Page 1

®
Intel
Express 550T
Routing Switch
User Guide
696939-004
Page 2

Year 2000 capable
An Intel product, when used in accordance with associated documentation, is “Year 2000 Capable” when, upon installation, it accurately stores, displays, processes, provides, and/or receives data from, into, and between the twentieth and twenty-first centuries,
including leap year calculations, provided that all other technology used in combination with said product properly exchanges date
data with it.
Copyright © 1999, Int el Co rporation. All rights re served.
Intel Corporation, 52 00 NE Elam Young Parkway, Hi ll sboro, OR 97124-6497
Intel Corporation assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions in this manual. Nor does Intel make any commitment to update the information contained herei n .
* Other product and corporate names may be trademarks of other companies and are used only for explanation and to the owners’
benefit, without inten t to inf ringe.
Forth edition August 1999 696939-004
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1 Intel Express 550T Routing Switch 1
Introduction to the product . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Before Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Positioning and Installing the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Installing a Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Connecting Other Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Connecting the Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
The Power Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Power up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Other LEDs on the front panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Chapter 2 Intel Device View 17
System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Installation and Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Removal of Intel Device View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Using Intel Device View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Before a switch is contacted . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
After a Switch or Stack is Contacted . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Setting the Preferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Installing and Managing Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Device Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Device View (Main Display) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Explorer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Diagnostics Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Trap Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
System Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Errors Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
iii
Page 4

CONTENTS
Chapter 3 Standard Configuration 41
Changing the Setup of the Switch or Stack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Internet Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Local Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Permanent Entries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Link Aggregation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Port Mirroring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Local Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
TFTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Switching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Adaptive Forwarding Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Spanning Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Changing the Setup of the Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
General Changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Port Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Port Specific Spanning Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Chapter 4 Advanced Configuration 65
VLANs (Virtual LANs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Routing Between VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
DVMRP Tunnels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
IP Multicast (IGMP pruning) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
IP Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Chapter 5 Managing the Switch 79
Management using Intel Device View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Information about the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Monitoring the Switch’s Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Monitoring using RMON . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Monitoring the Stack’s Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Monitoring VLANs and Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Monitoring the Port’s Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Tools for the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Ping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Report Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
iv
Page 5

CONTENTS
Telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Recovery Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
DNS IP Conversion Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Tools for the Stack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Stack Synchronization Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Switch Position Organizer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Color Code Matrix Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Chapter 6 Redirect TCP Packets 111
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Setting up redirection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Monitoring the status of the cache servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Chapter 7 Technical Specifications 117
Physical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Power Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Performance Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Chapter 8 Console Port Use and Troubleshooting 123
Use of the Console Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Recovering from Start-up Failure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Using Maintenance Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Troubleshooting Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Troubleshooting Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Isolating the Problem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Further Evaluation of the Problem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Typical Problems and Causes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Start-up Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Performance Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Communication Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Reporting the Problem to Intel Customer Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Retrieving Information for Customer Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Appendix A Limited Hardware Warranty 137
Limited Hardware Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Limited Hardware Warranty (Europe only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
v
Page 6

CONTENTS
Manufacturer Declaration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
WARNING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
WARNING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
AVERTISSEMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
WARNUNG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
AVVERTENZA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
ADVERTENCIAS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Automated Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Customer Support Technicians . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
vi
Page 7

Preface
Information sources for
this switch
This User Guide is one of three sources of informat ion delivered with
this switch.
Information type... Given in...
Getting started quickly Quick Start (printed)
How to customize your switch User Guide (printed)
Context sensiti ve help Help (online)
Quick Start description A printed guide that describes these basic steps:
•
Connect the switch
•
Start the switch (using the default settin gs)
•
Start Intel Device View
•
Change the setup
•
Save a new setup to the memory
•
Access Local Management
•
And, the legal declarations and warnings
User Guide description
(this guide)
Help description Online, context-sensitive help text for each dialog box, providing in-
A printed guide containing full instructions on h ow to install the
switch and operate the switch using Intel Device View.
formation about the p ermitted limits for the par ameters used.
vii
Page 8

PREFACE
Warning
Products covered This User Guide gives you instructions on how to use:
Electrostatic Sensitive Devi ce
Electrostatic Sensitive Device
Do not handle the printed circuit board unless the working area is static-free!
•
Intel Express 550T Routing Switch
•
Intel Device View
0887
Prerequisite knowledge This User Guide is i ntended for personnel autho rized to configure and
manage local area networks. We assume that the person has an advanced technical background within data communication and networks.
Opening this pro duct must be done only by a net work manager or person who is qualified and authorized to install electrical equipment,
and who is aware of the hazards to which he/she is exposed. This person must have an advanced technical background within data communications and networks.
Conven tion s in this manual This manual uses the following conventions:
File names, commands and examples
All file names, commands and exampl es are shown in the COURIER
typeface.
Menu and submenu names
Menus, for example File or View, are shown in normal typeface with
lowercase and uppercase letters displayed as shown on the screen.
viii
Page 9

PREFACE
Access to submenus
You access submenus using a menu hierarchy. These are shown by
use of angle brackets and the courier typeface. For example,
File>Configuration>Setup shows that to select t he Setup sub-
menu you must first click File and then Configuration.
Acronyms ARP Address Resolution Protocol
ASIC Application-Specific Integrated Circuit
AUI Attachment Unit Interface
BPDU Bridge Protocol Data Unit
CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DVMRP Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol
ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol
IGMP Internet Group Message Protocol (for IP Multicast)
IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers
IP Internet Protocol
LAN Local Area Network
MIB Management Information Base
RAM R andom Access Memory
RMON Remote Monitoring
RIP Routing Information Protocol
RSVP Resource Reservation Protocol
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol
STP Spanning Tree Protocol
TFTP Trivial File Tra nsfer Protocol
ToS Type of Service
UDP User Datagram Protocol
VLAN Virtual Local Area Network
ix
Page 10

Page 11
Intel Express 550T
1
In this chapter This chapter covers the following topics.
Routing Switch
Topic See Page
Introduction to the product 2
Front Panel 3
Rear Panel 5
Installation 5
1
Page 12

C H A P T E R 1 Intel Express 550T Routing Switch
Introduction to the product
Purpose of the switch The Intel Express 550T Routing Switch uses your existing network
cables to in tegrate switchi ng technolog y into your computer netw ork.
Each device in a workgroup or a network segment can communica te
at a full wire-speed of 10Mbps or 100Mbps to provide:
• High-speed connectivity
• Simultaneous two-way communication between connected
devices
• Increased network throughput and performance
• Increased server availability
Physical features This switch offers the following features:
• Plug-and-play—no need to configure the modu le to use the basic
operations
• 8 x 10/100Mbps, non-blocking connections
• Two option slots for modules
• Front panel LEDs that show switch, port and traffic status
• Automatic detection of 110V and 240V power supplies
Hardware features The switch offers the following features:
• Each port can operate in one of three switching modes: cut-
through, fragment-free or store-and-forward
• Each port supports half- and full-duplex operation
• Sim ultaneous full wire-speed switching on all ports
• RMON support for Statistics, History, Alarm, Host, HostTopN,
Matrix, Filter, Capture and Events
• Full RMON support on a limited number of ports
• Switch routing: IP and IPX protocols
• Spanning tree support on all ports
• Flow control
• Permanent MAC address entries
2
Page 13

C H A P T E R 1 Intel Express 550T Routing Switch
Software features
The switch offers the following features:
• Intel Device View for W i ndows* 95, W indows* 98 and W indows
NT* or Intel Device View for Web
• Adaptive forwarding mode
• Local Management via a direct terminal connection or via TEL-
NET
• SNMP Management support
• BOOTP and TFTP support
• Control over user access rights
• Creation of virtual LANs
• Stand-alone (per switch or stack) or distributed (swi tch networ k )
VLAN
• IP Multicast
• RSVP
• ToS (Type of Service)
• IP Filtering
Front Panel
Introduction The LEDs on the front panel show the status of the ports, so you
should position the switch with the front panel facing you. You can
also see which ports the cables are connected to on the switch.
View of the front panel The front panel of the switch is shown below:
123 87654
971126 Awaiting Drawing from EBZ
Slot BSlot A
Orange
LEDs
Green
Off
10Mbps
Halfduplex
100Mbps
Green
Link
Activity
PortStatus
Fullduplex
Orange
Disabled
Collision
Intel Express
550T Routing
Switch
Status
Temperature
RPS
Console
9600-8-N-1
Solid
LEDs
Solid
Blink
Power
Reset
1675
3
Page 14

C H A P T E R 1 Intel Express 550T Routing Switch
Front panel ports
These ports are on the front panel:
Port Function
CONSOLE port
(DB-9)
Connects a PC (running a VT100 emulation), a VT100 terminal or a modem to
access the built-in Local Management program.
8 x 10/100Base-TX
ports (RJ-45)
Connects devices using Unshiel ded T wisted
Pair (UTP) cab ling complying to EIA568A
Category 5 or ISO/IEC 11801 Category 5
level D.
Slots for modules After removing one or both of the cover plates, the modules can be
inserted to expand the functionality of the switch.
Front panel LED functions The LEDs on the front panel have the following functions:
LED
Shows the status for...
Port LEDs -
The operation of each port.
Green and Orange
Status The operation of the switch.
Power The internal power supply.
Temperature The internal temperature.
RPS (redundant
The external, redundant power supply.
power supply)
Buttons The buttons on the front panel have the following functions:
Button name Function
Port Status Shows the operational status of each port.
Reset Reset or enter Maintenance Mode or Recov-
ery Mode
4
Page 15

C H A P T E R 1 Intel Express 550T Routing Switch
Rear Pa nel
Introduction The rear panel has a cooling fan ou tlet and the main suppl y cable, so
you should position the switch with the rear panel f acing away fro m
you.
View of rear panel The rear panel of the switch is shown below:
Input
100-120VAC/2A
200-240VAC/1A
47Hz-63Hz
RedundantPower Supply (RPS)
1741
Rear panel parts The switch’s rear panel has the following parts:
Part Function
Fan outlet Cools the internal circuitry of the switch.
Power connection A socket to connect the power cord to the
main supply.
Redundant power
supply connector
Connects an external redundant power supply. If the internal power supply fails, the
redundant power supply starts immediately.
Installation
Important You must adhere to all local and national regulations governing the
installation and connection of electrical devices when installing the
switch.
5
Page 16

