Intel Express Router 9300, Express Router 9100, Express Router 9200, Express Router 9201, Express Router 9400 Specifications
Page 1

KEY FEATURESJ
■
Secure LAN to LAN
connectivity over the
Internet featuring
144 bit encryption
■
Multiple protocol
support including
Frame Relay, X.25,
EuroISDN and PPP
■
Easy configuration
and management
with Intel Device
View for Windows*
Intel Express Routers
The VPN routers for secure networking over the Internet.
Intel Express Routers can now secure your private business communications for safe
transmission over the Internet, while continuing to offer a simple and cost effective
solution for all your traditional WAN routing needs. With two or more Express Routers,
you can create a secure Virtual Private Network over the Internet. Powerful encryption
and tunneling capabilities safeguard your data. With the comparatively low cost of
Internet access, you can save as much as 80% of the cost of dedicated long distance
WAN connections.
Intel Express Routers provide a rich set of features while simplifying the traditional
complexity of router installation and management. An Intel Express Router can be
up and running in minutes, using simple menu-based options with default settings
that will satisfy most network situations. Management is also easy, with powerful
Windows* OS-based SNMP management tools that provide a hierarchal view of each
WAN and LAN connection for monitoring and troubleshooting.
You get sophisticated control of WAN link activity. Features such as advanced
filtering, data compression and Network Address Translation (NAT) are built in
to each router, ensuring efficient data transmission, a secure data link across the
public domain, and a safeguard that restricts public access to your private LAN.
Unlike other router solutions in which software and other important components
are costly add-ons, Intel Express Routers are complete, cost-effective solutions.
Each Intel Express Router includes all the hardware and software needed for full
installation. The only item packaged separately is the appropriate WAN interface
cable for the environment.
Intel Express Routers are designed for worldwide network environments worldwide,
with support for a range of WAN protocols and interfaces. They integrate with other
Intel networking products for a complete corporate internetworking solution.
NEW FEATURES
■
Secure Virtual Private Network
support
■
Even easier-to-use console interface
■
Robust new features added to
Intel Device View for Windows*
■
Enhanced SNMP support
■
Support for RMON groups 1, 2, 3 and 9
■
Frame Relay encryption (per link
■
Improved diagnostic tools
)
Page 2

Intel Express Routers
The features described below are supported by
all Intel Express Routers. The router models are
differentiated by the WAN support they provide.
Secure business communication over the Internet –
Virtual Private Networks and more
The Internet offers unprecedented savings as a means of
long distance corporate communication. In fact, Internet
access can easily cost as little as 20% of the cost of a traditional
WAN connection. But how do you keep your vital business
data secure as it crosses the public domain?
Intel Express Routers provide a simple and inexpensive
solution, enabling you to create a highly secure Virtual Private
Network (VPN) over the Internet and public Frame Relay
and X.25 networks. There’s no need to alter your existing
network architecture. Security is provided by using an Intel
router for each point at which you connect to the Internet.
Powerful encryption keeps your data private. (See the side
bar on tunneling for more information.)
Other security features include:
■
Data encryption. Encryption is available when used over
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) or Frame Relay links. Encryption
is performed using the Blowfish algorithm, with a 144 bit
encryption key. For best effectiveness, encryption is performed
across the entire data stream rather than on individual packets
only. All Express Router models come in two versions – with
or without encryption.
■
Network Address Translation (NAT). Network Address
Translation enhances security by hiding internal IP addresses
when data is sent over the Internet or WAN. NAT also provides
considerable savings in time and money by eliminating the need
to redesign your business’s internal TCP/IP addressing scheme
when connecting to the Internet or remote sites with conflicting
IP addressing schemes.
Using NAT, an Intel Express Router automatically assigns
a unique Internet IP address to each internal LAN address,
enabling transparent communication with those outside your
corporate network. Alternatively, the router can maintain a
pool of unique IP addresses, assigning a temporary address to
a workstation whenever it connects over the Internet or WAN.
This method requires fewer official Internet IP addresses.
■
Authentication – PAP, CHAP. To ensure that Intel
Express Routers communicate only with other authorized
devices, the routers can be configured to use the Password
Authentication Protocol (PAP) or the Challenge Handshake
Authentication Protocol (CHAP) when communicating
over PPP links. The routers will demand authentication
whenever the link is established.
