots should be occupied with typical add-in options.
5.6.4.2. Area and Size
The area and size of the intake vents should be designed with the size and shape of the fan(s) in mind.
Adequate air volume requires appropriately sized vents. Intake vents should be located in front of the
intake fan(s) and adjacent to the drive bays. Vents should be approximately 50% to 60% open in the
18 249660-001
Page 19

Intel
R
EMI containment area due to EMI constraints. Outside the EMI containment area, the open percentage
can be greater if needed for aesthetic appeal (i.e., bezel/cosmetics).
5.6.4.3. Vent Shape
Round, staggered pattern openings are best for EMI containment, acoustics, and airflow balance.
®
Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
249660-001 19
Page 20

Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
R
This page is intentionally left blank.
20 249660-001
Page 21

Intel
R
®
Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
6. Alternative Cooling Solutions
In addition to passive heatsinks, fan heatsinks and system fans, other solutions exist for cooling
integrated circuit devices. For example, ducted blowers, heat pipes and liquid cooling are all capable of
dissipating additional heat. Due to their varying attributes, each of these solutions may be appropriate for
a particular system implementation. More information on this topic can be located on Intel's web site at
http://developer.intel.com/
6.1. Ducting
Ducts can be designed to isolate the processor from the effects of system heating (such as add-in cards),
and to maximize the processor cooling temperature budget. Typical temperature rise from external
ambient to the local-ambient near the processor can be greater than 10°C. Air provided by a fan or
blower can be channeled to the processor and heatsink with little or no rise from the external ambient
temperature.
.
6.1.1. Ducting Placement
When ducting is to be used, it should direc t the airflow evenly fro m the fan through the length of the
heatsink. This should be accomplished, if possible, with smooth, gradual turns, as this will reduce air
impedance. Sharp turns in ducting should be avoided as they increase friction and drag and will greatly
reduce the volume of air reaching the processor heatsink.
6.2. System Components
6.2.1. Placement
Peripherals such as CD-ROMs, floppy drives, and hard drives can be placed to take advantage of the
fan's movement of ambient air (i.e., near intake or exhaust fans or venting). So me a dd-in cards often
have a low tolerance for temperature rise. These components should be placed near additional vents if
they are downstream of the processor to minimize temperature rise.
6.2.2. Power
Some types of drives, such as a floppy drive, do not dissipate much heat, while others (read/write CDROMs, hard drives) dissipate a great deal of heat. These hotter components should be placed near fans
or vents whenever possible. The same can be said for some types of add-in cards. Some PCI cards are
very low wattage (5W) while others can be as high as 25 watts, per PCI specification. Great care should
be taken to ensure that these cards have sufficient cooling.
249660-001 21
Page 22

Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
R
This page is intentionally left blank.
22 249660-001
Page 23

Intel
R
®
Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
7. Thermal Metrology for FC-PGA2
Packaged Processors
The following sections will discuss the thermal metrology used on the FC-PGA2 packaged processors.
These techniques should be followed to evaluate thermal performance of proposed solutions. Carefully
read the following instructions and interpretation steps to validate your cooling solution.
7.1. Thermal Resistance
The thermal resistance value from case to local-ambient (
θ
) for a FC-PGA2 package is used as a
CA
measure of the cooling solution's thermal performance. Thermal resistance is measured in units of °C/W.
The thermal resistance of the case to local-ambient,
θ
resistance (
), and the sink to local-ambient thermal resistance (
CS
θ
, is comprised of the case-to-sink thermal
CA
strongly dependent on the thermal conductivity and thickness of the TIM between the heatsink and
surface of the processor.
θ
is a measure of the thermal resistance from the bottom of the heatsink cooling solution to the local-
SA
θ
ambient air.
is dependent on the heatsink’s material, thermal conductivity, and geometry, and is
SA
strongly depend ent on the air velocity through the fins of t he heatsink.
Figure 7-1. Processor-Heatsink Thermal Resistance Relationships
T
Heatsink
Thermal Interface
Material
Processor Package
(IHS)
Socket
θ
) (see Figure 7-1). The
SA
ambient
T
sink
T
case
θθθθ
sa
θθθθ
cs
θ
value is
CS
θθθθca = θθθθcs + θθθθ
sa
The thermal parameters are related by the following equations:
Equation 1. Case to Ambient Thermal Resistance
249660-001 23
= (T
θ
CA
- TLA) / TDP
CASE
Page 24

Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
Equation 2. Case to Ambient Thermal Resistance
θ
=
θ
CA
+
CS
Where:
θ
CA
T
T
= thermal resistance from case to local-ambient (°C/W)
= processor case temperature (°C)
CASE
= local-ambient temperature in chassis around processor (°C)
LA
TDP = processor T hermal Design Power dissipation (W) (assume all power goes to the case)
θ
CS
θ
SA
= case-to-sink thermal resistance (°C/W)
= sink to local-ambient thermal resistance (°C/W)
7.2. Thermal Solution Performance
All processor thermal solutions interface to the processor at the IHS. The system thermal solution must
adequately control the local-ambient air around the processor (T
between the processor and the local-ambient air, the more efficient the thermal solution is. The required
θ
is dependent upon the maximum allowed processor temperature (T
CA
temperature (T
packaged processors, refer to the processor datasheet.
) and the processor thermal design power (TDP). For actual specifications on FC-PGA2
LA
R
θ
SA
). The lower the thermal resistance
LA
), the local-ambient
CASE
θ
Use Equatio n 1 and Equati on 2 (above) to determine a target
CA
and
assumptions.
T
T
= 67 °C, hypothetical maximum case temperature specification
CASE
= Assume 45°C, a typical value for desktop systems
LA
TDP = Assume 30 W, hypothetical thermal design power
θ
CS
= Assume 0.15 °C/W, hypothetical TIM resistance
Solving for the equation 1 from above:
θ
= (T
CA
- TLA) / TDP
CASE
= (67 – 45) / 30
= 0.73 °C/W
Solving for equation 2 from above:
θ
CA
θ
SA
=
=
θ
+
θ
−
SA
θ
CS
CS
θ
CA
= 0.73 − 0.15
= 0.58 °C/W
θ
using the following
SA
24 249660-001
Page 25

Intel
R
®
Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
7.3. Local-ambient Temperature Measurement Guidelines
Local-ambient temperature, TLA, is the temperature of the ambient air surrounding the processor. In a
system environment, ambient temperature is the temperature of the air upstream of the processor and in
its close vicinity; or in an active cooling system; it is the inlet air to the active cooling device.
It is worthwhile to determine the local-ambient temperature in the chassis around the processor to better
understand the effect it may have on the case temperature.
The following guidelines are meant to alleviate the non-uniform measurements found in typical systems.
The local-ambient temperature is best measured as an average of the localized air surrounding the
processor. The following guidelines are meant to enable accurate determination of the localized air
temperature around the processor during system thermal testing. These guidelines are meant as a
reasonable expectation to ensure the product specifications are met.
7.3.1. Local-ambient Temperature M easurement for a Passive
Heatsink
• During system thermal testing, a minimum of two thermocouples should be placed approximately
0.5 to 1.0 inches (12.7 to 25.4 mm) away from the leading edge of the heatsink fins as shown in
Figure 7-2. The two thermocouples should be placed 2.0 (50.8 mm) inches apart (see top view in
Figure 7-2). This placement guideline is meant to minimize localized hot spots due to the
processor, heatsink, or other system components.
• The thermocouples should be placed approximately 2 inches (50.8 mm) above the baseboard. This
placement guideline is meant to minimize localized hot spots from baseboard components.
• T
should be the average of the thermocouple measurements during system thermal testing.
LA
Figure 7-2. Local-ambient Thermocouple Measurement Locations (Passive Heatsink)
Note: Figure is not to scale. Locations are approximate and may vary depending on your system configuration.
249660-001 25
Page 26

Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
7.3.2. Local-ambient Temperature M easurement for an Active
Heatsink
• During system thermal testing, a minimum of two thermocouples should be placed approximately
0.5 to 1.0 inches (12.7 to 25.4 mm) above the fan inlet as shown in Figure 7-3. The two
thermocouples should be placed 1.0 to 2.0 (25.4 to 50.8 mm) inches apart. This placement
guideline is meant to minimize localized hot spots due to the processor, heatsink, or other system
components.
• The thermocouples should be centered relative to the fan and heatsink (see top view in Figure 7-3).
• T
Figure 7-3. Local-ambient Thermocouple Measurement Locations (Active Heatsink)
should be the average of the thermocouple measurements during system thermal testing.
LA
R
Note: Figure is not to scale. Locations are approximate and may vary depending on your system configuration.
7.4. Processor Measurements for Thermal Specifications
Temperature measurements must be made to accurately determine processor thermal performance.
Guidelines have been established for proper techniques for measuring processor temperatures. The
following sections describe these guidelines for temperature measurement.
26 249660-001
Page 27