C H A P T E R 1 Intel Express 550T Routing Switch
Before Installation
Contents of the pack Unpack the switch carefully and check that these parts are present:
Item Present?
One Intel Express 550T Rout i ng S wit ch
One power cord (suitable for your
power outlet)
One moun ting kit
One CD-ROM
One Console cable
One Quick Start
One User Guide (you are reading it)
Late-breaking News
Intel Support Service papers
Check the package
contents
If you have not received all of the parts, or any of the parts are damaged, contact your dealer immediately.
Keep all the packaging materials in case you need to repack the
switch.
Check all labels Read all labels and rating plates on the switch. If there is any thing that
you do not understand , or if any of th e informati on provided does no t
appear to comply with your local or national rules and regulations,
consult your dealer before proceeding with the installation.
Essential reading It is important that you read th e following:
• “Late-breaking News”.
This contains essential i nformat ion you sho uld be aware of when
installing and using the product; for example, limitations and
compatibility issues.
• Warnings and the instructions earlier in this guide.
• The README.TXT file on the CD-ROM. This gives a general
6
description of the software and specific requirements.
Page 17

C H A P T E R 1 Intel Express 550T Routing Switch
Positioning and Installing the Switch
Allow adequate ventilation The switch contains two fans to air-cool the internal circuitry. The air
is drawn in from the left of the unit and expelled through the outlet
grills on the right side and the rear.
To ensure correct airflow, leave 100 mm (4 inc hes) free space on both
sides and behind the switch. Do not allow t he intake or outle t grills to
become blocked.
On a desktop To install the switch in a desktop environment:
1 Find the four rubber feet in the pack that contains the rack
mounting kit.
2 Remove the backing strip from each of the four feet.
3 Attach the four rubber feet to the underside of the switch (to
ensure that the switch stands firmly).
4 Place the switch on a stable, flat surface.
5 Ensure tha t th e air intake (on the left) and fan outlets (on the
right side and rear ) are not blocked.
Warning The switch’s lifetime and operational reliability can
be seriously degraded by inadequate cooling.
Rack requirements Install the switch in a standard rack in accordance with IEC297 (or
similar); if th e minimum out side mea surements of the rack are 600 x
600mm (23.5 x 23.5inches), you must allow 190mm (7.5 inches) of
space at the rear.
Mounting kit The switch is delivered with a kit to attach it to a standard 19-inch
equipment rack (wit h side sup port rai ls). The ki t contains two mounting brackets and four screws (for attaching the brackets to the sides
of the switch).
Tools required for
positioning in a rack
In addition to the mounting kit, you need the following items to
mount the switch in a rack:
• Standard 19-inch rack with side support rails.
• 3 mm screwdriver.
7
Page 18

C H A P T E R 1 Intel Express 550T Routing Switch
• Customer-supplied screws for securing the switch in the rack.
Mounting screws are not provided because the required sizes
may vary from rack to rack.
In an equipment rack To mount the switch in a standard equipment rack:
1 Attach the mounting bracket marked “ Left” to t he left-hand side
of the switch, and attach the mounting bracket marked “Right”
to the right-hand side of the switch, using the four screws provided.
SlotA
971126 Awaiting Drawing from EBZ
2
1
4
3
SlotB
7
6
5
Orange
Green
LEDs
Halfduplex
10Mbps
Off
Intel Express
Fullduplex
100Mbps
Solid
550T Routing
PortStatus
Switch
Power
Status
Orange
Green
LEDs
Temperature
Disabled
Link
Solid
Collision
Activity
Blink
8
Reset
RPS
Console
9600-8-N-1
1679
Make sure that you attach the mounting brackets to the correct
sides. Otherwise the switch will not align correctly in the
equipment rack.
2 If the four rubber feet prevent the switch from standing firmly
on the equipment rack’s side support rails, remove them.
3 Set the switch in the equipment rack, and make sure there is
adequate space for air flow around the switch (see “Allow adequate ventilation ” in “Posit io ni ng and I nstall i ng t he Swit ch”, p.
7).
4 Screw the mounting brackets securely to the equipment rack.
Ambient temperature If the switch is installed in a closed or multi-rack assembly, the oper-
ating ambient temperature of the rack environment may be greater
than the ambient temperature of the room. Make sure that the temperature of the rack environment does not exceed the recommended operating temperature for the switch.
8
Page 19

C H A P T E R 1 Intel Express 550T Routing Switch
Installing a Module
Introduction You can increase the connecti vity options of your switch by installing
a module.
Warning Modules are not designed to be installed in, or removed
from, the switch while it is in operation. You must
power off the switch before attempting to install or
remove a module.
Static-free working area The m odule’s printed circu it board is an Electrostatic Sensitive De-
vice and should be handled only in a static-free working area; otherwise, the printed circuit board may fail or be degraded.
Avoiding damage to the
circuit board
If you remove the plate covering the slot on the front of the switch,
for example, to install or remove a module, follow this procedure to
avoid damage to your printed circuit board:
Warning Do not remove the plate unless the switch is discon-
nected from the main power supply.
1 Disconnect the switch from the main power supply.
2 Ground the switch before you handle the printed circuit board.
3 Connect yourself to a non-painted/non-isolated part of the
grounded switch (for example the back panel) using a wrist
strap wi th 1MΩ resistance to ensure that you carry the same
electrostatic charge as the enclosure.
4 Remove the plate covering the slot.
Installing a module To install a module:
1 If the switch is already operational, disconn ect it from th e main
power supply.
2 Follow the instructions in “Avoiding damage to the circuit
board” above.
3 Unscrew the screws of the plate covering the slot on the front of
the switch. Save these screws and plate.
4 Insert the module into the slot (following the instructions in the
module’s User Guide). Place your thumbs just beneath the
screws on the front panel of the modul e and push in th e module.
Secure it using the retaining screws.
9
Page 20

C H A P T E R 1 Intel Express 550T Routing Switch
Removing the module
To remove a module:
1 If the switch is already operational, disconnect it from the main
power supply.
2 Follow the instructions in “Avoiding damage to the circuit
board” above.
3 Unscrew the screws securing the module.
4 Pull the module gently to disengage the connectors fully from
the socket on the motherboard. Slide the module out completely.
5 Cover the empty module port with the plate and secure using
the screws.
Connecting Other Devices
Introduction Incorrect cabling is often the cause of network configuration prob-
lems
Use shielded cables Shielded cables normally comp ly with EMC and FCC emission lim-
its.
Only use unshielded cables when it is explicitly specified in the in-
stallation manual of the device in question.
Cables fo r the LAN Ports Ports on the switch are wired MDI-X, so use the following cable:
If you connect the switch to a... Then use a...
Workstation or server Straight-through cable 1:1
Device with MDI-X ports (for exam-
Crossover cable
ple another Intel switch or hub)
Device with MDI ports S traight-throug h cable 1:1
10
Page 21

C H A P T E R 1 Intel Express 550T Routing Switch
RJ-45 connector pin
assignments
Connecting a de vice to the
RJ-45 ports
The RJ-45 ports on the front of the switch have the following pin assignments:
Pin number Function
1RX+
2RX3TX+
6TX-
To connect a workstation compatible with IEEE 802 .3 (Ethernet Version 1.0 and 2.0) or a fast access device (such as a server) to the
switch’s RJ-45 ports using UTP cable (Category 5):
1 Make sure that the device has a 100Mbps (100Base-FX or 10/
100Base-TX) network interface card installed.
If not, use your network interface card’s documentation to
install and configure it c orrectly.
2 If your workstation is fitted with an RJ-45 interface then there i s
no problem. However, it is possible to attach to other connector
types using an appropriate adapter. For example, use a UTP/
10Base-FL adapter for fiber connections
3 Connect one end of the UTP cable to an RJ-45 port on the
switch.
According to IEEE 802.3, the cable le ngth must not exceed 100
meters (approximately 325 feet).
4 Connect the other end to the 100Base-TX connection on the
device.
Connecting the
management PC
To manage the switch from a PC connected directly to the switch, the
PC must not use frame tagging. To manage the switch from a PC with
IEEE 802.1Q tagged frames, management must be through a device
which untags the frames.
Cable fo r the C on sol e Port If you connect a PC (via the Console Port), then use a null-modem ca-
ble.
11
Page 22
C H A P T E R 1 Intel Express 550T Routing Switch
Connecting the Power
Introduction After connecting the d evi ces to the switch, con nect th e power cabl e.
There are certain practical and safety considerations to be made before powering the switch on.
The Po w er Cable
Ground warning The switch is delivered with a power cable that fits the power sockets
in your countr y. If thi s is no t the case , conta ct your dealer immed iately and ask for the correct power cable.
Power cable wiring color
code
The wires in the power cable provided are color coded:
Color Connection
Green and yellow Ground
Blue Neutral
Brown Live
Important for U K use If the colors of the wires in the power cable provided do not corre-
spond with the markings that identify the terminals in your plug:
1 Make sure that the green and yellow wire is connected to the
terminal marked with the letter E, or with the ground symbol
, or is colored green and yellow.
2 Make sure that the blue wire is connected to the terminal
marked with the letter N or colored black.
3 Make sure that the brown wire is connected to the terminal
marked with the letter L or colored red.
Power supply to a rack If the switch is installed in a rack, make sure the rack’s power supply
socket has a ground connection an d the rack is con nected to a branch
supply or a power supply socket with a ground connection.
To avoid overloadi ng the circui t and damagi ng the wiring of the power supply, the power supply to the rack must be adequ ate to c over the
extra power consumed by the switch.
12
Page 23

C H A P T E R 1 Intel Express 550T Routing Switch
Power up
Powering up the switch Follow these steps to power up the switch:
1 Push the female end of the power cable into the main socket (i n
the rear panel); plug the other end into the power supply outlet.
2 Make sure that the Power LED (on the front panel) is green.
If it isn’t green, make sure that the power outlet is working correctly (switched on). If the power outlet is on and the Power
LED is not green, then the re i s a fau lt within the switch and
you must contact your dealer.
3 Verify that an LED is lit for each of the front panel ports where
a powered on device is connected.
Start-up procedure Immediately after power-up, the following should happen during
start-up:
Stage STATUS LED... Then the switch...
1 Is red Is starting up
2 Turns to steady green Has started successfully
If the Status LED remains red, then the switch has no t started successfully. Try to restart it; if the switch does not sta rt, contact your dealer.
Look at the other front panel LEDs during start-up and check that
they are operating correctly.
Port LED s tates The LEDs reflect the state of each port:
LED Indicates
No lights Port enabled, no link.
Green, blinking
randomly
Port enabled, RX/TX traffic, link pulse
active.
Green, solid Port enabled, link pulse active.
13
Page 24