Over ISDN (EuroISDN only) and analog modems, PPP
Call Back can be used for authentication. If a user dials in for
access to the LAN, the router cuts the connection, then calls
back to ensure that it’s an authorized link. PPP Call Back is
compatible with the Microsoft Call Back standard.
■
Filtering. IP and IPX filtering eliminates unauthorized
communication over the WAN or LAN link. By tightly
defining filters to pass communication only to and from
authorized sources, links remain secure.
Comprehensive cost control of WAN links
Traditionally, WAN link traffic is by far the most expensive
cost component of WAN connections. Intel Express Routers
help control WAN link costs while also maximizing the available bandwidth for data communication. They do this in a
variety of ways:
■
Data compression. Data compression allows the transmission of more information over the same bandwidth on
a WAN connection. Software-based LZS data compression
is supported in the Intel Express 9100, 9200, 9201 and
9300 Routers for Frame Relay and PPP. LZS is an industry
accepted specification providing typical compression rates
of approximately 4:1 and interoperability with other routers.
The hardware-based data compression supported in the Intel
Express Router 9400 is also based on the LZS algorithm.
This distinctive feature allows compression while running at
full bandwidth. X.25 and LAPB compression is supported
in an implementation that requires Express Routers at both
ends of the connection.
■
Filtering. Filtering eliminates unnecessary communication
over the WAN link. With tightly defined filters, only essential
traffic passes through, thus lowering communication costs. The
Intel Express Routers support filters for IP, IPX and bridging.
2
Page 3
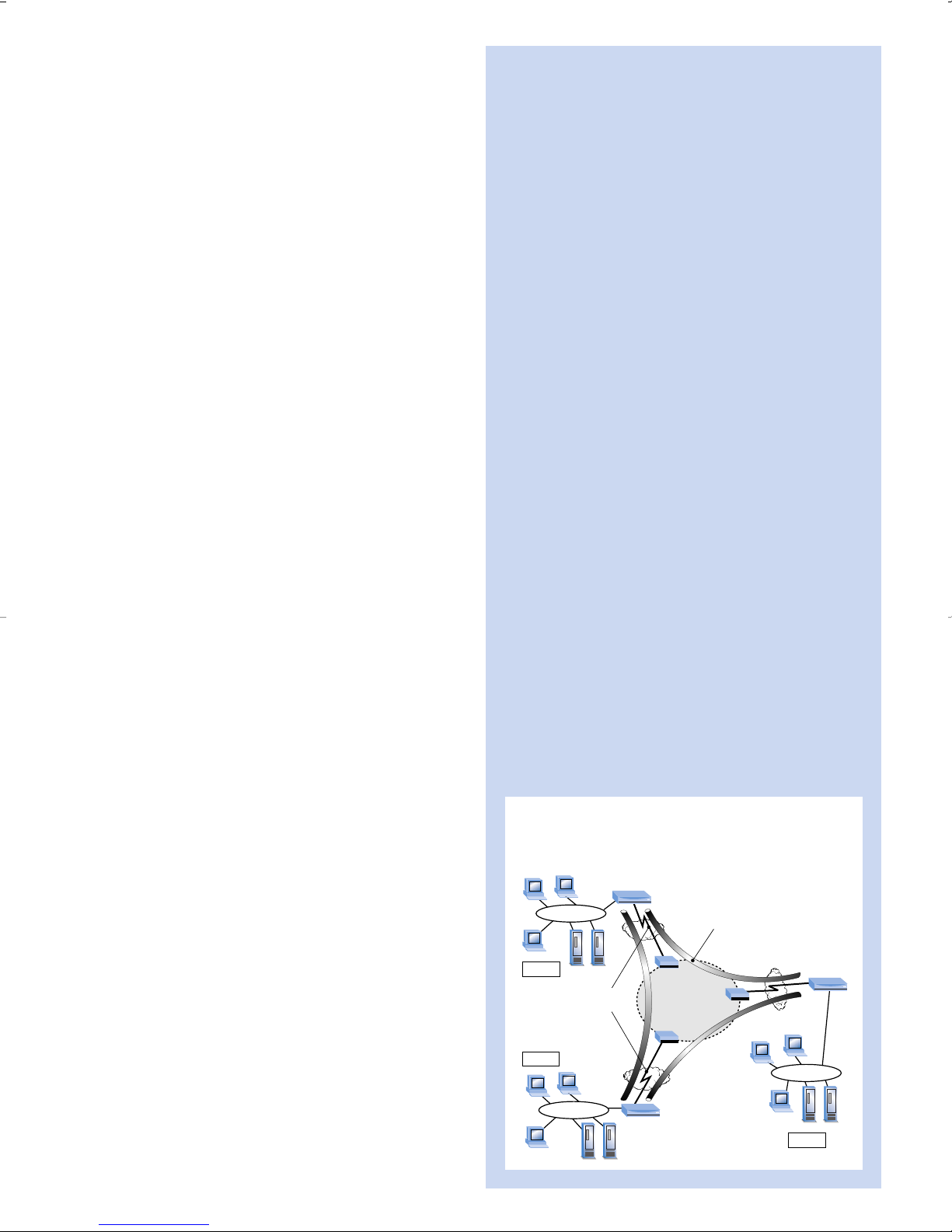
Intel Express Router
(with tunneling enabled)
ISP
POP
Public
Internet
Secure Tunnel:
IP, IPX or bridged LAN
traffic encrypted,
compressed by PPP
and encapsulated in IP
Local private
WAN link to ISP
(PPP, Frame
Relay or X.25)
Site A
Site C
Site B
ISP POP
ISP POP
Intel Express
Router
(with tunneling
enabled)
Intel Express Router
(with tunneling enabled)
■
IPX/SPX spoofing. The Novell IPX protocol sends IPX
Watchdog packets between servers and clients on a regular
basis to ensure that IPX sessions remain valid. Similarly, SPX
sends keep-alive packets between clients to ensure that SPX
sessions are still active. The packets continually activate the WAN
link, which significantly increases the cost of operation. Intel
Express Routers prevent these unnecessary dial-up connections
by answering the packets on behalf of remote clients until the
WAN link is established for data communication.
■
Triggered RIP. Standard RIP updates are transmitted
between routers at regular intervals and whenever a topology
change occurs. With Triggered RIP, the routers store these