Intel
R
®
Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
7.4.1. Processor Case Temperature M easurements
To ensure functionality and reliability, the FC-PGA2 packaged processors are specified for proper
operation when T
The measurement location for T
T
measurement.
CASE
is maintained at or below the value listed in their respective processor datasheets.
CASE
is the geometric center of the IHS. Figure 7-4 shows the location for
CASE
Special care is required when measuring the T
Thermocouples are often used to measure T
CASE
measurements are made. When measuring the temperature of a surface, which is at a different
temperature from the surrounding local-ambient air, errors could be introduced in the measurements. The
measurement errors could be due to having a poor thermal contact between the thermocouple junction
and the surface of the integrated heat spreader, heat loss b y radi ation, convection, by conduction through
thermocouple leads, or by contact between the thermocouple cement and the heatsink base. To minimize
these measurement errors, the following approach is recommended:
1. Obtain the necessary items needed for the quantity of thermocouple attachments and samples
desired. A list of necessary items is shown in Table 7-1.
Table 7-1. List of Items for Thermocouple Attach
FC-PGA2 Packaged Process or
Modified heatsink (see sec tion 7.4.1.1)
Fine point tweezers
Thermocouples (Type K, 36 gauge, 36 inch, Teflon* insulation)
Ex-acto* knife (#11 blade)
3M* Kapton* tape cut into strips (1/8” X ½”)
Epoxy cement
2. Use a scribe to mark the geometric center on the topside of the IHS package. This represents the
location where the bead of the thermocouple will be placed. The center of the package can be
obtained by measurement, or by drawing two diagonal lines across the length of the package. The
cross-point will be the geometric center of the package (see Figure 7-4).
to ensure an accurate temperature measurement.
CASE
and should be calibrated before any temperature
249660-001 27
Page 28

Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
Figure 7-4. Locating Geometric Center of Processor
R
3. After the marks are scribed, clean the desired thermocouple attach location with a mild solvent and
a lint-free wipe or cloth. Alcohol or acetone should suffice. Remember that the cleaner the part is,
the stronger the bond will be after curing.
4. Straighten the thermocouple wire by hand so that the first 4-6 inches are reasonably straight. Use
fine point tweezers to make sure that the bead and the two wires coming out are straight and
untwisted. Make sure that the second layer of thermocouple insulation, sometimes clear, is not
covering the bead.
5. Create a slight downward bend in the wires about a 1/16” from the bead. Once the thermocouple
is in place, this will ensure that the thermocouple is making contact with the surface.
6. Place the thermocouple bead on the geometric center of the IHS (previously scribed). Apply tape
across the wire about ¼” back from the bead to hold the thermocouple in place. Apply pressure to
the tape to ensure a good bond. Apply additional tape pieces along the length of the wire to ensure
a good temporary bond to the part (see Figure 7-5). Check the electrical continuity between the
thermocouple and the IHS using a multimeter. If there is no electrical continuity between the
thermocouple and the IHS, repeat st eps 4 through 6.
Figure 7-5. Thermocouple Preparation
28 249660-001
Page 29

Intel
R
7. With the thermocouple in place, the epoxy can now be mixed and applied. Follow the
manufacturer's directions for mixing t he epoxy.
8. Use a clean, finely pointed applicator to apply the epoxy to the bead. Dab the epoxy bond on the
bead and the exposed wires. Use only the appropriate amount of glue to cement the thermocouple
down. The entire bead should be submerged and it is best to have insulated wires protruding from
the glue (see Figure 7-6).
9. Additional beads of epoxy can be added, off of the IHS surface, along the length of wire to provide
additional attachment for the thermocouple wire. Only one bead should be on the IHS surface
Figure 7-6. Thermocouple Adhesive Placement
®
Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
.
10. To cure the epoxy, put the part(s) in an oven set @ 150°F (65°C) for a period of 1 hour. Make sure
the vibration in the oven is minimal to prevent the thermocouple bead from moving. Another
alternative is to cure the epoxy at room temperature for at least 12 hours. (Some epoxy may have
different cure times. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions.)
11. Once the epoxy has cured, remove all tape and check for any residual epoxy outside the
thermocouple attach area on the IHS. Run the tip of your finger around the IHS surface to find any
small glue dots. Remove any residual glue to prevent any impact on bond line or heatsink attach.
12. Verify the cured adhesive bead at the IHS center is smaller than 0.15 inches (3.8mm) in diameter
and 0.025 inches (0.63mm) in height so as to fit in the hole drilled in the heatsink base. Trim as
necessary.
13. Check the electrical continuity between the thermocouple and the IHS again. If there is no
electrical continuity between the thermocouple and the IHS, repeat steps 4 through 12.
14. Place the TIM on the heatsink base. If it is a semi-liquid type apply it on the IHS around the
thermocouple. The clamping force will spread the TIM. If the TIM is a solid type, punch a 0.15
inch (3.8mm) diameter hole in the center of the TIM pad and cut a line from a side to the hole.
This will allow the installation of the TIM to the IHS with the thermocouple already attached to the
IHS.
249660-001 29
Page 30

Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
7.4.1.1. Heatsink Preparation
In order to measure the case temperature as accurately as possibly, the heatsink must be modified to
allow for the thermocouple wires and attach points. Depending on the chosen solution the dimensions
may vary. It is imperative that the modifications made to the heatsink align to the location of the
thermocouple wires and attach point when properly installed. Any discrepancy will cause the heatsink to
not sit properly on the IHS surface and provide erroneous data. Figure 7-7 shows the modification on a
typical heatsink base. Figure 7-8 shows the groove dimensions required to route a thermocouple to the
center of the heatsink without interfering the IHS to heatsink attachment. The depth for the entire groove
including the circle area is 0.025 in (0.63 mm). The groove should be 0.04 in (1.0 mm) wide. It must be
noted that the center of the circle area needs to be located 0.05 in (1.3 mm) off center from the location
corresponding to the thermocouple bead. This is because the epoxy covers both the bead and the
exposed thermocouple wires so that the circle area needs to accommodate the whole epoxy location. It is
left to the designer to perform the appropriate tolerance stack-up and to define the placement
dimensioning for a specific heatsink design.
Figure 7-7. Example of Machined Heatsink with Thermocouple Groove
R
30 249660-001
Page 31

Intel
R
®
Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
Figure 7-8. Example of Dimensioning for Thermocouple Groove
Note: Dimensions are in inches. Centerlines in drawing correspond to the thermocouple location (geometric
center of IHS).
7.4.2. About the High Power Application
The High Power Application software (a.k.a. “HIPWR30.EXE” or “HIPWRMP2.EXE”) is intended for
thermal evaluation purposes only. This software is not a general-purpose application. The software may
not generate the absolute worst-case thermal power dissipation as defined in the processor datasheets.
Differences between the observed thermal power measurements and the maximum power dissipation
indicated in the datasheets can be attributed to processor manufacturing process variation, system voltage
regulation configuration differences, and potential High Power Application software optimizations. This
software does provide system designers with an application that will power a processor to very near the
TDP identified in the processor datasheets and is intended to be a tool for the analysis and validation of
system cooling solutions.
All systems should be designed with the ability to dissipate the thermal design power (TDP) indicated in
the datasheets. The High Power Application software, utilizing the methodologies presented in this
document, can enable system designers to design and validate robust cooling solutions that can
adequately cool the processor at the maximum specifications.
The High Power Application software maximizes the current consumption of the processor core. All
execution stages and various functional units of the core and L1 cache are fully utilized. The software
performs minimal system bus accesses, with minimal L2 cache utilization. This mode of operation
produces a large amount of thermal power from the processor.
Contact your Intel Field Sales representative to obtain a copy of the software.
7.4.3. Executing the High Power Application Software
The High Power Application software is a 32 bit Windows NT* or Windows* 95/98 application. The
application should be executed from a DOS window command prompt from within the Windows NT or
249660-001 31
Page 32

Intel® Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
R
Windows 95/98 environment, and not from a DOS onl y environment. The Hi gh Power Application
software puts the processor into an infinite loop and locks the command prompt environment. The
“HIPWR30.EXE” and “HIPWRMP2.EXE” utilities have an on-screen message with version number
information and usage help. To halt execution of the application, use the Windows NT Task Manager or
Windows 95/98 Task Bar to stop execution of the command prompt environment. For maximum
processor power consumption, the software should be the only application executing on the system under
evaluation. It is recommended that the Windows NT or Windows 95/98 operating environment be
configured to the default OS settings.
32 249660-001
Page 33

Intel
R
®
Pentium® III Processor in the FC-PGA2 Package Thermal Design Guidelines
8. Conclusion
As the complexity of today's microprocessors continues to increase, so do the power dissipation
requirements. Care must be taken to ensure that the additional power is properly dissipated. Heat can be
dissipated using passive heatsinks, fans and/or active cooling devices. Further thermal soluti ons can be
achieved through the use of ducting.
The simplest and most cost effective method is to use an extruded heatsink and a system fan. The size of
the heatsink and the output of the fan can be varied to balance size and space constraints with acoustic
noise. This document has presented the conditions and requirements for properly designing a heatsink
solution for an FC-PGA2 packaged processor based system. Properly designed solutions provide
adequate cooling to keep the processor within thermal specifications. This is accomplished by providing
a low local-ambient temperature and creating a minimal thermal resistance between the processor core
and the local-ambient airflow. Active fan heatsinks or ducting can be used to cool the processor(s) if
proper case and package temperatures cannot be maintained otherwise. By maintaining the processor's
case temperature at or below the values specified in the processor datasheet, a system can guarantee
proper functionality and reliability of these processors.
249660-001 33
 Loading...
Loading...