C H A P T E R 1 Intel Express 550T Routing Switch
LED Indicates
Default se ttin gs afte r st artup
Green and Orange both
blinking r andomly
Collision detected (with half duplex).
Port enabled, link pulse active.
Orange, solid Port disabled by management.
Green and Orange both
solid
Port dis abled by a hardware fault, or no
hardware connected.
Once the switch has started successfully, installation is complete and
the switch is using its default setti ng (al s o known as default confi guration):
• All ports are enabled.
• All ports operate in auto-negotiation mode.
• Spanning Tree is disabled on all ports.
• Addresses that have been silent for more than 15 minutes are
purged from t he swit ch’s address table (the MAC Add ress Agi ng
time).
• No access restrictions to Local Management (Telnet).
• No SNMP restrictions.
• No permanent MAC address entries defined. A permanent entry
is a MAC address that is defined as being permitted only on a
certain port. This can be a useful security feature.
• All ports are in the same VLAN (named <System>) and VLAN
mode (Stand-alone mode). VLANs allow you to create virtual
networks using specific switch ports, IP addresses, IP subnets
and MAC addresses.
• Flow Control is enabled on all ports.
• The connection with Local Management is timed-out after 10
minutes if there has been no input during this period.
After start-up This default confi guration is adequa te for simple wor kgroup environ-
ments to operate in basic switching mode.
Although the switch continues to operate without problems, we rec-
ommend that you change cert ain parameters t o suit your own requ irements.
14
Page 25

C H A P T E R 1 Intel Express 550T Routing Switch
Follow the instructions in Chapter 2 to change the configuration
while the switch is opera ting.
Other LEDs on the front panel
Introduction There are three other LEDs and one button on the front panel that
show how the switch is operating:
• Status LED
• Temperature LED
• Redundant Power Supply (RPS) LED
• Port Status button
LED colors and their
meanings
The LEDs give information about the state of the switch:
LED Color Meaning
Status Green Solid: The switch is operating norm ally.
Blinking (1 Hz): Updating software or
running in recovery mode.
Blinking (5 Hz): Running in maintenance mode.
Red The switch is resetting, or either hard-
ware or software errors are detected.
Temperature Green Normal operating temperature.
Orange Temperature is higher than normal.
Check that the area around the ai r in takes
and vents are clear of obstructions.
Red Temperature is too high and the switch
will shut down.
RPS Green Off: No RPS connected.
Solid: RPS connected, but not needed.
Orange Normal power supply has failed and the
RPS has taken over.
15
Page 26

C H A P T E R 1 Intel Express 550T Routing Switch
Port Status button
To see the speed and duplex set tings of al l the po rts, press the Port
Status
button. The function of the port LEDs changes for a period
of 5 seconds, where they have the following meaning:
LED Color Meaning
Left (Speed) Green Off: 10Mbps
Solid: 100Mbps
Right
(Duplex)
Orange Off: Half duplex
Solid: Full duplex
16
Page 27
2
In this chapter This chapter covers the following topics.
Intel Device View
Topic See Page
System Requirements 18
Installation and Removal 19
Using Intel Device View 20
Installing and Managing Switches 26
Device Tree 29
Device View (Main Display) 31
Explorer 37
Diagnostics Window 37
Trap Window 38
System Window 39
Errors Window 40
17
Page 28

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
System Requireme nts
Requirements f or Inte l
Device View under
Windows
You need a PC with the following minimum requirements to run Intel
Device View:
• Microsoft Windows NT workstation or server, version 4.0, or
Microsoft Windows 95 or Microsoft Windows 98.
(Windows NT 4.0 English language version workstation recommended.)
• A network adapter installed.
• 30 MB of free hard disk space.
• A color display with 800 x 600 resolution and 256 colors.
• The Microsoft IP protocol must be installed and configured
before installation of Intel Device View.
DHCP limitation Three important things to know:
• Do not use a PC running Windows NT server (with its DHCP
server installed) to run Intel Device View.
• Ensure the IP address for the PC is not changed by the DHCP
server.
Management PC
restrictions
Requirements f or Inte l
Device View on the Web
server
• PCs that use a network management system that uses BootP,
DHCP or SNMP Trap Receiving, may have their network management system disabled by Intel Device View.
To manage the switch from a PC connected directly to the switch, the
PC must not use frame tagging. To manage the switch from a PC with
IEEE 802.1Q tagged frames, management must be through a device
which untags the frames.
You need a PC with the following minimum requirements to run Intel
Device View:
• One of the following running: Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 Server
with Internet Information Server (IIS) 2.0 or later; or Windows
NT Workstation with Peer Web Services.
• 30 MB of free hard disk space.
• The Microsoft IP protocol must be installed and configured
before installation of Intel Device View.
18
Page 29

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Web server rest rictions
Requirements f or Inte l
Device View on the Web
client
Requirements f or Inte l
Device View with plugin
To manage the switch from a web server connected directly to the
switch, the web server must not use frame tagging. To manage the
switch from a web server with IEEE 802.1Q tagged frames , management must be through a device which untags the frames.
To run Intel Device View, the client requires:
• Microsoft Internet Explorer (4.00) running on Windows 95 or
Windows 98 or Windows NT 4.0.
• A color display with a minimum o f 80 0 x 6 00 resolution and 256
colors.
To run Intel Device View with a plugin , the PC must be r unning HP
OpenView* or Intel LANDesk Manager.
Installation and Removal
To start the installation of
Intel Device View
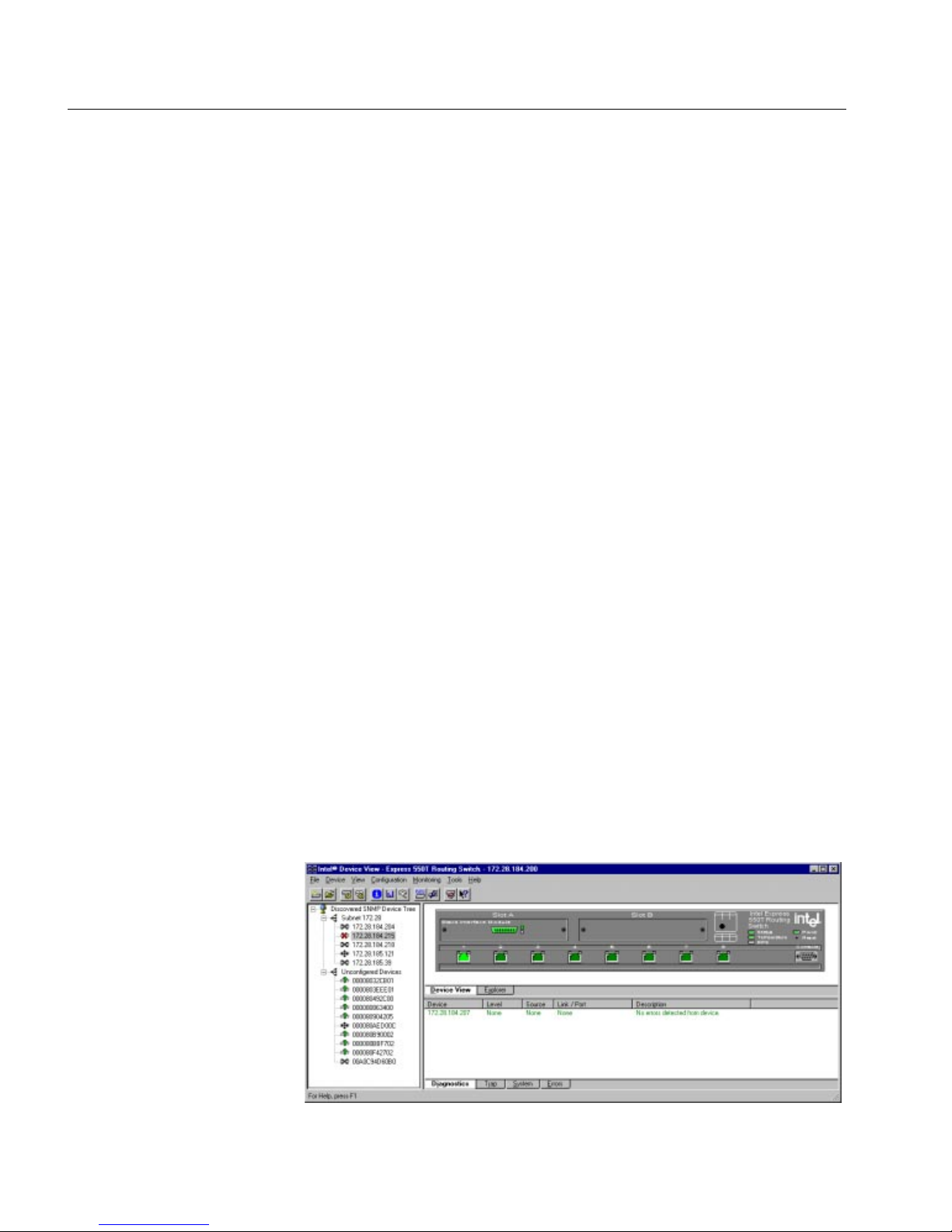
Normally, the Setup program for Intel Device Vie w will start automatically after you insert the compact disc (CD) in your CD ROM
drive. However, if it does no t, us e the sta ndard Win dows procedur es
for installing programs. A screen similar to the one below is displayed:
19
Page 30
C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
T o insta ll Intel Device Vie w
for Windows
Click Install Windows and follow the on-screen instructions.
When the installatio n is complete, Intel Device View will start auto-
matically when “Launch Intel Device View” is selected.
T o insta ll Intel Device Vie w
for Web
Click Install Web and follow the on-screen instructions. When
the installation is complete, Intel Device View will start automatically when “Launch Intel Device View” is selected.
T o insta ll Intel Device Vie w
when using HP
OpenView* or Intel
LANDesk
®
Manager
Click Install Plugin and follow the on-screen instructions.
When the installatio n is complete, Intel Device View starts automat-
ically when “Launch Intel Device View” is selected.
Removal of Intel Device View
Removal under Windows To remove Intel Device View under Windows:
1 Close all Intel Device View programs.
2 Use standard Windows procedures to uninstall Intel Device
View.
Using Intel Device View
Concept Intel Device View configures all the parameters on your switch, or
group of switches known from here on as a stack, (via SNMP) and
monitors their activities.
20
Page 31

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Navigating through Intel
Device View
The Intel Device View
window
Basic menu bar
commands
Many commands are available from within Intel Device View. These
are best accessed using mouse actions. However, Windows users c an
also access most of them through the menu bar.
There are three sections:
• Device Tree — displays the separate branches on your LAN,
including a branch showing all unconfigured devices.
• Interactive picture of the switch, or stack — shows the port state
or the Explorer, which provides port and VLAN details for the
switch or stack.
• Information section — provides details about diagnostics, traps,
errors and the system. Using this window, you can show activity
statistics for the switch (or the stack) and for individual ports.
Before a switch is contacted
Before a switch or stack is contacted, the following commands are
available through the menu bar. The toolbar buttons are for users using Intel Device View in Windows.
File menu This contains one command, Exit which enabl es you to exi t the Intel
Device View. When a switch or stack is open and the configuration
has been changed and not saved to the Flash Memory as the permanent configurati on, yo u are asked i f you want to save th e new conf iguration before exiting.
Device menu The Device menu contains the following switch commands:
• Install — enables you to install a new device, which does not
have an IP address, in Intel Device View. Can also be accessed
by selecting .
• Manage — enables a switch or stack that has an IP address
already assigned to be managed or configured. Can also be
accessed by selecting .
• Discover — enables you to set up how the Device T r ee discover s
devices and users.
Note: do not leave the Subnet Mask blank or set to 0.0.0.0, as
Intel Device View will continually broadcast device discovery
messages to all networks and use bandwidth.
21
Page 32