updates until the next WAN link is established, and thereafter
send only those updates that report a topology change. By
eliminating unnecessary information exchange between routers,
Triggered RIP reduces the cost of the WAN link and maximizes
the available bandwidth for data communication.
■
IP and IPX static routes. Even with Triggered RIP updates
sent via IP and IPX, keeping track of topology changes can
consume valuable bandwidth on the WAN link and increase
costs. To prevent routing updates from being sent over the
WAN link at all, users can establish static routes.
■
Controlled bridging. Intel Express Routers offer user-defined
control of the bridging functions. For example, the routers
can be configured to forward data only to known destinations,
helping to ensure that only essential information is forwarded.
■
EuroISDN cost control. Timer profiles and link accounting
are especially useful for controlling WAN link costs on ISDNbased (EuroISDN only) networks. Timer profiles (up to 16) can
be used to restrict outgoing and incoming access to the WAN link.
For example, access can be restricted to times when operating
tariffs are lowest. Link accounting allows usage monitoring of
the ISDN link, including the number of calls and cumulative
uptime. An activity alarm can be set to close the ISDN links
or send an alert when usage reaches a predefined threshold.
To control and consolidate the billing of dial-in connections
over analog or ISDN modems, the Call Back feature can be
used. In this case, the router cuts the inbound connection, then
immediately calls back the remote site so the billing originates
from the central site.
Tunneling – Secure Use of the Internet
Via a Virtual Private Network (VPN)
With two or more Intel Express Routers, you can use tunneling
and encryption to create a VPN that allows safe use of the Internet
to send and receive secure business data between LANs. You get
the security of a private network at the vastly lowered expense
of simple Internet connections. Typically, because of current
limitations in the Internet infrastructure, VPNs are most suitable
for non real-time or lower bandwidth traffic.
Tunneling with Intel Express Routers is supported by powerful
encryption, using the Blowfish algorithm, with a 144 bit encryption
key. Compare this with competing solutions providing key lengths
of only 40 to 128 bits – this is strong encryption. For even greater
security, you can use a different key for each tunnel.
Before any data enters the public domain, each packet is
encrypted and placed in a separate envelope for transmission.
For best effectiveness, the encryption is performed across the
entire data stream rather than on individual packets only. Even
the original source and destination address of the data stream
are hidden from potential hackers.