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
• A list of IP addresses — contains the last eight switches success-
fully contacted from Intel Device View. These can be used to
manage the switch.
View menu — for
Windows users only
The View menu allows you to customize the Intel Device View display to your own preferences: the Toolbar and Status Bar can be
switched on and off.
Monitoring menu This menu gives access to set t he Default Preferences for Intel Device
View, see “Setting the Preferences”, p. 24.
Tools menu The Tools menu has the following commands:
• Ping — sends ICMP echo packets to the switch. Can also be
accessed by selecting .
• A Report Manager — uploads reports, logs and the parameter
block from the switch. Can also be accessed by selecting .
• A Recovery Manager — regains control of your switch if you
have lost contact. This is described in “Recovery Manager”, p.
107.
• A DNS-IP conversion tool converts DNS names to IP addresses.
These are described in de tail, together with switc h specific tools, in
the Chapter “Managing the Switch”, p. 79.
Help menu The Help menu ha s the following commands for the switch:
• Help for Intel Device View. Can also be accessed by selecting the
• Help for switch specific topics.
22
Help icon then clicking on the feature of interest
Page 33

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
After a Switch or Stack is Contacted
Commands When Intel Device View contacts a switch, the basic commands are
supplemented with :
• Local Management access — provides Telnet access to monitor-
ing functions embedded in the switch.
• RMON facility — gathers information about the network traffic,
monitors traffic on subnets and enables you to define alarms on
the individual ports.
• Stack Synchronization Manager (for stacks only) — enables you
to establish a stack from a group of switches connected via a
Matrix Module, or add a swi tc h to an existing stack and then synchronize their configurations.
• Switch Position Organizer (for stacks only) — enables you to
move the switches displayed on screen around in the stack.
• Color Code Matrix Ports (for stacks only) — colors the individ-
ual ports on the Matrix Module. This simplifies the task of tracing cables, as the ports on the Stack Interface Modules become
the same color as the corresponding Matrix Module port.
• A color coding chart for Intel Device View to show the states of
switch’s LEDs
23
Page 34

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Setting the Preferences
Setting the polling
intervals
The polling intervals det ermine how often Intel Device View contacts
the switch or stack and updates the status and infor mation displayed.
To change the polling parameters:
1 Select Monitoring>Preferences.
2 Click Polling or Monitor.
3 If you want the polling to happen more frequently than just on
opening, click
Periodically.
4 Move the Interval slider to the requ ired time.
5 Click OK.
24
Page 35

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Setting the timeout
parameters for SNMP
The timeout determines the intervals between polling and the number
of times the req uest is retr ied if a de vice is not r esponding. T o change
the timeout parame ters:
1 Select Monitoring>Preferences.
2 Click Timeouts.
3 Change the values.
Setting the community for
SNMP polling
4 Click OK.
The community for SNMP polling determines access rights. To
change the community:
1 Select Monitoring>Preferences.
2 Click Community.
3 Type the new community name.
4 Click OK.
25
Page 36

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Installing and Managing
Switches
Following installation of
Intel Device View
Adding new s w itches To add new switches (that have not been assigned an IP address) to
The Install Wizard The Install Wizard requires that you enter a minimum amount of in-
After installing Intel Device View, you can add new switches, establish or expand stacks of switches, and manage existin g switches and
stacks.
Intel Device View, select
will start and guide you through the installation.
formation to set up the switch fo r management by Intel Device View.
To select th e correct new device, yo u need to know the device’s MAC
address. You can find this on a label on the rear panel of the device.
You must assign an IP address (and subnet mask) to the switch on
your Local Area Network (LAN).
Device>Install. The Install Wizard
Intel Device View uses this address for configuration and management purposes.
26
Page 37

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Matrix Module connected
to a new switch
When the Install wizard detects that a new switch is connected to a
Matrix Module, a message in forms that you must decide ho w to manage the switch.
If you want to manage it separately, the installation is completed and
the switch is displayed in the Intel Device View window. If you wan t
to manage it as part o f a stack, you have th e opportunity t o assign consecutive IP addresses in the next dialog.
Managing an existing
switch or stack
The Synchronization Wizard completes the installation. The complete stack, including the new switch, t hen appears in the Intel Device
View window. The Synchronization wizard is described in detail in
“Stack Synchronization Manager”, p. 108.
To manage a switch or stack that h as an IP add ress already assigned:
1 Select Device>Manage The Manage dialog box appears.
2 Type in the switch’s IP Address or MAC address.
27
Page 38

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
3 Select the box if you want to open the switch in a new Intel
Device View window.
4 Click OK.
Establishi ng and
expanding a stack
If you connect switches that already have IP addresses assigned together via a Matri x Modu le, you can ma nage the m as a stack . To create or expand an existing stack:
1 Select Device>Manage, and the Manage dialog opens.
2 Type in the IP Address or MAC address of one of the switches.
All the switches connected via the Matrix Module are di splayed
in this window, even switches that are already configured as a
stack.
3 If the switches don’t have compatible software, the Upgrade
4 Select Stack Mana ge me nt .
5 Select OK. The Upgrade W izard st arts a utomatica lly i f soft ware
28
box is checked. If one or more of the switches aren’t configured, the Configure IP address box is check.
needs to be upgraded.
Page 39

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Device Tree
Introduction The Device Tree displays the separate subnets on your LAN as
branches in a tree. This includes a branch that shows all the unconfigured devices on the LAN.
Identifying devices The Device Tree uses several ic ons to rep resent the i ndividual devic-
es:
Icons Device Description
Recognized as a switch.
Recognized as a router.
Recognized as a hub.
Device contacted, but not recognized.
Lost contact with device.
29
Page 40

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Installing and managing
switches
Right mouse button
commands
Double clicking the switch’s IP address or MAC address opens e xisting switches in the Intel Device View window, or start s the Install
Wizard for new switches.
By positioning t he mouse point er in th e Device Tr ee and cl icking th e
right mouse button, the following functions are available:
Functions Description
(without a device selected)
View
IP Address Sorts the devices by their IP addresses.
Name Sorts the devices by their DNS names.
Add Device If a device has not been auto-detected
then you can add it to the tree. You need
to know its IP address.
Find Locates a specific device by searching for
its IP address.
Refresh Polls the network and redisplays the tree.
If a new device has been connected, it
will appear after a refresh.
(additional functions with a device selected)
Launch With Opens the switch in In tel Device View.
Delete Removes a device from the Device Tree.
Edit Change the name, community settings
(read and write) and polling rate of the
device.
RMON
Statistics Provides subnet management statistics.
History Lists monitored traffic on a subnet.
Alarms Enables activity alarms to be set.
Logs Sets events defined by Log, Trap or Log
and Trap.
30
Page 41

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Device View (Main Display)
Switch contacted When Intel Device View contacts t he switch or st ack, the front (inter-
face side) of the switch or stack is displayed.
This view provides a real-time v iew of the switch, or stack and ports,
which behave in the same way as the physical switch. For example,
the LEDs change color acc ording to the stat e of the switch/stack. You
can fully manage the switch or stack using this display.
Mouse moves Using a mouse makes it easier to operate Intel Device View and saves
you time:
Mouse action Information
Right-click switch Shows the switch-related men us for
configuration and monitoring.
Right-click stack border Shows the stack-related menus for
configuration and monitoring.
Right-click a port S hows the port-related menus for
configuration and monitoring.
Double left-click switch Opens the Device Setup menu.
Double left-click a port Opens that port’s Setup menu.
31
Page 42

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Right mouse button
commands f or a sing le
switch
Right click a single switch and Intel Device View offers:
Functions Description
Device Setup Displays comprehensive information
about the switch’s overall setup.
VLAN/Routing Setup Provides an overview of existing VLANs
and the opportunity to add new ones or
change existing ones.
IP Filtering Setup Defines user groups and filter the packets
sent to them.
Device Information Informs you about the type of switch, its
location, who is responsible for it and the
amount of time passed since the switch
was restarted.
Port Overview Gives detailed monitoring information for
each port.
Device Activity Displays, in a graph fo rm a t, information
about the activity on the ports.
VLAN Displays monitoring information and the
status of the VLAN links.
IP Routing Provides information about the IP ro ut ing
links and networks, and the number of
packets sent via the different IP protocols.
IPX Routing Provides information about the IPX rout-
ing links and networks, and t he numb er of
packets sent via the IPX protocols.
32
Page 43

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Functions Description
Device Reboots the switch and provides informa-
Configuration Ensures the switch’s configuration is safe
Monitoring Provides comprehensive details for Span-
tion about the firmware in the switch. Also
enables the switch’s firmware to be
upgraded.
by saving it to the flash memory, by backing up to disk and by being able to restore
it again should it be lo st. If necessary, the
switch can be returned to the factory
default configuration.
ning Tree statistics and RMON facilities,
as well as Hardware information and an
Access Overview.
Right mouse button
commands f or a stack
border
When managing a stack of switches, r ight cl ick the stack border and
Intel Device View offers:
Functions Description
Stack Setup Displays compr eh ensive information
about the switch’s overall setup.
VLAN/Routing Setup Provides an overview of existing VLANs
and the opportunity to add new ones or
change existing ones.
IP Filtering Setup Defines user groups and filters the packets
sent to them.
Stack Health Monitor Provides the IP addresses for all the
switches in the stack, the type of switch
and whether they are responding to ping.
IntraStack Traffic Gives information about the traffic
through the Matrix Module.
System Information Gives the name and location of the stack,
together with a contact name and the
length of time the stack has been running.
Stack Activity Displays as graphs monitoring information
of traffic on the ports in the stack.
33
Page 44

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Functions Description
Port Overview Provides port performance, packet distri-
Device Enables you to reboot the stack and pro-
Configuration Ensures the stack’s configuration is safe
Monitoring Provides Hardware information about the
bution and spanning tree informa ti on fo r
all the ports in the stack.
vides information about the firmware in
the switches.
by saving it to the flash memory, by backing up to disk and by being able to restore
it again should it be lo st. If necessary, the
stack can be returned to the factory default
configuration.
separate switches in the stacks and the
access rights to the devices on the LAN.
Right mouse button
commands for a switch in
a stack
Tools Gives access to the Synchronization Man-
age, the Switch Position Organizer and
Color Code Matr ix Ports function.
When managing a stack o f switches, right cl ick a switch and Int el Device View offers:
Functions Description
IP and Name Setup Displays the switch’s IP address and Sub-
net mask.
Device Activity Displays, in a graph fo rm a t, information
about the activity on the ports in the switch
selected.
Spanning Tree Provides statistics about the Spanning
Tree on the selected switch.
VLAN Displays monitoring information and the
status of the VLAN links.
IP Routing Provides information about the IP ro ut ing
34
links and networks, and the number of
packets sent via the different IP protocols.
Page 45

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Functions Description
IPX Routing Provides information about the IPX rout-
Device Restarts the switch and provides informa-
Configuration Ensures the switch’s configuration is safe
Monitoring Displays, as a graph, the activity on all the
ing links and networks, and t he numb er of
packets sent via the IPX protocols.
tion about the fi rm ware in the switch.
by saving it to the flash memory.
ports in the switch and RMON facilities.
Right mouse button
commands f or a port
Right click a single port and Intel Device View offers:
Functions Description
Port Setup Displays the port status, the speed and
duplex settings, an d spa nni ng tr ee sett i ngs.
Add Port to VLAN Adds the port to a VLAN.
Port Details Displays comprehensive performance, dis-
tribution and spanning tree details.
Port Activity Displays, as a graph, the activity on the
port.
VLAN Port Monitor-
ing
Provides details about the MAC and IP
addresses on the VLANs.
RMON Statistics Provides RMON statistics for the selected
port.
35
Page 46

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Color coding
The switch and ports are displayed in different colors:
Color Means
Switch
Body
Gray The switch is operational (the soft-
ware is loaded and running) and it
can be contacted by Intel Device
View via the network.
Dark blue That switch is selected, and various
device-specific parameters can be
changed using the right-mouse button.
Ports Dark green Port enabled, but no plug connected.
Light green Port enabled and plug connected.
Brown Port disabled by management or a
hardware error.
Dark blue That port is selected, and various
port-specific parameters can be
changed using the right-mouse button.
Purple Port mirroring is enabled here.
Stack border Dark blue The stack is selected, and various
stack-specific parameters can be
changed using the right-mouse button.
Everything;
switches,
ports and
stack border
Light blue Intel Device View has lost contact
with the devices (for example, the
switch or your PC is disconnected
from the LAN).
36
Page 47

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Explorer
Intel Device View Explorer The Explorer within Intel Device View displays management infor-
mation, for example VLANs on this switch and other switches.
If a switch is disabled or not operational, it is displayed with a red
cross through it.
General management inf ormation for the swi tch is accessed from the
Monitoring menu.
Intel Device View
Diagnostics
Diagnostics Window
The Diagnostics window helps you troubleshoot the switch/stack to
get it working properly in case of problems.
The Diagnostics window lists any problems detected by the switch/
stack and notes the level of the problem (f atal error, error or note) and
the port on which the error occurred. Messages are automatically
cleared from the list when the problem no longer exists
37
Page 48

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Right mouse button
commands
Right click a message and Intel Device View offers:
Functions Description
Details Displays a diagnostic details window that
describes the problem and gives a possible
solution.
Refresh Reloads and updates all the diagnostic
information.
Clear Clears all the messages displayed.
Use Color Coding Displays the messages in different colors,
depending on their severity.
Diagnostic details window This window provides comprehensive details of the error.
Trap Window
Traps window The Traps window displays all traps generated by the switch.
Color coding Traps are generated by the switch for many events, both normal and
errors. Traps displayed in Intel Device View are color coded according to the severity of the trap.
38
Page 49

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Right mouse button
commands
Right click a message and Intel Device View offers:
Functions Description
Refresh Reloads and updat es all the infor mation i n
this window.
Clear Clears all the messages displayed.
Properties Enables color coding to be switched on
and off and define maximum number of
messages displayed.
System Window
System window The System window contains a log o f all the major switch e vents with
date and times (for example, return to factory default, filter entry settings, modules inserted in slots).
Right mouse button
commands
Right click a message and Intel Device View offers:
Functions Description
Refresh Reloads and updat es all the infor mation i n
this window.
Clear Clears all the messages displayed.
Pause Pauses the normal updating of informati on
in this window.
39
Page 50

C H A P T E R 2 Intel Device View
Errors Window
Errors window The Errors window is a log of all error messages generated by the
switch.
Right mouse button
commands
Right click a message and Intel Device View offers:
Functions Description
Refresh Reloads and updat es all the infor mation i n
this window.
Clear Clears all the messages displayed.
Pause Pauses the normal updating of informati on
in this window.
40
Page 51

Standard
3
In this chapter Configuration is th e way we chan ge t he set up o f the swi tc h or stack.
Configuration
In this chapter you will find all the instructions you need to change
setups that affect the switch, or stack, and the ports.
Topic
Changing the Setup of the Switch or
Stack
Changing the Setup of the Port 57
In chapter 4 you will find instructions to integrate VLANs and routing into your setup.
See Page
42
41
Page 52

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
Changing the Setup of the
Switch or Stack
Improving switch security To restrict the use of the switch or stack, you can:
• Change the administrator password for local management.
• Change the user password for local management.
• Limit access to Local Management via the Console port and/or
Telnet.
• Specify a time of “no input”, after which the connection with
Local Management is terminated.
• Change the password for moving files with TFTP.
• Specify use of TFTP.
• Restrict access to include only the stations named on the Authen-
tications list.
Using the mouse There are two ways to access the Device Setup (for single switch-
es) or
• Double-click the switch or the stack border.
• Right-click the switch or the stack border.
Stack Setup window:
42
Page 53

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
System
Identifying the switch To assist with switch identification and administration, you can
change certain switch details (name, location and contact person).
With a switch or stack in the Device View window:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
Click System.
2
3 Change the details.
4 Click OK.
These details are used by SNMP management centers.
43
Page 54

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
Internet Protocol
Changing IP details To change the main IP address and network mask:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click IP.
3 Change the details.
4 Click OK.
This is used to contact the switch via IP (TFTP, SNMP, TELNET etc.) protocols.
44
Page 55

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
Local Time
Setting the date and clock
to local time
To change the clock in the switch to your lo cal time:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Date/Time.
3 Click Insert Current PC Date/Time to show the present
settings. If this is satisfactory, click
OK.
Note The clock displays the time at which it is accessed
and not the current time.
4 If the time or the date is not satisfactory, click the date and/or
time opti ons and type the new time and date.
5 Click OK.
Authentication
Purpose SNMP is a fully de fine d, i nt er ope ra ti ve standard that helps you man-
age both the switch and the network. To do this you can:
• Specify the names of the hosts to access the SNMP agent on the
switch (authentication) by defining the source IP and community
• Specify read-write or read-only for authenticated hosts
• Request a trap to be sent if authentication is violated
Note If no hosts are defined in the Authentication List, any host
can access the SNMP agent in the switch.
45
Page 56

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
Security
The authentications list defines the hosts that can carry out SNMP,
TFTP or Telnet management on the switch, have read-write or readonly rights and access to communities. You can:
• Add a new entry to the list
• Dele te a n entry
• Edit existing entries
Adding a device To add a host that i s al l owed to carry out management on the switch:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Authentications.
3 Click Send trap when authentication violation.
4 Click Add.
5 In IP address, type the IP address of the device to manage
6 Click Protocol and select one.
7 Click Rights and specify the leve l of access to the switch
8 For SNMP only, click Community and type the SNMP request
46
A message will be sent to the
Traps window if unauthorized
hosts try to carry out management on the switch.
the switch.
You can have a maximum of eight addresses in the list. The
address 0.0.0.0 indicates that all IP addresses are accepted.
name accepted by the SNMP agent.
If no community name is specified, all community names are
accepted by the SNMP agent.
Page 57

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
9 Click OK.
Traps
Purpose A trap alerts you of events occurring in the switch. The traps list
shows where SNMP traps (generated by the switch) are sent. You
can:
• Add a new entry to the list
• Dele te a n entry
• Edit existing entries
Adding a trap Note If there are no entries in the Traps list, then no SNMP traps
are sent.
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Traps.
3 Click Add.
4 Type the Destination IP address, or click This PC.
5 Type the community (SNMP password).
6 Click OK.
47
Page 58

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
Permanent Entries
Purpose Enables you to allocate a port to a device t hat does not send out dev ice
information. These devices are not removed from the switch’s address table, regardless of how long they are quiet. This is useful for
connections to printers and other similar devices. You can:
• Add a new entry to the list
• Dele te a n entry
• Edit existing entries
Adding a Permanent Entry To add a device to the switch’s address table:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Permanent Entries.
3 Click Add.
4 Type the device’s MAC address.
5 Click Port number and select one. A permanent entry is
6 Click OK.
48
only made on the defined port.
Page 59

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
Link Aggregation
Purpose Combines two or four adjacent ports to increase the bandwidth be-
tween two switches or stacks. You can:
• Add a new entry to the list
• Dele te a n entry
Adding an Aggregate Link To set up and add an aggregate link:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Link Aggregation.
3 Click Add.
4 For a stack, click Switch and select one from the list.
5 Click Aggregation width: and select 2 Ports or 4
Ports
.
6 Click Anchor Port and select a port.
7 Type a unique name for the link.
8 Click OK. For further configuration of a link, for example in a
VLAN, use the Anchor Port.
49
Page 60

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
Port Mirroring
Purpose Provides a facility to debug or monitor traffic on a specific port, by
duplicating th e traffic an d sending it to a speci fied port. Only one pair
of ports can be mirrored per switch. Within Port Mirroring, you can:
• Add a new entry to the list
• Dele te a n entry
• Edit existing entries
Important When a switch has Port Mirroring enabled, the switch cannot collect
RMON data from the RMON groups 4 to 8.
Adding Port Mirroring To add a mirrored port to a switch:
Note If Port Mirroring is ena bled, the source po rt will be in store-
and-forward mode. Therefor e, Runt s, C RCs, et c. wil l not be
forwarded or mirrored.
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Port Mirroring.
3 Click Add.
4 For a stack, click Switch and select one.
5 Click Reflect from and select the port that you want.
6 Click Reflect to and select the port to where the traffic can
7 Click OK.
50
be debugged/monitored.
Page 61

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
Local Management
Changing password
details
The administrator has read-write access at all levels. The user can
read the monitoring screens, but can not chang e the configurat ion, update software or r eset th e station . To p revent unauthor ized person nel
changing configurations:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Local Management.
3 You can change the passwords for the Administrator and User.
4 Type the old password.
5 Type the new password.
6 Retype the new password (in Retype new).
7 Click OK.
Changing timeout details When ther e has been no input during thi s period, the connecti on with
Local Management is terminated. To change the timeout interval:
1 Select Configuration>Device Setup.
2 Click Local Management.
3 Type the new time.
4 Click OK.
51
Page 62