With Intel Express Routers, configuring a tunnel is simple.
You don’t have to modify applications or add any specialized
software to your LAN. Just enter the IP address of the router at
the remote site and enter the same encryption key on both ends
of the communication. The connection will work with virtually
any ISP and travel as easily as open traffic through the Internet.
Because Intel’s solution encapsulates tunneled traffic in
standard IP, Intel Express Routers can tunnel any LAN protocol
they can route or bridge, including IPX. This allows existing
LAN applications to be used unchanged over the Internet tunnel.
LAN to LAN Connectivity Via
Virtual Private Network Over the Internet
Page 4

10BASE-T
AUI WAN 1 WAN 2 CONSOLE
LAN
WAN 1
WAN 2
MAINT
SYSTEM
Intel Express Routers
Easy setup and management
Intel Device View for Windows* is included with each
Intel Express Router for simple and comprehensive SNMPbased management within Windows 95 and Windows NT*
environments. This powerful tool offers a simple graphical
interface for real-time monitoring, configuring and troubleshooting of the router and all WAN and LAN links.
Features include:
■
Quick Setup. Intel Express Routers are easy to install
and configure, even for users who have little or no WAN or
router expertise. The configuration of just a few parameters
using the simple menu-assisted format will satisfy the needs
of most installations. Intelligent cross-checking helps the
user avoid “impossible” configurations, and auto-detection
of cables and WAN port type ensures proper connections.
For more demanding applications, advanced configuration
capabilities are easily accessed and can be implemented
with the router online.
■
SNMP Monitoring and Configuration. Intel Device View
for Windows uses standard and proprietary MIBs to manage
Express Routers over the LAN, providing support for most
SNMP counters and allowing MIB viewing with other SNMP
management tools. The data is clearly organized by port, and
you can quickly navigate down protocol layers to access the
level of information you need.
■
RMON Support. Intel Express Routers support groups 1-3
and group 9 of the RMON standard for monitoring of the local
area network and the router. The supported groups include
statistics, history, alarm and events.
■
Clear Informational Graphs. Built-in graphical analysis
tools offer a clear look at real-time traffic statistics. Use built-in
or user-defined parameter combinations for both statistical
displays and graphs.
Intel Device View for Windows* includes a new explorer view that
presents all WAN connections in an easy-to-navigate protocol tree.
This, coupled with intelligent diagnostics, can literally save hours
troubleshooting a tough link problem by directing you to the level
where the problem exists.
■
Straightforward Diagnostics. Unlike most log-based
diagnostic tools, Device View for Windows sorts errors by
link and prioritizes them in order of seriousness. It also
provides an ordered list of suggestions for corrective action.
■
Management Platform Independence. Intel Device View for
Windows can be integrated in Windows NT and Windows 95
management platforms. Its logical, easy-to-use, menu-based
layout offers full integration with the Windows user interface.
Intel Express Router 9100
Wide area networking among multiple sites.
■
Easy Firmware Upgrades. The included Software Upgrade
Wizard is an integrated Windows-based interface that guides
you step-by-step through the upgrade process. In addition,
Intel Express Routers let you pretest new software while you
continue to run the original software. This avoids downtime
by allowing full testing of any new configuration before it is
released for full-scale operation.
4
The Intel Express Router 9100 features two WAN
ports, and can support one protocol on one port while
simultaneously supporting a different protocol on the
other. This ensures maximum flexibility in connecting
simultaneously to two networks.
WAN links:
■
Two HDLC Serial Interfaces supporting Frame Relay,
X.25, PPP, LAPB, Leased Line (TI/EI)
Page 5

10BASE-T
AUI WAN 1 WAN 2 CONSOLE
LAN
WAN 1
WAN 2
MAINT
SYSTEM
■
Intel Support Services. Intel provides a broad range of support
services including free 90-day phone support and a 1 year limited
warranty. Hardware Maintenance Agreements are also available
as added protection for your investment in Express Routers.
Intel Express Routers overview
Intel offers five models of the Intel Express Router, each
one supporting all the features previously discussed. The
difference among the first four models (9100 - 9300) is in
the type of WAN connections they support. The Express
Router 9400 is a high-performance ISDN Primary Rate
Interface (EuroISDN) alternative. It provides hardwarebased data compression for the fastest possible throughput.