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
TFTP
Changing password
details
Changing the MAC
address ageing time
To give added security, you can limit the number of staff authorized
to transfer TFTP file s by changing the TFTP password. To change the
password:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click TFTP.
3 Type the old password.
4 Type the new password.
5 Retype the new password (in Retype new).
6 Select OK.
Switching
To change the time a MAC address is kept in the filter before being
purged:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
Click Switching.
2
3 Click MAC Address Ageing.
4 Type the required number of minutes.
5 Click OK.
52
Page 63

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
Changing the flow control
Changing the default
forwar di ng mod e
Flow control prevents the loss of frames during busy periods. Note
that the individual port settings overrule the default setting. To
change the default flow mechanism on all ports:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Switching.
3 Click Default Flow Control.
4 Click Enabled or Disabled.
5 Click OK.
To change the forwarding mode to be used on all ports:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Switching.
3 Click Default Switch Forwarding Mode.
4 Click the default forwarding mode you want.
5 Click OK.
Enable forward learn
packets mode
When this mode is enabled, all packets are forwarded. However, if
there is not enough memory in the switch, due to heavy load, the
packet is discarded . When t his mode is disa bled, on ly “IPX Get server” request packets are forwarded. To enable or disable this mode:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Switching.
3 Check the box to enable this mode.
4 Click OK.
53
Page 64

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
Adaptive Forwarding Mode
Purpose You can:
• Change the Sample Time
• Define the minimum and maximum errors acceptable before
changing the forwarding mode
Note While CRC errors and runts are the most likely parameters
to cause the switching mode to ch ange, they are not the onl y
ones.
Changing the time to
measure errors
The sample time should be the shortest time needed to detect errors.
If the sample time is too great, there may be too many errors before
the forwarding mode changes. To chang e the t ime the switch ret ai ns
error counters:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Switching.
3 Click Advanced.
4 Click Sample Time.
5 Type the required number of seconds.
6 Click OK.
Changing number of
errors before adaptive
forwarding mode operates
54
Adaptive forwardin g changes the f orwarding mode d epending on th e
upper and lower limits of specifi c error types. To change the number
of upper and lower limits:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Switching.
3 Click Advanced.
Page 65

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
4 Click the required parameter.
5 Type the percentage of errors or runts.
6 Click OK.
Spanning Tree
Purpose You can change the:
• Priority given to the switch
• Maximum length of time information is retained by the switch
• Time between tra nsmitted Configura tion BPDUs
• Time the switch spends in the Listening and Learning states
Warning when using
VLANs
It is important to be aware of problems that may arise when using
Spanning Tree and VLANs. The Spanning Tree can use alternative
paths (such as different ports) to get messages to their destination.
VLAN STP
A
123 87654
123 87654
A
SlotBSlotA
SlotBSlotA
VLAN
B
SlotBSlotA
Orange
LEDs
Green
Off
10Mbps
Halfduplex
IntelExpress
Solid
100Mbps
Fullduplex
550TRouting
PortStatus
Switch
Power
Status
Orange
LEDs
Green
Temperature
Solid
Link
Disabled
Reset
Blink
Activity
Collision
RPS
Orange
LEDs
Green
Off
10Mbps
Halfduplex
IntelExpress
Solid
100Mbps
Fullduplex
550TRouting
PortStatus
Switch
Status
Orange
LEDs
Green
Temperature
Solid
Link
Disabled
Blink
Activity
Collision
RPS
Switch 1
Console
9600-8-N-1
Power
Reset
Console
Switch 2
9600-8-N-1
123 87654
WX
Y
123 87654
Orange
LEDs
Green
Off
10Mbps
Halfduplex
IntelExpress
Solid
100Mbps
Fullduplex
550TRouting
PortStatus
Switch
Power
Status
Orange
LEDs
Green
Temperature
Solid
Link
Disabled
Reset
Blink
Activity
Collision
RPS
Console
9600-8-N-1
SlotBSlotA
Z
Orange
LEDs
Green
Off
10Mbps
Halfduplex
IntelExpress
Solid
100Mbps
Fullduplex
550TRouting
PortStatus
Switch
Power
Status
Orange
LEDs
Green
Temperature
Solid
Link
Disabled
Reset
Blink
Activity
Collision
RPS
Console
9600-8-N-1
B
1684
The diagram above, shows two switches. On th e l eft, we see the two
switches connected and the por t s ar e grou ped i n t wo VLANs: A and
B. On the right, we have enabled ST P; ST P blocks t he pat h bet ween
X and Z (to avoid looping) and, theref ore, dest roys t he VLAN setup
(because VLAN B needs these ports to receive messages).
Why change these from
their defaults?
The switch is deli vered with Spanning Tr ee default values set to those
recommended by the IEEE 8 02.1d standard. These values are conservative worst-case estimates for LANs consisting of a large number of
switches. Therefore, changing these default values may improve the
performance of your netw ork.
55
Page 66

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
Changing the spanning
tree priority
The higher the value, the lower the chance of the switch being used
as the root bridge. To change the priority value:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Spanning Tree.
3 Click Priority.
Changing the message
age expiry time
Changing the hello expiry
time
4 Type the required value.
5 Click OK.
To change the maximu m time between pro tocol informatio n being received and discarded:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Spanning Tree.
3 Click Message Age Timer Expiry.
4 Type the required number of seconds.
5 Click OK.
To change the time between transmissions of configuration BPDUs
from a switch that is, or a ttempting to become, the root:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Spanning Tree.
3 Click Hello Timer Expiry.
4 Type the required number of seconds.
56
Page 67

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
5 Click OK.
Changing the forward
delay expiry time
Changing the state of the
ports
To change the time between port states while the bridge attempts to
become the root:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Spanning Tree.
3 Click Forward Delay Timer Expiry.
4 Type the required number of seconds.
5 Click OK.
To specify that all ports are using Spanning Tree Protocol:
1 Select Device Setup or Stack Setup.
2 Click Spanning Tree.
3 Click Enable All Ports.
The ports are able to resolve problematic network loops using
STP.
4 Click OK.
Changing the Setup of the
Port
Purpose You can configure the port to op erate in d ifferent ways, a ccording to
your network’s requirements:
• Change the port state
• S elect the auto-ne gotiation mode
• Change each port to half or full duplex
(If auto-negotiation is not enabled)
• Specify the speed of the port
(If auto-negotiation is not enabled)
• Change the forwarding mode of the port
• Change the flow control setting of the port
57
Page 68

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
• Specify the spanning tree
Using the mouse There are two ways to access the Port Setup window:
• Double-click the port
• Right-click on the port, and click Port Setup
General Changes
Renaming a port To give a port a new name, for example, i ts use or the user(s) connec t-
ed:
1 Click the port you want to rename.
2 Select Port Setup.
3 Click General.
4 In Description, type the new name.
5 Click OK.
Location for a port To specify the location (for example, an office number or depart-
ment) of the device attached to a port:
1 Click the port you want to give a home to.
2 Select Port Setup.
3 Click General.
4 In Location, type where the device is.
5 Click OK.
58
Page 69

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
Port Mode
Disabling the port If you disable the port, the devices attached to it cannot use the
switch. The MAC address of those devices are removed from the
switch’s address table. If those addresses are defined as permanent
entries, they are not purged but are unable to use the switch. To disable the port:
1 Click the port you want to disable.
2 Select Port Setup.
3 Click Port Mode.
4 Click Enable Port.
If there is a check mark in the box, the port is operational. If
the box is empty, the port is disabled.
5 Click OK.
Disabling auto-negotiation To disable auto-negotiation, and reset the speed to the values speci-
fied in
1 Click the port you want to disable auto-negotiation.
2 Select Port Setup.
3 Click Port Mode.
4 Click Enable Auto-negotiation.
Speed:
If there is a check mark in the box, the port automatically
detects the line-speed and duplex setting. If the box is empty,
auto-negotiation is disabled and the port uses the values specified in
Duplex and Speed.
59
Page 70

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
5 Click OK.
Changing duplex mode To change the port’s duplex mode (when auto-negotiation is dis-
abled):
1 Click the port you want to change.
2 Select Port Setup.
3 Click Port Mode.
4 Click Half Duplex or Full Duplex.
Half allows either transmission or receipt of the data and
Full allows both transmission and receipt of the data.
5 Click OK.
Changing the port speed To change the speed a port accepts data (when auto-negotiation i s dis-
abled):
Changing the forwarding
mode on a port
1 Click the port you want to change.
2 Select Port Setup.
3 Click Port Mode.
4 Click Speed 10 or Speed 100.
10 limits data entering to 10Mbps and 100 allows data speeds
up to 100Mbps.
5 Click OK.
To change the forwarding mode to be used on a port:
1 Click the port you want to change.
2 Select Port Setup.
3 Click Port Mode.
4 In Switch Forwarding Mode, click the forwarding mode
you want.
Default uses the same forwarding mode as specified in
Device Setup.
5
60
Click OK.
Page 71

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
Changing the flow control
on a port
Flow control prevents the loss of frames during busy periods. To
change the flow mechanism on a port:
Note This feature is over-ridden by disabling the flow control set-
1 Click the port you want to change.
2 Select Port Setup.
3 Click Port Mode.
4 In Flow Control, click the flow control you want.
Default uses the same flow control as specified in Device
Setup.
Click OK.
5
Port Specific Spanning Tree
Purpose You can:
ting in
Device Setup>Switching.
Changing the state of a
port
• View the Spanning Tree setups for the port
• Specify whether STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) is enabled on the
port
• Define which ports are going to be used most frequently
To specify that a port is using STP:
1 Click the port you want to change.
2 Select Port Setup.
61
Page 72

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
3 Click Spanning Tree.
4 Click Enable spanning tree on this port.
If there is a check mark in the box, the port is used in STP. If
the box is empty, the port is not used in STP.
Changing the cost of the
path
Changing priority of the
port in the spanning tree
5 Click OK.
The higher the cost, the lower the chance of this port being used for
forwarding traffic, if there is an alternative route. When possi ble, give
a port a low cost if it is connected to a faster network segment. To
change the overall cost of the path between a port and the segment:
1 Click the port you want to change.
2 Select Port Setup.
3 Click Spanning Tree.
4 Select the Port status box.
5 In Path cost, type the required value.
6 Click OK.
The higher the value, the lower the cha nce of th is por t being used as
the designated or root port. To change the priority value:
1 Click the port you want to change.
2 Select Port Setup.
3 Click Spanning Tree.
4 Select the Port status box.
62
Page 73

C H A P T E R 3 Standard Configuration
5 In Priority, type the required value.
If there are two ports with the same value, the port with the
lowest port number is chosen.
6 Click OK.
63
Page 74