Models 9100, 9200, 9201 and 9300 each provide one or more
High-level Data Link Control (HDLC) WAN ports. These ports
will support as many as 62 links to user-defined sites. This is a
unique feature that provides an ideal solution for building wide
area networks linking many locations with Frame Relay, X.25
or EuroISDN. Data compression is also supported for each link
to improve throughput and reduce costs.
With an X.25 connection, each link can be defined as
a Switched Virtual Circuit (SVC) or a Permanent Virtual
Circuit (PVC). Switched Virtual Circuits are established
only when data is awaiting transmission; Permanent Virtual
Circuits are always available.
Intel Express 9400Intel Express 9300Intel Express 9201Intel Express 9200Intel Express 9100Feature
LAN Interface
WAN Interfaces
WAN Protocol
All products come in two versions: one with encryption and one without.
†
EuroISDN support only.
1, 10BASE-5
(AUI) or 10BASE-T
(RJ-45)
2, HDLC Serial
Interfaces
Frame Relay,
X.25, PPP
1, 10BASE-5
(AUI) or 10BASE-T
(RJ-45)
1, HDLC Serial
Interface
1, PC Card slot for
analog modem
Frame Relay,
X.25, PPP
Intel Express Router 9200
Wide area networking using an analog
modem connection as a back-up link.
1, 10BASE-5
(AUI) or 10BASE-T
(RJ-45)
1, HDLC Serial
Interface
1, PC Card Slot for
analog or ISDN
BRI modem
Frame Relay,
X.25, PPP
†
1, 10BASE-5
(AUI) or 10BASE-T
(RJ-45)
Interface
1, ISDN†BRI
PPP, Multilink PPP
1, 10BASE-5
(AUI) or 10BASE-T
(RJ-45)
†
1, ISDN
PRI1, HDLC Serial
PPP, Multilink PPFrame Relay, X.25,
WAN links:
■
One HDLC Serial Interface supporting Frame Relay,
X.25, PPP, LAPB, Leased Line (TI/EI)
■
One PC Card slot supporting the following analog modems
(modem not included):
The Intel Express Router 9200 is an excellent solution for
environments requiring maximum reliability. The dial-up
connection can be used as a back-up in case the primary
link fails. It can also be used for separate Internet access,
or for occasional connections to other sites that are not
connected to a WAN on a permanent basis.
– Xircom CreditCard Modem 28.8
– Xircom CreditCard Modem 33.6
– US Robotics Sportster PC Card 28.8 V.34 Faxmodem
– US Robotics Sportster 33.6Kbps PC Card 33.6 V.34+ Faxmodem
– US Robotics Courier V.Everything 33.6Kbps PC Card Modem
– US Robotics Worldport* PCMCIA V.34 CE Data/
Faxmodem 28.8Kbps
– US Robotics Worldport PCMCIA V.34+ CE Data/
Faxmodem 33.6Kbps
5
Page 6

10BASE-T ISDN S/T
AUI CONSOLE
LAN
WAN 1
WAN 2
MAINT
SYSTEM
10BASE-T ISDN S/T
AUI WAN CONSOLE
LAN
WAN 1
WAN 2
MAINT
SYSTEM
10BASE-T
AUI WAN 1 WAN 2 CONSOLE
LAN
WAN 1
WAN 2
MAINT
SYSTEM
Intel Express Routers
Intel Express Router 9201
Flexible wide area networking using an analog
modem or ISDN as backup (EuroISDN only).
The flexibility of the Intel Express Router 9201 makes it
an ideal solution for the company with changing WAN
connectivity requirements. For example, a company can
start with dial-up support using the analog modem. Then,
if a faster dial-up link is required, the router offers support
for BRI (Basic Rate Interface) ISDN through the PC Card
slot. The BRI ISDN connection could be used as the primary
(or only) link to the WAN. It could also provide a safety
backup, while using the WAN port as the main connection.
WAN links:
■
One HDLC Serial Interface supporting Frame Relay,
X.25, PPP, LAPB, Leased Line (TI/EI)
■
One PC Card slot supporting either analog or BRI ISDN
(EuroISDN only) communications using the following
(modem not included):
For BRI ISDN (EuroISDN only):
– Eicon Diva* PCM
For analog modem communications:
– Xircom CreditCard Modem 28.8
– Xircom CreditCard Modem 33.6
– US Robotics Sportster PC Card 28.8 V.34 Faxmodem
– US Robotics Sportster 33.6Kbps PC Card 33.6 V.34+ Faxmodem
– US Robotics Courier V.Everything 33.6Kbps PC Card Modem
– US Robotics Worldport* PCMCIA V.34 CE Data/
Faxmodem 28.8Kbps
– US Robotics Worldport PCMCIA V.34+ CE Data/
Faxmodem 33.6Kbps
Intel Express Router 9300
Wide area networking with ISDN as the
primary or secondary link (EuroISDN only).
The BRI ISDN port can be a permanent or dial-up
connection. The Intel Express Router support for
Multilink PPP makes it possible to use the ISDN
connection to gain extra bandwidth (bandwidth on
demand) with a leased line connection running PPP
at the same speed. In this case, the ISDN connection
is made whenever WAN traffic exceeds a given amount,
then closes when traffic levels return to normal.
WAN links:
■
One HDLC Serial Interface supporting Frame Relay,
X.25, PPP, LAPB, Leased Line (TI/EI)
■
One integrated BRI ISDN port (EuroISDN only)
Intel Express Router 9400
Full Primary Rate Interface (PRI) ISDN performance
for central sites or high-bandwidth environments
(EuroISDN only).
The Intel Express Router 9400 features a PRI ISDN
(EuroISDN only) port that allows 62 connection profiles or
links to be defined and up to 30 simultaneous connections.
This high-performance capability makes the 9400 ideally
suited as a central-site solution.
To reduce WAN costs, the Intel Express Router 9400
takes unique advantage of hardware-based data compression.
This allows data compression at full line speed for the fastest
possible throughput – a powerful feature not found in most
other PRI ISDN routers in its category.
6
WAN links:
■
One PRI ISDN port (EuroISDN only) supporting
PPP and Multilink PPP
Page 7

SPECIFICATIONS
Feature Intel Intel Intel Intel
Express Router Express Router Express Router Express Router
9100 9200/9201 9300 9400
Physical Dimensions (WxHxD) 305.5 x 72 x 245mm 305.5 x 72 x 245mm 305.5 x 72 x 245mm 305.5 x 72 x 245mm
Weight approx. 3kg approx. 3kg approx. 3kg approx. 3kg
Maximum power consumption 25W 25W 25W 25W
Hardware:
LAN interface connectors
WAN interface connectors
ISDN interface connectors
CPU 32 bit RISC 32 bit RISC 32 bit RISC 32 bit RISC
Memory 5MB DRAM, 5MB DRAM, 5MB DRAM, 4MB DRAM,
Performance:
Forwarding rate
Filtering rate
MTBF 47,200 hours 61,840 hours 54,800 hours 51,600 hours
Physical and Link Layer:
Number of LAN & WAN links available
Standards
Frame Relay Standards
X.25 Standards
ISDN Standards
(EuroISDN)
Bridging
Network Layer:
RFCs
Routing protocols IP (RIP-1 & RIP-2) IP (RIP-1 & RIP-2) IP (RIP-1 & RIP-2) IP (RIP-1 & RIP-2)
Approvals:
Safety
Telecommunications
Emission
Susceptibility
CE Mark
10BASE-T (RJ-45) 10BASE-T (RJ-45) 10BASE-T (RJ-45) 10BASE-T (RJ-45)
10BASE-5 (AUI) 10BASE-5 (AUI) 10BASE-5 (AUI) 10BASE-5 (AUI)
X.21/lV11, V.24/V.28, 2 ports:X.21/lV11, V.24/V.28, X.21/lV11, V.24/V.28,