Page 75

Advanced
4
In this chapter In this chapter you will le arn how to use Advanced Configura tion ef-
Configuration
fectively. This chapter covers the V i rtual LAN (VLAN), Routing and
IP Filtering features.
You can create logical network groups (VLANs) by segmenting the
switch; for example, according to the su bnettin g scheme wit hin your
network. Each VLAN is an isolated group and the switch only forwards traffic between members of the same group. Communication
between groups can be implemented using routers.
Routing can be implemented using an external router or the internal
routing feature. The switch can run either stand-alone or distributed
VLANs. For single switches using stand-alone VLANs, the local
configuration (for example, ports) must be configured on each
switch. This does not apply to a stack. For distributed VLANs, the
global configuration of MAC and IP addresses is automatically distributed. Local policies are distributed within a stack, regardless of
the VLAN mode.
IP Filtering enables selective filtering of data traffic. It is available
when you are routing between nets or VLANs. It enables you to send
data packets to specific workstations or user groups across the
VLANs.
Note This switch is able to forward tagged frames from devices
supporting IEEE 802.1p/Q. These frames are only forwarded to ports that are in the same VLAN.
65
Page 76

C H A P T E R 4 Advanced Configuration
However, IP policies cannot be used for devices using tagged VLANs
and IP learning is not p ossible . In add ition to t his, tagged frames cannot be routed between VLANs.
VLANs (Virtual LANs)
Purpose You can use VLANs to:
• Create up to 128 separate user groups
• Limit broadcast and multicast traffic
• Increase security by limiting communication between groups
• Allocate network resources (such as servers) to groups
For a more comprehensive explanation of the VLAN concept, refer
to the online help.
Warning when using STP It is important to be aware of problems that may arise when using
Spanning Tree and VLANs. The Spanning Tree can use alternative
paths (such as different ports) to get messages to their destination.
VLANs specify which ports can receive messages (see “Spanning
Tree”, p. 55).
Warning When using the Spanning Tree facility, use only one
VLAN. If you use two or more VLANs, unexpected
changes in your network topology may occur.
Policy-based VLANs The swi tch or stack uses “Policy-based VLANs”. This means that the
devices attached to t he swit ch/s t ack can be grouped by any combi nation of MAC address, IP address, IP net and port number; therefore,
devices can belong to one or more VLANs.
Policy hierarchy To avoid conflicts between two VLANs, a strict p r iority of the poli-
cies is used:
1. MAC address
2. IP address and IP net
66
Page 77

C H A P T E R 4 Advanced Configuration
3. Port
Warning This means that a station learned by a MAC rule is not
learned by an IP or Port rule, and a station learned by an
IP rule is not learned by a Port rule. Only stations that
are not learned by MAC or IP rules are learned by a
Port rule.
Note IP policies can be used only when IP learning is enabled on
the respective ports.
Adding a VLAN The task of adding VLANs is simplified by using the VLAN Wizard.
VLANs are not switch specific when managing a stack. Therefore,
right-click the stack border to a ccess VLAN/Routing Setup. To add a
VLAN:
1 Select VLAN/Routing Setup.
2 Click Add, and follow the instructions in the Wizard windows.
Policy Information required
Switch Ports Port numbers
IP Subnet IP Subnet and Mask
Mixed policy IP Subnet and Mask,
Port numbers,
MAC address and/or
IP address
IP routing Subnet and router link
67
Page 78

C H A P T E R 4 Advanced Configuration
Deleting a VLAN
To delete a VLAN:
1 Select VLAN/Routing Setup.
2 Click the name of the VLAN you want to delete. (Note: you
cannot delete a VLAN if it is the
ment VLAN]
and then click Use this VLAN for SNMP
ties
management
. To do this, click another VLAN, click Proper-
; you can now delete th e first VLAN.)
[Designated Manage-
3 Click Delete.
Adding a policy to a VLAN You may want to add another policy (that is, a port, IP address, IP
subnet or MAC address) to an existing VLAN. To add a policy:
1 Select VLAN/Routing Setup.
2 Click the nam e of the VLAN you want to edit.
3 Select Policies>Add.
4 Select the New policy type.
5 Fill in th e appropriate field(s).
Adding a new switch to a
distributed VLAN
6 Click Close.
If Intel Device View is connected to an existing switch, the new
switch needs to be learned by the management VLAN before Intel
Device View can access it.
We recommend that you connect Intel Device View directly to the
new switch, or use a port-policy rule to learn it.
If you do not add the port on which the new switch is connected (using the port-po licy rul e), y ou must add t he MAC addr ess for the ne w
switch instead.
For example, if you define the membership of a VLAN using a MAC
policy, you need to use two MAC addresses. If the System MAC address is 00A0C9xxxxxx, you must enter 00A0C9xxxxxx and
02A0C9xxxxxx in the MAC policy.
68
Page 79

C H A P T E R 4 Advanced Configuration
Changing VLAN mode
To change the mode of operation of a VLAN:
1 Select VLAN/Routing Setup.
2 Click Advanced. The VLAN mode is shown.
3 Click th e VLAN mode to see the full ra nge of choices.
VLAN Mode Description
Stand-alone For single switches: the re is no exchange of
information with VLANs on other swi tches;
each switch is its own domain
(STDALONE).
For switches in a stack: there is an ex change
of information using VLANs between the
switches in the stack; these switches are in
their own domain (STDALONE).
Distributed A domain is a collection of switches and
can contain up to 128 VLANs. If you select
distributed, each switch will be able to communicate with all the others in this domain.
4 Click the new mode and make sure the rest of the details are
correct.
5 Click OK.
Your switch may turn blue (for a few seconds) while the network stability return s; this is normal.
69
Page 80

C H A P T E R 4 Advanced Configuration
Adding a station to a
Switch VLAN Link
Changing VLAN domain
name
To place a station on the link between two switches or two stacks,
configure the station as a permanent entry. If you have a stack, rightclick a stack border and select Stack Setup instead of Device Setup:
1 Choose one of the switches, and select Device Setup>Per-
manent Entries>Add
in Intel Device View.
2 Enter the MAC address.
3 Select th e number of the port to wh ich the link is connec ted.
4 Make a MAC address policy in the VLANs to which this station
is joining.
This is relevan t only for a Dist ribute d VLAN. To cha nge th e domain
name for all VLANs:
1 Select VLAN/Routing Setup.
2 Click Advanced The VLAN mode is highlighted.
3 Double-click the VLAN Domain Name, and type the new
domain name (note that domain names are case sensitive).
Changing the priority of
the server
Changing the time before
the server is removed
4 Click OK.
This is relevant only for a Distributed VLAN. You can specify a
switch in the domain to be the VLAN database server. The switch
with the lowest value will be the server. To change the priority:
1 Select VLAN/Routing Setup.
2 Click Advanced. The VLAN mode is highlighted.
3 Double-click the Server priority, and type the new value.
If two switches have the same priority, the switch with the lowest MAC address will be the server.
4 Click OK.
This is relevant only for a Distributed VLAN. After receiving a packet from the server, the switch/stack waits for a specific length of time
before it assumes the server is lost. The switch /stack then start s to listen for a new server and, if none is found, it becomes the server. To
change the length of time before the server is assumed to be lost:
1 Select VLAN/Routing Setup.
2 Click Advanced. The VLAN mode is highlighted.
70
Page 81

C H A P T E R 4 Advanced Configuration
3 Double-click Server Expiry Time-out, and type the new
value.
4 Click OK.
Ports with IP learning IP learning must be enabled when using IP policies. (IP learning is
enabled on all ports by defaul t.) If you want to change the settings for
individual ports, for examp le if you are usi ng pro to col s oth er tha t IP
protocols and don’t want these stations to be learned using IP rules,
you should:
1 Select VLAN/Routing Setup.
2 Click Advanced.
3 Click IP Traffic to specify which ports support IP learning.
4 Click OK.
Routing Between VLANs
Introduction After you have created the VLAN groups, you can move (or route)
packets of data between VLANs using the IP and IPX protocols.
71
Page 82

C H A P T E R 4 Advanced Configuration
Adding a routing link
To add a routing link to a VLAN that is not already configured:
1 Select VLAN/Routing Setup>Add.
2 Select the Setup an IP routing interface box.
3 Click Next, and follow the instructions in the W izard win dows.
Changing IP and IPX
details
To change the routing protocol details for an existing VLAN:
1 Select VLAN/Routing Setup.
2 Click Routing.
3 Select the Use IP routing or Use IPX routing box to
make active (if possible).
4 Double-click the required field, type the new value and select
the correct protocol parameters.
5 Click OK.
Adding a static route A static route is a permanent entry in the routing table and is a pat h to
IP network which is not announced by the RIP. A static route is announced to other switches or stacks using RIP. To add a static route:
1 Select VLAN/Routing Setup.
2 Click Advanced>IP Routing
Click Add
3
4 Double-click the required field, and type the new value.
5 Click OK.
72
Page 83

C H A P T E R 4 Advanced Configuration
Changing the number of
BOOTP request hops
This parameter specifies the maximum number of ho ps that a BOOTP
request can make before being discarded. To change the number of
hops:
1 Select VLAN/Routing Setup.
2 Click Advanced>IP Routing.
3 Double-click the Maximum BootP request hops, and type
the new value.
4 Click OK.
Changing RSVP settings This ReSe rVa tion Protocol (RSVP) facility allows bandwidth to be
reserved, enabling guaranteed delivery of data. To change the settings:
1 Select VLAN/Routing Setup.
2 Click Advanced>IP Routing.
Click box to enable/disable RSVP, set Refresh Timer period and
3
Cleanup timeout factor.
4 Click OK.
Changing Type of Service
priorities
This uses IP packet preferen ce settings to prioritize t raffic through the
switch. Packets with a higher setting are handled in preference to
packets with lower settings. To change the priority level:
1 Select VLAN/Routing Setup.
2 Click Advanced>IP Routing.
3 Double-click the ToS, and type the new value (range 1-7).
73
Page 84

C H A P T E R 4 Advanced Configuration
4 Click OK.
DVMRP Tunnels
Introduction This routing switch supports the Distance Vector Multicast Routing
Protocol (DVMRP). This enables IP multicast packet s to be encapsulated in an IP header, and sent through a tunnel bet ween two specific
switches on a network that does not support DVMRP routing. The
tunnel is defined using IP addresses, a source IP address and a destination IP address.
Adding a tunnel A DVMRP tunnel must be set up in both switches over the tunnel.
1 Select VLAN/Routing Setup.
Click Advanced>IP Routing>DVMRP Tunnels.
2
3 Click Add.
4 Type the required information in the fields provided.
5 Click OK.
IP Multicast (IGMP pruning)
Warning when using
pruning
It is important to be aware of problems that may arise when using
IGMP pruning and IP Multicast addresses.
Warning When using the IGMP pruning, IP multicast packets not
74
based on IGMP are discarded.
Page 85

C H A P T E R 4 Advanced Configuration
IGMP pruning can only be used in VLANs that have an IP link. Enabling IGMP pruning stops Layer 2 forwar di ng o f IP mul t ica st p ackets in all other VLANs without IP links.
Only enable IGMP pruning (on this device) when it is connected between the device receiving the packe ts and an IP multicast routing device. Or, disable IGMP pr uning (on t his device) when it is conn ected
between the device t ransmi t ting t he pack ets an d a n IP mu lti cast rou ting device.
IP multicast routing in a
stack
When enabling IP multicast routing on the management VLAN in a
stack, you MUST assign the IP addresses consecutively to the management VLAN, for example, x.x.x.77, x.x.x.78, x.x.x.79 etc.
Enabling IGMP pruning IGMP pruning implements a system where only the necessary
amount of IP multicast packets are bridged . To enable IGMP pr uning:
1 Select VLAN/Routing Setup.
2 Click Advanced>IP Routing>IGMP.
3 Check Enabled.
4 In Pruning timeout, type the new value.
5 Click OK.
IP Filtering
Purpose IP filtering is availabl e when you are routing between nets or VLANs.
It enables you to send data packets to specific workstati ons or user
groups across the VLANs. You define the members in these user
groups and the type of IP filterin g. IP filtering uses either IP addresses
or specified IP protocols. It i s specific for the individual switches, an d
therefore, right-click the switch to access the IP filtering functions.
Before you start Look at the architecture of your network before starting. Make a list
of proposed user groups and their filter parameters. Then look at the
individual members t o be included i n the groups. T his prevents workstations or subnets from being excluded when IP filtering is enabled.
75
Page 86

C H A P T E R 4 Advanced Configuration
Enabling IP Filtering
IP Filtering is enabled by default . There are two default user group s,
which allow all traffic to pass. Enable is a toggle function, which also
allows you to disable IP Filtering:
1 Select IP Filtering Setup.
2 Select Enabled.
3 Set up any User Groups and Members required.
4 Click OK.
Adding a User Group Before filtering can take place, you must define the different user
groups. To add a user group:
1 Select IP Filtering Setup>User Groups.
2 Click Add.
3 Type a unique name for the User Group.
4 Click OK.
5 When the User Group list is complete, click Close.
76
Page 87

C H A P T E R 4 Advanced Configuration
Adding a Member
To add a member to a user group:
1 Select IP Filtering Setup>Add member.
2 In Type, select whether the member is defined by Port (Proto-
col) or by Address.
3 For port selections, define th e IP fi lter protocol, while for
Address define the IP Address (and subnet if necessary).
Checking Member
connections
4 Select the User Group for this new member.
5 Click OK.
This checks which members a specific member can communicate
with, and lists them on screen. To check connections:
1 Select IP Filtering Setup.
77
Page 88

C H A P T E R 4 Advanced Configuration
2 Click a Me mber in the list.
3 Click Show member connections
Verify that the connections for this member are correct.
4
5 Click Close.
78
Page 89

5
In this chapter This chapter covers the following topics.
Managing the Switch
Topic See Page
Management using Intel Device View 80
Monitoring the Switch’s Performance 81
Monitor ing the Stack’s Performance 86
Monitoring VLANs and Routing 91
Monitoring the Port’s Performance 99
To ols for the Switch 103
Tools for the Stack 108
79
Page 90

C H A P T E R 5 Managing the Switch
Management using Intel
Device View
Why use Intel Device
View?
Intel Device View allows you to:
• Configure system, switching, IP, spanning tree, authentication,
and trap paramete rs for the switch.
• Configure port-related parameters.
• View traps, logs, traces, and reports generated by the switch.
• Monitor port activity.
• Monitor port faults.
• M on itor switch activity.
• Monitor VLANs and Routing.
Information about the Switch
Identifying the switch To see the name of the switch, the IP address, the administrator’s
name and how long the switch has been running:
1 Select Device Information.
2 To update the information, click Refresh.
80
Page 91

C H A P T E R 5 Managing the Switch
Hardware details
Monitoring the tota l packe t
activity
To see the MAC address, hardware version and memory size:
1 Click Monitoring>Hardware Information.
2 To update the information, click Refresh.
Monitoring the Switch’s Performance
To view the total activ ity of the packets on all the ports:
1 Select Device Activity>Total Packets.
Each column represents a port and its activity level.
2 To see the exact value, hold the mouse pointer over a port.
3 Click View and change the presentation style: 3D- to 2D-
Graph, with or without a peak value indicator and vertical to
horizontal bars.
81
Page 92

C H A P T E R 5 Managing the Switch
Monitoring the total
activity of transmitted
packets
Monitoring the total
activity of received
packets
To view the total ac tivity of the packets being transmitted on all the
ports:
1 Select Device Activity>Tx Packets.
Each column represe nts the activity level on t hat p ort.
2 To see the exact value, hold the mouse pointer over a port.
3 Click View and change the presentation style: 3D- to 2D-
Graph, with or without a peak value indicator and vertical to
horizontal bars.
To view the total activity of the packets being received on all the
ports:
1 Select Device Activity>Rx Packets.
Each column represe nts the activity level on t hat p ort.
2 To see the exact value, hold the mouse pointer over a port.
3 Click View and change the presentation style: 3D- to 2D-
Graph, with or without a peak value indicator and vertical to
horizontal bars.
Monitoring the total
number of errors
To view the total error activity of the packets on all the ports:
1 Select Device Activity>Errors.
Each column represe nts the activity level on t hat p ort.
2 To see the exact value, hold the mouse pointer over a port.
3 Click View and change the presentation style: 3D- to 2D-
Graph, with or without a peak value indicator and vertical to
horizontal bars.
82
Page 93

C H A P T E R 5 Managing the Switch
Monitoring the spanning
tree statistics
Overview of all the ports To view the setups of all the ports on the switch:
To view the spanning tree statistics for the whole switch, select
Spanning Tree Statistics.
1 Select Port Overview.
2 Double-click a port to get the specific details for that port: port
performance, faults, packet distribution, link aggregation and
spanning tree information.
83
Page 94

C H A P T E R 5 Managing the Switch
Stations on the switch
To view the IP addresses of the devices that have accessed management on the switch:
1 Click Monitoring>Access Overview.
2 To change the order of the information, click the appropriate
title bar.
Monitoring using RMON
Purpose The switch contains several RMON functions. These function pro-
vide a tool for collecting information about network traffic. The following information, History, Alarm and Event Log are switch
specific. Right-click the switch to access the relevant RMON facility.
RMON History To monitor traffic on a subnet over a period of time:
1 Right-click a switch and select Monitoring>RMON His-
tory.
2 To open a graph showing the statistics, select a history and
press
This opens a window listing all history collections.
View.
84
Page 95

C H A P T E R 5 Managing the Switch
RMON Alarms
Alarm is a useful RMON feature; it enables you to set your own
thresholds for when the network activity requires some attention.
1 Right-click a switch and select Monitoring>RMON
Alarms>Configure. The Alarm Table window opens,
which lists all alarms.
2 Click Add to add an alarm to the list.
After defining the alarm, a trap is sent every time the threshold
is exceeded.
RMON Events Event is a useful RMON feature; it enables you to set your own
events, defined by type; Log, Trap or Log and Trap:
1 Right-click a switch and select Monitoring> RMON
Alarms>Events
. The Events Table window opens, whic h
lists all events defined.
2 Click Add to add an event to the list.
Note Events can be created automatically through the alarm
configurations.
Online Help For more information about the use of the RMON facilities, please re-
fer to the online
Help.
85
Page 96

C H A P T E R 5 Managing the Switch
Monitoring the Stack’s Perform ance
Monitoring the health of
the stack
The Stack Health Moni tor provides a n overal l stat us for t he switche s
in the stack. To view the health of the stack: Right-click the stack border and select
Stack Health Monitor.
If the condition of any of the switches alters, the changes are displayed on screen.
86
Page 97

C H A P T E R 5 Managing the Switch
Monitoring IntraStack
activity
To view the total activity of the packets between the switches in the
stack, or across the Matrix Module:
1 Right-click the stack border and select IntraStack Traf-
fic
Each column represents a Matrix Module port and its activity
level.
2 To see the exact value, hold the mouse pointer over a port.
87
Page 98

C H A P T E R 5 Managing the Switch
Monitoring the tota l packe t
activity per port
To view the total ac tivity of the packets on all the ports:
1 Right-click the stack border and select Stack Activ-
ity>Total Packets per Port
.
Each column represents a port and its activity level.
Monitoring the tota l packe t
activity of the switches
2 To see the exact value, hold the mouse pointer over a port.
To view the total ac tivity of the packets on all the ports:
1 Right-click the stack border and select Stack Activ-
ity>Total Packets
.
2 To see the exact value, hold the mouse pointer over a switch.
88
Each column represe nts a switch and its activity level.
Page 99

C H A P T E R 5 Managing the Switch
3 Click View and change the presentation style: 3D- to 2D-
Graph, with or without a peak value indicator and vertical to
horizontal bars.
Monitoring the total
activity of transmitted
packets
Monitoring the total
activity of received
packets
To view the total activ ity of the packets being transmitted o n a ll the
switches:
1 Right-click the stack border and select Stack Activ-
ity>Tx Packets
.
Each column represe nts the activity level on a switch.
2 Hold the cursor on a column to see the exact value.
3 Click View and change the presentation style: 3D- to 2D-
Graph, with or without a peak value indicator and vertical to
horizontal bars.
To view the total activity of the packets being received on all the
switches:
1 Right-click the stack border and select Stack Activ-
ity>Rx Packets
.
Each column represents the activity level on t hat switch.
2 Hold the cursor on a column to see the exact value.
3 Click View and change the presentation style: 3D- to 2D-
Graph, with or without a peak value indicator and vertical to
horizontal bars.
Monitoring the total
number of errors
To view the total error activity of the packets on all the switches:
1 Right-click the stack border and select Stack Activ-
ity>Errors
.
Each column represents the activity level on t hat switch.
2 Hold the cursor on a column to see the exact value.
3 Click View and change the presentation style: 3D- to 2D-
Graph, with or without a peak value indicator and vertical to
horizontal bars.
89
Page 100

C H A P T E R 5 Managing the Switch
Overview of all the ports
Monitoring the spanning
tree statistics
To view the setups of all the ports in the stack:
1 Right-click the stack border and select Port Overview.
2 Double-click a port to get the specific details for that port: port
performance, faults, distribution and spanning tree information.
To view the spanning tree statistics for the whole switch, right-click
a specific switch and select
Spanning Tree.
90
 Loading...
Loading...