V.35 or V.36 by use of V.35 or V.36 by use of V.35 or V.36 by use of
an adapter cable an adapter cable an adapter cable
ISDN Basic Rate Interface ISDN Basic Rate Interface ISDN E1 Primary Rate
via an Eicon/Diehl Diva via an RJ-45 connector Interface via RJ-45
PCM Card connector
3MB FlashPROM preloaded 3MB FlashPROM preloaded 3MB FlashPROM preloaded 4MB FlashPROM preloaded
with router software with router sof tware with router software with router software
(self-booting) (self-booting) (self-booting) (self-booting)
4513 packets/sec 4276 packets/sec 4419 packets/sec 3174 packets/sec
Line speed (LAN - Line speed (LAN - Line speed (LAN - Line speed (LAN -
up to 14,800 packets/sec) up to 14,800 packets/sec) up to 14,800 packets/sec) up to 14,800 packets/sec)
62 62 62 62
Microsoft Call-Back Control Microsoft Call-Back Control Microsoft Call-Back Control
CSMA/CD (ISO 8802/3) CSMA/CD (ISO 8802/3) CSMA/CD (ISO 8802/3) CSMA/CD (ISO 8802/3)
LLC (ISO 8802/2) LLC (ISO 8802/2) LLC (ISO 8802/2) LLC (ISO 8802/2)
IEEE 802.3 IEEE 802.3 IEEE 802.3 IEEE 802.3
LAPB (ISO 7776) LAPB (ISO 7776) LAPB (ISO 7776) LAPB (ISO 7776)
HDLC (ISO 3309) HDLC (ISO 3309) HDLC (ISO 3309) PPP LCP (RFC 1681)
PPP LCP (RFC 1681) PPP LCP (RFC 1681) PPP LCP (RFC 1681) PPP ML (RFC 1990)
PPP over HDLC (RFC 1662) PPP over HDLC (RFC 1662) PPP over HDLC (RFC 1662) PPP Stac compression(RFC 1974)
PPP ML (RFC 1990) PPP ML (RFC 1990) PPP ML (RFC 1990) PPP encryption (RFC 1968)
PPP Stac compression(RFC 1974) PPP Stac compression(RFC 1974) PPP Stac compression(RFC 1974) PPP compression (RFC 1962)
PPP encryption (RFC 1968) PPP encryption (RFC 1968) PPP encryption (RFC 1968) PPP over ISDN (RFC 1618)
PPP compression (RFC 1962) PPP compression (RFC 1962) PPP compression (RFC 1962)
PPP over ISDN (RFC 1618) PPP over ISDN (RFC 1618)
ANSI T1.606 ANSI T1.606 ANSI T1.606
ANSI T1.606 Add.1 ANSI T1.606 Add.1 ANSI T1.606 Add.1
ANSI T1.617-DSS1 ANSI T1.617-DSS1 ANSI T1.617-DSS1
ANSI T1.618-DSS1, ANSI T1.618-DSS1, ANSI T1.618-DSS1,
FRF.1, FRF.3 FRF.1, FRF.3 FRF.1, FRF.3
CCITT I.233.1, CCITT I.370, CCITT I.233.1, CCITT I.370, CCITT I.233.1, CCITT I.370,
CCITT Q.922 CCITT Q.922 CCITT Q.922
Multi-protocol (RFC 1490) Multi-protocol (RFC 1490) Multi-protocol (RFC 1490)
ITU-T(CCITT) X.121, X.25 ITU-T(CCITT) X.121, X.25 ITU-T(CCITT) X.121, X.25
ISO/IEC 7776, ISO/IEC 8208 ISO/IEC 7776, ISO/IEC 8208 ISO/IEC 7776, ISO/IEC 8208
(RFCs 877, 1356) (RFCs 877, 1356) (RFCs 877, 1356)
For the 9201, refer to the BAPT 223 ZV 25 BAPT 223 ZV 25
Eicon Diva PCM card ETS 300 047 part 3 ETS 300 046 part 3
specifications ITU-T (CCITT) I.430, Q.850, ITU-T (CCITT) I.430, Q.850,
Q.921, Q.922, Q.931 Q.921, Q.922, Q.931
ETS 300 012 ETS 300 156
ETS 300 153 and ETS 300 104 and ETS 300 011
IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1D
IEEE 802.1G IEEE 802.1G IEEE 802.1G IEEE 802.1G
768, 783, 791, 792, 793, 826, 768, 783, 791, 792, 793, 826, 768, 783, 791, 792, 793, 826, 768, 783, 791, 792, 793, 826,
919, 922, 950, 951, 1027, 1055, 919, 922, 950, 951, 1027, 1055, 919, 922, 950, 951, 1027, 1055, 919, 922, 950, 951, 1027, 1055,
1058, 1155, 1166, 1212, 1213, 1058, 1155, 1166, 1212, 1213, 1058, 1155, 1166, 1212, 1213, 1058, 1155, 1166, 1212, 1213,
1256, 1315, 1332, 1334, 1490, 1256, 1315, 1332, 1334, 1490, 1256, 1315, 1332, 1334, 1490, 1256, 1315, 1332, 1334, 1490,
1493, 1552, 1631 1638, 1700, 1493, 1552, 1631 1638, 1700, 1493, 1552, 1631 1638, 1700, 1493, 1552, 1631 1638, 1700,
1717, 1723, 1812, 1994, 2091 1717, 1723, 1812, 1994, 2091 1717, 1723, 1812, 1994, 2091 1717, 1723, 1812, 1994, 2091
Novell IPX RIP/SAP Novell IPX RIP/SAP Novell IPX RIP/SAP Novell IPX RIP/SAP
UL 1950, CSA-C22.s No. 950, UL 1950, CSA-C22.s No. 950, UL 1950, CSA-C22.s No. 950, UL 1950, CSA-C22.s No. 950,
IEC 950, EN60950 IEC 950, EN60950 IEC 950, EN60950 IEC 950, EN60950
CTR 2, NET2 9200: CTR 2, NET 2 CTR 2, I-CTR 3, NET 2, NET 3 I-CTR 4, NET 5, BAKOM, BZT
9201: CTR 2, NET 2 BAKOM, BZT
47 CFR part 15 Class A 47 CFR part 15 Class A 47 CFR part 15 Class A 47 CFR part 15 Class A
EN55022 Class A EN55022 Class A EN55022 Class B EN55022 Class B
CISPR 22 Class A CISPR 22 Class A CISPR 22 Class B CISPR 22 Class B
EN 50082-1 EN 50082-1 EN 50082-1 EN 50082-1
Yes Yes Yes Yes
Page 8

Intel Express Routers
ORDER CODES
Express Router 9100 with encryption ER9100
Express Router 9100 no encryption ER9100C
Express Router 9200 with encryption ER9200
Express Router 9200 no encryption ER9200C
Express Router 9201 with encryption ER9201W
Express Router 9201 no encryption ER9201WC
Express Router 9300 with encryption ER9300W
Express Router 9300 no encryption ER9300WC
Express Router 9400 with encryption ER9400W
Express Router 9400 no encryption ER9400WC
Rack Mount Kit for Express Routers ER0001
Hardware Maintenance Agreement HMAROUTER
Hardware Maintenance Agreement Plus HMAPLUSROUTER
For the Express Routers 9100, 9200, 9201 and 9300, please order the appropriate WAN cable.
V.24 DTE interface cable ER1801
V.35 DTE interface cable ER1802
V.11 DTE interface cable ER1804
Optional test cables
V.24 DCE interface cable ER1811
V.35 DCE interface cable ER1812
V.11 DCE interface cable ER1814
Additional cables are also available. Please refer to the Intel Branded Products Price List for more information.
COMPANION PRODUCTS
Consider these related
Intel products as a factor
in your network planning:
■
Intel Express Switches
■
Intel Express Hubs
■
Intel EtherExpress
TM
PRO/100 LAN Adapters
J
CUSTOMER SUPPORT
Intel Customer Support Services offer a broad selection of tiered suppor t programs. For more information: visit us on the
World Wide Web at http://support.intel.com or call 800-538-3373, ext. 276, or order FaxBack* 8549 at 800-525-3019.
FOR PRODUCT INFORMATION
World Wide Web http://www.intel.com/network
U.S. and Canada 800-538-3373 or
503-264-7354
Europe +44-1793-431-155
Japan +81-298-47-0800
FOR MORE INFORMATION,
ORDER THESE FAXBACK*DOCUMENTS
Intel Express Routers Application Guide 1753
Virtual Private Networking White Paper 1747
Hardware Maintenance Agreement Information 8549
Intel Branded Products Price List 9000
Hong Kong +852-2-844-4524
Taiwan, Korea, Singapore and ASEAN +65-735-3811
To order call 503-264-6835, 800-525-3019, or find us on
the World Wide Web: http://www.intel.com/network
Australia +61-2-9937-5800
■
Intel NetportExpress
PRO/100 Print Servers
■
Intel LANDesk
®
Network Manager
TM
© Intel Corporation, 1997.
*Third party trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Please Recycle.
NP0803.02
 Loading...
Loading...